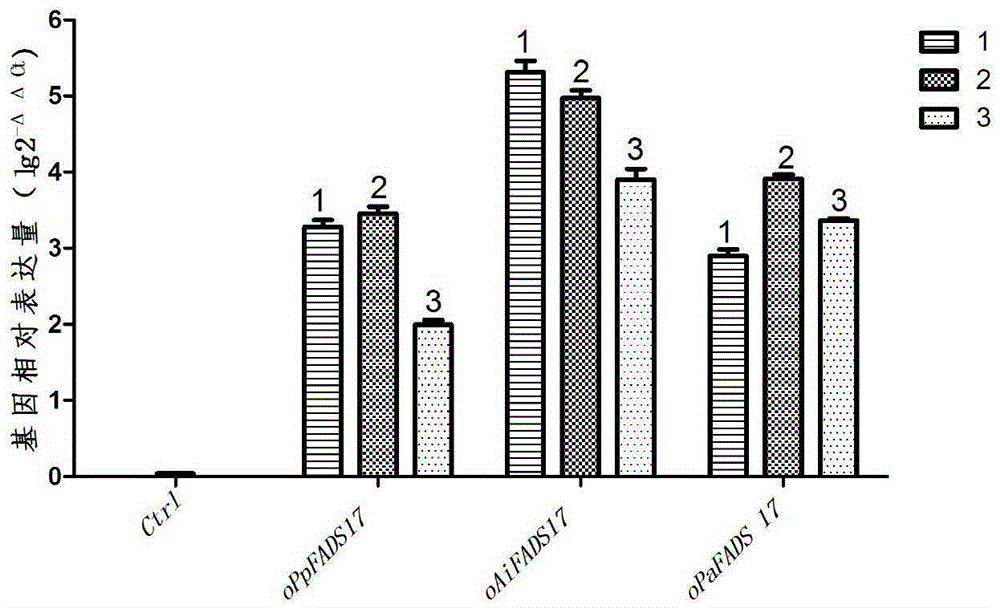
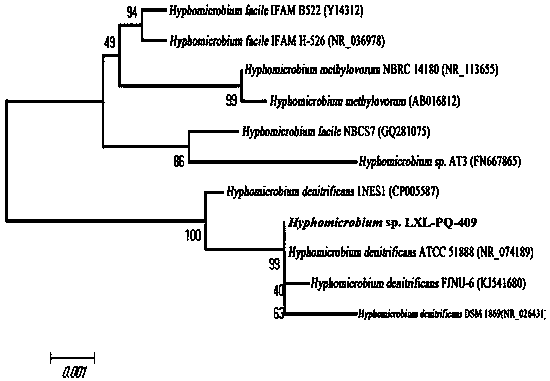
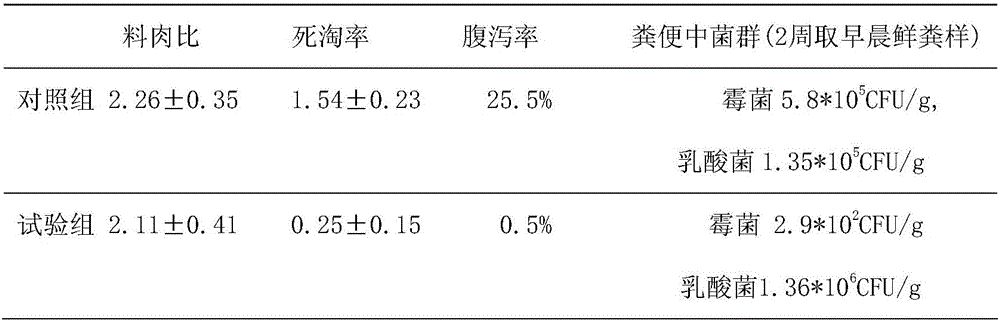
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
189 results about "Saccharomyces paradoxus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Saccharomyces paradoxus is a wild yeast and the closest known species to the baker's yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae. It is used in population genomics and phylogenetic studies to compare its wild characteristics to laboratory yeasts.
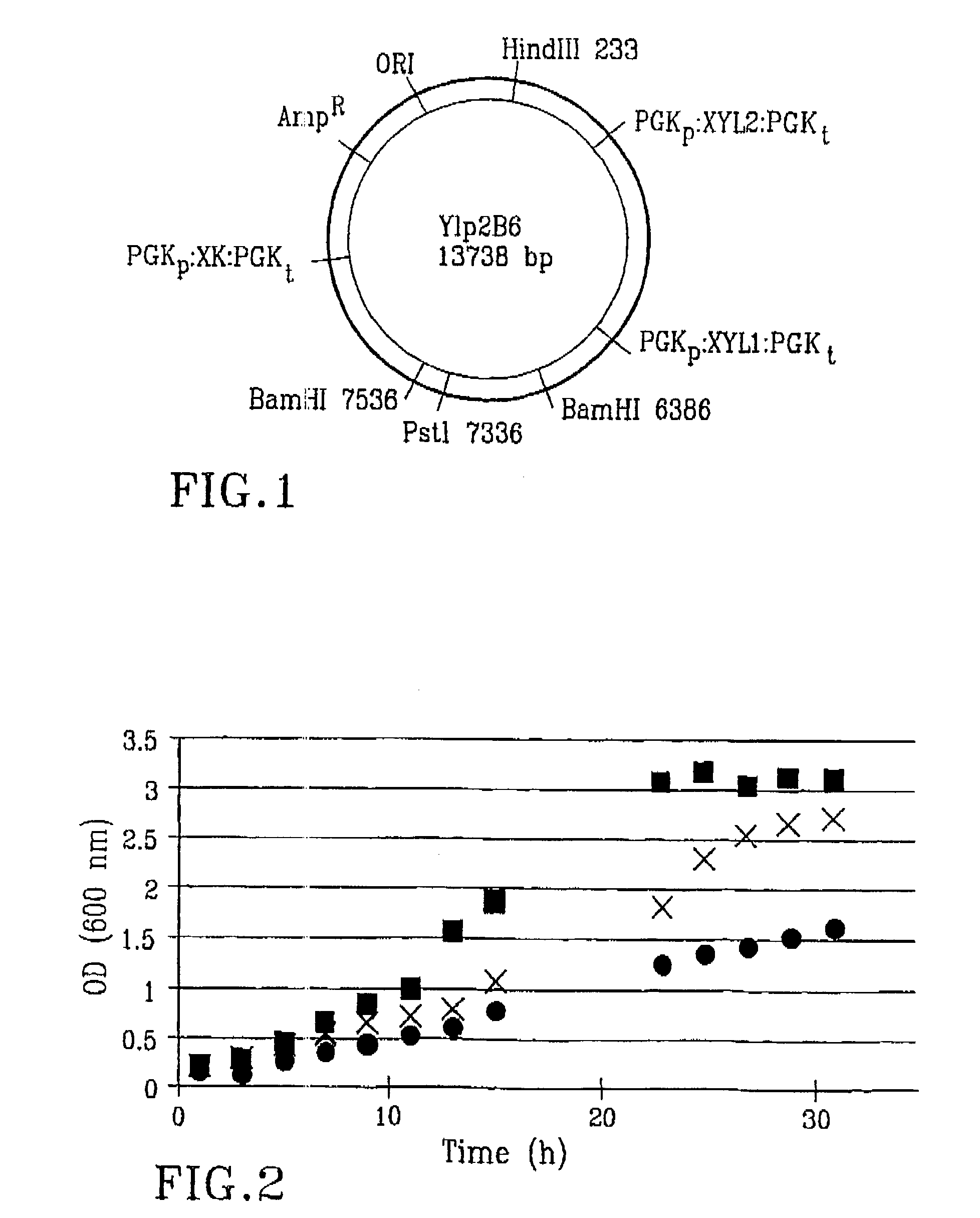
Transformed Saccharomyces cerevisiae Engineered for Xylose Utilization
InactiveUS20100112658A1High ethanol productionEfficient growth processFungiBacteriaHeterologousNucleotide
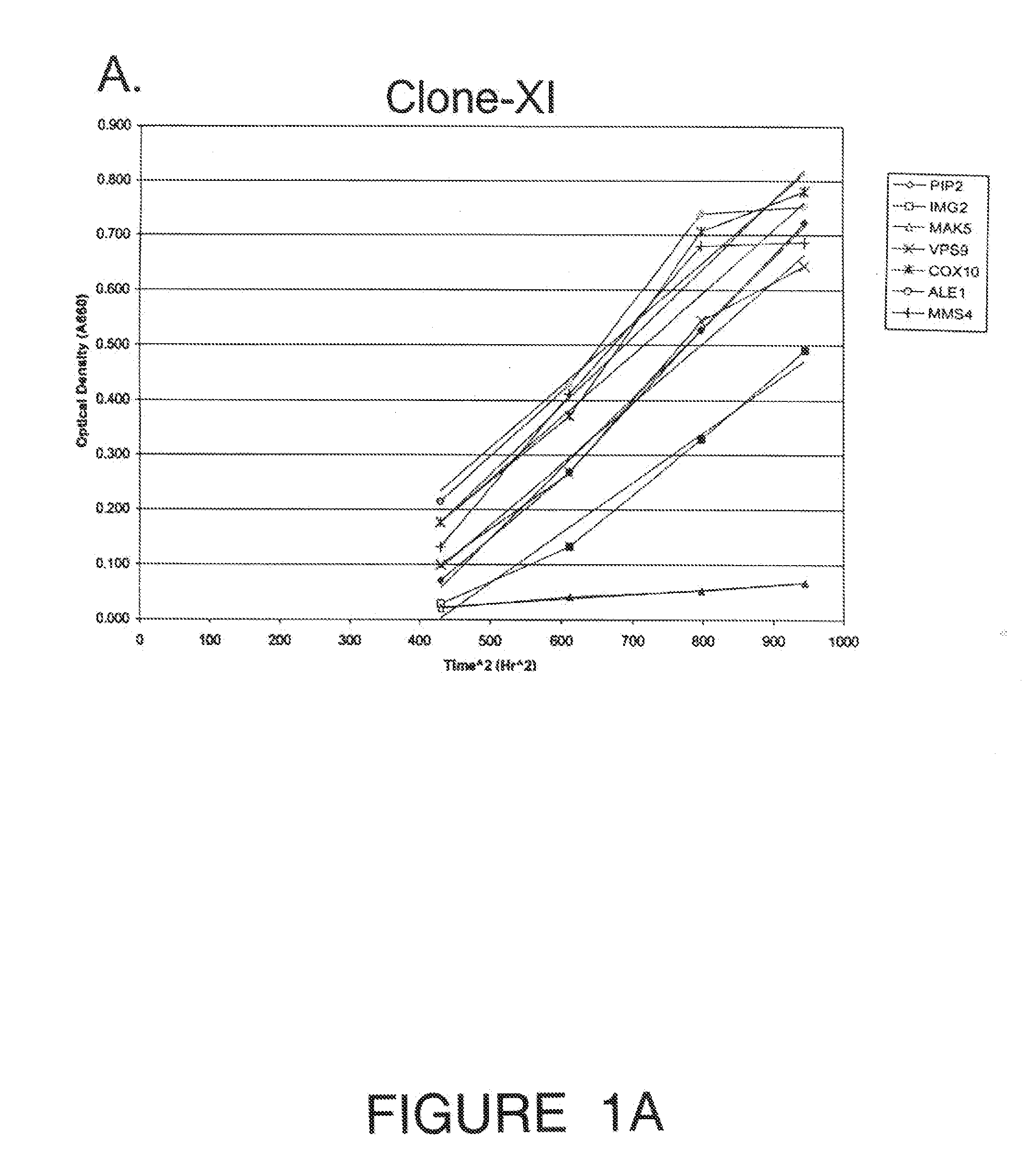
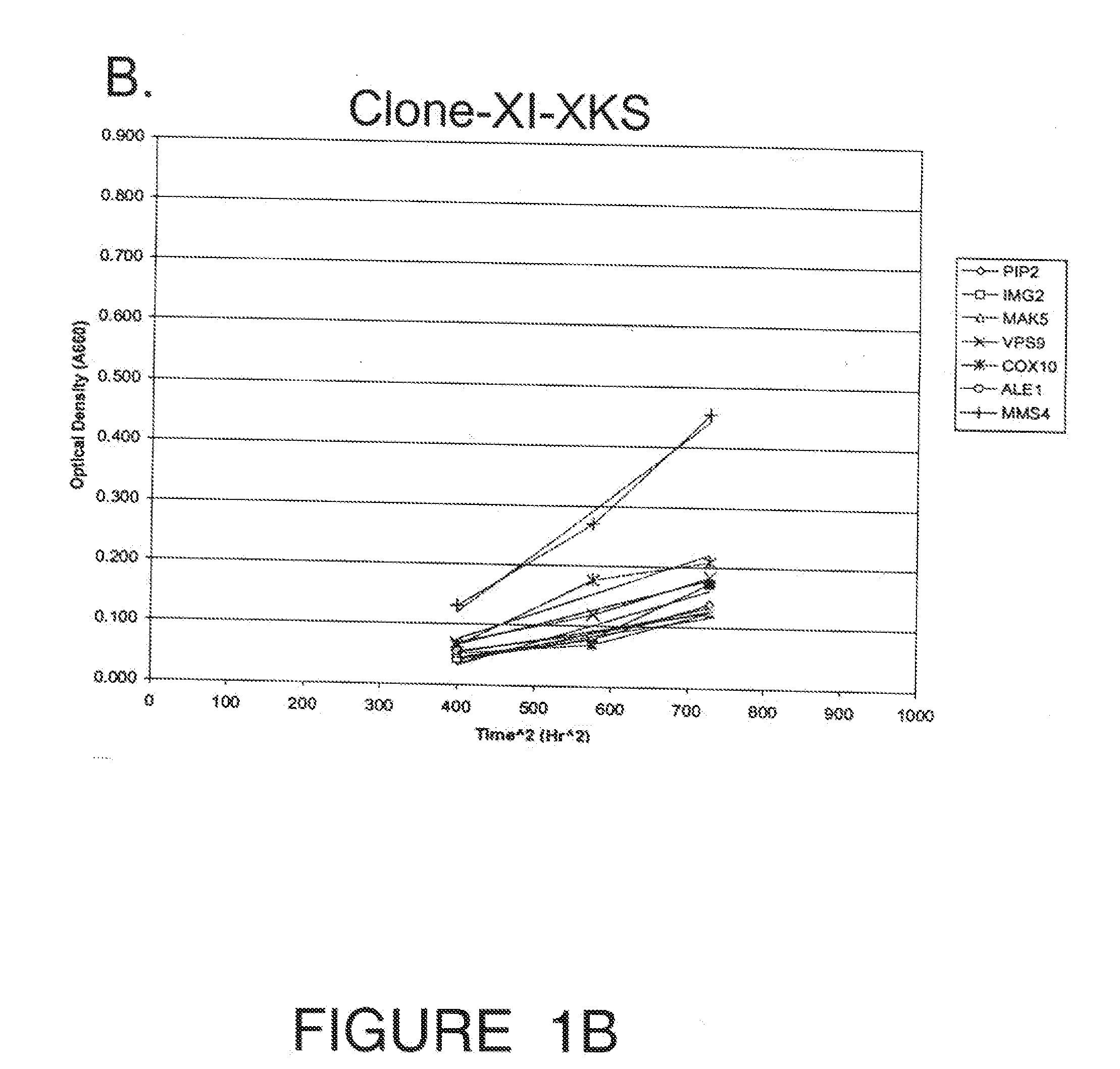
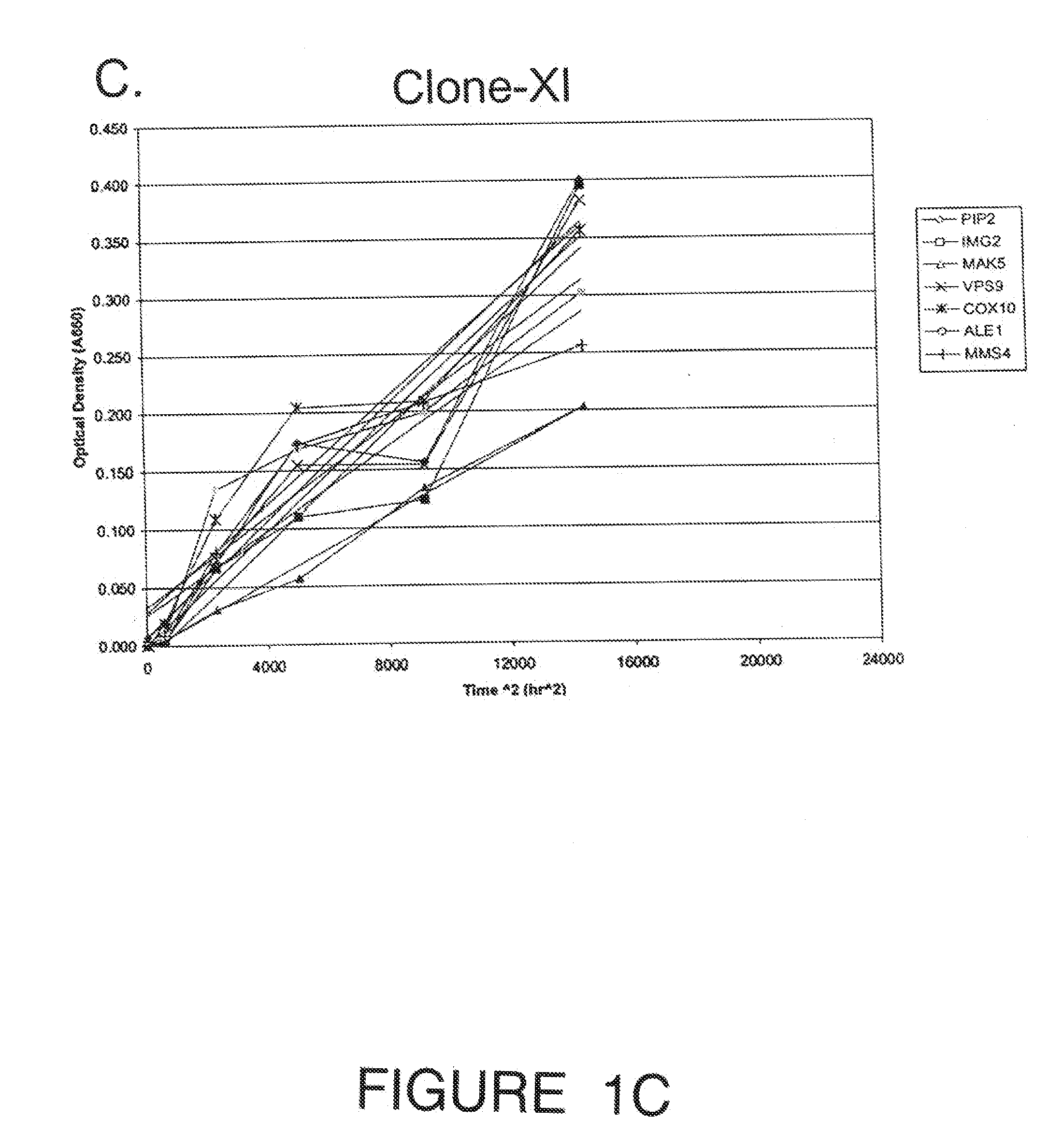
Recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae produced by transformation with heterologous polynucleotide sequences coding for xylulokinase (XKS) from Yersinia pestis and xylose isomerase (XI) are capable of xylose utilization. The transformants express these heterologous polynucleotides at a sufficient functional level to grow aerobically on xylose as the sole carbon source. Further transformation of the recombinant yeasts to overexpress one or more of the S cerevisiae genes PIP2, IMG2, MAK5, VPS9, COX10, ALE1, CDC7, and MMS4, permits the yeast to grow anaerobically on xylose as the sole carbon source. When grown under anaerobic conditions on a culture medium comprising both glucose and xylose, the transformed yeast exhibit increased ethanol productivity, with the yeast growing on the xylose to increase their biomass and fermenting the glucose to ethanol.
