Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
602 results about "Charge retention" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
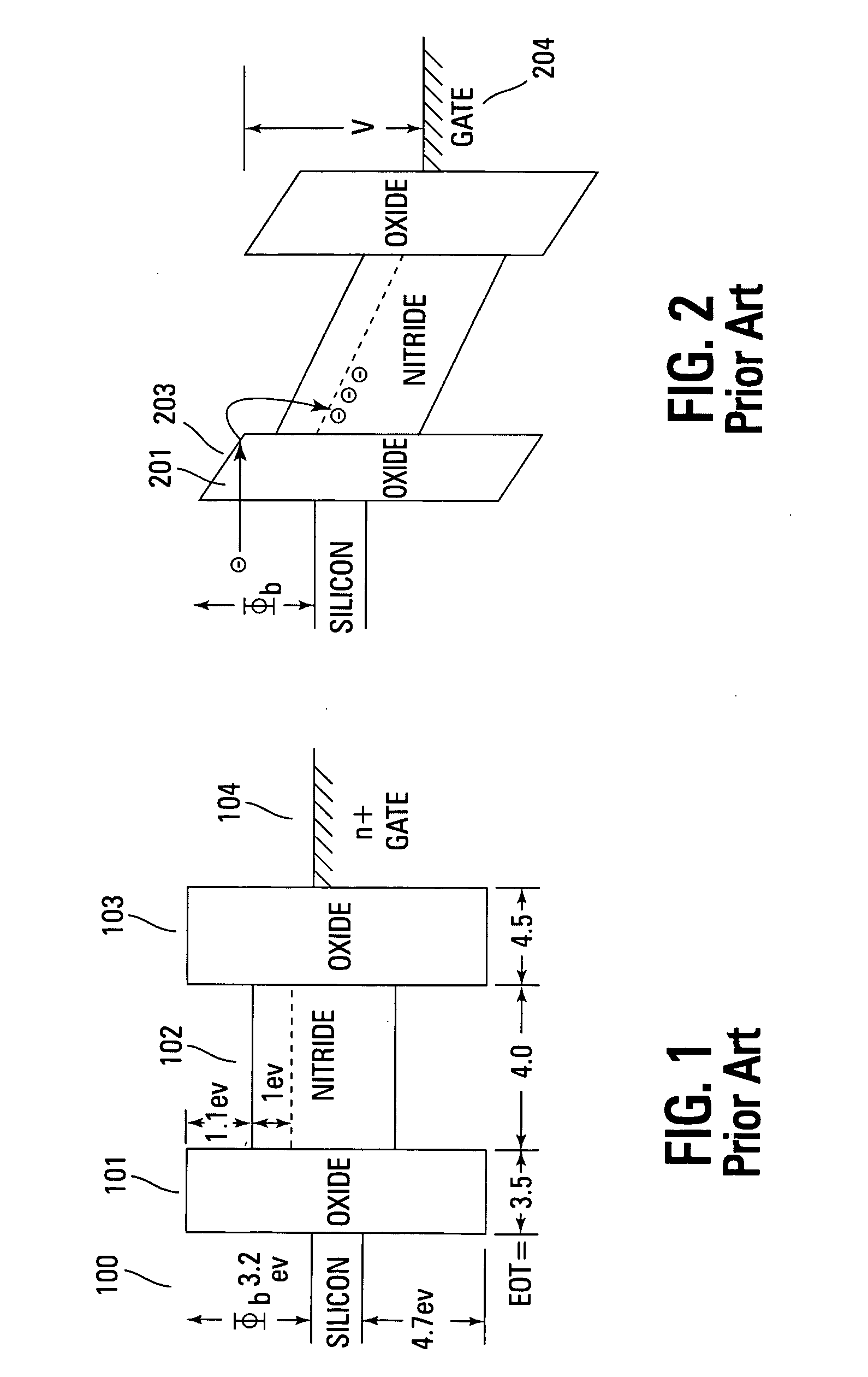
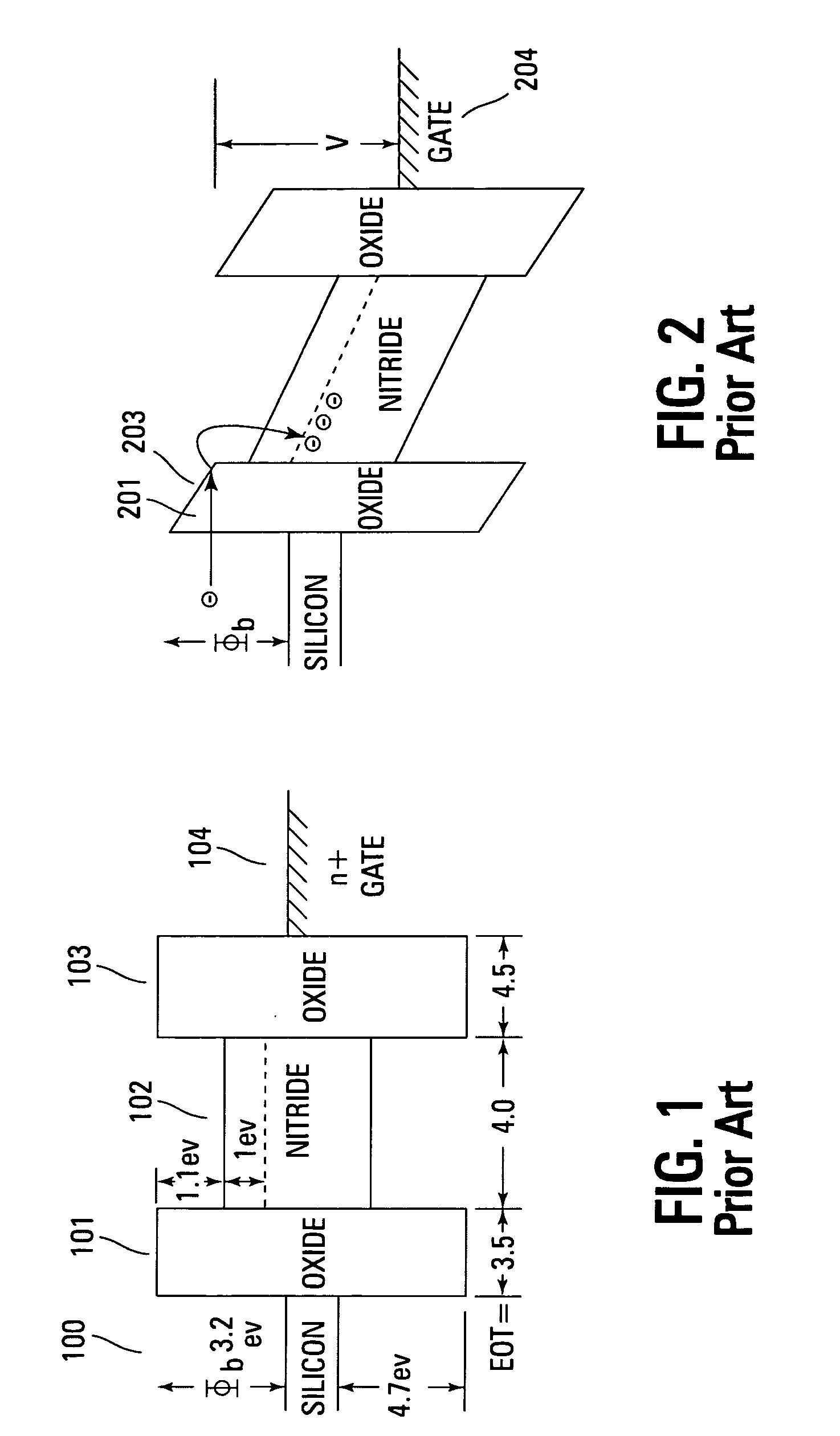
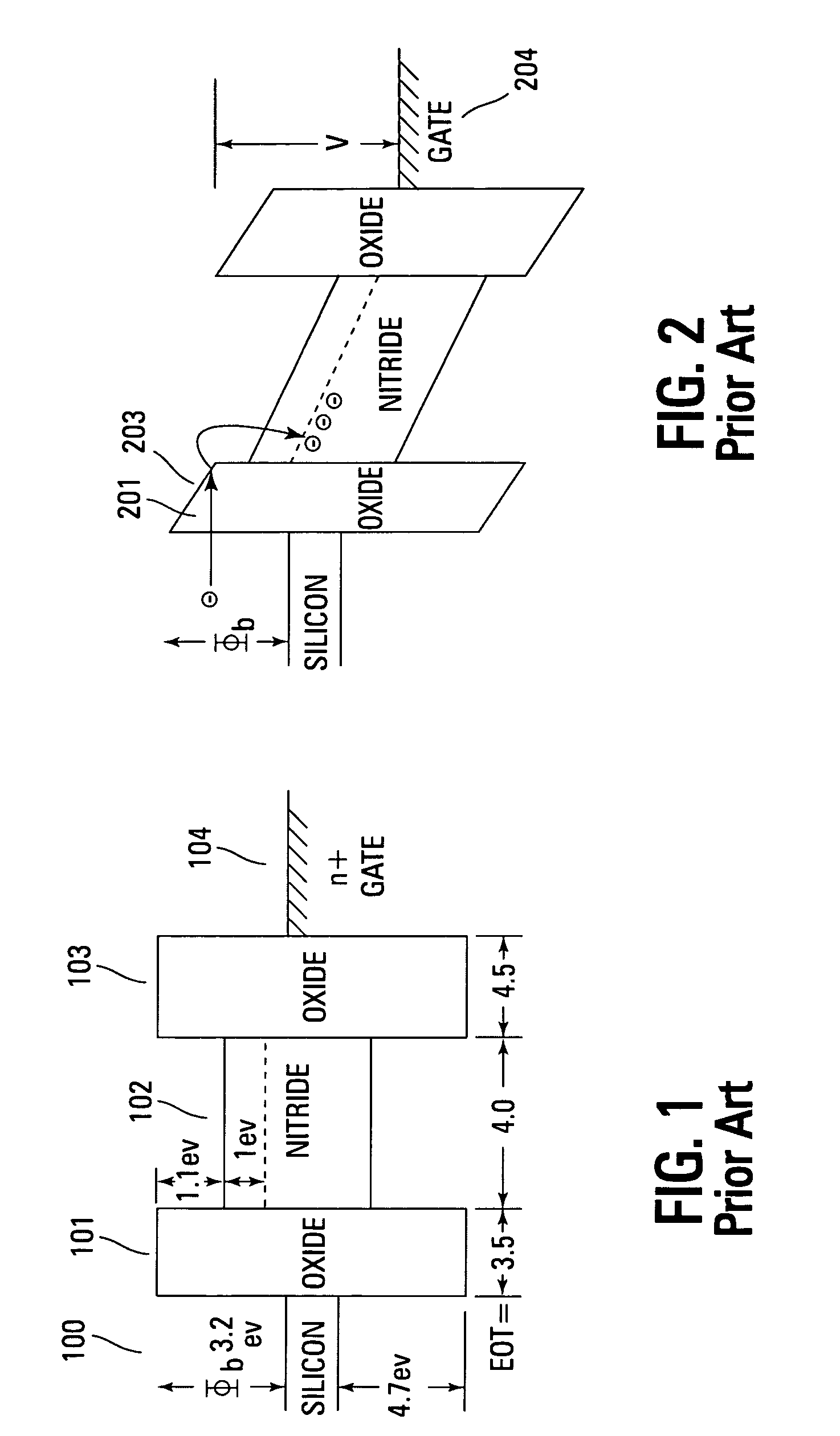
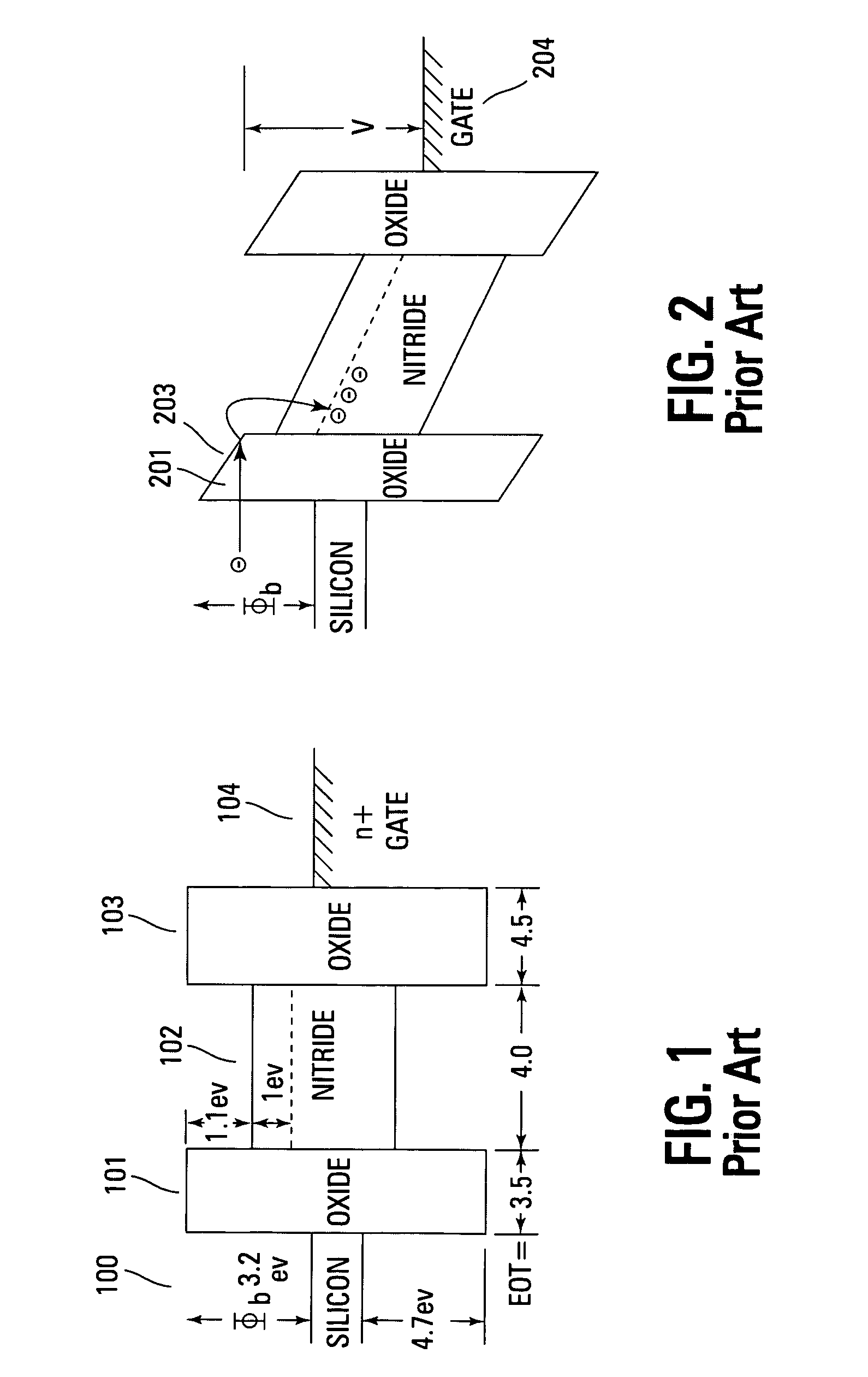
The dielectric absorption of a capacitor is the inability of a capacitor to completely discharge to zero. It is sometimes referred to battery action or capacitor memory, because of this charge retention, and this is due to the dielectric of the capacitor retaining a charge after it is supposedly discharged.
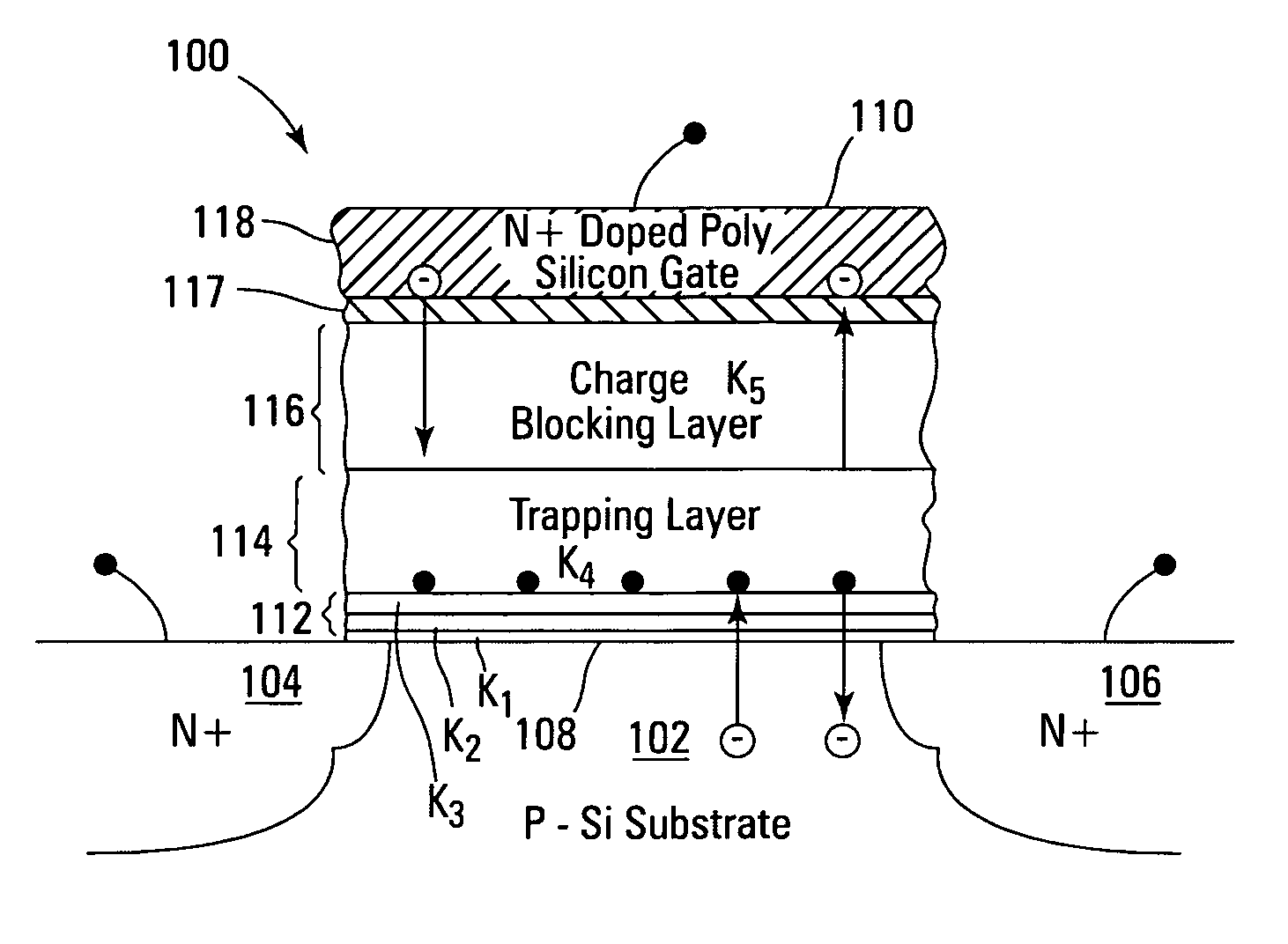
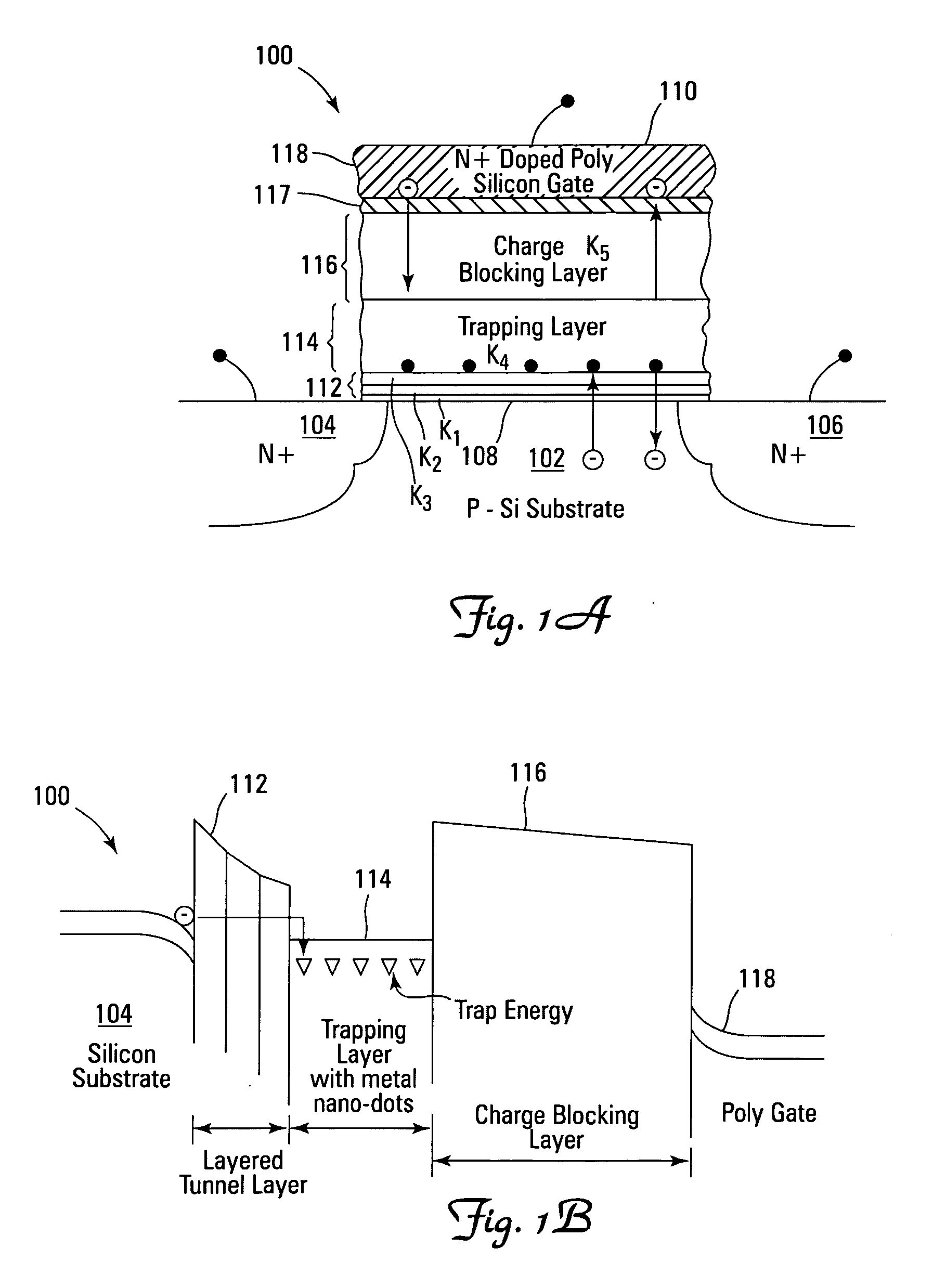
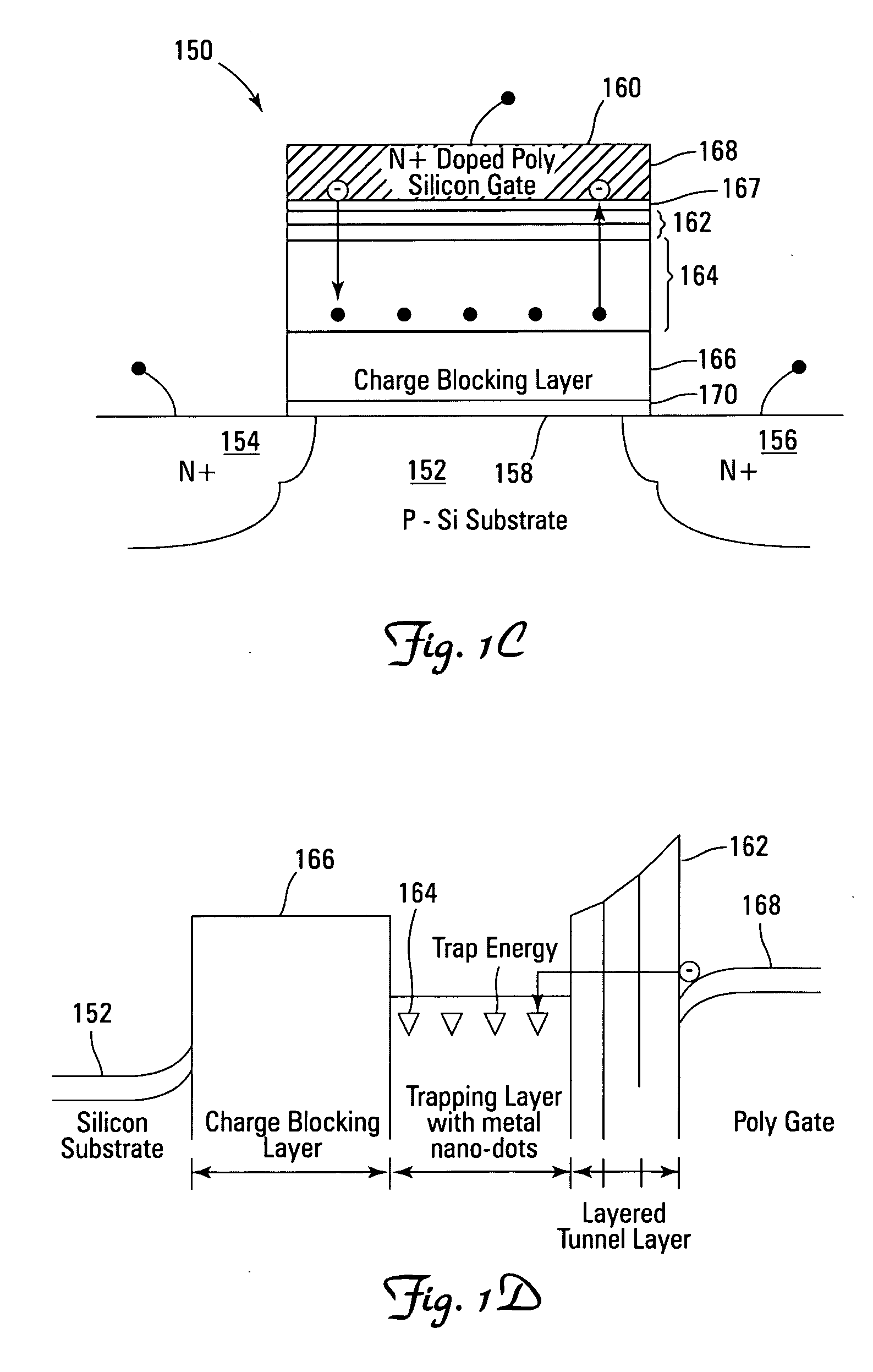
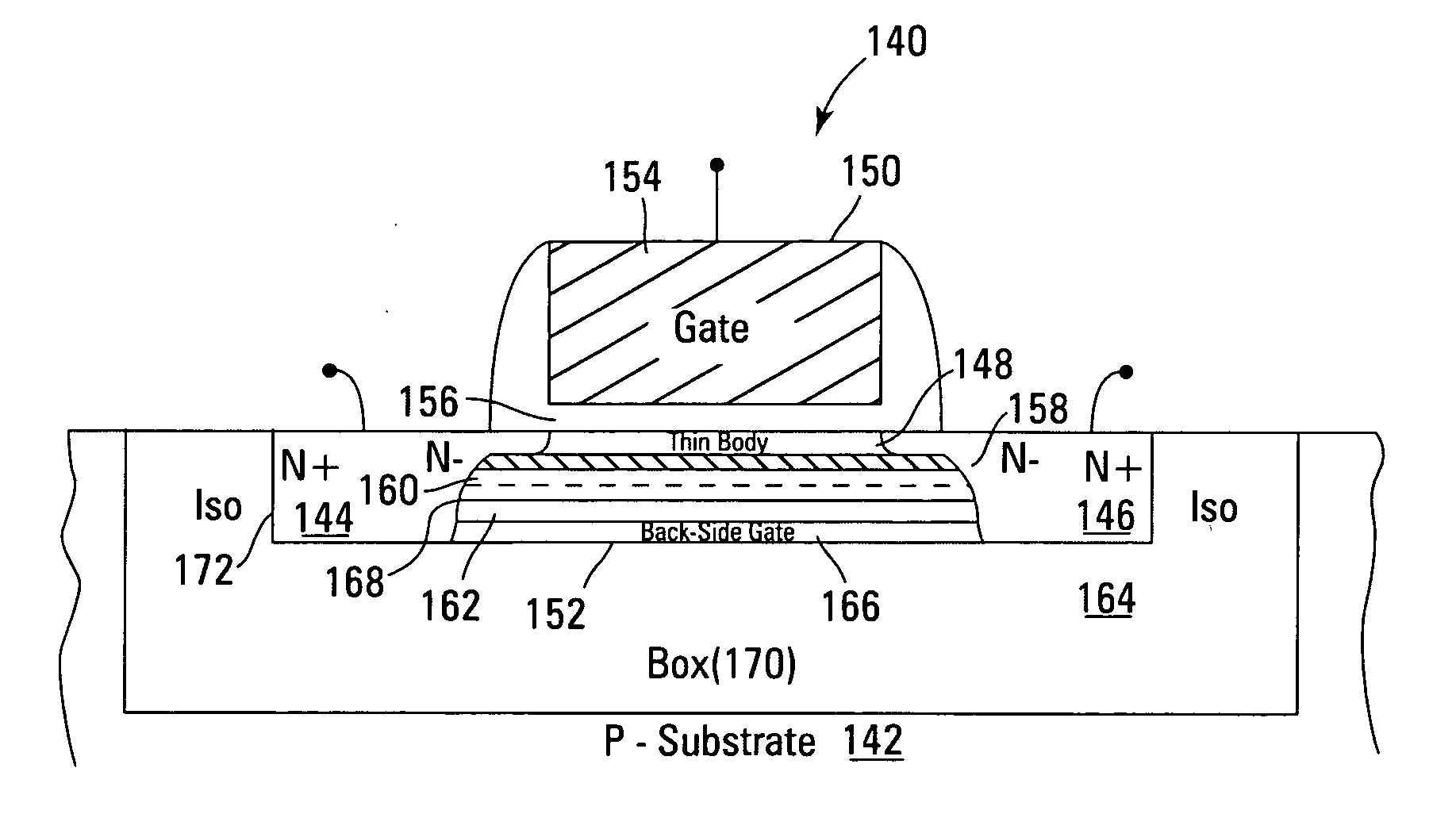
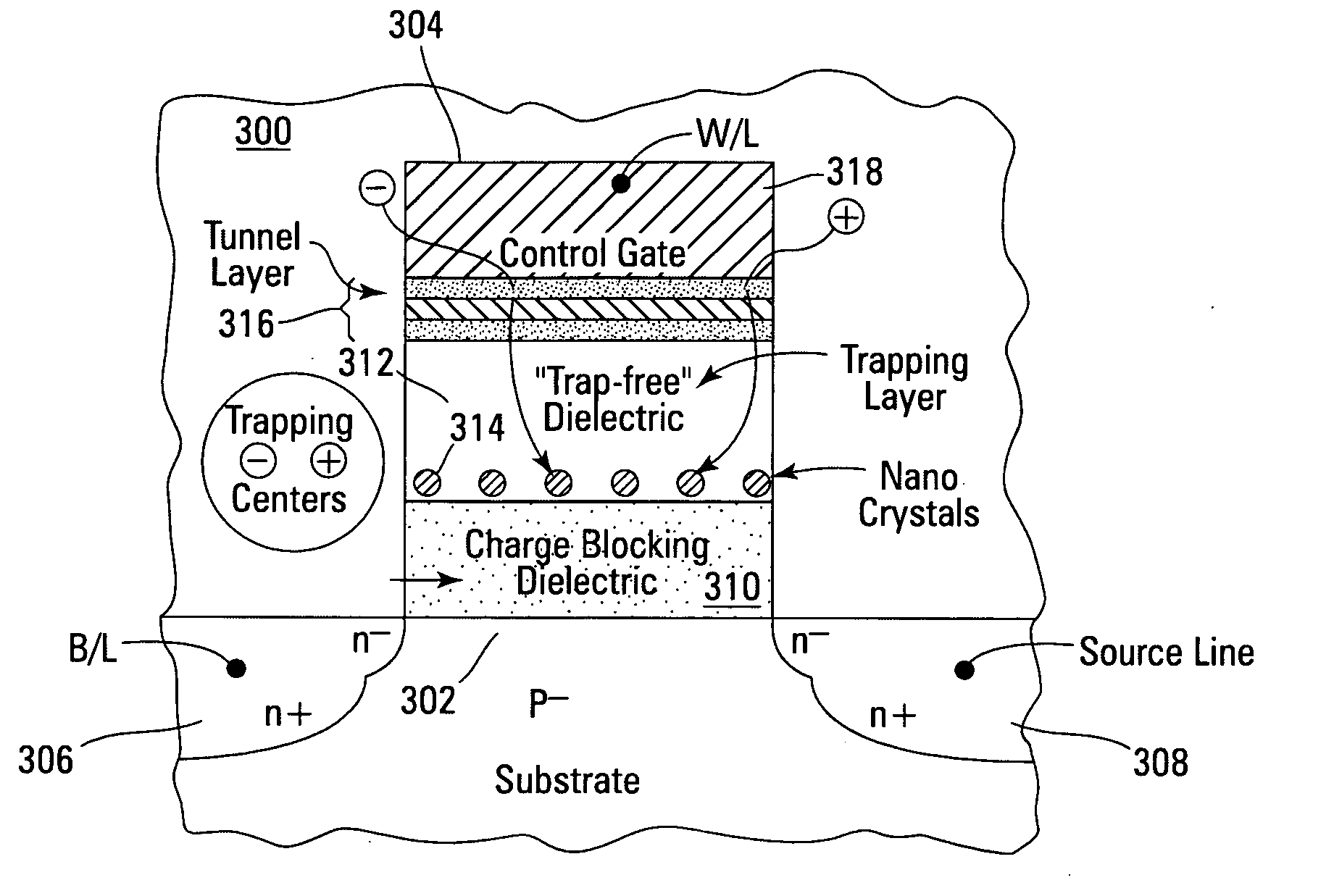
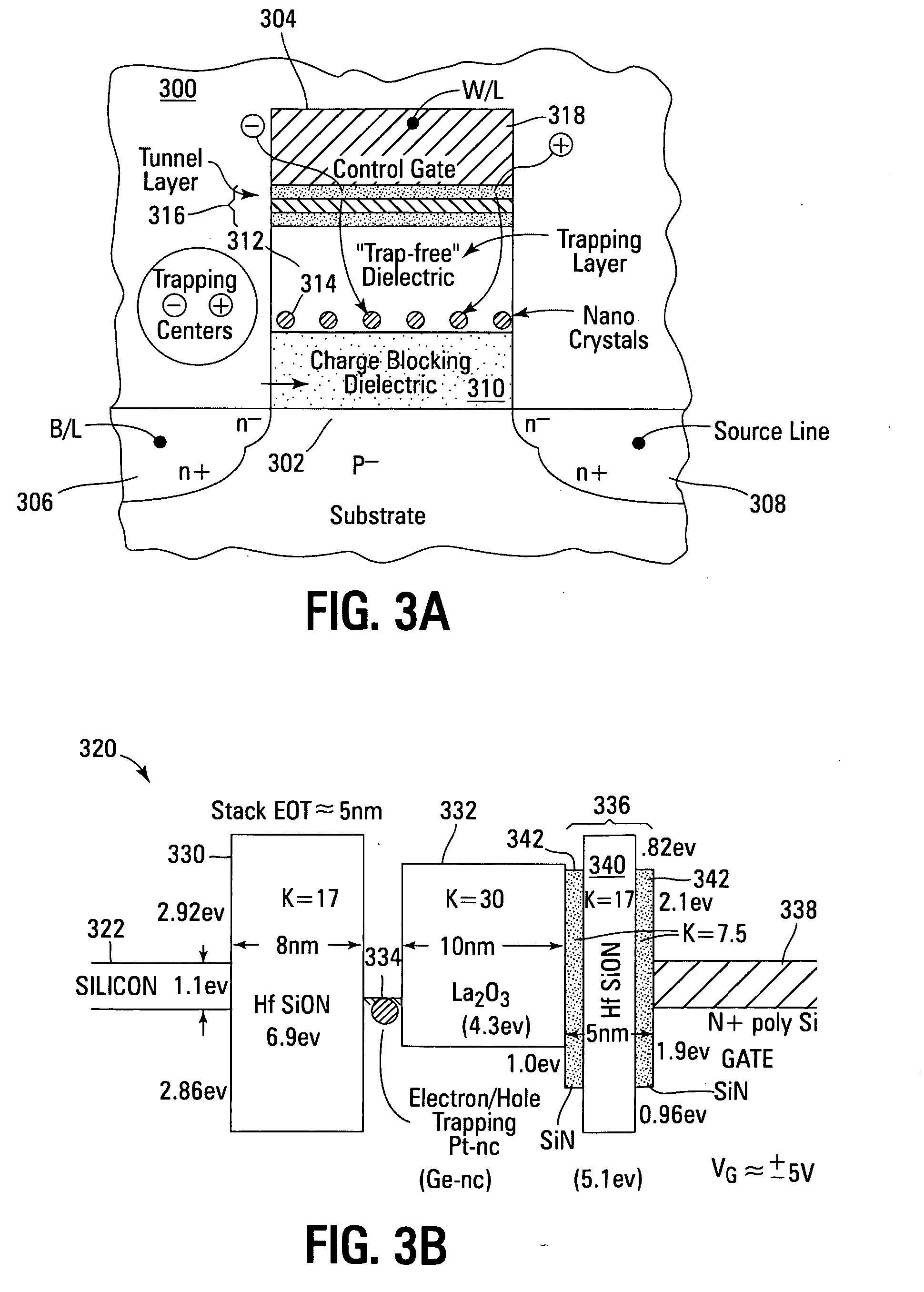
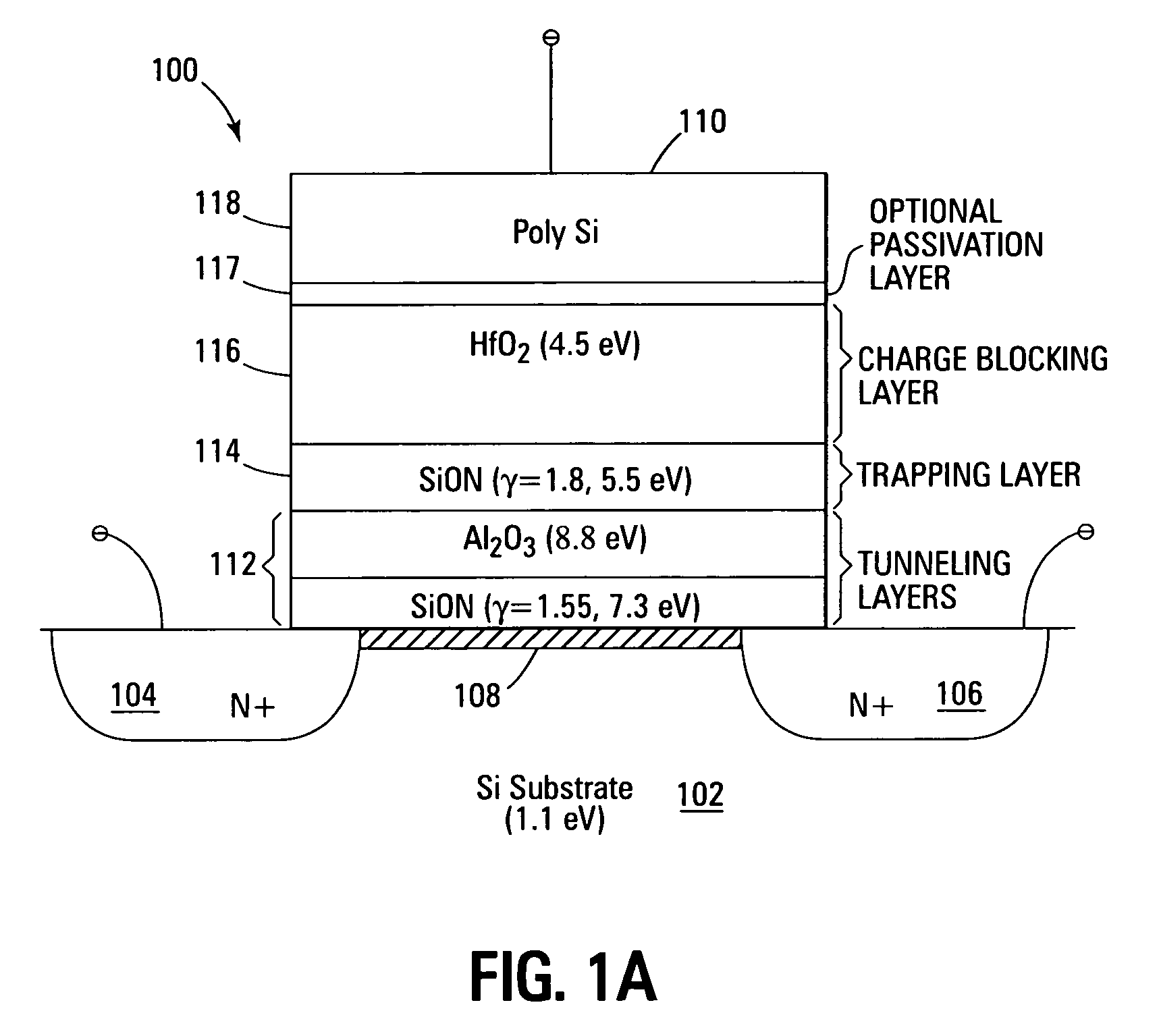
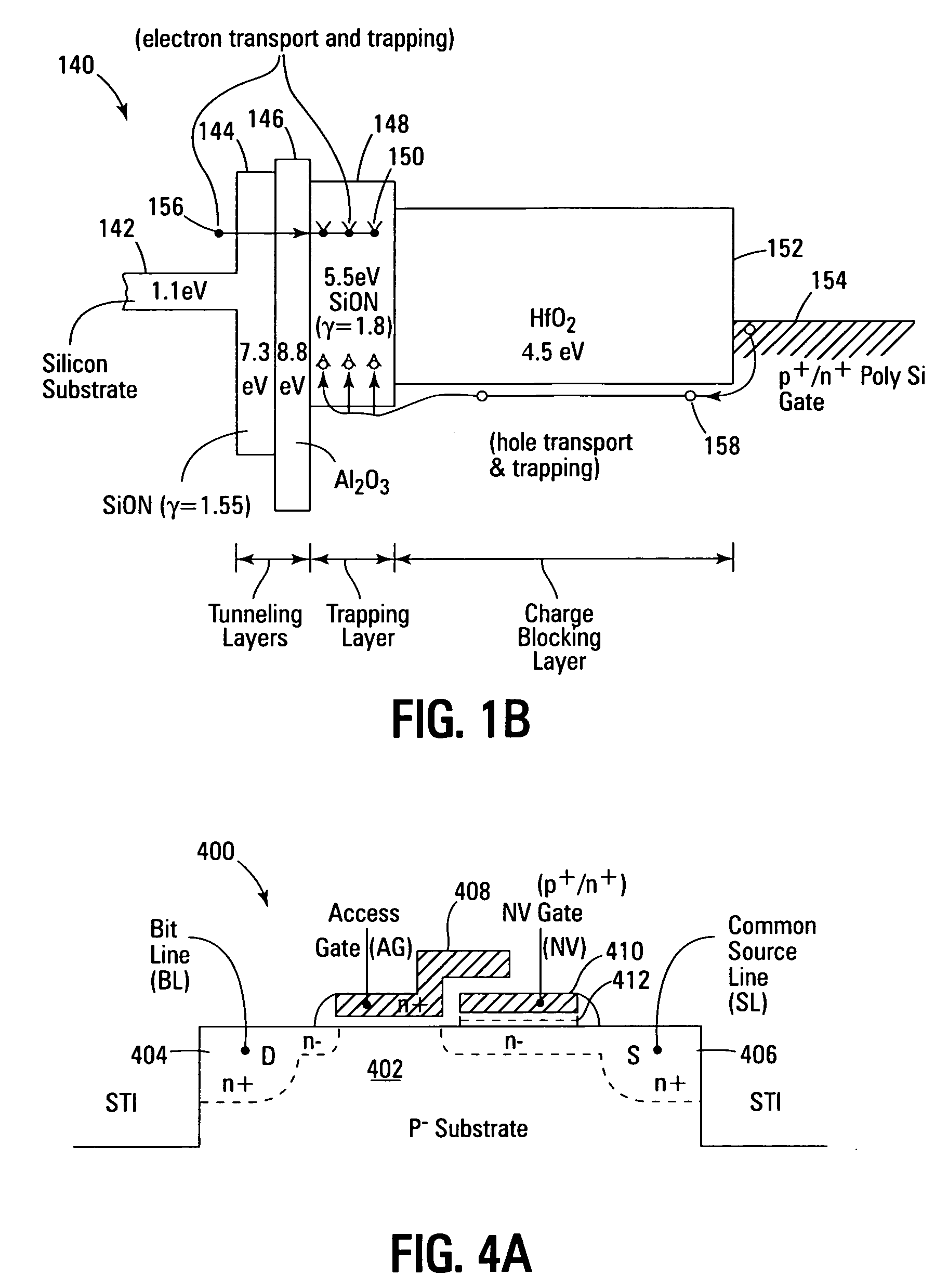
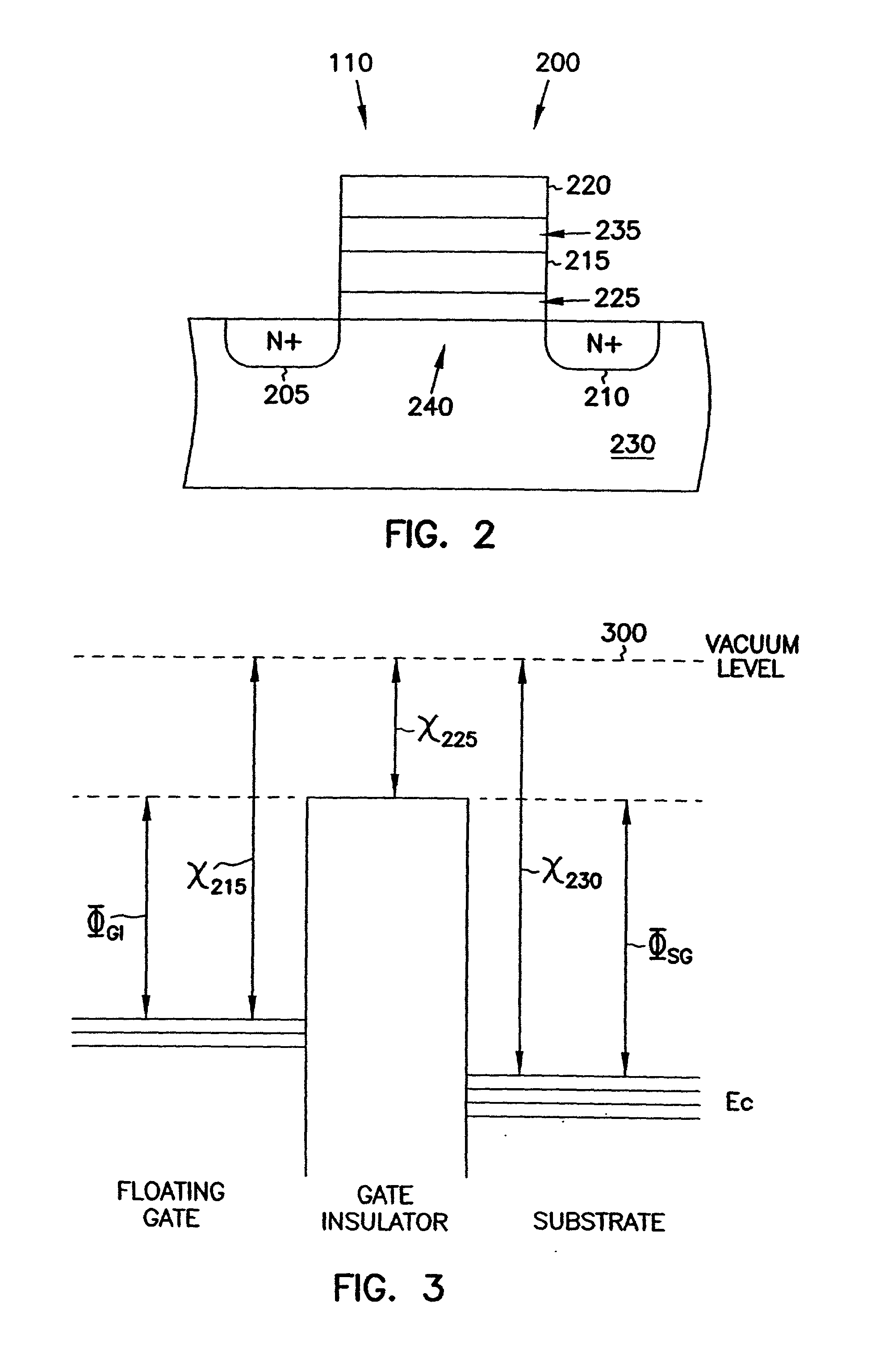
Novel low power non-volatile memory and gate stack
ActiveUS20060261401A1High charge blocking barrierExcellent charge retentionTransistorNanoinformaticsCharge retentionLow voltage
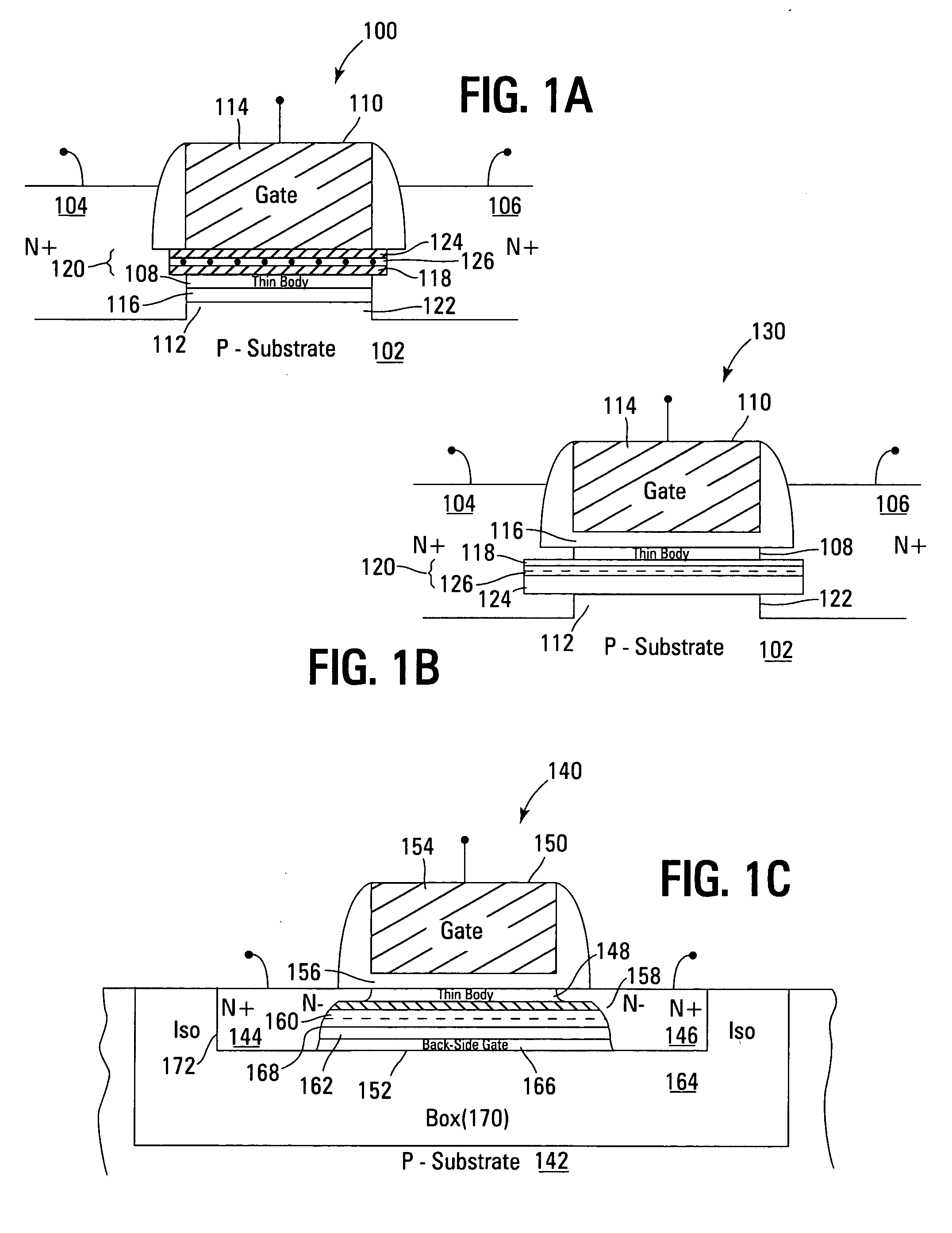
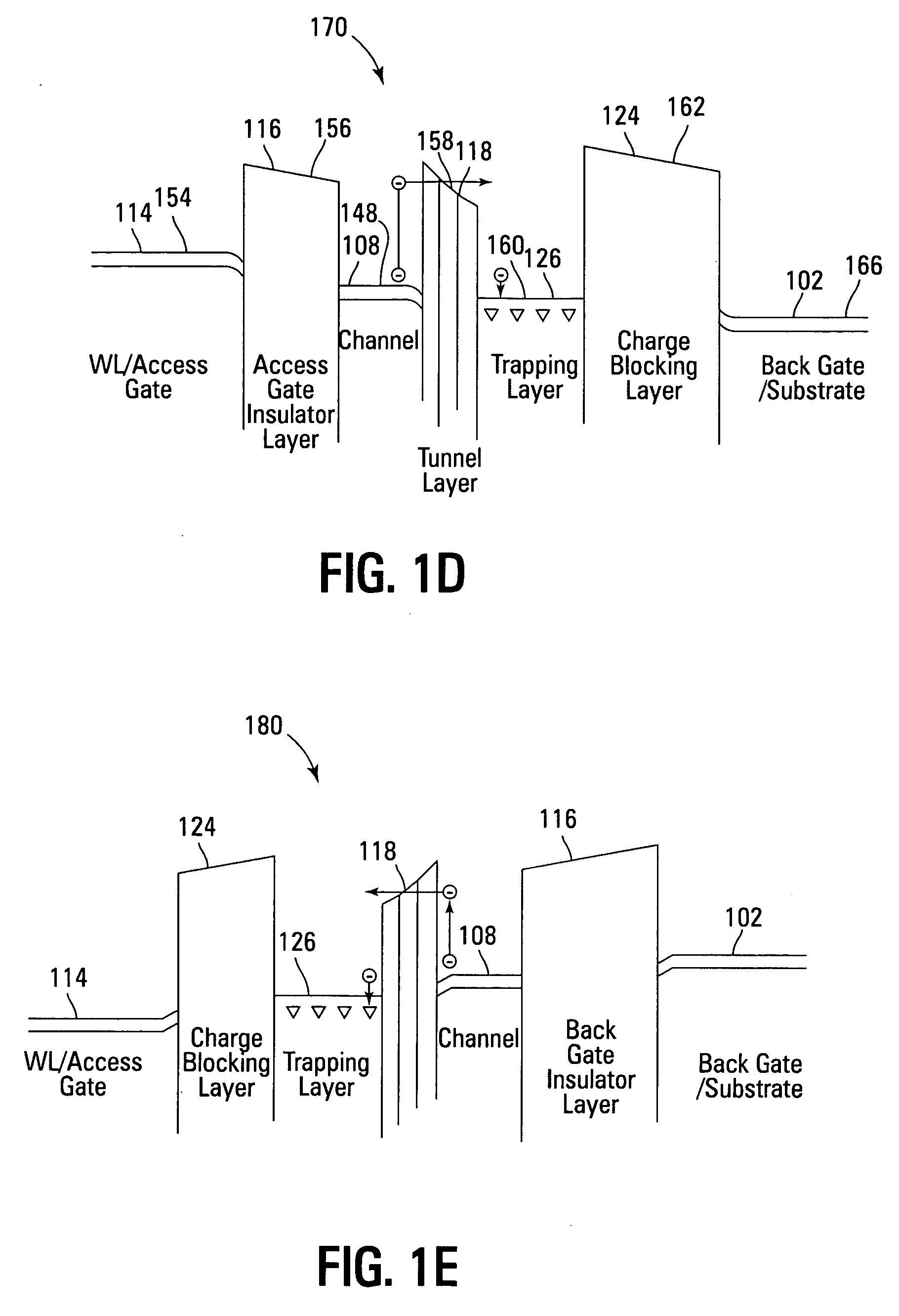
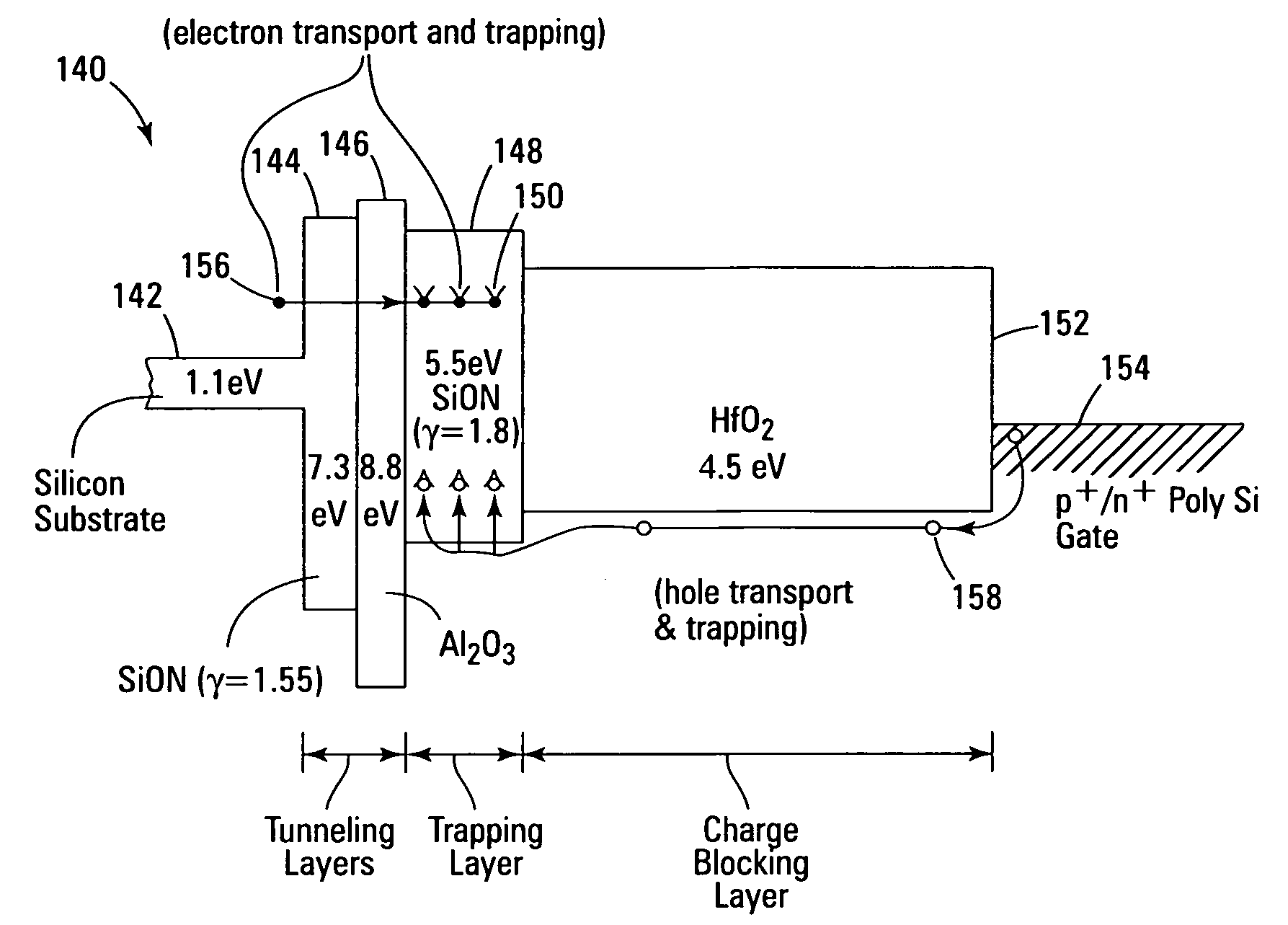
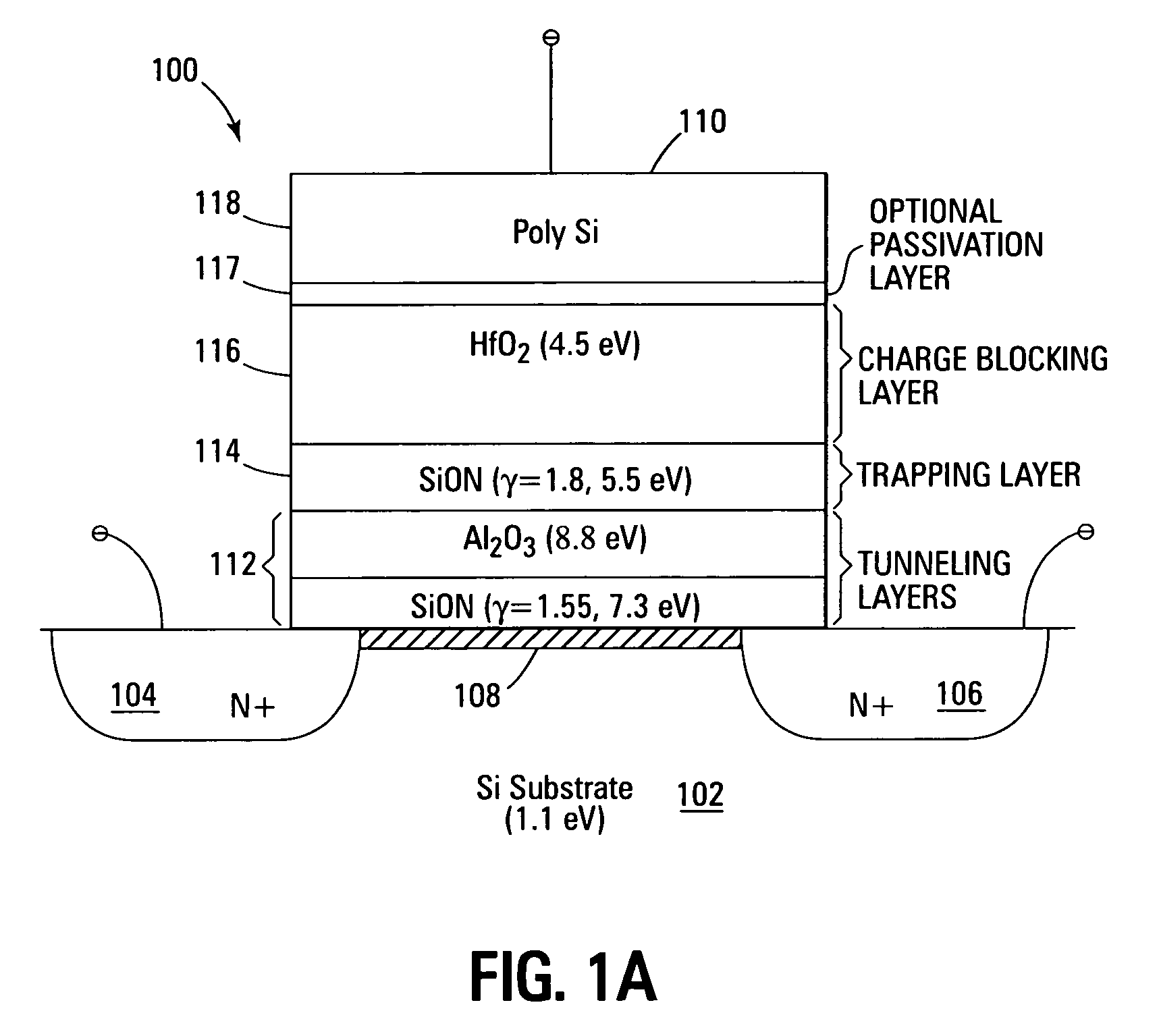
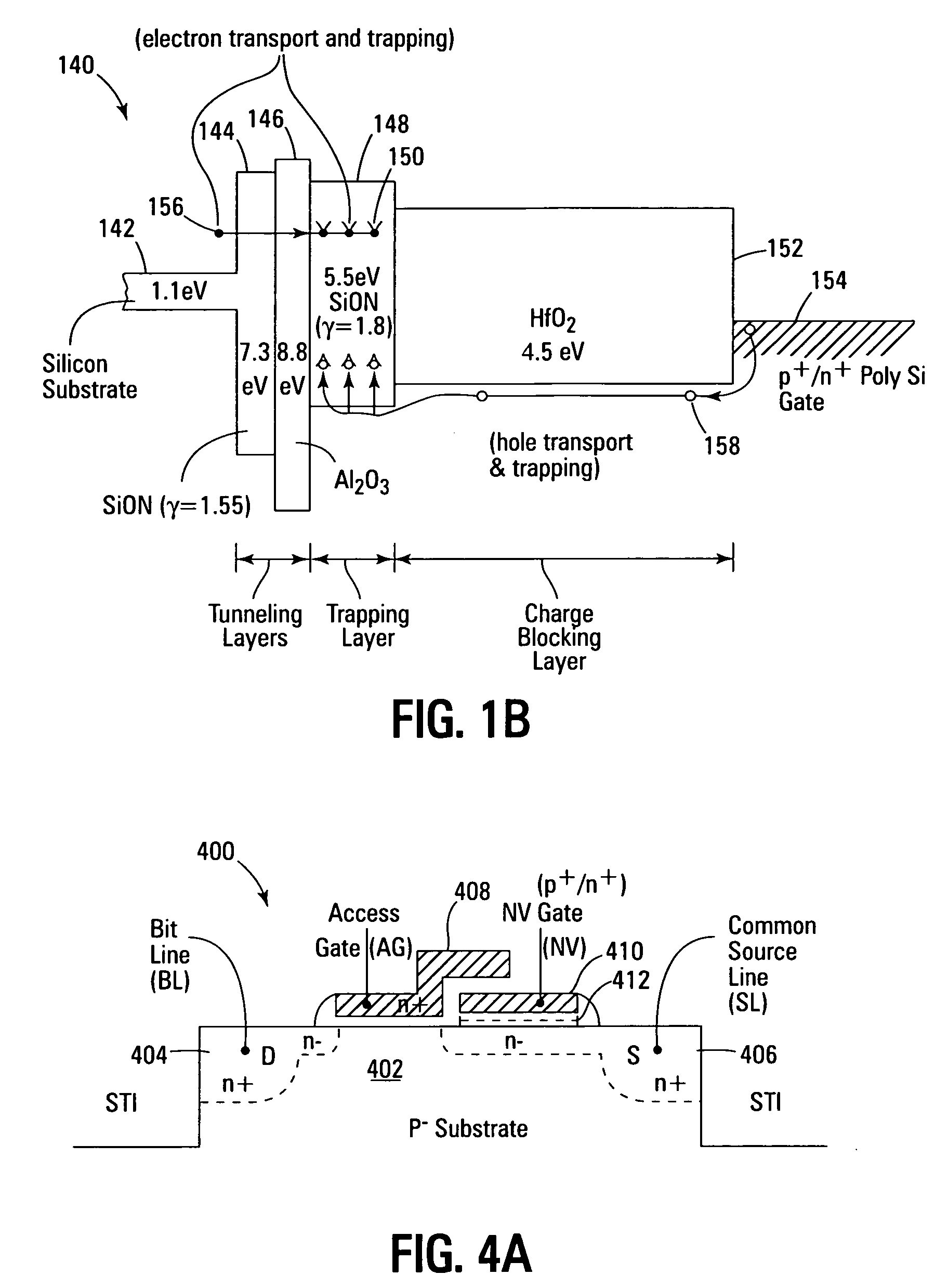
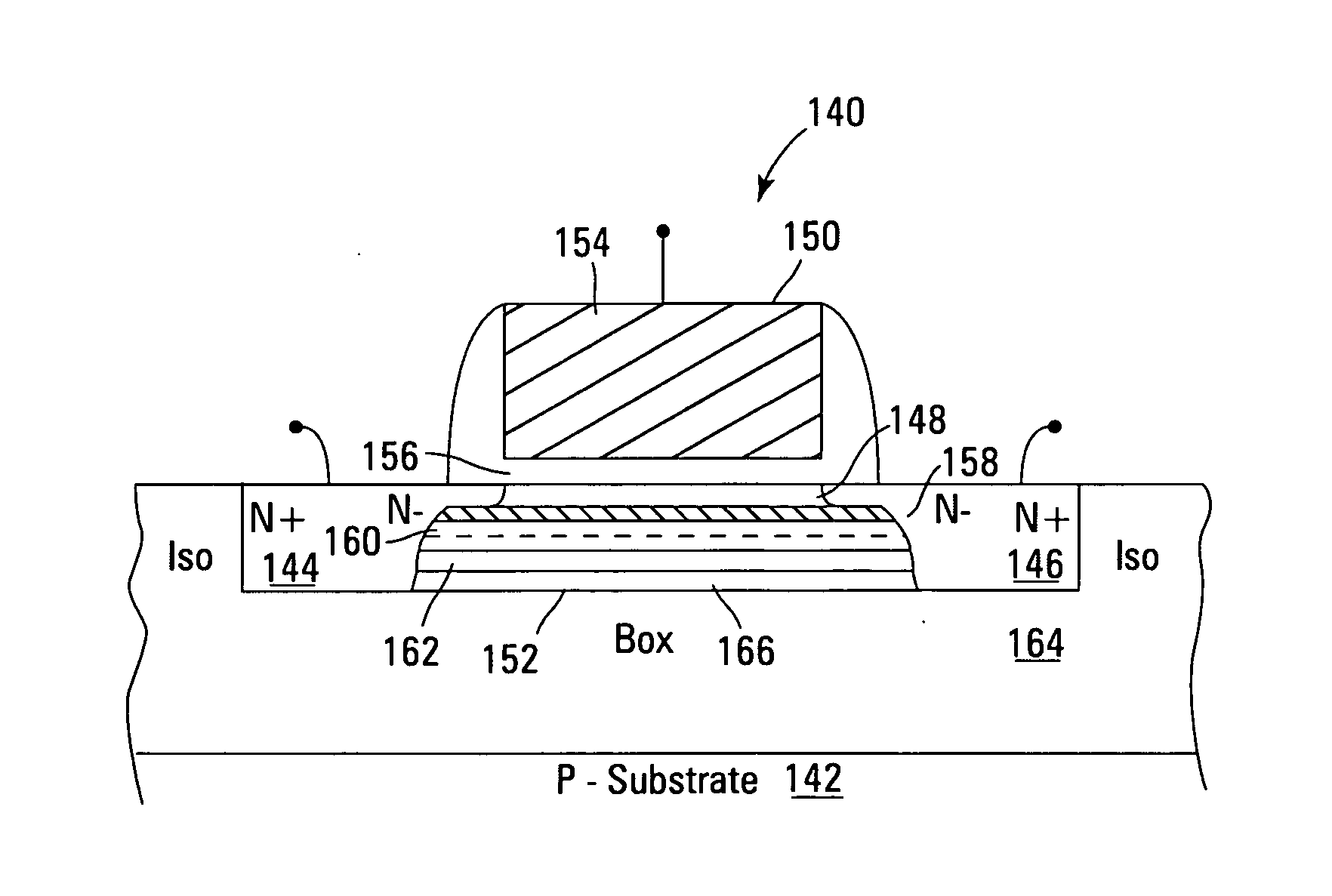
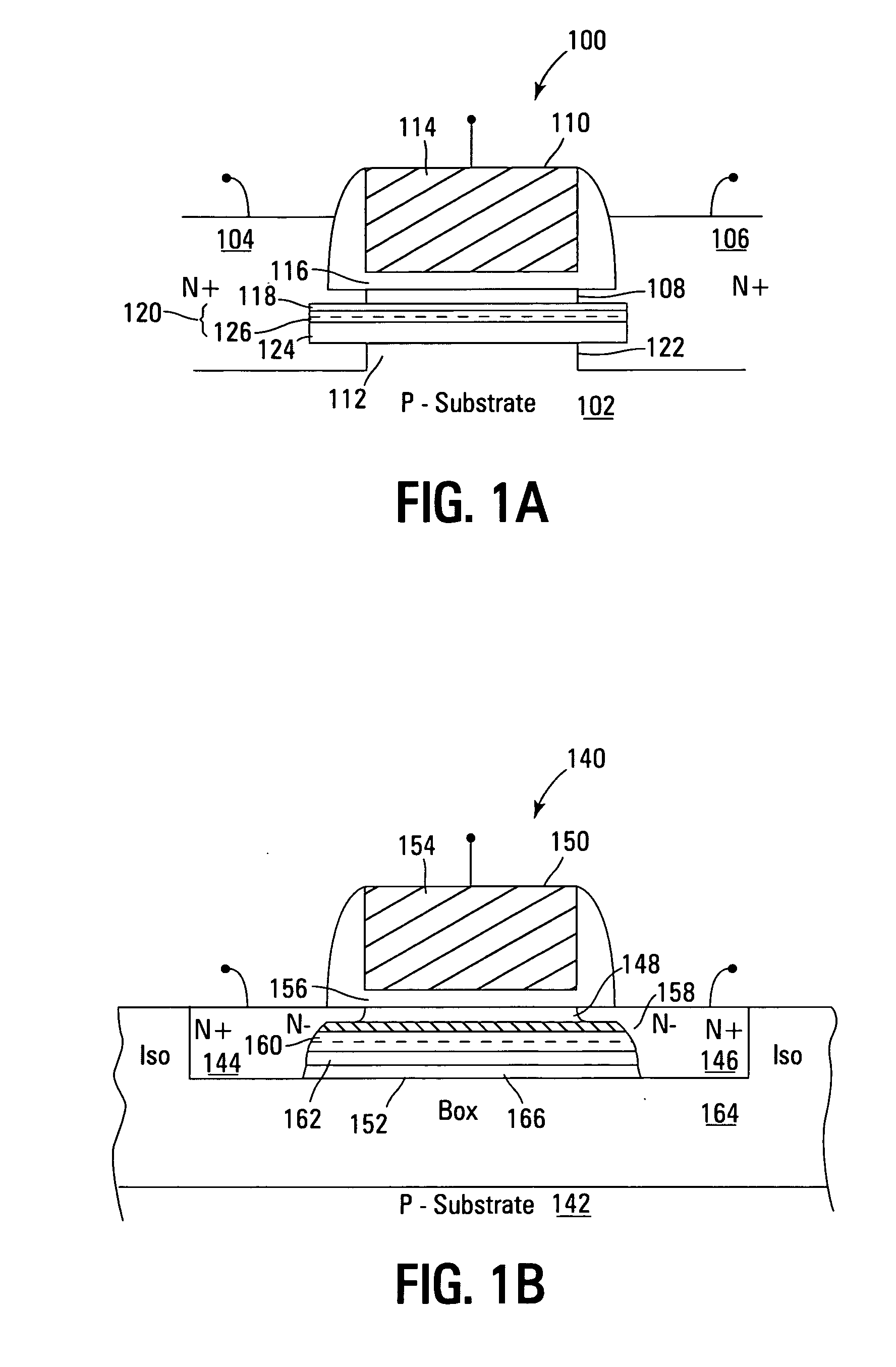
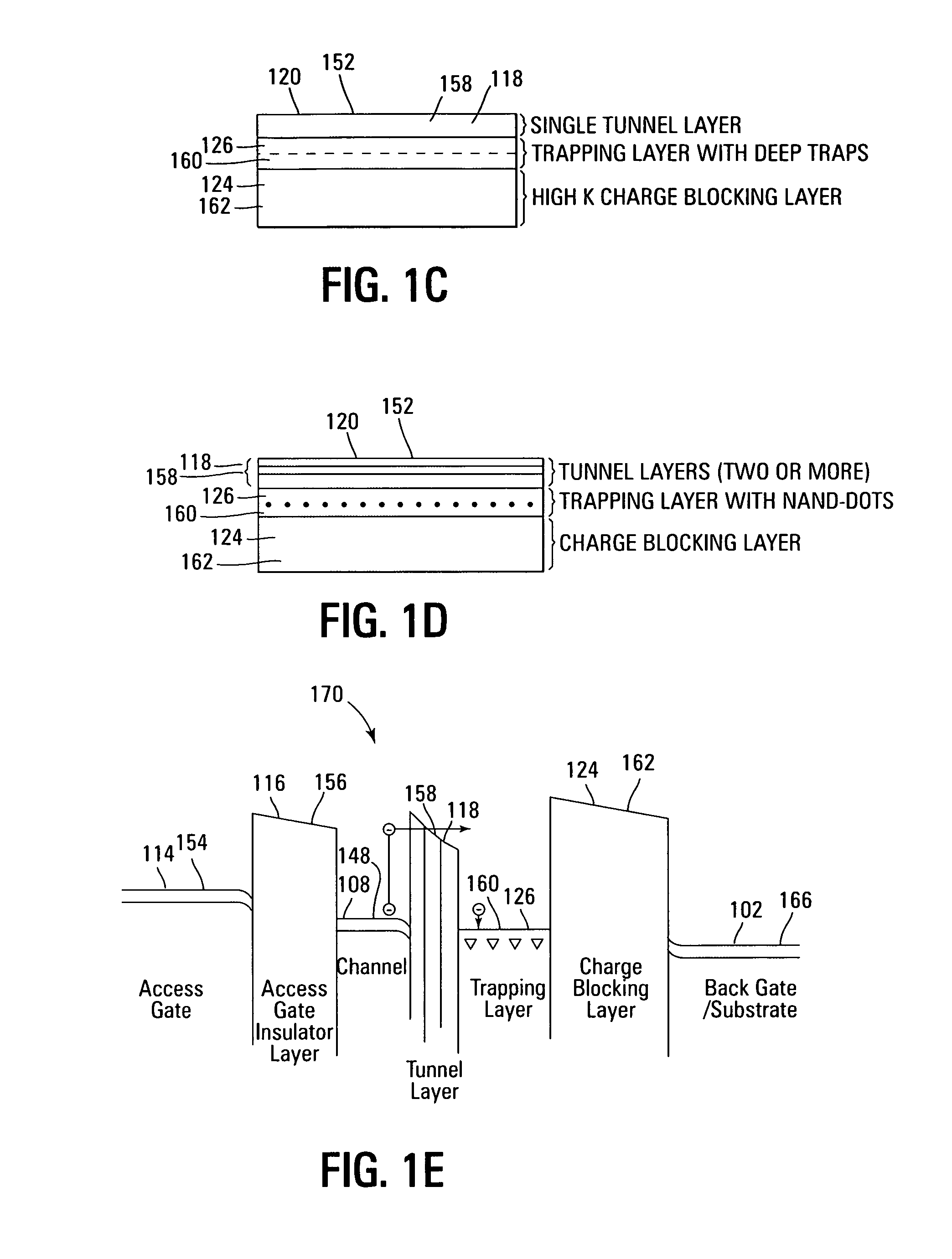
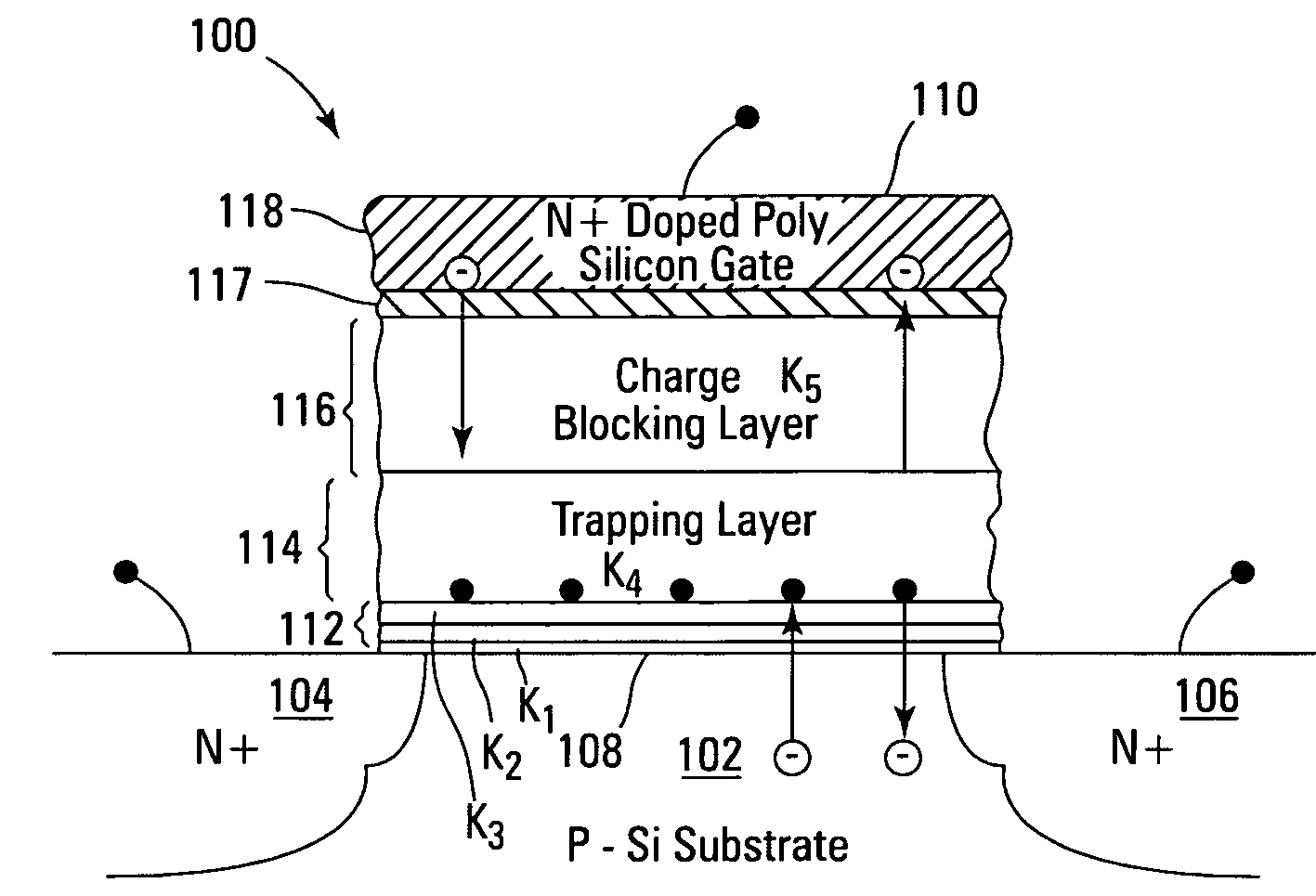
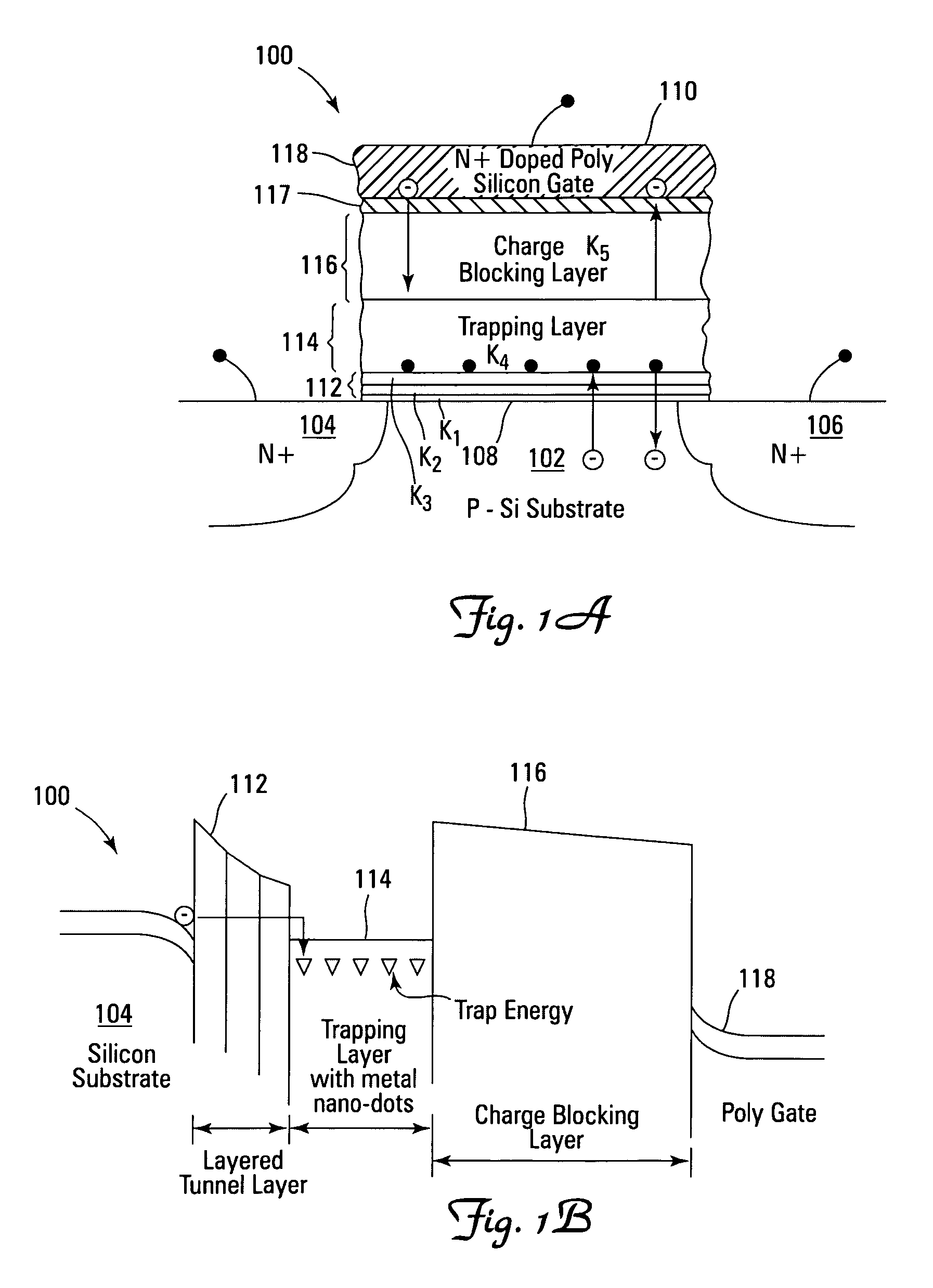
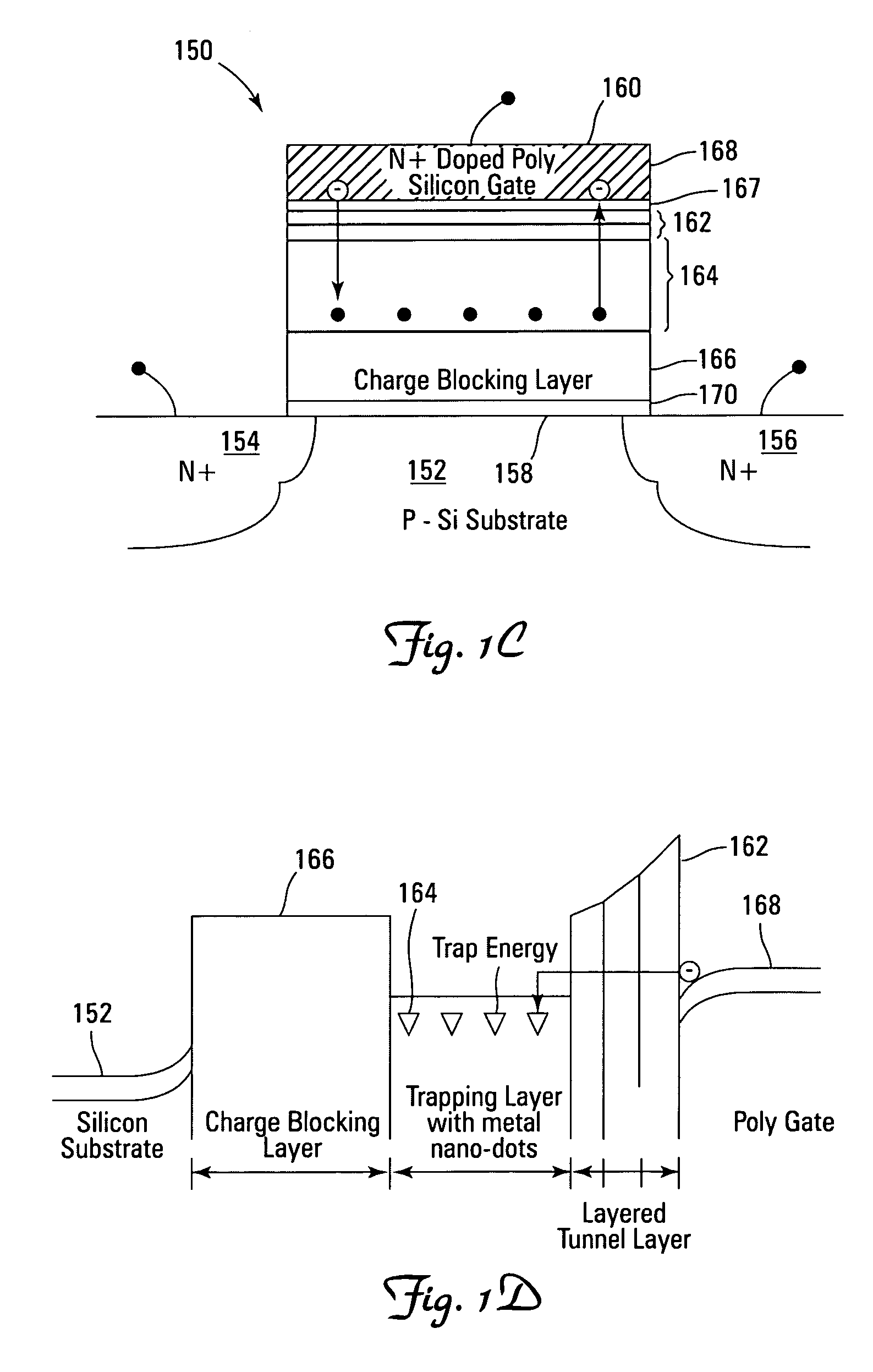
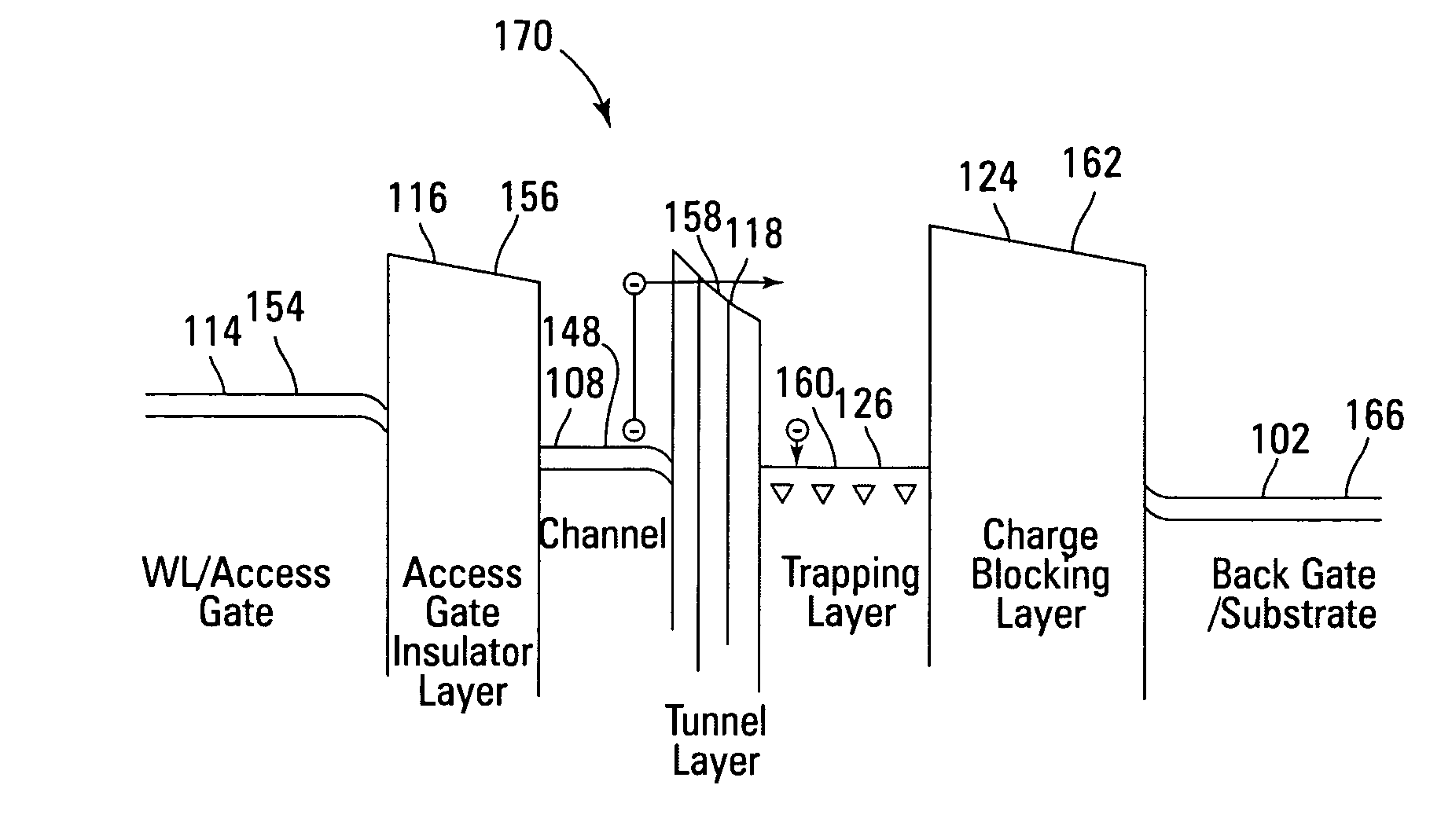
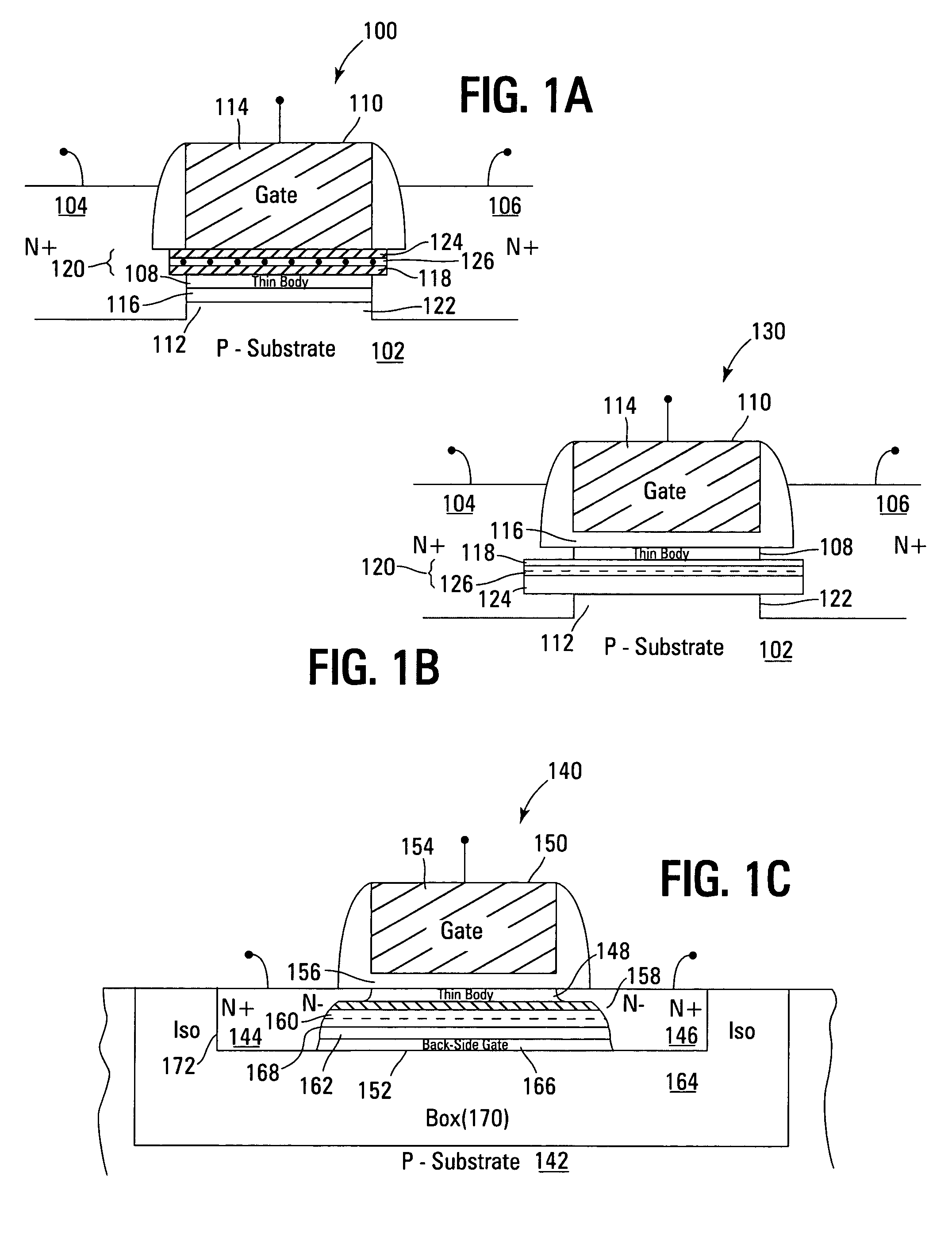
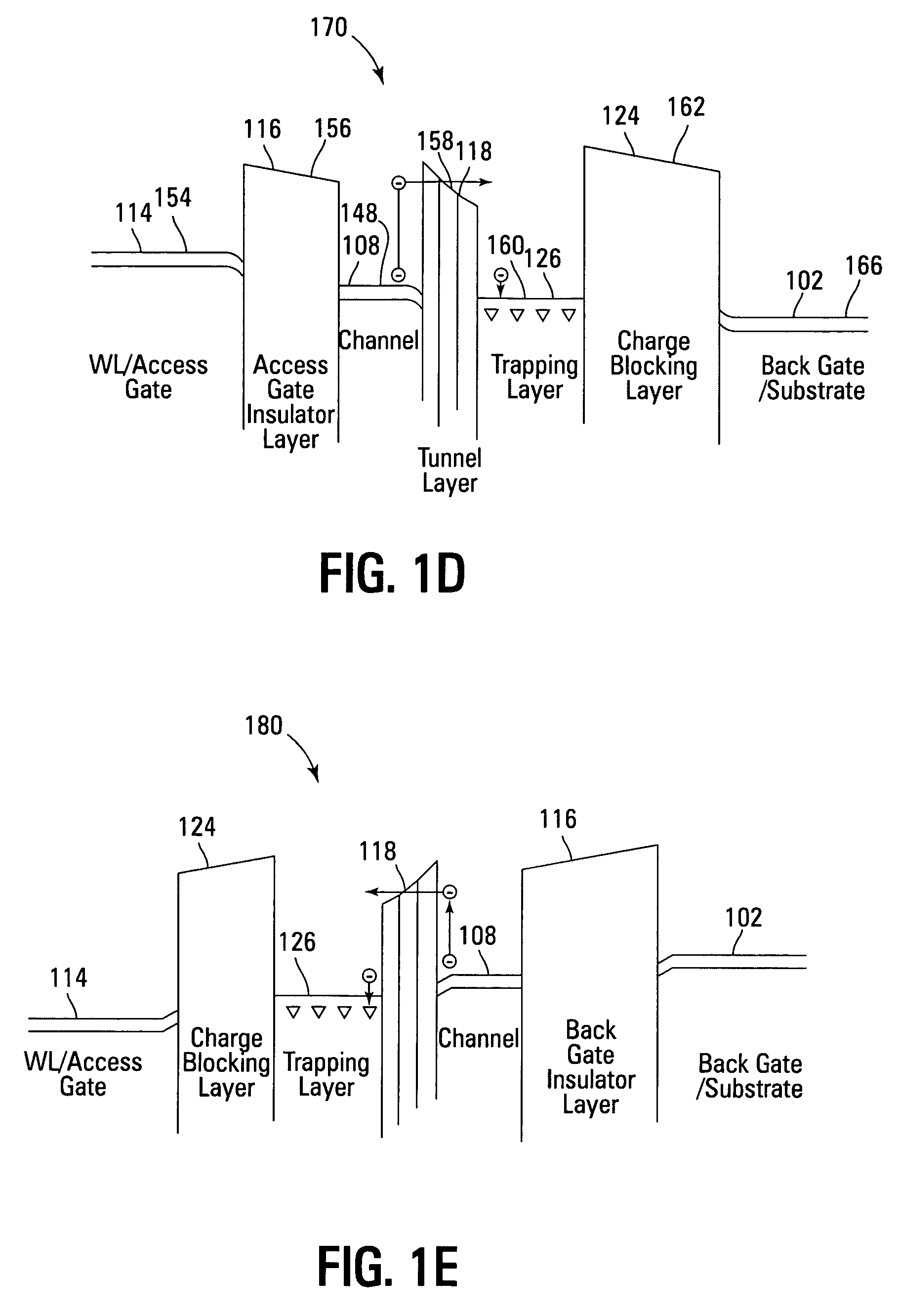
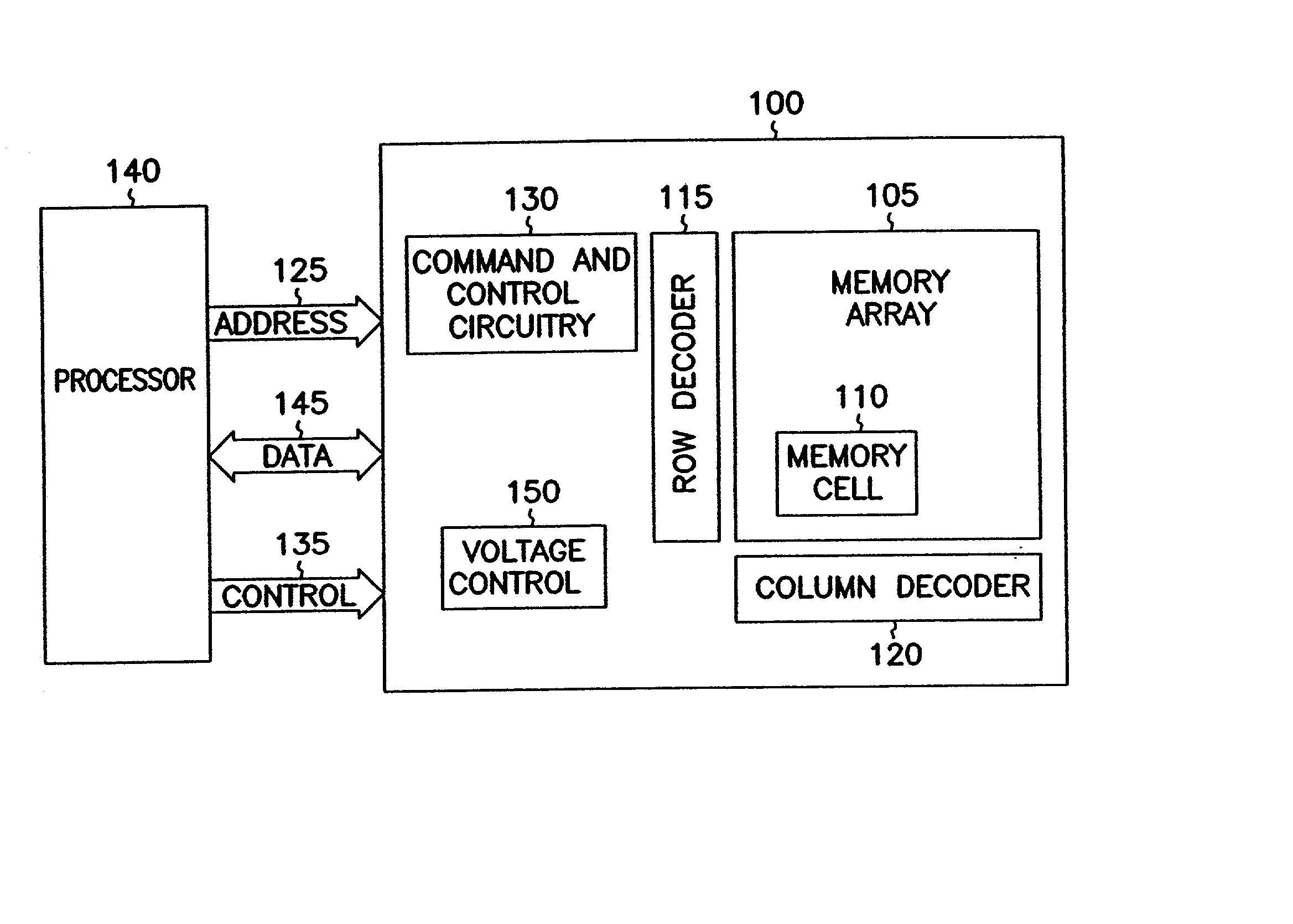
