Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
1746 results about "Impurity ions" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
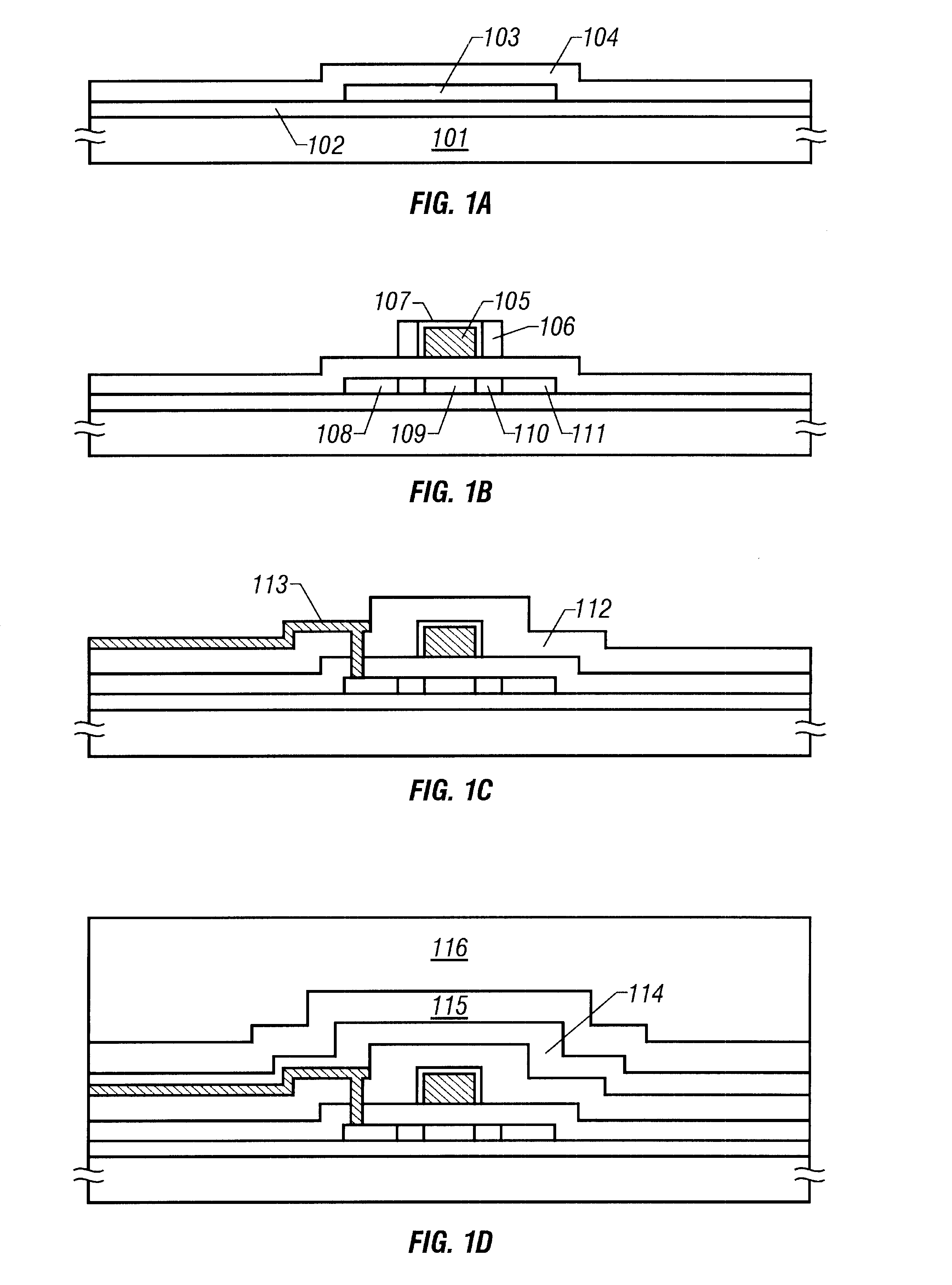
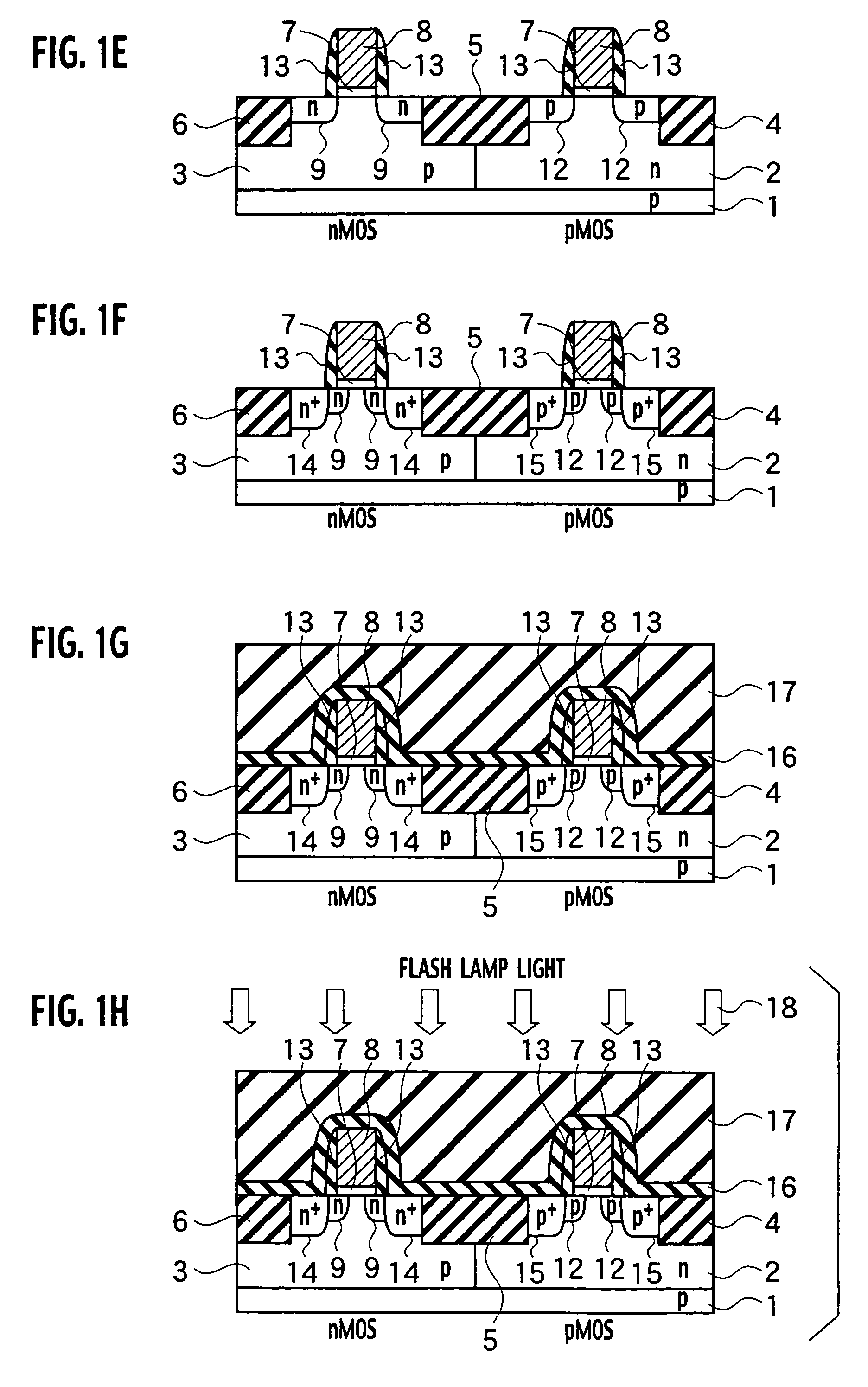
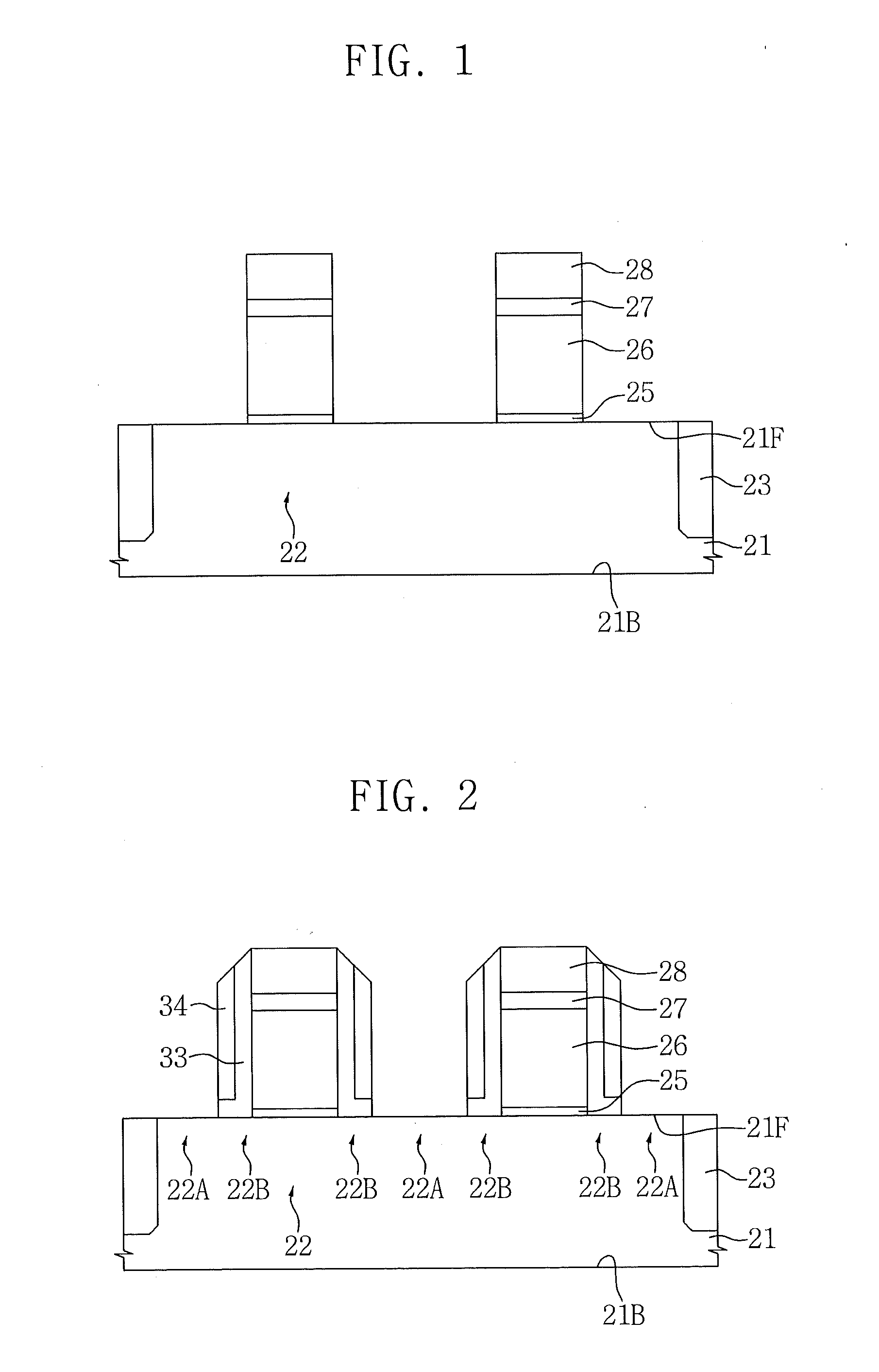
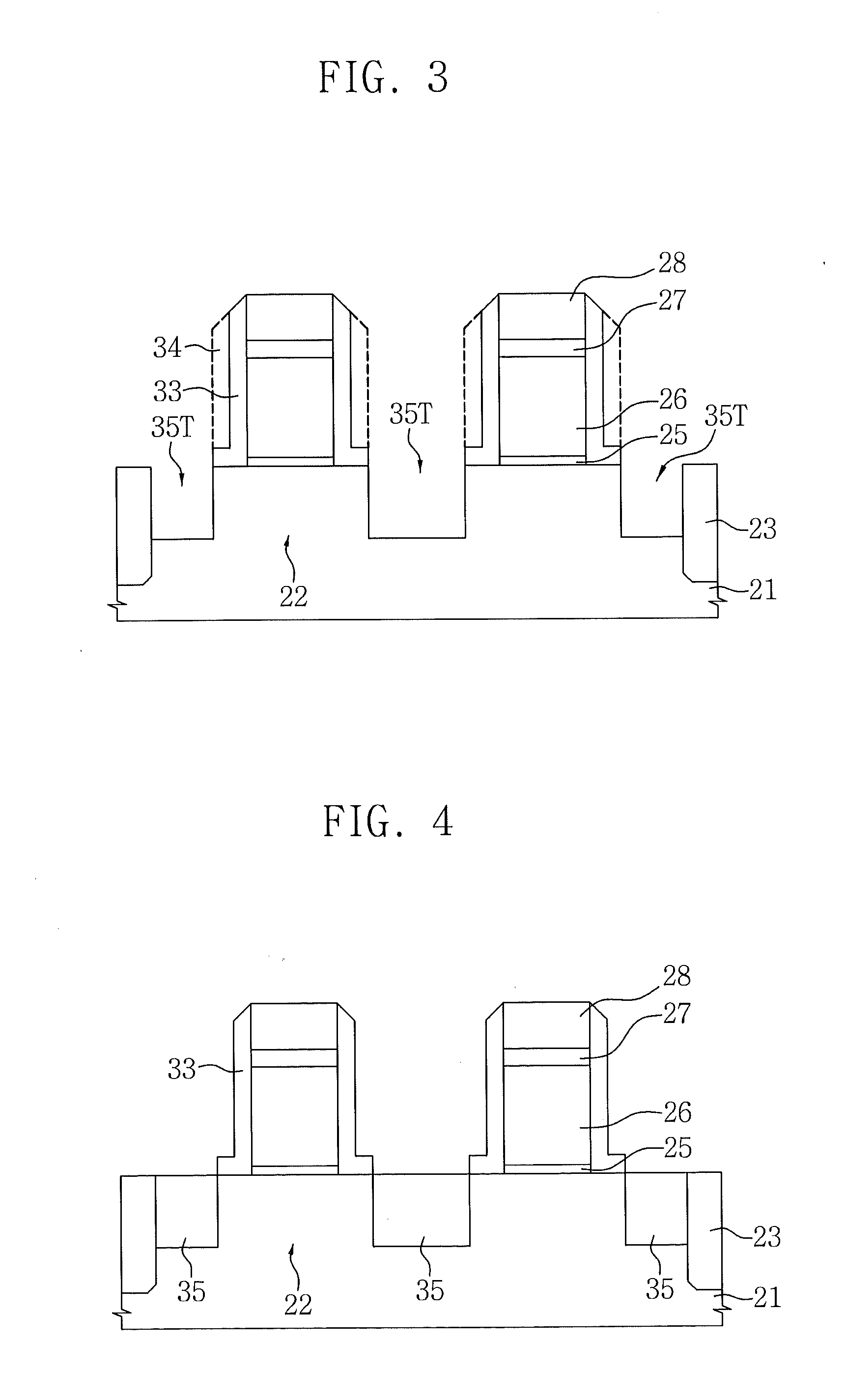
Method for doping impurities, methods for producing semiconductor device and applied electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20050181566A1Low level of contaminationReduce usageTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice materialImpurity ions
A solution containing impurity ions is applied onto the surface of a silicon film to form a solution layer, followed by drying into a compound layer containing the impurities. Heat treatment is performed by irradiation with an energy beam so as to diffuse the impurity atoms in the compound layer toward the silicon film into a source region and a drain region. Subsequently, the compound layer is removed.
