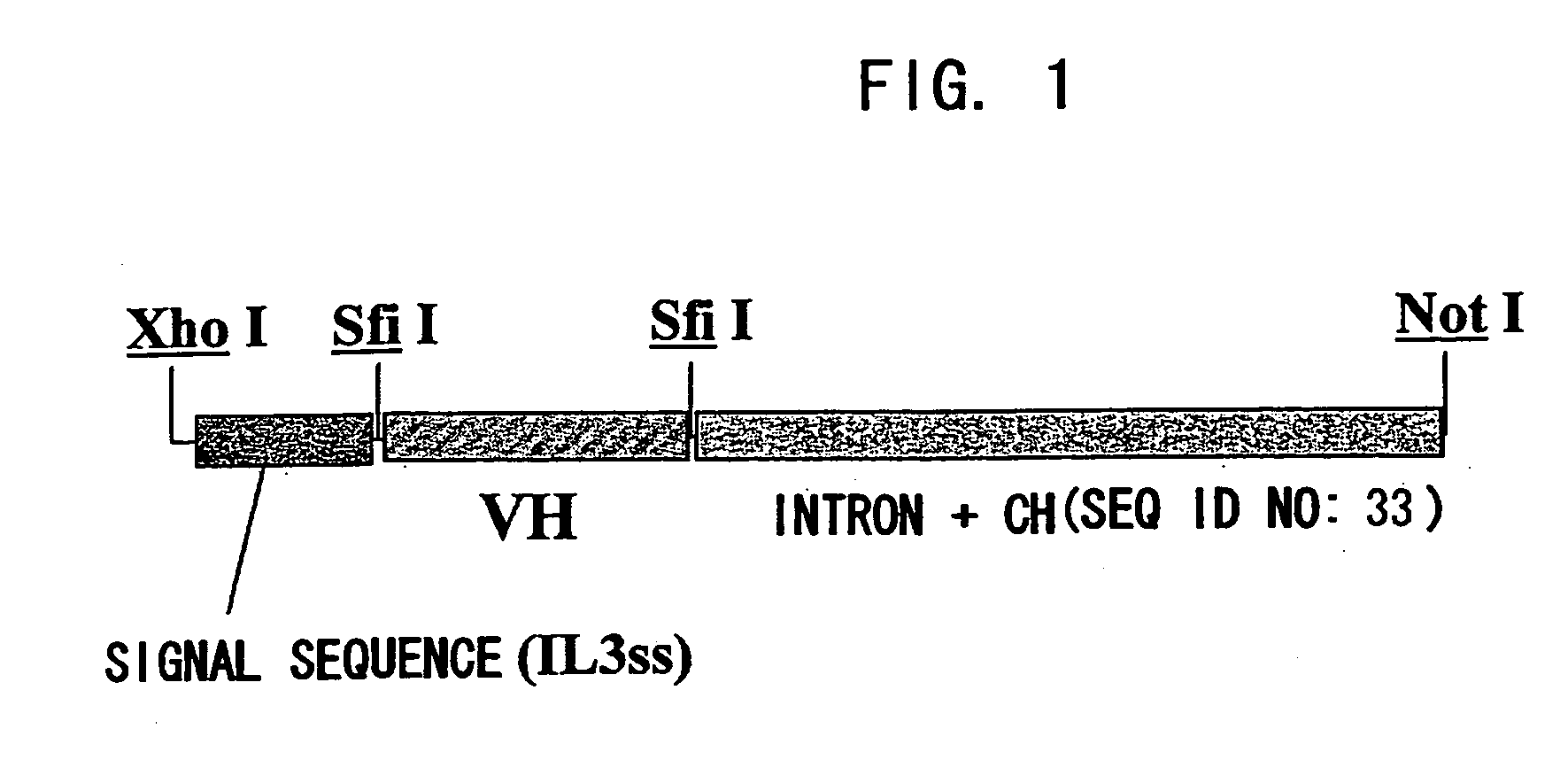
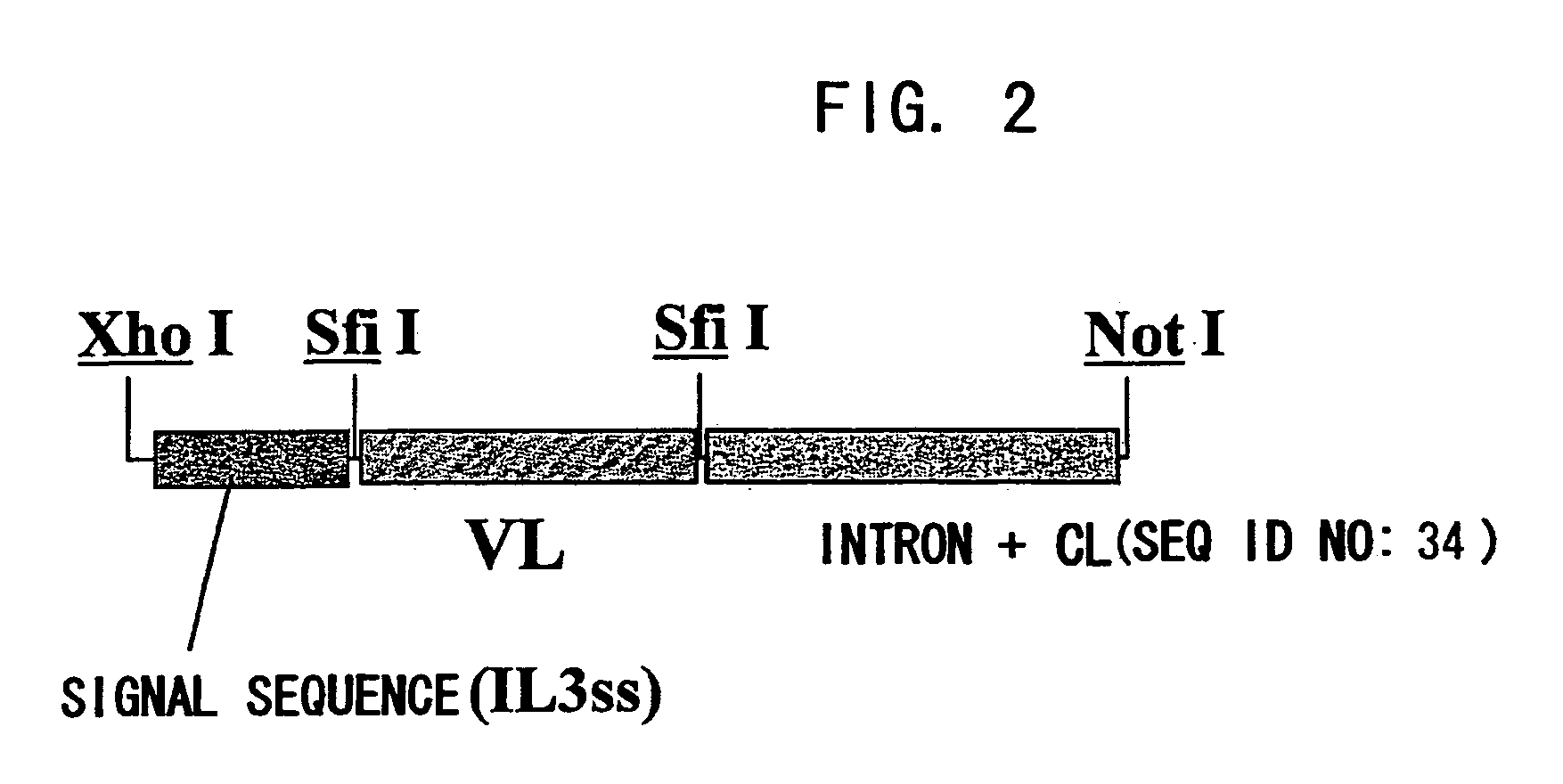
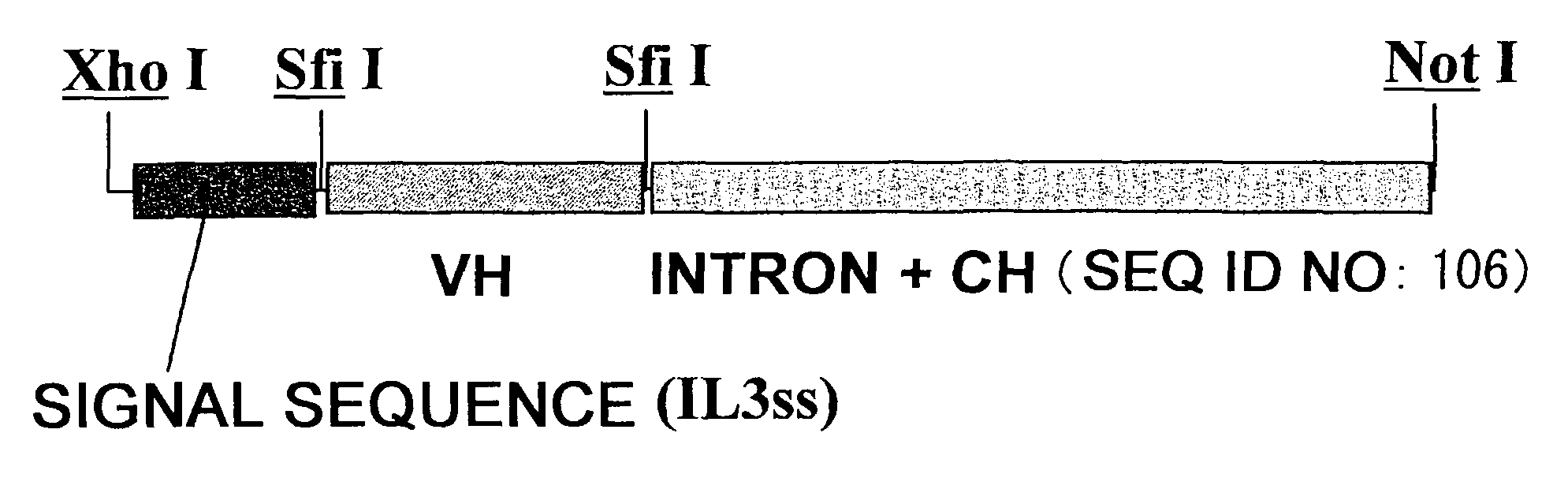
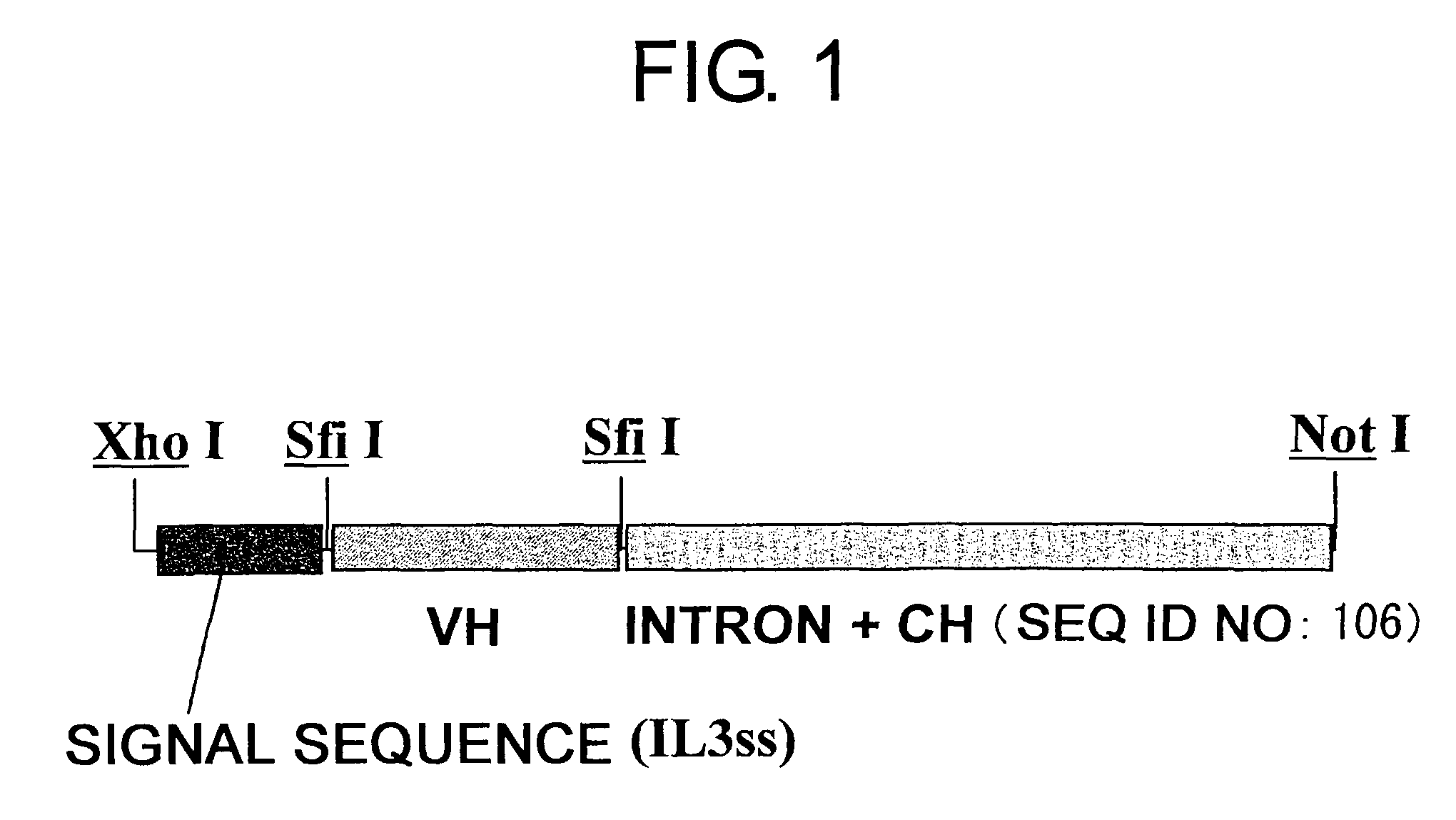
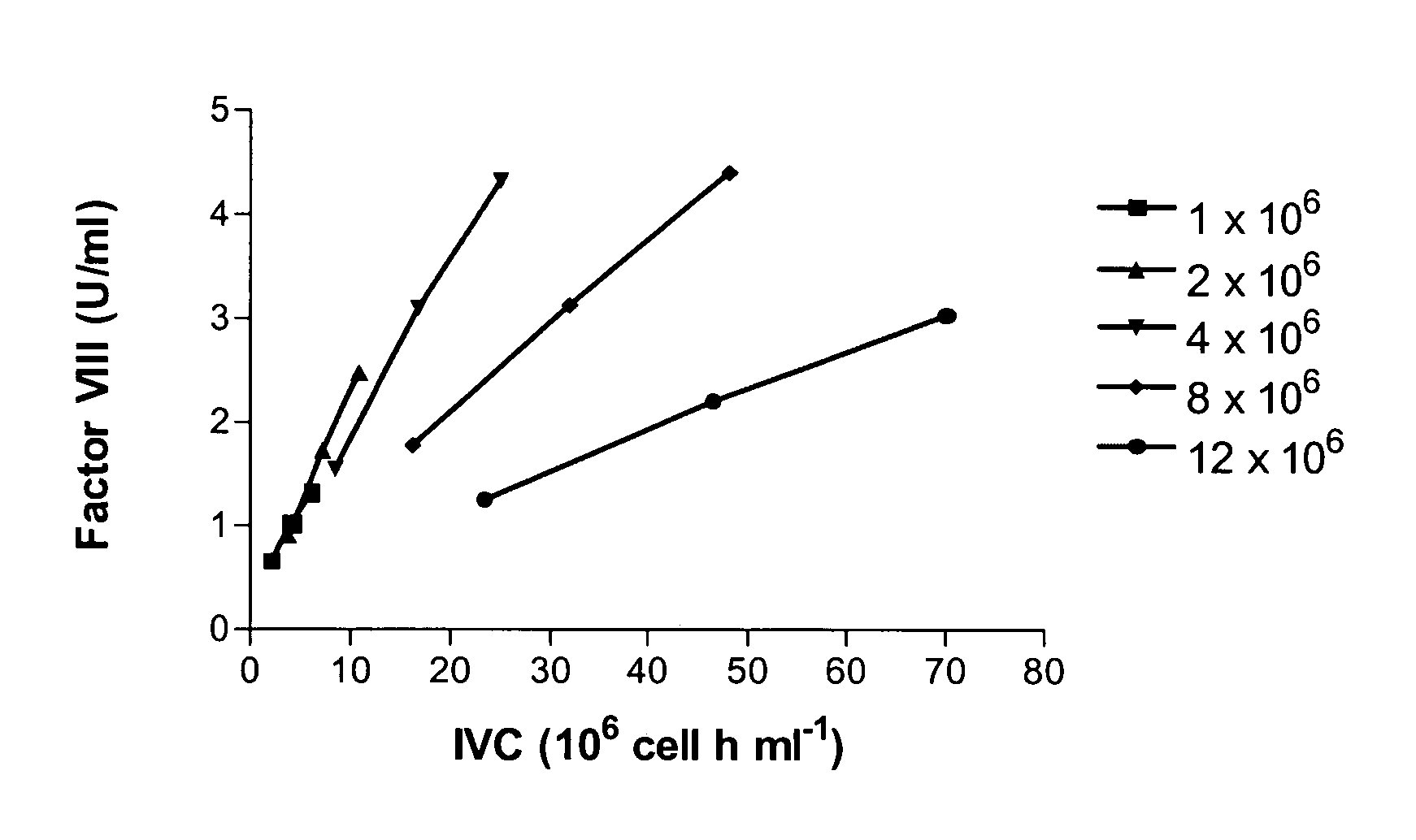
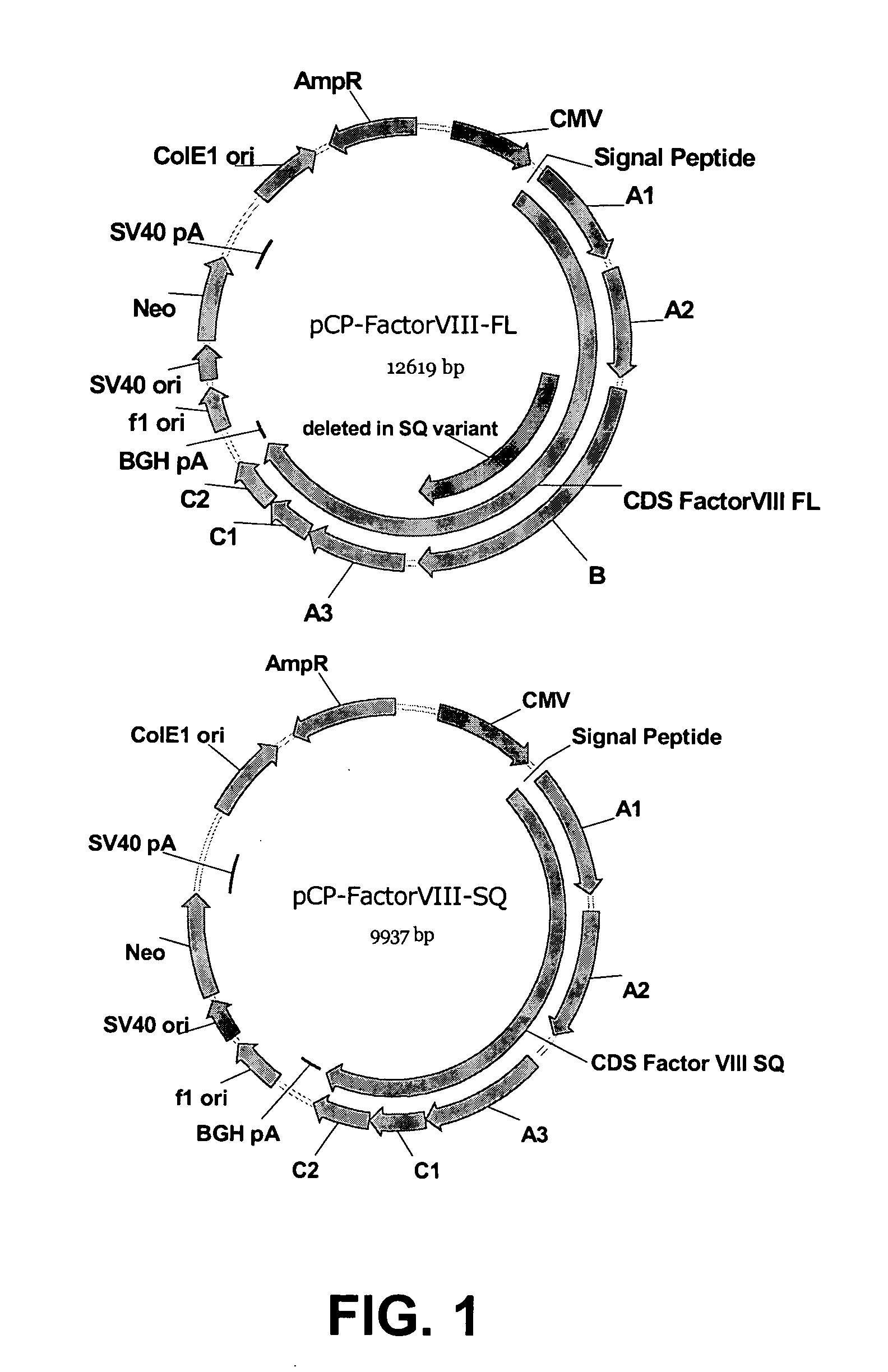
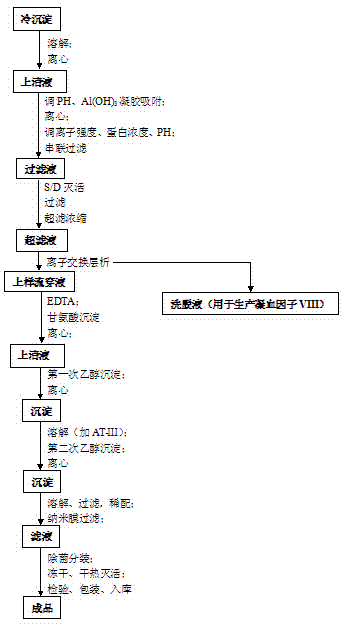
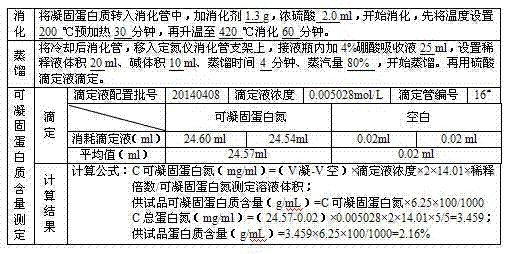
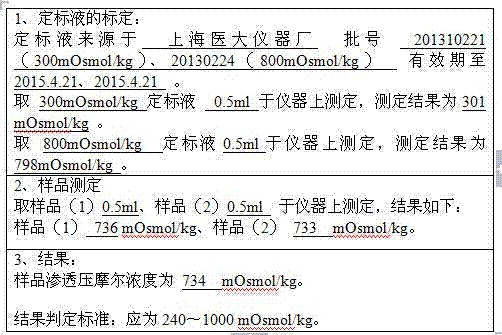
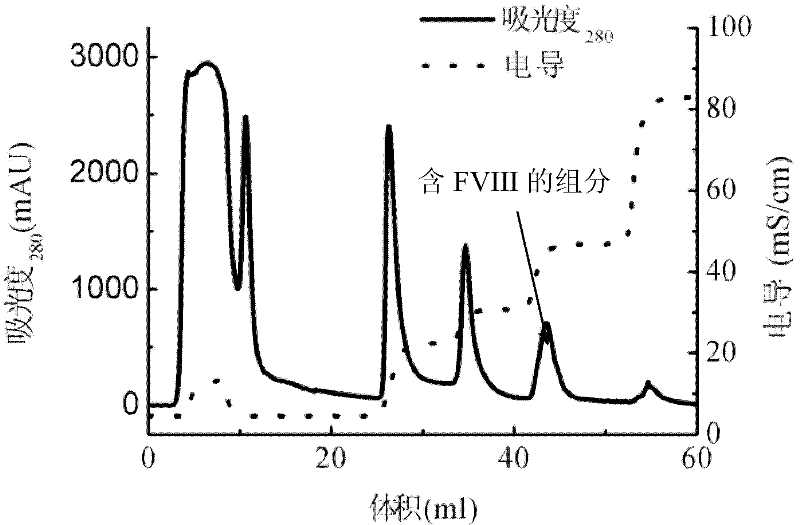
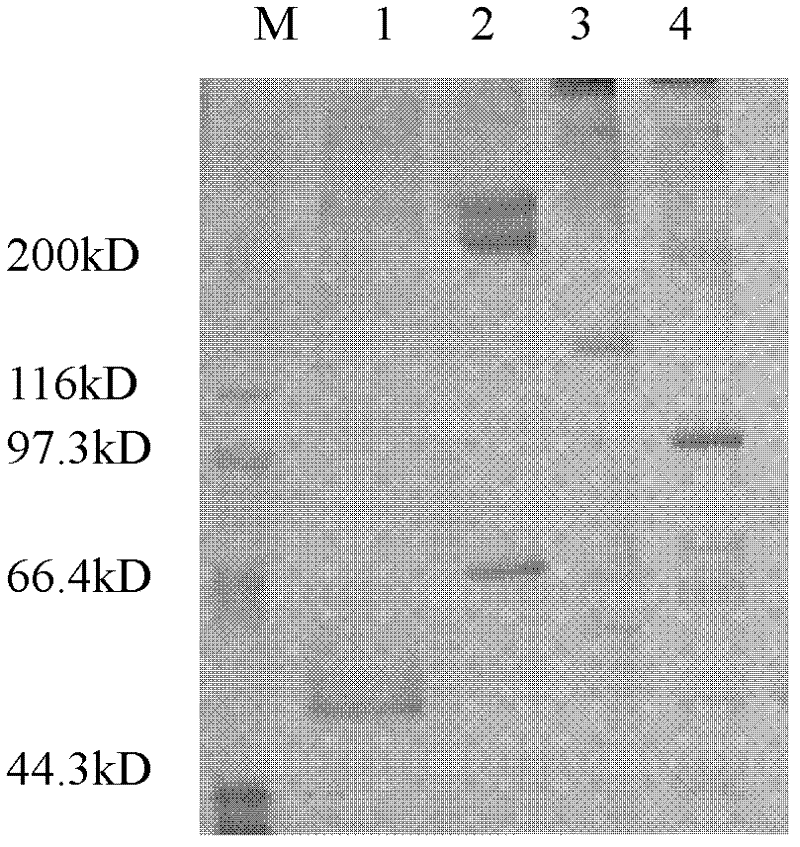
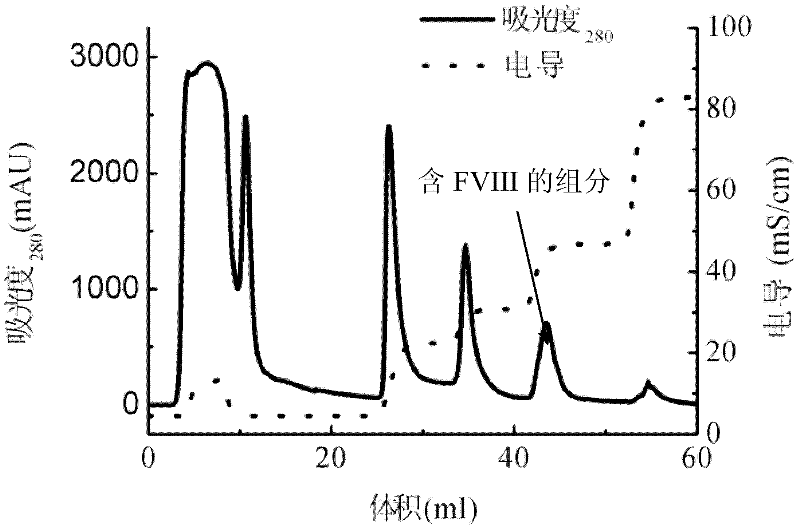
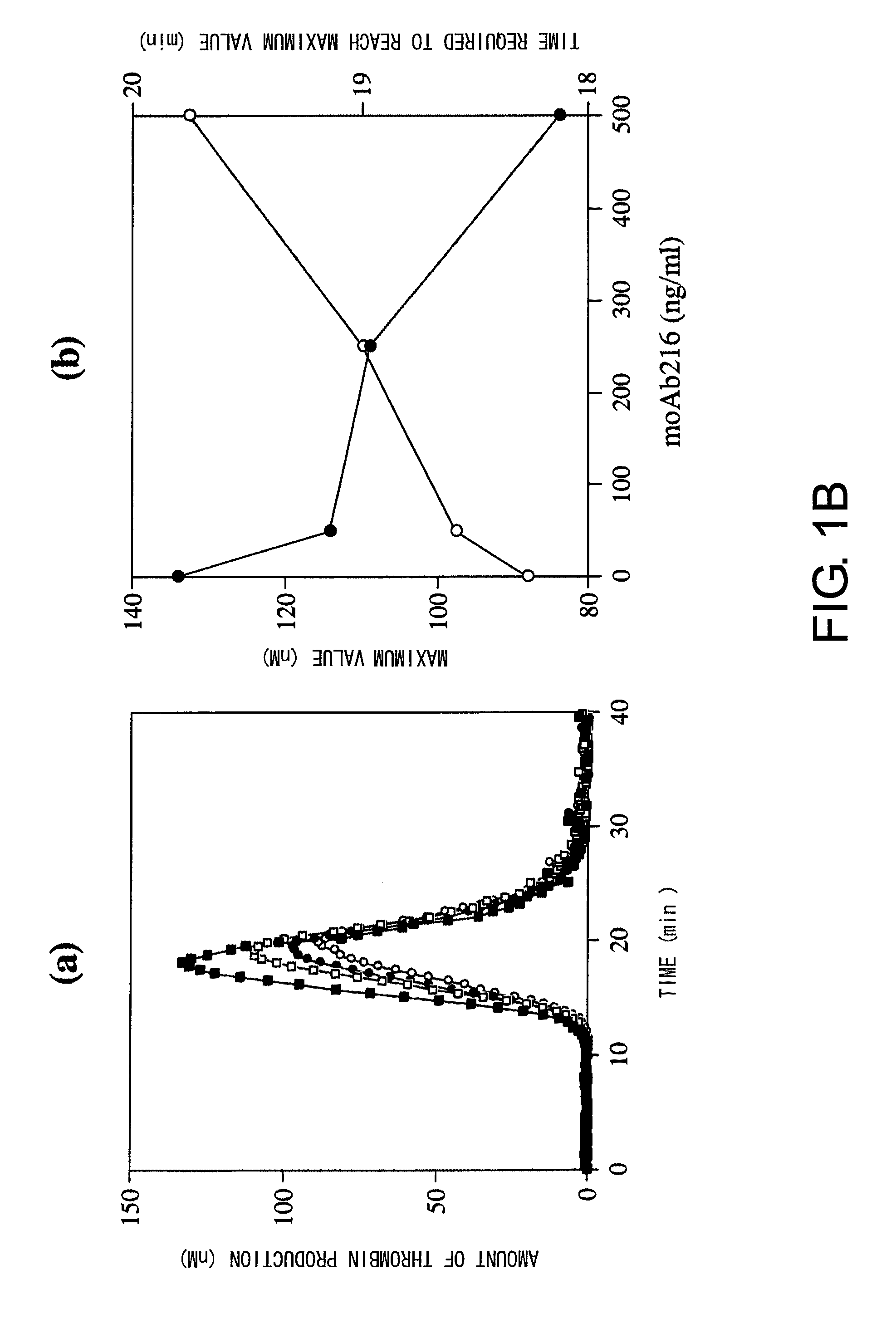
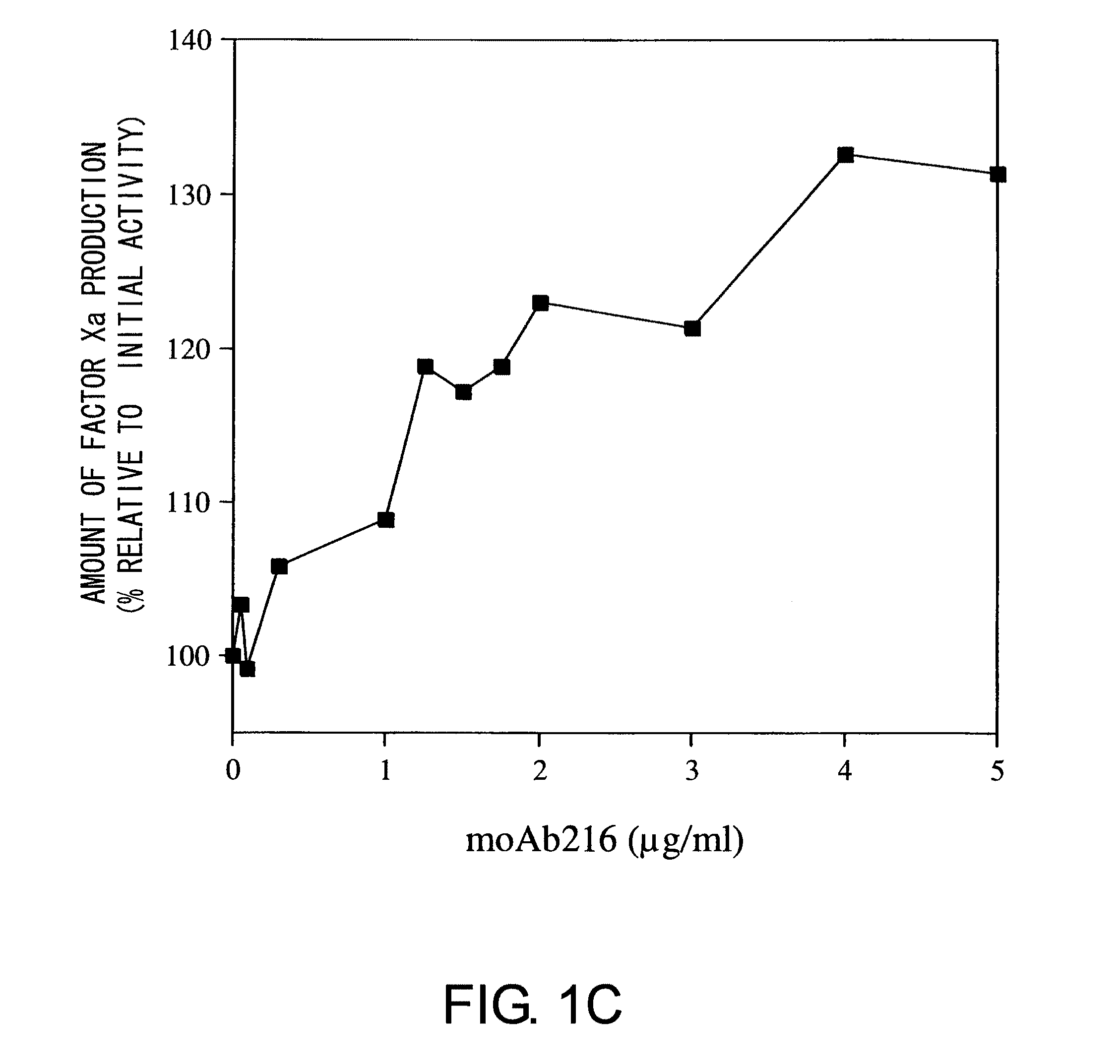
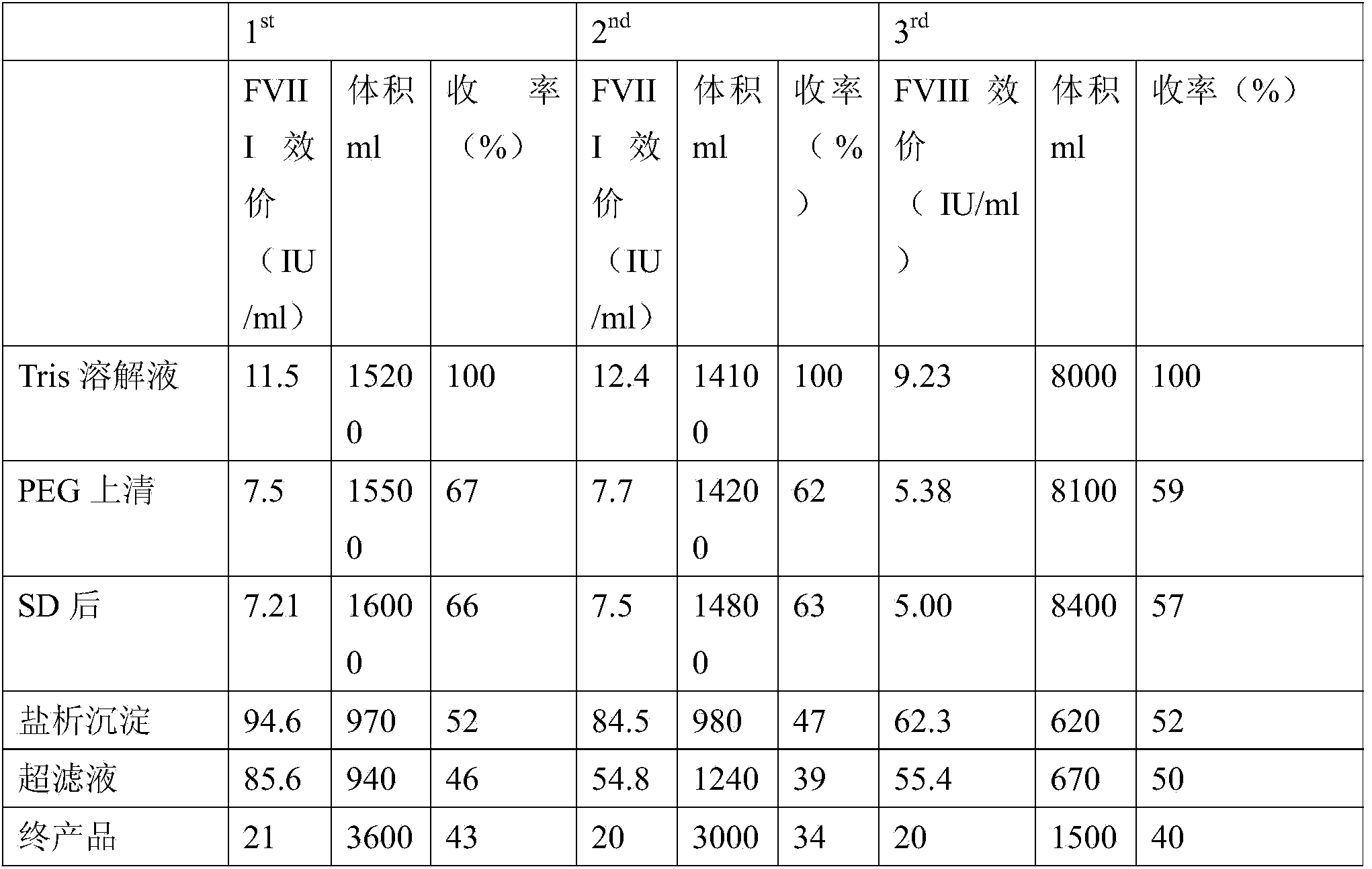
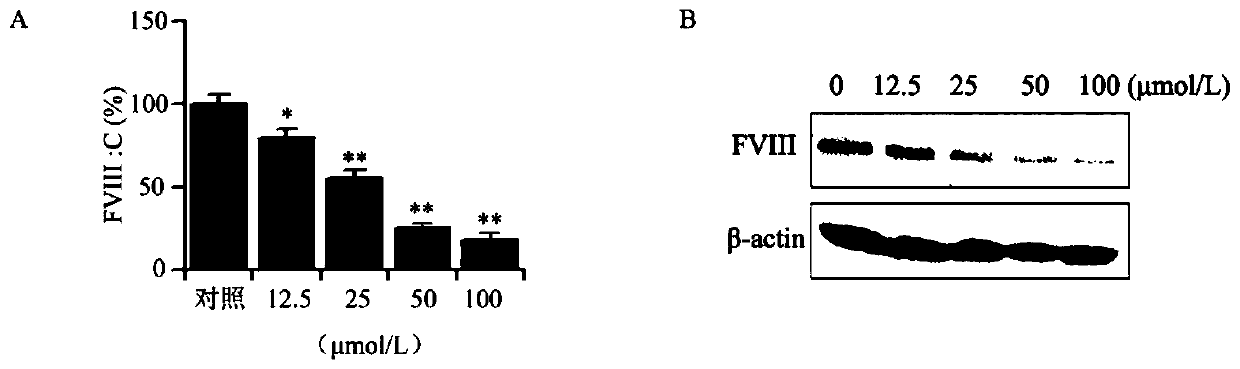
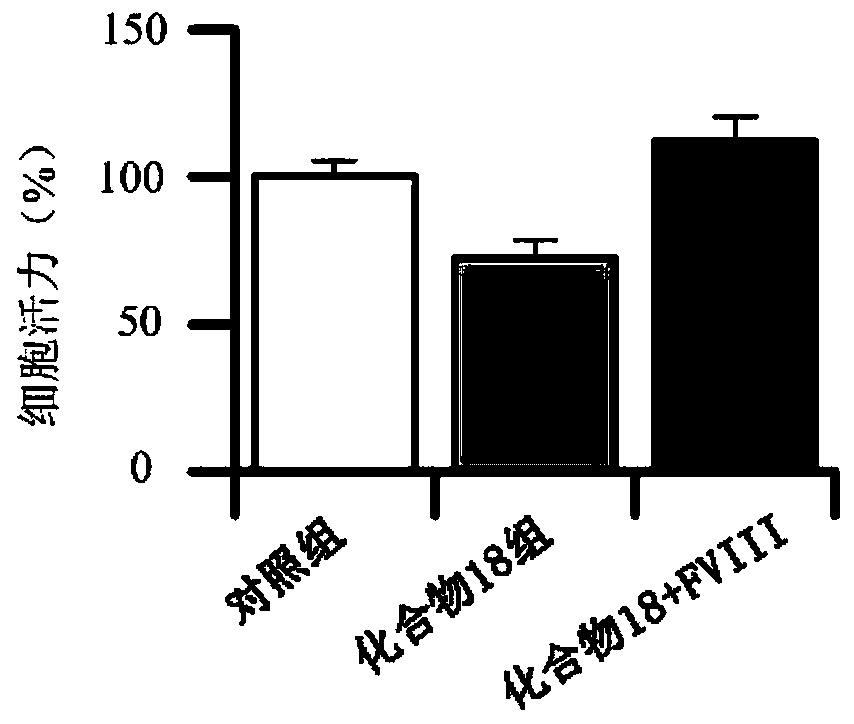
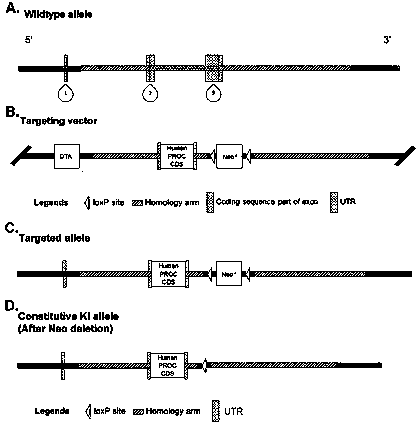
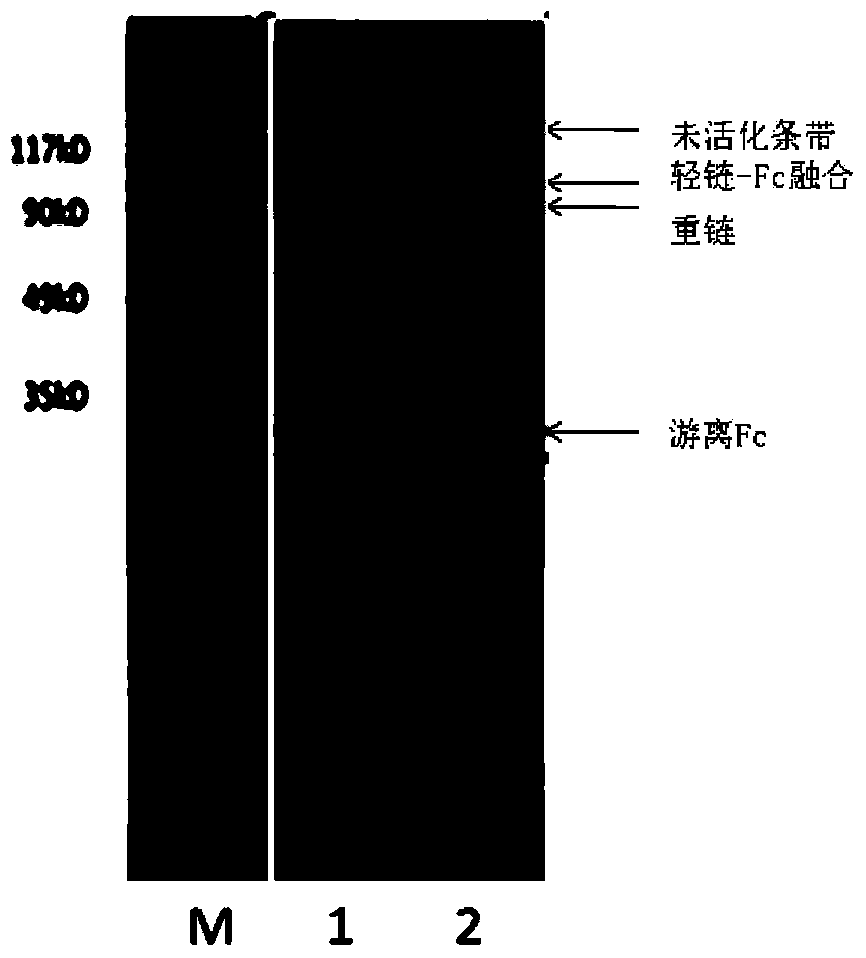
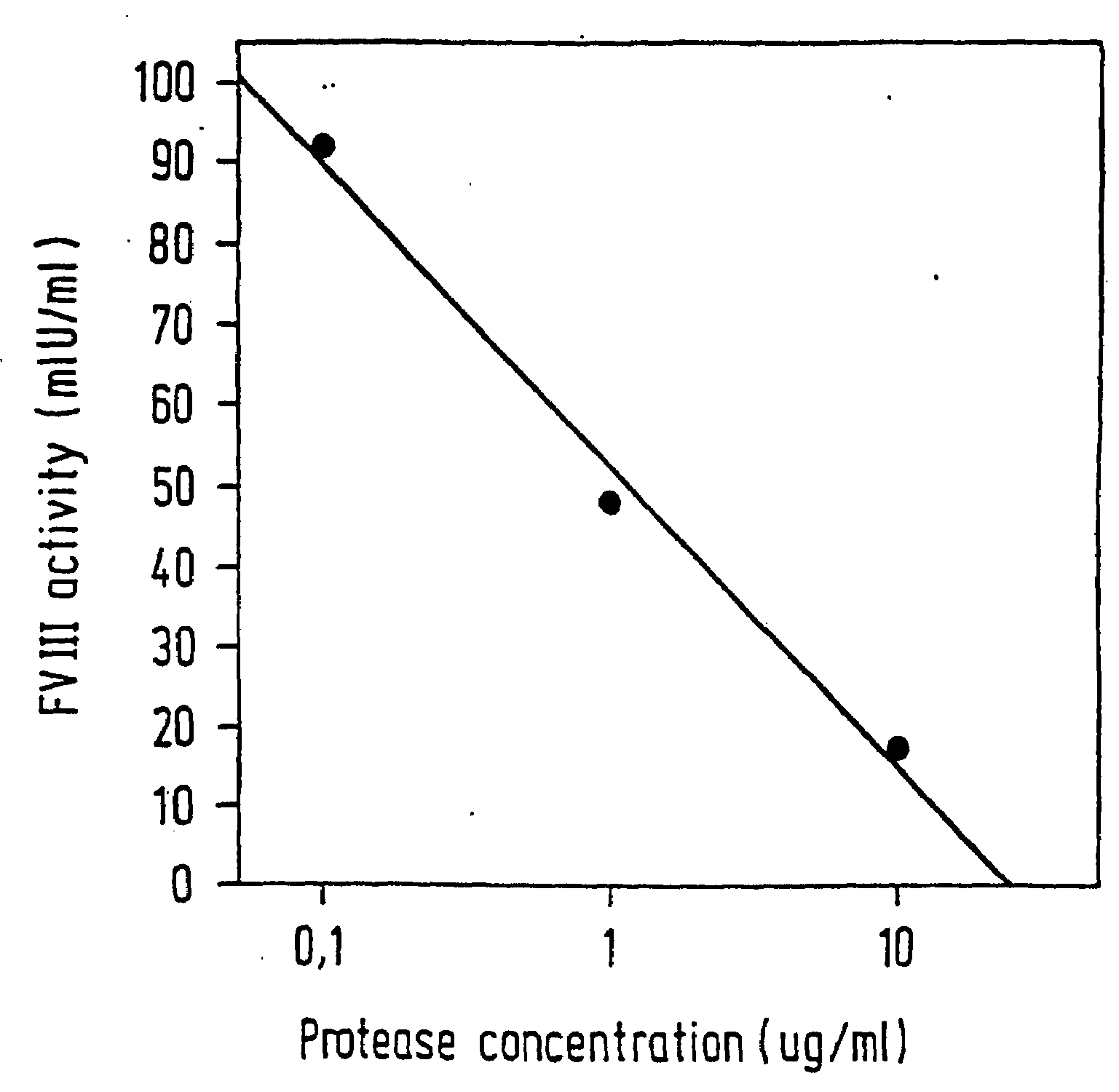
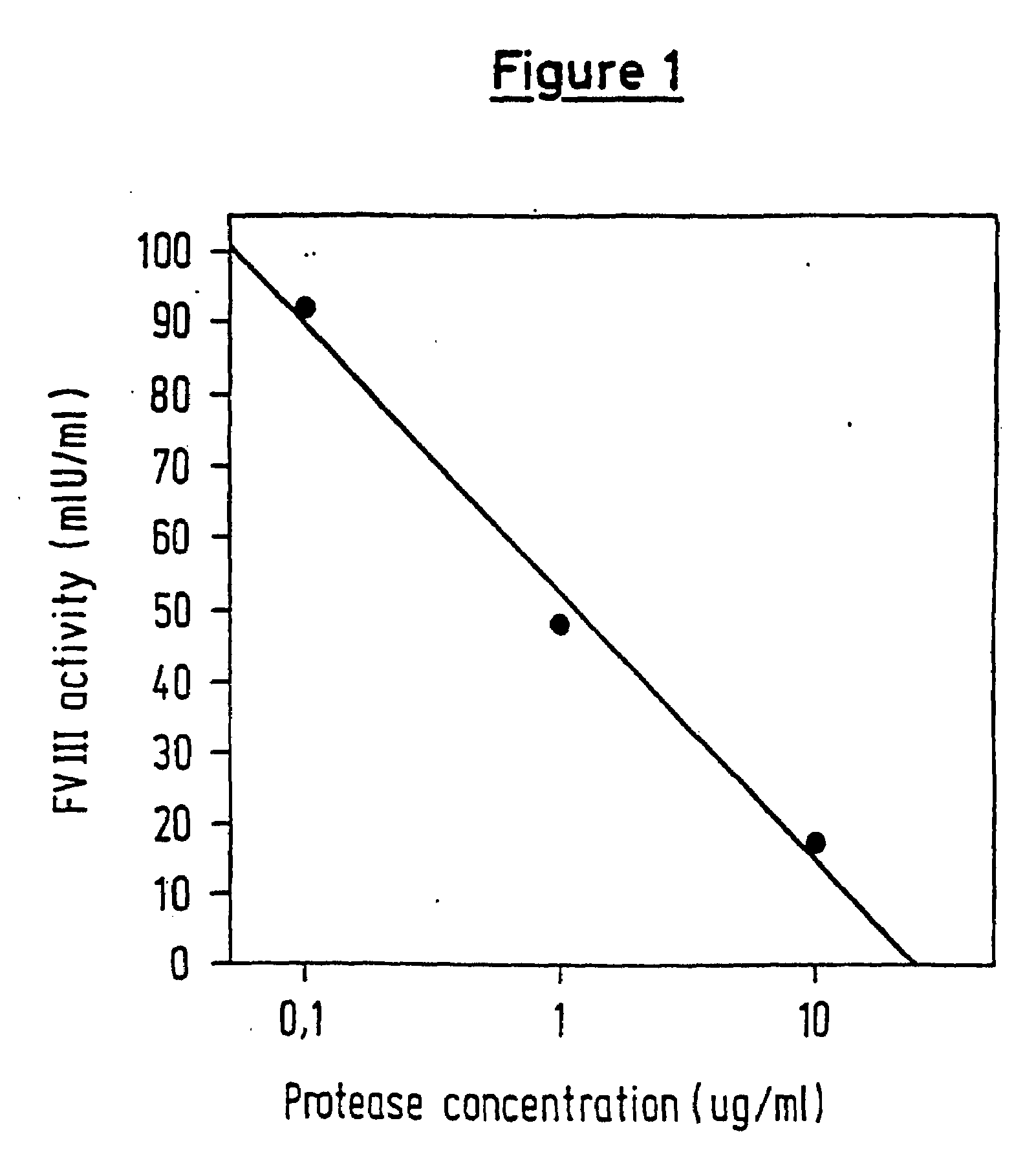
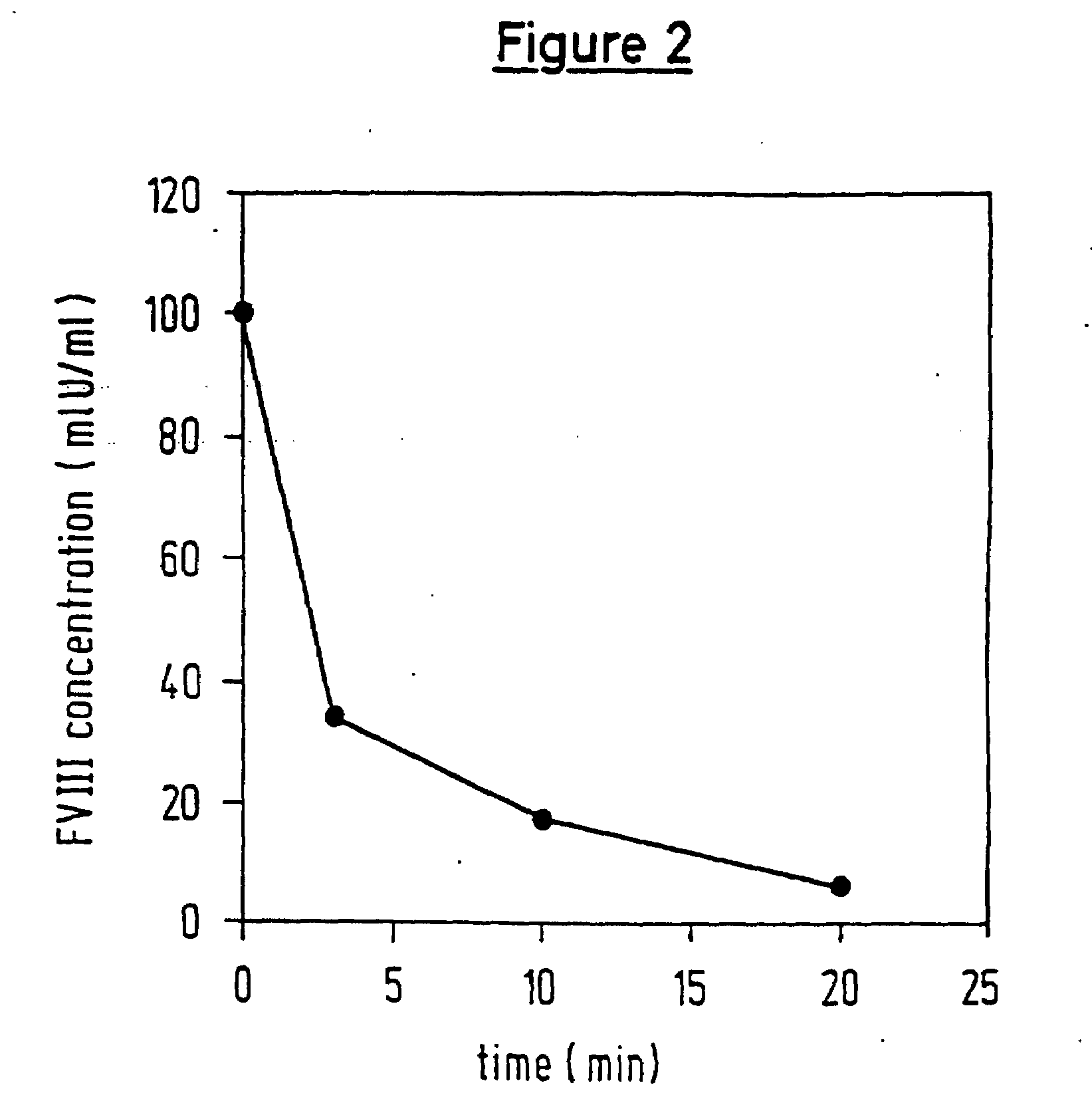
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
72 results about "Blood coagulation factor VIII" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Bispecific antibody substituting for functional proteins
ActiveUS20070041978A1Enhances enzymatic reactionImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIBlood coagulation factor VIIIBlood Coagulation Factor X
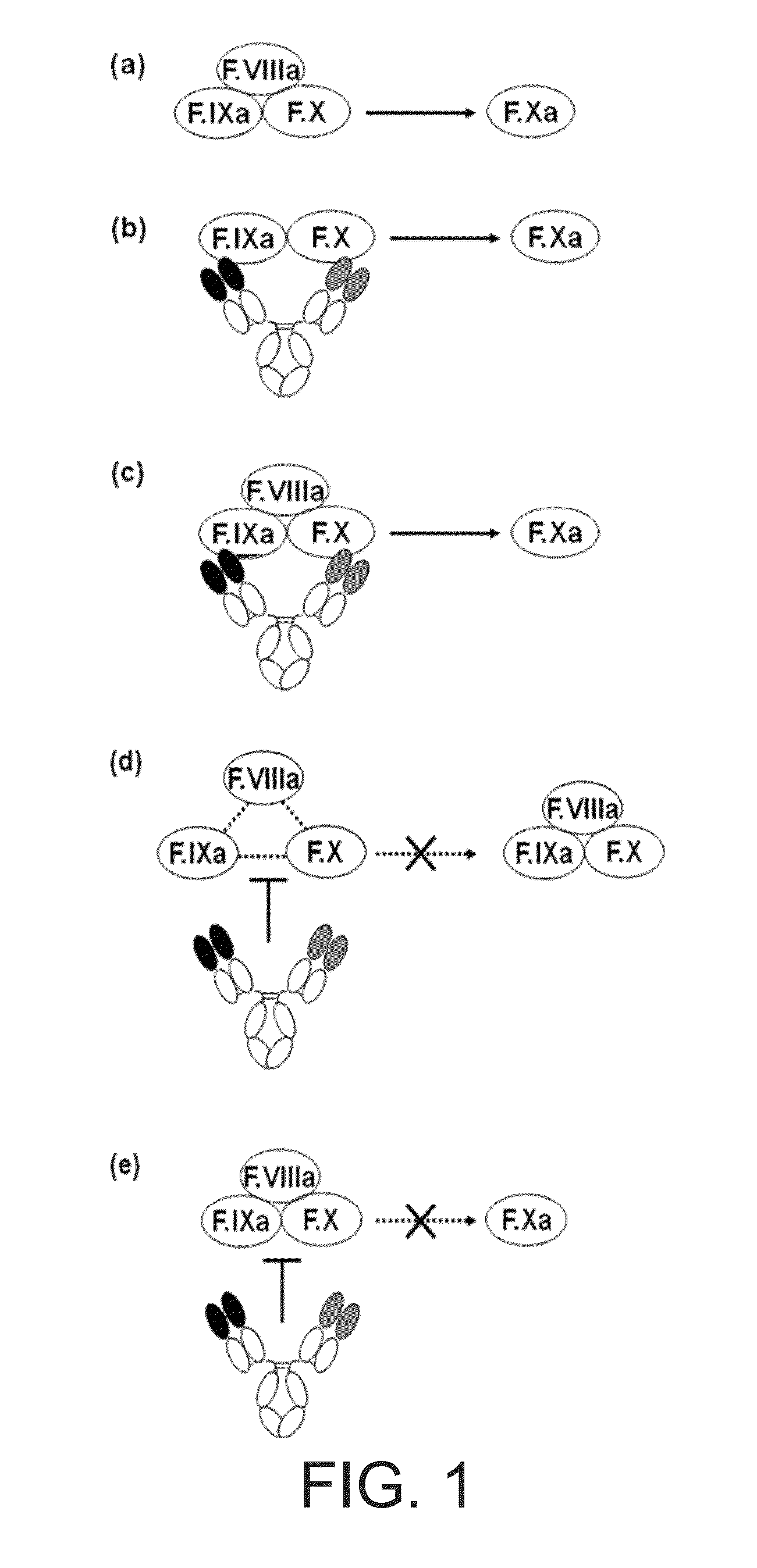
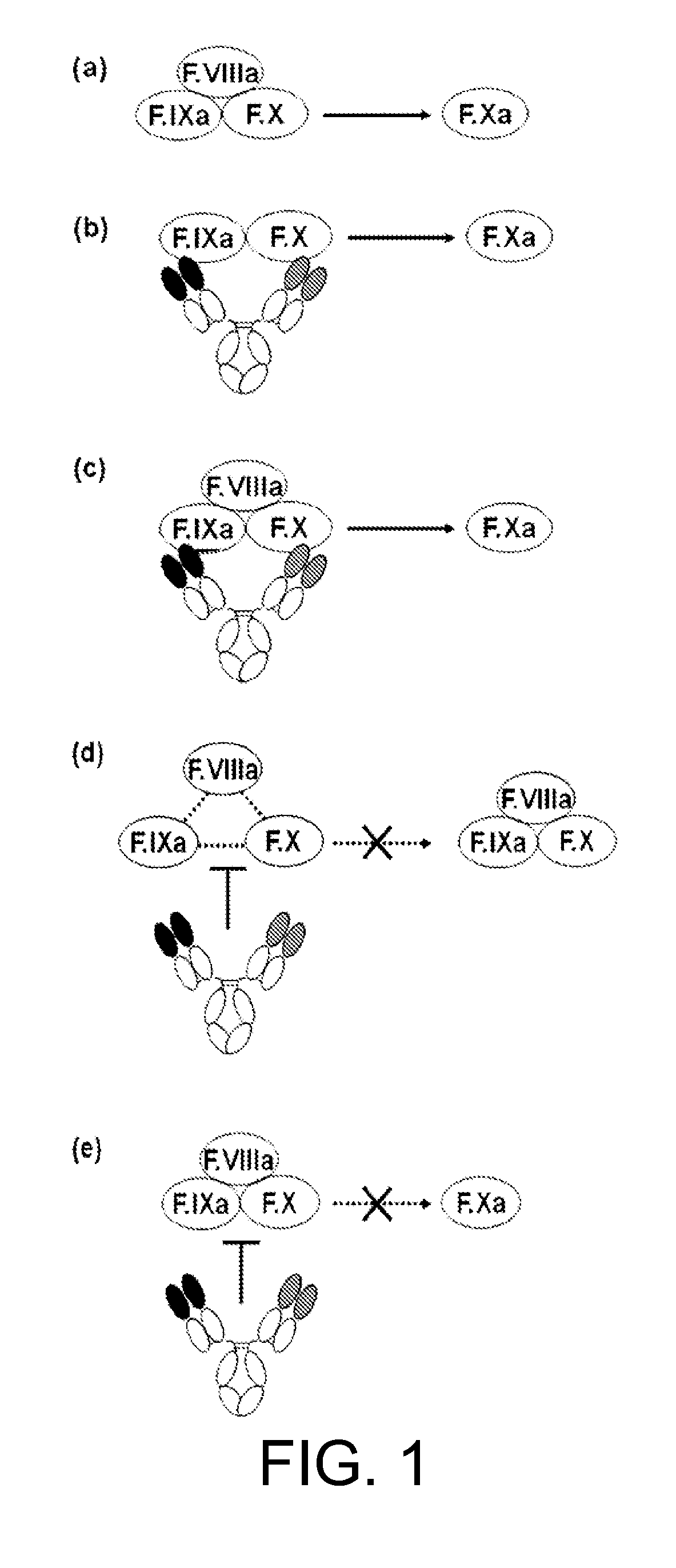
The present inventors succeeded in constructing bispecific antibodies, which bind to both the blood coagulation factor IX / activated blood coagulation factor IX and blood coagulation factor X, and functionally substitute for blood coagulation factor VIII / activated blood coagulation factor VIII which enhances the enzymatic reaction.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Double Specific Antibodies Substituting For Functional Proteins
InactiveUS20080075712A1Reduced activityOutstanding sustainabilityImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsNervous disorderBlood coagulation factor VIIIBlood Coagulation Factor X
