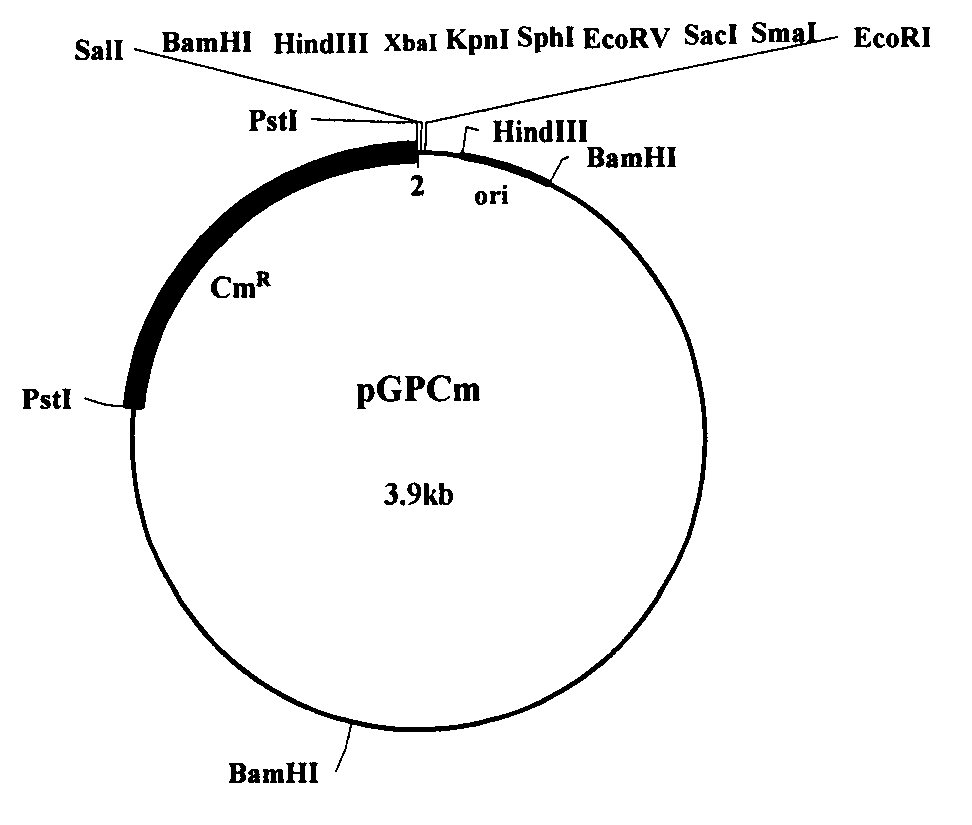
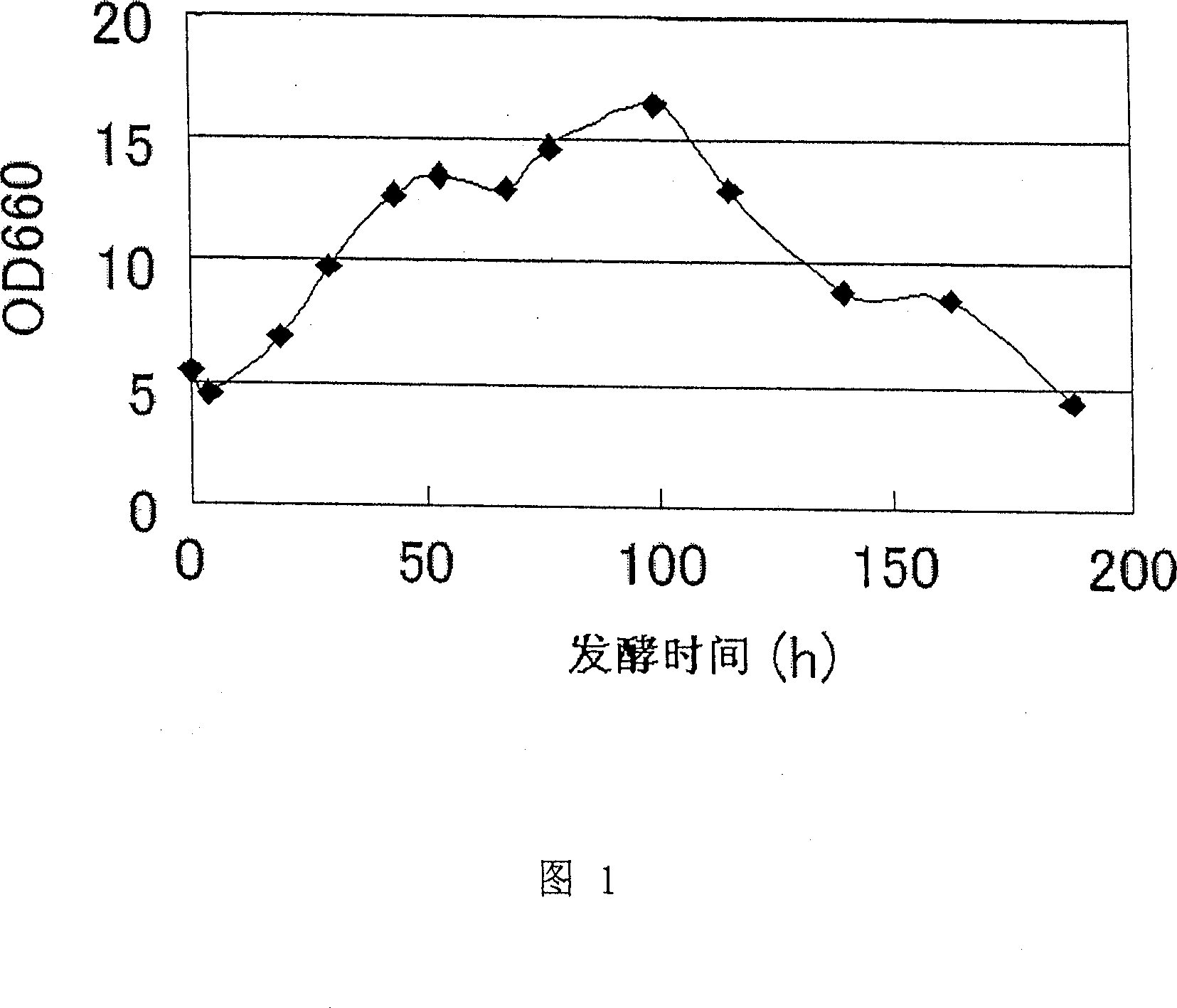
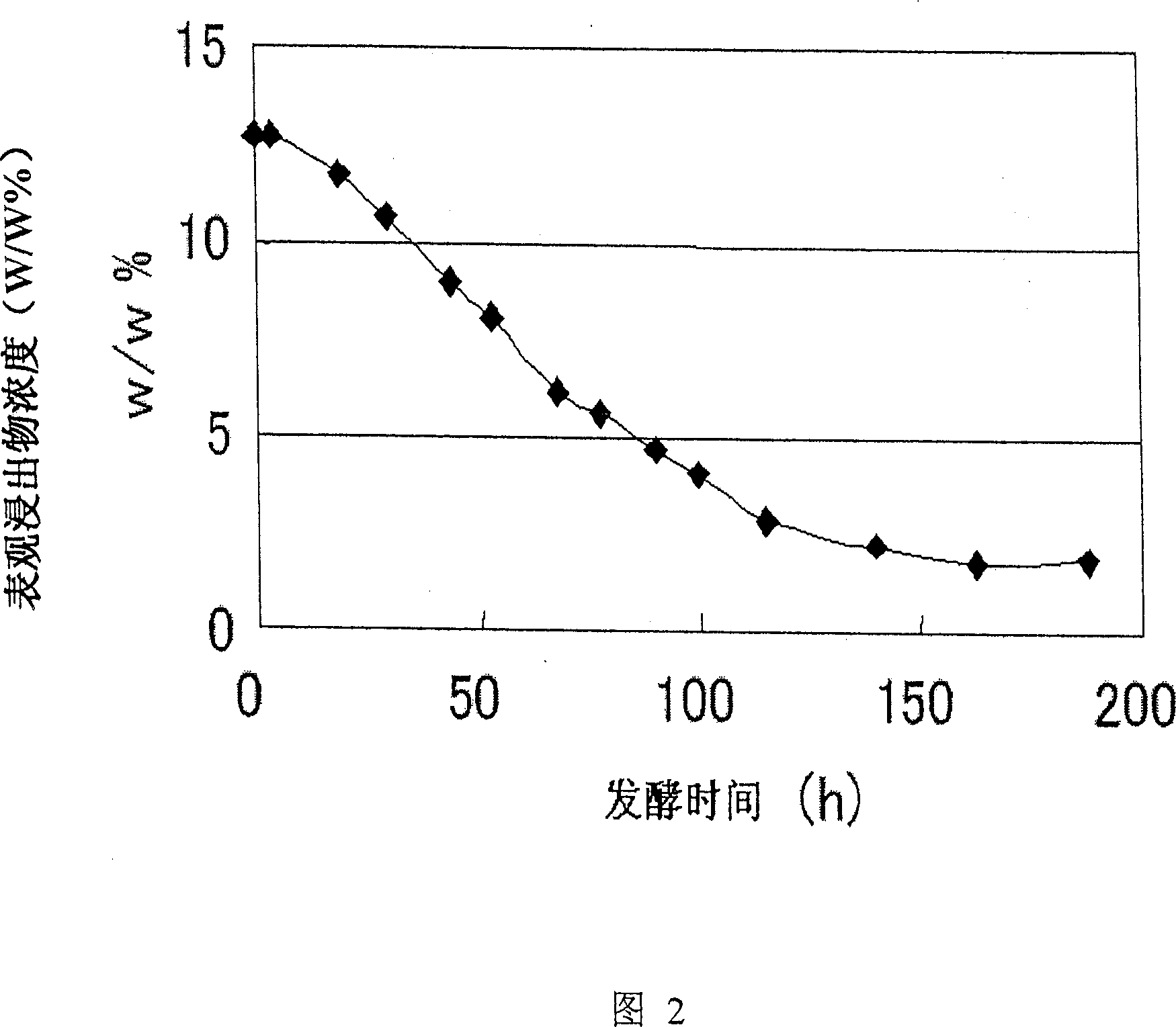
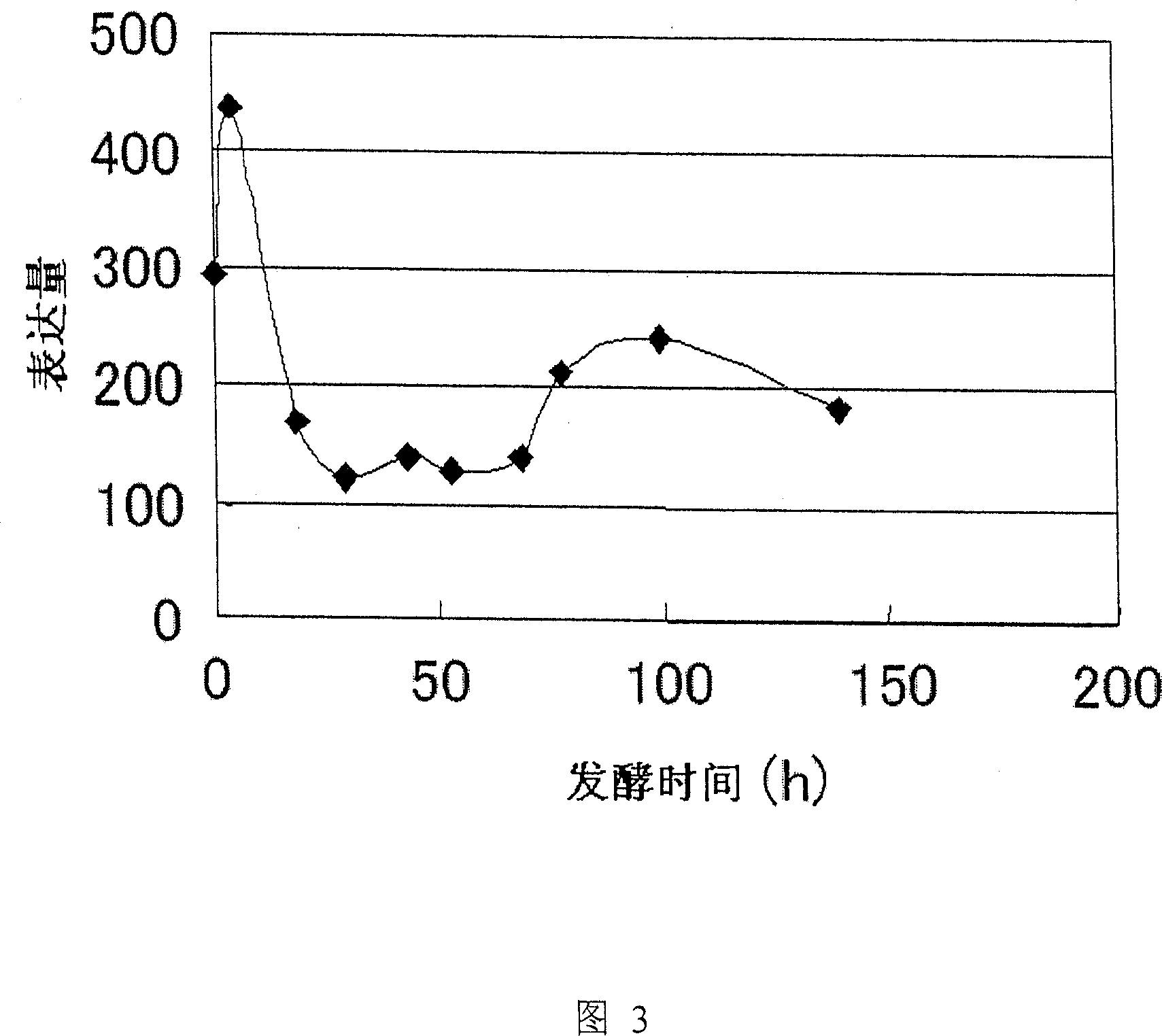
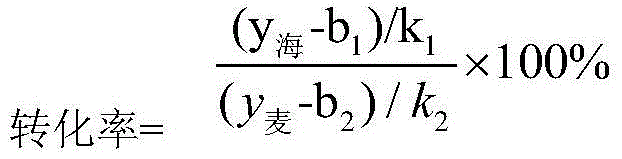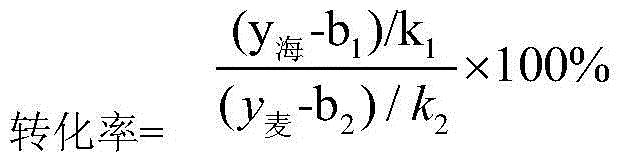Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
81 results about "Acetolactate Synthetase" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Recombinant bacillus subtilis increased in yield of acetylglucosamine
ActiveCN104498394AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processes2,3-ButanediolAcetolactate Synthetase
The invention discloses a recombinant bacillus subtilis increased in yield of acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis increased in yield of acetylglucosamine, the recombinant bacillus subtilis BSGN6-PxylA-glmS is taken as an original strain, an alpha-acetolactate synthetase encoding gene and an alpha-acetolacetate decearboxylase encoding gene are knocked out by virtue of homologous recombination, and therefore, the approach by which acetoin and butanediol are generated from 2,3-pyroracemic acid in host bacteria is blocked. In the host bacteria from which the alsS and alsD are knocked out, the glucosamine acetylase encoding gene derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae is excessively expressed, and therefore, the route of synthesis of the acetylglucosamine is enhanced, the yield of the acetylglucosamine in the recombinant bacillus subtilis is increased to 38.46g / L, and a foundation is laid for producing the glucosamine by modifying the bacillus subtilis in the metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Protein for endowing wheat with herbicide resistance and application of protein in plant breeding
The invention provides an acetolactate synthetase (ALS) protein for endowing a plant with herbicide resistance. The ALS protein is derived from a wheat variety Ningchun 4, and carries Ala179 and / or Ser627 mutation. In addition, the invention also provides corresponding nucleic acid, an expression kit, a vector, a cell, a plant, application and method of obtaining the plant with the herbicide resistance, and a method for identifying the plant.
