Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89results about How to "Reduce die area" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
MMIC DC-to-DC converter
InactiveUS20050242795A1Improve efficiencyImprove reliabilityDc-dc conversionElectric variable regulationConvertersLow noise
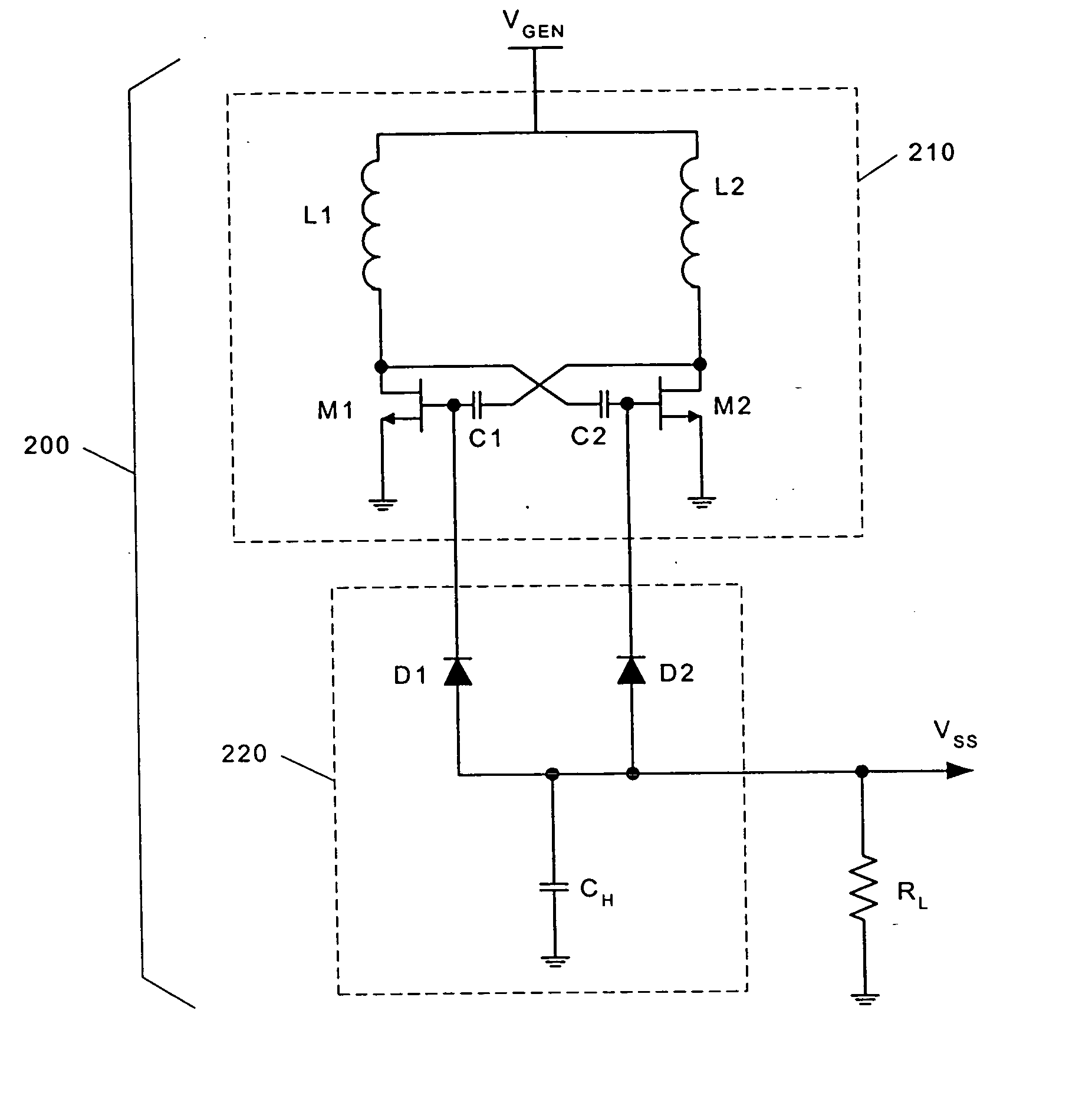
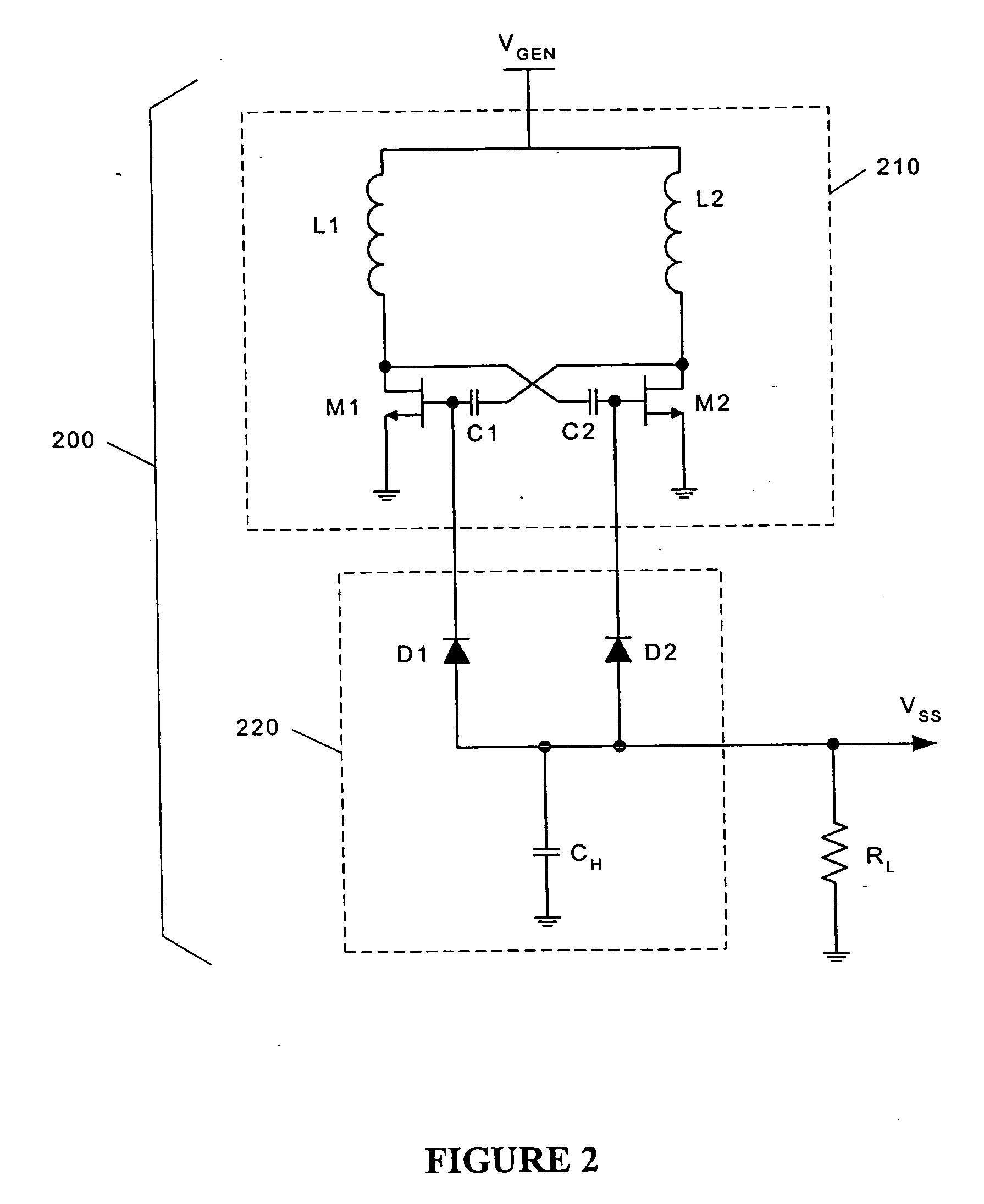
An improved Monolithic Microwave Integrated Circuit DC-to-DC voltage converter fabricated in GaAs MESFET technology is introduced. The converter comprises a differential oscillator having crossed-coupled symmetrical inductors that ensure low-noise operation. The converter further comprises a highly-efficient synchronous rectifier and a start-up enable circuit.
Owner:AL KURAN SHIHAB +1
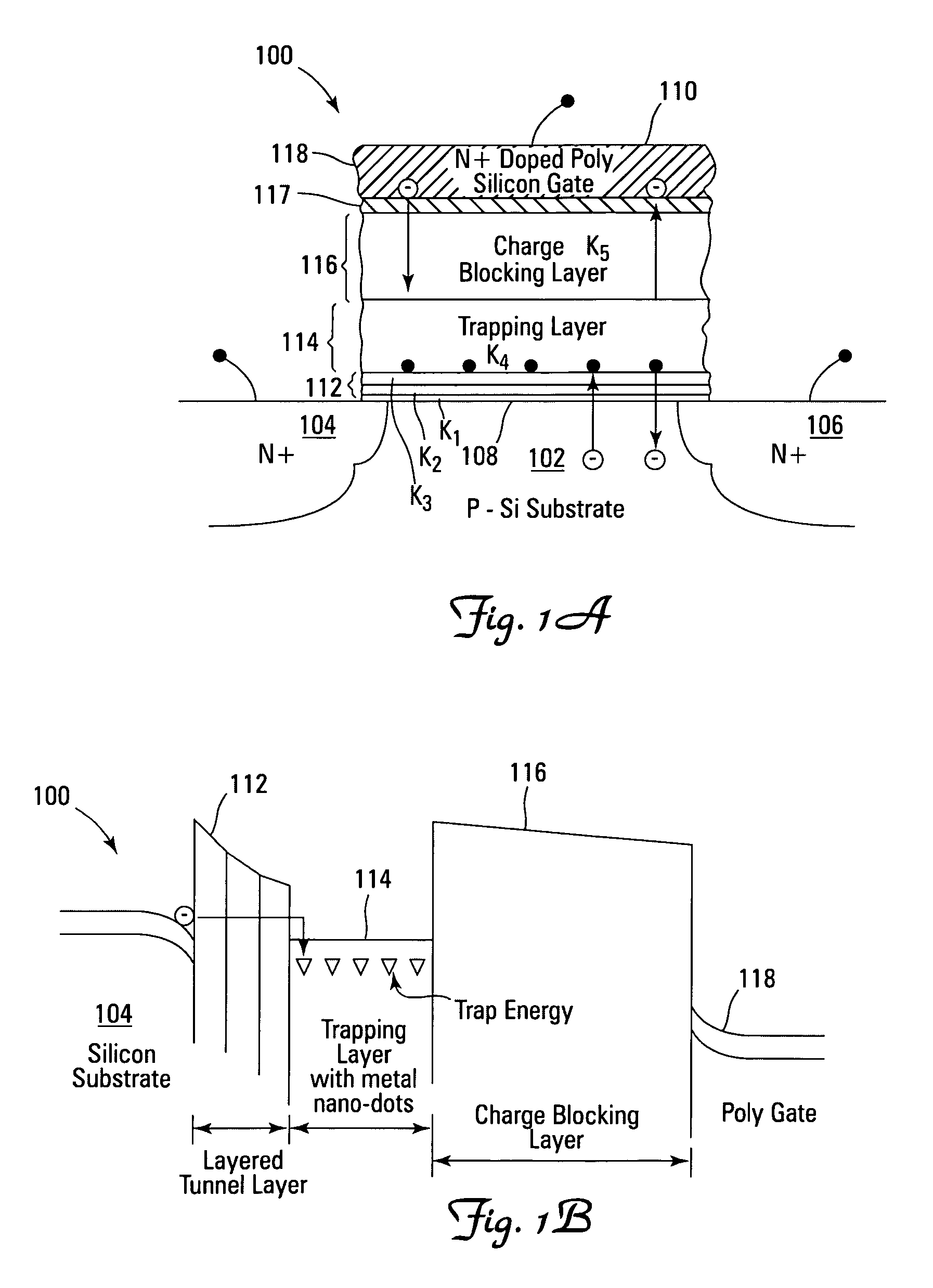
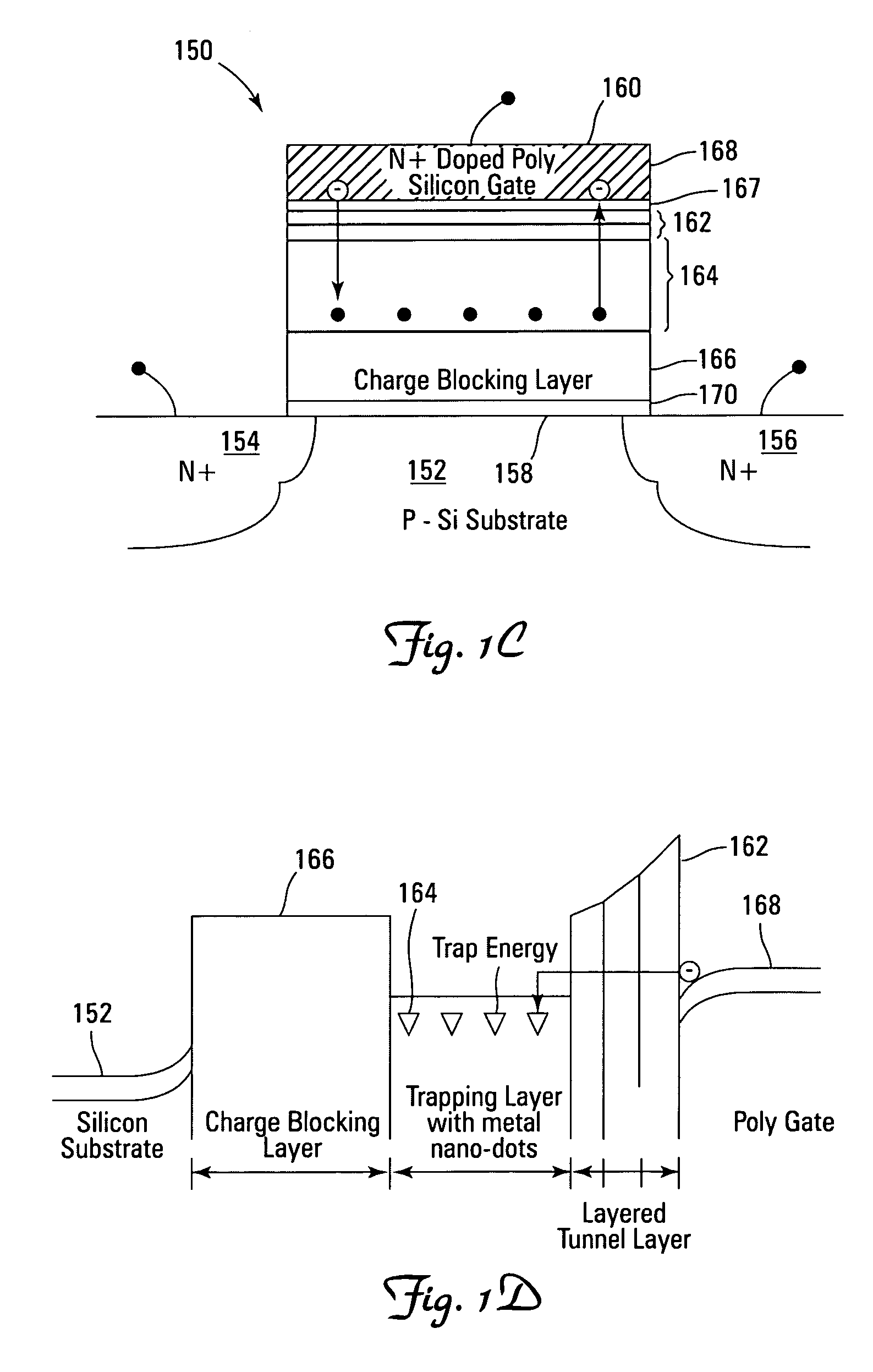
Low power non-volatile memory and gate stack
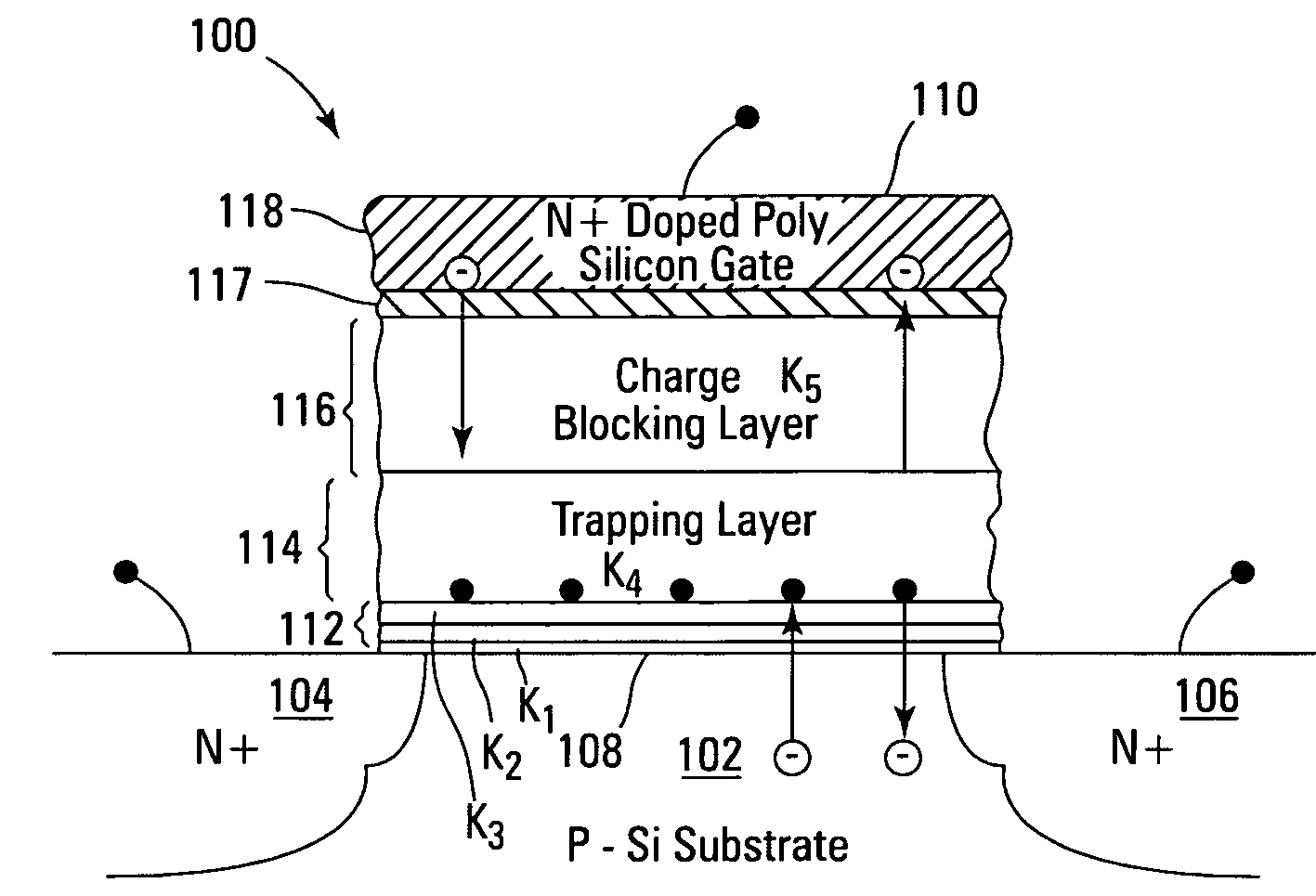
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that facilitate the use of band-gap engineered gate stacks with asymmetric tunnel barriers in reverse and normal mode floating node memory cells in NOR or NAND memory architectures that allow for direct tunnel programming and erase, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. The low voltage direct tunneling program and erase capability reduces damage to the gate stack and the crystal lattice from high energy carriers, reducing write fatigue and enhancing device lifespan. The low voltage direct tunnel program and erase capability also enables size reduction through low voltage design and further device feature scaling. Memory cells of the present invention also allow multiple bit storage. These characteristics allow memory device embodiments of the present invention to operate within the definition of a universal memory, capable of replacing both DRAM and ROM in a system.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