The present inventors succeeded in separating bispecific antibodies that functionally substitute for ligands of type I interferon receptors comprising two types of molecules: AR1 chain and AR2 chain. Furthermore, the present inventors succeeded in producing bispecific antibodies that substitute for the enzyme reaction-accelerating function of blood coagulation factor VIII / activated blood coagulation factor VIII, which bind to both blood coagulation factor IX / activated blood coagulation factor IX and blood coagulation factor X.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Antibody Substituting for Function of Blood Coagulation Factor VIII
InactiveUS20100003254A1Enhances enzymatic reactionShorten clotting timeImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibody ingredientsBlood coagulation factor VIIIAntiendomysial antibodies
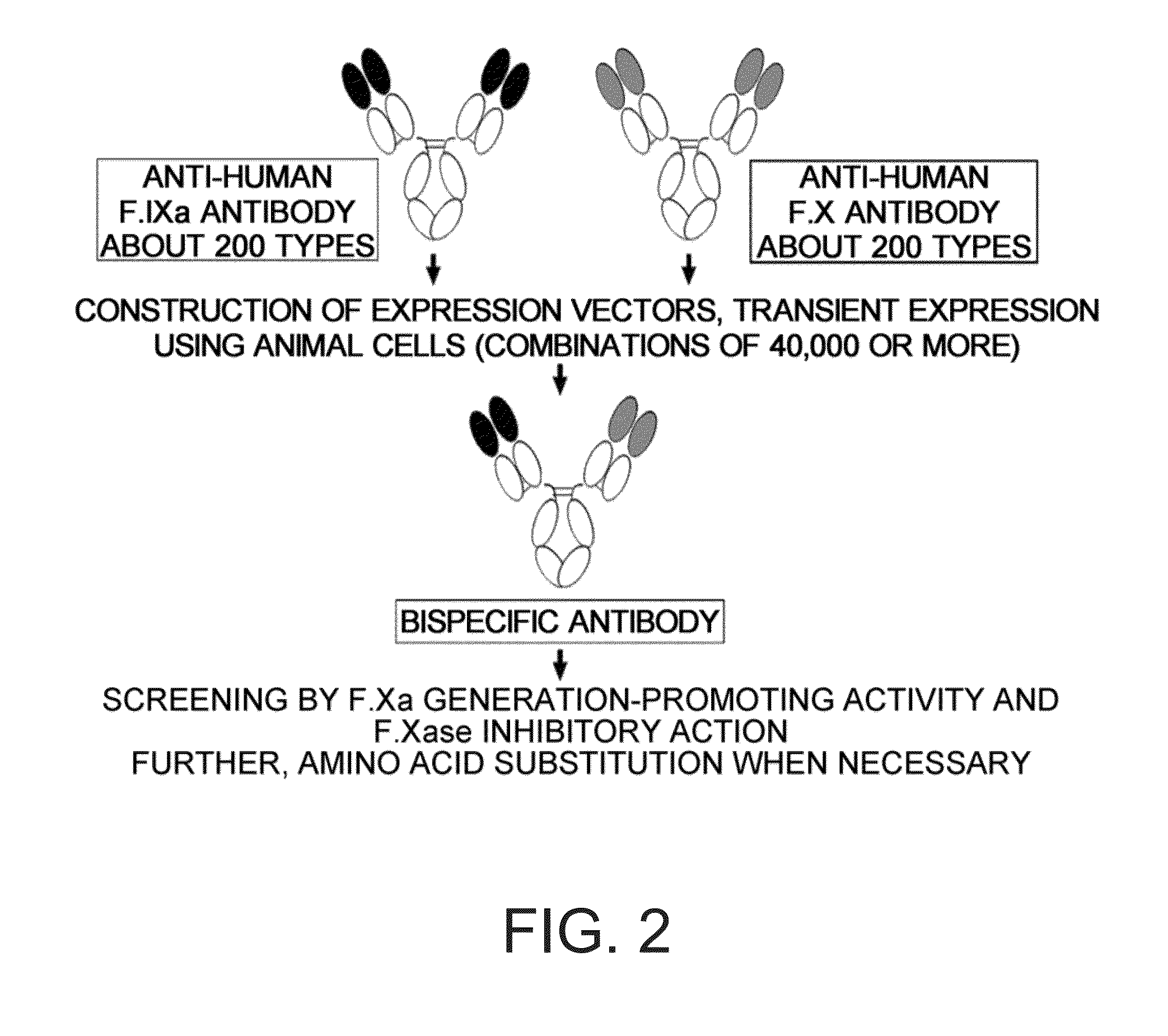
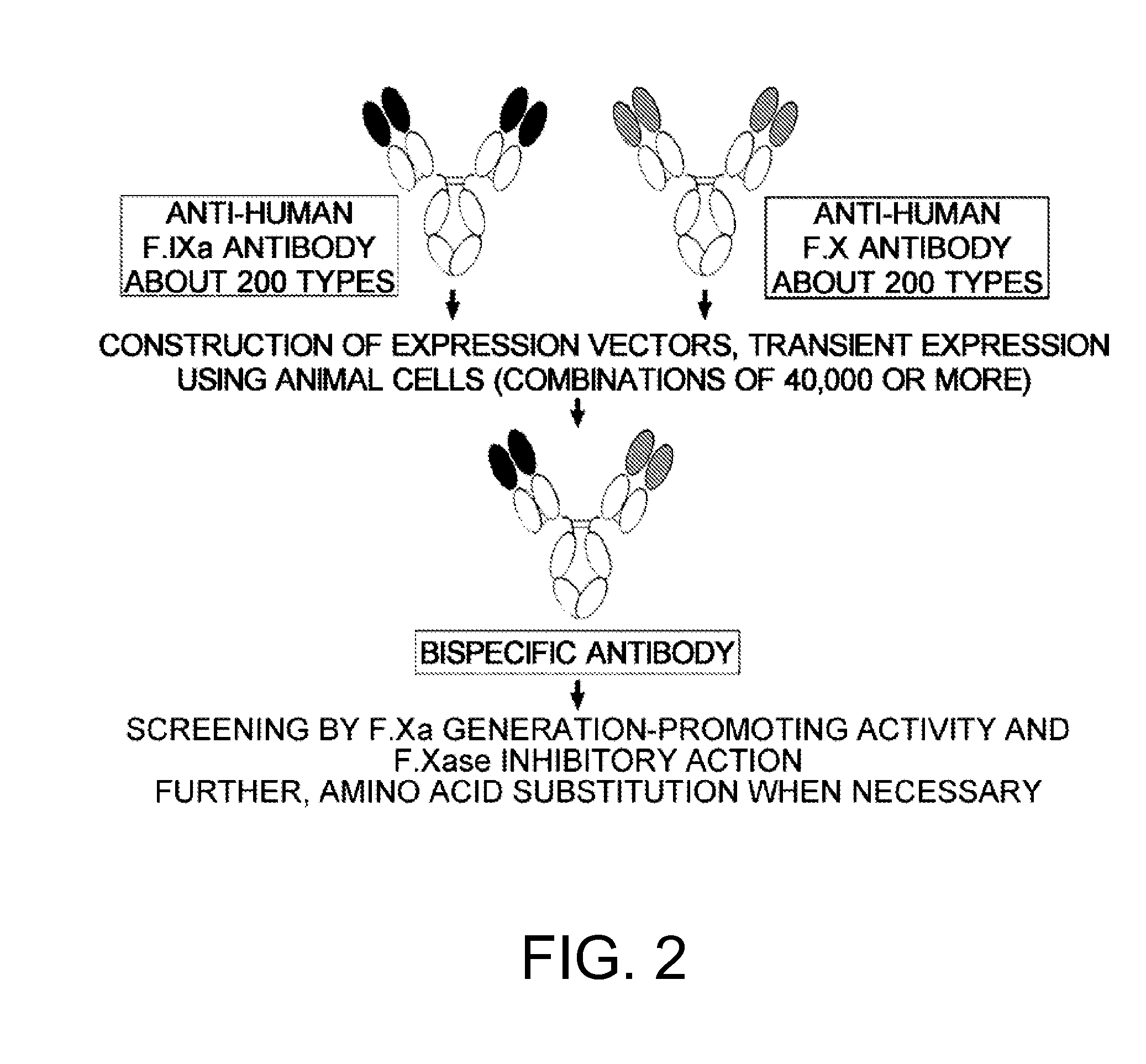
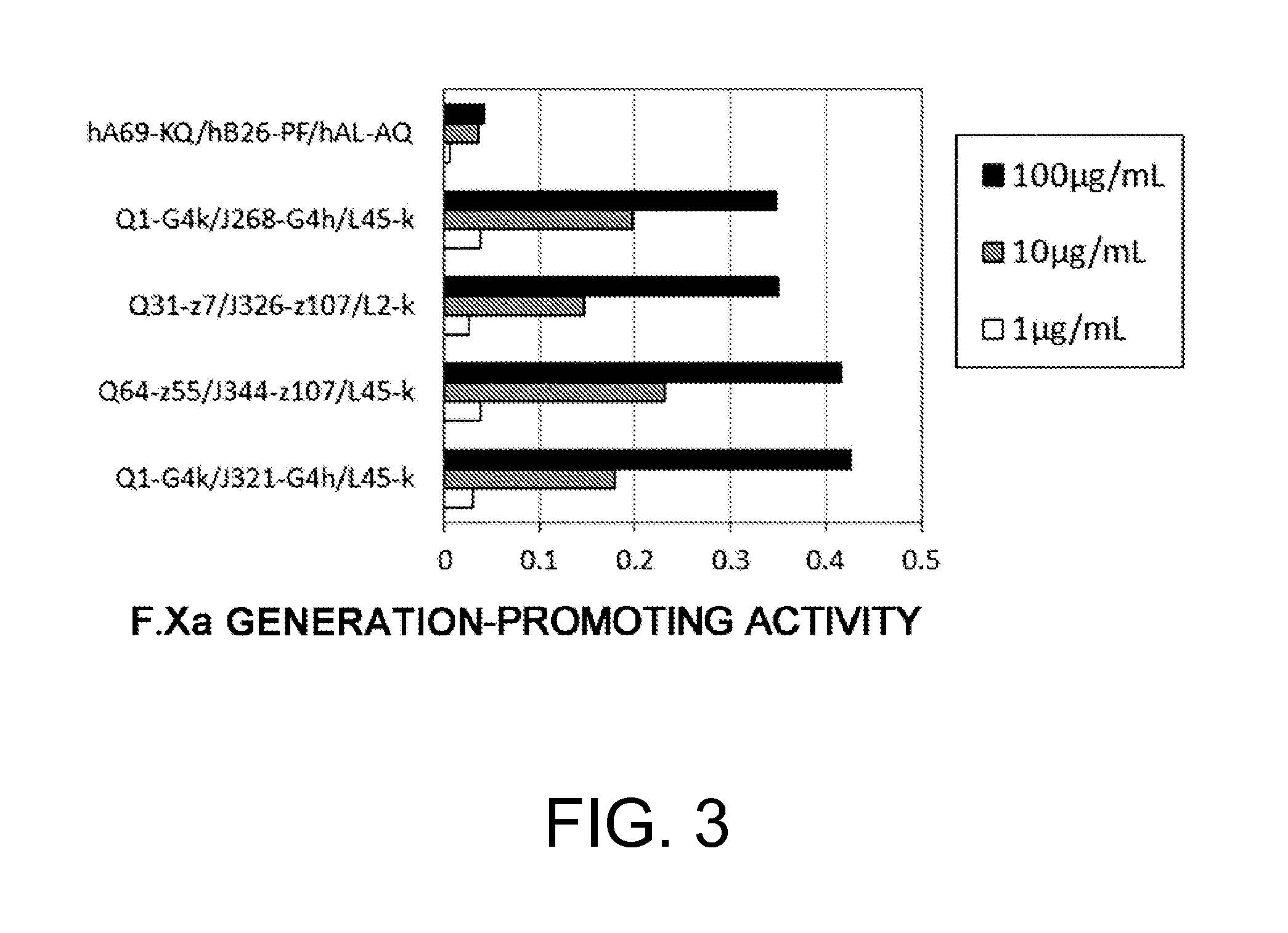
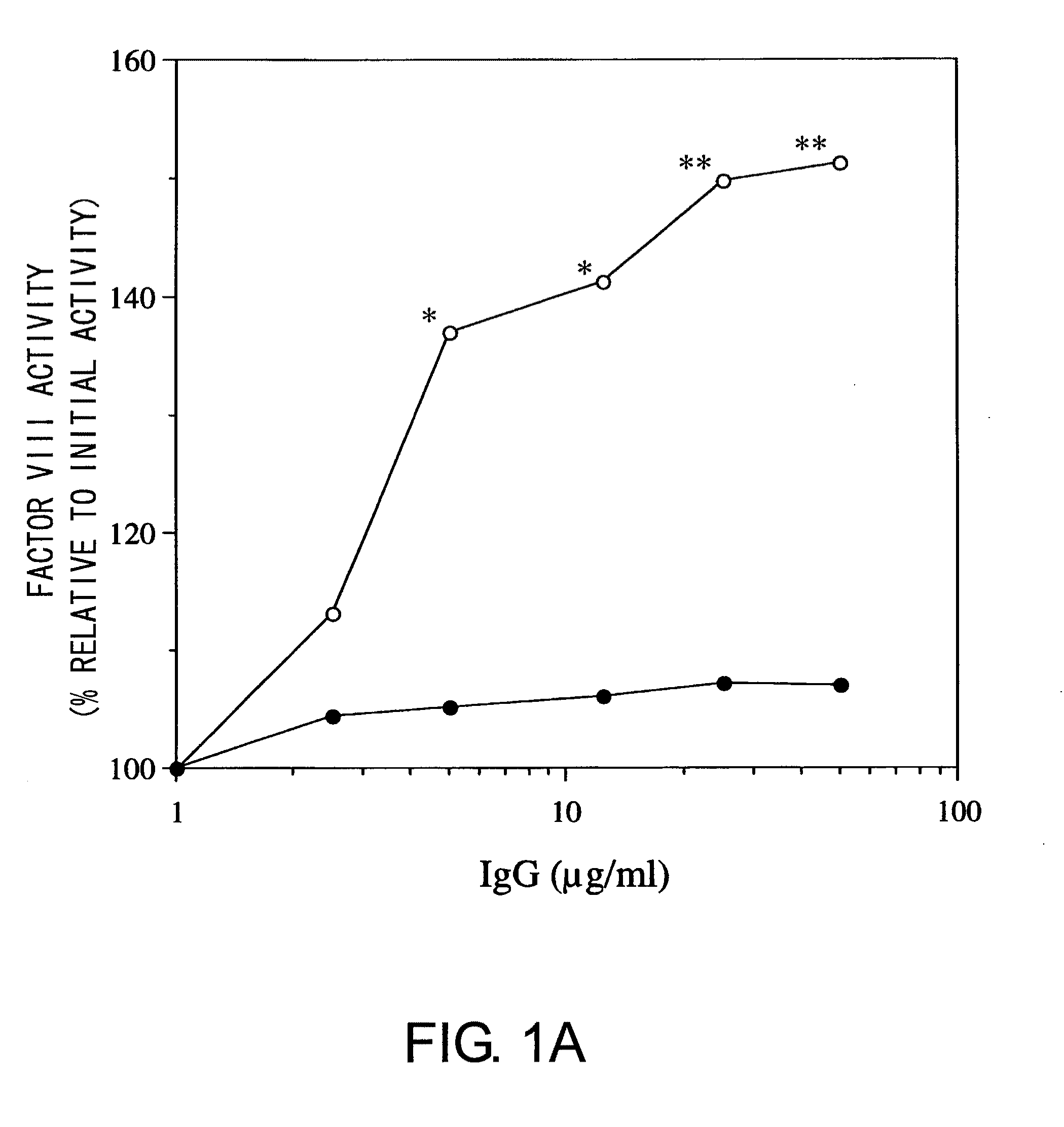
The present inventors produced a variety of bispecific antibodies that specifically bind to both F. IX / F. IXa and F. X, and functionally substitute for F. VIIIa, i.e., have a cofactor function to promote F. X activation via F. IXa. Among these antibodies, the antibody A44 / B26 reduced coagulation time by 50 seconds or more as compared to that observed when the antibody was not added. The present inventors produced a commonly shared L chain antibody from this antibody using L chains of A44, and showed that A44L can be used as commonly shared L chains, although the activity of the resulting antibody is reduced compared to the original antibody (A44HL-B26HL). Further, with appropriate CDR shuffling, the present inventors successfully produced highly active multispecific antibodies that functionally substitute for coagulation factor VIII.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Bispecific antibody substituting for functional proteins
ActiveUS8062635B2Enhances enzymatic reactionImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIBlood coagulation factor VIIIBlood Coagulation Factor X
