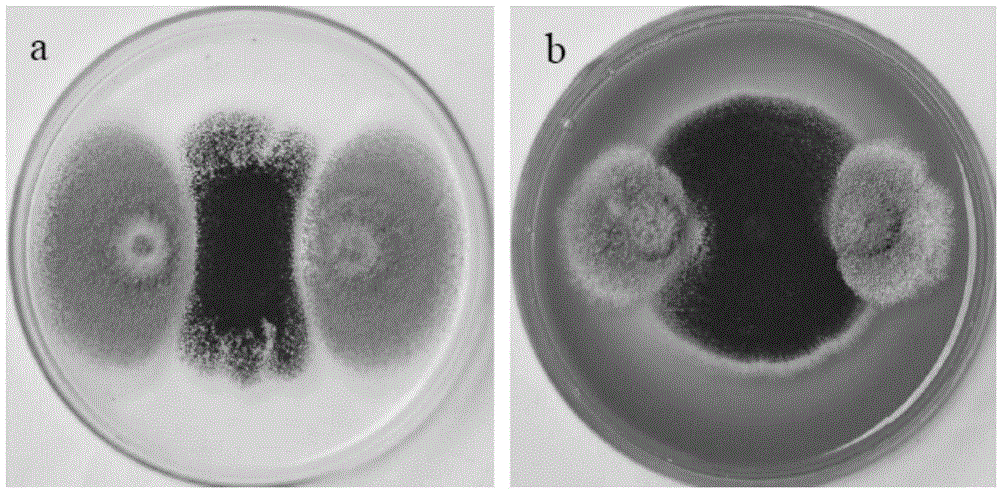
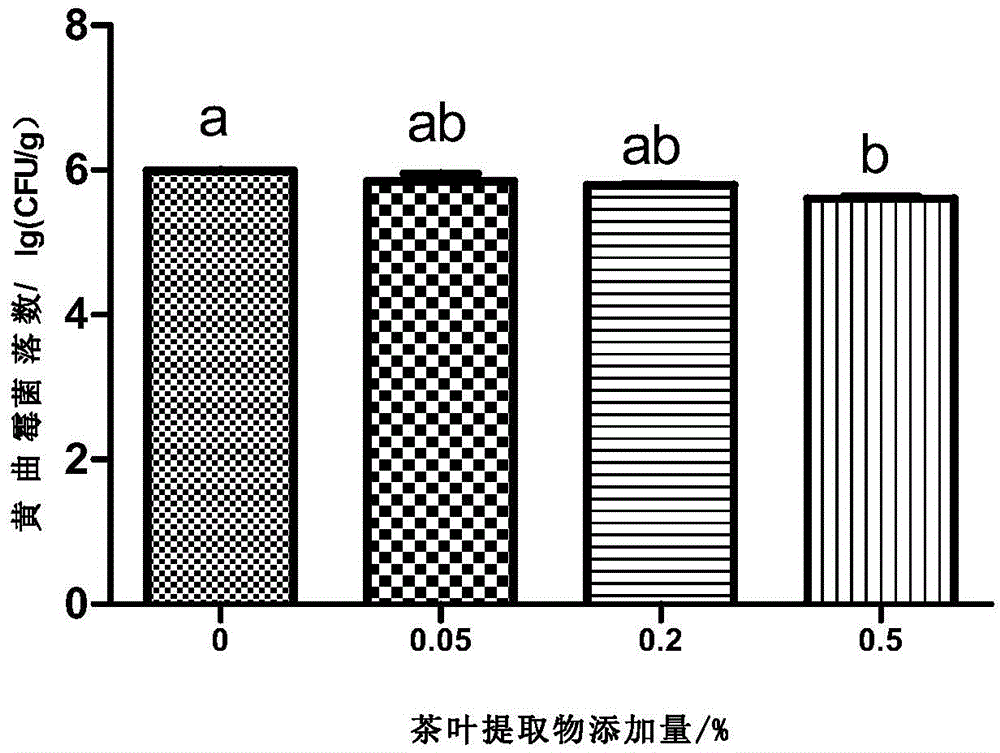
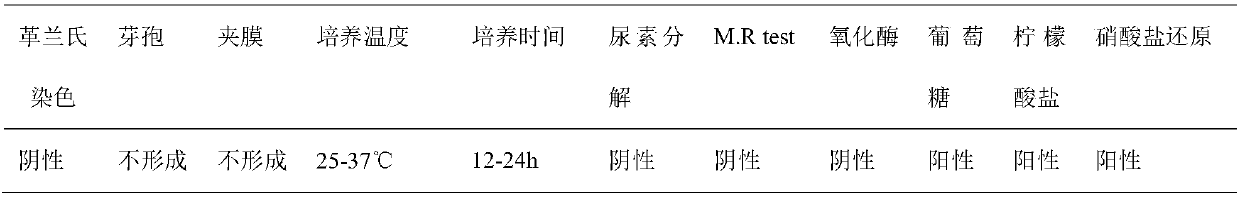
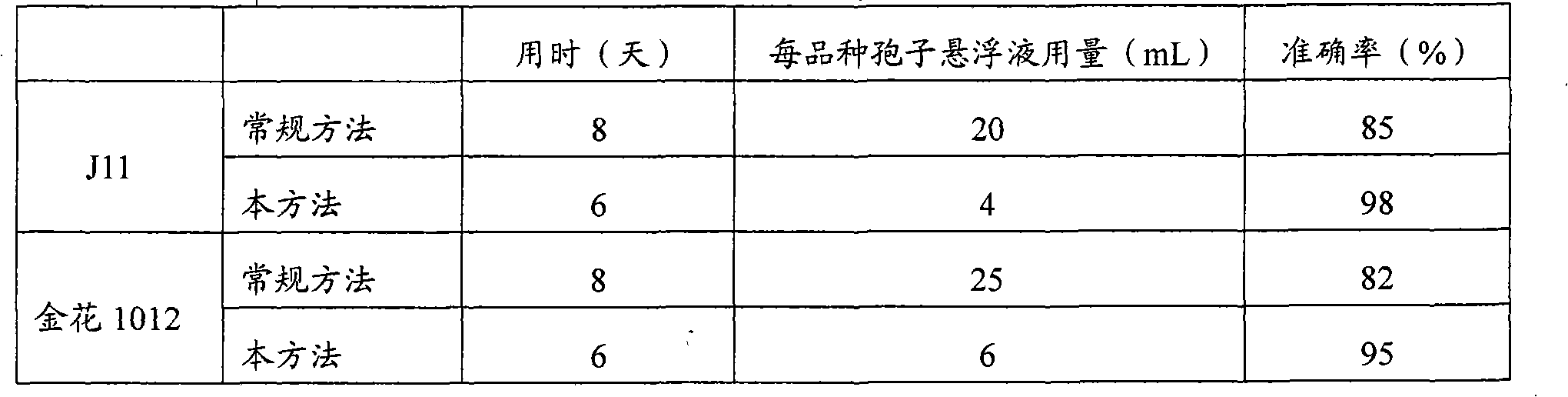
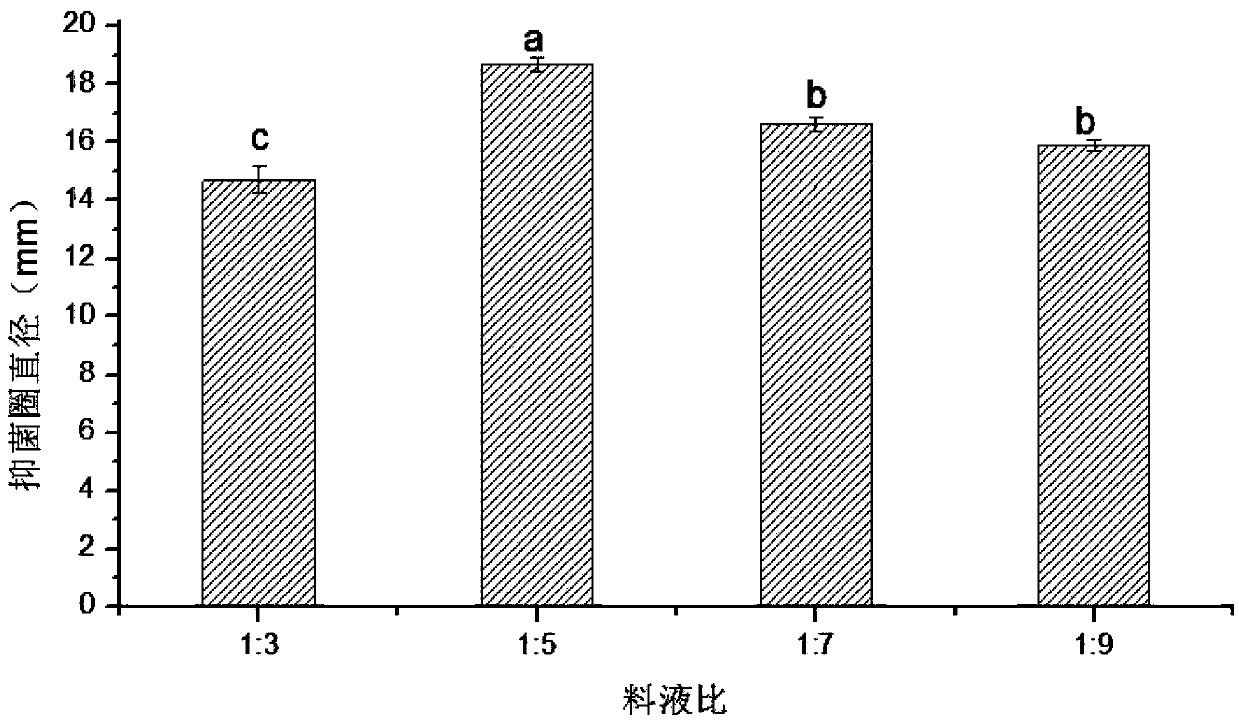
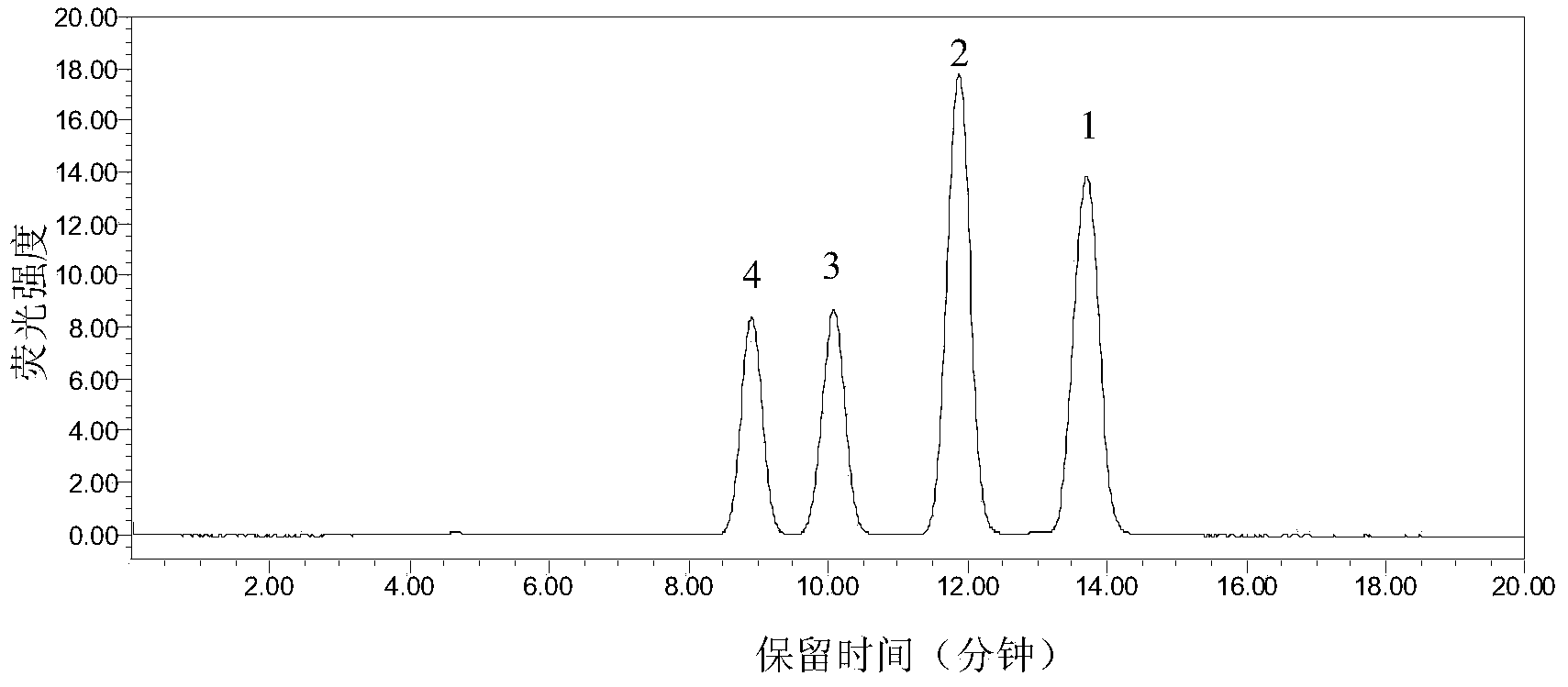
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
73 results about "Trimeresurus flavoviridis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Protobothrops flavoviridis is a species of venomous pit viper endemic to the Ryukyu Islands of Japan. No subspecies are currently recognized. Local common names include "habu", "Okinawa habu", and "Kume Shima habu".
