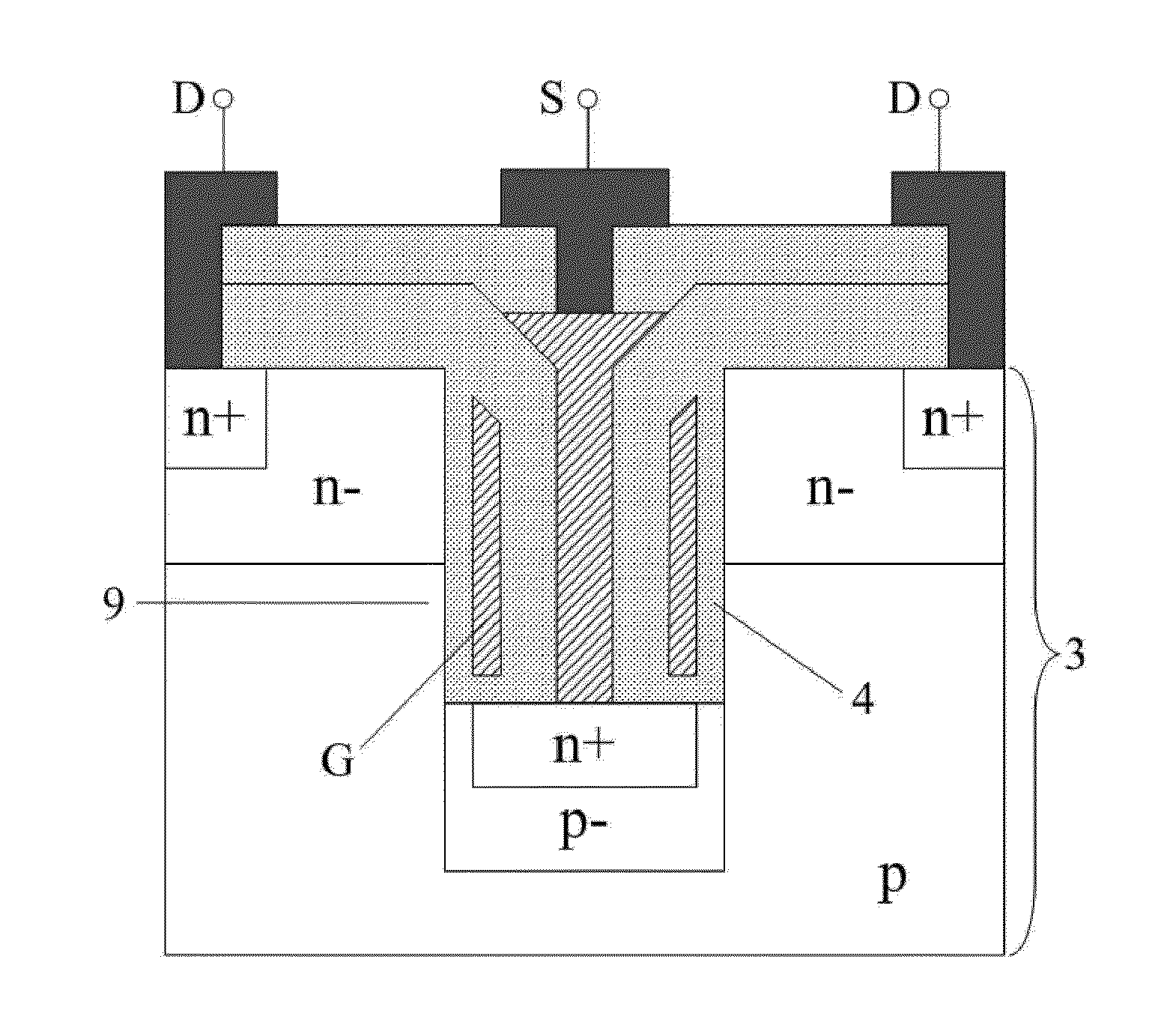
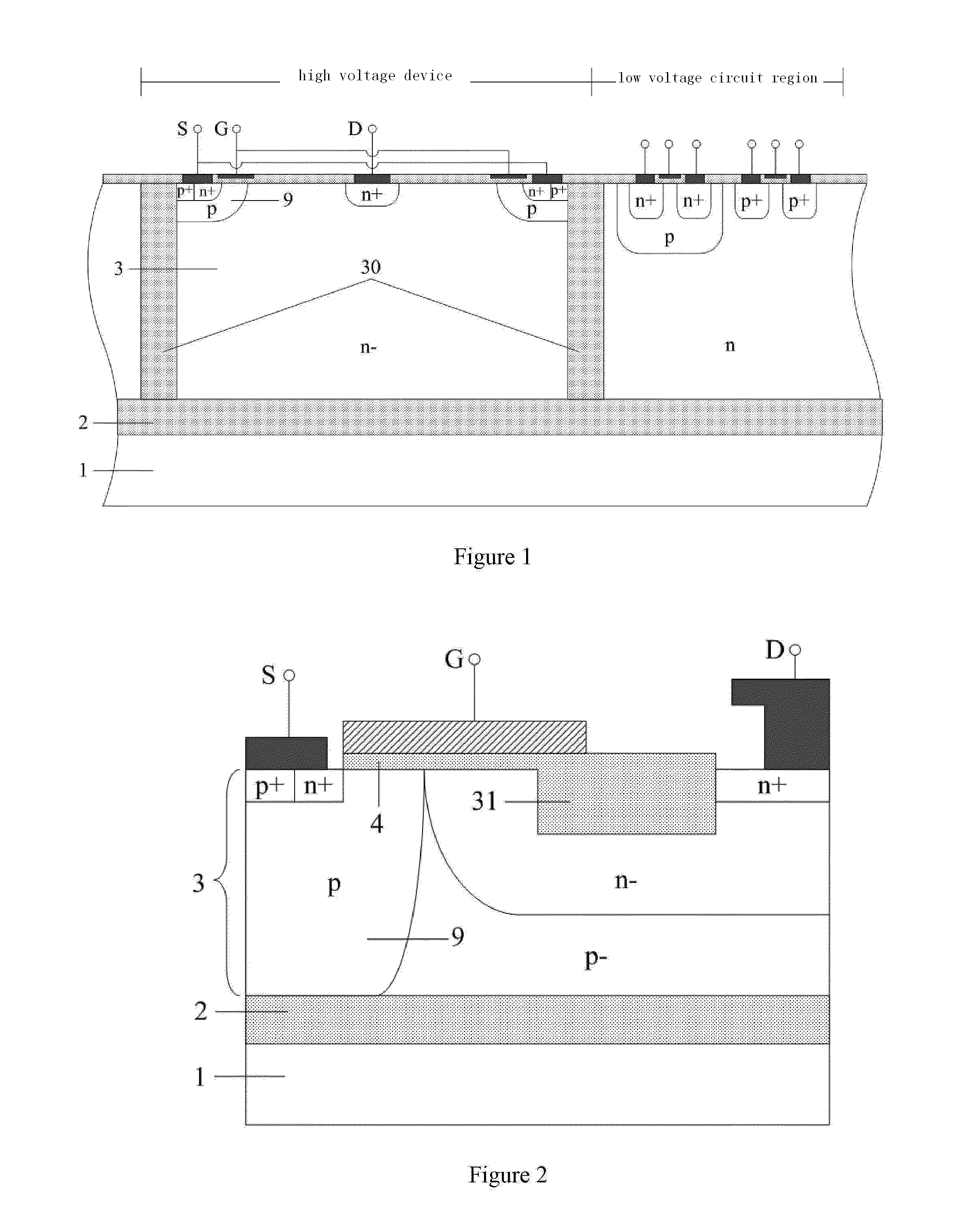
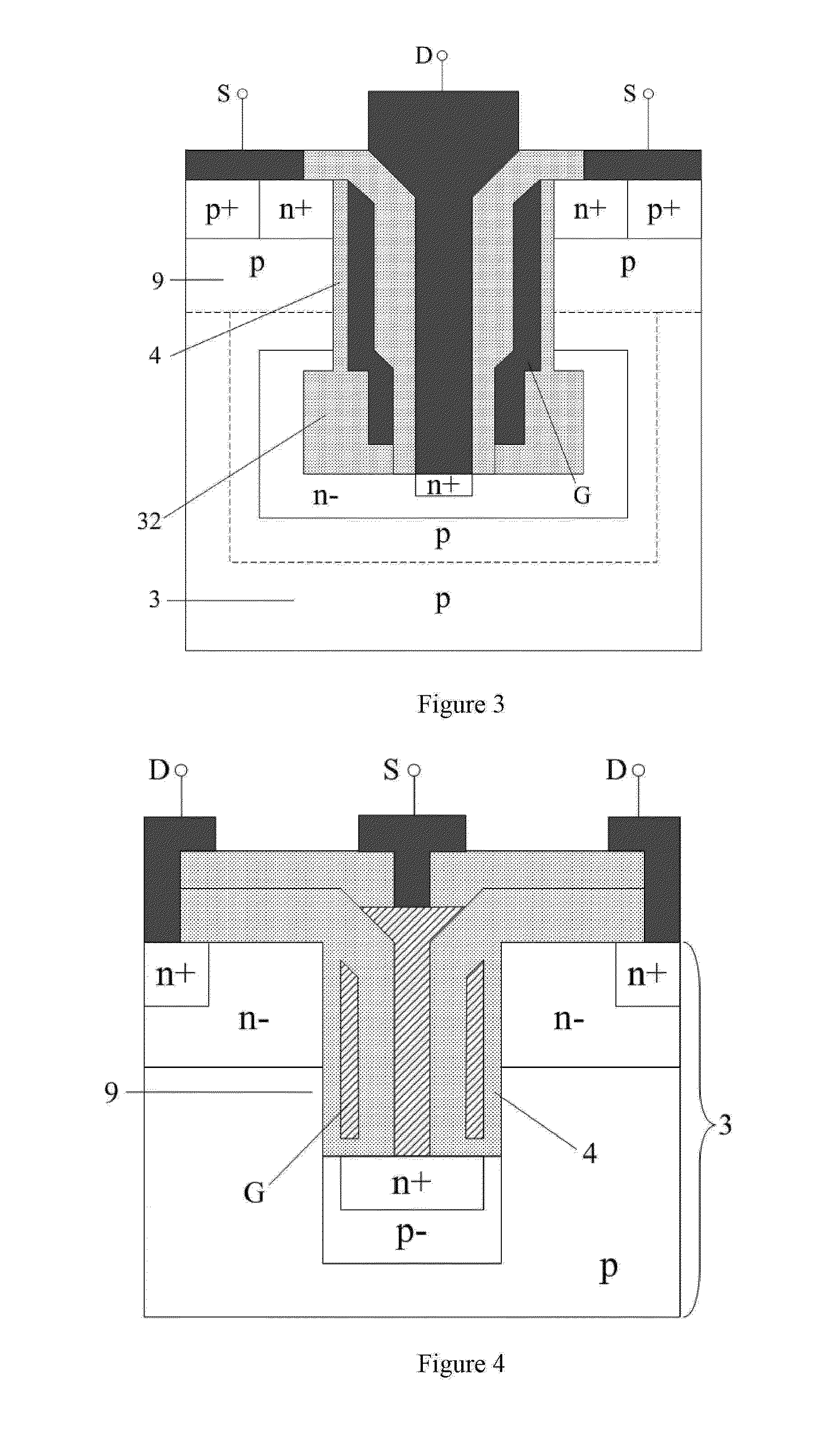
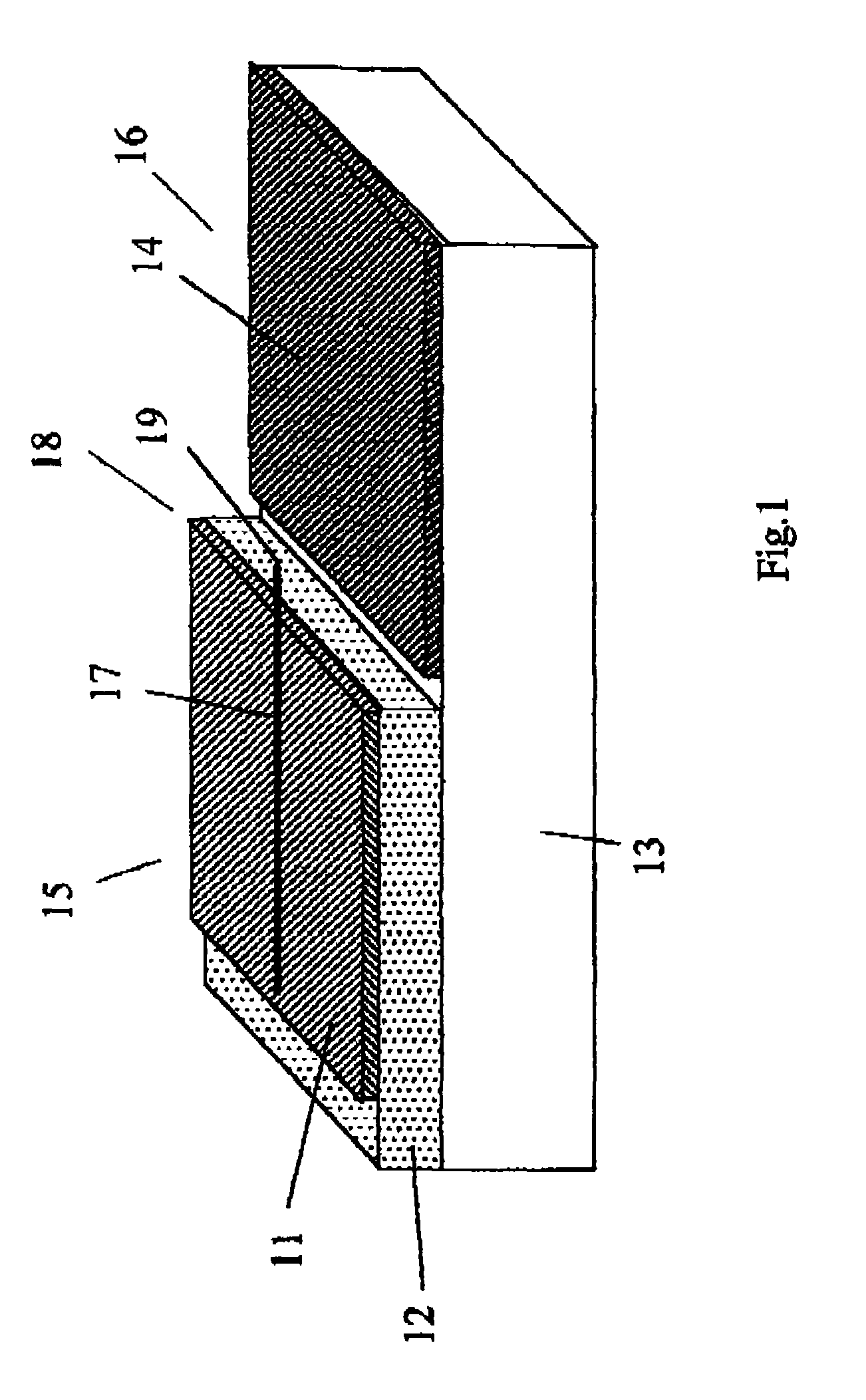
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
233results about How to "Improve transconductance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
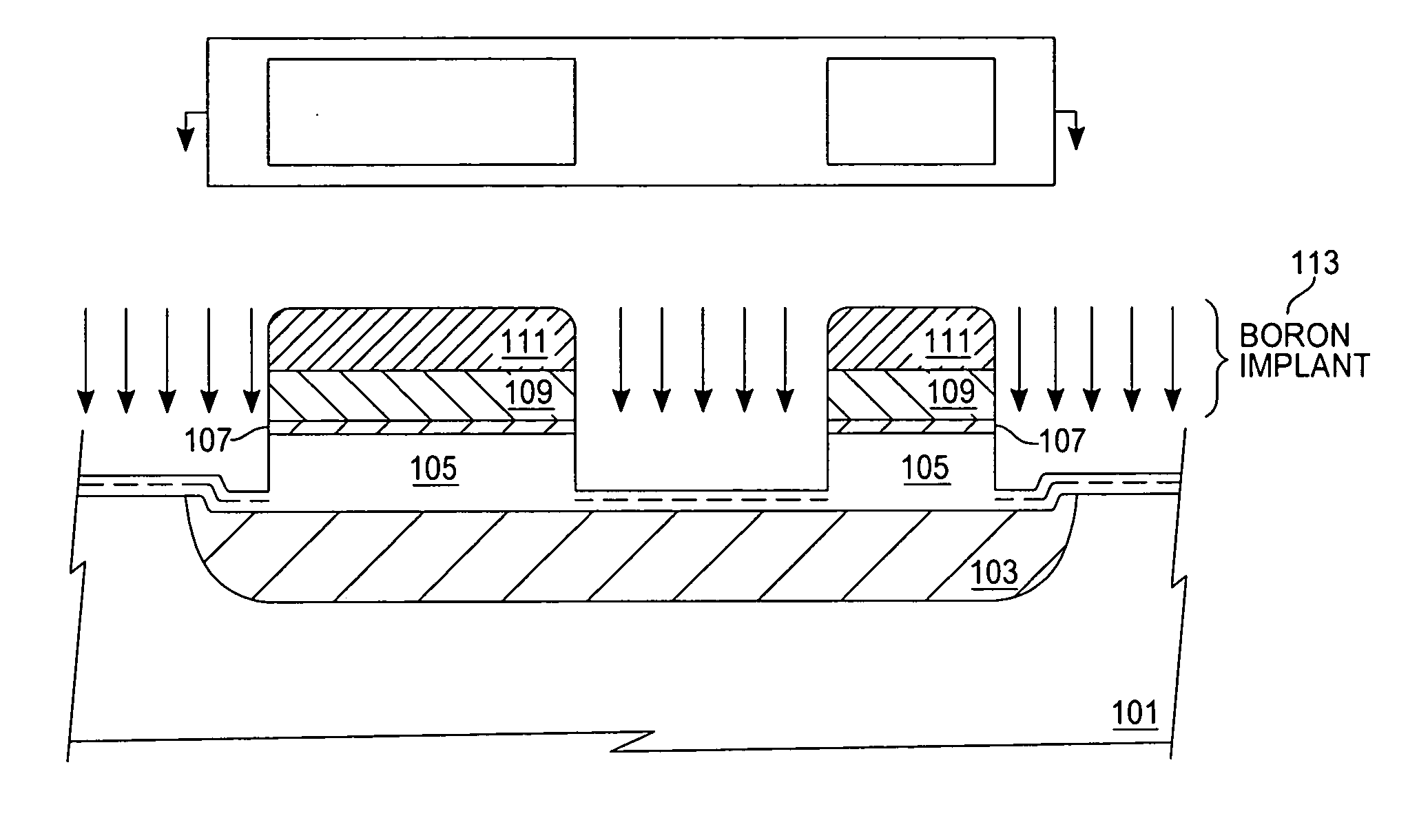
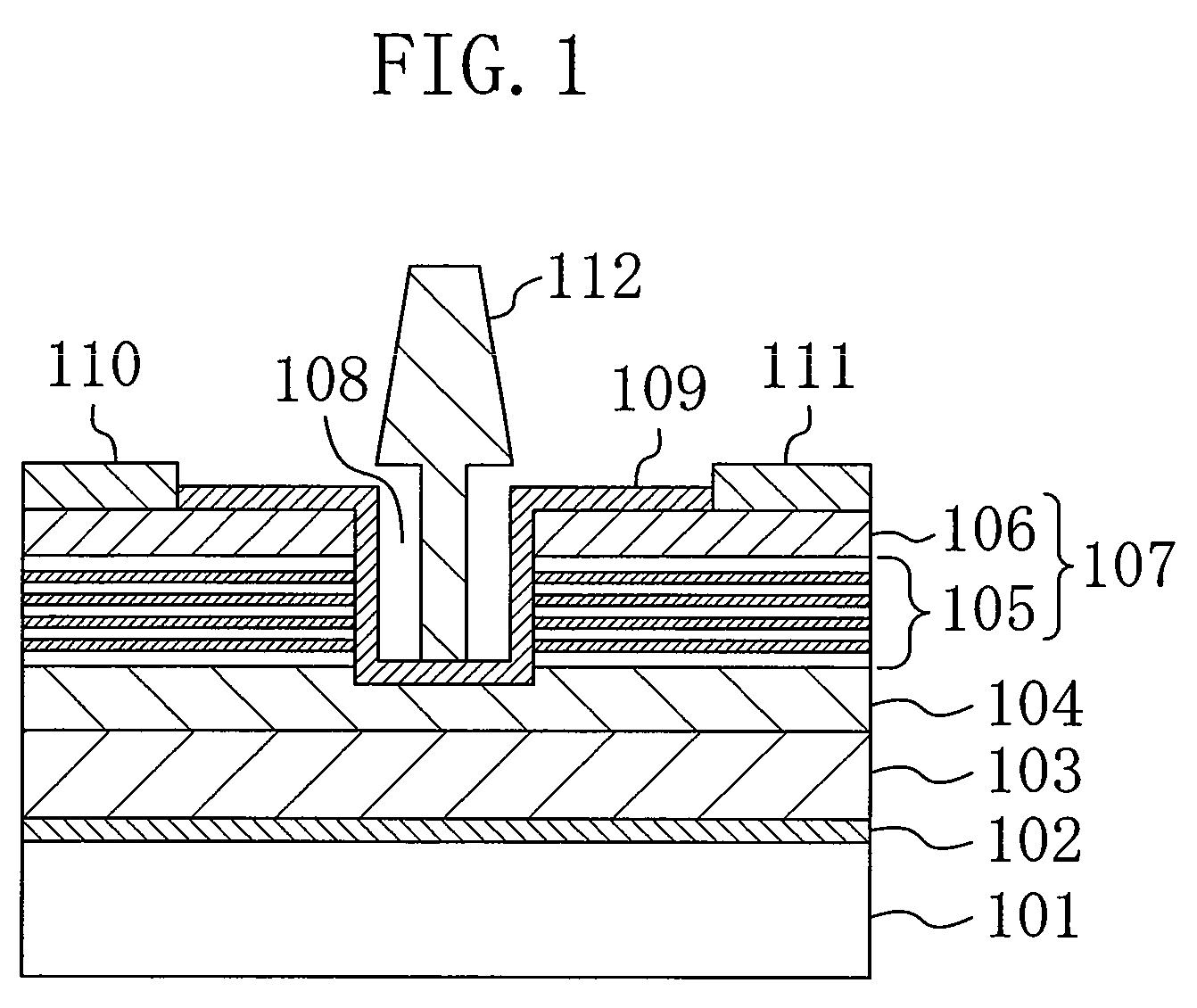
SOI structure having a sige layer interposed between the silicon and the insulator
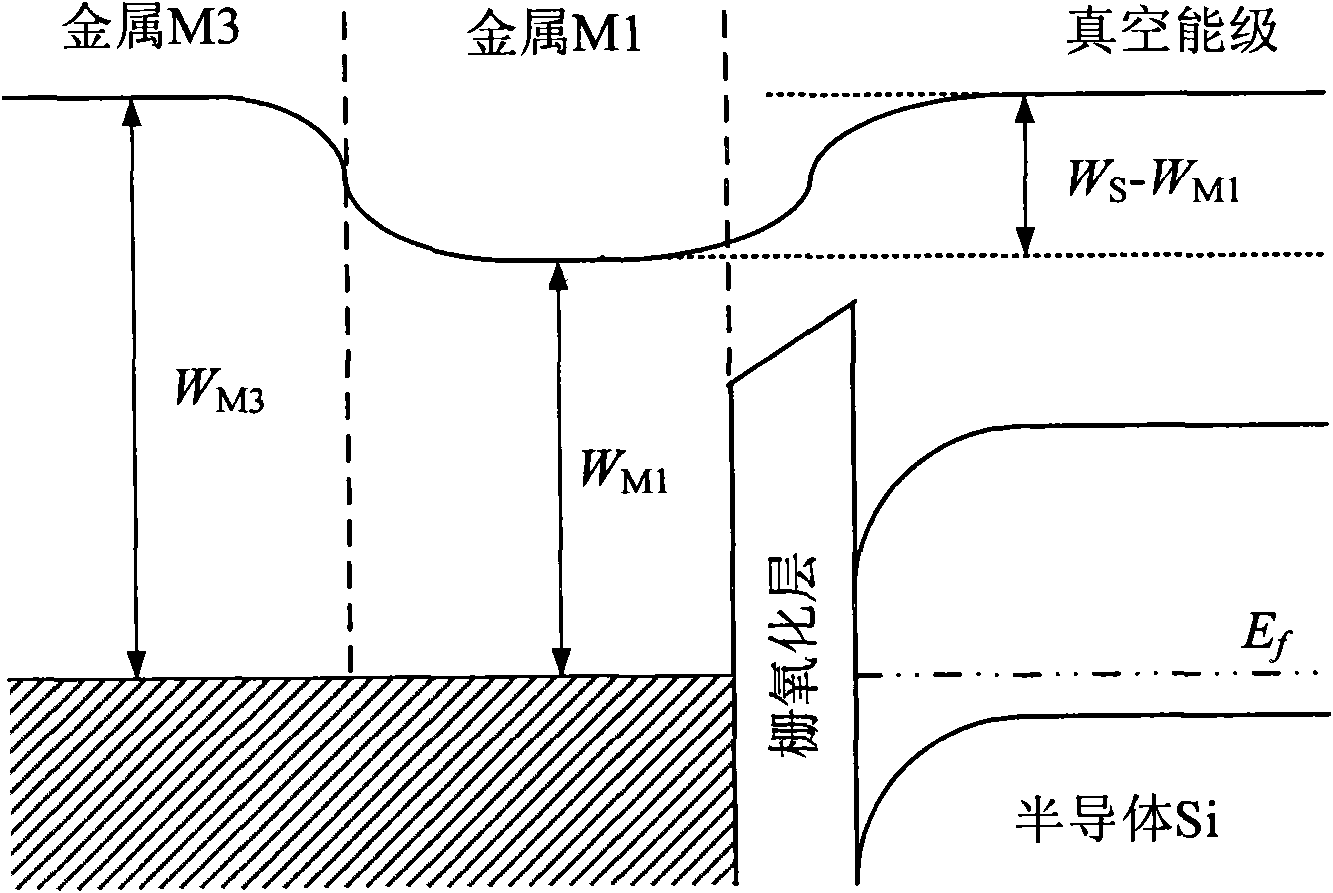
InactiveUS20050242396A1Improve breakdown voltageImprove transconductanceTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor structureImpurity ions
A semiconductor structure and a method of manufacturing a silicon on insulator (SOI) structure having a silicon germanium (SiGe) layer interposed between the silicon and the insulator. According to one manufacturing method, a first SiGe layer, a silicon layer, and a second SiGe layer are epitaxially grown in sequence over a first substrate, and then an insulating layer is formed on the second SiGe layer. Then, impurity ions are implanted into a predetermined location of the first substrate underlying the first SiGe layer to form an impurity implantation region. A second substrate is bonded to the insulating layer on the first substrate. After the first substrate is separated along the impurity implantation region and removed, the first SiGe layer remaining on the surface of the separated region is removed so that the surface of the silicon layer may be exposed.