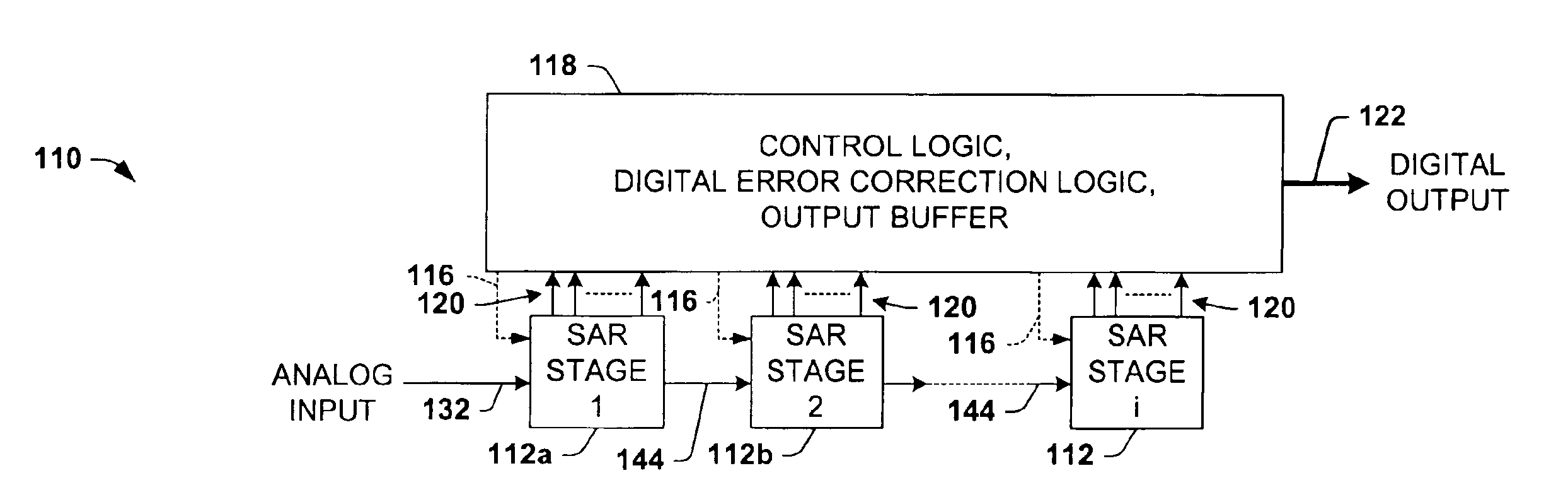
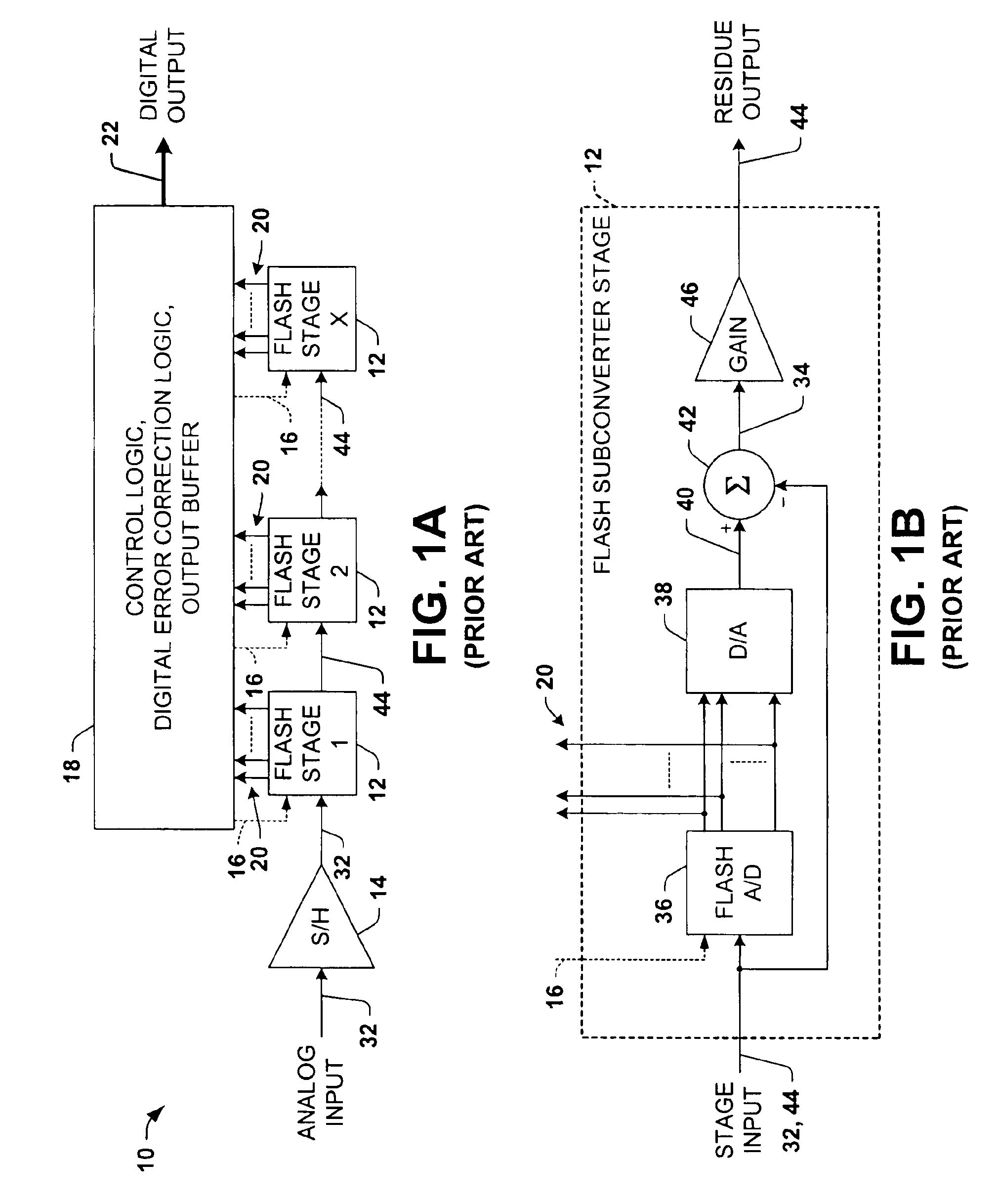
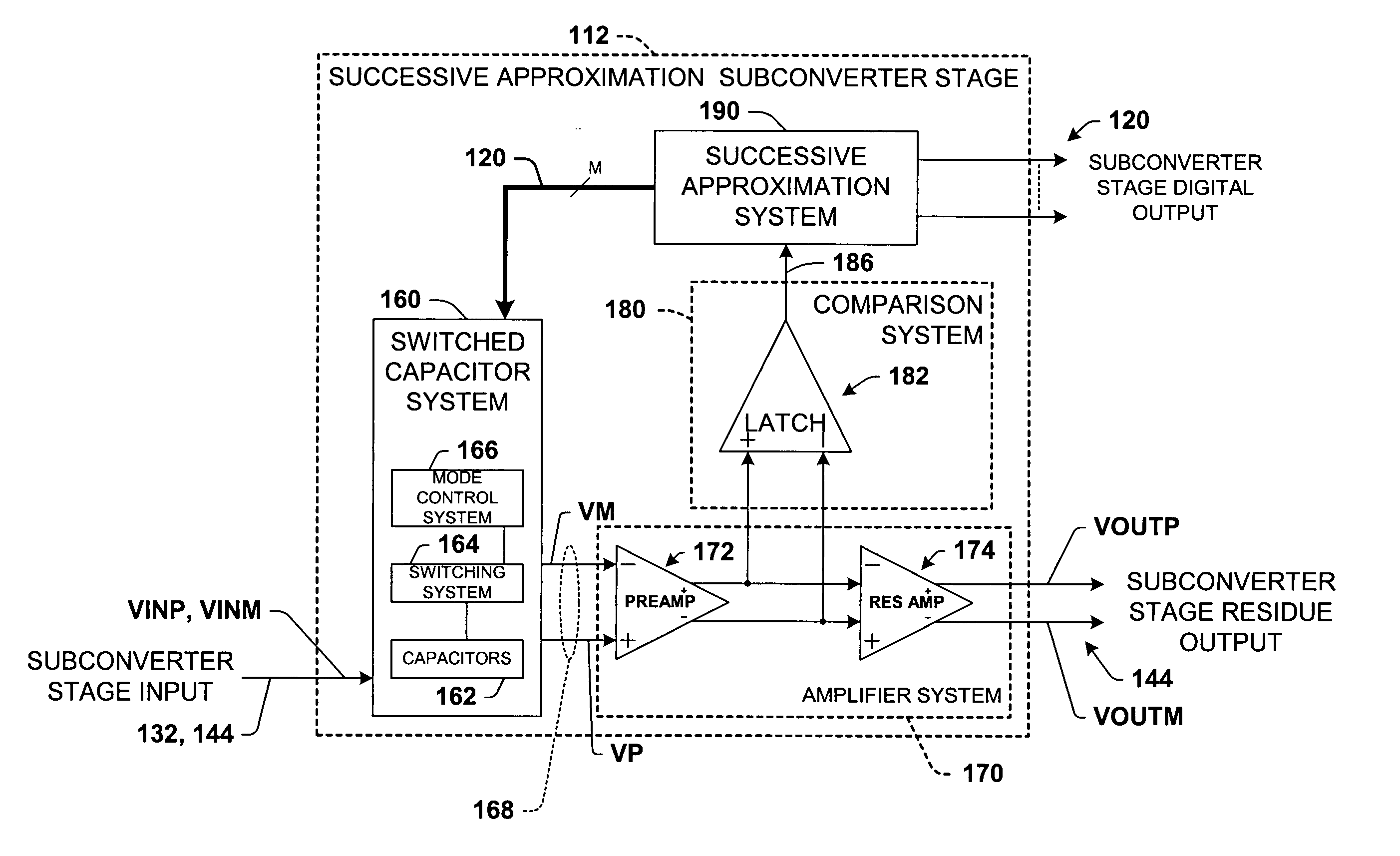
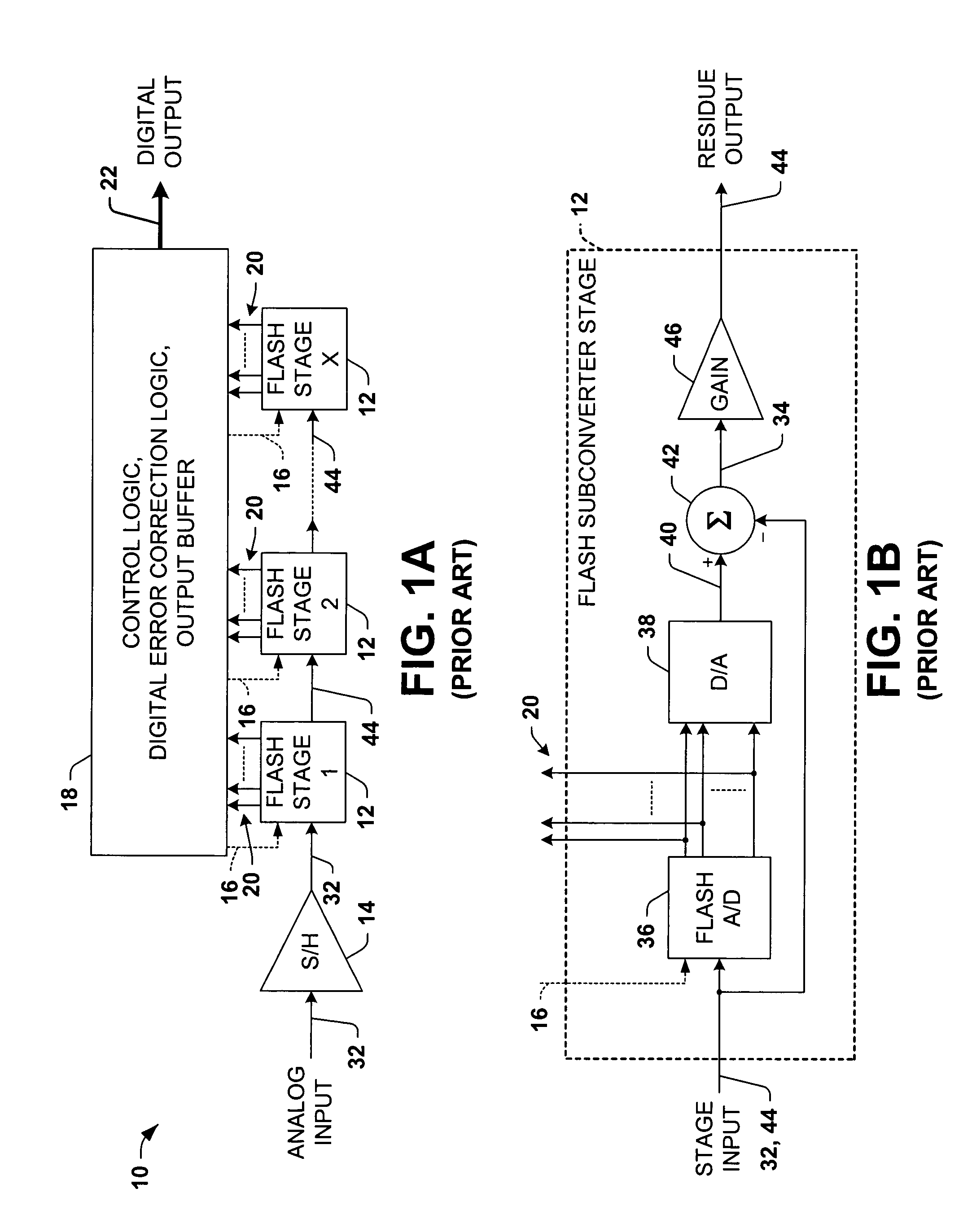
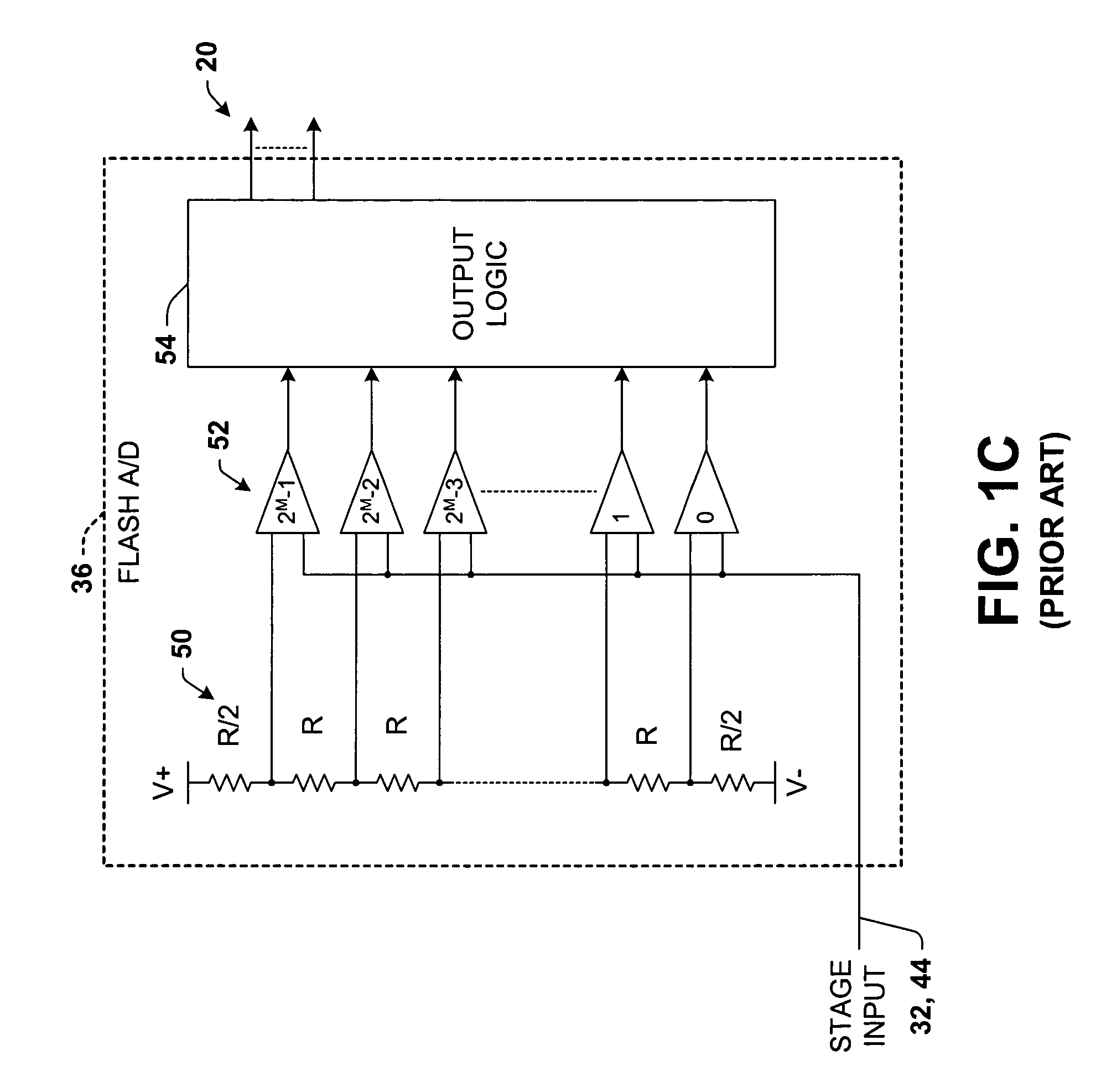
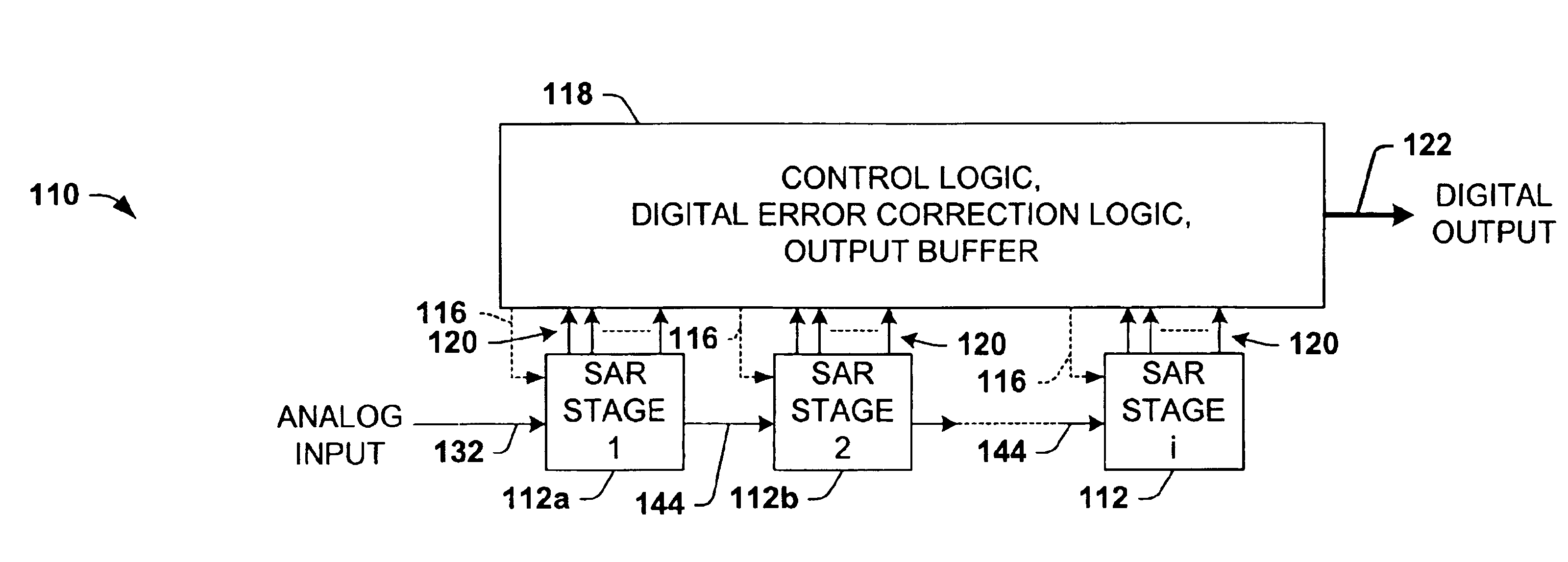
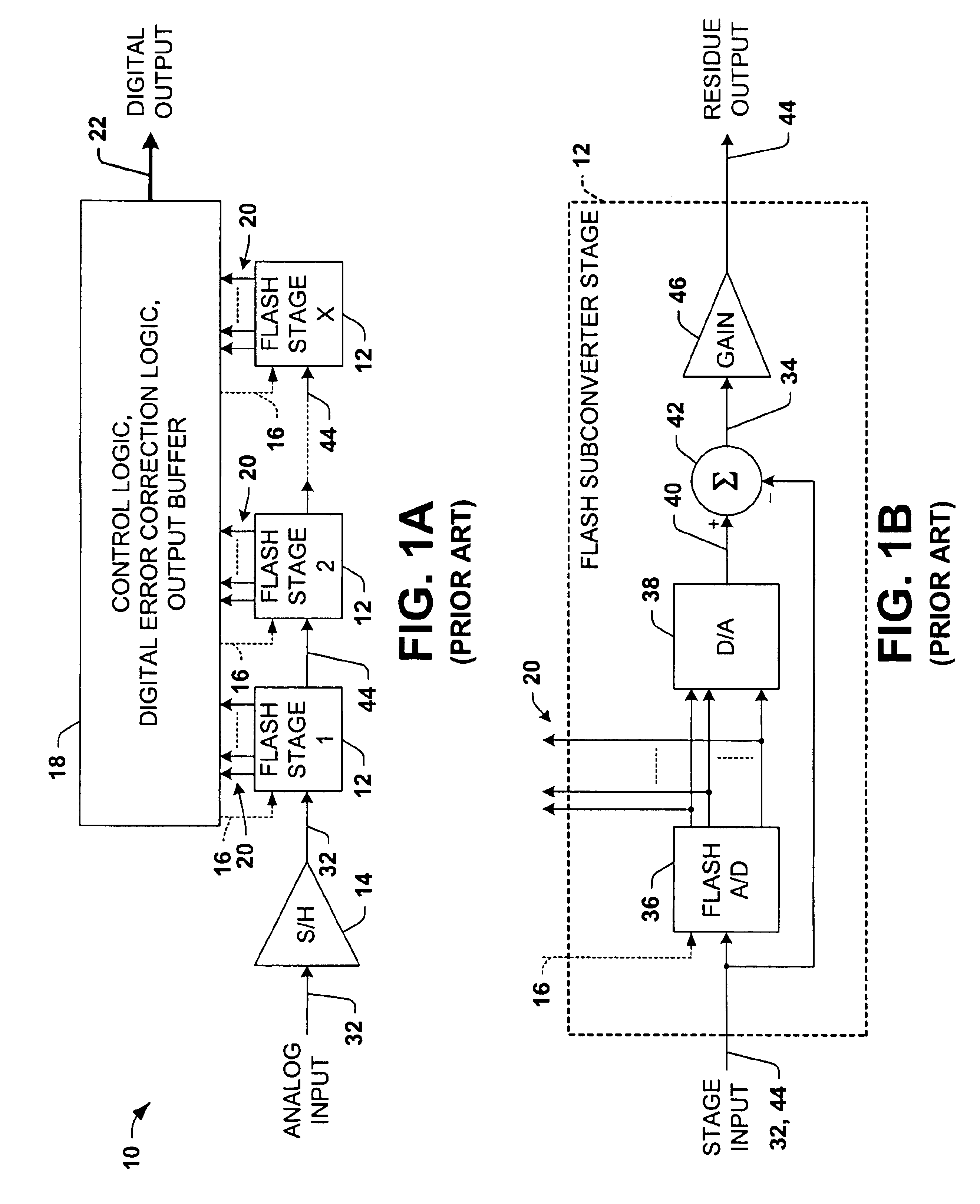
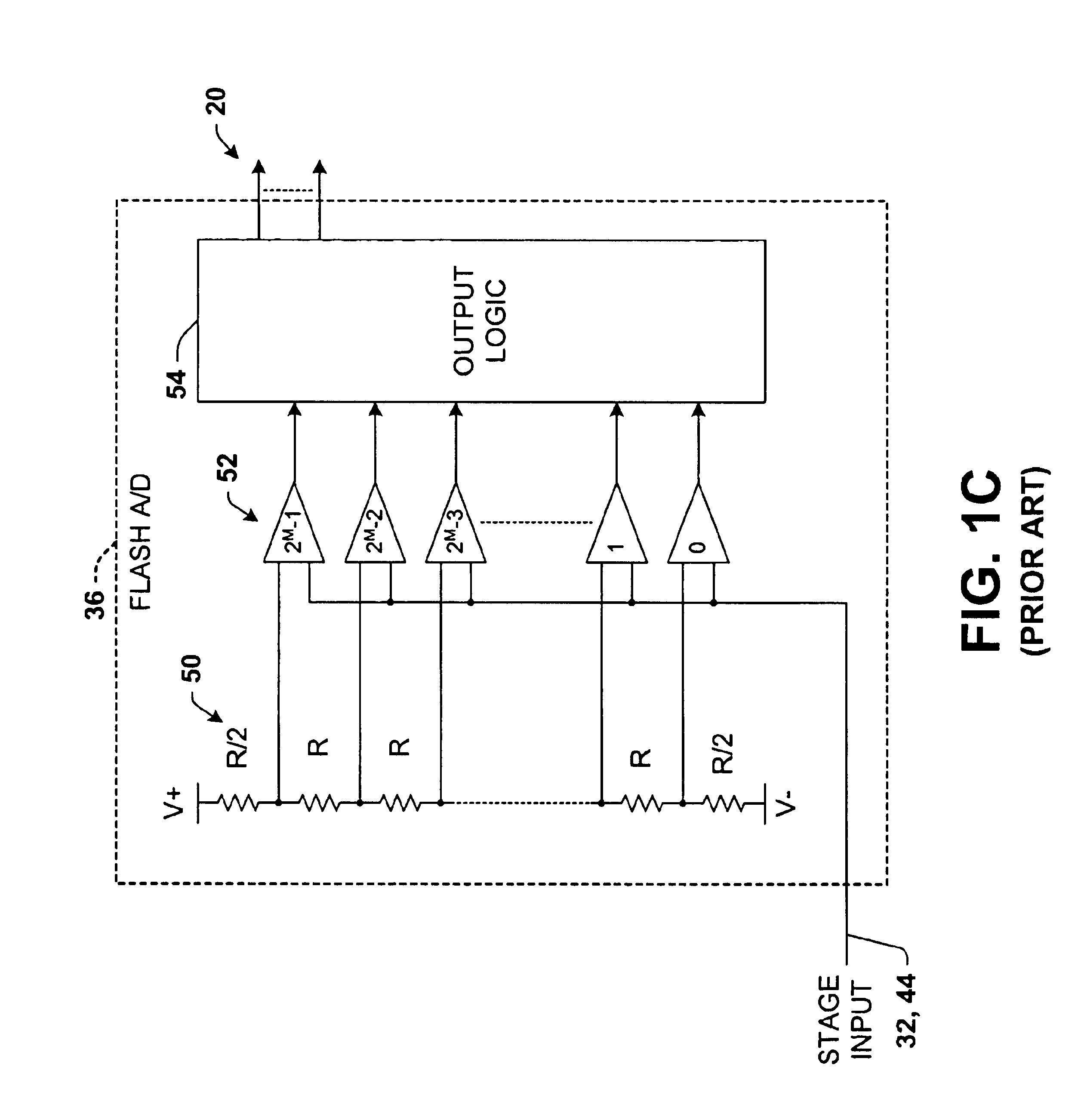
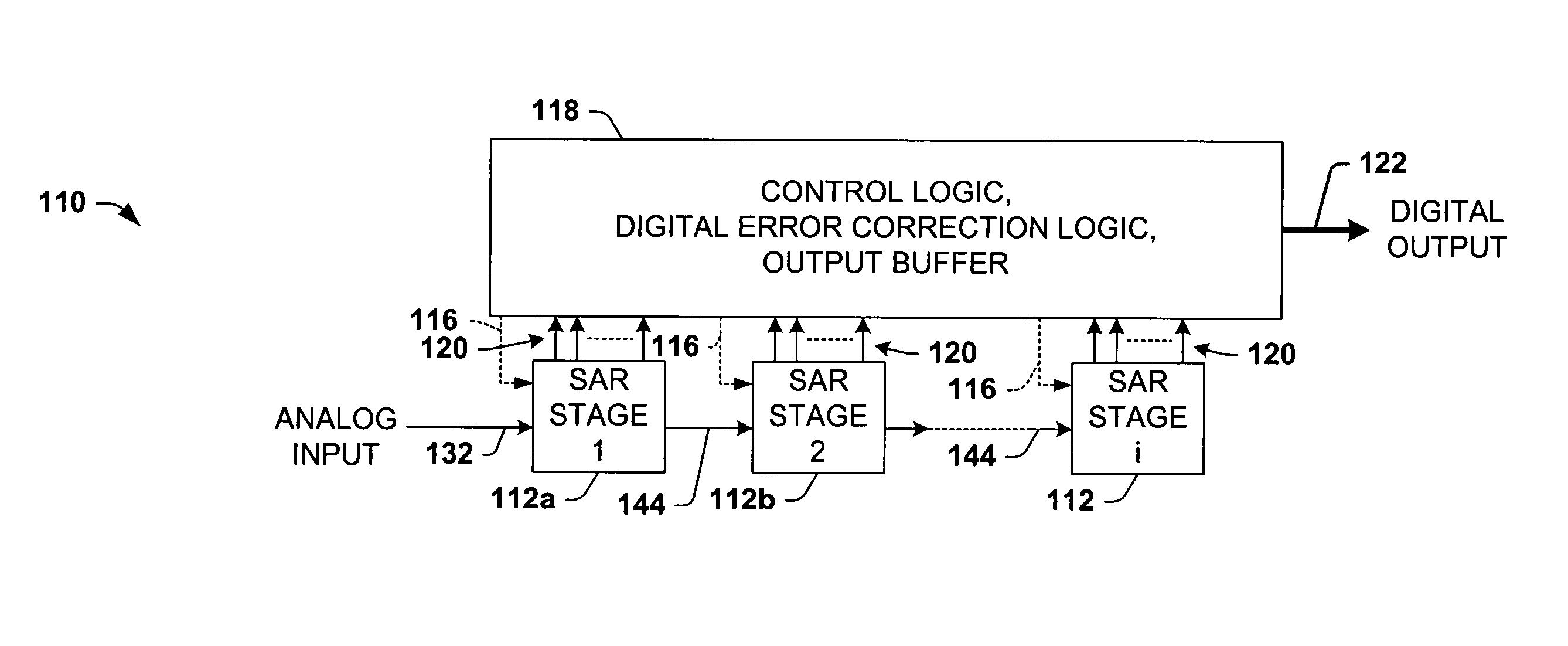
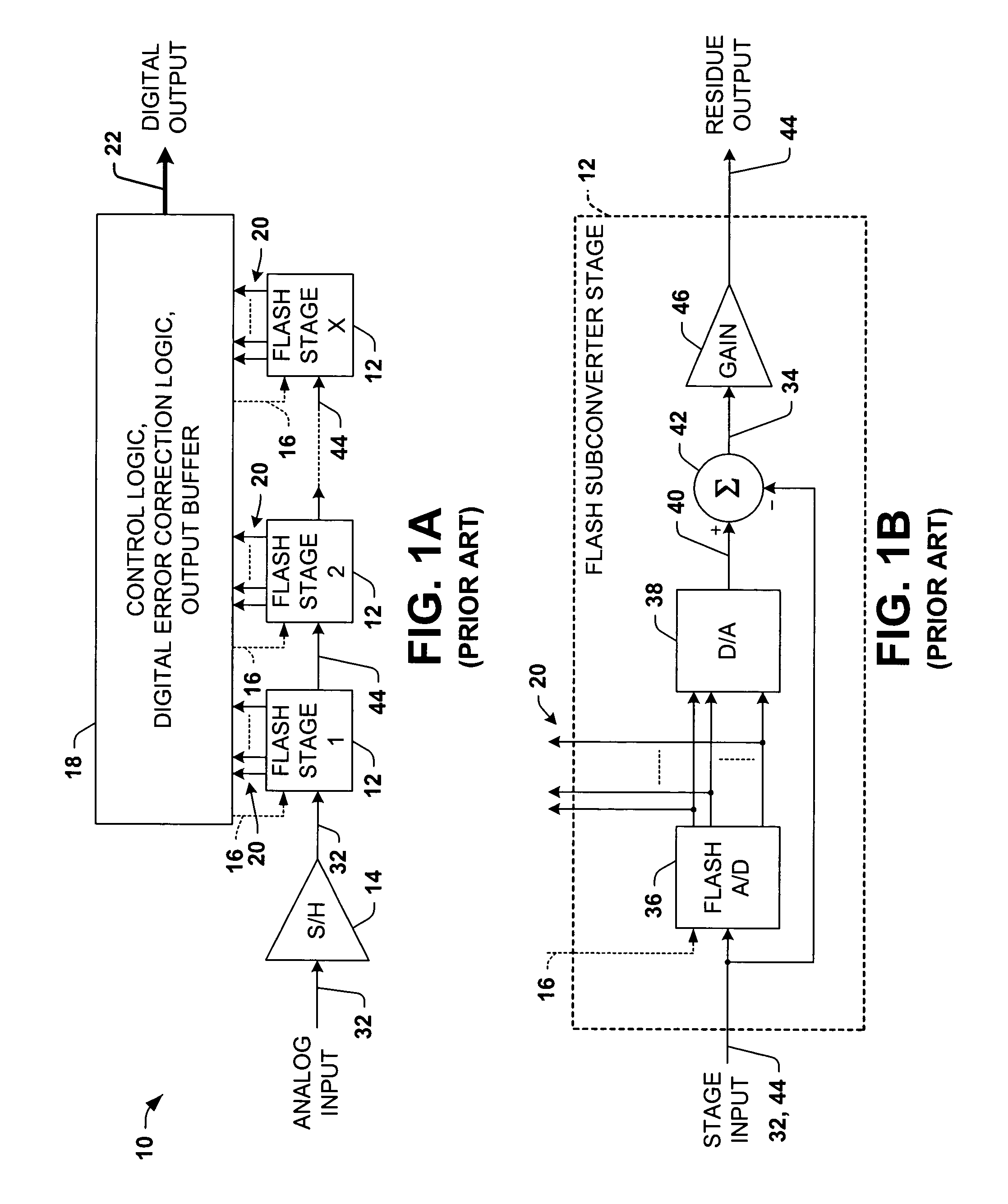
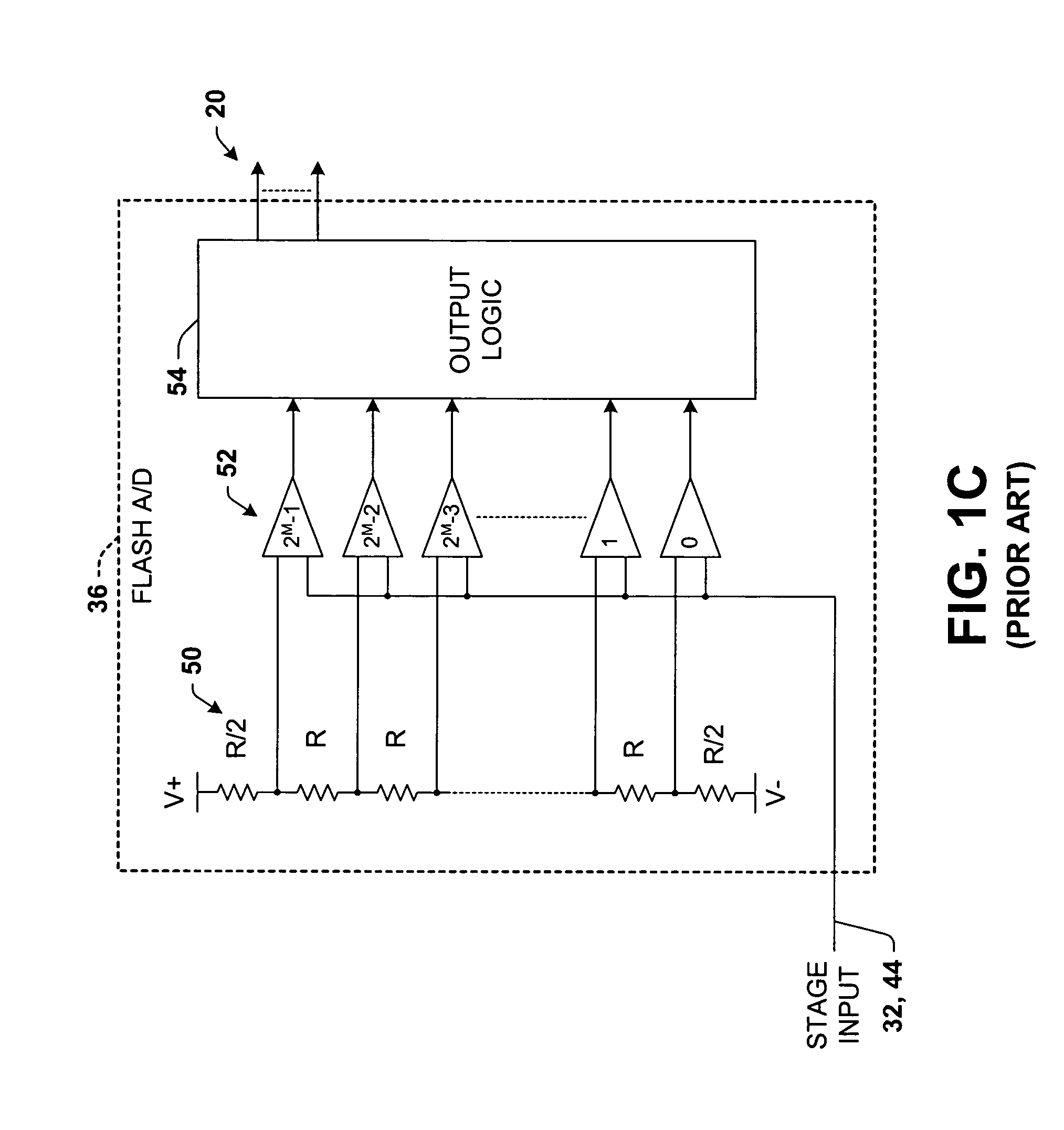
Differential pipelined analog to digital converter with successive approximation register subconverter stages using thermometer coding
InactiveUS6914550B2Improve conversion speedReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersEngineeringAnalog-to-digital converter
Pipelined analog to digital conversion systems are provided having cascaded multi-bit successive approximation register subconverter stages using thermometer coding. Capacitor arrays are provided in the subconverter stages, where switching logic selectively couples the capacitors to operate in sample, conversion, and residue amplification modes for generating multi-bit subconverter digital outputs and analog subconverter residue outputs, wherein the capacitors are switched according to a thermometer code to reduce differential converter non-linearity.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
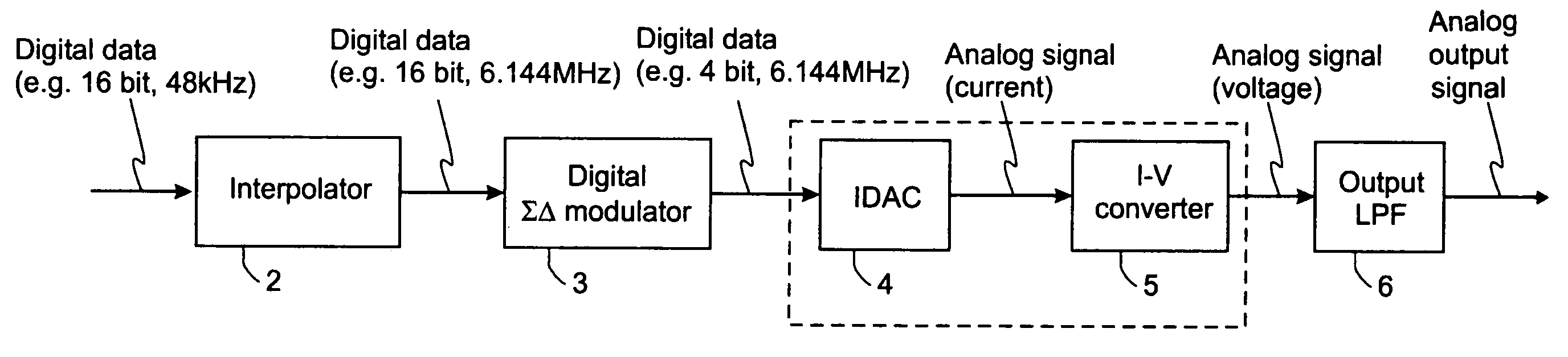
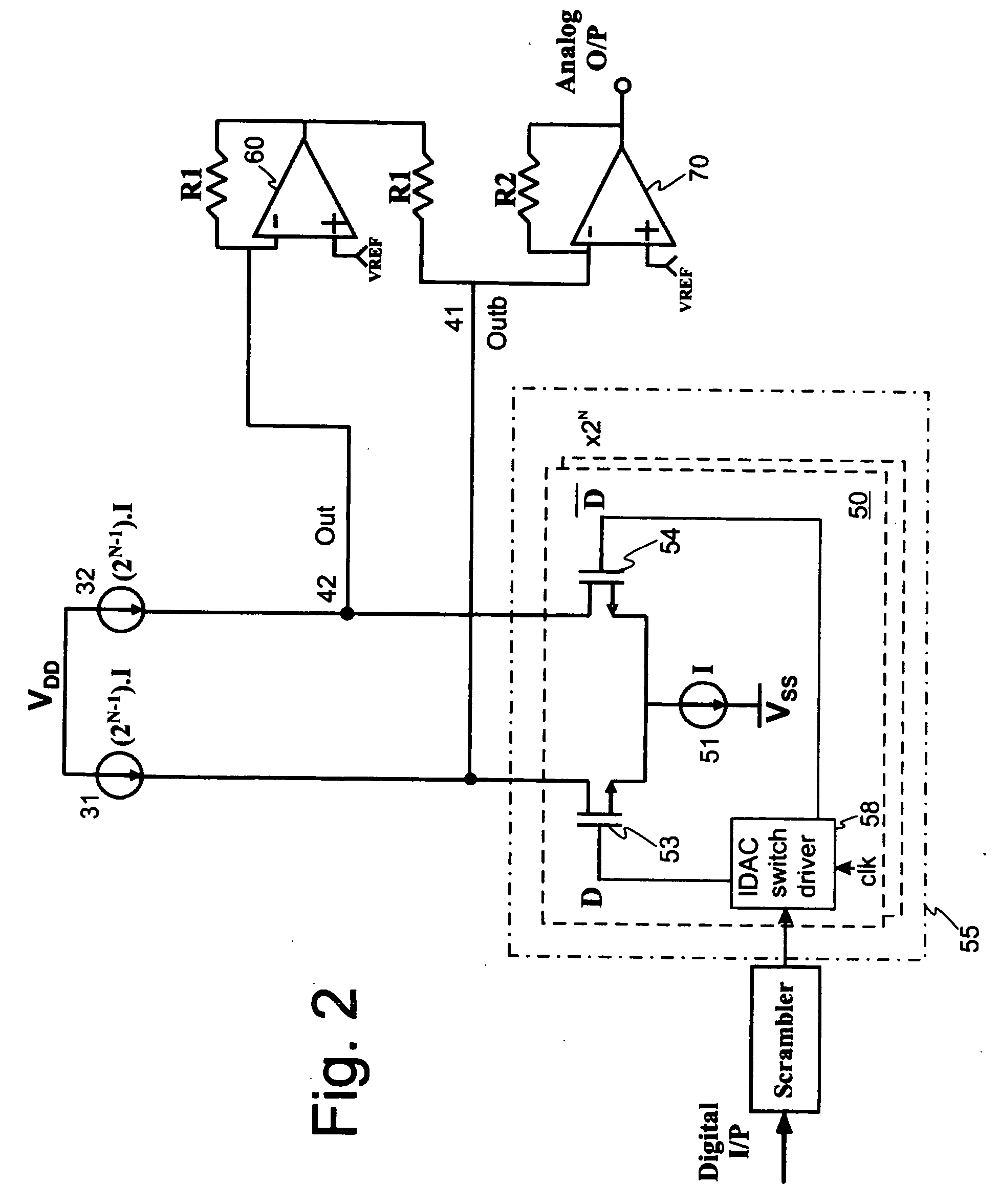
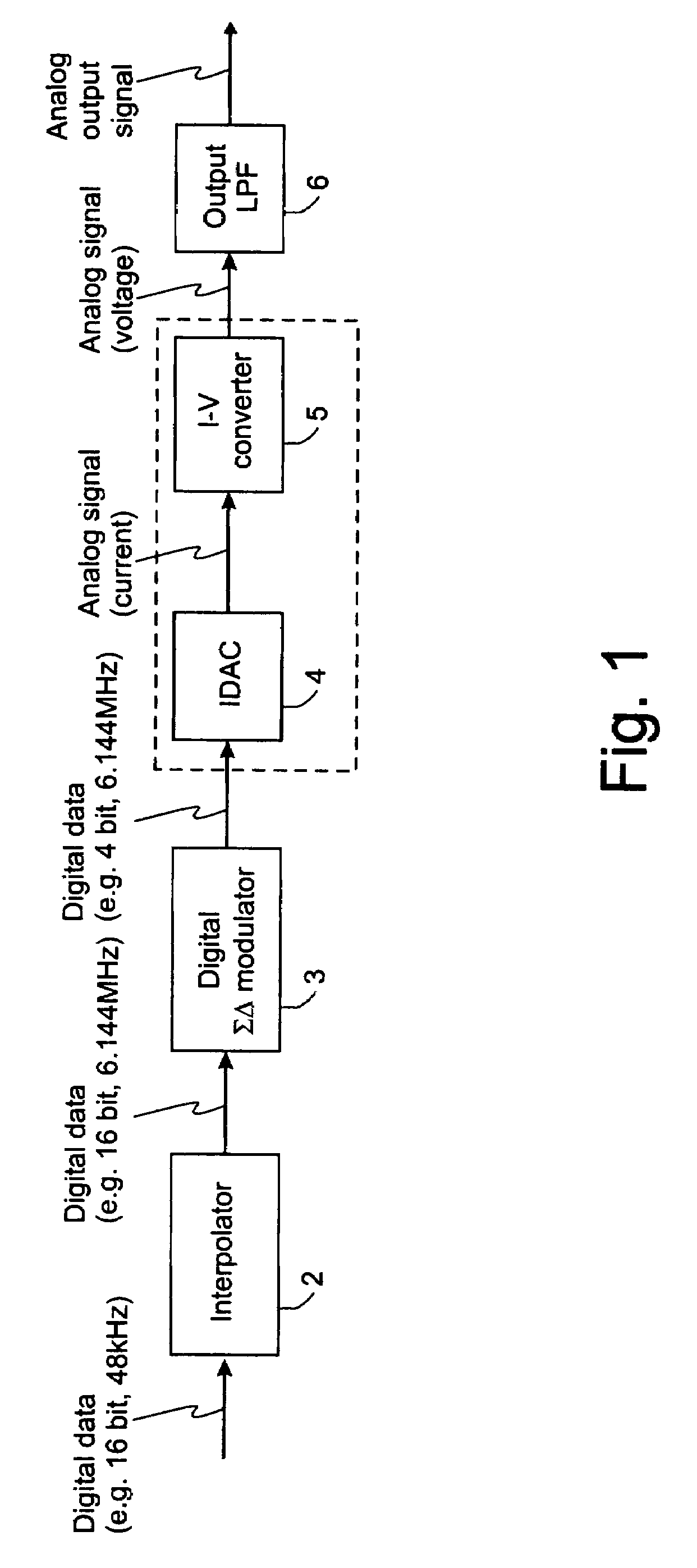
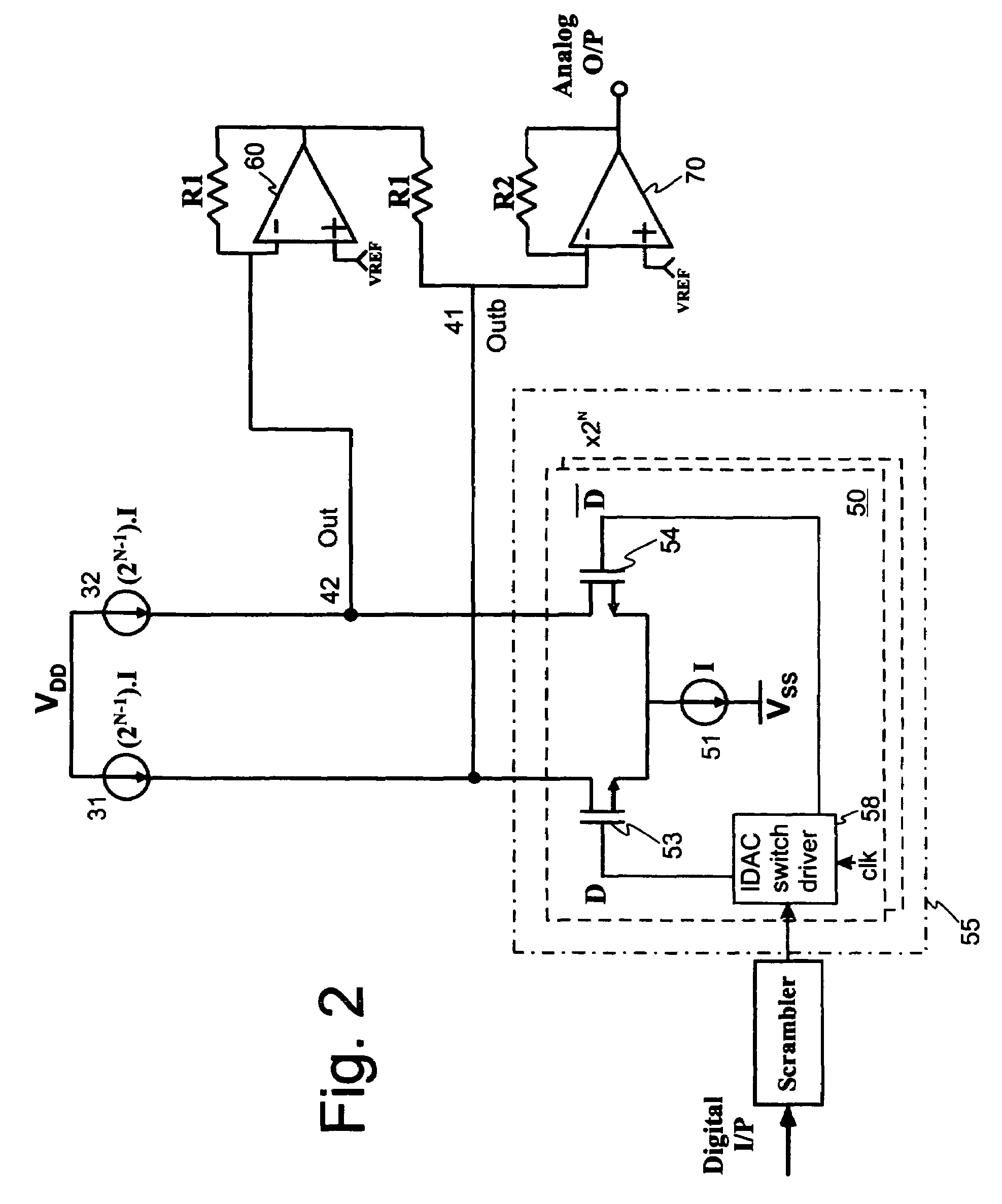
Continuous-time-sigma-delta DAC using chopper stabalisation
ActiveUS20060139193A1Reduce flicker noiseRemove flicker noiseElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionVoltage converterGreek letter sigma
