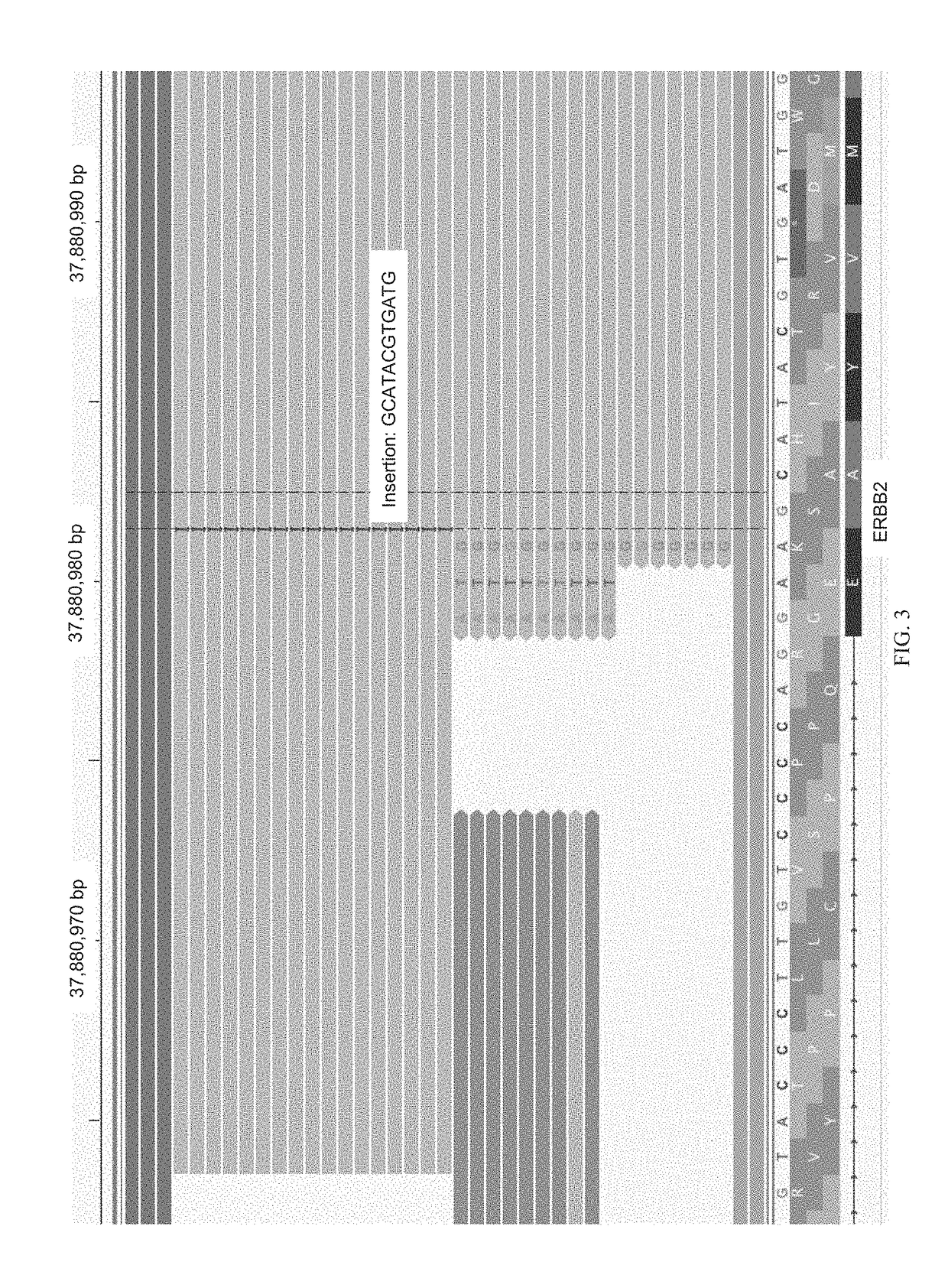
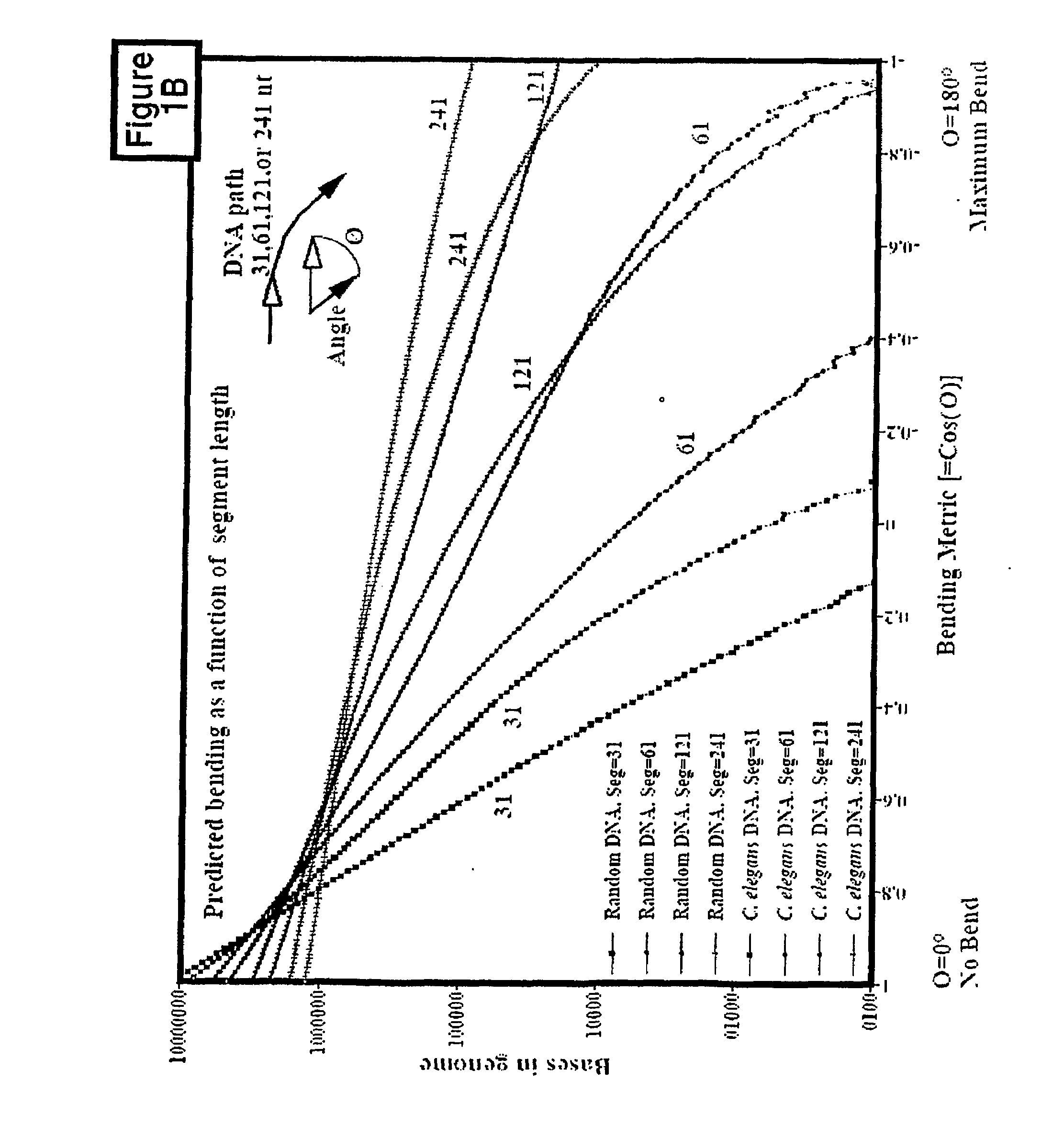
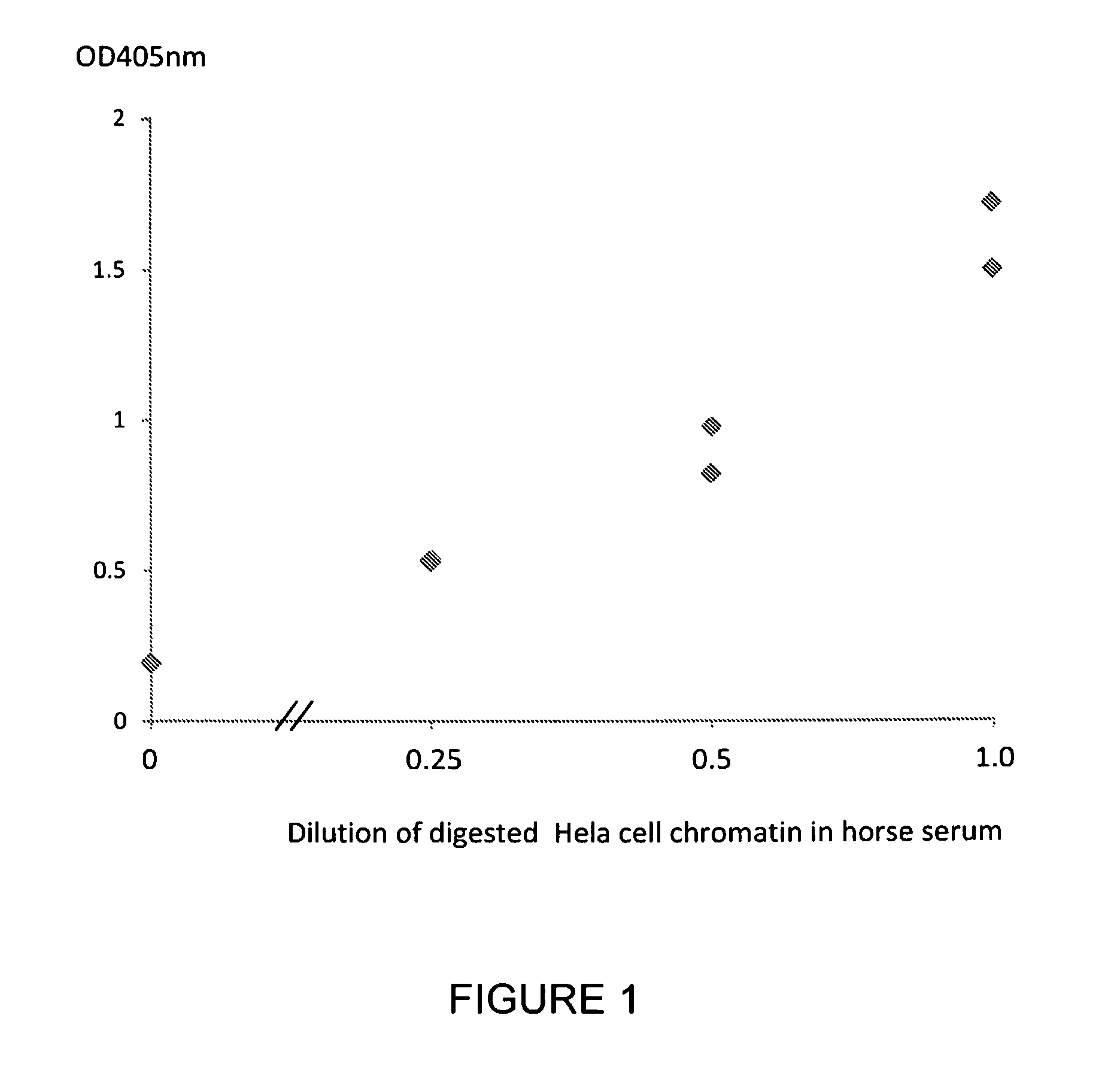
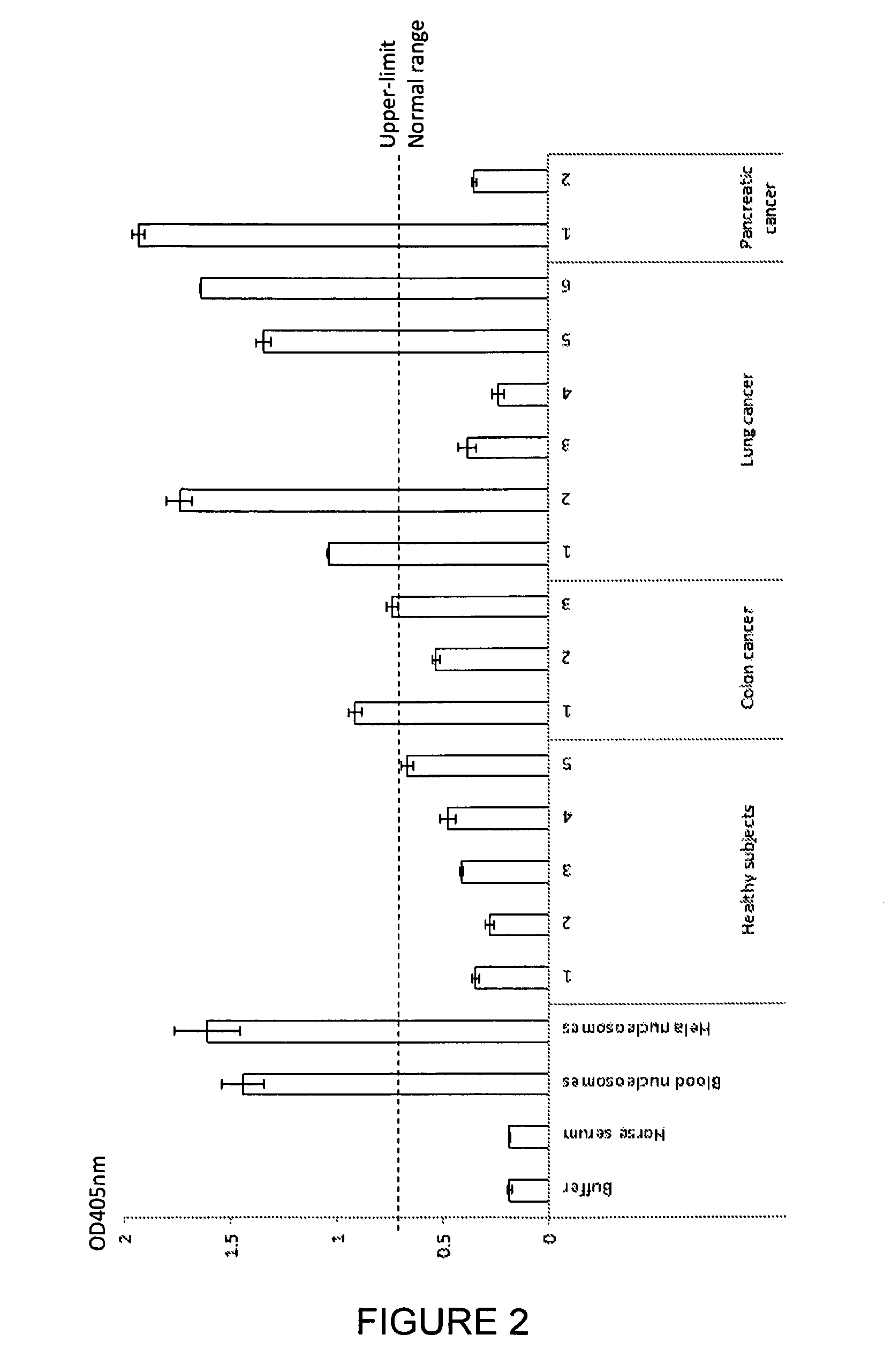
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
82 results about "Nucleosome" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
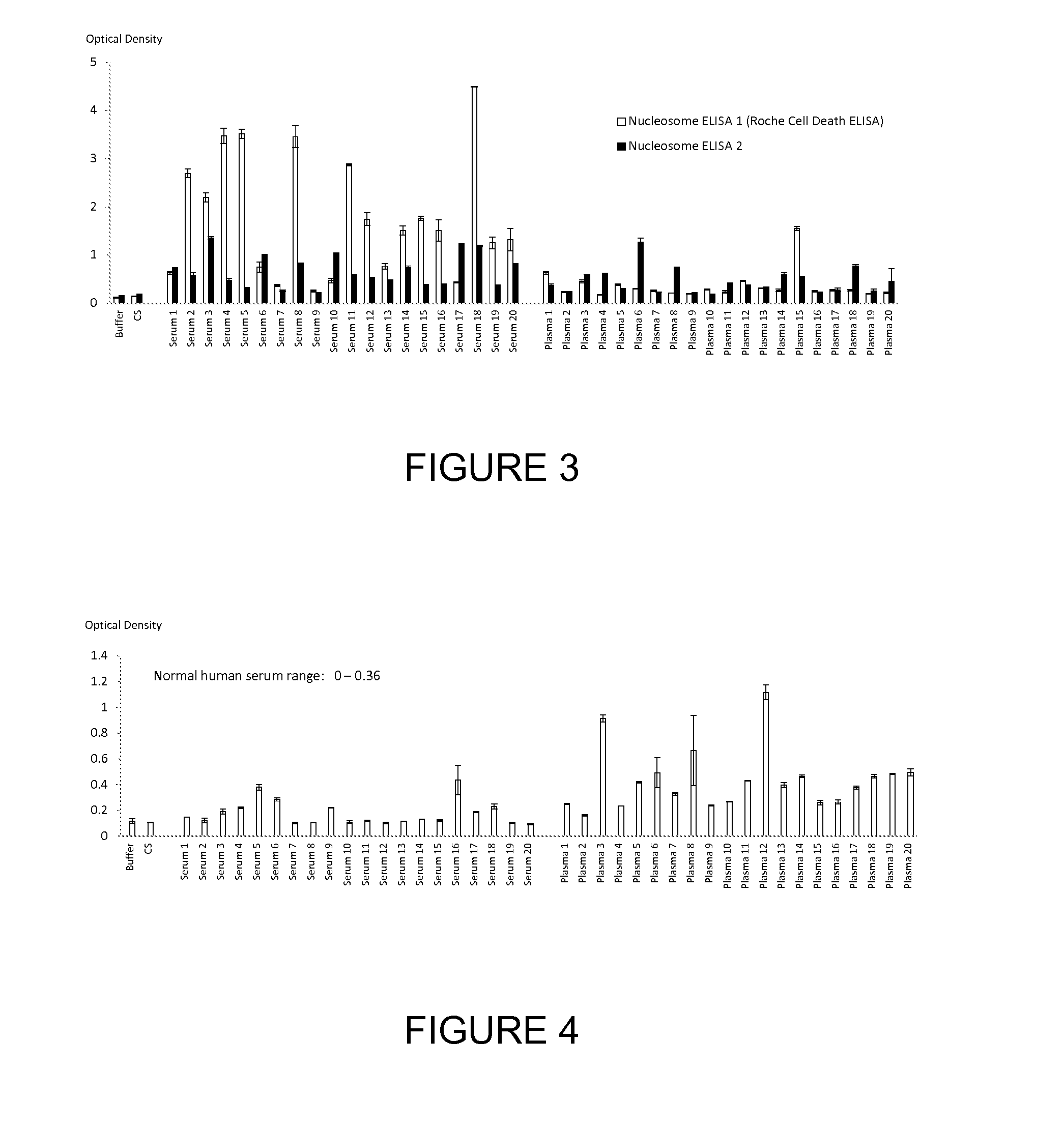
A nucleosome is a fundamental unit of DNA packaging in eukaryotes, consisting of a segment of DNA wound in sequence around eight histone protein cores. This structure is often compared to thread wrapped around a spool.
Enrichment of circulating fetal DNA
InactiveUS20070243549A1High accuracy of resultsMicrobiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against animals/humansNon invasiveMolecular diagnostics
A non-invasive screening or diagnostic method for determining the likelihood of a fetus with a genetic abnormality or a potential pregnancy complication, which utilizes a liquid blood sample from a pregnant woman. Antibodies specific to a section of histone 3.1 which is exposed to a far greater extent in chromatin of fetal origin than in chromatin of maternal origin are used to sequester and isolate such fetal nucleosomes including the associated fetal DNA. Following isolation / enrichment of such fetal DNA, genetic analysis is carried out using known molecular diagnostics.
Owner:BAYLOR COLLEGE OF MEDICINE
Method enabling use of extracellular RNA extracted from plasma or serum to detect, monitor or evaluate cancer
InactiveUS20020106684A1Low tumor burdenImmunologic function is relatively intactSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementA lipoproteinNeoplasm
This invention relates to the use of tumor-derived or associated extracellular ribonucleic acid (RNA) found circulating in the plasma or serum fraction of blood for the detection, monitoring, or evaluation of cancer or premalignant conditions. Extracellular RNA may circulate as non-bound RNA, protein-bound RNA, lipid-RNA complexes, lipoprotein (proteolipid)-RNA complexes, protein-RNA complexes including within or in association with ribonucleoprotein complexes, nucleosomes, or within apoptotic bodies. Any intracellular RNA found in plasma or serum can additionally be detected by this invention. Specifically, this invention enables the extraction of circulating RNA from plasma or serum and utilizes nucleic acid amplification assays for the identification, detection, inference, monitoring, or evaluation of any neoplasm, benign, premalignant, or malignant, in humans or other animals, which might be associated with that RNA. Further, this invention allows the qualitative or quantitative detection of tumor-derived or associated extracellular RNA circulating in the plasma or serum of humans or animals with or without any prior knowledge of the presence of cancer or premalignant tissue.
Owner:ONCOMEDX
Methods for multi-resolution analysis of cell-free nucleic acids
ActiveUS9850523B1Improve capture efficiencyImprove detection accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationDiseaseMulti resolution analysis
The present disclosure provides a method for enriching for multiple genomic regions using a first bait set that selectively hybridizes to a first set of genomic regions of a nucleic acid sample and a second bait set that selectively hybridizes to a second set of genomic regions of the nucleic acid sample. These bait set panels can selectively enrich for one or more nucleosome-associated regions of a genome, said nucleosome-associated regions comprising genomic regions having one or more genomic base positions with differential nucleosomal occupancy, wherein the differential nucleosomal occupancy is characteristic of a cell or tissue type of origin or disease state.
Owner:GUARDANT HEALTH
Method Enabling the Use of Extracellular Ribonucleic Acid (RNA) Extracted from Plasma or Serum to Detect, Monitor or Evaluate Cancer or Premalignant Conditions
InactiveUS20080261292A1Assess prognosisPredict prognosisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNeoplasmCirculating RNA
