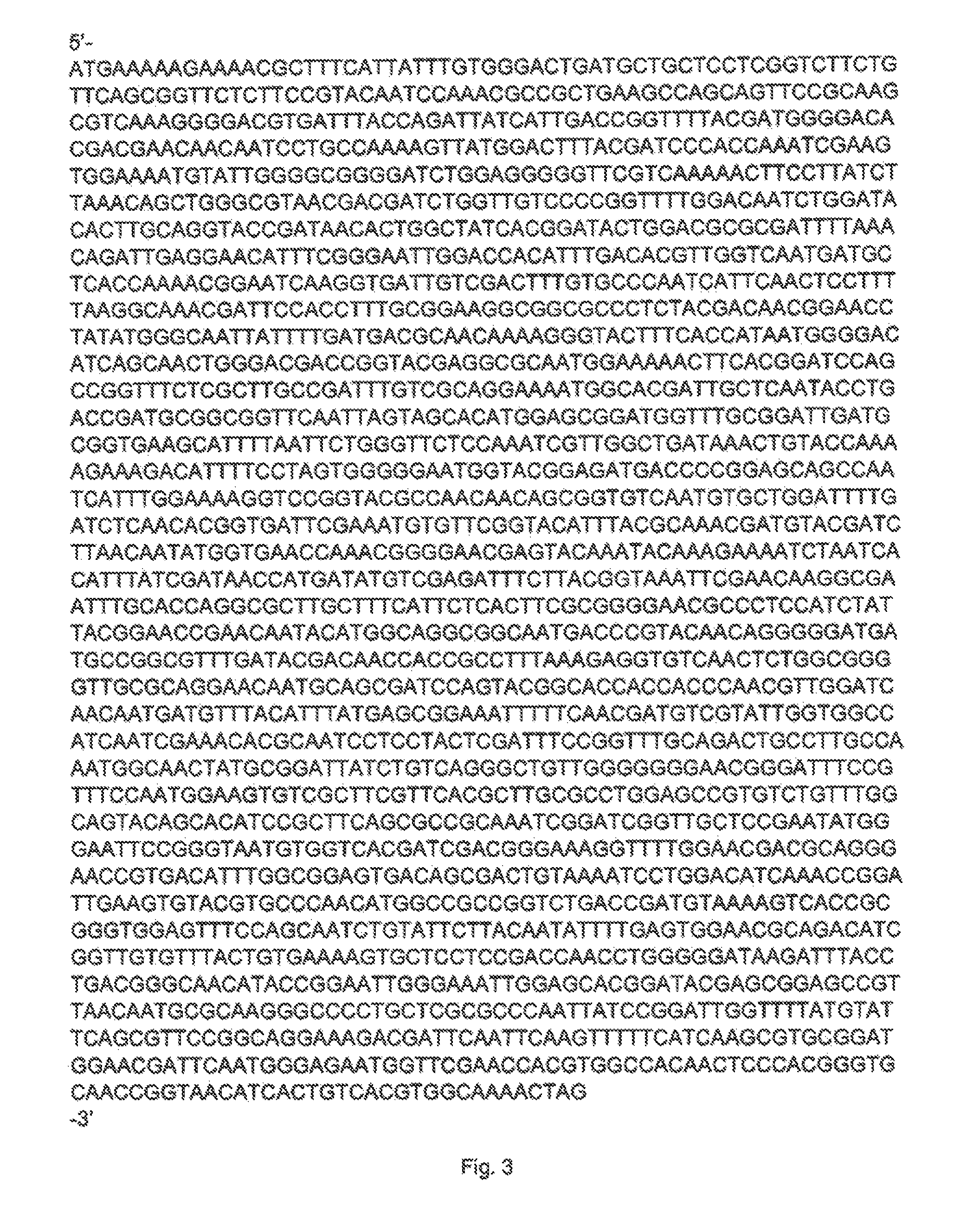Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
615 results about "Functional protein" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Functional proteins carry out a function in the body unlike structual proteins which produce structures (eg bones and muscles). An example of a functional protein is antibodies as they carry out the function of fighting off bacteria and virus'.
Shotgun scanning
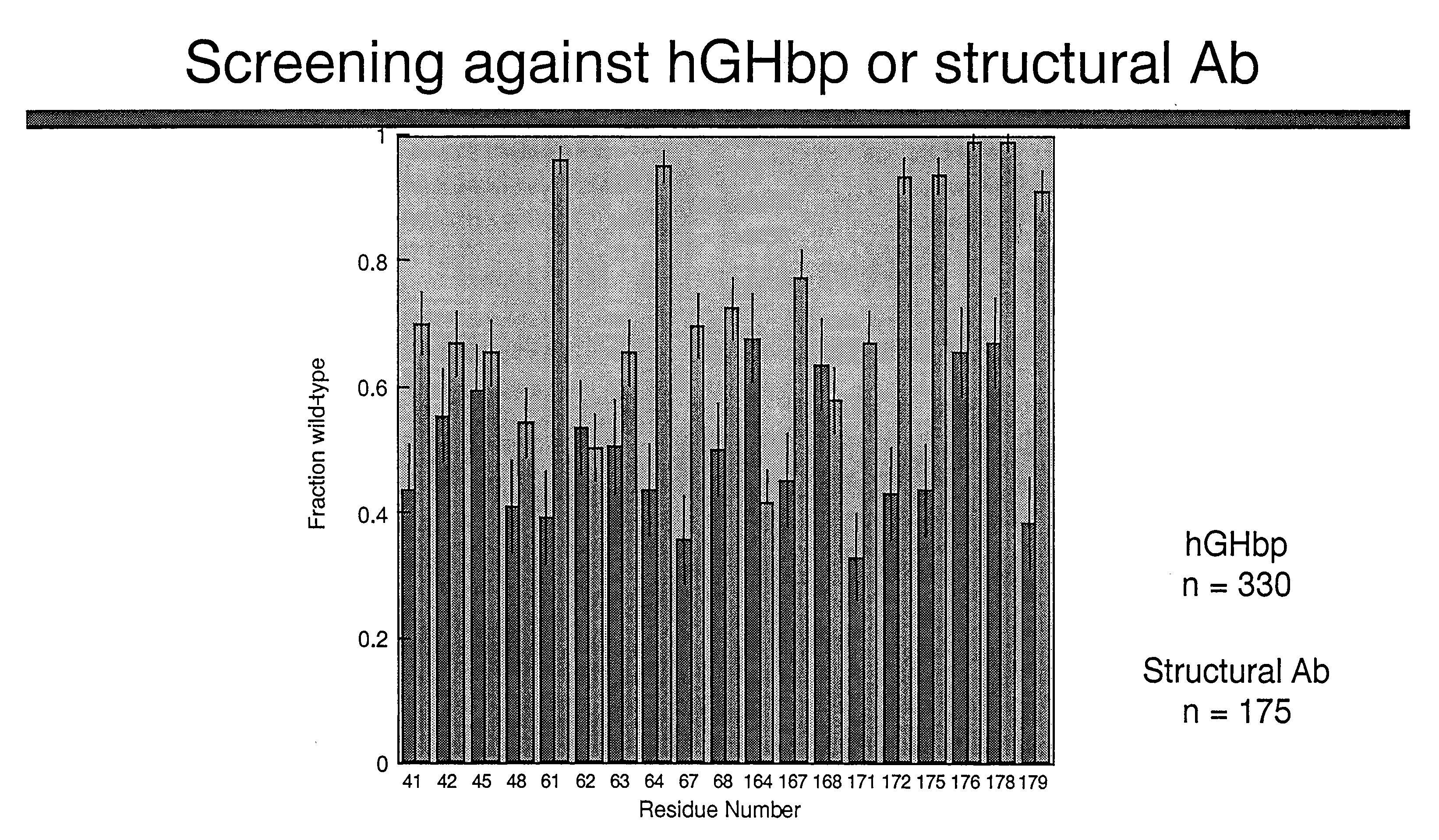
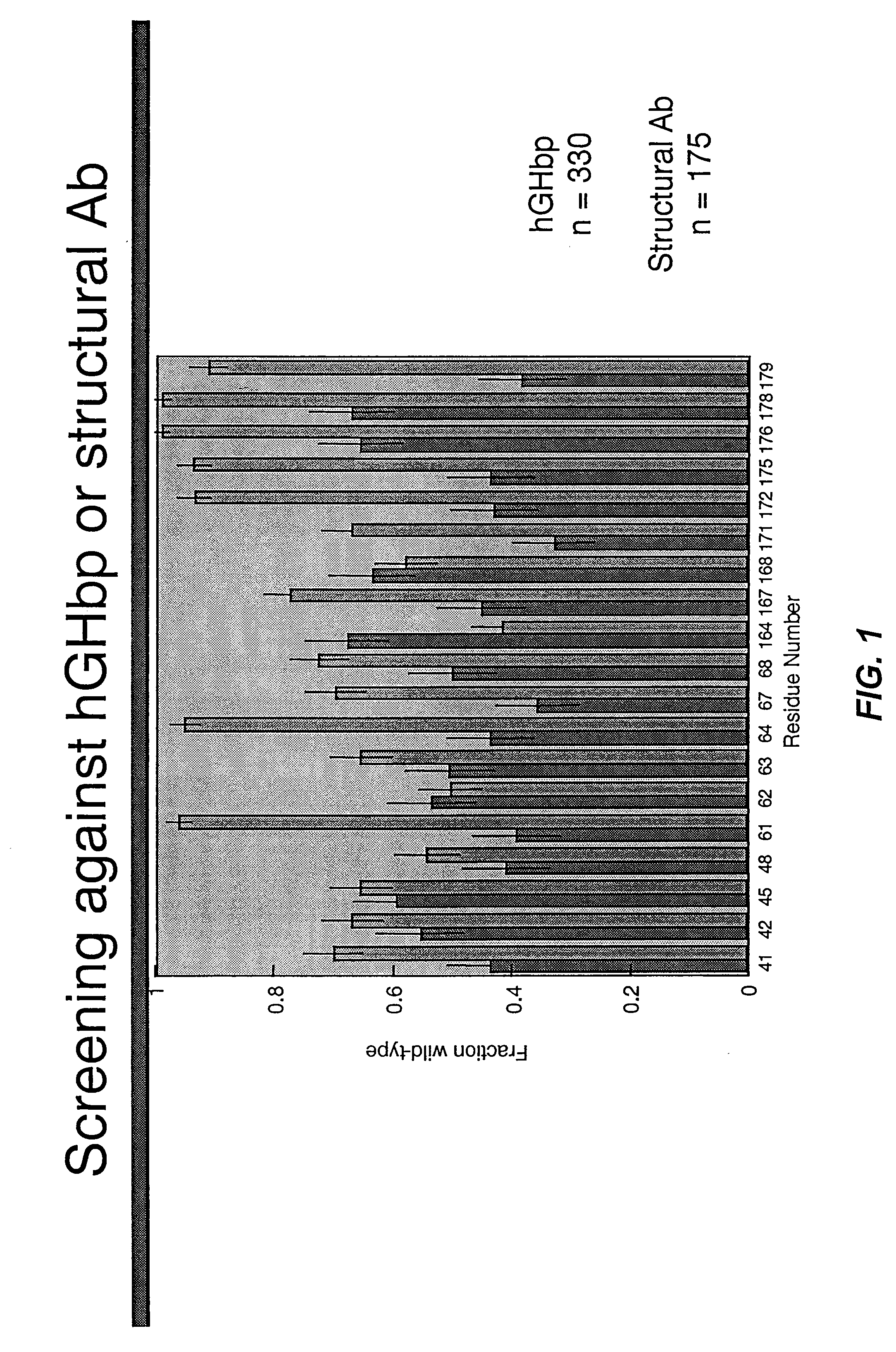
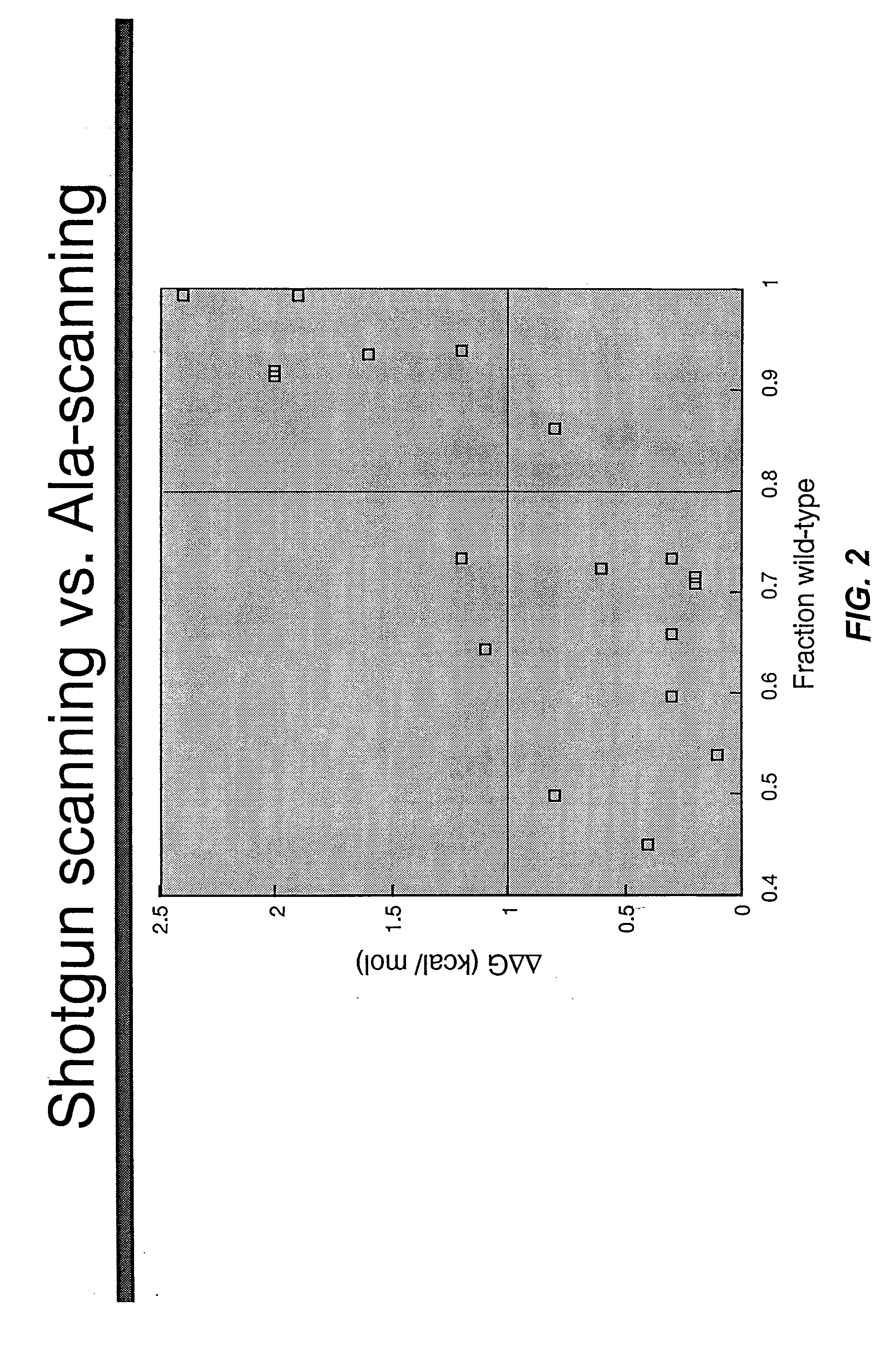
A combinatorial method that uses statistics and DNA sequence analysis rapidly assesses the functional and structural importance of individual protein side chains to binding interactions. This general method, termed “shotgun scanning”, enables the rapid mapping of functional protein and peptide epitopes and is suitable for high throughput proteomics.
Owner:GENENTECH INC
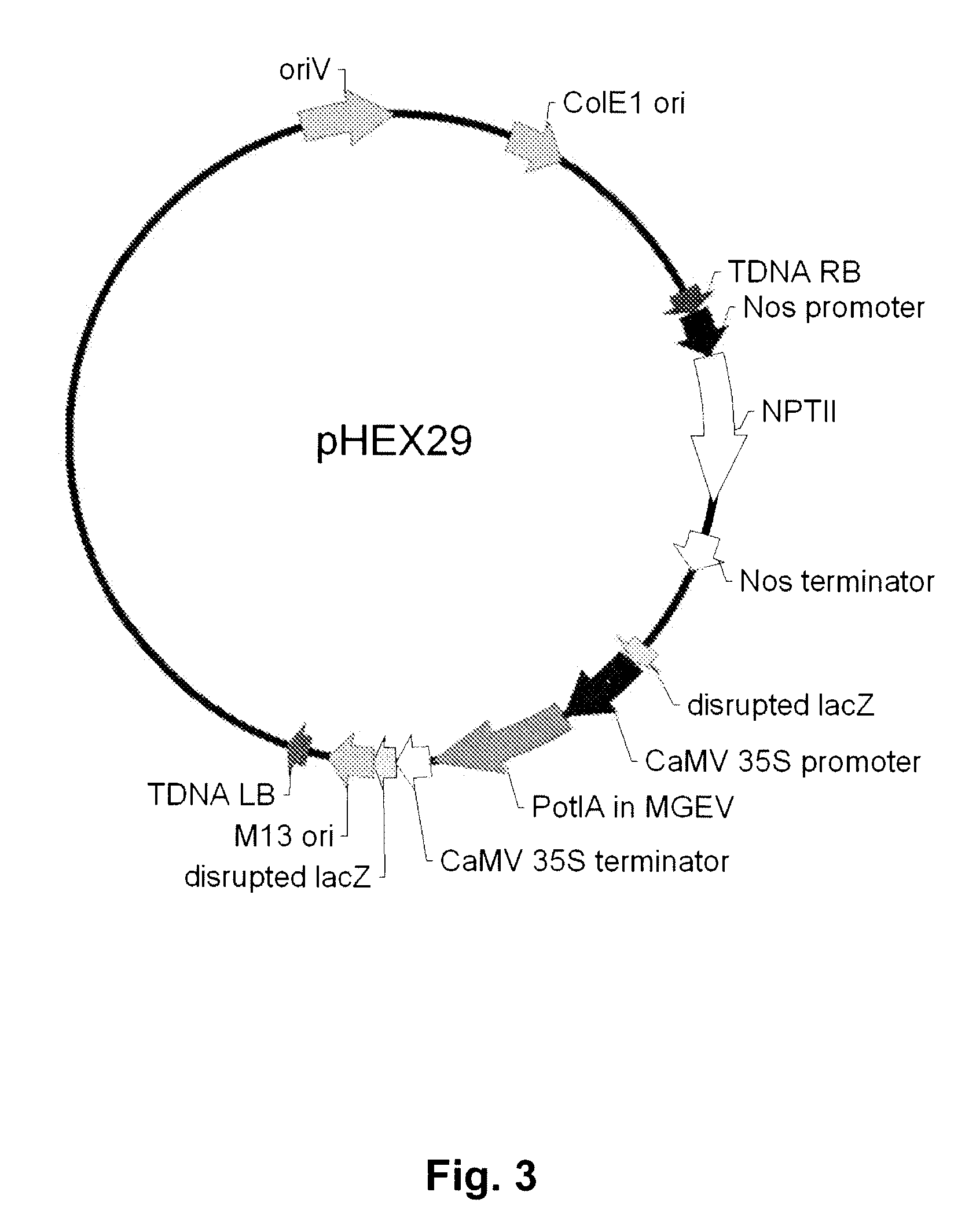
Multi-gene expression vehicle
InactiveUS20070277263A1Lack featureClimate change adaptationOther foreign material introduction processesMultigene expressionNucleotide
A multigene expression vehicle (MGEV) consisting essentially of a polynucleotide comprising 2 to 8 domain segments, D, each domain encoding a functional protein, each domain being joined to the next in a linear sequence by a Linker (L) segment encoding a Linker peptide, the D and L segments all being in the same reading frame, and at least one of the domains is not a type two protease inhibitor.