A sigma-delta digital-to-analog converter comprises a current digital-to-analog converter (IDAC) stage which generates a current depending on an input digital signal. An output current-to-voltage converter converts the generated signal to a voltage on a continuous-time basis. The amplifier used in the output current-to-voltage converter is chopper-stabilized. The converter can be single bit or multi-bit. The IDAC stage can be implemented with a pair of branches, a first branch comprising a first biasing current source and a second branch comprising a second biasing current source. The biasing current sources can be chopper-stabilized by connecting the bias current sources to the output current-to-voltage converter by a set of switches. The switches connect the biasing current sources to the output current-to-voltage converter in a first configuration and a second, reversed, configuration. This modulates flicker noise contributed by the bias current sources to the chopping frequency. from where it can be removed by filtering downstream of the current-to-voltage converter.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
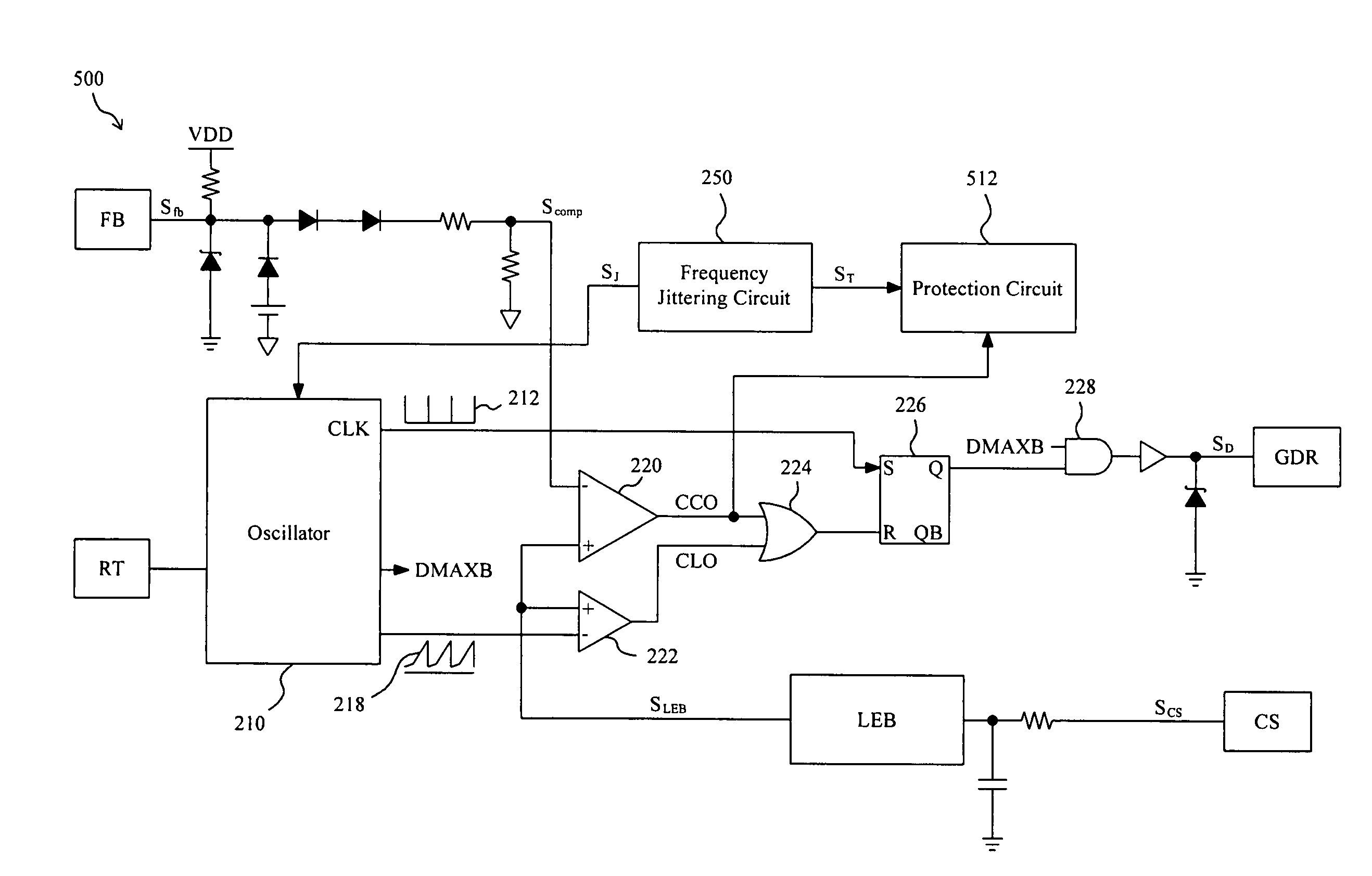
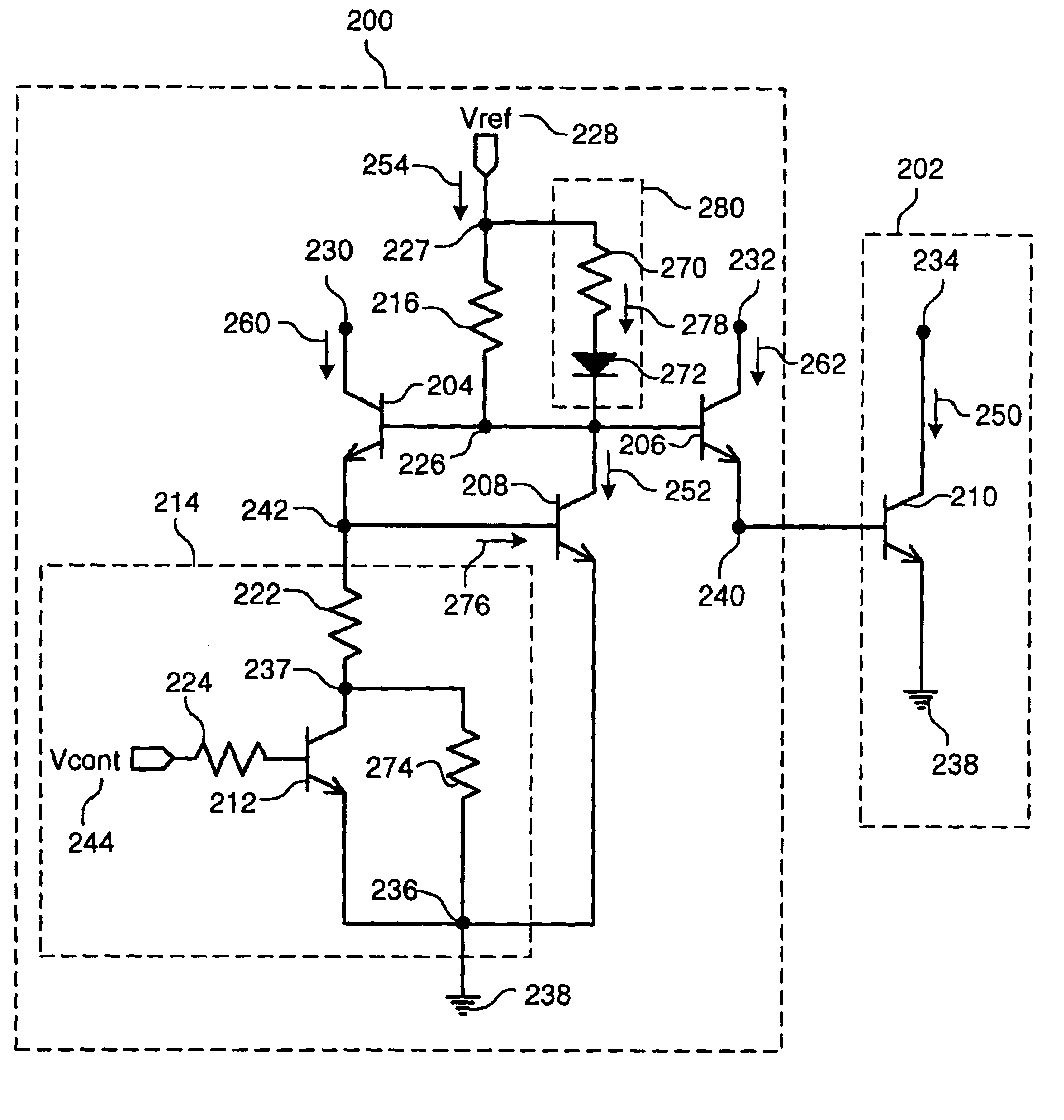
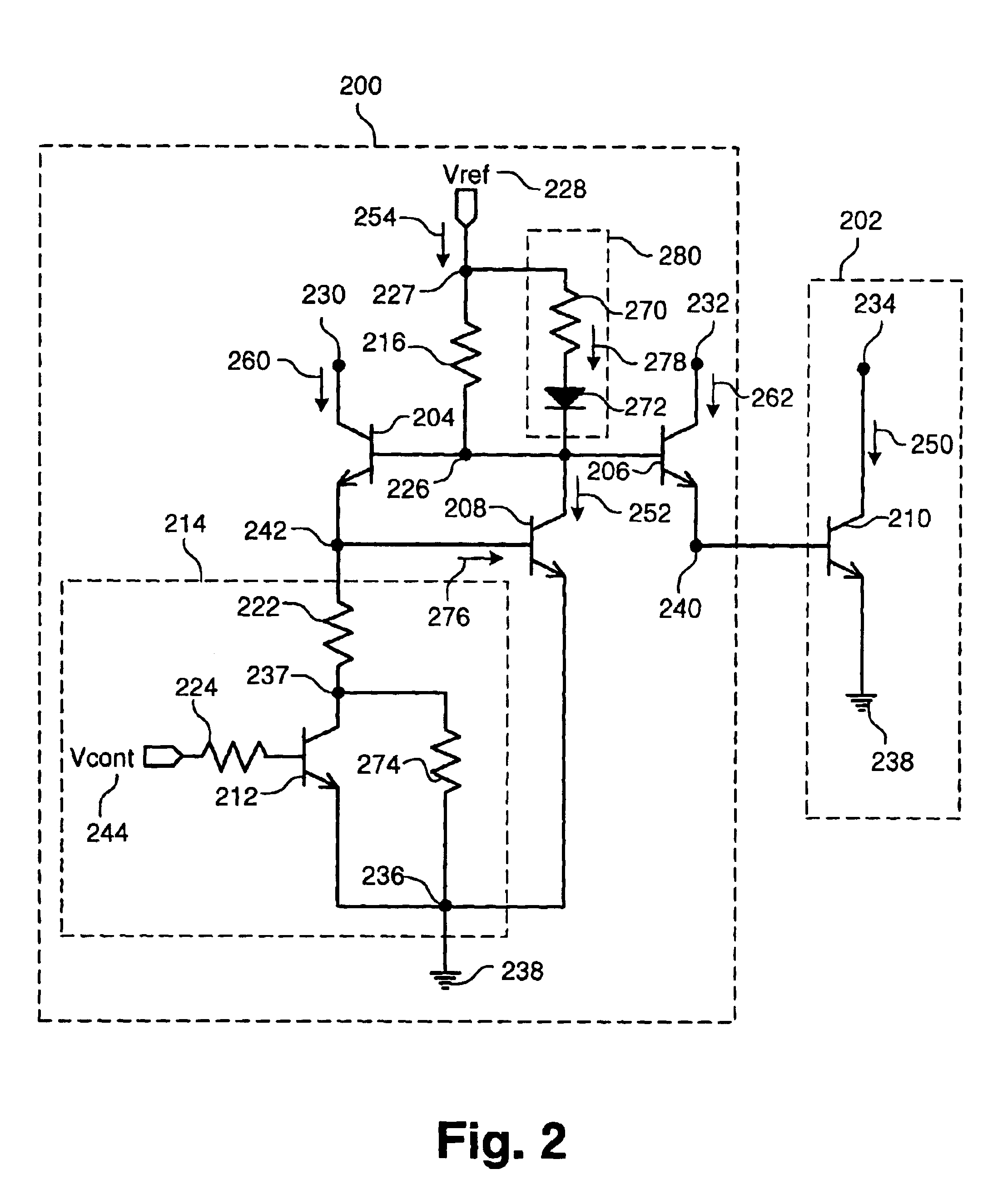
Apparatus and method for reducing the die area of a PWM controller
InactiveUS20080298099A1Reduce die areaLow costEmergency protective arrangements for automatic disconnectionPower conversion systemsDelayed timePwm controller
An apparatus and method for reducing the die area of a PWM controller include a protection circuit triggered by a fault index signal for counting, and the counting time is provided for a delay time required by fault verification. Therefore, fault detection circuits can be eliminated and the purpose of reducing the die area can be achieved.