Owner:SONY CORP
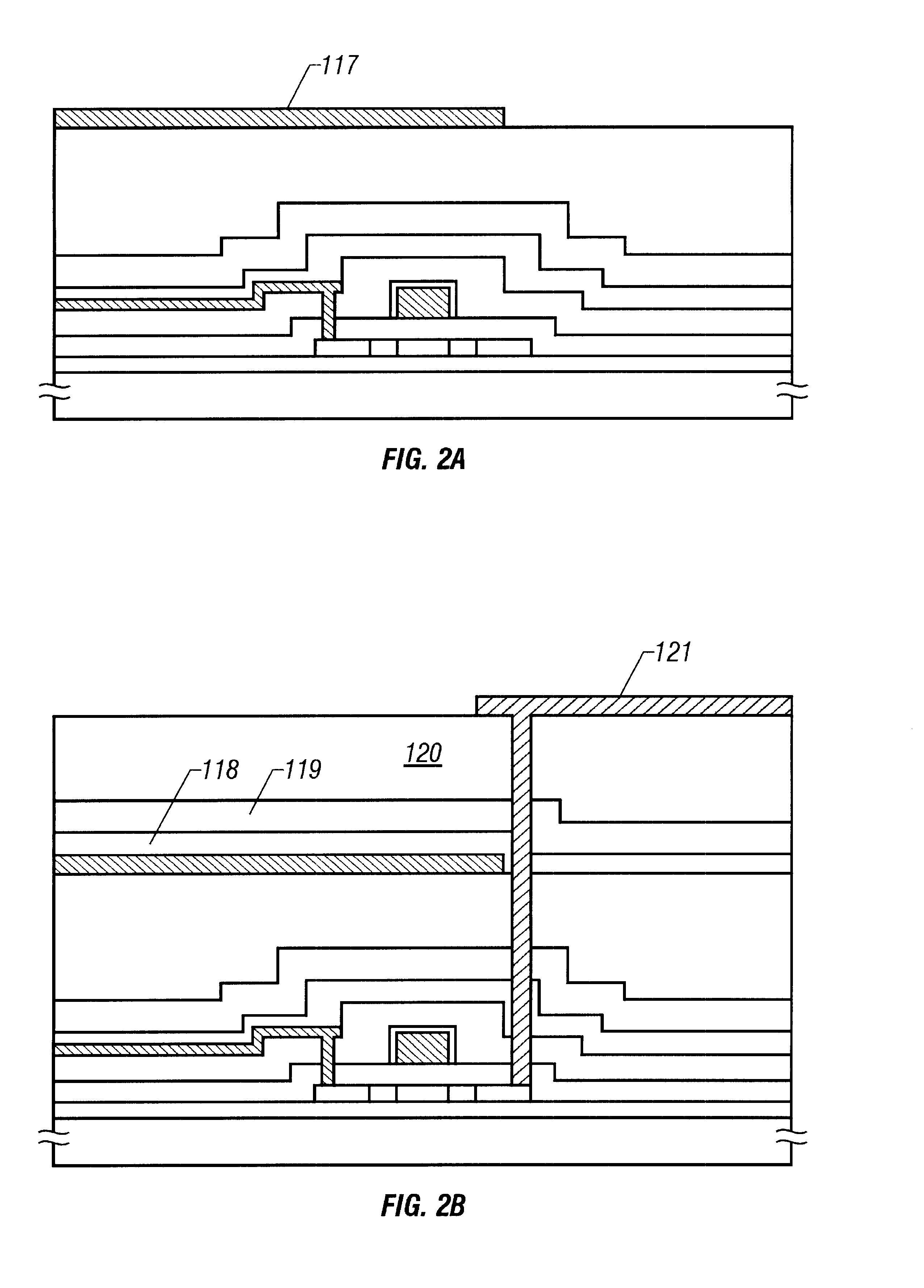
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS6445059B1Capacity producedReduce capacityTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsInter layerSilicon oxide
A resin material having low dielectric constant is used as an inter-layer insulating film and its bottom surface is contacted with a silicon oxide film across the whole surface thereof. Thereby, the surface may be flattened and capacity produced between a thin film transistor and an pixel electrode may be reduced. Further, it allows to avoid a problem that impurity ions and moisture infiltrate into the lower surface of the resin material, thus degrading the reliability of whole semiconductor device.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Semiconductor devices and dynamic random access memories having a retrograde region and methods of forming the same
InactiveUS20080169493A1Raise the threshold voltageEasy to limitTransistorFuel supply apparatusDevice materialImpurity ions
Semiconductor devices include an active region defined in a semiconductor substrate having first type impurity ions. A retrograde region is in the active region and has second type impurity ions. An upper channel region is on the retrograde region in the active region and has the first type impurity ions. Source and drain regions are on the upper channel region in the active region and spaced apart from each other. A gate electrode fills a gate trench formed in the active region. The gate electrode is disposed between the source and drain regions and extends into the retrograde region through the upper channel region. DRAM devices and methods are also provided.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Preparation method of suspension liquid and powder of graphene quantum dot
The invention discloses a preparation method of a suspension liquid and a powder of graphene quantum dots. The method includes following steps: preparing the suspension liquid of the graphene quantum dots in one step from fullerene in a manner of chemical oxidation cleavage, removing impurity ions from the suspension liquid, and then performing a drying process to obtain the powder of the graphene quantum dots. In the invention, problems of complex technology and high cost in preparation of the suspension liquid and the powder of the graphene quantum dots are solved. The preparation method is simple in operation, can quickly prepare the suspension liquid and the powder of the graphene quantum dots in macro scale in an amplifying manner and is high in yield. The graphene quantum dots are uniform in size distribution and are excellent in water solubility.
Owner:UNIV OF SCI & TECH OF CHINA
SOI structure having a sige layer interposed between the silicon and the insulator
InactiveUS20050242396A1Improve breakdown voltageImprove transconductanceTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureImpurity ions
