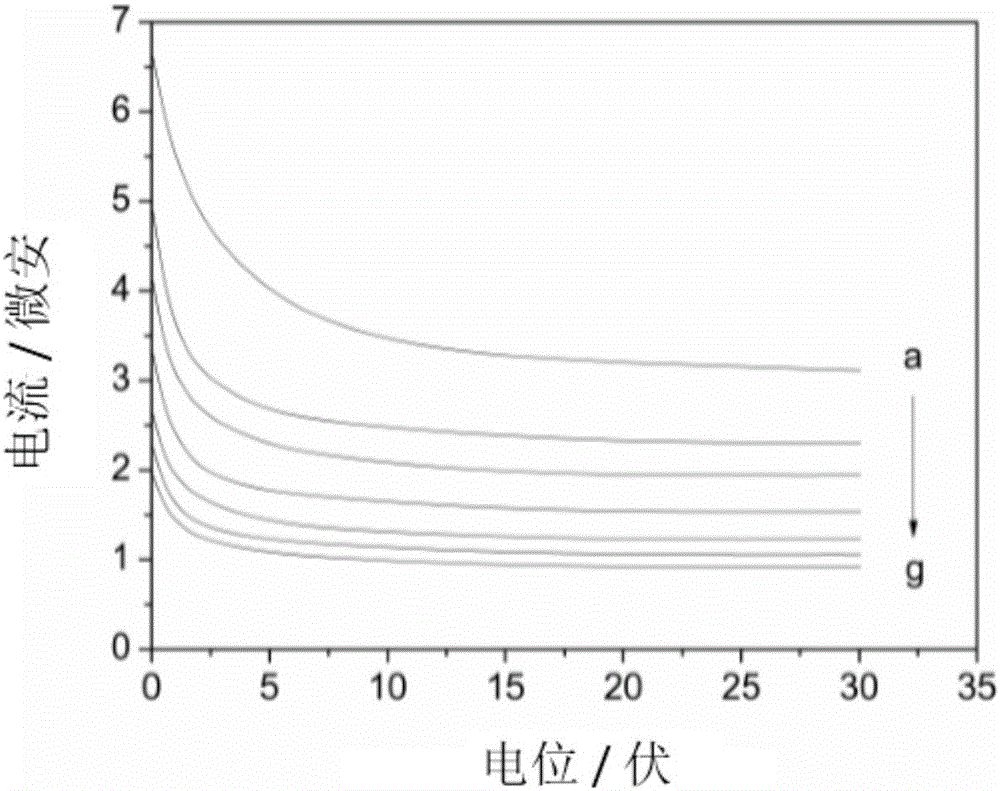
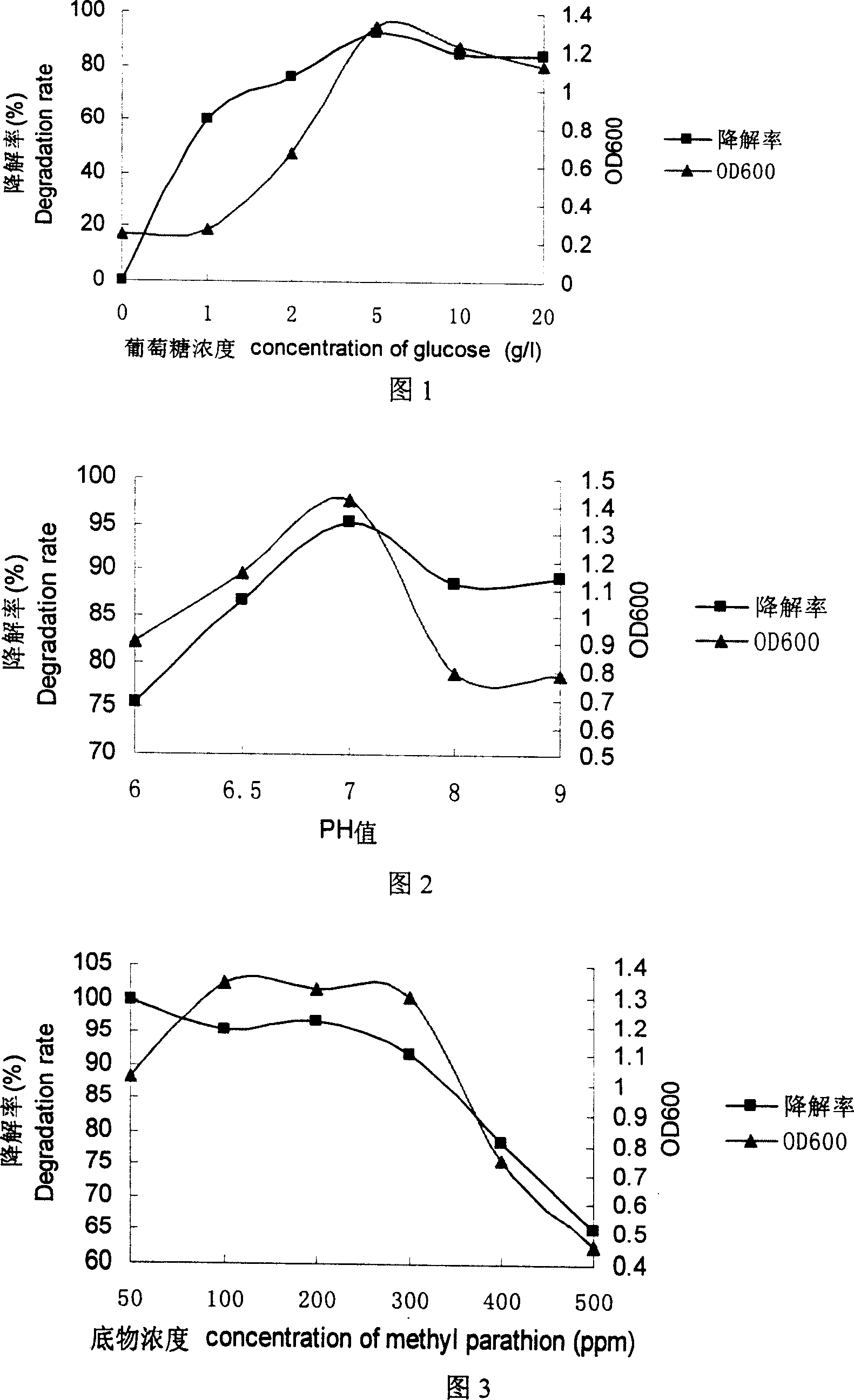
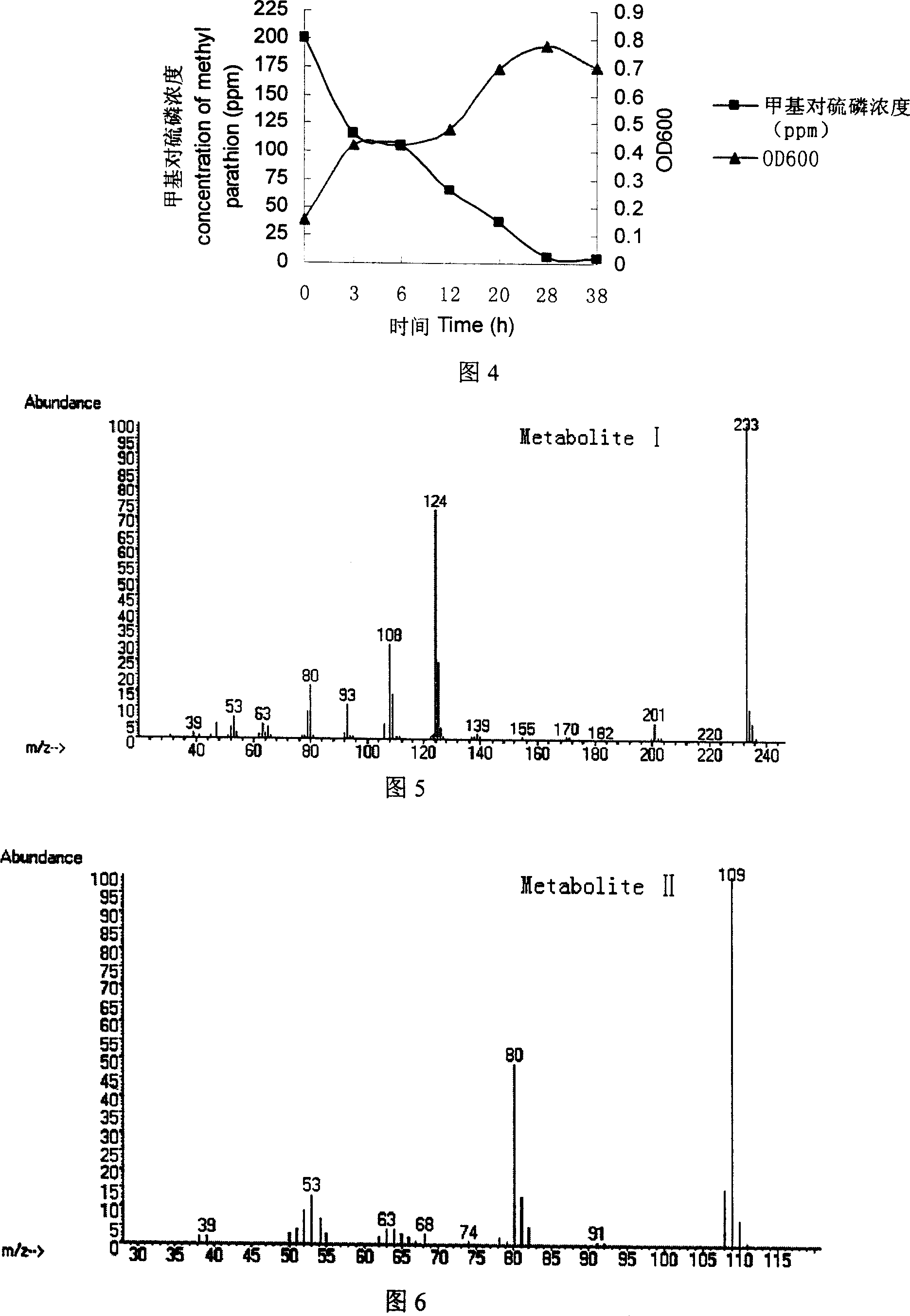
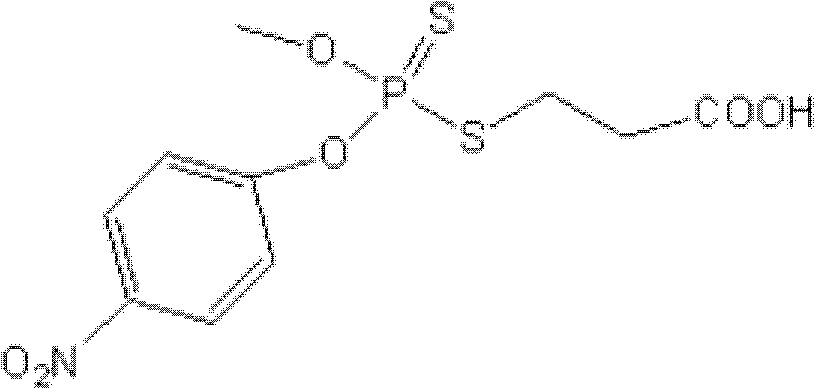
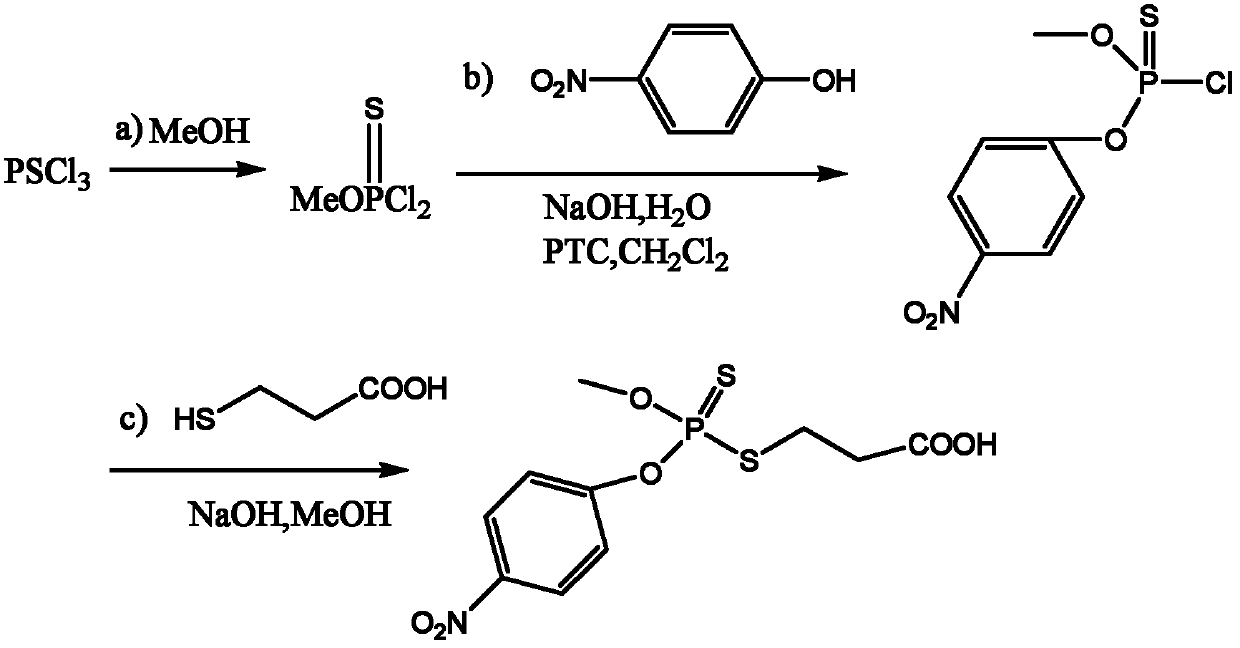
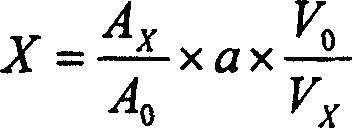Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
93 results about "Methyl parathion" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Parathion methyl, or methyl parathion, is an organophosphate pesticide and insecticide, possessing a organothiophosphate group. It is structurally very similar to parathion-ethyl. It is not allowed for sale and import in nearly all countries around the world, while a few allow it under subject to specified conditions only.