Owner:RICHTEK TECH
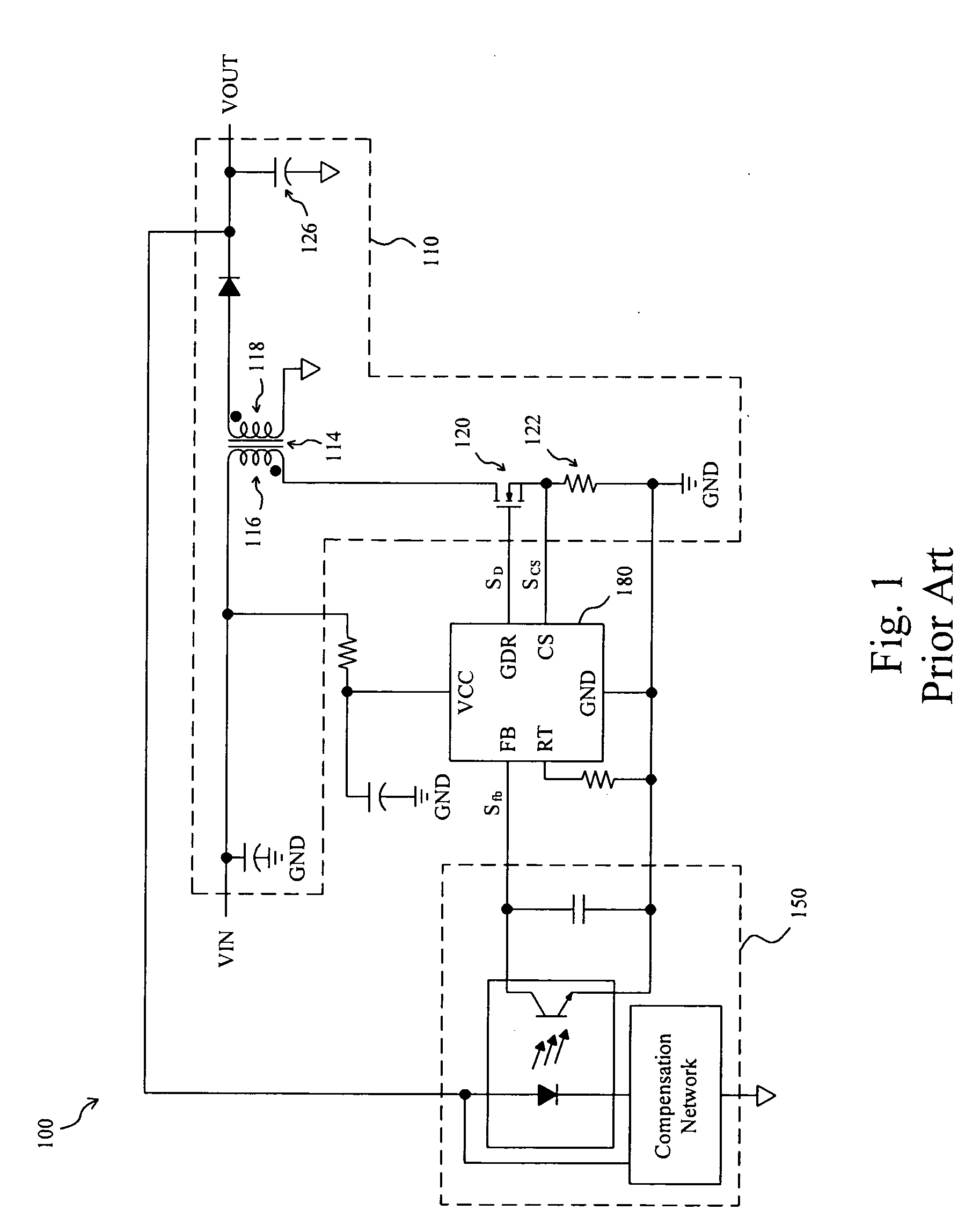
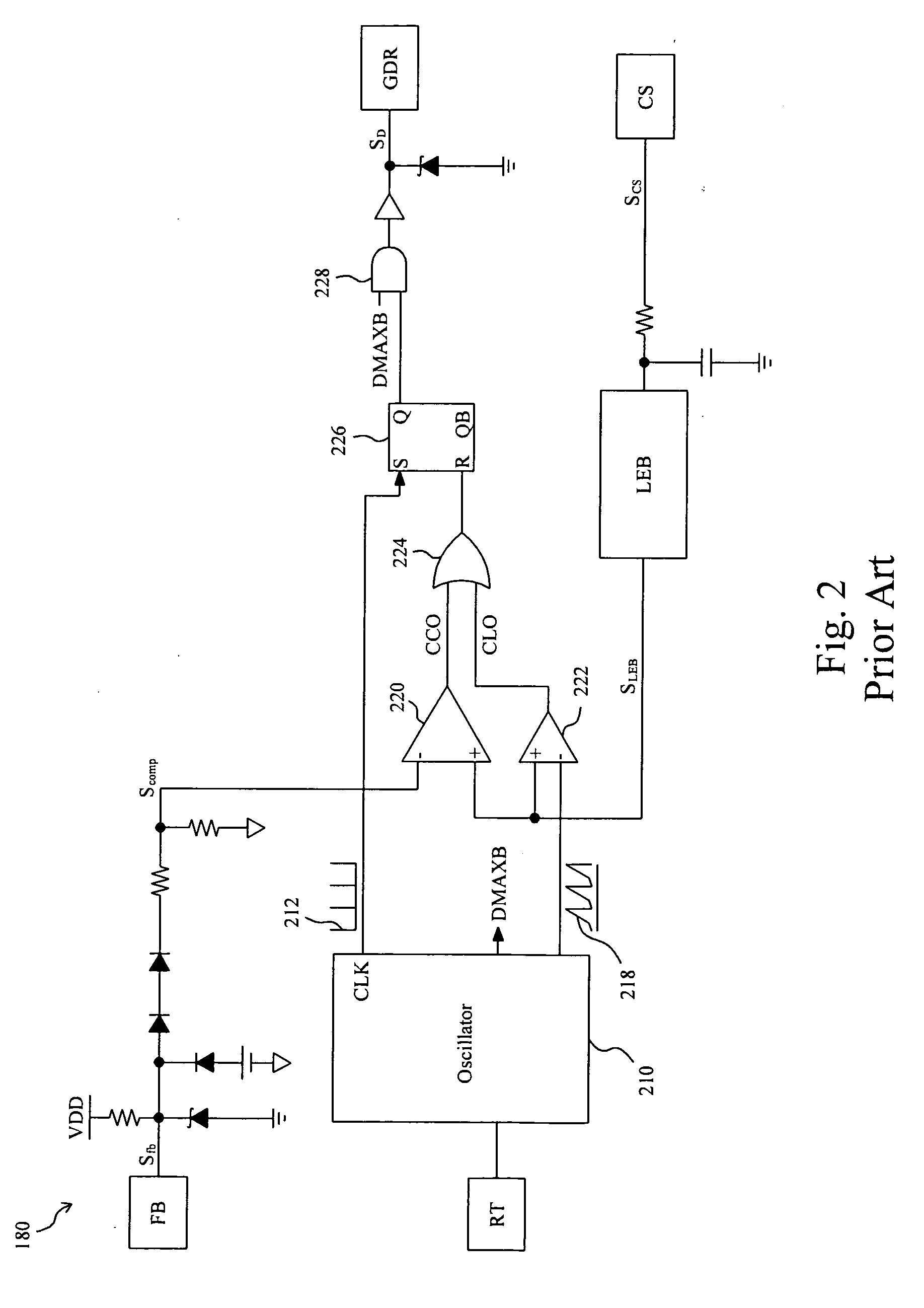
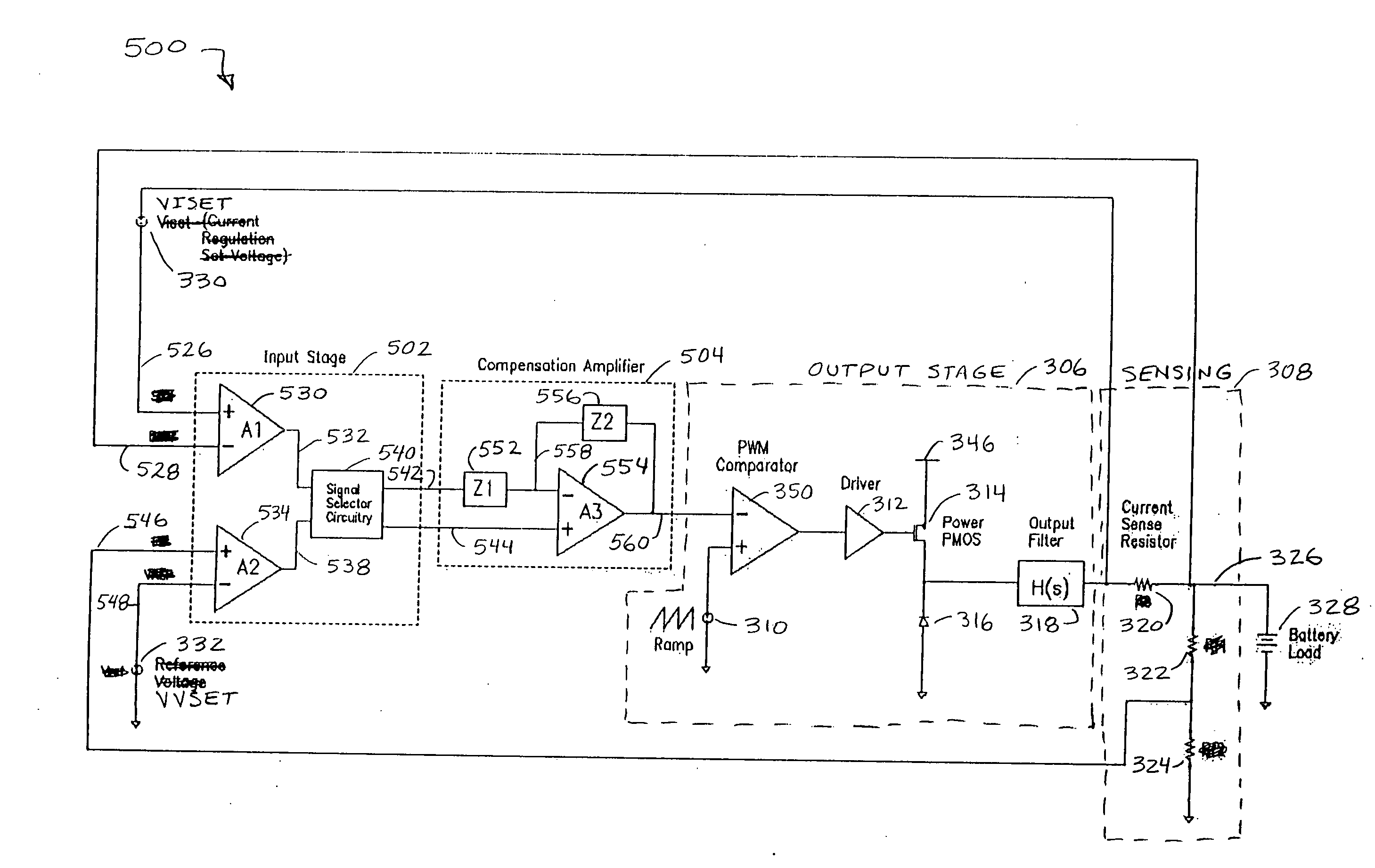
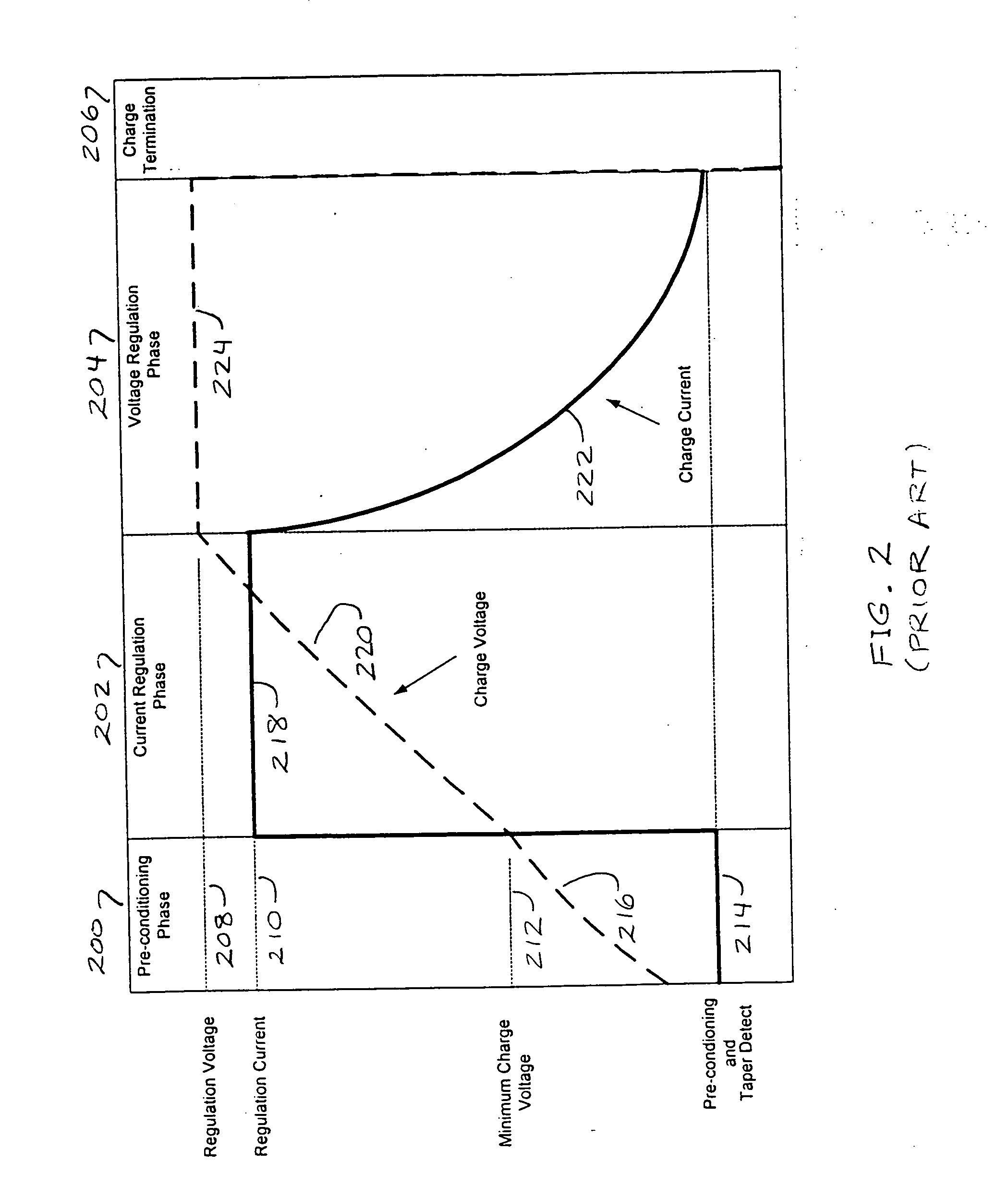
Area-efficient compensation circuit and method for voltage mode switching battery charger
InactiveUS20050134220A1Reduce die areaImproved compensation amplifier performanceBatteries circuit arrangementsElectric powerAudio power amplifierFeedback control
A feedback-controlled battery charger circuit (500) provides, alternatively, constant current and constant voltage to a battery (328) being charged. Current and voltage at the charger output (326) are sensed in sensing elements (308) and compared to preset reference values from reference generators for current (330) and voltage (332), thus generating error signals for both current and voltage. These error signals are amplified in separate amplifiers (530, 534); then, depending on battery voltage, one of the amplified error signals is automatically selected by a signal selector (540). The selected error signal is applied to a single compensation amplifier (554) with reactive feedback loop (552, 556); the output of the compensation amplifier with feedback (504) then controls the output current or voltage of the output stage (306). This output stage is a voltage controlled current source. The output of this voltage controlled current source is connected through an output filter (318) and sensing elements (308) to the battery (328) being charged.
Owner:BROHLIN PAUL L +2
Differential pipelined analog to digital converter with successive approximation register subconverter stages
InactiveUS20050078026A1Improve conversion speedReduce power consumptionElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersA d converterEngineering
Pipelined analog to digital conversion systems are provided having cascaded multi-bit successive approximation register subconverter stages. Capacitor arrays are provided in the subconverter stages, where switching logic selectively couples the capacitors to operate in sample, conversion, and residue amplification modes for generating multi-bit subconverter digital outputs and analog subconverter residue outputs. In one implementation, the capacitors are switched according to a thermometer code to reduce differential converter non-linearity, and the first subconverter stage gain is reduced to improve the conversion system bandwidth.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Differential pipelined analog to digital converter with successive approximation register subconverter stages
ActiveUS6879277B1Improve system bandwidthReduce rangeElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersAnalog to digital conversionAnalog-to-digital converter
Pipelined analog to digital conversion systems are provided having cascaded multi-bit successive approximation register subconverter stages. Capacitor arrays are provided in the subconverter stages, where switching logic selectively couples the capacitors to operate in sample, conversion, and residue amplification modes for generating multi-bit subconverter digital outputs and analog subconverter residue outputs. In one implementation, the capacitors are switched according to a thermometer code to reduce differential converter non-linearity, and the first subconverter stage gain is reduced to improve the conversion system bandwidth.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Die attach pad for use in semiconductor manufacturing and method of making same
ActiveUS7227245B1Reduce riskReduce die areaSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesAdhesiveEngineering
Broadly speaking, the invention pertains to substrates for use in semiconductor manufacturing. A peripheral ledge or similar structure can be provided in a die attach pad, so as to retain adhesive that may flow from the die support surface when the die is attached to the die attach pad. In this manner, adhesive is prevented from flowing off the die attach pad, where it can create unwanted conductive areas on the outer surface of an IC package. The accompanying reduction in area of the die support surface, and retention of adhesive from any downbond areas, also prevents delamination of the adhesive.