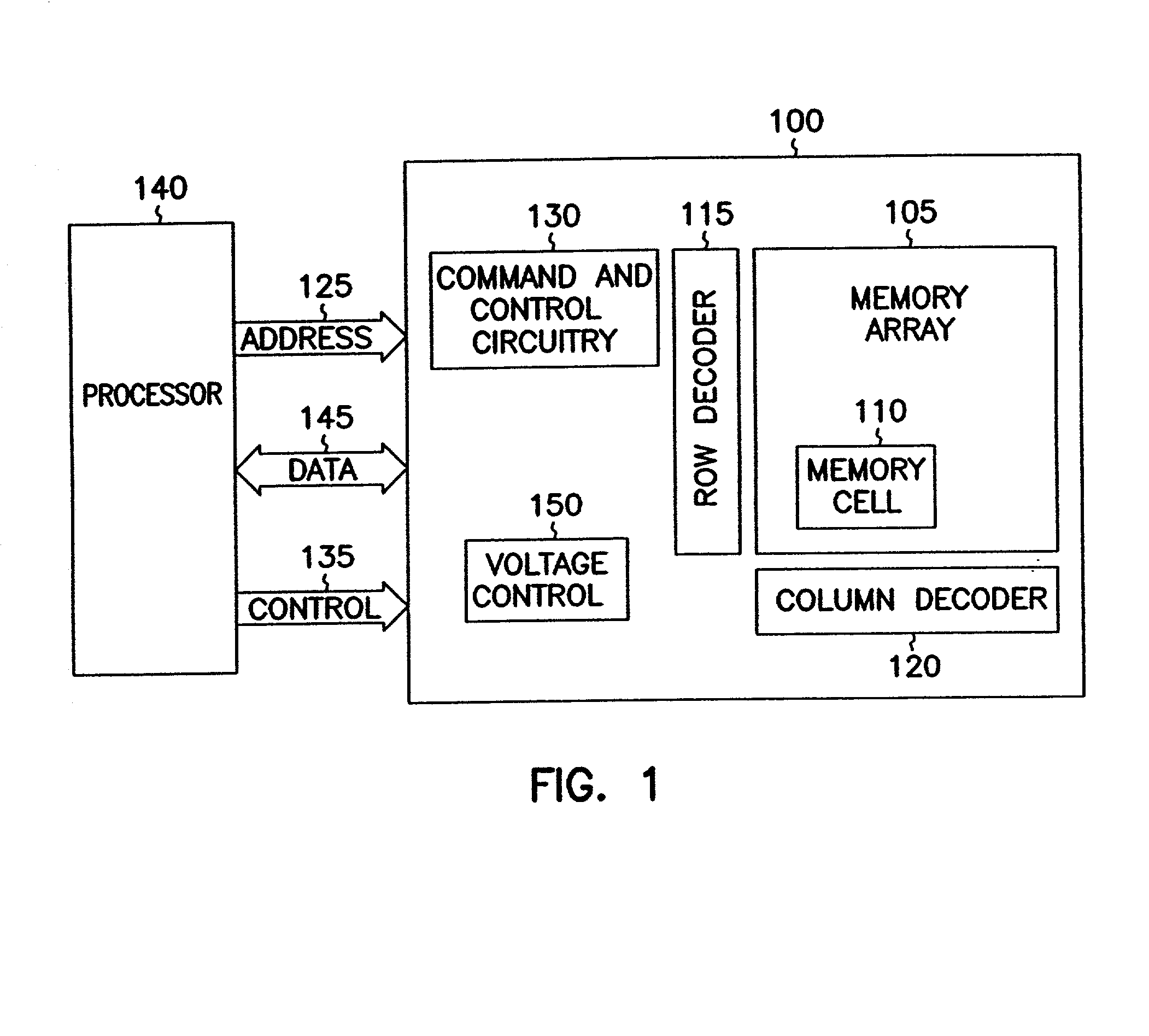
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that facilitate the use of band-gap engineered gate stacks with asymmetric tunnel barriers in reverse and normal mode floating node memory cells in NOR or NAND memory architectures that allow for direct tunnel programming and erase, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. The low voltage direct tunneling program and erase capability reduces damage to the gate stack and the crystal lattice from high energy carriers, reducing write fatigue and enhancing device lifespan. The low voltage direct tunnel program and erase capability also enables size reduction through low voltage design and further device feature scaling. Memory cells of the present invention also allow multiple bit storage. These characteristics allow memory device embodiments of the present invention to operate within the definition of a universal memory, capable of replacing both DRAM and ROM in a system.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
High density NAND non-volatile memory device
ActiveUS20070012988A1Efficient eraseReduce harmSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCharge retentionLow voltage
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that utilize dual gate (or back-side gate) non-volatile memory cells with band engineered gate-stacks that are placed above or below the channel region in front-side or back-side charge trapping gate-stack configurations in NAND memory array architectures. The band-gap engineered gate-stacks with asymmetric or direct tunnel barriers of the floating node memory cells of embodiments of the present invention allow for low voltage tunneling programming and efficient erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. The memory cell architecture also allows for improved high density memory devices or arrays with the utilization of reduced feature word lines and vertical select gates.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