Owner:HEXIMA LTD
Bispecific antibody substituting for functional proteins
ActiveUS20070041978A1Enhances enzymatic reactionImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIBlood coagulation factor VIIIBlood Coagulation Factor X
The present inventors succeeded in constructing bispecific antibodies, which bind to both the blood coagulation factor IX / activated blood coagulation factor IX and blood coagulation factor X, and functionally substitute for blood coagulation factor VIII / activated blood coagulation factor VIII which enhances the enzymatic reaction.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Double Specific Antibodies Substituting For Functional Proteins
InactiveUS20080075712A1Reduced activityOutstanding sustainabilityImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsNervous disorderBlood coagulation factor VIIIBlood Coagulation Factor X
The present inventors succeeded in separating bispecific antibodies that functionally substitute for ligands of type I interferon receptors comprising two types of molecules: AR1 chain and AR2 chain. Furthermore, the present inventors succeeded in producing bispecific antibodies that substitute for the enzyme reaction-accelerating function of blood coagulation factor VIII / activated blood coagulation factor VIII, which bind to both blood coagulation factor IX / activated blood coagulation factor IX and blood coagulation factor X.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Modular protein libraries and methods of preparation
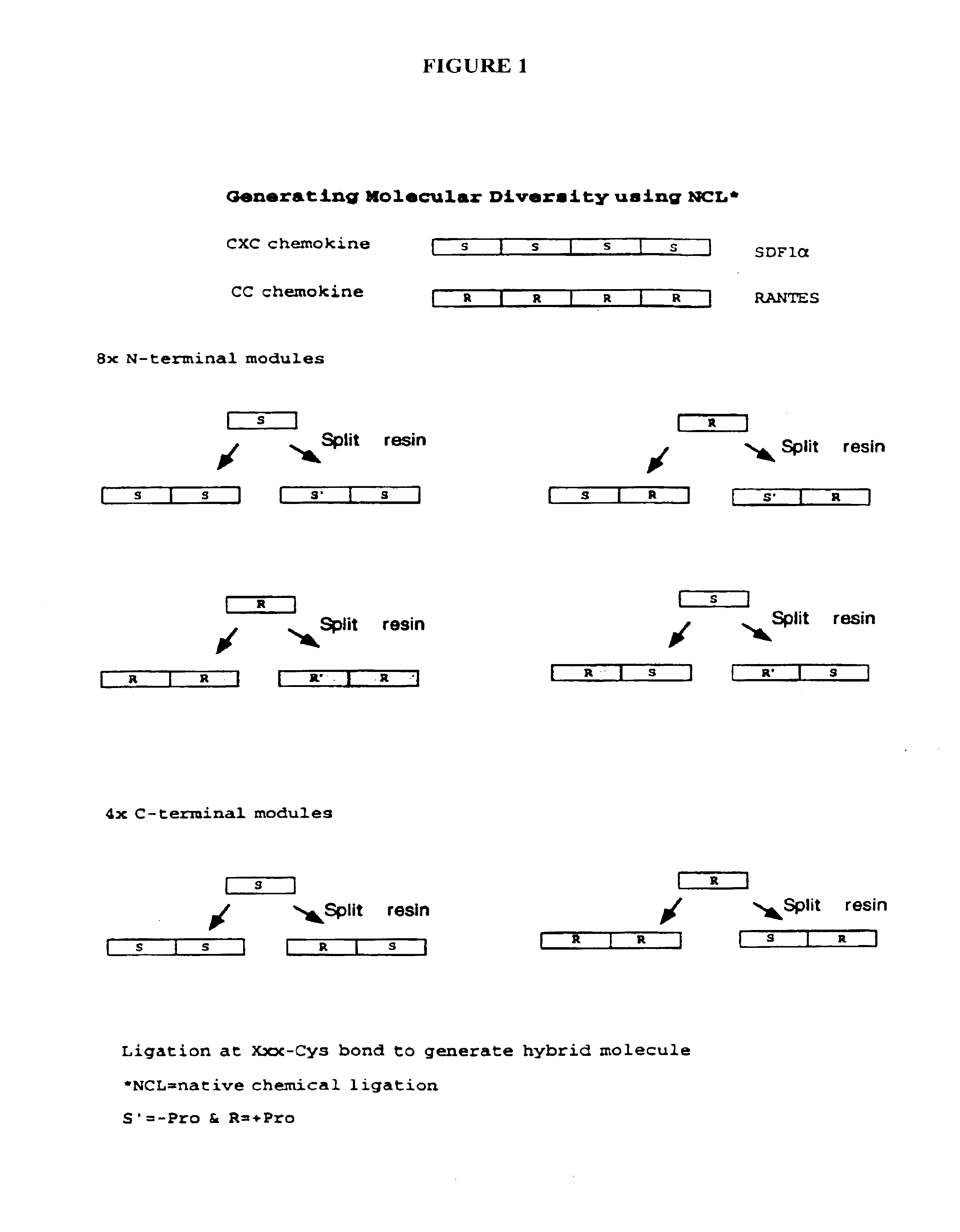
InactiveUS6844161B2Efficient and high-yieldPeptide librariesChemokinesHigh-Throughput Screening AssaysProtein molecules
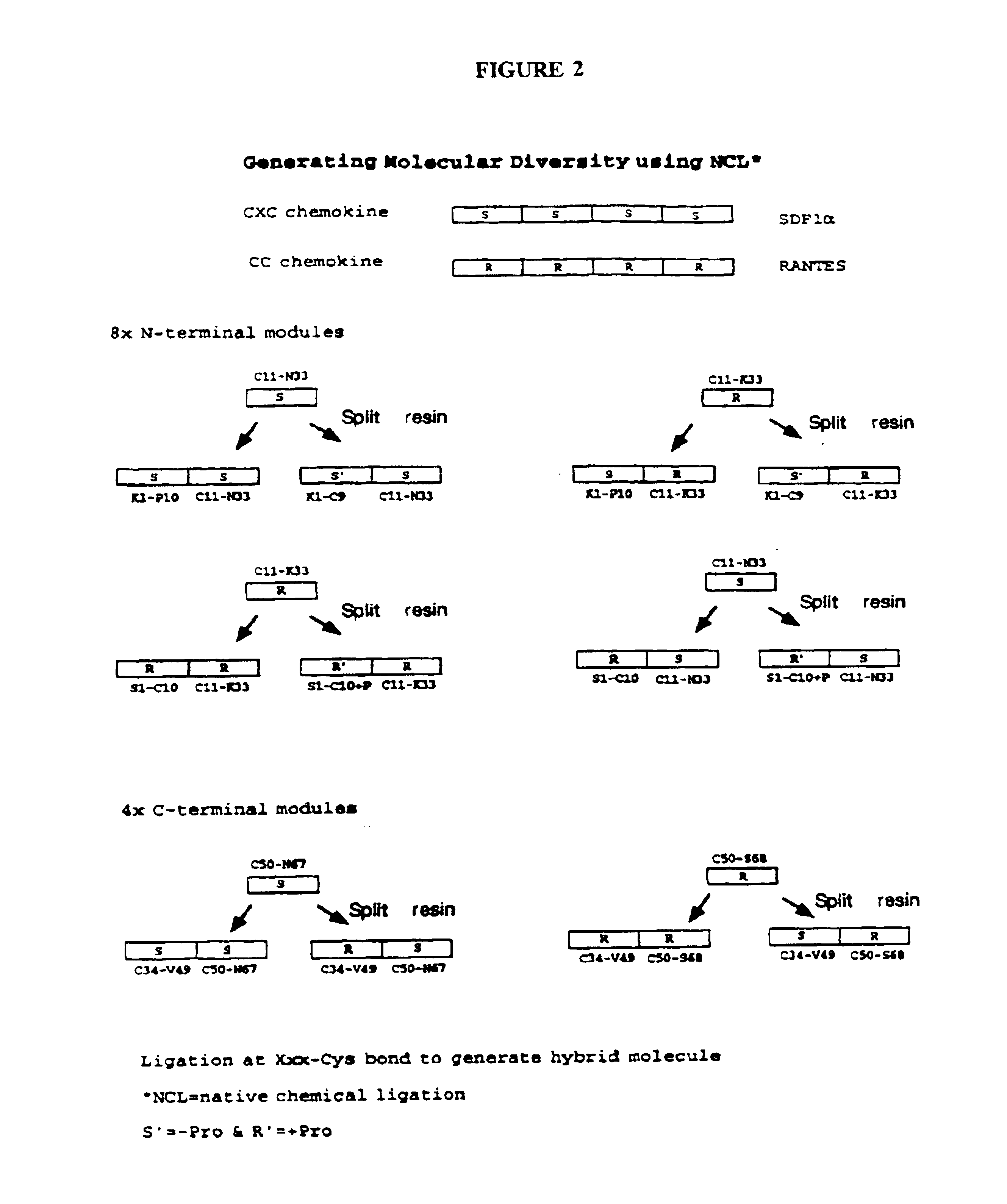
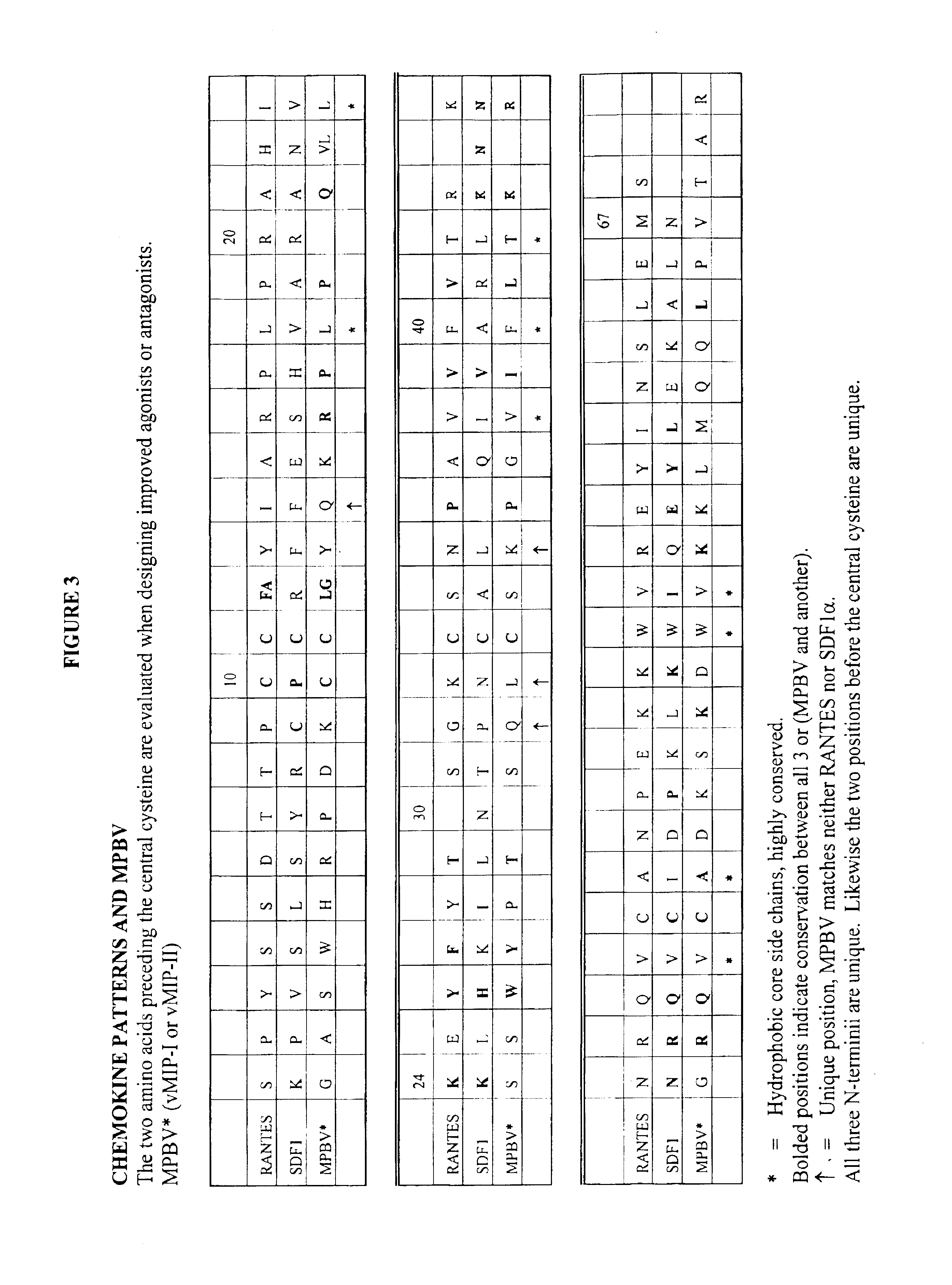
Novel proteins and protein libraries are disclosed. The proteins possess one or more functional protein modules from different parent protein molecules. The proteins and protein libraries are exemplified by the preparation of cross-over chemokines that contain various combinations of peptide segments derived from RANTES, SDS-1 and vMIP-I and to vMIP-II. The proteins and libraries are extremely pure and can be provided in non-limiting high yields suitable for diagnostic and high-throughput screening assays.
Owner:AMYLIN PHARMA INC
Hormone receptor functional dimers and methods of their use
InactiveUS7057015B1Enhance possibility of producingIncrease flexibilityFusion with DNA-binding domainSugar derivativesADAMTS ProteinsProtein Unit
The invention provides chimeric proteins having at least two functional protein units, each containing the dimerization domain of a member of the steroid / thyroid hormone nuclear receptor superfamily. The chimeric proteins can fold under crystallization conditions to form functional entities. The functional entities optionally contain a novel flexible peptide linker of variable lengths between at least two of the protein units. In a preferred embodiment, the linker is designed to be increased in increments of 12 amino acids each to aid in preparation of variant chimeric proteins. The DNA binding characteristics of the invention functional entities differ from those of wild-type complexes formed between “monomeric” receptors and their binding partners. Some functional entities, e.g. dimers expressed as fusion proteins, transactivate responsive promoters in a manner similar to wild-type complexes, while others do not promote transactivation and function instead essentially as constitutive repressors. The invention further provides nucleotide sequences encoding the invention chimeric proteins, cells containing such nucleotide sequences, and methods for using the invention chimeric proteins to modulate expression of one or more exogenous genes in a subject organism. In addition, isolated protein crystals suitable for x-ray diffraction analysis and methods for obtaining putative ligands for the invention chimeric proteins are provided.