Aspergillus flavus strain without producing aspergillus flavus toxin and uses thereof
InactiveCN101363006AControl latent infestationReduce the risk of contaminationBiocideFungiMicroorganismAspergillus
The invention discloses an Aspergillus flavus strain for not producing toxins of Aspergillus flavus, the Aspergillus flavus strain belongs to the Aspergillus flavus of Aspergillus, the collection name is: Aspergillus flavus strain A051, the collection unit is: China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, the collection data is: June 24, 2008, and the collection No. is: CGMCC NO.2556. The invention further discloses the use of the Aspergillus flavus strain, and the use is characterized in that: the Aspergillus flavus strain is used for inhibiting Aspergillus flavus pathogenic bacteria groups of the toxins of the Aspergillus flavus in peanut field soil.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Bacillus amyloliquefacien for degrading aflatoxin B1 in peanut meal
ActiveCN103966147AGrowth inhibitionInhibitionBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismBacillus amyloliquefaciens
The invention discloses a bacillus amyloliquefacien for degrading aflatoxin B1 in peanut meal, and belongs to the technical field of applied microbiology. According to the invention, a bacillus amyloliquefacien capable of significantly inhibiting the growth of Aspergillus flavus and efficiently degrading aflatoxin B1 can be obtained by screening and the content of aflatoxin B1 in detoxified peanut meal is lower than the national limited standard and achieves the safe feeding level after the bacillus amyloliquefacien is applied to moldy peanut meal. Furthermore, the detoxification mechanism of the strain is the degradation effect of extracellular metabolites, and generation of the active substance is of a non-induced type, which is an inherent attribute of the strain. The features of the strain provide the possibility for biocontrol of Aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin B1 in industries such as feed and foods and the strain has very high application values.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Bacillus subtilis and application of same in resisting aspergillus
InactiveCN102965306AImprove the level of prevention and controlPromote export tradeBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementBacteroidesActinomyces flaveolus
The invention discloses bacillus subtilis and an application of the same in resisting aspergillus. The bacillus subtilis has antagonistic action in aspergillus flavus. A method for screening the bacillus subtilis which has antagonistic action in the aspergillus flavus from soil comprises the following steps: a, bacteria isolating; b, aspergillus culturing and spore liquid preparing; c, aspergillus-resistant strain screening; and d, aspergillus-resistant strain rescreening. Through aflatoxin panel screening tests and toxin production aspergillus flavus antagonistic tests, aspergillus flavus antagonistic strains in the peanut cultivation fields and storage warehouses are screened. A method for reasonably and effectively screening the aspergillus flavus antagonistic strains is established, so that the appropriate required aflatoxin inhibition strains are obtained. The bacillus subtilis is applied to the easy aflatoxin contamination stages which are before and after harvesting crops of peanuts and the like and during storage periods and the like, the aflatoxin prevention and control levels of the crops of export peanuts and the like can be improved, export risks are lowered, and the export trade of the crops and products thereof are promoted.
Owner:中华人民共和国潍坊出入境检验检疫局
Aspergillus niger and application thereof in biological prevention and control of aflatoxin
ActiveCN104673682AGrowth inhibitionInhibition of toxin productionBiocideFungiMicroorganismAflatoxin contamination
The invention discloses Aspergillus niger and application thereof in biological prevention and control of aflatoxin. The strain is Aspergillus niger RAF106 collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on August 27, 2014 with a collection number of CGMCC NO.9608 at Yard NO.1, Building NO.3, Beichen West Road, Chaoyang District, Beijing. Under the synergistic effect of plant polyphenol, the competition inhibiting effect of the Aspergillus niger strain screened in the invention is increased greatly. The strain is capable of remarkably inhibiting growth of Aspergillus flavus and generation of aflatoxin, and is also capable of efficiently degrading aflatoxin with high specificity, thereby having very high industrial application values. For agricultural products or feed polluted by aflatoxin, aflatoxin can be decomposed through fermentation of the strain, and the content of aflatoxin is reduced by 80.7% after corn containing aflatoxin is fermented for 48h.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
Technical process for inhibiting Aspergillus flavus from hazarding peanut production and preservation
The invention aims at the shortcoming of the prior art in preventing aspergillus flavus from damaging crops, and provides a complete production technology for preventing aspergillus flavus in the processes of peanut growth, reproduction and storage. The production technology can effectively reduce the content of aflatoxin in peanuts, and reduce the risks of aflatoxin infection of peanuts in the sowing, storing and processing links. The production technology can reduce the content of aflatoxin in peanuts, improve food safety, promote import and export trade of peanuts, and prevent Aspergillus flavus from damaging the production and storage of peanuts.
Owner:长沙水地沙生物科技有限公司
Serratia marcescens biocontrol bacterium for efficiently inhibiting aspergillus flavus compounded aflatoxin and its application
The invention belongs to the field of a microorganism, and particularly relates to serratia marcescens biocontrol bacterium for efficiently inhibiting aspergillus flavus compounded aflatoxin and its application. The serratia marcescens biocontrol bacterium 3J4SM has been preserved in the China typical culture preservation center (CCTCC for short) on June 13, 2017; the preservation address is WuhanUniversity of Wuhan of China; the preservation number is CCTCC No. M2017328. The enterobacter cloacae biocontrol strain 3J4SM can be used for inhibiting aspergillus flavus compounded aflatoxin and preventing the aflatoxin pollution of grain crops.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
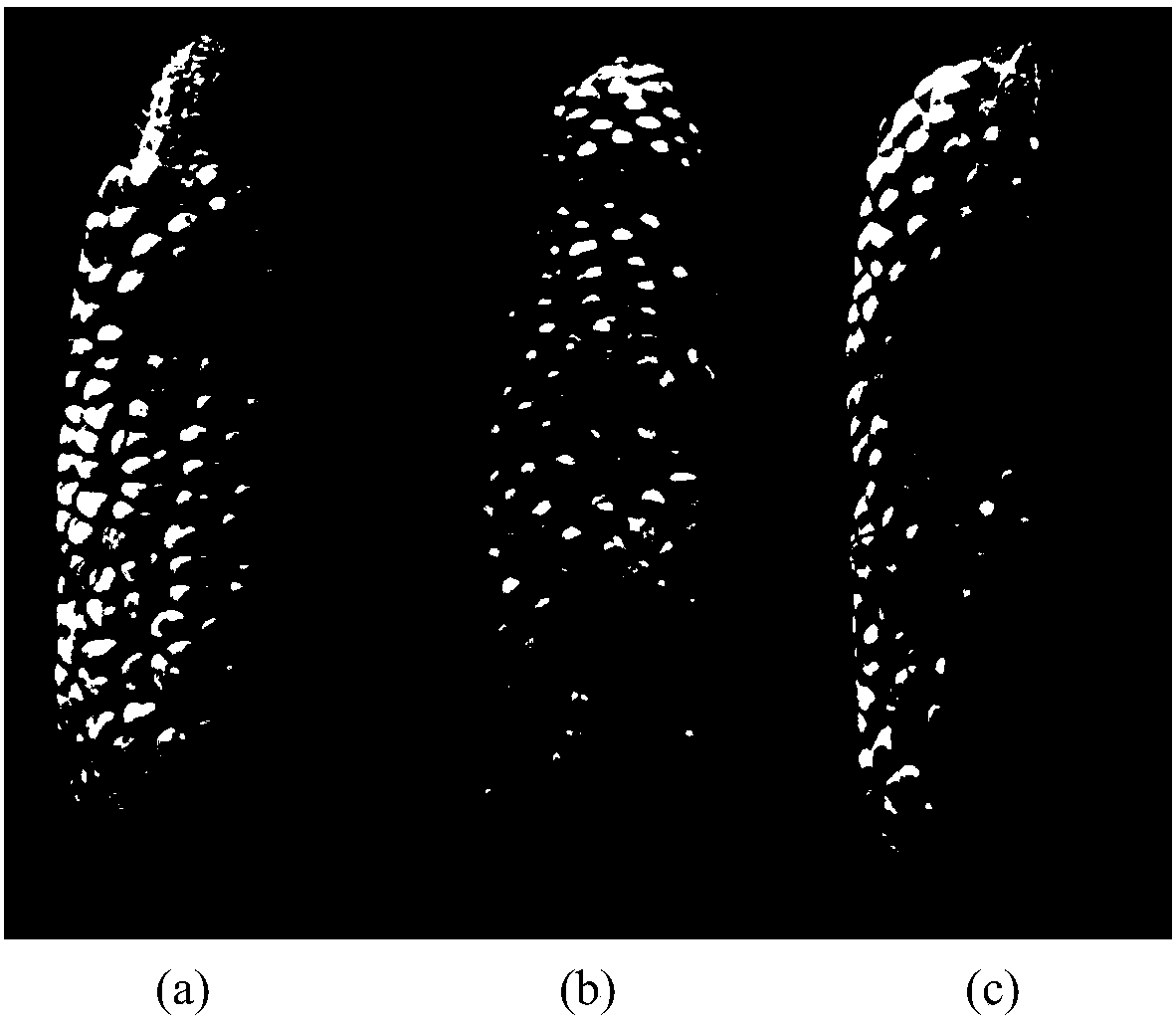
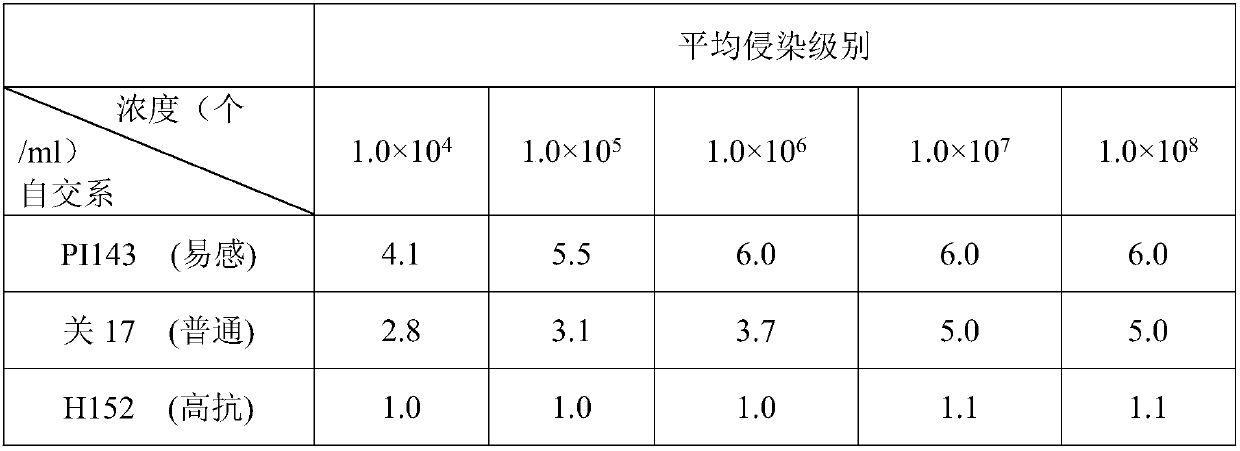
Indoor detection method for resistance of peanuts to infection of Aspergillus flavus
InactiveCN101608211ASpeed up the infection processTo achieve the purpose of resistance identification at the same timeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMaximum diameter
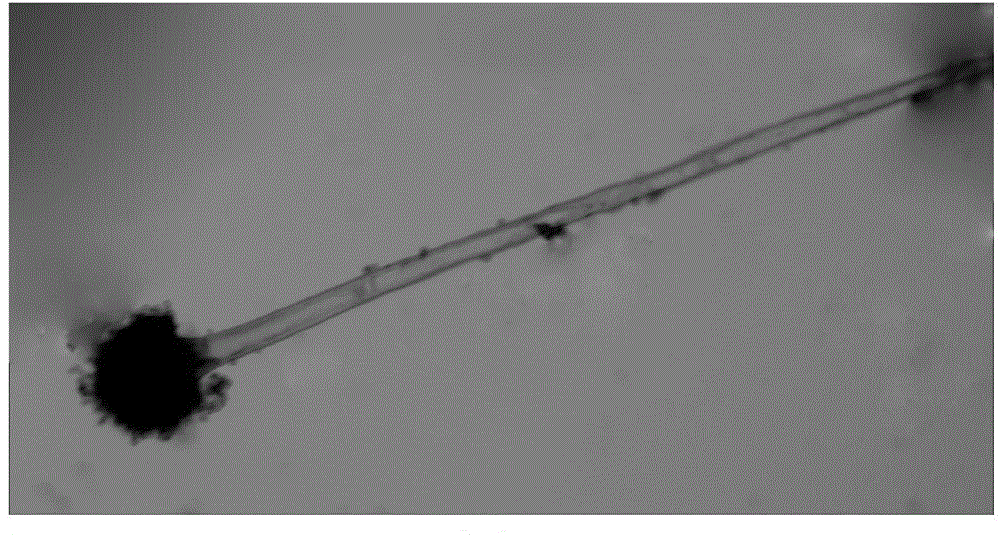
An indoor detection method for resistance of peanuts to infection of Aspergillus flavus includes the following steps of: drying the harvested seeds of peanuts to reach the water content of 8-10 percent, blending the bacterial strain of Aspergillus flavus into spore suspension with the concentration of 0.05-1*10 pieces / mL; sterilizing the dried peanut seeds with a regular method and bleaching the seeds with sterile water to recover the water content of the seeds to 15-20 percent; creating a cut ready for the infection of Aspergillus flavus on the peanut seeds by adopting a method of transverse girdling of testa and uniformly drilling a place which has the maximum diameter of kernel and is perpendicular to the section of seed leaf; putting filter paper in a culture dish, adding the spore suspension to moisten the filter paper, soaking the treated peanut seeds in the spore suspension for 3-5min, taking out the seeds, then using sterile filter paper to suck the surfaces of the seeds dry, putting the seeds on the filter paper of the culture dish, subsequently shielding the culture dish with a dish cover, and putting the culture dish in an incubator to cultivate the seeds for 5-6days under the culture conditions including humidity being 80-90 percent and temperature being 28-30 DEG C; and evaluating the resistance according to the result that the kernel surface and hole of peanuts are infected with the Aspergillus flavus.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Preparation method of tartary buckwheat yellow koji rice wine
PendingCN105112200AWith health functionKeep active ingredientsMetabolism disorderAntinoxious agentsBiotechnologyPolygonum fagopyrum
The invention discloses a preparation method of tartary buckwheat yellow koji rice wine. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating Aspergillus flavus into a medium according to an inoculation amount of 0.5-2%; adding traditional Chinese medicinal material fine powder with the mass fraction of 0.5-2%, and culturing to generate mycelia; collecting a liquid carrying strain in the medium to obtain medicinal koji; and steaming a fermentation substrate, mixing the steamed substrate with the medicinal koji and yeast, naturally fermenting, squeezing, filtering, and disinfecting to obtain the tartary buckwheat yellow koji rice wine. Tartary buckwheat and other traditional Chinese medicinal materials are co-fermented under the action of Aspergillus flavus, yeast is added to ferment the fermentation substrate rice or other cereals in order to prepare the yellow rice wine with health functions, effective components of tartary buckwheat and the traditional Chinese medicinal materials are maximally reserved, and new functional components are generated through the fermentation process.