Owner:US SEC AGRI +1
Complex bacterium for bean pulp fermentation and application of complex bacterium
The invention provides a complex bacterium for bean pulp fermentation. The complex bacterium is composed of bacillus subtilis, bacillus coagulans, aspergillus niger, aspergillus oryzae, lactobacillus plantarum and saccharomyces cerevisiae. The complex bacterium provided by the invention is obtained through repeated scientific experiment and reasonable combination based on physiological metabolism feature of the microorganism, the complex bacterium is vigorous in growth metabolism, is capable of secreting a plurality of enzymes, acids and other metabolites, and is capable of efficiently decomposing macromolecule protein, anti-nutritional factors and sensitization factors in the bean pulp, obviously increasing content of soluble protein, small peptide, organic acid, protease and vitamin and the number of probiotics and antibacterial peptide, improving the digestion utilization rate, inhibiting the growth of pathogenic bacteria and reducing the use of antibiotic; and meanwhile, the complex bacterium has acid fragrance of fermentation and is good in food attractant effect. The bacteria strains forming the complex bacterium are included in a feed additive variety catalogue (2013) issued by the department of agriculture, the complex bacterium is safe and reliable, and can be directly used for the industrial production for the bean pulp fermentation.
Owner:HENAN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY
Genetic recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of degrading and utilizing kitchen wastes
The invention relates to the field of genetic engineering and fermentation engineering and in particular discloses genetic recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae capable of degrading and utilizing kitchen wastes. The genetic recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae is constructed by transferring alpha-amylase (alpha-amylase) genes, glucoamylase (glucoamylase) genes and acid protease (acid protease) genes through a multi-gene coexpression vector of the saccharomyces cerevisiae and obtaining accurate secretory expression. The previous three enzyme genes are simultaneously transferred into the saccharomyces cerevisiae for realizing the secretory expression, so that the saccharomyces cerevisiae can simultaneously secrete the alpha-amylase, glucoamylase and acid protease. Therefore, main nutritional ingredients such as starch and proteins in the kitchen wastes can be efficiently degraded and become carbon sources and nitrogen sources needed by growth and fermentation of recombinant yeasts, and high-efficiency conversion between the kitchen wastes and ethanol is realized.
Owner:GUANGDONG RECYCLEAN LOW CARBON TECH CO LTD
Recombinant bacillus subtilis increased in yield of acetylglucosamine
ActiveCN104498394AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processes2,3-ButanediolAcetolactate Synthetase
The invention discloses a recombinant bacillus subtilis increased in yield of acetylglucosamine and belongs to the field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant bacillus subtilis increased in yield of acetylglucosamine, the recombinant bacillus subtilis BSGN6-PxylA-glmS is taken as an original strain, an alpha-acetolactate synthetase encoding gene and an alpha-acetolacetate decearboxylase encoding gene are knocked out by virtue of homologous recombination, and therefore, the approach by which acetoin and butanediol are generated from 2,3-pyroracemic acid in host bacteria is blocked. In the host bacteria from which the alsS and alsD are knocked out, the glucosamine acetylase encoding gene derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae is excessively expressed, and therefore, the route of synthesis of the acetylglucosamine is enhanced, the yield of the acetylglucosamine in the recombinant bacillus subtilis is increased to 38.46g / L, and a foundation is laid for producing the glucosamine by modifying the bacillus subtilis in the metabolic engineering.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Process for producing feeding micro-ecological preparation by solid fermentation of brewery mash with various bacterium and fermentation culture medium thereof
ActiveCN101139560AReduce manufacturing costSimple production facilitiesFungiBacteriaAnimal ForagingFreeze-drying
The invention provides a process for producing forage micro ecologic preparations by a multi-bacteria solid fermentation beer draff and a fermentation culture medium for the preparations. Delbrueckii subsp bulgaricus (preservation no. CCTCC M 207096), bacillus subtilis (preservation no. CCTCC M 207097) and saccharomyces paradoxus (preservation no. CCTCC M 207098) are respectively inoculated to corresponding liquid culture media, cultured 18-24 h thermostatically under 37 DEG C; then the suspension fluids are inculcated in certain proportion into a disinfected solid fermentation culture media taking beer draff as main raw materials, fermented for 36-48h under 30-34 DEG C, and frozen dry. In this way the forage micro ecologic preparations are got. The production process in the invention is of low investment, low energy consumption, high yield and free from pollution from waste fluid, and opens a new means for changing waste into a treasure for beer draff.
