Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
132 results about "Drain resistance" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
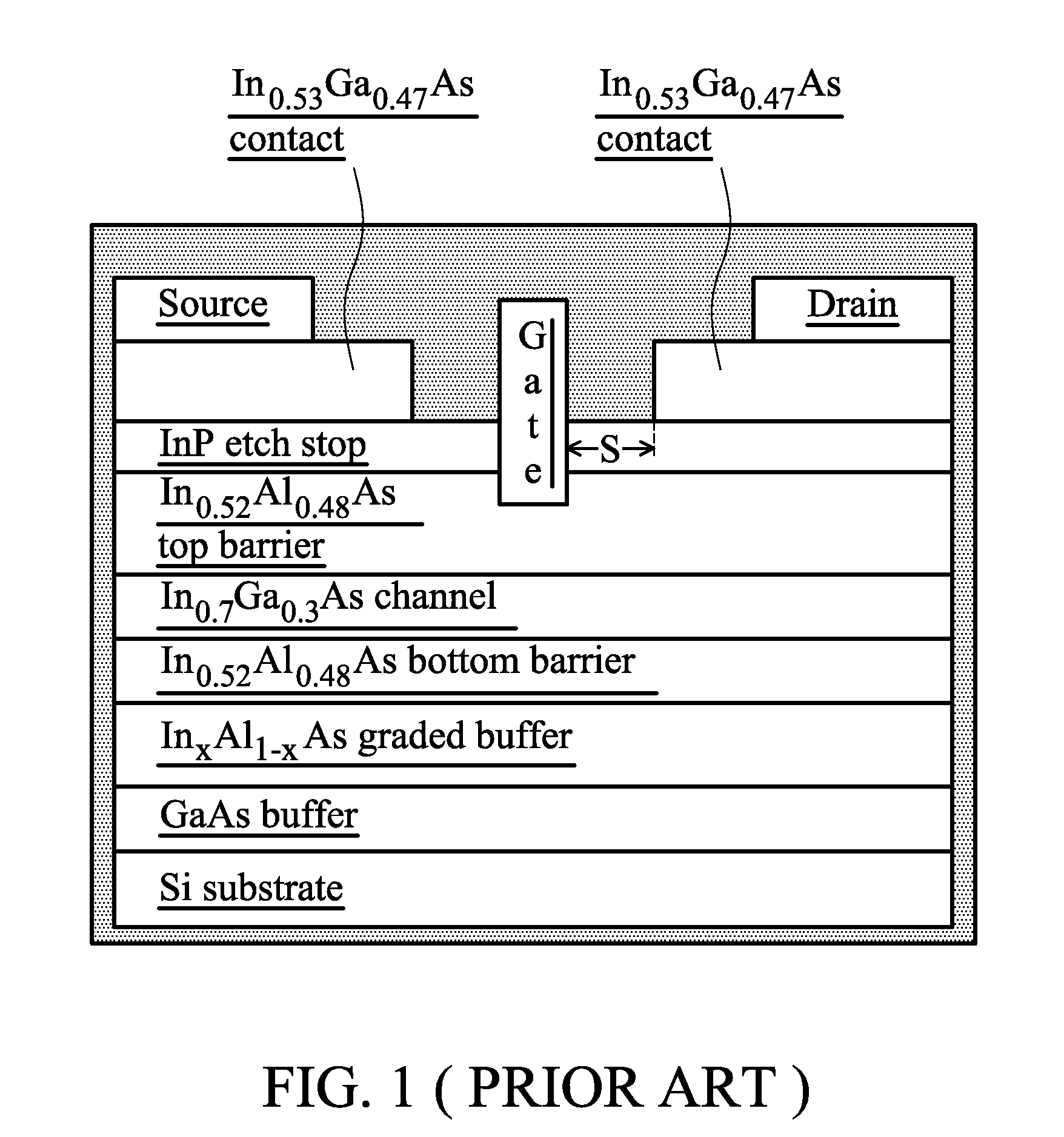
Hetero-junction field effect transistor having an intermediate layer
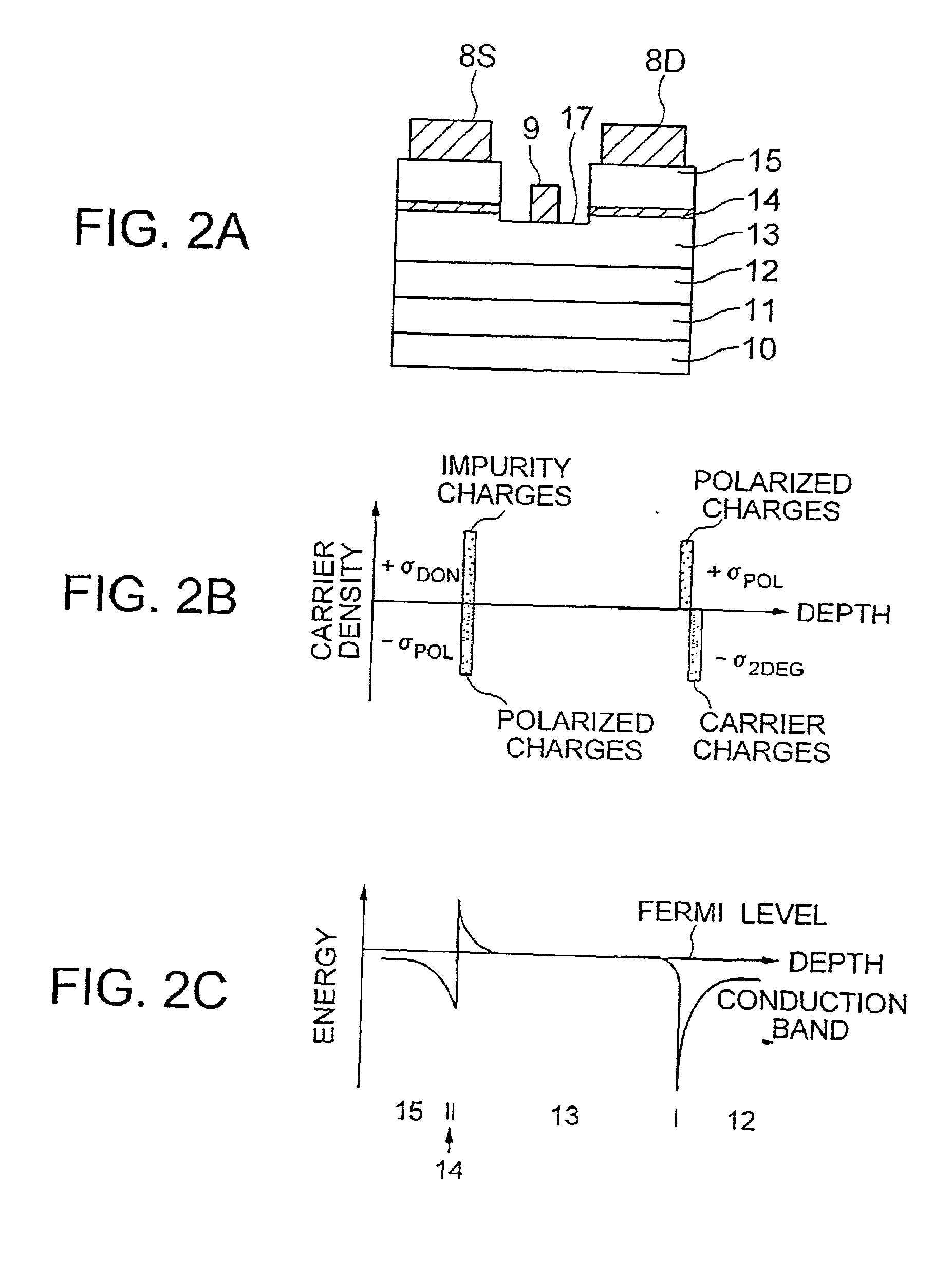
InactiveUS20010040247A1Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingImpurityElectron
A hetero-junction FET has an intermediate layer including n-type-impurity doped layer between an electron supply layer and an n-type cap layer. The intermediate layer cancels the polarized negative charge generated between the electron supply layer and the n-type cap layer by ionized positive charge, thereby reducing the barrier against the electrons and source / drain resistance.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Hetero-junction field effect transistor having an intermediate layer
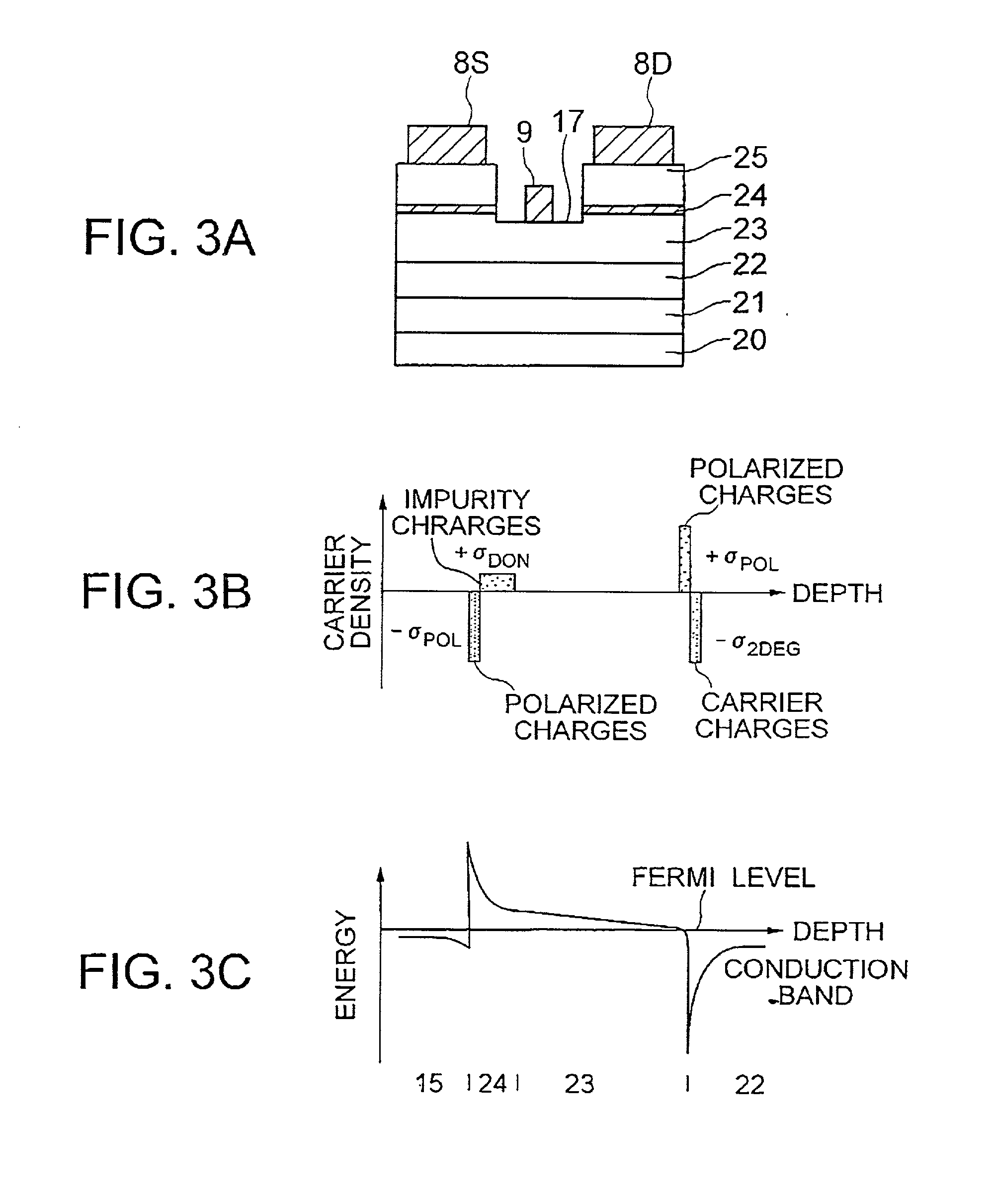
InactiveUS6552373B2Solid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectronImpurity
A hetero-junction FET has an intermediate layer including n-type-impurity doped layer between an electron supply layer and an n-type cap layer. The intermediate layer cancels the polarized negative charge generated between the electron supply layer and the n-type cap layer by ionized positive charge, thereby reducing the barrier against the electrons and source / drain resistance.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Fully-depleted SOI MOSFETs with low source and drain resistance and minimal overlap capacitance using a recessed channel damascene gate process
InactiveUS6841831B2Good effectLower resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSalicideCapacitance
A sub-0.05 μm channel length fully-depleted SOI MOSFET device having low source and drain resistance and minimal overlap capacitance and a method of fabricating the same are provided. The sub-0.05 μm channel length fully-depleted SOI MOSFET device includes an SOI structure which contains at least an SOI layer having a channel region of a first thickness and abutting source / drain regions of a second thickness present therein, wherein the second thickness is greater than the first thickness and the source / drain regions having a salicide layer present thereon. A gate region is present also atop the SOI layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Method of forming an N channel and P channel finfet device on the same semiconductor substrate
InactiveUS7187046B2Lower gate resistanceReduce resistanceTransistorSolid-state devicesDevice formGate insulator
A method of forming a FINFET CMOS device structure featuring an N channel device and a P channel device formed in the same SOI layer, has been developed. The method features formation of two parallel SOI fin type structures, followed by gate insulator growth on the sides of the SOI fin type structures, and definition of a conductive gate structure formed traversing the SOI fin type structures while interfacing the gate insulator layer. A doped insulator layer of a first conductivity type is formed on the exposed top surfaces of a first SOI fin type shape, while a second doped insulator layer of a second conductivity type is formed on the exposed top surfaces of the second SOI fin type shape. An anneal procedure results creation of a source / drain region of a first conductivity type in portions of the first SOI fin type shape underlying the first doped insulator layer, and creation of a source / drain region of a second conductivity type in portions of the second SOI fin type shape underlying the second doped insulator layer. Selective deposition of tungsten on exposed top surface of the source / drain regions is then employed to decrease source / drain resistance.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Reducing Source/Drain Resistance of III-V Based Transistors
ActiveUS20100276668A1Reduced sourceReduced drain resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricIntegrated circuit
An integrated circuit structure includes a substrate; a channel layer over the substrate, wherein the channel layer is formed of a first III-V compound semiconductor material; a highly doped semiconductor layer over the channel layer; a gate dielectric penetrating through and contacting a sidewall of the highly doped semiconductor layer; and a gate electrode on a bottom portion of the gate dielectric. The gate dielectric includes a sidewall portion on a sidewall of the gate electrode.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Device improvement by source to drain resistance lowering through undersilicidation
InactiveUS6133124ATransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCrystal structureOptoelectronics
Various methods of fabricating a silicide layer, and devices incorporating the same are provided. In one aspect, a method of fabricating a silicide layer on a substrate is provided. The method includes the steps of damaging the crystal structure of a portion of the substrate positioned beneath the spacer and depositing a layer of metal on the substrate. The metal layer and the substrate are heated to react the metal with the substrate and form the silicide layer, whereby a portion of the silicide layer extends laterally beneath the spacer. Any unreacted metal is removed. The method enables fabrication of silicide layers with substantial lateral encroachment into LDD structures, resulting in lower possible source-to-drain resistance and enhanced performance for transistors.