Owner:CHENGDU UNIV
Trichoderma viride strain and application of metabolites thereof
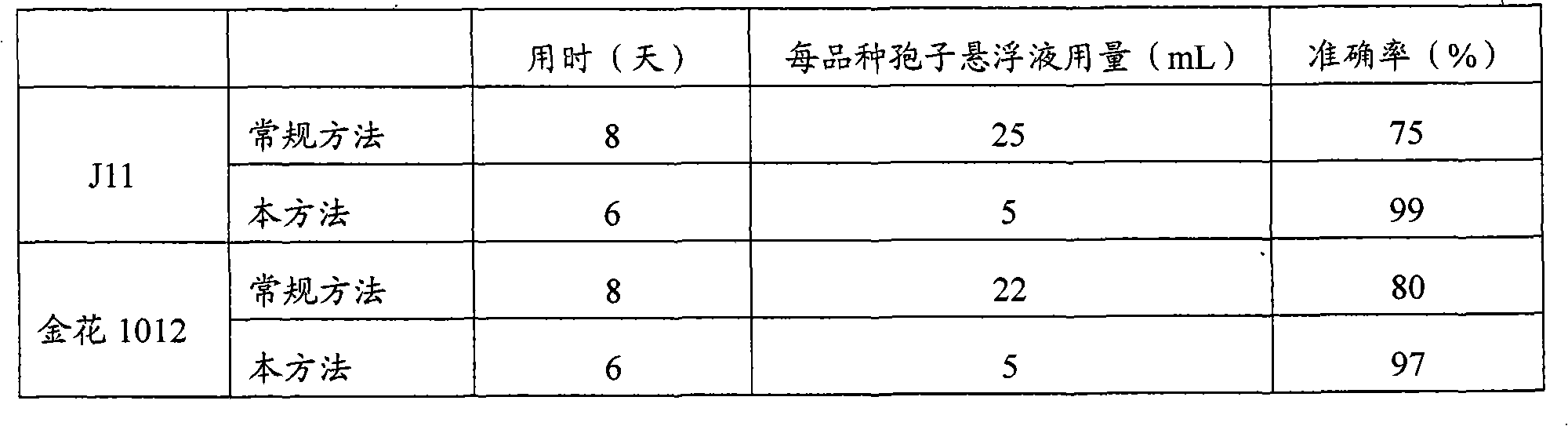
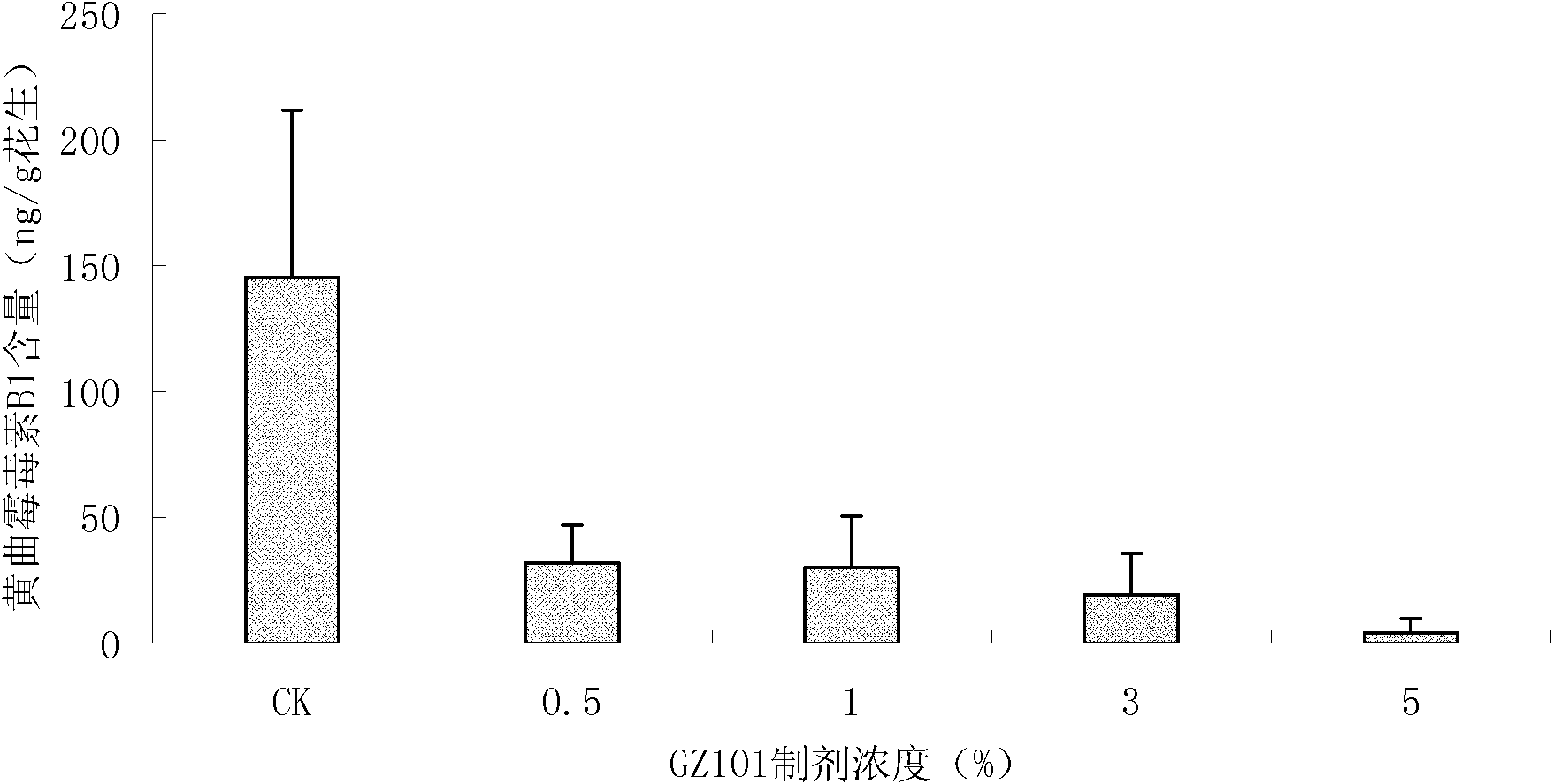
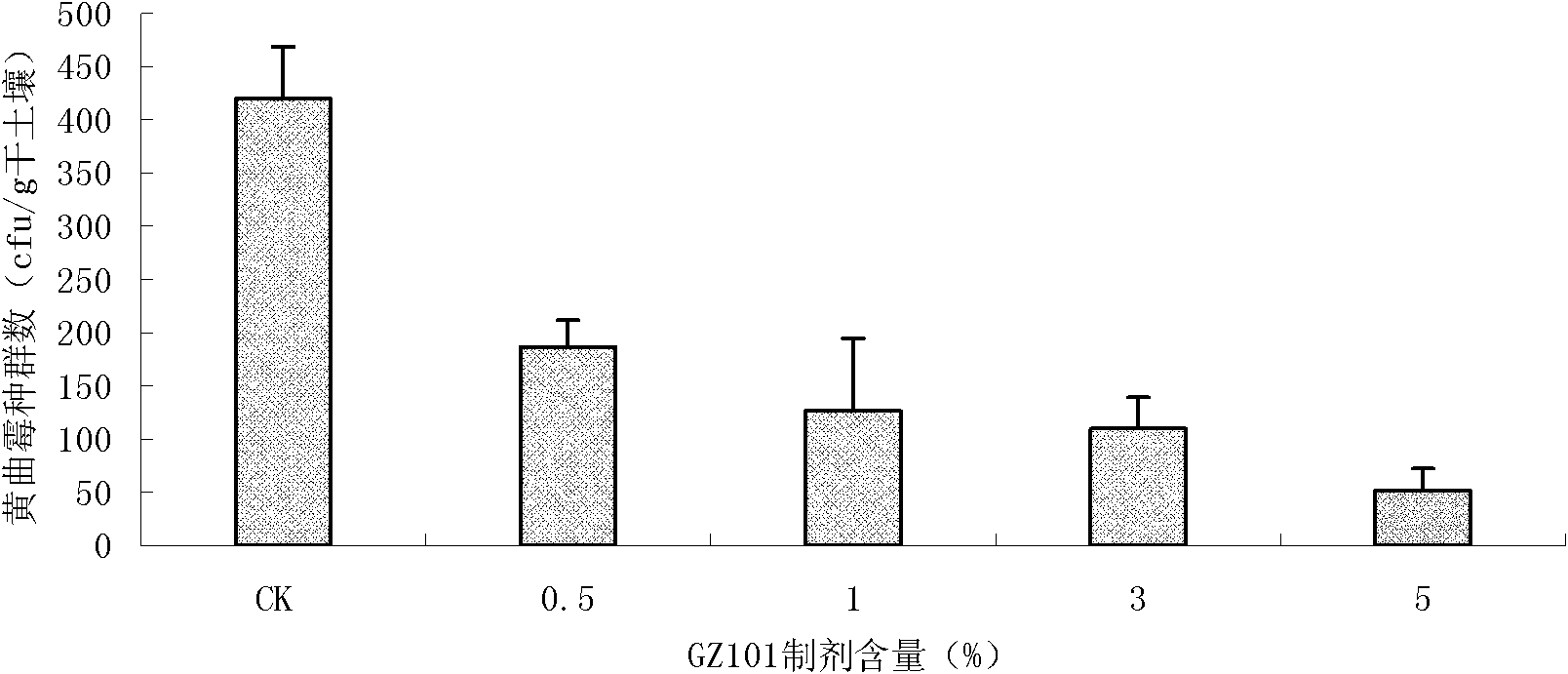
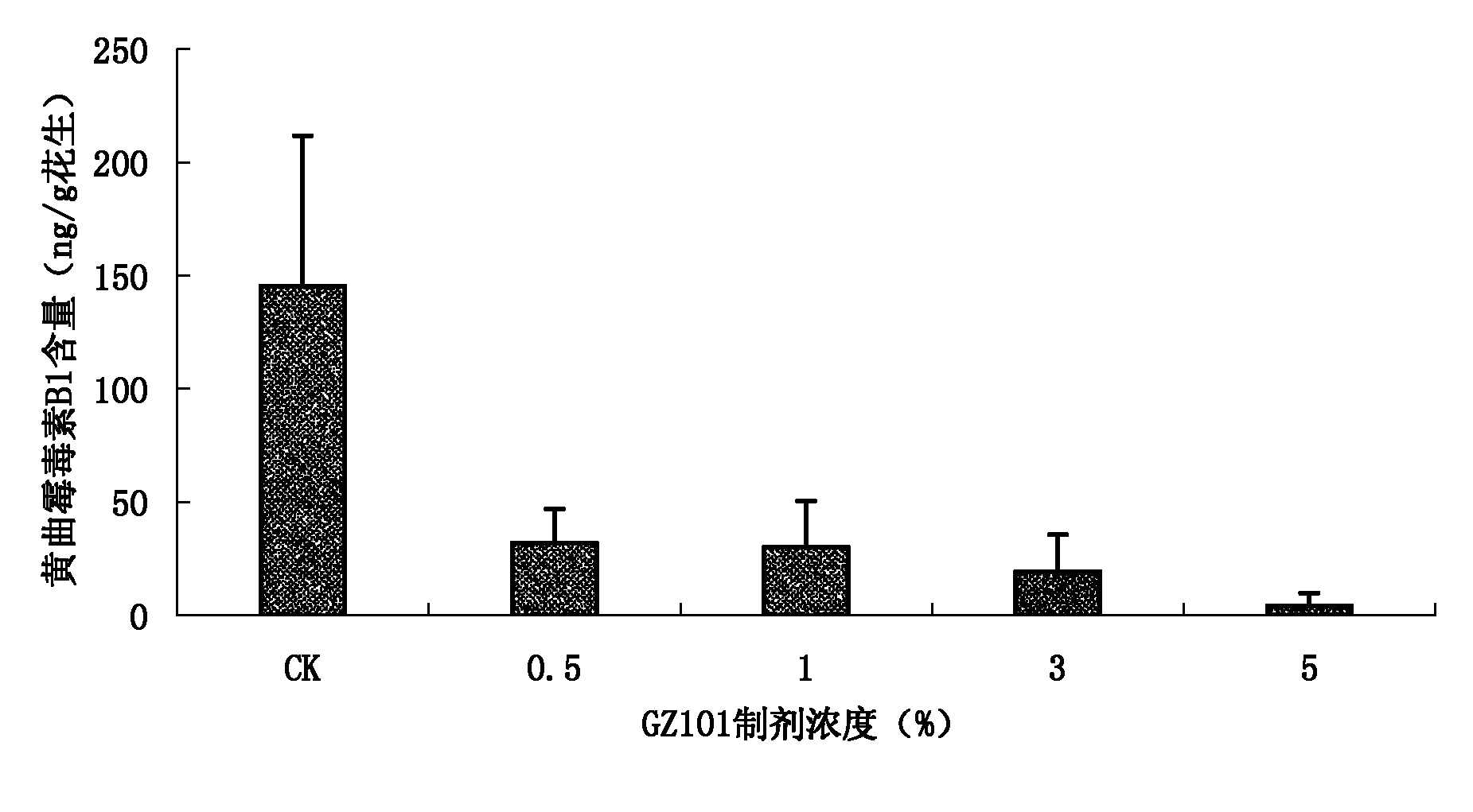
The invention discloses a trichoderma viride strain and application of metabolites thereof and belongs to the field of microorganisms and agriculture. The trichoderma viride strain has the effective antagonistic action on growth of aspergillus flavus, the name of trichoderma viride strain is the trichoderma viride GZ101 which was collected in China Center for Type Culture Collection on Nov. 4th, 2010, and the collection number is CCTCC NO: M 2010291. When the supernatant obtained by fermenting the trichoderma viride strain in the potato-dextrose agar (PDA) liquid culture medium is sprayed in the soil where peanuts are planted, the aflatoxin pollution before the peanut harvest can be effectively reduced, and the reducing rate reaches 97 percent, so that the metabolites of the trichoderma viride strain can be used for preparing a preparation for reducing the aflatoxin pollution before the peanut harvest.