This invention relates to the use of tumor-derived or associated extracellular ribonucleic acid (RNA) found circulating in the plasma or serum fraction of blood for the detection, monitoring, or evaluation of cancer or premalignant conditions. Extracellular RNA may circulate as non-bound RNA, protein-bound RNA, lipid-RNA complexes, lipoprotein (proteolipid)-RNA complexes, protein-RNA complexes including within or in association with ribonucleoprotein complexes, nucleosomes, or within apoptotic bodies. Any intracellular RNA found in plasma or serum can additionally be detected by this invention. Specifically, this invention enables the extraction of circulating RNA from plasma or serum and utilizes nucleic acid amplification assays for the identification, detection, inference, monitoring, or evaluation of any neoplasm, benign, premalignant, or malignant, in humans or other animals, which might be associated with that RNA. Further, this invention allows the qualitative or quantitative detection of tumor-derived or associated extracellular RNA circulating in the plasma or serum of humans or animals with or without any prior knowledge of the presence of cancer or premalignant tissue.
Owner:ONCOMEDX
Levels and/or Sustainability of DNA-based Gene Expression
InactiveUS20090311786A1Easy to testImproving level and sustainabilityGenetic material ingredientsTissue cultureBiotechnologyDNA
The invention encompasses methods for improving the level and / or sustainability of expression for a target nucleic acid in a eukaryotic cell comprising: (a) modifying the target nucleic acid to introduce or to comprise signals that limit or constrain the positions of nucleosome cores, and (b) introducing the modified target nucleic acid into the eukaryotic cell, wherein the modified target nucleic acid has improved levels and / or sustainability of expression compared to original unmodified nucleic acid.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Method for detecting nucleosome adducts
The invention relates to a method for detecting and measuring the presence of nucleosome-protein adducts and the use of such measurements for the detection and diagnosis of disease. The invention also relates to a method of identifying nucleosome adduct biomarkers for the detection and diagnosis of disease and to biomarkers identified by said method.
Owner:SINGAPORE VOLITION PTE LTD
Method for detecting nucleosomes
The invention relates to a method for detecting and measuring the presence of mono-nucleosomes and oligo-nucleosomes and the use of such measurements for the detection and diagnosis of disease.
Owner:SINGAPORE VOLITION PTE LTD +1
Tumor screening kit based on high-throughput sequencing technology for free DNA in peripheral blood plasma and system and method of tumor screening kit
ActiveCN110272985AOvercome limitationsEnable non-invasive screeningMicrobiological testing/measurementSequence analysisInformation analysisBlood plasma
Owner:广州市雄基生物信息技术有限公司
Preparation of circulating tumor free DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) standard product for simulating plasma matrix
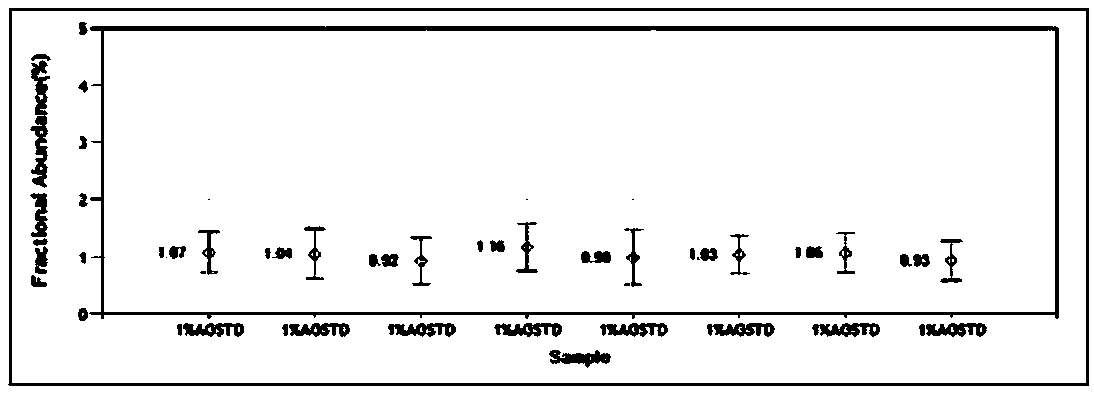
InactiveCN109055487AArbitrarily set gene mutation frequencyMicrobiological testing/measurementHuman bodyEnzyme digestion
The invention provides preparation of a circulating tumor free DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) standard product for a simulating plasma matrix. The preparation comprises the following steps of A, purchasing a natural cell line carrying gene mutation, or editing the gene to obtain a cell line carrying the gene mutation; B, cracking a wild cell line and a gene mutation cell line, and obtaining fragmented DNA by a nucleosome enzyme digestion or ultrasonic intercepting method; mixing the fragmented DNA of the wild cell line and one or multiple fragmented DNA of the gene mutation cell line according toa ratio, so that the mixture has the required gene mutation points and mutation frequency; D, preparing simulating plasma; E, feeding the mixture in step D into the simulating plasma, fully and uniformly mixing, and verifying the property. The preparation has the advantages that a standard product of a ctDNA sample approximate to a natural sample of the human body is provided, and a standard reference substance is provided for a circulating tumor free DNA detection platform, development of detection reagents, and evaluation on laboratory detection ability.