Owner:ADVANCED MICRO DEVICES INC
MOS transistor having a T-shaped gate electrode
InactiveUS7250655B2Minimize source/drain resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCapacitanceHigh concentration
A MOS transistor having a T-shaped gate electrode and a method for fabricating the same are provided, wherein the MOS transistor includes a T-shaped gate electrode on a semiconductor substrate; an L-shaped lower spacer disposed at both sides of the gate electrode to cover a top surface of the semiconductor substrate; and low-, mid-, and high-concentration impurity regions formed in the semiconductor substrate of both sides of the gate electrode. The high-concentration impurity region is disposed in the semiconductor substrate next to the lower spacer and the mid-concentration impurity region is disposed between the high- and low-concentration impurity regions. A MOS transistor according to the present invention provides a decrease in a capacitance, a decrease in a channel length, and an increase in a cross-sectional area of the gate electrode. At the same time, the mid-concentration impurity region provides a decrease in a source / drain resistance Rsd.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
MOSFETS (metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistors) with low source-drain contact resistance and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103000675ALower the altitudeImprove performanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesDielectricSalicide
The invention discloses a MOSFET (metal-oxide-semiconductor field effect transistor) which effectively lowers source-drain contact resistance in post grid process and a manufacturing method thereof. The MOSFET comprises a substrate, a grid stacking structure, formed by a grid medium layer and a grid metal layer, on the substrate, source-drain areas in substrate parts on two sides of the grid stacking structure, grid side walls on substrate parts on two sides of the grid stacking structure, interlevel dielectric on the substrate, a source-drain contact plug in the interlevel dielectric on the source-drain areas and metal silicide between the source-drain areas and the source-drain contact plug and is characterized in that the interface of the metal silicide and the source-drain areas is provided with an ion-doped dephlegmation area, and the grid medium layer is located below and on the side of the grid metal layer. By the MOSFET which effectively lowers source-drain contact resistance and the manufacturing method thereof and the ion-doped dephlegmation area disposed on the interface between the metal silicide and the source-drain areas, Schottky barrier height can be reduced effectively, and accordingly source-drain resistance is reduced greatly, and device performance is further improved.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Integrated circuit structure
ActiveCN101908543ALower resistanceImprove drive currentTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingDriving currentSemiconductor materials
An integrated circuit structure includes a substrate, and a channel over the substrate. The channel includes a first III-V compound semiconductor material formed of group III and group V elements. A gate structure is over the channel. A source / drain region is adjacent the channel and includes a group-IV region formed of a doped group-IV semiconductor material selected from the group consisting essentially of silicon, germanium, and combinations thereof. By re-growing silicon / germanium source / drain regions, the existing silicidation technique can be used to reduce the source / drain resistance and to improve drive currents of the resulting transistors. Buffer layers have the effect of smoothening the lattice constant transition between the channel of the transistor and the source / drain regions, resulting in a reduced defect density and reduced junction leakage currents.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
