Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
134 results about "Palate muscle" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
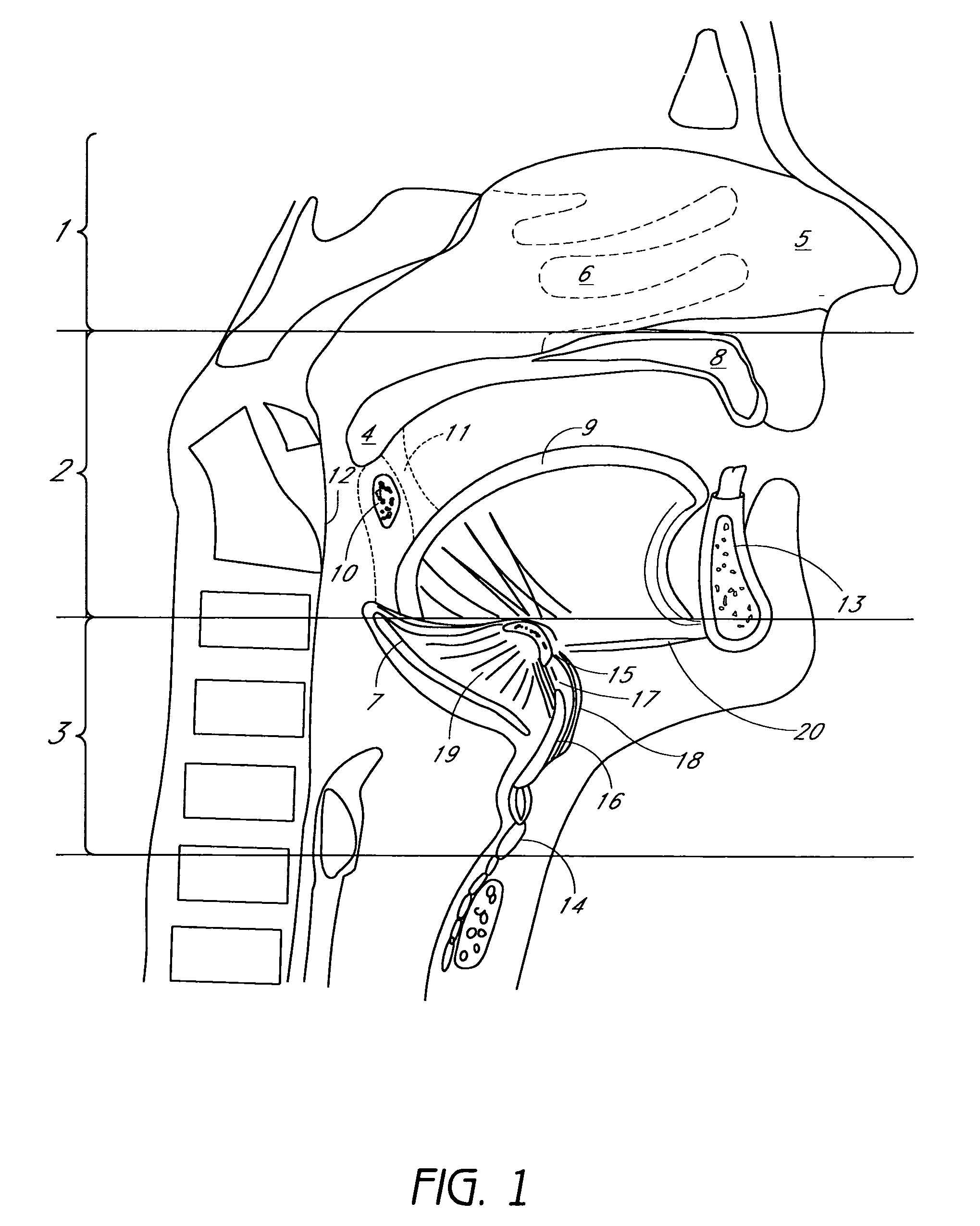
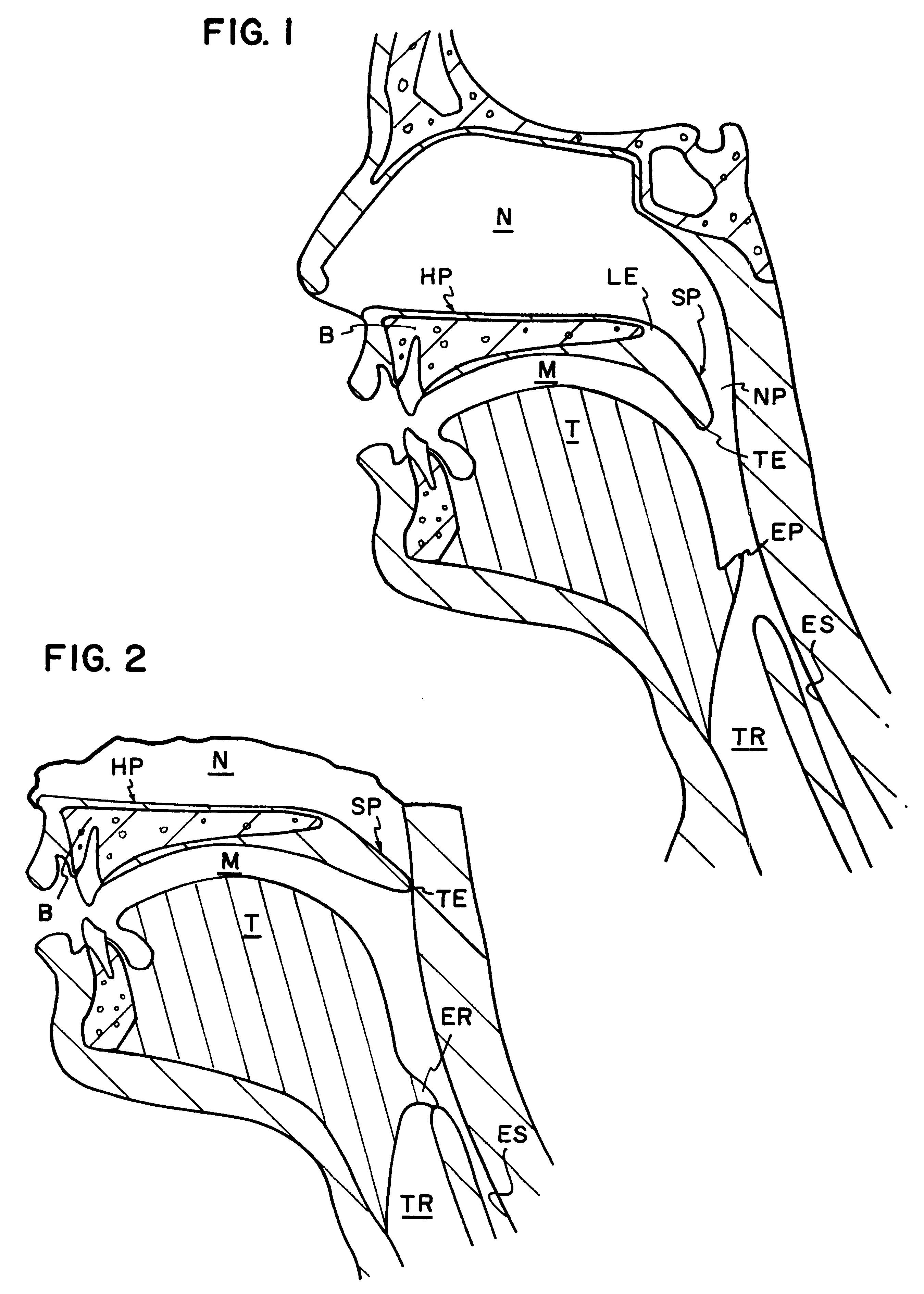