Owner:苏州她他基因科技有限公司
Method enabling use of extracellular RNA extracted from plasma or serum to detect, monitor or evaluate cancer
InactiveUS20020155469A1Predict prognosisHigh sensitivitySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLipid formationCirculating RNA
Owner:ONCOMEDX
Method enabling use of extracellular RNA extracted from plasma or serum to detect, monitor or evaluate cancer
InactiveUS20080050783A1Assess prognosisPredict prognosisSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLipid formationNeoplasm
This invention relates to the use of tumor-derived or associated extracellular ribonucleic acid (RNA) found circulating in the plasma or serum fraction of blood for the detection, monitoring, or evaluation of cancer or premalignant conditions. Extracellular RNA may circulate as non-bound RNA, protein-bound RNA, lipid-RNA complexes, lipoprotein (proteolipid)-RNA complexes, protein-RNA complexes including within or in association with ribonucleoprotein complexes, nucleosomes, or within apoptotic bodies. Any intracellular RNA found in plasma or serum can additionally be detected by this invention. Specifically, this invention enables the extraction of circulating RNA from plasma or serum and utilizes nucleic acid amplification assays for the identification, detection, inference, monitoring, or evaluation of any neoplasm, benign, premalignant, or malignant, in humans or other animals, which might be associated with that RNA. Further, this invention allows the qualitative or quantitative detection of tumor-derived or associated extracellular RNA circulating in the plasma or serum of humans or animals with or without any prior knowledge of the presence of cancer or premalignant tissue.
Owner:ONCOMEDX
Method enabling use of extracellular RNA extracted from plasma or serum to detect, monitor or evaluate cancer
InactiveUS20070009934A1Assess prognosisMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationLipid formationCirculating RNA
This invention relates to the use of tumor-derived or associated extracellular ribonucleic acid (RNA) found circulating in the plasma or serum fraction of blood for the detection, monitoring, or evaluation of cancer or premalignant conditions. Extracellular RNA may circulate as non-bound RNA, protein-bound RNA, lipid-RNA complexes, lipoprotein (proteolipid)—RNA complexes, protein-RNA complexes including within or in association with ribonucleoprotein complexes, nucleosomes, or within apoptotic bodies. Any intracellular RNA found in plasma or serum can additionally be detected by this invention. Specifically, this invention enables the extraction of circulating RNA from plasma or serum and utilizes nucleic acid amplification assays for the identification, detection, inference, monitoring, or evaluation of any neoplasm, benign, premalignant, or malignant, in humans or other animals, which might be associated with that RNA. Further, this invention allows the qualitative or quantitative detection of tumor-derived or associated extracellular RNA circulating in the plasma or serum of humans or animals with or without any prior knowledge of the presence of cancer or premalignant tissue.
Owner:KOPRESKI MICHAEL
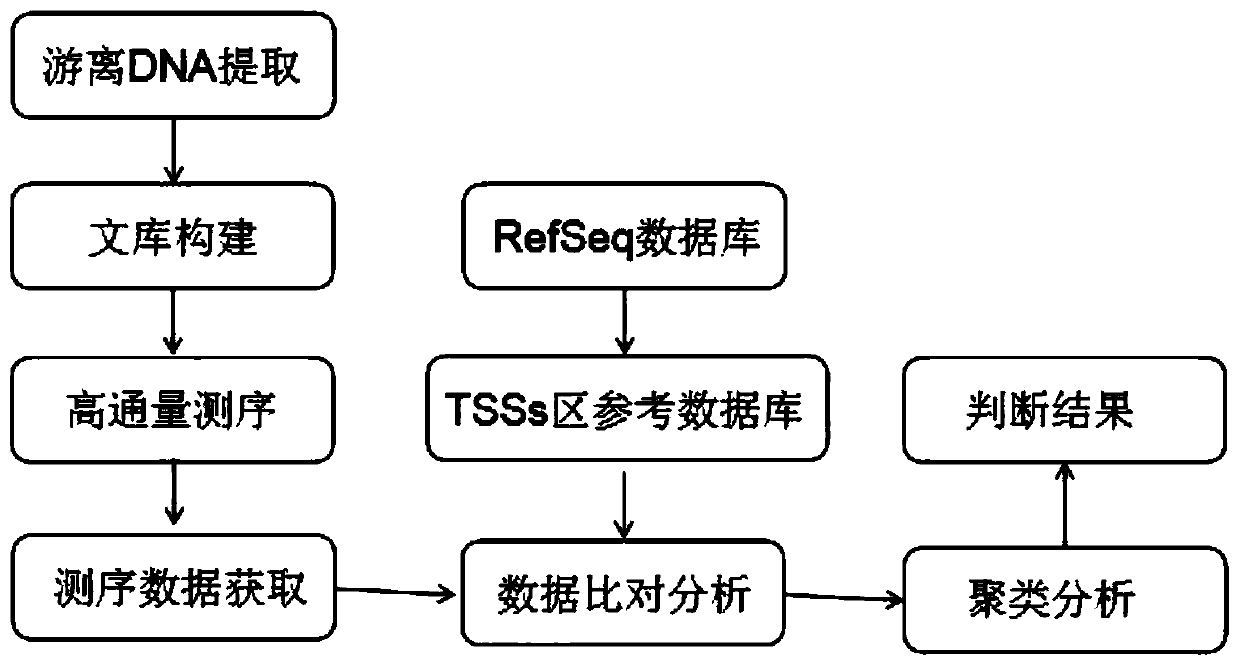
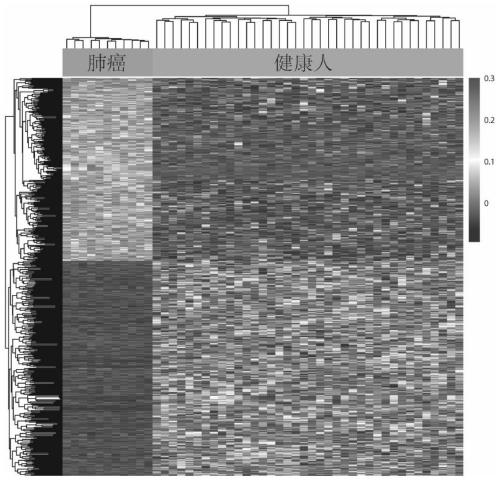
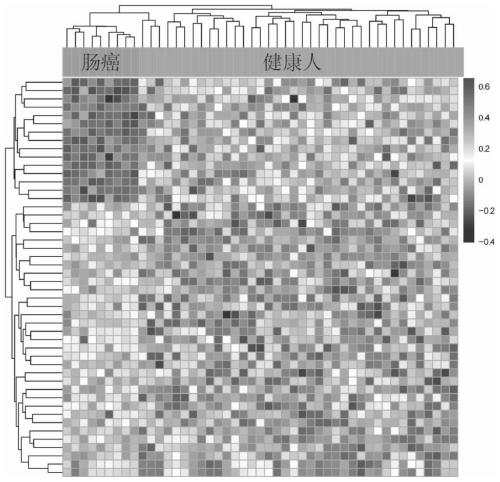
Cluster analysis method based on peripheral blood plasma free DNA nucleosome footprint difference, and application thereof
InactiveCN110189798AAvoid dependenceIncrease coverageBiostatisticsSequence analysisSample sequenceNucleosome
The invention discloses a cluster analysis method based on a peripheral blood plasma free DNA nucleosome footprint difference, and an application thereof. The method comprises the steps of (1), acquiring peripheral blood plasma free DNA high-flux sequencing data; (2), constructing a standard nucleosome positioning area database; (3), performing comparative analysis on each sample sequencing data and the standard nucleosome positioning area database; (4), screening coverage data of the nucleosome footprint difference and performing standardizing; and (5), performing cluster analysis on the standardized data by means of a hierarchical clustering method according to correlation between the samples. The method according to the invention has advantages of effectively preventing dependence of anexisting method to tissues or cells, comprehensively improving depth and accuracy in high-flux sequencing data analysis, realizing noninvasive radiotherapy and chemotherapy sensitivity prediction toa tumor patient, and realizing high comprehensiveness, high accuracy and high coverage. The method belongs to the field of biotechnology.
Owner:广州市雄基生物信息技术有限公司
Methylation analysis method and device for active region of circulating cell-free nucleosome, terminal equipment and storage medium
ActiveCN112735531AAuxiliary early diagnosisAid early screeningProteomicsGenomicsCell freeTerminal equipment
The invention provides a methylation analysis method and device for an active region of circulating cell-free nucleosome, terminal equipment and a storage medium, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining capture sequencing data of a to-be-detected plasma sample, and extracting cfDNA molecular fragments from the capture sequencing data; based on the extracted cfDNA molecular fragments, adopting windows to perform sliding operation in genome intervals of the cfDNA molecular fragments, and calculating the ratio of the number of cfDNA molecules crossing the whole window end to end in each window to the number of all cfDNA molecules in different conditions covered by the window; based on the calculated ratio, screening out an interval having significant difference with a baseline nucleosome activity difference area created according to the healthy person sample through a Kolmonov Schmidov test method to obtain a nucleosome activity area; calculating the methylation phenotypic characteristics of the screened nucleosome active area, completing methylation analysis of the circulating acellular nucleosome active area. The method can effectively assist in distinguishing the source of the plasma sample to be detected.
Owner:臻和(北京)生物科技有限公司 +1
Polypeptide and application thereof to preparation of medicament for treatment and/or prevention of tumor
ActiveCN107474115ASignificant effectSmall toxicityPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptidesSide chainMedicine
The invention provides a polypeptide and an application thereof to preparation of medicament for treatment and / or prevention of tumor. An amino acid sequence of the polypeptide is shown in a sequence table SEQ ID No.1, or shown in the sequence table SEQ ID No.1 amino acid sequence with two or more amino acids substituted by unnatural amino acids with connectable side chains, and a derivative comprises a chimeric peptide formed by connection of the polypeptide and a cell-penetrating peptide, a fusogenic peptide formed by the polypeptide and a virus, a methylated polypeptide, a glycosylated polypeptide, and a pegylated polypeptide. The polypeptide or the polypeptide derivative can targetedly increase number of PML nucleosomes, and can be applied to preparation of medicament for treatment and / or prevention of tumor.
Owner:胡卓伟
Cancer detection model and construction method and kit thereof
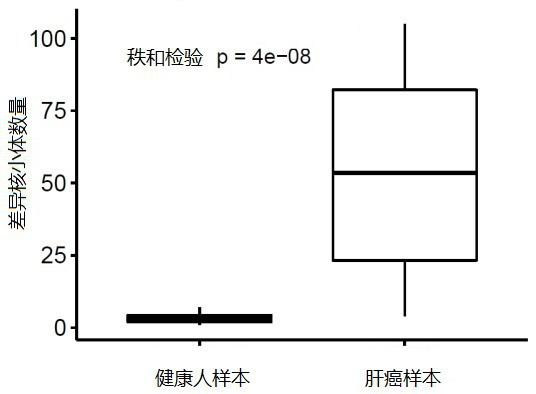
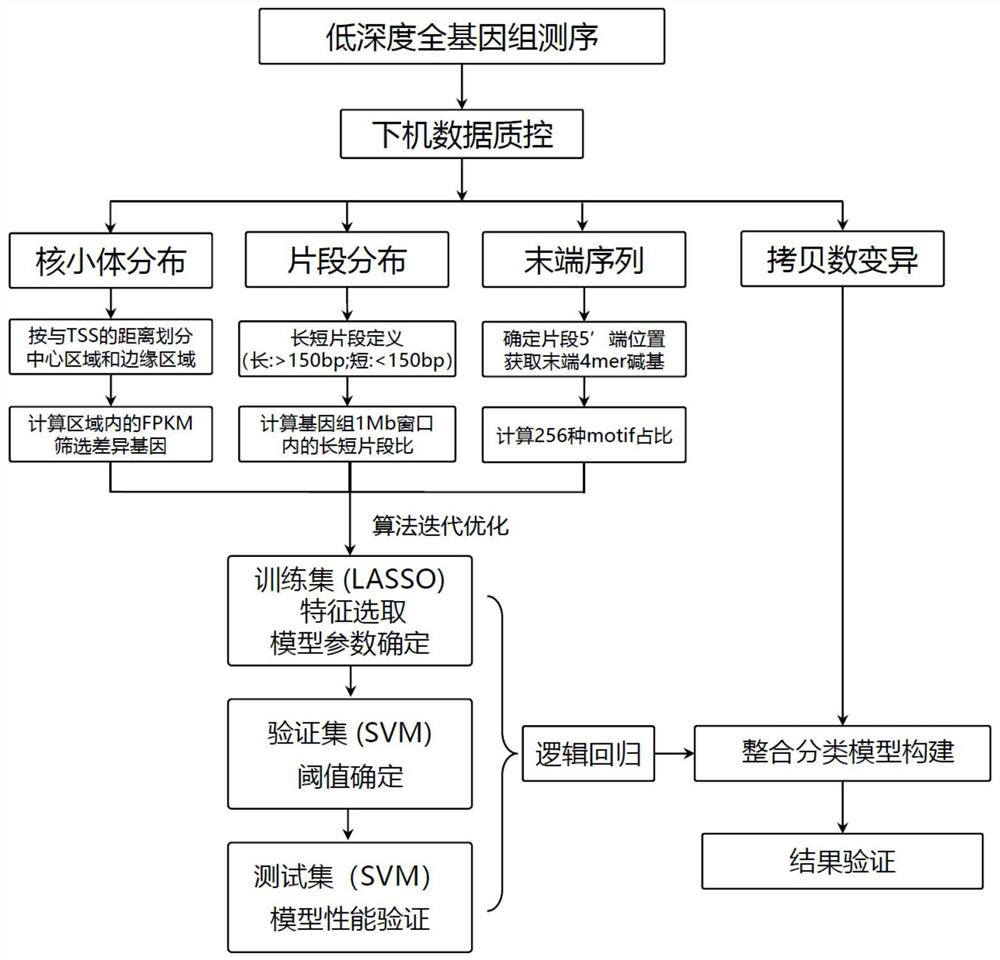
PendingCN113838533AImprove efficiencyImprove accuracyBiostatisticsProteomicsWhole genome sequencingCancer detection
The invention discloses a cancer detection model, a construction method thereof and a kit, and relates to the technical field of cancer detection. The method comprises the following steps: excavating nucleosome distribution characteristics, terminal sequence characteristics and fragment size distribution characteristics which can be applied to cancer detection through whole genome sequencing of plasma free DNA; constructing a classification model of the three indexes to obtain a prediction score of each index for a sample, and then using a logic regression model to integrate the scores and add copy number variation feature information to obtain a final classification prediction model. According to the cancer detection model, the efficiency and accuracy of cancer detection are remarkably improved, the amount of data needed for analysis is small, the detection cost is low, different cancers can be detected, and the cancer detection model is suitable for analyzing and predicting tumors in all periods. In addition, the kit provided by the invention can complete detection of indexes required by a detection model, so the kit can be innovatively applied to the field of cancers in ctDNA detection.