High-performance one-transistor memory cell
ActiveUS20050001232A1Reduce standby powerAddressing slow performanceTransistorThyristorCharge retentionSemiconductor
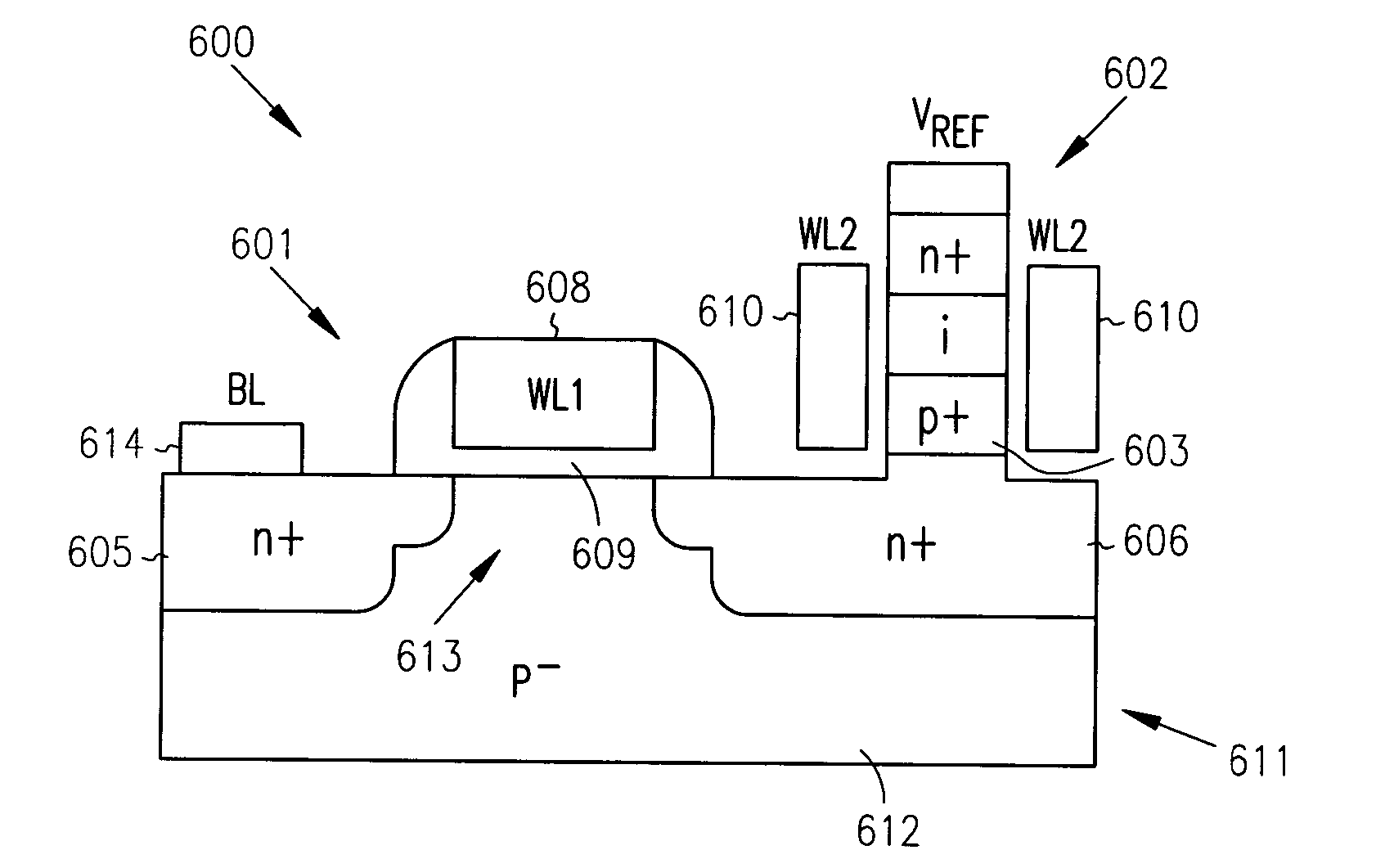
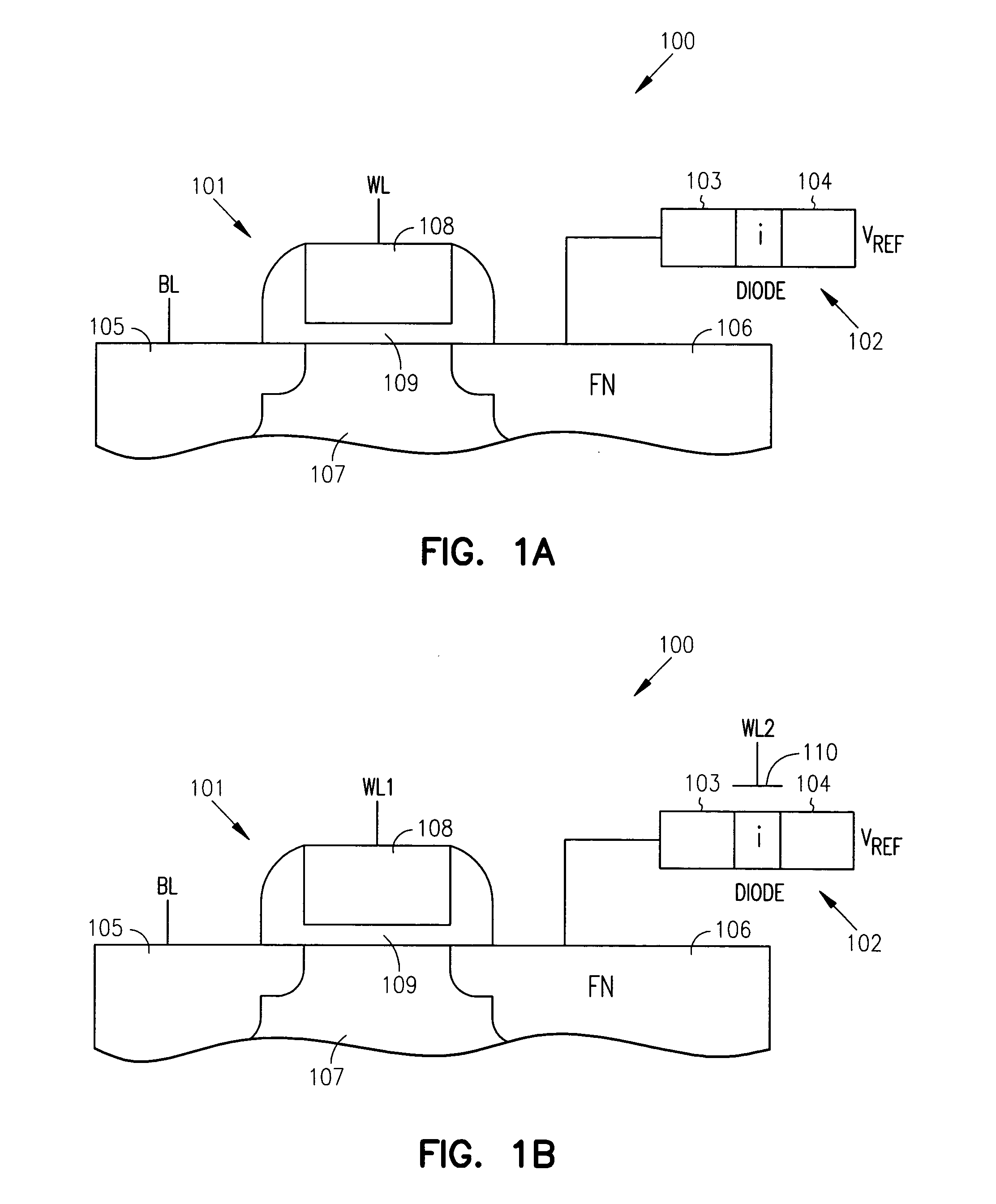
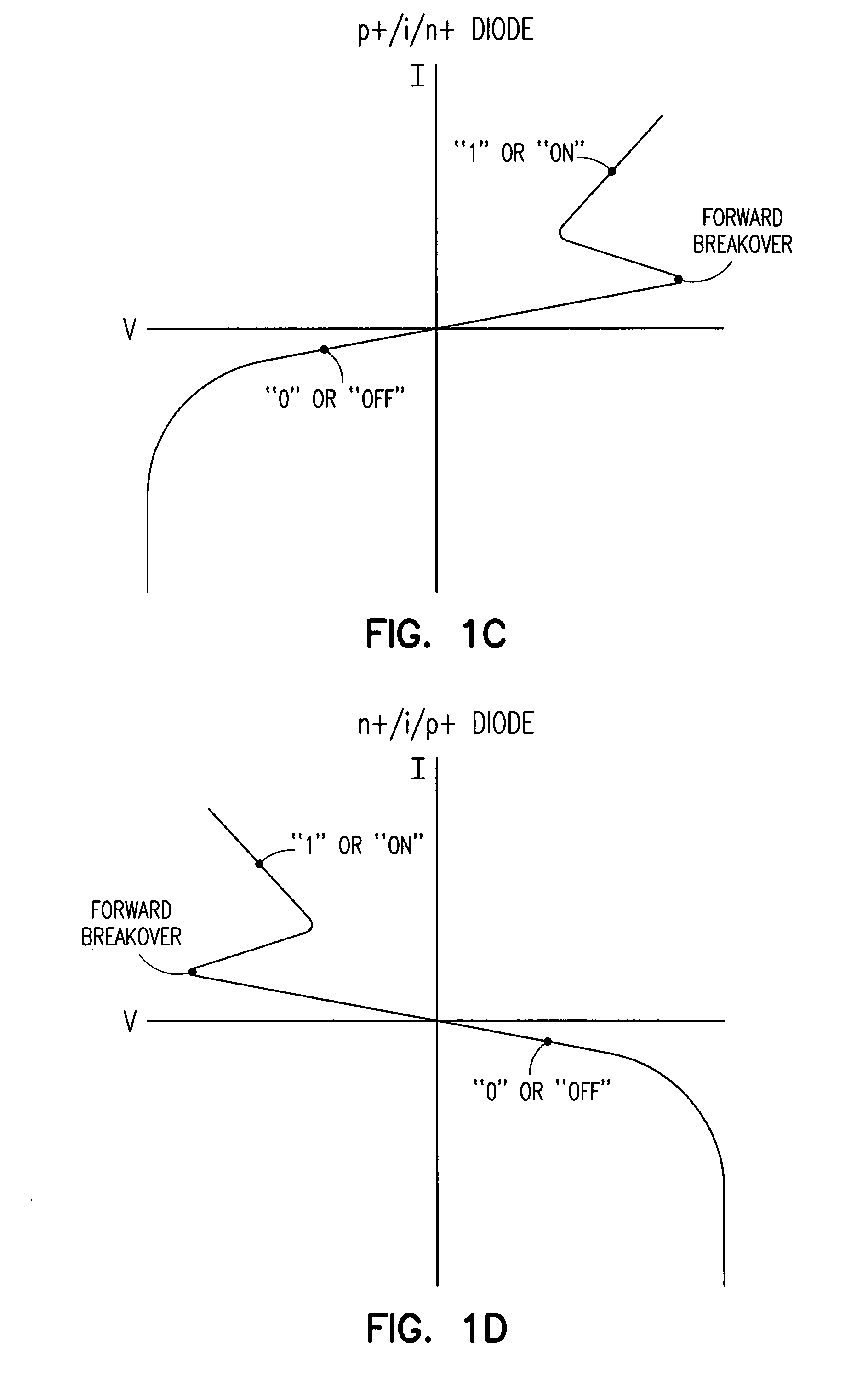
One aspect of this disclosure relates to a memory cell. In various embodiments, the memory cell includes an access transistor having a floating node, and a diode connected between the floating node and a diode reference potential line. The diode includes an anode, a cathode, and an intrinsic region between the anode and the cathode. A charge representative of a memory state of the memory cell is held across the intrinsic region of the diode. In various embodiments, the memory cell is implemented in bulk semiconductor technology. In various embodiments, the memory cell is implemented in semiconductor-on-insulator technology. In various embodiments, the diode is gate-controlled. In various embodiments, the diode is charge enhanced by an intentionally generated charge in a floating body of an SOI access transistor. Various embodiments include laterally-oriented diodes (stacked and planar configurations), and various embodiments include vertically-oriented diodes. Other aspects and embodiments are provided herein.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
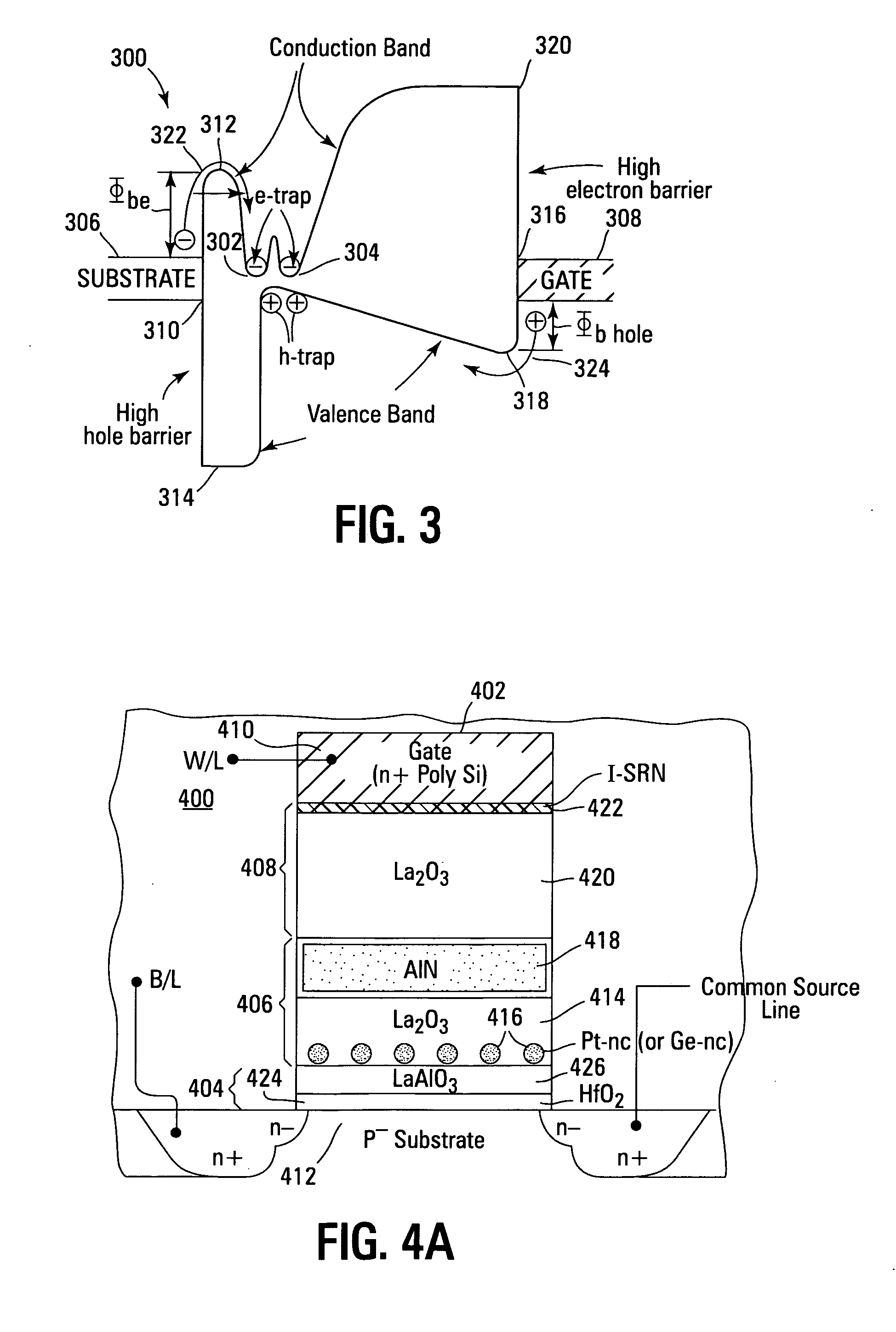
Band-engineered multi-gated non-volatile memory device with enhanced attributes
ActiveUS7279740B2Reduce harmExcellent charge retentionSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCharge retentionHigh energy