Owner:SUMITOMO MITSUBISHI SILICON CORP +1
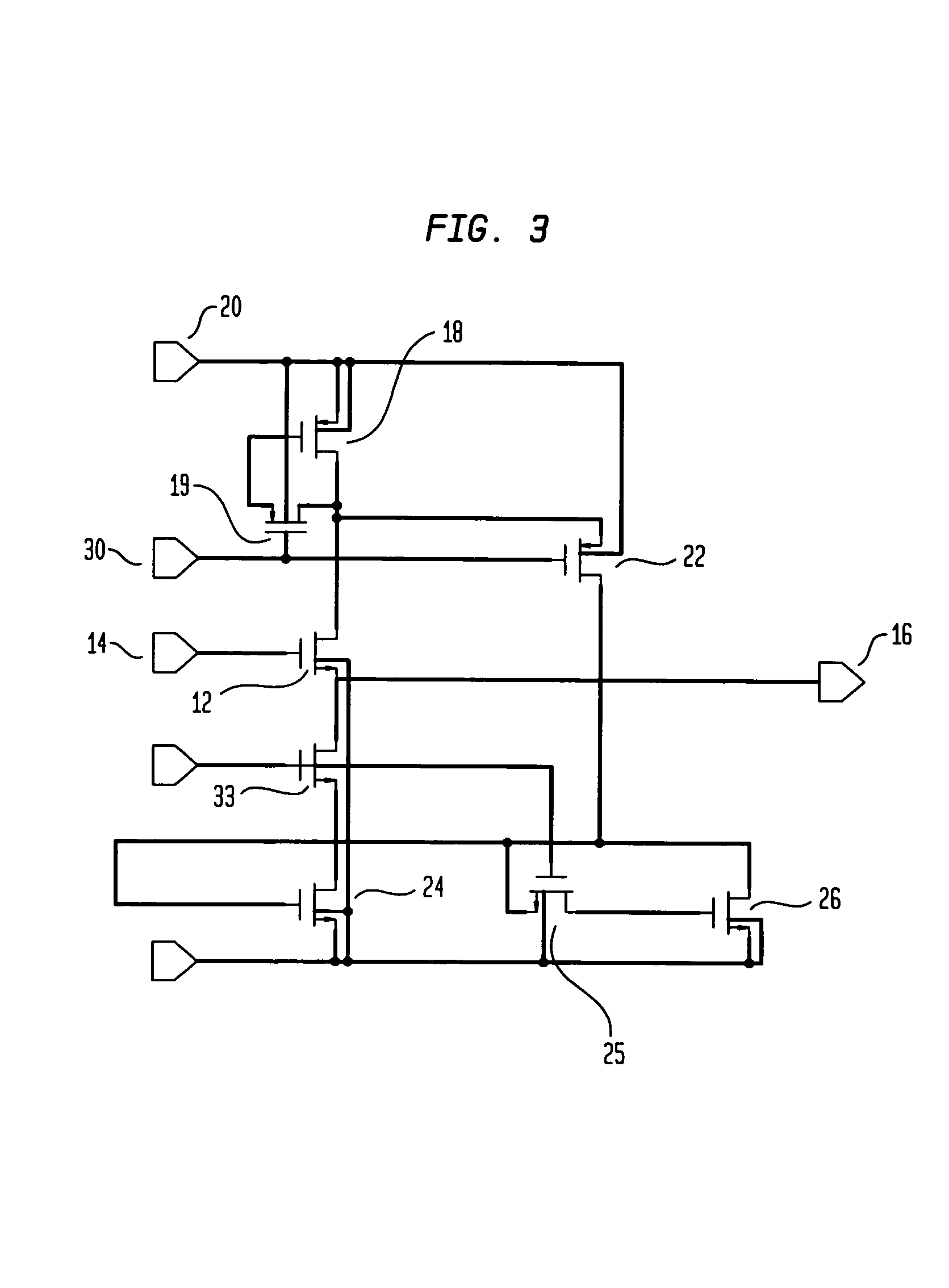
Power amplifier module with distortion compensation
InactiveUS7068099B2Reduce conductionImprove transconductanceNegative-feedback-circuit arrangementsAmplifier combinationsAudio power amplifierEngineering
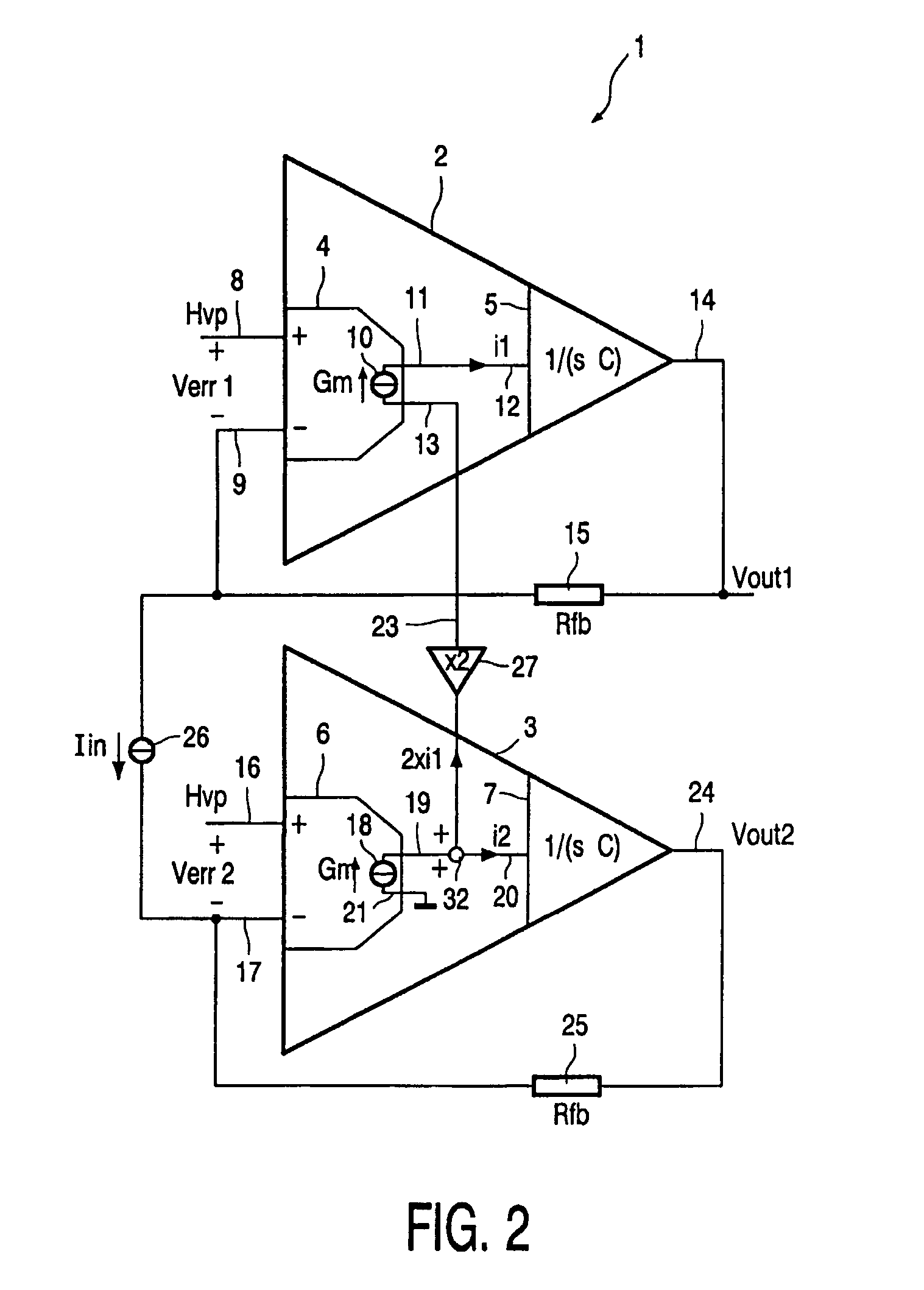
The invention relates to a power amplifier module comprising a first amplifier 2 having a first front-end 4 and a first backend amplifier stage 5 and a second amplifier 3 having a second front-end 6 and a second backend amplifier stage 7, the first amplifier and the second amplifier being arranged in a Bridge Tied Load (BTL) configuration with feedback over the load,characterized in thatthe first and the second backend amplifier stages having point symmetrical transfer functions with respect to the origin,the input current i1 of the first backend amplifier stage being substantially equal to the input current i2 of the second backend amplifier stage.
Owner:NXP BV
Vertical MOSFET SRAM cell
InactiveUS20070007601A1Improve transconductanceMore drivabilityTransistorSolid-state devicesMOSFETEngineering
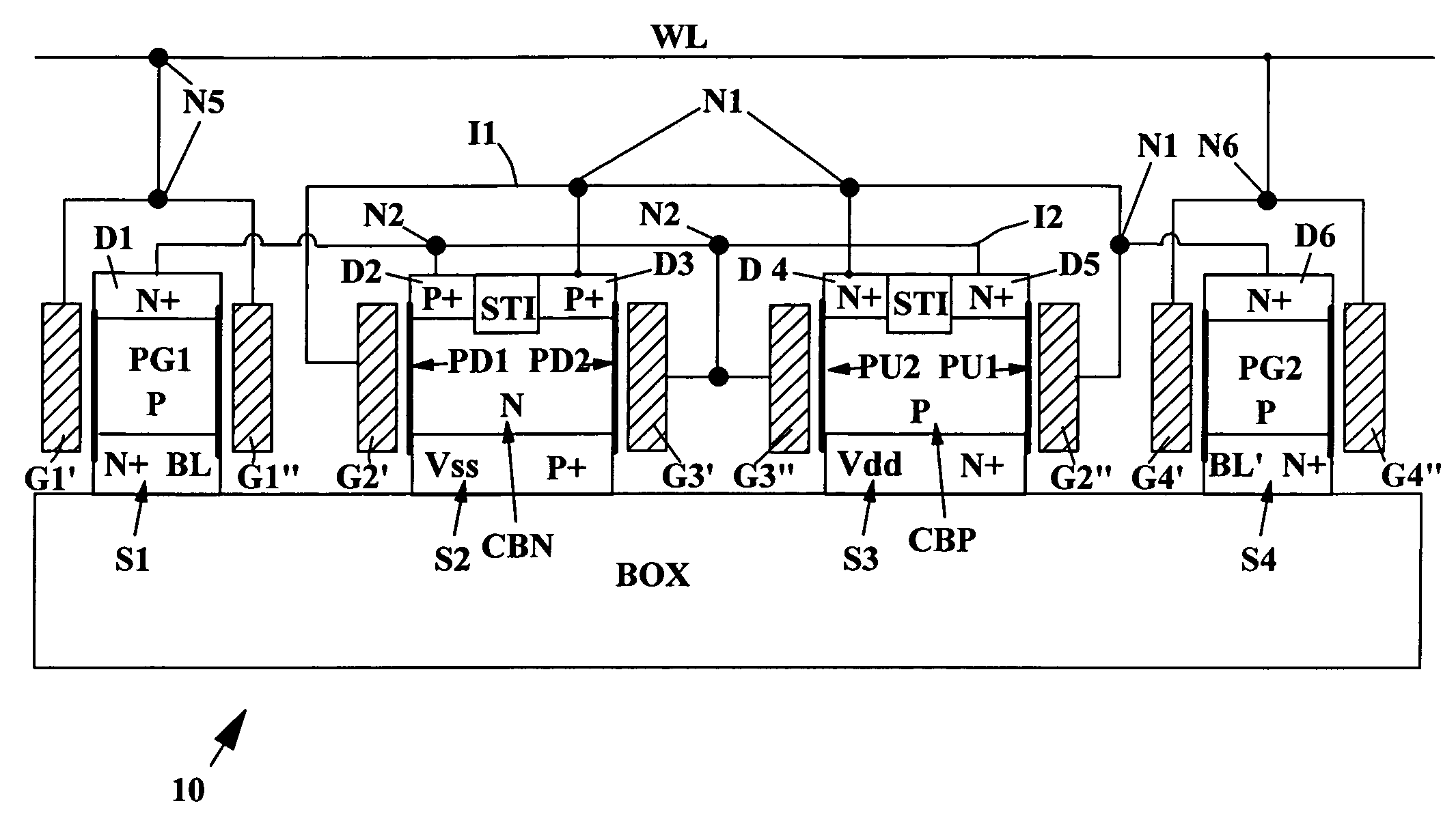
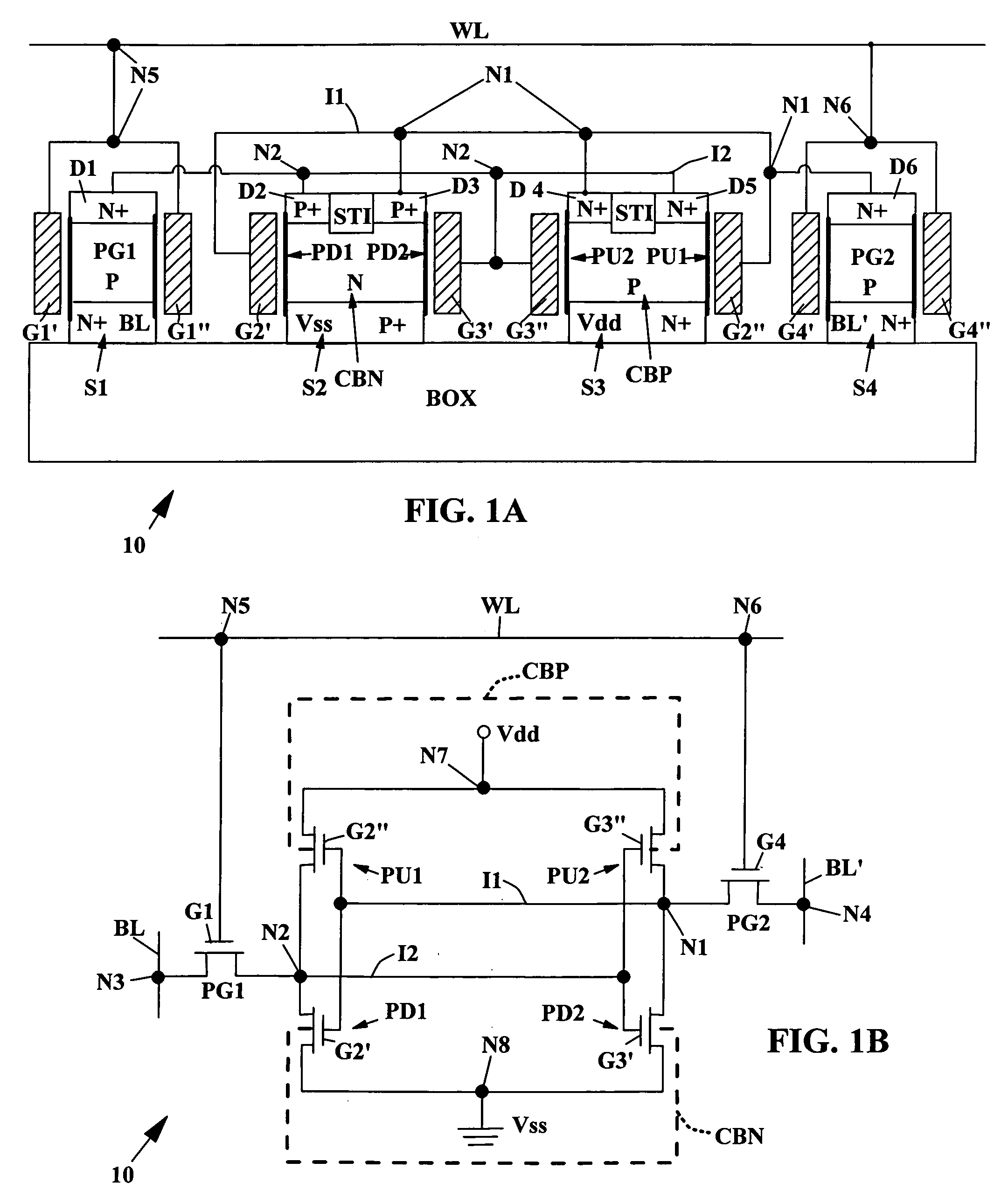
A method of forming an SRAM cell device includes the following steps. Form pass gate FET transistors and form a pair of vertical pull-down FET transistors with a first common body and a first common source in a silicon layer patterned into parallel islands formed on a planar insulator. Etch down through upper diffusions between cross-coupled inverter FET transistors to form pull-down isolation spaces bisecting the upper strata of pull-up and pull-down drain regions of the pair of vertical pull-down FET transistors, with the isolation spaces reaching down to the common body strata. Form a pair of vertical pull-up FET transistors with a second common body and a second common drain. Then, connect the FET transistors to form an SRAM cell.
