Recombinant saccharomyces cerevisiae for producing ethanol by xylose fermentation and construction method thereof
A technology for recombining Saccharomyces cerevisiae and xylose isomerase, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of no enzyme activity of xylose isomerase, unfavorable yeast growth, slow xylose metabolism, etc., and achieve important economic and social benefits. Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0032] Example 1 Identification of xylose metabolism characteristics of Candida boidinii
[0033]Candida boidinii (CGMCC 2.1645, purchased from China General Microorganism Culture Collection and Management Center) was inoculated on YPD medium at 30°C for activation, and then inoculated on YP (without Glucose) plate medium, cultivated for 2 to 3 days, and as a result, all strains on the plate can use xylose to grow. Pick the cells with the largest colonies on the plate and inoculate them in YP liquid medium containing only xylose as the sole carbon source, and they can grow at 25-32°C and pH4.0-6.0. Explain that Candida boidinii can metabolize xylose.
Embodiment 2
[0034] The mensuration of xylitol content during the xylose fermentation of embodiment 2
[0035] Ferment xylose according to the conditions of Example 1, homogenate and break the cells, centrifuge at 5000 rpm for 5 minutes to obtain supernatant, take 10 mL of supernatant and boil at 100 ° C for 5 minutes, centrifuge to remove protein, and the supernatant after centrifugation is used for chromatographic detection. Agilent HPLC 2D chromatographic workstation: the chromatographic column is ZORBAX carbohydrate, the column temperature is 30°C, the mobile phase is acetonitrile:water (80:20 (V / V)), the flow rate is 1.5mL / min, and the differential refractive index detector detects. Xylitol was detected well within the range of 0.3-50.0 mg / mL. The results showed that xylitol was not detected.
Embodiment 3
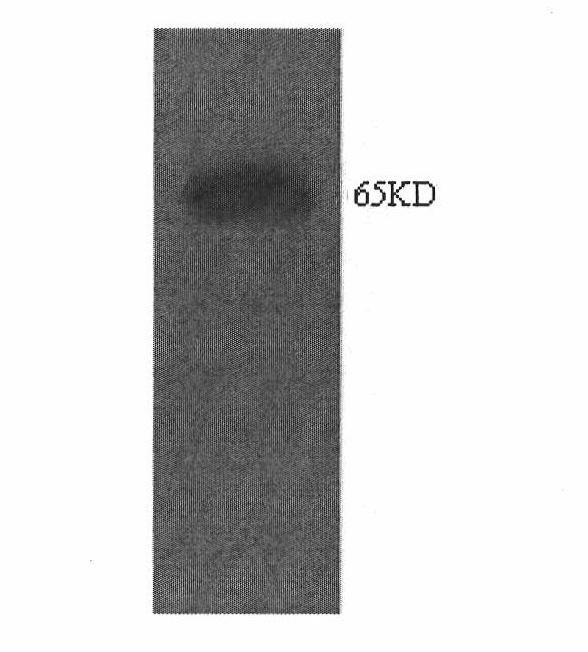
[0036] Example 3 Separation and purification of xylose isomerase and enzyme characteristics
[0037] The activated Candida boidinii is inoculated in YPD liquid medium containing 1% xylose, fermented at 25-32 DEG C and pH 4.0-6.0, and the fermented liquid is obtained for purification.
[0038] 1. Purification: ①. Adjust the pH of the fermentation broth to 7.0, add 2% protamine sulfate dropwise, let it stand for 30 minutes, and centrifuge to remove the precipitate. ②. Add 30% ammonium sulfate under the condition of pH 7.0, let it stand for 1 hour after dissolving, centrifuge to remove impurity protein, then add ammonium sulfate to make the saturation to 80%, stand overnight at 4°C, collect the precipitate by centrifugation, and re-dissolve in a small amount of buffer. ③. The above-mentioned concentrated enzyme solution is loaded onto DEAE-Sepharose column chromatography, and the active part is eluted by 0.1M NaCl and further concentrated. ④. The sample in step ③ was purified b...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com