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that facilitate the use of band-gap engineered gate stacks with asymmetric tunnel barriers in floating gate memory cells in NOR or NAND memory architectures that allow for direct tunneling programming and erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. The direct tunneling program and erase capability reduces damage to the gate stack and the crystal lattice from high energy carriers, reducing write fatigue and leakage issues and enhancing device lifespan. Memory cells of the present invention also allow multiple bit storage in a single memory cell, and allow for programming and erase with reduced voltages. A positive voltage erase process via hole tunneling is also provided.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
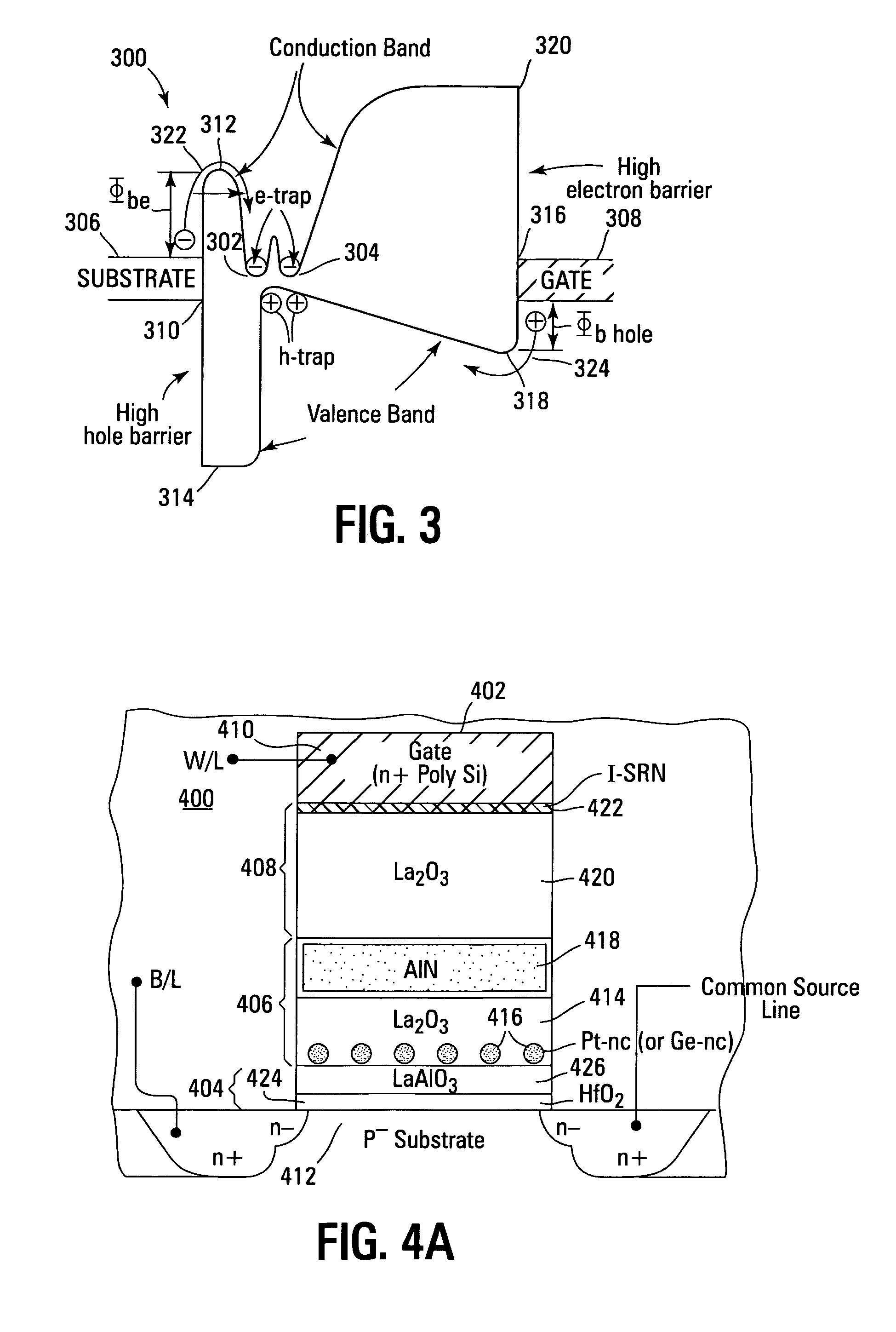
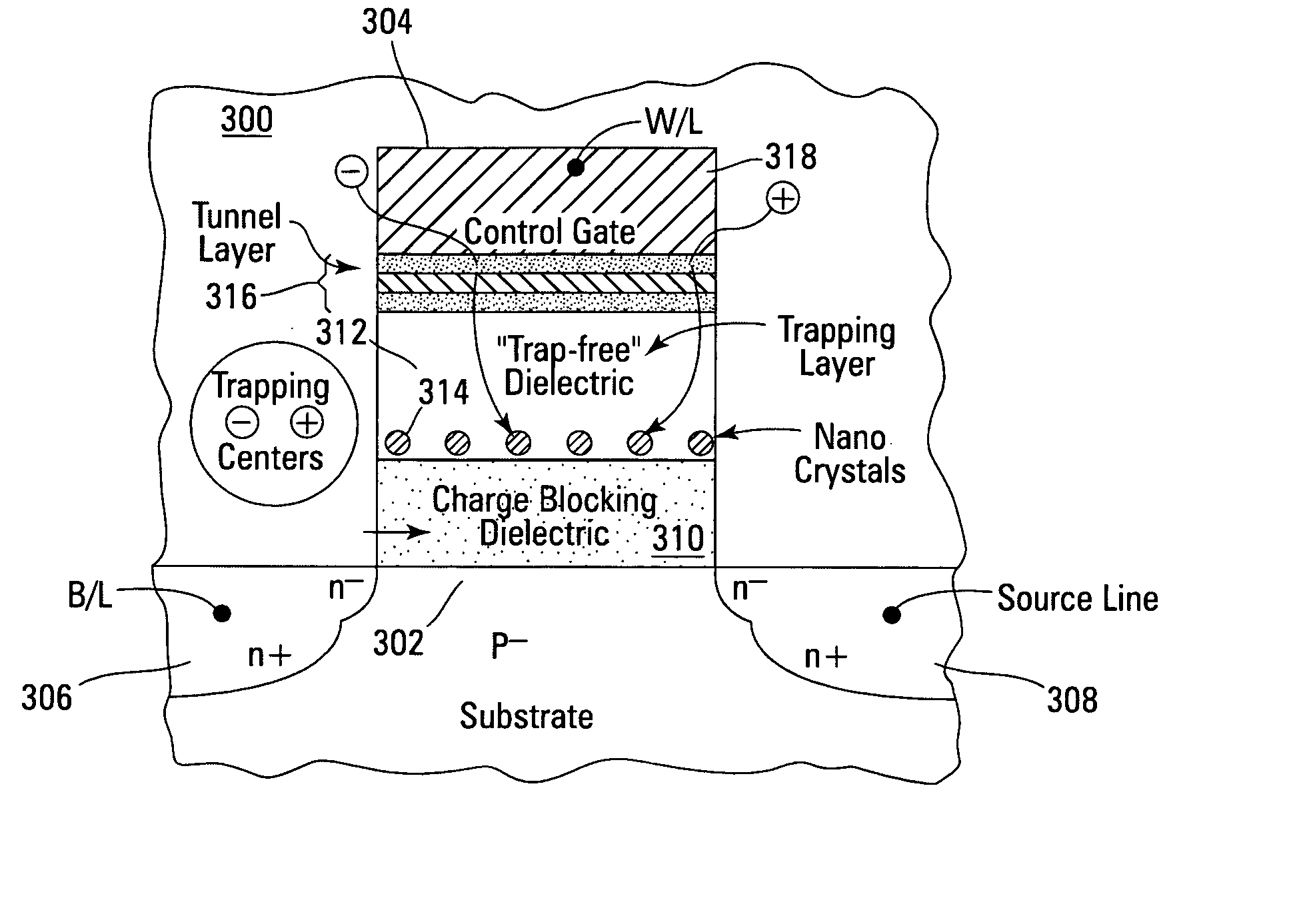
Band engineered nano-crystal non-volatile memory device utilizing enhanced gate injection
ActiveUS20070045718A1Increased device feature scalingEfficient erasureTransistorNanoinformaticsCharge retentionNon symmetric
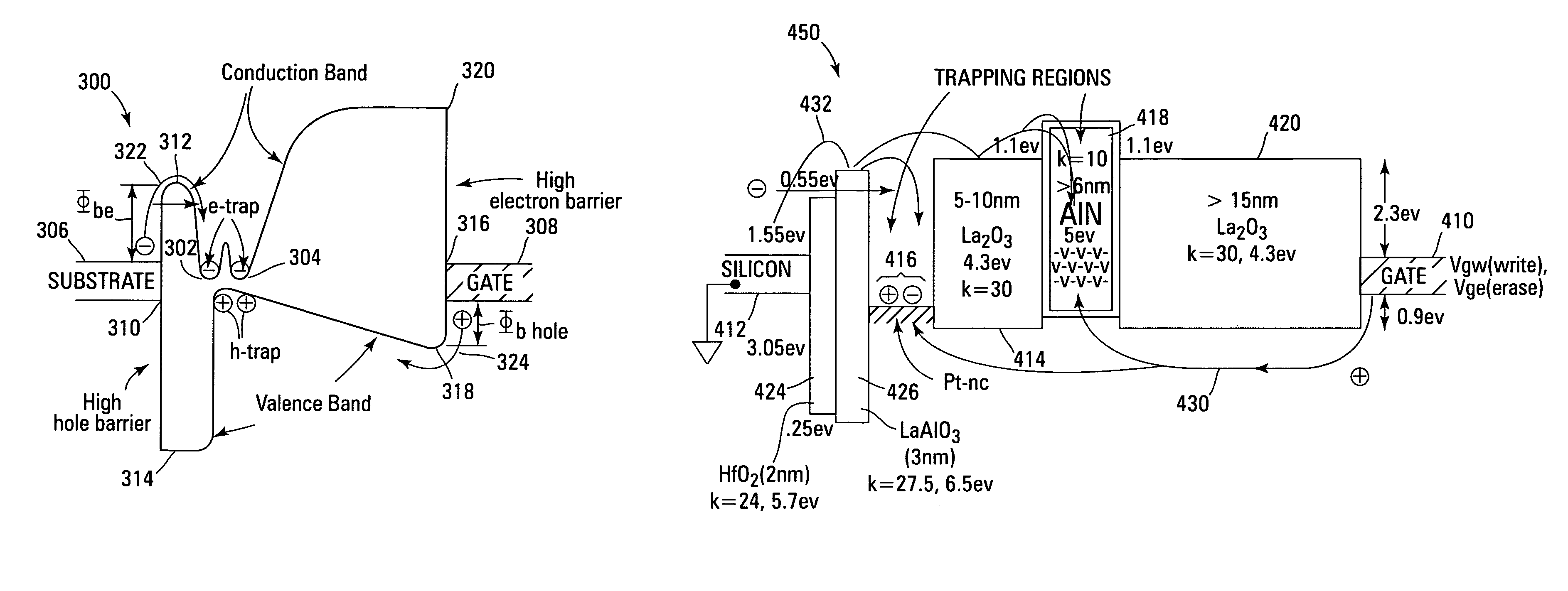
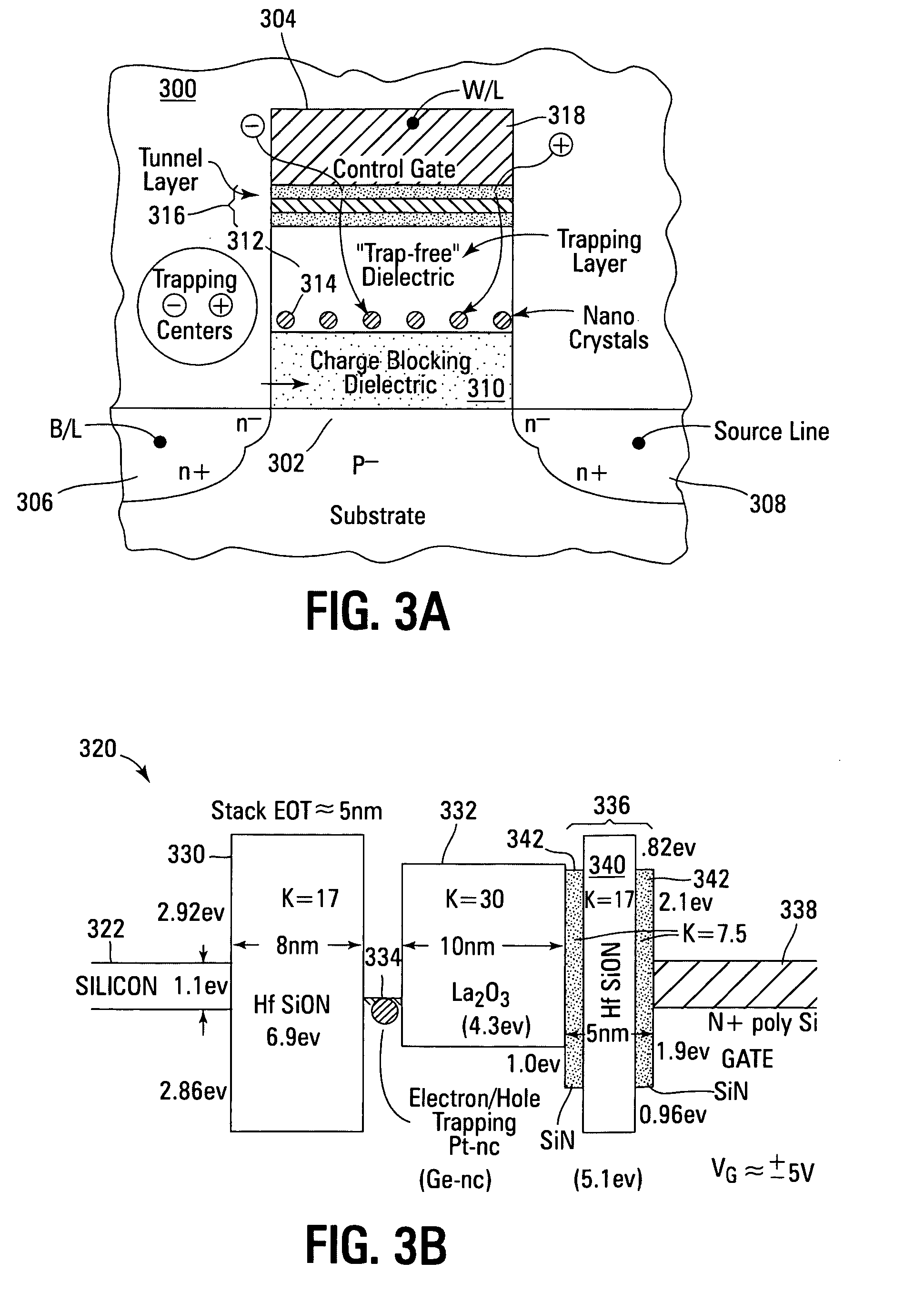
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that utilize reverse mode non-volatile memory cells that have band engineered gate-stacks and nano-crystal charge trapping in EEPROM and block erasable memory devices, such as Flash memory devices. Embodiments of the present invention allow a reverse mode gate-insulator stack memory cell that utilizes the control gate for programming and erasure through a band engineered crested tunnel barrier. Charge retention is enhanced by utilization of high work function nano-crystals in a non-conductive trapping layer