Owner:SALK INST FOR BIOLOGICAL STUDIES
Bispecific antibody substituting for functional proteins
ActiveUS8062635B2Enhances enzymatic reactionImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIBlood coagulation factor VIIIBlood Coagulation Factor X
The present inventors succeeded in constructing bispecific antibodies, which bind to both the blood coagulation factor IX / activated blood coagulation factor IX and blood coagulation factor X, and functionally substitute for blood coagulation factor VIII / activated blood coagulation factor VIII which enhances the enzymatic reaction.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
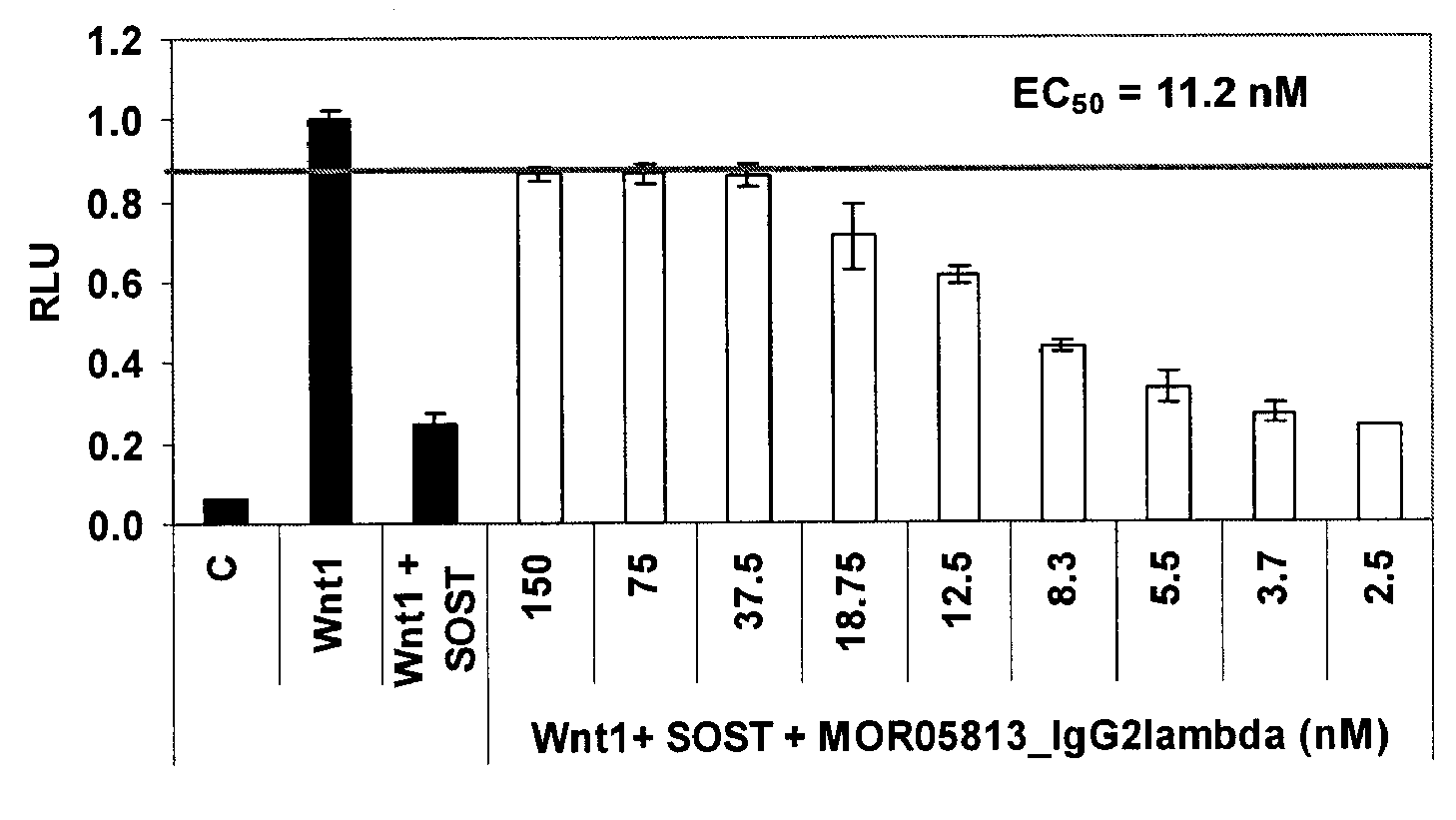
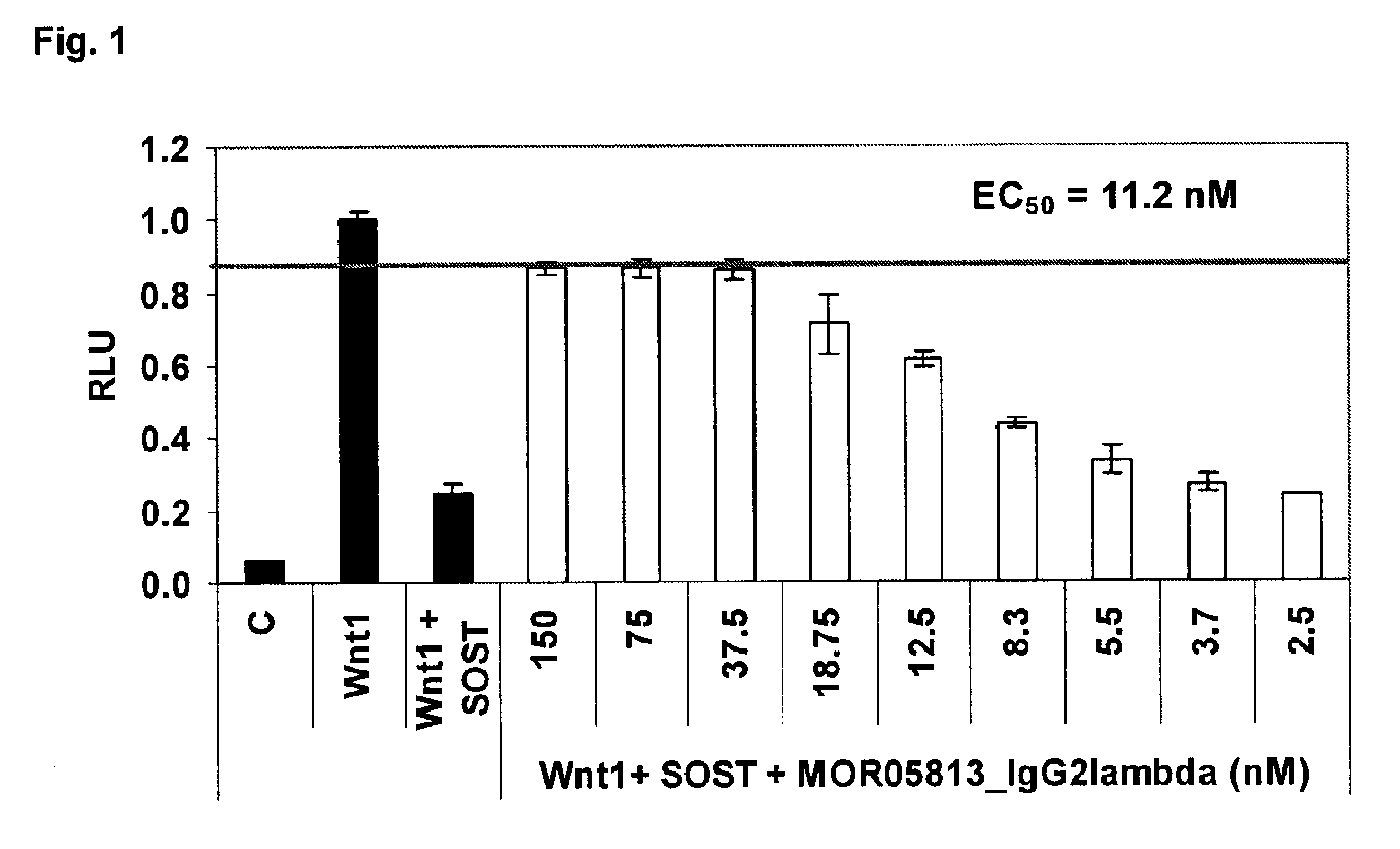
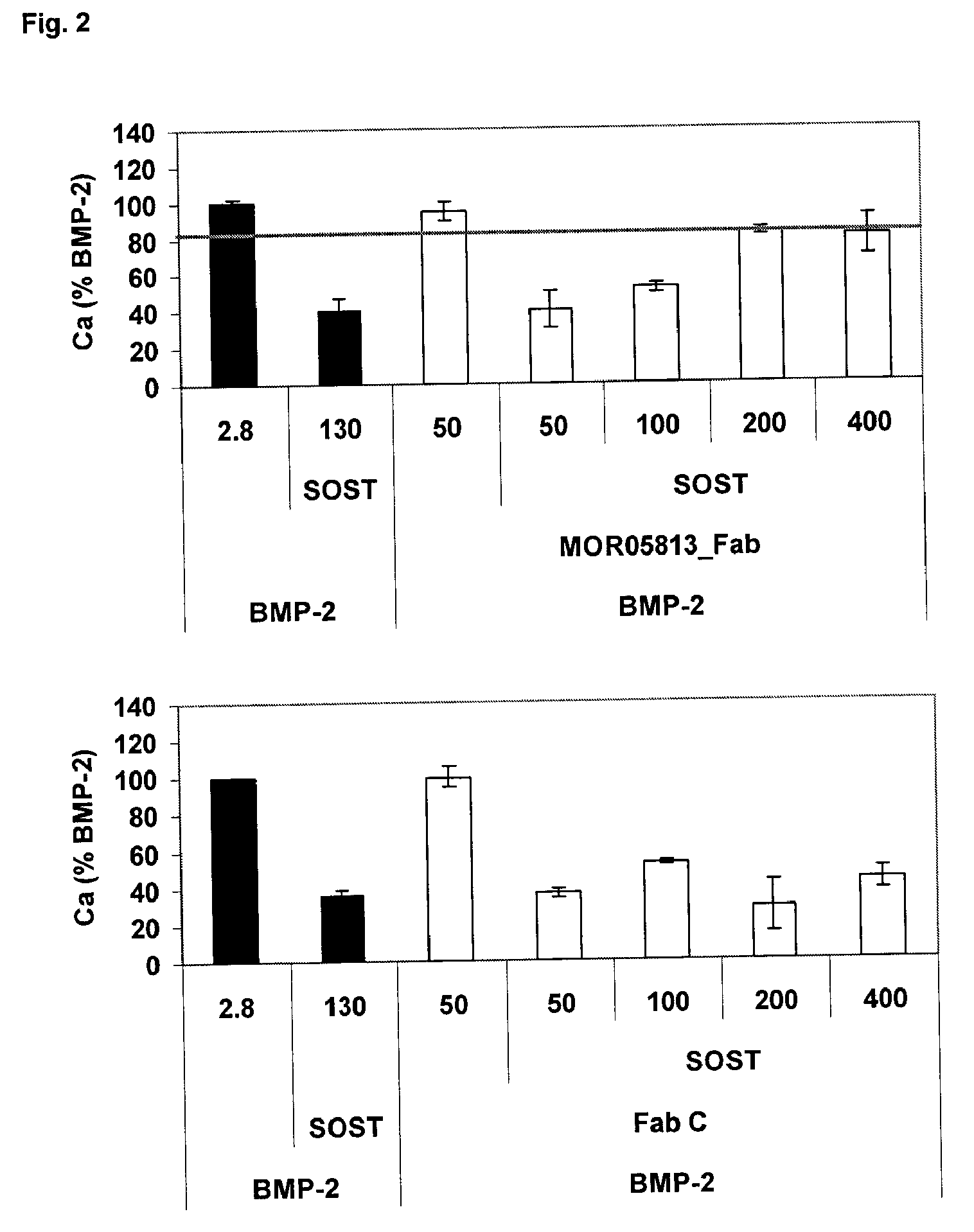
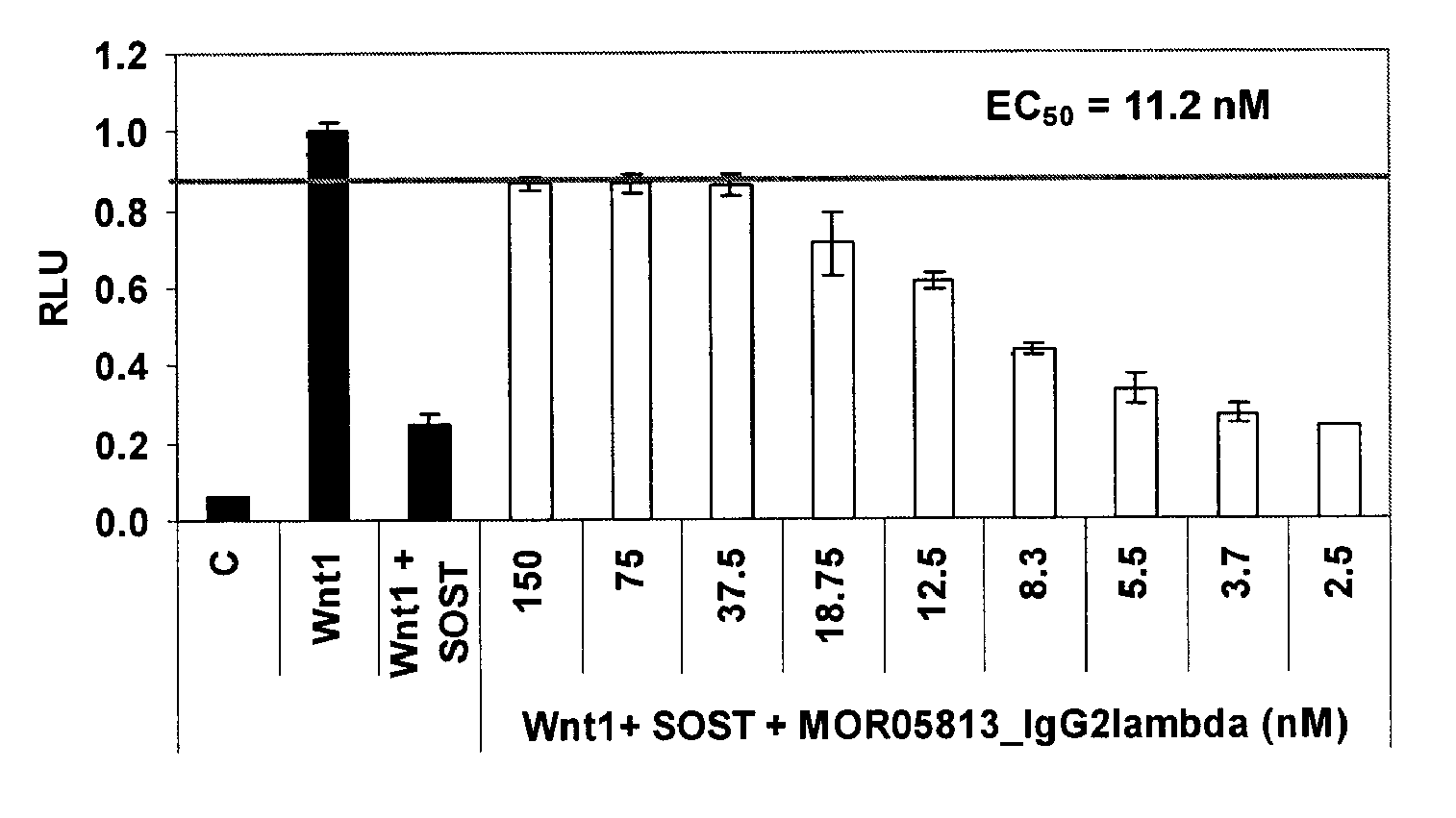
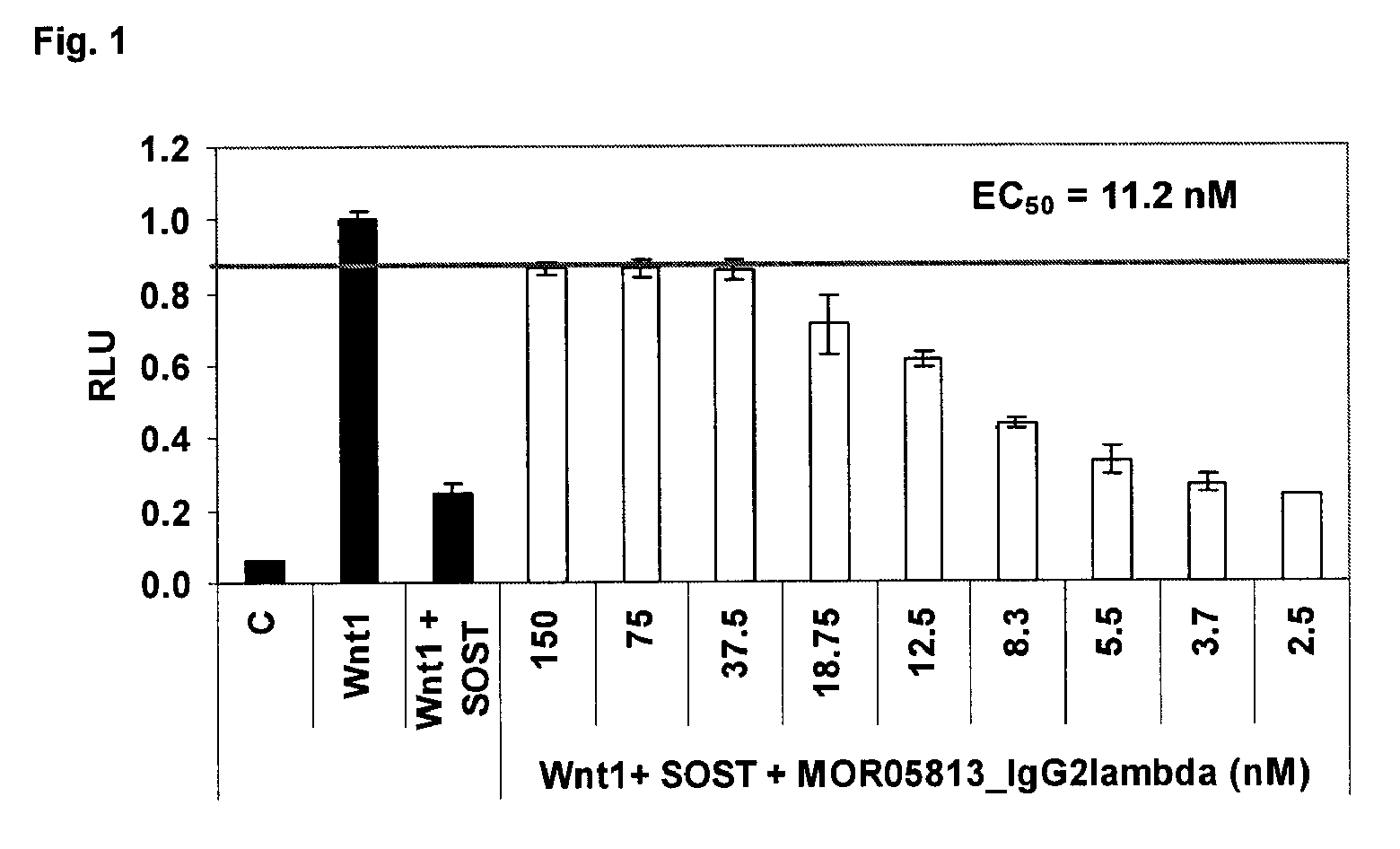
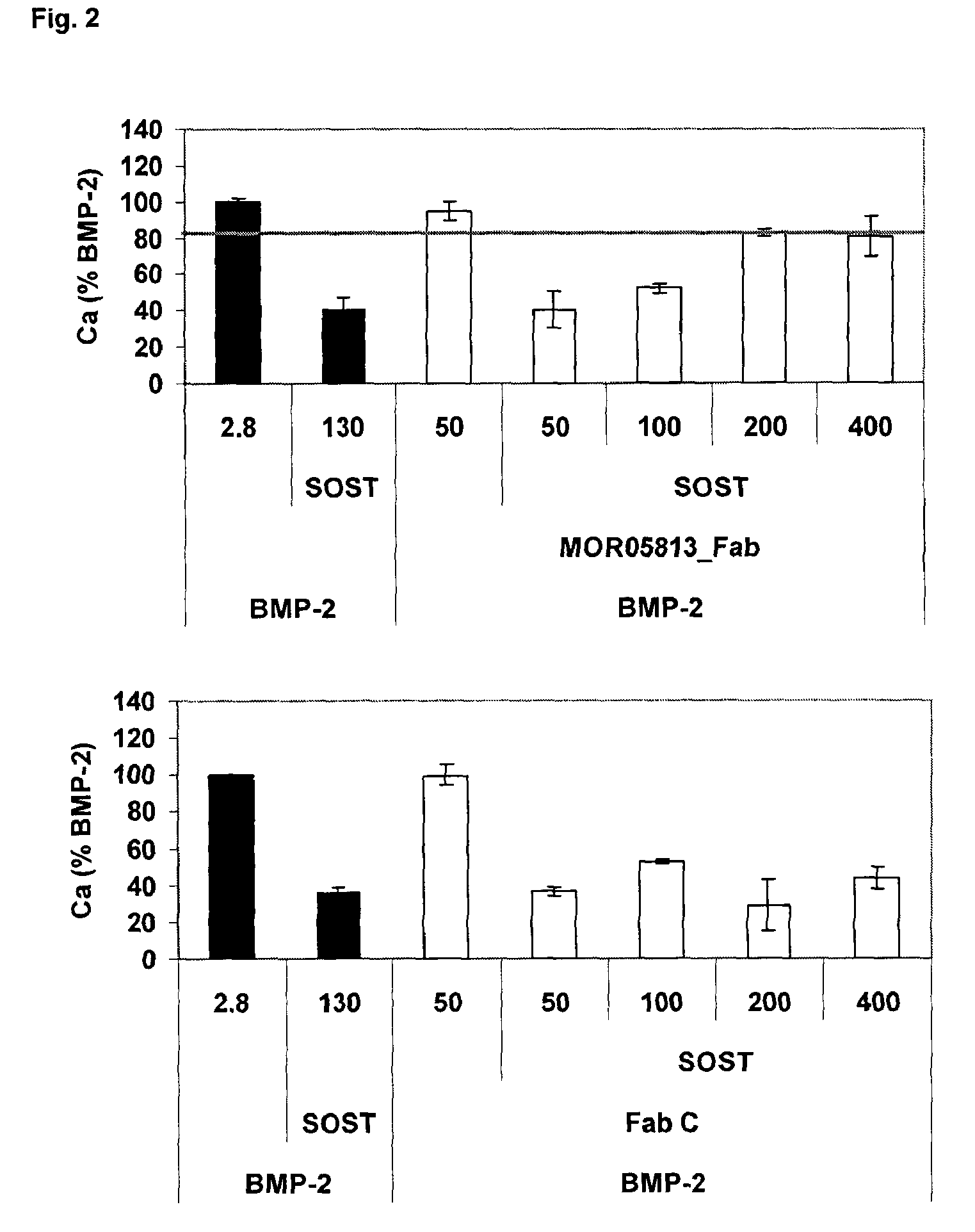
Compositions and methods for use for antibodies against sclerostin
The present invention relates to antibodies against sclerostin and compositions and methods of use for said antibodies to treat disease related to bone abnormalities such as osteoporosis. An embodiment of the invention herein provides an antibody or a functional protein comprising an antigen-binding portion of said antibody for a target in sclerostin polypeptide, characterized in that the antibody or functional protein specifically binds to sclerostin polypeptide and can increase at least one of bone formation, bone mineral density, bone mineral content, bone mass, bone quality and bone strength in a mammal.
Owner:MEREO BIOPHARMA 3 LTD
Compositions and methods for use for antibodies against sclerostin
The present invention relates to antibodies against sclerostin and compositions and methods of use for said antibodies to treat disease related to bone abnormalities such as osteoporosis. An embodiment of the invention herein provides an antibody or a functional protein comprising an antigen-binding portion of said antibody for a target in sclerostin polypeptide, characterized in that the antibody or functional protein specifically binds to sclerostin polypeptide and can increase at least one of bone formation, bone mineral density, bone mineral content, bone mass, bone quality and bone strength in a mammal.
Owner:MEREO BIOPHARMA 3 LTD
Food compositions having a realistic meat-like appearance, feel, and texture
InactiveUS20100233347A1Improve palatabilityHighly palatableAnimal feeding stuffWorking-up animal fodderBiotechnologyPlasticizer
The invention provides novel food compositions having a realistic meat-like appearance, feel, and texture. The compositions comprise from about 40 to about 90% functional proteins, from about 0.05 to about 2% of one or more cross-linking agents, and from about 60 to about 10% of a meat slurry, wherein the meat slurry comprises meat and one or more humectant plasticizers in a meat:humectant plasticizer ratio of from about 20:80 to about 80:20. The compositions are produced by heating a preconditioned mixture of the food components under pressure and then expanding the heated composition to form the food composition.