Owner:CROP RES INST GUANGDONG ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Enterobacter cloacae biocontrol strain capable of effectively inhibiting aspergillus flavus from synthesizing aflatoxins and application thereof
InactiveUS20190159463A1Enhanced inhibitory effectObstruction is producedBiocideBacteriaMicroorganismEnterobacter cloacae
The present invention belongs to the field of microorganisms, and particularly relates to an Enterobacter cloacae biocontrol strain capable of effectively inhibiting Aspergillus flavus from producing aflatoxins and an application thereof. Enterobacter cloacae biocontrol strain 3J1EC was deposited in China Center for Type Culture Collection on Jun. 13, 2017, with the deposit address being Wuhan University, Wuhan, China, and the deposit number being CCTCC No. M 2017330. The strain can be used for inhibiting Aspergillus flavus from producing aflatoxins to prevent and control the contamination of food crops by aflatoxins.
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Establishment and application of brewing yeast engineering bacterium strain for producing L-malic acid
ActiveCN105400711ARealize accumulationFungiMicroorganism based processesPyruvate carboxylaseTrimeresurus flavoviridis
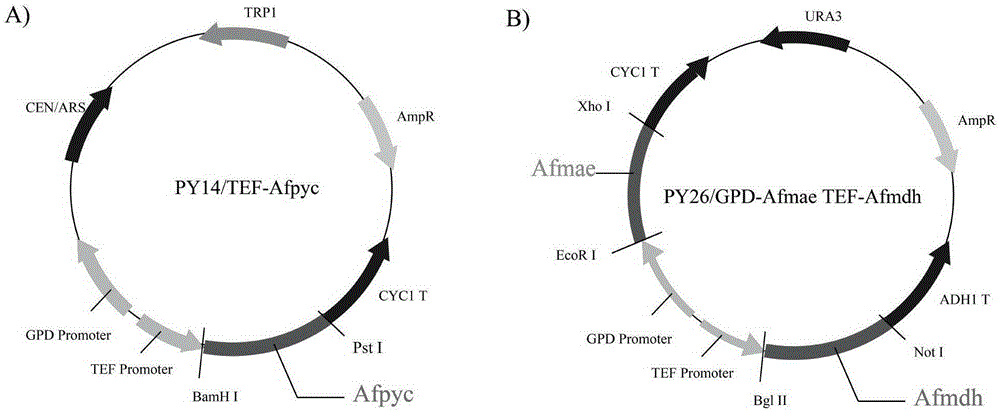
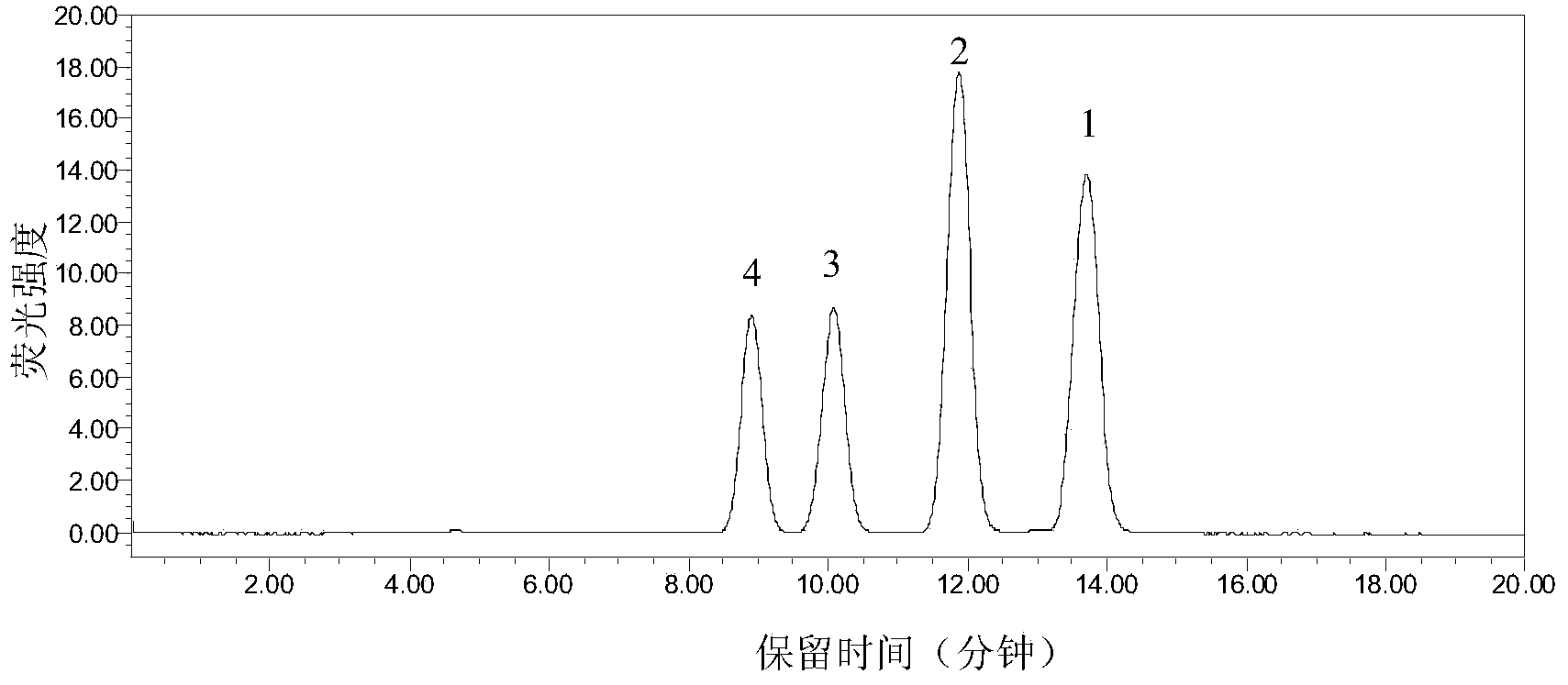
The invention discloses establishment and application of a brewing yeast engineering bacterium strain for producing L-malic acid, and belongs to the field of fermentation engineering. Genes of pyruvic carboxylase (Afpyc), malic dehydrogenase (Afmdh) and malic acid transport protein (Afmae) coming from Aspergillus flavus ATCC13697 are excessively and dissociatively expressed in the bacterium strain S.cerevisiae tTAM(delta)ura3(delta)trpl high in pyruvic acid yield, the malic acid accumulation path is established, and the bacterium W1101 is obtained. The bacterium strain is used for producing L-malic acid through fermentation; after fermentation is conducted for 84 h, the malic acid yield is 27.3 g / L; an original starting bacterium strain does not accumulate malic acid, the metabolism path of aspergillus flavus of the high-yield L-malic acid bacterium strain is successfully applied to brewing yeast, and a new strategy is provided for establishing the high-yield L-malic acid bacterium strain.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Aspergillus flavus resisting composite oil with natural essence and its prepn
InactiveCN1548508ABlock metabolic pathwaysSignificantly resistant to Aspergillus flavusBiocideFungicidesWater vaporDistillation
The Aspergillus flavus resisting composite oil of natural essence is prepared with cubeba fruit, lemon grass, Qulongcao grass, citronella grass and orange peel as material and through mixing in certain proportion, distillation with water vapor, condensation and separation. The Aspergillus flavus resisting composite oil of natural essence may be sprayed directly or processed into delayed releasing agent. It has fast volatilizing and diffusion speed and obvious Aspergillus flavus resisting effect, is suitable for oil, grains and their product and safe to human body and animal, and has no residue and environmental pollution.
Owner:罗曼 +1
Aspergillus flavus mixed strain incapable of producing aflatoxin and application thereof
The invention discloses an Aspergillus flavus mixed strain incapable of producing aflatoxin. The mixed strain is formed by mixing Aspergillus flavus AF-8 and Aspergillus flavus AF-20; and the collection numbers of the Aspergillus flavus AF-8 and Aspergillus flavus AF-20 at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center are respectively CGMCC No.8964 and CGMCC No.8966. The experiment proves that the mixed strain has an inhibiting action on toxin production of the Aspergillus flavus strain capable of producing aflatoxin; the mixture of the two strains has better inhibiting effect on the bacterium capable of toxin production than a single strain; and when the spore concentration ratio of the AF-8 and AF-20 incapable of toxin production to the GD-1 capable of toxin production is 5*10<4>:5*10<4>:1*10<5>, the toxin production inhibition rate of the mixed strain incapable of toxin production for the bacterium capable of toxin production is approximately 100%. The strain has important meanings for inhibiting the toxin production Aspergillus flavus from infecting the agricultural products and lowering the aflatoxin pollution in the agricultural products.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Biocontrol strain of Aspergillus flavus resistant to fungicides and not producing aflatoxin and its application
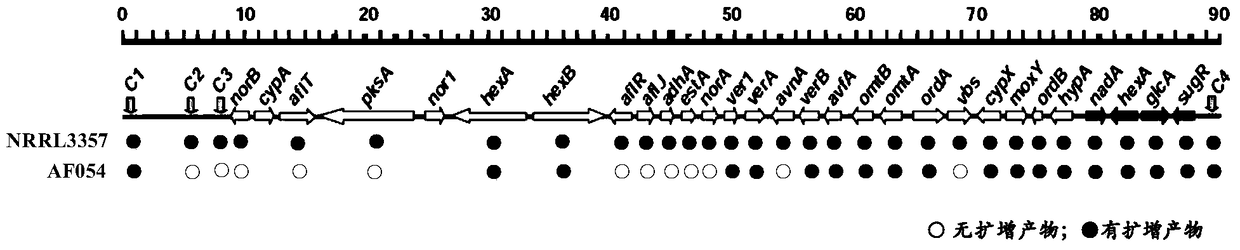
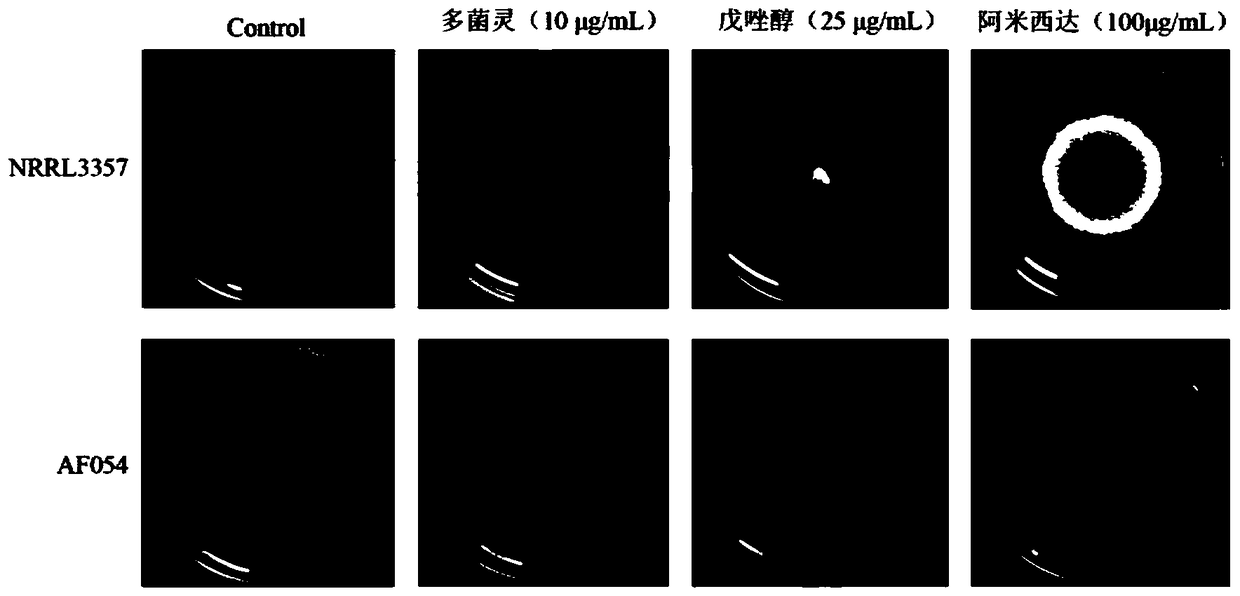
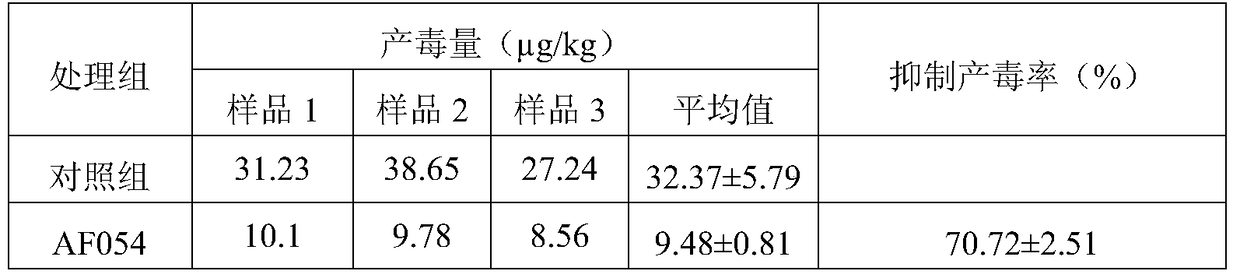
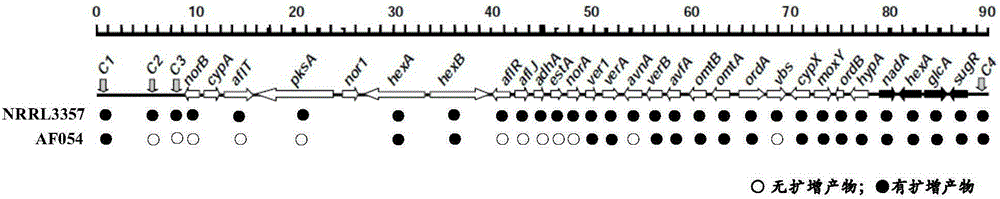
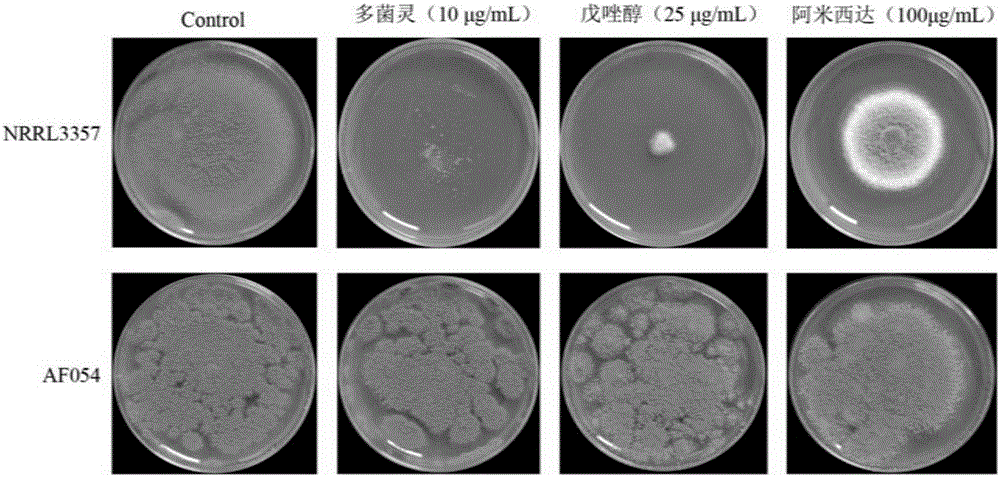
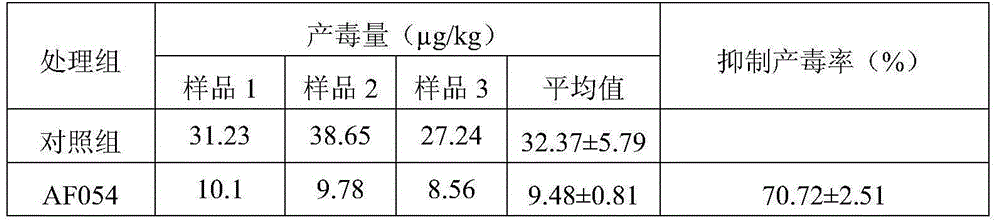
ActiveCN105219655BInhibition formationReduce pollutionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAspergillusTrimeresurus flavoviridis