Owner:HSU LOUIS L +3
Transistor with A-Face Conductive Channel and Trench Protecting Well Region
ActiveUS20090146154A1High voltage blocking abilityMinimize JFET effectThyristorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingTrench gateSemiconductor
A transistor structure optimizes current along the A-face of a silicon carbide body to form an AMOSFET that minimizes the JFET effect in the drift region during forward conduction in the on-state. The AMOSFET further shows high voltage blocking ability due to the addition of a highly doped well region that protects the gate corner region in a trench-gated device. The AMOSFET uses the A-face conduction along a trench sidewall in addition to a buried channel layer extending across portions of the semiconductor mesas defining the trench. A doped well extends from at least one of the mesas to a depth within the current spreading layer that is greater than the depth of the trench. A current spreading layer extends between the semiconductor mesas beneath the bottom of the trench to reduce junction resistance in the on-state. A buffer layer between the trench and the deep well further provides protection from field crowding at the trench corner.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Method and apparatuses for high pressure gas annealing
ActiveUS20090148965A1Reduce in quantityImprove device performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSolid-state devicesGate dielectricForming gas
Novel methods and apparatuses for annealing semiconductor devices in a high pressure gas environment. According to an embodiment, the annealing vessel has a dual chamber structure, and potentially toxic, flammable, or otherwise reactive gas is confined in an inner chamber which is protected by pressures of inert gas contained in the outer chamber. The incoming gas delivery system and exhaust gas venting system are likewise protected by various methods. Embodiments of the present invention can be used, for example, for high-K gate dielectric anneal, post metallization sintering anneal, and forming gas anneal in the semiconductor manufacturing process.
Owner:HPSP CO LTD
Vertical MOSFET SRAM cell
InactiveUS7138685B2Improve transconductanceMore drivabilityTransistorCurrent/voltage measurementMOSFETCommon drain
A method of forming an SRAM cell device includes the following steps. Form pass gate FET transistors and form a pair of vertical pull-down FET transistors with a first common body and a first common source in a silicon layer patterned into parallel islands formed on a planar insulator. Etch down through upper diffusions between cross-coupled inverter FET transistors to form pull-down isolation spaces bisecting the upper strata of pull-up and pull-down drain regions of the pair of vertical pull-down FET transistors, with the isolation spaces reaching down to the common body strata. Form a pair of vertical pull-up FET transistors with a second common body and a second common drain. Then, connect the FET transistors to form an SRAM cell.
Owner:IBM CORP
Transistor with A-face conductive channel and trench protecting well region
ActiveUS7989882B2Improve abilitiesMinimize JFET effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesTrench gateSemiconductor
A transistor structure optimizes current along the A-face of a silicon carbide body to form an AMOSFET that minimizes the JFET effect in the drift region during forward conduction in the on-state. The AMOSFET further shows high voltage blocking ability due to the addition of a highly doped well region that protects the gate corner region in a trench-gated device. The AMOSFET uses the A-face conduction along a trench sidewall in addition to a buried channel layer extending across portions of the semiconductor mesas defining the trench. A doped well extends from at least one of the mesas to a depth within the current spreading layer that is greater than the depth of the trench. A current spreading layer extends between the semiconductor mesas beneath the bottom of the trench to reduce junction resistance in the on-state. A buffer layer between the trench and the deep well further provides protection from field crowding at the trench corner.
Owner:WOLFSPEED INC
Fabrication of asymmetric field-effect transistors using L-shaped spacers
ActiveUS8101479B2Facilitated DiffusionShortening the channel zoneSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDopantGate dielectric
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
Nanotube-based vacuum devices
InactiveUS7102157B2Minimize threshold voltageLow inputNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCapacitanceTerminal equipment
New, hybrid vacuum electronic devices are proposed, in which the electrons are extracted from the nanotube into vacuum. Each nanotube is either placed on the cathode electrode individually or grown normally to the cathode plane. Arrays of the nanotubes are also considered to multiply the output current. Two- and three-terminal device configurations are discussed. In all the cases considered, the device designs are such that both input and output capacitances are extremely low, while the efficiency of the electron extraction into vacuum is very high, so that the estimated operational frequencies are expected to be in a tera-hertz range. New vacuum triode structure with ballistic electron propagation along the nanotube is also considered.
Owner:ITUS
Gain increased operational transconductance amplifier
InactiveCN105141265ADoubling the transconductanceIncrease transient slew rateAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationDifferential amplifiersAutomatic controlPower flow