Owner:NESTEC SA
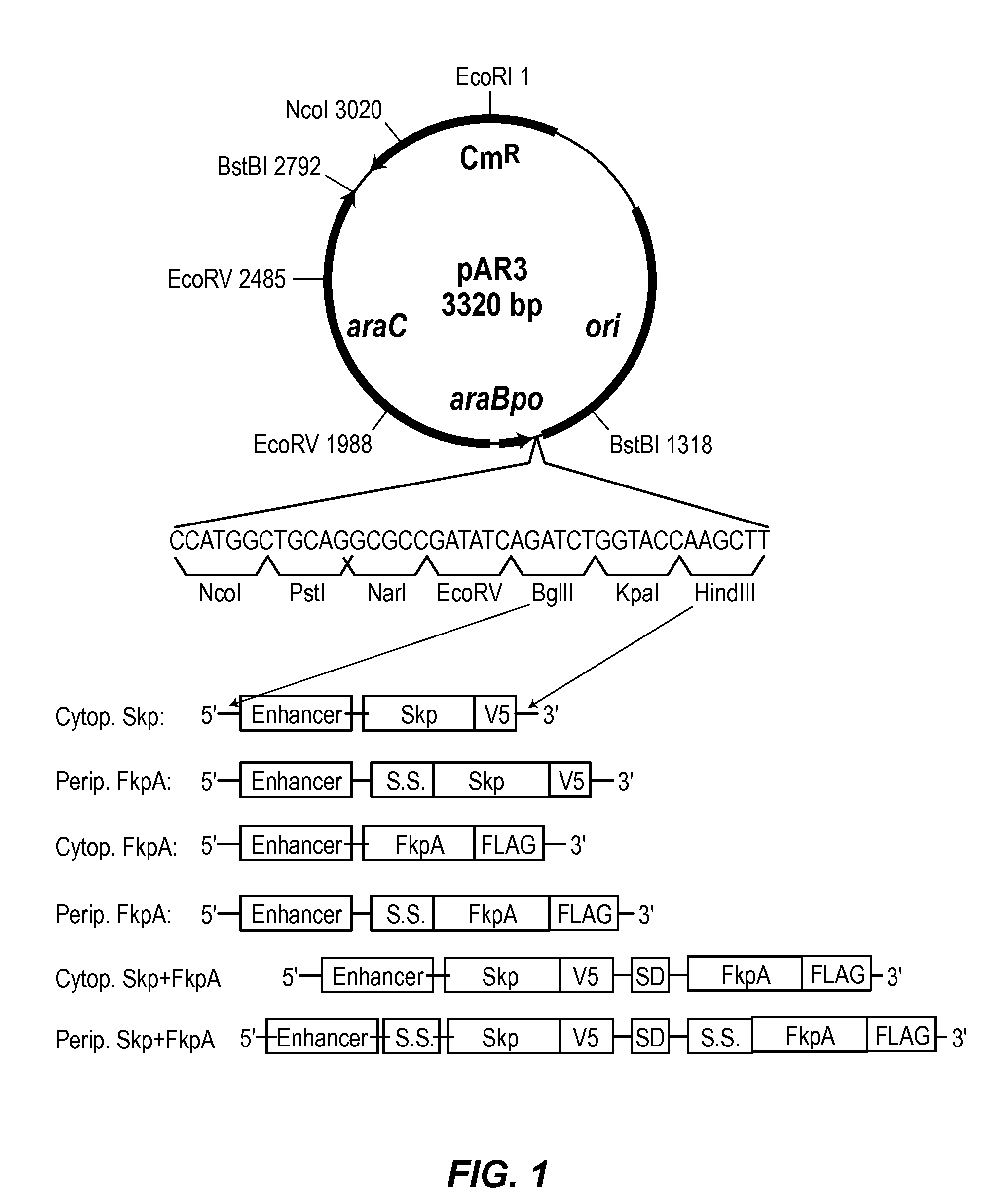
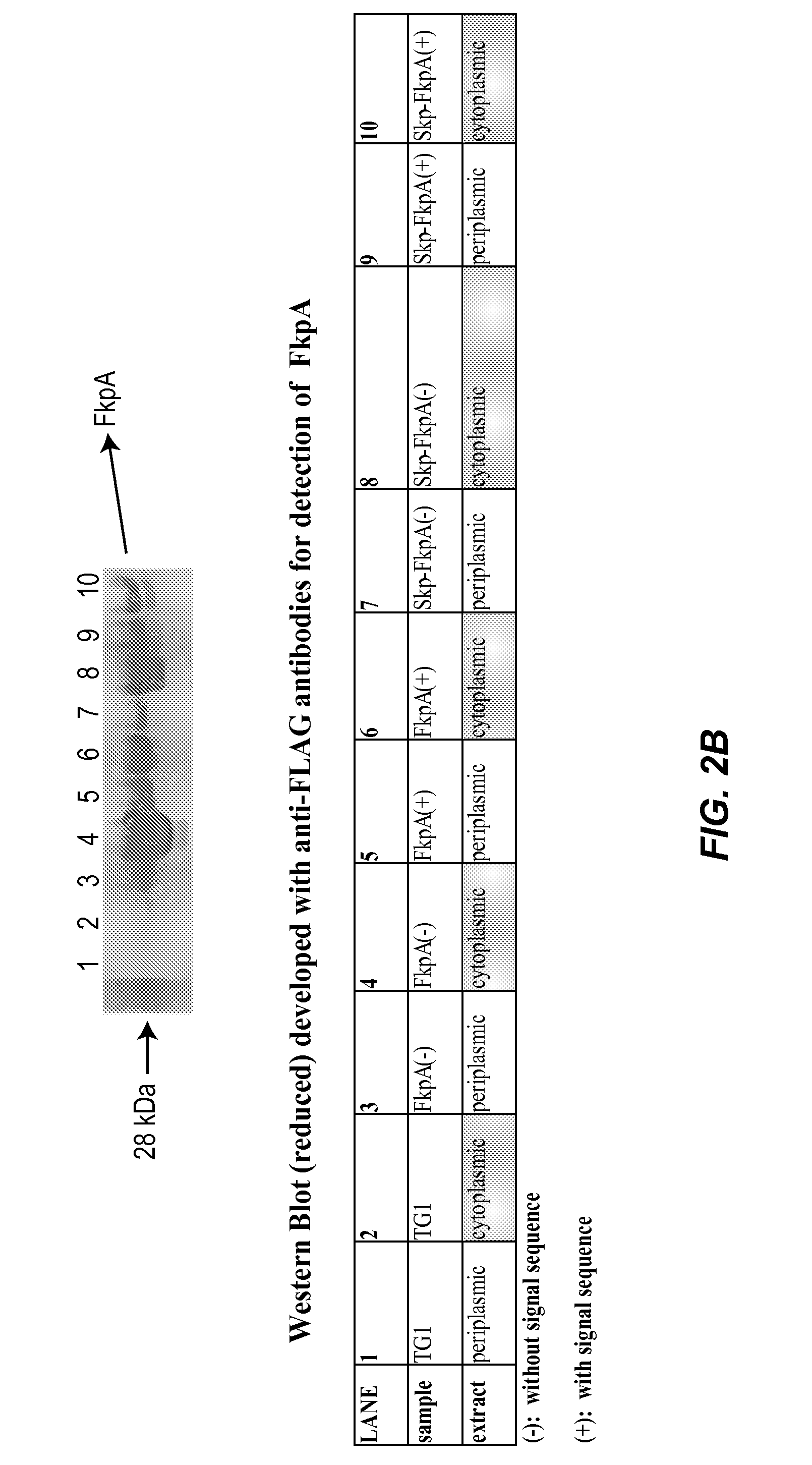
Methods and materials for enhancing functional protein expression in bacteria
ActiveUS20140154743A1Increase productionIncrease volumeBacteriaAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHeterologousBiochemistry
Novel materials and methods useful for expressing heterologous proteins in prokaryotic cells are provided, including prokaryotic cells expressing FkpA and / or Skp.
Owner:XOMA TECH LTD
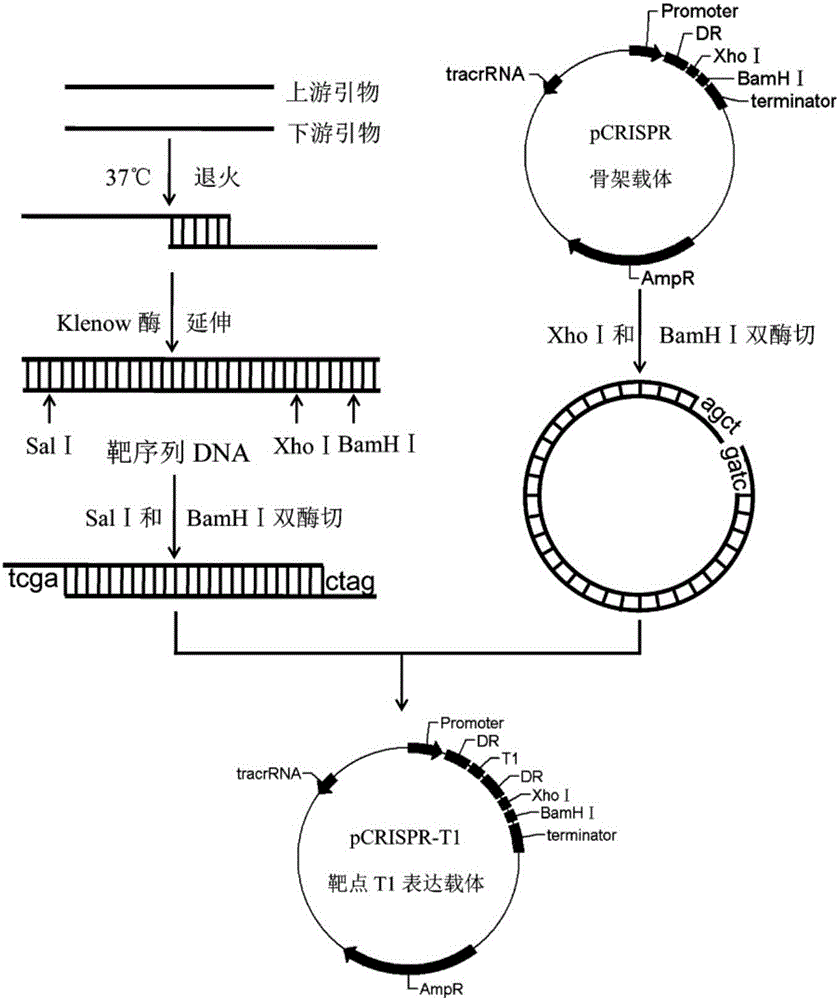
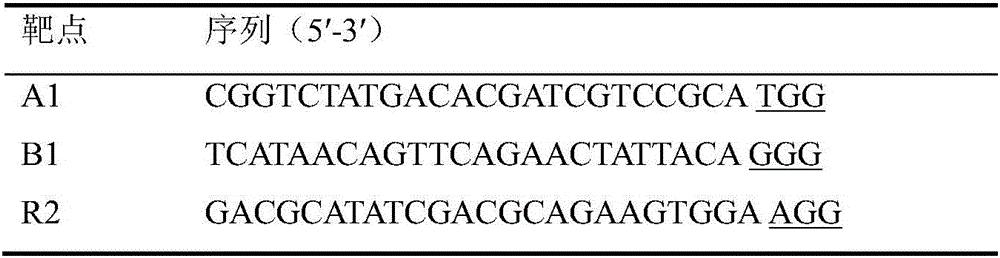
Multi-target-point CRISPR/Cas9 expression vector based on bacteriostasis and sterilization
InactiveCN106554969ATo achieve the effect of antibacterial and bactericidalVectorsOxidoreductasesA-DNADihydrofolate reductase
The invention discloses a multi-target-point CRISPR / Cas9 expression vector based on bacteriostasis and sterilization. The gene sequence of the multi-target-point CRISPR / Cas9 expression vector is SEQ ID NO1 and the gene sequence of a Cas9 expression vector is SEQ ID NO2. A construction method of the expression vector comprises: using a DNA segment of an oriented RNA specific recognition gene, mediating Cas9 protein to cut a DNA double strand to produce a double strand incision and break a DNA sequence, and therefore breaking the principle of DNA coding of functional protein to construct the multi-target-point CRISPR / Cas9 expression vector. Through comparison with a negative contrast, after CRISPR / Cas9 acts on DNA gyrase and dihydrofolate reductase, the survival rate of bacteria is only 10%, and the sterilization effect can reach no less than 90%.
Owner:SHAANXI UNIV OF TECH
Universal donor cells
InactiveUS6916654B1Inhibition of activationHigh degreePeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsClass II major histocompatibility complex geneT cell
Genetically engineered cells are provided which can serve as universal donor cells in such applications as reconstruction of vascular linings or the administration of therapeutic agents. The cells include a coding region which provides protection against complement-based lysis, i.e., hyperacute rejection. In addition, the cell's natural genome is changed so that functional proteins encoded by either the class II or both the class I and the class II major histocompatibility complex genes do not appear on the cell's surface. In this way, attack by T-cells is avoided. Optionally, the cells can include a self-destruction mechanism so that they can be removed from the host when no longer needed.
Owner:OKLAHOMA MEDICAL RES FOUND +1
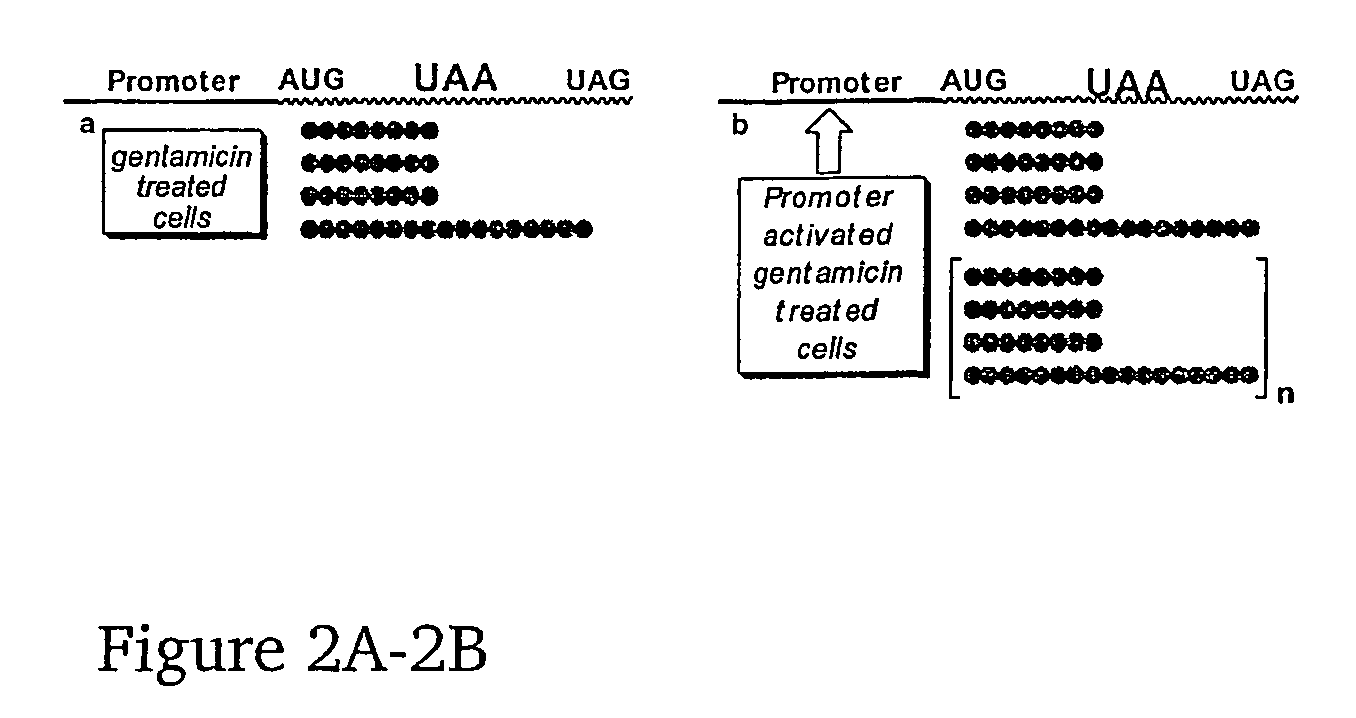
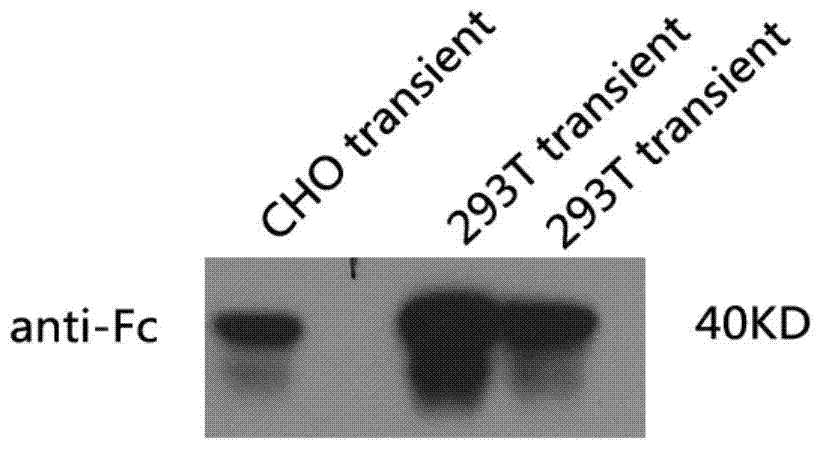
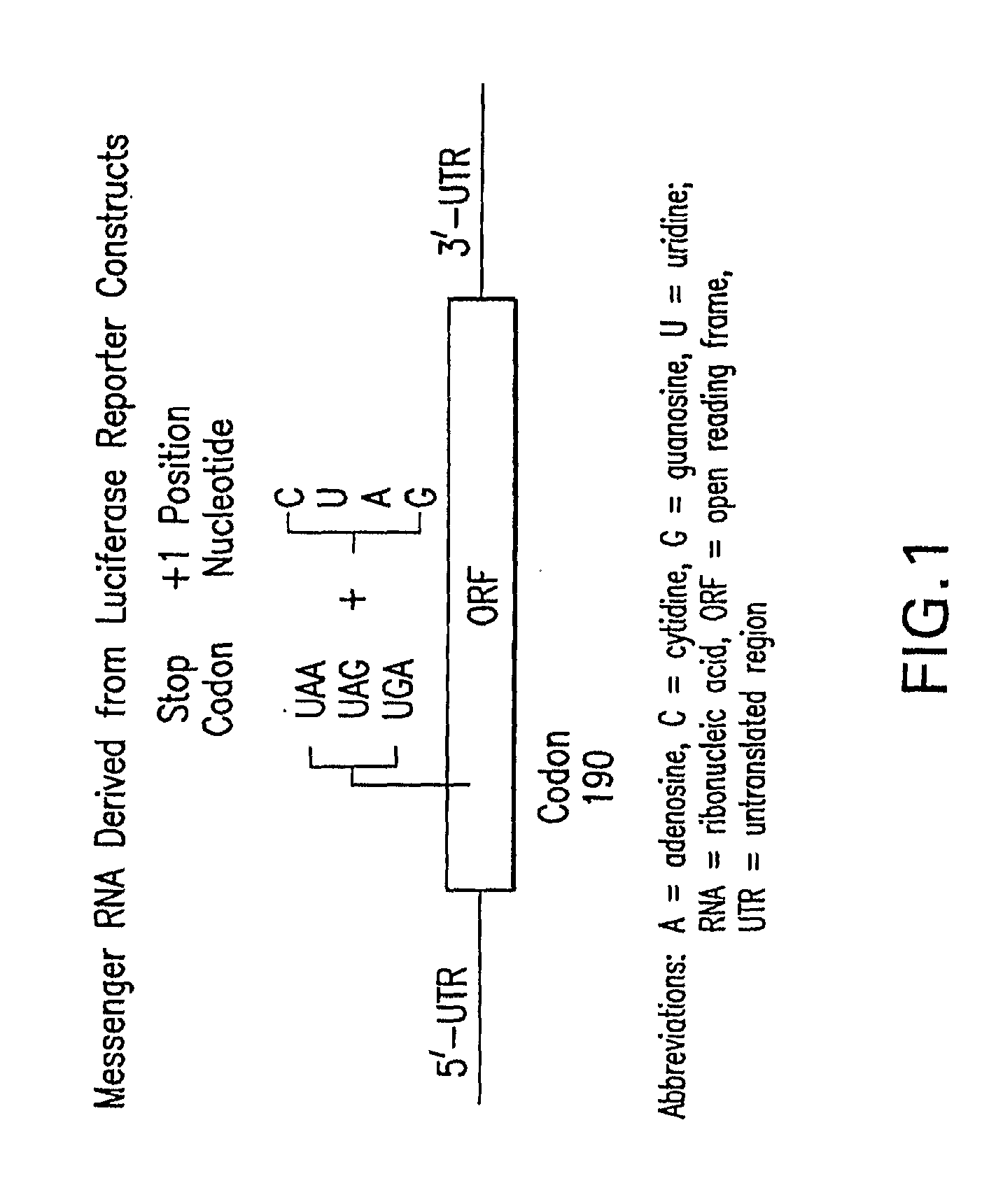
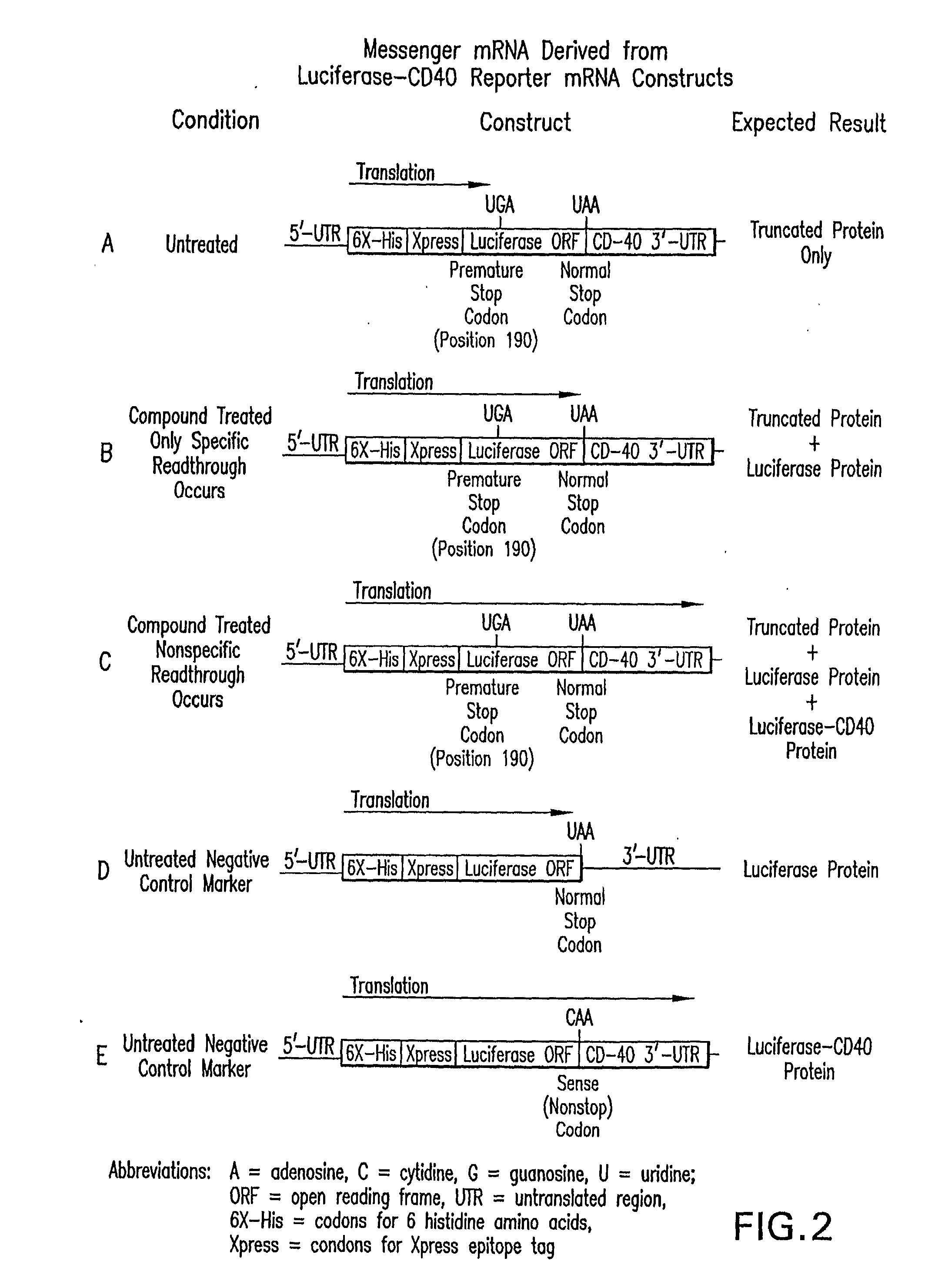
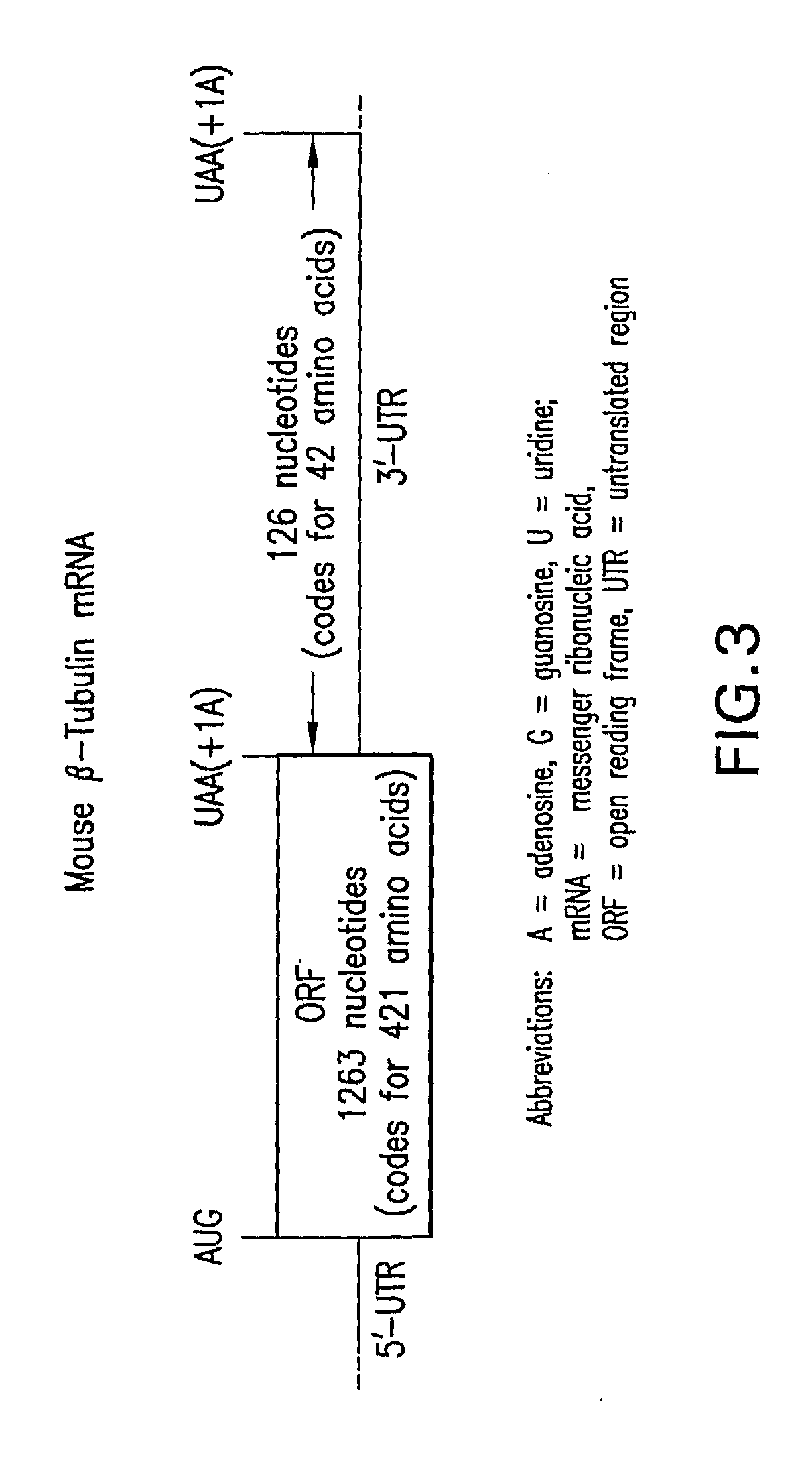
Enhanced Production of Functional Proteins From Defective Genes
InactiveUS20080207538A1Increase productionIncrease transcriptionBiocideAntibioticsPremature Stop CodonADAMTS Proteins
This invention provides methods for enhancing production in a subject of a functional protein from a gene disrupted by a mutation, for example by the presence of a premature stop codon or by an exon skipping mutation, comprising administering to the subject an amount of an agent effective to suppress the mutation and an amount of an agent effective to increase transcription of the gene.