and a high K dielectric charge blocking layer. The band-gap engineered gate-stack with symmetric or asymmetric crested barrier tunnel layers of the non-volatile memory cells of embodiments of the present invention allow for low voltage tunneling programming and erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Band-engineered multi-gated non-volatile memory device with enhanced attributes
ActiveUS20060258090A1Reduce harmExcellent charge retentionSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCharge retentionHigh energy
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that facilitate the use of band-gap engineered gate stacks with asymmetric tunnel barriers in floating gate memory cells in NOR or NAND memory architectures that allow for direct tunneling programming and erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. The direct tunneling program and erase capability reduces damage to the gate stack and the crystal lattice from high energy carriers, reducing write fatigue and leakage issues and enhancing device lifespan. Memory cells of the present invention also allow multiple bit storage in a single memory cell, and allow for programming and erase with reduced voltages. A positive voltage erase process via hole tunneling is also provided.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
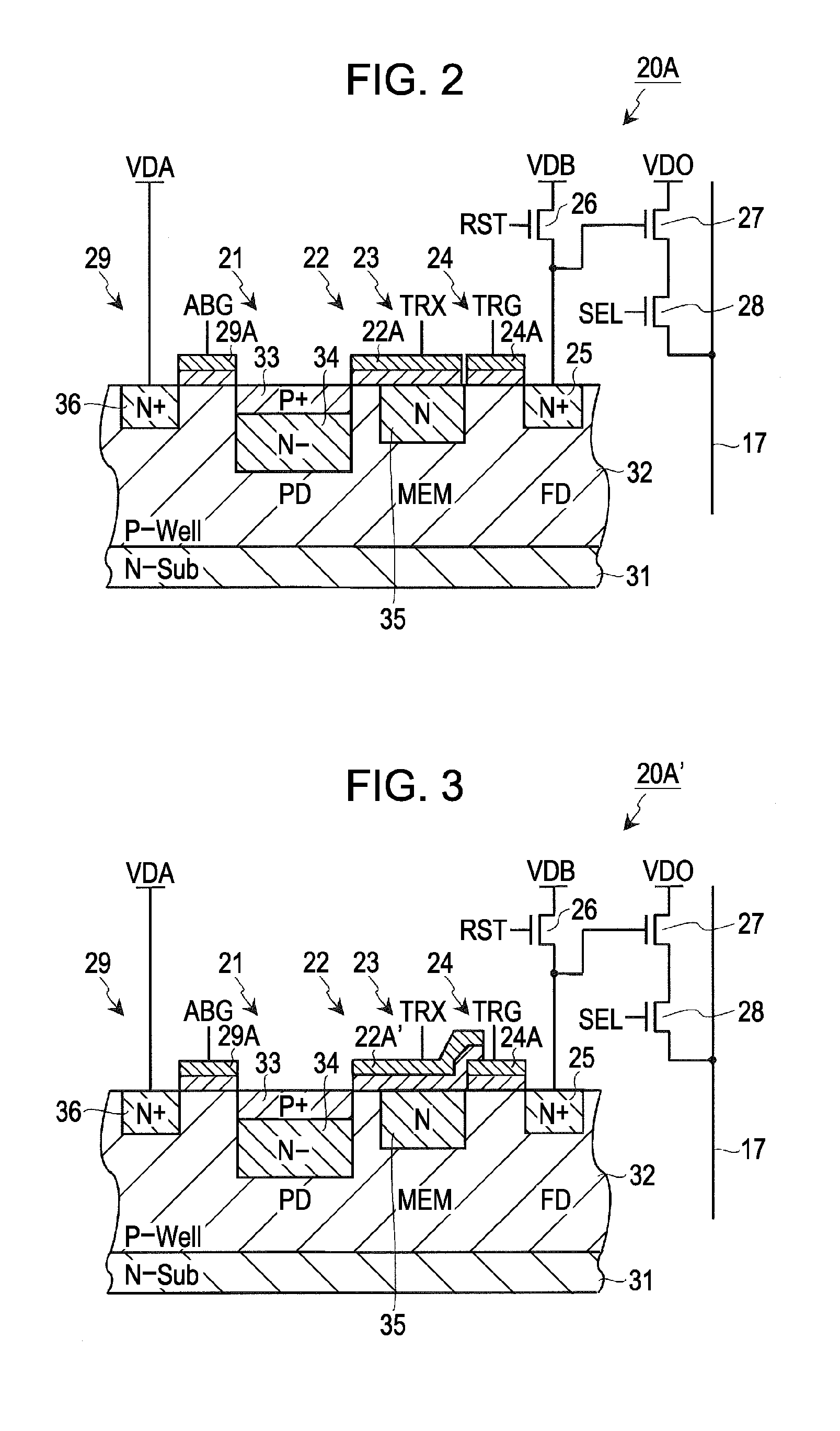
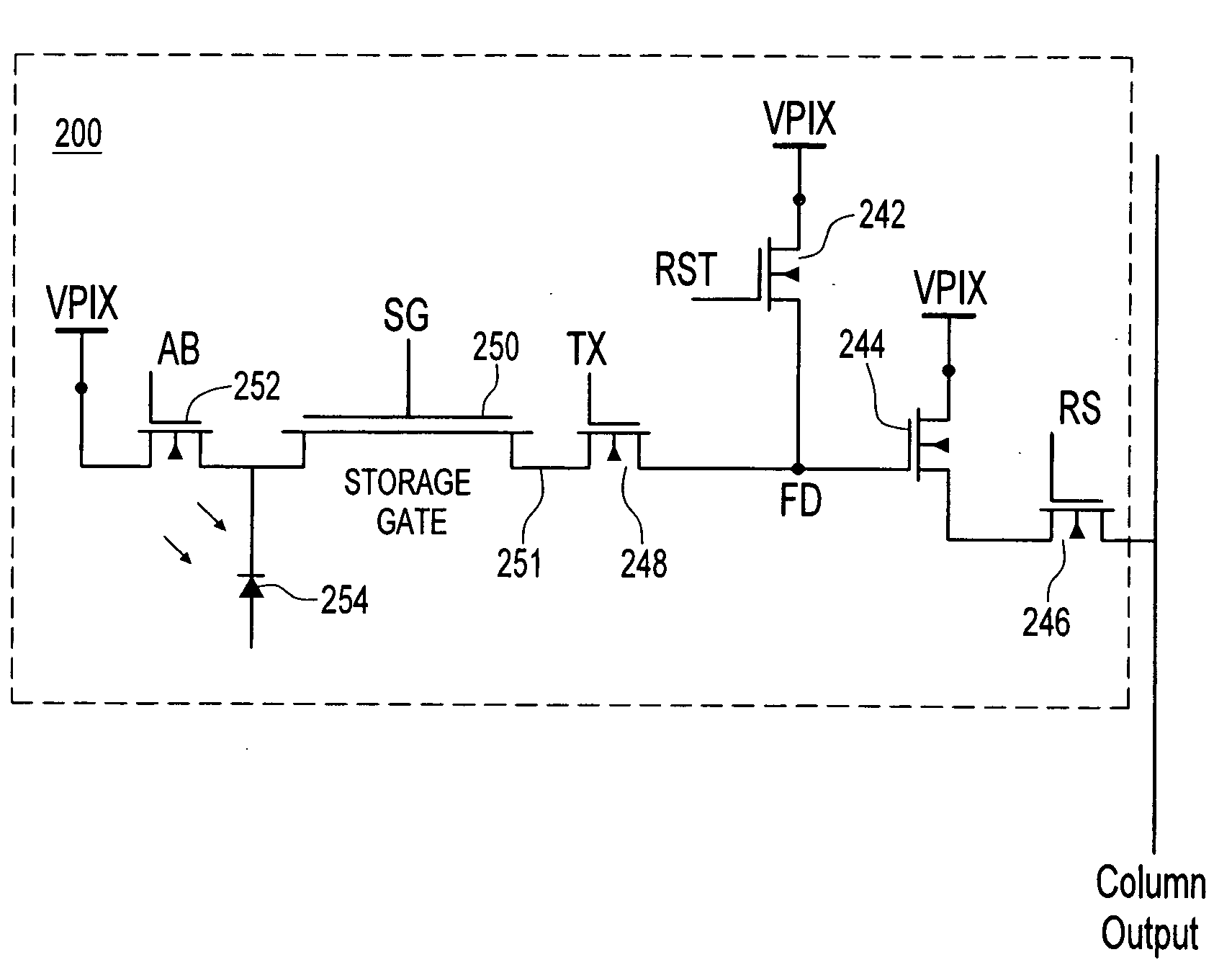
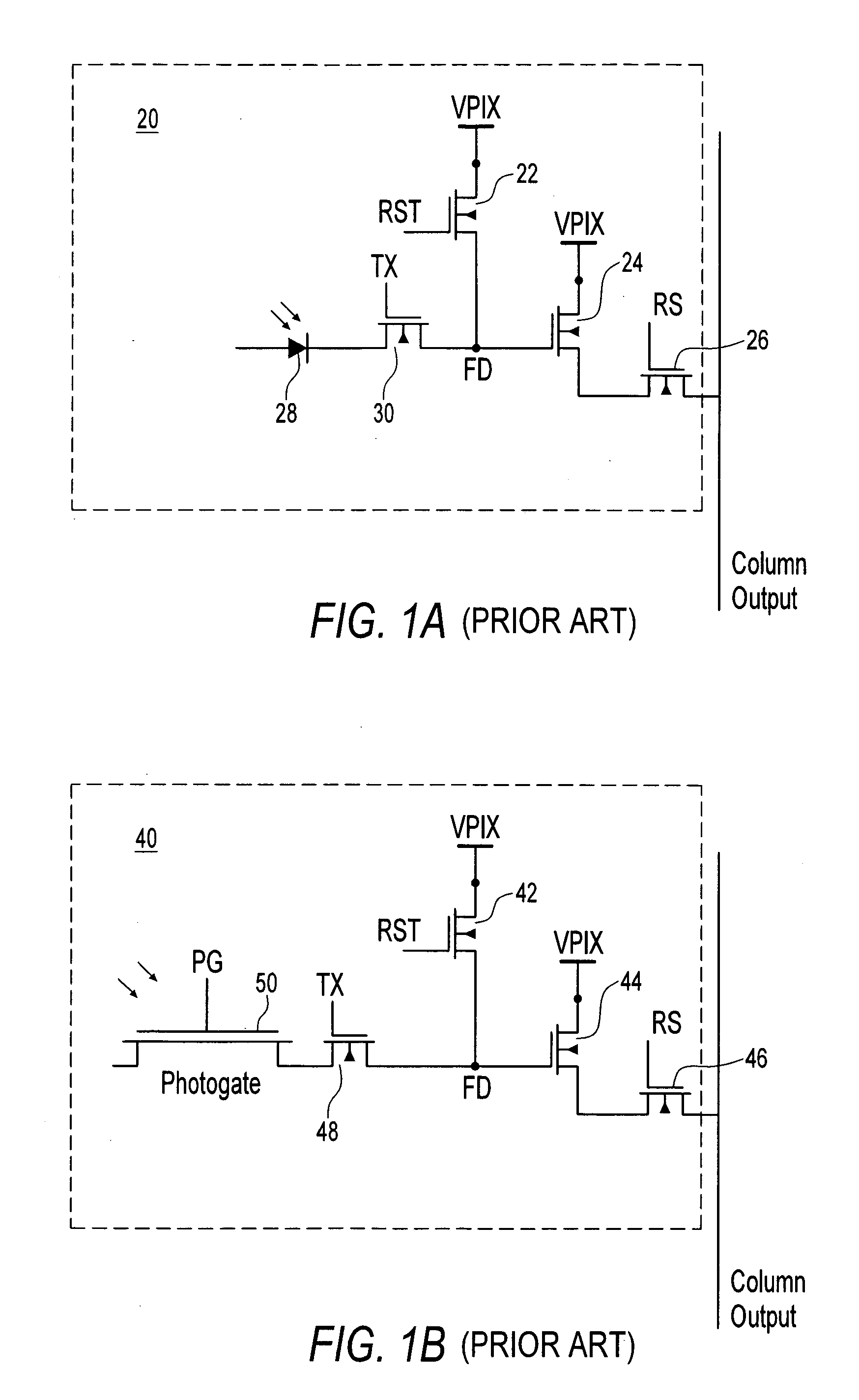
Solid state imaging device, driving method of the solid state imaging device, and electronic equipment
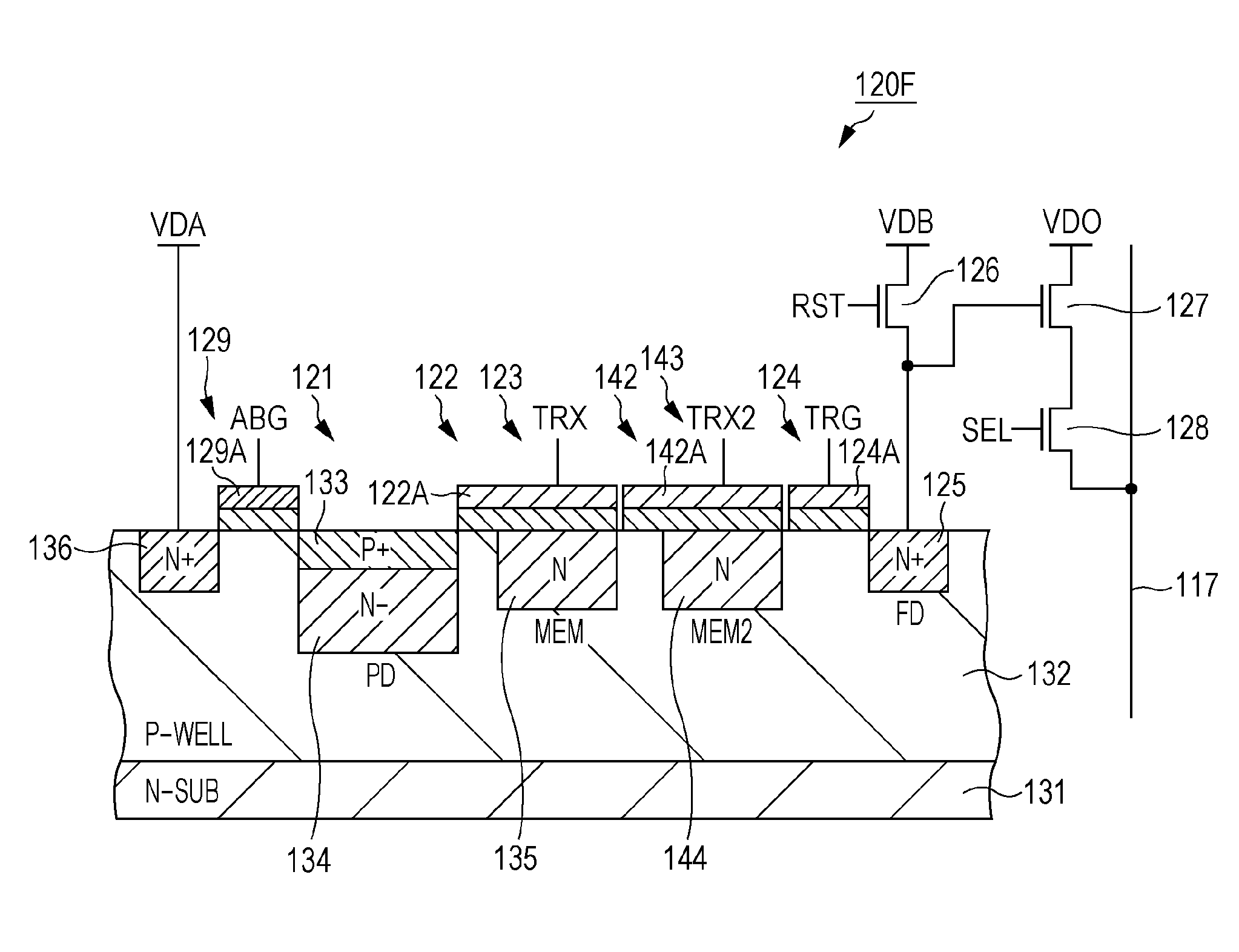
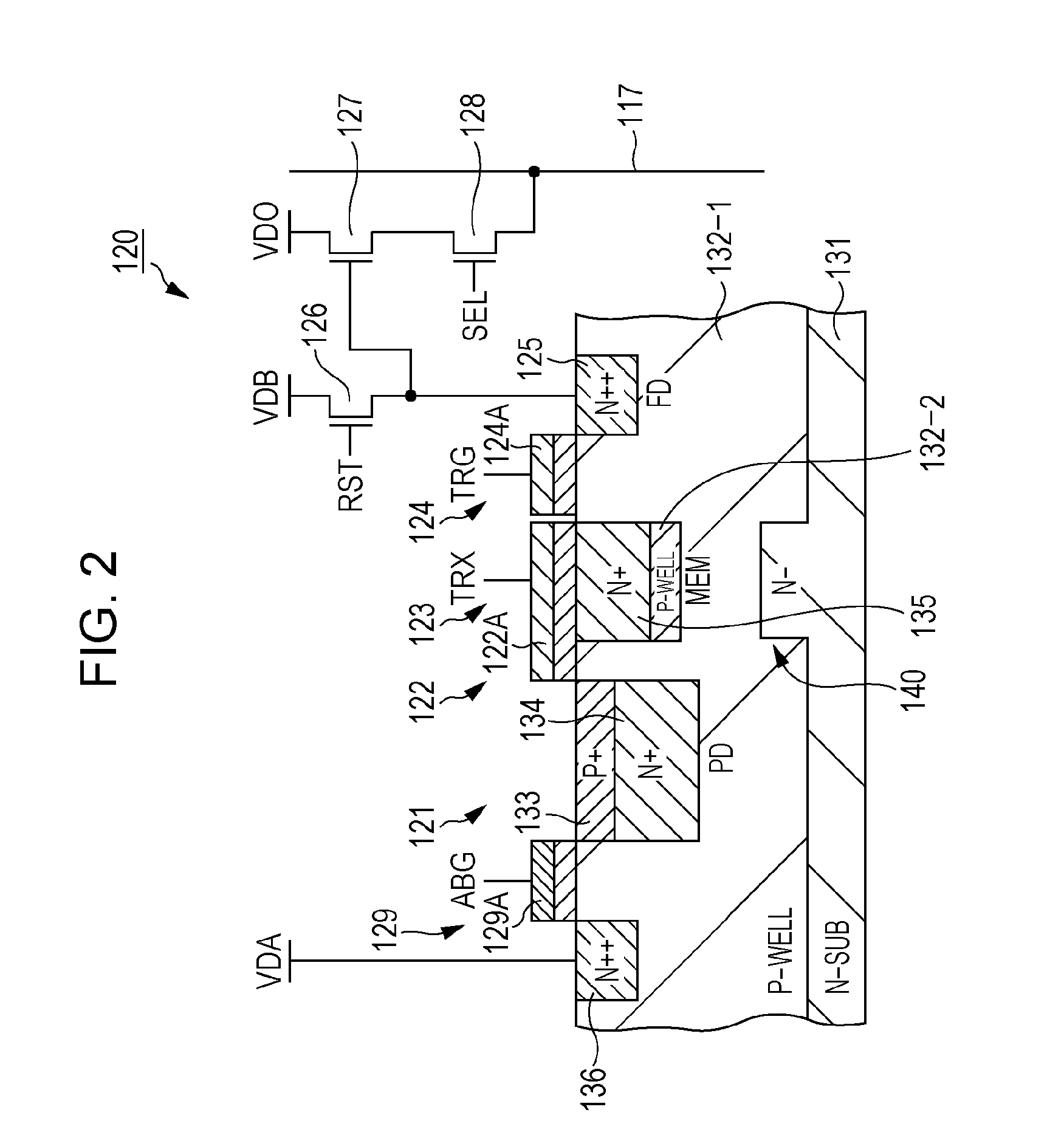
ActiveUS20090251582A1Reduce noiseImprove image qualityTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsCharge retentionFloating diffusion