A semiconductor structure and a method of manufacturing a silicon on insulator (SOI) structure having a silicon germanium (SiGe) layer interposed between the silicon and the insulator. According to one manufacturing method, a first SiGe layer, a silicon layer, and a second SiGe layer are epitaxially grown in sequence over a first substrate, and then an insulating layer is formed on the second SiGe layer. Then, impurity ions are implanted into a predetermined location of the first substrate underlying the first SiGe layer to form an impurity implantation region. A second substrate is bonded to the insulating layer on the first substrate. After the first substrate is separated along the impurity implantation region and removed, the first SiGe layer remaining on the surface of the separated region is removed so that the surface of the silicon layer may be exposed.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP +1
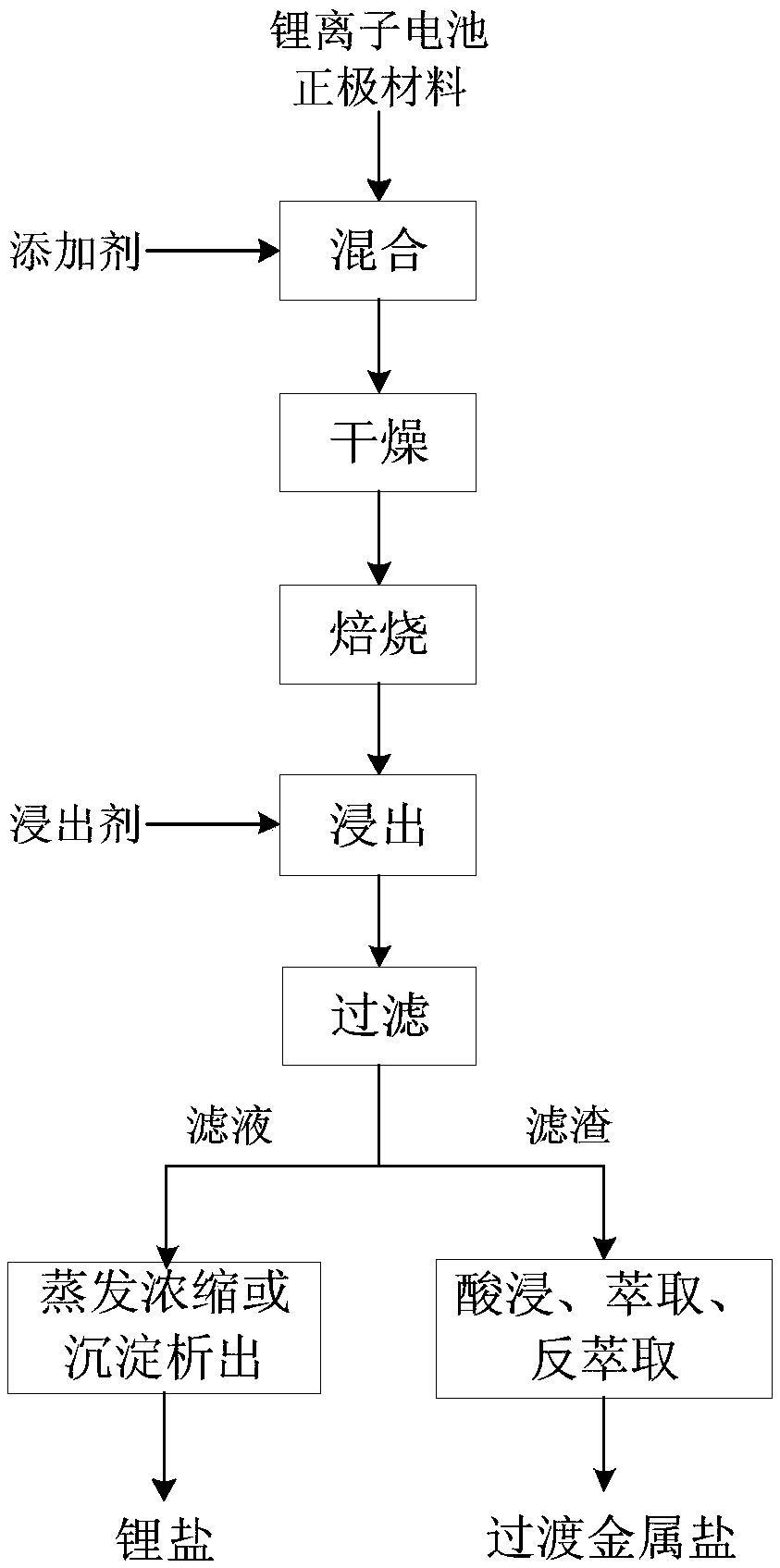
Full-component resource reclamation method for waste positive electrode materials of lithium ion batteries
ActiveCN102751549AAvoid secondary pollutionImprove separation efficiencyWaste accumulators reclaimingBattery recyclingRecovery methodDistillation
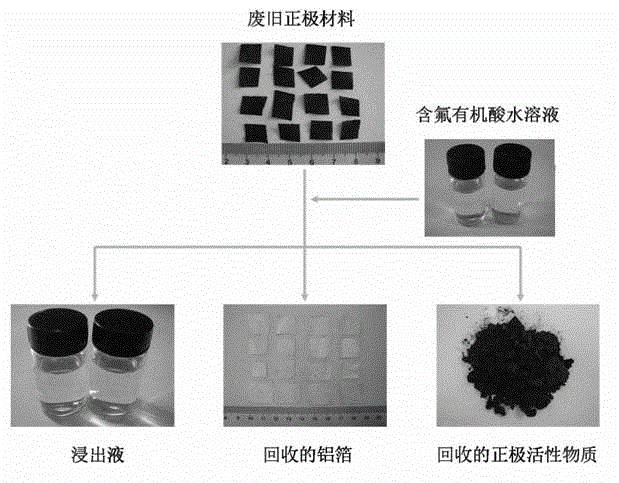
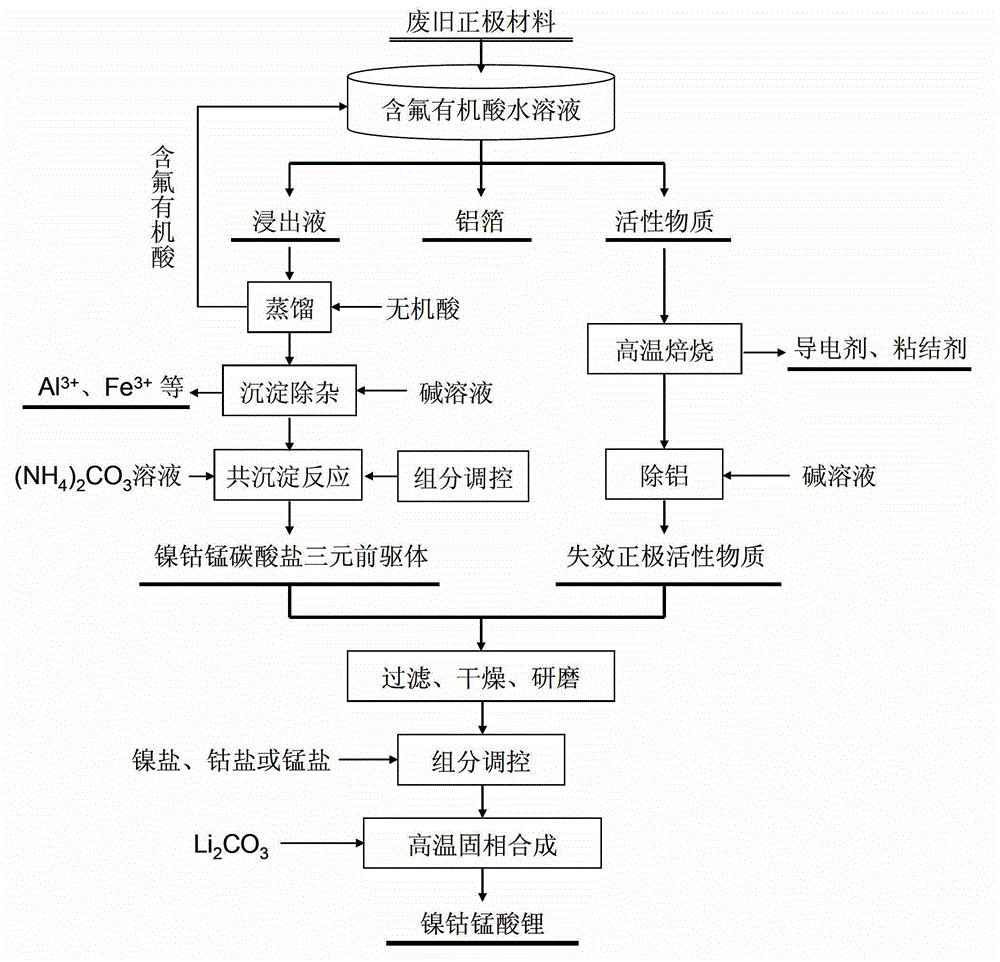
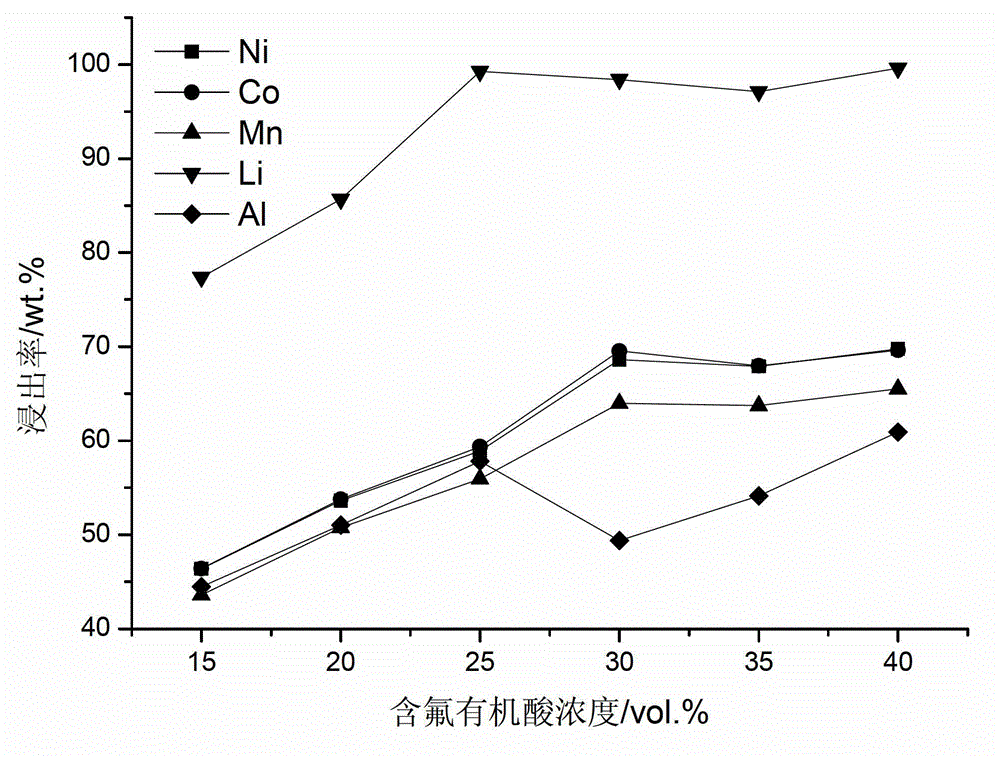
The invention provides a full-component resource reclamation method for waste positive electrode materials of lithium ion batteries. The method comprises the following steps: 1) separating active substances and aluminum foils in waste positive electrode materials of lithium ion batteries by using an aqueous solution of fluorine-containing organic acid and carrying out liquid-solid-solid separation so as to obtain leachate, the lithium-containing active substances and the aluminum foils; 2) respectively carrying out high temperature roasting and impurity removal with alkali liquor on the lithium-containing active substances; 3) respectively carrying out recovery of the fluorine-containing organic acid through addition of acid and distillation, deposition of impurity ions through addition of alkali and ammonium carbonate coprecipitation on the leachate so as to prepare nickel-cobalt-manganese carbonate ternary precursor; and 4) carrying out component regulation on a mixture of the treated active substances and the nickel-cobalt-manganese carbonate ternary precursor, adding lithium carbonate in a certain proportion and carrying out high temperature solid phase sintering so as to prepare a lithium nickel cobalt manganese oxide ternary positive electrode material. The method provided in the invention has the following advantages: the application scope of the method is wide; separation efficiency of the lithium-containing active substances and the aluminum foils is high; short-flow direct re-preparation of positive electrode materials in waste lithium ion batteries is realized; and the method is applicable to large-scale resource reclamation of waste lithium ion batteries.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
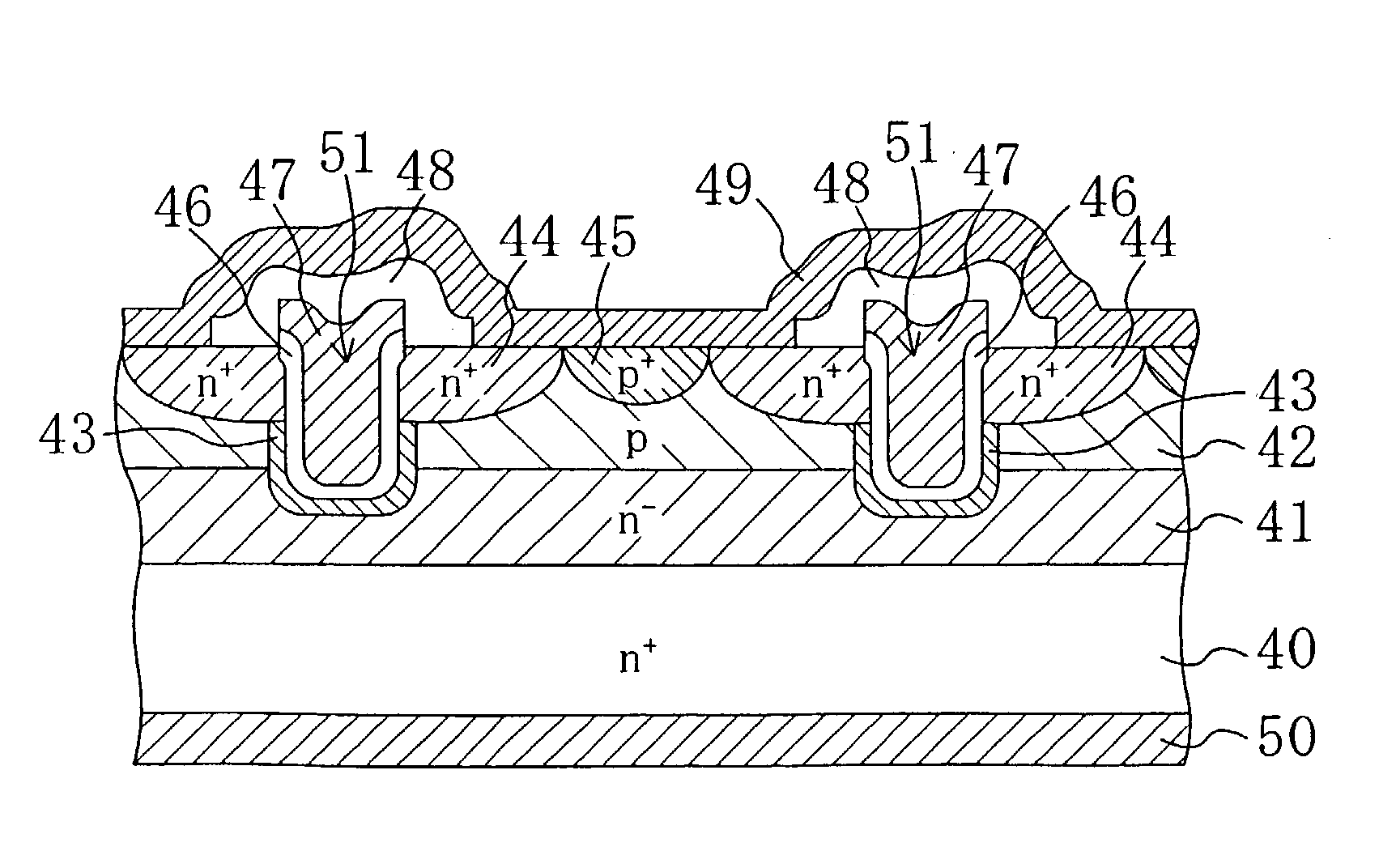
Fabrication method for a semiconductor device including a semiconductor substrate formed with a shallow impurity region
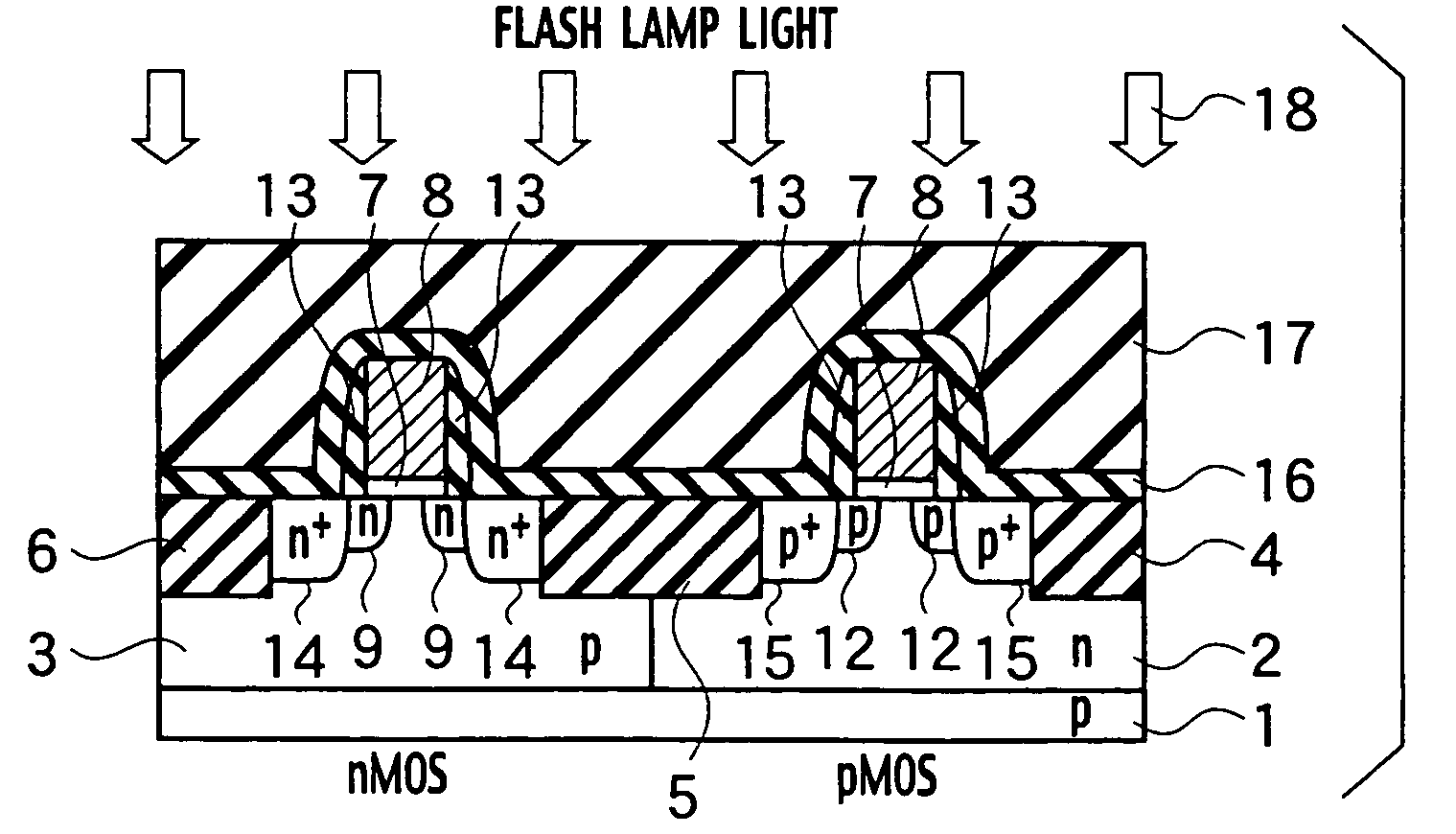
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device includes forming isolation regions, a gate insulator film and gate electrodes, implanting in the silicon substrate with impurity ions, annealing to recover crystallinity of the implanted silicon substrate without diffusing the impurity ions, depositing an interlayer insulator film on the isolation regions, the silicon substrate, and the gate electrodes, and heating the silicon substrate by irradiating a light having a wavelength that the light is absorbed by the silicon substrate without being absorbed by the interlayer insulator film, activating the impurity ions so as to form source and drain regions.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