MOS transistors having higher drain current without reduced breakdown voltage
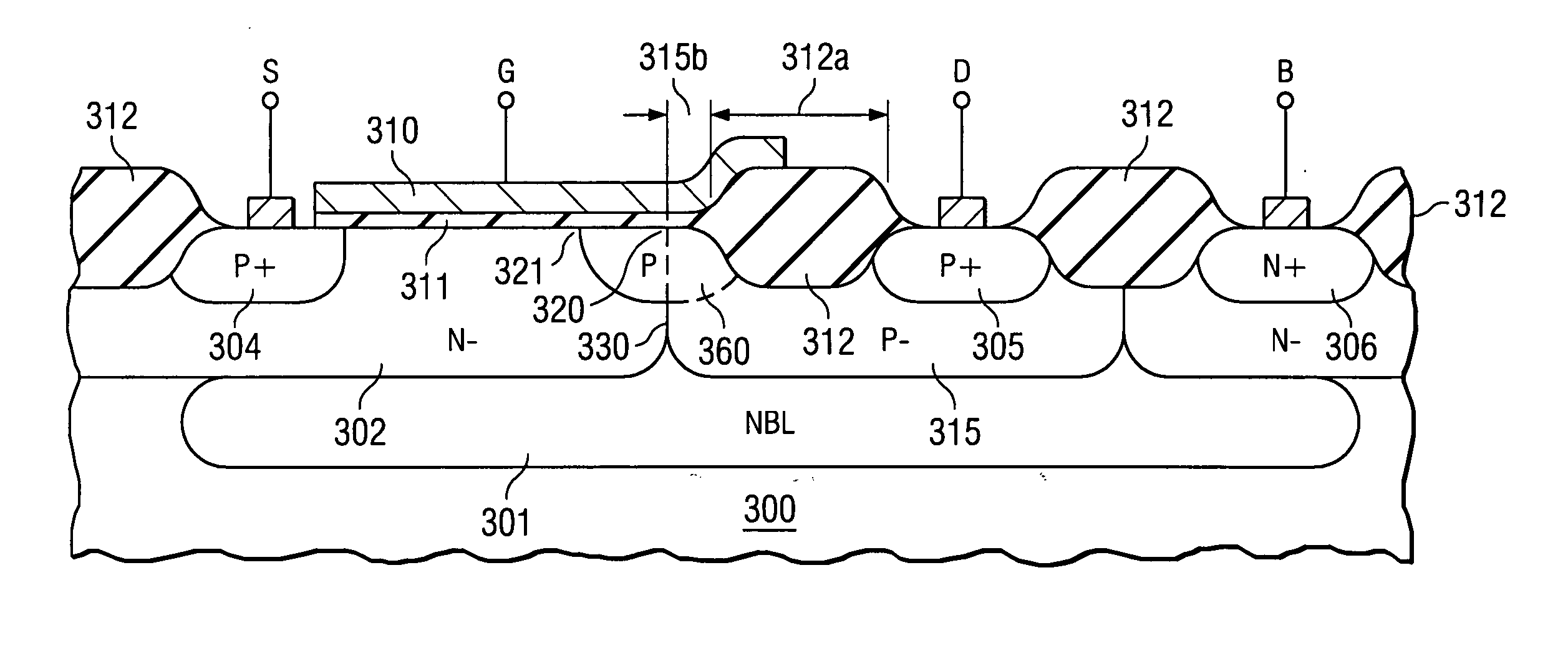
ActiveUS6873021B1Reduce resistanceEliminating resistance uncertaintyTransistorSolid-state devicesDrain resistanceDrain current
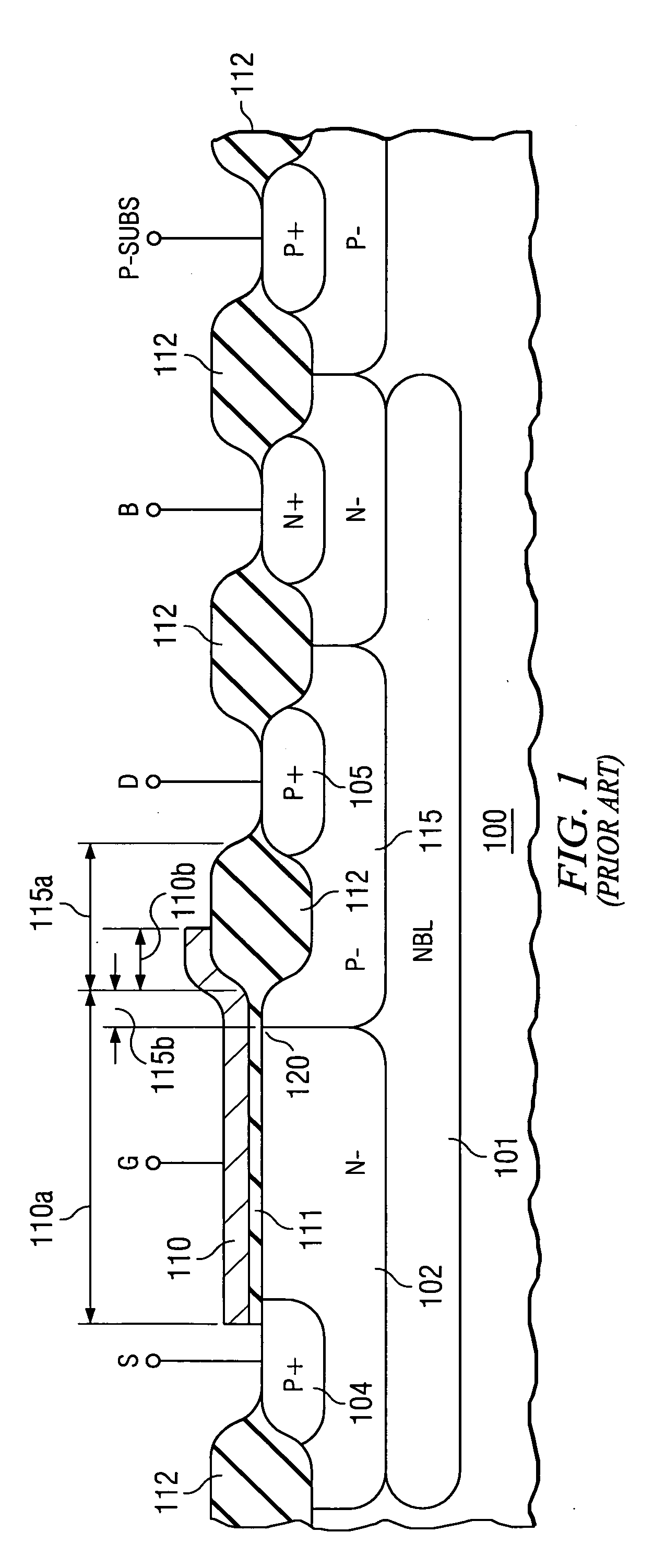
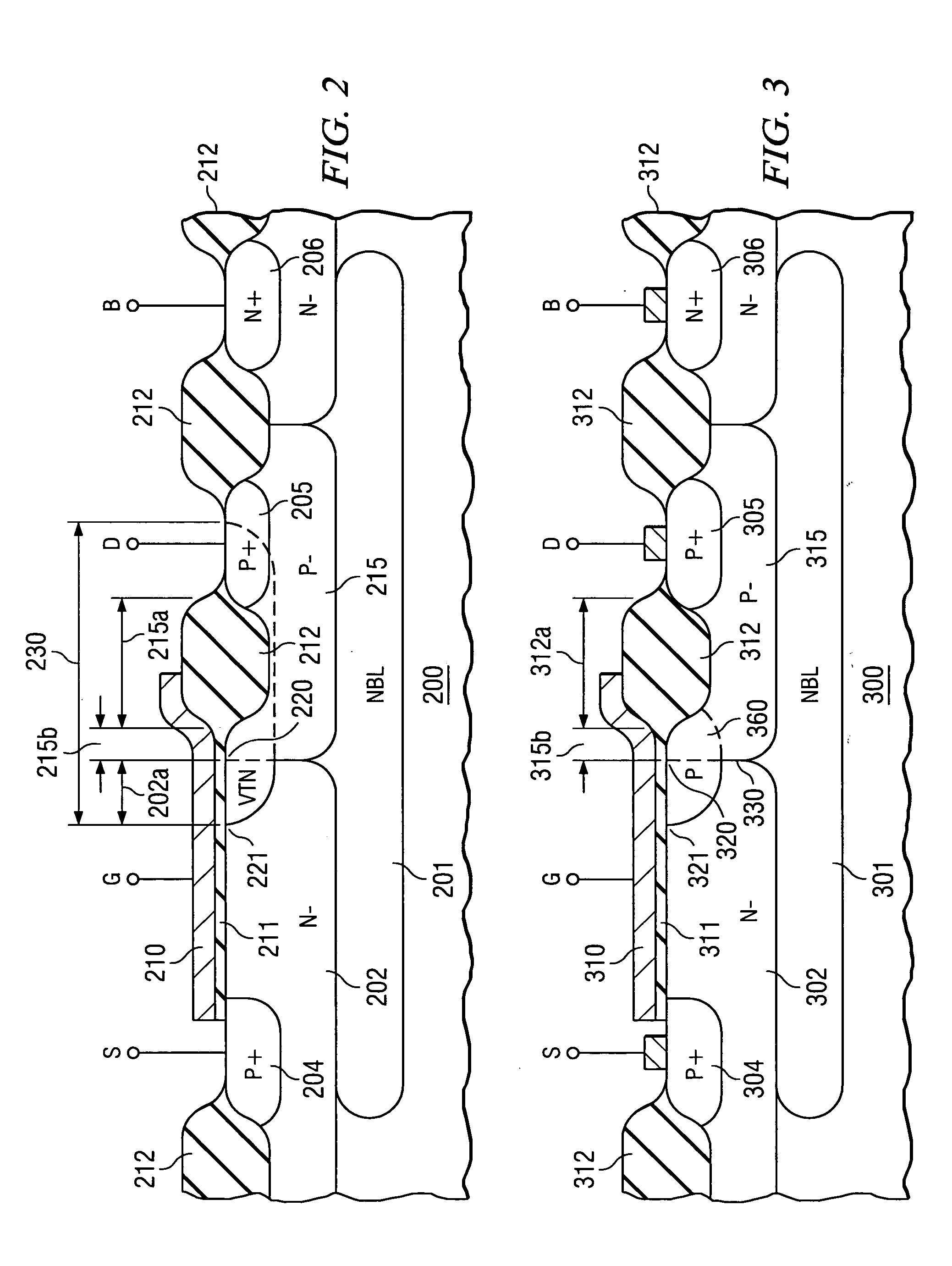
A drain-extended MOS transistor in a semiconductor wafer (300) of a first conductivity type comprises a first well (315) of the first conductivity type, operable as the extension of the transistor drain (305) of the first conductivity type, and covered by a first insulator (312) having a first thickness, and further a second well (302) of the opposite conductivity type, intended to contain the transistor source (304) of the first conductivity type, and covered by a second insulator (311) thinner than said first insulator (312). First and second wells form a junction (330) that terminates (320, 321) at the second insulator. The first well has a region (360) in the proximity of the junction termination, which has a higher doping concentration than the remainder of the first well and extends not deeper than the first insulator thickness. Region (360) of higher doping concentration reduces the transistor drain resistance so that the drain current is increased to approximately twice the value it had without the higher doping concentration, while the transistor breakdown voltage remains determined by the (low) doping concentration of the remainder of first well (315).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor device
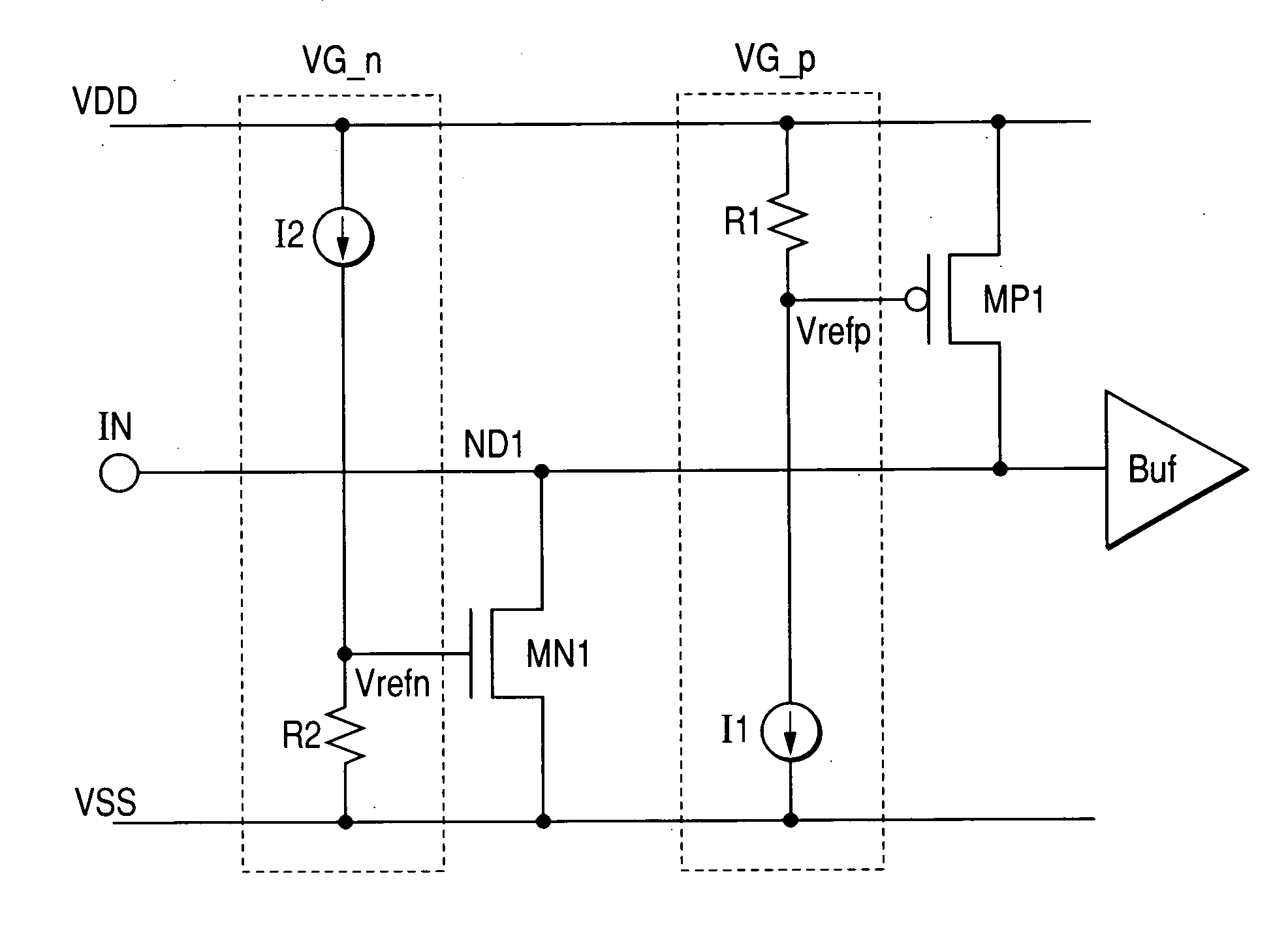
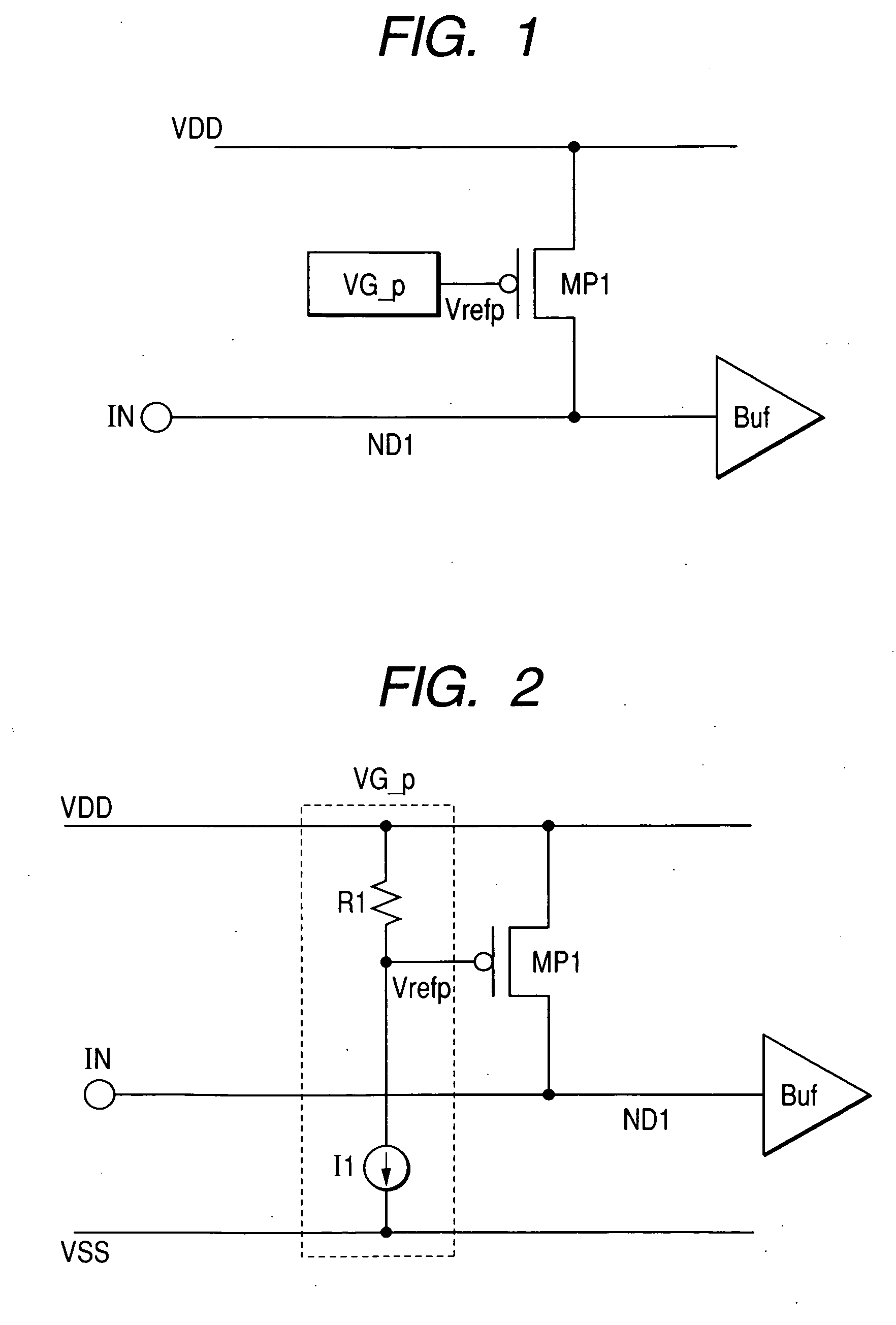
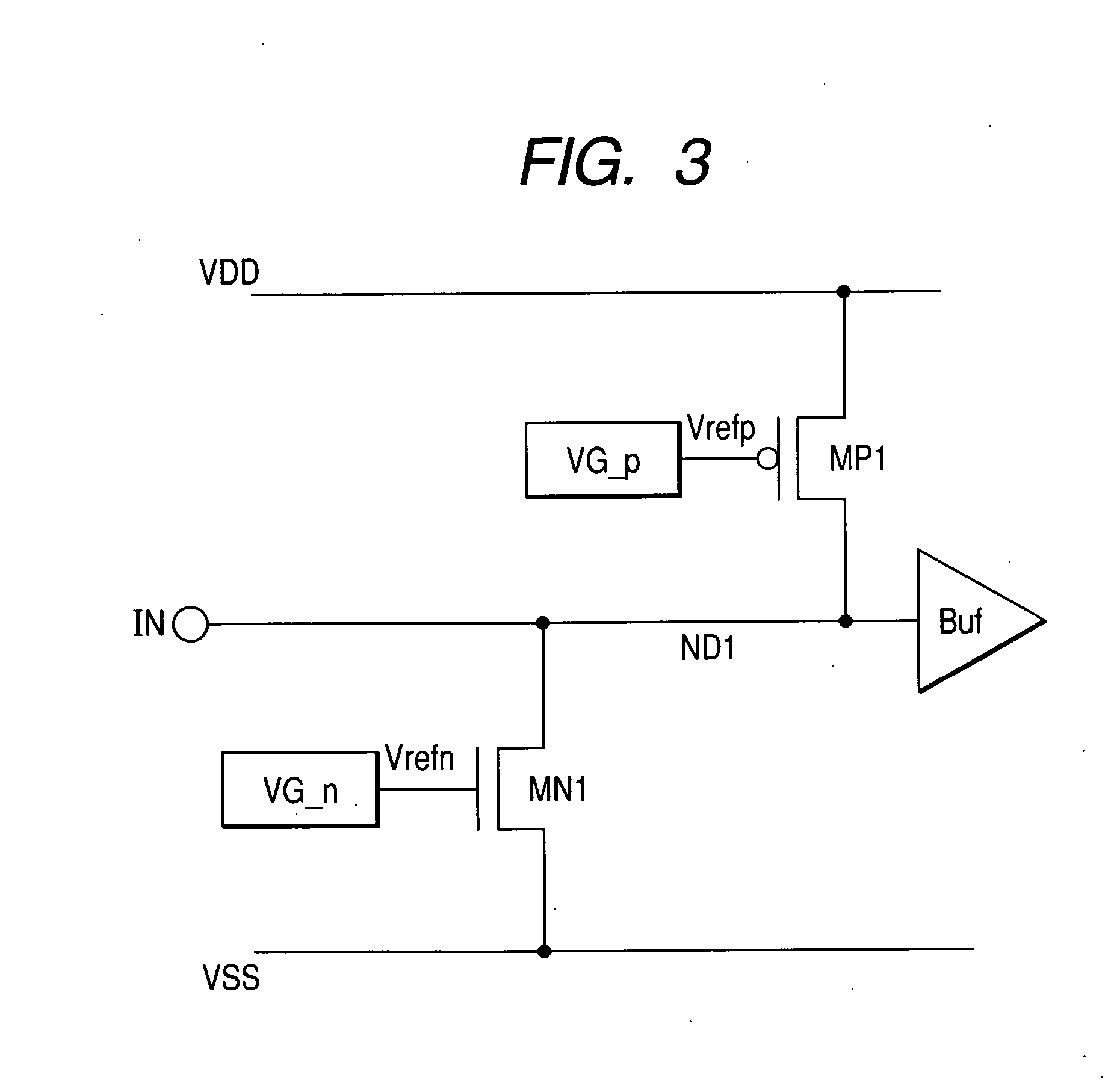
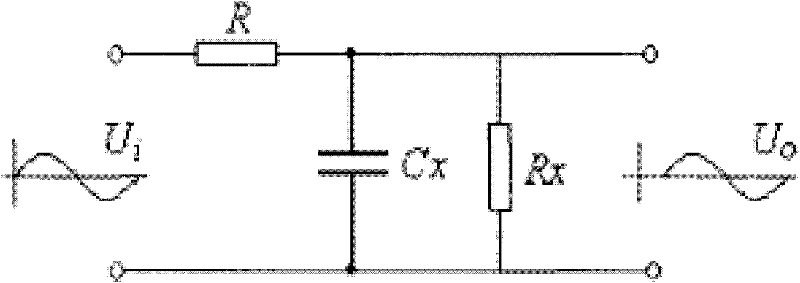
InactiveUS20060158802A1Reduce die areaTransistorReliability increasing modificationsVoltage referenceDrain resistance
This invention provides a semiconductor device in which an ESD protection circuit and a termination circuit can be realized with a small die area. A PMOS transistor having an ESD protection function is placed between a signal node on a line from an signal terminal to an input buffer and a supply voltage node. Furthermore, a voltage generator circuit is placed to supply a reference voltage to the gate of the PMOS transistor. By the reference voltage controlled by the voltage generator circuit, a source-drain resistance of the PMOS transistor is set. Thereby, the PMOS transistor can be made to function as a terminating resistor whose resistance can be set adaptively to a characteristic impedance of a transmission line, for example, connected to the signal terminal in addition to the ESD protection function.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
Low cost fabrication method for high voltage, high drain current MOS transistor
ActiveUS20050118753A1Reduce resistanceEliminating resistance uncertaintySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHigh pressureDrain current