The invention discloses a gain increased operational transconductance amplifier which is formed in a manner that a bias constant current source is sequentially connected with differential input, a load current mirror, a cascode output stage and an adjustable auxiliary differential pair in sequence, wherein the differential input is composed of four PMOS pipes namely M1a, M2a, M1b and M2b; the load current mirror is composed of six NMOS pipes namely M3, M4, M5a, M6a, M5b and M6b; the cascode output stage is composed of six MOS pipes namely M7, M8, M9, M10, M11 and M12; the adjustable auxiliary differential pair is composed of M13, M14 and M15. Reutilization of current and the output stage increased adjustable auxiliary differential pair thoroughly solve the inherent contradiction among gain, bandwidth, power dissipation and the like in a circuit; the gain increased operational transconductance amplifier is slightly influenced by output voltage, an additional pole is not introduced, the simulation results show same static power dissipation, and multiplication is realized for gain and bandwidth; the gain increased operational transconductance amplifier further has the characteristics of fine tuning and high accuracy and is applicable to communication, electronic measurement and automatic control systems.
Owner:GUANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Method for growth and optimization of heterojunction bipolar transistor film stacks by remote injection
InactiveUS20060292809A1Avoid spreadingEliminates and minimizes deleterious effectSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceDopant
A method, and a resulting device, for fabricating a heterojunction bipolar transistor (HBT). HBT devices have a high transconductance typical of bipolar devices and are additionally capable of high-power operation. To achieve the aforementioned characteristics, HBT devices are generally of the npn type, preferably with a thin, heavily doped base. The thin, heavily doped base maintains a low base-spreading resistance, leading to a high maximum oscillation frequency. In order to maintain a high doping concentration while minimizing outdiffusion of the dopant material, carbon is remotely doped into the base region. Details of the carbon dopant techniques and procedures are described with respect to fabrication of an exemplary HBT device.
Owner:ATMEL CORP
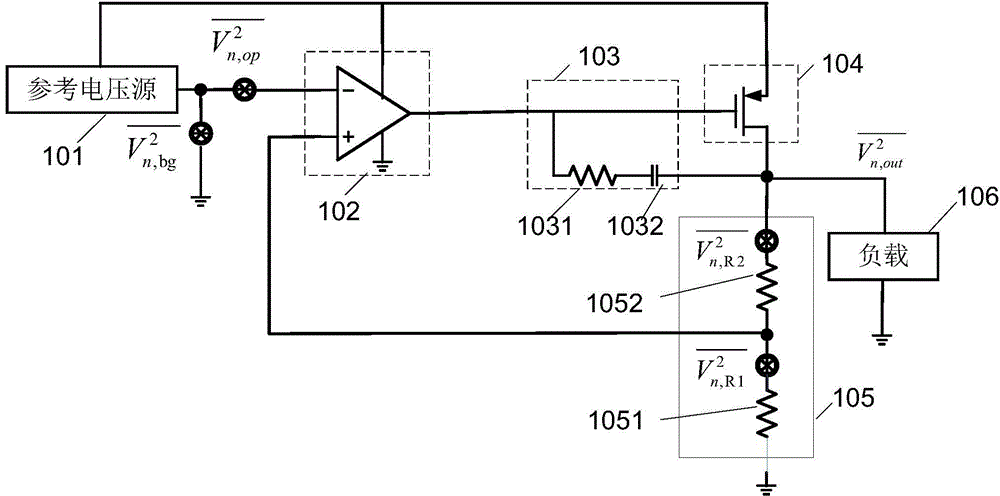
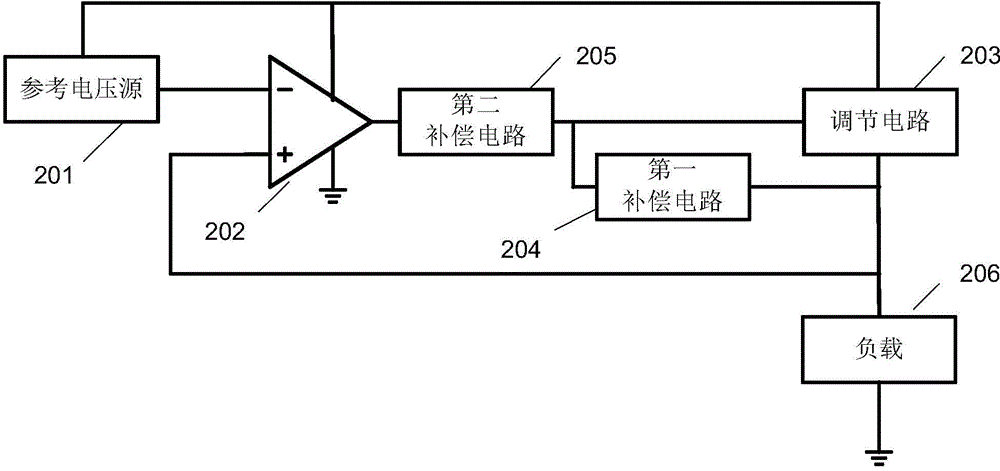
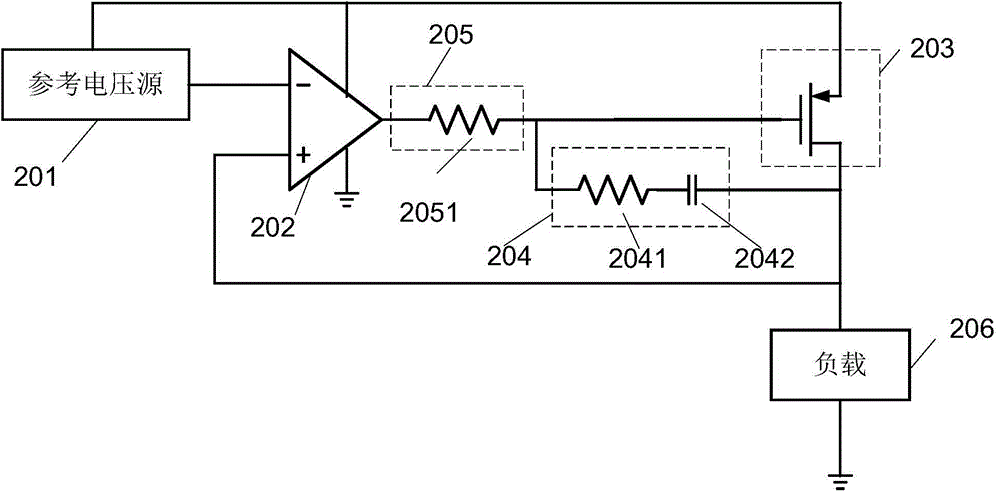
Low dropout linear regulator, method for improving stability of low dropout linear regulator and phase-locked loop
ActiveCN104950974AMagnification StabilityHigh gain-bandwidth productPulse automatic controlElectric variable regulationPhase marginVoltage reference
The embodiment of the invention discloses a low dropout linear regulator, a method for improving the stability of the low dropout linear regulator and a phase-locked loop. The low dropout linear regulator comprises a reference voltage source, an error amplifier, an adjustment circuit, a load, a first compensating circuit and a second compensating circuit. The first compensating circuit is coupled with the adjustment circuit and used for adjusting a dominant pole and a secondary dominant pole of the low dropout linear regulator to adjust the phase margin. The second compensating circuit is used for adjusting the dominant pole of the low dropout linear regulator on the basis that the dominant pole and the secondary dominant pole of the low dropout linear regulator are adjusted by the first compensating circuit, further increasing the secondary dominant pole to adjust the phase margin and adjusting the gain bandwidth product of the low dropout linear regulator. By means of the low dropout linear regulator, the value of the gain bandwidth product and the dominant pole can be remarkably reduced, the secondary dominant pole can be increased, and therefore the error amplifier has the better noise performance.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Radio frequency (RF) laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) component and manufacture method
ActiveCN103035727AImprove transconductanceLower base resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesRadio frequencyTransconductance
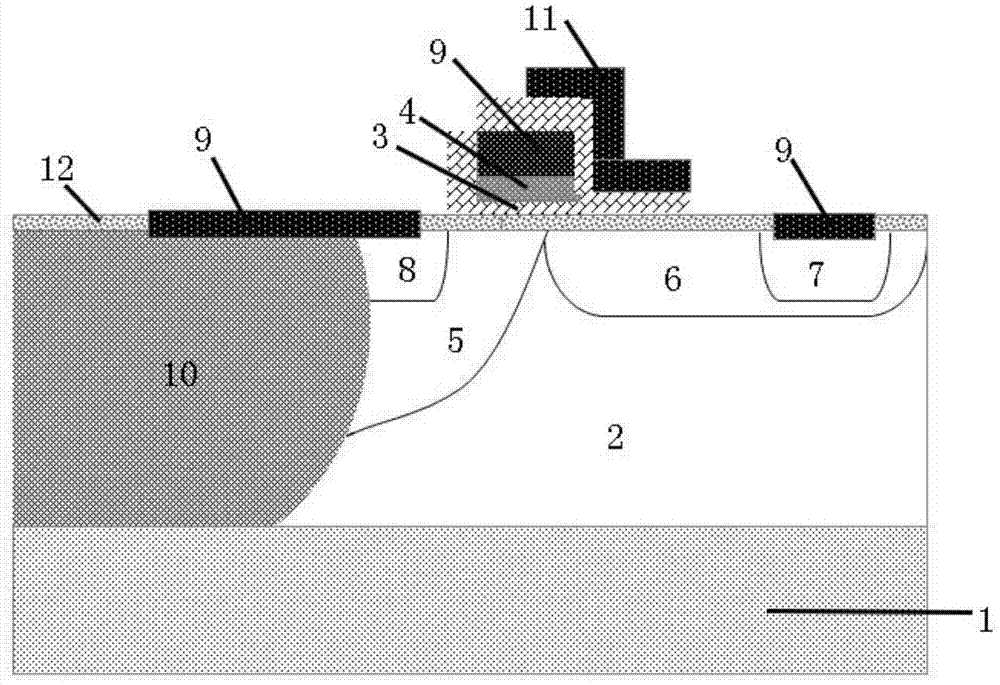
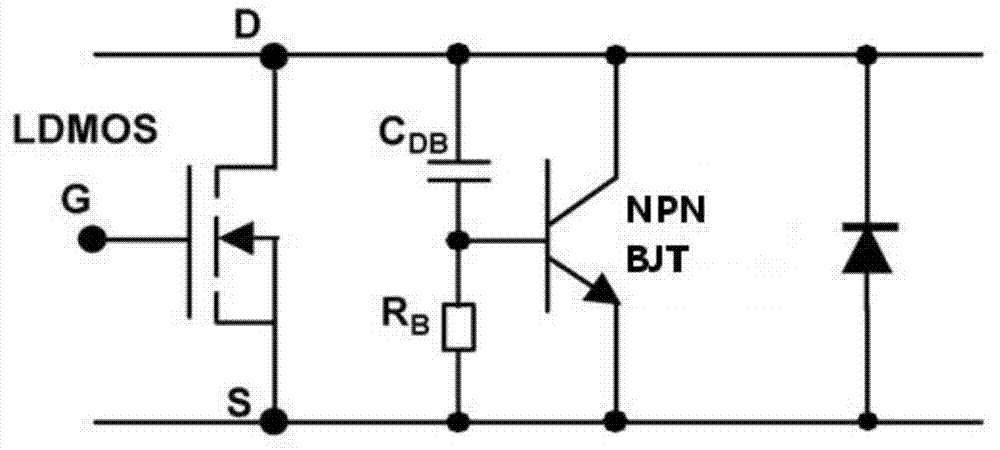
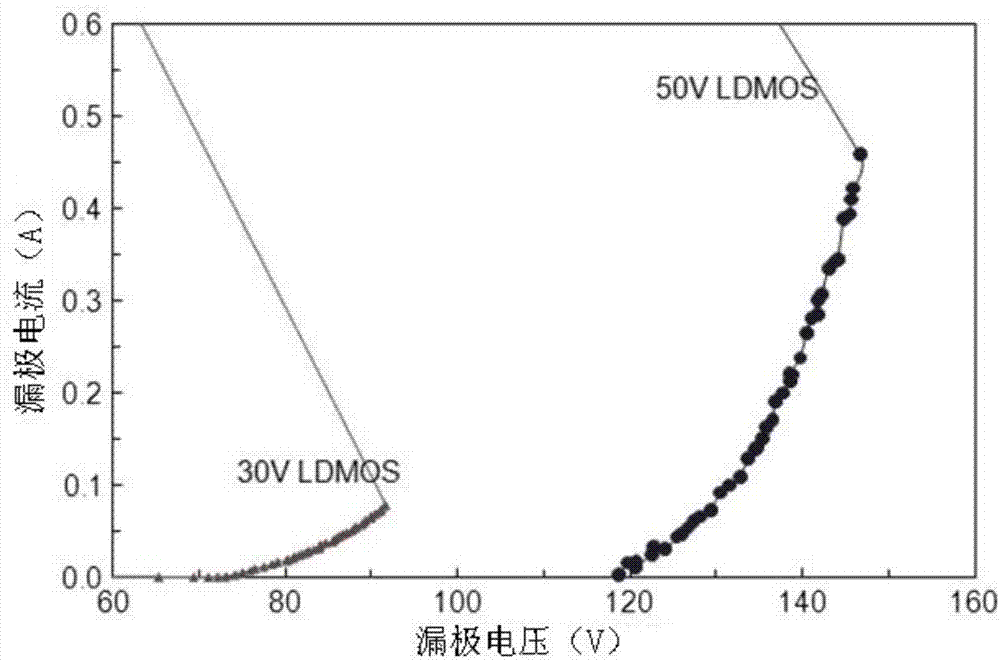
The invention discloses a radio frequency (RF) laterally diffused metal oxide semiconductor (LDMOS) component. A light dope P type buried layer and a middle dope buried layer in the light dope P type buried layer are additionally arranged under a P type channel region. The base electrode resistance of a parasitic non-protein nitrogen (NPN) pipe can be reduced, so that snapback effect is not prone to be generated. A reversed diode formed by a source electrode, the channel and the buried layer can strangulate drain-source voltage of an LDMOS and can sink extra current on a substrate. Thick gate oxide at the drain electrode end can reduce hot carrier effect, and thin gate oxide at the source electrode end can improve transconductance of the component. The invention further discloses a manufacture method of the RF LDMOS component. In process realization, the manufacture method only adds two photoetching steps in an existing process so as to be easy to implement.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG GRACE SEMICON MFG CORP
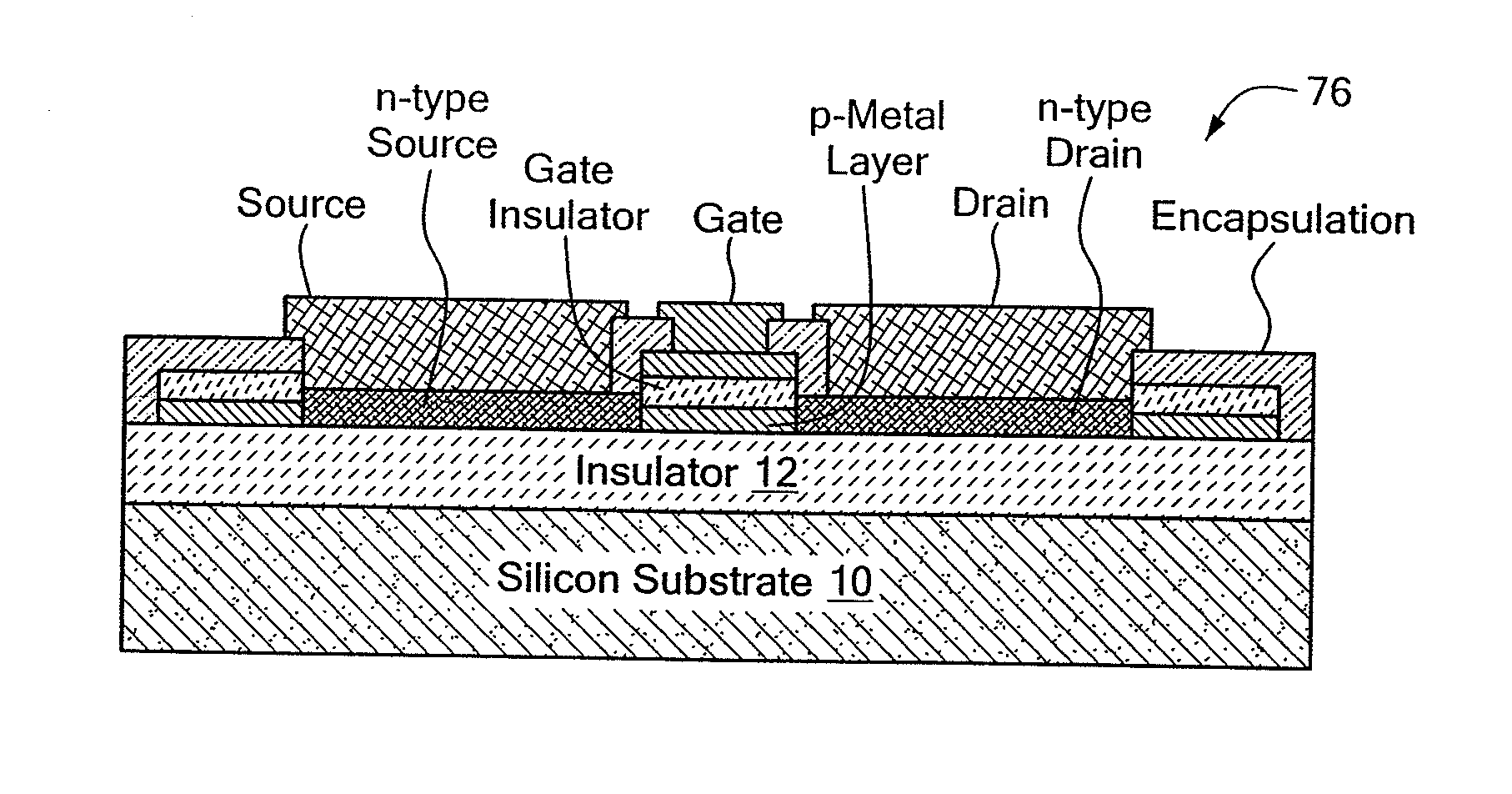
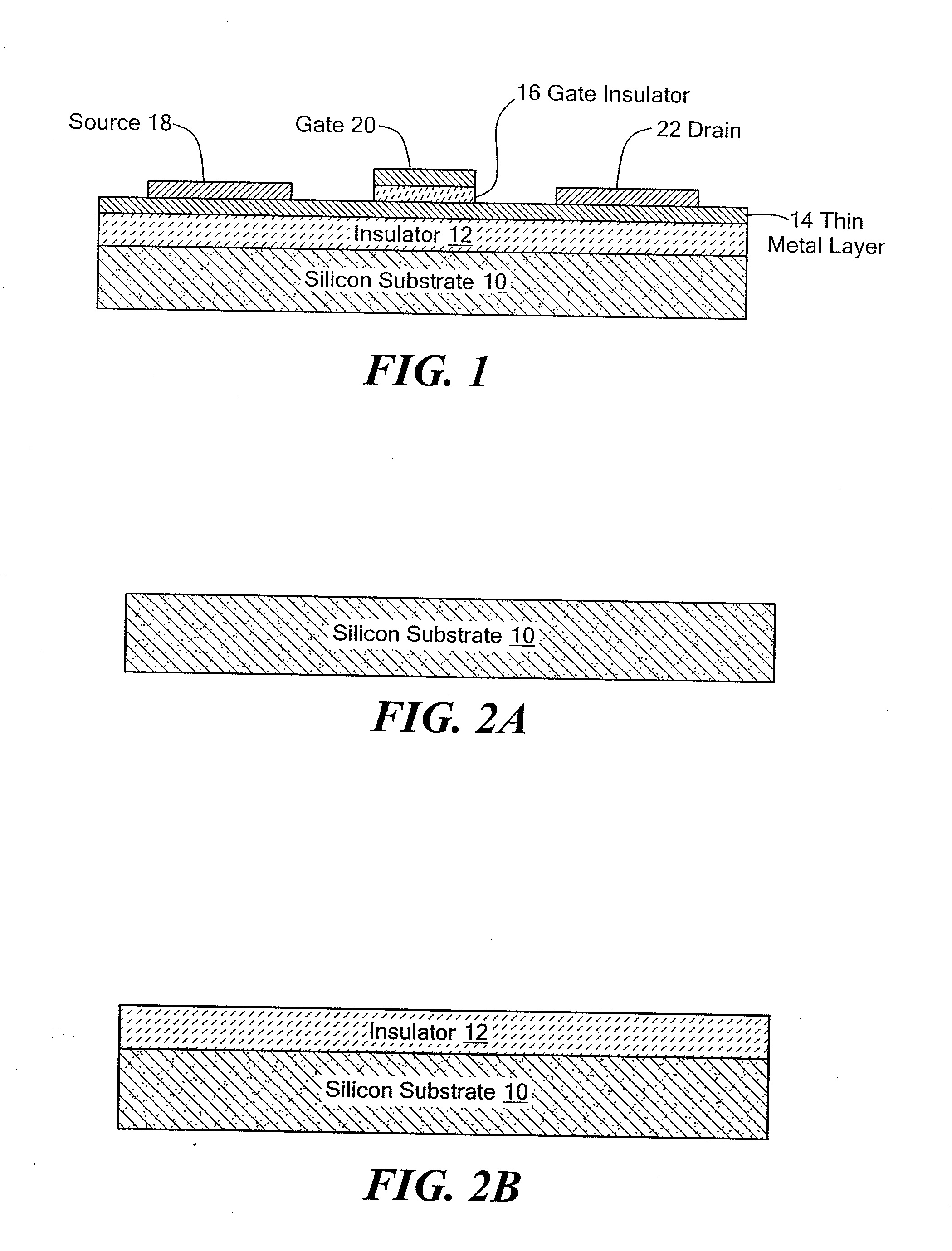
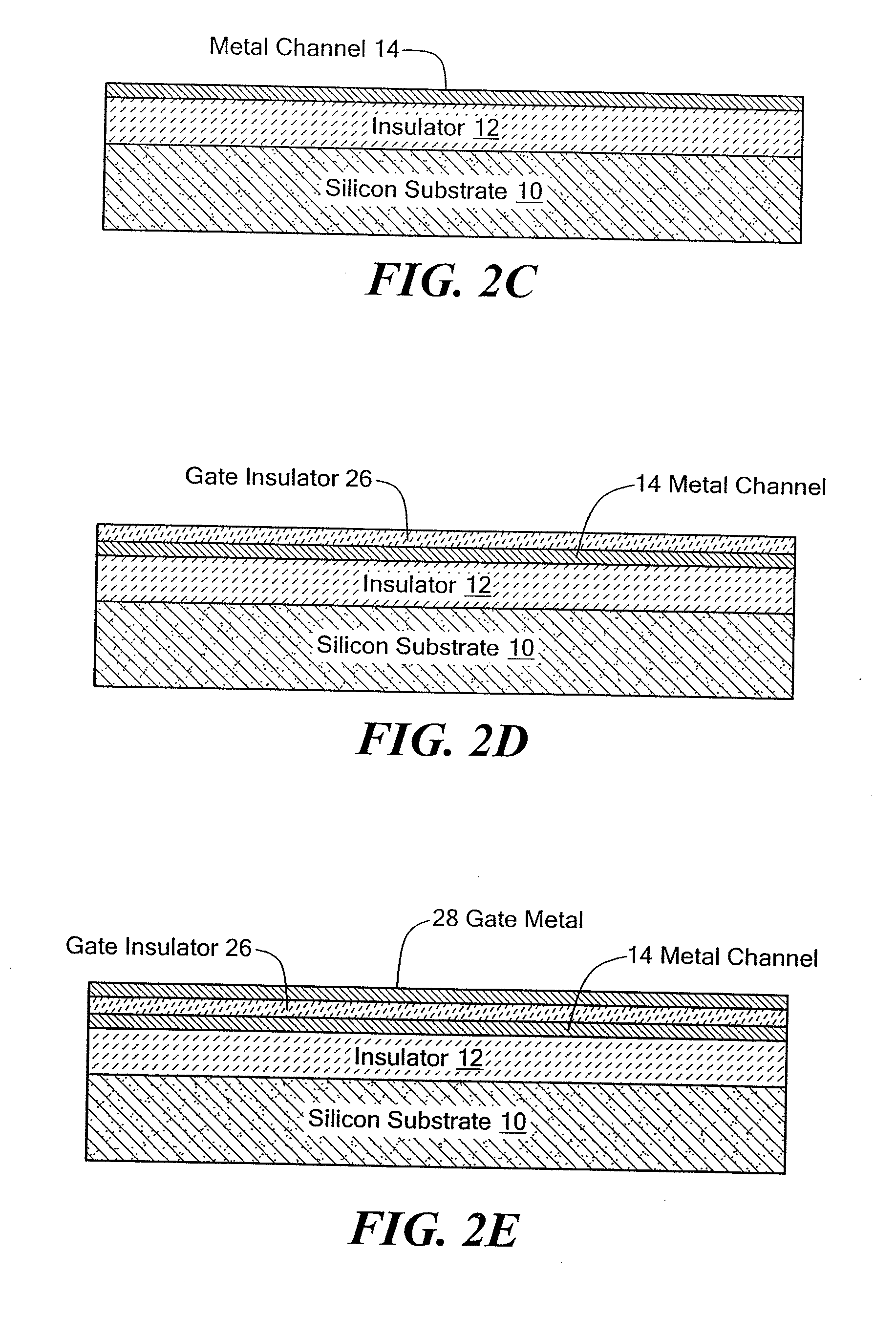
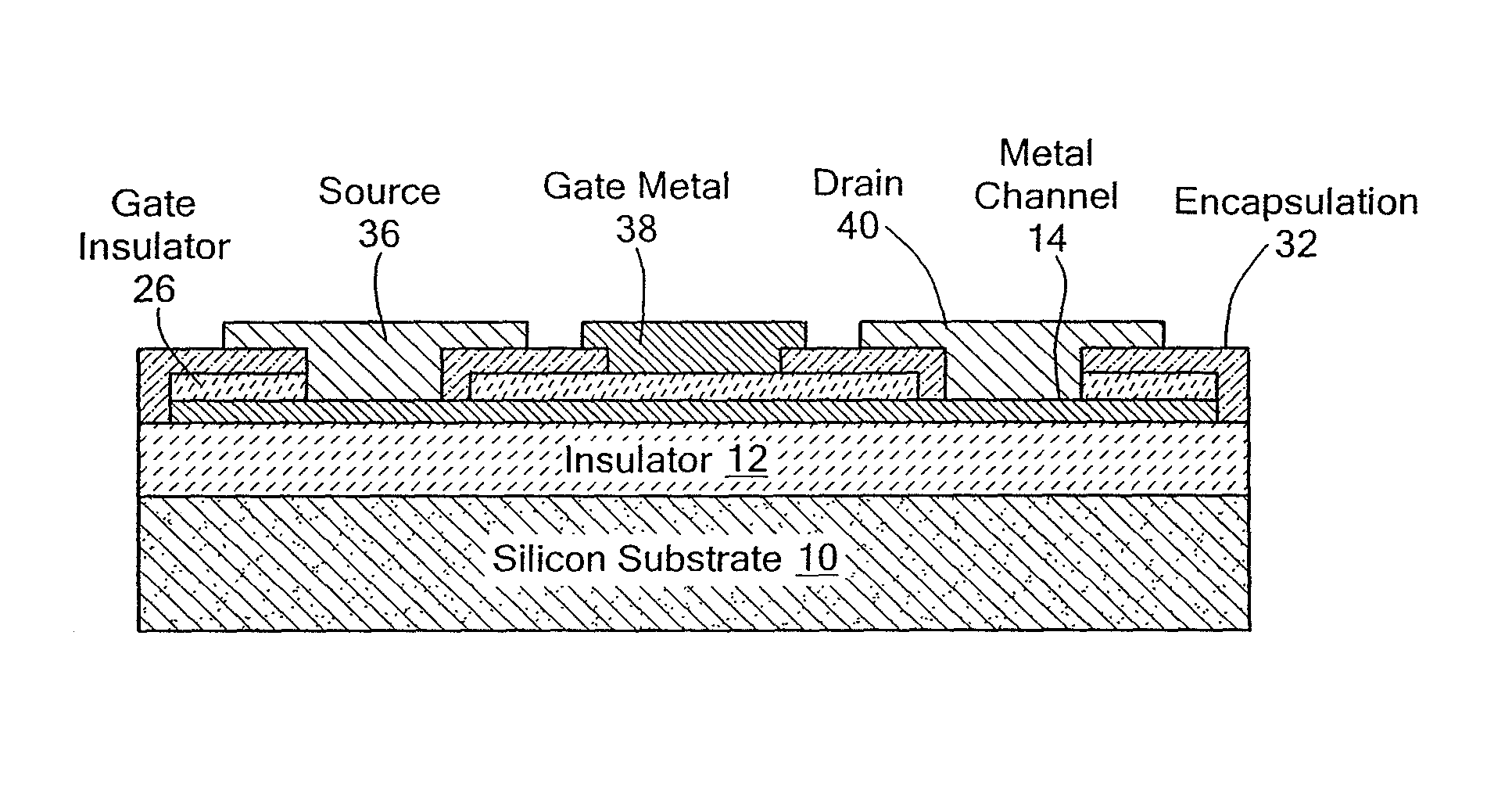
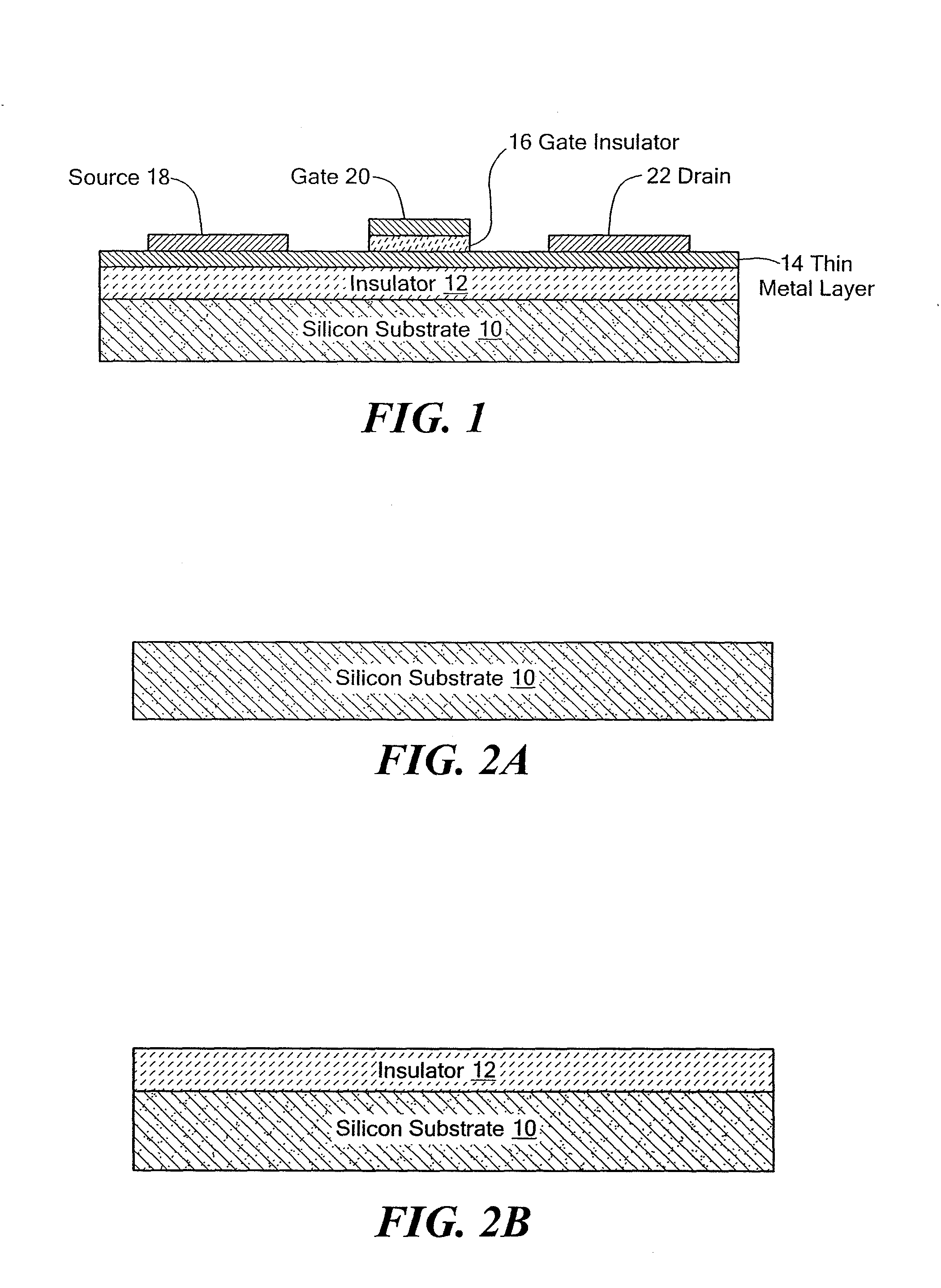
Metal transistor device
ActiveUS20110180867A1Small sizeImprove performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMaterials scienceMetal
The present invention is related to a depletion or enhancement mode metal transistor in which the channel regions of a transistor device comprises a thin film metal or metal composite layer formed over an insulating substrate.