The present inventors succeeded in constructing bispecific antibodies, which bind to both the blood coagulation factor IX / activated blood coagulation factor IX and blood coagulation factor X, and functionally substitute for blood coagulation factor VIII / activated blood coagulation factor VIII which enhances the enzymatic reaction.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Multi-specific antigen-binding molecule having alternative function to function of blood coagulation factor viii
ActiveUS20130330345A1High activityLow F.Xase inhibitory actionImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAnimal cellsBlood coagulation factor VIIIAntigen
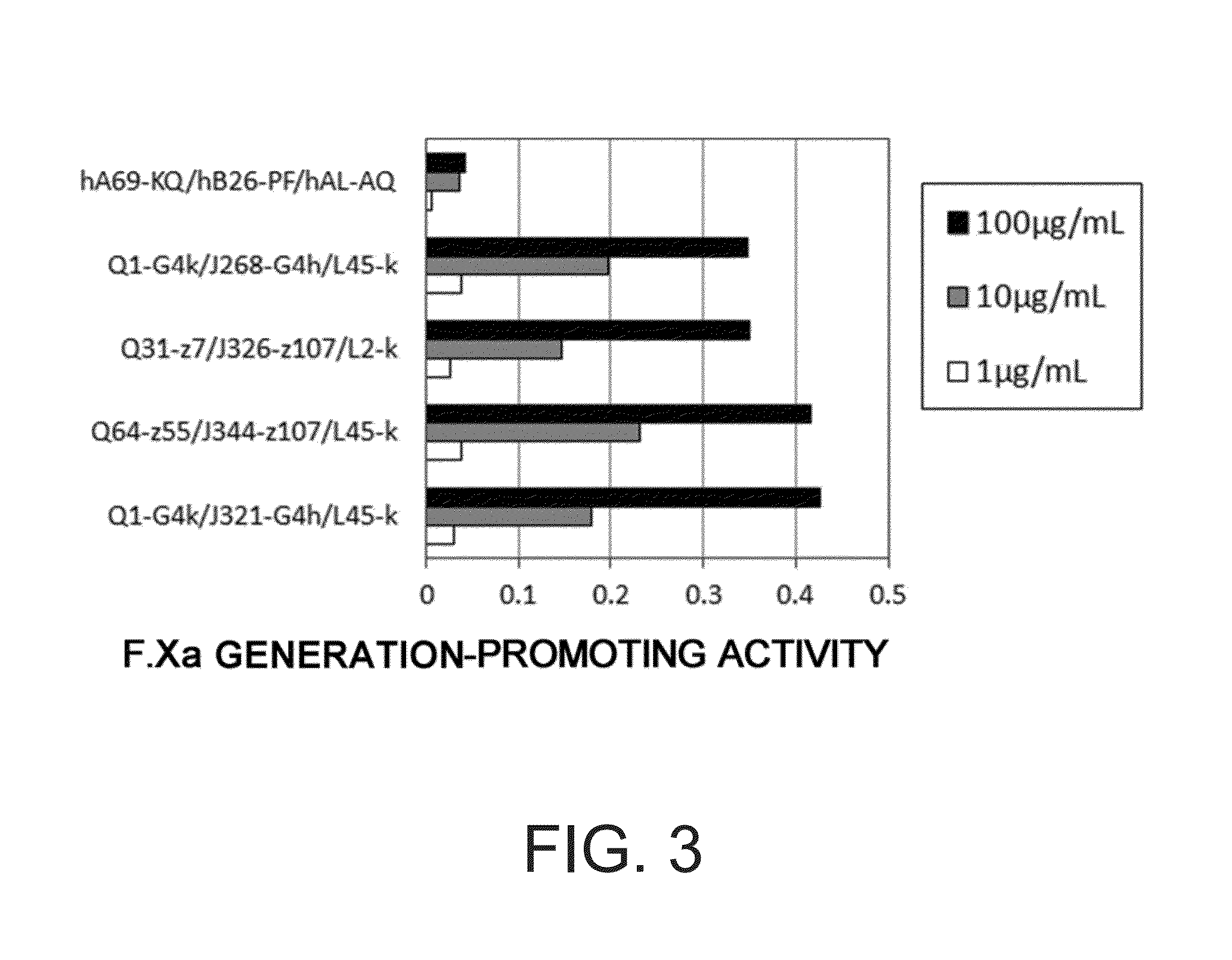
Various bispecific antibodies that specifically bind to both blood coagulation factor IX / activated blood coagulation factor IX and blood coagulation factor X and functionally substitute for the cofactor function of blood coagulation factor VIII, that is, the function to promote activation of blood coagulation factor X by activated blood coagulation factor IX, were produced. From these antibodies, multispecific antigen-binding molecules having a high activity of functionally substituting for blood coagulation factor VIII were successfully discovered.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Antibody Substituting for Function of Blood Coagulation Factor VIII
InactiveUS20120237517A1Shorten clotting timeImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibody ingredientsBlood coagulation factor VIIIBispecific antibody
The present inventors produced a variety of bispecific antibodies that specifically bind to both F. IX / F. IXa and F. X, and functionally substitute for F. VIIIa, i.e., have a cofactor function to promote F. X activation via F. IXa. Among these antibodies, the antibody A44 / B26 reduced coagulation time by 50 seconds or more as compared to that observed when the antibody was not added. The present inventors produced a commonly shared L chain antibody from this antibody using L chains of A44, and showed that A44L can be used as commonly shared L chains, although the activity of the resulting antibody is reduced compared to the original antibody (A44HL-B26HL). Further, with appropriate CDR shuffling, the present inventors successfully produced highly active multispecific antibodies that functionally substitute for coagulation factor VIII.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Factor VII polypeptides for preventing formation of inhibitors in subjects with haemophilia