Pseudomonas stutzeri JSD-008 and its degradation function for organophosphorus pesticide
InactiveCN101096644APromote degradationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesChlorpyrifosMethyl parathion
The invention discloses a Pseudomonas stutzeri JSD-008 and degradation for organophosphorus pesticide, which is preserved in the 'Chinese germ management committee center (CGMCC)' with preservation number at CGMCC No.1738, wherein the strain is separated from the soil at pollution discharge pore of pesticide processing plant polluted by organophosphorus pesticide; the thallus and ferment liquid with the thallus can be degradation agent of organophosphorus pesticide to degrade the chlorpyrifos into trichlopyridinenol and methyl parathion into nitrophenol; fitting for rapid in-situ rehabilitation polluted by field soil pesticide.
Owner:谢明
Acetylcholinesterase biosensor and application thereof
ActiveCN106248748AImprove electrocatalytic activityGood biocompatibilityMaterial electrochemical variablesWater bathsElectrochemical biosensor
The invention relates to an acetylcholinesterase biosensor and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of electrochemical detection. The biosensor is produced through the following steps: 1, preparing a MnO2-nanoflakes composite nano-material and a Pd-Pt@MnO2-nanoflakes composite nano-material from KMnO4, CTAB, PdCl2, PEG400, H2PtCl6, sodium citrate and sodium borohydride used as initial raw materials through a water bath technology; and 2, immobilizing acetylcholinesterase by using chitosan (CS), and immobilizing acetylcholinesterase (AChE) on the surface of a Pd-Pt@MnO2 modified glassy carbon electrode through adopting physical adsorption to construct the electrochemical biosensor. The biosensor adopting an electrochemistry and enzyme sensing combination technology realizes high-sensitivity detection of methyl parathion and carbofuran pesticides, has the advantages of small amount of a required sample, short detection time, high sensitivity and low cost, and is suitable for analyzing and detecting pesticide residual.
Owner:云南省产品质量监督检验研究院
Gas chromatographic method for detecting residues of high-toxic organophosphorus pesticides in soil
InactiveCN103472175AEasy to separateMeet testing requirementsComponent separationPhosphamidonMethyl parathion
The invention relates to a gas chromatographic method for detecting residues of five high-toxic organophosphorus pesticides in different texture soils(loam, clay and sandy soil) so as to realize the qualitative and quantitative detection on the residues of methamidophos, parathion, methyl parathion, monocrotophos and phosphamidon pesticides in the soils. The gas chromatographic method is characterized in that acetonitrile is taken as an extracting agent, and after an extraction solution is concentrated with constant volume and is filtered, the trace analysis is directly carried out by using a gas chromatograph. The gas chromatographic method has the advantages that firstly a chromatographic column has a good separation effect on a target object, the accuracy degree of detection results is high, the reproducibility is good, and the sensitivity of the method meets the detection requirements of the residual pesticides; secondly compared with a GB / T14552-2003 (gas chromatographic method for determining organophosphorus pesticides in water and the soil), the national standard method is easier and more convenient, a pretreatment process of soil samples is simplified, the detection time is shortened, and the cost is saved.
Owner:邬金飞
DU-E4LP seudomonas putida and use in degradating parathionmethyl
The invention supplies a methyl parathion degradation fungus DM-1 that the preservation NO is CGMCC No.1620. The classification designation is Bacillus subtilis. It is separated and selected from soil polluted by agricultural chemical. The fungus has good degradation effect to 50-500ppm methyl parathion at 30 degree centigrade.