Owner:TSANG DEAN Z
Amplitude controlled quartz oscillator with broad voltage and temperature range
ActiveUS7598821B2High transconductance levelImprove transconductancePulse automatic controlApparatus using electrochemical resonatorsVoltage shiftAmplitude control
The invention concerns an oscillator including an input terminal, an output terminal, a resonator, and an oscillator circuit including: first and second power supply terminals, two capacitors connected between the first power supply terminal and the input terminal, and respectively the output terminal of the oscillator; first and second active transistors of complementary type, forming therewith an inverting amplifier, first and second means for respectively polarizing the first and the second active transistors, a first current source formed by a transistor of the same type as the second active transistor, between the second power supply terminal and the second active transistor, current control means for the second polarizing means, characterized in that in an steady operating conditions, said second polarizing means are arranged for providing a polarization voltage across the gate of the second active transistor corresponding to the transistor gate voltage of the first current source to within one voltage shift.
Owner:EM MICROELECTRONIC-MARIN
Fully-differential operation transconductance amplifier
InactiveCN103095234AImprove transconductanceHigh gainDifferential amplifiersDc-amplifiers with dc-coupled stagesEngineeringP channel
The invention discloses a fully-differential operation transconductance amplifier which is provided with a first branch path and a second branch path. The first branch path receives differential input signals Vin and Vip and comprises an N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) tube (M31), an NMOS tube (M32), an NMOS tube (M35), an NMOS tube (M314) and an NMOS tube (M315), and the second branch path is a sleeve type common source and common grid structure, receives the differential input signals Vin and Vip, outputs differential output signals Von and Vop, and comprises a P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) tube (M38) and a PMOS tube (M39). Source electrodes of the PMOS tube (M38) and the PMOS tube (M39) are connected on a power source VDD, grid electrodes of the PMOS tube (M38) and the PMOS tube (M39) are connected into bias voltage Vbp1, a drain electrode of the PMOS tube (M38) is connected with a drain electrode of the NMOS tube (M314), and a drain electrode of the PMOS tube (M39) is connected with a drain electrode of the NMOS tube (M315).
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
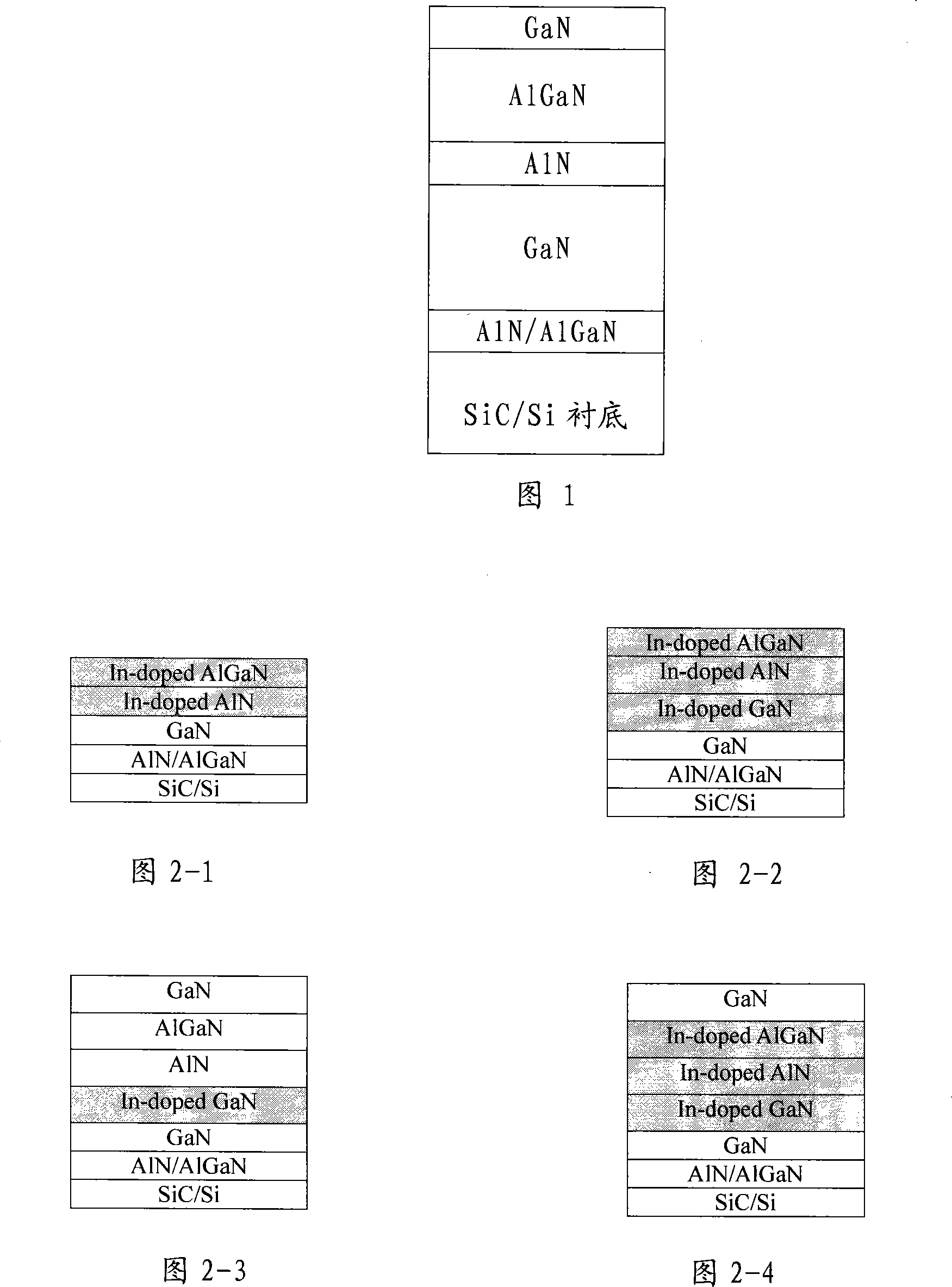
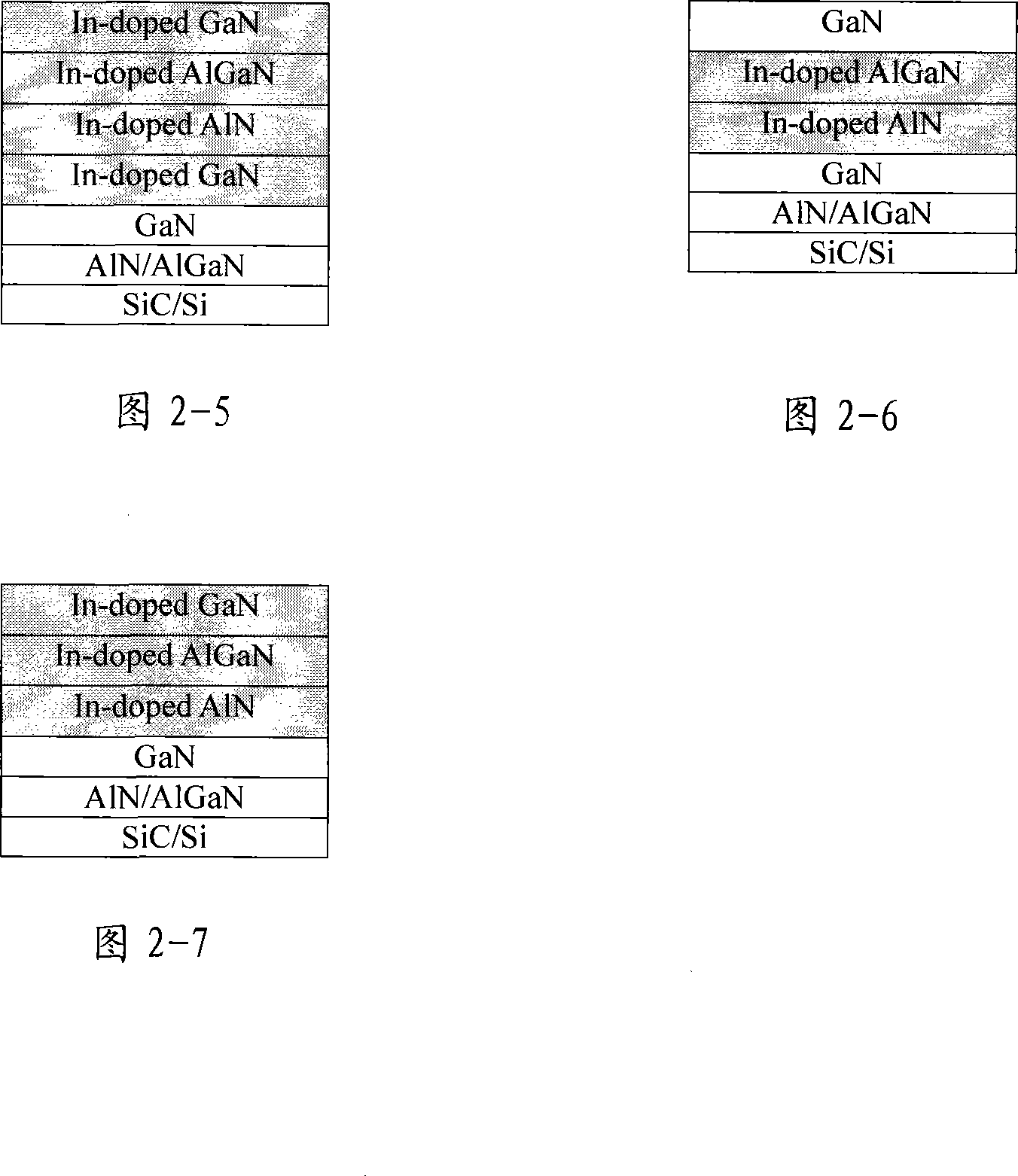
Method for improving gallium nitride based transistor material and device performance using indium doping
ActiveCN101114594AFree diffusionIncrease the diffusion distanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGas phaseSingle crystal
The invention discloses a method of increasing the properties of the gallium nitride-based transistor material and device with indium doping and applies in the field of making gallium nitride-based HEMT or HFET materials and devices. The method and process is to form the gallium nitride-based high electron mobility transistor or heterostructure field effect transistor materials on SiC or Si single crystal substrate grown by metal-organic chemical vapor deposition epitaxial growth system. After the AlN or AlGaN nucleating layer and the GaN buffer layer are grown on the SiC or Si single crystal substrate, a GaN channel layer, an AlN insert layer, an AlGaN barrier layer and a GaN capped layer are grown, and trimethyl indium is added in the growth atmosphere to do epitaxial growth with indium doping. The dislocation of the material or device made by the method of the invention is reduced greatly. The invention improves the interfacial smoothness, increases the electron mobility of the material, increases the growth window, ensures the material grow easier, improves the current collapse of the device, reduces the leakage current and increases transconductance and gain and increases the output power of microwave power devices.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
Diamond semiconductor element and process for producing the same
ActiveUS20080134960A1Reduce generationImprove transconductanceSolid-state devicesVacuum evaporation coatingRefractive indexWaveguide
An integrated optical waveguide has a first optical waveguide, a second optical waveguide, and a groove. The second optical waveguide is coupled to the first optical waveguide and has a refractive index that is different from the first optical waveguide. The groove is disposed so as to traverse an optical path of the first optical waveguide and is separated from an interface between the first optical waveguide and the second optical waveguide by a predetermined spacing. The spacing from the interface and the width of the groove are determined such that reflection at a boundary between the first optical waveguide and the second optical waveguide is weakened. A semiconductor board may be disposed at a boundary between the first optical waveguide and the second optical waveguide. In this case, the width of the groove and the thickness of the semiconductor board are determined such that light reflected off an interface between the first optical waveguide and the groove is weakened by light reflected from an interface between the groove and the semiconductor board, and by light reflected from an interface between the semiconductor board and the second optical waveguide.
Owner:NIPPON TELEGRAPH & TELEPHONE CORP
Semiconductor device
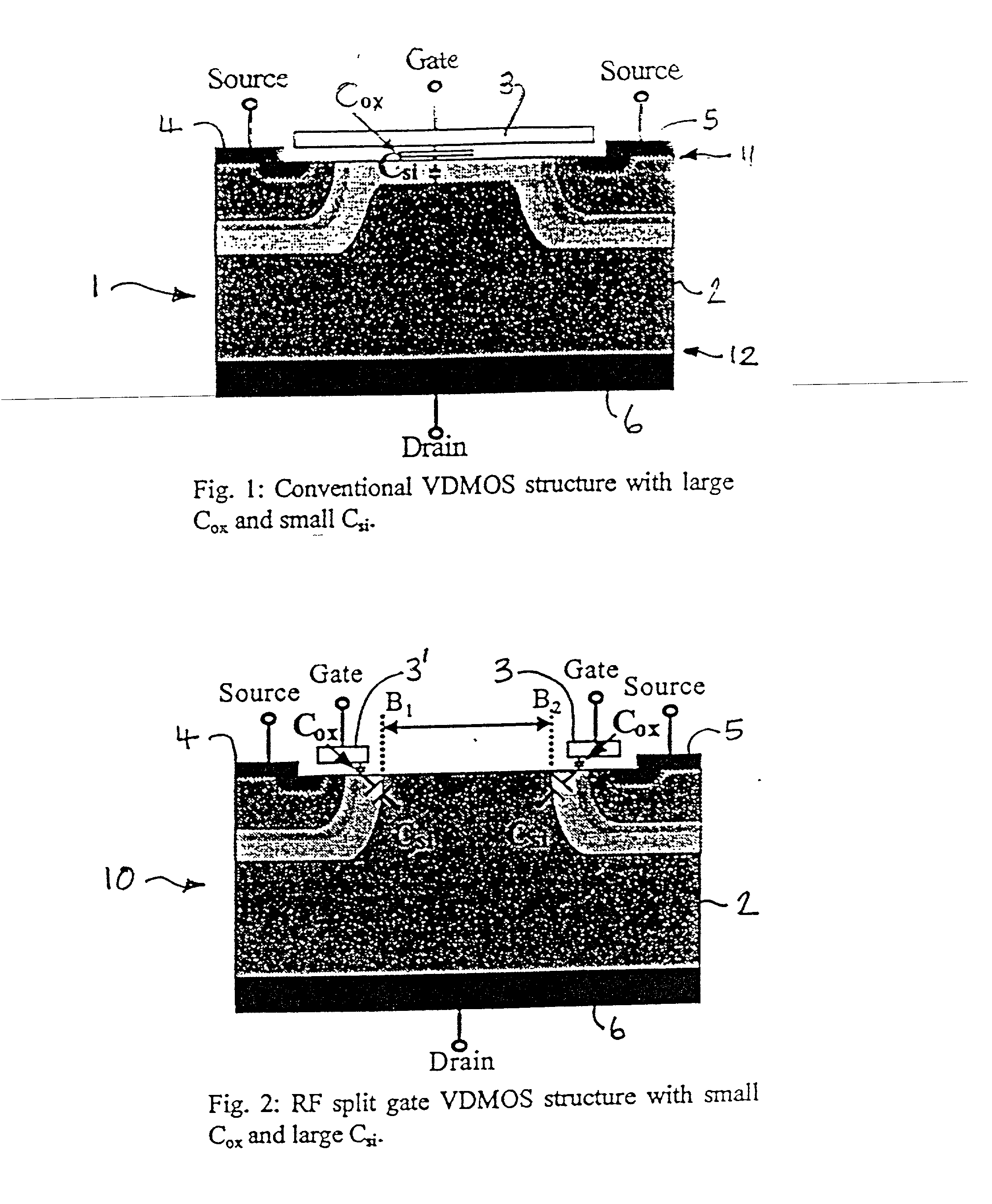
InactiveUS20020017682A1Efficient and reliable for applicationImprove breakdown voltageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMOSFETPower application