InactiveUS20050032690A1Inhibition formationImprove stabilityOrganic active ingredientsFactor VIIFactor VIIaBlood coagulation factor VIII
The invention provides a method for preventing formation of inhibitors to blood coagulation factor VIII or factor IX in a subject having haemophilia, the method comprising administering (via intravenous, subcutaneous, intradermal, or intramuscular routes) to a previously untreated subject an effective dosage of factor VIIa or a factor VII-related polypeptide.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
Multi-specific antigen-binding molecules and uses thereof
InactiveUS20140037632A1High activityHigh stability in bloodImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsAntibody ingredientsBlood coagulation factor VIIIAntigen
Various bispecific antibodies that specifically bind to both blood coagulation factor IX / activated blood coagulation factor IX and blood coagulation factor X and functionally substitute for the cofactor function of blood coagulation factor VIII, that is, the function to promote activation of blood coagulation factor X by activated blood coagulation factor IX, were produced. From these antibodies, multispecific antigen-binding molecules having a high activity of functionally substituting for blood coagulation factor VIII were successfully discovered.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Recombinant expression of factor VIII in human cells
InactiveUS20060099685A1SsRNA viruses negative-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood coagulation factor VIIIHeterologous
The invention discloses a process for recombinant production of blood coagulation Factor VIII in an immortalized human embryonic retina cell, said cell expressing at least an adenoviral E1A protein and comprising a nucleic acid sequence encoding said Factor VIII, said nucleic acid sequence being under control of a heterologous promoter, said process comprising culturing said cell and expressing the Factor VIII in said cell, and harvesting the expressed Factor VIII. Cells that can be used in the process of the invention are also provided.