Methods for fabricating a stressed MOS device
InactiveUS20070032024A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesStress inducedImpurity ions
A method for fabricating a stressed MOS device in and on a semiconductor substrate is provided. The method comprises the steps of forming a gate electrode overlying the semiconductor substrate and etching a first trench and a second trench in the semiconductor substrate, the first trench and the second trench formed in alignment with the gate electrode. A stress inducing material is selectively grown in the first trench and in the second trench and conductivity determining impurity ions are implanted into the stress inducing material to form a source region in the first trench and a drain region in the second trench. To preserve the stress induced in the substrate, a layer of mechanically hard material is deposited on the stress inducing material after the step of ion implanting.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES INC
Benzene selection noncrystalline catalyst with hydrogen added and containing ruthenium, boron as well as its preparing method
InactiveCN1446625AHigh catalytic efficiencyHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCatalyst activation/preparationBenzeneHydrogen
A non-crystal catalyst for preparing cyclodexene by selectively hydrogenating benzene is prepared from Ru, B meta or metal oxide modified M, and the oxide or metal hydroxide carrier L through reducing Ru ions and M in oxide form, and removing ions of impurities. Its advantage is high selectivity and hydrogenating activity.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
MEMS device and fabrication method thereof
InactiveUS20080093684A1Reduce resistanceLower the resistance valueSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingFlexible microstructural devicesImpurity ionsSilicon
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
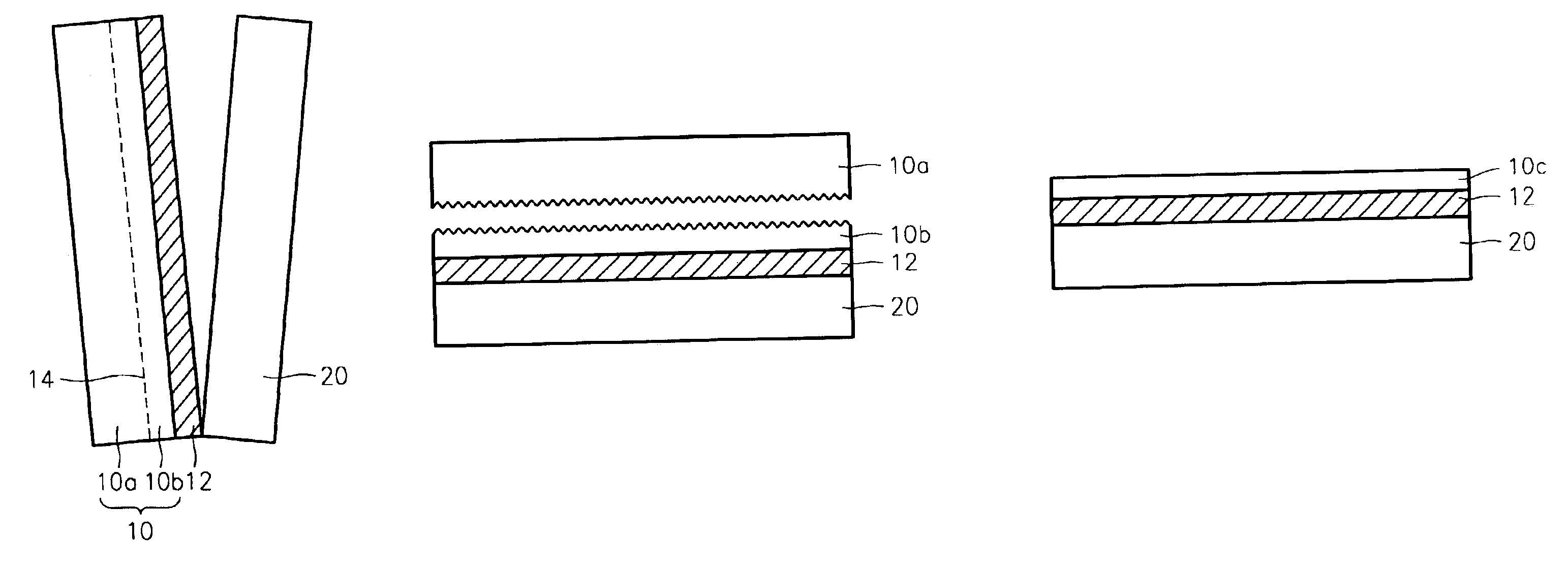
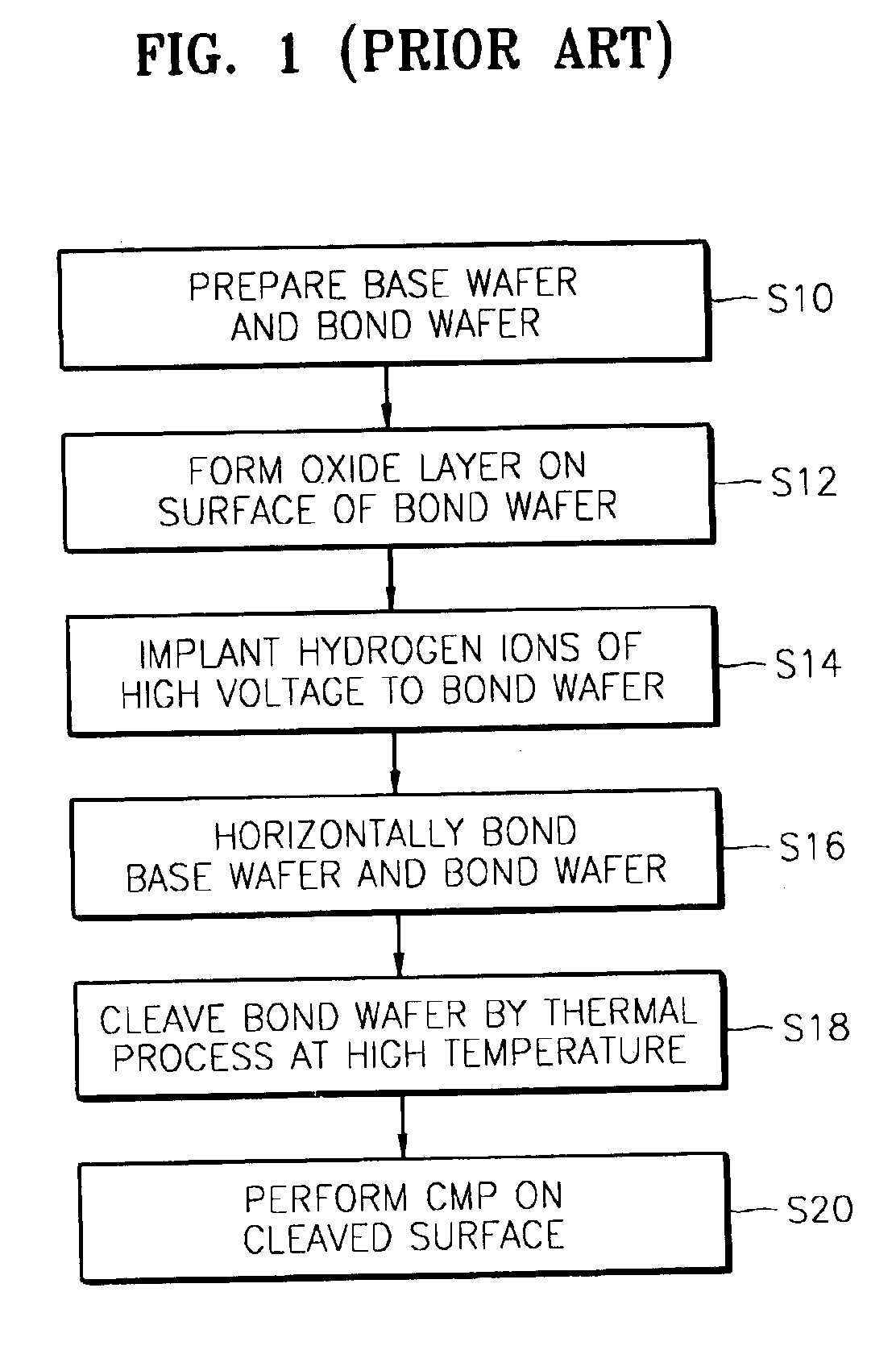
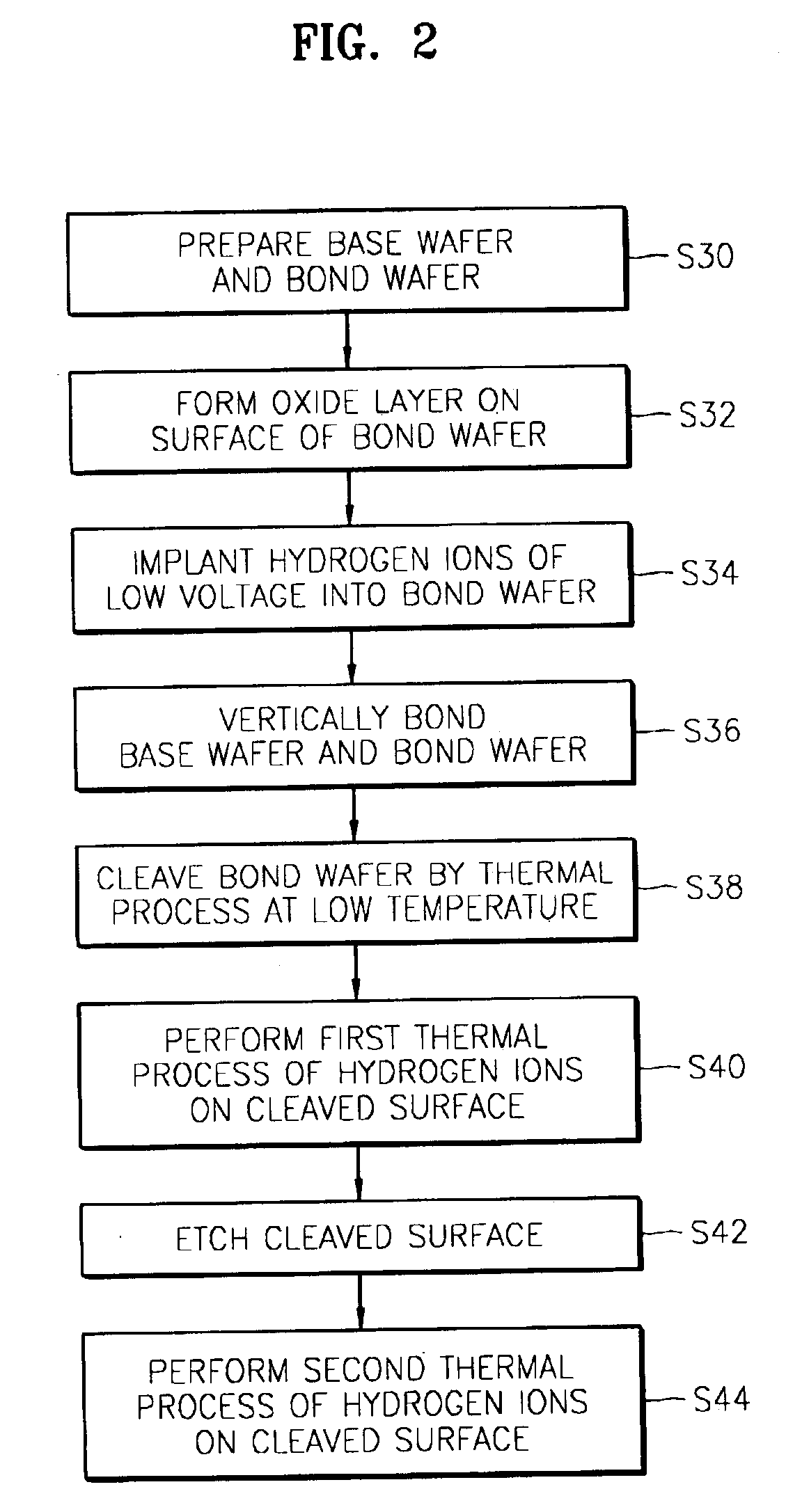
Method of fabricating nano SOI wafer and nano SOI wafer fabricated by the same
InactiveUS6884694B2Improve the bonding force between layersEtch thickness can be made uniformSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDielectricNano silicon
A method of fabricating a nano silicon on insulator (SOI) wafer having an excellent thickness evenness without performing a chemical mechanical polishing (CMP) and a wafer fabricated by the same are provided. The provided method includes preparing a bond wafer and a base wafer, and forming a dielectric on at least on surface of the bond wafer. Thereafter, an impurity ion implantation unit is formed by implanting impurity ions into the bond wafer to a predetermined depth from the surface of the bond wafer at a low voltage. The dielectric of the bond wafer and the base wafer contact each other in order to be bonded. Next, a thermal process of low temperature is performed to cleave the impurity ion implantation unit of the bond wafer. In addition, the cleaved surface of the bond wafer bonded to the base wafer is etched to form a nano scale device region. Here, the cleaved surface may be etched by performing a hydrogen surface process and a wet etching.