Owner:BERRY ONCOLOGY CO LTD
New method for capturing chromatin nucleosome vacancy district at high-throughput complete genome level and use therefor
InactiveCN102691111AMicrobiological testing/measurementLibrary creationTranscriptional regulationFunctional genomics
The invention relates to a new method for high-efficiently capturing a chromatin nucleosome vacancy district at a whole-cell level. The new method can locate the chromatin nucleosome vacancy district more accurately and sensitively in the range of a complete genome. The method for capturing the chromatin nucleosome vacancy district at a high-throughput complete genome level can be used to search the chromatin nucleosome vacancy district of the transcriptional regulation of eukaryotic cells, and is an effective means for functional genomics research.
Owner:CAPITAL UNIVERSITY OF MEDICAL SCIENCES
Combinatorial single molecule analysis of chromatin
ActiveUS20190284603A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingMolecular analysisNucleosome
The present invention provides for single-molecule profiling of combinatorial protein modifications and single-molecule profiling of combinatorial protein modifications combined with single-molecule sequencing of protein / nucleic acids complexes. High-throughput single-molecule imaging was applied to decode combinatorial modifications on millions of individual nucleosomes from pluripotent stem cells and lineage-committed cells. Applicants identified bivalent nucleosomes with concomitant repressive and activating marks, as well as other combinatorial modification states whose prevalence varies with developmental potency. Applying genetic and chemical perturbations of chromatin enzymes show a preferential affect on nucleosomes harboring specific modification states. The present invention also combines this proteomic platform with single-molecule DNA sequencing technology to simultaneously determine the modification states and genomic positions of individual nucleosomes. This novel single-molecule technology can be used to address fundamental questions in chromatin biology and epigenetic regulation leading to novel therapeutics and diagnostics.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP +1
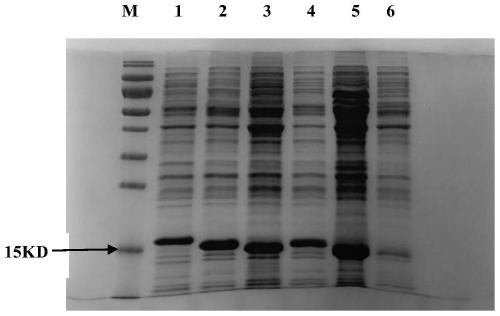
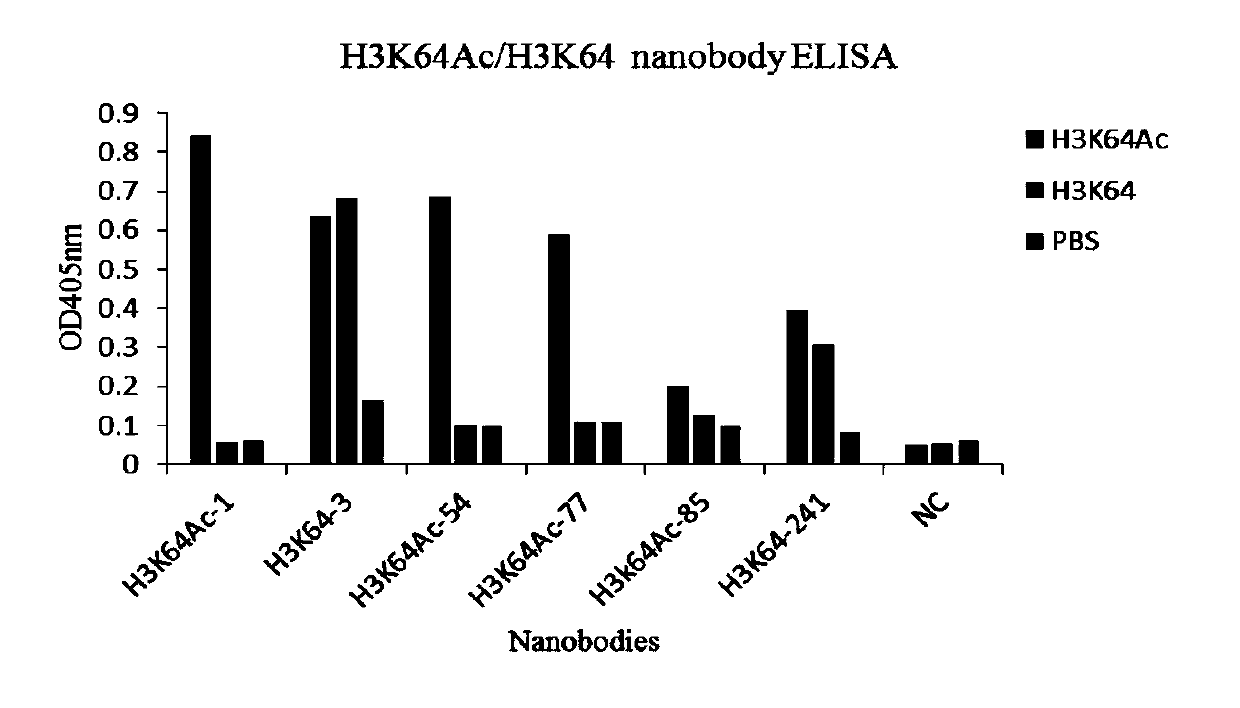
Nano-antibody aiming at H3K64Ac/H3K64 fragments and application thereof
ActiveCN109734804AReduce research costsImmunoglobulins against animals/humansBiological testingNucleosome CoreAntibody