A VD (vertical diffusion) MOSFET device for use in RF power applications has a split gate structure and an additional, dummy gate is provided between the spaced apart gates and, in operation of the device, is electrically coupled to source electrodes provided outside of the gates. The split gate structure reduces gate overlap capacitance and the dummy gate induces depletion in the semiconductor body of the device and reduces the substrate capacitance. The gate overlap capacitance and the substrate capacitance both contribute to the feedback capacitance of the device which has to be as low as possible for high frequency operation. By reducing both of these components, the invention provides advantageous high frequency operation.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Metal transistor device
ActiveUS7838875B1Small feature sizeEnhanced transistor performanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesMaterials scienceMetal
The present invention relates to a depletion or enhancement mode metal transistor in which the channel region of a transistor device comprises a thin film metal or metal composite layer formed over an insulating substrate.
Owner:TSANG DEAN Z
Soi lateral mosfet devices
InactiveUS20130193509A1High critical electric filedIncrease the electric field strengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor devicesMOSFETPermittivity
The present invention relates to a semiconductor power device and power integrated circuits (ICs). The lateral SOI MOSFET in the present comprises a trench gate extended to the dielectric buried layer, one or multiple dielectric trenches in the drift region, and a buried gate in said dielectric trench. The permittivity of the dielectric in said dielectric trench is lower than that of said active layer. Firstly, said dielectric trench not only greatly improves breakdown voltage, but also reduces pitch size. Secondly, the trench gate widens the effective conductive region in the vertical direction. Thirdly, dual gates of said trench gate and buried gate increase channel and current densities. Thereby, specific on-resistance and the power loss are reduced. The device of the present invention has many advantages, such as high voltage, high speed, low power loss, low cost and ease of integration. The device in the present invention is particularly suitable for power integrated circuits and RF power integrated circuits.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
AlGaN/GaN HEMT multilayer field plate device of concave grid groove and manufacturing method thereof
InactiveCN101276837AImprove breakdown voltageEliminate collapseSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesSemiconductor materialsGrid connection
The invention relates to the technical field of microwave power device in semiconductor materials, discloses a AlGaN / GaN HEMT multilayer field board device of recessed grid, and meanwhile discloses a method for manufacturing AlGaN / GaN HEMT multilayer field board device of the recessed grid; on the basis of common AlGaN / GaN HEMT device manufacturing process, the method comprises the steps of photo-etching grid images after forming Ohm contact of a source electrode and a drain electrode, etching AlGaN extension layer of a part of the grid image, after evaporating grid metal, firstly manufacturing a grid connection field board and then a source connection field board to form the AlGaN / GaN HEMT multilayer field board device of the recessed grid. Utilization of the invention can efficiently improve puncturing characteristic, transconductance and threshold value voltage of the AlGaN / GaN HEMT device, and at the same time of improving the device plus, availably suppress phenomenon of current collapse of the AlGaN / GaN HEMT device.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Secondary extension structure of silicon carbide
ActiveCN101246899AWork lessIncrease powerSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesOhmDrain resistance
The present invention discloses a carborundum secondary epitaxy material structure used for carborundum preparation comprising of: a carborundum single crystal substrate, a first homoepitaxy layer on surface of substrate, a secondary epitaxy material on surface of first homoepitaxy which comprises of p-type carborundum buffer layer, n-type carborundum active layer and unintentional doped intrinsic carborundum layer. Corresponding to MESFET (metal mosfet) with common structure, the MESFET fabricated by secondary epitaxy type has merits of small source-drain resistance, large ohm interface and uniform electric field distribution of working field in MESFET, can enhance transconductance, improve working voltage and power of appliance, and at the same time, the technique of preparation is simplified and the stability of appliance is ensured.
Owner:THE 13TH RES INST OF CHINA ELECTRONICS TECH GRP CORP
Nanotube-based vacuum devices
InactiveUS7176478B2Improve transconductanceRaise the ratioNanoinformaticsCold cathodesCapacitanceTerminal equipment
New, hybrid vacuum electron devices are proposed, in which the electrons are extracted from the nanotube into vacuum. Each nanotube is either placed on the cathode electrode individually or grown normally to the cathode plane. Arrays of the nanotubes are also considered to multiply the output current. Two- and three-terminal device configurations are discussed. In all the cases considered, the device designs are such that both input and output capacitances are extremely low, while the efficiency of the electron extraction into vacuum is very high, so that the estimated operational frequencies are expected to be in a tera-hertz range. New vacuum triode structure with ballistic electron propagation along the nanotube is also considered.