Owner:LG SILTRON +1
Method for forming a raised source and drain without using selective epitaxial growth
InactiveUS6090691AEasily controllable depthGood coplanaritySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor structureEngineering
A method for forming a raised source and drain structure without using selective epitaxial silicon growth. A semiconductor substrate is provided having one or more gate areas covered by dielectric structures. Doped polysilicon structures are adjacent to the dielectric structures on each side and are co-planar with the dielectric structures from a CMP process. The first dielectric structures are removed to form gate openings and a liner oxide layer is formed on the bottom and sidewalls of the gate openings. Dielectric spacers are formed on the liner oxide layer over the sidewalls of the gate openings, and the liner oxide layer is removed from the bottom of the gate openings and from over the doped polysilicon structures. Source and drain regions are formed in the semiconductor substrate by diffusing impurity ions from the doped polysilicon layer. A gate oxide layer and a gate polysilicon layer are formed over the semiconductor structure and the gate polysilicon layer is planarized to form a gate electrode. In a key step, the dielectric spacers are removed to form spacer openings, and impurity ions are implanted through the spacer openings and annealed to form source and drain extensions. The dielectric spacers are reformed and a self-aligned silicide layer is formed on the doped polysilicon structure and the gate electrode. Alternatively, the self-aligned silicide layer can be formed prior to removing the dielectric spacers and implanting ions to form source and drain extensions.
Owner:CHARTERED SEMICONDUCTOR MANUFACTURING
Method of manufacturing semiconductor device comprising high voltage regions and floating gates
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device includes the steps of preparing a substrate having a high-voltage applied region, a peripheral region, a cell region with at least first and second portions, the high-voltage applied region having a well formed therein; simultaneously forming a plurality of spaced floating gates on the first and second portions of the cell region and a plurality of spaced first gates on the high-voltage applied region; implanting first impurity ions in the high-voltage applied region of the substrate using the first gates as a mask to form a first impurity region, the floating gates masking the cell region from the first impurity ions; simultaneously forming control gates on the respective floating gates of the cell region and a plurality of spaced second gates on the peripheral region; selectively etching one of the control gates and one of the floating gates to form a plurality of gate patterns in the first portion of the cell region; and implanting second impurity ions in the substrate at sides of the gate patterns and at sides of the first gates to simultaneously form second impurity regions at sides of the gate patterns and twice implanted first impurity regions at sides of the first gates.
Owner:HYUNDAI MICRO ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Misfet
InactiveUS20030227061A1Improve electronic propertiesAvoid harmful effectsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImpurity ionsSic substrate
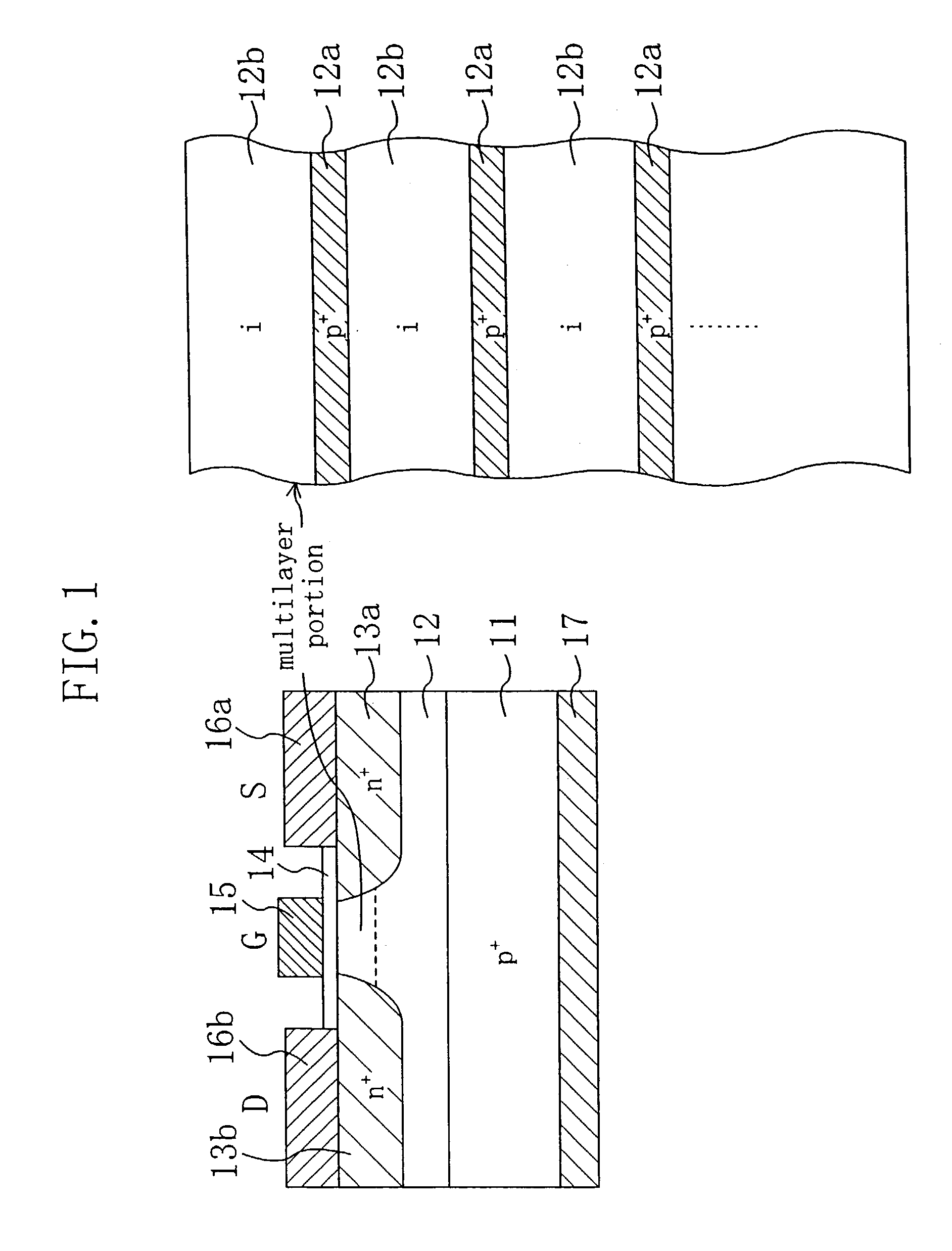
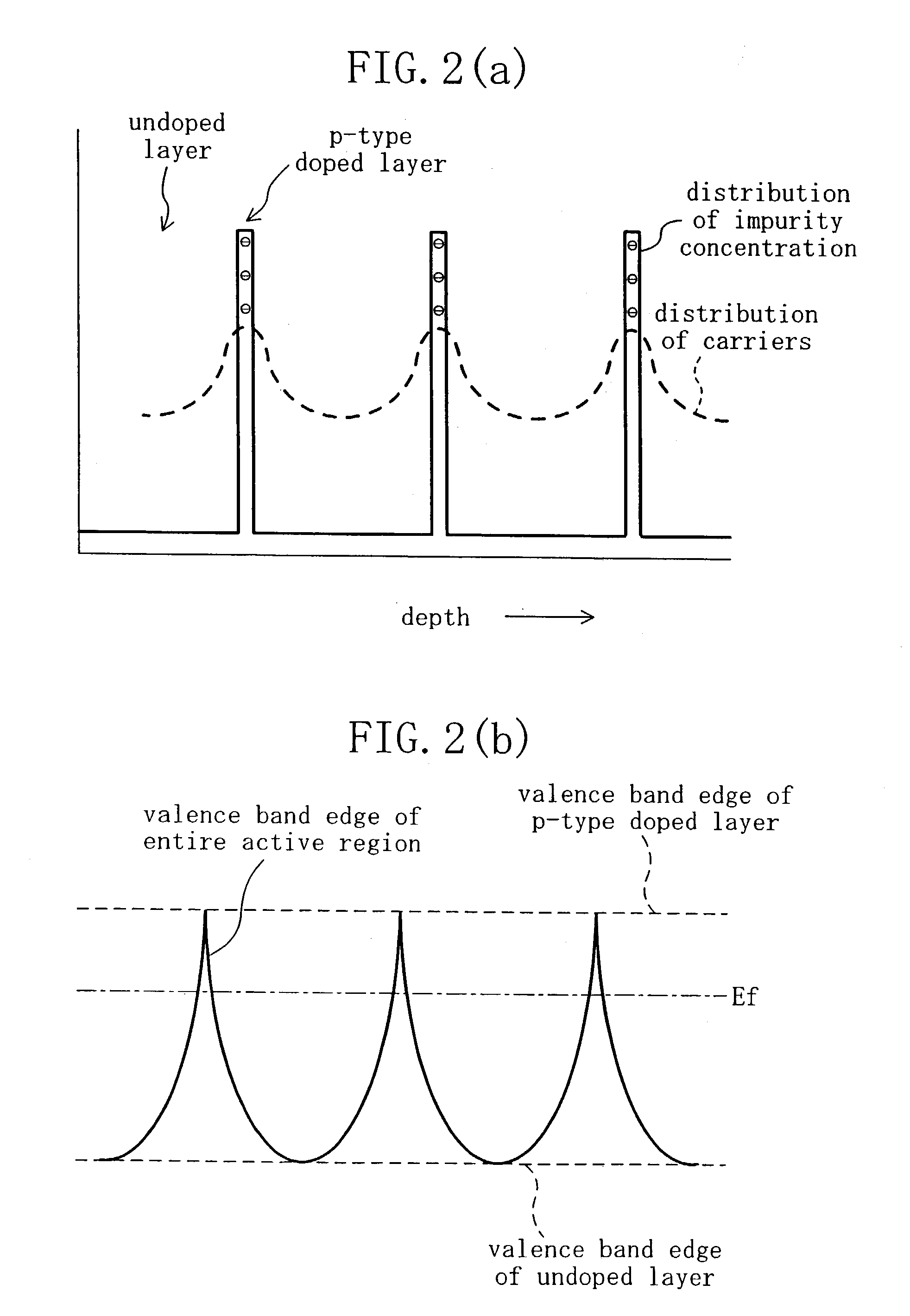
P-type active region 12; n-type source / drain regions 13a and 13b; gate insulating film 14 made of a thermal oxide film; gate electrode 15; source / drain electrodes 16a and 16b, are provided over a p-type SiC substrate 11. In the active region 12, p-type heavily doped layers 12a, which are thin enough to create a quantum effect, and thick undoped layers 12b are alternately stacked. When carriers flow, scattering of impurity ions in the active region is reduced, and the channel mobility increases. In the OFF state, a depletion layer expands throughout the active region, and the breakdown voltage increases. As a result of reduction in charges trapped in the gate insulating film or near the interface between the gate insulating film and the active region, the channel mobility further increases.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
CMOS image sensor and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS20050156213A1Minimise currentNot to damageSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCMOSImpurity ions
A CMOS image sensor and a method for fabricating the same are disclosed, in which the boundary between an active region and a field region is not damaged by ion implantation. The method for fabricating a CMOS image sensor includes forming a trench in a first conductive type semiconductor substrate, forming a first conductive type heavily doped impurity ion region in the semiconductor substrate at both sides of the trench, forming a device isolation film by interposing an insulating film between the trench and the device isolation, sequentially forming a gate insulating film and a gate electrode on the semiconductor substrate, and forming a second conductive type impurity ion region for a photodiode in the semiconductor substrate between the gate electrode and the device isolation film.