Owner:FRONTIER LAB OF SYST CROP DESIGN CO LTD +1
Genetically engineered bacteria realizing high-density fermentation co-production of 2,3-butanediol as well as construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN104560848AReduce culture volumeLess investmentBacteriaHydrolasesBiotechnologyEscherichia coli
The invention discloses genetically engineered bacteria realizing high-density fermentation co-production of 2,3-butanediol as well as a construction method and an application thereof. The genetically engineered bacteria are constructed by integrating three key enzyme genes such as alpha-acetolactate synthetase encoding genes, alpha-acetolacetate decearboxylase encoding genes and 2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase encoding genes onto Escherichia coli chromosomes in a 2,3-butanediol synthesis path. According to the strain fermentation process, the content of the byproduct acetic acid is reduced, so that high-density fermentation can be realized, and 2,3-butanediol with high additional value is co-produced. In addition, the invention also discloses a method for realizing high-density fermentation co-production of other compounds and 2,3-butanediol genetically engineered bacteria and an application thereof. The 2,3-butanediol can be produced by virtue of high-density fermentation, and polyhydroxyalkanoates or functional proteins also can be co-produced, so that low-cost and high-efficiency co-production of the polyhydroxyalkanoates or functional proteins and the 2,3-butanediol is realized, and the genetically engineered bacteria have important industrial application values.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
ALS mutant type gene and application thereof in herbicide resistance