Owner:NAT INST OF HEALTH REPRESENTED BY THE SEC OF THE DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES NAT INST OF HEALTH
Compositions increasing moisture content and distribution in muscle-derived food products
InactiveUS20090269440A1Increase moisture contentIncrease contentProtein composition from fishFatty substance preservation using additivesMuscle tissueMuscle protein
Methods for making dry protein powder or aqueous functional protein suspension compositions which provide increased moisture content and moisture retention in meats and other animal muscle tissue-based products have been developed. An important aspect is the use of alkali rather than an acid or a series of acid and alkaline treatments to dissolve the protein in the starting material. This includes both muscle and connective tissue proteins and fats, yielding a product in higher yield than acid based and other processes in which fat and connective tissue is removed and then only the remaining muscle dissolved in the acid. The connective tissue and fat increases water retention in meat into which it is injected, as compared to meat extracts containing only muscle proteins.
Owner:GENESIS GLOBAL
Genes encoding novel proteolytic enzymes
InactiveUS7323327B2Efficient productionProduce defectBacteriaHydrolasesProteinase activityNovel gene
The invention relates to newly identified gene sequences that encode novel proteases obtainable from Aspergillus niger. The invention features the full length gene sequence of the novel genes, their cDNA sequences as well as the full-length functional protein and fragments thereof. The invention also relates to methods of using these enzymes in industrial processes and methods of diagnosing fungal infections. Also included in the invention are cells transformed with DNA according to the invention and cells wherein a protease according to the invention is genetically modified to enhance or reduce its activity and / or level of expression.
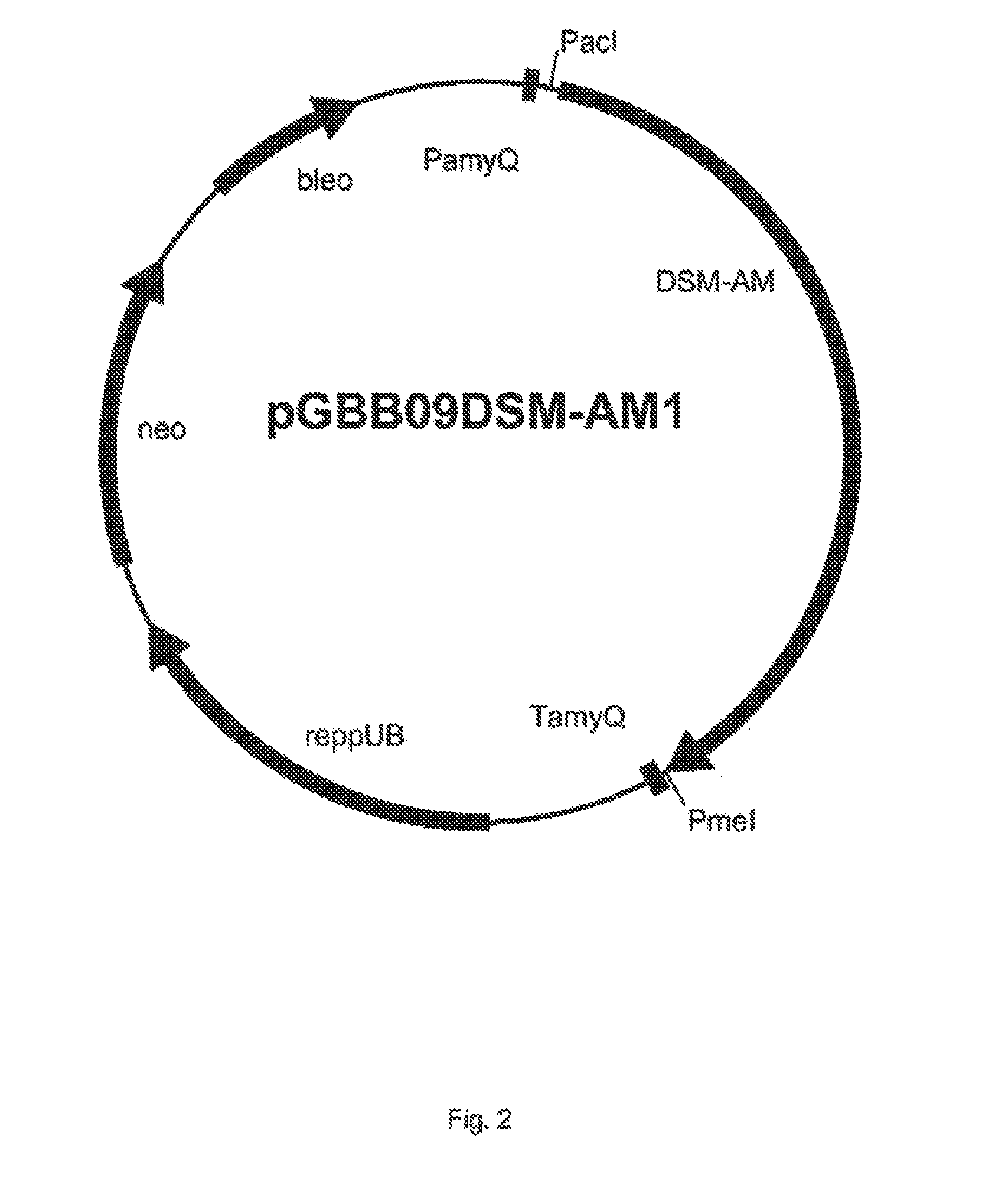
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
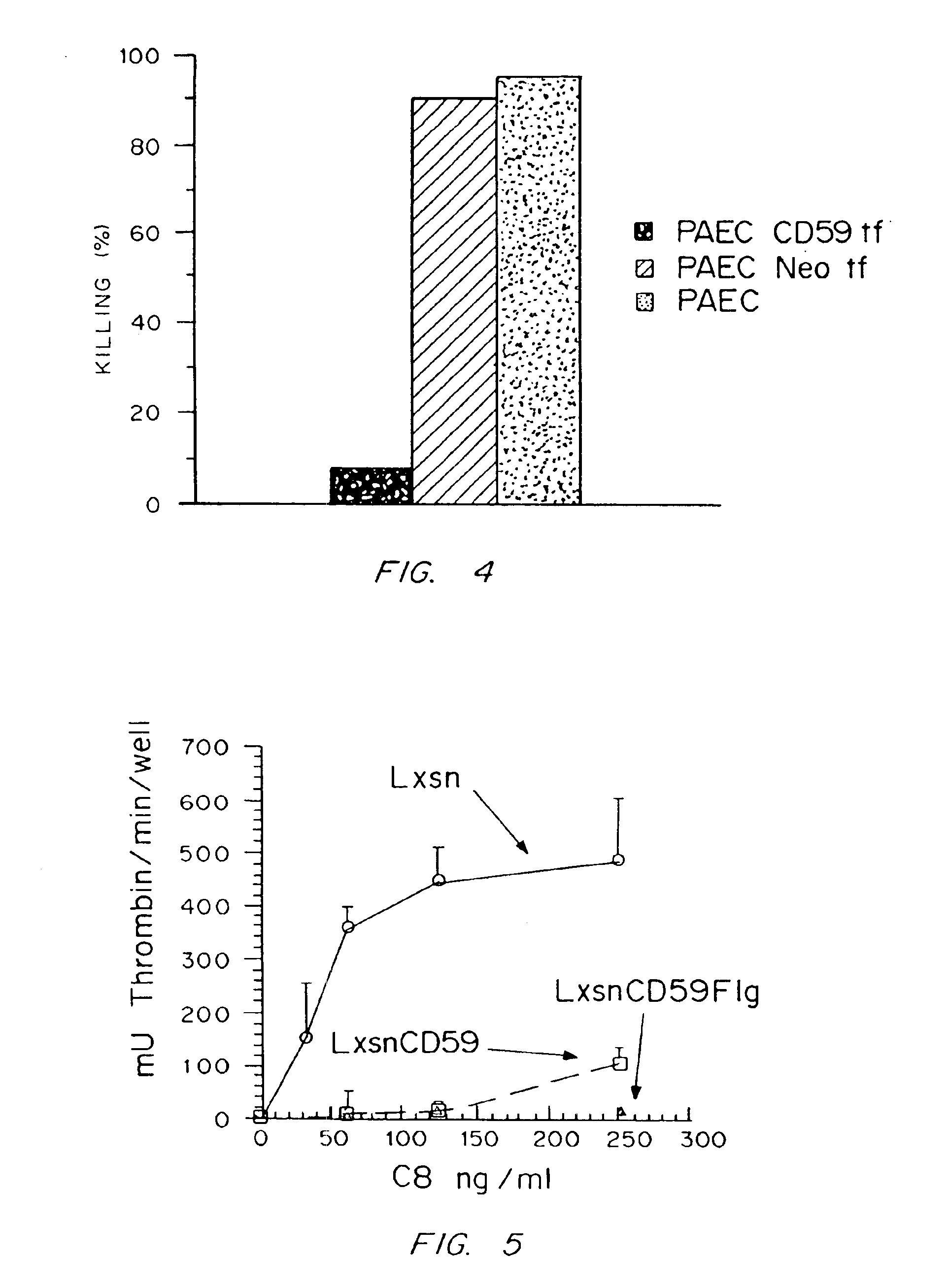
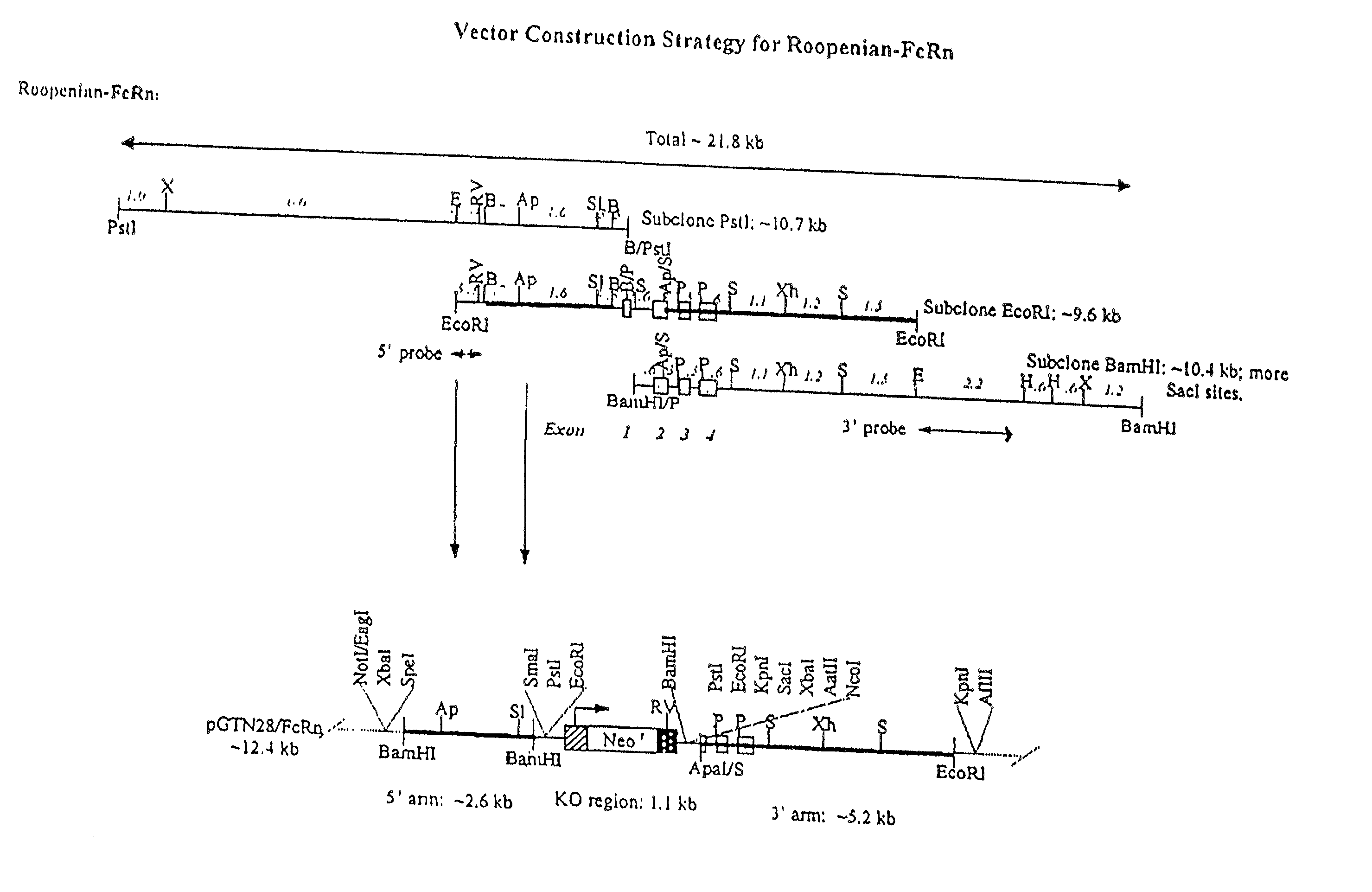
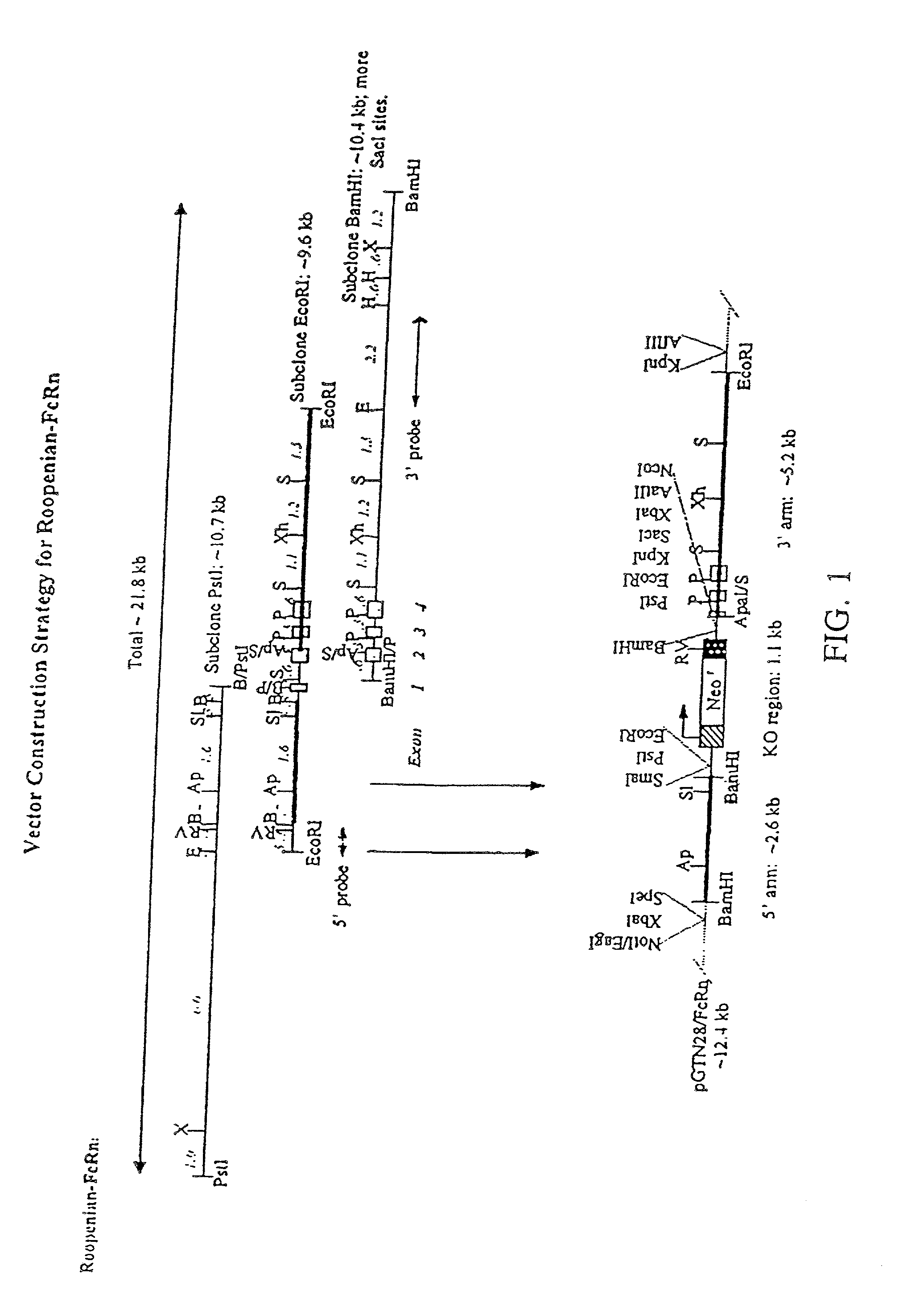
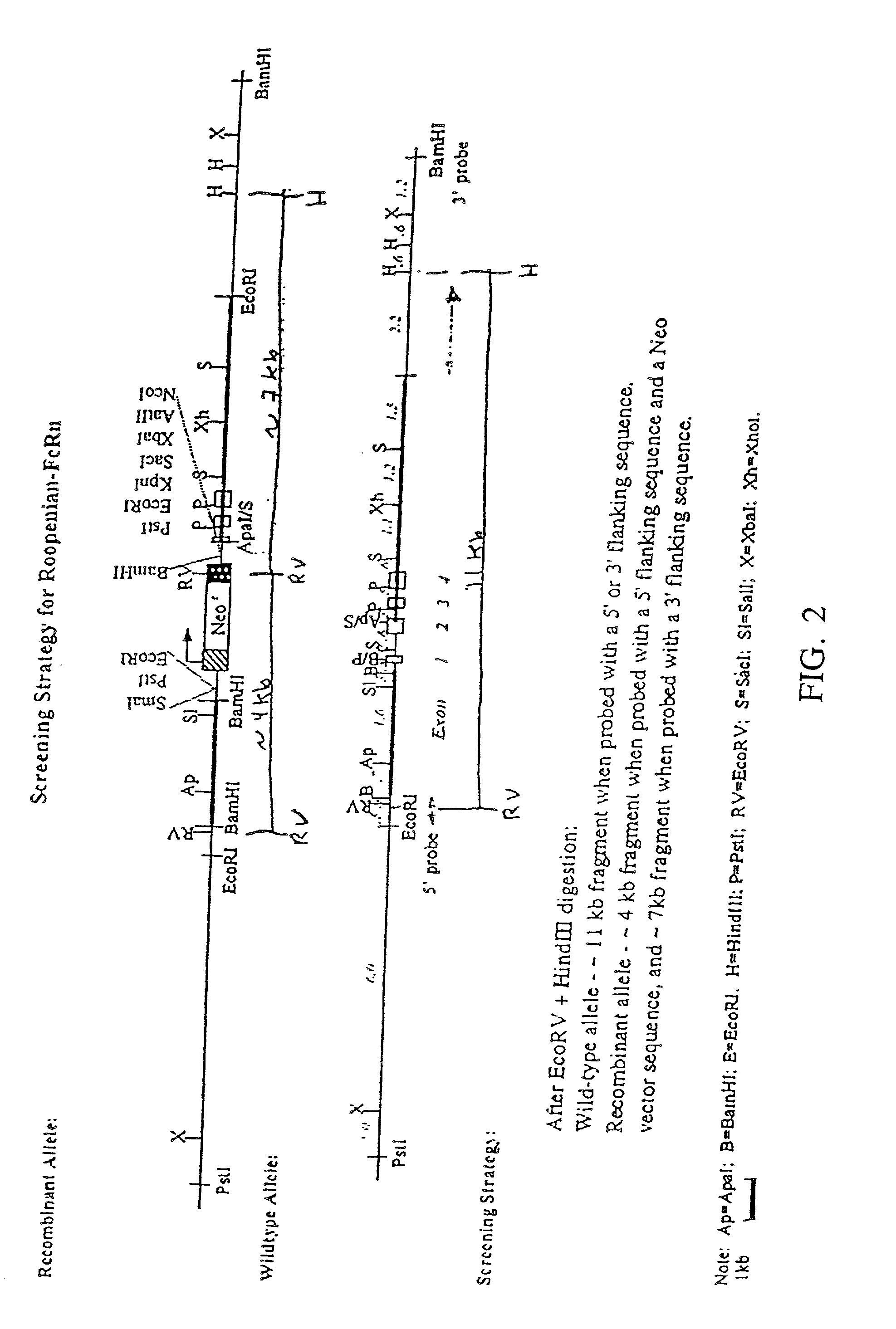
FcRn-based therapeutics for the treatment of auto-immune disorders
InactiveUS20020138863A1Increased catabolismShort livedDepsipeptidesAntibody ingredientsDiseaseTransgenic knockout
Disclosed is a transgenic knockout mouse whose genome comprises a homozygous disruption in its endogenous FcRn gene, wherein said homozygous disruption prevents the expression of a functional FcRn protein, resulting in a transgenic knockout mouse in which exogenously administered IgG1 exhibits a substantially shorter half-life, as compared to the half-life of exogenously administered IgG1 in a wild-type mouse. Also disclosed is a transgenic knockout mouse whose genome comprises a homozygous disruption in its endogenous FcRn gene, wherein said homozygous disruption prevents the expression of a functional FcRn protein, resulting in a transgenic knockout mouse which is unable to absorb maternal IgG in the prenatal or neonatal stage of development Methods of using the transgenic knockout mouse, and cells derived therefrom, are also disclosed.