The invention relates to the field of biotechnology and biomedicine, and relates to a nano-antibody aiming at H3K64Ac / H3K64 fragments and application thereof. Specifically, a VHH chain of the nano-antibody of the anti-histone 3 64 lysine acetylation (H3K64Ac) fragment has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:33 or SEQ ID NO:34 or SEQ ID NO:35 or SEQ ID NO:36. A VHH chain of the nano-antibody of the anti-histone 3 64 lysine non-modified (H3K64) fragment has an amino acid sequence shown in SEQ ID NO:37 or SEQ ID NO:58. The nano-antibody is efficiently expressed through microorganisms. The molecular weight of the nano-antibody does not reach 1 / 10 that of a conventional antibody, and therefore research on the nucleosome core region H3K64 acetylation site biological functions can be achieved.
Owner:REGENECORE BIOTECH CO LTD
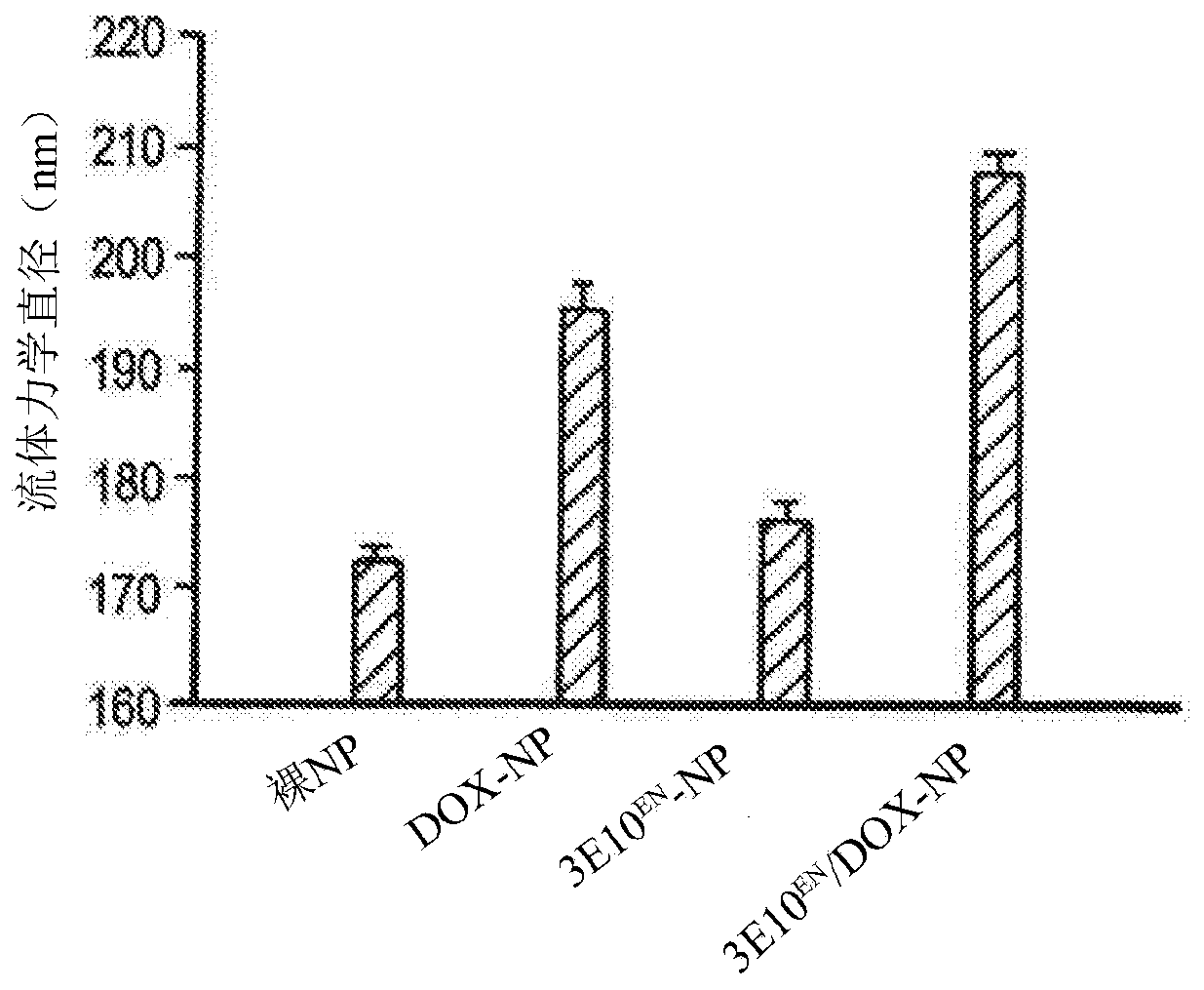
Antibody-mediated autocatalytic, targeted delivery of nanocarriers to tumors
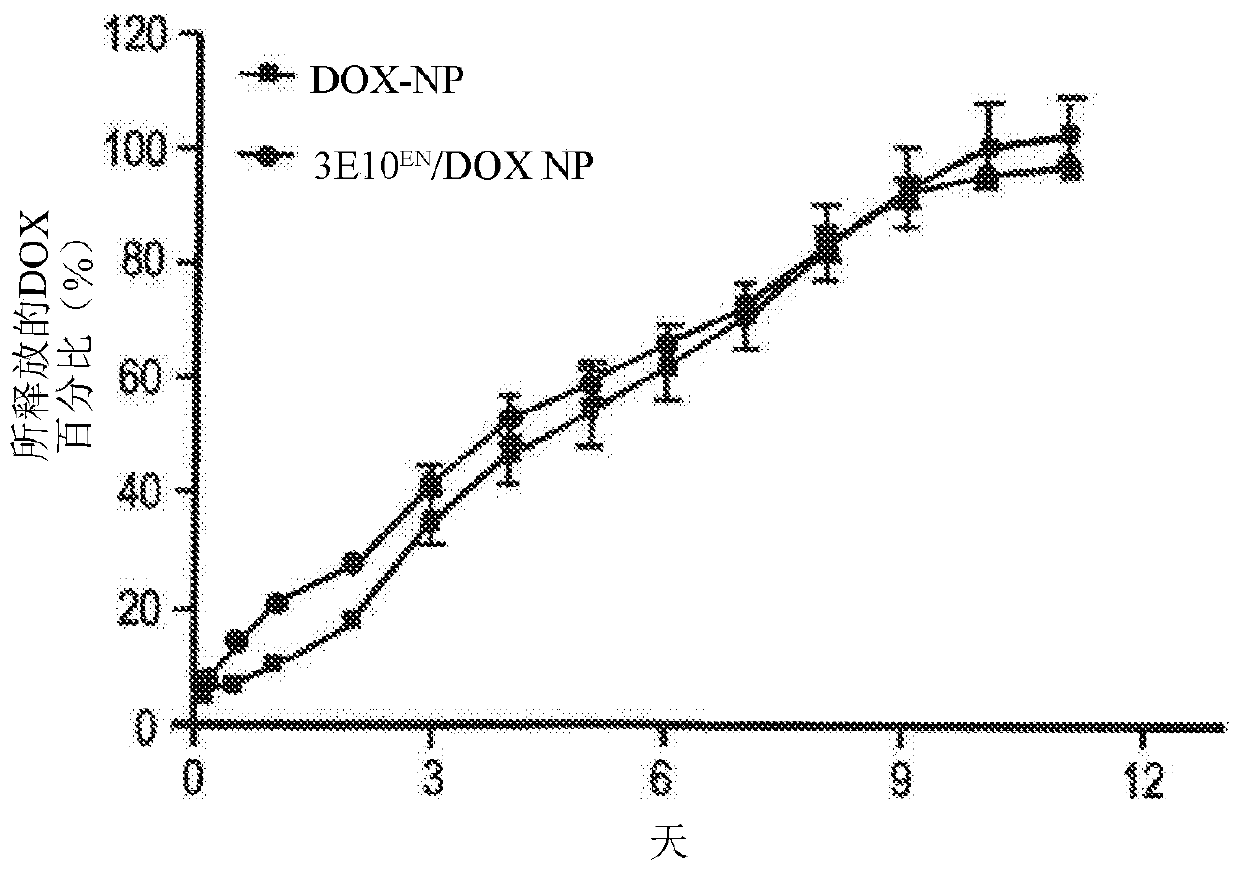
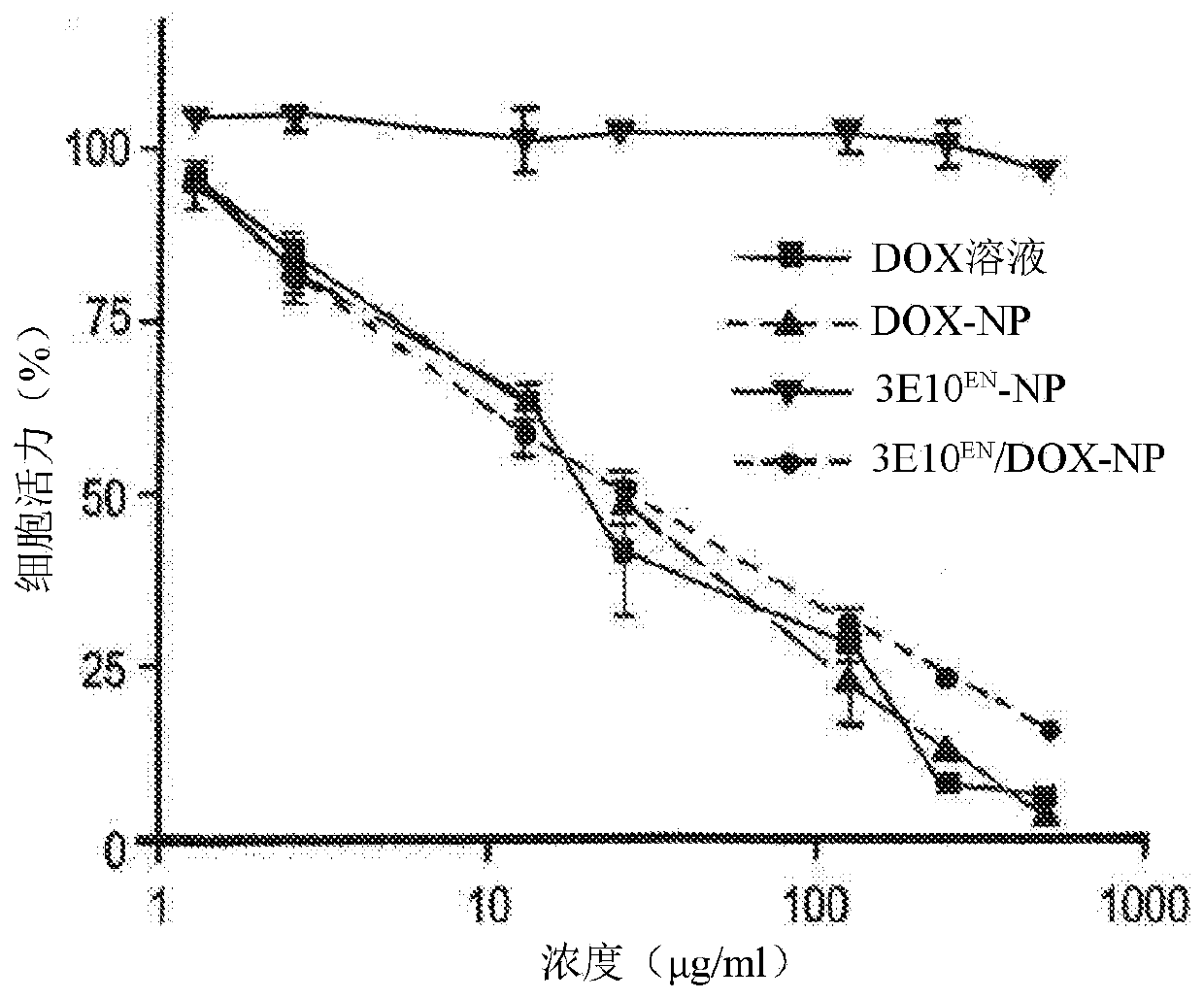
The present invention provides DNA-targeted nanocarriers for encapsulating an active agent and delivering it to extracellular DNA. The nanocarriers, for example, polymeric particles, liposomes, and multilamellar vesicles have targeting moiety that targets DNA conjugated thereto. The targeting moiety that targets DNA is typically an antibody, or variant, fragment, or fusion protein derived therefrom that binds to DNA or nucleosomes. The targeting moiety can be a circulating autoantibody that binds DNA such as those commonly found in patients with SLE. In some embodiments, the targeting moiety is antibody 3E10 or a variant, fragment, or fusion protein derived therefrom. Pharmaceutical compositions, methods of use, and dosage regimens are also provided.
Owner:YALE UNIV
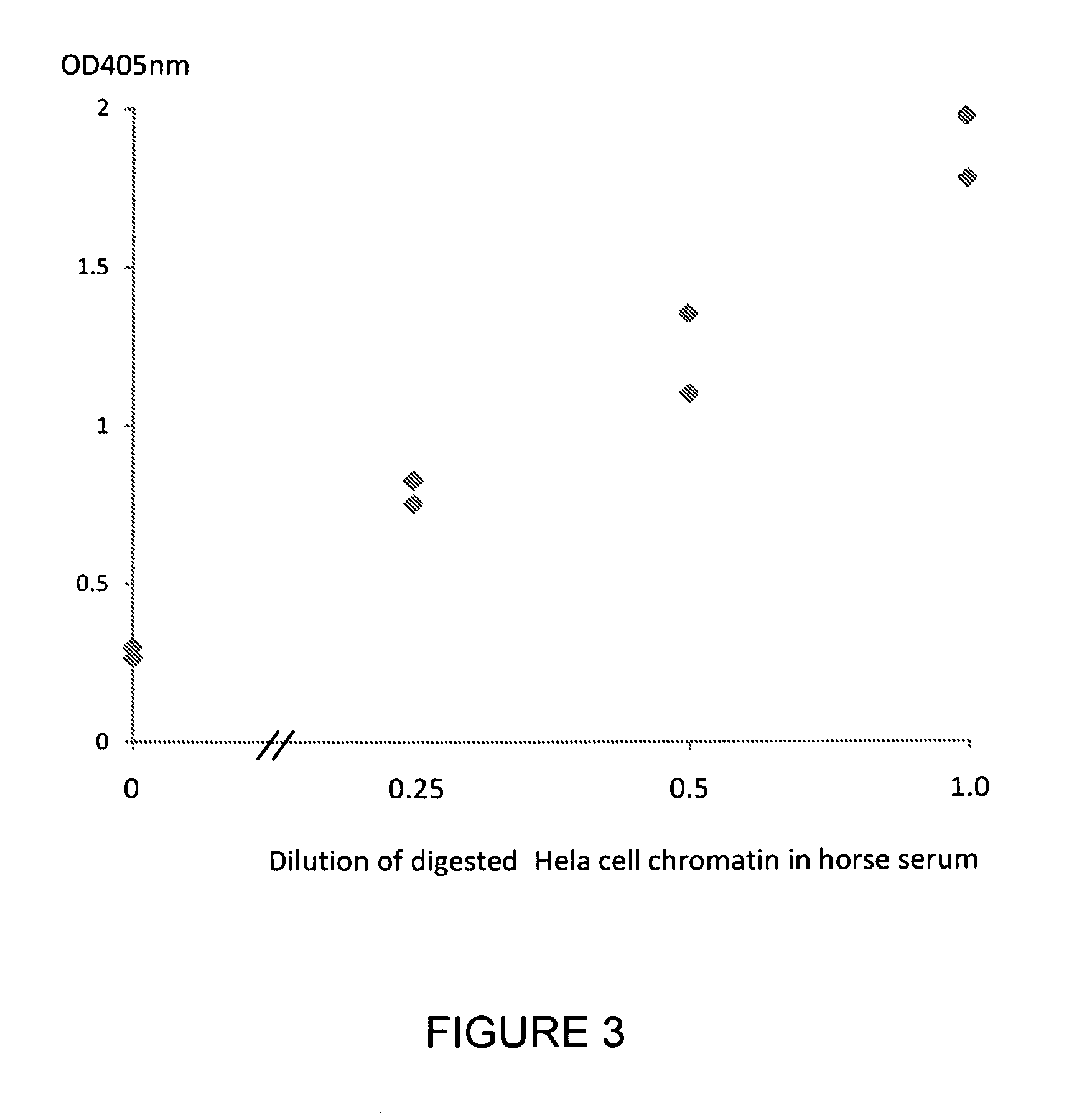
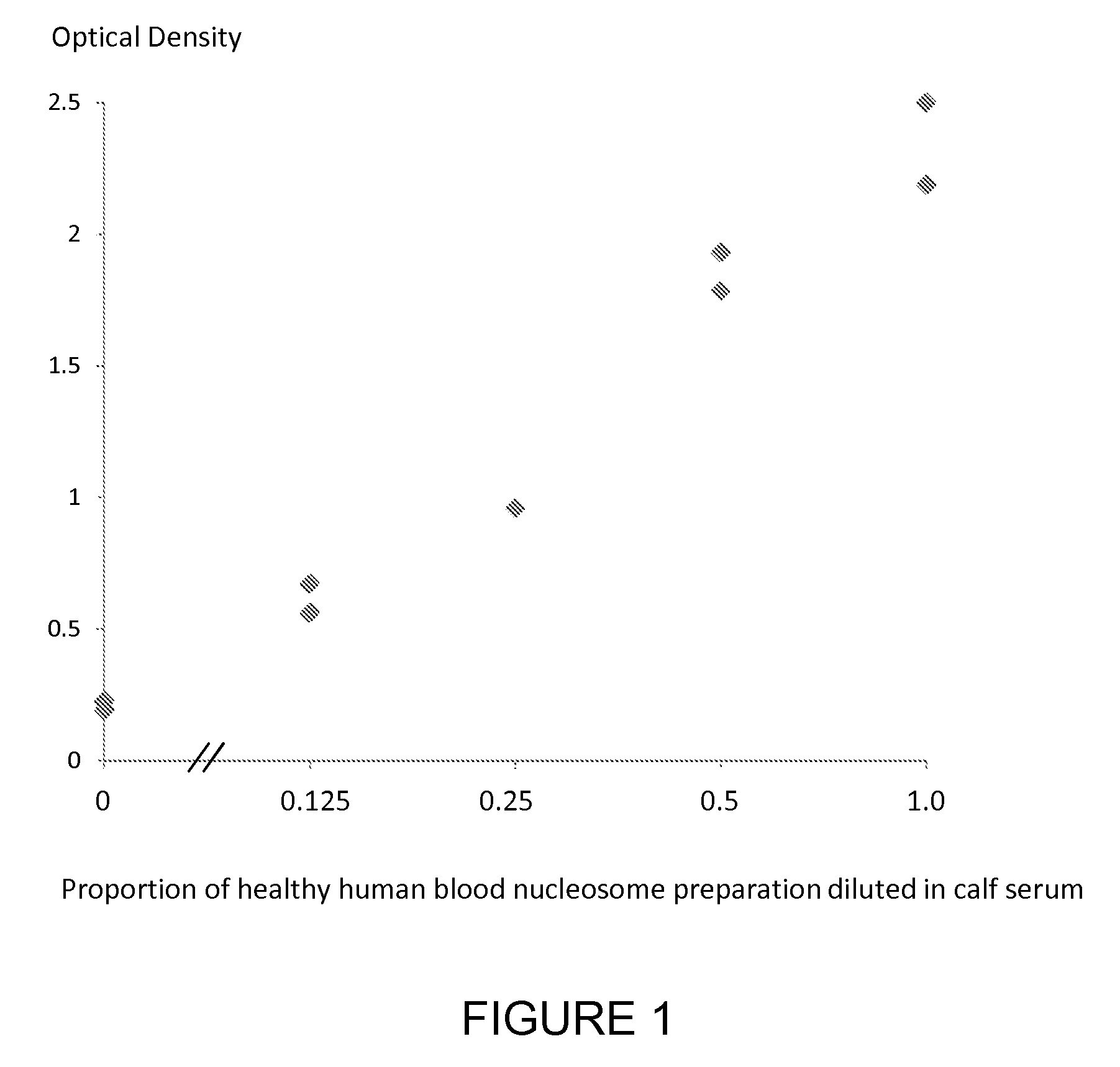
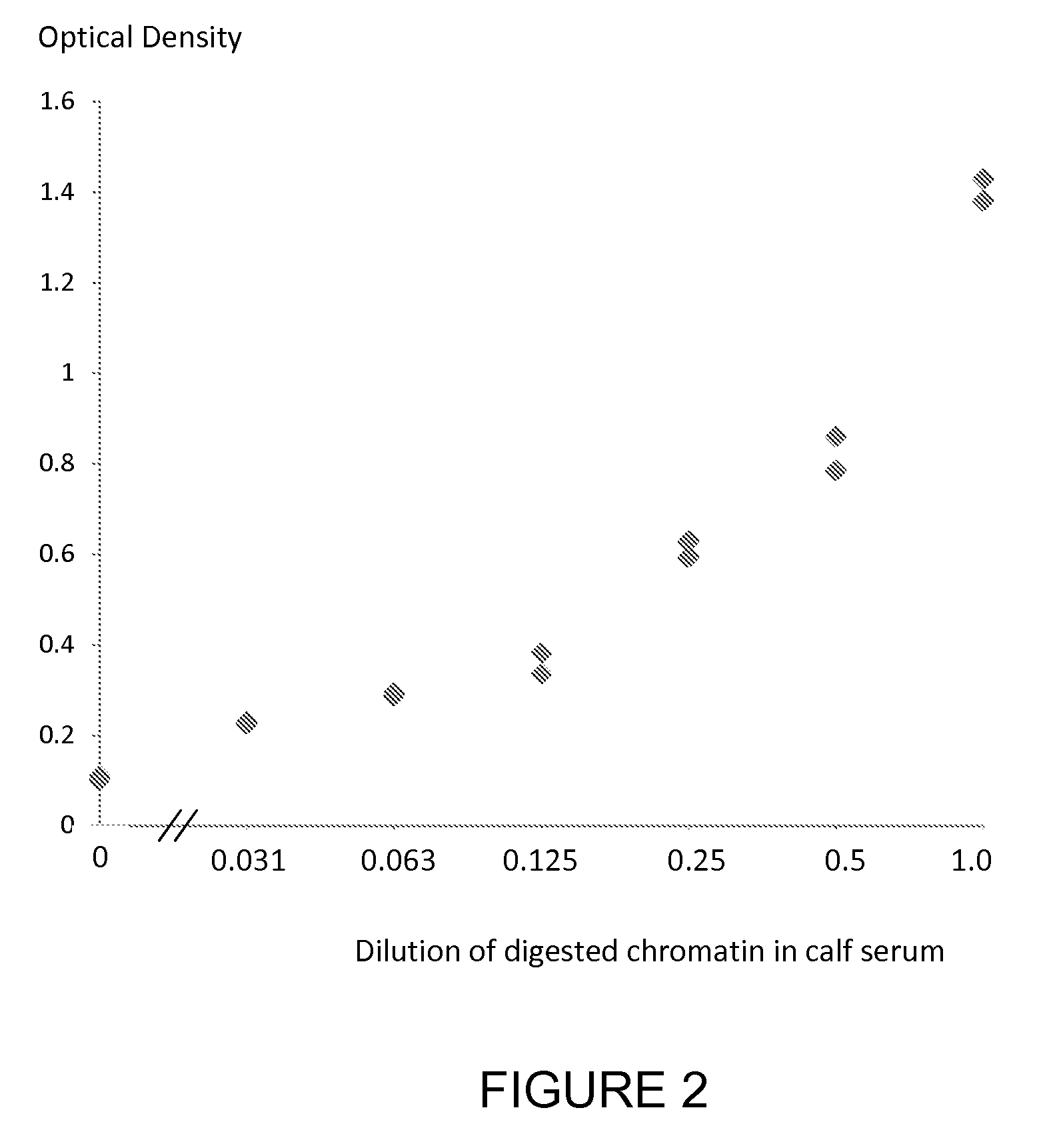
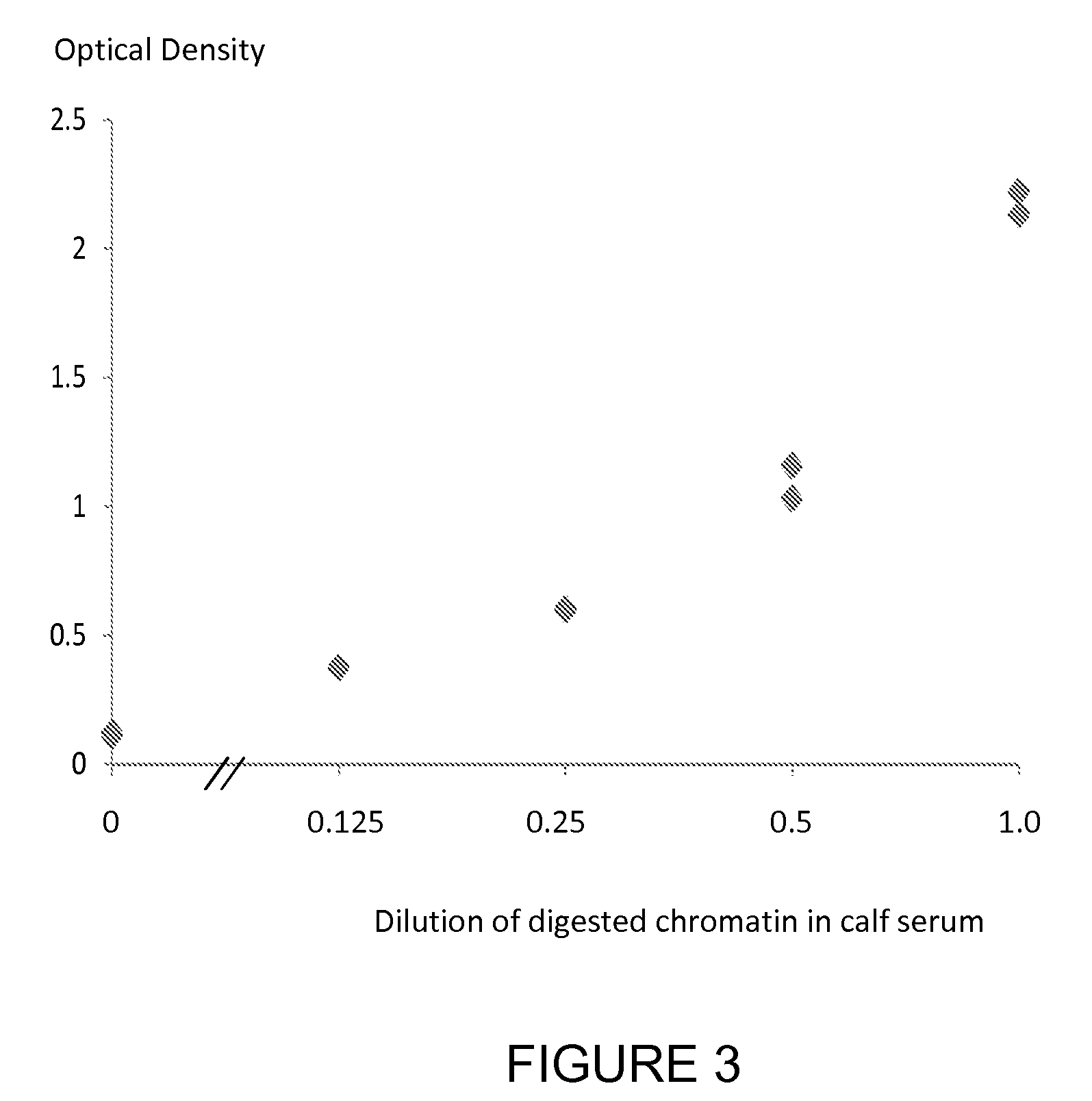
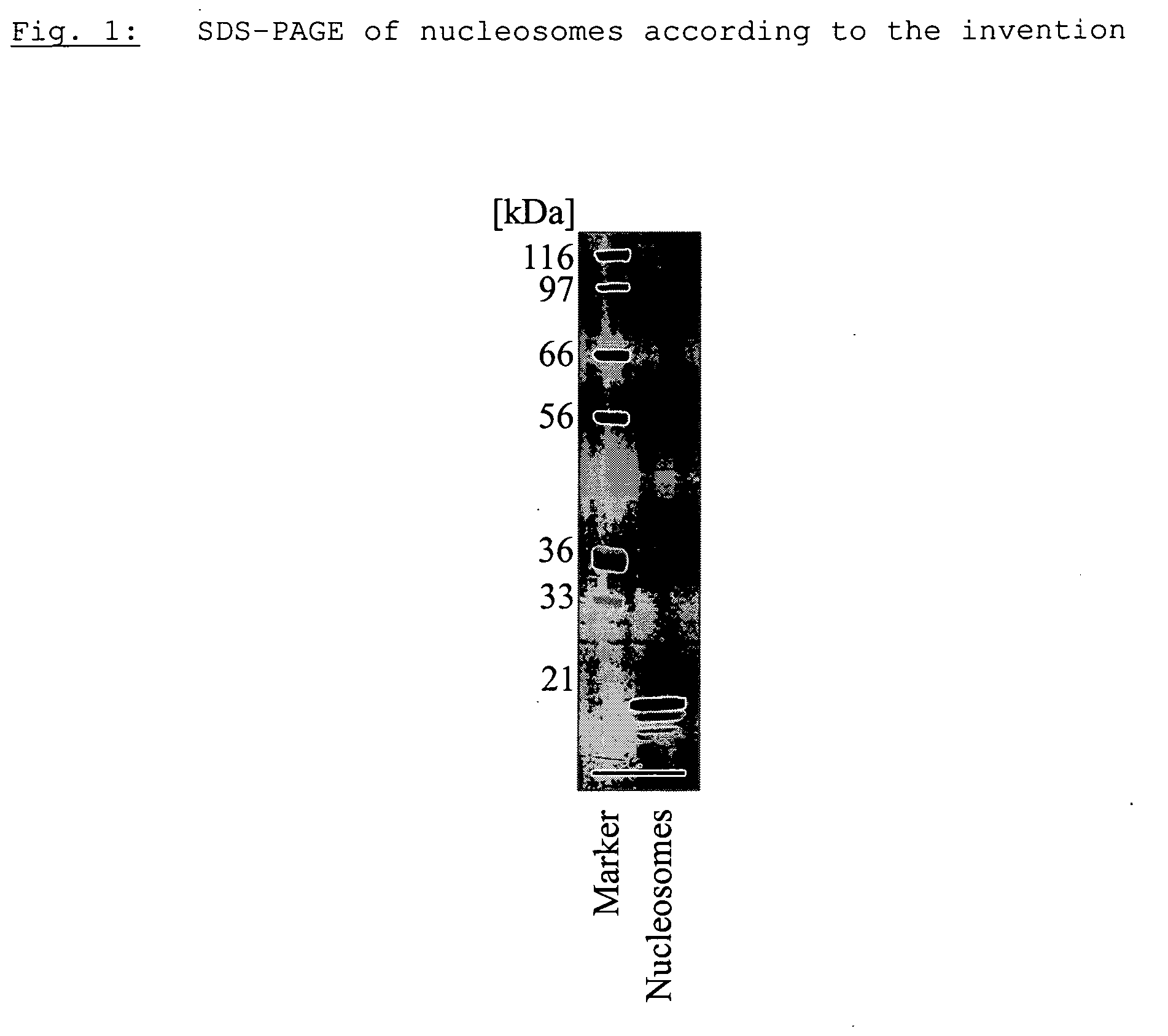
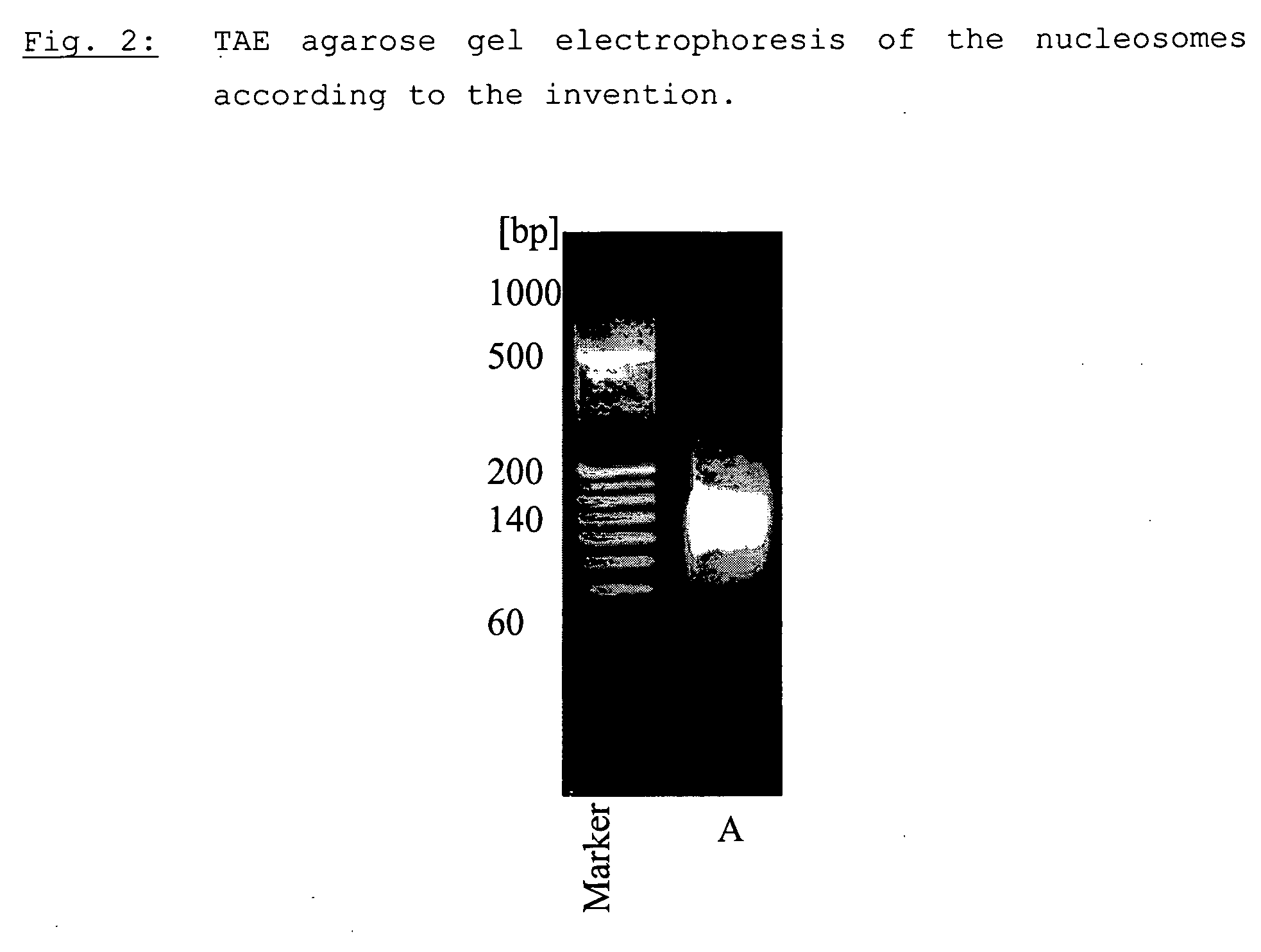
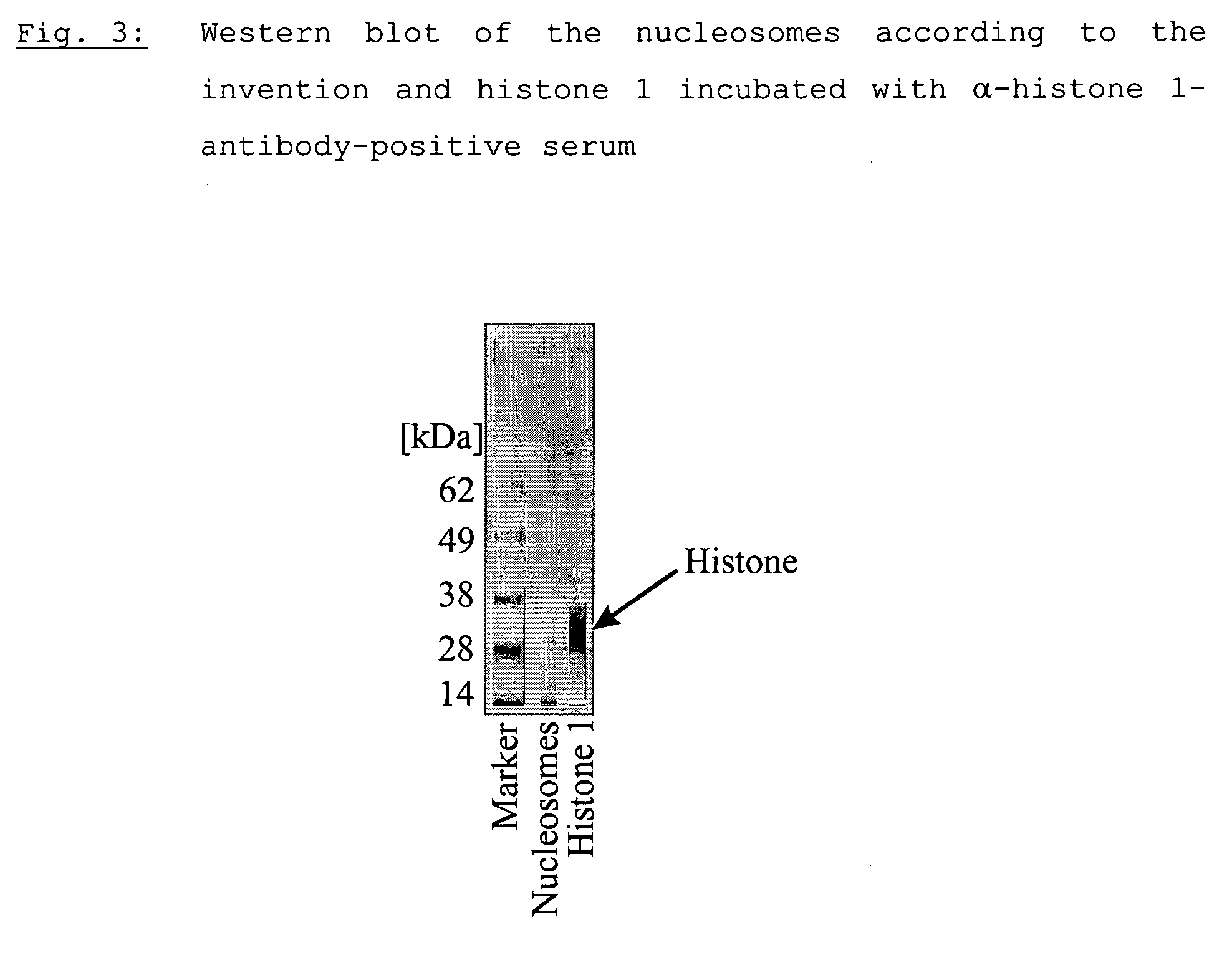
Method for producing a nucleosome preparation and use thereof in in vitro diagnosis of disseminated lupus erythematosus (dle)
InactiveUS20050233322A1Peptide/protein ingredientsMicroorganismsImmunofluorometric AssaysImmunofluorescence
The present invention relates to a method for producing a nucleosome preparation that is characterised by being suitable for use in immunofluorescence assays of specific antibodies directed against the nucleosomes in human samples and thus for a more specific diagnosis of disseminated lupus erythematosus (LED) compared with the state of the art.
Owner:EUROIMMUN MEDIZINISCHE LABORDIAGNOSTIKA
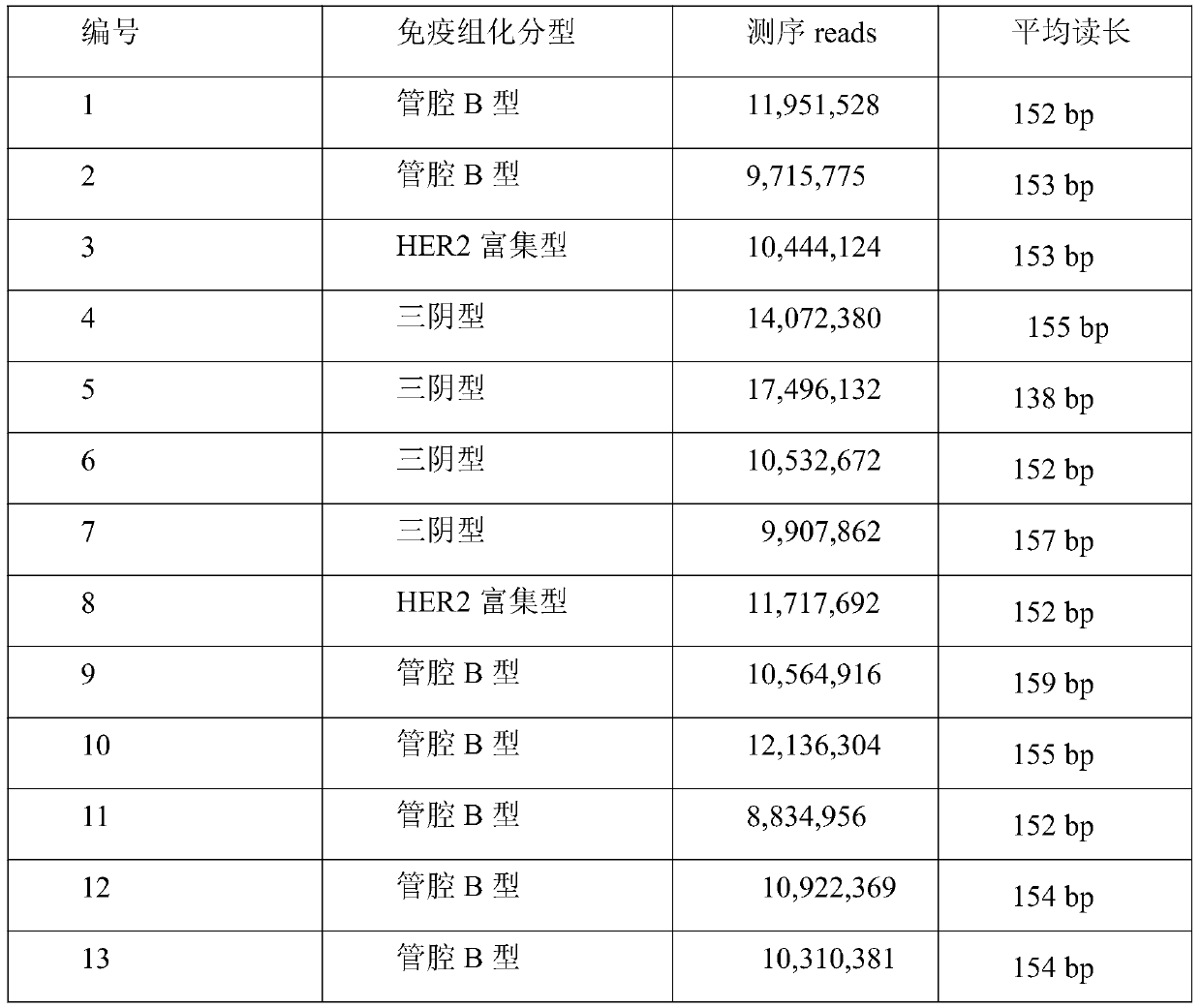
Noninvasive molecular subtyping kit and method for breast cancer
InactiveCN110106244AGood choiceEasy to get samplesMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsDiseaseCancer research