The invention discloses an ALS mutant type gene and further discloses ALS protein coded by the ALS mutant type gene and application of the ALS protein. In a rice ALS gene sequence, 75 nucleotide G changes into nucleotide C, and 339 nucleotide A changes into nucleotide C. The protein is derived from a rice mutant plant resisting an ALS inhibitor herbicide, and compared with a rice wild type ALS sequence, the protein sequence of the ALS protein mutates at the site of Gln25 or Gln113 or Ala237. If green plants express the protein sequence, the green plants can resist an acetolactate synthetase inhibitor herbicide and especially an imidazolone and sulfonylurea herbicide.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
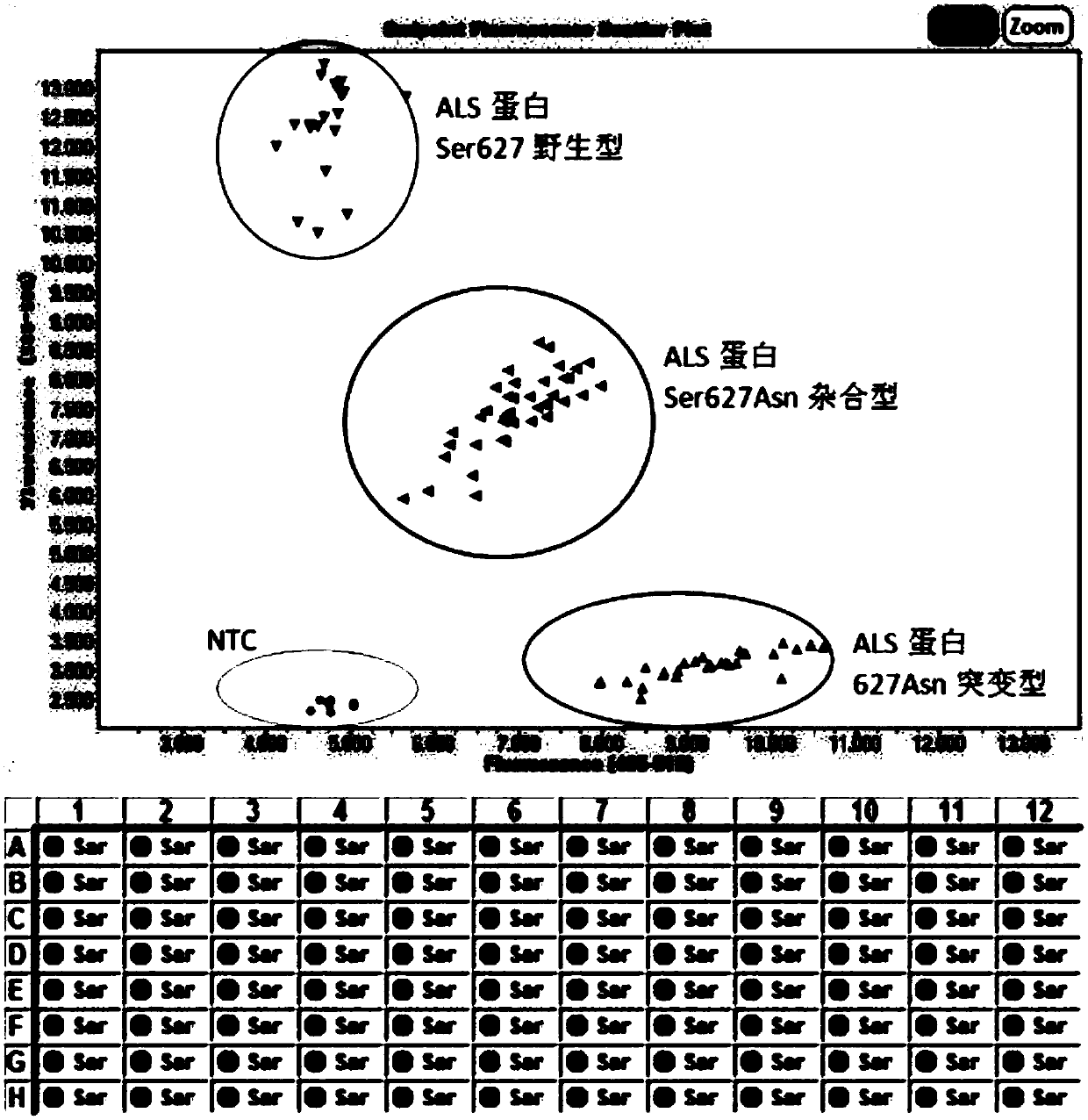
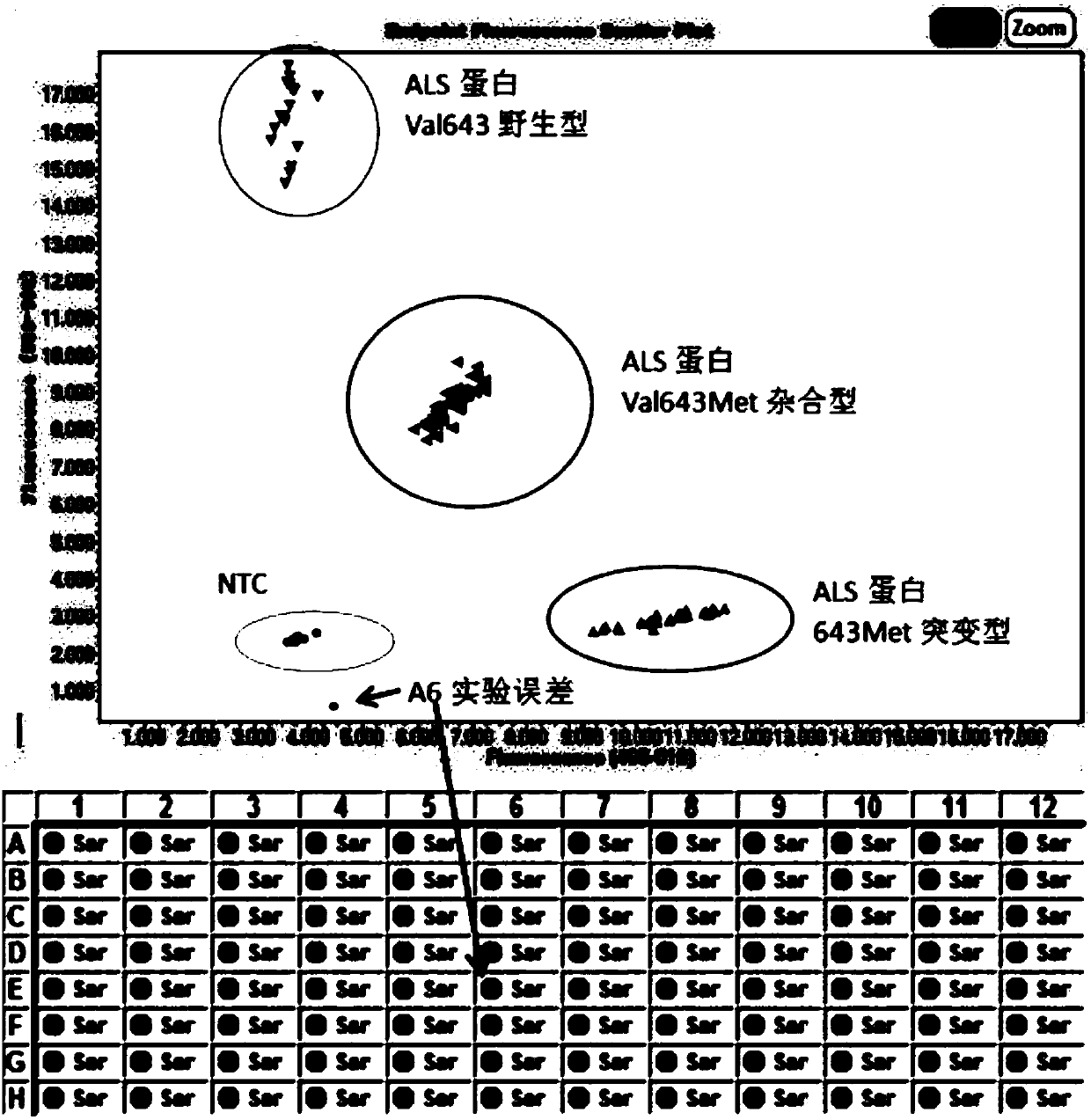
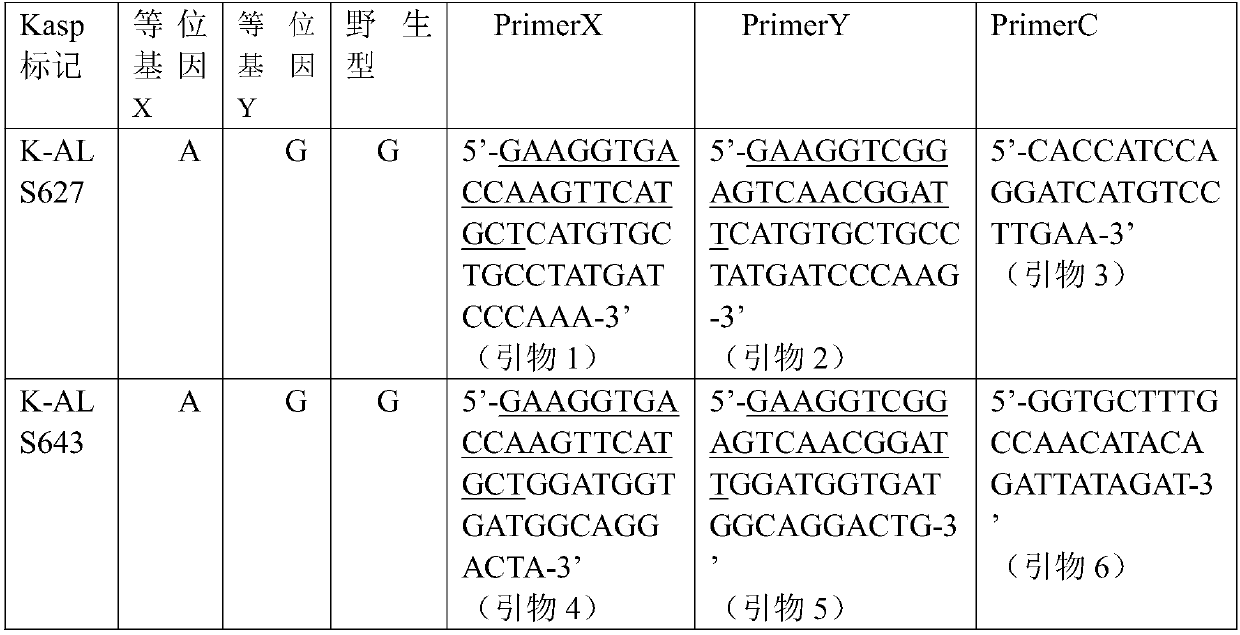
KASP marker primers for detecting SNP mutations in rice ALS genes and application thereof
InactiveCN107653337ARapid identificationImprove throughputMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAgricultural scienceAcetolactate Synthetase
The invention discloses KASP marker primers for detecting simultaneous SNP mutations in Ser627Asn and Val643Met of rice ALS genes. In terms of the simultaneously generated SNP mutations in the Ser627Asn and the Val643Met of the rice ALS genes, when the phenotype of the double mutant ALS genes is labeled, the sequence of the double mutant ALS genes is a new unreported gene sequence which can primarily determine the labeled material, and then accurately determine the labeled rice material throughdouble KASP markers in the genes so as to carry out quick, highly accurate and high-throughput identification of anti-acetyl lactate synthase inhibitor herbicides of the rice. When the KASP marker primers are used for molecular marker-assisted breeding of hybrid rice varieties with herbicide resistance, the results of two pairs of KASP markers are validated mutually in order to effectively remove sterile line seedlings obtained via 'Tako' selfing by spraying herbicides.