Owner:INST OF ZOOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
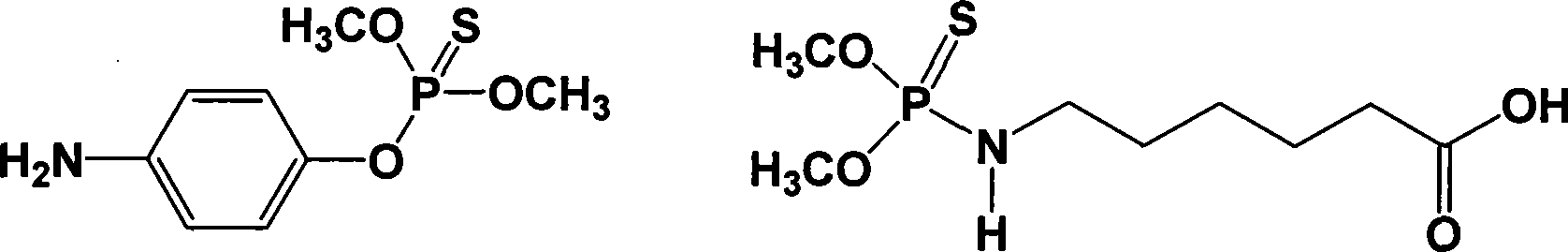
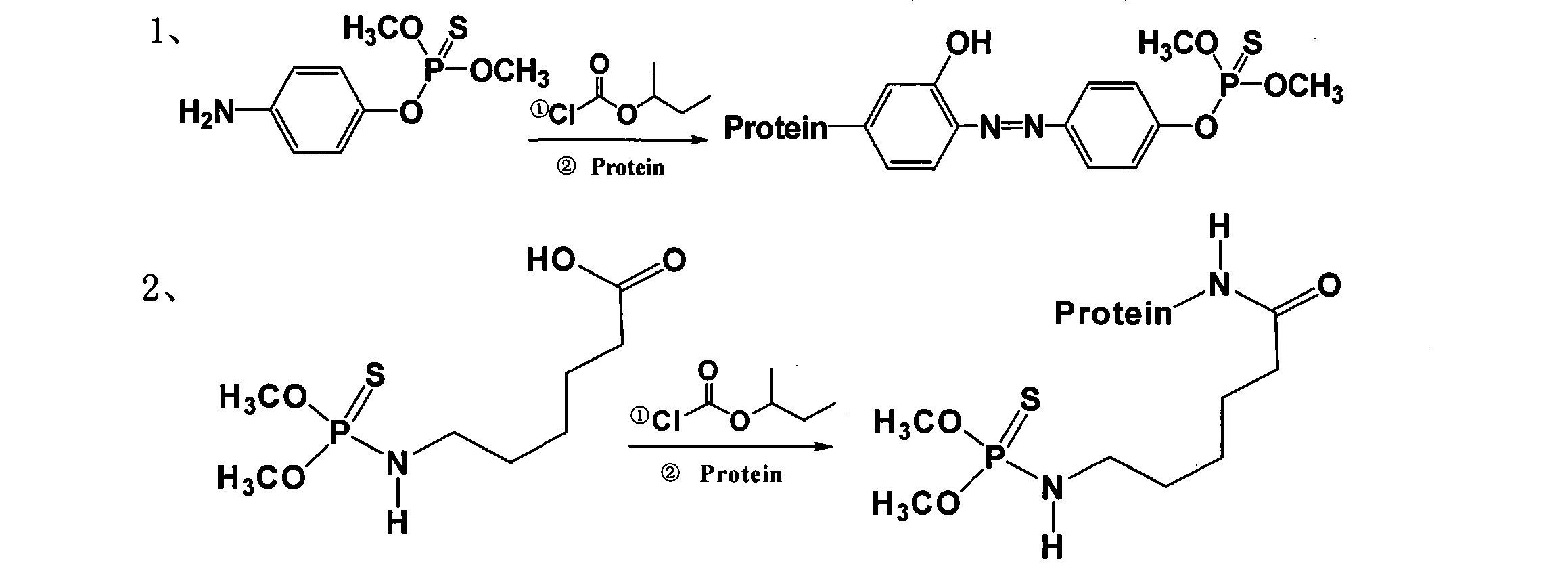
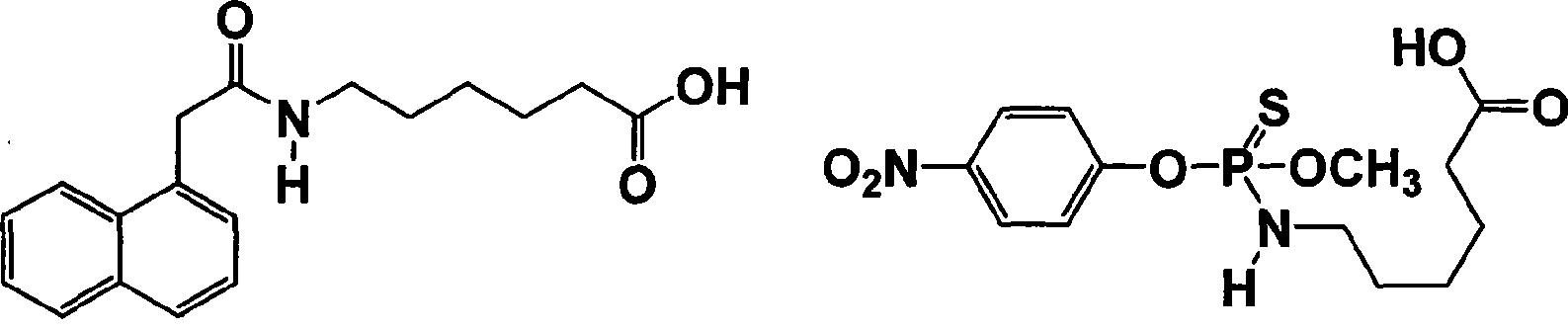
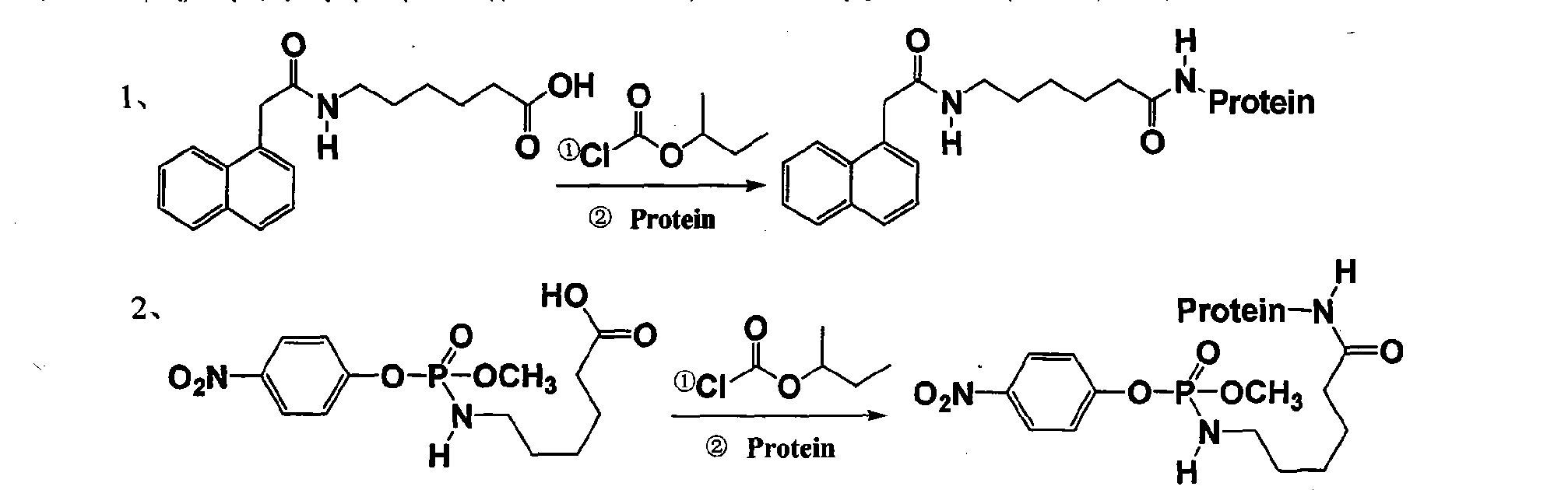
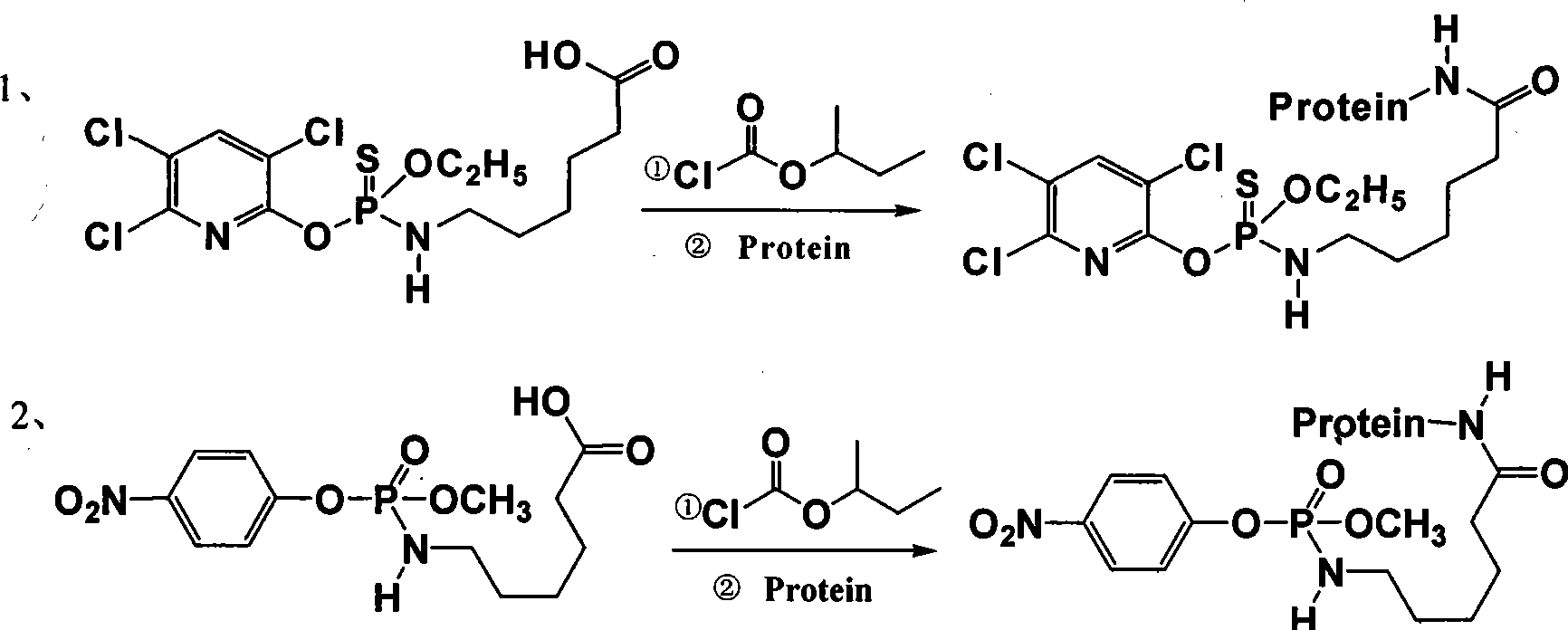
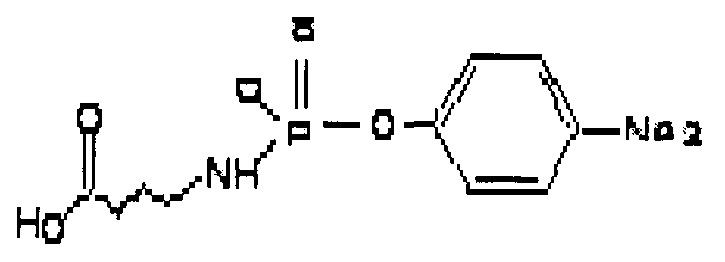
Methyl parathion hapten, and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103288872ARetain chemical structureGood potencyFibrinogenOvalbuminMethyl parathionMethyl group
The invention discloses a hapten, and a preparation method and application thereof, particularly a methyl parathion hapten. The invention also discloses a preparation method and application of the hapten. The kit quick detection product established on the basis of the methyl parathion hapten is convenient to use and low in detection cost; and the detection method is efficient, accurate and quick, can be used for simultaneously detecting mass samples, and is suitable for on-site supervision of methyl parathion residues in corn and apple samples and screening of mass samples.
Owner:BEIJING KWINBON BIOTECH
Nanometer molecular biosensor, preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101624568AReduced preparation stepsAssembly SynchronizationBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsNanowireFluorescence
The invention discloses a nanometer molecular biosensor and a preparation method thereof. The biosensor is mainly characterized in that a molecular biosensor is self-assembled into a nanometer molecular biosensor by adopting nanowire protein, and compared with an unassembled molecular biosensor, the detection sensitivity is greatly improved. The preparation method adopts the protein fusion technology, and fuses nanowire protein with self-assembled function, special enzyme molecule used as a biology identification element and fluorescence protein used as a transducer element, therefore, functional protein with self-assembled nanowire, identification and transduction output signal functions simultaneously, and after the functional protein is expressed and purified, the functional protein is self-assembled into a nanometer molecular biosensor which can be used for inspecting object molecules in various clinical samples and environment samples. The invention simultaneously discloses an application of the nanometer molecular biosensor prepared by the preparation method in pesticide methyl parathion detection.
Owner:WUHAN INST OF VIROLOGY CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of electrochemical sensor for detecting organophosphorus pesticide methyl parathion
InactiveCN103196968AImprove stabilityReduce manufacturing costMaterial electrochemical variablesElectricityComposite electrode
The invention relates to a preparation method of an electrochemical sensor for detecting organophosphorus pesticide methyl parathion. 0.1wt% functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes and 10mgml-1beta-cyclodextrin are taken as materials, directly dropped and coated on the surface of a glassy carbon electrode after being evenly mixed by ultrasonic, and then dried by using an infrared drying oven to prepare an electrochemical sensing composite electrode with good electrochemical properties and selectivity. The composite electrode constructed by the preparation method has good electrocatalytical properties on the methyl parathion, has the characteristics of fast current response, wide linear range, high sensitivity, low detection limit, good stability and the like, and has the advantages of low preparation cost, simple process, simpleness and easiness in operation, strong selectivity and the like. The prepared composite electrode is successfully applied in the analysis and the detection on methyl parathion residues in vegetables such as onion, lettuce, spinach and cole, and has a good application prospect and a potential application value in the field of detection and analysis on environmental pollution.