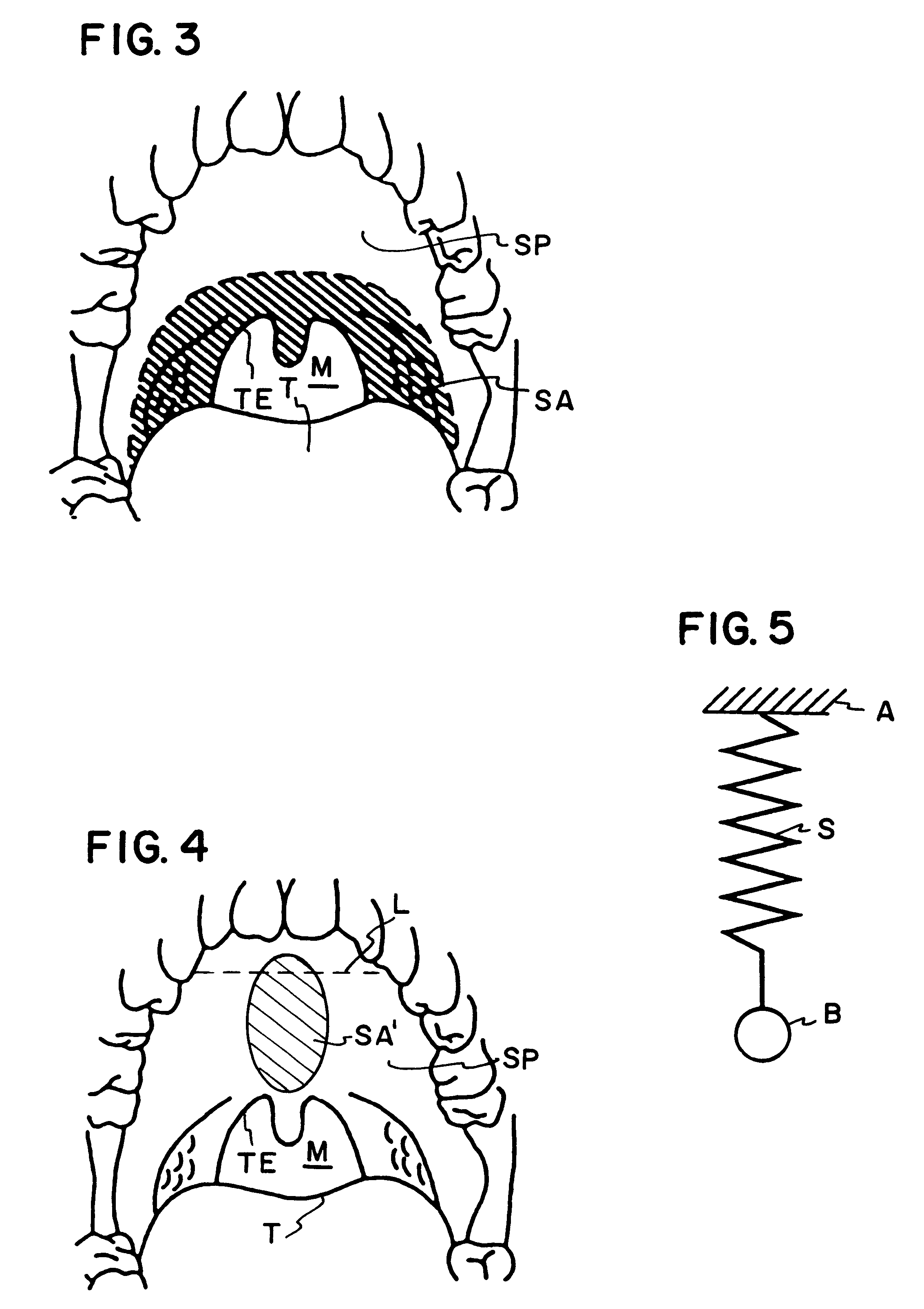
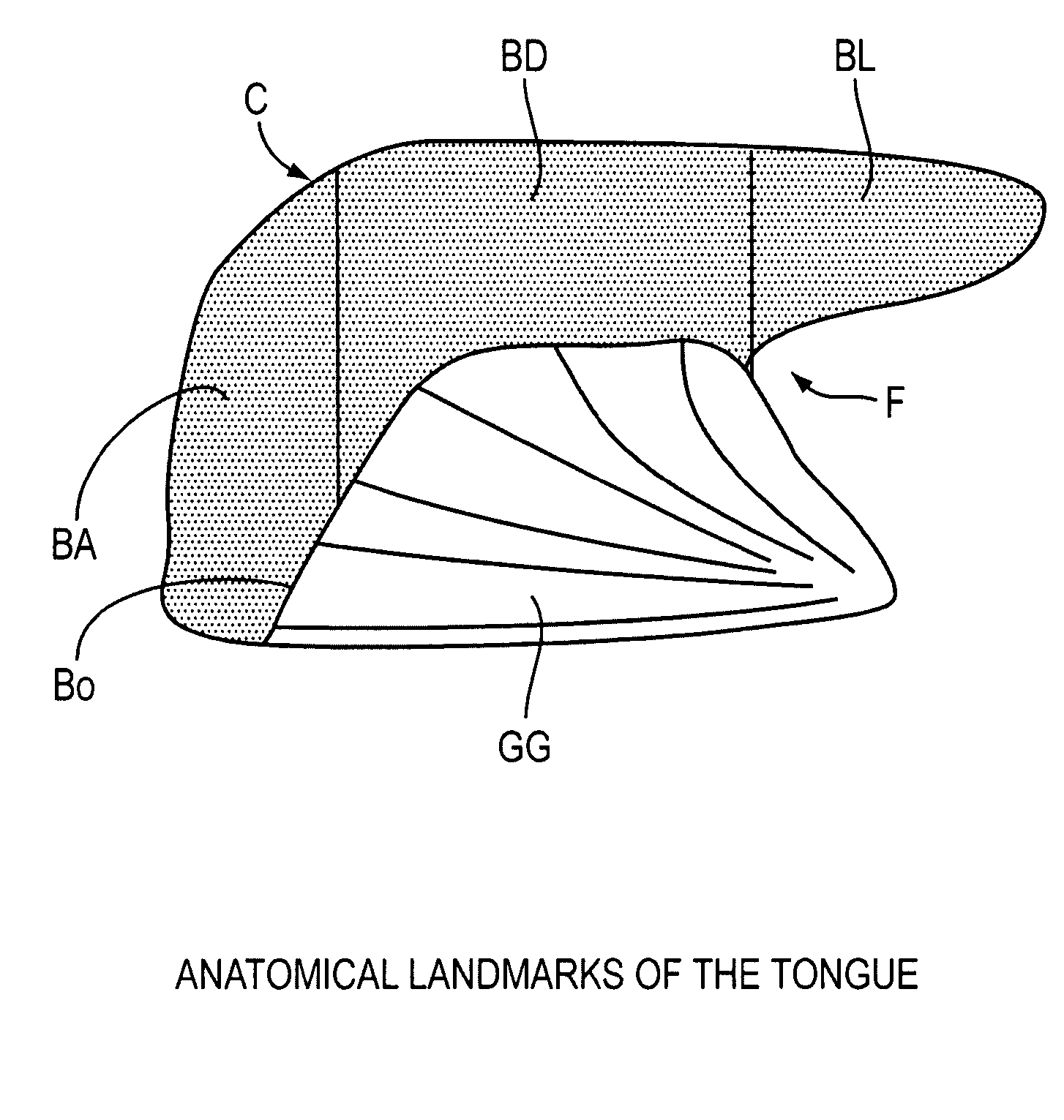
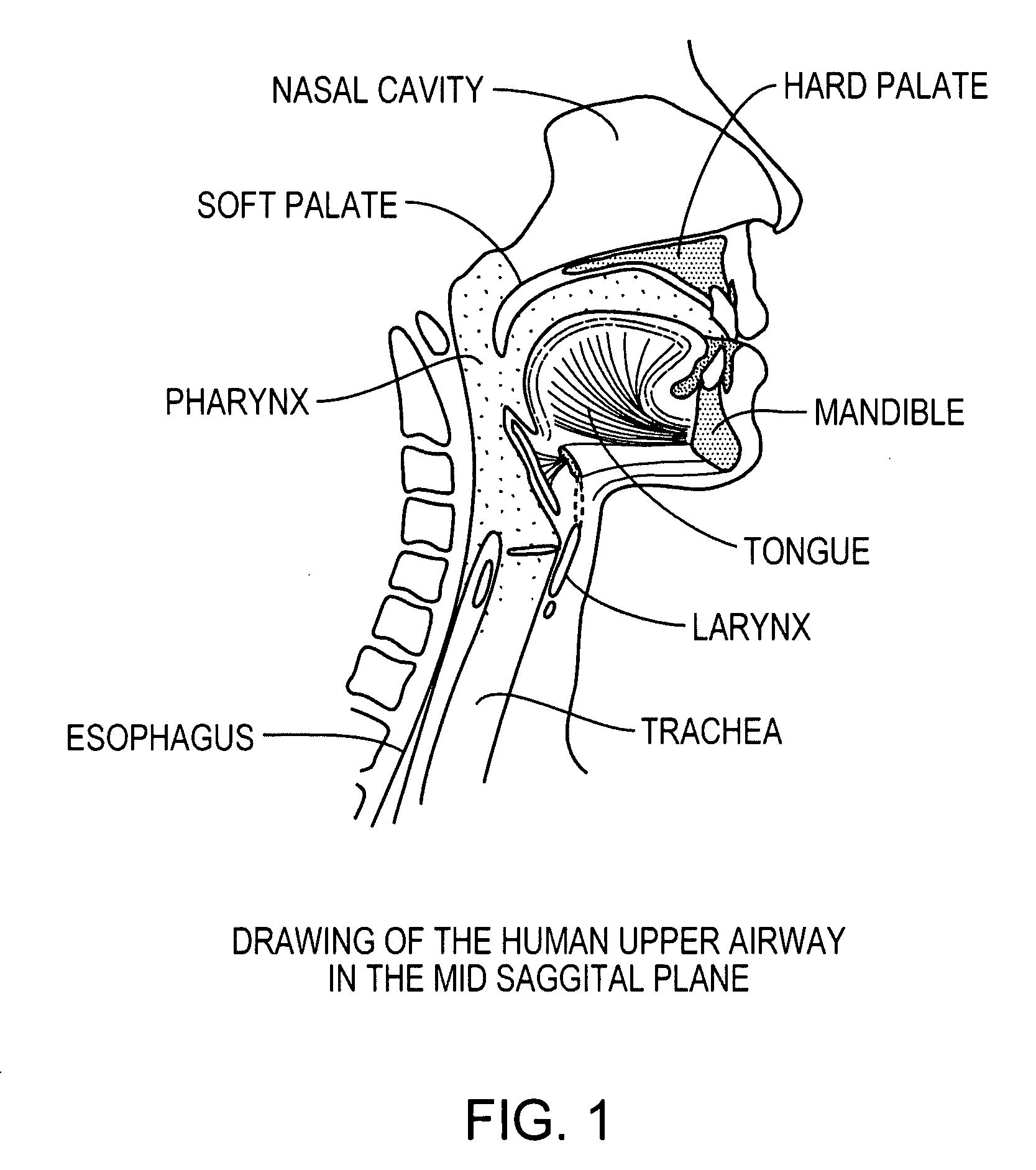