Owner:NAT SEMICON CORP
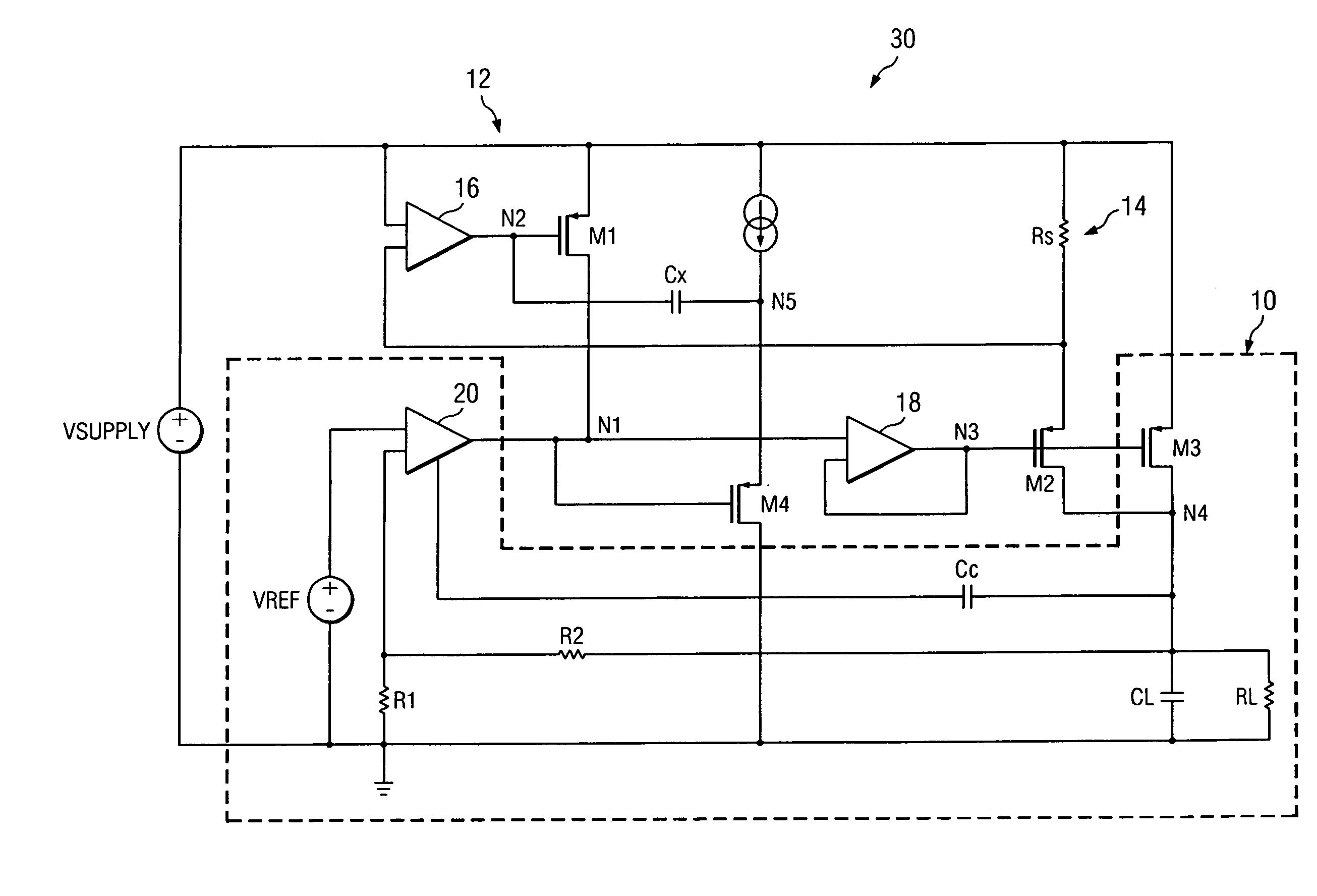
Switch mode power converter current sensing apparatus and method
ActiveUS20140049238A1Reduce die areaImprove accuracyDc-dc conversionCurrent measurements onlyEngineeringField-effect transistor
Methods and apparatus are presented for sensing current flowing in a power transistor of a switch mode converter, in which a voltage is sensed across a first field effect transistor connected in a series circuit branch in parallel with the power transistor, and the sensed voltage is used to generate output signal to indicate the current flowing in the power transistor.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
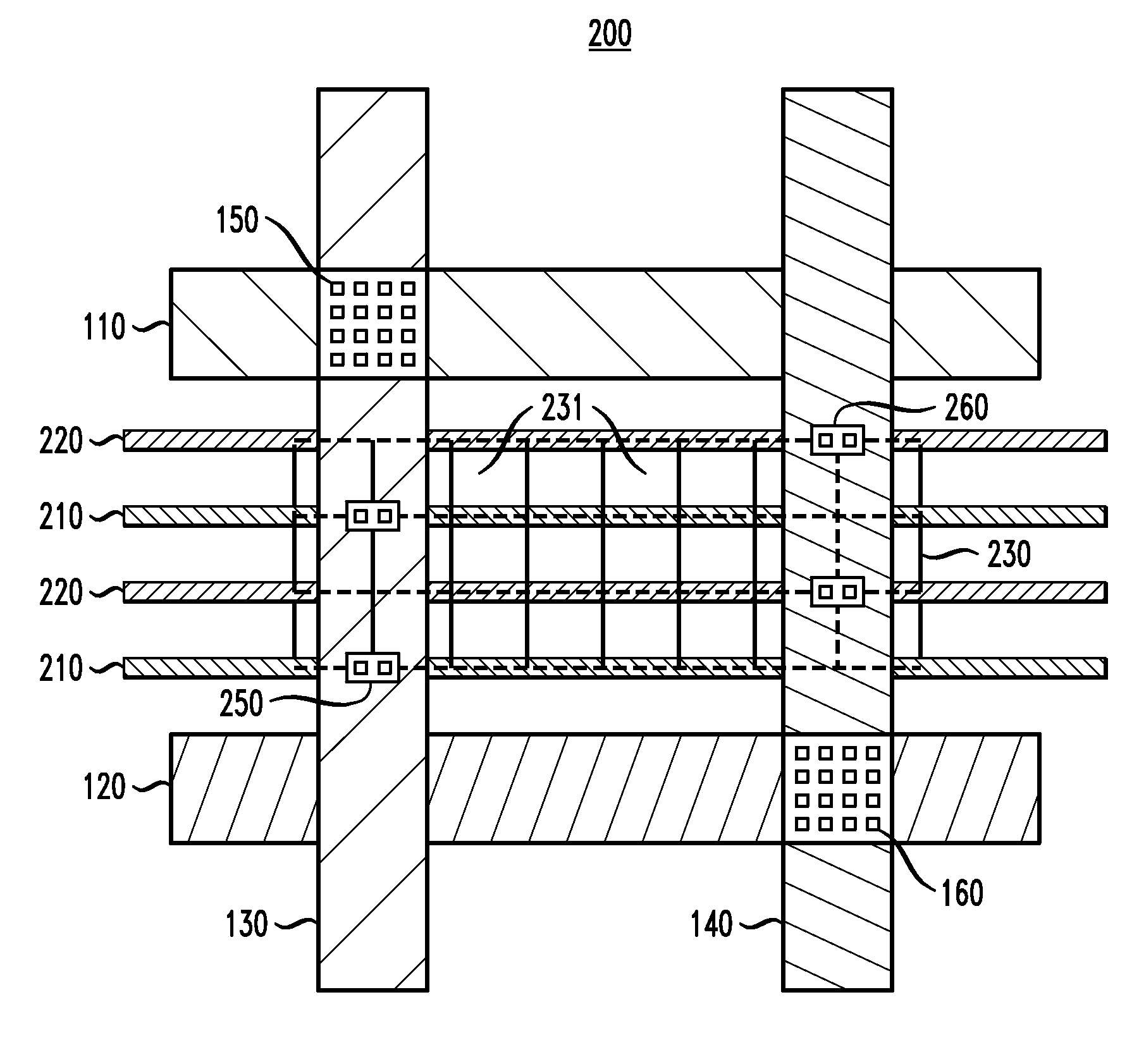
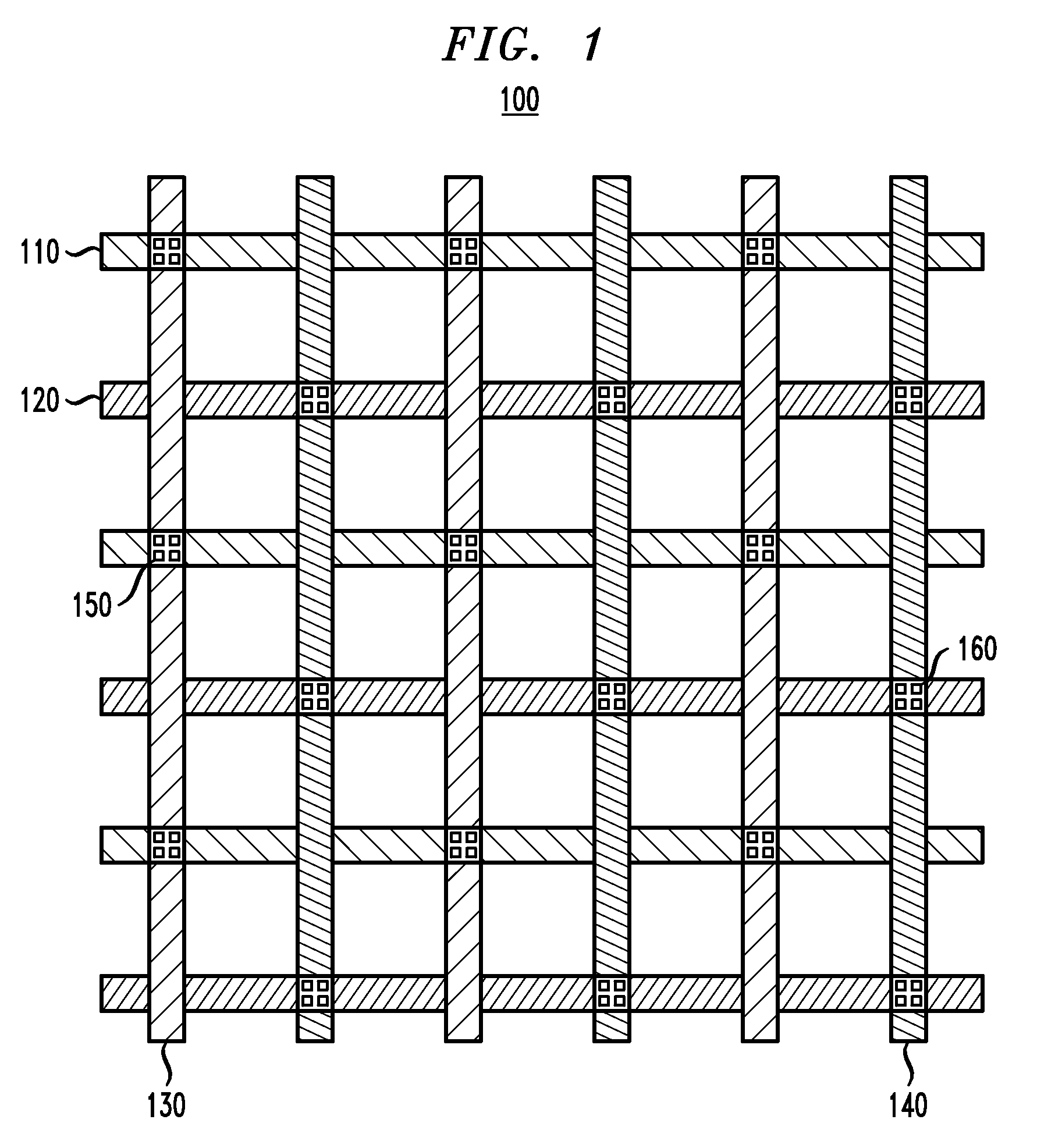
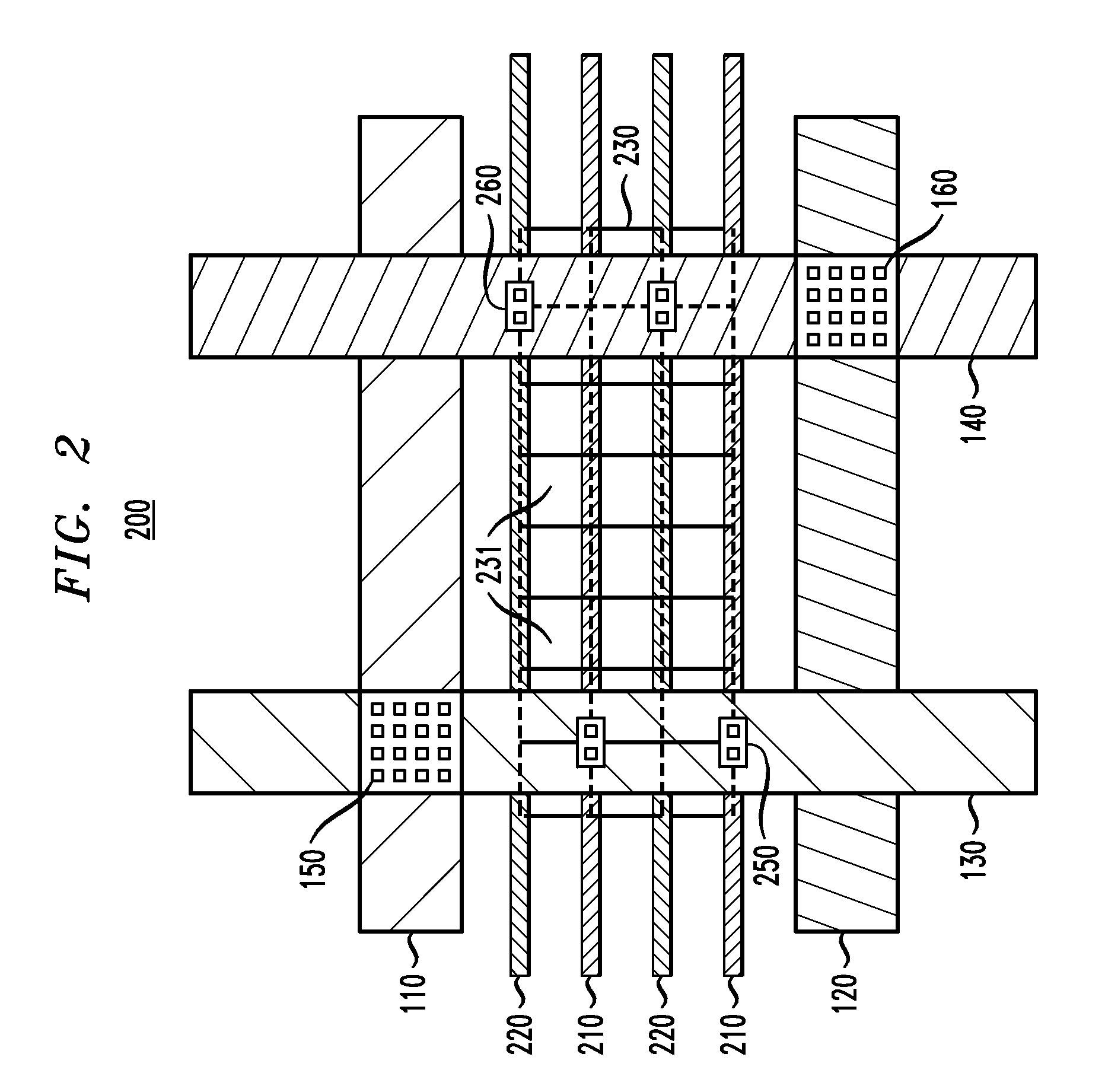
Enhanced Power Distribution in an Integrated Circuit
InactiveUS20100097875A1Efficiently delivering powerCost ICsSolid-state devicesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingElectrical batteryAbutment
An integrated circuit structure for distributing power to one or more standard cells in an integrated circuit includes a first plurality of standard cells and a power mesh power connection structure coupled to the cells. Each of the standard cells includes first and second power rails adapted for connection to a voltage supply and a voltage return, respectively, of the standard cells. Each standard cell in a subset of the standard cells is arranged in direct abutment with at least two other standard cells, and at least first and second end cells are arranged in direct abutment with at least one other standard cell of the first plurality of standard cells. The power mesh power connection structure includes a plurality of conductive elements formed in a plurality of different conductive layers in the integrated circuit. The power mesh power connection structure is operative to connect the first and second power rails of the first plurality of standard cells to the voltage supply and voltage return, respectively, and is configured so as to reduce a first voltage differential between respective first power rails of the standard cells and to reduce a second voltage differential between respective second power rails of the standard cells.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
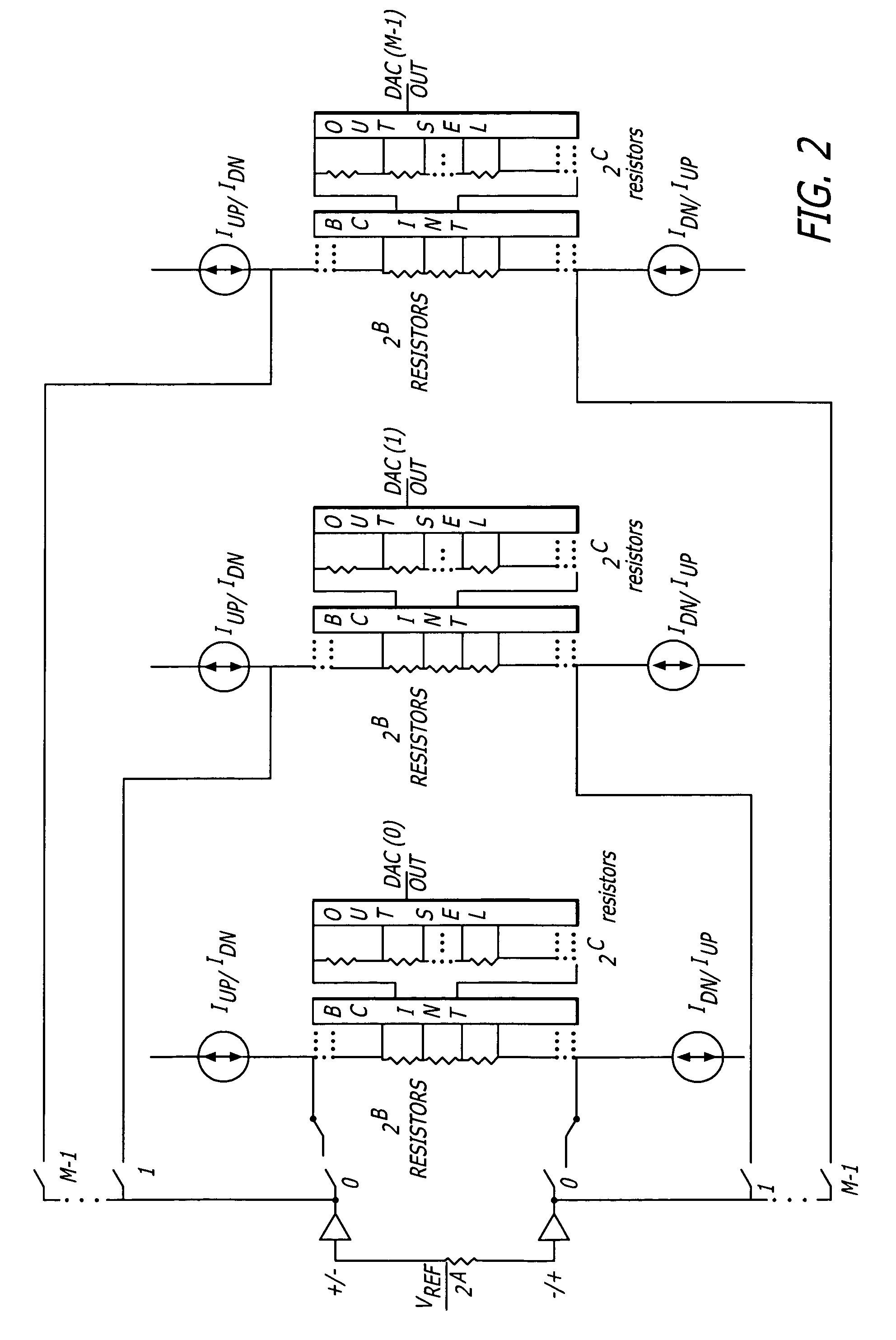
Digitally-switched impedance with multiple-stage segmented string architecture
ActiveUS6885328B1Reduce countReduce die areaElectric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsImage resolutionDigital input
A multiple-stage digitally-switched impedance has one “type B” stage and at least two “type A” stages. The type A stages are cascaded between high and low reference nodes and the type B stage. Each stage comprises a string of series-connected impedances and a switch network. A decoder responds to an digital input signal by controlling the switch networks to switch selectable portions of the strings in the type A stages into a series connection with the type B stage's string, and to control the type B stage's switch network to tap its string at a location to provide a impedance corresponding to the n-bit digital input signal between the final output node and at least one of the high and low reference nodes. Each stage provides a portion of the impedance's n-bit resolution, and the sum of the bits of resolution provided by each stage equals the total n-bit resolution.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
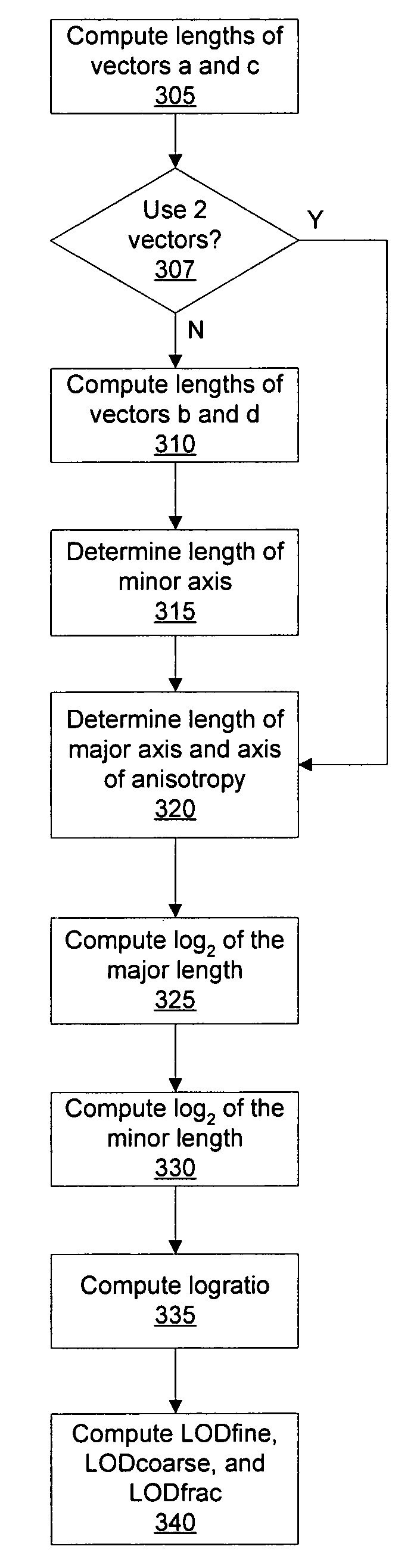
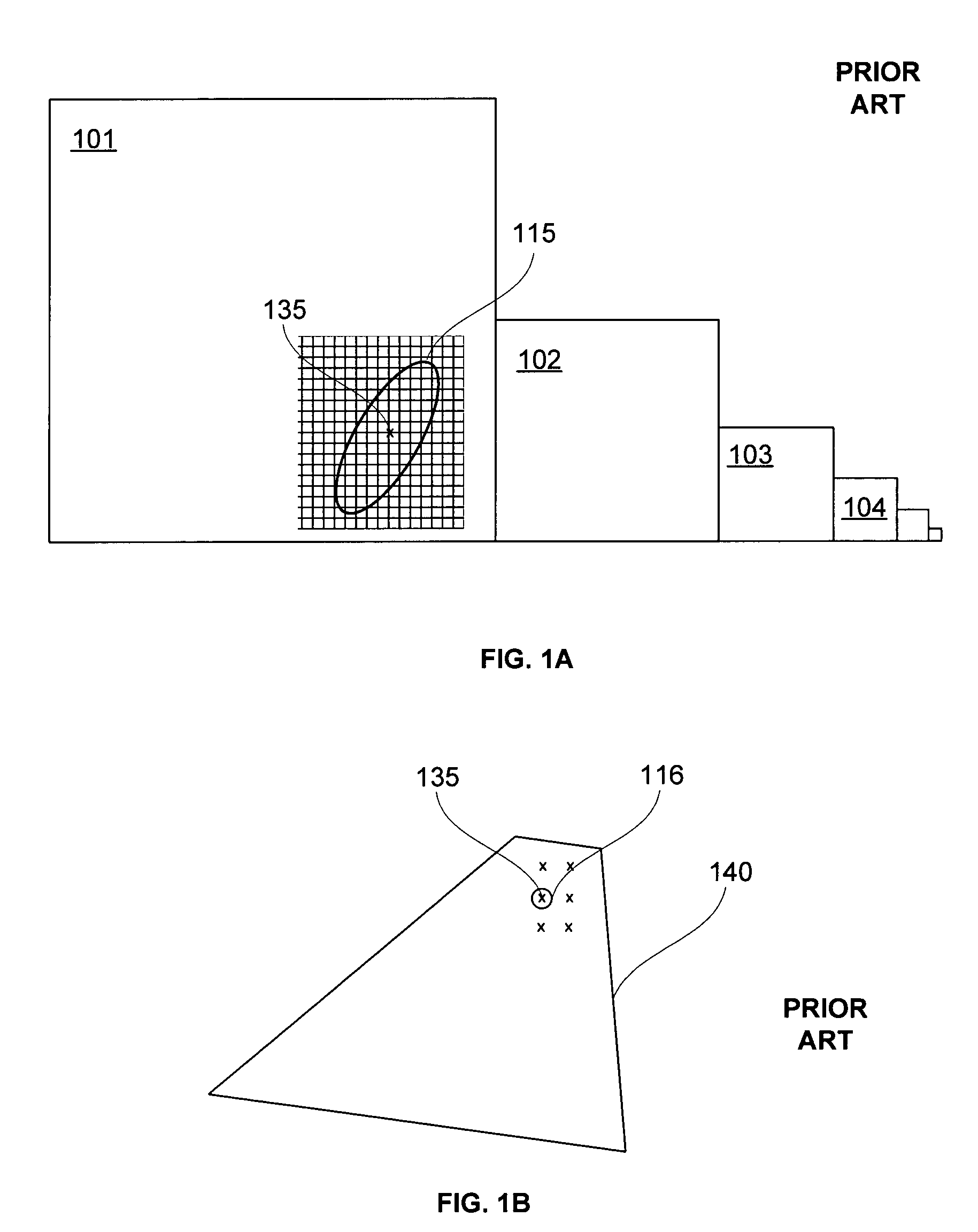
Computing anisotropic texture mapping parameters
InactiveUS7369136B1Less die areaMaintaining anisotropic texture filtering qualityCathode-ray tube indicators3D-image renderingComputational scienceGraphics
A system and method for computing anisotropic texture mapping parameters by using approximation techniques reduces the complexity of the calculations needed to perform high quality anisotropic texture filtering. Anisotropic texture mapping parameters that are approximated may be computed using dedicated processing units within a graphics processor, thereby improving anisotropic texture mapping performance. Specifically, the major axis and minor axis of anisotropy are determined and their respective lengths are calculated using approximations. Other anisotropic texture mapping parameters, such as a level of detail for selecting a particular level are computed based on the calculated lengths of the major and minor axes.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
Integrated RF circuits
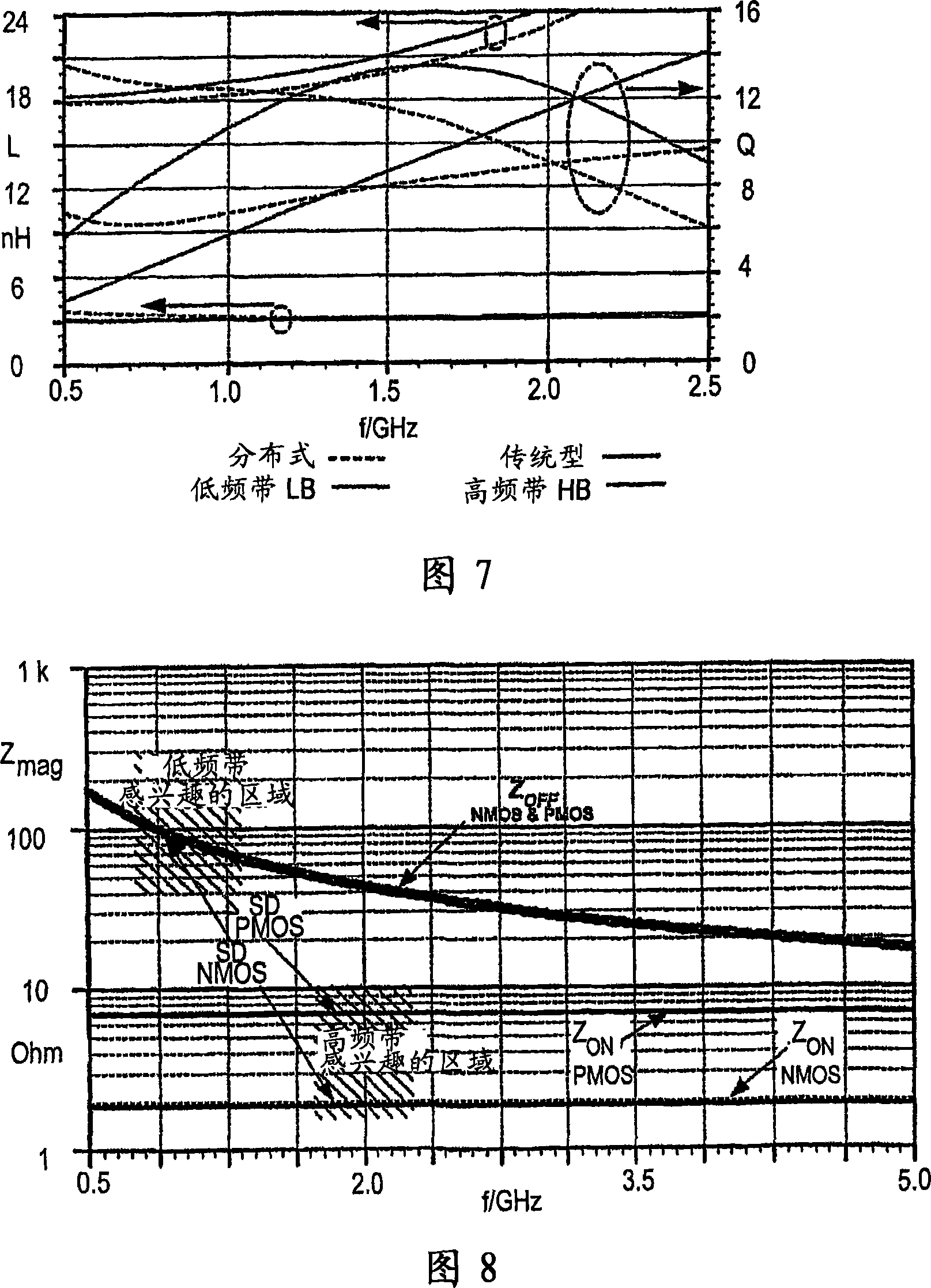
InactiveUS20070037544A1Large response tuning rangeReduce die areaAmplifier modifications to reduce non-linear distortionHigh frequency amplifiersSignal responseOperating point
An on-chip response adjuster is based on an on-purpose generated and dominant transfer pole or zero of a signal response so as to provide a process-stable phase behavior of the circuitry. The signal response is defined directly by a passive frequency variant component (Lfold) and by transistor operation point, e.g. biasing, of a transistor configuration (Qcas,Qaux). As a result, electrically controlled signal response adjusters can be provided with fully integrated, single-chip integrated or system-on-chip (SoC) techniques.