A solid state imaging device includes: multiple unit pixels including a photoelectric converter generating electrical charge in accordance with incident light quantity and accumulating the charge, a first transfer gate transferring the accumulated charge, a charge holding region holding the transferred charge, a second transfer gate transferring the held charge, and a floating diffusion region converting the transferred charge into voltage; an intermediate charge transfer unit transferring, to the charge holding region, a charge exceeding a predetermined charge amount as a first signal charge; and a pixel driving unit setting the first transfer gate to a non-conducting state, set the second transfer gate to a conducting state, transfer the first signal charge to the floating diffusion region, set the second transfer gate to a non-conducting state, set the first transfer gate to a conducting state, and transfer the accumulated charge to the charge holding region as a second signal charge.
Owner:SONY CORP
Operation scheme for spectrum shift in charge trapping non-volatile memory
ActiveUS7209390B2Improve reliabilityMinimize damageRead-only memoriesDigital storageCharge retentionFrequency spectrum
A memory cell with a charge trapping structure is programmed using refill cycles that include a program pulse followed by a charge balancing pulse that causes ejection of electrons from the charge trapping structure. The refill cycle causes a blue spectrum shift in the charge trap distribution in the charge trapping structure. The algorithm includes program verify operations after the program pulse, and completes when a successful program verify operation occurs after a number of refill cycles. The charge retention properties can be greatly improved by these refill cycles.