The invention provides a noninvasive molecular subtyping kit and method for a breast cancer and aims to provide a kit which is simple to use and high in detection accuracy and a noninvasive molecularsubtyping method for a breast cancer, which makes samples easy to obtain, is simple in sampling process, good in clinical experience, capable of achieving processized operation and very suitable for clinical application and non-disease diagnosis purposes. The technical scheme of the invention is that the noninvasive molecular subtyping kit for the breast cancer comprises a plasma free DNA extraction reagent, a library construction reagent, a sequencing reagent and a sequencing chip. The method is based on high-throughput sequencing data of plasma free DNA, nucleosome footprint difference information of a promoter region in the whole genome range in the plasma free DNA is obtained by means of bioinformatic analysis, and thus noninvasive molecular subtyping of four categories of a lumen A type, a lumen B type, an HER2 enrichment type and basal cell type of a breast cancer patient is achieved according to the difference of footprint information. The invention belongs to the technical field of biology.
Owner:广州市雄基生物信息技术有限公司
Methods for multi-resolution analysis of cell-free nucleic acids
ActiveUS11062791B2Improve capture efficiencyMaximizing of loadMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsMulti resolution analysisGenomic clone
The present disclosure provides a method for enriching for multiple genomic regions using a first bait set that selectively hybridizes to a first set of genomic regions of a nucleic acid sample and a second bait set that selectively hybridizes to a second set of genomic regions of the nucleic acid sample. These bait set panels can selectively enrich for one or more nucleosome-associated regions of a genome, said nucleosome-associated regions comprising genomic regions having one or more genomic base positions with differential nucleosomal occupancy, wherein the differential nucleosomal occupancy is characteristic of a cell or tissue type of origin or disease state.
Owner:GUARDANT HEALTH
Method for detecting nucleosomes
The invention relates to a method for detecting and measuring the presence of mono-nucleosomes and oligo-nucleosomes and the use of such measurements for the detection and diagnosis of disease.
Owner:SINGAPORE VOLITION PTE LTD +1
Method for detecting nucleosomes containing nucleotides
The invention relates to a method for detecting and measuring the presence of mono-nucleosomes and oligo-nucleosomes and nucleosomes that contain particular nucleotides and the use of such measurements for the detection and diagnosis of disease. The invention also relates to a method of identifying nucleosome associated nucleotide biomarkers for the detection and diagnosis of disease and to biomarkers identified by said method.
Owner:BELGIAN VOLITION SPRL
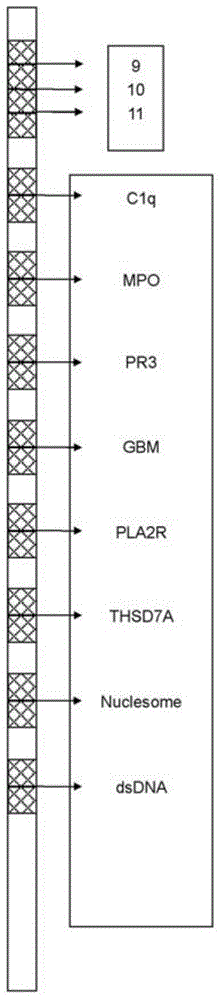