The invention discloses an aspergillus flavus biocontrol strain realizing resistance on bactericides without producing aflatoxin and application of the aspergillus flavus biocontrol strain. The aspergillus flavus biocontrol strain is named as aspergillus flavus AF054; the preservation number is CGMCC NO.9860; and the preservation date is November 20, 2014. The aspergillus flavus obtained through separation does not generate the aflatoxin; the formation of the aflatoxin in agricultural products can be effectively inhibited; the aflatoxin pollution in the agricultural products is reduced; the agricultural product quality is improved; the resistance on common-use bactericides such as carbendazol, tebuconazole and amistar is realized; the problem of sensitivity of the existing biocontrol strain on the bactericides in a farmland system is solved; and the colonizing capacity and the adaptability of the biocontrol strain in the field are effectively improved, so that the biocontrol effect of biocontrol bacteria is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Aspergillus flavus biocontrol strain realizing resistance on bactericides without producing aflatoxin and application of aspergillus flavus biocontrol strain
ActiveCN105219655AInhibition formationReduce pollutionBiocidePlant growth regulatorsAspergillusTrimeresurus flavoviridis
The invention discloses an aspergillus flavus biocontrol strain realizing resistance on bactericides without producing aflatoxin and application of the aspergillus flavus biocontrol strain. The aspergillus flavus biocontrol strain is named as aspergillus flavus AF054; the preservation number is CGMCC NO.9860; and the preservation date is November 20, 2014. The aspergillus flavus obtained through separation does not generate the aflatoxin; the formation of the aflatoxin in agricultural products can be effectively inhibited; the aflatoxin pollution in the agricultural products is reduced; the agricultural product quality is improved; the resistance on common-use bactericides such as carbendazol, tebuconazole and amistar is realized; the problem of sensitivity of the existing biocontrol strain on the bactericides in a farmland system is solved; and the colonizing capacity and the adaptability of the biocontrol strain in the field are effectively improved, so that the biocontrol effect of biocontrol bacteria is improved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Microorganism used for decolouring molasses alcohol waste water and decolouring method
ActiveCN102839128AHigh decolorization rateImprove decolorization efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBacterial strainTrimeresurus flavoviridis
The invention relates to a microorganism used for decolouring molasses alcohol waste water, namely aspergillus flavus, preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on November 1, 2010. During screening and separation of the aspergillus flavus, pigment melanoidins simulating molasses alcohol waste water is taken as a substrate, a dilution spread plate method is adopted for screening in natural environment to obtain the melanoidins decolouring microorganism, bacterial strains with an obvious decolouring ring are transferred into an untreated actual molasses alcohol waste water culture medium to carry out secondary screening, the bacterial strains with decolouring capability are transferred into a culture medium to be cultured, and spores are eluted to prepare spore suspension. The molasses alcohol waste water is diluted until A 475 is about 3.5, a nutrient source is added, the spore suspension is inoculated into the molasses alcohol waste water liquid culturemedium for carrying out decolouring reaction, after reaction is finished, thallus is leached and separated, and decolouring rate is calculated by testing variation of absorbance at 475nm.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
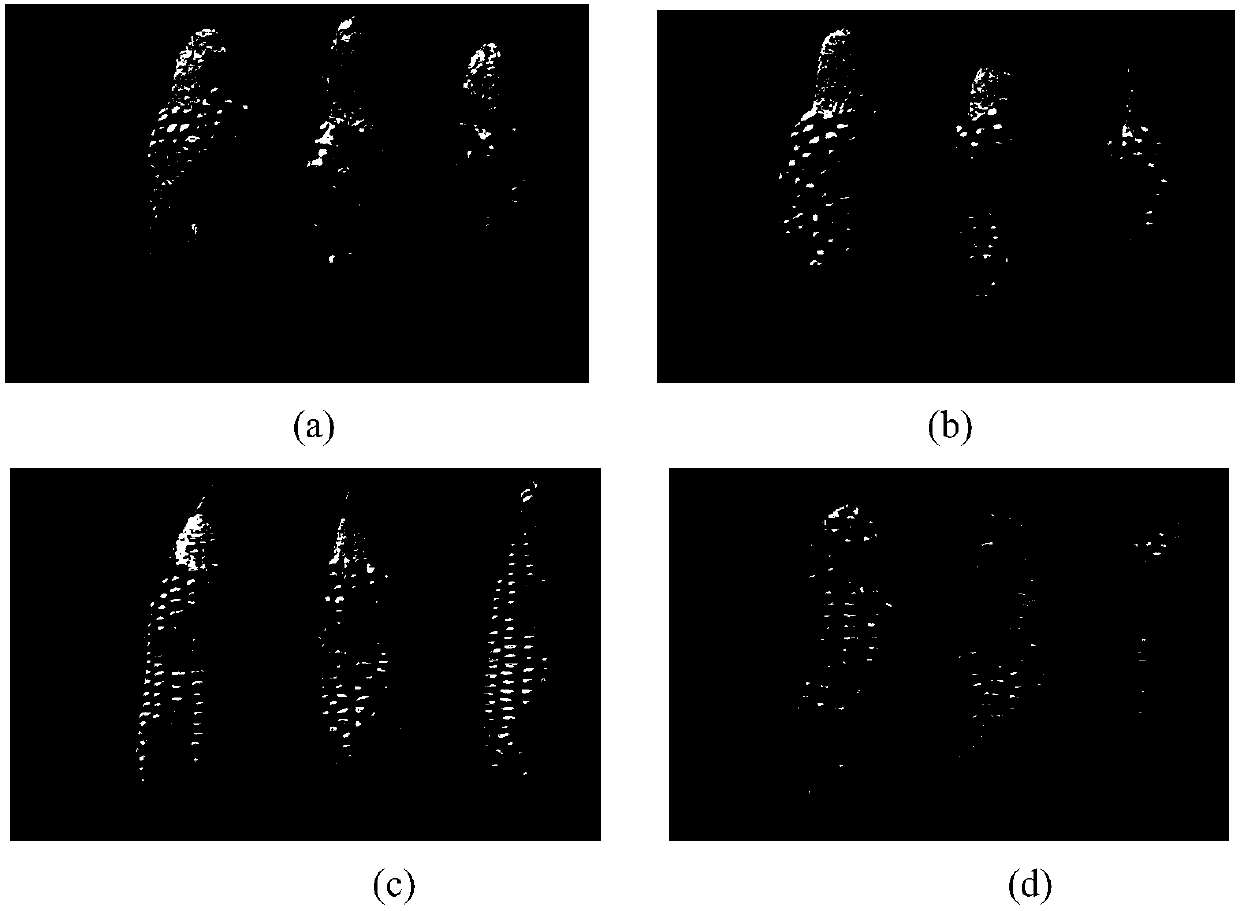
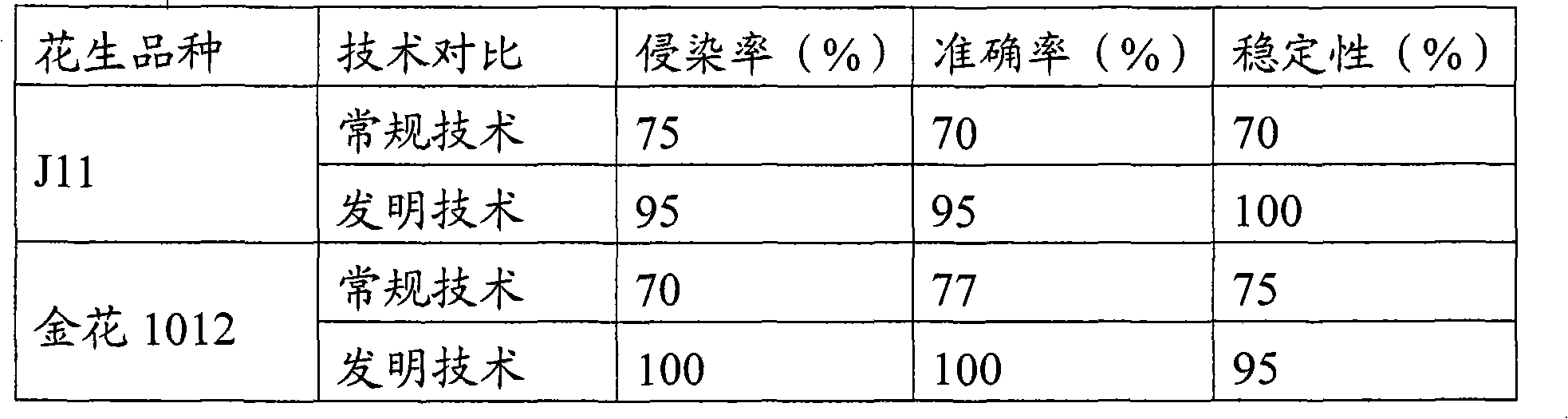
Field identification method for evaluating aspergillus flavus infection resistance of corn
InactiveCN107870224AImprove test repeatabilityGuaranteed test reproducibilityMaterial analysisAgricultural scienceSelfing
The invention provides a field identification method for evaluating aspergillus flavus infection resistance of corn. The method comprises steps as follows: 1), a czapek's solid medium is inoculated with aspergillus flavus; 2), aspergillus flavus spores on the surface of the medium are scraped off, and aspergillus flavus spore suspension with concentration being 1.0*10<6> / ml is prepared from distilled water; 3), the aspergillus flavus spores are inoculated by a scale syringe in 15-20 days after pollination of corn ears, the upper part, the middle part and the lower part of each corn ear are inoculated with 0.5 ml of spore suspension respectively, and a syringe needle is obliquely pierced into a bracteal leaf of the corn ear with 45 degrees; 4), resistance of a corn selfing line to aspergillus flavus infection is determined according to ear incidence area and aflatoxin B1 content. Compared with the prior art, the method is based on the natural environment of the corn growing field and meets the agricultural production rule, an identification result is accurate, the stability is high, and the method has no adverse effect on body health.