Owner:JIANGXI SCI & TECH NORMAL UNIV
Liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for measuring 18 semi-volatile organic pollutants in water
InactiveCN106053622AImprove accuracyHigh quantitative sensitivityComponent separationRelative standard deviationMethyl parathion
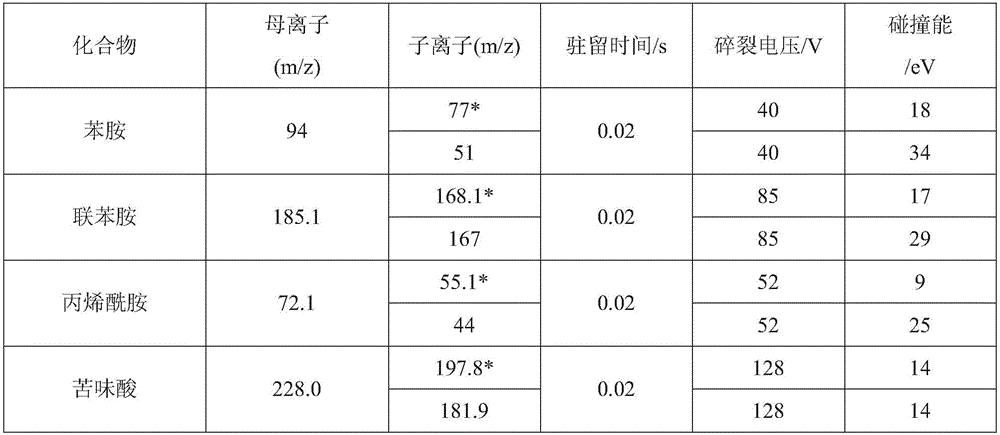
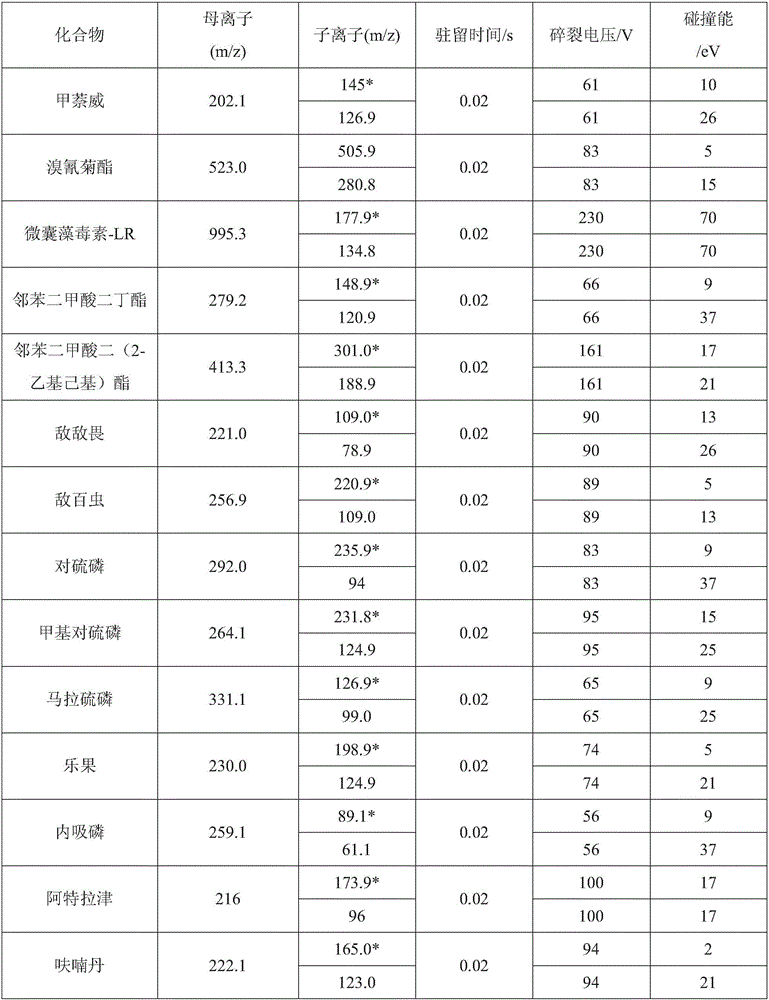
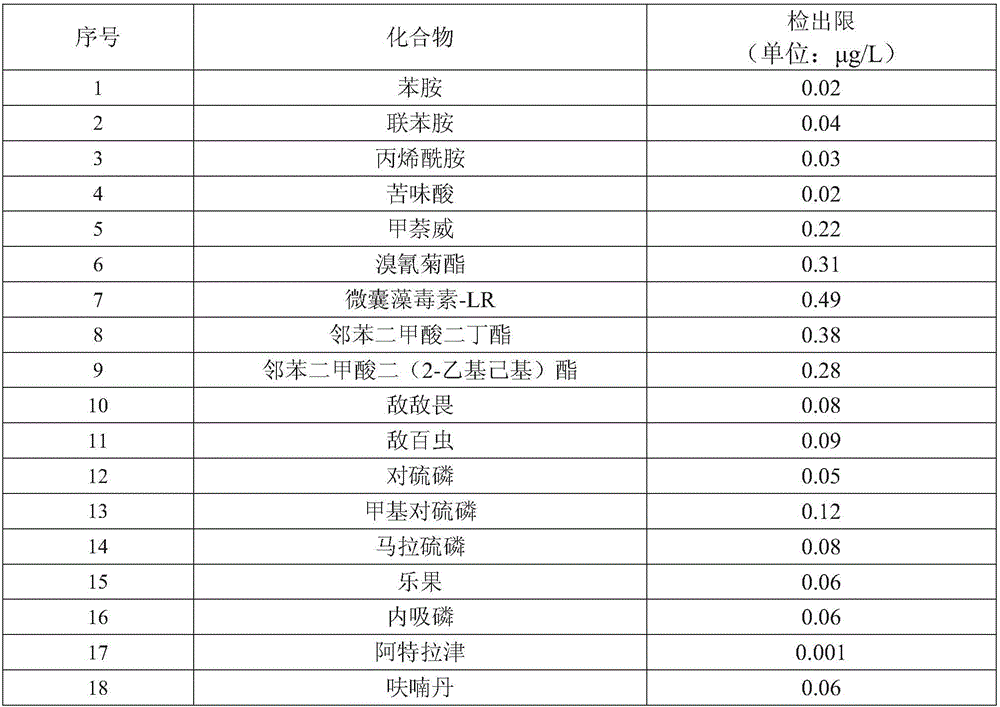
The invention discloses a liquid chromatography-tandem mass spectrometry method for measuring 18 semi-volatile organic pollutants in water. According to the method, a clean water sample such as surface water, drinking water, and the like is simply filtered by a 0.22 [mu]m micro-porous filter membrane, and then a liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry instrument is used to separate and detect the following 18 compounds in water: aniline, benzidine, acrylamide, picric acid, carbaryl, deltamethrin, microcystic toxin-LR, dibutyl phthalate, bis(2-ethylhexyl) phthalate, dichlorvos, trichlorphon, parathion, methyl parathion, malathion, dimethoate, demeton, atrazine, and carbofuran. The provided method can detect many target substances. The detection range of the method is 0.001 to 0.49 [mu]g / L, the relative standard deviation is 0.7 to 15.4%; and the analysis method has the advantages of high sensitivity, quick analysis speed, little pollution, and simple and efficient pretreatment, is especially suitable for standard analysis of drinking water source monitoring, and solves the problems of bad conformability, large labor strength, and low analysis efficiency of the conventional standard method.
Owner:广西壮族自治区环境监测中心站
Methyl-parathion molecularly-imprinted electrochemical sensor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103675050AGood selectionHigh detection sensitivityMaterial electrochemical variablesMethyl parathionParathion
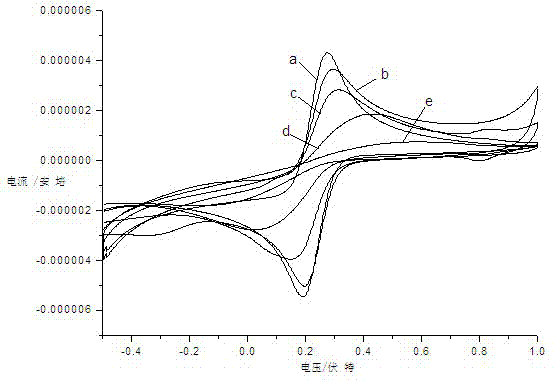
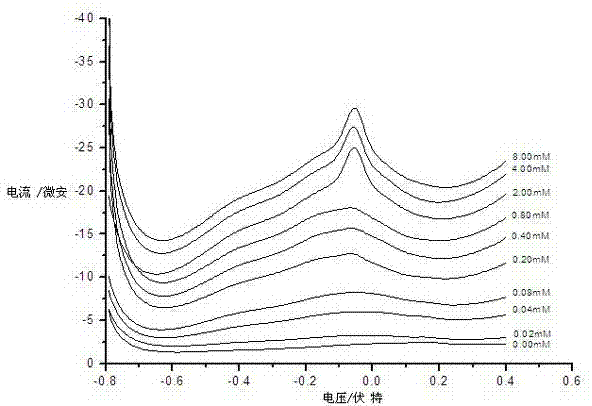
The invention discloses a methyl-parathion molecularly-imprinted electrochemical sensor and a preparation method thereof. The sensor comprises a glassy carbon electrode, wherein the glassy carbon electrode is covered with a carboxyl graphene-nanogold composite coating, and molecularly-imprinted holes corresponding to methyl-parathion molecules are formed in the carboxyl graphene-nanogold composite coating. The preparation method comprises four steps as follows: synthetizing a carboxyl graphene-nanogold composite; using the carboxyl graphene-nanogold composite to modify the glassy carbon electrode; forming a methyl-parathion molecularly-imprinted template; removing methyl-parathion molecularly-imprinted template molecules. Through an electrochemical performance test, the sensitivity of the methyl-parathion molecularly-imprinted electrochemical sensor is high. A methyl-parathion solution with the concentration being 4*10-8 mol.L<-1> is compared with a methyl-parathion solution with the concentration being 0, current curves are obviously changed, and thus micro trace detection on the low-concentration methyl parathion is realized.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV
Preparation of multi-organophosphor universal antibody and universal envelope antigen
InactiveCN101477116AThe pre-processing process is simpleReduce testing costsMaterial analysisAntigenFenitrothion
The invention discloses preparation of various common antibodies of an enzyme-linked immunoadsorption determination reagent kit suitable for analyzing different residues at the same time and common envelope antigen, which comprise preparation methods of common organophosphorus pesticide semiartificial antigen structure, different organophosphorus pesticide common antibodies and common envelope antigen. The organophosphorus pesticide common antibodies and the common envelope antigen prepared by the preparation methods can be used to prepare the enzyme-linked immunoadsorption determination reagent kit suitable for analyzing different organophosphorus pesticide residues at the same time; moreover, the reagent kit can be used for quick detection of different organophosphorus pesticides such as methyl parathion, fenitrothion, fenthion, acephate, Cygon and malathion in water, soil, foodstuff such as vegetables and poisoned samples; in addition, the invention has the advantages of simple preliminary treatment process of samples, simultaneous detection of samples in batches and lower sample detection cost than the prior detection method.
Owner:孙家隆
Preparation of carbaryl and methyl parathion universal antibody and universal envelope antigen
InactiveCN101475637AReduce testing costsThe pre-processing process is simpleSerum immunoglobulinsSerum albuminMethyl parathionHapten
The invention discloses the preparation for a carbaryl and methyl parathion general antibody and general envelope antigen suitable for an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit capable of simultaneously carrying out the carbaryl and methyl parathion retention analysis. The invention comprises a preparation method for a carbaryl artificial hapten and methyl parathion artificial hapten structure, and the carbaryl and methyl parathion general antibody and general envelope antigen. The carbaryl and methyl parathion general antibody and general envelope antigen can be used for the preparation of the enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit capable of simultaneously carrying out the carbaryl and methyl parathion retention analysis. The kit can be used for the quick detection of the carbaryl residue and methyl parathion in the water, soil, vegetable, food and poisoned samples. The preliminary treatment of the samples is simple; the kit can be used for the detecting a batch quantity of samples; and the sample detection cost is lower than that of a conventional detection method.
Owner:孙家隆
Composite microbial degradation agent for organic pollutants and preparation method of degradation agent
InactiveCN108585216AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsBacillus megateriumMethyl parathion
The invention relates to the field of environmental protection, and relates to degradation of organic waste materials by biological materials and / or photocatalytic materials. A microbial strain is oneor more selected from bacillus subtilis, bacillus megaterium, and aspergillus sydowii, wherein the bacillus subtilis is preferably bacillus subtilis with a preservation number of CGMCC NO.1.9083, thebacillus megaterium is preferably bacillus megaterium with a preservation number of CGMCC NO.1.16094; and the aspergillus sydowii is preferably aspergillus sydowii with a preservation number of CGMCCNO.3.13937. According to a method disclosed by the invention, photocatalyst nano titanium dioxide is used to cooperate with the above microorganisms, and the degradation agent has a very good effecton an application of degradation of pesticides, especially degradation of methamidophos, methyl parathion and triazophos.
Owner:佛山市尚柏科技有限公司
Method for degrading pyrethrins pesticide by magnetic polyurethane foam plastic immobilized cell
The present invention belongs to a plant magnetism polyurethane foam plastic immobilized microorganism cell and the technology field of the biological degradation chemical pesticide, and relates to the magnetic immobilization to a strain cell which highly and effectively degrades the pyrethroid pesticide. The bacterial strain is acinetobacter (Acinetobacter sp.) JCX22D strain, which uses botanical wastes as polymerization material, and Fe 3 O 4 as a magnetic component, a cold curing technology is adopted to perform the immobilization of the strain cell, and the immobilized cell can be recycled through adding the magnetic field. The degradation efficiency of the immobilized cell to highly effective cypermethrin, lamba cyhalothrin and bifenthrin is more than 70 percent, the degradation efficiency to naled, methyl parathion, phoxim and chlorpyrifos is over 60 percent, and the degradation efficiency to avermectins is 85 percent. The magnetic immobilized cell can be used for the biolobical repair or biological purification of a water body polluted by the pesticide.
Owner:许雷
Compound microbial degradation agent for organic pollutants and preparation method of compound microbial degradation agent
InactiveCN108585217AWater/sewage treatment by irradiationWater treatment compoundsMicroorganismBacillus megaterium
The invention relates to the field of environmental protection, and relates to degradation of organic waste by using biological materials and / or photocatalytic materials. Microbial strains are selected from one or more of Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus megaterium and Aspergillus sydowii, wherein Bacillus subtilis with a preservation number of CGMCC No.1.9083 is preferably selected for the Bacillus subtilis, Bacillus megaterium with a preservation number of CGMCC No.1.16094 is preferably selected for the Bacillus megaterium, and Aspergillus sydowii with a preservation number of CGMCC No.3.13937 ispreferably selected. A photocatalyst nano-titanium dioxide is adopted to cooperate with the microorganisms, a very good result is achieved in degradation of pesticide, especially in degradation application of methamidophos, methyl parathion and triazophos.