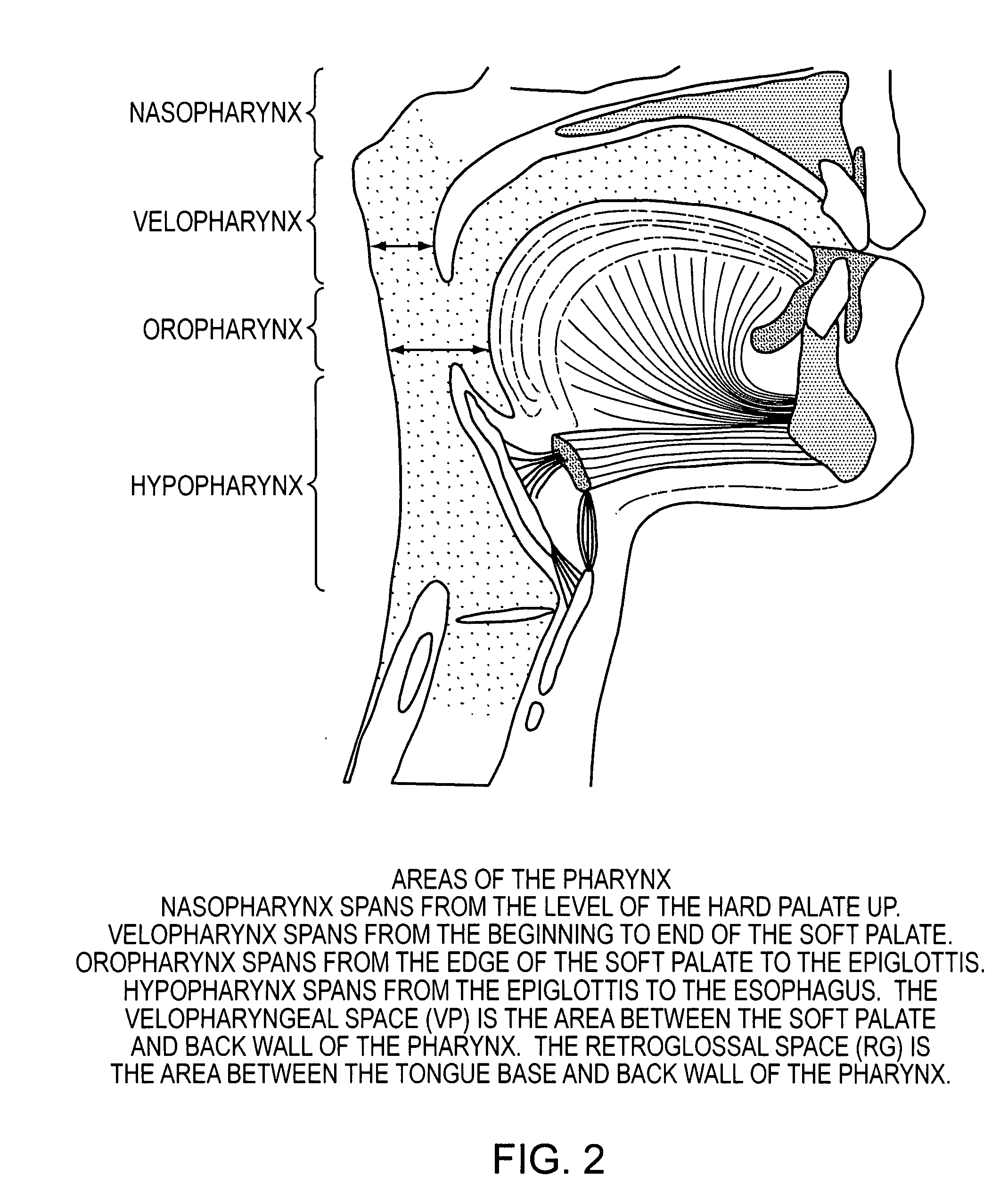
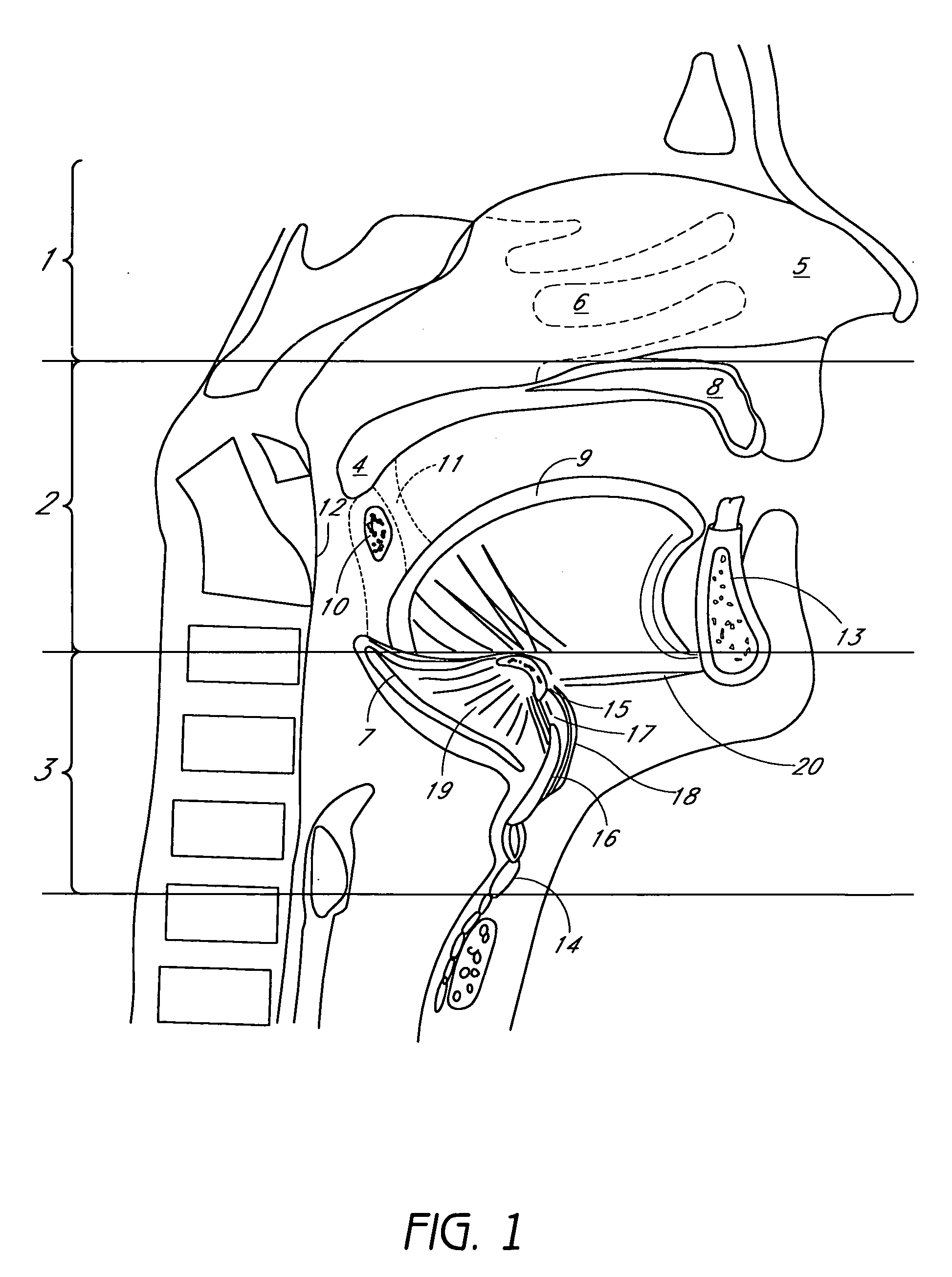