Owner:CHANGSHA LVYE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
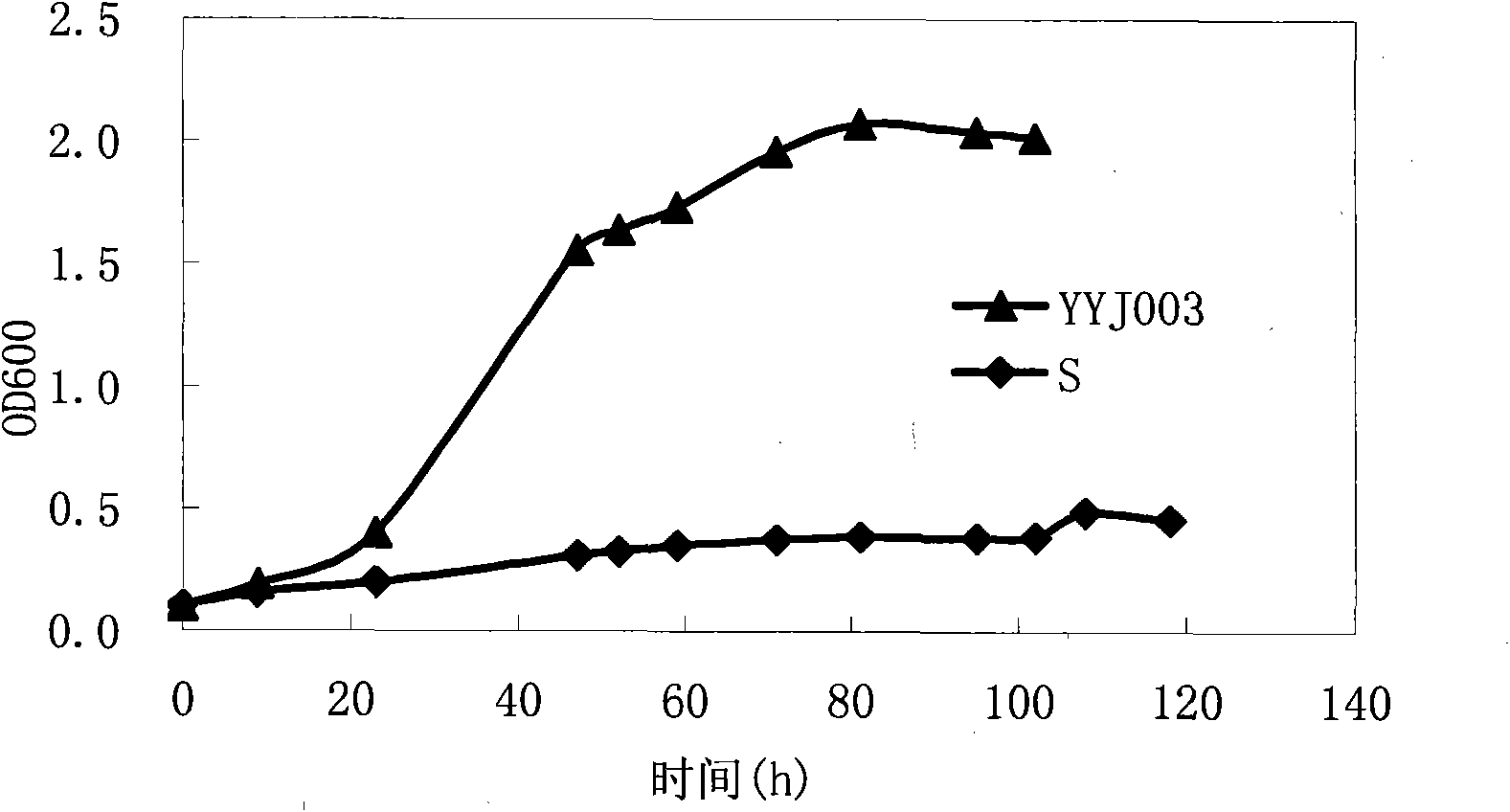
Bacterial strain tolerant with various inhibitors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
The invention discloses a bacterial strain tolerant with various inhibitors of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which is named as Saccharomyces cerevisiae YYJ003 and is collected in China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms (CCCCM) with the collection number of CGMCC NO.2757. The bacterial strain tolerant with the various inhibitors of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae in the invention can be in normal growth in a culture medium containing inhibitors produced by diluted acid pretreatment and can realize efficient ethanol production. The bacterial strain in the invention breaks through the bottleneck problem that a dilute acid pretreatment method is limited to produce cellulosic ethanol.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
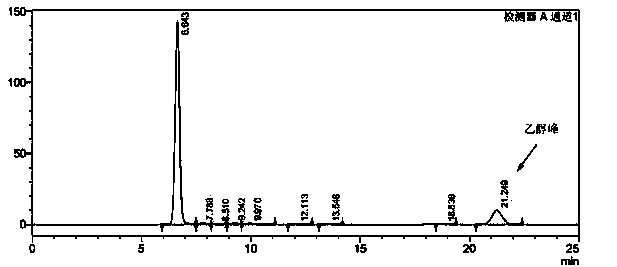
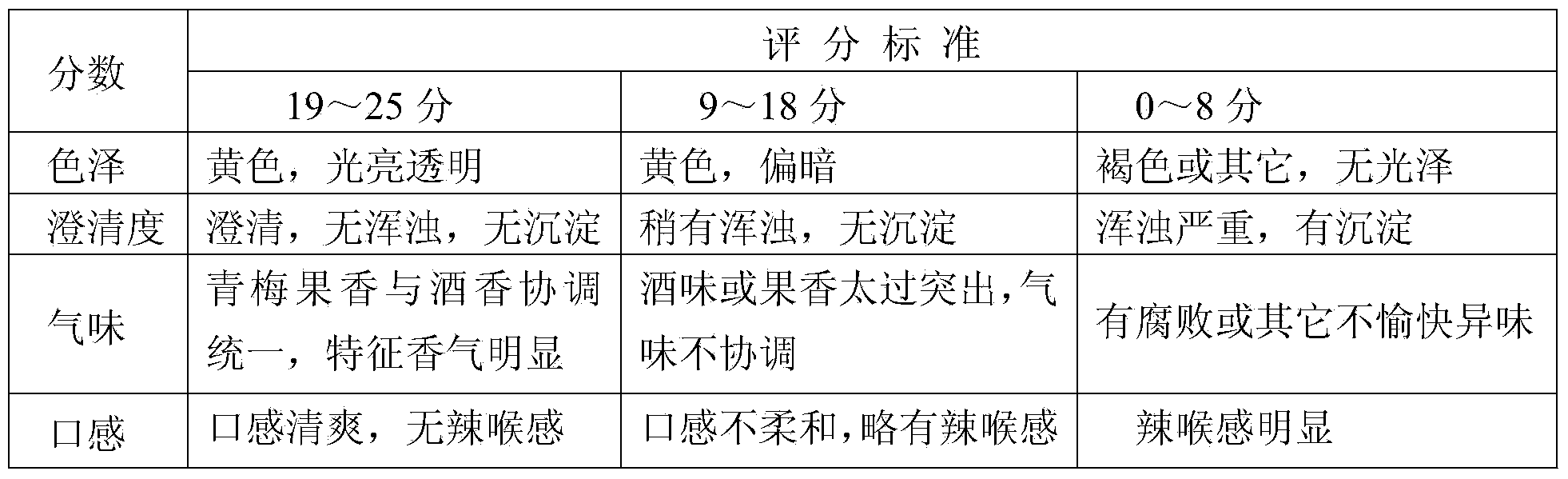
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and green plum fruit wine prepared by using saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
ActiveCN103773702ARetain and enrich nutrientsEmbodies and fills with characteristic aromaFungiAlcoholic beverage preparationFlavorMicroorganism
The invention discloses a strain QM5236 special for fermenting green plum fruit wine. The strain is collected in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center with the collection number CGMCC No.8485 on November 19, 2013. The green plum fruit wine and a preparation method thereof are further disclosed. The green plum fruit wine is obtained through preparing and treating green plum fruit pulp serving as a raw material by taking the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain QM5236 as a production strain, and performing the processes of primary fermentation, secondary fermentation, aging, filtering, sealing and sterilizing. The saccharomyces cerevisiae strain QM5236 in the technical scheme is suitable for a green plum fruit pulp fermentation system, and the product fruit wine is outstanding in particular flavor and excellent in organoleptic quality.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and method for preparing blueberry fruit wine by using saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
ActiveCN102911885AFruityStrong targetingFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyNutritive values
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and a method for preparing a blueberry fruit wine by using the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. The saccharomyces cerevisiae strain is used for preparing the blueberry fruit wine by fermentation, and can maintain the blueberry flavor and the nutritive value of the fruit wine. The method comprises the following steps: activating the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain in a liquid seed culture medium; crushing blueberry and then adding an activated strain for carrying out primary fermentation for 7-9 days, filtering to obtain a fermentation liquor; and adding SO2 into the fermentation liquor for secondary fermentation for 12-14 days, and filtering to obtain a wine base. The blueberry fruit wine obtained through the method is fruity enough, and is high in nutritive value and stability.
Owner:INST OF BOTANY JIANGSU PROVINCE & CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
High-yielding ethanol yeast and method for improving quality of traditional fermented foods through symbiotic fermentation of high-yielding ethanol yeast and ester-producing yeast
ActiveCN109810910AIncreased ethanol productionOptimizing the Culture Conditions of Symbiotic FermentationFungiAlcoholic beverage preparationHydrolysateEthyl acetate
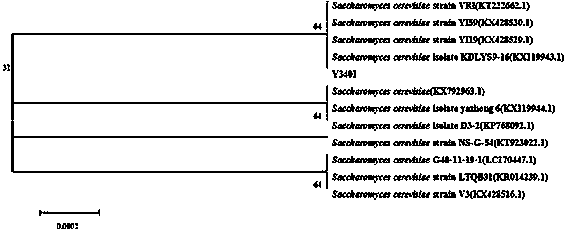
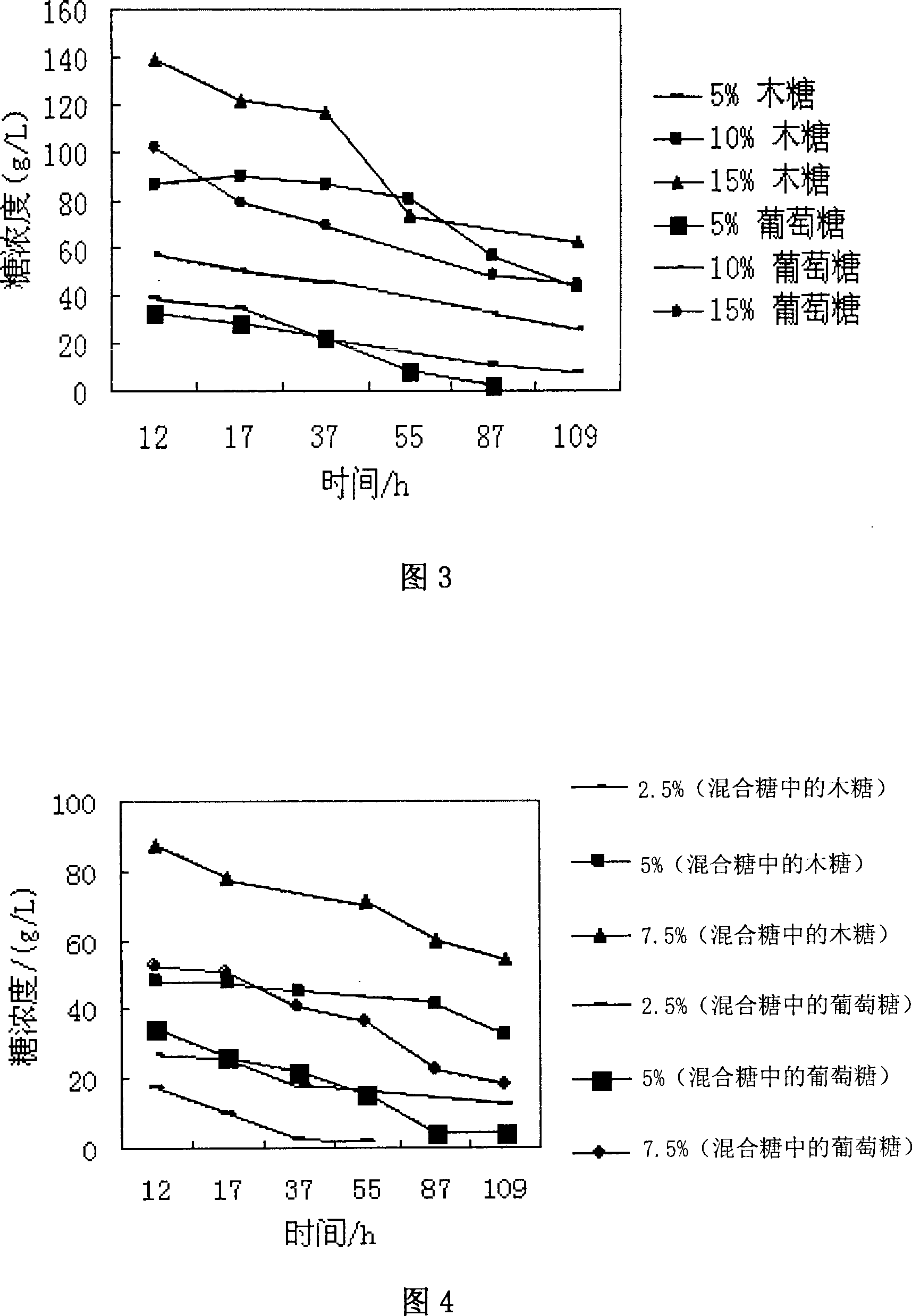
The invention relates to a saccharomyces cerevisiae Y3401 strain for high-yielding ethanol and a symbiotic fermentation culture method of the saccharomyces cerevisiae Y3401 strain and a Wickerhamomyces anomalus Y3604 strain for high-yielding ethyl acetate as well as application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae Y3401 strain. The saccharomyces cerevisiae Y3401 was preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on October 20th, 2017, with a preservation number of CGMCC No.14828; the similarity of 26S rDNA D1 / D2 sequence of the saccharomyces cerevisiae Y3401 strain to 26S rDNA D1 / D2 sequence of other saccharomyces cerevisiae strains; symbiotic fermentation of two yeast strains in a sorghum enzymatic hydrolysate culture medium by a standing or shaking mode has the advantages that the content of the ethyl acetate is favorably improved and the contents of flavor substances such as total ester, beta-phenylethanol and isoamyl alcohol also can be improved. In a solid brewing system, the symbiotic fermentation of the two strains can enhance the characteristics of ester-improving and flavor-enhancing of yeast. The symbiotic fermentation method of the two strains, disclosed by the invention, can be applied to the brewing industries, having demands on the ethyl acetate, such as Baijiu, yellow rice wine and soy sauce.