Owner:JANSSEN VACCINES & PREVENTION BV
Factor VIII:Ca chromogenic assay
InactiveUS6100050AGood reproducibilityHigh degree of sensitivityHydrolasesMicrobiological testing/measurementBlood coagulation factor VIIIFactor ii
A chromogenic assay for determination of blood coagulation Factor VIII:Ca, using an indicator of Factor Xa simultaneously as a measure of Factor VIII:Ca concentration and as an inhibitor of Factor Xa. This technique can be applied to measure the concentration of an activating enzyme using the rate of conversion of the indicator molecule of the product of that enzyme as an indirect indicator of enzyme concentration.
Owner:DADE BEHRING
Technology for extracting human blood coagulation factor VIII and human fibrinogen from plasma constituent precipitation
The invention provides a technology for extracting human blood coagulation factor VIII and human fibrinogen from plasma constituent precipitation. The preparation technology comprises the following steps: fresh plasma is subjected to primary sedimentation, so that blood coagulation factor VIII and fibrinogen precipitation can be jointly precipitated from the plasma; the primary precipitation is subjected to suspension; the suspension liquid is subjected to centrifugal separation to obtain supernatant; the centrifugally separated supernatant is subjected to virus inactivation and chromatography refining to respectively obtain human blood coagulation factor VIII refined liquid used for preparing human blood coagulation factor VIII products and chromatography effluent used for preparing human fibrinogen products. According to the invention, the human blood coagulation factor VIII and the human fibrinogen are precipitated through the one-step plasma constituent precipitation, and an ion-exchange column chromatography technology is adopted to perform purification preparation of the human blood coagulation factor VIII and the human fibrinogen, so that the deficiency that the human fibrinogen cannot be normally produced as the human blood coagulation factor VIII is prepared through cryoprecipitation is overcome.