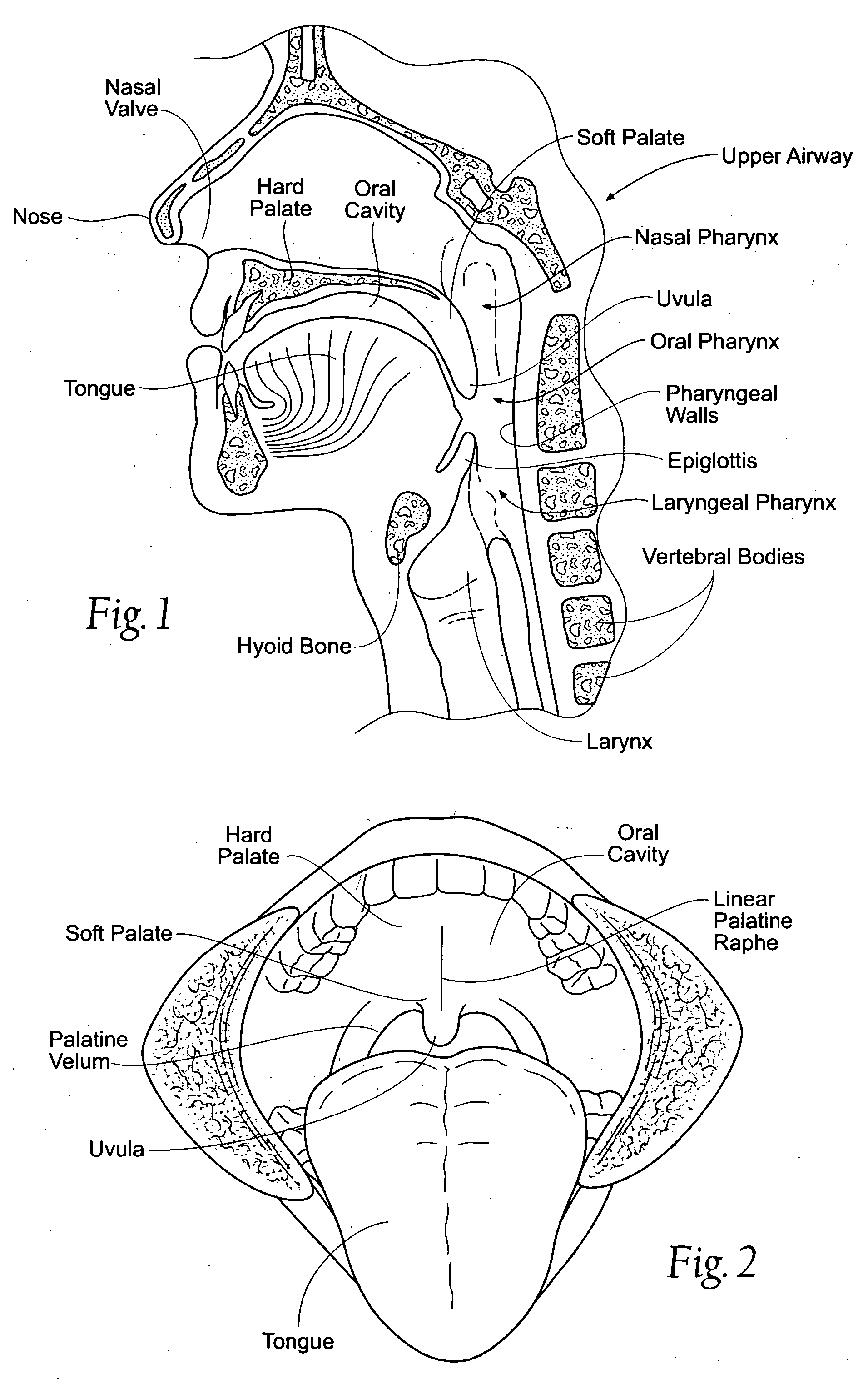
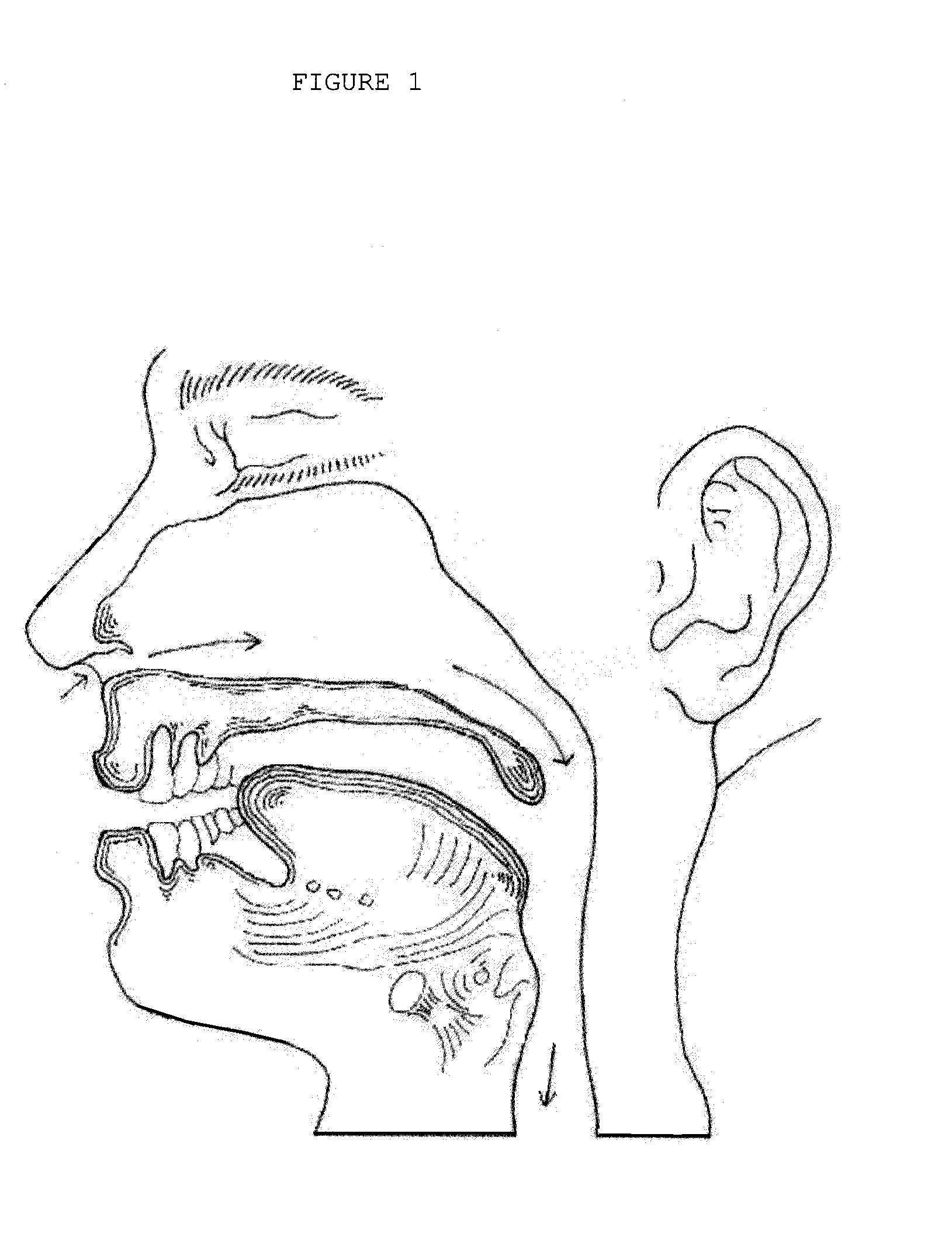
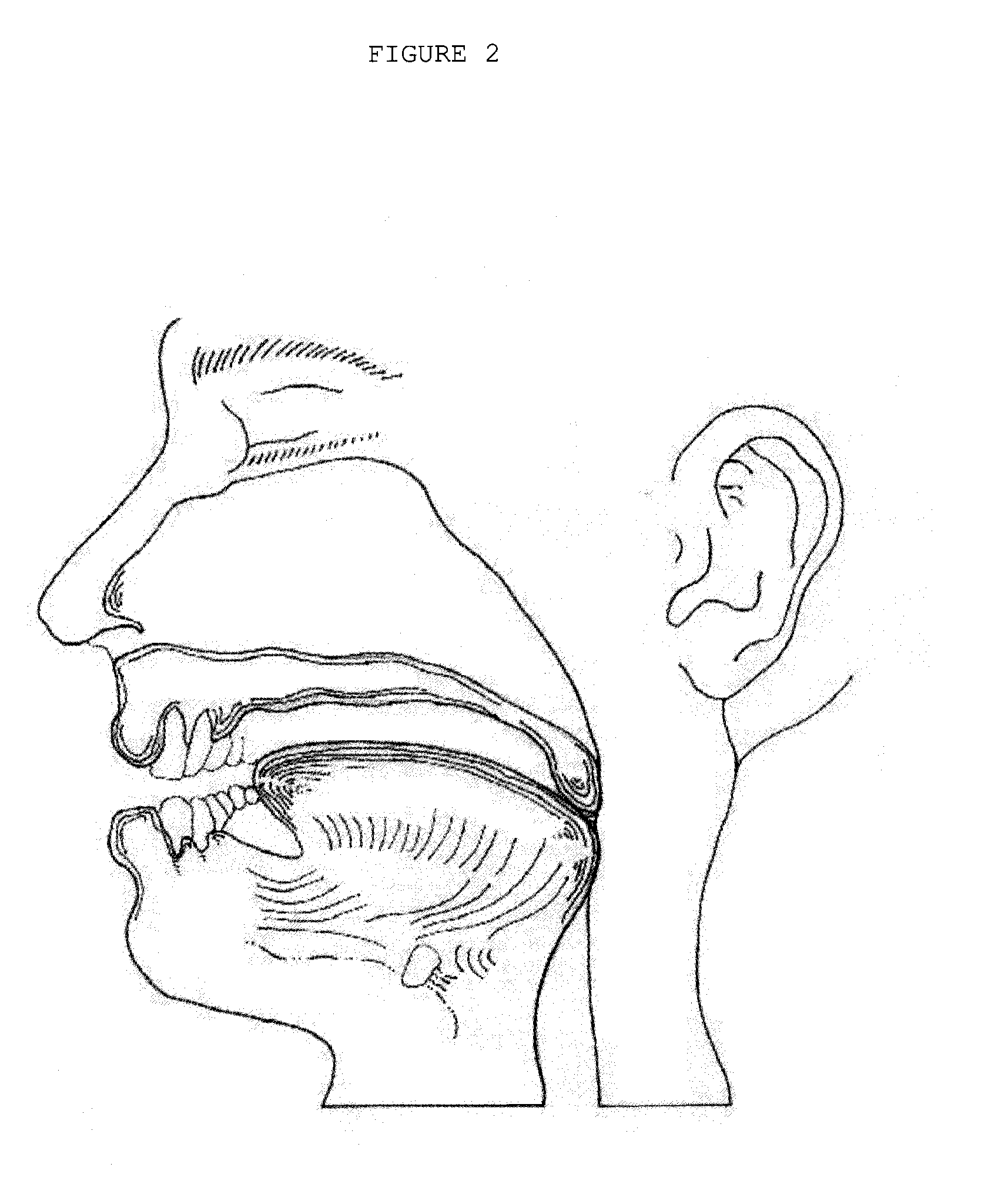