Owner:NOKIA CORP
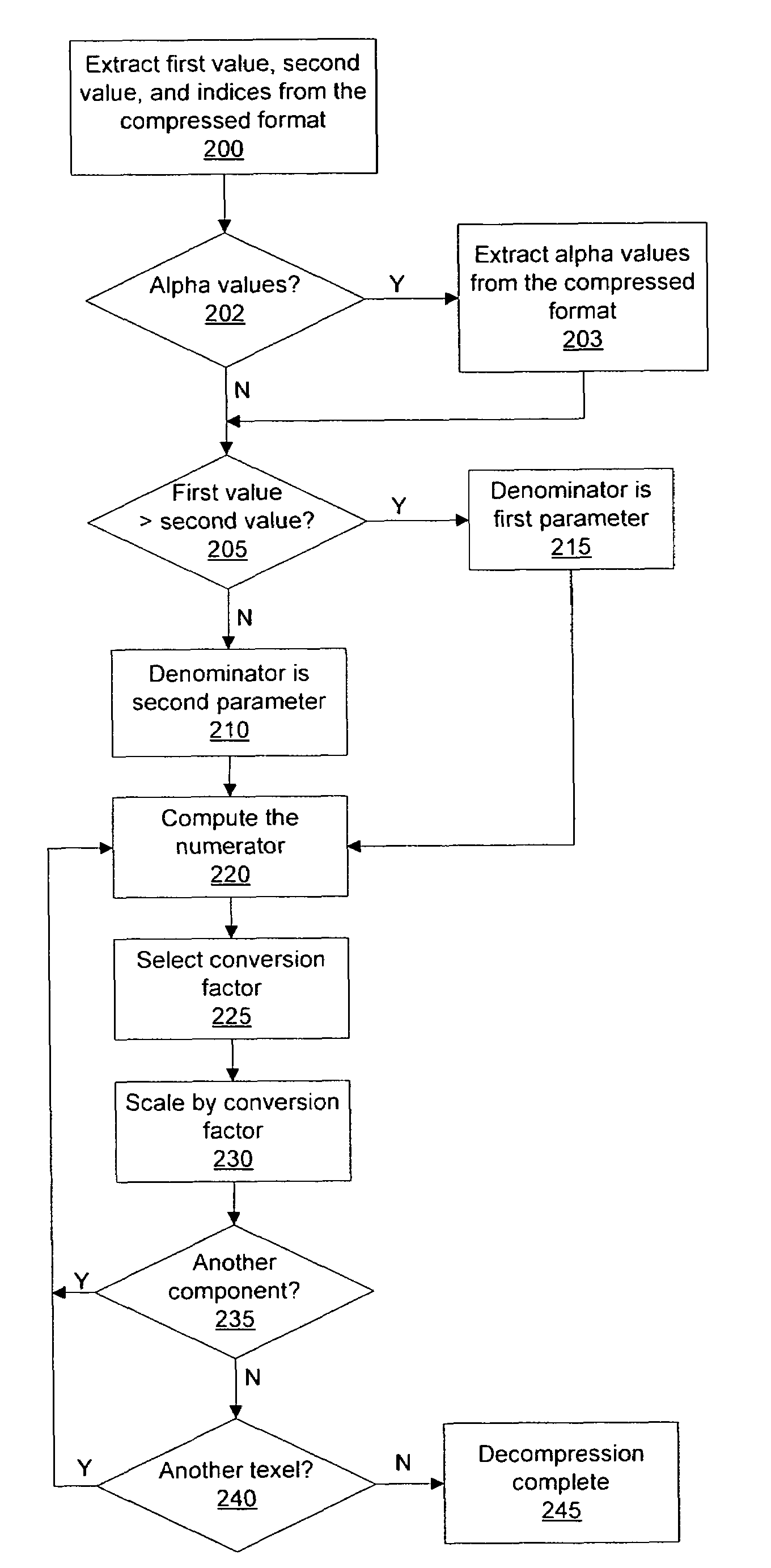
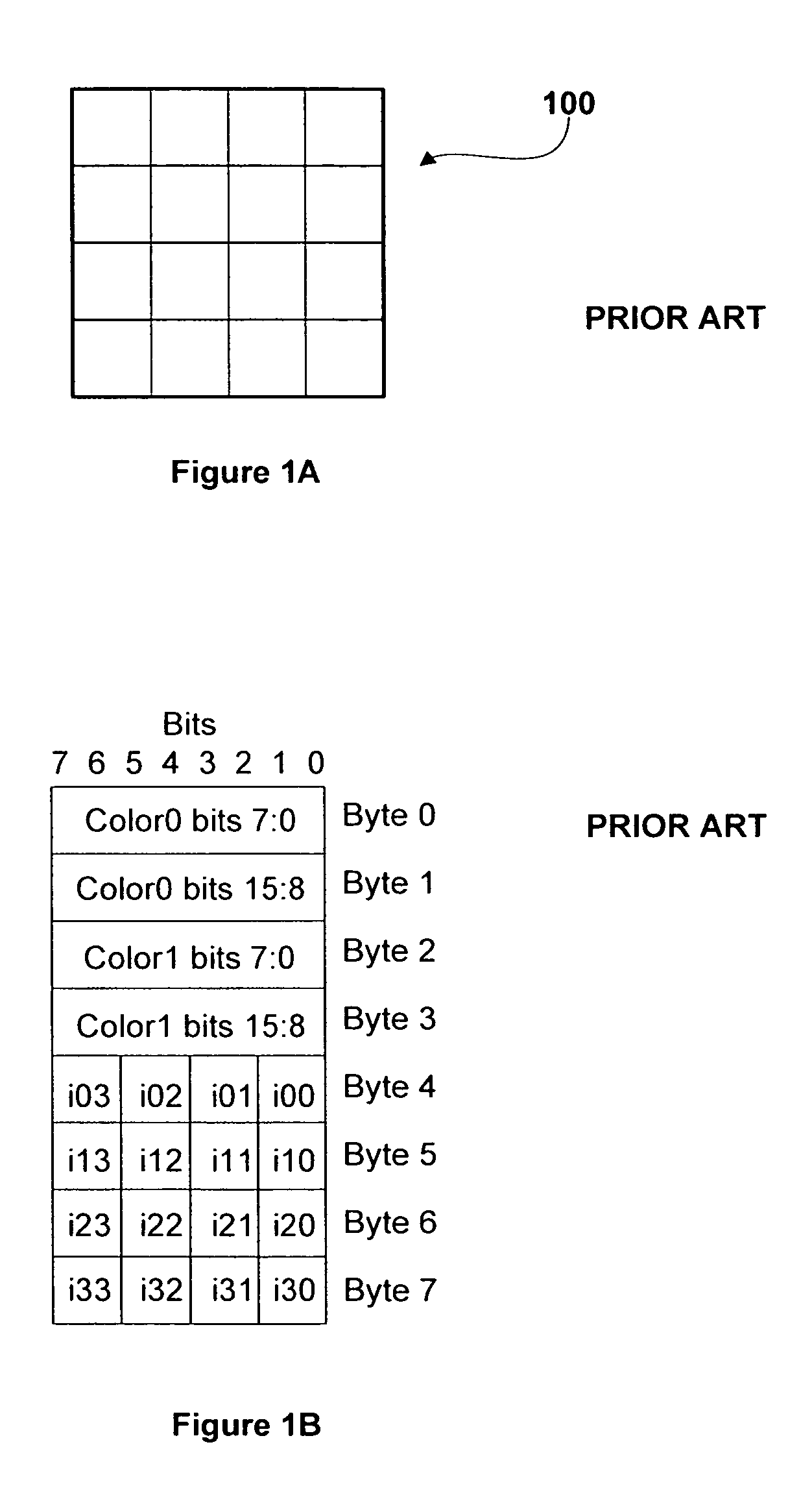
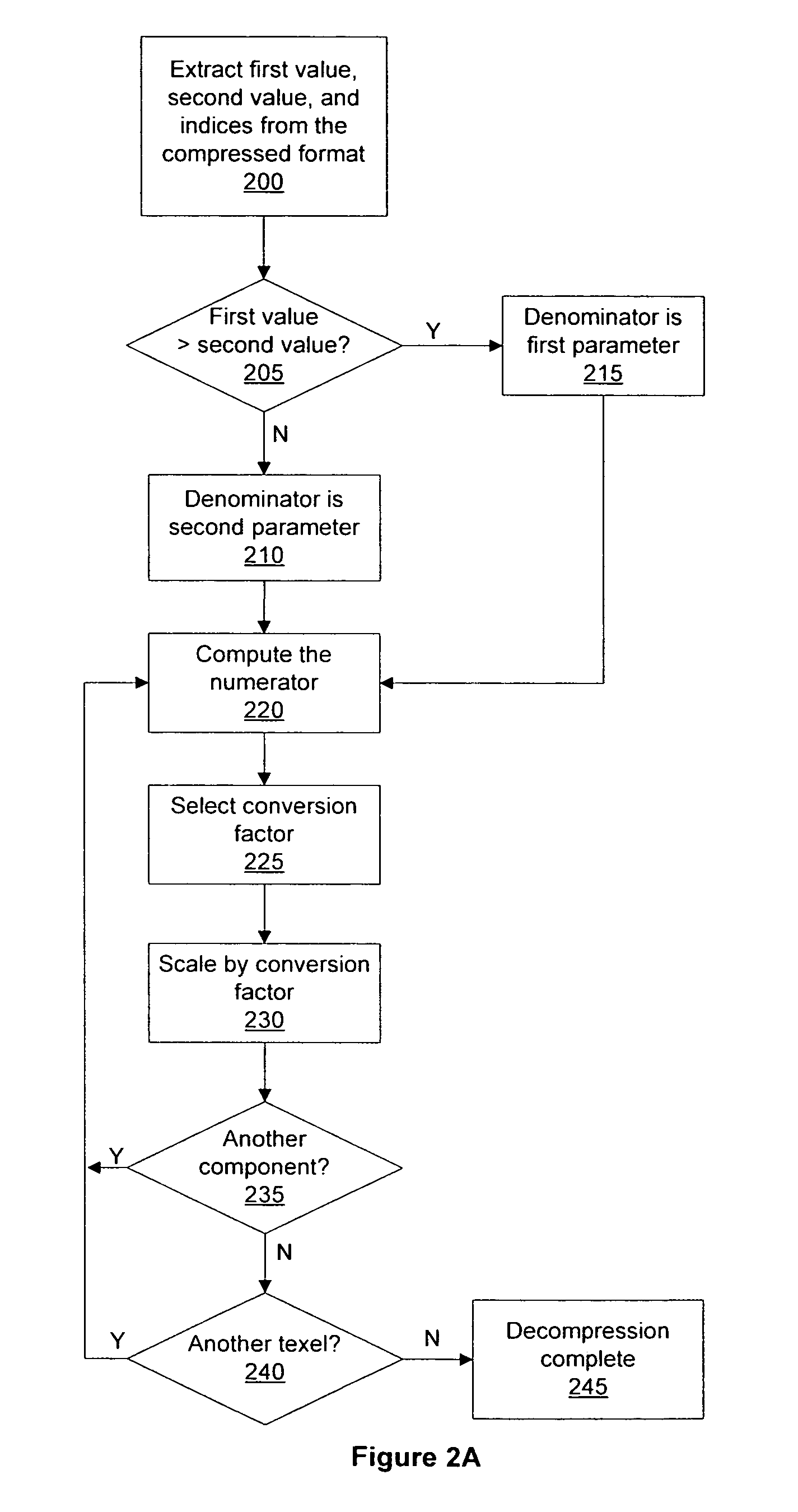
Decompression of block encoded texture data
ActiveUS7385611B1Simple calculationReduce die areaCharacter and pattern recognitionCathode-ray tube indicatorsPattern recognitionData system
Systems and methods that decompress block compressed texture data may decompress the texture data while simplifying computations to reduce die area while maintaining the required accuracy. Reducing the die area permits more texture data to be decompressed in the same die area compared with a more accurate decompression, thereby increasing texture decompression throughput. Computations are simplified by combining denominators for linear interpolation with format conversion to decompress texture data components compressed using conventional block compression formats.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
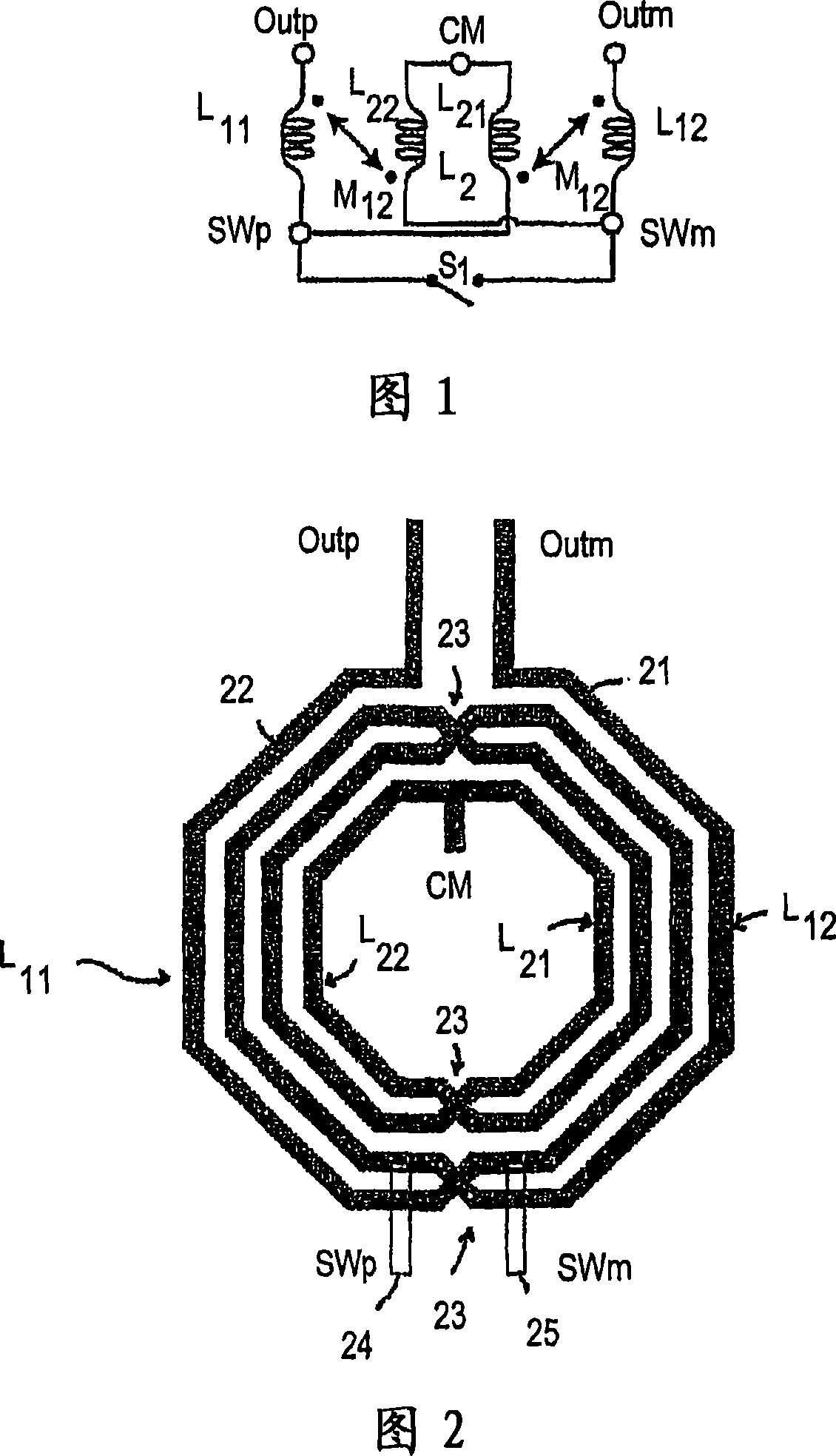
On-chip differential inductor and applications thereof
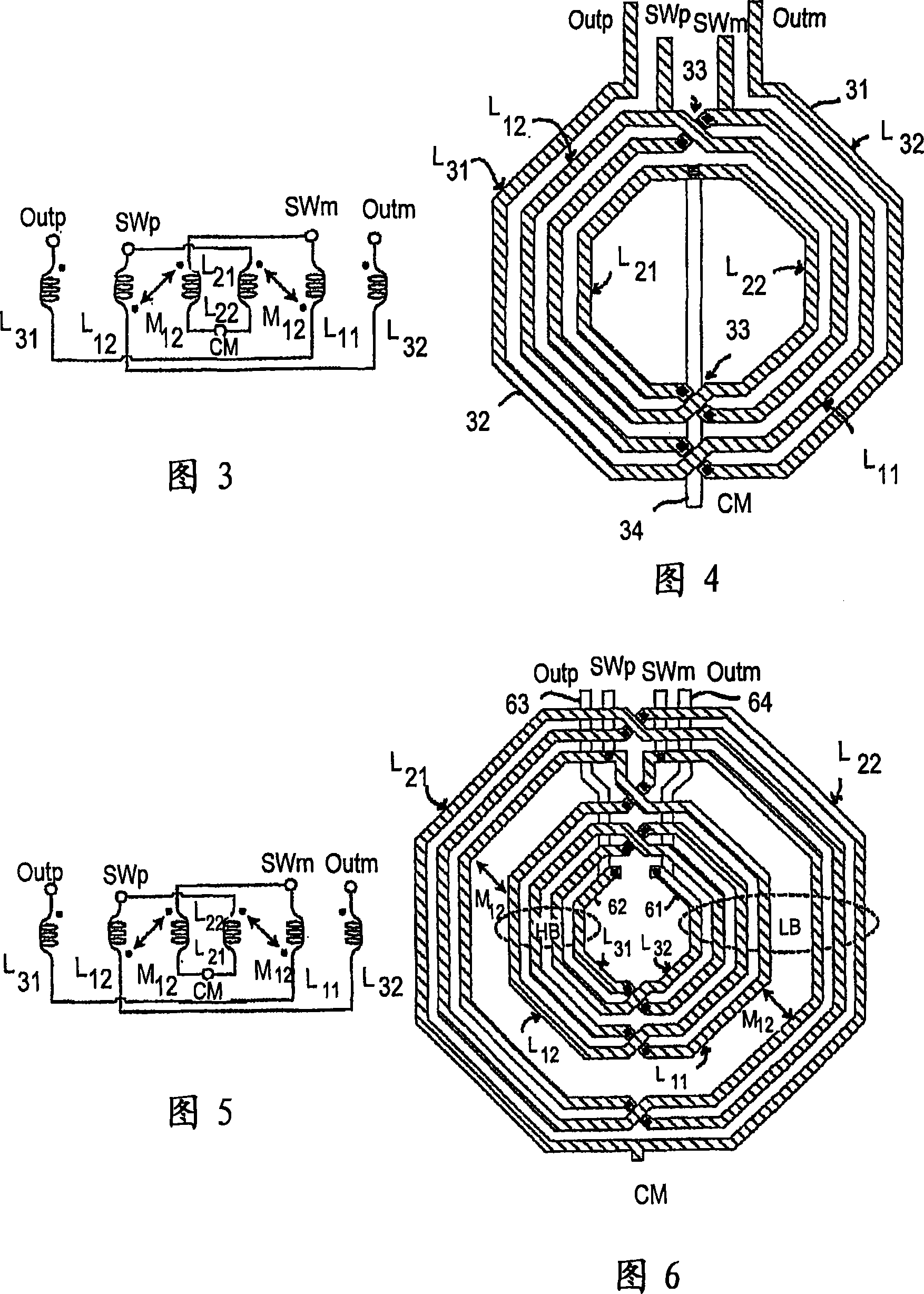
ActiveUS7039381B2Optimal integrated circuit layoutHigh quality factorSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesEngineeringInductor
An on-chip differential inductor includes a 1st interwound winding having a substantially octagonal shape, or rectangular octagonal shape, and a 2nd interwound winding having a substantially octagonal shape, or rectangular octagonal shape, that is interwound with the 1st interwound winding. Both the 1st and 2nd interwound windings are on the same layer of the integrated circuit. Each interwound winding includes two nodes; one of node of each winding is commonly coupled to a reference potential. The other node of each winding is operably coupled to receive a respective leg of a differential signal.