A method for reducing the drain resistance of a drain-extended MOS transistor in a semiconductor wafer, while maintaining a high transistor breakdown voltage. The method provides a first well (502) of a first conductivity type, operable as the extension of the transistor drain (501) of the first conductivity type; portions of the well are covered by a first insulator (503) having a first thickness. A second well (504) of the opposite conductivity type is intended to contain the transistor source (506) of the first conductivity type; portions of the second well are covered by a second insulator (507) thinner than the first insulator. The first and second wells form a junction (505) that terminates at the second insulator (530a, 530b). The method deposits a photoresist layer (510) over the wafer, which is patterned by opening a window (510a) that extends from the drain to the junction termination. Next, ions (540) of the first conductivity type are implanted through the window into the first well; these said ions have an energy to limit the penetration depth (541) to the first insulator thickness, and a dose to create a well region (560) of high doping concentration adjacent to the junction termination (530a).
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS20120267709A1Avoid defectsMiniaturizationSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesMiniaturizationSemiconductor
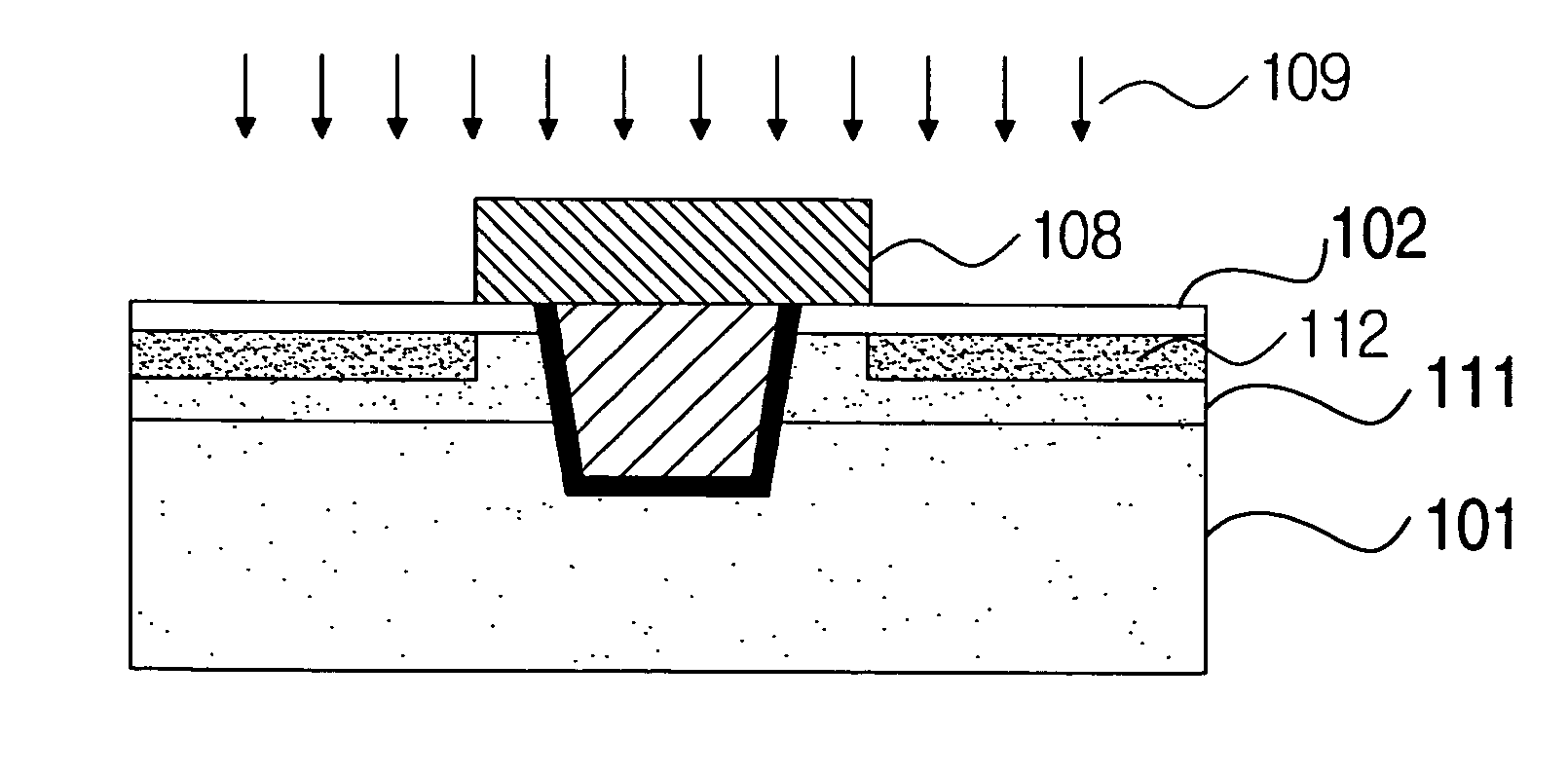
To provide a highly reliable semiconductor device. To provide a semiconductor device which prevents a defect and achieves miniaturization. An oxide semiconductor layer in which the thickness of a region serving as a source region or a drain region is larger than the thickness of a region serving as a channel formation region is formed in contact with an insulating layer including a trench. In a transistor including the oxide semiconductor layer, variation in threshold voltage, degradation of electric characteristics, and shift to normally on can be suppressed and source resistance or drain resistance can be reduced, so that the transistor can have high reliability.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
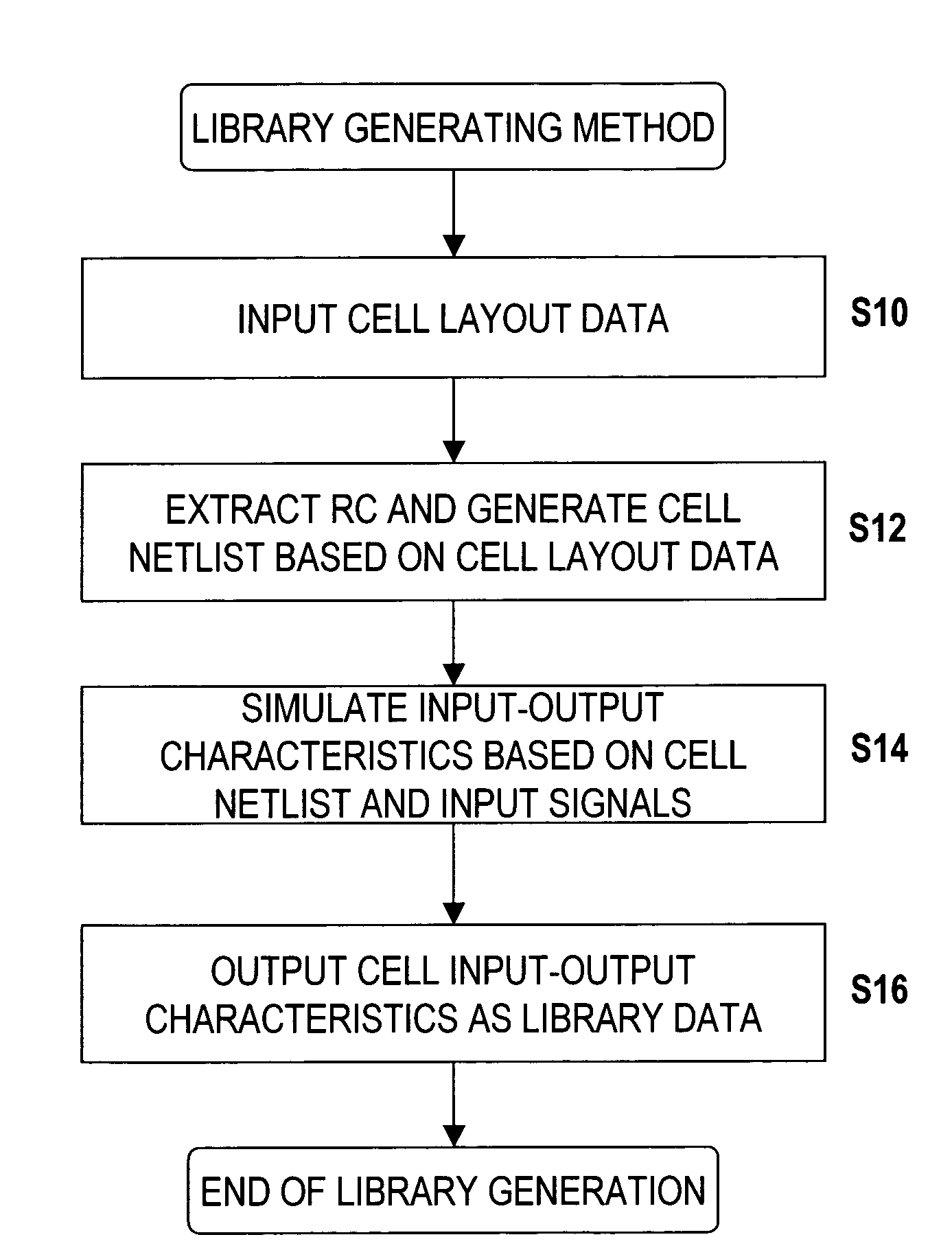
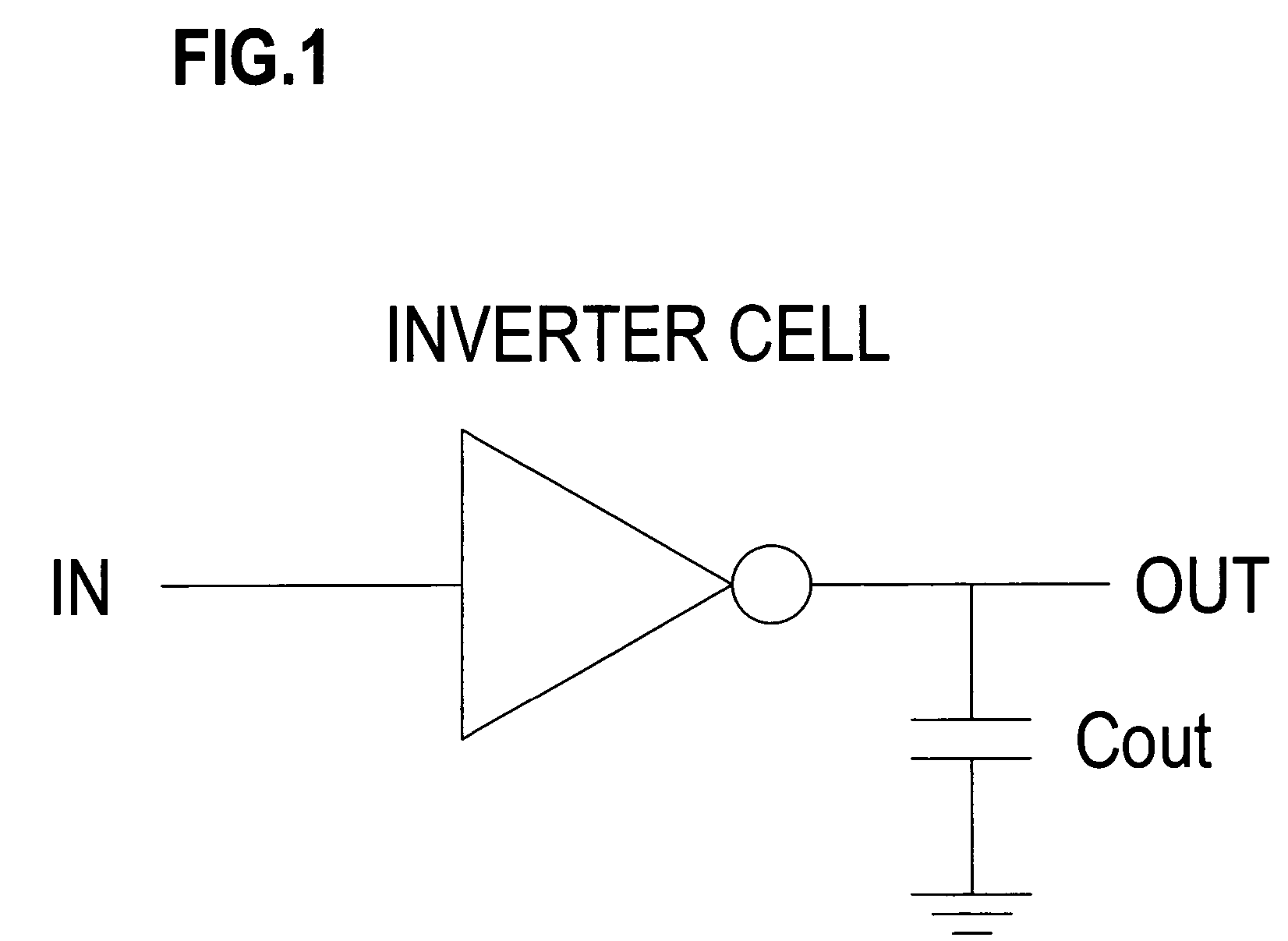
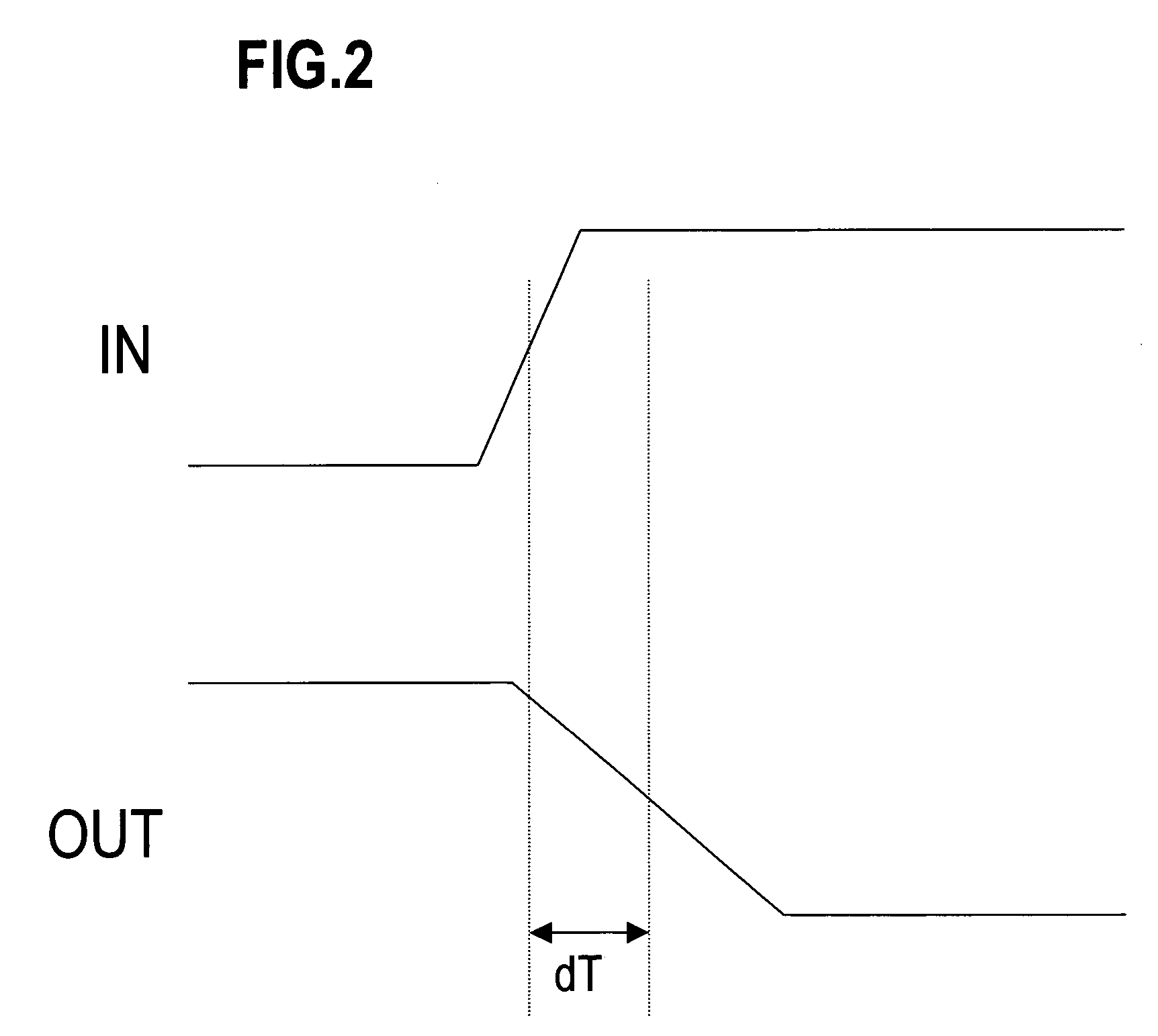
Method of generating cell library data for large scale integrated circuits
InactiveUS7320116B2Accurate representationAccurate extractionDetecting faulty computer hardwareRead-only memoriesElectrical resistance and conductanceNetlist
A method of generating library data for a cell constructed of interconnected MOS transistors, includes a resistance extraction step which extracts source and drain resistances according to source and drain region surface areas by using a resistance calculating formula or referring to a resistance extraction reference file which, when the source and drain regions have a first surface area region, treats the source and drain resistances as resistance values depending on the surface areas, and when the source and drain regions have a second surface area region larger than the first surface area region, treats the source and drain resistances as fixed resistance values; and a simulation step which generates an input-output characteristic for the cell from a netlist containing a MOS transistor model that includes the extracted source resistances and drain resistances and connection information for the model, and from input signals.
Owner:SOCIONEXT INC
Method to Accurately Estimate the Source and Drain Resistance of a MOSFET
ActiveUS20090079446A1Semiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical resistance and conductanceThreshold potential