Owner:HUNAN HYBRID RICE RES CENT
Engineering bacteria of inactivated acetolactate synthetase, and applications thereof in producing 1,3-propanediol
InactiveCN103305543AReduce production processExtraction pressure after reductionBacteriaHybrid cell preparationBiotechnologyButanediol
The invention discloses an engineering bacteria of inactivated acetolactate synthetase, and a construction method and applications thereof in producing 1,3-propanediol. The acetolactate synthetase in wild type strain for producing 1,3-propanediol is silenced by utilizing homologous recombination and gene insertion inactivation methods, thus obtaining 2,3-butanediol metabolic pathyway-blocked engineering bacteria. By using the engineering bacteria to ferment and produce 1,3-propanediol, the production of side product 2,3-butanediol can be greatly reduced, the metabolism shunting effect of the side product 2,3-butanediol can be greatly decreased, and the conversion rate for producing 1,3-propanediol can be improved; in addition, the side product 2,3-butanediol is reduced to lower the post-extraction pressure, so that the production cost can be lowered. Proved by experiments, the concentration of 1,3-propanediol can achieve 72g / L by fermenting the engineering bacteria for 36 hours through adopting a conventional method. The engineering bacteria and the construction method and applications thereof can play an important role in the industrial production of 1,3-propanediol through adopting a microbial fermentation method, and have wide application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
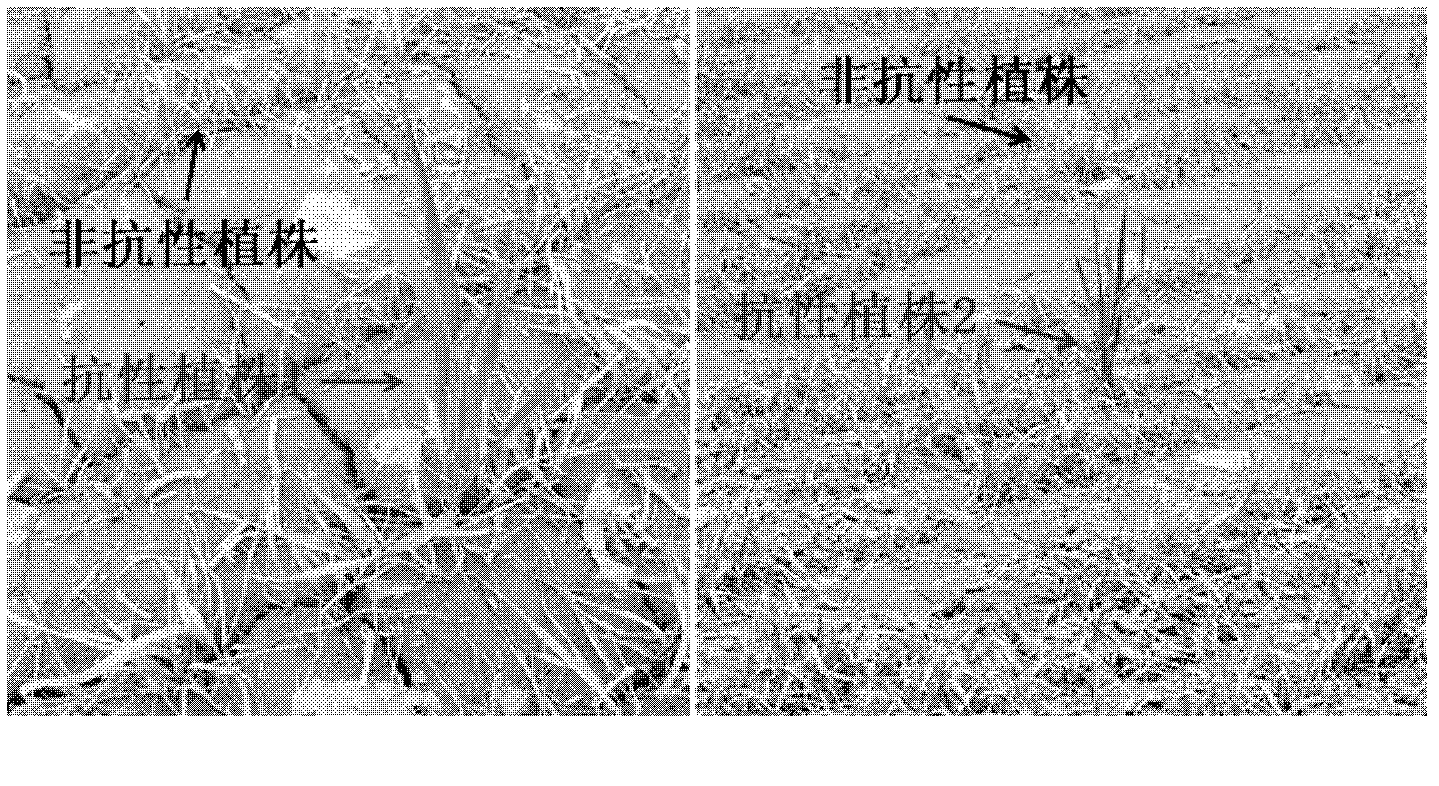
Method for preservation of pure state of hybrid plants by chemical emasculation
InactiveCN101595836AFor the purpose of weedingBiocideAnimal repellantsF1 generationAcetolactate Synthetase
The invention discloses a method for preservation of pure state of hybrid plants by chemical emasculation. In the method, a breed sensitive to acetolactate synthase inhibitory type herbicide is selected as female parent and a breed resistant to acetolactate synthase inhibitory type herbicide is selected as male parent, acetolactate synthase inhibitory type herbicide with activity of chemical hybridizing agent is used for processing the female parent to obtain male sterility, the male parent pollinates the female parent, the seeds of the female parent line are harvested to be cross breeds, the obtained F1 generation cross breed has herbicide resistance, after the F1 generation cross breed is planted, and acetolactate synthase inhibitory type herbicide seedling stage processing is used for removing uncrossed female parent seedling, so as to remain real cross breed. The method utilizes herbicide for preservation of pure state while realizing weeding. The invention has more advantages than common breed in the aspect of adapted breed simplified culture requirement.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Double-gene knockout engineering bacteria and construction method and application thereof in fermentation production of 1,3-propylene glycol
InactiveCN105936915AReduce synthesisIncrease percentageBacteriaTransferasesLactate dehydrogenaseMetabolite