Owner:WUHAN ZHONGYUAN RUIDE BIOLOGICAL PROD CO LTD
Preparation process for extracting human fibrinogens from waste for extracting cryoprecipitated blood coagulation factor VIII
ActiveCN104231072AHigh purityShort reconstitution timeFactor VIIFibrinogenBlood coagulation factor VIIIEthanol precipitation
The invention discloses a preparation process for extracting human fibrinogens from waste for extracting cryoprecipitated blood coagulation factor VIII. The preparation process is characterized by comprising the steps of cryoprecipitation dissolution, 2% aluminium hydroxide gel absorption, ion strength adjustment, series connection filtering, S / D viral inactivation, ion-exchange chromatography, EDTA Ca2+ removal, glycine precipitation, primary low-temperature ethanol precipitation, AT-III thrombin inhibition, secondary low-temperature ethanol precipitation, nanofilm filtering and dry-heat inactivation. For ensuring the safety, a nanofilm ia added to filter virus except S / D and dry-heat inactivation. By means of an added AT-III inactivated thrombin and EDTA Ca2+ removal process, fibrinogen in the production process is effectively prevented from being activated into fibrous protein. The glycine precipitation is utilized to remove fibrous protein monomers and polymers in products so as obtain high-purity human fibrinogen. The preparation products are safe and reliable, redissolution time is short, the clinic first-aid demand is met, and meanwhile the preparation process has important significance on indirect saving of scarce plasma resources.
Owner:华润博雅生物制药集团股份有限公司
Method for separating and purifying blood coagulation factor VIII
InactiveCN102584983AReduce transfer rateFacilitate dissociationFactor VIIPeptide preparation methodsBlood coagulation factor VIIIWhole blood product
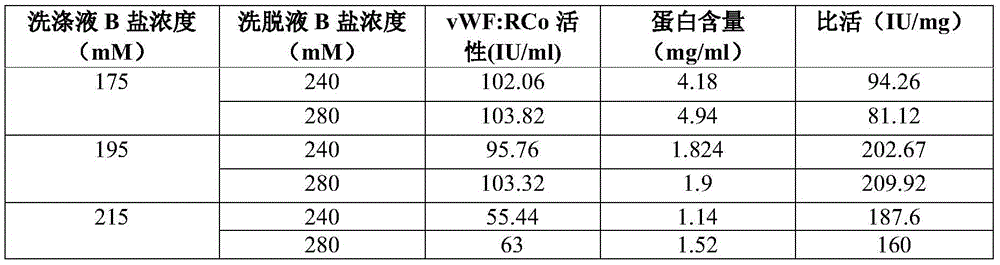
The invention relates to the field of separation and purification of blood products, in particular to a method for separating and purifying blood coagulation factor VIII. According to the method, a chromatographic raw material containing the blood coagulation factor VIII is separated by using super-macroporous ion exchange chromatography. The method also comprises a step of performing coarse separation treatment before separation of the super-macroporous ion exchange chromatography. According to the method, F VIII chromatography recovery rate stably reaches up to about 85 percent, the specific activity reaches up to 154 IU / mg protein, and the process is stable and easy to amplify; while in the prior art, the F VIII chromatography recovery rate is normally stabilized at about 25 percent, and the specific activity is 20-50 IU / mg protein; and thus, compared with the prior art, the method provided by the invention has the advantage of achieving an unexpected technical effect.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Human-type anti-blood coagulation factor VIII antibody
InactiveUS7214785B2Immunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIBlood coagulation factor VIIIRandom combination
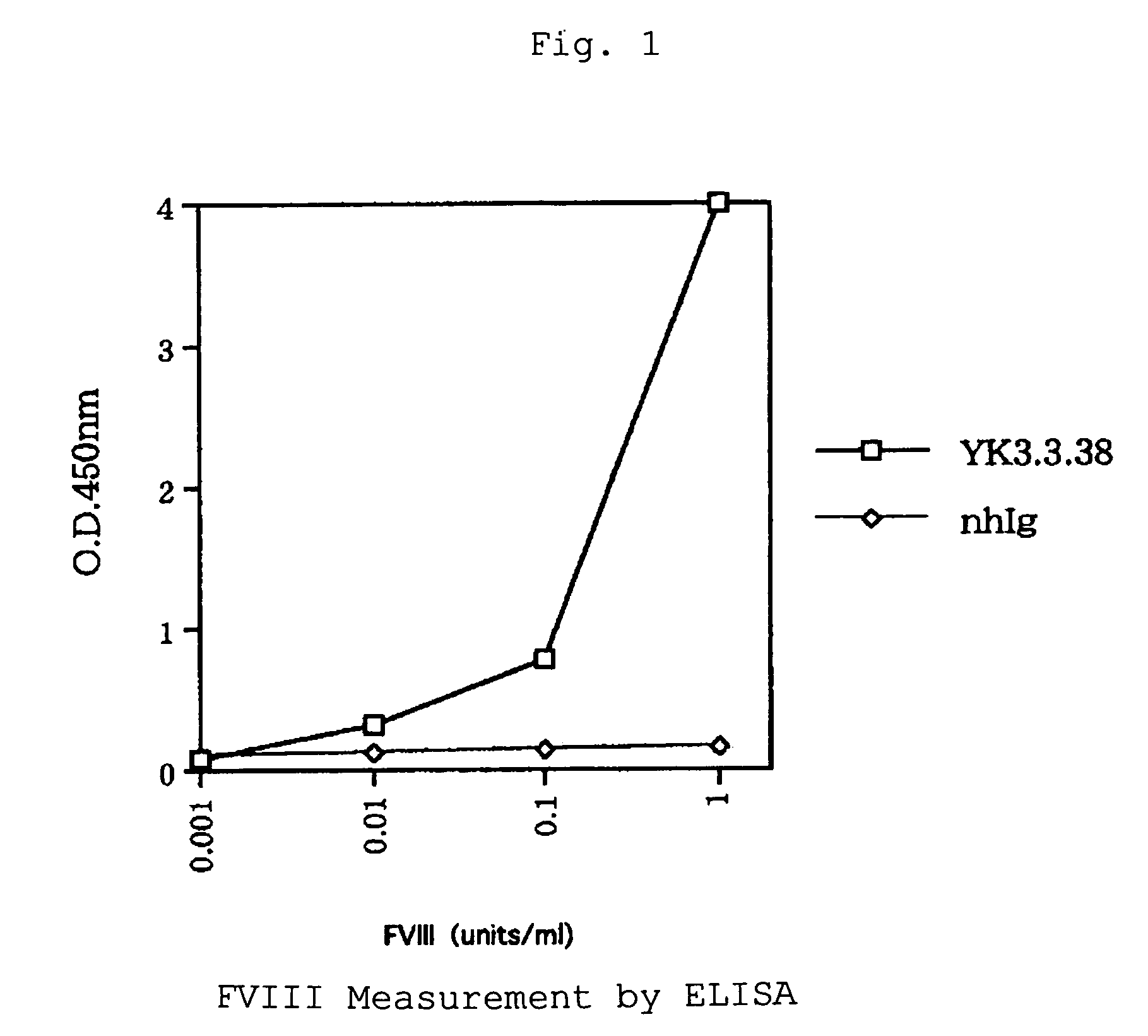
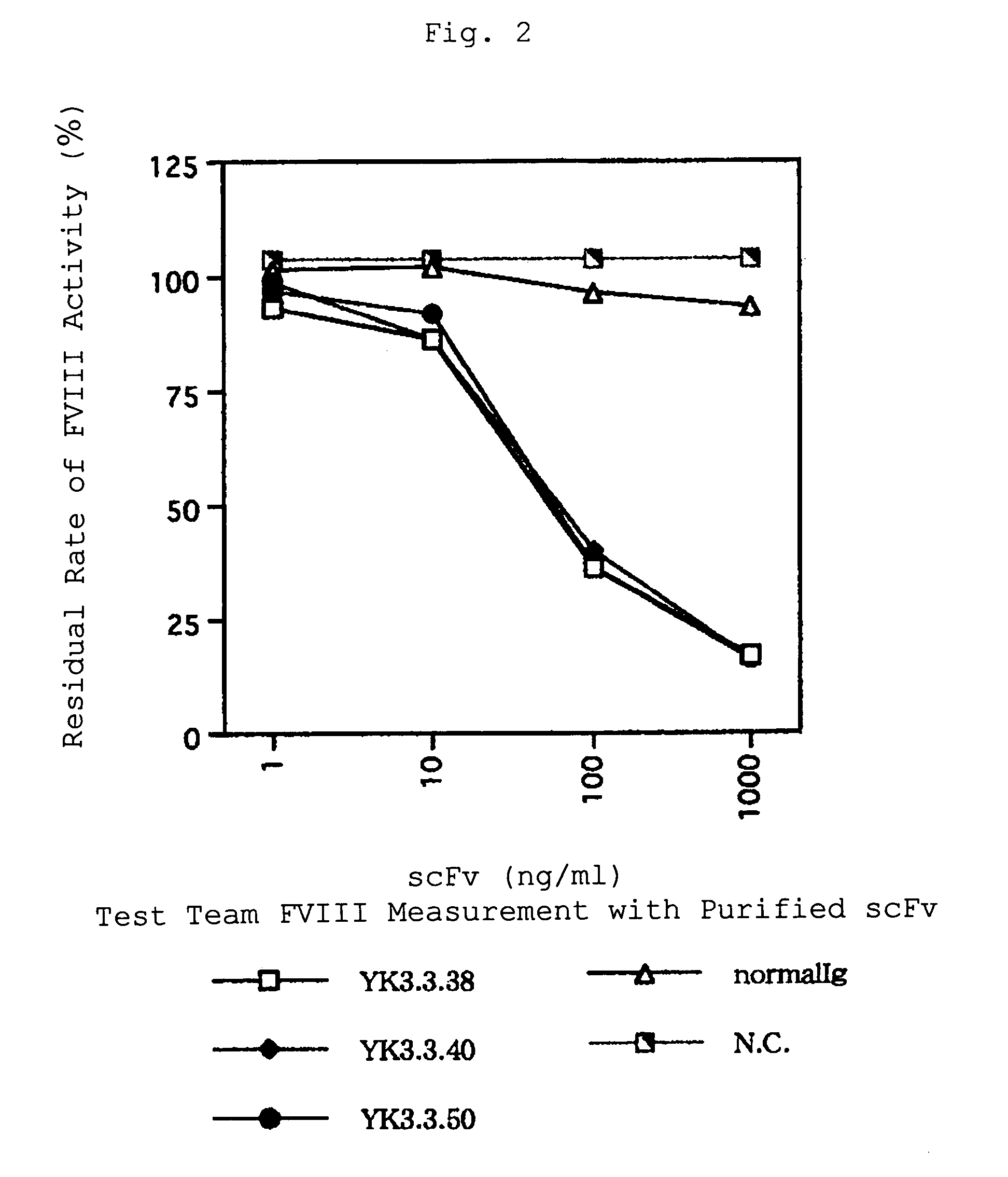
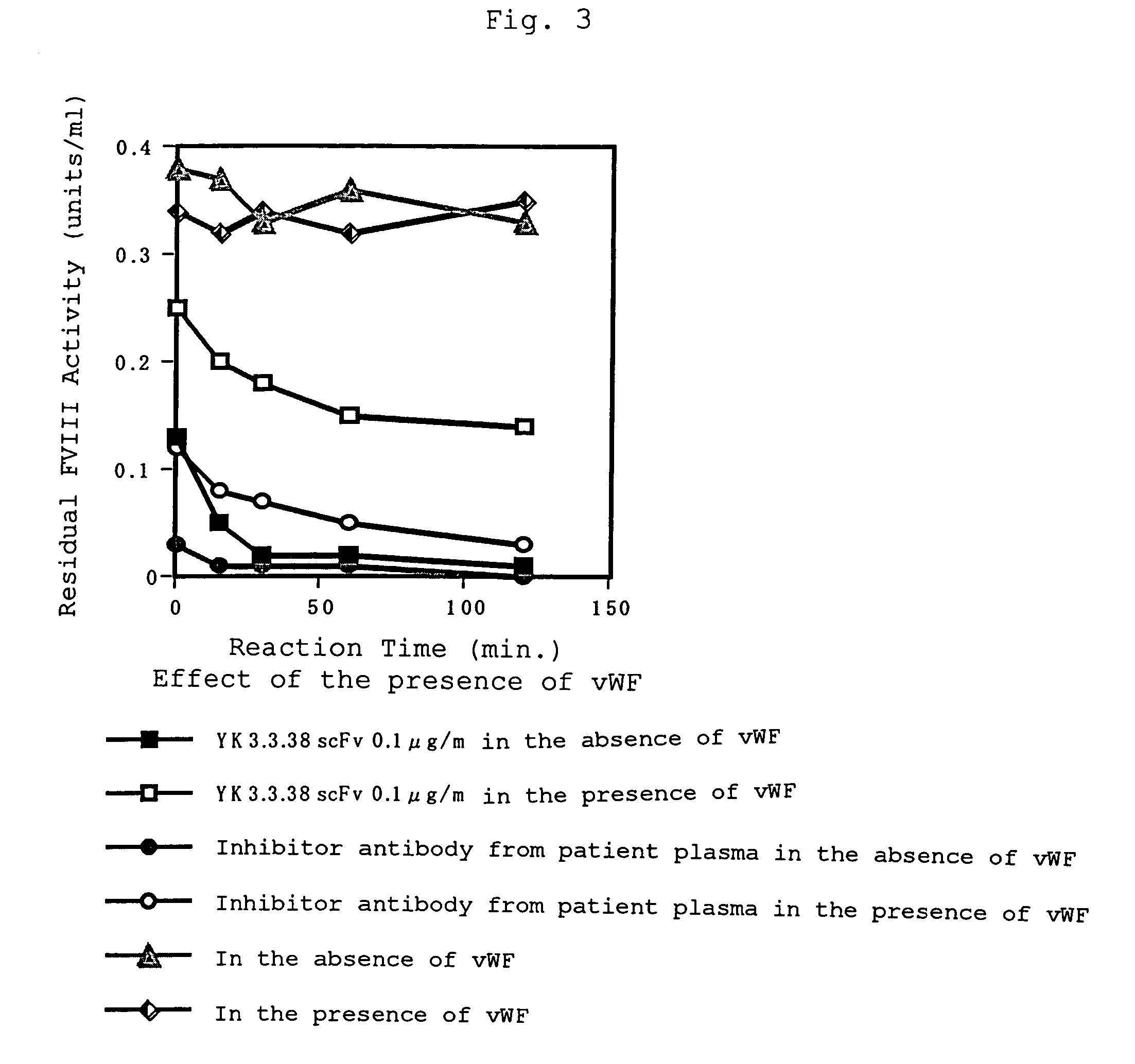
The present invention provides a human antibody against blood coagulation factor VIII (hereinafter also referred to as “FVIII”) and an antibody fragment that binds to human FVIII and specifically inhibits the coagulation activity of human FVIII. ScFv display phage libraries, prepared by using scFv DNAs constructed by random combinations of immunoglobulin VH chain genes and VL chain genes from lymphocytes from hemophilia A patients, is reacted with FVIII immobilized to a solid phase via anti-FVIII monoclonal antibody, and scFv clones capable of binding to FVIII are cloned to reveal VH and VL chains of FVIII-specific antibody.
Owner:JURIDICAL FOUND THE CHEMO SERO THERAPEUTIC RES INST
Glycosylated, low antigenicity, low immunogenicity factor VIII
InactiveUS20050009148A1Factor VIIMammal material medical ingredientsBlood coagulation factor VIIIVaccine Immunogenicity
The development of inhibitory antibodies to blood coagulation factor VIII (fVIII) results in a severe bleeding tendency. These antibodies arise in patients with hemophilia A (hereditary fVIII deficiency) who have been transfused with fVIII. They also occur in non-hemophiliacs, which produces the condition acquired hemophilia. We describe a method to construct and express novel recombinant fVIII molecules which escape detection by existing inhibitory antibodies (low antigenicity fVIII) and which decrease the likelihood of developing inhibitory antibodies (low immunogenicity fVIII). In this method, fVIII is glycosylated at sites that are known to be antibody recognition sequences (epitopes). This produces the desired properties of low antigenicity fVIII and low immunogenicity fVIII. The mechanism is similar to one used by viruses such as the AIDS virus, which glycosylates its surface proteins to escape detection by the immune system.
Owner:LOLLAR JOHN S
Method for improving separation efficiency, purity and biological specific activity of blood coagulation factor VIII and analog thereof by using affine aqueous two-phase system
InactiveCN102584933AHigh partition coefficientImprove separation efficiencyPeptide preparation methodsBlood coagulation factor VIIIPhosphate
The invention discloses a simple and quick method for improving separation efficiency, purity and biological specific activity of blood coagulation factor VIII and an analog thereof. The method is based on application of an affine aqueous two-phase technology, i.e., a characteristic hydrophilic macromolecular compound, preferably polyethylene glycol (PEG), forms a stable aqueous two-phase system with phosphate, glucan or other second component in aqueous solution; and one of core technologies is that: covalent linkage of the PEG and the blood coagulation factor VIII specific affine small peptide ligand is realized. The blood coagulation factor VIII is preferably located in a characteristic hydrophilic macromolecular compound phase connected to the affine small peptide ligand; and most of protein (or hybrid protein) from cell extract tends to move to another phase. By changing existence of target protein or polypeptide in one phase or another phase, the protein or polypeptide is efficiently purified with high purity.