Immunoblotting kit for detecting autoimmune nephrosis and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN105823873AOvercoming Detection SensitivityOvercoming featureDisease diagnosisCelluloseDisease
The invention relates to an immunoblotting kit for detecting autoimmune nephrosis and a preparation method thereof, which belong to the field of biomedicine. The immunoblotting kit comprises a reaction membrane strip, an enzyme conjugate, a chromogenic substrate, a washing solution, a sample diluent and a stopping solution; the reaction membrane strip is composed of a carrier and a cellulose nitrate membrane or a nylon membrane which are fixed on the carrier, the cellulose nitrate membrane or the nylon membrane contains parallel detection lines specifically combined and coated by 4-8 kinds of natural or recombinant antigens in C1q, MPO, PR3, GBM, Nucleosome, dsDNA, PLA2R and YHSD7A, a strip of determination indication strip with high concentration being 30-50 [mu]L / mL, a strip of the determination indication strip with medium concentration being 15-25 [mu]L / mL, and a strip of the determination indication strip with low concentration being 1-10 [mu]L / mL. The kit can overcome the disadvantages of detection sensitivity and specificity of a single autoantibody as well as tedious operation for individually detecting several kinds of disease-associated autoantibodies, and can greatly increase the detection efficiency and result determination accuracy.
Owner:SHENZHEN YHLO BIOTECH
Use of cell-free nucleosomes as biomarkers in sputum samples
The invention relates to the use of a cell-free nucleosome as a biomarker in a sputum sample for the diagnosis or detection of cancer, adenoma, autoimmune disease or inflammatory disease. The invention also relates to methods of detecting said cell free nucleosomes in sputum samples, in particular in methods of diagnosis.
Owner:BELGIAN VOLITION SPRL
MNase digestion optimization method applied to nucleosome loci in tissue samples
InactiveCN108048543AEfficient acquisitionSpeed up the research processMicrobiological testing/measurementBiostatisticsEnzyme digestionBinding site
The invention relates to an MNase digestion optimization method applied to nucleosome loci in tissue samples. The MNase digestion optimization method includes chromatin preparation, DNA preparation, MNase digestion, DNA fragment recycle, high-throughput sequencing and frequency detection. The MNase digestion optimization method has the advantages that pre-collection methods for tissue cell nucleuses are improved, enzyme digestion reaction conditions are optimized, and enzyme digestion efficiency and recycle rate are increased; correct chromatin fragments can be acquired effectively, binding loci of regulation elements on whole genomes can be positioned and transcribed accurately, and research progresses of clinical samples are improved.