Owner:BEIJING TECHNOLOGY AND BUSINESS UNIVERSITY
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing ethanol by using xylose and glucose
The invention belongs to the bioengineering technical field and discloses a Saccharomyces cerevisiae YPH499-3 which has been collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center of China Committee for Culture Collection of Microorganisms with a collection number of CGMCC No.2255. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae of the invention can well utilize xylose and also can simultaneously transport the xylose and glucose to produce ethanol, and utilization rate reaches over 80 percents.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Recombinant yeast for lignocellulose raw materials
The present invention relates to a method for obtaining a recombinant yeast of Saccharomyces cerevisiae, which ferments lignocellulose raw materials to ethanol, including introducing DNA into a yeast so as to cause the yeast to have introduced genes encoding xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase and xylulokinase.
Owner:SCANDINAVIAN TECH GRP AB
Method for simultaneous production of ergosterol and glutathione by yeast fermentation
ActiveCN1844407AIncrease profitEasy to synthesizeMicroorganism based processesFermentationSucroseMetabolite
The invention discloses a method of yeast fermentation coproduction ergot sterol and glutathion, utilizing conspecific yeast bacterial fermentation to produce simultaneous two kinds of metabolite-ergot sterol and glutathion, the utilization bacterial of fermentation is Saccharomyces cerevisiae, candida utilis, candida tropicalis or engineering bacterial reconstructed by mutagenesis and gene engineering, the utilization yeast culture medium contain the carbon source such as glucose, cereal mash, sucrose molasses and so on, the nitrogen source such as maize milk, yeast powder, protease leather, carbonyldiamide, ammonia and so on, inorganic salt and the metallic ion that the yeast need. The invention utilizes fermentation coproduction ergot sterol and glutathion, simultaneously, accomplish high-density culture of the yeast cell, and make the biomass of yeast expression coproduction come up to the standard of the high level in individual fermentation ergot sterol and glutathion, full utilization culture medium substrate, increasing availability ratio of raw material, decreasing the cost of manufacture.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Production of saccharomyces cerevisiae and lactobacillus acidophilus composite microbe preparation used for feed
The invention relates to a microbe preparation, and concretely relates to a production method of a saccharomyces cerevisiae and lactobacillus acidophilus composite microbe preparation used for feed, the production method is characterized in that concentrated saccharomyces cerevisiae mother liquor containing saccharomyces cerevisiae greater than or equal to 50 hundreds million / ml and the concentrated lactobacillus acidophilus mother liquor with high density containing lactobacillus acidophilus greater than or equal to 100 hundreds million / ml are mixed according to 1:1 with the volume ratio, and the composite microbe preparation product containing saccharomyces cerevisiae greater than or equal to 50 hundreds million / ml and containing lactobacillus acidophilus greater than or equal to 100 hundreds million / ml. The saccharomyces cerevisiae and lactobacillus acidophilus composite microbe preparation takes glucose, cane sugar, cane sugar honey and corn steep liquor as main fermentation raw materials, the fermental cultivation can be carried out at 30-34 DEG C, the product bacteria number is high, the quality is good, pH value is between 5.0-6.6, and the quality guarantee period is 18 monthes. The saccharomyces cerevisiae and lactobacillus acidophilus composite microbe preparation used for feed has simple production technology and good product application effect, can purify the culture environment, and can be used in the culture industries such as aquatic product and livestock and poultry.
Owner:辽宁威兰生物技术有限责任公司
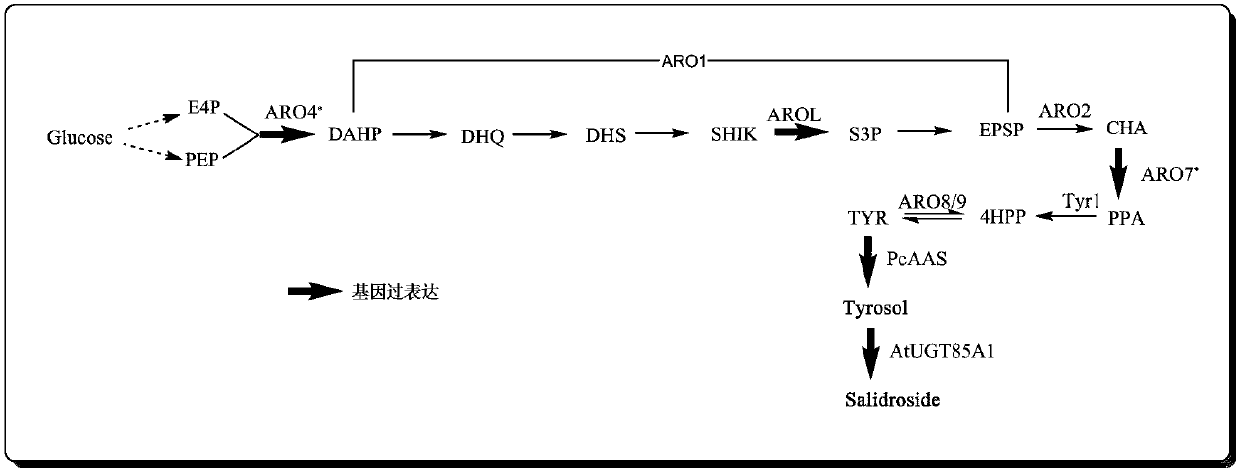
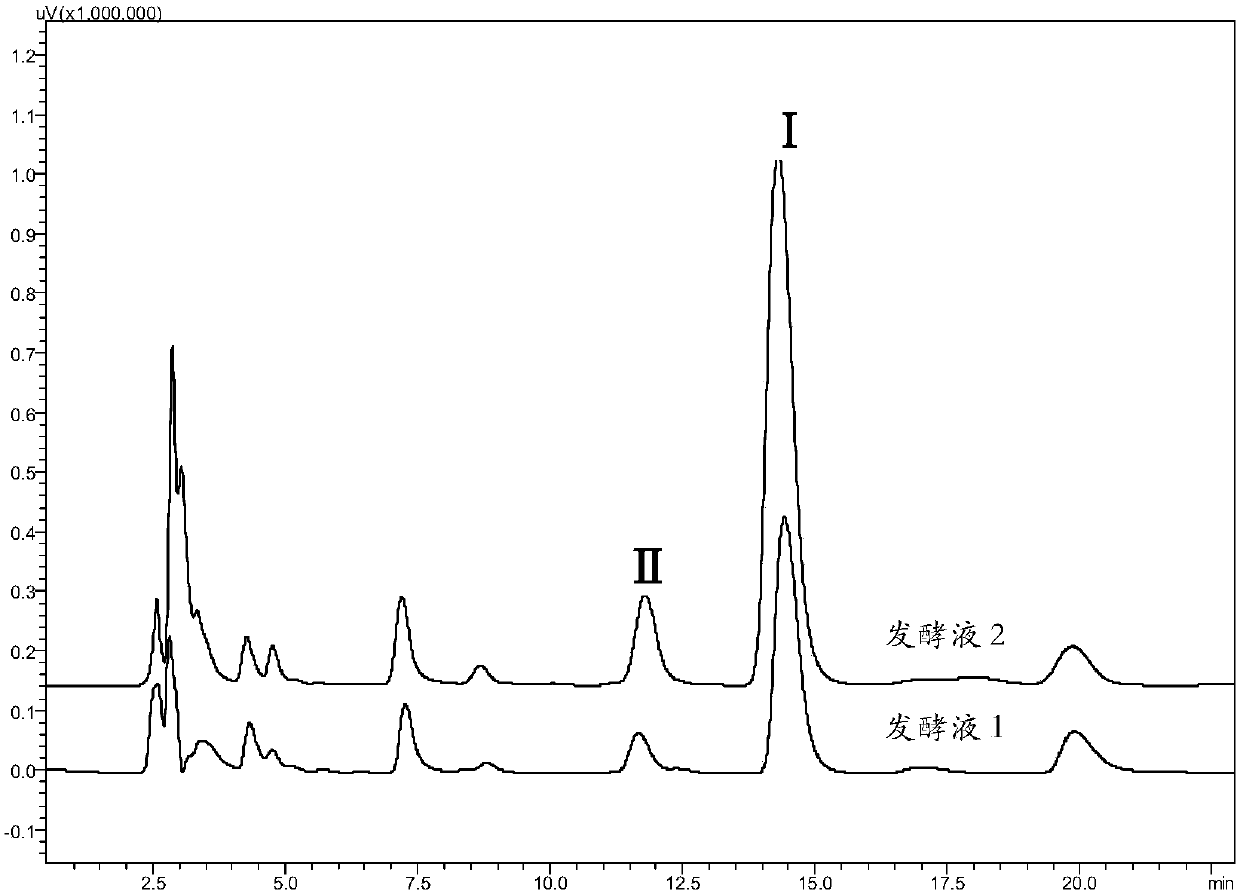
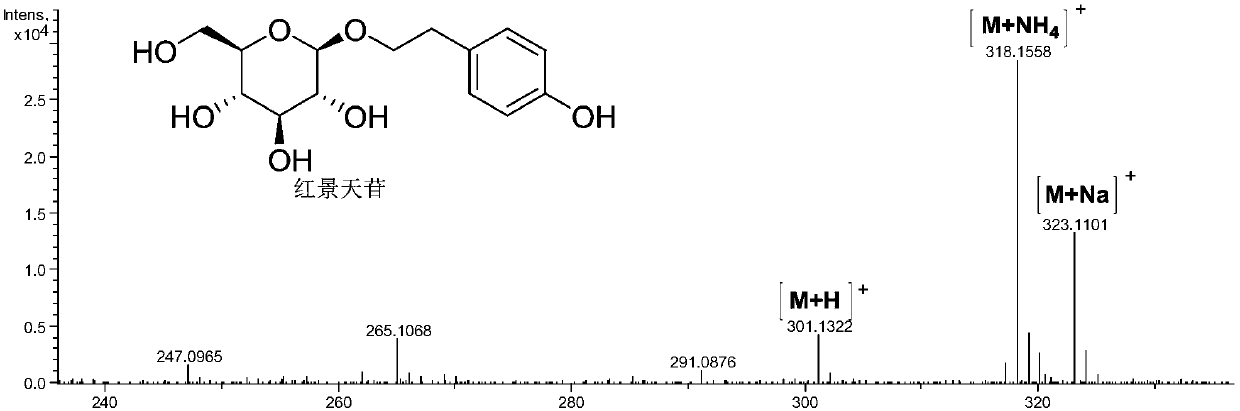
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and application thereof to producing tyrosol and/or salidroside
The invention provides a recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for producing tyrosol and / or salidroside and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of genetic engineering. According to the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for producing the tyrosol and / or salidroside, applied exogenous genes comprises AROL gene, PcAAS gene, AtUgt85A1 gene, ARO4* gene and ARO7* gene,which serve as five key enzyme encoding genes during biosynthesis of the tyrosol and / or salidroside and are introduced and overexpressed in saccharomyces cerevisiae, so that metabolic flux from glucose to tyrosine can be reduced to enhance the biosynthesis of the tyrosol and / or salidroside and further to achieve construction of a route of de novo synthesis from glucose to the tyrosol and / or salidroside for the saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Torulaspora delbrueckii strain and application thereof in brewing of wine