The invention discloses double-gene knockout engineering bacteria and a construction method and an application thereof in fermentation production of 1,3-propylene glycol. A D-lactic dehydrogenase gene and an alpha-acetolactate synthetase gene in a genome of a wild type strain for production of 1,3-propylene glycol are knocked out to obtain the engineering strain; the wild type strain for production of 1,3-propylene glycol takes glycerol as a raw material for fermentation production of 1,3-propylene glycol. The engineering bacteria obtained after simultaneous knockout of the two genes of lactic dehydrogenase and acetolactate synthetase are applied in the process of fermentation-process production of 1,3-propylene glycol; the accounting proportion of 1,3-propylene glycol in a fermentation liquid in metabolites is increased, synthesis of lactic acid and 2,3-butylene glycol are simultaneously greatly reduced, and other by-products are not significantly increased. In the process of microbiological fermentation-process production of 1,3-propylene glycol, the role in improving the accounting proportion of 1,3-propylene glycol synthesized by the engineering bacteria and reducing the proportion of the synthesized by-products are played, the production cost is facilitated to be reduced, and the engineering bacteria have important application prospects.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA SEA INST OF OCEANOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
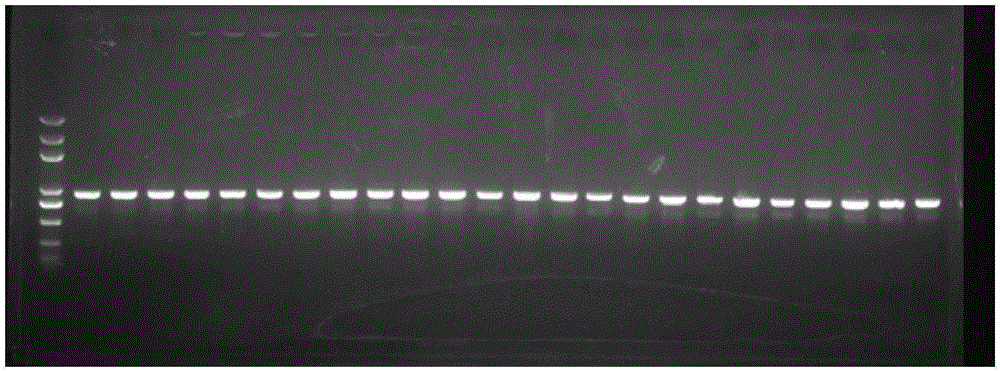
PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection method and kit of ALS (acetolactate synthetase) inhibitor herbicide-resistant descurainia sophia
ActiveCN103923996AImprove featuresIncreased sensitivityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationAcetolactate synthaseNucleotide
The invention provides a specific PCR (polymerase chain reaction) primer pair for detecting ALS (acetolactate synthetase) inhibitor herbicide-resistant descurainia sophia. The primer pair comprises a primer pair (Seq ID No.1-2) for specific amplification of a B-ALS-1 gene of the descurainia sophia and a primer pair (Seq ID No.3-4) for specific amplification of a B-ALS-2 gene of the descurainia sophia. A PCR detection method adopting the primer pair is excellent in specificity and sensitivity, and a specificity test proves that the two ALS genes of the descurainia sophia can be amplified (figures 1 and 2). As the PCR method is simple, convenient and quick to operate, the sampling detection can be carried out in season based on nucleotide detection, and only 2-4 days are required for a process from sampling to results. The sensitivity and specificity of the method can realize quick identification of suspended ALS inhibitor herbicide-resistant descurainia sophia in the field and confirmation of mutation sites, thus the scientific control of resistant weeds in production practice is guided.
Owner:INST OF PLANT PROTECTION CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
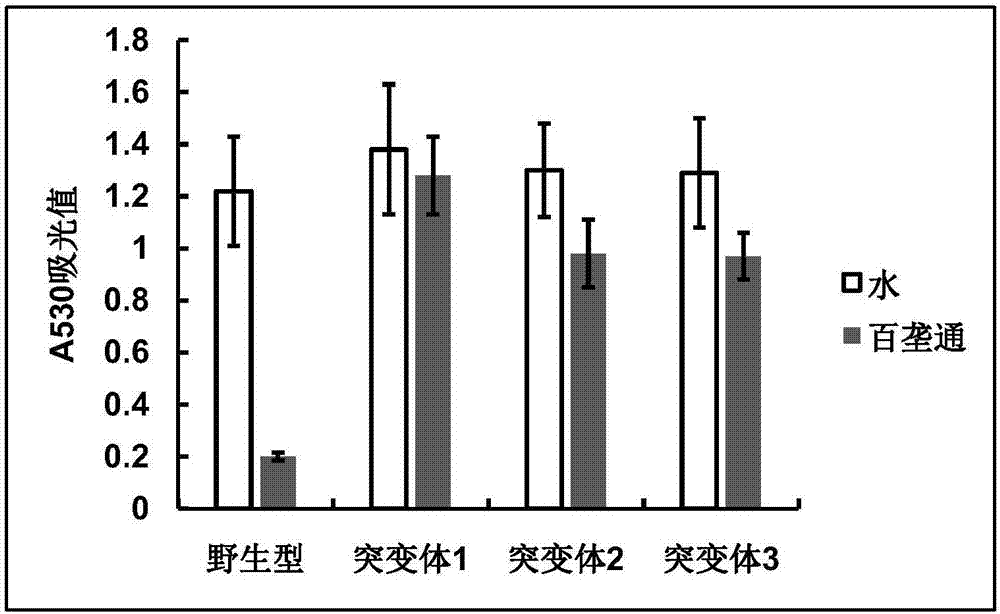
Rice ALS (acetolactate synthetase) mutant-type protein enabling plants to have herbicide resistance and application thereof
ActiveCN108004224AHigh ALS enzyme activityHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAcetolactate SynthetaseWild type
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
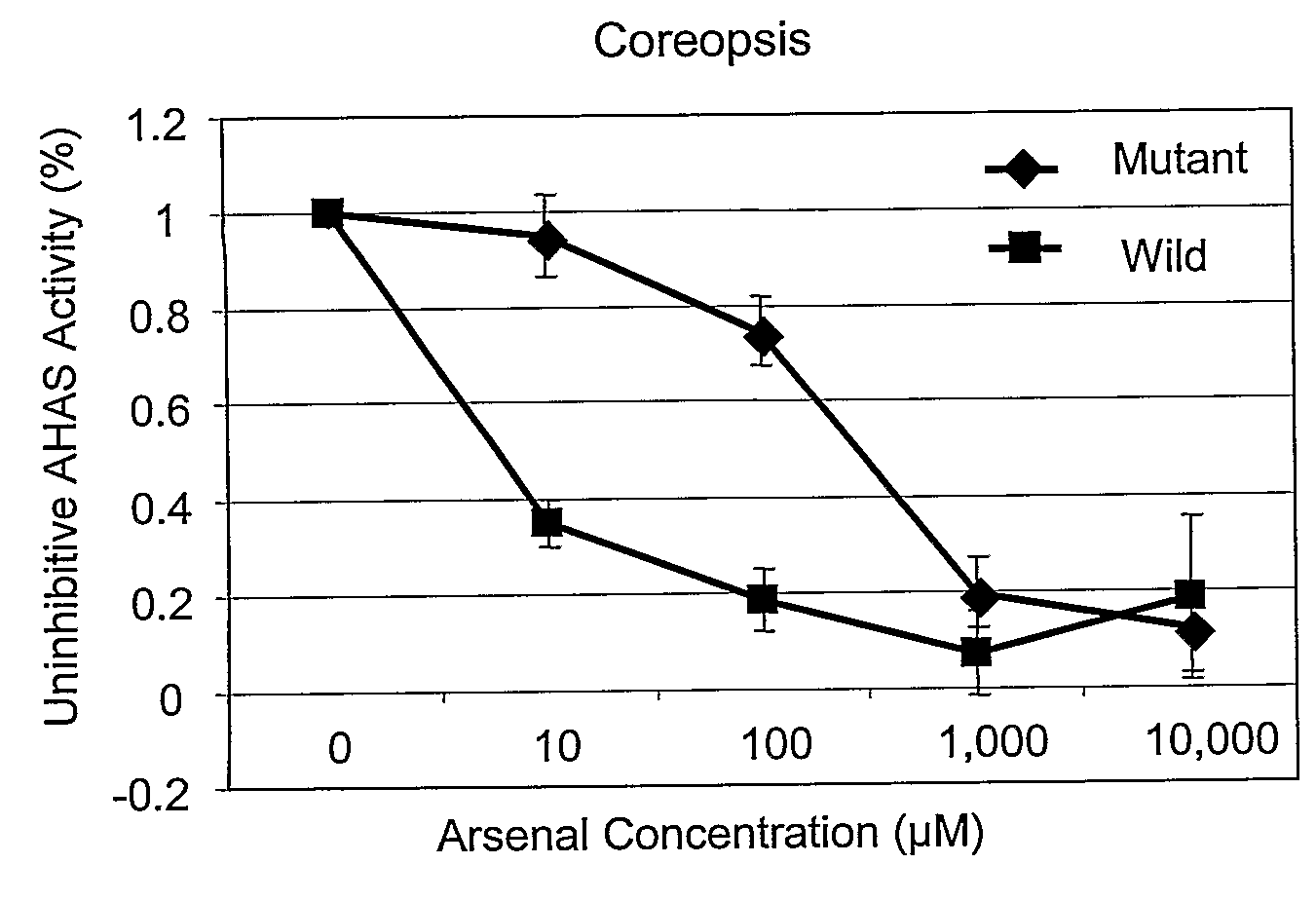
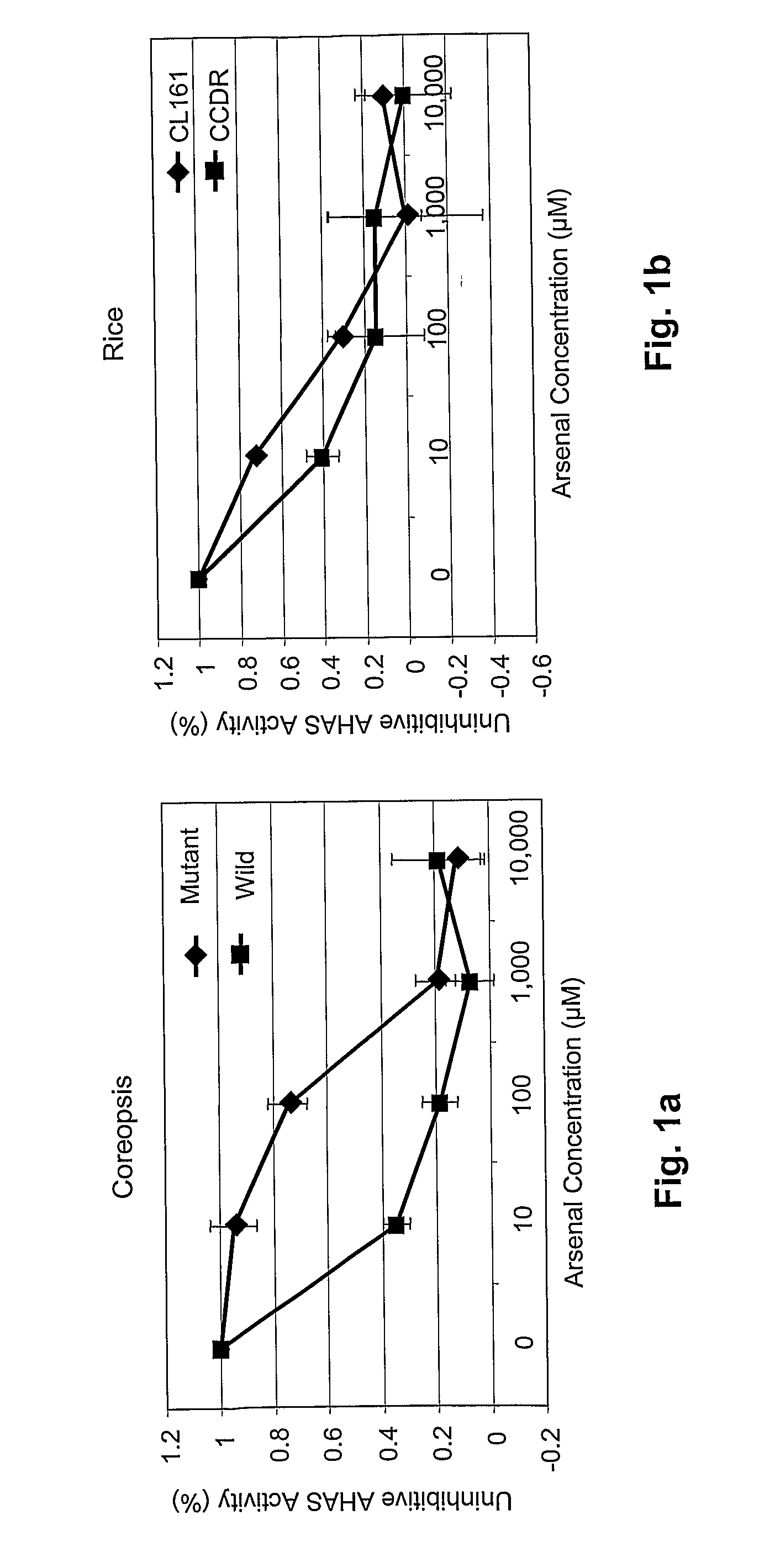
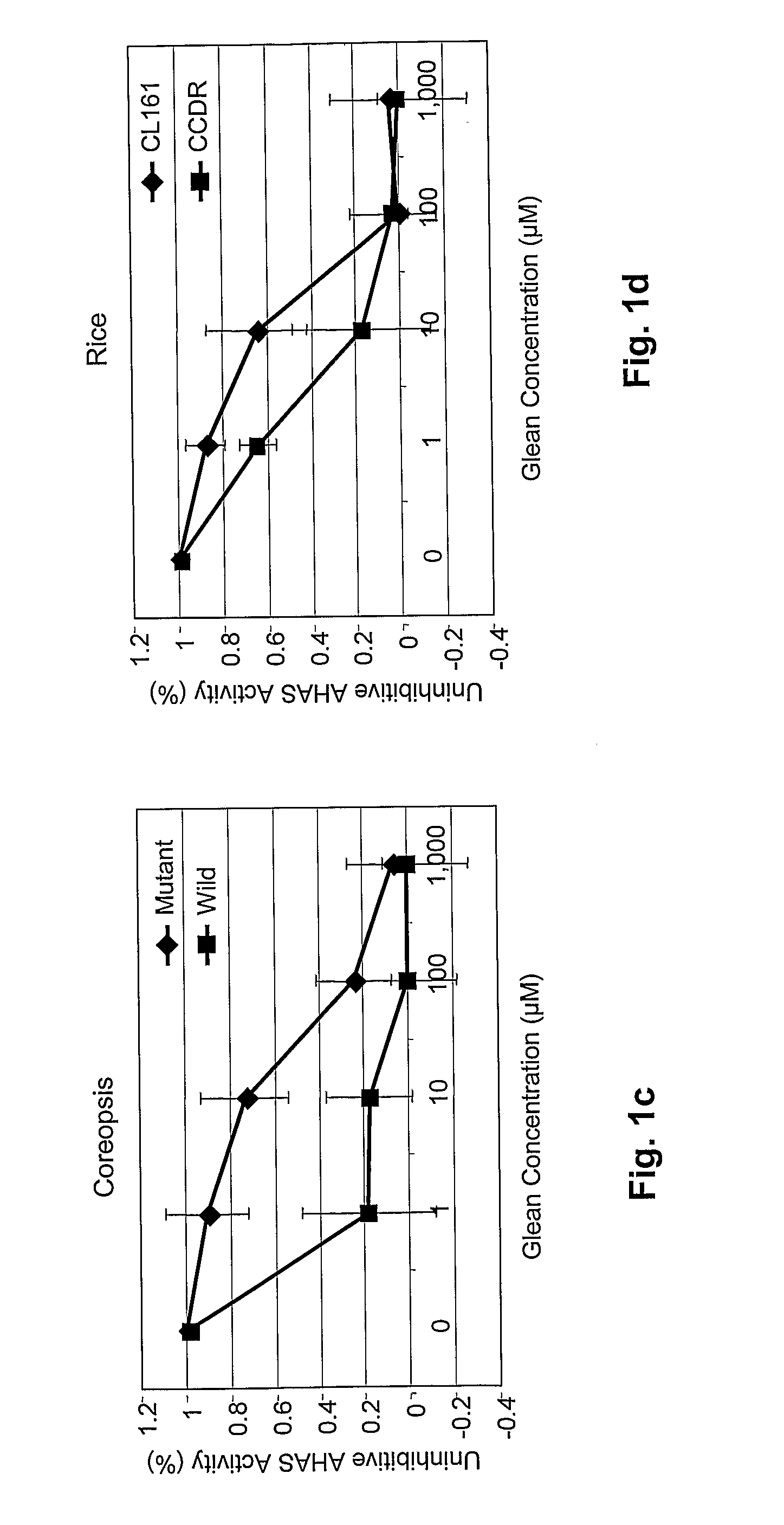
Resistance to Acetolactate Synthase-Inhibiting Herbicides
Nucleotide sequences are disclosed that may be used to impart herbicide resistance to green plants. The sources of novel herbicide resistance were originally isolated in mutant Coreopsis plants. Green plants transformed with these sequences are resistant to herbicides that normally inhibit acetolactate synthase (ALS), particularly imidazolinone and sulfonylurea herbicides.