Owner:佛山市尚柏科技有限公司
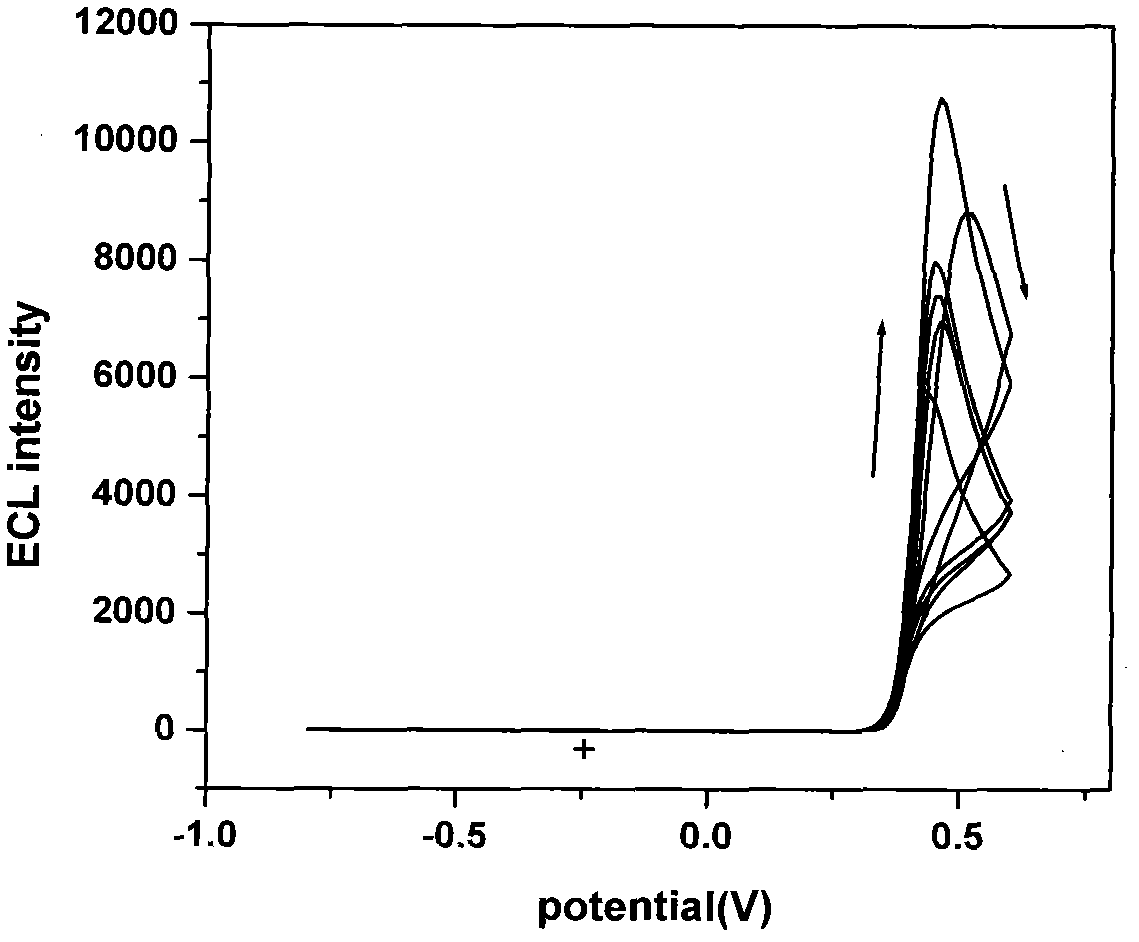
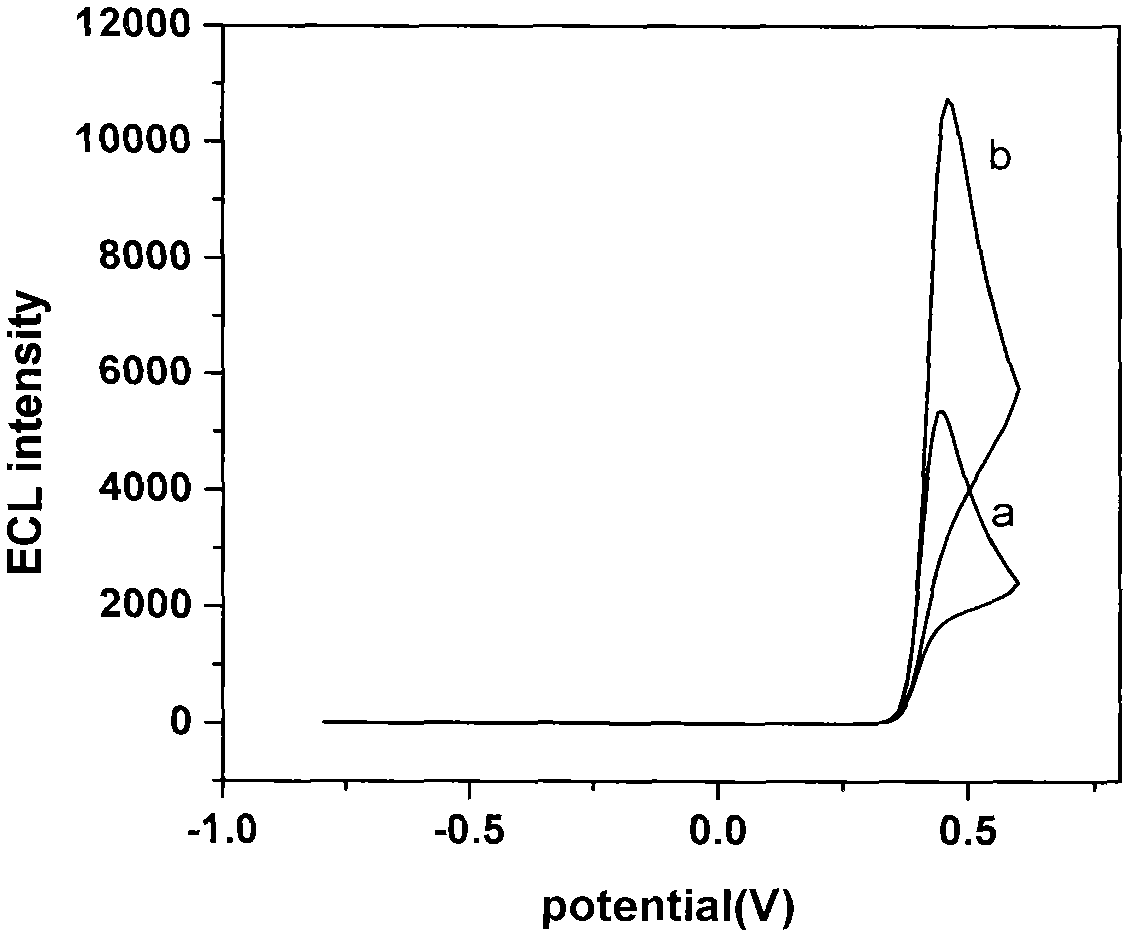
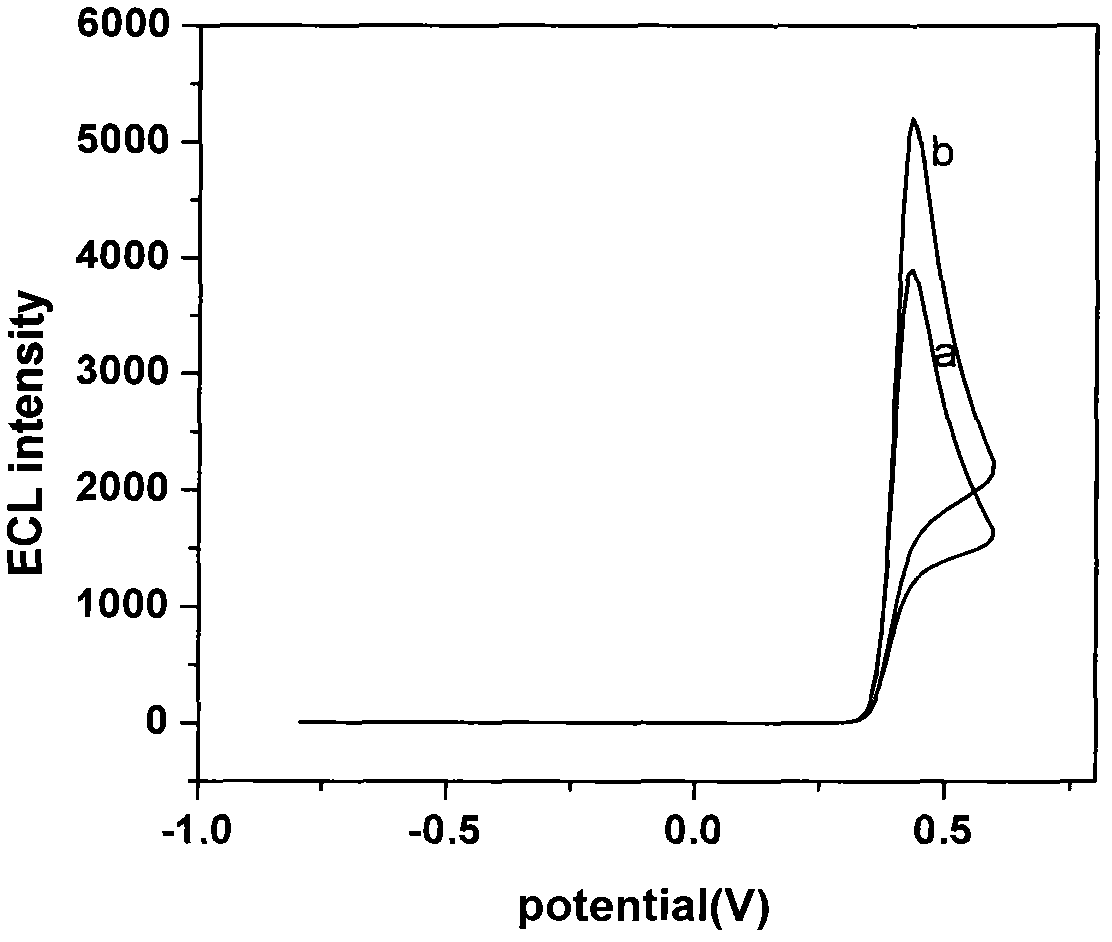
Device for detecting methyl parathion pesticide residue through electrochemiluminescence
InactiveCN102539417AQuick checkChemiluminescene/bioluminescenceMaterial electrochemical variablesMethyl parathionPesticide residue
The invention relates to a device for detecting methyl parathion pesticide residue through electrochemiluminescence, and belongs to the field of analysis and detection. Researching and developing a methyl parathion pesticide residue detection technique which is highly sensitive, quick, efficient and easy to operate is an important focus of attention in the field of pesticide residue analysis. Highlighting the focus, the device provided by the invention is a three-electrode electrochemiluminescence detection device, wherein the base solution in an electrolytic bath in the device is Luminol / KCl solution; the working electrode is a glassy carbon electrode; and nano zirconium oxide is modified on the working face of the glassy carbon electrode. The working electrode of the device has special sensitivity to the pesticide methyl parathion, so that the device can sensitively and quickly detect the methyl parathion pesticide residue.
