Biocontrol strain of Aspergillus flavus resistant to fungicides and not producing aflatoxin and its application
A technology of aflatoxin and biocontrol strains, applied in the application, biocide, microorganism and other directions, can solve the problems of biocide sensitivity, affecting biocontrol effect and control effect stability, etc. Colonization ability, effectiveness in overcoming biocide susceptibility issues
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Example 1 Isolation and identification of Aspergillus flavus strain AF054 that does not produce aflatoxin
[0028] 1. Isolation of Aspergillus flavus strains from soil, corn, peanut and other habitats
[0029] Soil was collected from corn and peanut fields in Jiangsu, Zhejiang, Shandong, Fujian, Anhui and other places, and the soil was cultured with YES medium to isolate Aspergillus flavus strains. Ingredients per liter of YES medium: Yeast extract 1g, sucrose 10g, NaCl 60g, agar 20g, add CuSO after sterilization 4 .ZnSO 4 1 mL, 0.4% clonamide 5 ml, streptomycin 100 μg / mL.
[0030] 2. Use bioassay, thin-layer chromatography and enzyme-linked immunoassay to analyze the aflatoxin production of the strain.
[0031] details as follows:
[0032] Bioassay method: Inoculate the isolated Aspergillus flavus strain on YES medium containing 0.3% cyclodextrin, culture it at 30°C for 7 days, fumigate the colony with 25% ammonia water for 3 minutes, if the back of the colony is p...
Embodiment 2
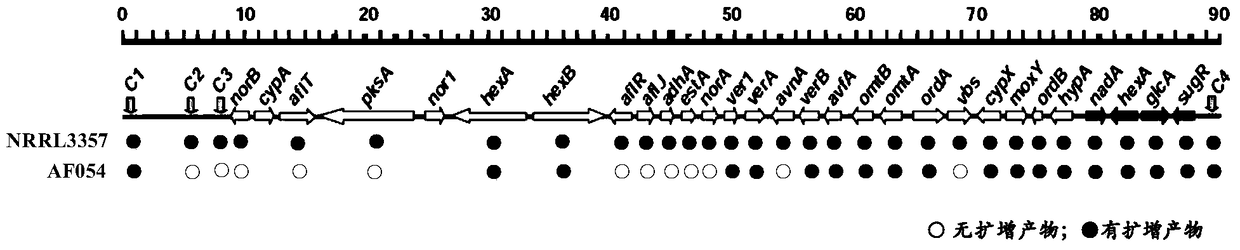
[0051] Example 2 Deletion Identification of Aflatoxin Synthetic Gene in Aspergillus flavus Strain AF054 That Does Not Produce Aflatoxin
[0052] (1) Primer synthesis
[0053] In order to clarify the deletion of the aflatoxin synthesis gene in the non-aflatoxin-producing Aspergillus flavus strain AF054, the test refers to the literature Perng-Kuang Chang (Chang, P.K., Horn, B.W. and Dorner, J.W. (2005) Sequence breakpoints in the aflatoxin biosynthesis Gene cluster and flanking regions in nonaflatoxigenic Aspergillus flavus isolates. Fungal Genet Bio 42,914–923.) The identification primers for toxin synthesis genes were designed to identify the deletion of related genes in strain AF054.
[0054] (2) Gene deletion identification
[0055] Using the extracted DNA of Aspergillus flavus strain AF054 as a template, conventional PCR reactions were carried out with the above primers, and each reaction had a DNA control and a negative control (use sterile water as a template) of the to...