Owner:上海嘉因生物科技有限公司
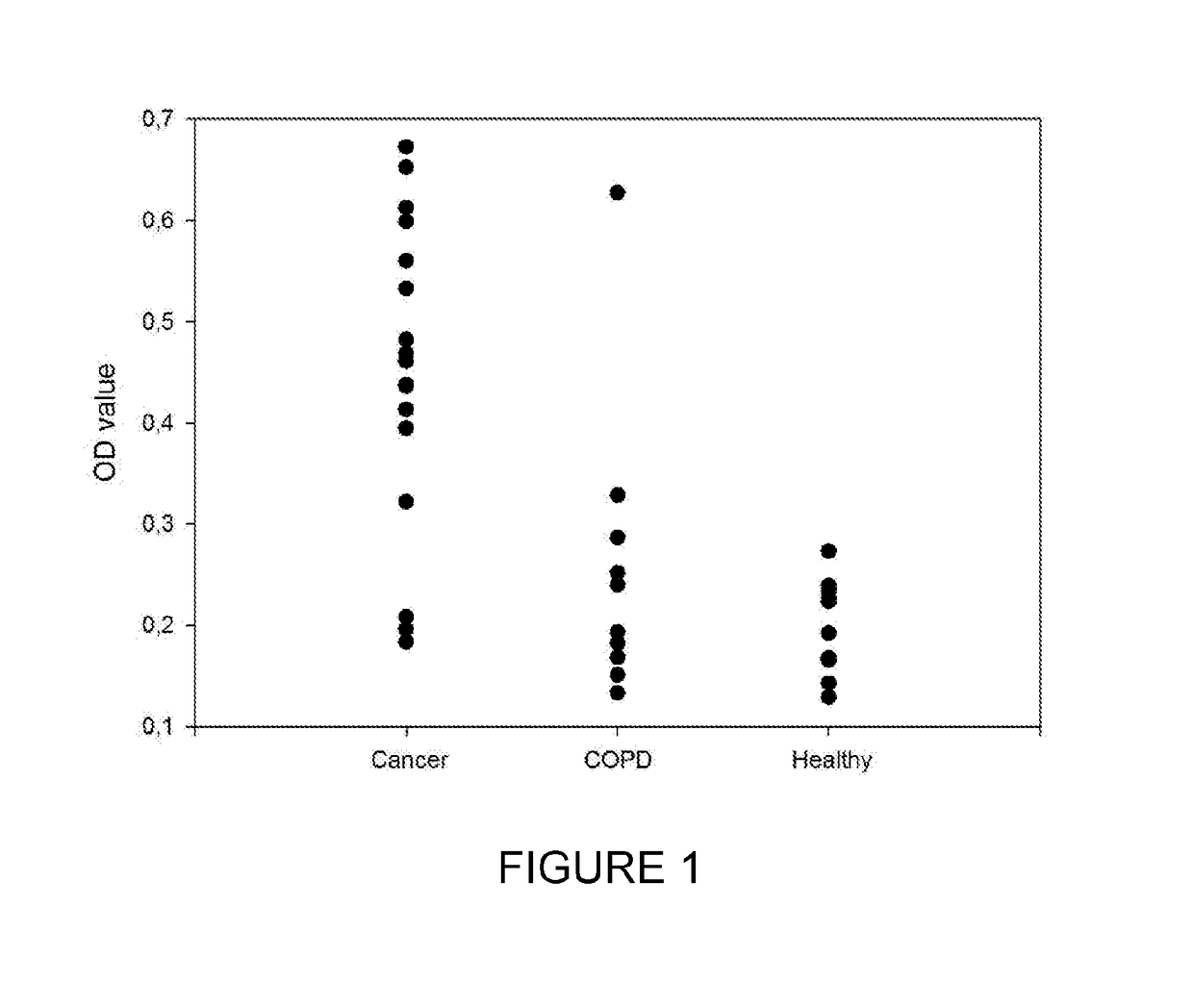
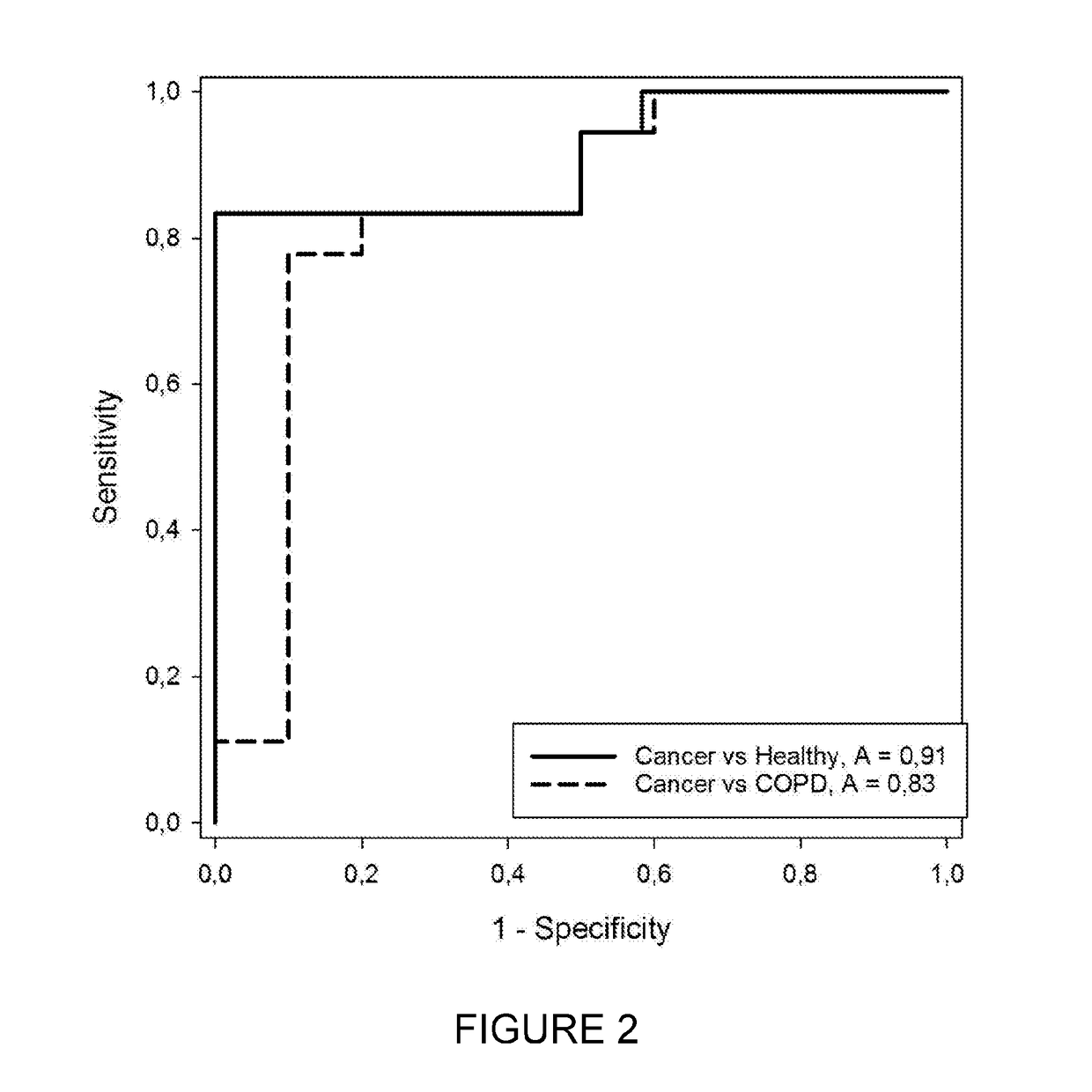
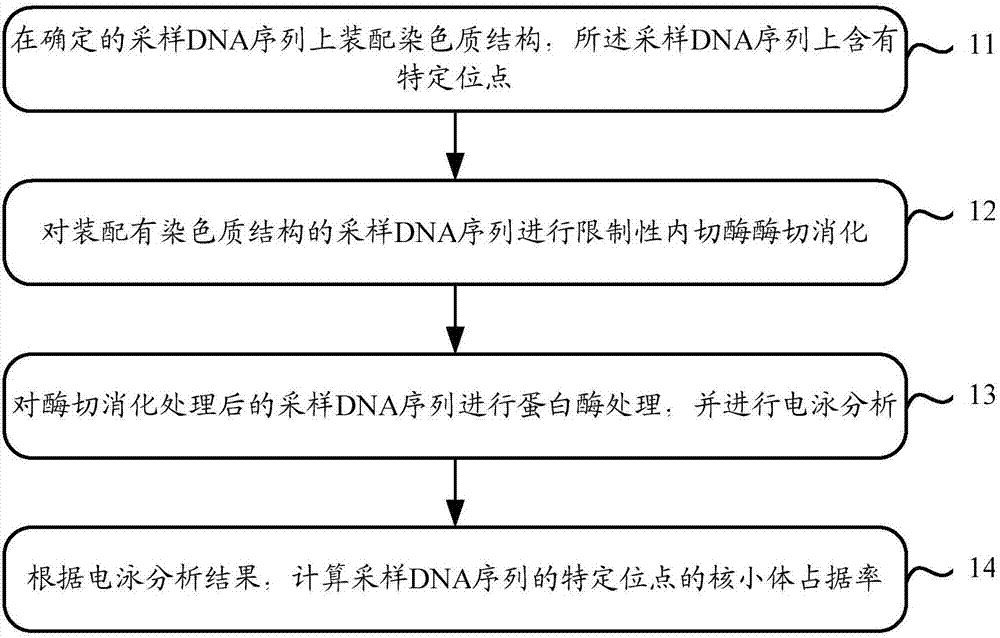
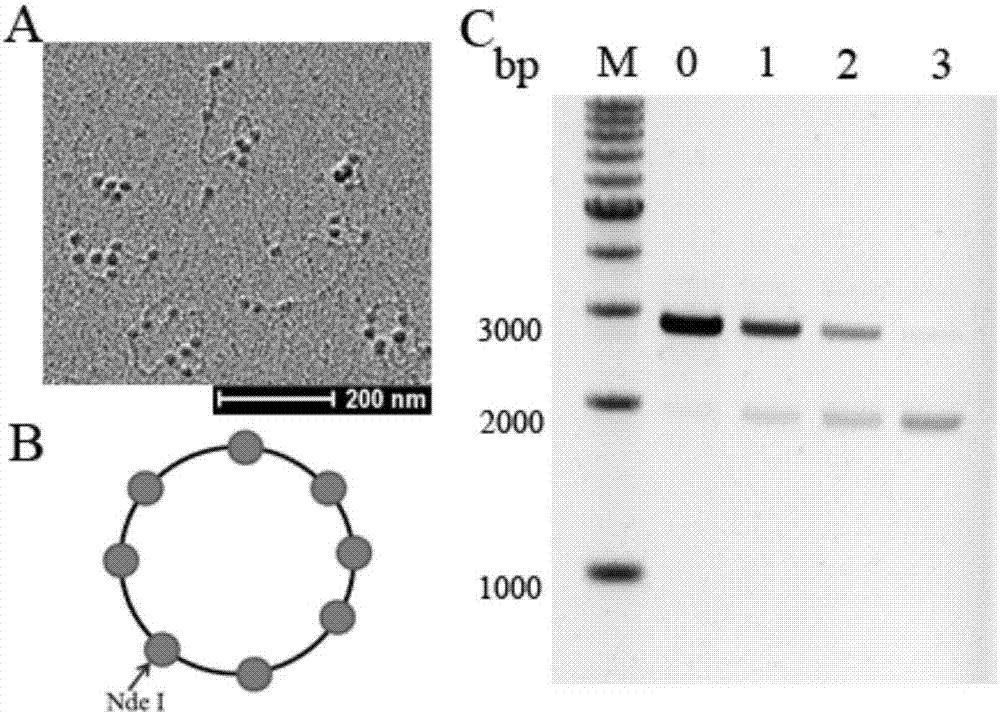
Capacity detection method for assembling chromatin structure on specific site of DNA sequence
ActiveCN107541558AThe implementation process is simpleThe realization process is convenientMicrobiological testing/measurementEnzyme digestionElectrophoresis
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology, in particular to a capacity detection method for assembling a chromatin structure on a specific site of a DNA sequence, and aims to solve the problem that an existing technology cannot detect the nucleosome occupying rate at a fixed site to determine the chromatin structure assembling capacity. The method is mainly to assemble the DNA sequence containing a specific restriction enzyme site into the chromatin structure; enzyme digestion is carried out through restriction enzyme to remove various types of protein, then electrophoresis detection is carried out, and the site and the nucleosome occupying rate of the DNA sequence near the site are quantitatively calculated to judge a local chromatin structure near the site. Therefore, the efficiency of assembling the chromatin structure on the specific site on the DNA sequence and the nucleosome assembling capacity are analyzed. The detection method is simple and quick in realizing process, and high in specificity and accuracy.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Improved apoptotic DNA ladder extraction kit
The invention relates to an improved apoptotic DNA ladder extraction kit, which comprises a cell lysis buffer used for extracting an apoptotic nucleosome of an apoptotic cell within 10 seconds, an extraction reagent enzyme A solution and an extraction reagent enzyme B solution both used for removing an RNA enzyme and nucleosome protein mixed in the apoptotic nucleosome, an ammonium acetate solution formed by an aqueous solution in which 1 mL aqueous solution contains 790 mg ammonium acetate, and a DNA ladder solution formed by a TE buffer solution of 1.667 mL and an aqueous solution in which 0.333 mL aqueous solution contains 4.4 g EDTA, 250 mg bromophenol blue and 250 mg Xylene Cyanol FF. The improved apoptotic DNA ladder extraction kit used for detecting ligand has the characteristics of quickness, high sensitivity (cells with the apoptosis rate more than 10% can be detected), capability of qualitative detection, and strong specificity.
Owner:张根
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com