Owner:NINGBO UNIV
Method for preparing methyl parathion degradation bacterium and enzyme preparation thereof
InactiveCN101168731AWill not affect the use effectEasy to useBacteriaPesticide residueMethyl parathion
The invention relates to methyl parathion degradation fungus and the preparing method of the enzyme preparation thereof, and belongs to the biological high technical field. The methyl parathion degradation fungus strain is plesiomus shigelloides, and the production process of liquid enzyme preparation adopts the steps of slant culture, seed liquid shaking, seed fermenter, fermenter, bacterial collection, mechanical cell crushing, clear liquid collection, (NH4)2SO4 fractional precipitation, HEPES buffer solution suspension, dialysis, and crude enzymes production. Enzyme dry powder preparation which is easy to be stored or transported can also be further refined, and processing steps added on the basis of the crude enzymes production are as follows: DEAE-Sephadex-A50 anion column chromatography, CM Sepharose Fast Flow cation column chromatography, dialysis, cryodesiccation and enzyme dry powder production. The direct application of the liquid crude enzymes preparation can ensure the organic phosphorus pesticide residue quantity in agricultural crops to be reduced by more than 90 percent, and the residual on the surface of garden spgarden stuff washed to be reduced by about 98 percent; after the enzyme dry powder preparation is diluted according to a specific proportion, the pesticide residue quantity can be reduced by more than 95 percent. The enzyme preparation product resolves the problem that the pesticide residue is over-standard in the agricultural production.
Owner:SHENYANG INST OF APPL ECOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Construction method of electrochemical sensor for rapidly and quantitatively detecting pesticide residues
ActiveCN112147195ALow costEasy to operateMaterial electrochemical variablesMethyl parathionPesticide residue
The invention discloses a construction method of an electrochemical sensor for rapidly and quantitatively detecting pesticide residues, relates to the technical field of food safety detection and analysis, overcomes the defects of various existing methyl parathion detection technologies, and has the advantages of low detection limit, rapidness and accuracy in detection, convenience in carrying, less required equipment, low cost and the like. According to the specific scheme, the construction method comprises the following steps of S1, carrying out self-assembly on 4-aminothiophenol on a sulfhydrylated graphene modified silk-screen printing electrochemical sensor; S2, self-assembling methyl parathion on the sulfhydrylated graphene modified silk-screen printing electrochemical sensor; and S3, preparing a sulfhydrylated graphene loaded gold platinum nanoparticle modified molecularly imprinted silk-screen printing electrochemical sensor: preparing the methyl parathion molecularly imprintedpolymer electrochemical sensor by adopting an electro-polymerization method. The construction method of the electrochemical sensor for rapidly and quantitatively detecting pesticide residues providesa miniature pesticide residue detection chip which is rapid, sensitive, portable, low in cost and easy to operate.
Owner:河北地质大学
Preparation method of chemiluminescence immunoassay detection kit used for detecting methyl parathion
InactiveCN105319354AReduce testing costsThe electrophoretic method is fast and easyMaterial analysisMethyl parathionCarrier protein
The invention provides a chemiluminescence immunoassay detection kit used for detecting methyl parathion (MP), and belongs to the field of immunological detection. The chemiluminescence immunoassay detection kit is composed of a non-transparent white enzyme label plate coated with a methyl parathion (MP)-carrier protein conjugate, a methyl parathion standard substance, a methyl parathion-peroxidase labelled antibody working liquid, a luminescent substrate liquid, a concentrated sample diluent, and a concentrated washing liquid. The methyl parathion (MP)-carrier protein conjugate is obtained via coupling of methyl parathion with a carrier protein via mixed anhydride method or carbodiimide method; and the concentrated washing liquid contains 0.05% of tween-20. The chemiluminescence immunoassay detection kit is high in sensitivity; detection time is short; cost is low; and the chemiluminescence immunoassay detection kit can be used for residual amount detection of methyl parathion (MP) in samples such as fruits, vegetables, and crops.
Owner:JIANGSU WISE SCI & TECH DEV
Time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay kit detecting methyl parathion and detection method thereof
InactiveCN105319366ASensitive methodSimple and fast operationMaterial analysisPorous coatingTime resolved fluorescence immunoassay