Owner:BOARD OF SUPERVISORS OF LOUISIANA STATE UNIV & AGRI & MECHANICAL COLLEGE
Protein for endowing wheat with herbicide resistance and application of protein in plant breeding
Owner:FRONTIER LAB OF SYST CROP DESIGN CO LTD +1
Paddy rice ALS (Acetolactate Synthase) mutant protein for endowing plants with resistance to herbicides, gene and application thereof
PendingCN107090447AHigh ALS activityMicrobiological testing/measurementGenetic engineeringMutated proteinAcetolactate synthase
The invention discloses a paddy rice ALS (Acetolactate Synthase) mutant protein for endowing plants with resistance to herbicides. The invention further discloses a nucleic acid for coding the protein. The protein comes from a paddy rice mutant plant resisting ALS inhibitor type herbicides, and in comparison with the ALS sequence in the genome of wild paddy rice, the protein sequence of the protein is simultaneously mutated at sites Ser 627 and Gly 628 or only mutated at the site Gly 628. Plants which express the protein sequence can resist (tolerate) acetolactate synthase inhibitor type herbicides, particularly imidazolinone herbicides. The herbicide-resistant effect of the mutant mutated simultaneously at the sides Ser 627 and Gly 628 disclosed by the invention is about 30 percent higher than the herbicide-resistant capability of the mutant plant only contains mutation at the site Ser 627 or Gly 628.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Application of ALS mutant type genes in aspect of herbicide resistance
The invention discloses ALS mutant type genes. The 75th nucleotide of the ALS mutant type genes in an ALS gene sequence of rice mutates from G to nucleotide C, the 339th nucleotide of the ALS mutant type genes in the ALS gene sequence of the rice mutates from A to nucleotide C, and the 710th nucleotide of the ALS mutant type genes in the ALS gene sequence mutates from C to nucleotide T. The invention further discloses application of ALS protein coded by the ALS mutant type genes in the aspect of herbicide resistance. The protein comes from a rice mutant plant resisting ALS inhibitor herbicide. Compared with the rice wild type ALS sequence, the protein sequence of the ALS mutant type genes mutates at Gln25, Gln113 and Ala237 sites. Green plants express the protein sequence, and acetolactate synthetase resistant inhibitor herbicide, particularly imidazolone and sulfonylurea herbicide, can be resisted.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for improving beet salt-resistance, draught-resistance and anti-herbicide chlorsulfuron characteristics by multi-gene transformation and application
InactiveCN1768575AImprove salt and drought toleranceImprove featuresPlant phenotype modificationPlant genotype modificationEscherichia coliTransgene
The invention provides a method of improving the sugar beet property of salt and drought resistance and weedicide resistance of green-yellow ron through polygene inversion and the application; recombining gene NHX1 of sodium hydrogen inversing transferring protein from the plant racuolar membrane, gene Ppase of racuolar membrane pyrophosphatase , gene beta of choline dehydrogenase from bacillus coli and gene als of acetolactate synthetase resisting the accident mutation of weed killer of green-yellow ron from quasi-mustard in the plant expression carrier, transferring into the sugar beet cell for high effective expression and getting trans genetic plant; choosing trans plants of salt and drought resistance and weedicide resistance of green-yellow ron dramatically increased from the trans genetic plants and their generations; getting the trans genetic plants with 3-4 target genes by a second conversion or making the plants with different trans genes mate with each other; choosing individuals with outstanding properties of salt and drought resistance and weedicide resistance of green-yellow ron from generations of polygenetic inversed plants, and then producing the sugar beet of new strain with properties of salt and drought resistance and weedicide resistance of green-yellow ron.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
ALS mutant gene and application of protein thereof to herbicide resistance
The invention discloses an ALS mutant gene. The nucleotide at the 75th locus of the ALS mutant gene in an ALS gene sequence of rice is changed from G to C, the nucleotide at the 339th locus is changed from A to C, the basic group at the 1099th locus is changed from C to T, and the basic group at the 1880th locus is changed from G to A. The invention further discloses ALS protein coded by the ALS mutant gene and application of the ALS protein. The protein comes from a rice mutant plant resistant to ALS inhibitor herbicide. Compared with a wild ALS sequence of rice, the sequence of the protein is subjected to mutation at the loci of Gln25, Gln113, His367 and Ser627. It is expressed by green plants that the sequence of the protein can resist acetolactate synthetase inhibitor herbicide and particularly imidazolone and sulfonylurea herbicide.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for constructing genetic engineering strains for producing (R)-acetoin and application of genetic engineering strains
ActiveCN107129959AReduce pathogenicityNon-pathogenicBacteriaTransferasesBiotechnologyAcetolactate synthase
The invention discloses a method for constructing genetic engineering strains for producing (R)-acetoin and application of the genetic engineering strains. The method includes optimizing codons of nucleotide sequences of alpha-acetolactate synthase genes, alpha-acetolactate decarboxylase genes and NADH (reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide) oxidase genes and acquiring each gene cluster with three genes by the aid of artificial synthesis processes; inserting the gene clusters into expression vectors to obtain polycistron recombinant plasmids; introducing the polycistron recombinant plasmids into host bacteria E. coli and knocking out key genes of main byproduct synthesis paths to obtain the genetic engineering strains for producing the (R)-acetoin. The method and the application have the advantages that raw materials for the genetic engineering strains can come from wide sources and are low in cost, the strains are free of pathogenicity, oxidized form coenzymes NAD+ (nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide+) can be effectively regenerated, the strains are high in (R)-acetoin yield and production efficiency, the maximum yield can reach 72.1 g / L, and the optical purity can reach 99% at least; the (R)-acetoin is produced by the aid of non-grain cassava flour and inexpensive nitrogen sources which are used as fermentation raw materials, and accordingly the production cost can be reduced.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Acetolactate Synthase Herbicide Resistant Sorghum
ActiveUS20080216187A1Confer resistanceBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyPlant tissue
The present invention provides for compositions and methods for producing sorghum crop plants that are resistant to herbicides. In particular, the present invention provides for sorghum plants, plant tissues and plant seeds that contain altered acetolactate synthase (ALS) genes and proteins that are resistant to inhibition by herbicides that normally inhibit the activity of the ALS protein.
Owner:KANSAS STATE UNIV RES FOUND
Method for improving transformation efficiency of soybean
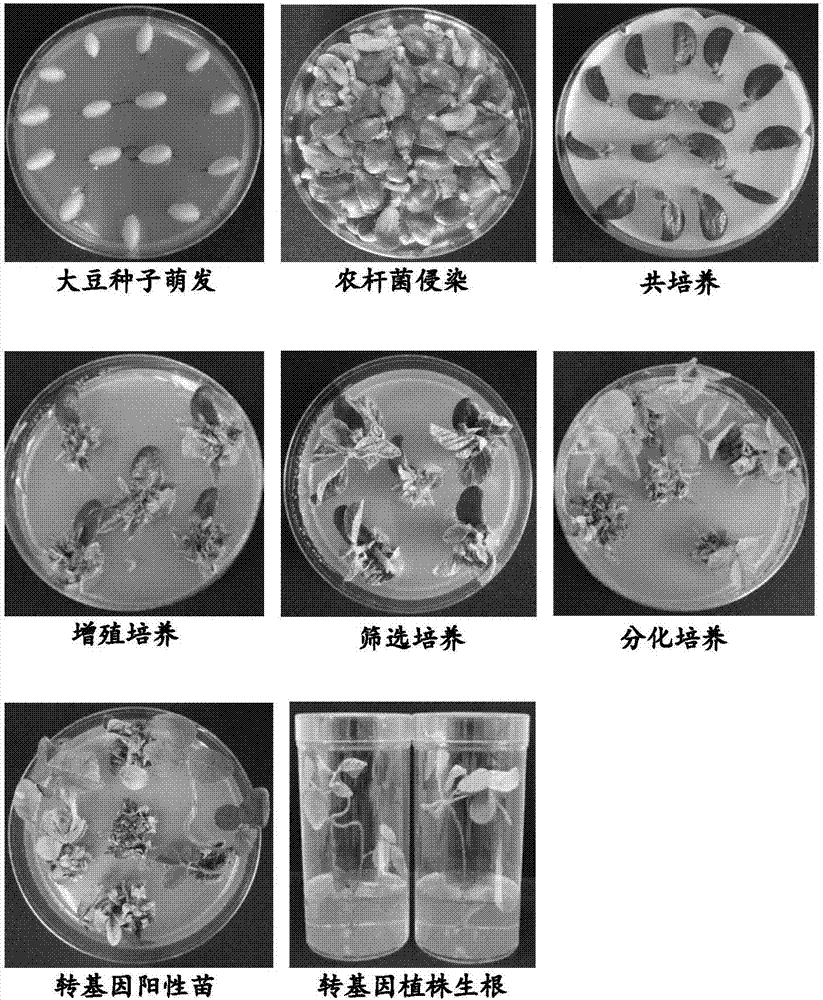
ActiveCN107099548AIncreased rate and conversion efficiencyToleratedVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsHydrolase GenePlant cell
The invention relates to a method for improving the transformation efficiency of soybean. A method for selecting transformed plant cells comprises the following steps: transforming the plant cells by using a recombinant carrier of a gene containing a target gene and a gene for encoding sulfonylurea herbicide hydrolase; carrying out screening culture on the transformed plant cells by externally applying an ALS (Acetolactate Synthetase) inhibitor, and using the gene for encoding the sulfonylurea herbicide hydrolase as a selected marker; selecting the plant cells which are not killed and / or not inhibited. According to the method disclosed by the invention, a method of adding a selective agent into an enrichment culture medium and a differential culture medium by an external application mode (in particular to dropping) in the plant transforming process is put forward for the first time, and effective concentration screening range of the selective agent is optimized, and the proportion and the transformation efficiency of positive plants obtained by an offspring are remarkably improved; meanwhile, transgenic plants obtained by transformation using the sulfonylurea herbicide hydrolase as the selected marker have the advantages of high commercial value, good resistance and genetic stability.