Owner:JACKSON LAB THE
Process for preparing nutritional, therapeutic or organoleptic products from crude glycerol
The present invention relates to a process for preparing a nutritional, therapeutic or organoleptic product by growing non-recombinant yeast under aerobic conditions, in a medium that includes crude glycerol, as one possible carbon source to produce a yeast product. The yeast product can be processed to obtain such nutritional, therapeutic or organoleptic products as yeast paste, yeast metabolites, carbohydrates, proteins, functional proteins, nucleotides, yeast autolysates, yeast extract, yeast cell walls, beta-glucans, mannans or a product derived from a mineralized yeast product.
Owner:BIO PROCESSING AUSTRALIA
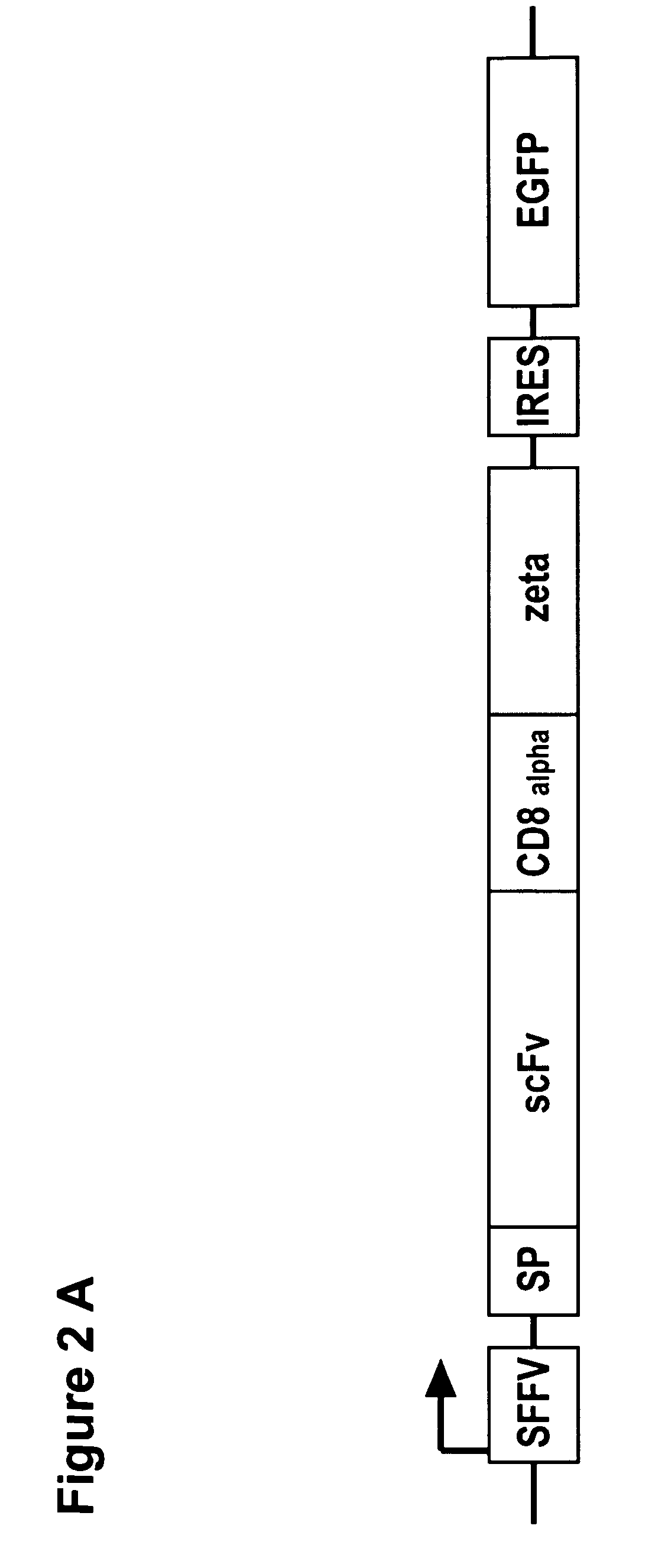
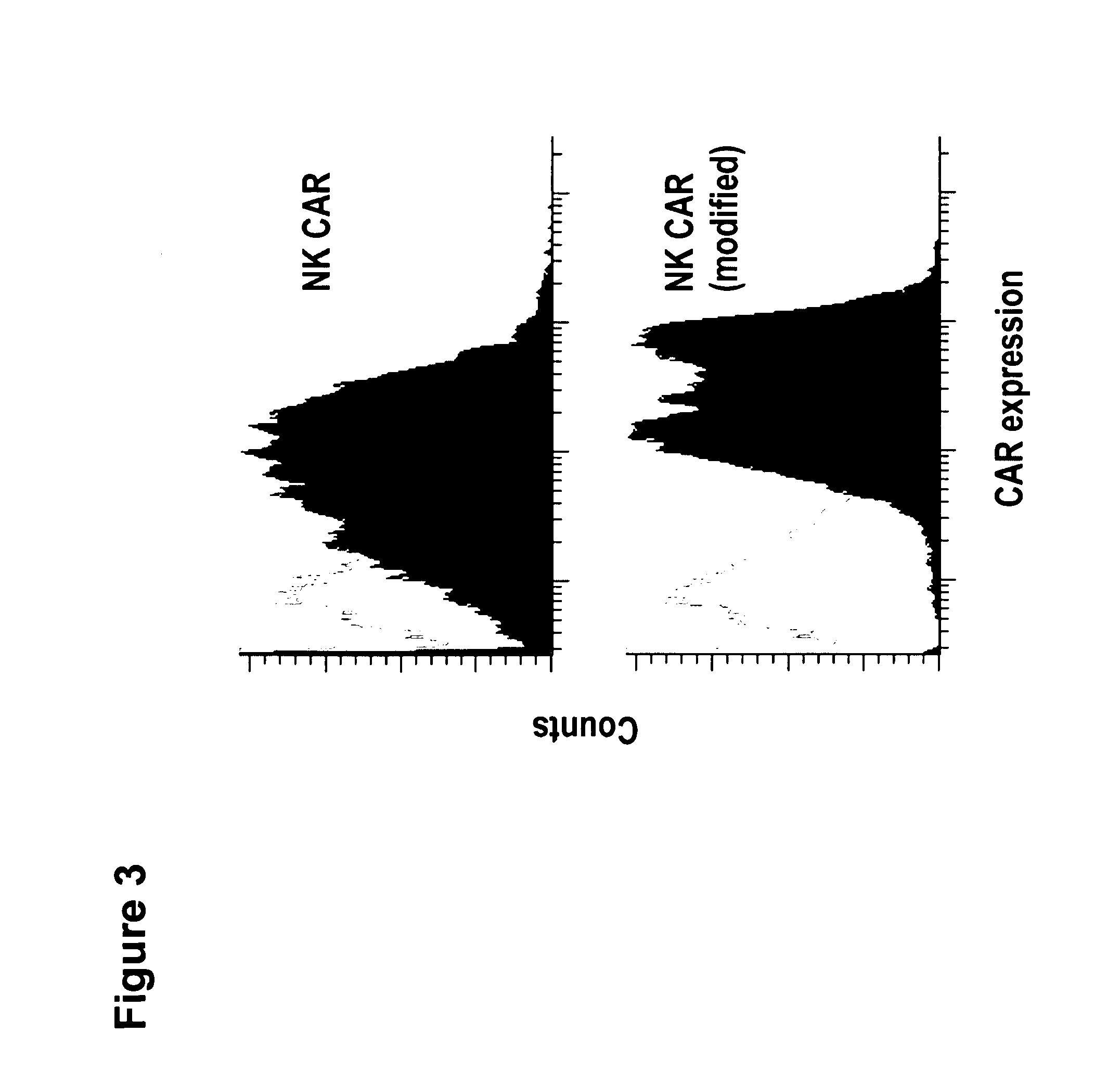
Chimeric antigen receptors with an optimized hinge region
The present invention relates to multi-functional proteins which comprise (i) a signal peptide, (ii) a target specific recognition domain, (iii) a linker region, connecting domain (ii) and domain (iv) which comprises a specific modified hinge region of the human CD8 alpha-chain, and (iv) an effector domain. The present invention furthermore relates to nucleic acids encoding the proteins, expression constructs for expressing the protein in a host cell and host cells. The proteins of the invention are chimeric antigen receptors with an optimized linker or hinge region that are suitable for generating target-specific effector cells, for use as a medicament, in particular in the treatment of cancer and in adoptive, target-cell specific immunotherapy.
Owner:CHEMOTHERAPEUTISCHES FORSCHUNGINSTITUT GEORG SPEYER HAUS
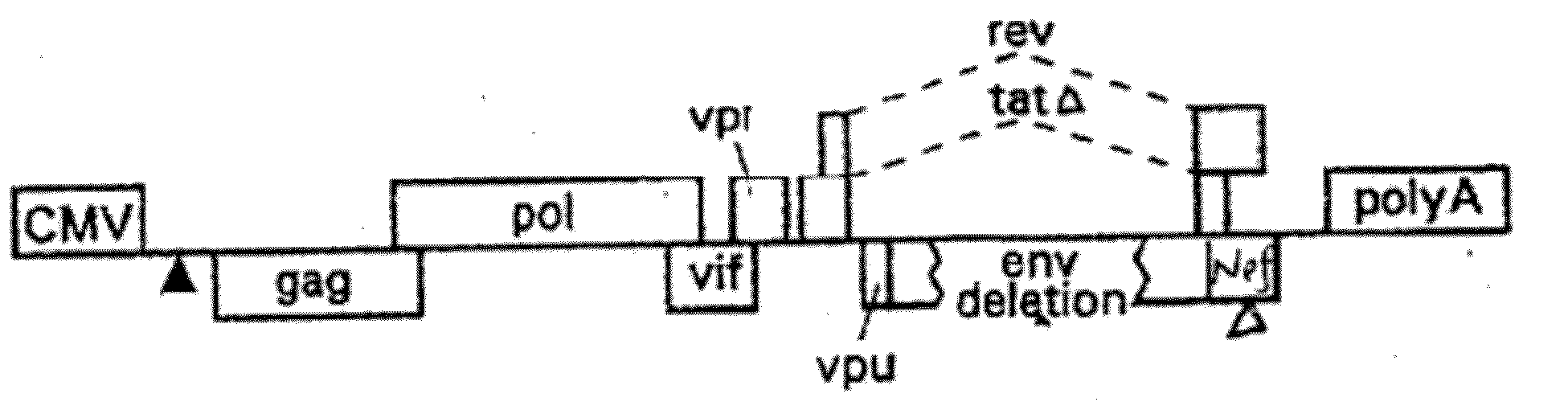
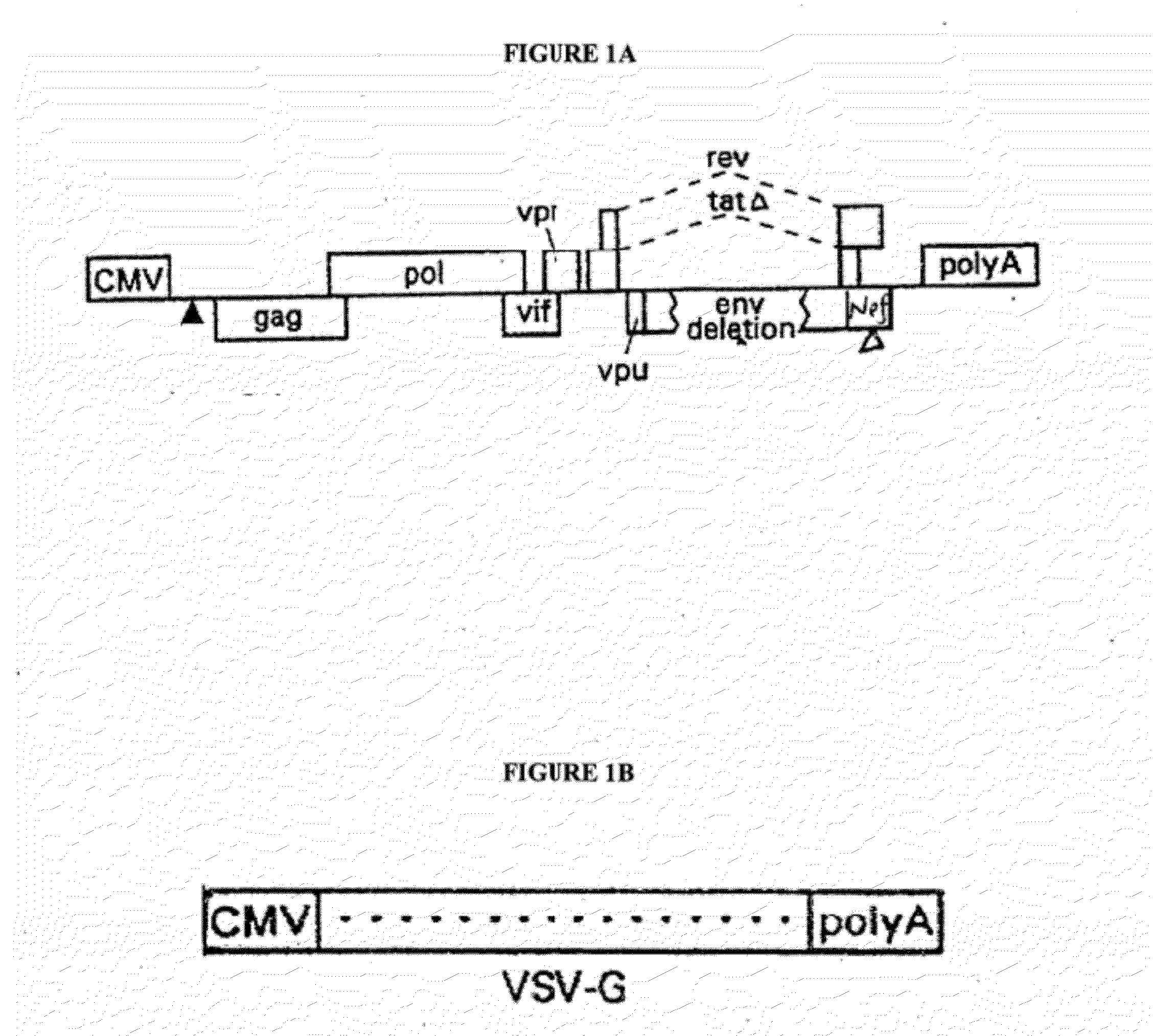
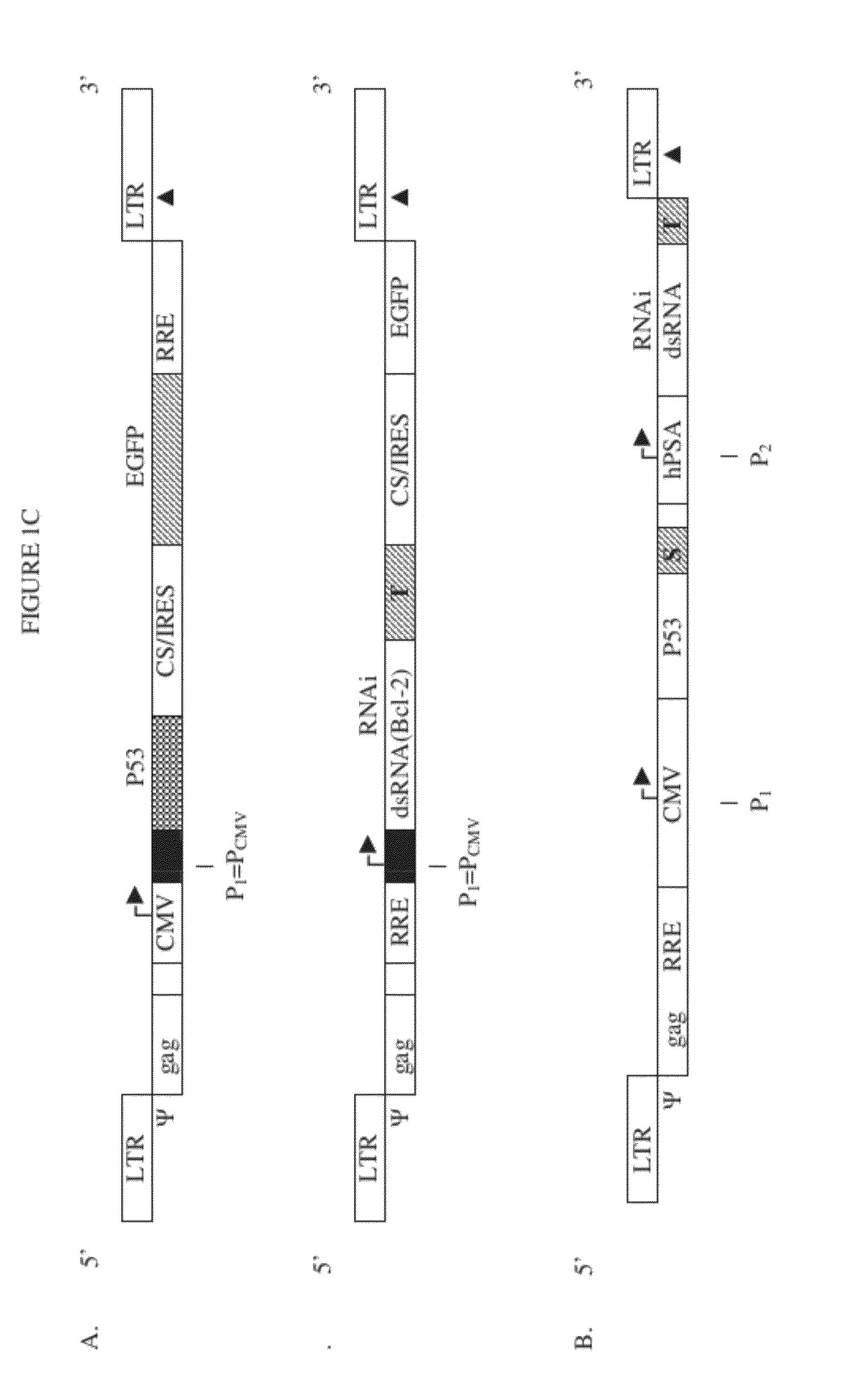
Safe lentiviral vectors for targeted delivery of multiple therapeutic molecules
Owner:AMERICAN GENE TECH INT
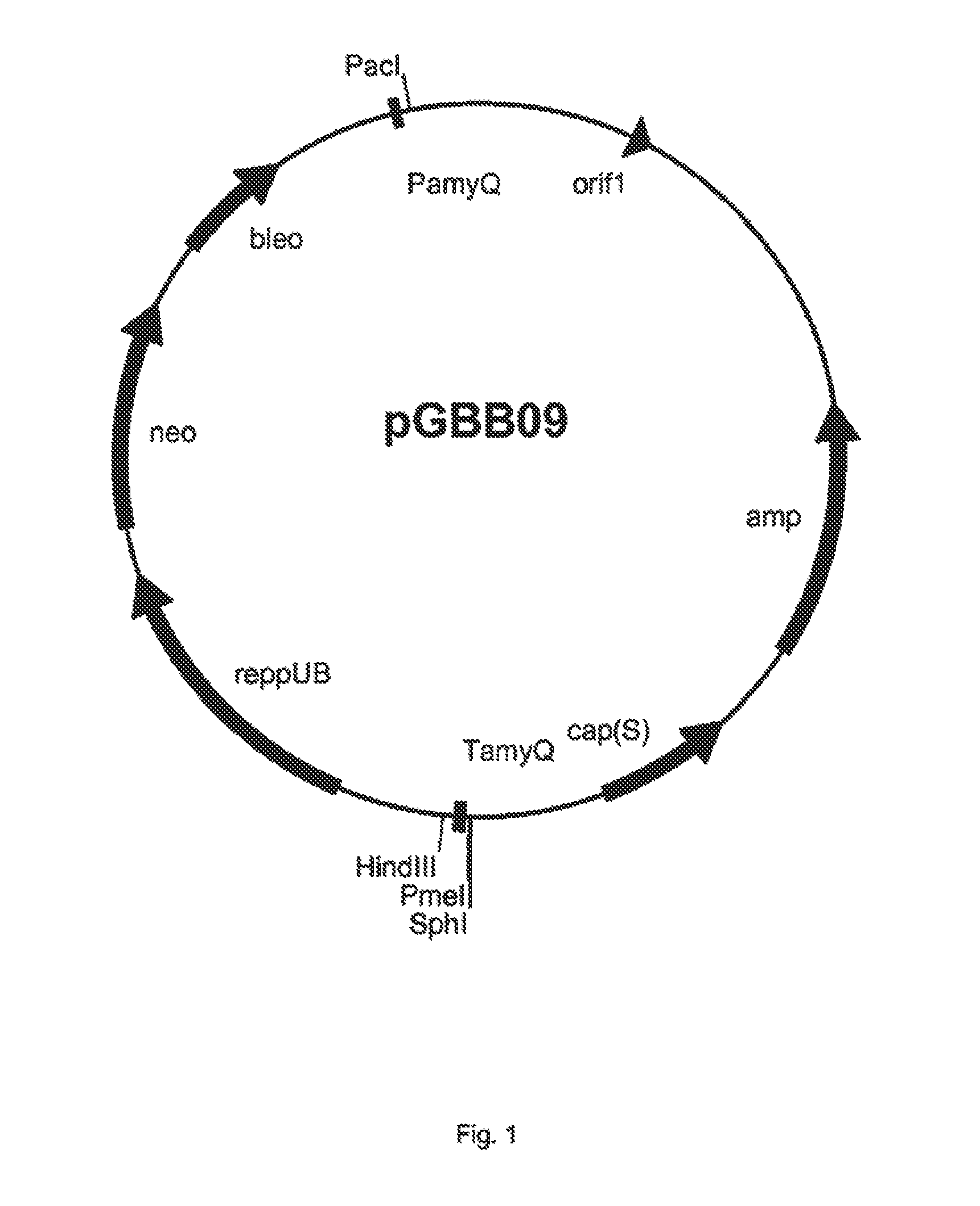
Alpha-amylase
This invention relates to an alpha-amylase, a process for its preparation and the use of the amylase. The invention relates to a newly identified polynucleotide sequence from Alicyclobacillus pohliae comprising a gene that encodes the alpha-amylase enzyme. The invention features the full-length coding sequence of the gene as well as the amino acid sequence of the full-length functional protein of the gene. The invention also relates to methods of using these proteins in industrial processes, for example in food industry, such as the baking industry. Also included in the invention are cells transformed with a polynucleotide according to the invention suitable for producing these proteins and cells.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Anti-adhesion biological membrane and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103405811AGood biocompatibilityGood physical barrier anti-adhesion effectSurgeryLight whitePharmaceutical Substances