ActiveCN108239608ARich fruityImprove qualityFungiMicroorganism based processesVitis viniferaMicroorganism
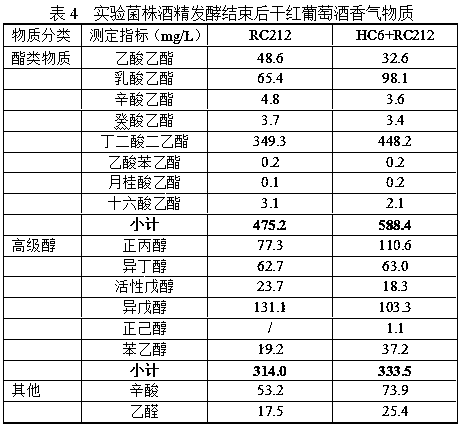
The invention discloses a Torulaspora delbrueckii strain and application thereof in the brewing of wine. The Torulaspora delbrueckii strain is characterized in that a Torulaspora delbrueckii HC6 culture is preserved on January, 2018 in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center and has a preservation number of CGMCC No.15179. The strain is separated from natural fermented mash of cabernet sauvignon in a grape region in Hebei province, and the Torulaspora delbrueckii HC6 capable of highly producing ester fragrance is prepared through a series of screening and identification experiments; the screened Torulaspora delbrueckii HC6 is matched with brewer's yeast so as to brew wine through fermentation and is accordant with the national standard on the production of the wine, and thecontents of esters such as fragrant substances is remarkably increased; and the strain can be applied to the brewing of the wine and can play important roles in the improvement of the quality of thewine, the increase of the fragrance complexity of the wine and the richness of the fruit fragrance of the wine.
Owner:YANTAI CHANGYU PIONEER WINE CO LTD
Acetyl-glucosamine accumulating recombinant bacillus subtilis and application thereof
InactiveCN103045527AEasy to buildEasy to useBacteriaMicroorganism based processesGlucose polymersMicrobiology
The invention discloses an acetyl-glucosamine accumulating recombinant bacillus subtilis and an application thereof, belonging to the field of genetic engineering. According to the invention, bacillus subtilis 168 is used as an expression host, a glucosamine acetylase coding gene (GNA1) derived from saccharomyces cerevisiae S288C is over-expressed, and the synthesis route of the glucosamine is strengthened so as to obtain the genetic engineering bacteria of the acetyl-glucosamine accumulating bacillus subtilis, wherein the yield is up to 115 mgL. The invention lays the foundation for the further metabolic engineering transformation of bacillus subtilis to produce the glucosamine.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing oligo-galactose by cyclic utilization of recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN101475914AIncrease productionEasy to produceFungiMicroorganism based processesSurface displayLactose
The present invention relates to a method of using recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce galactooligosaccharides, specifically to a recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae with surface display of beta-galactosidase and method for making same and a method of recycling the recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae fermentation lactose to produce galactooligosaccharides. The method includes: first of all, building a beta-galactosidase yeast surface display vector, displaying the beta-galactosidase on cell surface of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae, and then recycling the recombinant yeast fermentation lactose to produce galactooligosaccharides. The inventive recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae of the surface display beta-galactosidase can be recycled to produce galactooligosaccharides, and has high yields, low production cost, simple process and broad industrialization application prospects.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
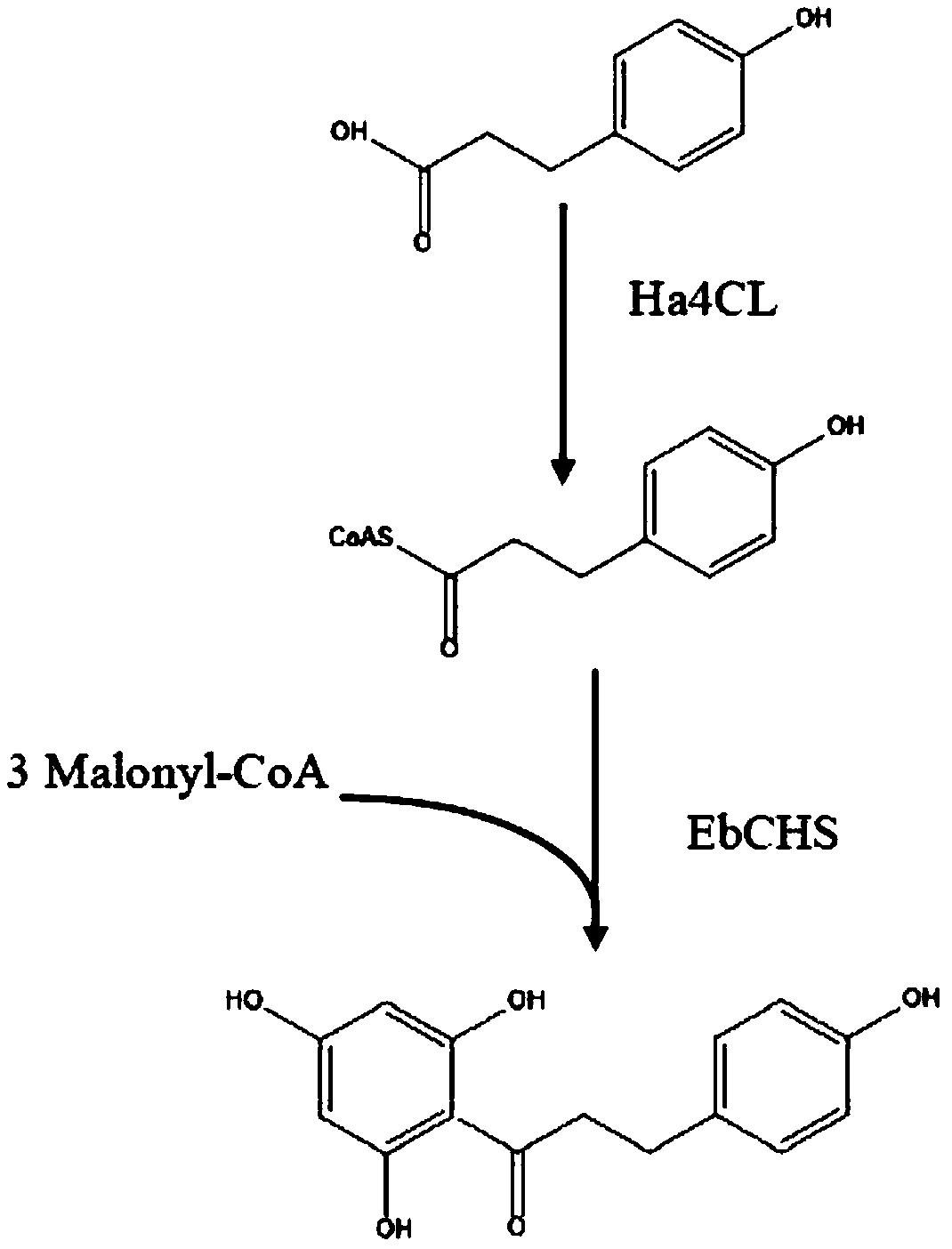
Method for producing phloretin by fermentation of saccharomyces cerevisiae
ActiveCN107586795ALow costFriendly and easy to controlMicroorganism based processesFermentationFermentationPollution
The invention relates to a method for producing phloretin by fermentation of saccharomyces cerevisiae. The method is completed by performing catalysis on p-hydroxyphenylpropionic acid serving as a rawmaterial and the saccharomyces cerevisiae serving as host bacteria through a plurality of enzymes in the host bacteria. Compared with the prior art, the method disclosed by the invention is characterized in that (1) by taking a low-cost compound as the raw material, the technological raw material is low in cost; (2) on the technical basis of modification of microorganisms, catalytic synthesis ofbiological enzymes is carried out in the microorganisms, so that large-scale extraction, separation and purification processes are avoided, and the production cost and the environmental protection areeasy to control; (3) the scale and the quantity of production equipment in the process are less than the scale and the quantity in other methods, and industrial transformation is facilitated; (4) separation and purification procedures are only carried out in the last step of the production in the process, so that a product purification process is simple, the product quality is higher than that ina general method, and the content is higher; (5) no waste liquid is discharged in a synthesis process, so that the method is environmentally friendly and pollution-free and can realize sustainable production.