Measurements of parameters of MOS transistors, also known as MOSFETs, such as threshold potentials, require accurate estimates of source and drain series resistance. In cases where connections to the MOSFET include significant external series resistance, as occurs in probing transistors that are partially fabricated or deprocessed, accurate estimates of external resistances are also required. This invention comprises a method for estimating series resistances of MOSFETs, including resistances associated with connections to the MOSFET, such as probe contacts. This method is applicable to any MOSFET which can be accessed on source, drain, gate and substrate terminals, and does not require other test structures or special connections, such as Kelvin connections.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Recessed Single Crystalline Source and Drain For Semiconductor-On-Insulator Devices
ActiveUS20130105898A1Reduce parasitic capacitive couplingLow source resistanceSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingGate dielectricCapacitive coupling
After formation of a gate stack, regions in which a source and a drain are to be formed are recessed through the top semiconductor layer and into an upper portion of a buried single crystalline rare earth oxide layer of a semiconductor-on-insulator (SOI) substrate so that a source trench and drain trench are formed. An embedded single crystalline semiconductor portion epitaxially aligned to the buried single crystalline rare earth oxide layer is formed in each of the source trench and the drain trench to form a recessed source and a recessed drain, respectively. Protrusion of the recessed source and recessed drain above the bottom surface of a gate dielectric can be minimized to reduce parasitic capacitive coupling with a gate electrode, while providing low source resistance and drain resistance through the increased thickness of the recessed source and recessed drain relative to the thickness of the top semiconductor layer.
Owner:GLOBALFOUNDRIES US INC
Three-dimensional semiconductor device and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN104393046AImprove efficiencyHigh strengthSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCouplingEngineering
The invention discloses a three-dimensional semiconductor device which comprises a plurality of storage units and a plurality of selection transistors. Each of the plurality of storage units comprises a channel layer which is distributed along a direction perpendicular to the surface of a substrate; a plurality of interlayer insulating layers and a plurality of grid stack structures which are alternately stacked along the side wall of the channel layer; a plurality of floating gates which are arranged between the plurality of interlayer insulating layers and the side wall of the channel layer; a drain electrode which is arranged at the top of the channel layer; and a source electrode which is positioned in the substrate between two adjacent storage units of the plurality of storage units. According to the three-dimensional semiconductor device and a manufacturing method thereof, the floating gates are arranged at the side walls of the vertical channels, and the starting of the source and drain regions generated on the side walls of the channels due to induction is controlled through the coupling between the gate electrodes and the floating gates, thereby improving induction efficiency and intensity of the source and drain regions, reducing source and drain resistance of the storage units, and improving read current and read speed of a storage array.