Owner:BEIJING DABEINONG BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Wheat ALS mutation gene and application of protein thereof in aspect of herbicide resistance
ActiveCN106755019AGood growthBiocideMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyAcetolactate synthase
The invention discloses a wheat ALS mutation gene. The 331th nucleotide of an ALS gene sequence of 6BL chromosome of a wheat B genome is changed into nucleotide A from G. The invention further discloses wheat ALS mutation protein encoded by the wheat ALS mutation gene and application of the wheat ALS mutation protein. The protein is from a wheat mutant plant of an anti-ALS inhibitor herbicide. Compared with a wheat mild ALS sequence, the protein sequence mutates at a Val111 site. A green plant expresses that the mutation protein sequence can be resistant and tolerant to an acetolactate synthase inhibitor herbicide, especially an imidazolone herbicide. After 3mL of imazameth / L water (9-fold recommended concentration) is applied to a wheat seedling with one leaf and one core of the wheat ALS mutation protein, the plant can still normally grow, develop and fruit.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cyanobacterial nucleic acid fragments encoding proteins useful for controlling plant traits via nuclear or plastome transformation
InactiveUS7285701B2Improve methodEasy to identifySugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementPhylum CyanobacteriaBiotechnology
This invention provides cyanobacteria as an alternative source of ahas and pds genes for plant transformations and for selectable markers. In particular, it provides for cyanobacteria, for example, Synechocystis, as a source of genes encoding herbicide insensitive proteins, and elements of genes for control of expression in plastids. Nucleic acid fragments, both the acetolactate synthase (ahas) large subunit and the ahas small subunit, were found to provide herbicide resistance. Also, the present invention provides novel Synechocystis mutant phytoene desaturase (PDS) gene conferring resistance to 4′-fluoro-6[(alpha,alpha,alpha,-trifluoro-m-tolyl)oxy]-picolinamide, a bleaching herbicide. The present invention provides improvements to method involving cyanobacteria for the screening of compounds, including a new high-through-put protocol that is a rapid and cost effective way to identify target site genes.
Owner:BASF PLANT SCI GMBH
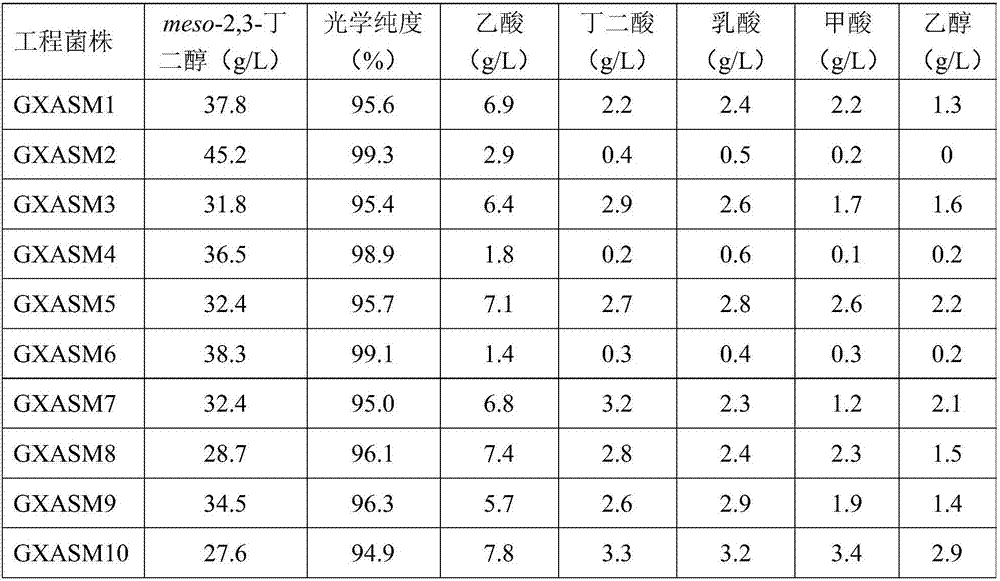
Construction method and application of high-yield engineering strain for optically pure meso-2,3-butanediol
The invention discloses construction of a high-yield engineering strain for optically pure meso-2,3-butanediol. A construction method comprises the following steps of carrying out codon optimization on nucleotide sequences of an alpha-acetolactic acid synthetase gene, an alpha-acetolactic acid decarboxylase gene and a meso-2,3-butanediol dehydrogenase gene, afterwards, splicing to obtain a gene cluster containing the three genes, then introducing the gene cluster into an expression vector to obtain a polycistronic recombinant plasmid, and finally introducing the recombinant plasmid into a host bacterium E. coli again, so that a high-yield engineering bacterium is obtained. Synthesis raw materials used by the bacterium are wide in sources and low in costs; the strain has no pathogenicity; the strain is high in yield, high in production efficiency and good in stability, has the highest yield which can reach 91.5g / L and the optical purity which can reach 99 percent or above. The invention discloses application of the high-yield engineering strain to the production of the optically pure meso-2,3-butanediol by utilizing cheap cassava meal as a carbon source and utilizing cottonseed protein powder, soybean pulp powder, soybean cake powder or peanut protein powder as a nitrogen source at the same time. The production cost is lowered.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Wheat ALS (anti-lymphocyte serum) mutant type protein endowing plants with herbicide resistance as well as gene and application thereof
ActiveCN107022540AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisTriticeaeAcetolactate Synthetase
The invention discloses a wheat ALS (anti-lymphocyte serum) mutant type protein endowing plants with herbicide resistance, and also discloses nucleic acid for coding the protein. The protein is from a wheat mutant plant with ALS-inhibitor herbicide resistance; compared with an ALS sequence in a wild type wheat A-genome, a protein sequence mutates at an Ser630 site. The plant expressed protein sequence can be resistant to an acetolactate synthetase-inhibitor herbicide, in particular to an imidazolinone herbicide. In the wheat ALS mutant type protein, after imazameth and water at the volume ratio of 3:1,000 (9 times of using concentration is recommended) is applied to a wheat seedling with one leaf and one core, the plant can still grow and develop normally and bear fruits.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Escherichia coli for synthesis of propane through pathway of valine and establishing method of escherichia coli
InactiveCN105296410ADecreased aldehyde reductase activityDoes not affect normal growthBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliFormate
The invention discloses escherichia coli for synthesis of propane through the pathway of valine and an establishing method of the escherichia coli, and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the escherichia coli, nine sorts of aldose reductase genes, a lactic dehydrogenase gene, a fumarate reductase gene, a formate-lyase gene and an overall transcription factor gene are eliminated. Meanwhile, overexpression of an acetolactate synthetase gene, a ketol-acid reductoisomerase gene, a DHAD gene, a 2-ketoacid decarboxylase gene and an aldehyde deformylating oxygenase gene is achieved. The invention provides the establishing method of the escherichia coli at the same time. Through overexpression of the propane synthesis pathway in an improved strain, the strain successfully achieves biosynthesis of propane.
Owner:QINGDAO INST OF BIOENERGY & BIOPROCESS TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Method for increasing purity of plant variety