Owner:AVAGO TECH INT SALES PTE LTD
Inductor device for multiband radio frequency operation
InactiveCN101253586AOperation steps can be controlledEasy to operateTransformers/inductances coils/windings/connectionsAmplifier with semiconductor-devices/discharge-tubesAudio power amplifierPlanar inductor
Owner:NOKIA CORP
Semiconductor device
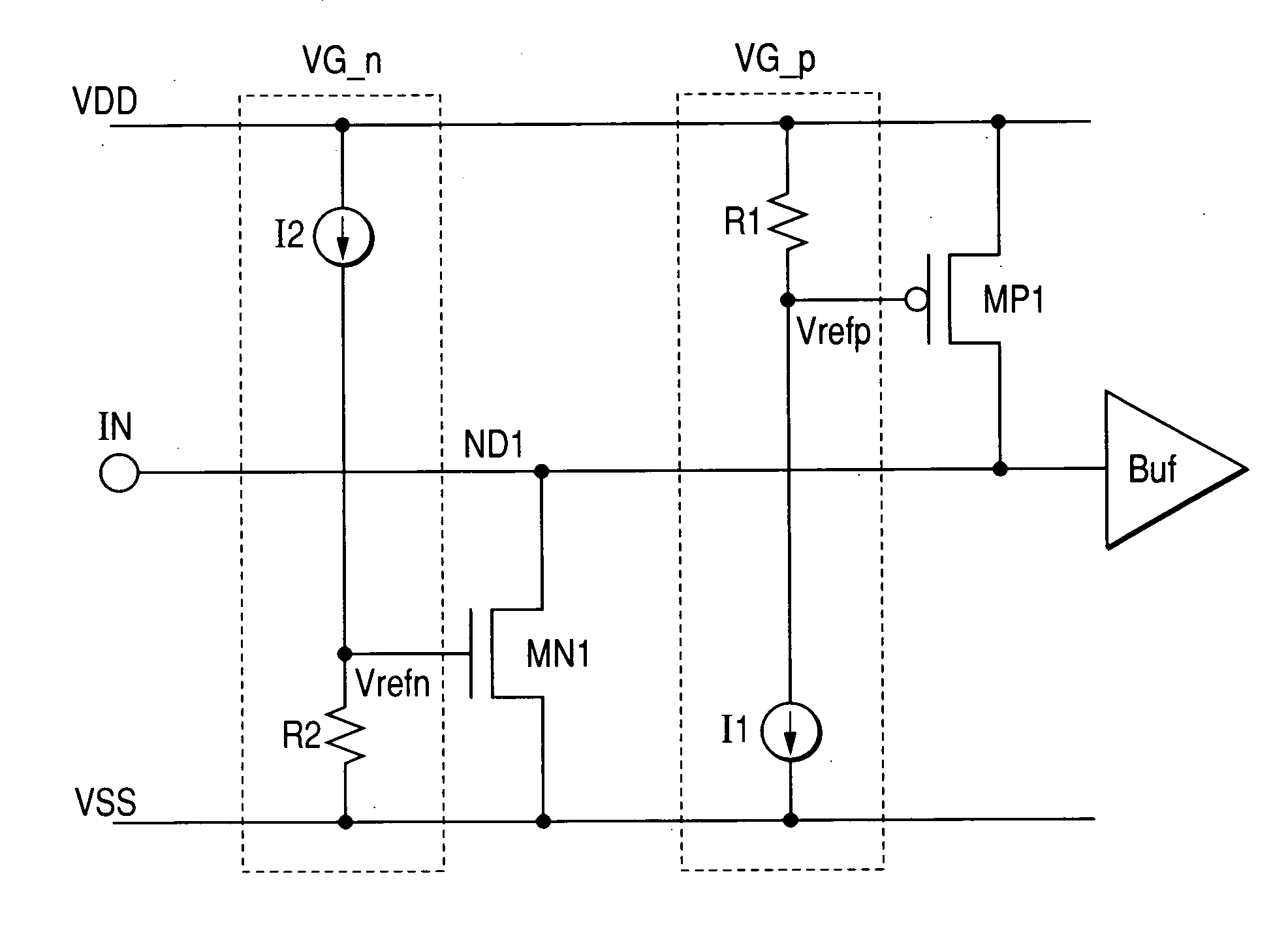
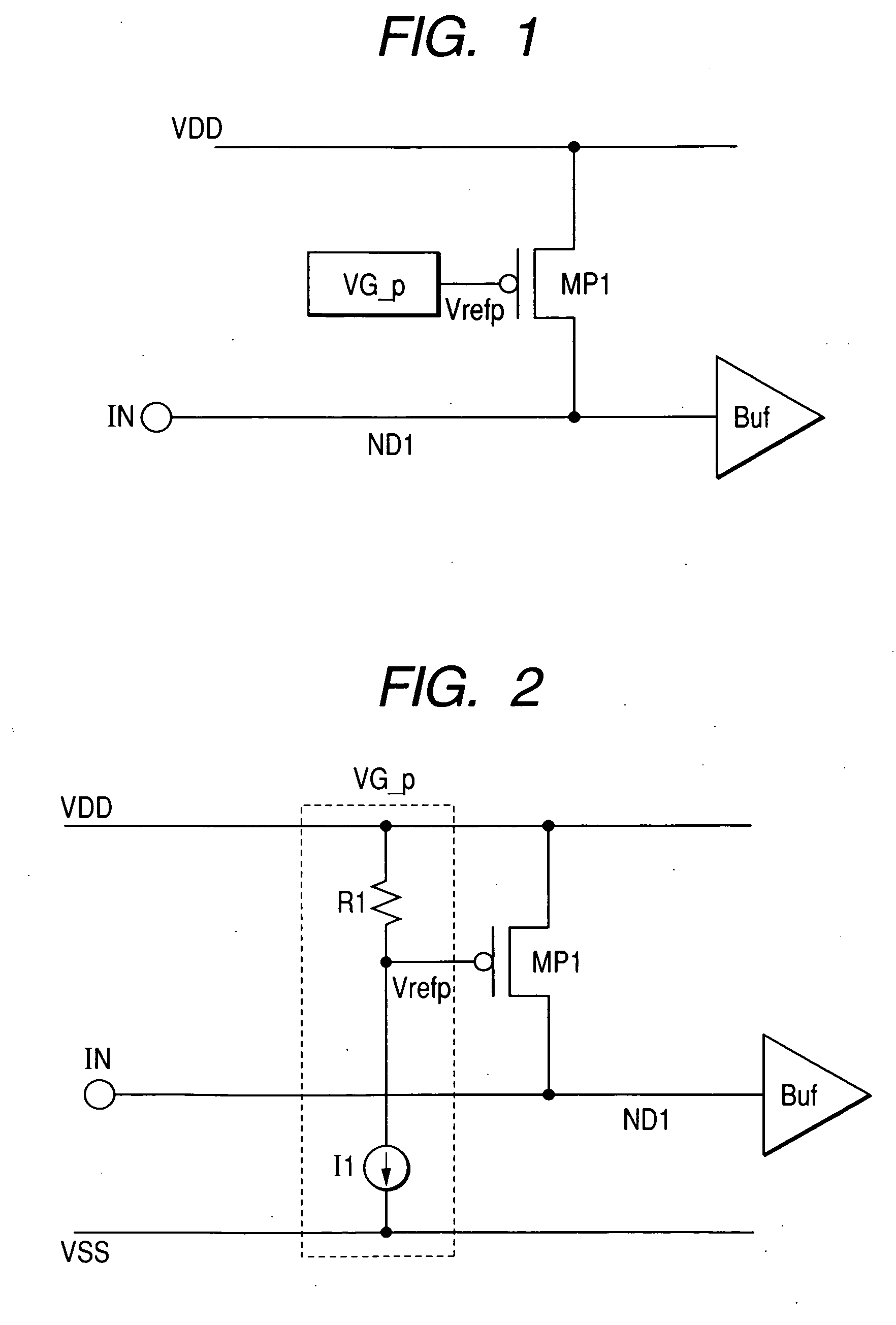
InactiveUS20060158802A1Reduce die areaTransistorReliability increasing modificationsVoltage referenceDrain resistance
This invention provides a semiconductor device in which an ESD protection circuit and a termination circuit can be realized with a small die area. A PMOS transistor having an ESD protection function is placed between a signal node on a line from an signal terminal to an input buffer and a supply voltage node. Furthermore, a voltage generator circuit is placed to supply a reference voltage to the gate of the PMOS transistor. By the reference voltage controlled by the voltage generator circuit, a source-drain resistance of the PMOS transistor is set. Thereby, the PMOS transistor can be made to function as a terminating resistor whose resistance can be set adaptively to a characteristic impedance of a transmission line, for example, connected to the signal terminal in addition to the ESD protection function.
Owner:HITACHI LTD
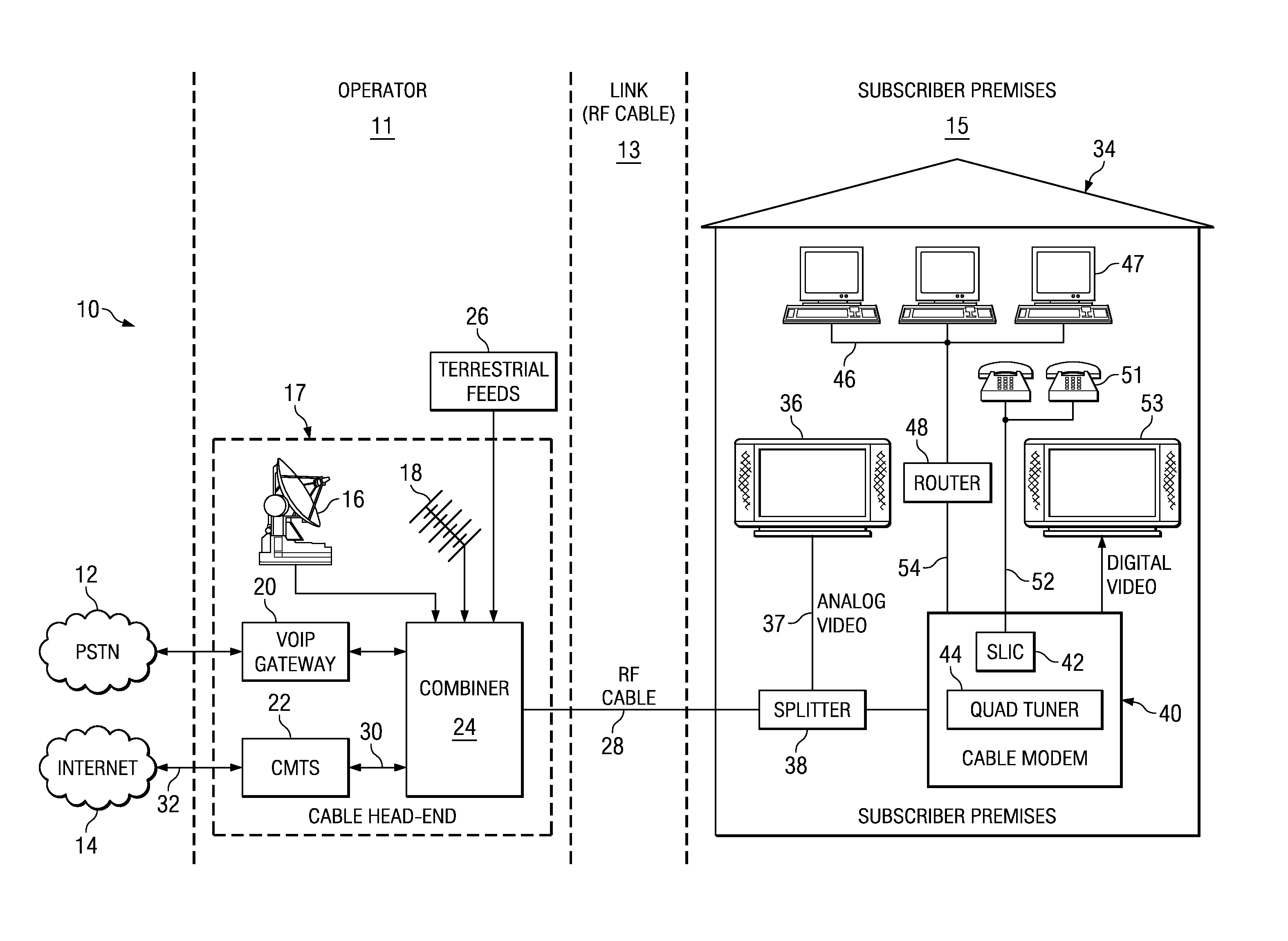
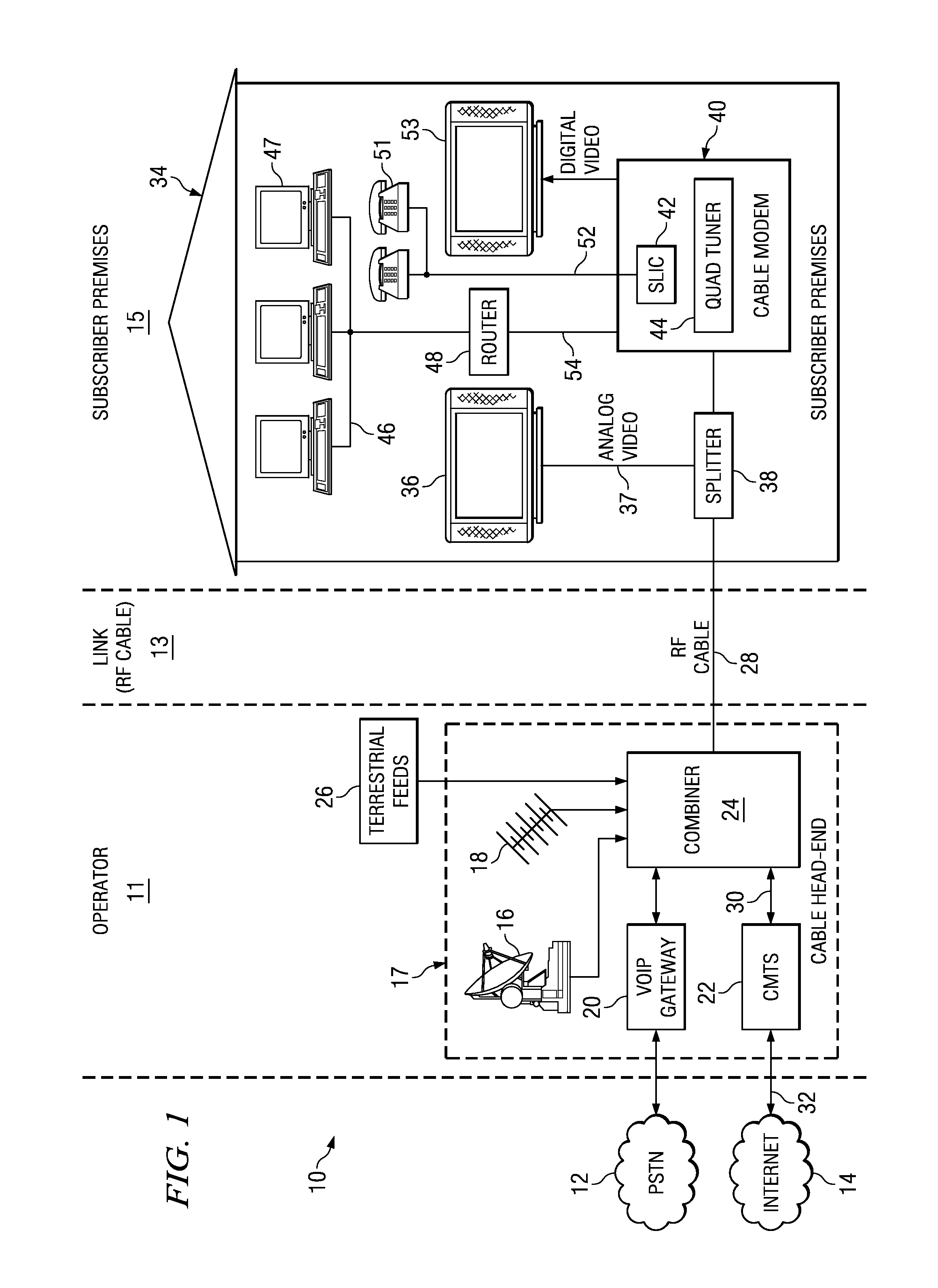
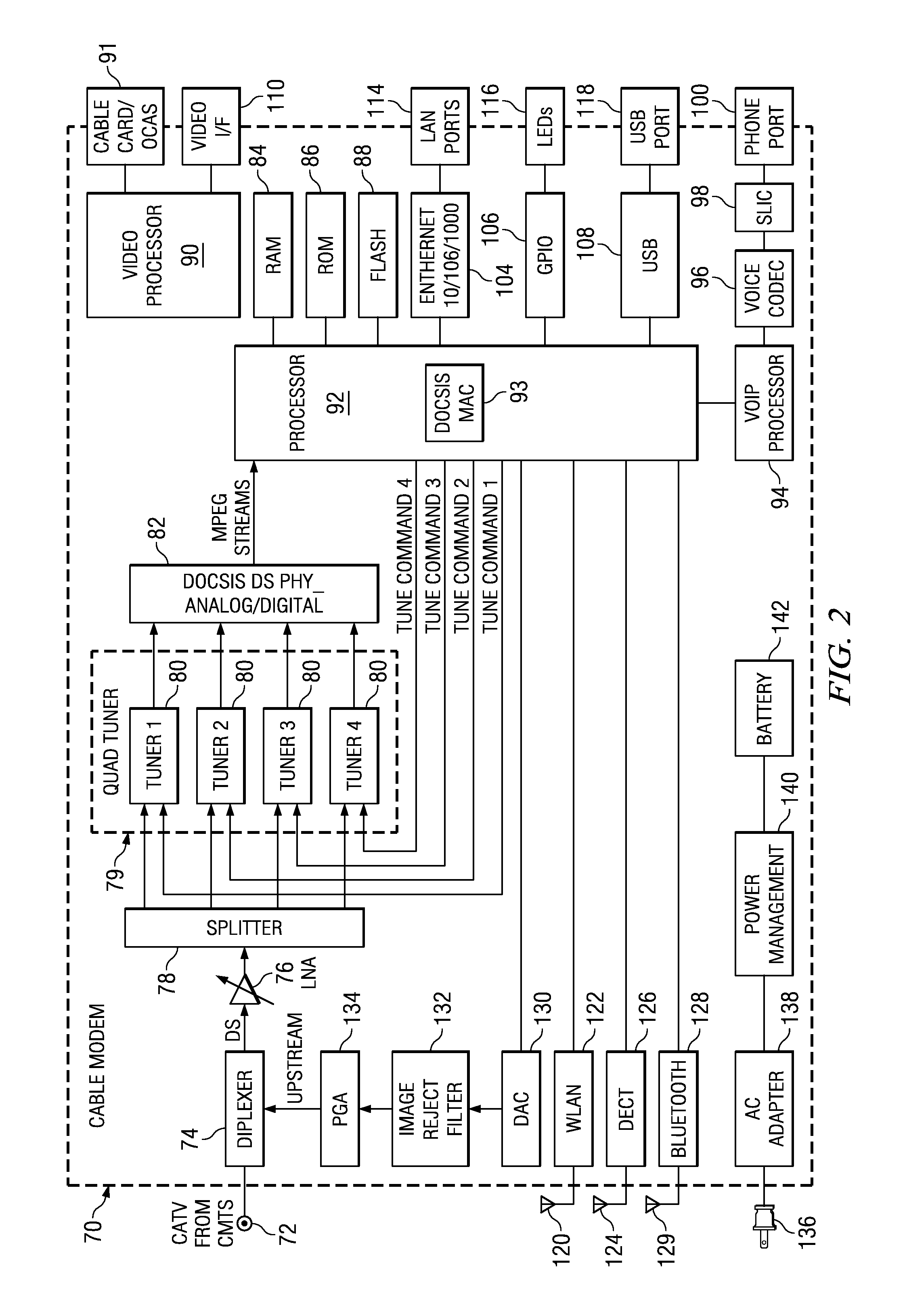
Single chip tuner integrated circuit for use in a cable modem
ActiveUS20080089362A1Simple designLow costTelevision system detailsBroadband local area networksDOCSISSingle chip
A novel single chip tuner integrated circuit (IC) for multiple video reception in a cable modem. The tuner circuit is well suited for use in cable modem systems adapted to implement the DOCSIS 3.0 specification which specifies multiple simultaneous video channel reception. The single-chip tuner integrated circuit comprises a plurality of tuner sub-circuits wherein each tuner sub-circuit is operative to generate a single output channel, determined in accordance with a tune commend input. The tune command input is used to generate a frequency reference signal that is input to a corresponding tuner sub-circuit. The frequency reference signal for a tuner sub-circuit is mixed with an input RF receive signal from the CATV input to the cable modem to generate a baseband channel. The baseband channel is subsequently filtered, amplified and input to the PHY circuit wherein undergoes analog to digital conversion (ADC) before being input to a baseband processor.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
Continuous-time-sigma-delta DAC using chopper stabalization
ActiveUS7205920B2Improve performanceReduce die areaElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue conversionVoltage converterAudio power amplifier
A sigma-delta digital-to-analog converter comprises a current digital-to-analog converter (IDAC) stage which generates a current depending on an input digital signal. An output current-to-voltage converter converts the generated signal to a voltage on a continuous-time basis. The amplifier used in the output current-to-voltage converter is chopper-stabilized. The converter can be single bit or multi-bit. The IDAC stage can be implemented with a pair of branches, a first branch comprising a first biasing current source and a second branch comprising a second biasing current source. The biasing current sources can be chopper-stabilized by connecting the bias current sources to the output current-to-voltage converter by a set of switches. The switches connect the biasing current sources to the output current-to-voltage converter in a first configuration and a second, reversed, configuration. This modulates flicker noise contributed by the bias current sources to the chopping frequency. from where it can be removed by filtering downstream of the current-to-voltage converter.
Owner:ANALOG DEVICES INC
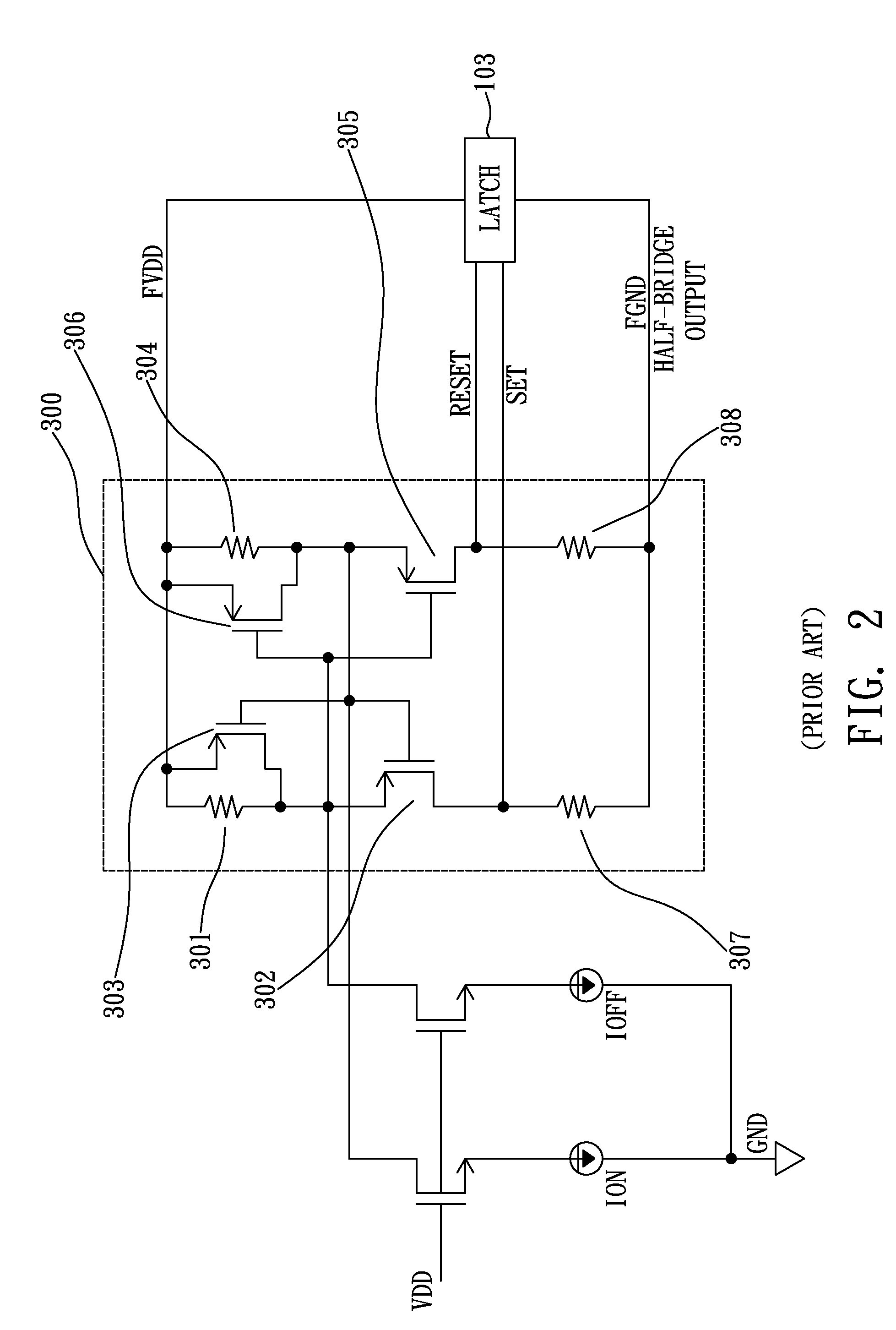
Active-load dominant circuit for common-mode glitch interference cancellation
ActiveUS7719325B1Die area be minimizedMinimize power consumptionElectronic switchingElectric pulse generatorSymmetric structureGlitch
An active-load dominant circuit for common-mode glitch interference cancellation, biased between a first voltage potential and a second voltage potential with an accompanying common-mode glitch interferer. The active-load dominant circuit includes a pair of pull-up networks and a pair of active-load networks. The common-mode glitch interferer is cancelled out due to a symmetric structure of the pair of pull-up networks. At least one set signal and at least one reset signal are provided to a latch in response to a clock signal or a complemented clock signal. At least one of the set signal and the reset signal can be pulled up to the first voltage potential or pulled down to the second voltage potential. The voltage difference of the set signal and the reset signal is large enough for a latch.