Owner:INST OF TOBACCO ANHUI ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Field identification method for peanut aspergillus flavus infection resistance
ActiveCN101603073AIncrease costStrong costMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSporeGram
The invention provides a field identification method for peanut aspergillus flavus infection resistance, which comprises the following steps: 1) crushing corn until the diameter thereof is between 3 and 5 millimeters, and producing aspergillus flavus spores according to 50 to 75 grams of corn / m<2> of peanut inoculation aspergillus flavus; 2) stopping watering 5 to 6 weeks before harvesting peanuts, making ditches of which the depth is about 2 to 3 centimeters among peanut rows before the inoculation, broadcasting the aspergillus flavus spores in the ditches among the rows for three times before harvesting the peanuts, and covering the ditches with soil for 2 to 3 millimeters; and 3) using a watering can to water the near-earth surface evenly after the inoculation according to 100 to 150 grams / m<2> to create an environment of which the temperature and the moisture are suitable for the propagation of the aspergillus flavus. Compared with the prior art, the method is the most similar field peanut growing environment, and has accurate identification result and high stability; and the used devices can be used for a plurality of years with only once investment, and generate no adverse effects on environmental pollution and human body health.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Antibiological inoculant for toxin production aspergillus flavus, and preparation method and application of antibiological inoculant
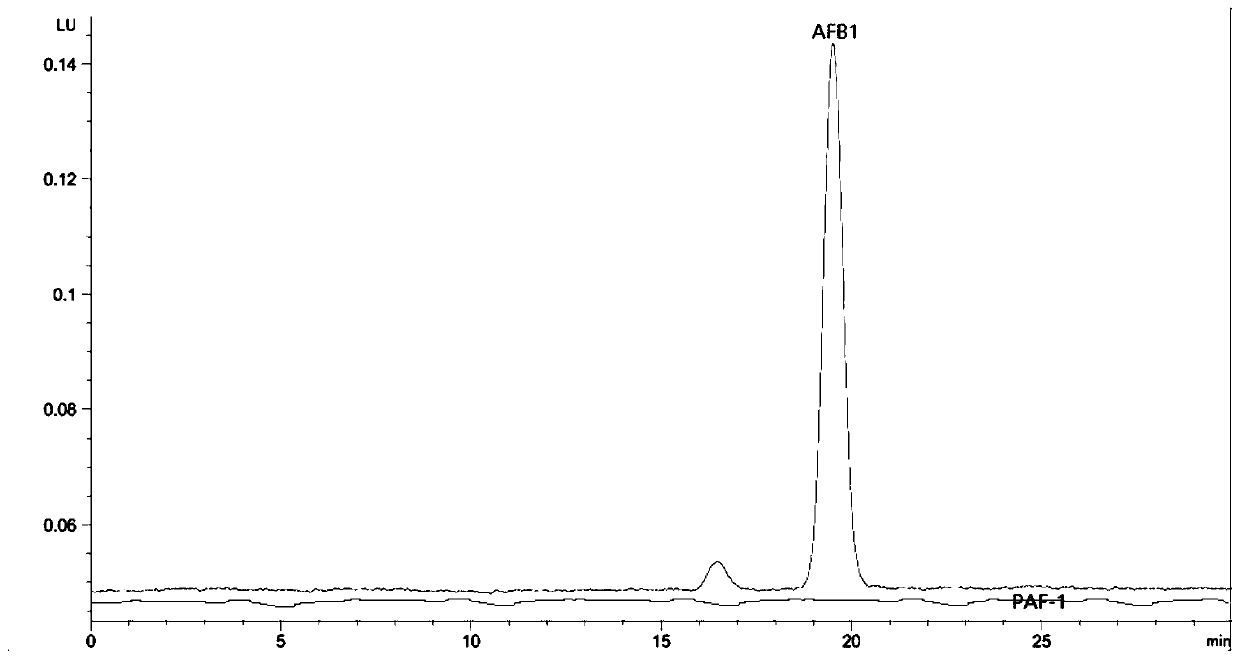
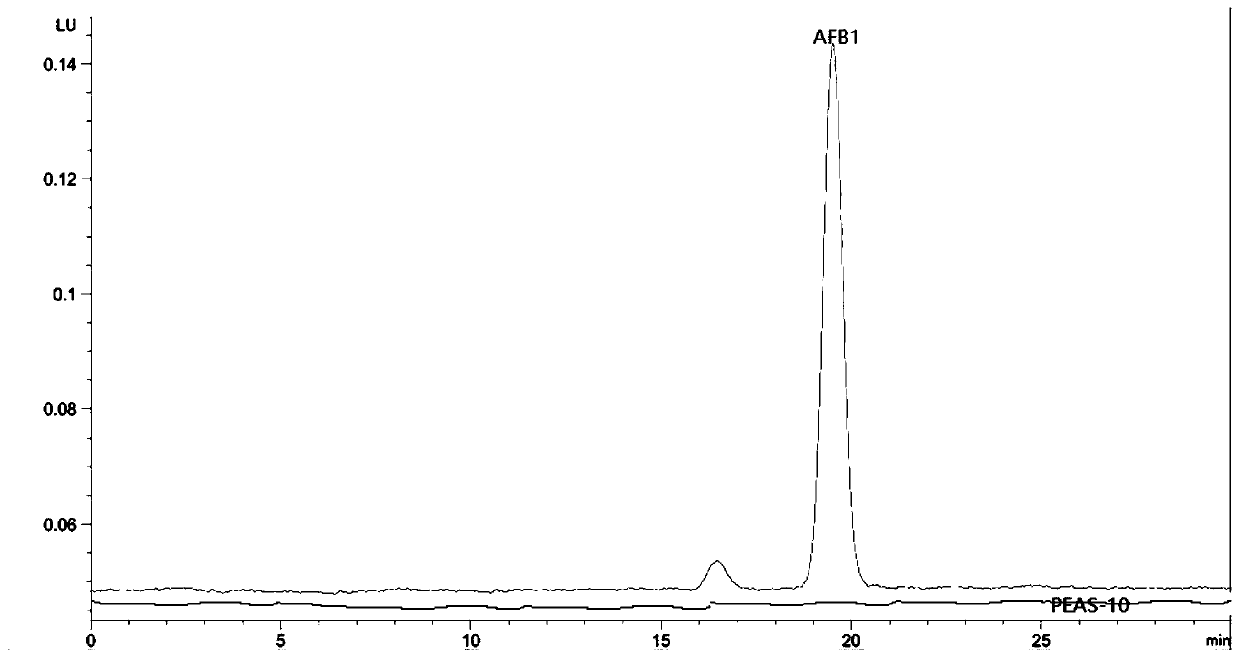
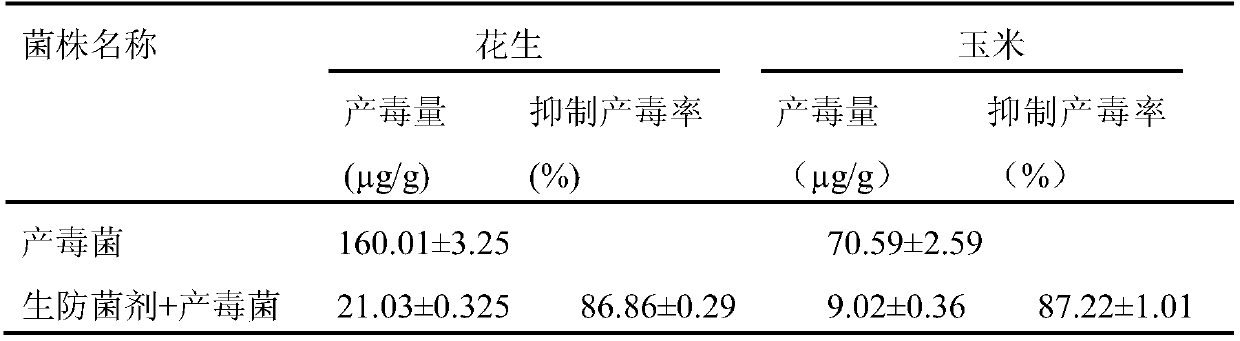
The invention discloses an antibiological inoculant for toxin production aspergillus flavus, and a preparation method and an application of the antibiological inoculant, and belongs to the technical field of the antibiological inoculant for harmful microorganisms. The effective ingredients of the antibiological inoculant for the toxin production aspergillus flavus are aspergillus flavus PEAS-10 producing no aflatoxin and aspergillus flavus PEF-1 producing no aflatoxin; a aspergillus flavus strain in the antibiological inoculant can rapidly grow and propagate in the field, the growth, the propagation and the toxin production of the toxin production aspergillus flavus are efficiently inhibited, the disease of a peanut is obviously reduced, the content of the aflatoxin in the harvested peanutis low, the storage period of the peanut is long, and compared with the treatment with a single microbial agent, the effect is excellent.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
New aspergillus flavus and use thereof
The present invention discloses new aspergillus flavus and use thereof. The aspergillus flavus is aspergillus flavus LB-Y4 preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center, and the accession number is CGMCC No. 3.15413. Metabolites of the aspergillus flavus have activity for inhibition of staphylococcus aureus and other bacteria, can be used for preparing anti-bacterial drugs or disinfectants, and has good prospects for clinical application.