ActiveCN102763506ASeed and root treatmentPlant genotype modificationBiotechnologyAcetolactate synthase
The present invention relates to a method for increasing purity of a plant variety. The method comprises step of: providing a plurality of plant seeds, wherein at least a portion of the plant seeds express an acetolactate synthase mutant and have herbicide resistance; and cultivating the seeds to obtain plants with herbicide resistance. Before the seed cultivation or in the cultivation process, at least one of the following treatments is carried out: before cultivation, a herbicide is utilized to treat the seeds, in order to remove seeds without herbicide resistance; and during the cultivation, herbicide is utilized to treat seedlings, so as to remove the seedlings without herbicide resistance. The method can improve and guarantee purity of hybrid varieties in the field and endow the hybrid seeds and seedlings with herbicide resistance activity.
Owner:BEIJING XINGBOYA BIOLOGICAL TECH
Method of producing D-(-)-acetoin by in-vitro enzyme reaction
ActiveCN107653259AAchieve productionIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesEscherichia coliThiamine pyrophosphate
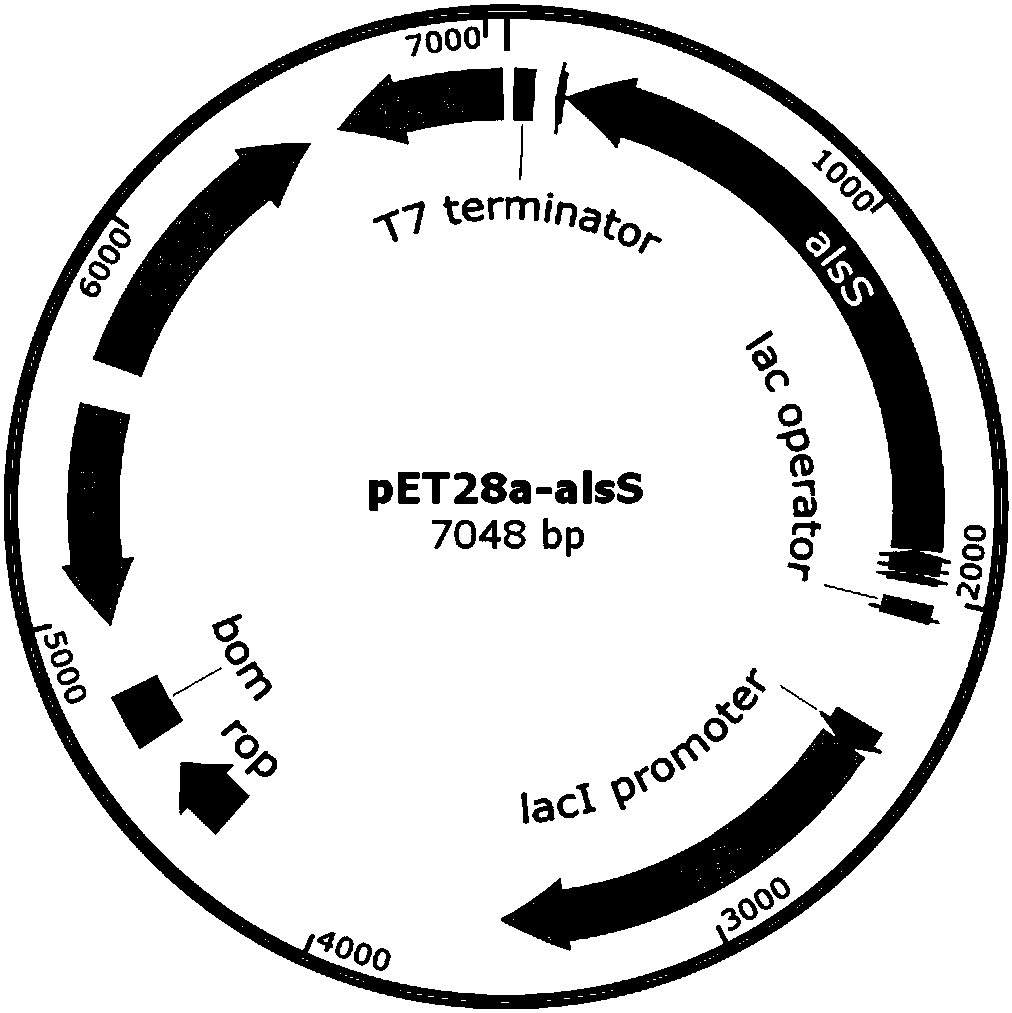
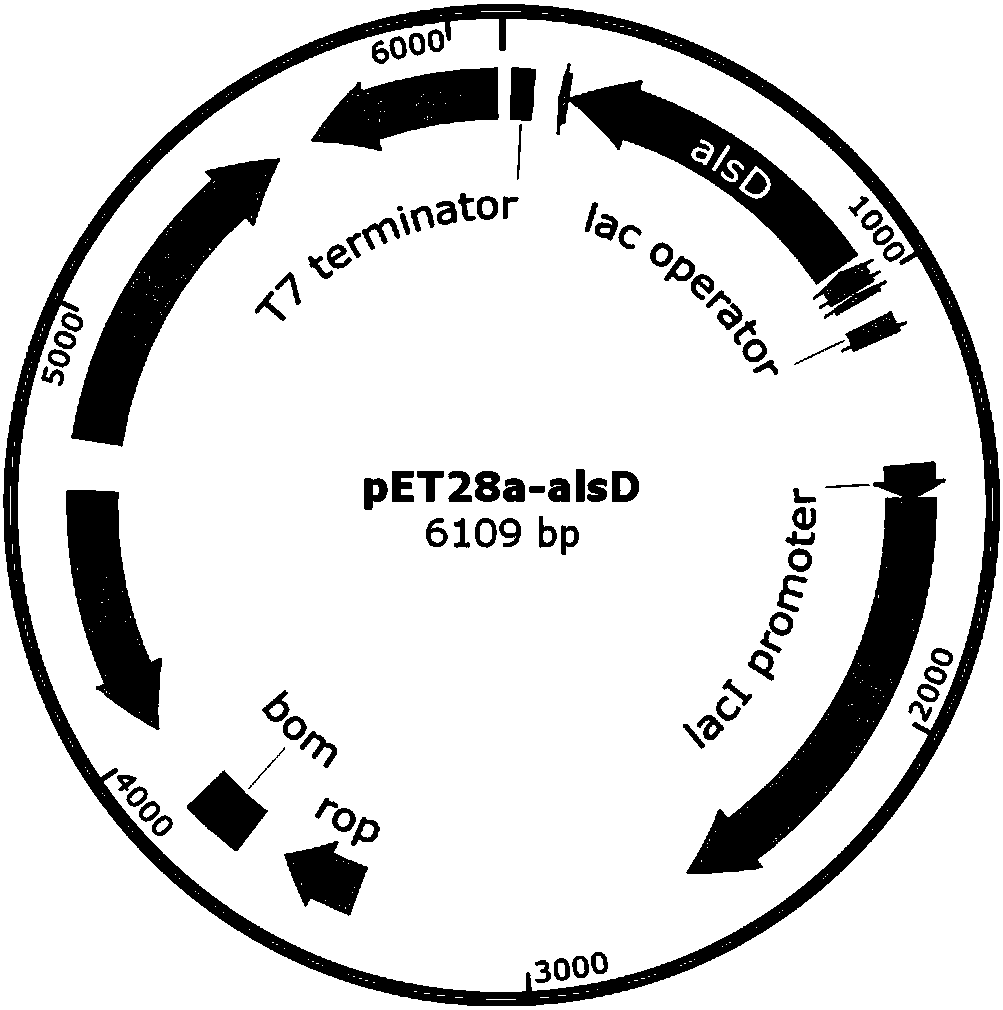
The invention discloses a method of producing D-(-)-acetoin by in-vitro enzyme reaction, comprising the steps of (1) linking the carrier pET28a and alpha-acetolactate synthase encoding gene alsS to obtain pET28a-alsS, introducing the pET28a-alsS into Escherichia coli, fermenting, purifying, and concentrating to obtain alpha-acetolactate synthase concentrate; linking the carrier pET28a and alpha-acetolactate decarboxylase encoding gene alsD to obtain pET29a-alsD, introducing the pET29a-alsD to Escherichia coli, fermenting, purifying, and concentrating to obtain alpha-acetolactate decarboxylaseconcentrate; (2) mixing well the two concentrates, sodium pyruvate, Mg2+ and thiamine pyrophosphate, and allowing reaction to obtain the D-(-)-acetoin. The sodium pyruvate low in cost is used as a substrate to provide in-vitro efficient production of high-added-value chiral D-(-)-acetoin, and the finished D-(-)-acetoin has high purity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Wheat ALS mutant gene and application thereof in resisting herbicide
ActiveCN106591334AGood growthMicrobiological testing/measurementTransferasesAgricultural scienceMutated protein
The invention discloses a wheat ALS mutant gene. According to the mutant gene, the 1180th nucleotide of the ALS gene sequence of the wheat B genome 6BL chromosome is changed from nucleotide G to nucleotide A. The present invention further provides a wheat ALS mutant protein encoded by the wheat ALS mutant gene and an application of the mutant protein. The mutant protein originates from wheat mutant plants capable of resisting ALS inhibition herbicide. Compared with the wheat wild type ALS order, the mutant protein order is mutated in the Ala 394 site. The expression of the protein order through a green plant can resist (endure) acetyl lactate synthase inhibitor herbicide, particularly imidazolidinone herbicide. The 1-leave-1-core wheat seedlings with the wheat ALS mutant protein can still grow, develop and bear fruits normally after an imazameth aqueous solution with a concentration of 3mL imazameth per liter of water (nine times of the recommended concentration) is applied to the seedlings.
Owner:JIANGSU ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Acetolactate synthetase AHAS restrainer combination
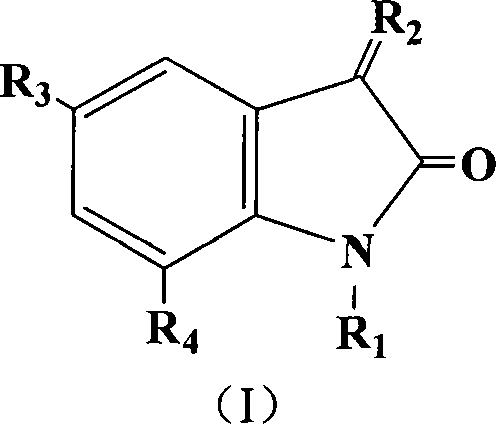
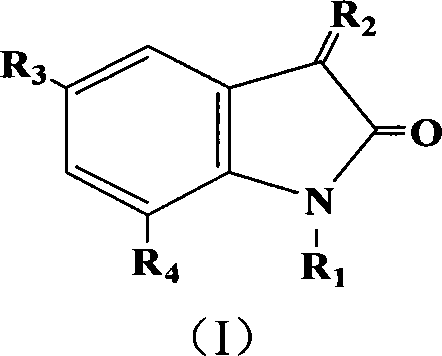
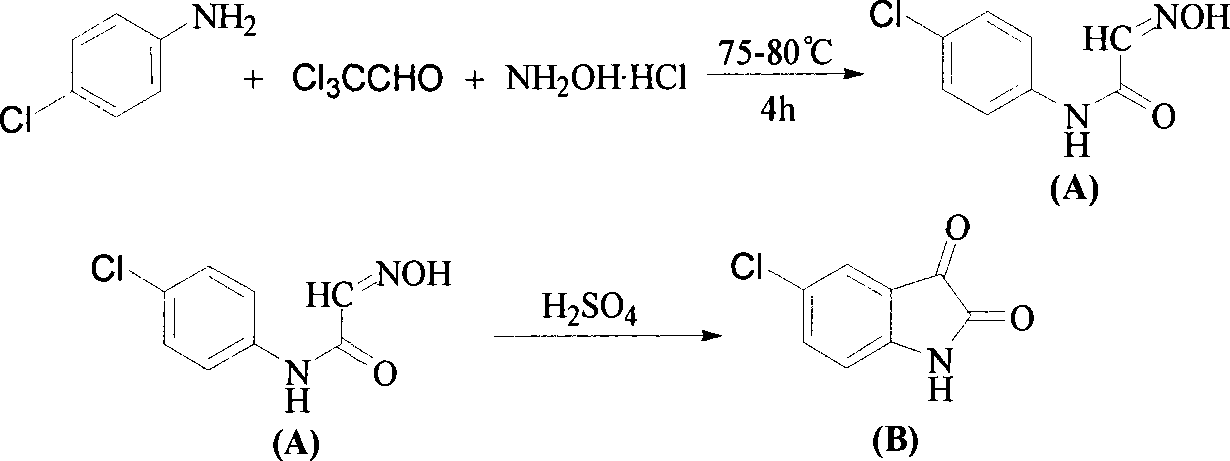
InactiveCN101243793ABreak through structural featuresGrowth inhibitionBiocideAnimal repellantsDiketoneAcetolactic acid
The invention relates to an inhibitor compound for acetolactate synthetase AHAS, which is indoline diketone compound (I); wherein, R1 is H or CH3, R2 is O or N-OH, R3 is F, Cl, Br, I, CH3, OCH3, NO2, SO3H, OCF3 or CF3, R4 is F, Cl, Br, I, CH3 or OCH3. The inhibitor compounds for acetolactate synthetase has the advantages of having herbicidal activity, having inhibiting action upon arabidopis thaliana aceto-lactic acidsynzymeas well as upon growth of rape root and being used for designing new environmentally friendly herbicide molecule.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
Gene encoding acetolactate synthase and use thereof
InactiveCN101024838AEasy to manufactureOutstanding fragranceFungiBeer fermentationAlcohol drinkAcetolactate synthase
The present invention relates to an acetolactate synthase gene and use thereof, in particular, a brewery yeast for producing alcoholic beverages with superior flavor, alcoholic beverages produced with said yeast, and a method for producing said beverages. More particularly, the present invention relates to a yeast, whose capability of producing vicinal diketones, especially diacetyl, that are responsible for off-flavors in products, is reduced by repressing expression level of ILV2 gene encoding an acetolactate synthase (Ilv2p), especially non-ScILV2 gene specific to a lager brewing yeast, and to a method for producing alcoholic beverages with said yeast.
Owner:SUNTORY HLDG LTD
Wheat ALS mutant protein and nucleic acid and application thereof
ActiveCN107354139AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisMutated proteinTriticeae
The invention discloses a wheat ALS mutant protein. The sequences of an ALS gene of a wheat A genome 6AL chromosome, an ALS gene of a B genome 6BL chromosome and an ALS gene of a wheat D genome 6DL chromosome are mutated. The invention further discloses nucleic acid of the wheat ALS mutant protein and further discloses application of the wheat ALS mutant protein. By expressing the protein sequence, green plants can resist (tolerate) acetolactate synthetase inhibitor type herbicides, especially imidazolone type herbicides. Wheat one-leaf one-core seedlings with the wheat ALS mutant protein still can normally grow, develop and fruit after a herbicide is applied according to the concentration of 1 mL of imazameth per L of water (three times of recommended use concentration).
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com