Owner:DONGBU HITEK CO LTD
Methods of fabricating a single transistor floating body DRAM cell having recess channel transistor structure
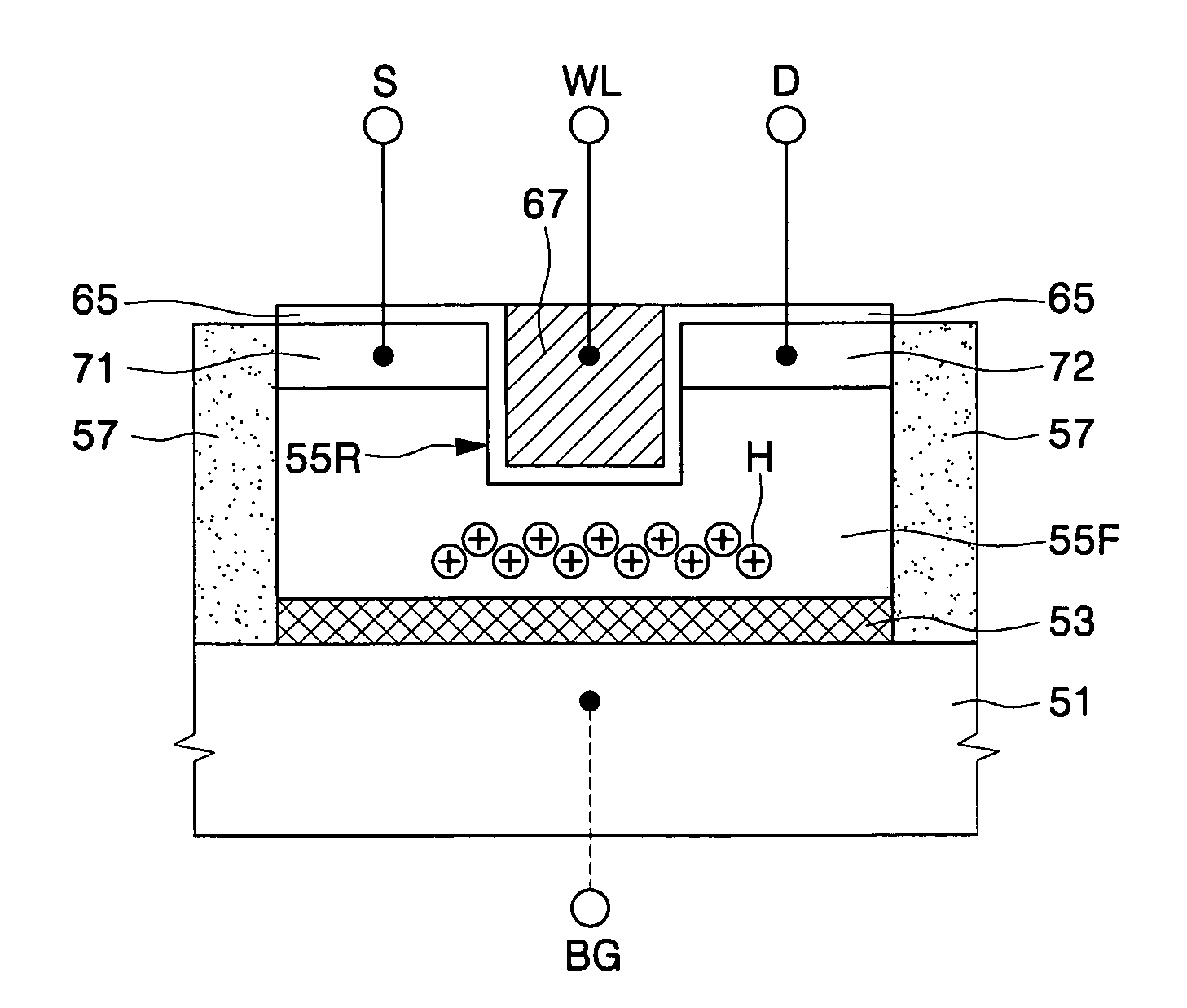
Methods of fabricating a single transistor floating body dynamic random access memory (DRAM) cell include forming a barrier layer on a semiconductor substrate. A body layer is formed on the barrier layer. An isolation layer is formed defining a floating body region within the body layer. A recess region is formed in the floating body region. A gate electrode is formed in the recess region. Impurity ions of a first conductivity type are implanted into a portion of the floating body region on a first side of the recess region to define a source region and into a portion of the floating body on an opposite side of the recess region to define a drain region to provide a floating body.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Titanium white for dry acrylic spinning delustering its preparing method
InactiveCN1858309ADry spinning methodsPigment treatment with organosilicon compoundsWeather resistanceWhite powder
The present invention discloses a kind of titanium white powder for extinction in dry spinning acrylic fiber and its preparation process. The titanium white powder is prepared with anatase type titanium white as material and through pulping, sanding milling, grading, purifying and other steps to eliminate coarse grains and impurity ions, coating with compact Al2O3 to obtain high weather resistance, water washing and coating with organic material. It has excellent dispersivity in spinning solution for dry spinning acrylic fiber and is used for extinction. It can result in excellent filtering performance and spinnability, low end breakage, high tow strength, high whiteness and high dyeability.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Methods of Forming Semiconductor Devices Having Faceted Semiconductor Patterns
ActiveUS20110230027A1TransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDevice materialImpurity ions
Provided are methods of forming semiconductor devices. A method may include preparing a semiconductor substrate including a first region and a second region adjacent the first region. The method may also include forming sacrificial pattern covering the second region and exposing the first region. The method may further include forming a capping layer including a faceted sidewall on the first region using selective epitaxial growth (SEG). The faceted sidewall may be separate from the sacrificial pattern. The sacrificial pattern may be removed. Impurity ions may be implanted into the semiconductor substrate.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
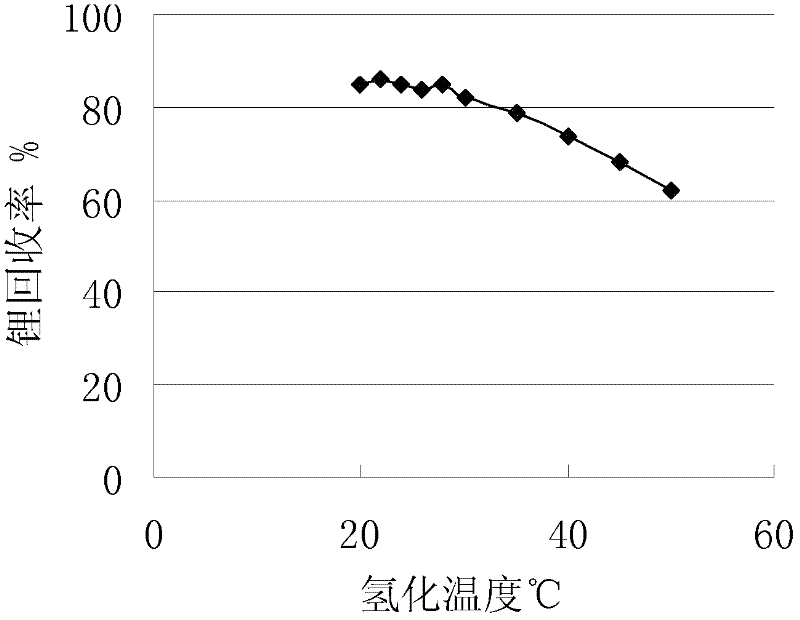
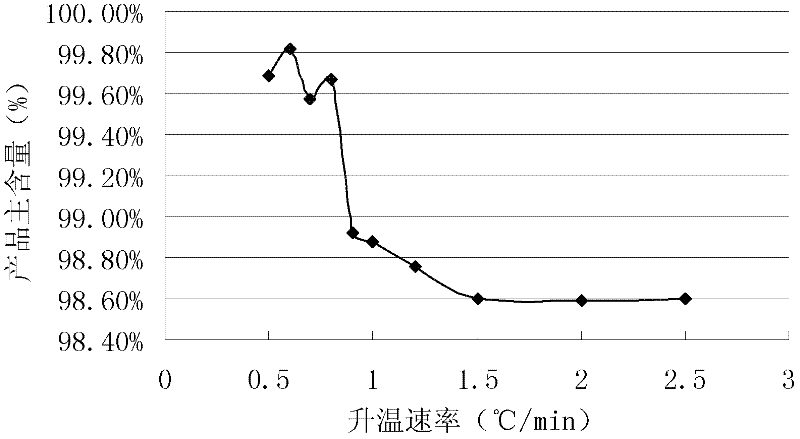
Method for purifying lithium carbonate
ActiveCN102531002ALow impurity contentImprove qualityLithium carbonates/bicarbonatesLithium oxideHydrogenation reaction
The invention relates to a method for purifying lithium carbonate, belonging to the technical field of the preparation of high-purity lithium carbonate. The method is characterized by safe production process and high lithium yield. The method comprises the following specific steps: (1) washing lithium carbonate to be purified to remove impurities, and adding water to prepare lithium carbonate slurry; (2) introducing CO2 into the lithium carbonate slurry prepared in the step (1) to carry out hydrogenation reaction, stopping introducing CO2 when the concentration of lithium oxide concentration in a solution is 10-30g / L, and filtering the solution to obtain a hydrogenated solution, wherein the hydrogenation reaction is carried out at the pressure of 0.2-0.6Mpa and the temperature of 20-30 DEG C; (3) subjecting the hydrogenated solution obtained in the step (2) to an ion exchange resin to remove impurity ions in the hydrogenated solution; and (4) heating the hydrogenated solution in which the impurity ions are removed in the step (3) to 70-90 DEG C to carry out decomposition reaction, separating solid from liquid to obtain the wet lithium carbonate, and drying the wet lithium carbonate. The produced battery-level lithium carbonate has high main content, excellent quality and stable performance.