Owner:嘉兴欣贝莱生物科技有限公司
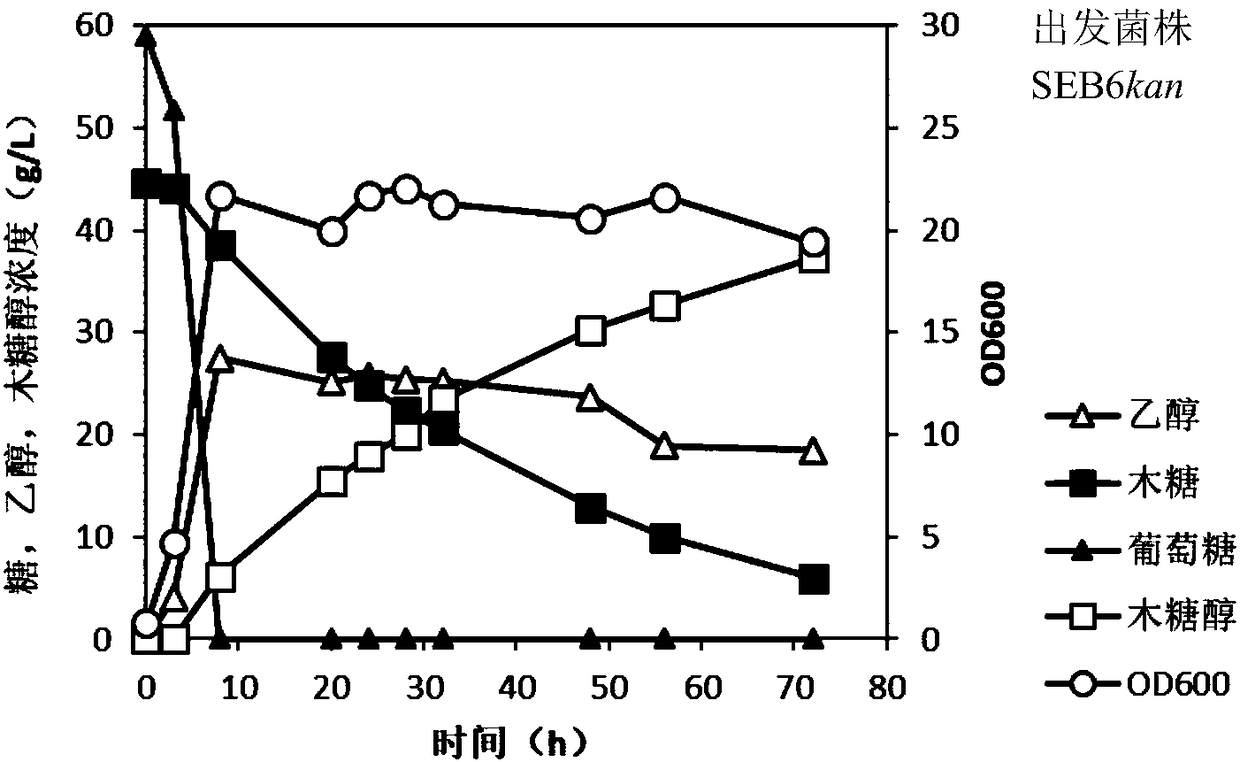
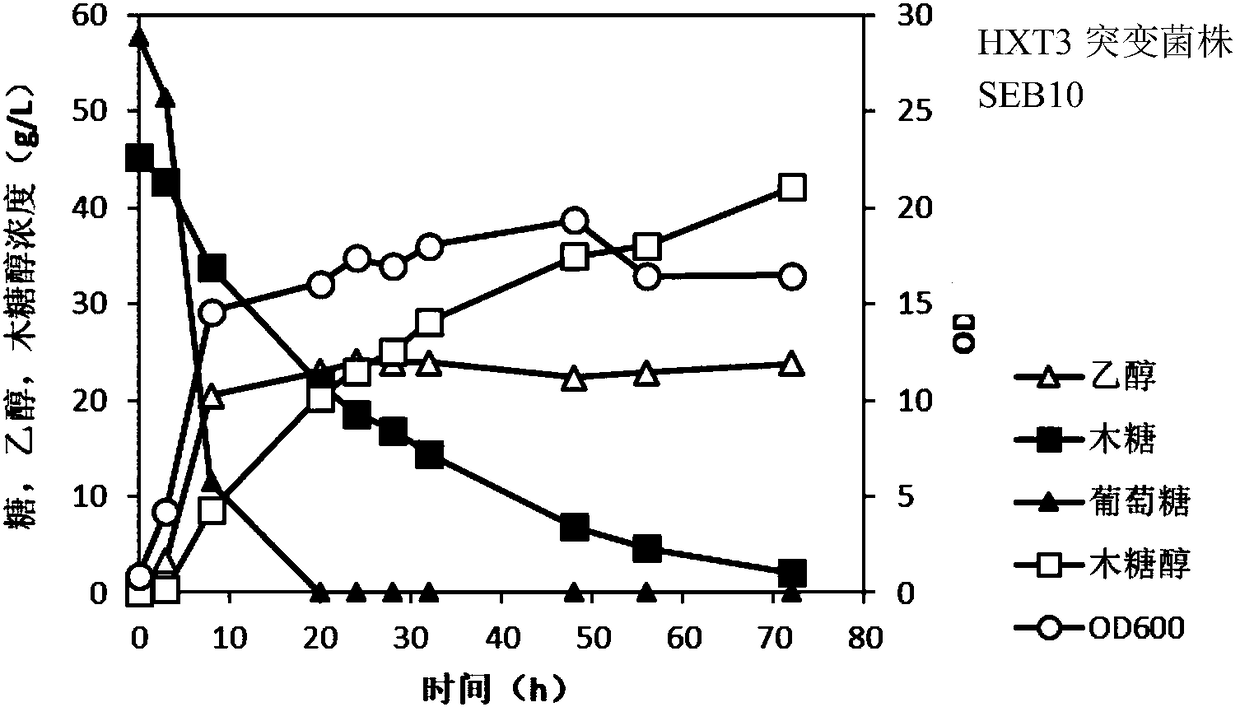
Industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for high-yield production of xylitol and ethanol by co-fermenting xylose and glucose and construction method
InactiveCN108300671AAccurate and fast positioningIncrease consumption rateFungiVectorsConcentrations glucoseXylose
The invention discloses an industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain for high-yield production of xylitol and ethanol by co-fermenting xylose and glucose. The industrial Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain is SEB10 with a preservation number of CGMCC NO. 14777. The invention further relates to a construction method of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain, and the method comprises the following steps:selecting an original strain; using a Cre-LoxP system to knock out a KanMX gene of the original strain and construct an SEB6kan strain; mutating an HXT3 gene of the SEB6kan strain by using a CRISPR / Cas9 system to construct an SEB6kan-M-HXT3 strain. Through a CRISPR / CasS9 gene editing technology, the 367th site of a transport protein HXT3 can be rapidly and accurately mutated from asparagine to alanine at a fixed point; under the condition with high initial glucose concentration, the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain prepared according to the construction method provided by the invention improvesthe xylose transport rate, thereby improving the capability of Saccharomyces cerevisiae to co-ferment xylose and glucose and improving the performance of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce xylitol and ethanol; under the condition with a fermentation tank, the xylose consumption rate is increased by 12%, the xylitol production is increased by 13%, the ethanol production is increased by 22%, and the xylitol yield is close to a theoretical value of 1.0.
Owner:SINOPEC SHANGHAI ENG +2
Secretion expression of antibiotic peptide cad in bacillus subtilis and expression system of recombination bacillus subtilis
ActiveUS20120009625A1Easy culture conditionIncrease the propagation speedBacteriaPeptidesAntimicrobial peptidesFeed additive
The present invention relates to a method for expressing antimicrobial peptide CAD by means of a recombinant Bacillus subtilis expression system. The SUMO protease expression operon is first artificially synthesized. The protein expression operon genes of Saccharomyces cerevisiae small ubiquitin-related protein is then fused with the antibacterial peptide AD. The fusion protein is further cloned into the pNF11 plasmid to be introduced into Bacillus subtilis, thereby ensuring the induced expression of recombined Bacillus subtilis in shake flasks. The method has the advantages of a simple expression system, large-scale production, low production cost, strong biological activity and no toxic or harmful substance production. Moreover, the method provides a medicine with low price and strong antibacterial capacity for clinic disease prevention and treatment. This invention can also be used as a feedstuff additive.
Owner:LINZHOU SINAGRI YINGTAI BIOLOGICAL PEPTIDES CO LTD
Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain and application thereof in comprehensive utilizing xylose mother liquor and corn cob residues to produce xylitol
ActiveCN107384815AImprove toleranceEffective fermentationFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismAlcohol sugars
The invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae strain. The strain is named as saccharomyces cerevisiae genetically engineered bacterium X3kZPM, the strain is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection in twenty seventh of June, 2017, and a preservation number is CGMCC No.14362. The invention further discloses application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae in utilizing xylose mother liquor to produce xylitol or comprehensively utilizing the xylose mother liquor and corn cob residues to produce the xylitol. Experiments prove that a sugar alcohol converting rate is high and can reach 100% of a theoretical value when the saccharomyces cerevisiae genetically engineered bacterium disclosed by the invention is used; a concentration of the xylitol in fermentation liquor is obviously improved and reaches 83 to 91g L<-1>; the saccharomyces cerevisiae strain basically has actual industrialization potency and a wide industrialized application prospect.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Rhizopus strains, yeast strains, distiller's yeast containing same and production method for distiller's yeast
ActiveCN102041234AMeet different needsGuarantee standardized controlFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMixed culture
The invention relates to rhizopus strains, yeast strains, distiller's yeast containing the same and a production method for the distiller's yeast. The invention relates to rhizopus oryzae strains CCTCC No: M209191 and CCTCC No: M209232, saccharomyces cerevisiae strains CCTCC No: M209190 and CCTCC No: M209231, and rice distiller's yeast containing the strains. The method for producing the rice distiller's yeast comprises the following steps of: inoculating the rhizopus strains and the yeast strains into a culture medium, and performing mixed culture to obtain mixed culture yeast; inoculating the rhizopus strains into the culture medium, and performing rhizopus culture to obtain pure yeast; and blending the pure yeast and the mixed culture yeast in a certain ratio to obtain the rice distiller's yeast. The rhizopus strains and the yeast strains have good adaptability during mixed culture. The method can meet different requirements of customers on mouthfeel, and meanwhile guarantees standard control of product quality.