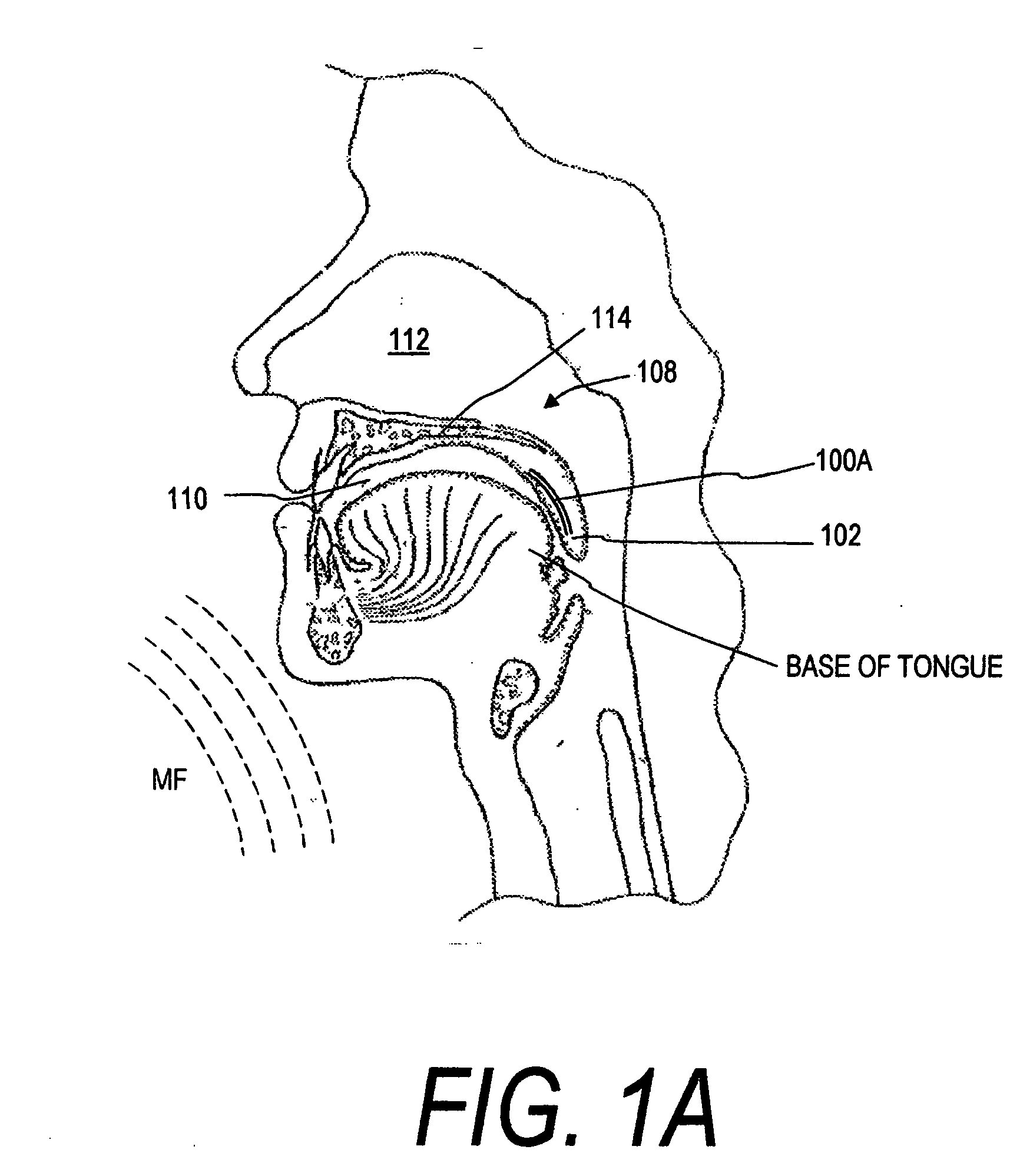
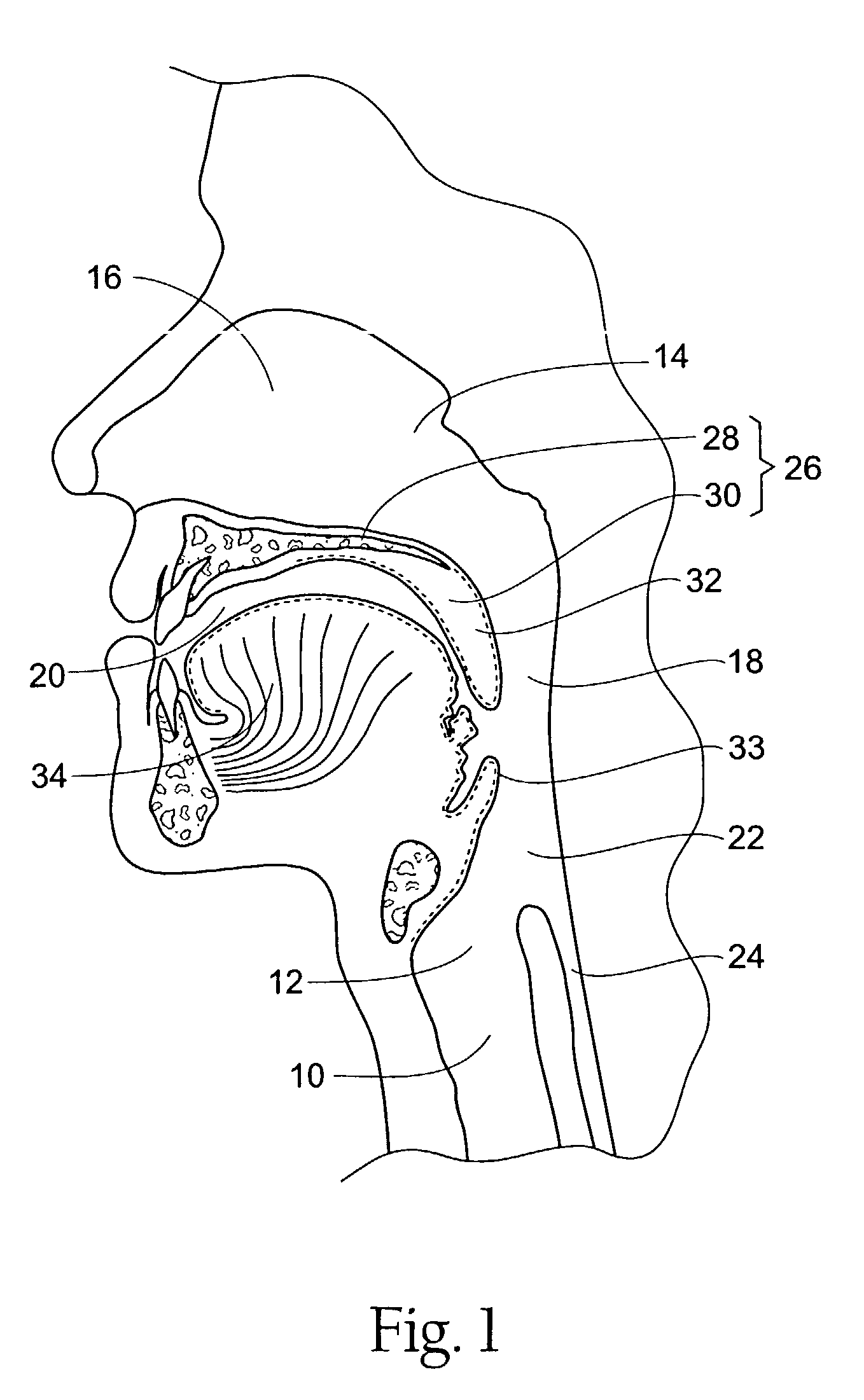
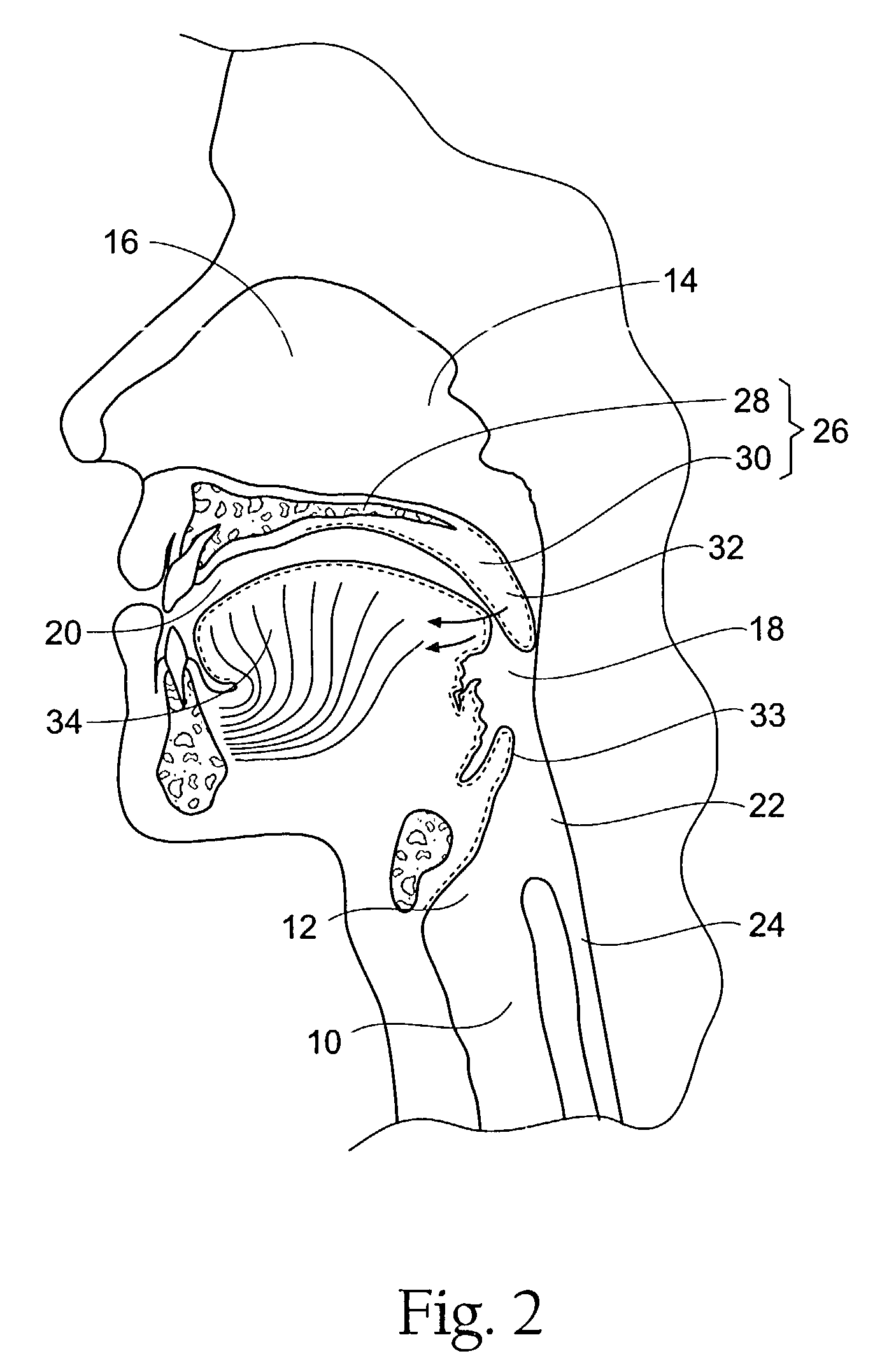