Owner:MACRONIX INT CO LTD
Back-side trapped non-volatile memory device
ActiveUS20060284236A1Efficient eraseReduce voltageNanoinformaticsSolid-state devicesCharge retentionHigh energy
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that utilize back-side trapped floating node memory cells with band-gap engineered gate stacks with asymmetric tunnel barriers. Embodiments of the present invention allow for direct tunneling programming and efficient erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention and reduces the possibility of damage to the channel / insulator interface. The direct tunneling program and efficient erase capability reduces damage to the gate stack and the crystal lattice from high energy carriers, reducing write fatigue and leakage issues and enhancing device lifespan. Memory device embodiments of the present invention are presented that are arranged in NOR or NAND memory architecture arrays. Memory cell embodiments of the present invention also allow multiple levels of bit storage in a single memory cell, and allow for programming and erase with reduced voltages.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device having excellent charge retention and manufacturing process of the same
InactiveUS20060118853A1Improve adhesionIncrease production capacityNanotechRead-only memoriesCharge retentionManufacturing technology
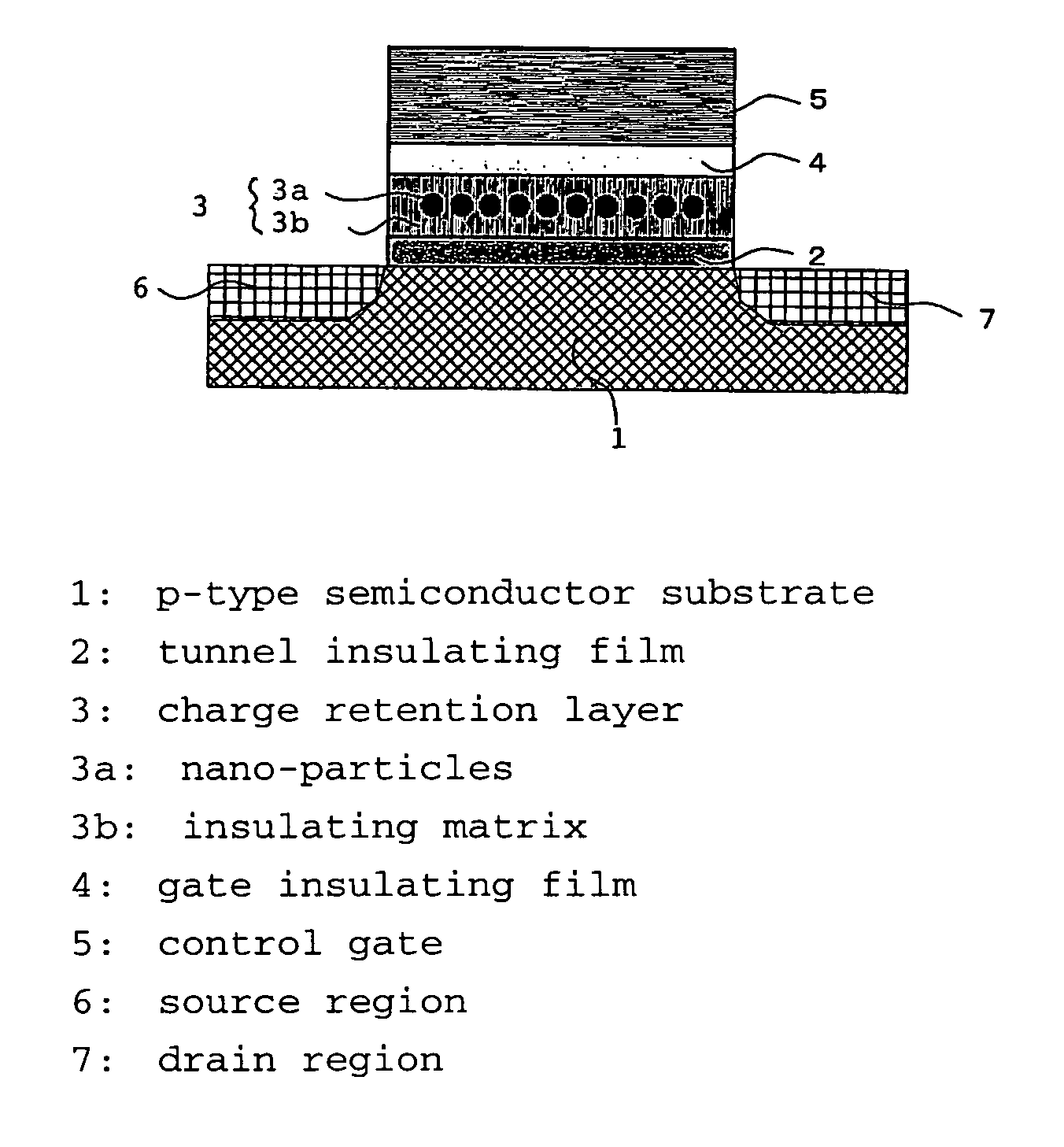
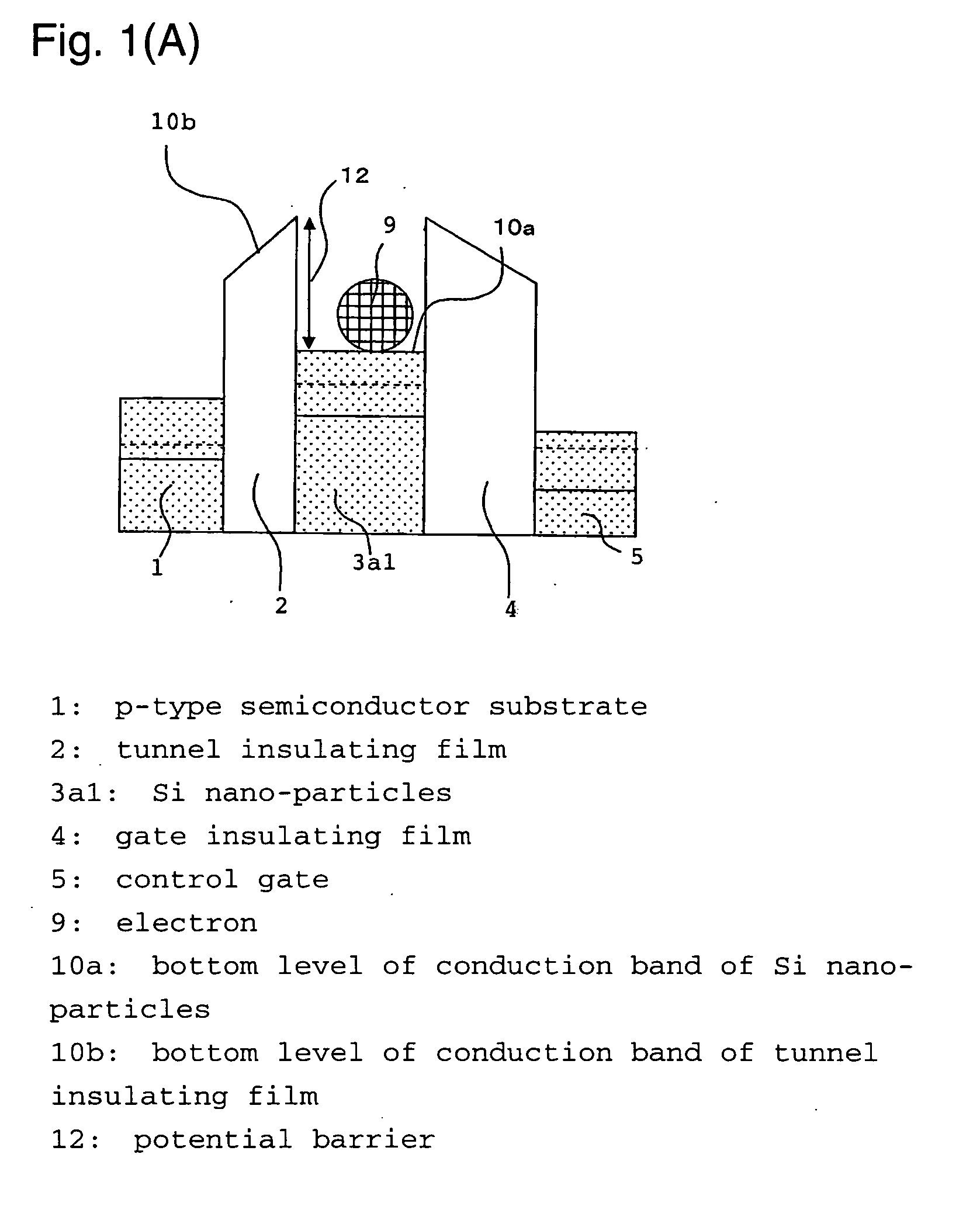
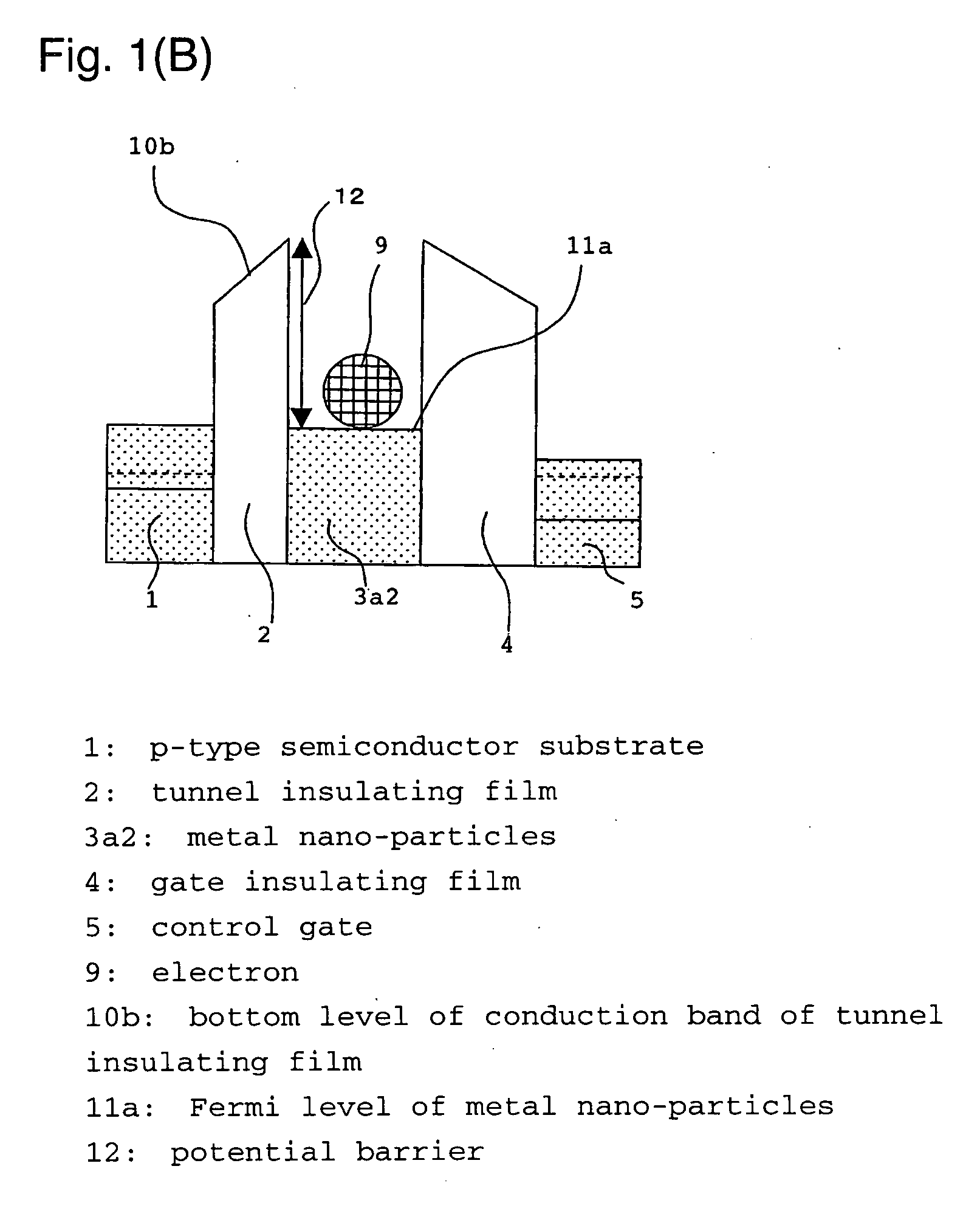
There has been a problem in conventional Si-type floating-gate type nonvolatile semiconductor memory devices that the charge retention characteristic is low due to insufficiently large electron affinity of Si, therefore improvement of the memory performances, such as scaling down of a memory cell and increasing operation speed, have been difficult to be achieved due to the essential problem. In order to solve the above problem, in the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device of the present invention, a material having large work function or large electron affinity or a material having a work function close to that of semiconductor substrate or of a control gate, is employed for a floating gate retaining charges. Further, an amorphous material having small electron affinity for an insulating matrix is used. Further, at a time of deposition of charge retention layer, the supply ratio of the nano-particle material and the insulating matrix material, such as the mixture ratio of materials of both phases in a target in a sputtering method, is adjusted. By these methods, the charge retention characteristic of the floating-gate type nonvolatile semiconductor memory device can be improved, and the above-mentioned problem of the nonvolatile semiconductor memory device can be solved.
Owner:ASAHI GLASS CO LTD +1
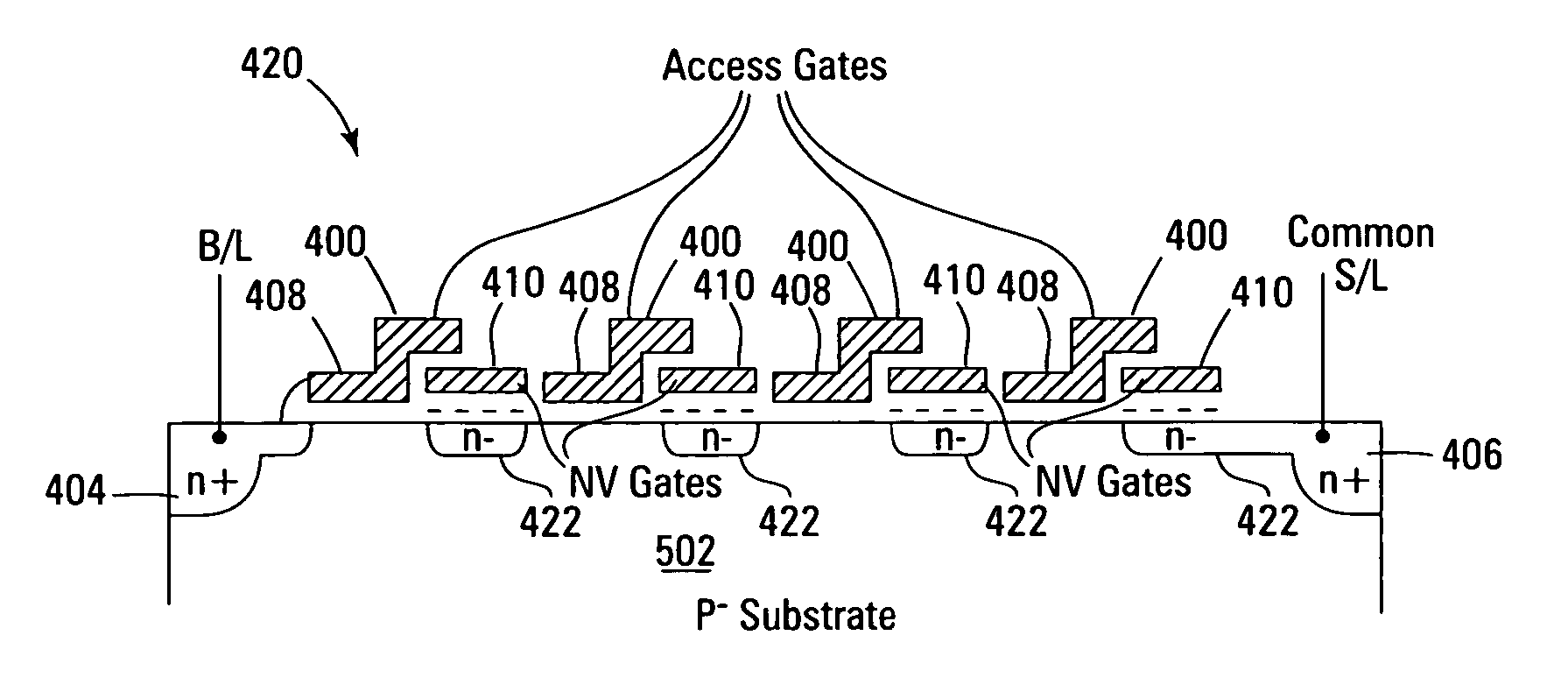
NAND based NMOS NOR flash memory cell, a NAND based NMOS nor flash memory array, and a method of forming a NAND based NMOS NOR flash memory array
InactiveUS20090279360A1Fast and asynchronous random accessReduce processingSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesBit lineCharge retention
A NOR flash nonvolatile memory device provides the memory cell size and a low current program process of a NAND flash nonvolatile memory device and the fast, asynchronous random access of a NOR flash nonvolatile memory device. The NOR flash nonvolatile memory device has an array of NOR flash nonvolatile memory circuits. Each NOR flash nonvolatile memory circuit includes a plurality of charge retaining transistors serially connected in a NAND string. A drain of a topmost charge retaining transistor is connected to a bit line associated with the serially connected charge retaining transistors and a source of a bottommost charge retaining transistor is connected to a source line associated with the charge retaining transistors. Each control gate of the charge retaining transistors on each row is commonly connected to a word line. The charge retaining transistors are programmed and erased with a Fowler-Nordheim tunneling process.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Electron blocking layers for electronic devices
InactiveUS20080150003A1Improve performanceEnhancement of charge retention propertySemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingSemiconductor devicesCharge retentionHafnium
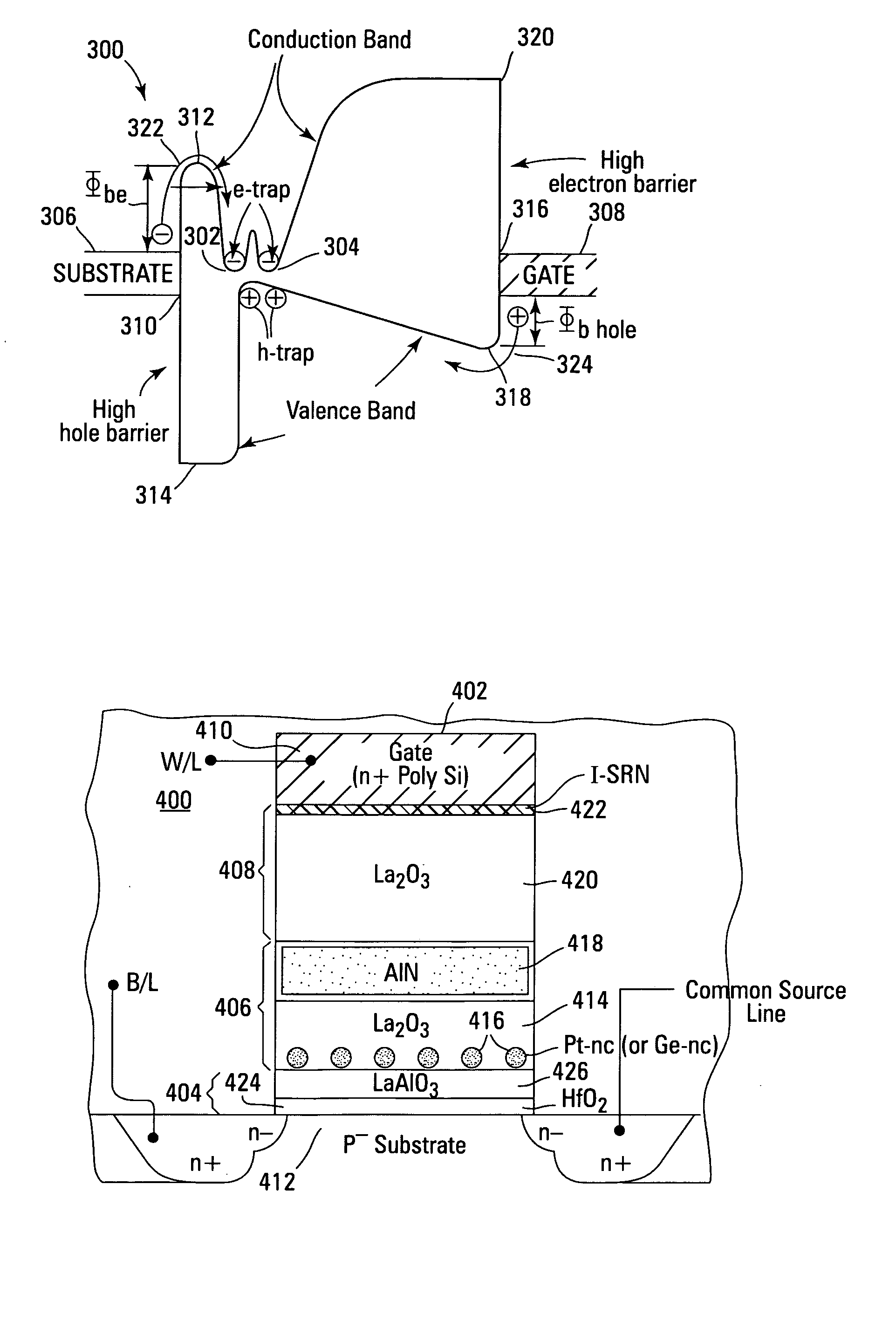
Methods and apparatuses for electronic devices such as non-volatile memory devices are described. The memory devices include a multi-layer control dielectric, such as a double or triple layer. The multi-layer control dielectric includes a combination of high-k dielectric materials such as aluminum oxide (Al2O3), hafnium oxide (HfO2), and / or hybrid films of hafnium aluminum oxide. The multi-layer control dielectric provides enhanced characteristics, including increased charge retention, enhanced memory program / erase window, improved reliability and stability, with feasibility for single or multistate (e.g., two, three or four bit) operation.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
Security display with central control system
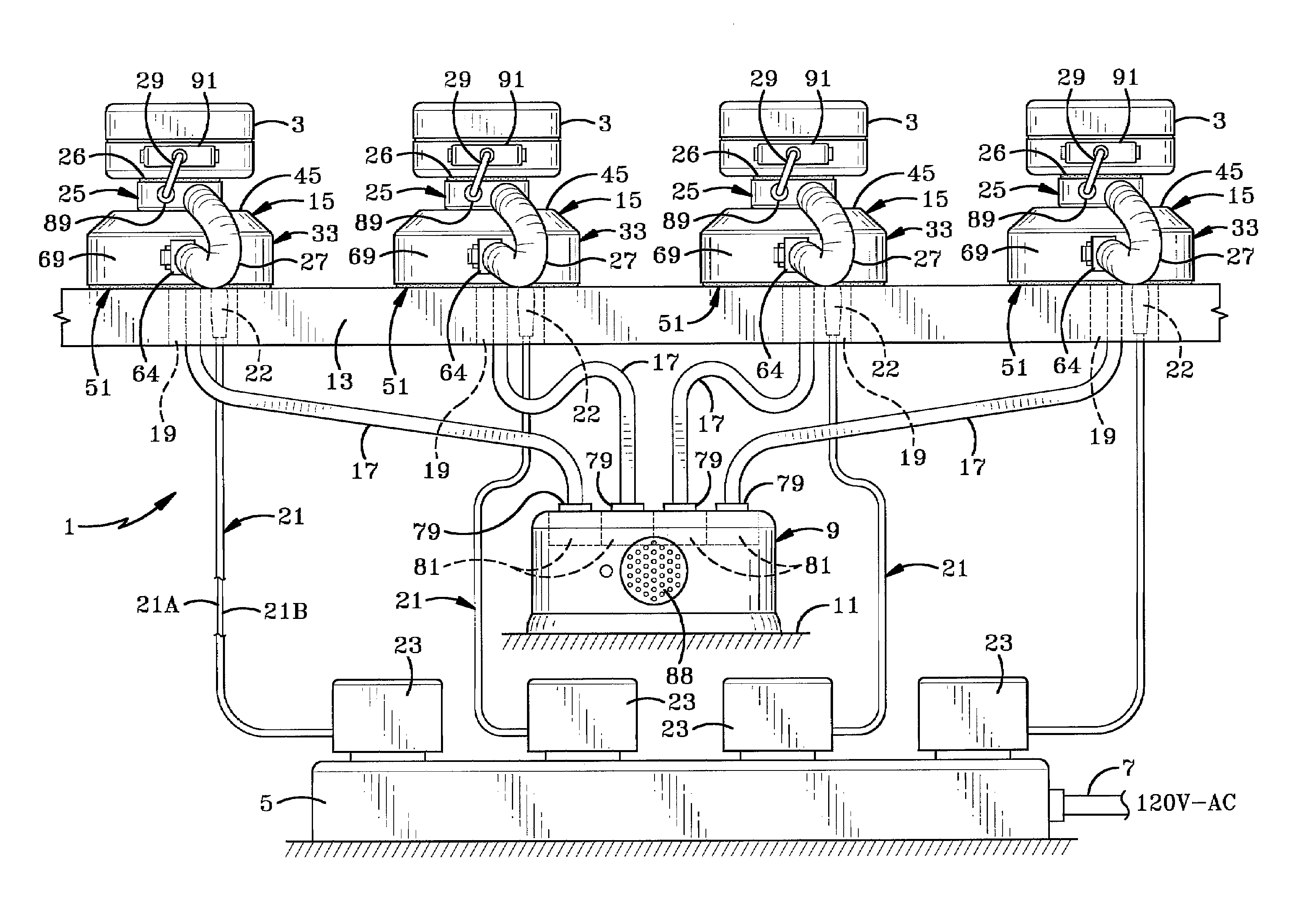
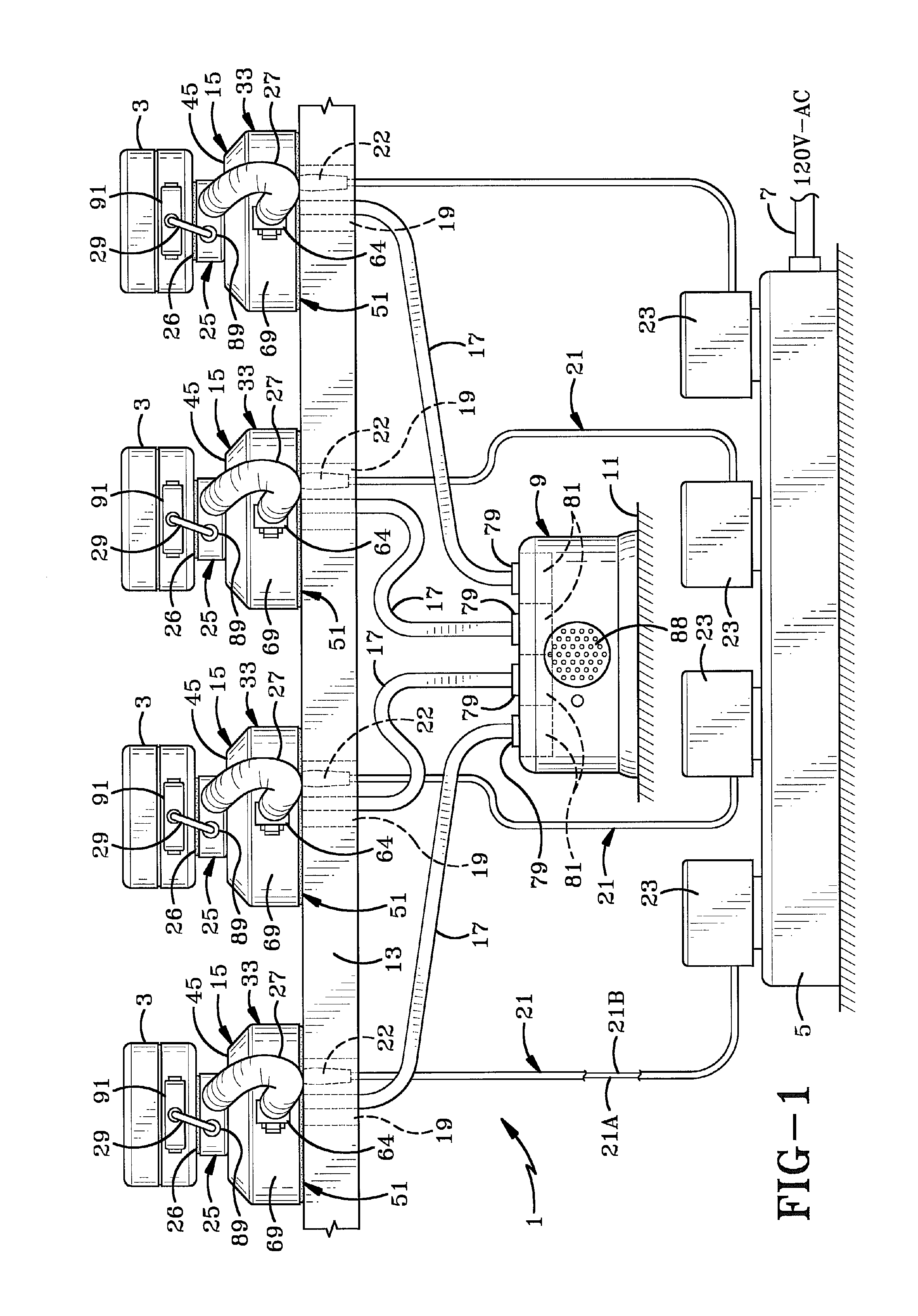
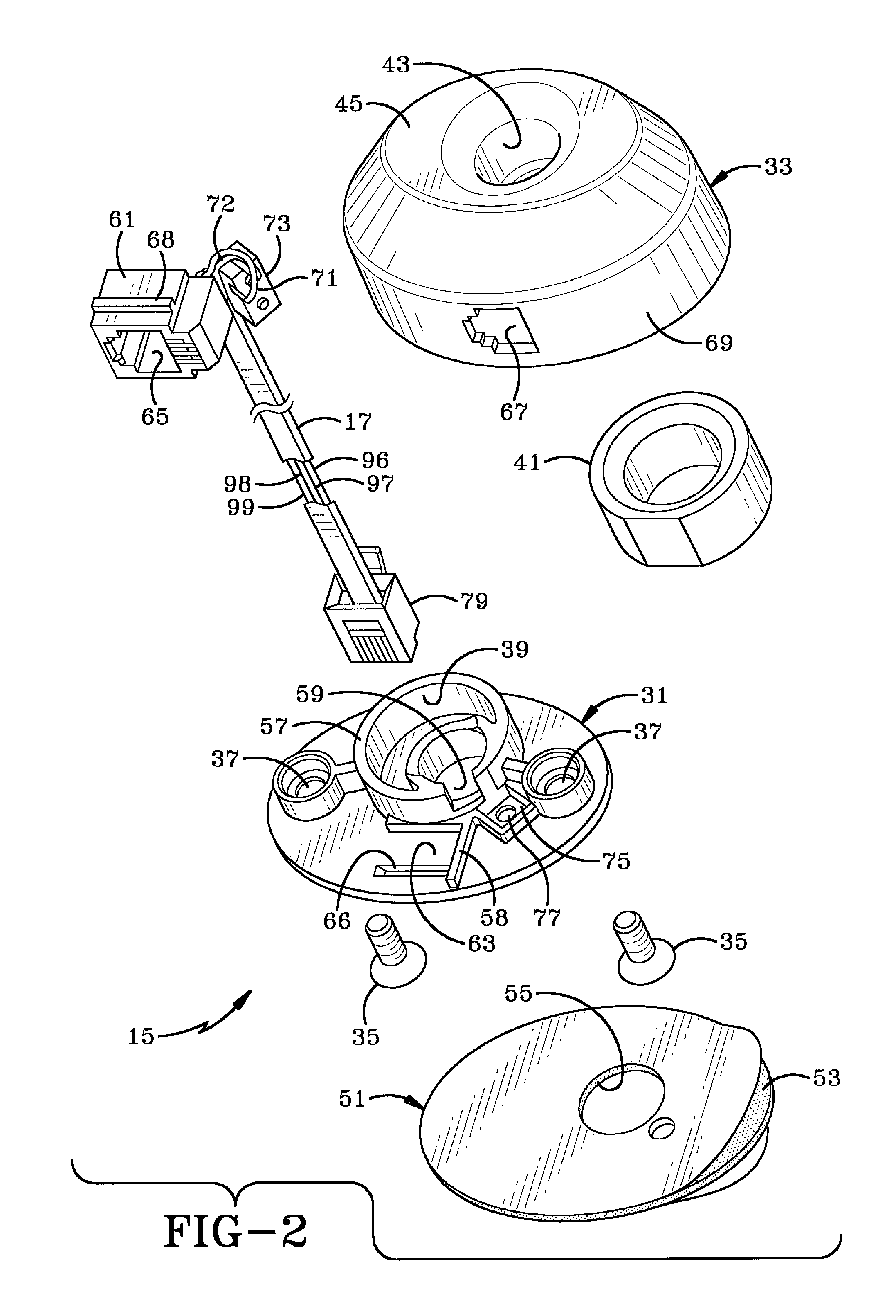
InactiveUS7626500B2Locks for portable objectsElectric connection structural associationsElectricityCharge retention
A security system for protecting a plurality of items of merchandise on display in a retail environment. Each of the items is connected to a sensor which is removably mounted in a display module and connected thereto by a power cord. A single alarm module located in an inaccessible location is connected to each of the display modules by another power cord. A power cord connects each of the display modules to a source of electricity for supplying electric power to the sensor through the display module and then to the displayed item for maintaining the charge on a battery of the displayed item. The alarm unit contains an internal power source for controlling the alarm circuitry. A plunger switch and LED may be contained in the sensor.