Owner:天齐锂业(射洪)有限公司
Benzene selective hydrogenation carried ruthenium based catalyst and its preparation
InactiveCN1424293AHigh catalytic efficiencyHigh selectivityHydrocarbon by hydrogenationCatalyst activation/preparationBenzeneHydrogen
A Ru-base catalyst for selective hydrogenation of benzene to prepare cyclohexene is prepared from Ru, carrier (metal oxide), modifier M chosen from Cr, Mo, W, Fe, Co, Cu and La, and salt solution N through introducing hydrogen gas to aqueous solution to reduce Ru(OH)3 and M, and centrifugal washing to remove impurity ions. Its advantages are high activity and selectivity, and easy storage.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
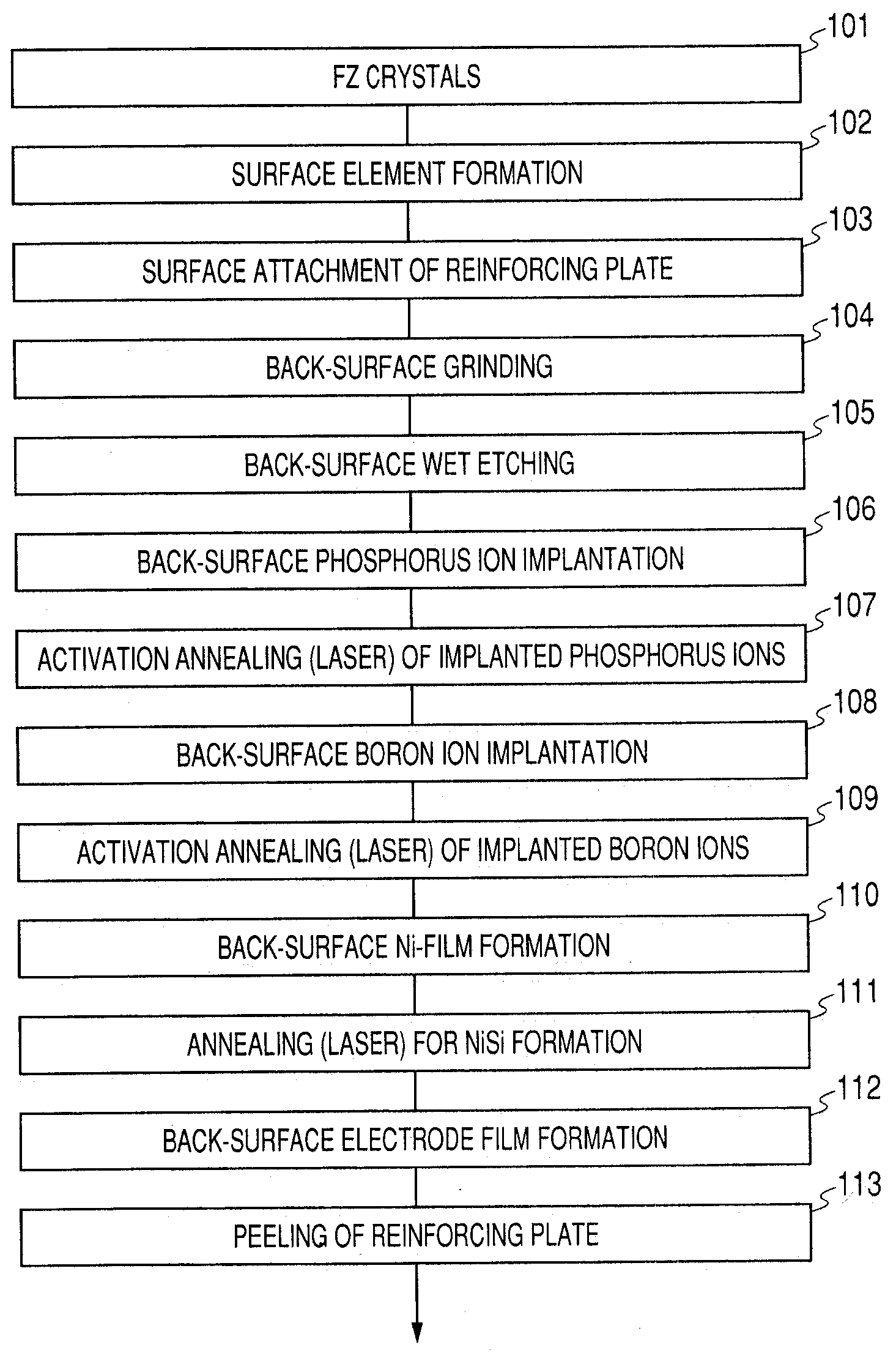
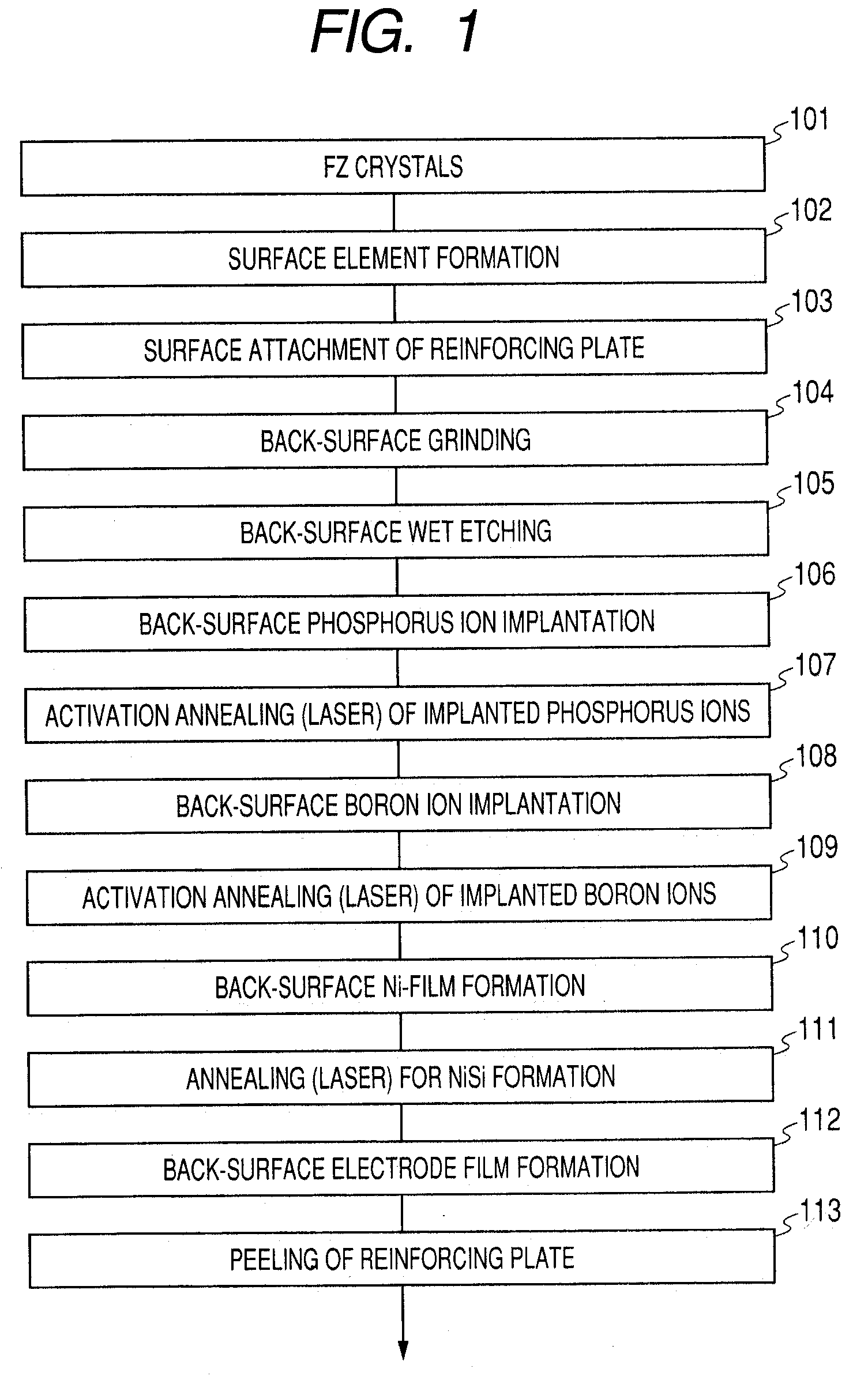
Doping method and manufacturing method for a semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050227463A1Semiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDevice materialImpurity ions
A doping method includes implanting first impurity ions into a semiconductor substrate, so as to form a damaged region in the vicinity of a surface of the semiconductor substrate, the first impurity ions not contributing to electric conductivity; implanting second impurity ions into the semiconductor substrate through the damaged region, the second impurity ions having an atomic weight larger than the first impurity ions and contributing to the electric conductivity; and heating the surface of the semiconductor substrate with a light having a pulse width of about 0.1 ms to about 100 ms, so as to activate the second impurity ions.
Owner:KIOXIA CORP
Semiconductor device including a semiconductor substrate formed with a shallow impurity region, and a fabrication method for the same
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device includes forming isolation regions, a gate insulator film and gate electrodes, implanting in the silicon substrate with impurity ions, annealing to recover crystallinity of the implanted silicon substrate without diffusing the impurity ions, depositing an interlayer insulator film on the isolation regions, the silicon substrate, and the gate electrodes, and heating the silicon substrate by irradiating a light having a wavelength that the light is absorbed by the silicon substrate without being absorbed by the interlayer insulator film, activating the impurity ions so as to form source and drain regions.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
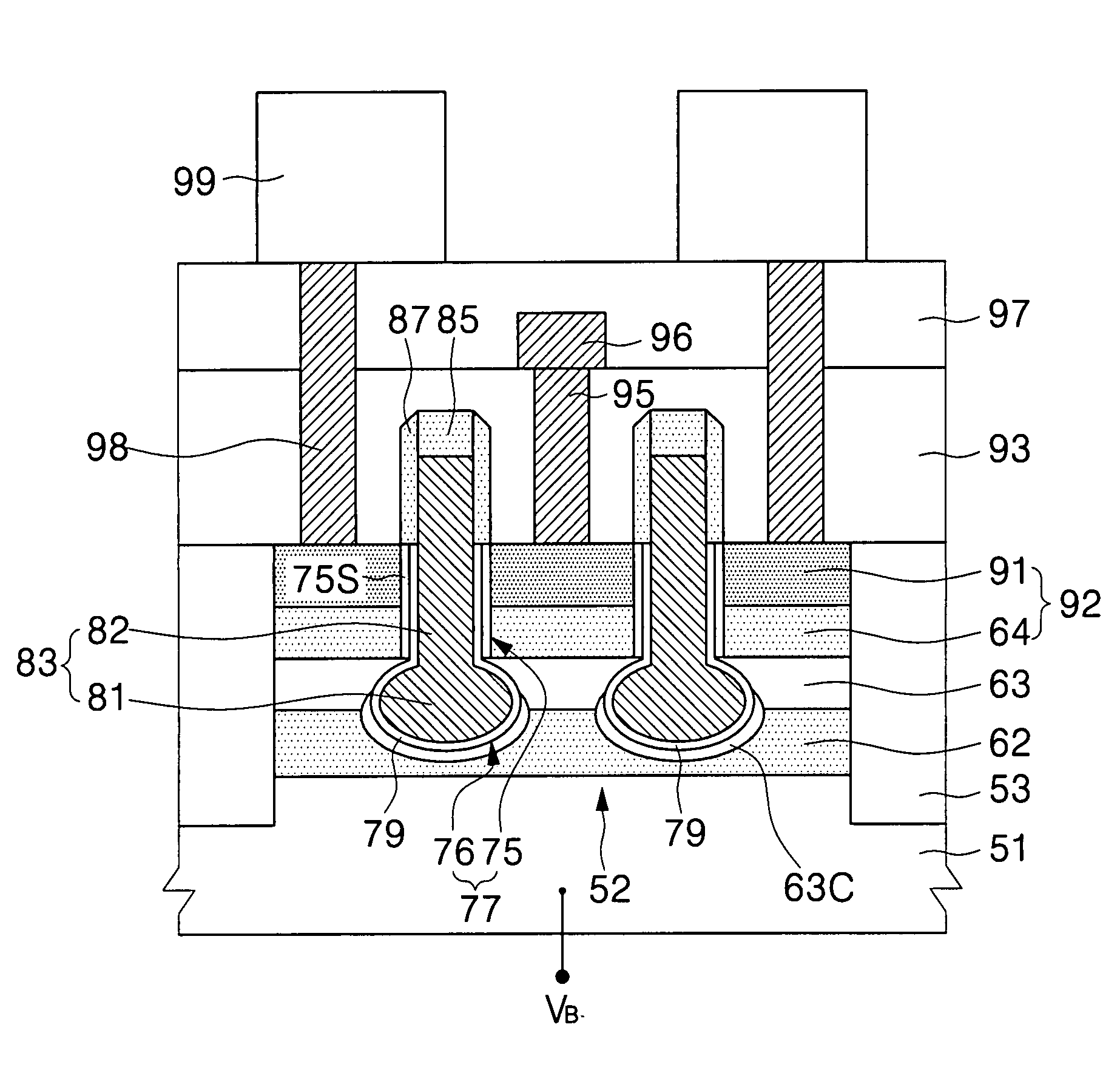
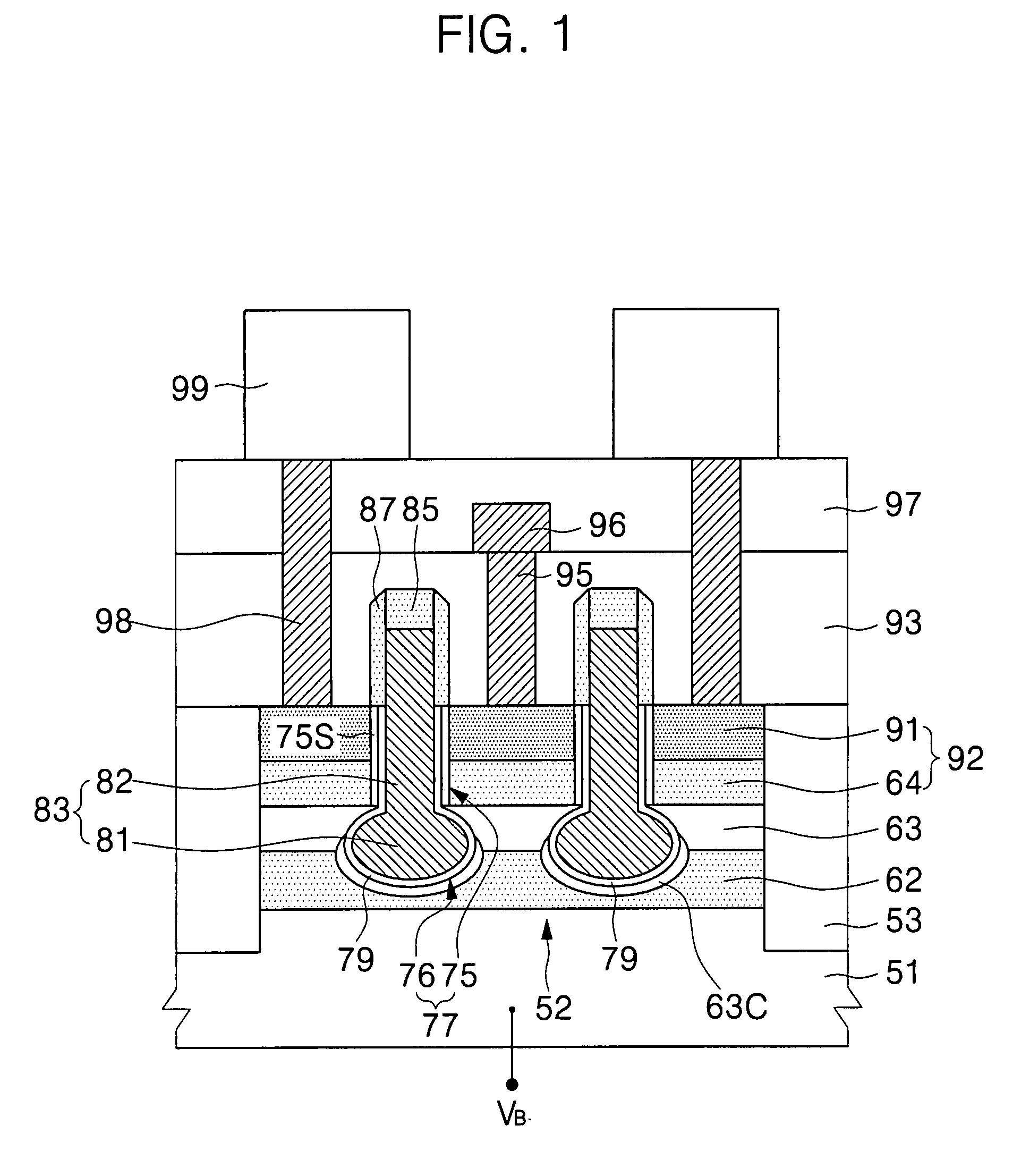
SONOS type memory device
InactiveUS7053448B2Shorten programming timeErasing timeTransistorSolid-state devicesData memoryImpurity ions
A SONOS type memory includes a semiconductor substrate, first and second impurity regions in the semiconductor substrate doped with impurity ions of a predetermined conductivity, separated a predetermined distance from each other, a channel region between the first and second impurity regions, and a data storage type stack on the semiconductor substrate between the first and second impurity regions. The data storage type stack includes a tunneling oxide layer, a memory node layer for storing data, a blocking oxide layer, and an electrode layer, which are sequentially formed. A dielectric constant of the memory node layer is higher than dielectric constants of the tunneling and the blocking oxide layers, and a band offset of the memory node layer is lower than band offsets of the tunneling and the blocking oxide layers. The tunneling oxide layer and the blocking oxide layer are high dielectric insulating layers.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Semiconductor device and method for fabricating the same
ActiveUS7348243B2Avoid short channel effectsProvide uniformSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesImpurity ionsOptoelectronics
A transistor and a method for fabricating the same is disclosed, to uniformly provide impurity ions in impurity areas, and to prevent a short channel effect, in which the method for fabricating the transistor includes steps of forming a plurality of channel ion implantation areas having different depths in a first conductive type semiconductor substrate; forming a pillar by selectively etching the first conductive type semiconductor substrate; sequentially depositing a gate insulating layer and a conductive layer for a gate electrode on the first conductive type semiconductor substrate including the pillar; forming the gate electrode by selectively patterning the conductive layer; and forming second conductive type source / drain impurity ion areas in the first conductive type semiconductor substrate corresponding to the top of the pillar and both sidewalls of the pillar.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD +1
Wiring material and a semiconductor device having wiring using the material, and the manufacturing method
InactiveUS6614083B1Improve adhesionHigh melting pointTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsActive matrixOxygen ions
An object of the present invention is to realize a semiconductor device having a high TFT characteristic. In manufacturing an active matrix display device, electric resistivity of the electrode material is kept low by preventing penetration of oxygen ion into the electrode in doping of an impurity ion. A display device having a low electric resistivity can be obtained.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
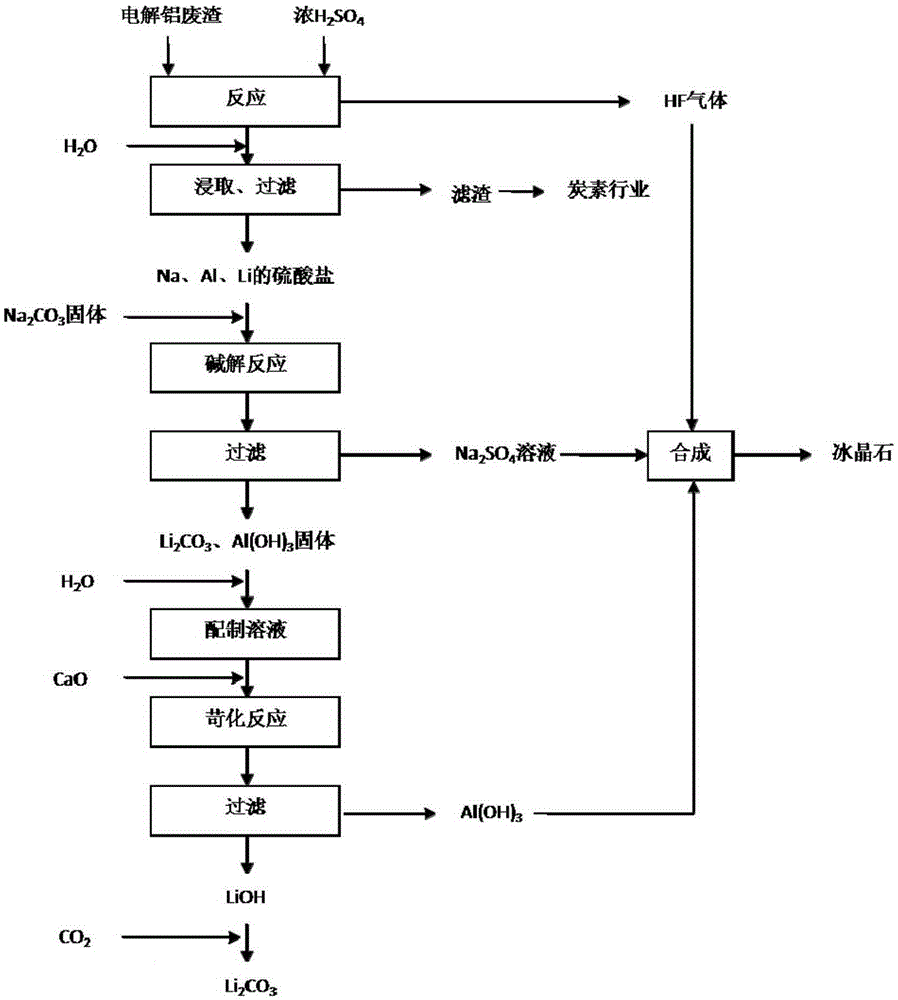
Method of extracting lithium from electrolytic aluminium waste residues
ActiveCN105293536ALow content of impurity ionsImprove product qualityProductsReagentsSocial benefitsLithium carbonate