Owner:ANGELYEAST CO LTD
Activity expression and application of thermobifida fusca xylose isomerase in wine brewing yeast
The invention discloses a method for extraction of xylose isomerases by taking brown hot crack loving spore fungus as sources and the activity expression and application of the brown hot crack loving spore fungi xylose isomerases in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. The molecule weight of the brown hot crack loving spore fungi xylose isomerases is 43 kilodaltons; the most suitable reaction temperature of the xylose isomerases is 80 to 85 DEG C; and the most suitable reaction pH of the xylose isomerases is 7.0. The xylose isomerases can convert xyloses into xyluloses under normal biochemical reaction conditions; genes of the xylose isomerases can be recombined into the Saccharomyces cerevisiae in which the activity expression is realized, and the xyloses or other carbon sources such as lignocellulose hydrolysate and so on can be utilized for production of various fermentation products such as alcohols and so on. The method utilizes the genetic engineering means to expand substrates which are converted by the alcohols and has important theoretical significance and application value on full utilization of lignocellulose resources.
Owner:GUANGXI ACAD OF SCI
Saccharomyces cerevisiae integrated expression vector
InactiveCN103911371AGood toolMicroorganism based processesVector-based foreign material introductionProtein targetEukaryotic plasmids
The present invention discloses a saccharomyces cerevisiae integrated expression vector, and provides a double-stranded DNA fragment, which sequentially comprises elements such as a saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome upstream homology arm, an eukaryotic promoter, a saccharomyces cerevisiae IRES sequence, an eukaryotic screening gene, an eukaryotic transcription termination sequence and a saccharomyces cerevisiae chromosome downstream homology arm from upstream to downstream. The invention further relates to plasmid containing the double-stranded DNA fragment, wherein the plasmid is a saccharomyces cerevisiae integrated expression vector, can be provided for making exogenous or endogenous genes express in saccharomyces cerevisiae without induction, can adopt saccharomyces cerevisiae to produce the target protein, or can be used for metabolic pathway construction of genetic engineering strains. The saccharomyces cerevisiae integrated expression vector provides a good tool for protein expression and metabolic pathway construction of saccharomyces cerevisiae.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Micro-zoology preparations for feeding
The present invention provides a feed micro-ecological preparation. The preparation contains beneficial live bacteria whose total amount is 9 multiplied by 108CFU / g to 1 multiplied by 1010CFU / g; the lactobacillus delbrueckii content is 4multiplied by 108CFU / g to 1 multiplied by 1010CFU / g; the bacillus subtilis content is 4 multiplied by 108CFU / g to 1 multiplied by 1010CFU / g; the saccharomyces paradoxus content is 1multiplied by 108CFU / g to 1multiplied by 1010CFU / g. The present invention of a feed micro-ecological preparation contains live bacteria which are selected according to the features of animal intestinal tracts and have strong applicability on the intestinal tracts and are beneficial to keeping the micro-ecological balance in the internal environment of animal intestinal tracts; in this way, the present invention is important for the safety of livestock and fowl products and environmental protection.
Owner:CHANGSHA LVYE BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
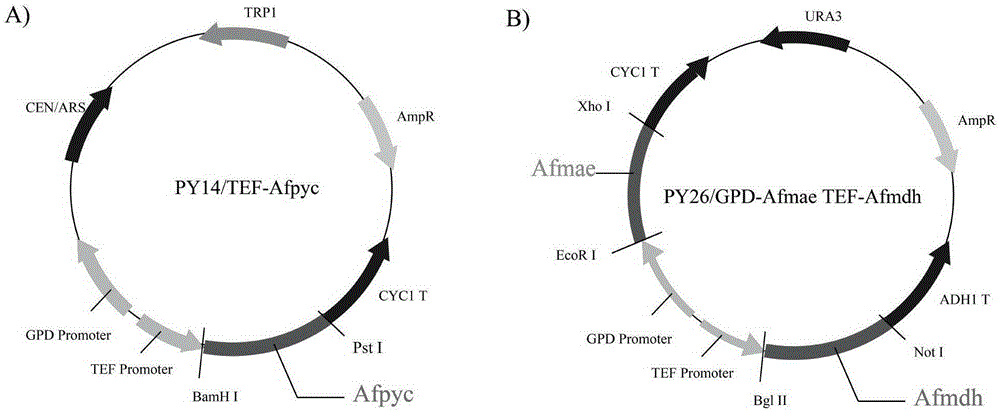
Establishment and application of brewing yeast engineering bacterium strain for producing L-malic acid
ActiveCN105400711ARealize accumulationFungiMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseTrimeresurus flavoviridis
The invention discloses establishment and application of a brewing yeast engineering bacterium strain for producing L-malic acid, and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. Genes of pyruvic carboxylase (Afpyc), malic dehydrogenase (Afmdh) and malic acid transport protein (Afmae) coming from Aspergillus flavus ATCC13697 are excessively and dissociatively expressed in the bacterium strain S.cerevisiae tTAM(delta)ura3(delta)trpl high in pyruvic acid yield, the malic acid accumulation path is established, and the bacterium W1101 is obtained. The bacterium strain is used for producing L-malic acid through fermentation; after fermentation is conducted for 84 h, the malic acid yield is 27.3 g / L; an original starting bacterium strain does not accumulate malic acid, the metabolism path of aspergillus flavus of the high-yield L-malic acid bacterium strain is successfully applied to brewing yeast, and a new strategy is provided for establishing the high-yield L-malic acid bacterium strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing ethanol by xylose fermentation and construction method thereof
The invention provides recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing ethanol by xylose fermentation and a construction method thereof. In the invention, candida boidinii is led to the saccharomyces cerevisiae to metabolize a DNA fragment of a coding gene of related enzymes of the xylose, so that the saccharomyces cerevisiae can secrete and express xylose isomerase the enzymatic reaction conditions of which are close to growth conditions of the saccharomyces cerevisiae, so the recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae can effectively utilize the xylose to produce the ethanol, thus solving the technical problem that the saccharomyces cerevisiae can not utilize the xylose to produce the ethanol. The invention lays a foundation for industrial application of the saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing the ethanol by using xylose fermentation, thus having great economic benefit and social benefit.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
Omega-3 desaturase from Phytophthora nicotianae, vector containing desaturase, recombinant microorganism and their application
The invention relates to a recombinant nucleotide sequence as shown in SEQ ID NO. 3 and used for encoding Omega-3 desaturase from Phytophthora nicotianae, a vector containing the Omega-3 desaturase, and a recombinant microorganism containing the vector, in particular recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae and also relates to a construction method of the recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae as well as application of the Saccharomyces cerevisiae containing the desaturase in the biological synthesis of polyunsaturated fatty acids. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae can catalyze C20:4<Delta5,8,11,14> into C20:5<Delta5,8,11,14,17> at normal temperature, with catalytic efficiency up to 65%.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Method for producing pyrroloquinoline quinine-containing table vinegar through co-culture and fermentation of microorganisms
ActiveCN110564580AImprove nutrition and health valueNovel methodBacteriaMutant preparationMicroorganismHyphomicrobium
The invention discloses a method for producing pyrroloquinoline quinone table vinegar through co-culture and fermentation of microorganisms, and belongs to the technical field of table vinegar brewing. A co-culture system is constructed by saccharomyces cerevisiae, hyphomicrobium and acetobacter pasteurianus, and the table vinegar rich in pyrroloquinoline quinone is produced. The table vinegar rich in pyrroloquinoline quinone is prepared by adopting a method of co-culturing saccharomyces cerevisiae, hyphomicrobium and acetobacter pasteurianus microorganisms through the stages of alcoholic fermentation, acetic fermentation, fermentation stopping, product filtering and packaging and the like, and the concentration of pyrroloquinoline quinone is 0.05-0.2 mg / L. The method is novel, the microorganism co-culture method is adopted, nutritional factors are combined with the table vinegar, the nutritional and healthy value of the table vinegar is increased, and feasibility is achieved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG GONGSHANG UNIVERSITY
Poultry and livestock intestinal ecological restoration microbial agent with virus and pathogenic bacteria-resisting functions and antibiotic-replacing effect and preparation method thereof
The invention discloses a poultry and livestock intestinal ecological restoration microbial agent with virus and pathogenic bacteria-resisting functions and antibiotic-replacing effect and a preparation method thereof. The poultry and livestock intestinal ecological restoration microbial agent is prepared by mixing saccharomyces cerevisiae, candida utilis, bacillus subtilis, bacillus licheniformis, rhodopseudomonas palustris, lactobacillus plantarum, and lactobacillus rhamnosus. The preparation method comprises the following steps of respectively inoculating each strain into a corresponding sterilization culture medium, activating, and preparing a first-level seed liquid; according to the neighboring and mutualism principle, during second-level and third-level fermenting, mixing and fermenting the saccharomyces cerevisiae and candida utilis, mixing and fermenting the bacillus subtilis and bacillus licheniformis, and mixing and fermenting the rhodopseudomonas palustris, lactobacillus plantarum and lactobacillus rhamnosus; mixing the three mixed and enlarged culture bacteria liquids according to the equal volume of 1:1:1, absorbing onto sterilizing wheat bran-rice bran, and performing solid fermenting and low-temperature drying, so as to obtain the solid microbial agent. The poultry and livestock intestinal ecological restoration microbial agent has the characteristics that the good properties of high density and high activity are realized; the probiotics microbial agent and the lemon and radix astragali seu hedysari water extracting liquid are compounded for first time; the usage amount is less, and the use method is simple and convenient.
Owner:道拓百旗(天津)房地产信息咨询有限责任公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com