Owner:WUXI WENXIN ELECTRONICS TECH CO LTD
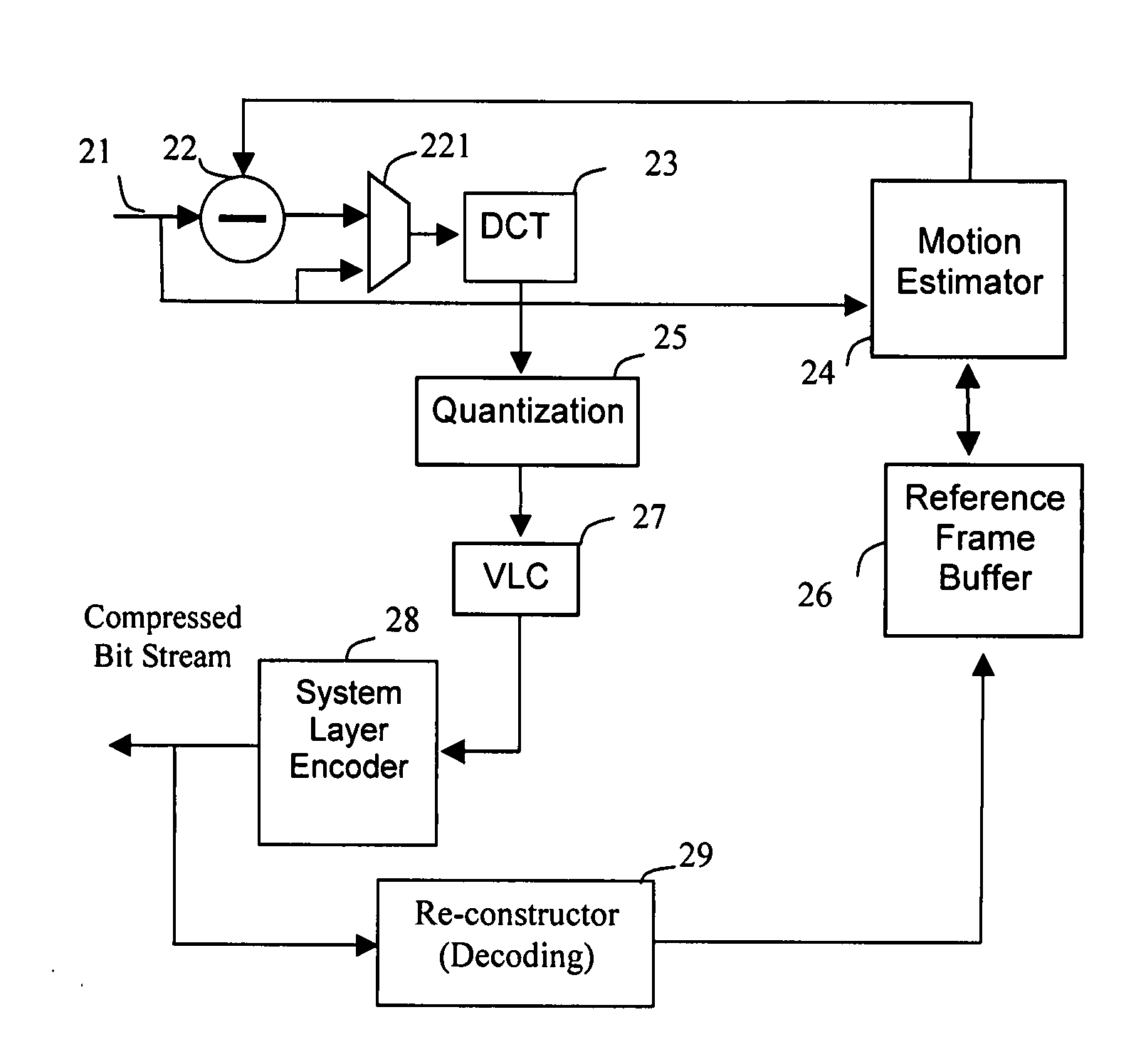
Video decompression, de-interlacing and frame rate conversion with frame buffer compression
InactiveUS20080267295A1Reduces the semiconductor die area/cost sharplyLow densityColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionDigital videoInterframe coding
Inter-frame and intra-frame block pixel compression means are applied to re-compress the decompressed video field / frame for future digital video decompression, de-interlacing and frame conversion. The motion vectors, MVs, decompressed from the compressed video field / frame are temporarily saved in a buffer for future inter-frame coding of block by block re-compression. If the input video frames are uncompressed or decompressed fields / frames, they will be compressed before saving into an off-chip frame buffer, later, the accessed lines of compressed pixels of at least two fields / frames will be used for de-interlacing and frame rate conversion. If the corresponding MV is out of the predetermined threshold, inter-frame coding will be skipped and only intra-frame coding is applied.
Owner:TAIWAN IMAGINGTEK
Multichannel high resolution segmented resistor string digital-to-analog converters
ActiveUS6995701B1Guaranteed monotonicityHigh-channel densityElectric signal transmission systemsDigital-analogue convertorsElectrical resistance and conductanceDigital analog converter
Multi-channel high resolution segmented resistor string digital-to-analog converters (DACs) suitable for realization in a single integrated circuit. The DACs incorporate a primary resistor string shared by all channels, and one or more additional pluralities of additional resistor strings for additional resolution. The primary resistor string may be buffered to limit the effect of loading thereon by the plurality of resistor strings coupled thereto. Current sources may also be coupled to the resistor strings coupled to the primary resistor string to also avoid loading of the primary resistor string. A trimmable resistor string of fewer bits may be connected to the primary resistor string for laser trimming. In the embodiment disclosed, a plurality of secondary and tertiary resistor strings are used, with leapfrogging minimizing the switches required.
Owner:MAXIM INTEGRATED PROD INC
Differential pipelined analog to digital converter with successive approximation register subconverter stages using thermometer coding
ActiveUS20050078025A1Facilitates improved system bandwidthIncreased gain factorElectric signal transmission systemsAnalogue-digital convertersA d converterAnalog to digital conversion
Pipelined analog to digital conversion systems are provided having cascaded multi-bit successive approximation register subconverter stages using thermometer coding. Capacitor arrays are provided in the subconverter stages, where switching logic selectively couples the capacitors to operate in sample, conversion, and residue amplification modes for generating multi-bit subconverter digital outputs and analog subconverter residue outputs, wherein the capacitors are switched according to a thermometer code to reduce differential converter non-linearity.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Temperature-insensitive bias circuit for high-power amplifiers
InactiveUS6946911B2Reduce die areaAmplifier modifications to reduce temperature/voltage variationGain controlAudio power amplifierEngineering
An exemplary bias circuit is coupled to an amplifier. The bias circuit comprises a first bipolar transistor, a second bipolar transistor and a third bipolar transistor. The first bipolar transistor has a base connected to a first node, and the first node is connected to a reference voltage through a first resistor. The second bipolar transistor has a base connected to the first node. The third bipolar transistor has a collector connected to the first node and a base connected to an emitter of the first bipolar transistor at a second node. An emitter of the second bipolar transistor is connected to a base of a fourth bipolar transistor associated with the amplifier, and the second bipolar transistor does not have a resistor connected to the emitter of the second bipolar transistor.
Owner:SKYWORKS SOLUTIONS INC
Methods and systems for decoupling the stabilization of two loops
ActiveUS7135912B2Small capacitanceReduce die areaAmplifier modifications to reduce detrimental impedenceDifferential amplifiersCapacitanceCurrent loop
Circuits and methods for dynamically stabilizing a circuit having a relatively small capacitive load two current loop sub circuits are provided. A main current loop and an associated sensing loop are coupled such that a compensation capacitance supplied to each sub circuit loop individually will remain isolated and will not be cumulative with respect to the remainder of the circuit.
Owner:TEXAS INSTR INC
Multiple tile output using interface compression in a raster stage
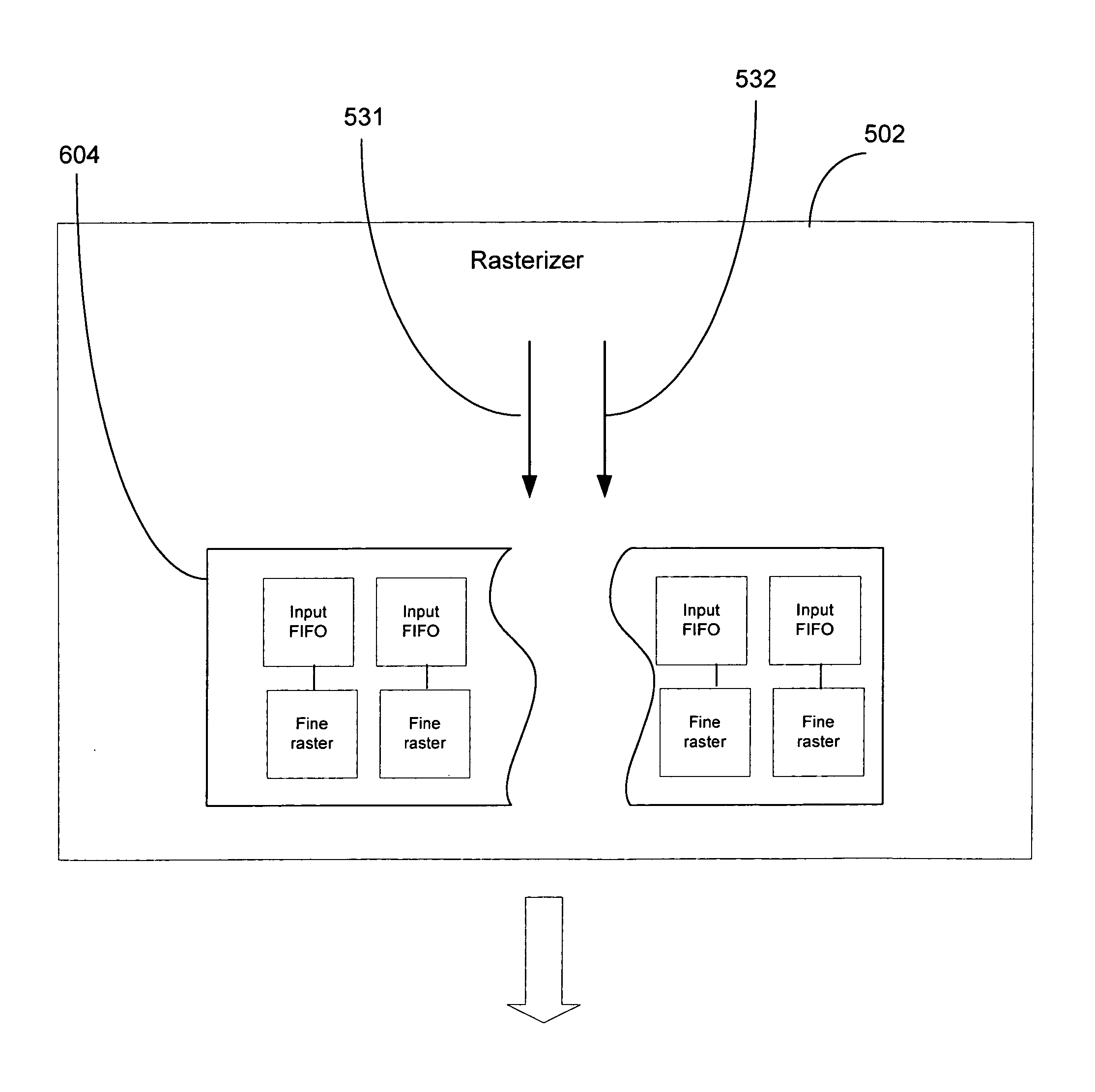
ActiveUS8427487B1Reduce the amount requiredReduced silicon die areaDigital computer detailsProcessor architectures/configurationComputational scienceGraphics
A method and system for interface compression in a raster stage of a graphics processor. The method includes receiving a graphics primitive for rasterization in a raster stage of a graphics processor and rasterizing the graphics primitive at a first level in a coarse raster component to generate a plurality of tiles related to the graphics primitive. The method determines whether a window ID operation is required for the plurality of tiles. If the operation is required, a respective plurality of uncompressed coverage masks for the tiles are output from the coarse raster component to a fine raster component on a one coverage mask per clock cycle basis. If the operation is not required, a compressed coverage mask for the tiles is output in a single clock cycle. The tiles are subsequently rasterized at a second-level in the fine raster component to generate pixels related to the graphics primitive.
Owner:NVIDIA CORP
1:N MEM switch module
InactiveUS7157993B2Reduce areaReduce the numberElectrostatic/electro-adhesion relaysWaveguide type devicesCapacitancePhase shifted
A 1:N MEM switch module comprises N MEM switches fabricated on a common substrate, each of which has input and output contacts and a movable contact which bridges the input and output contacts when the switch is actuated. The input contacts are connected to a common input node, and the output contacts are connected to respective output lines. Each output line has an associated inductance and effective capacitance, and is arranged such that its inductance is matched to its effective capacitance. The switches are preferably arranged symmetrically about the terminus point of the signal input line. A phase shifter employs at least two switch modules connected together with N transmission lines having different lengths, operated such that an input signal is routed via one of the transmission lines to effect a desired phase-shift.
Owner:TELEDYNE SCI & IMAGING
Single chip tuner integrated circuit for use in a cable modem
ActiveUS7978735B2Low costImprove performanceTelevision system detailsBroadband local area networksDOCSISSingle chip
A novel single chip tuner integrated circuit (IC) for multiple video reception in a cable modem. The tuner circuit is well suited for use in cable modem systems adapted to implement the DOCSIS 3.0 specification which specifies multiple simultaneous video channel reception. The single-chip tuner integrated circuit comprises a plurality of tuner sub-circuits wherein each tuner sub-circuit is operative to generate a single output channel, determined in accordance with a tune commend input. The tune command input is used to generate a frequency reference signal that is input to a corresponding tuner sub-circuit. The frequency reference signal for a tuner sub-circuit is mixed with an input RF receive signal from the CATV input to the cable modem to generate a baseband channel. The baseband channel is subsequently filtered, amplified and input to the PHY circuit wherein undergoes analog to digital conversion (ADC) before being input to a baseband processor.
Owner:MAXLINEAR INC
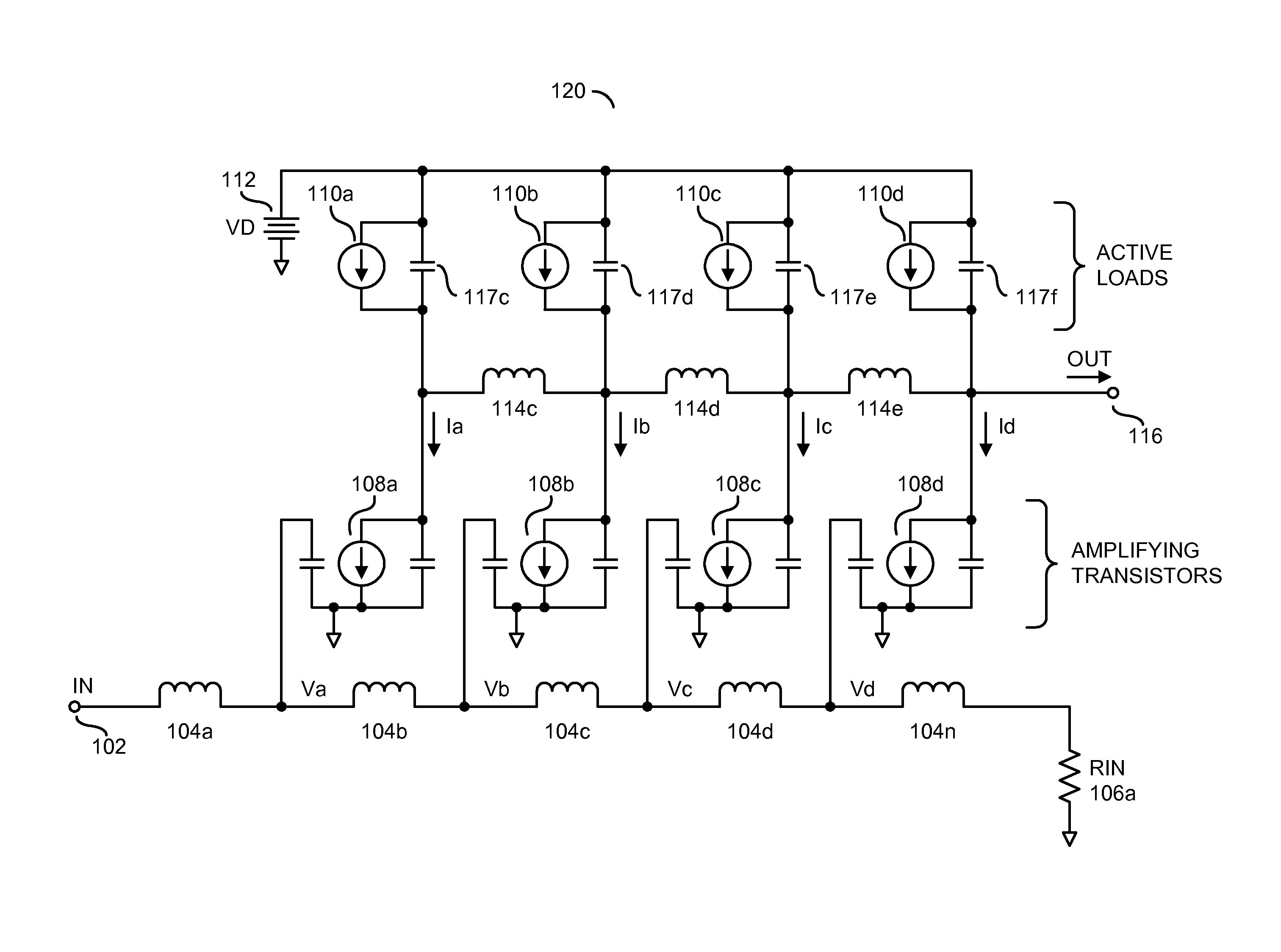
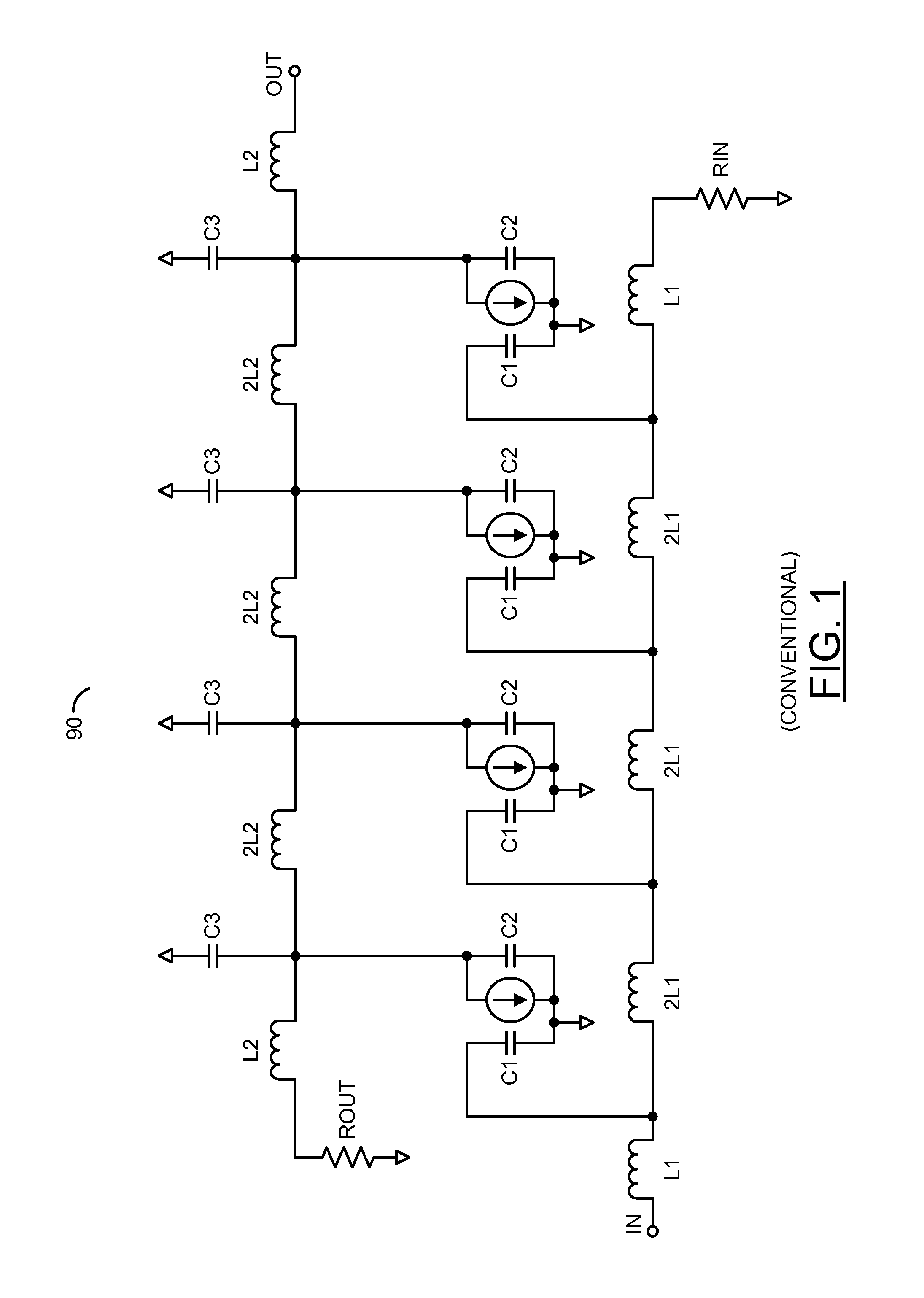
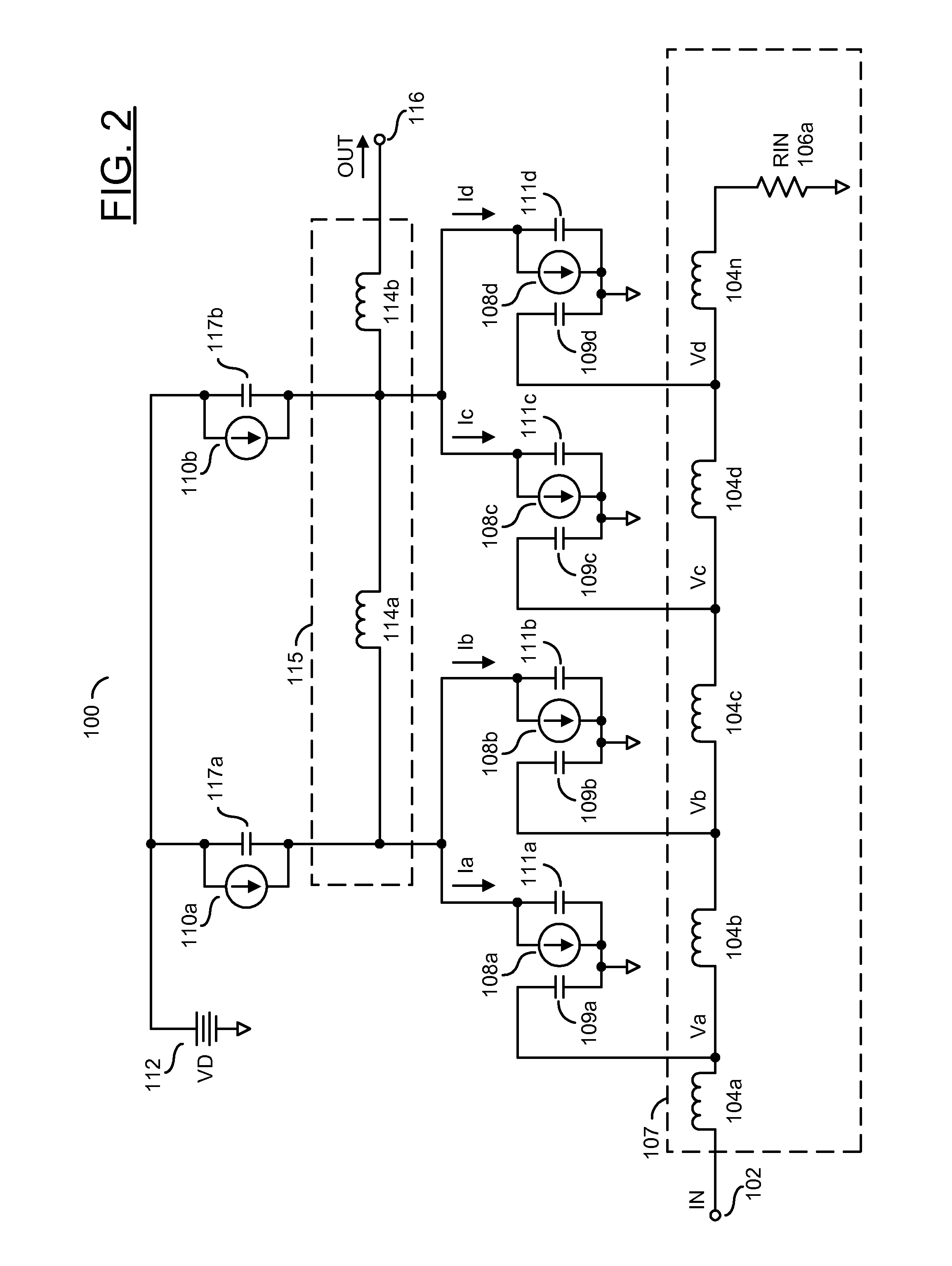
Distributed transconductance amplifier
ActiveUS9013237B1Improve transconductanceReduce die areaAmplifiers wit coupling networksAudio power amplifierInductor
An apparatus having an input transmission line, a plurality of amplifiers and an output transmission line is disclosed. The input transmission line may include a plurality of first inductors configured to receive an input voltage. The amplifiers may be configured to generate a plurality of intermediate currents by amplifying a plurality of intermediate voltages at a plurality of first nodes between the first inductors. The output transmission line generally includes a plurality of second inductors configured to generate an output current at an output node by combining the intermediate currents. Each of a plurality of second nodes connected to the second inductors may transfer a plurality of the intermediate currents. Each of the second inductors generally has a different one of a plurality of inductance values.
Owner:MACOM TECH SOLUTIONS HLDG INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com