Owner:汪志友
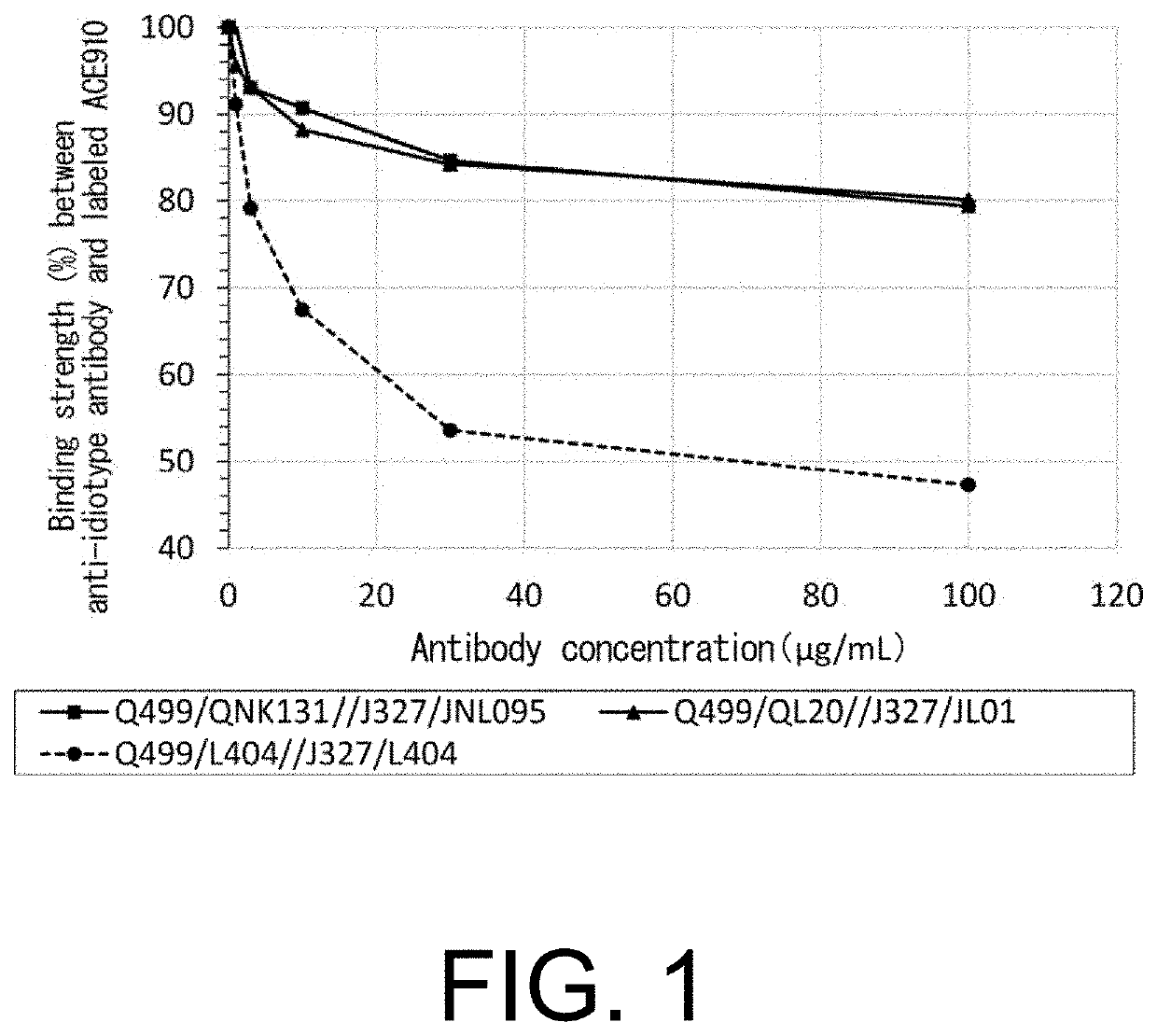
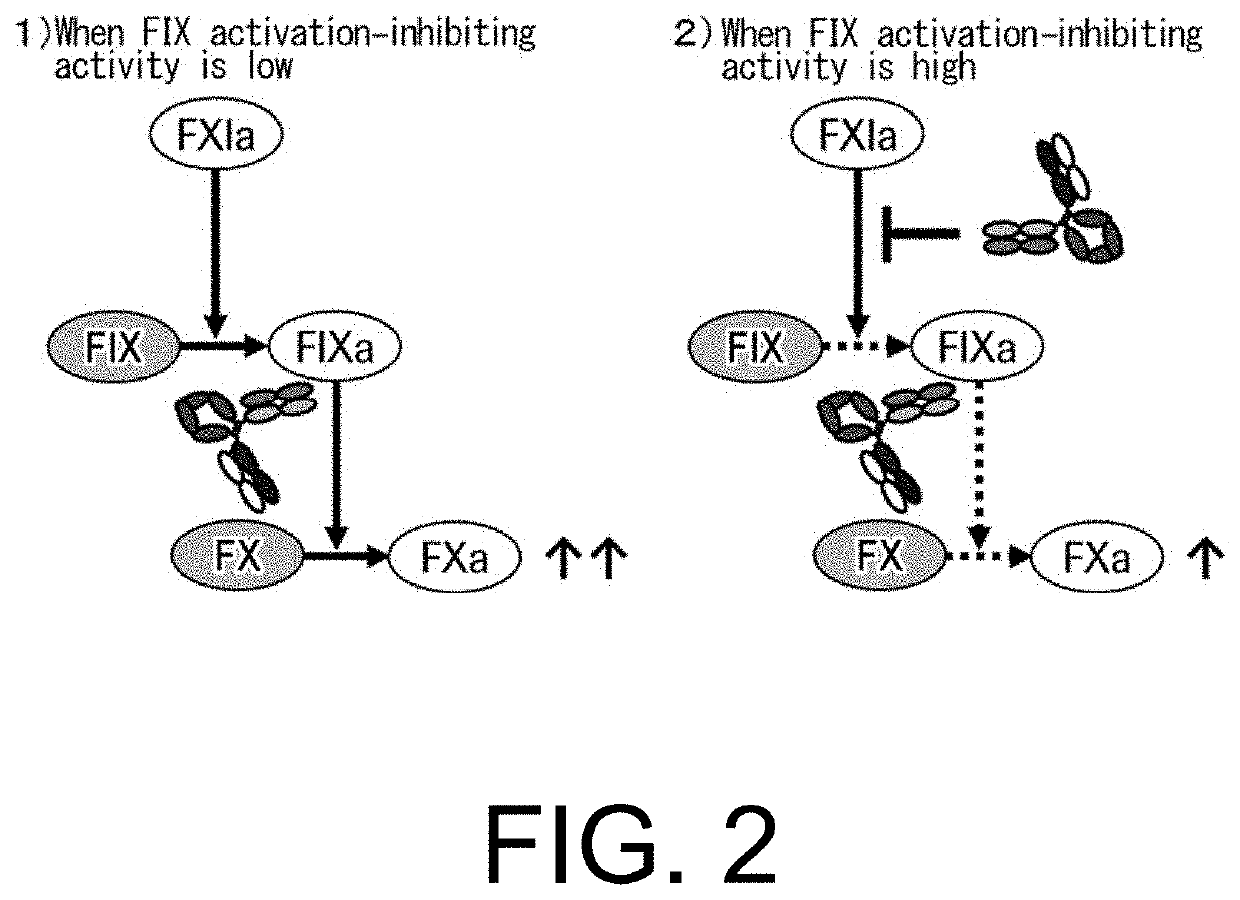
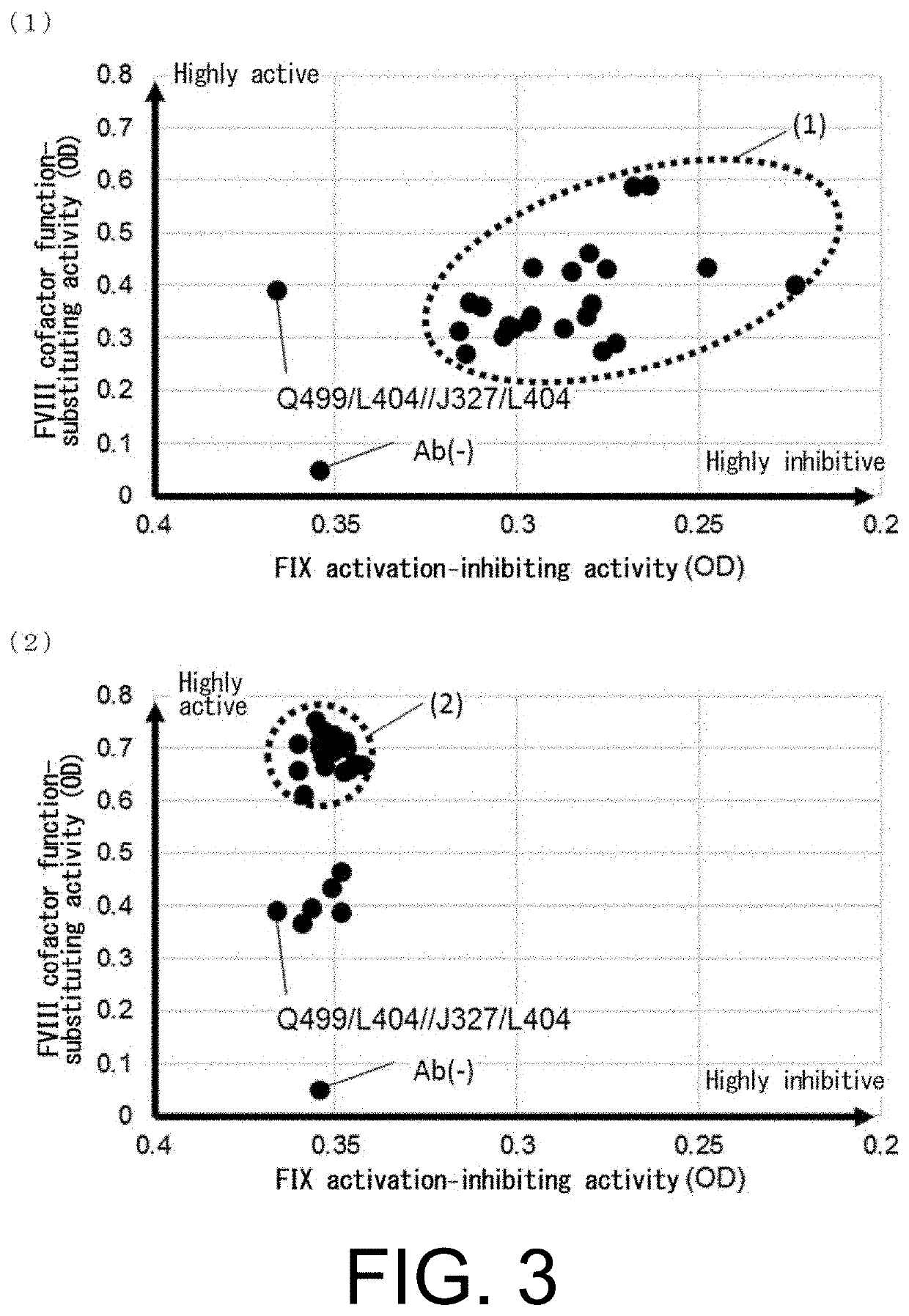
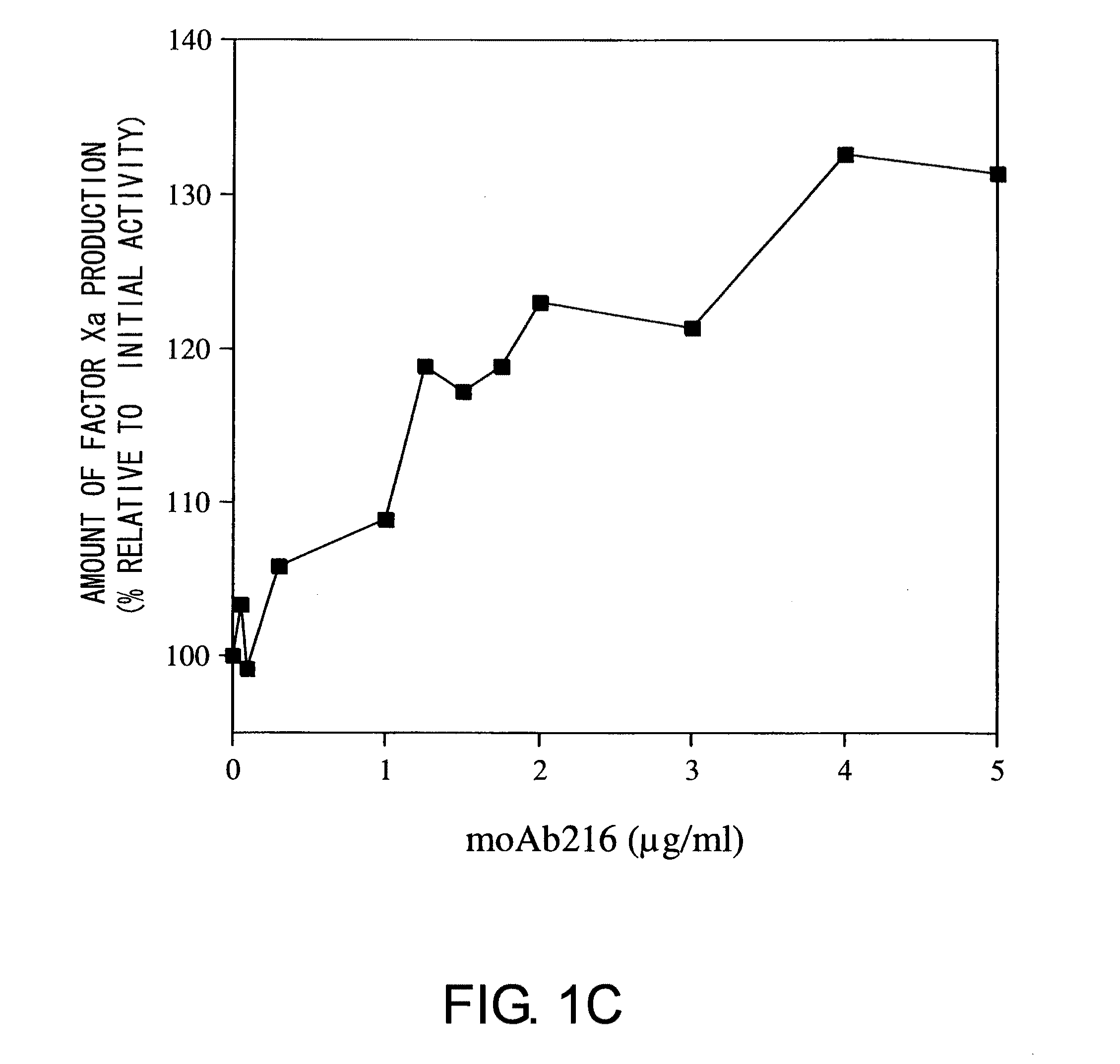
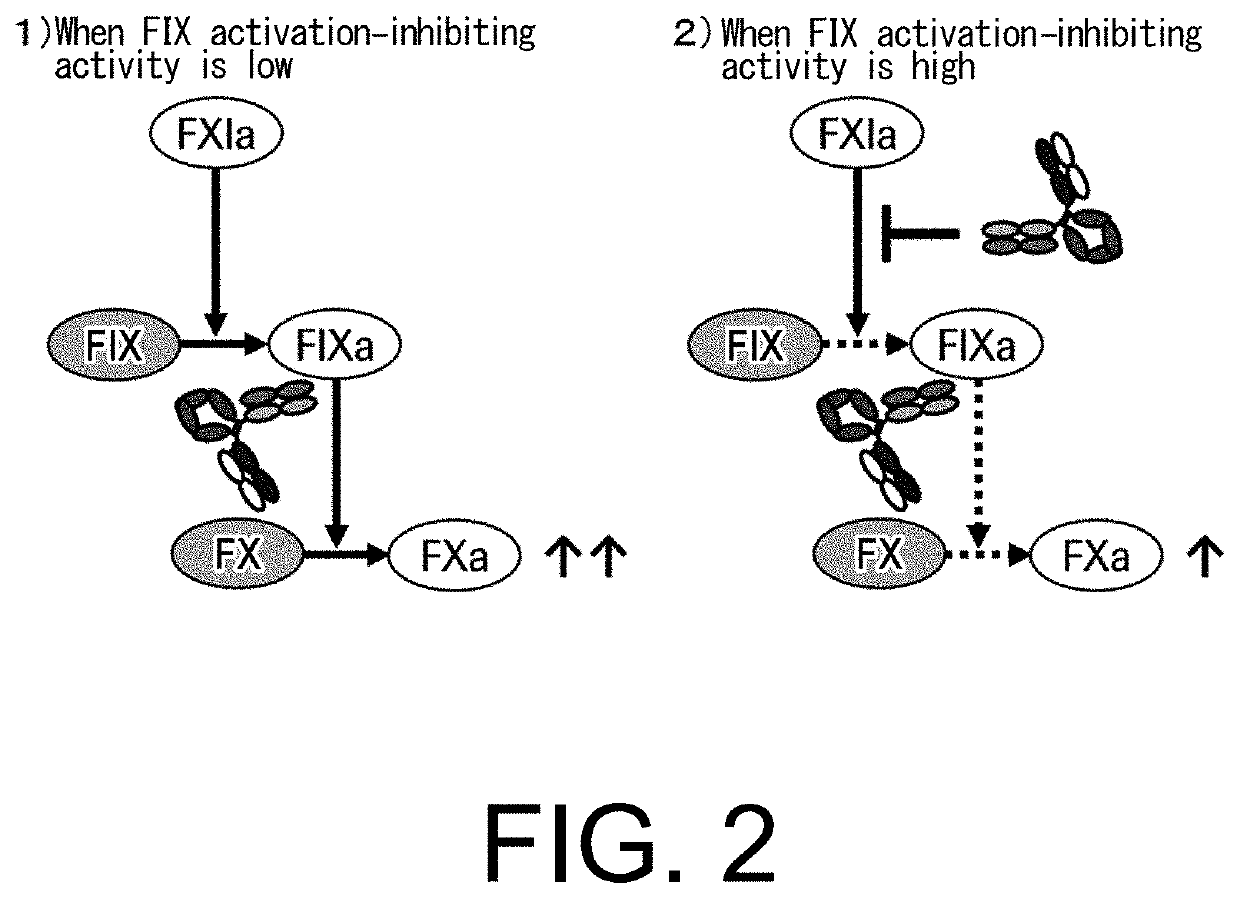
Multispecific antigen-binding molecules having blood coagulation factor VIII (FVIII) cofactor function-substituting activity and pharmaceutical formulations containing such a molecule as an active ingredient
ActiveUS10759870B2Efficiently formedImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsHybrid immunoglobulinsBlood coagulation factor VIIIAntigen
Bispecific antibodies whose FIX activation-inhibiting activity is not elevated and whose FVIII cofactor function-substituting activity is elevated have been successfully discovered.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
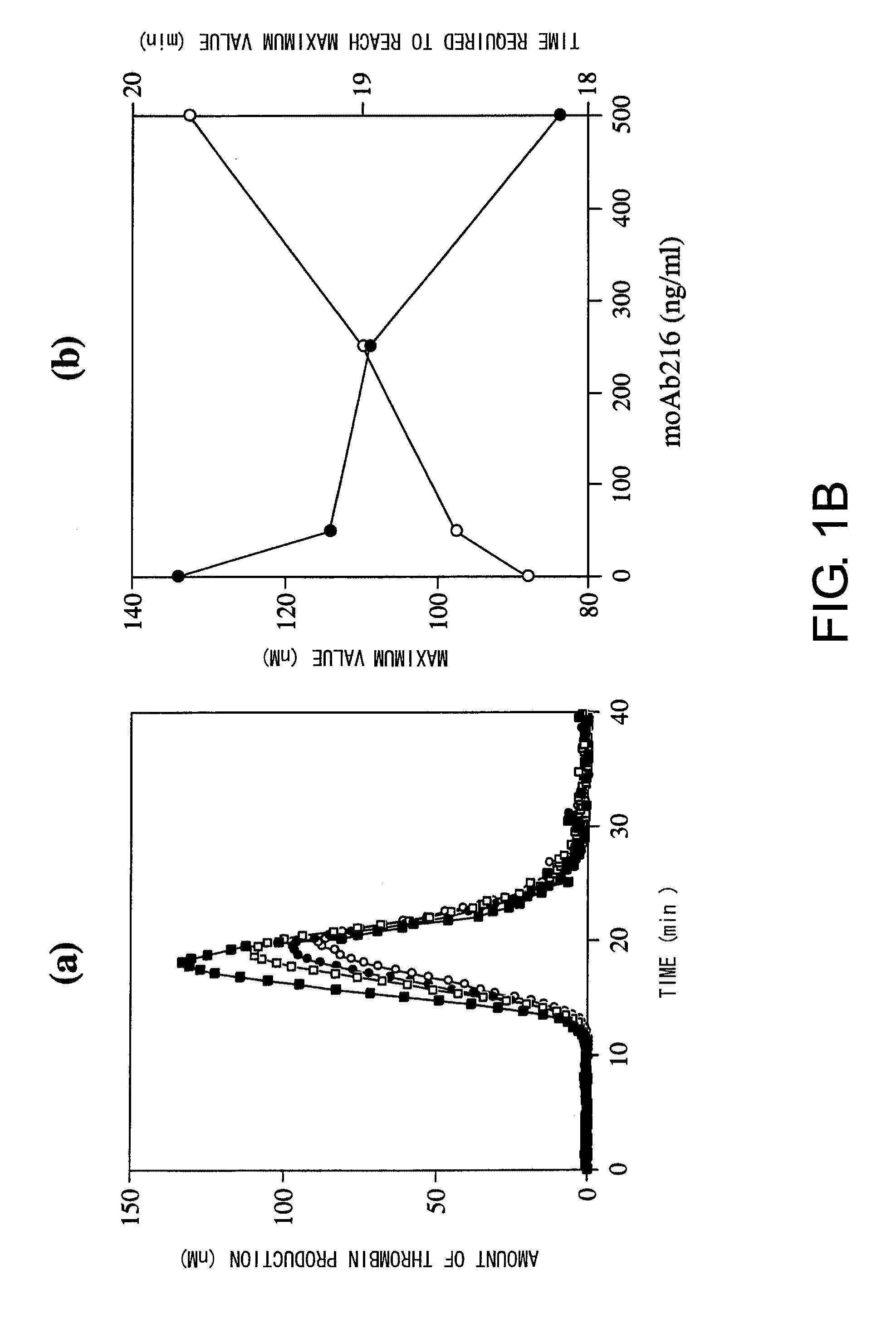
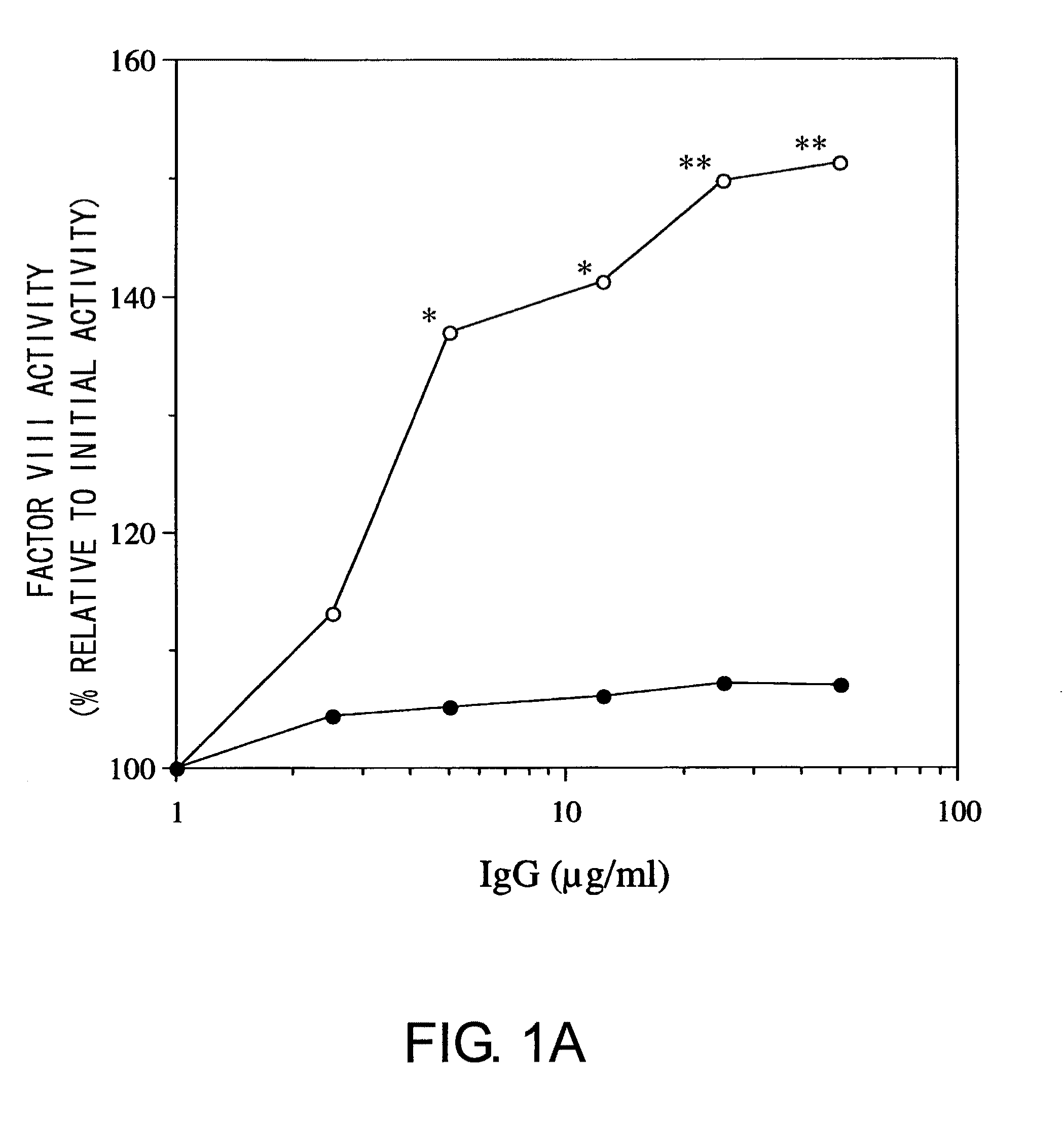
Blood Coagulation Factor VIII Activation-Enhancing Antibodies
ActiveUS20090297503A1Increases coagulation-enhancing activity of Factor VIIIHigh activityImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIBlood coagulation factor VIIIVon willebrand
For the first time, the present invention provides antibodies that enhance the generation of activated blood coagulation factor VIII. The antibodies enhance the cleavage of blood coagulation factor VIII at the Arg of position 372 and suppress the cleavage at the Arg of position 336 by recognizing and binding to the A2 domain of blood coagulation Factor VIII. Such antibodies are expected to be useful in preventing or treating diseases that develop or progress due to decrease or loss of the blood coagulation factor VIII activity, for example, hemophilia A, acquired hemophilia, and von Willebrand's disease.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +1
Multispecific antigen-binding molecules having blood coagulation factor viii (FVIII) cofactor function-substituting activity and pharmaceutical formulations containing such a molecule as an active ingredient
PendingUS20200354473A1Undesirable CH1 and CL association can be suppressedEfficiently formedImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsHybrid immunoglobulinsBlood coagulation factor VIIIAntigen
Bispecific antibodies whose FIX activation-inhibiting activity is not elevated and whose FVIII cofactor function-substituting activity is elevated have been successfully discovered.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD
Blood coagulation factor VIII activation-enhancing antibodies
ActiveUS8252287B2Increases coagulation-enhancing activity of Factor VIIIHigh activityImmunoglobulins against blood coagulation factorsFactor VIIBlood coagulation factor VIIIVon willebrand
For the first time, the present invention provides antibodies that enhance the generation of activated blood coagulation factor VIII. The antibodies enhance the cleavage of blood coagulation factor VIII at the Arg of position 372 and suppress the cleavage at the Arg of position 336 by recognizing and binding to the A2 domain of blood coagulation Factor VIII. Such antibodies are expected to be useful in preventing or treating diseases that develop or progress due to decrease or loss of the blood coagulation factor VIII activity, for example, hemophilia A, acquired hemophilia, and von Willebrand's disease.
Owner:CHUGAI PHARMA CO LTD +1
Method for preparing cryoprecipitate and method for preparing blood coagulation factor VIII preparation by using cryoprecipitate
ActiveCN103848886AReduce the amount of solutionFactor VIIPeptide preparation methodsBlood coagulation factor VIIICryoprecipitate
The invention discloses a method for preparing a cryoprecipitate. The method comprises the steps of (1) thawing: selecting fresh frozen plasma, and heating to obtain thawed plasma of which the temperature is 0-5 DEG C; (2) filtering: filtering under the condition that the temperature of the thawed plasma is 0-5 DEG C to obtain filtrate and filter residues; (3) centrifuging: centrifuging under the condition that the temperature of the filtrate is 0-5 DEG C to obtain a precipitate; (4) combining the filter residues obtained in step (2) and the precipitate obtained in step (3) to obtain the cryoprecipitate. The preparation method disclosed by the invention is simple, and the prepared cryoprecipitate is high in yield and human blood coagulation factor VIII content, so the preparation method has a good industrial application prospect.
Owner:CHENGDU RONGSHENG PHARMA
Cyclopentanopolyhydrophenanthrene skeleton compound capable of regulating and controlling blood coagulation factor VIII level to play anti-tumor role and application thereof
ActiveCN110028546APrevent proliferationInhibition of adhesionSteroidsAntineoplastic agentsBlood coagulation factor VIIIFactor ii
The invention provides a cyclopentanopolyhydrophenanthrene skeleton compound capable of regulating and controlling the blood coagulation factor VIII level to play an anti-tumor role, and application of the cyclopentanopolyhydrophenanthrene skeleton compound to preparation of drugs for treating blood coagulation factor VIII-mediated tumors, in particular to drugs for treating a blood coagulation factor VIII-mediated tumor which is blood coagulation factor VIII-mediated liver cancer. Experiments prove that the cyclopentanopolyhydrophenanthrene skeleton compound can inhibit expression and secretion of HUVEC endothelial cells FVIII, inhibit HUVEC endothelial cell FVIII mediated hepatoma carcinoma cell proliferation, and inhibit adhesion of tumor cells and platelets mediated by FVIII secreted by HUVEC cells, and in-vivo experiments prove that the cyclopentanopolyhydrophenanthrene skeleton compound can inhibit lung metastasis of liver cancer by inhibiting the level of FVIII.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Genetically-modified non-human animal and application thereof
The invention relates to a genetically-modified non-human animal and application thereof, in particular to a transgenic mouse model and application thereof in the aspect of screening of a targeted medicine. According to the transgenic mouse model and application thereof in the aspect of screening of the targeted medicine, by targetedly knocking out and replacing a mouse protein C gene by means ofa human protein C gene expression cassette, a humanized protein C knock-in mouse is generated. The mouse has fertility, and can hybridize with another mouse disease model (such as a mouse in the deficiency of a blood coagulation factor VIII or a blood coagulation factor IX) to produce a humanized protein C mouse disease model (such as a humanized protein C factor VIII-deficient mouse model or a humanized protein C factor IX-deficient mouse model). The mouse model can be used for studying functions in vivo of human protein C and human activated protein C (APC). The mouse model is the first mouse model used for testing a therapeutic candidate medicine, which targets the human protein C or the APC, in vivo, and has very high economic value and scientific research value.