Embodiment 3
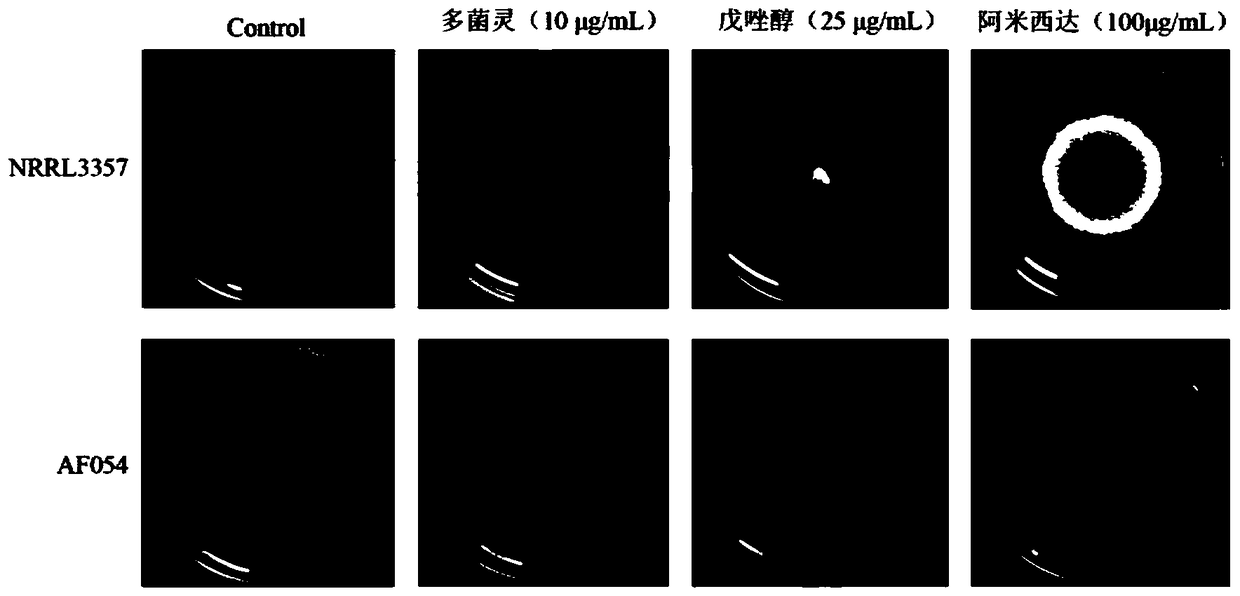
[0059] Example 3 Indoor test to evaluate the resistance of the non-aflatoxin-producing Aspergillus flavus strain AF054 to amida, carbendazim and tebuconazole
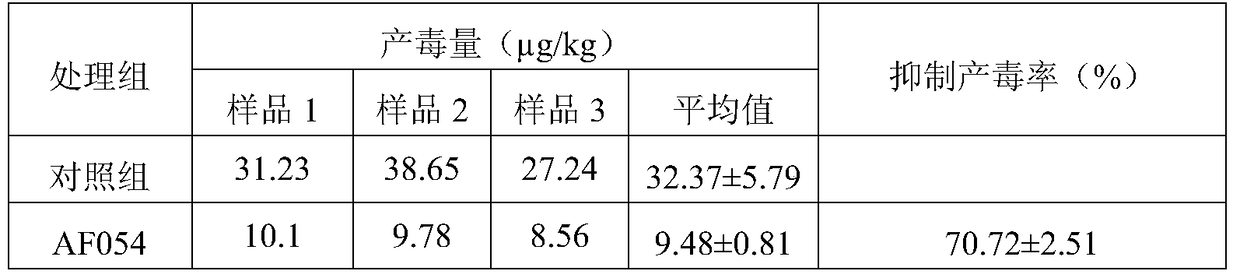
[0060] Inoculate AF054 or toxin-producing Aspergillus flavus standard strain NRRL3357 on PDA plates containing 10 μg / mL carbendazim or 25 μg / mL tebuconazole or 100 μg / mL amida, respectively, and observe the effect of the strains on fungicides after culturing at 25 degrees for 3 days. resistance. The experiment took PDA without fungicide as the control. from figure 2 It can be seen that the non-toxin-producing Aspergillus flavus strain AF054 of the present invention can resist carbendazim, tebuconazole and amida. And AF054 on the plate containing fungicide will not affect its ability to produce conidia.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com