Immobilized microspheres for degrading bacteria of PAEs (phthalic acid esters) and preparation method and application of such immobilized microspheres
A technology for degrading bacteria and microspheres, applied in the field of agricultural biology, can solve the problems of low DBP degradation efficiency and inability to use efficiently, and achieve the effect of simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1 Screening and Identification of Phthalate Degrading Bacteria
[0036] (1) Screening of phthalate-degrading bacteria
[0037] A certain amount of soil samples were collected in vegetable greenhouses in the suburbs of Qingdao, 10g of fresh soil samples were accurately weighed, added to a conical flask filled with 90mL of distilled water and 10mL of glass beads, placed in a shaker at 30°C, 175rpm and oscillated to mix evenly. Set aside.
[0038] Take 1mL from the above mixed solution according to the inoculum size of 1%, add it to 100mL inorganic salt culture solution with an initial concentration of 100mg / L phthalate (both DBP and DEHP are 50mg / L), and place it on a shaker Shaking culture was carried out at 30°C and 175rpm in the dark for 7 days. Gradually increase the concentration of phthalates (including 200mg / L, 500mg / L, 800mg / L, 1000mg / L, 1500mg / L and 2000mg / L) for each transfer, transfer once every seven days as an acclimation cycle, After a total of 6 ...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2 Detection of Pseudomonas putida RXX-01's ability to degrade phthalates
[0044] The culture solution of the RXX-01 strain was inoculated in an inorganic salt medium (50 mL) with a DBP and DEHP concentration of 50 mg / L according to an inoculum amount of 1%, and was shaken at 25° C. and 150 r / min. After culturing for 3 days, the concentrations of DBP and DEHP in the culture medium were measured, and the degradation rates of DBP and DEHP were calculated. The results showed that the degradation rate of DBP was 90.8%, and the degradation rate of DEHP was 54.7%, which indicated that the RXX-01 strain had a high ability to degrade phthalates.
[0045] Degradation rate calculation formula: degradation rate (%)=((initial concentration of phthalates-residual concentration of phthalates) / initial concentration of phthalates)×100%.
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3 The preparation method of Pseudomonas putida RXX-01 immobilized microspheres
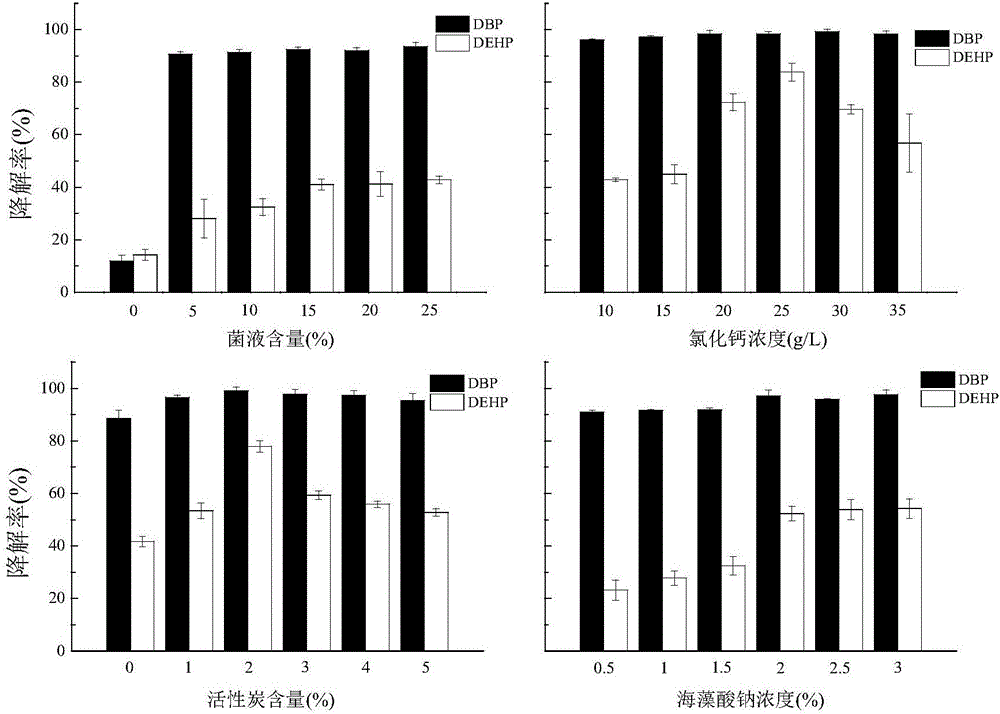
[0047] In order to determine the optimal ratio of immobilized materials in this embodiment, different bacterial liquid content, sodium alginate concentration, activated carbon content, and calcium chloride concentration were selected as factors to determine the concentration of immobilized microsphere terephthalate. The degradation rate was targeted, and the immobilization conditions were optimized.
[0048] A total of 4 factors (bacterial suspension content, sodium alginate concentration, activated carbon content, and calcium chloride concentration) were set in the single factor experiment, and 6 concentration levels were set for each factor. The percentages involved are all mass percentages. The bacterium suspension refers to the OD that the bacterium is made with physiological saline 600 = 1.0 suspension.
[0049] Under the conditions of sodium alginate concentration of 2%, ac...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com