Owner:INST OF MICROELECTRONICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Reducing source/drain resistance of III-V based transistors
ActiveUS8455860B2Increase drive currentReduce resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate dielectricCondensed matter physics
An integrated circuit structure includes a substrate; a channel layer over the substrate, wherein the channel layer is formed of a first III-V compound semiconductor material; a highly doped semiconductor layer over the channel layer; a gate dielectric penetrating through and contacting a sidewall of the highly doped semiconductor layer; and a gate electrode on a bottom portion of the gate dielectric. The gate dielectric includes a sidewall portion on a sidewall of the gate electrode.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Germanium-based NMOS (N-metal-oxide-semiconductor) device and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102222687AHigh switching current ratioSmall subthreshold slopeSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesHafniumOxygen
The invention provides a germanium-based NMOS (N-metal-oxide-semiconductor) device and a preparation method thereof, belonging to the technical field of ultra large scale integration (ULSI) circuit manufacturing. Two layers of insulation medium material are inserted among metal source and drain electrodes and a substrate of the germanium based-NMOS device, and the bottom layer is S medium material with high pinning coefficient, such as hafnium oxide, silicon nitride or hafnium silica, and the upper layer of medium material is delta EC medium material with low conduction band offset, such as titanium dioxide, gallium oxide or strontium titanium oxygen. According to the invention, the fermi energy level pinning effect can be weakened, the electronic potential barrier is reduced, and furtherthe performances of a germanium-based schottky NMOS device are improved; and compared with the traditional method in which a single layer of insulation medium material such as AL2O3 is adopted, the preparation method can be used for effectively reducing the schottky potential barrier and maintaining lower source and drain resistance, therefore, the performances of the device are improved to a large extent.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (BEIJING) CORP +1
Semiconductor device and method of fabricating the same
InactiveUS20050082603A1Desirable levelReduce resistanceTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsEngineeringBody region
The present invention is aimed at providing a DMOSFET and a method of fabricating the same, capable of keeping a desirable level of drain voltage resistance and, at the same time, of reducing the drain resistance. In a DMOSFET configured as having a drain region composed of an epitaxial layer formed on a P-type semiconductor substrate while placing an N-type buried layer in between, and as having, in the drain region, a P-type body region having an N-type source region nested therein and a drain extraction region, formation of N-type, heavily-doped buried layers prior to the epitaxial growth is proceeded so as not to form them at least in the region under the P-type body region, and so as to make an impurity concentration in the region under the P-type body region smaller than that in the region under a drift region when viewed after the impurity is diffused by the succeeding annealing. This makes it possible to suppress breakdown and thereby to suppress lowering in the drain voltage resistance, and at the same time to reduce the drain resistance by raising the impurity concentration of the N-type buried layer in the region under the drift region.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
A segmented capacitive liquid level sensor and its liquid level measurement method
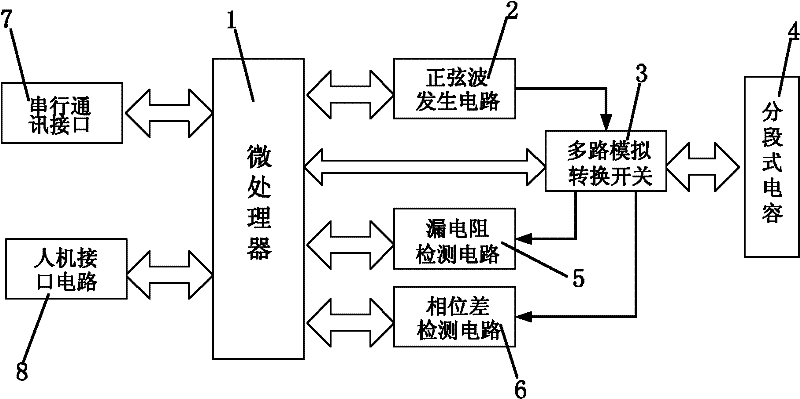
InactiveCN102288259AOvercoming structural complexityOvercoming structural reliabilityLevel indicators by physical variable measurementElectrical resistance and conductancePhase difference
A segmented capacitive liquid level sensor and a liquid level measuring method thereof, comprising a microprocessor, a sine wave generating circuit connected with the microprocessor, and a multiplex switch connected with the microprocessor and the sine wave generating circuit, A segmented capacitor connected to the multi-way switch, the segmented capacitor is composed of at least two mutually insulated capacitor arrangements, the multi-way switch is connected to each segment of the capacitor in the segmented capacitor respectively, and the microprocessor A leakage resistance detection circuit and a phase difference detection circuit are respectively connected between the multi-way switch and the multi-way switch; the microprocessor controls the multi-way switch to connect the input terminals of each segment capacitor in the segmented capacitor to the sine wave through a charging resistor The generating circuit is connected to the leakage resistance detection circuit and the phase difference detection circuit respectively at the output end. The invention adopts a leakage resistance detection circuit and a phase difference detection circuit to accurately measure the capacitance of each segment of the segmented capacitor, so that the liquid level measurement is more accurate, the reliability is high, and the anti-interference ability is strong.
Owner:JIAXING UNIV
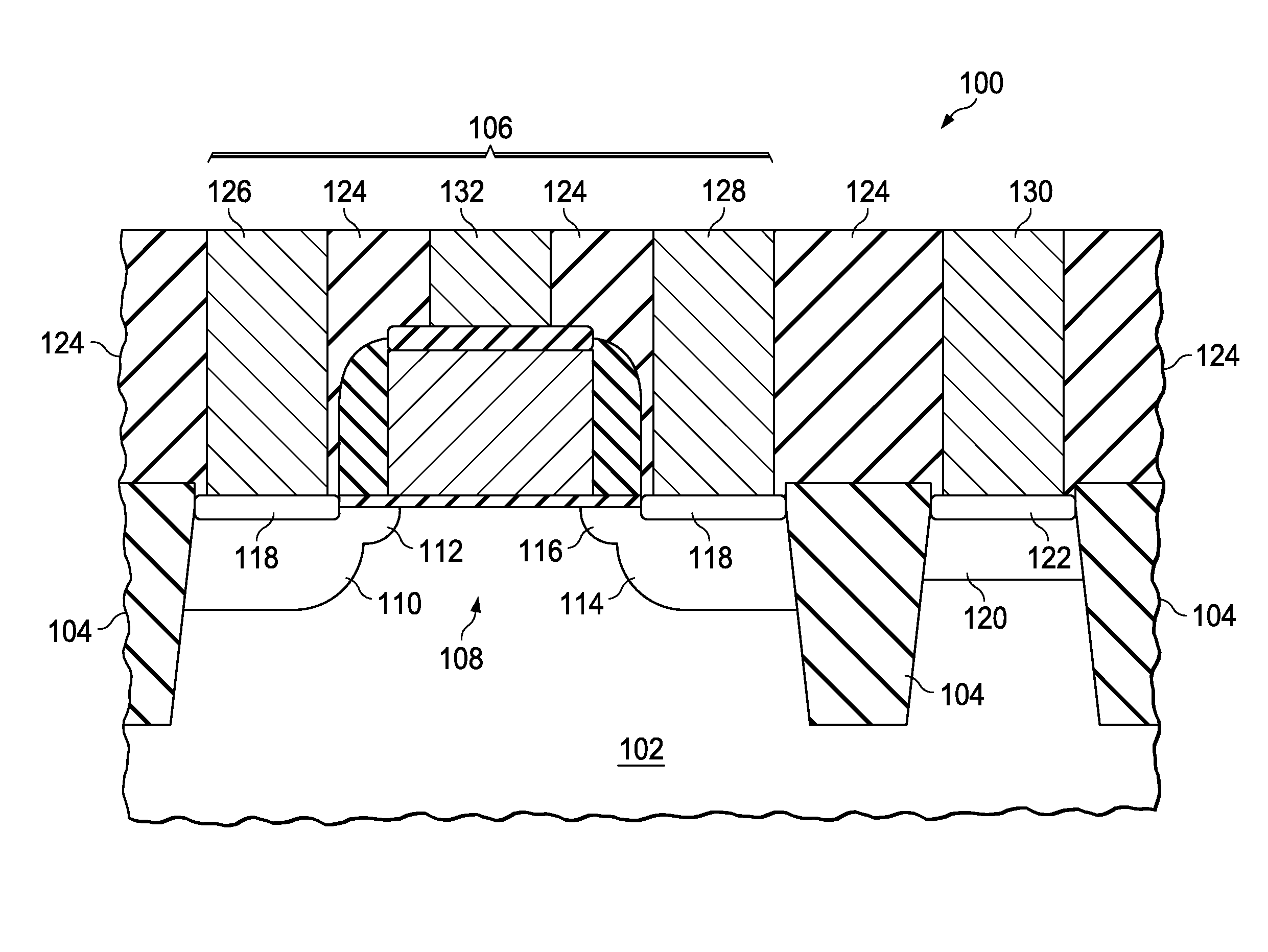
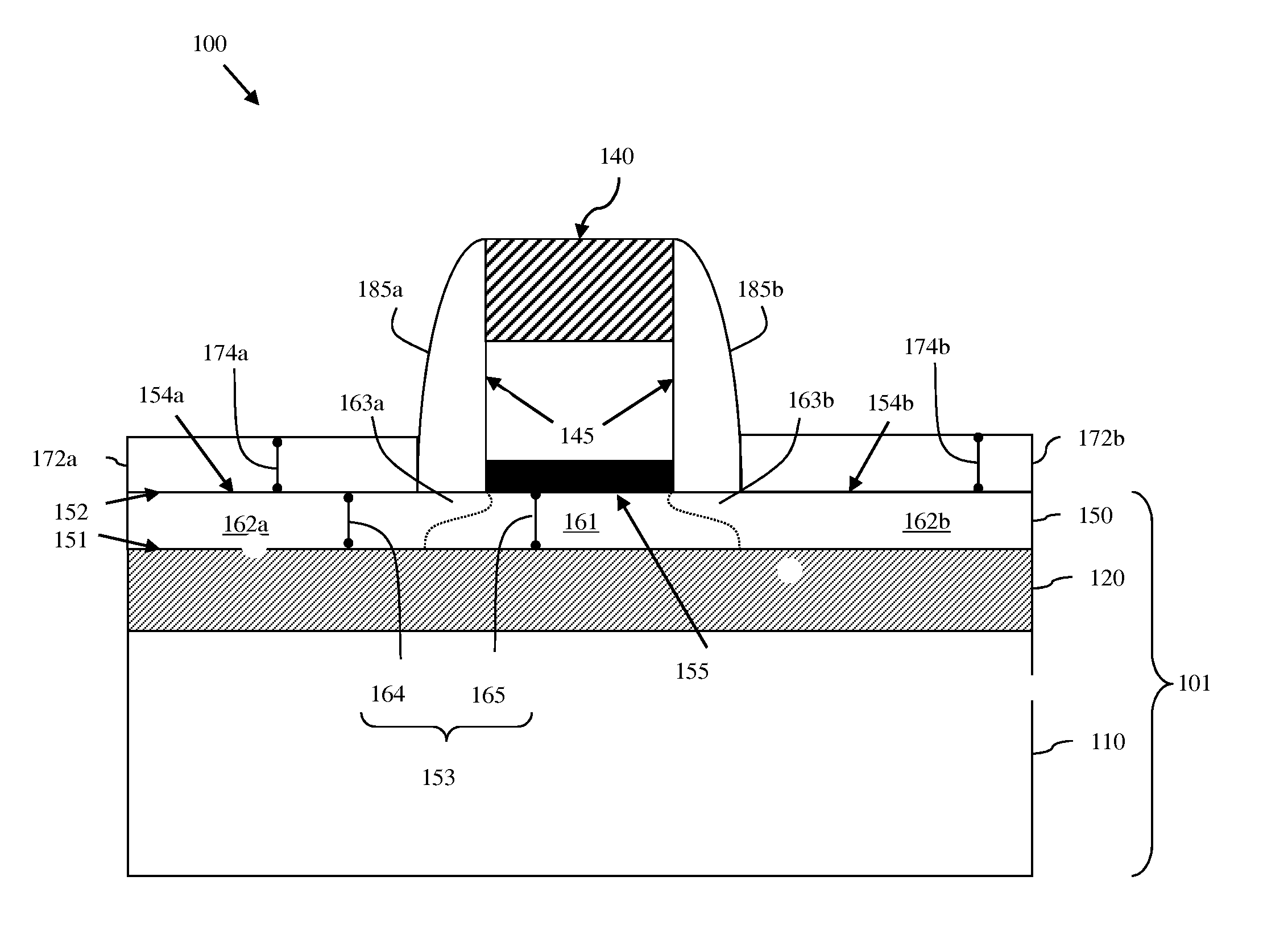
Field effect transistor (FET) and method of forming the fet without damaging the wafer surface