Owner:GANZI TIBETAN AUTONOMOUS PREFECTURE INST OF ANIMAL HUSBANDRY SCI
Method for identifying infection resistance of peanuts to aspergillus flavus and application thereof
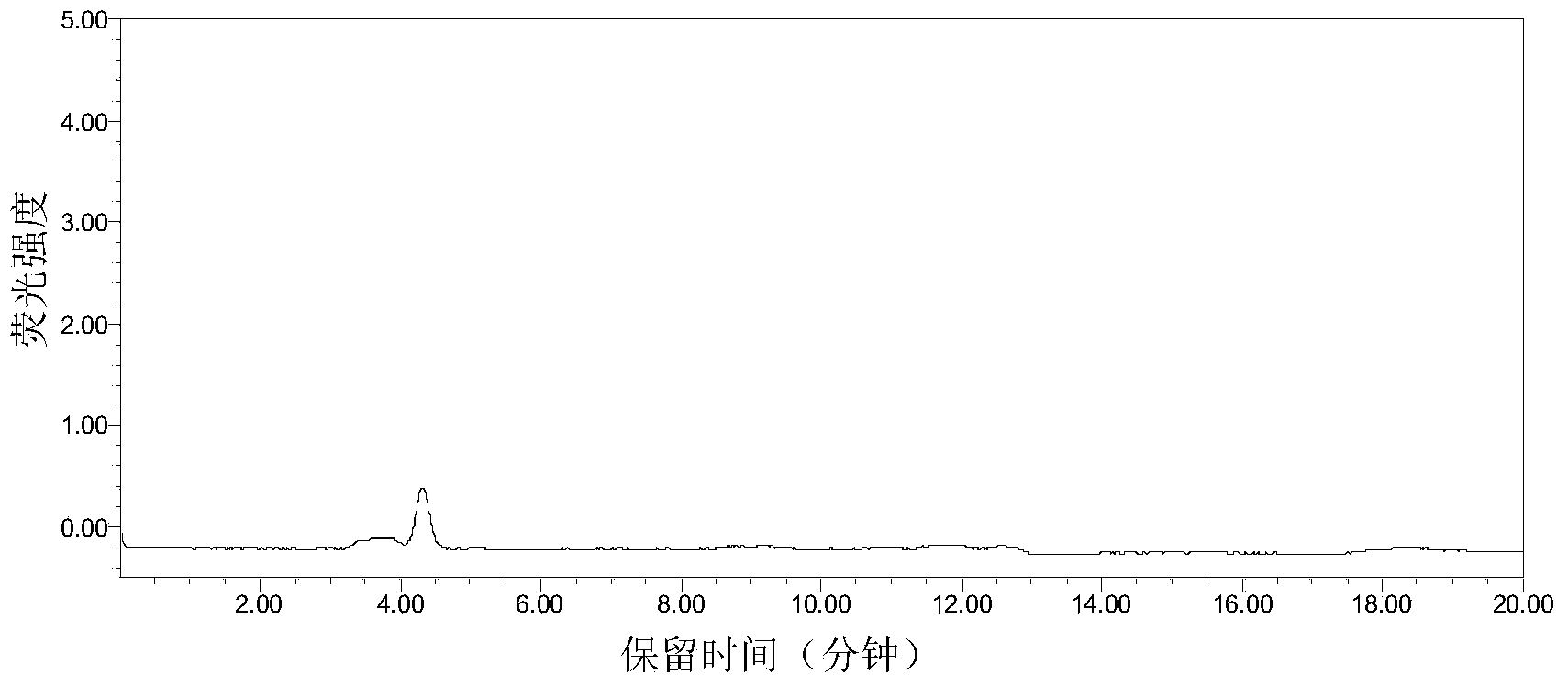
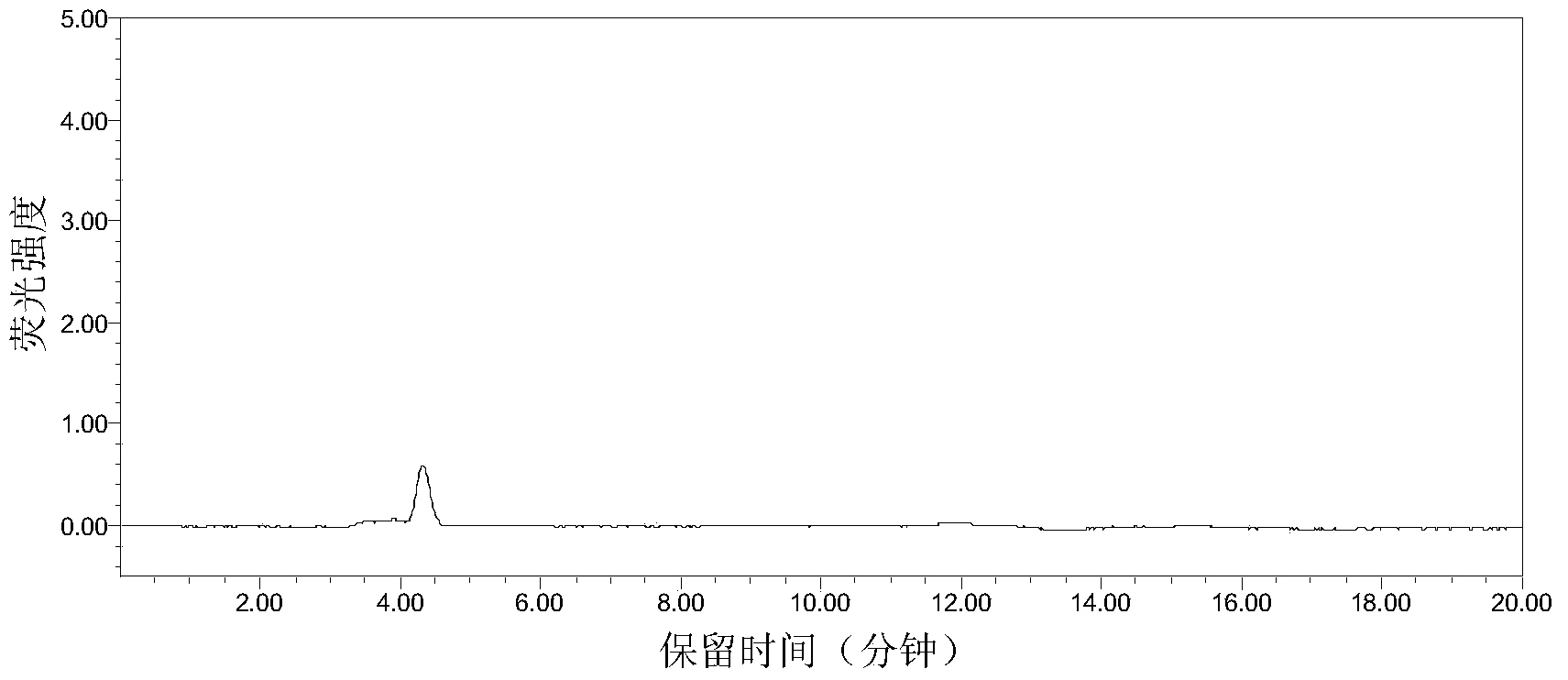
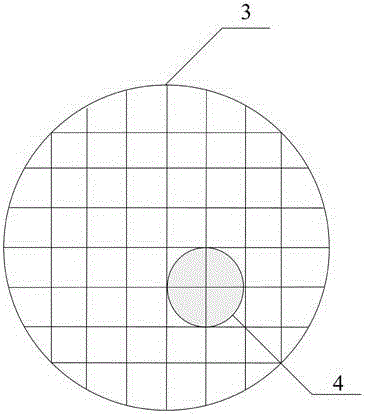
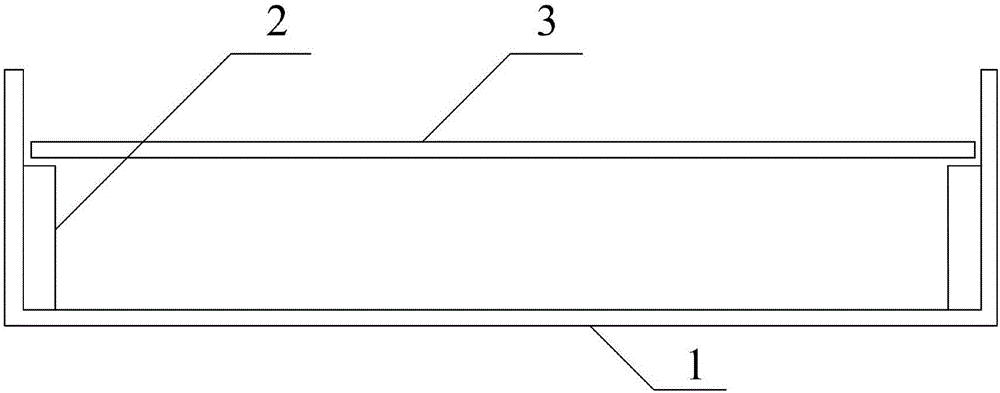
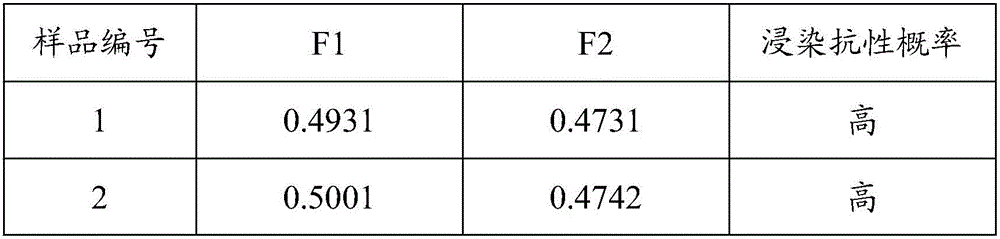
InactiveCN106596492ASolve the problem of large operating errorsAddressing Aflatoxin ContentPreparing sample for investigationFluorescence/phosphorescenceSporePhysical health
The invention discloses a method for identifying infection resistance of peanuts to aspergillus flavus. The method comprises the following steps: inoculating prepared aspergillus flavus spore suspension into healthy and aseptic peanut seeds; meanwhile, using a Czapek's medium as a reference product, and designing a special culture device; calculating the infection index of the aspergillus flavus according to the area of a mold ring to evaluate the infection resistance of a seed sample to the aspergillus flavus. The method has the advantages of convenience in operation, short time, low cost and high reliability; in an operation process, no complicated extraction process is needed, so that direct and long-time contact of a human body with the aspergillus flavus is reduced, and the physical health of an operation experimenter is benefited; the method is suitable for being popularized widely, and particularly applied to rapid and large-scale screening of peanut varieties having aspergillus flavus infection resistance.
Owner:SHANGQIU ACADEMY OF AGRI & FORESTRY
Bacillus siamensis and application thereof
ActiveCN109112086AGrowth inhibitionEfficient degradationBacteriaEdible seed preservationMicroorganismTrimeresurus flavoviridis
The invention discloses a bacillus siamensis and application thereof and belongs to the technical field of microorganisms. The bacillus siamensis provided by the invention is bacillus siamensis A2025and is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) on April 12, 2018; the preservation number is CGMCC NO: 15611 and the address is #3, No. 1 Yard, West Beichen Road,Chaoyang District, Beijing; and the preservation requesting unit is Shandong Peanut Research Institute. The bacillus siamensis A2025 obtained by the invention can be used for remarkably inhibiting thegrowth of aspergillus flavus and can be used for efficiently degrading aflatoxin.
Owner:SHANDONG PEANUT RES INST
Enterobacter cloacae biocontrol strain for efficiently inhibiting aspergillus flavus compounded aflatoxin and its application
Owner:INST OF OIL CROPS RES CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Cladosporium sp. strain, and extract and application thereof
The invention discloses a Cladosporium sp. strain, and an extract and application thereof. The Cladosporium sp. FS86 is collected to China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) on March 27th, 2014, wherein the address is Wuhan University, Wuhan City, PRC, and the collection number is CCTCC NO: M2014108. The fermentation extract has obvious inhibitory effects on Candida albicans, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus flavus, Trichoderma viride, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Cylindrocladium scoparium or Curvularia lunata. Therefore, the invention provides scientific references for developing new anti-pathogenic fungus drugs and exploring deep-sea-fungus-derived natural active substances.
Owner:GUANGDONG INST OF MICROORGANISM
Aspergillus flavus-resistant ceramic product and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN107459333APromote metabolic functionRegulate body metabolismClaywaresPollenTrimeresurus flavoviridis
The invention relates to an aspergillus flavus-resistant ceramic product and a preparation method thereof. The ceramic product comprises the following the components in parts by weight: 40 to 50 parts of Dongxing sand, 41 to 50 parts of pure white sand, 9 to 16 parts of Fuming sand, 13 to 20 parts of grind grain with water, 5 to 10 parts of calcined talc, 4 to 8 parts of bentonite, 5 to 15 parts of Huidong original mud, 5 to 15 parts of quartz powder, 0.4 to 1 part of an auxiliary agent, 100 to 140 parts of radix glehniae, 100 to 160 parts of the root of kudzu vine, 60 to 120 parts of plumula nelumbinis, 50 to 150 parts of lily, 110 to 130 parts of radices trichosanthis, 100 to 150 parts of astragalus membranaceus, 100 to 180 parts of the root of red-rooted salvia, 60 to 100 parts of Chinese yam, 100 to 150 parts of sculellaria barbata and 80 to 160 parts of dandelion. The ceramic product provided by the invention effectively improves the body function of a human body, has an aspergillus flavus-resistant function and has wide market prospect.