Owner:ITUS
Nanowire based vertical circular grating transistor and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN103531635AReduce parasitic resistanceImprove transconductanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceGrating
The invention discloses a nanowire based vertical circular grating transistor and a preparation method thereof. According to the structure, a conducting channel material is an intrinsic or low doped nanowire perpendicular to a substrate; a low-resistance nanowire is connected above the intrinsic or low doped nanowire in a gapless manner; the intrinsic or low doped nanowire is surrounded by a source electrode, a gate medium and a gate electrode sequentially from bottom to top; the source electrode and the gate medium as well as the gate medium and the grate electrode are connected in the position of the side wall of the nanowire in a gapless manner; the low-resistance nanowire is surrounded by a drain electrode; and three isolation layers are arranged among the electrodes. The invention further provides the preparation method of the transistor. Both the source electrode and the gate electrode are obtained with the method that firstly, a metal film is plated and then metal above BCB (benzocyclobutene) is eroded by using BCB as a mask; and the low-resistance nanowire is obtained through heavy doping of the intrinsic or low doped nanowire or through metal alloy. According to the short-channel transistor structure and the preparation method, a device with a short channel can be prepared, the parasitic resistance and the parasitic capacitance can be effectively reduced, and the device performance is improved.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Group III-nitride semiconductor device with a cap layer
ActiveUS7800116B2Improve transconductanceReduce resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical conductorDevice material
A semiconductor device includes: a first semiconductor layer which is made of a first group III nitride semiconductor; a cap layer which is formed on the first semiconductor layer, which is made of a second group III nitride semiconductor, and which has an opening for exposing the first semiconductor layer; and a source electrode and a drain electrode which are formed on the cap layer so as to oppose to each other with the opening interposed. A gate electrode is formed on the bottom face of the opening with an insulating film interposed. The insulating film is formed on at least a part of the first semiconductor layer which is exposed through the opening.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
Split compensation two-stage operational amplifier based on inverter input structure
InactiveCN103199807AInhibition effectOffset the impactDifferential amplifiersAmplifier modifications to extend bandwidthCapacitanceFrequency compensation
The invention belongs to the technical field of electronics and relates to the frequency compensation technology of operational amplifiers in analog integrated circuits. The split compensation two-stage operational amplifier comprises a two-stage operational amplifier. A first-stage operational amplifier is composed of N-channel metal oxide semiconductor (NMOS) tubes (M1N, M2N, M3 and M4) and P-channel metal oxide semiconductor (PMOS) tubes (M1P, M2P and M0). A second-stage operational amplifier is composed of a PMOS tube M5P and an NMOS tube M5N. A traditional Miller capacitor is divided into a Cm1 portion and a Cm2 portion to finish frequency compensation of the operational amplifier. A first frequency compensation capacitor Cm1 is connected with the position between the output end of the first operational amplifier and the output end of the whole two-stage operational amplifier. A second frequency compensation capacitor Cm2 is connected with the position between a connection point of a source of the NMOS tube M2N and a drain of the NMOS tube M4 in the first-stage operational amplifier and the output end of the whole two-stage operational amplifier. The split compensation two-stage operational amplifier has strong robustness and higher unit grain bandwidth and output slew rate due to the fact that non-dominant poles and stray parameter are not related.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
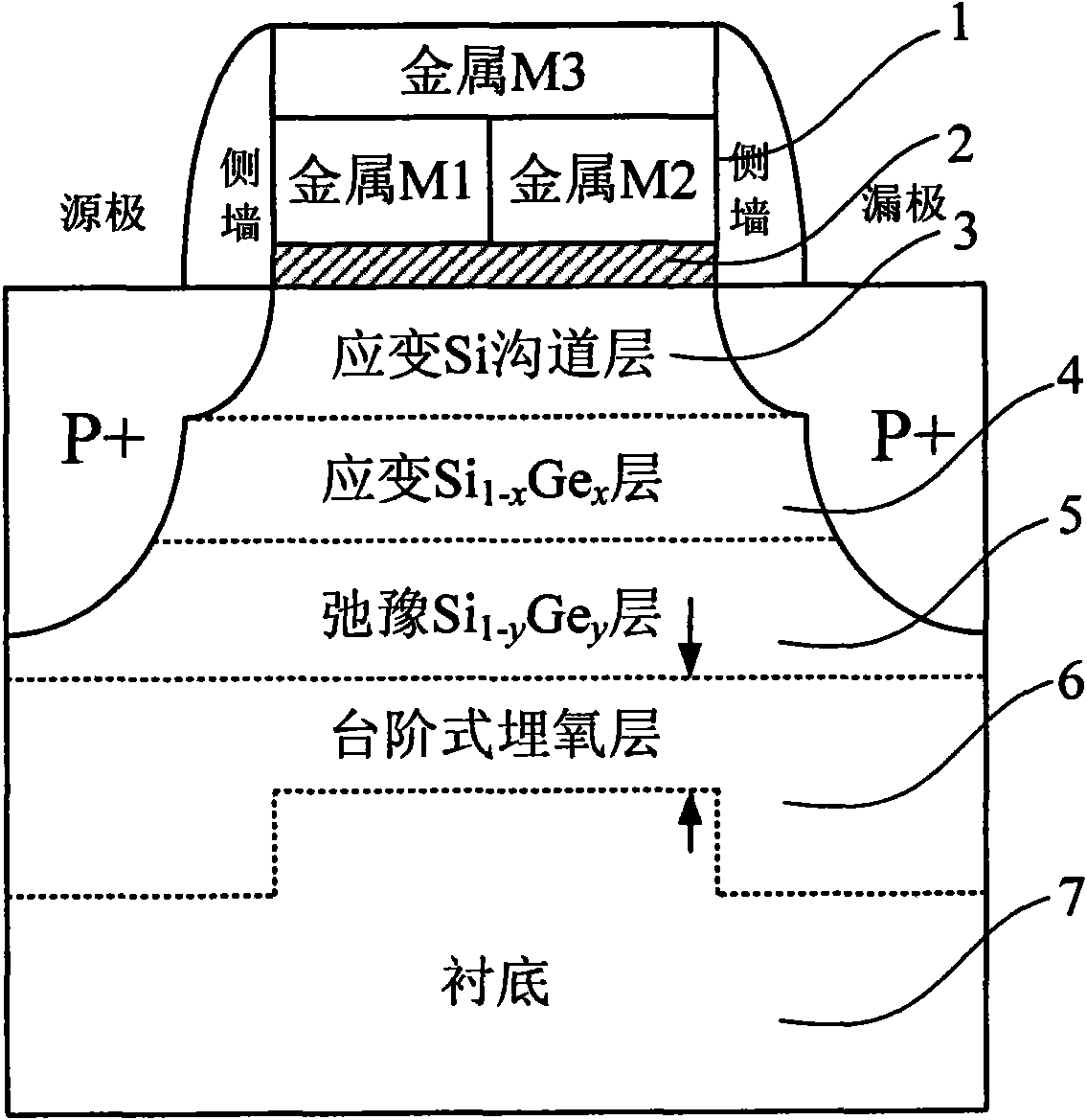
Heterogeneous metal stacked grid strained silicon-germanium on insulator p-channel metal oxide semiconductor field effect tube (SSGOI pMOSFET) device structure
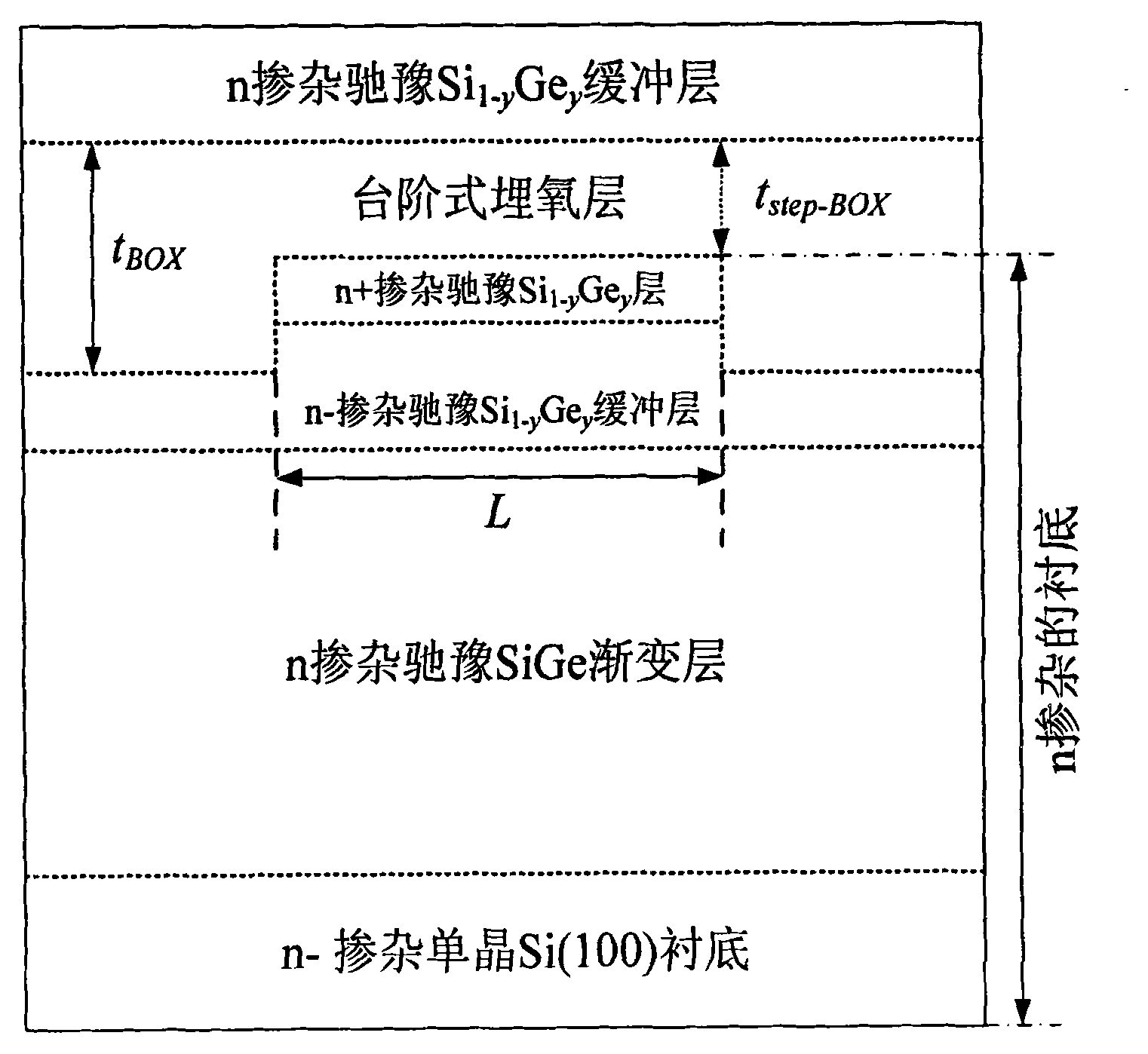
InactiveCN102214694AImprove shipping speedImprove transmission efficiencySemiconductor devicesInsulation layerOxygen
The invention discloses a heterogeneous metal stacked grid strained silicon-germanium on insulator p-channel metal oxide semiconductor field effect tube (SSGOI pMOSFET) device structure, which comprises a heterogeneous metal stacked grid structure, a grid insulation layer, an intrinsic or n-doped strained Si channel layer, a strained Si1-xGex layer of which an intrinsic or n-doped component is changed gradually, an n-doped relaxation Si1-yGey layer, a stepped oxygen buried layer and an n-doped substrate part sequentially from top to bottom, wherein the n-doped substrate part consists of four parts, namely an n<+>-doped relaxation Si1-yGey layer, an n<->-doped relaxation Si1-yGey buffer layer, an n-doped relaxation SiGe gradient layer and an n<->-doped monocrystal Si(100) substrate. The device has a simple structure, can be totally compatible with the conventional Si silicon on insulator (SOI) process, is integrated with the advantages of grid engineering, strain engineering and substrate engineering, and makes a complementary metal-oxide-semiconductor structure process simply integrated.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Nanotube-based vacuum devices
InactiveUS20050161668A1Improve transconductanceRaise the ratioNanoinformaticsCold cathodesCapacitanceTerminal equipment
New, hybrid vacuum electron devices are proposed, in which the electrons are extracted from the nanotube into vacuum. Each nanotube is either placed on the cathode electrode individually or grown normally to the cathode plane. Arrays of the nanotubes are also considered to multiply the output current. Two- and three-terminal device configurations are discussed. In all the cases considered, the device designs are such that both input and output capacitances are extremely low, while the efficiency of the electron extraction into vacuum is very high, so that the estimated operational frequencies are expected to be in a tera-hertz range. New vacuum triode structure with ballistic electron propagation along the nanotube is also considered.
Owner:ITUS
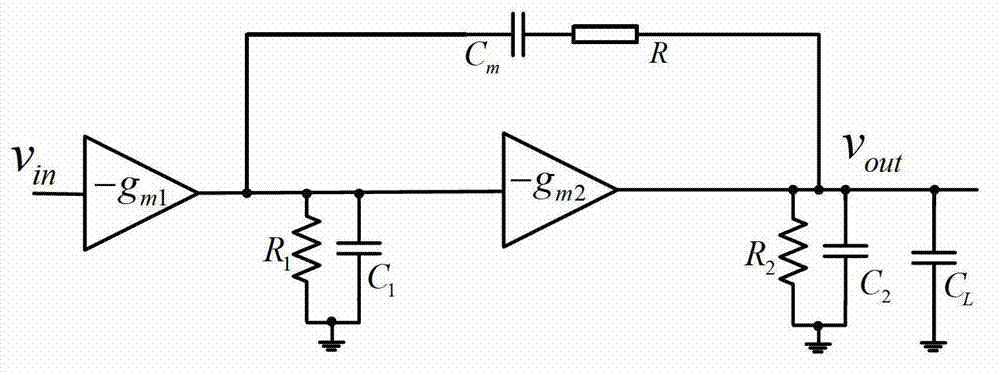
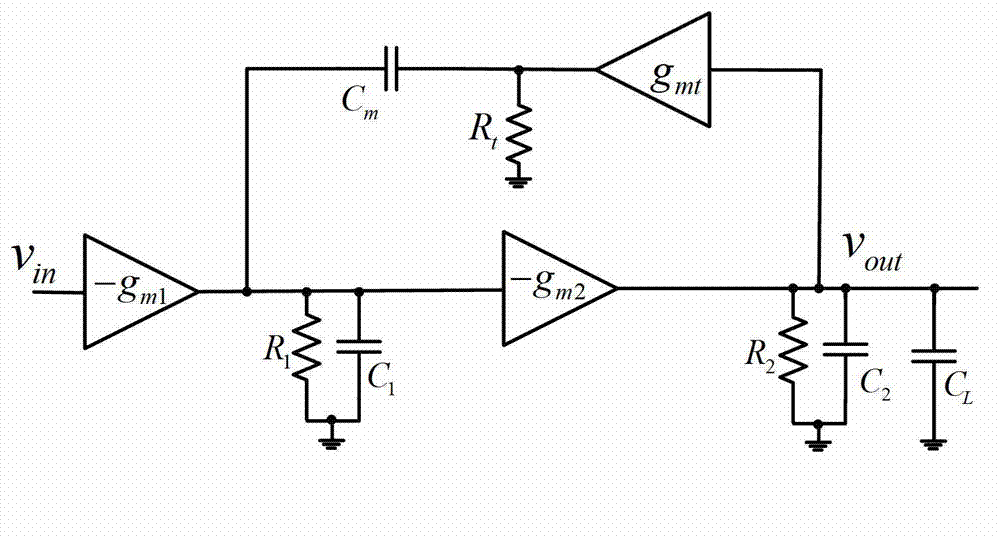
Class AB enhanced transconductance source follower
ActiveUS7151410B2Maintaining large bandwidthReduce voltageAmplifier combinationsAmplifier detailsLow voltageCascode
A low voltage, high bandwidth, enhanced transconductance, source follower circuit constructed from MOS FET devices, which operates in a class AB mode. The drain current of the source follower is sensed with a folded cascode device. The sensed current is multiplied by a common source device of same type (NMOS or PMOS) as the source follower, and directed to the output load. Over limit current load at the source follower drain is sensed by a common source device of the opposite type (NMOS or PMOS), which also supplies the necessary extra current to the output load. This allows the device to supply significantly more than the quiescent current in both sourcing and sinking the output. Average power consumption for driving a given load is significantly reduced, while maintaining the large bandwidth of traditional source follower designs, and the capability for use in either voltage regulators or in a current conveyor.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com