The invention provides an anti-adhesion biological membrane and a preparation method thereof. The anti-adhesion biological membrane is a dry membrane which is formed by SIS (styrene isoprene styrene block copolymer) as a support material, compound hyaluronic acid, functional proteins and anti-inflammotary medicines. The anti-adhesion biological membrane is semi-transparent from light white to faint yellow. The thickness of the anti-adhesion biological membrane is 0.01-0.5mm. Compared with the prior art, the anti-adhesion biological membrane has very good biocompatibility, good physical barrier anti-adhesion effect and the effects of resisting inflammatory, stopping bleeding and promoting fiber degradation. The effects of the anti-adhesion biological membrane are obviously superior to those of existing anti-adhesion biological membrane products. Animal experiments prove that the effective rate of the anti-adhesion biological membrane prepared by the method for preventing the adhesion after abdominal surgery reaches above 90%, the effective rate for preventing the adhesion after pelvic cavity surgery reaches above 80%, and the effective rate for preventing the adhesion after tendon surgery reaches above 70%.
Owner:XIAN TISSUE ENG & REGENERATIVE MEDICINE RES INST
Synergistic bifunctional protein for regulating blood sugar and lipid
The invention relates to a synergistic bifunctional protein for regulating blood sugar and lipid. The synergistic bifunctional protein comprises a human GLP-1 analog and human FGF21. In one aspect, the invention provides a method for preparing the synergistic bifunctional protein, and on the other hand, the invention also provides an application of the synergistic bifunctional protein for treatment of type 2 diabetes, obesity, dyslipidemia, fatty liver disease and / or metabolism syndrome drugs. The synergistic bifunctional protein provided by the invention can synergistically regulate blood sugar and lipid levels in vivo, and meet the multiple needs of hypoglycemia, alleviation of liver fatty degeneration, weight reduction and improvement of circulating lipid metabolism disorder in type 2 diabetic patients.
Owner:AMPSOURCE BIOPHARMA (SHANGHAI) INC
Methods for producing protein domains and analyzing three dimensional structures of proteins by using said domains
InactiveUS20020142387A1Easy and rapid methodEfficient preparationBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA fragmentationA-DNA
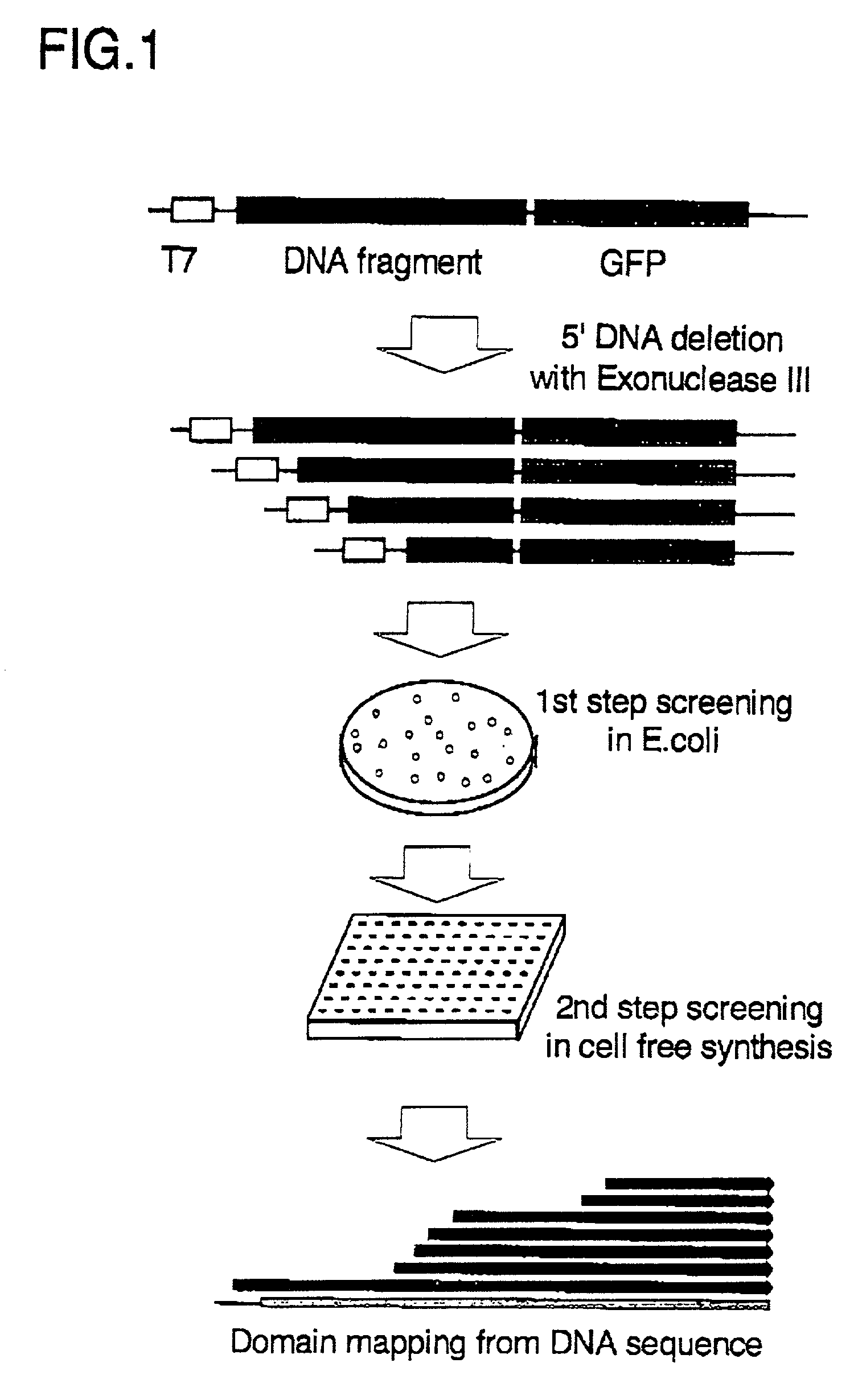
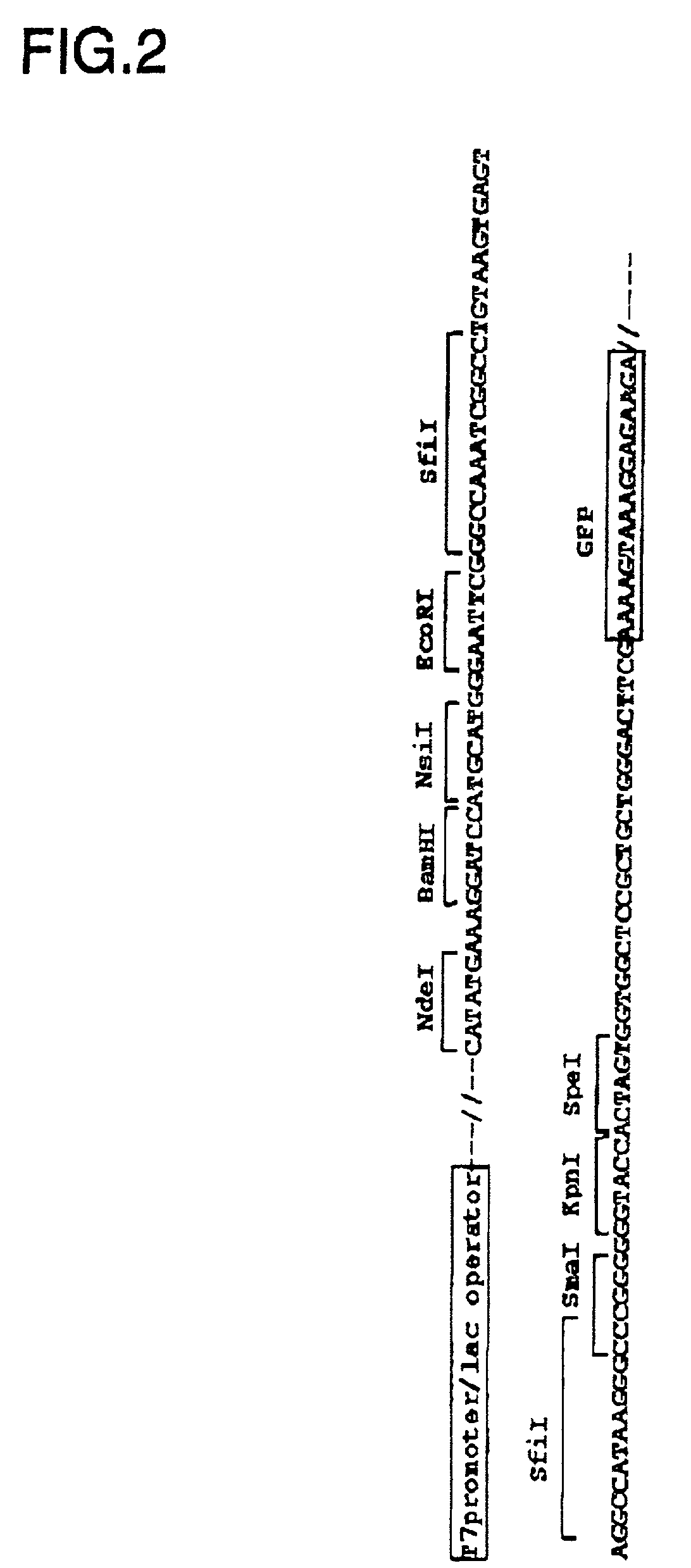
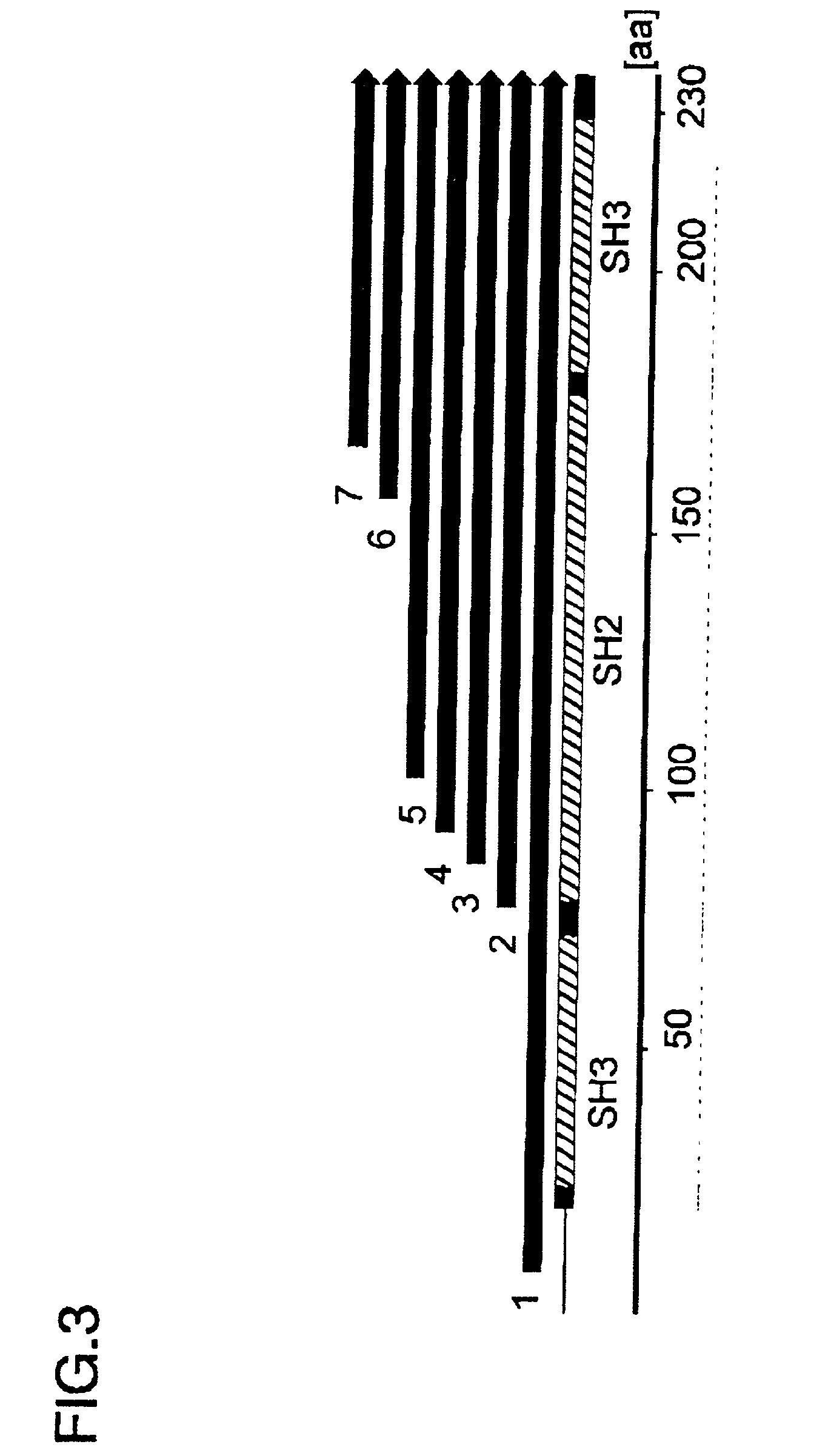
There is provided a method for producing a soluble protein domain comprising: (a) preparing two or more DNA fragments by partially digesting a DNA coding for a protein; (b) expressing the protein which is coded on each of said DNA fragments, as a fusion protein with a functional protein; (c) selecting the fusion protein exhibiting said function among two or more fusion proteins synthesized in step (b); and, (d) synthesizing the soluble protein domain which is coded on said DNA fragment in a cell-free system, wherein said soluble protein domain is included in said fusion protein selected in step (c). By using this method, it can be easy and efficient to analyze the three dimensional structure of proteins of many clones.