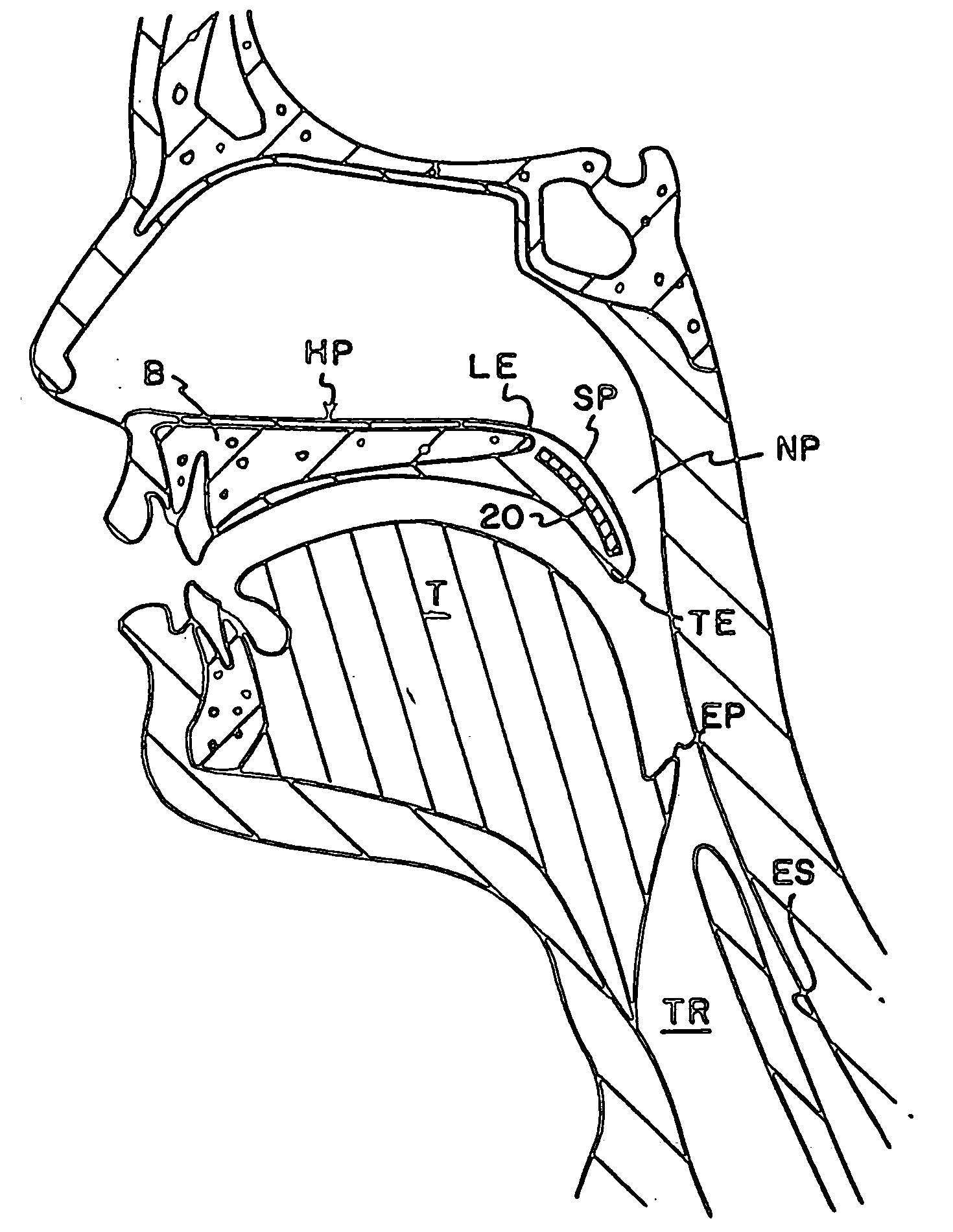
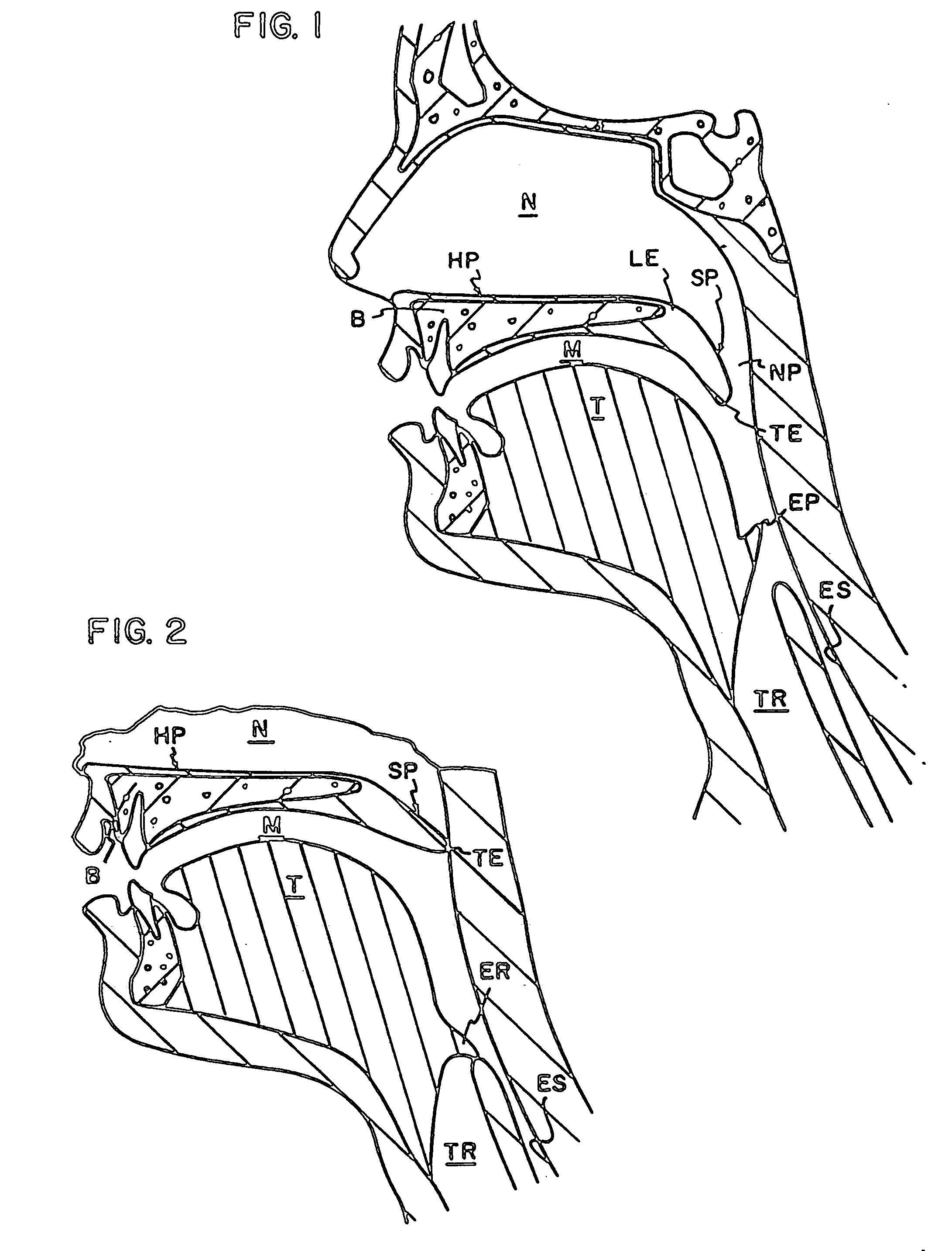