Owner:SHANGHAI RAAS BLOOD PRODUCTS CO LTD
Zone B partially-deleted type recombinant human blood coagulation factor VIII
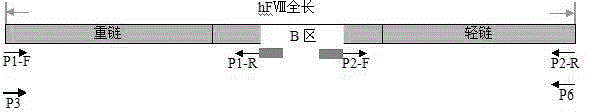
ActiveCN105017410AConsistent biological activityImprove stabilityFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsBlood coagulation factor VIIIClotting factor
The invention belongs to the field of biological medicines, and in particular relates to a gene recombinant human blood coagulation factor VIII for treating hemophilia A. By performing zone B partially-deleted type mutation on a full-length blood coagulation factor VIII, the obtained novel gene recombinant human blood coagulation factor VIII product has a characteristic that the structure is more stable.
Owner:BEIJING NORTHLAND BIOTECH
Factor VII Polypeptides for Preventing Formation of Inhibitors in Subjects with Haemophilia
InactiveUS20110059894A1Reduce riskFactor VIIPeptide/protein ingredientsFactor VIIaBlood coagulation factor VIII
The invention provides a method for preventing formation of inhibitors to blood coagulation factor VIII or factor IX in a subject having haemophilia, the method comprising administering (via intravenous, subcutaneous, intradermal, or intramuscular routes) to a previously untreated subject an effective dosage of factor VIIa or a factor VII-related polypeptide.
Owner:NOVO NORDISK AS
vWF (von willebrand factor) activity protection fluid
InactiveCN105622747AIncrease profitGuaranteed purityFactor VIIPeptide preparation methodsChromatographic separationBlood coagulation factor VIII
The invention discloses a vWF (von Willebrand factor) activity protection fluid. The vWF activity protection fluid is used in preparation for extracting von Willebrand factors from cryoprecipitated blood coagulation factor VIII waste. In a preparation technology of the von Willebrand factors, glycine is added into a chromatographic buffer solution, and lysine, glycine and albumin are added into protein fluid before freeze drying after chromatography to protect vWF activity. The vWF activity protection fluid has the advantages that by means of adding the glycine into the chromatographic buffer solution, vWF activity loss can be reduced in a chromatographic separation and purification process; the albumin, the lysine and the glycine are added into protein dialysate to serve as freeze-drying protectants, so that von Willebrand factor molecules can be stabilized; the albumin serving as an excellent protein stabilizer is capable of effectively adsorbing protein surfaces; the lysine and the glycine, serving as micromolecular amino acids, are capable of protecting a protein structure, increasing collapse temperature of a finished product and stopping protein damage caused by collapse during freeze-drying, so that biological activity is kept.
Owner:华润博雅生物制药集团股份有限公司
Expression vector for expressing blood coagulation factor VIII and application thereof
InactiveCN102277379APromote safe productionEfficient productionUnicellular algaeMicroorganism based processesBlood coagulation factor VIIIFactor VIII preparation
The invention discloses an expression vector for expressing a coagulation factor VIII and application thereof. In the invention, a plant expression vector of a B domain delete recombinant human coagulation factor VIII (BDD-rhFVIII) is constructed by using a nitrate reducase promoter (NRpro) as a starting element; and the B domain delete recombinant human coagulation factor VIII (BDD-rhFVIII) is expressed by taking chlorella as a receptor. The recombinant human coagulation factor VIII expressed in the chlorella has a strong blood coagulation effect. The result can be applied to the preparationof coagulation factor VIII preparations.
Owner:INST OF GENETICS & DEVELOPMENTAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Blood coagulation factor VIII fusion protein as well as preparation method and use thereof
ActiveCN104292341AImprove in vitro biological activityReduce ADCC effect functionPeptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsBlood coagulation factor VIIIHalf-life
The invention provides a blood coagulator factor VIII fusion protein as well as a preparation method and a use thereof. The fusion protein comprises a block B-missing blood coagulator factor VIII, a connecting peptide and a human IgGFc variant. In the blood coagulator factor VIII fusion protein, the specifically designed connecting peptide is added between the block B-missing blood coagulator factor VIII and the human IgGFc variant, so that an Fc area is far away an enzyme activity center of a blood coagulator factor VIII molecule, and thus, the in-vitro biological activity of the fusion protein is improved; moreover, the human IgGFc variant contains amino acid mutations on loca 228, 235 and 445 of an area CH2, so that an ADCC (antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity) effector function of an antibody segment Fc is lowered. Compared with the similar products, the blood coagulator factor VIII fusion protein has similar or relatively high in-vitro biological activity, relatively low binding force of vWF protein, a relatively long half-life period, a relatively long dosing interval and a relatively low drug-use dose.
Owner:SYNDEGEN SHANGHAI BIOTECH
Protease for activating clotting factor VII
Owner:CSL BEHRING GMBH
Recombinant blood coagulation factor VIII and application thereof
ActiveCN113248594AReduced responseEfficient coagulation functionFactor VIIVectorsBlood coagulation factor VIIITherapeutic effect
The invention relates to a recombinant blood coagulation factor VIII and application thereof. The B domain of the recombinant blood coagulation factor VIII comprises more than 80% of an amino acid sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO: 1 or SEQ ID NO: 2. The B domain of the recombinant blood coagulation factor VIII is subjected to gene modification, and is rich in glycosylation sites, so that the recombinant blood coagulation factor VIII has an efficient blood coagulation function, is easy to secrete outside cells, is easy to interact with auxiliary factors such as thrombin (FIIa) and the like, is low in antibody reaction, and can effectively guarantee the treatment effect, reduce the immunological rejection risk and save the treatment cost.
Owner:BEIJING MEIKANG JIMIAN BIOTECH CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com