Owner:INVUE SECURITY PROD INC
Method and apparatus providing dark current reduction in an active pixel sensor
An imager has one or more pixel circuits arranged to receive negatively biased control signals at one or more gates associated with charge holding regions to reduce dark current generation and flow.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Storage nitride encapsulation for non-planar sonos NAND flash charge retention
InactiveUS20100006974A1Reduced dimensionSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesCharge retentionNitride
The present disclosure provides a method of manufacturing a microelectronic device. The method includes forming recessed shallow trench isolation (STI) features in a semiconductor substrate, defining a semiconductor region between adjacent two of the recessed STI features; forming a tunnel dielectric feature within the semiconductor region; forming a nitride layer on the recessed STI features and the tunnel dielectric feature; etching the nitride layer to form nitride openings within the recessed STI features; partially removing the recessed STI features through the nitride openings, resulting in gaps between the nitride layer and the recessed STI features; and forming a first dielectric material on surfaces of the nitride layer, sealing the nitride openings.
Owner:TAIWAN SEMICON MFG CO LTD
Nonvolatile semiconductor memory device
InactiveUS20070278563A1Easy to keepReduce charge leakageSolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCharge retentionSemiconductor package
An object is to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device which is excellent in a writing property and a charge retention property. In addition, another object is to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor memory device capable of reducing writing voltage. A nonvolatile semiconductor memory device includes a semiconductor layer or a semiconductor substrate including a channel formation region between a pair of impurity regions that are formed apart from each other, and a first insulating layer, a plurality of layers formed of different nitride compounds, a second insulating layer, and a control gate that are formed in a position which is over the semiconductor layer or the semiconductor substrate and overlaps with the channel formation region.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
Low power non-volatile memory and gate stack
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that facilitate the use of band-gap engineered gate stacks with asymmetric tunnel barriers in reverse and normal mode floating node memory cells in NOR or NAND memory architectures that allow for direct tunnel programming and erase, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. The low voltage direct tunneling program and erase capability reduces damage to the gate stack and the crystal lattice from high energy carriers, reducing write fatigue and enhancing device lifespan. The low voltage direct tunnel program and erase capability also enables size reduction through low voltage design and further device feature scaling. Memory cells of the present invention also allow multiple bit storage. These characteristics allow memory device embodiments of the present invention to operate within the definition of a universal memory, capable of replacing both DRAM and ROM in a system.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
High performance multi-level non-volatile memory
ActiveUS20070045711A1Increased device feature scalingEfficient erasureTransistorSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingCharge retentionNon symmetric
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that utilize band engineered gate-stacks and multiple charge trapping layers allowing a multiple trapping site gate-insulator stack memory cell that utilizes a band engineered direct tunneling or crested barrier tunnel layer and charge blocking layer for high speed programming / erasure. Charge retention is enhanced by utilization of nano-crystals and / or bulk trapping materials in a composite non-conductive trapping layer and a high K dielectric insulating layers. The band-gap engineered gate-stack with asymmetric direct tunneling or crested barrier tunnel layers of the non-volatile memory cells of embodiments of the present invention allow for low voltage high speed tunneling programming and erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. Memory cell embodiments of the present invention allow multiple levels of bit storage in a memory cell through multiple charge centroids and / or multiple threshold voltage levels.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Exposed hollow carrier perforation gun and charge holder
InactiveUS20100089643A1Easily assembled and armedIncrease powerNuclear explosivesFluid removalCharge retentionDetonation
The perforation gun is comprised of a tubular carrier, a charge holder, a plurality of sealed charges, and a detonating cord. The tubular carrier has a length and a plurality of openings. The charge holder has a length and is comprised of a plurality of mounting locations which are each capable of receiving one of the sealed charges. The charge holder is capable of being secured within the carrier. The detonating cord is coupled to at least one sealed charge. In the mounted position and when the charge holder is secured within the carrier, the charges are aligned with the openings in the carrier such that, upon detonation, charge blasts emitted from the charges exit though the carrier openings and perforate a well casing and cement. In one aspect of the invention, the carrier openings are spirally arranged and spaced along the length of the carrier. In still another aspect of the invention, the openings are vertically arranged and spaced along the length of the carrier. In still another aspect of the invention, the carrier is closed at the top and bottom. In still another aspect of the invention, the carrier is capable of capturing debris created by a charge blast emitted from the sealed charges.
Owner:VIDAL MIRABEL
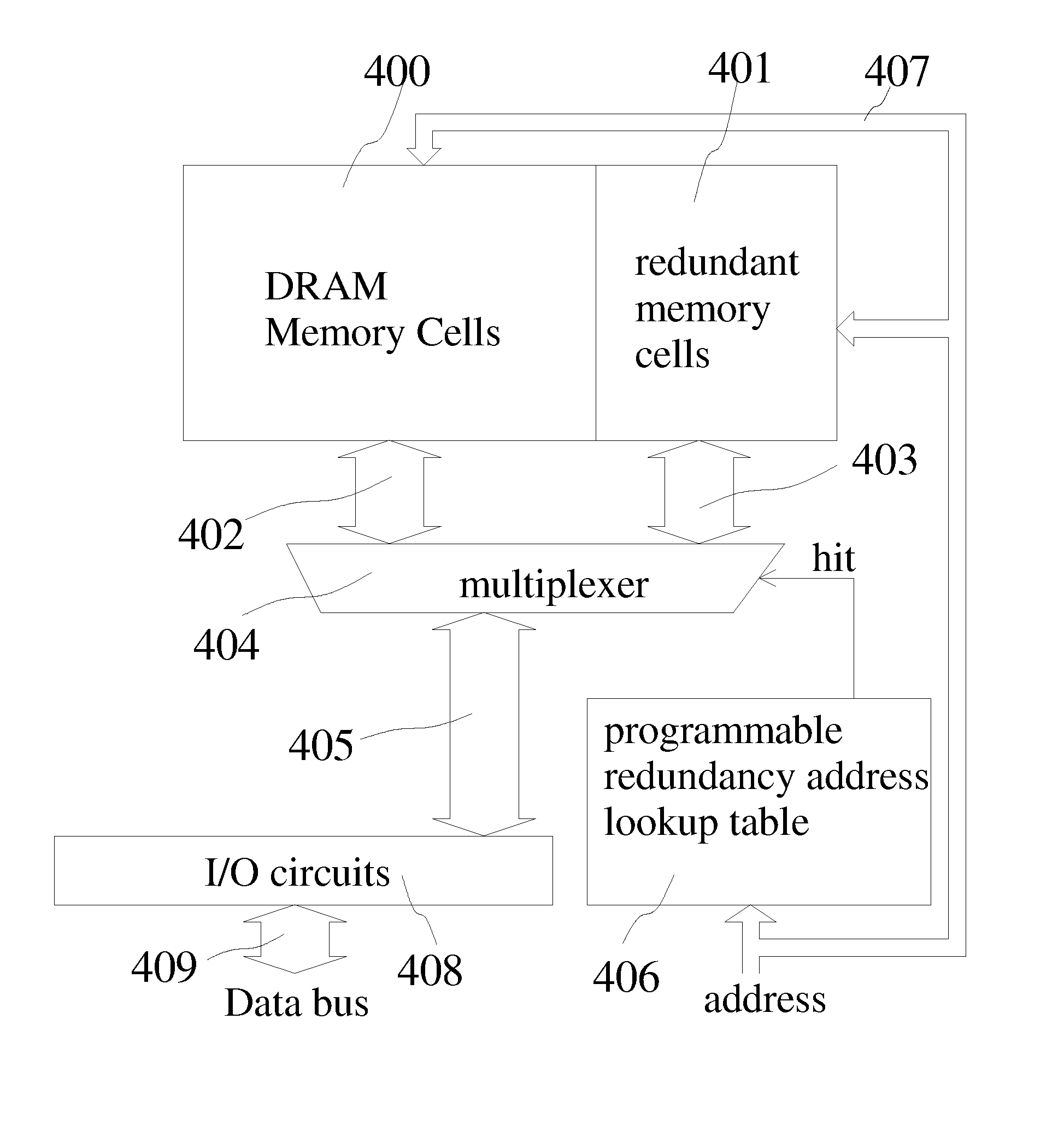
Power efficient dynamic random access memory devices
InactiveUS20120243299A1Improve DRAM power efficiencyReduce DRAM refresh powerDigital storagePower efficientCharge retention
The present invention provides methods and structures for improving refresh power efficiency of dynamic random access memory devices. By measuring charge retention properties of reference cells that have substantially the same structures as normal DRAM memory cells, the refresh rate of DRAM devices can be adjusted with better reliability. The reliability is further improved by using ECC circuits and / or field programmable redundancy circuits.
Owner:SHAU JENG JYE
Nonvolatile semiconductor storage device and method for manufacturing the same
InactiveUS20070228452A1Reduce etch timeEtching of the semiconductor layer is suppressedTransistorSolid-state devicesElectrical resistance and conductanceCharge retention
It is an object to provide a nonvolatile semiconductor storage device that prevents increase in a contact resistance value due to etching of a semiconductor layer when etching an interlayer insulating film and that has superiority in a writing characteristic and an electric charge-holding characteristic, and a manufacturing method thereof. A conductive layer is provided between a source or drain region and a source or drain wiring. The conductive layer is made of the same conductive layer that forms a control gate electrode. An insulating film is provided so as to cover the conductive layer, and the insulating film has a contact hole for exposing part of the conductive layer. The source or drain wiring is formed so that the contact hole is filled.
Owner:SEMICON ENERGY LAB CO LTD
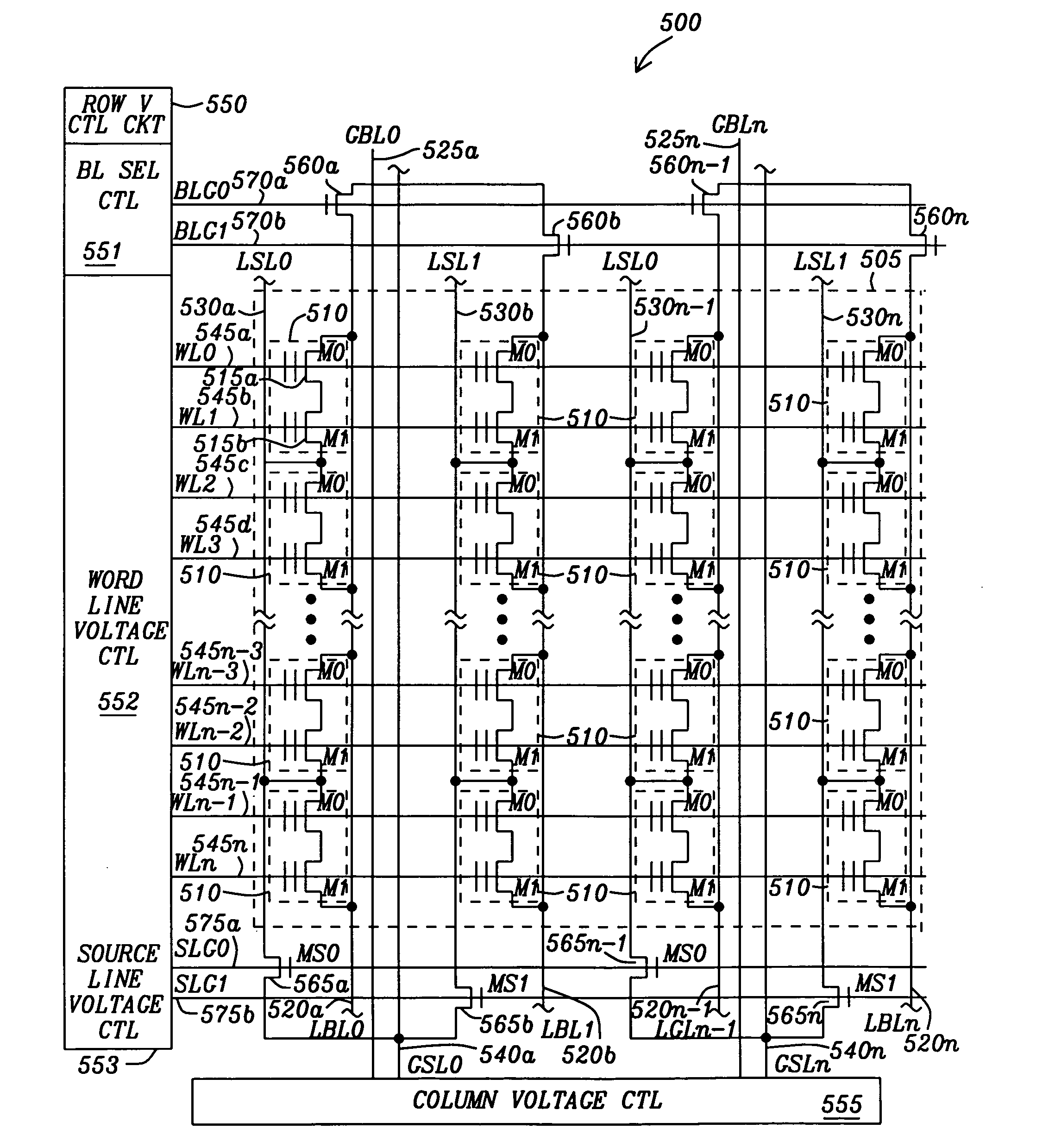
NAND string based NAND/NOR flash memory cell, array, and memory device having parallel bit lines and source lines, having a programmable select gating transistor, and circuits and methods for operating same
InactiveUS20090310414A1Eliminate the effects ofRead-only memoriesDigital storageBit lineDriver circuit
A nonvolatile memory device includes a nonvolatile memory array including a plurality of charge retaining transistors arranged in rows and columns. The device has a plurality source lines formed in parallel with the bit lines associated with each column. Row decode / driver circuits are connected to blocks of the charge retaining transistors for controlling the application of the necessary read, program, and erase signals. Erase count registers, each of the erase count registers associated with one block of the array of the charge retaining transistors for storing an erase count for the associated block for determining whether a refresh operation is to be executed. Groupings on each column of the array of charge retaining transistors are connected as NAND series strings where each NAND string has a select gating charge retaining transistor connected to the top charge retaining transistor for connecting the NAND series string to the bit lines.
Owner:APLUS FLASH TECH
Electron blocking layers for electronic devices
Methods and apparatuses for electronic devices such as non-volatile memory devices are described. The memory devices include a multi-layer control dielectric, such as a double or triple layer. The multi-layer control dielectric includes a combination of high-k dielectric materials such as aluminum oxide, hafnium oxide, and / or hybrid films of hafnium aluminum oxide. The multi-layer control dielectric provides enhanced characteristics, including increased charge retention, enhanced memory program / erase window, improved reliability and stability, with feasibility for single or multi state (e.g., two, three or four bit) operation.
Owner:SANDISK TECH LLC
High density cluster based perforating system and method
A perforating short gun for use in a horizontal well casing. The gun includes a gun carrier and a charge holder to carry shaped charges. The charge holder is inserted into the gun carrier and a selected length of the gun carrier includes internal features created therein to a depth in an inside wall of the gun carrier. The internal features are located and configured to align with a shaped charge, creating a standoff between the shaped charge and the internal feature such that when the charge is detonated it creates an opening through the internal feature.
Owner:WELLS FARGO BANK NAT ASSOC +1
High density NAND non-volatile memory device
ActiveUS7829938B2Reduce harmImproved high density memory device and arraySolid-state devicesRead-only memoriesCharge retentionTrapping
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that utilize dual gate (or back-side gate) non-volatile memory cells with band engineered gate-stacks that are placed above or below the channel region in front-side or back-side charge trapping gate-stack configurations in NAND memory array architectures. The band-gap engineered gate-stacks with asymmetric or direct tunnel barriers of the floating node memory cells of embodiments of the present invention allow for low voltage tunneling programming and efficient erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. The memory cell architecture also allows for improved high density memory devices or arrays with the utilization of reduced feature word lines and vertical select gates.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
High performance multi-level non-volatile memory device
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that utilize band engineered gate-stacks and multiple charge trapping layers allowing a multiple trapping site gate-insulator stack memory cell that utilizes a band engineered direct tunneling or crested barrier tunnel layer and charge blocking layer for high speed programming / erasure. Charge retention is enhanced by utilization of nano-crystals and / or bulk trapping materials in a composite non-conductive trapping layer and a high K dielectric insulating layers. The band-gap engineered gate-stack with asymmetric direct tunneling or crested barrier tunnel layers of the non-volatile memory cells of embodiments of the present invention allow for low voltage high speed tunneling programming and erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention. Memory cell embodiments of the present invention allow multiple levels of bit storage in a memory cell through multiple charge centroids and / or multiple threshold voltage levels.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Ultrasonic transducer cell
ActiveUS20080089181A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsSeismologyUltrasonic sensorCharge retention
An ultrasonic transducer cell according to the present invention includes: a substrate; a charge holding portion provided on the substrate; a lower electrode provided on the charge holding portion and used to input and output a signal; and a vibration membrane provided above the lower electrode to be separated from the lower electrode with a cavity, and configured to include at least an insulating film and an upper electrode provided on the insulating film.
Owner:OLYMPUS CORP
Solid-state imaging device, method of manufacturing solid-state imaging device, and electronic apparatus
InactiveUS20110248371A1Suppress noiseTransistorTelevision system detailsCharge retentionPhotoelectric conversion
Provided is a solid-state imaging device including: a first-conductivity-type substrate; a second-conductivity-type well formed in a surface side of the first-conductivity-type substrate; a photoelectric conversion area configured with a first-conductivity-type-impurity area formed in the second-conductivity-type well to convert incident light to charges; a first-conductivity-type-charge retaining area configured with the first-conductivity-type-impurity area formed in the second-conductivity-type well to retain the charges converted by the photoelectric conversion area until the charges are read out; a charge voltage conversion area configured with the first-conductivity-type-impurity area formed in the second-conductivity-type well to convert the charges retained in the charge retaining area to a voltage; and a first-conductivity-type-layer area configured by forming a first-conductivity-type-in a convex shape from a boundary between the first-conductivity-type substrate and the second-conductivity-type well to a predetermined depth of the surface side under at least one portion of the charge retaining area and the charge voltage conversion area.
Owner:SONY CORP
Deaprom and transistor with gallium nitride or gallium aluminum nitride gate
InactiveUS20020126536A1Detect signal easilyReduced barrier energyTransistorRead-only memoriesProgrammable read-only memoryCharge retention
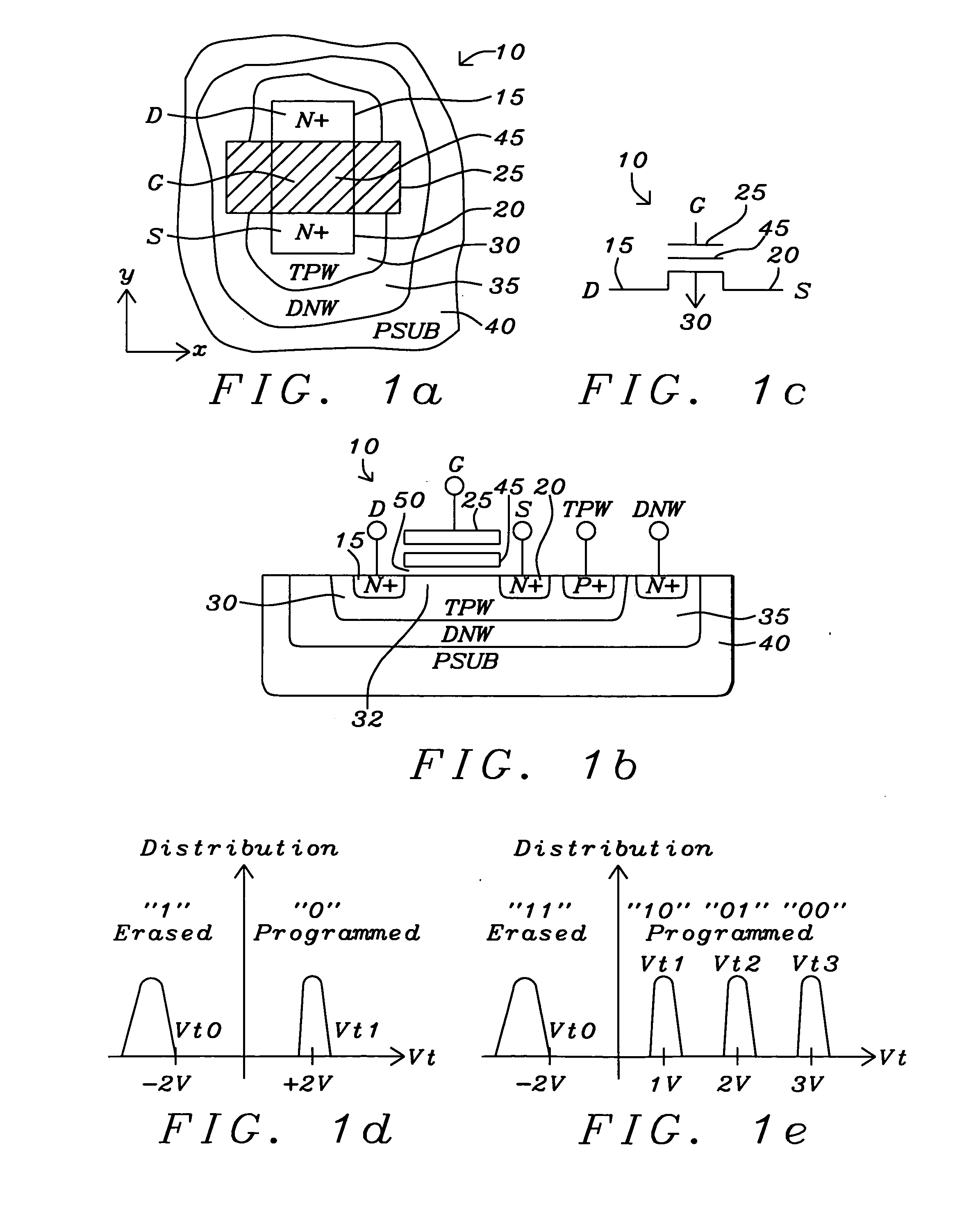
A floating gate transistor has a reduced barrier energy at an interface between a gallium nitride (GaN) or gallium aluminum nitride (GaAlN) floating gate an adjacent gate insulator, allowing faster charge transfer across the gate insulator at lower voltages. Data is stored as charge on the floating gate. The data charge retention time on the floating gate is reduced. The data stored on the floating gate is dynamically refreshed. The floating gate transistor provides a dense and planar dynamic electrically alterable and programmable read only memory (DEAPROM) cell adapted for uses such as for a dynamic random access memory (DRAM) or a dynamically refreshed flash EEPROM memory. The floating gate transistor provides a high gain memory cell and low voltage operation.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Band engineered nano-crystal non-volatile memory device utilizing enhanced gate injection
Non-volatile memory devices and arrays are described that utilize reverse mode non-volatile memory cells that have band engineered gate-stacks and nano-crystal charge trapping in EEPROM and block erasable memory devices, such as Flash memory devices. Embodiments of the present invention allow a reverse mode gate-insulator stack memory cell that utilizes the control gate for programming and erasure through a band engineered crested tunnel barrier. Charge retention is enhanced by utilization of high work function nano-crystals in a non-conductive trapping layer and a high K dielectric charge blocking layer. The band-gap engineered gate-stack with symmetric or asymmetric crested barrier tunnel layers of the non-volatile memory cells of embodiments of the present invention allow for low voltage tunneling programming and erase with electrons and holes, while maintaining high charge blocking barriers and deep carrier trapping sites for good charge retention.
Owner:MICRON TECH INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com