The invention discloses a method of extracting lithium from electrolytic aluminium waste residues. The method comprises the following steps of performing a reaction on the electrolytic aluminium waste residues containing the lithium and concentrated sulfuric acid under the condition of 200 to 400 DEG C, and a mixture A is obtained; adding water into the mixture A, filtering after leaching to obtain filtrate A and a filter residue A; adding the filtrate A into sodium carbonate, and performing an alkaline hydrolysis reaction under the condition of 20 to 40 DEG C, then filtering to obtain filtrate B and a filter residue B; adding water into the filter residue B to prepare slurry, then adding lime into the slurry for a causticizing reaction, then filtering to obtain filtrate C and a filter residue C; feeding CO2 into the filtrate C in step 4) for a carbonization reaction, then filtering, washing, drying so as to obtain the lithium. The content of impurity ions in the obtained cell grade lithium carbonate is low, the quality of a product is excellent, and the problems of low yield, high production cost, weak market competitiveness when the lithium is extracted from ore to prepare the cell grade lithium carbonate at present are solved; a new process that a high value-added and high quality lithium product is produced by low-grade lithium resources is developed, the process is simple, the industrialized operation is liable to be realized, and the economic and social benefit is remarkable.
Owner:焦作多氟多实业集团有限公司
Akali zinc secondary cell and method for preparation thereof
InactiveUS20020164530A1Excellent in maintaining alkaline aqueous solutionIncrease internal resistanceCell seperators/membranes/diaphragms/spacersNon-aqueous electrolyte cellsAlkaline waterElectrical battery
An alkaline zinc secondary battery in accordance with the present invention comprises a separator layer comprising a gel electrolyte comprising a water absorbent polymer and an alkaline aqueous solution, disposed between a negative electrode comprising at least one selected from the group consisting of zinc and zinc oxide and a positive electrode. Because the separator layer is in a gel form, transfer of zinc ions is limited. Thereby, deformation of the negative electrode and generation of dendrite due to charge and discharge of the battery are substantially inhibited. Moreover, since impurity ions such as nitrate ions become less prone to move, self-discharge of the battery is also inhibited.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Method for selectively recycling positive electrode materials for lithium ion batteries
ActiveCN108832215AImplement selective extractionEasy to separateWaste accumulators reclaimingProcess efficiency improvementLiquid wasteSlag
The invention provides a method for selectively recycling positive electrode materials for lithium ion batteries. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out transformation processing aftermixing the recycling positive electrode materials for lithium ion batteries with an additive; leaching an obtained transformation product with a leaching agent, and carrying out solid-liquid separation to obtain a lithium-rich solution and a solid slag; and preparing the obtained lithium-rich solution into a lithium salt and the obtained solid slag into a transition metal salt. According to the method, recycling of valuable metals in the positive electrode materials for lithium ion batteries is realized by using in situ crystal transformation and mild leaching methods, particularly, selectiveextraction for lithium is realized, the recycle rate reaches 95% or above, and the recycle rate of other valuable metals such as nickel, cobalt and manganese reaches 98% or above; the method is shortin flow, other impurity ions are not introduced, the product purity is high, secondary pollution and liquid waste disposal can also be avoided, the recycle cost is saved, and the method is easy to realize industrial application.
Owner:INST OF PROCESS ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Solid-state imaging device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS7198976B2Quality improvementMiniaturizationTransistorSolid-state devicesImpurity ionsEngineering
Channel stop sections are formed by multiple times of impurity ion implanting processes. Four-layer impurity regions are formed across the depth of a semiconductor substrate (across the depth of the bulk), so that a P-type impurity region is formed deep in the semiconductor substrate; thus, incorrect movement of electric charges is prevented. Other four-layer impurity regions of another channel stop section are decreased in width step by step across the depth of the substrate, so that the reduction of a charge storage region of a light receiving section due to the dispersion of P-type impurity in the channel stop section is prevented in the depth of the substrate.
Owner:SONY CORP
Manufacturing method of a semiconductor device
ActiveUS20080076238A1Improve breakdown voltageImprove switching characteristicsSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesOhmic contactGold film
Provided is a technology of carrying out activation annealing of n type impurity ions implanted for the formation of a field stop layer (n+ type semiconductor region) and activation annealing of p type impurity ions implanted for the formation of a collector region (p+ type semiconductor region) in separate steps to adjust an activation ratio of the n type impurity ions in the field stop layer to 60% or greater and an activation ratio of the p type impurity ions in the collector region to from 1 to 15%. This makes it possible to form an IGBT having a high breakdown voltage and high-speed switching characteristics. Moreover, use of a film stack made of nickel silicide, titanium, nickel and gold films for a collector electrode makes it possible to provide an ohmic contact with the collector region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com