InactiveUS20110186914A1High selectivityNot to damageSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesGate stackEngineering
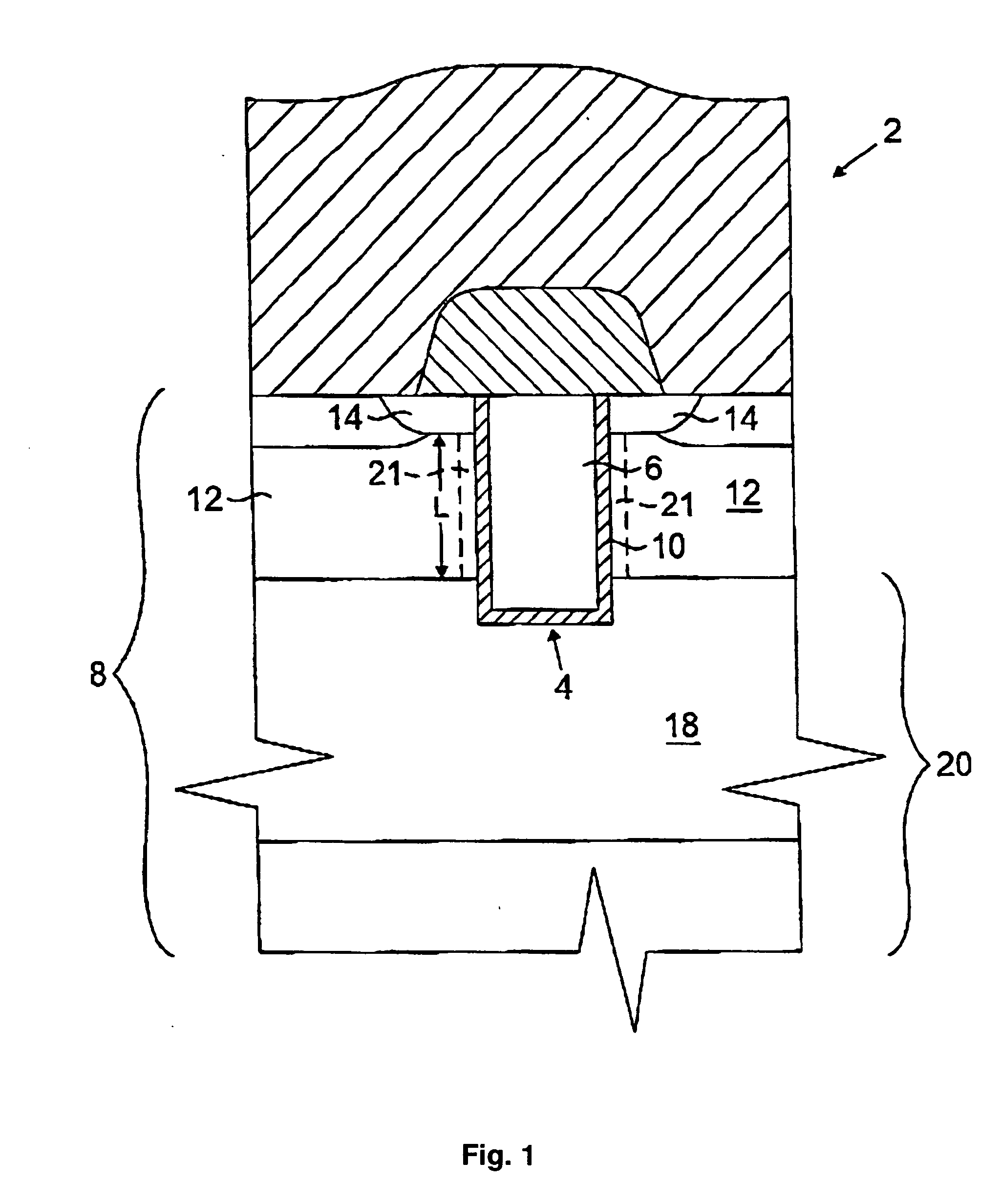
Disclosed are a field effect transistor structure and a method of forming the structure. A gate stack is formed on the wafer above a designated channel region. Spacer material is deposited and anisotropically etched until just prior to exposing any horizontal surfaces of the wafer or gate stack, thereby leaving relatively thin horizontal portions of spacer material on the wafer surface and relatively thick vertical portions of spacer material on the gate sidewalls. The remaining spacer material is selectively and isotropically etched just until the horizontal portions of spacer material are completely removed, thereby leaving only the vertical portions of the spacer material on the gate sidewalls. This selective isotropic etch removes the horizontal portions of spacer material without damaging the wafer surface. Raised epitaxial source / drain regions can be formed on the undamaged wafer surface adjacent to the gate sidewall spacers in order to tailor source / drain resistance values.
Owner:ALSEPHINA INNOVATIONS INC
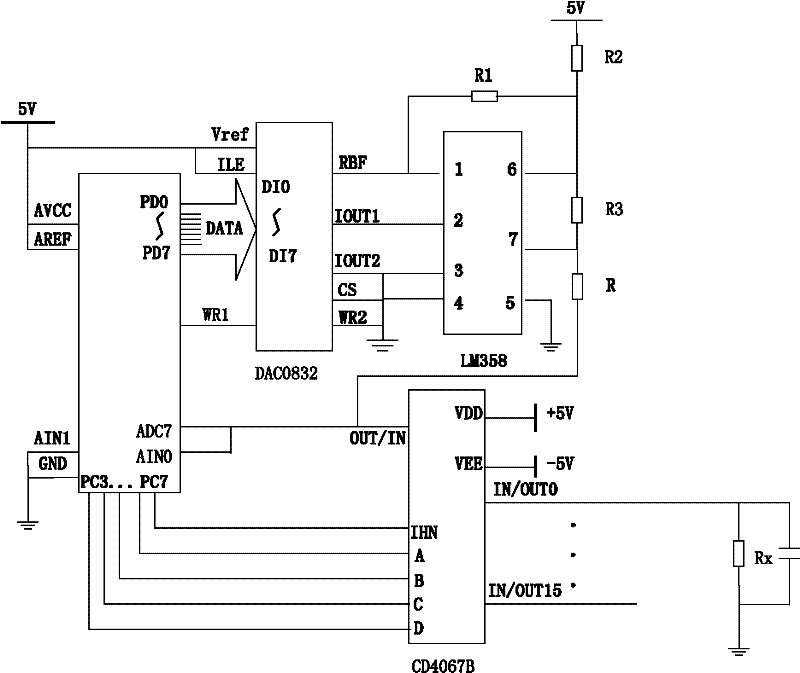
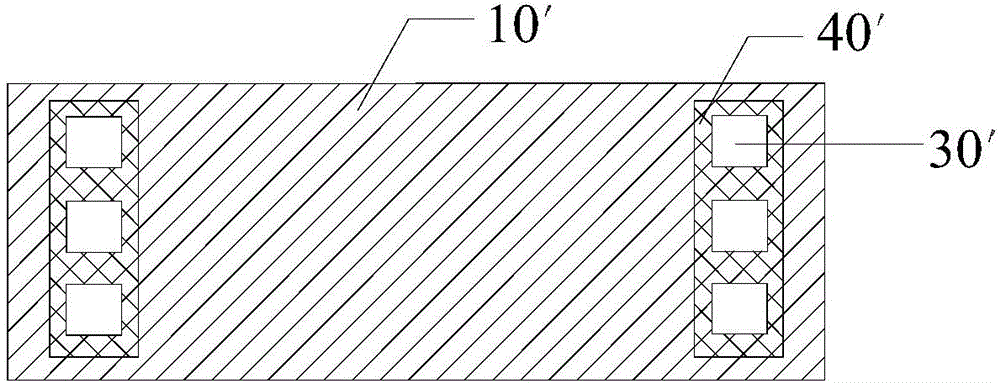
Test structure, manufacturing method of the test structure and test method
ActiveCN105336728AImprove accuracyStructural difference is smallSemiconductor/solid-state device testing/measurementSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsElectrical resistance and conductanceEngineering
The invention discloses a test structure, a manufacturing method of the test structure and a test method. The test structure comprises a gate structure, at least two groups of contact hole structure units and at least two layers of metal layers, wherein the at least two groups of contact hole structure units are arranged on an active area of one side of the gate structure; each group of contact hole structure units comprises at least one contact hole structure; the at least two layers of metal layers are arranged on a surface of each group of the contact hole structure units and are arranged with the contact hole structure units in a one-to-one correspondence mode. In the test structure, the metal layers on any two groups of contact hole structure units are taken as probe contact points during a resistance test so as to obtain a source-drain resistance in the test structure so that a structure difference between the test structure and a real device, which is generated because the gate structure is not formed in the test structure, is reduced; and further a difference between the source-drain resistance in the test structure and a source-drain resistance in the real device is reduced and measured value accuracy of the source-drain resistance in the test structure is increased.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP
Self-aligned double-layer channel metallic oxide thin film transistor and manufacturing method thereof
ActiveCN103346089AImprove mobilityImprove the degree of influence by ambient lightSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesPower flowOxide thin-film transistor
The invention provides a self-aligned double-layer channel metallic oxide thin film transistor and a manufacturing method of the self-aligned double-layer channel metallic oxide thin film transistor. The manufacturing method comprises the following steps that a thick high-resistivity metallic oxide semiconductor layer and a thin low-resistivity metallic oxide layer deposit on a substrate, so that double layers of channels are formed; photoetching and etching are carried out on the double layers of channels, so that an active area graph is formed; a gate medium layer and a gate electrode are formed on the double layers of channels; a covering layer with H deposits on the whole substrate, then heat processing is carried out so that H can diffuse to metallic oxide outside the channel area not covered by the gate electrode and the gate medium, and a heavily doped low-resistivity source drain area is formed; a contact hole and a contact electrode are prepared. The self-aligned double-layer channel metallic oxide thin film transistor and the manufacturing method of the self-aligned double-layer channel metallic oxide thin film transistor adopt self-aligned double-layer channel top gate structure, can lower source drain resistance, lower the influence of ambient light on elements, lower off-state current, and improve on-state current and migration rate of the elements.
Owner:PEKING UNIV SHENZHEN GRADUATE SCHOOL
Method for fabricating transistor of semiconductor device
ActiveUS20050090068A1Effective controlLower resistanceSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesElectrical conductorDevice material
A method for fabricating a semiconductor transistor including forming a first insulating layer on a semiconductor substrate; forming an LDD region using ion implantation; patterning the first insulating layer; forming a trench in the substrate; forming a trench gate by depositing and planarizing a second insulating layer and a conductor on the substrate with the trench formed therein; forming a photoresist pattern on the substrate; forming source / drain regions by performing an ion implantation using the photoresist pattern as a mask; and removing the photoresist pattern and the first insulating layer. Thus, a method for fabricating a semiconductor transistor according to the present invention can reduce source / drain resistances and gate resistance by forming a trench type gate and can efficiently control a short channel effect.