Owner:RIKEN
Protein related to rice ear sprouting period and encoding genes and uses thereof
InactiveCN101353376AIncrease planting areaIncrease productionFungiBacteriaAgricultural scienceRibonucleotide synthesis
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Chimeric promoter for cone photoreceptor targeted gene therapy
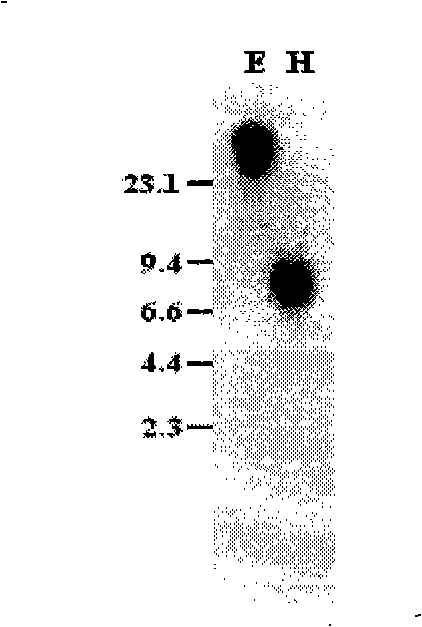
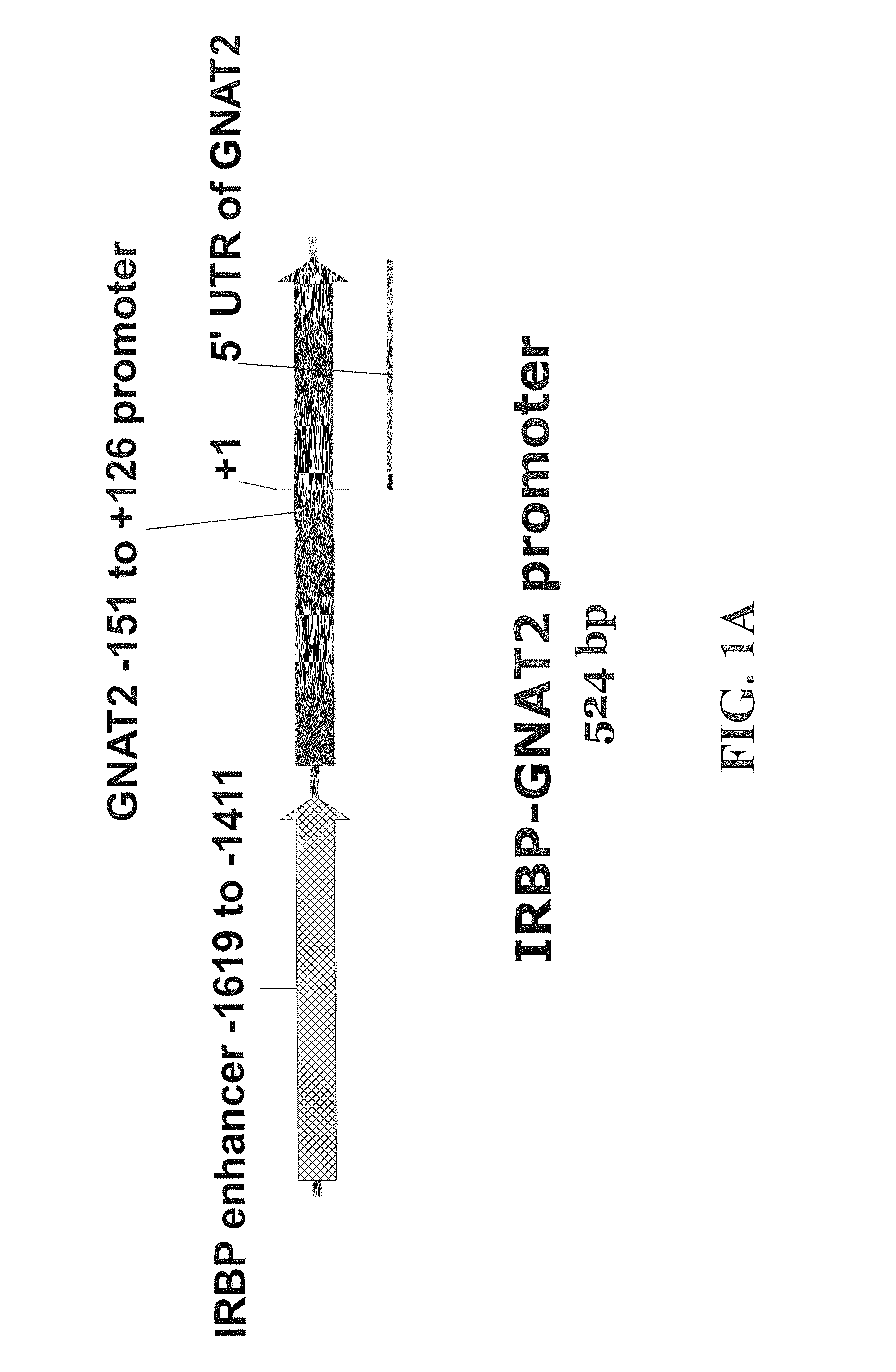
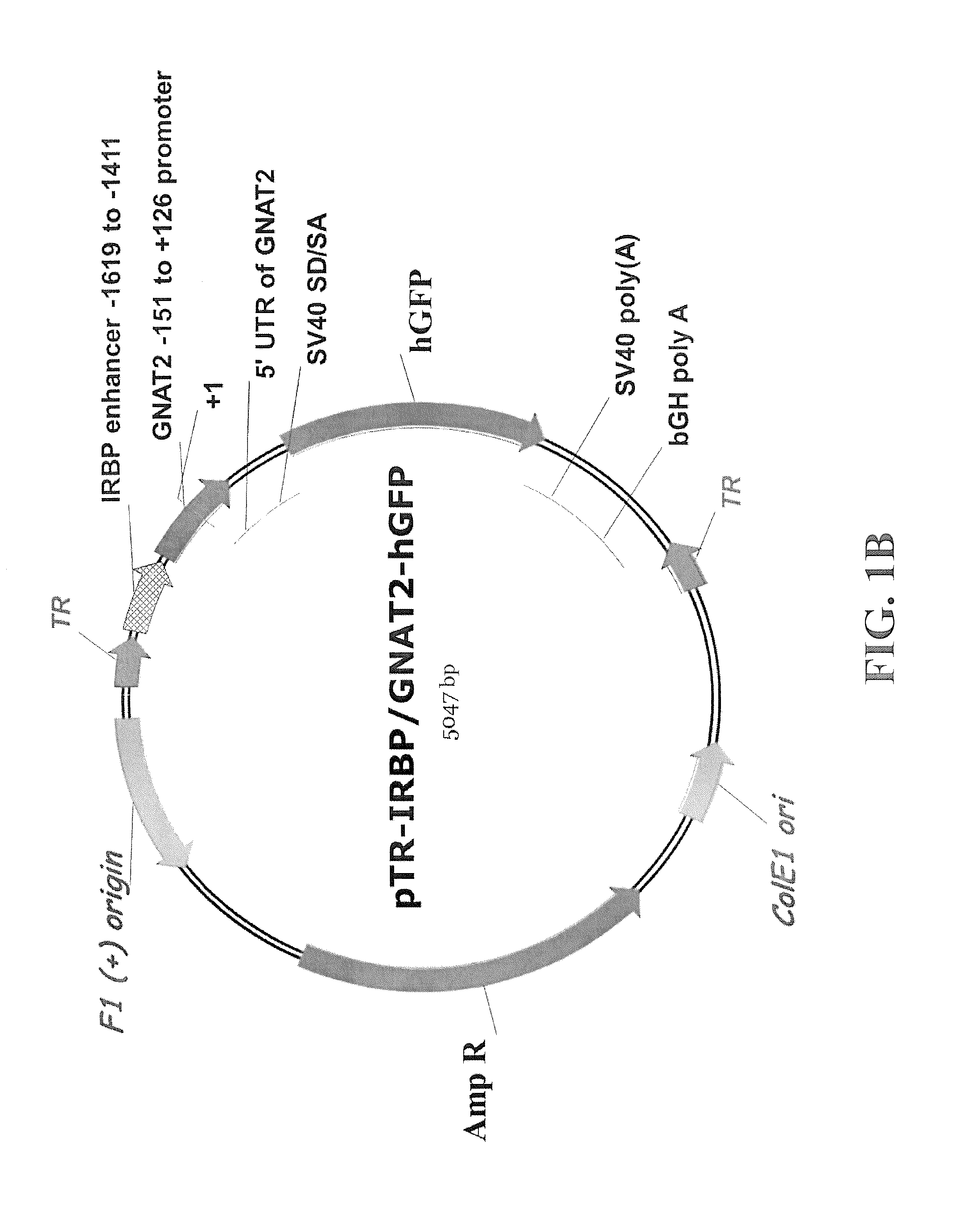
The subject invention concerns materials and methods for providing for cone cell specific expression of a polynucleotide in a human or animal. One aspect of the invention concerns a polynucleotide promoter sequence that directs expression of an operably linked polynucleotide in cone cells. In one embodiment, a polynucleotide of the invention comprises a nucleotide sequence of an interphotoreceptor retinoid-binding protein (IRBP) gene that is positioned upstream of a promoter nucleotide sequence of a cone transducin alpha-subunit (GNAT2) gene. Another aspect of the subject invention concerns methods for expressing a selected polynucleotide in cone cells. The selected polynucleotide can be provided in a polynucleotide of the invention wherein the selected polynucleotide is operably linked to a polynucleotide promoter sequence of the invention. In one embodiment, the selected polynucleotide sequence is provided in a polynucleotide vector of the invention. The vector comprising the selected polynucleotide is then introduced into a cell. The selected polynucleotide is expressed only in cone cells, with very little, if any, expression in rods or other cells. A selected polynucleotide can be one that encodes, for example, a therapeutic protein or a functional protein that is defective or underexpressed in the targeted cone cells.
Owner:UNIV OF FLORIDA RES FOUNDATION INC
Genetically engineered bacteria realizing high-density fermentation co-production of 2,3-butanediol as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN104560848AReduce culture volumeLess investmentBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria realizing high-density fermentation co-production of 2,3-butanediol as well as a construction method and an application thereof. The genetically engineered bacteria are constructed by integrating three key enzyme genes such as alpha-acetolactate synthetase encoding genes, alpha-acetolacetate decearboxylase encoding genes and 2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase encoding genes onto Escherichia coli chromosomes in a 2,3-butanediol synthesis path. According to the strain fermentation process, the content of the byproduct acetic acid is reduced, so that high-density fermentation can be realized, and 2,3-butanediol with high additional value is co-produced. In addition, the invention also discloses a method for realizing high-density fermentation co-production of other compounds and 2,3-butanediol genetically engineered bacteria and an application thereof. The 2,3-butanediol can be produced by virtue of high-density fermentation, and polyhydroxyalkanoates or functional proteins also can be co-produced, so that low-cost and high-efficiency co-production of the polyhydroxyalkanoates or functional proteins and the 2,3-butanediol is realized, and the genetically engineered bacteria have important industrial application values.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
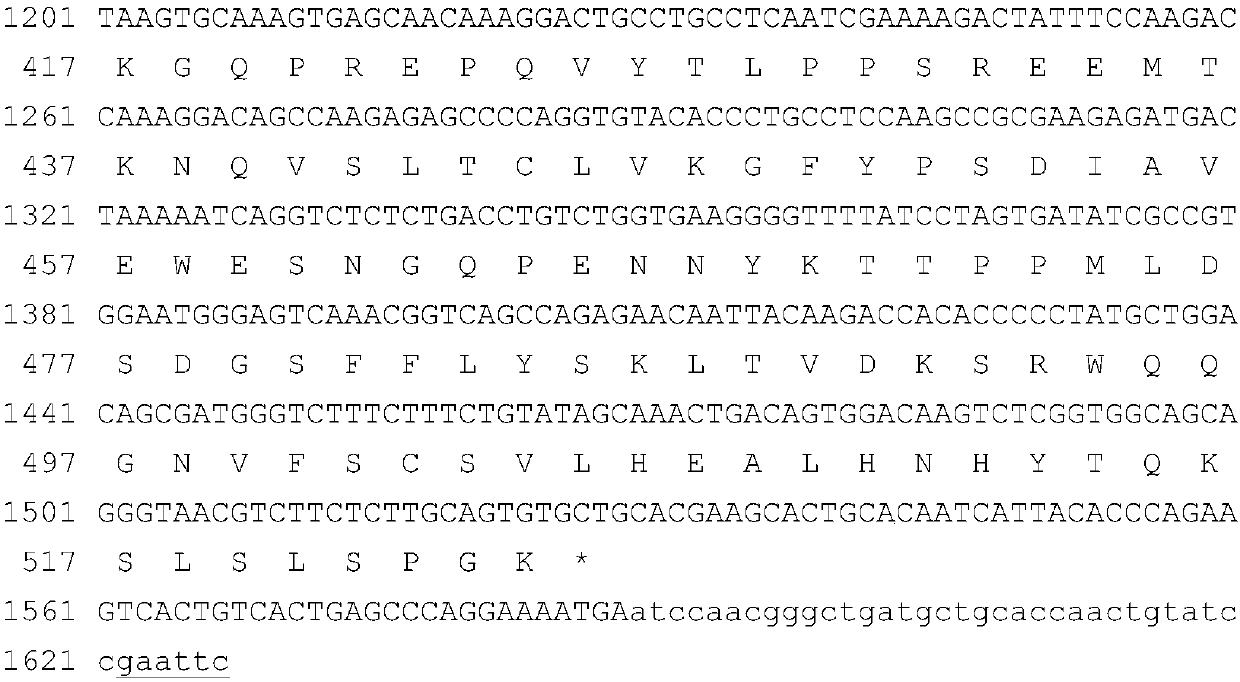
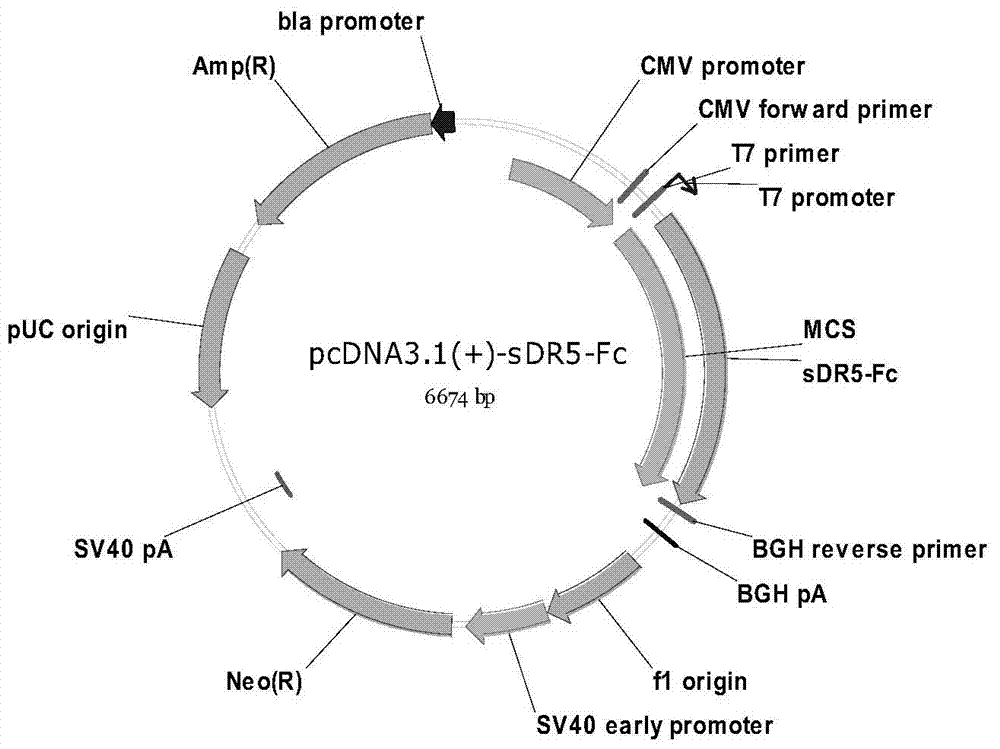
Sdr5-fc fusion protein and uses thereof
InactiveCN104710533ARelieve painLow cost of treatmentPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsHalf-lifeIn vivo
The present invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and relates to disease treatment, particularly to sDR5-Fc fusion protein and uses thereof. The sDR5-Fc fusion protein comprises an sDR5 functional sequence part and an immunoglobulin Fc region, wherein the sDR5 functional sequence part and the immunoglobulin Fc region are directly connected and / or are connected through a connection fragment. According to the present invention, the natural protein DR5 is adopted to fuse with the antibody Fc fragment, such that the in vivo half-life is prolonged on the base of provision of the biological activity of the functional protein, the frequent administration is not required, and the pain and the treatment cost of patients are reduced.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
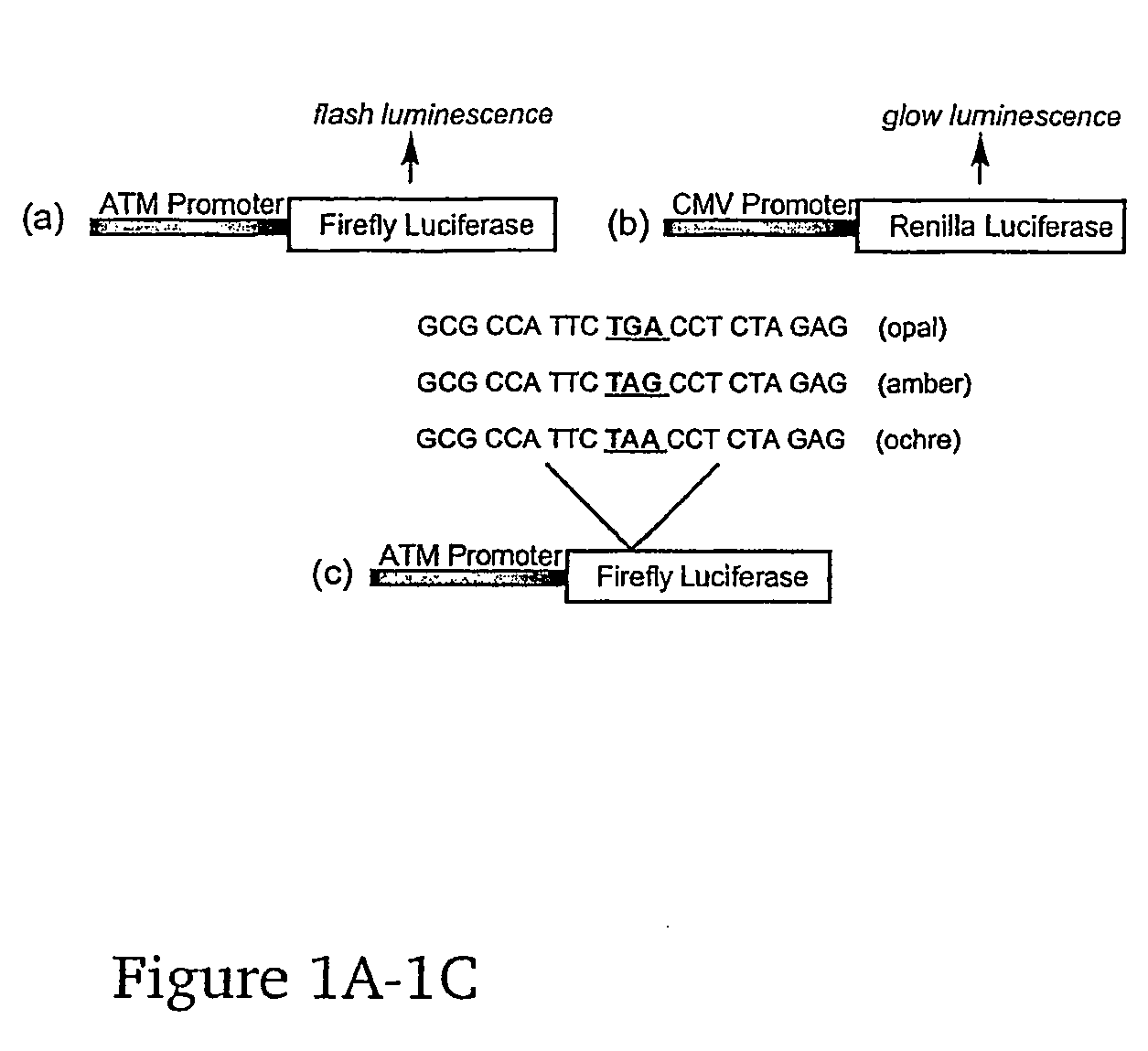
Methods for the production of functional protein from DNA having a nonsense mutation and the treatment of disorders associcated therewith
InactiveUS20110046136A1Eliminate riskImprove the quality of lifeBiocideSenses disorderDiseaseNucleic acid sequencing
The present invention relates to functional proteins encoded by nucleic acid sequences comprising a nonsense mutation. The present invention also relates to methods for the production of functional proteins encoded by nucleic acid sequences comprising a nonsense mutation and the use of such proteins for prevention, management and / or treatment of diseases associated with a nonsense mutation(s) in a gene.
Owner:PTC THERAPEUTICS INC
Composite membrane based on functional protein
ActiveCN105498559AEasy to embedImprove bindingMembranesSemi-permeable membranesPolyelectrolyteNetwork structure
The invention relates to a composite membrane based on a functional protein and a preparation method thereof. The composite membrane consists of a polyelectrolyte active layer on which the functional protein is embedded, and a supporting layer, wherein the functional protein is used as a functional unit and is directly embedded into a formed network structure in the process of assembling layer by layer to prepare the polyelectrolyte active layer, and by cross-linking and curing, combination firmness of the functional protein in the active layer is improved. The preparation method is simple in operation process, and embedding content of the functional protein in the composite membrane is improved. The functional protein composite membrane has a wide application prospect in the fields of water treatment and membrane separation.
Owner:YANTAI LVSHUIFU MEMBRANE MATERIAL
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com