The invention discloses a time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay kit detecting methyl parathion (MP) and a detection method thereof. The time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay kit detecting methyl parathion is composed of a porous coating plate, a buffer, a methyl parathion standard sample, a methyl parathion antibody freeze-dried sample, an europium-labelled goat anti-mouse antibody, a washing liquid and an enhancing liquid. The detection method employing the time-resolved fluorescence immunoassay kit detecting methyl parathion comprises the following steps: (1) preparing an immunogen; (2) preparing a coating antigen; (3) preparing a monoclonal antibody; and performing pretreatment and detection on a sample. The kit and the method are short in detection time, high in average recovery rate, simple for sample pretreatment, capable of realizing on-site operation detection, wide in application scope and low in detection cost, and also possess the advantages of being strong in detection specificity, small in intra- and inter-assay difference, high in sensitivity, simple and rapid in operation, especially suitable for detection of a large bath of samples, and the like.
Owner:JIANGSU WISE SCI & TECH DEV
Solid phase microextraction head and preparation method and application thereof
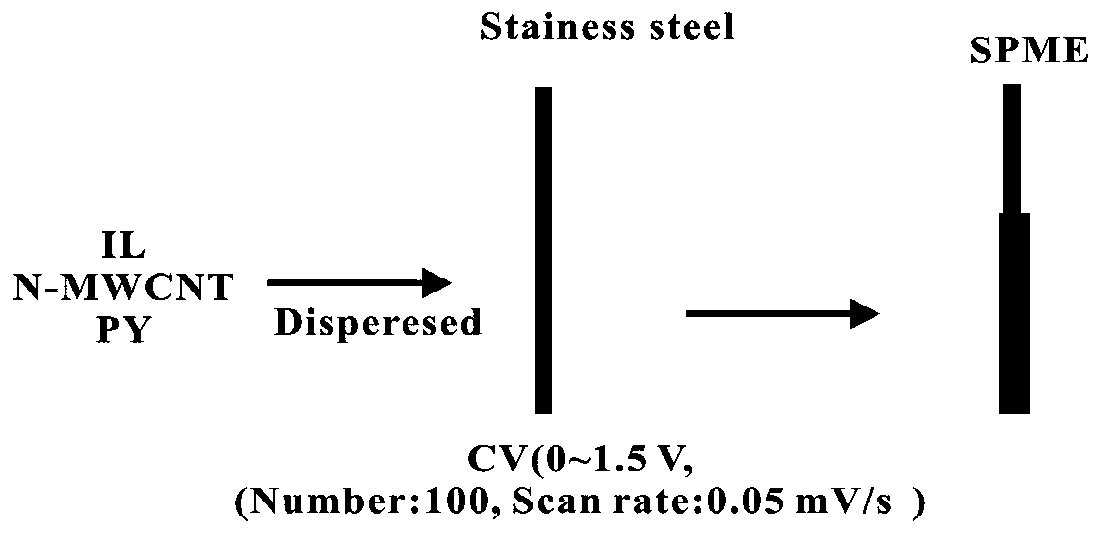
ActiveCN110694601AImprove adsorption capacityImprove mechanical stabilityIon-exchange process apparatusComponent separationFunctional monomerGas liquid chromatographic
The invention discloses a solid phase microextraction head and a preparation method thereof. A polypyrrole-ionic liquid-nitrogen doped multi-walled carbon nanotube extraction head is prepared by cyclic voltammetry by taking pyrrole as a functional monomer, and ionic liquid and nitrogen doped multi-walled carbon nanotubes as dopants. By combining the extraction with gas chromatography-mass spectrometry, an analytical method for the analysis and detection of methyl parathion, malathion and fenitrothion in food is established. Due to the large adsorption capacity and stability of IL and N-MWCNT,the sensitivity of the analysis method is improved and the analysis of the methyl parathion, malathion and fenitrothion in the food is further expanded. In addition, the PPY-IL-N-MWCNT extraction headcan also be used to detect other volatile pesticide residues.
Owner:HONGHE COLLEGE
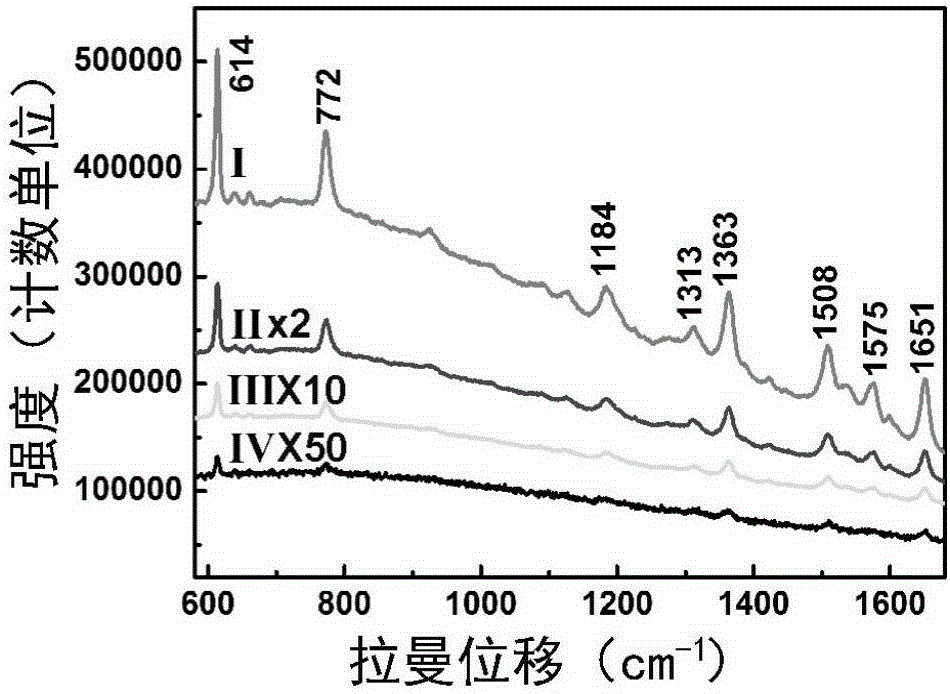
Silver-germanium-copper composite structural component and preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN104897638AAchieve enrichmentHigh SERS activityMaterial nanotechnologyPolycrystalline material growthNanowireGas phase
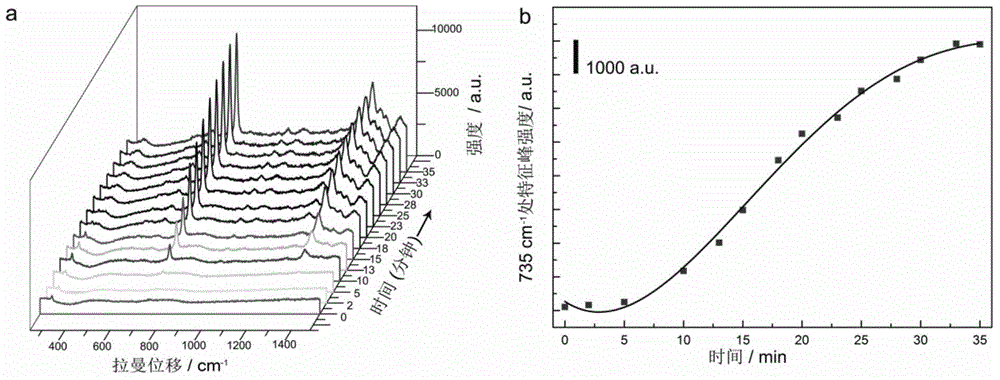
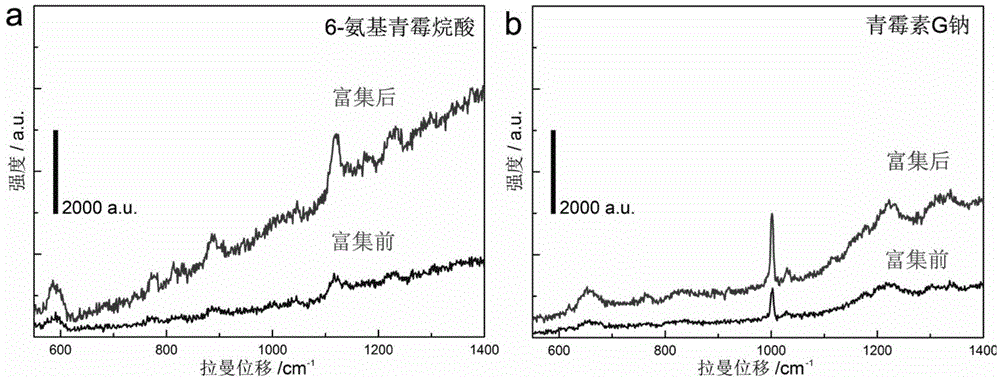
The invention discloses a silver-germanium-copper composite structural component and a preparation method and use thereof. The silver-germanium-copper composite structural component is prepared by constructing of germanium nanowires modified with silver nanoparticles on the surface and the mesh wall of a copper mesh, the mesh diameter of the copper mesh is 35-45 mum, the germanium nanowire line diameter is 100-150 nm, the line length is 5-15 mum, the silver nanoparticle grain diameter is 15-35 nm; and the method is as follows: the copper mesh is put at a position 1.5-2.5 cm from a gold target of a sputtering device for sputtering in the sputtering current of 15-25 mA for 1.5-2.5 min to obtain the copper mesh on which the surface and the mesh wall are evaporated with gold nanoparticles, then the germanium nanowires are grown on the copper mesh by chemical gas phase method to obtain the copper mesh on which the surface and the mesh wall are constructed with the germanium nanowires, and the sputtering device is used for sputtering the silver nanoparticles on the copper mesh on which the surface and the mesh wall are constructed with the germanium nanowires to obtain an objective product. The silver-germanium-copper composite structural component can be used as surface enhanced Raman scattering active base, and can be widely used for measuring the content of rhodamine 6G, or methyl parathion-methyl, or adenine, or 6-aminopenicillanicacid or alkanes acid or penicillin G sodium salt attached on the silver-germanium-copper composite structural component.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
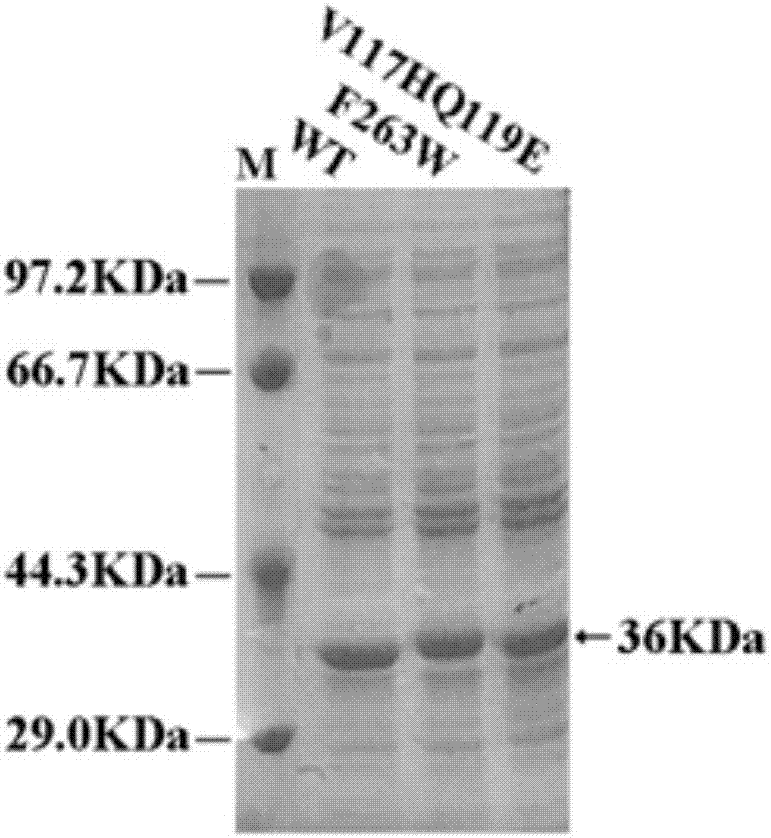
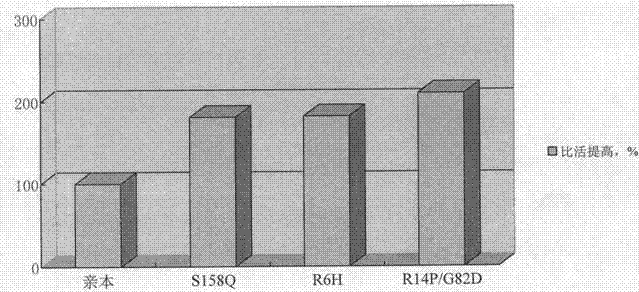
Enzymatic performance improved methyl parathion hydrolase mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN107189993AImprove enzymatic performanceBroaden the field of applicationHydrolasesFermentationMethyl parathionWild type
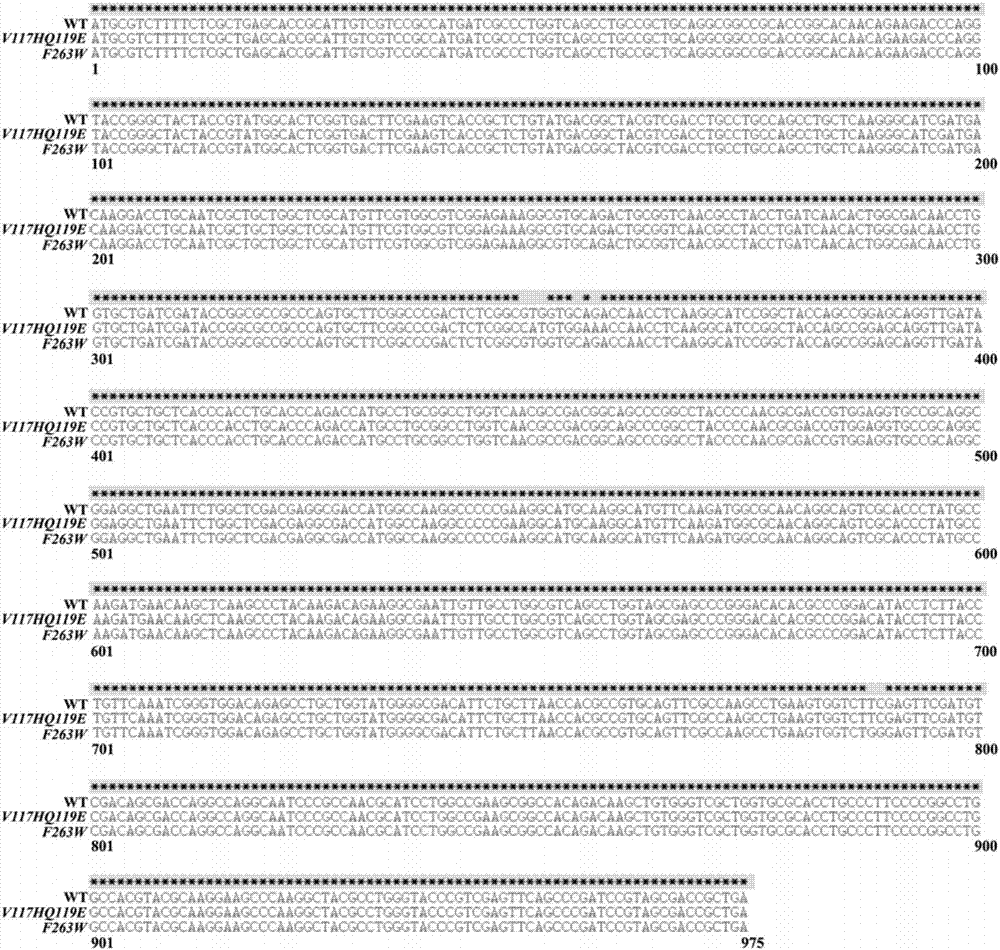
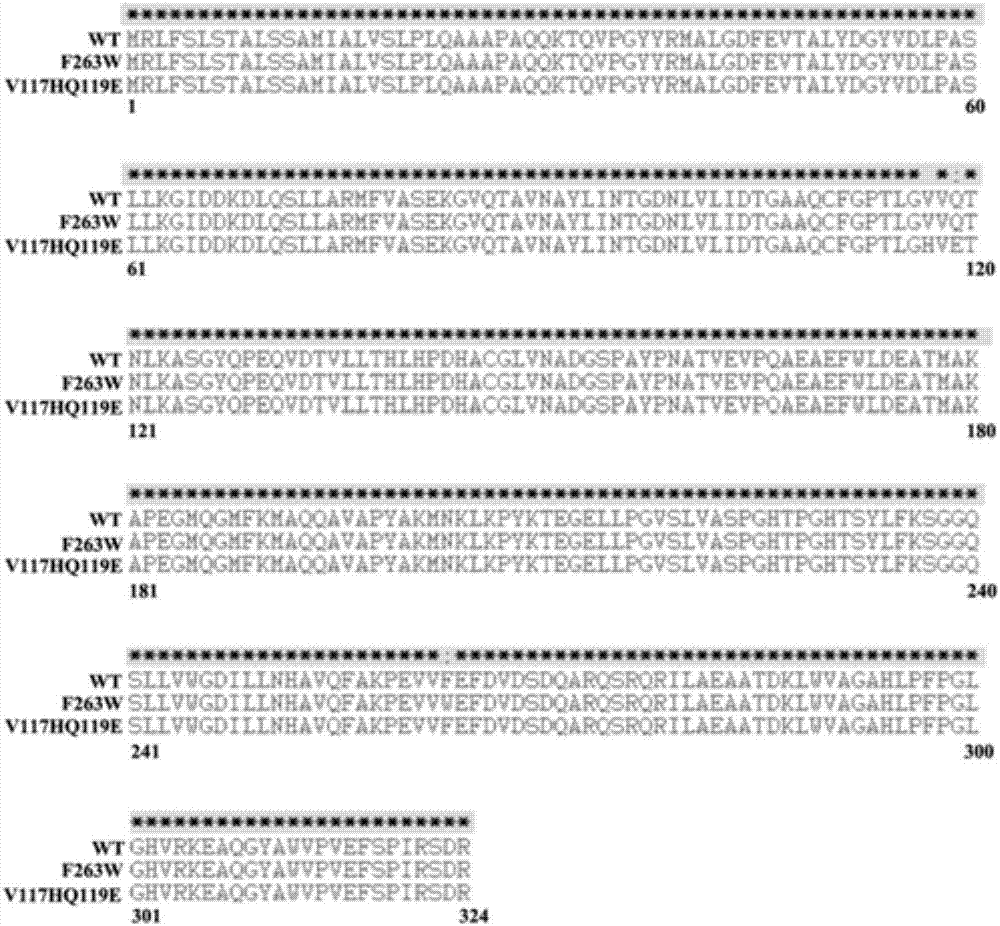
The invention discloses an enzymatic performance improved methyl parathion hydrolase mutant and application thereof. Wild-type enzymatic performance improved methyl parathion hydrolase is targetedly modified, mutation in vitro and expression to OPHC2 are performed by combining with a protein structure calculation and stimulation technology and a molecular biology technology, and kinetic parameters and the stability of protease are detected by applying biochemical means, so that a mutant V117HQ119E with remarkably improved thermal stability and substrate affinity and a mutant F263W with remarkably improved catalytic efficiency and improved stability in a surfactant are obtained through screening, wherein amino acid sequences of the mutant V117HQ119E and the mutant F263W are shown as SEQ ID No. 2 and SEQ ID No. 4 respectively. The enzymatic performance improved methyl parathion hydrolase mutant remarkably improves the enzymatic performance of the OPHC2, widens the application field and the action efficiency of the OPHC2 and has a wide application prospect on the aspects of degradation of an organophosphorus pesticide, organism detoxication, washing and disinfection of a nerve agent and the like.