Owner:MARVELL ASIA PTE LTD
Semiconductor device
InactiveUS8878288B2Improve reliabilityReduced deterioration and variationTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingMiniaturizationEngineering
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Variable gain control transformer and RF transmitter utilizing same
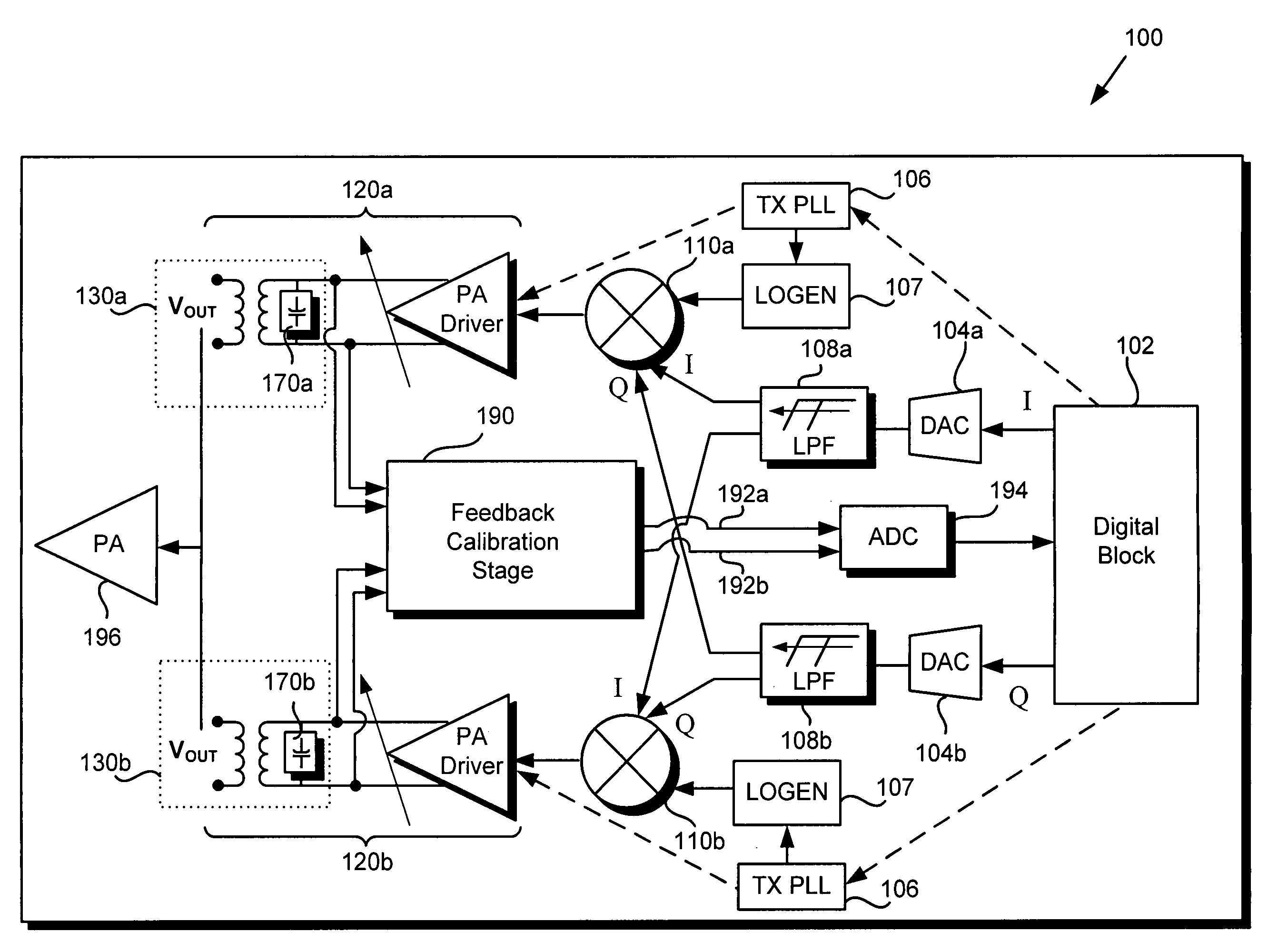
ActiveUS20120052824A1Resonant long antennasAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesCapacitanceTransformer
According to one embodiment, a variable gain control transformer comprises a primary winding connected to differential inputs of the variable gain control transformer, a secondary winding for providing a single ended output to a load, and an output control circuit coupled to the secondary winding, the output control circuit configured to provide up to approximately 12 dB of gain control. Variable gain control may be achieved using first and second variable resistors of the output control circuit, wherein the first and second variable resistors are implemented by respective first and second pluralities of source-drain resistances produced by respective corresponding first and second pluralities of selectable field-effect transistors (FETs). In one embodiment, the variable gain control transformer further comprises a variable capacitance tuning circuit coupled between the differential inputs, the variable capacitance tuning circuit implemented using a plurality of selectable fixed capacitance unit cells.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Semiconductor integrated circuit device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20090243658A1InhibitionReduce resistanceTransistorReliability increasing modificationsElectrical resistance and conductanceResonance
A circuit for attaining reduction in AC noise on power supply line caused by IR drop upon use of a decoupling capacitor represented by a cross-coupled decoupling capacitor with enhanced resistance to electrostatic breakdown, required in the case of a process of a high technology. There is also provided a circuit for suppressing the AC noise on power supply line due to resonance. MOS transistors composing the cross-coupled decoupling capacitor with enhanced resistance to electrostatic breakdown are caused to have lower threshold voltages Vth, thereby reducing a resistance between a source and a drain of each of the MOS transistors, resulting in reduction in IR drop. Further, a damping resistance is effective for suppressing the AC noise on power supply line, and the source-to-drain resistance of each of the MOS transistors is utilized as the damping resistance. At this point in time, a resistance value as desired is attained through combination of decoupling capacitors having threshold voltages Vth differing from each other.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
High Electron Mobility Transistors with Minimized Performance Effects of Microcracks in the Channel Layers
In HEMTs based on III-nitrides epitaxial films or GaAs, AlGaAs and InGaAs epitaxial films, unwanted microcracks are often formed in the composite epitaxial layers in the channel region during fabrication and operation. These microcracks are caused by strain or stresses due to lattice mismatch and thermal expansion coefficient differences between materials and substrate's. Those microcracks will bring about an increase in source to drain resistance and lead to performance and reliability degradation of the HEMTs and the MMICs containing them. The present invention provides HEMTs with minimized effects of the unwanted microcracks by aligning the channel region long axis to a certain direction so that the channel region long axis forms a right angle with axis of at least one type of the microcracks.
Owner:SHIH ISHIANG +3
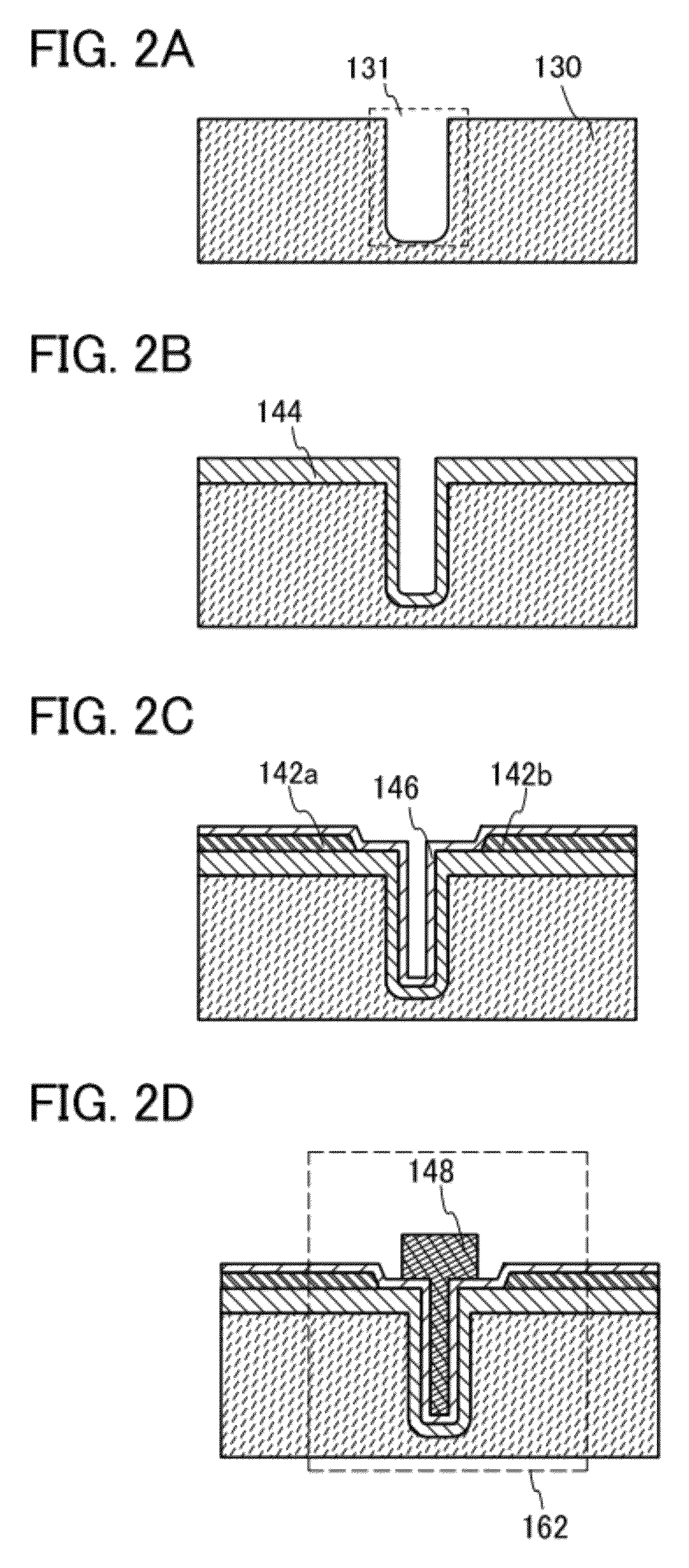
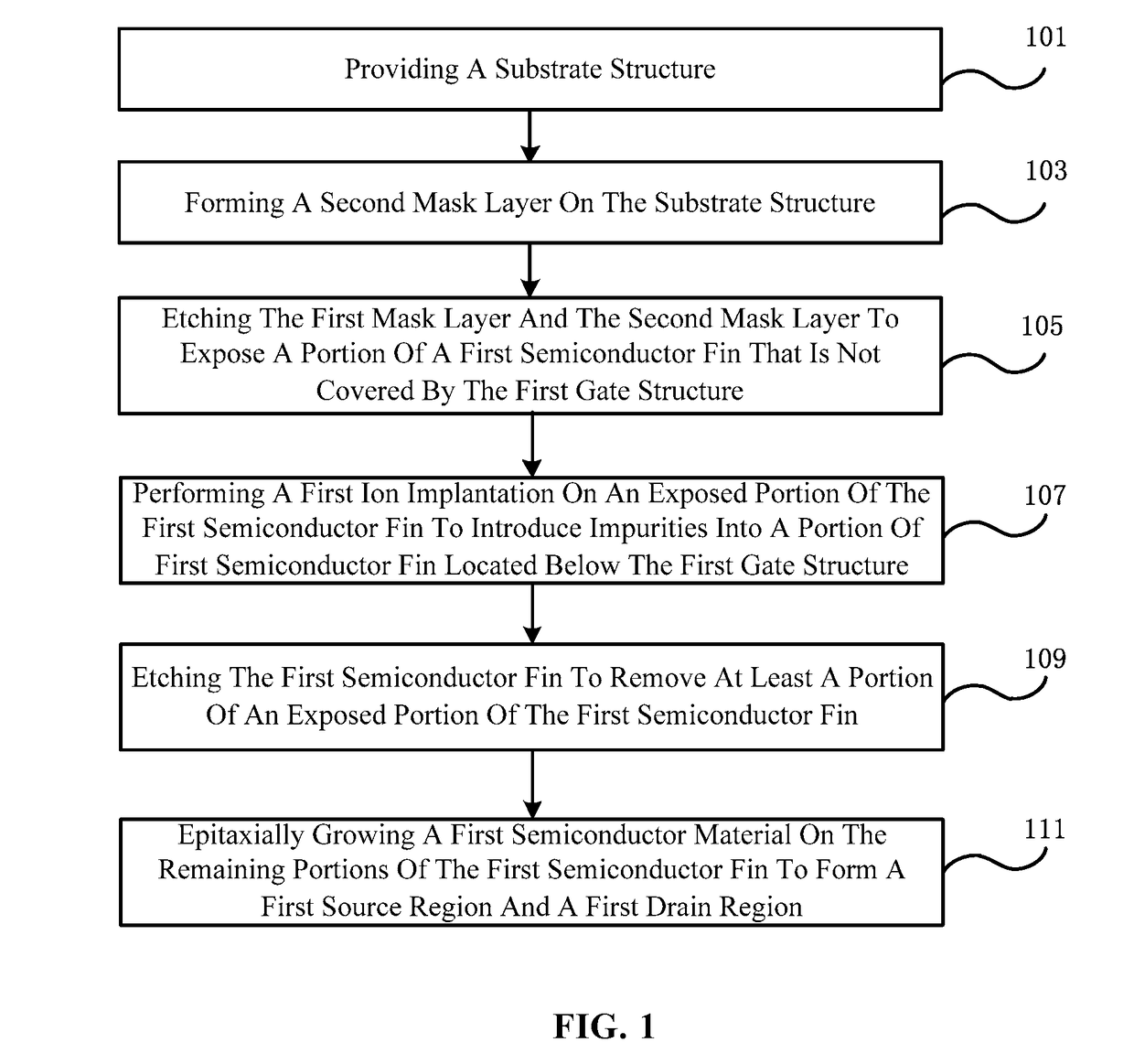
Method for reducing n-type finfet source and drain resistance
ActiveUS20170352595A1Increase in sizeBring more stressTransistorSolid-state devicesSemiconductor materialsEngineering
A method of manufacturing a semiconductor device includes providing a substrate structure, the substrate structure having a semiconductor substrate including a first semiconductor fin, a first gate structure, and a first mask layer on a first semiconductor region. The method includes forming a second mask layer on the substrate structure, etching first mask layer and second mask layer to expose a portion of a first semiconductor fin not covered by the first gate structure, performing a first ion implantation on an exposed portion of the first semiconductor fin to introduce impurities into a portion of the first semiconductor fin located below the first gate structure, etching the first semiconductor fin to remove a portion of an exposed portion of the first semiconductor fin, and epitaxially growing a first semiconductor material on the remaining portions of the first semiconductor fin to form a first source region and a first drain region.
Owner:SEMICON MFG INT (SHANGHAI) CORP +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com