Owner:GUANGDONG KANGSHITAI NEW MATERIAL TECH CO LTD
Chili antibacterial peptide extraction and purification method
ActiveCN108586570AGood extraction conditionsBroad antibacterial spectrumPeptide preparation methodsPurification methodsSpore germination
The invention discloses an optimized chili antibacterial peptide extraction and purification method. Particularly, an inventor acquires the best conditions of chili antibacterial peptide extraction byresearching the influence of different extracting liquid, solid-liquid ratios, extracting time and ammonium sulfate saturability on chili seed antibacterial peptide extraction, and further, components with good antibacterial effects are selected after ultrafiltration and crude separation and subjected to Sephadex gel filtration chromatography to obtain an electrophoresis pure antibacterial peptide sample. The extraction and purification method is simple, the antibacterial effect of an extracted antibacterial peptide is improved by 50.32% as compared with the antibacterial effect before optimization, the antibacterial peptide has a wide antibacterial spectrum, particularly has a strong inhibiting effect on Aspergillus flavus, can effectively inhibit Aspergillus flavus spore germination andmycelial growth and can further inhibit absorption and utilization of nutrient substances in a culture medium by the Aspergillus flavus. The antibacterial peptide extracted by the method is used as acorn mildew preventive, corn quality can be effectively kept, the service life is prolonged, and the antibacterial peptide is better in effect when being used with other mildew preventives.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
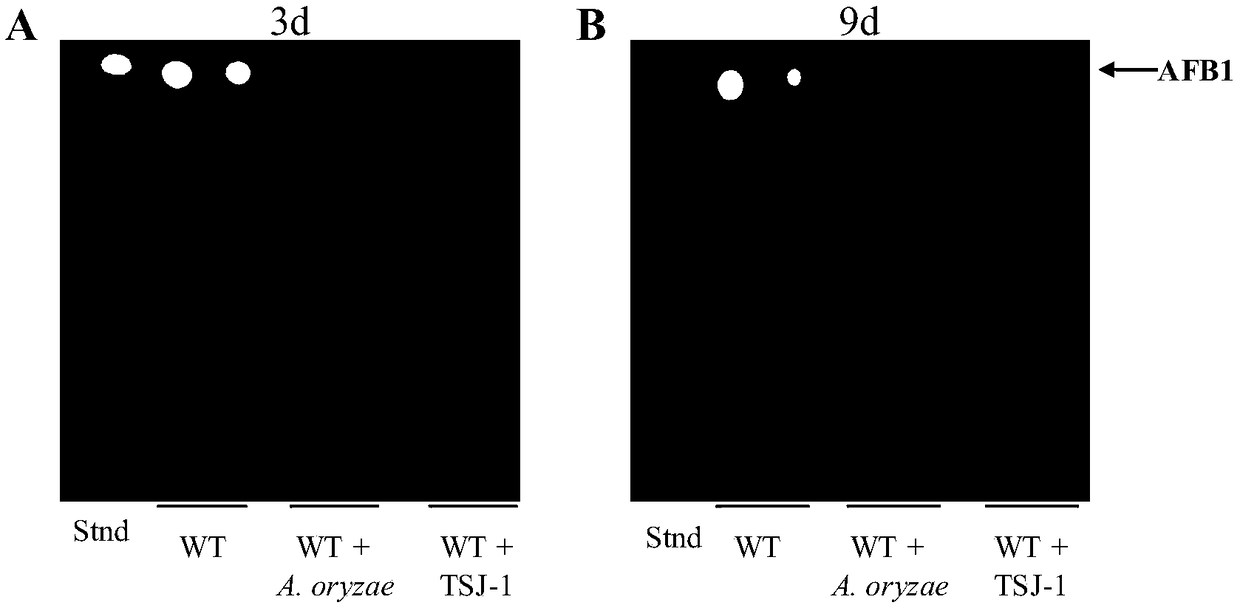
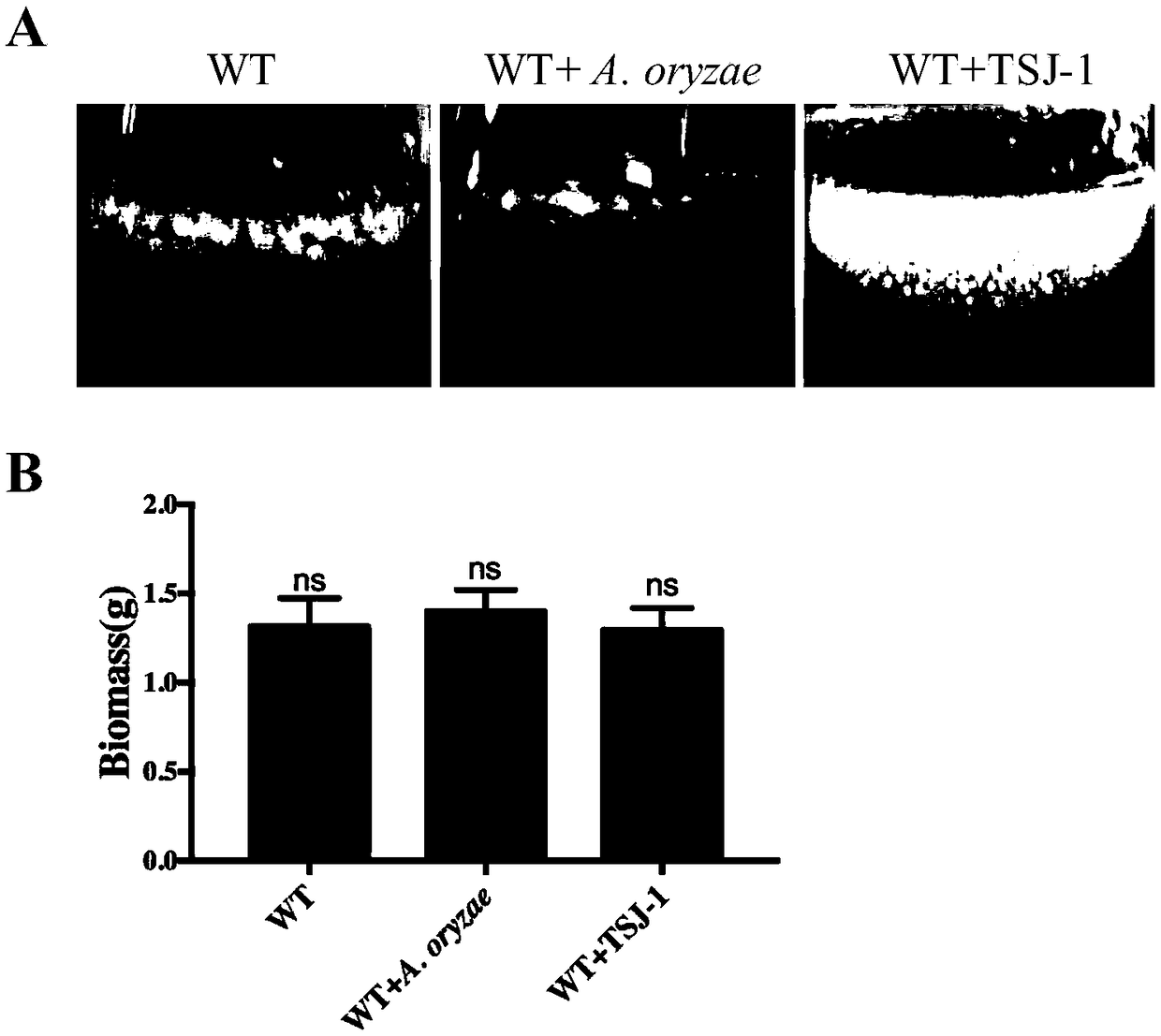
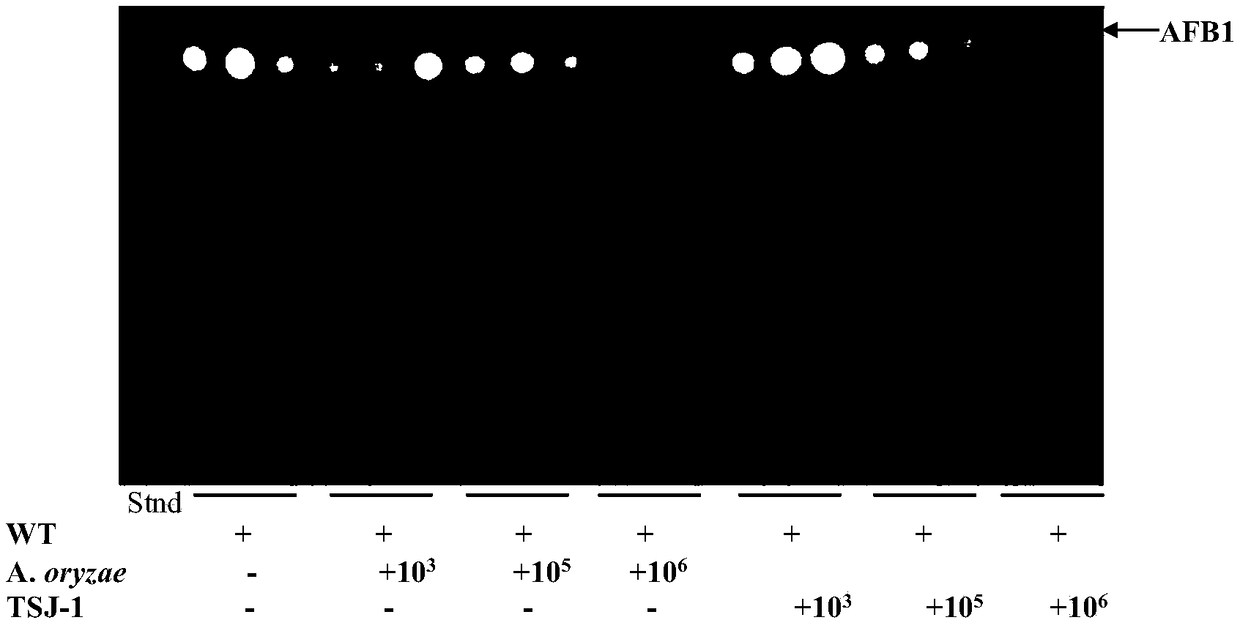
Biological control method for toxicogenic aspergillus flavus
The invention relates to a biological control method for toxicogenic aspergillus flavus, and belonging to the field of biological control. Aspergillus oryzae and an aflatoxin-free aspergillus flavus mutant TSJ-1 strain can inhibit the growth and production of the toxicogenic aspergillus flavus. The synthesis of aflatoxin can be significantly inhibited by co-cultivating the toxicogenic aspergillusflavus with aspergillus oryzae or the TSJ-1 non-toxicogenic mutant. The vegetative growth of wild type aspergillus flavus the production of conidia, and the amount of aflatoxin synthesis are also decreased significantly; further the toxicogenic aspergillus flavus is treated with the aspergillus oryzae and a culture medium of the TSJ-1 strains to inhibit the growth and conidiospore development of aspergillus flavus and aflatoxin synthesis. The biological control method for the toxicogenic aspergillus flavus can reduce the infection against many agricultural products and synthesis of the aflatoxin, and achieve the effect of preventing and controlling in advance and reducing economic loss.
Owner:XUZHOU NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Aspergillus flavus mixed strain incapable of producing aflatoxin and application thereof
The invention discloses an Aspergillus flavus mixed strain incapable of producing aflatoxin. The mixed strain is formed by mixing Aspergillus flavus AF-15 and Aspergillus flavus AF-20; and the collection numbers of the Aspergillus flavus AF-15 and Aspergillus flavus AF-20 at China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center are respectively CGMCC No.8965 and CGMCC No.8966. The experiment proves that the mixed strain has an inhibiting action on toxin production of the Aspergillus flavus strain capable of producing aflatoxin; the mixture of the two strains has better inhibiting effect on the bacterium capable of toxin production than a single strain; and when the spore concentration ratio of the AF-15 and AF-20 incapable of toxin production to the GD-1 capable of toxin production is 5*10<4>:5*10<4>:1*10<5>, the toxin production inhibition rate of the mixed strain incapable of toxin production for the bacterium capable of toxin production is approximately 100%. The strain has important meanings for inhibiting the toxin production Aspergillus flavus from infecting the agricultural products and lowering the aflatoxin pollution in the agricultural products.
Owner:INST OF AGRO FOOD SCI & TECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Method for extracting streptomyces antibacterial product
InactiveCN101897730AGood antibacterial broad spectrumEnhanced inhibitory effectBiocideAntimycoticsDesorptionAntibacterial activity
The invention relates to a method for extracting a streptomyces antibacterial product, and belongs to the technical field of biology. Streptomyces sp S24 is activated and fermented; the fermentation solution is sterilized, centrifuged, absorbed by macroporous absorption resin AB-8 and desorbed by 75 to 85 percent acetone; and a solvent is reclaimed from the desorption solution, and the desorptionsolution is evaporated and dried to obtain an antibacterial product extract. Experiments prove that the antibacterial product has broad-spectrum antibacterial activity for main mildewing fungi such as aspergillus flavus, aspergillus niger, aspergillus ochraceus and aspergillus fumigatus in food and feed and human pathogenic fungi such as aspergillus flavus and aspergillus fumigatus. Because the antibacterial product provided by the invention has obvious inhibiting effect on various food and geed mildewing fungi and human pathogenic fungi, the antibacterial product shows efficient broad-spectrum properties; and the method for extracting the antibacterial product is simple and convenient, has low cost, and has high practical application value and broad market prospect on the aspects of foodpreservative, feed additive and medicaments.
Owner:SHANDONG AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Aspergillus flavus strains and mixed flora that do not produce aflatoxin and their application
InactiveCN104789480BInhibition formationReduce pollutionFungiFood preservationAgricultural scienceTrimeresurus flavoviridis
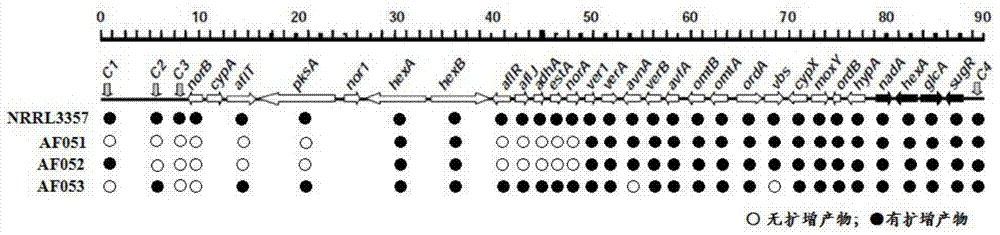
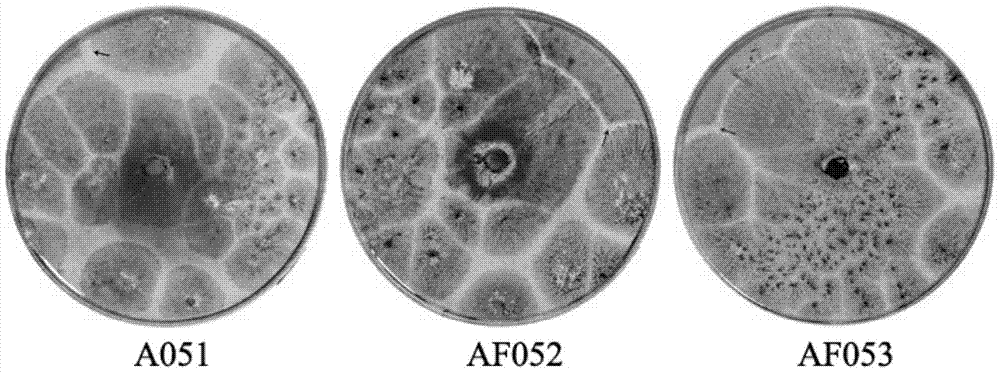
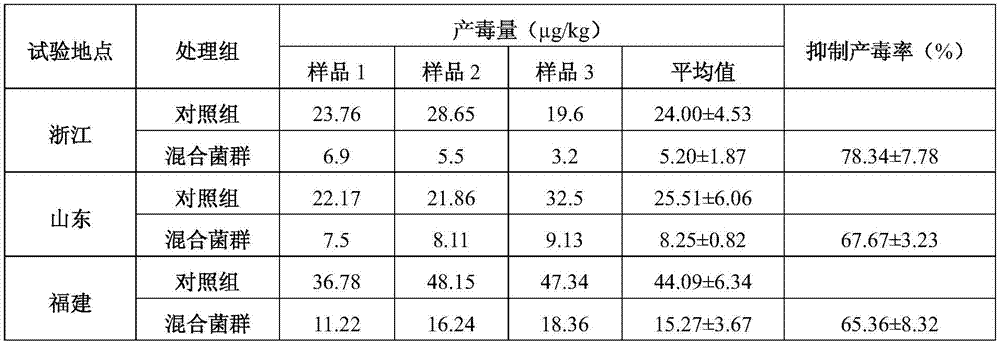
The invention discloses a non-aflatoxin-producing Aspergillus flavus strain and mixed flora and application thereof. The strains are Aspergillus flavus AF052, the preservation number is CGMCC NO.9858, and the preservation date is November 20, 2014 , and Aspergillus flavus AF053, deposit number CGMCC NO.9859, deposit date November 20, 2014. Both the strain and the flora can effectively inhibit the formation of aflatoxin in corn and peanuts and improve the quality of agricultural products; in addition, A051, AF052 and AF053 can also secrete cellulase, and the corn treated with the biocontrol flora prepared by using the Aspergillus flavus When the straw and straw are used as animal feed, the biocontrol bacteria carried will produce cellulase, which can degrade cellulose and improve the utilization efficiency of animal feed.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com