Owner:北京森根比亚生物工程技术有限公司
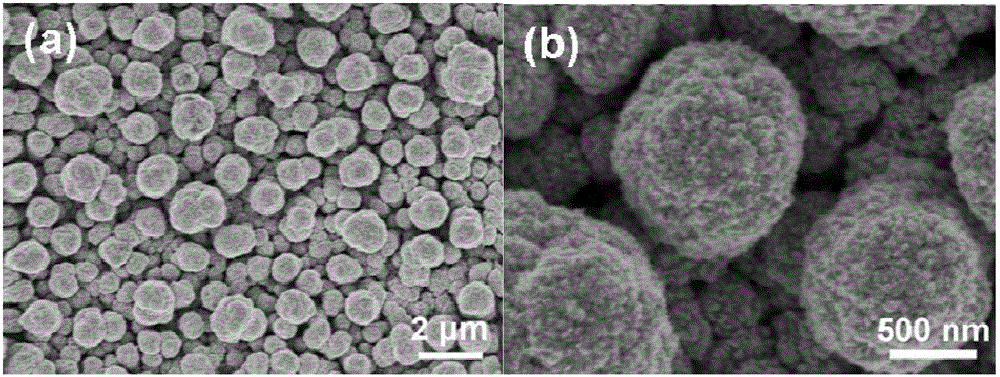
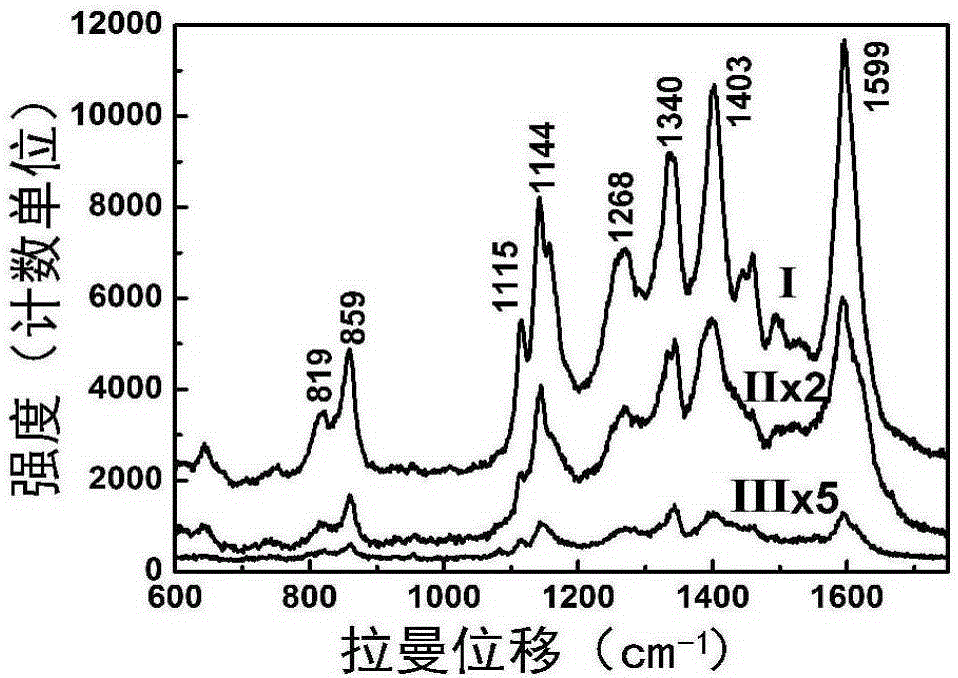
Gold micro-nano structure array and preparation method as well as application thereof
InactiveCN105174194AEfficient detectionImprove consistencyMaterial nanotechnologySemi-permeable membranesMicro nanoMethyl parathion
The invention discloses a gold micro-nano structure array and preparation method as well as application thereof. The array comprises a substrate coated with a gold film, a gold microprism array is arranged on the gold film, tops of gold microprisms forming the gold microprism array are hemispheric; each gold microprism with the hemispheric top has the prismdiameter of 200nm-3[mu]m and the prism height of 300nm-6[mu]m, and is composed of gold nano particles; and the particle size of the gold nano particles is 3-30nm. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, forming the gold film on the substrate through sputtering, then, adding the substrate coated with the gold film into a gold electrolyte as a cathode, performing electrodeposition for 8-20 hours with 30-500[mu]A / cm<2> direct current, wherein, the gold electrolyte is a mixed solution of 0.2-5g / L chloroauric acid solution and 2-50g / L polyvinyl pyrrolidone solution, thereby obtaining the target product. The gold micro-nano structure array can be used as an SERS (Surface Enhanced Raman Scattering) active substrate, and the content of rhodamine or methyl parathion attached on the gold micro-nano structure array is measured through a laser Raman spectrometer.
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Preparation of chlorpyrifos and methyl parathion universal antibody and universal envelope antigen
InactiveCN101477115AReduce testing costsThe pre-processing process is simpleMaterial analysisAntigenChlorpyrifos
The invention discloses preparation of chlorpyrifos and methyl parathion common antibody of an enzyme-linked immunoadsorption determination reagent kit suitable for analyzing chlorpyrifos and methyl parathion residue at the same time and common envelope antigen, which comprises preparation methods of chlorpyrifos semiartificial antigen, methyl parathion semiartificial antigen structure, chlorpyrifos and methyl parathion common antibody and common envelope antigen. The chlorpyrifos and methyl parathion common antibody and the common envelope antigen prepared by the preparation methods can be used to prepare the enzyme-linked immunoadsorption determination reagent kit suitable for analyzing chlorpyrifos and methyl parathion residue at the same time; moreover, the reagent kit can be used for quickly detecting chlorpyrifos residue and methyl parathion in water, soil, foodstuff such as vegetables and poisoned samples; in addition, the invention has the advantages of simple preliminary treatment process of samples, simultaneous detection of samples in batches and lower sample detection cost than the prior detection method.
Owner:孙家隆
Method used for rapid separation and detection of organophosphorus pesticides in water
The invention discloses a method used for rapid separation and detection of organophosphorus pesticide in water. The method comprises following steps: an appropriate amount of surface modified TiO2 with a particle size of 500nm, silica gel G and sodium carboxymethylcellulose are mixed and stirred uniformly; a glass plate of 2.5*10cm is coated with the mixture, is dried and activated for half an hour at a temperature of 105 DEG C so as to obtain a thin-layer chromatography plate; a mixture of hexane, acetone, methanol and water is taken as a developing solvent, and it is possible to separate six kinds of organophosphorus pesticides including chlopyrifos, malathion, parathion, methyl parathion, phoxim, and methamidophos by 12min of chromatography in dark; and the organophosphorus compounds are degraded to phosphates after 15 to 20min of sun light treatment, and the phosphates are subjected to color development in dark. Standard solution of each organophosphorus pesticide is prepared in a corresponding linear concentration range, thin-layer chromatography sample plates prepared under the same conditions are used as reference chromatograms, and kind and concentration of the organophosphorus pesticides in water samples can be determined by comparison. The linear concentration range is 0.02mg / L to 0.6mg / L, and detection requirements of drinking water are satisfied.
Owner:MINNAN NORMAL UNIV
Enzyme linked immunosorbent assay reagent kit for simultaneously analyzing carbaryl and methyl parathion
InactiveCN101477119AThe pre-processing process is simpleReduce testing costsMaterial analysisMethyl parathionMethyl group
The invention discloses an enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit suitable for residue analysis of carbaryl and methyl parathion simultaneously, which comprises a kit body, an ELISA plate / tube and reagents arranged in the kit body. Each hole of the ELISA plate is provided with general coating antigen, wherein the general coating antigen is coated by a coating liquid and can undergo specific reaction with co-anti-antibody against carbaryl and methyl parathion, and is sealed with gelatin; the regents in the kit comprise a washing liquid, a substrate diluent, a standard solution of carbaryl and methyl parathion , antibodies against carbaryl and methyl parathion, enzyme-labeled antibodies against carbaryl and methyl parathion, a substrate, a coloration substance and a reaction terminating solution. The enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay kit can be used to detect carbaryl and methyl parathion residues in food such as water, soil, vegetable and poisoned samples simultaneously and rapidly, has simple pretreatment process of the samples, and detect batch samples simultaneously, and has sample detection cost lower than the prior detection method.
Owner:孙家隆
Treatment agent for organic phosphorus contaminated soil and preparation method of treatment agent
InactiveCN108085014AReduce contentSimple preparation processAgriculture tools and machinesOrganic fertilisersPullulanSodium Caseinate
The invention discloses a treatment agent for organic phosphorus contaminated soil. The treatment agent for the organic phosphorus contaminated soil comprises the following components: dry cow dung, pullulan, sodium caseinate, selenium-enriched capsicum stems, sodium tripolyphosphate, magnesium chloride, calcium sulfate crystal whiskers, desalinated sea sand, hydrated zinc borate, molybdenum disulfide, calcite, pineapple leaf powder, dry moss, and a silica sol. The treatment agent provided by the invention can effectively treat the organic phosphorus contaminated soil, and can obviously reducethe content of methyl parathion, phorate and methidathion in the soil; the preparation process is simple, production preparation is facilitated; and the use method is simple and not restricted by environmental conditions, and has better social value.
Owner:苏州艾捷尔斯生物科技有限公司
Gold nano structure with cone-shaped surface and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN109722683AEfficient detectionImprove consistencyMaterial nanotechnologyRaman scatteringNano structuringMethyl parathion
Owner:HEFEI INSTITUTES OF PHYSICAL SCIENCE - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
High-activity methyl parathion hydrolase mutant and use thereof
InactiveCN104726426AHigh catalytic activityImprove catalytic performanceBacteriaHydrolasesMethyl parathionCleansing Agents
The invention discloses high-activity methyl parathion hydrolase and a use thereof. Compared with the existing methyl parathion hydrolase, the recombinant methyl parathion hydrolase obtained by site directed mutagenesis design and screening has substantially improved activity, and has a good capability of degrading organophosphorus pesticide such as methyl parathion. A fruit and vegetable pesticide cleaning agent prepared from the methyl parathion hydrolase has effects better than those of the same kind products on the market. The high-activity methyl parathion hydrolase can be used for removing pesticide on fruits and vegetables, tea and traditional Chinese medicine raw materials in processing, can be used in soil restoration and has a wide application prospect. The invention also discloses a preparation method of the recombinant methyl parathion hydrolase.
Owner:BIOTRAND
Hybridoma cell line F3A2, monoclonal antibody produced by hybridoma cell line F3A2 and application
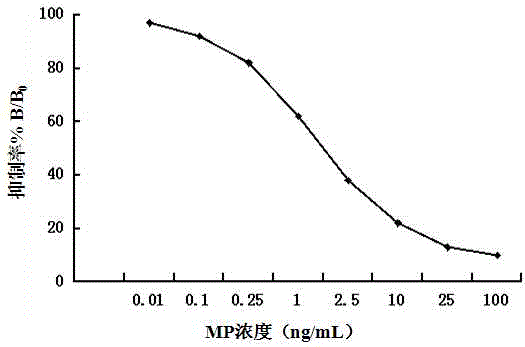
ActiveCN105131119AHigh sensitivityStrong specificityTissue cultureImmunoglobulinsReaction rateMethyl parathion
The present invention relates to a monoclonal antibody for detecting organophosphorus pesticide methyl parathion and application. F3A2 hybridoma cell line provided by the invention can be used in the preparation of the methyl parathion efficient identifying monoclonal antibody, and the titer measured by mouse hydroperitoneum antibody enzyme-linked immunosorbent analysis method is 1.2 * 10<4>. The anti-methyl parathion monoclonal antibody is high in sensitivity, the methyl parathion 50% inhibitory concentration (IC50) is 21.2ng / mL, the intercrossing reaction rates of the monoclonal antibody and the organophosphorus pesticides such as fenitrothion, isocarbophos, chlorpyrifos-methyl, phoxim and the like similar in structure to methyl parathion are less than 0.1%, and the monoclonal antibody can be used for rapid detection of organophosphorus pesticide methyl parathion residues.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com