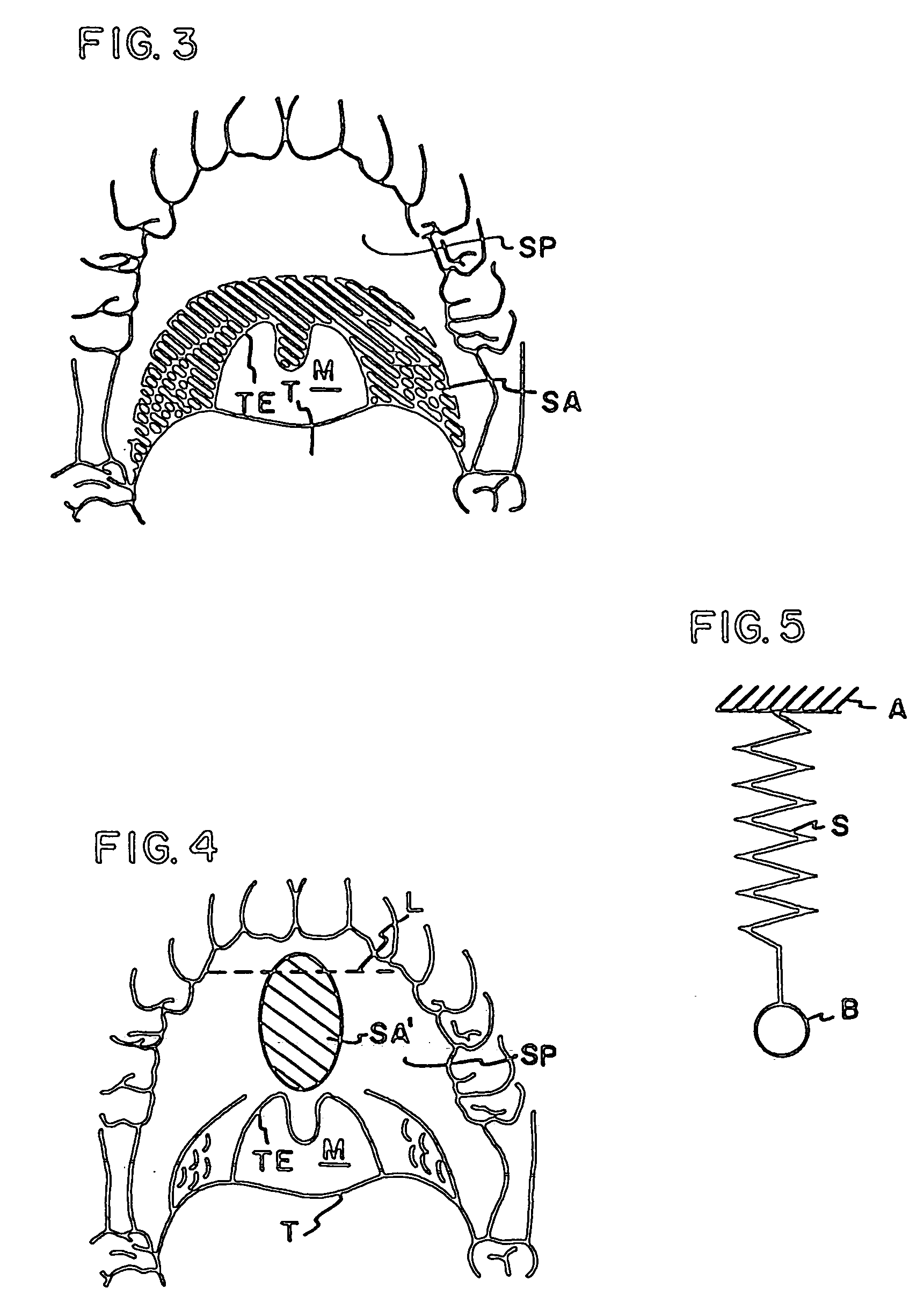
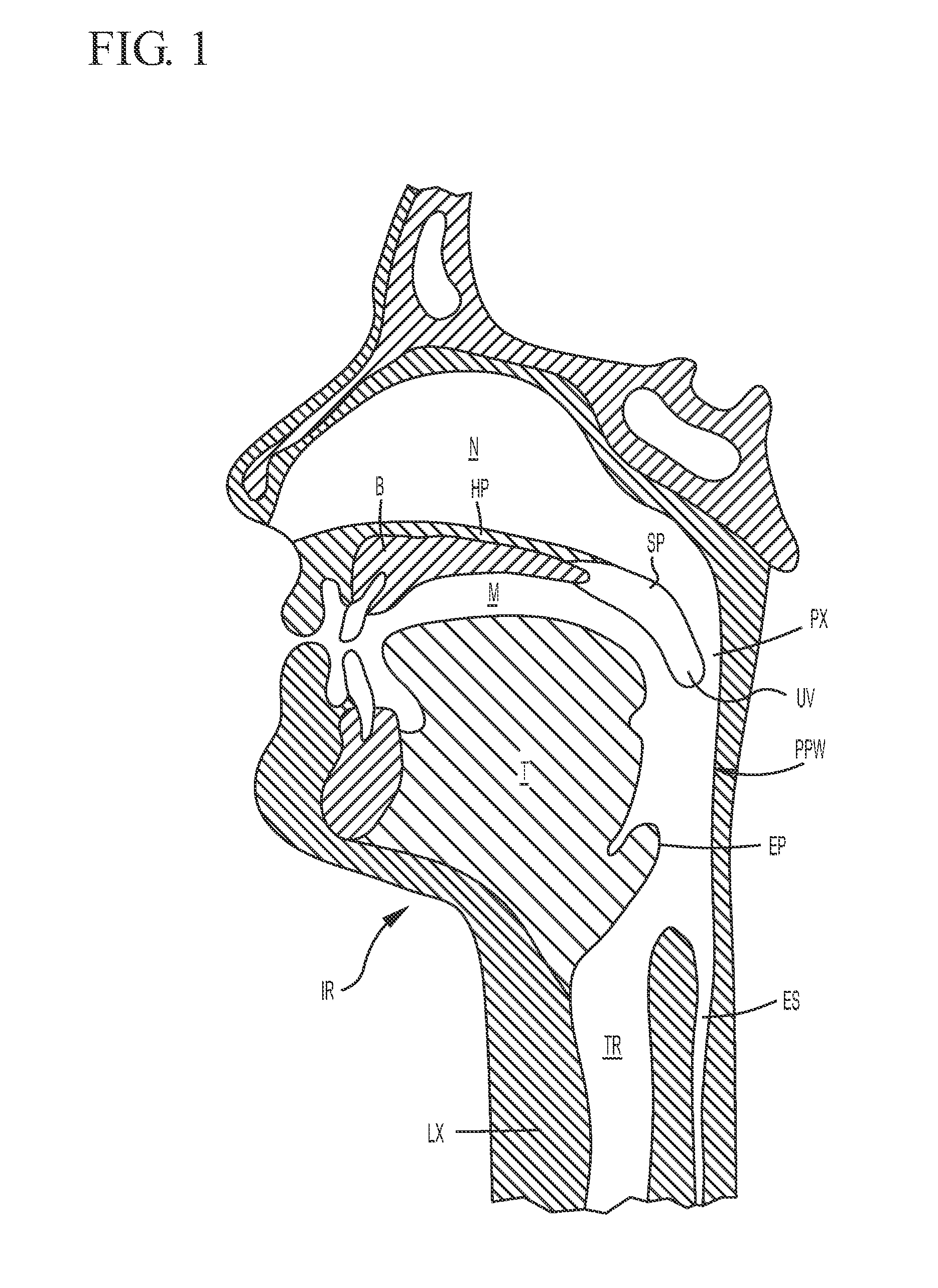
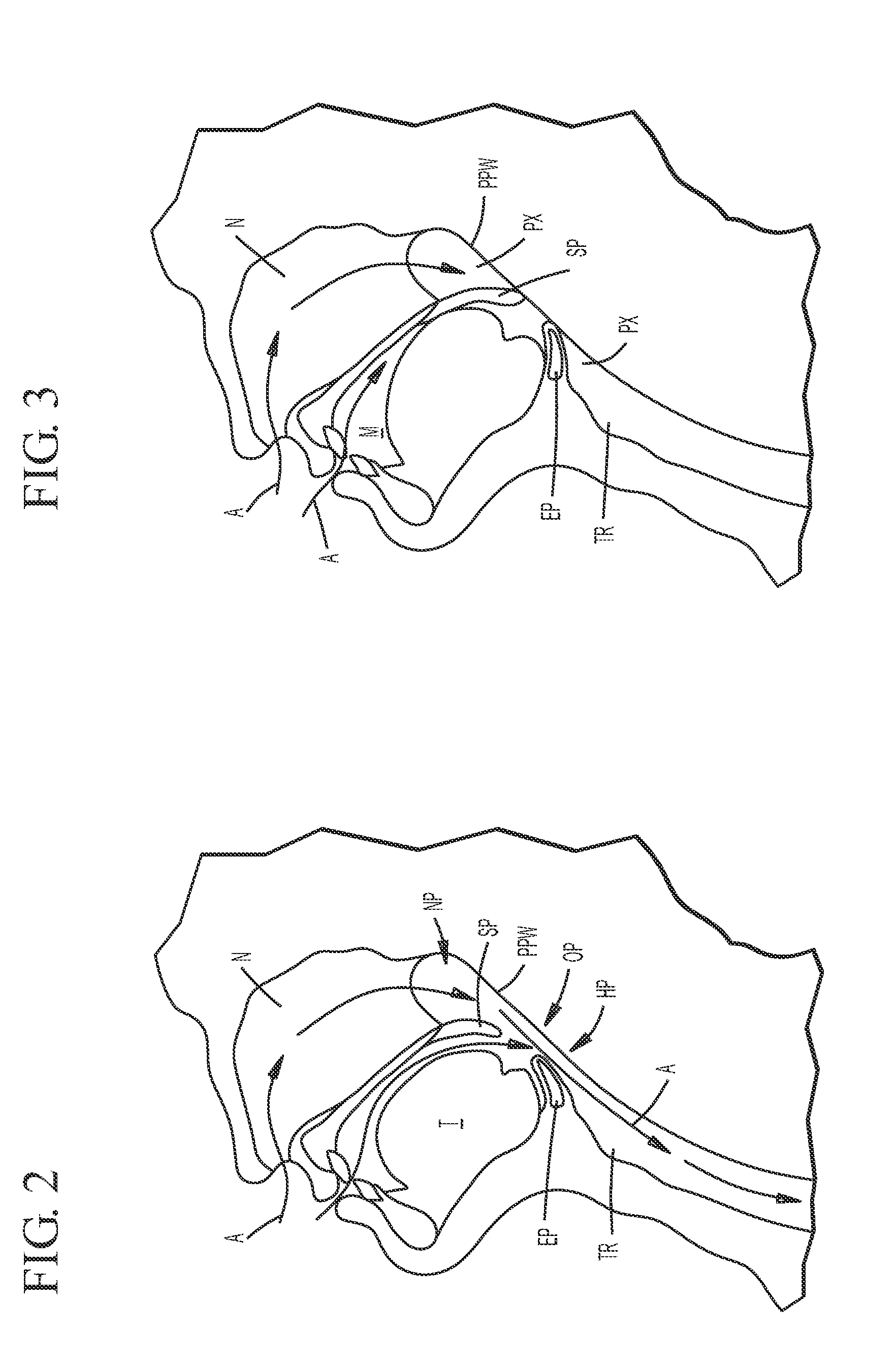
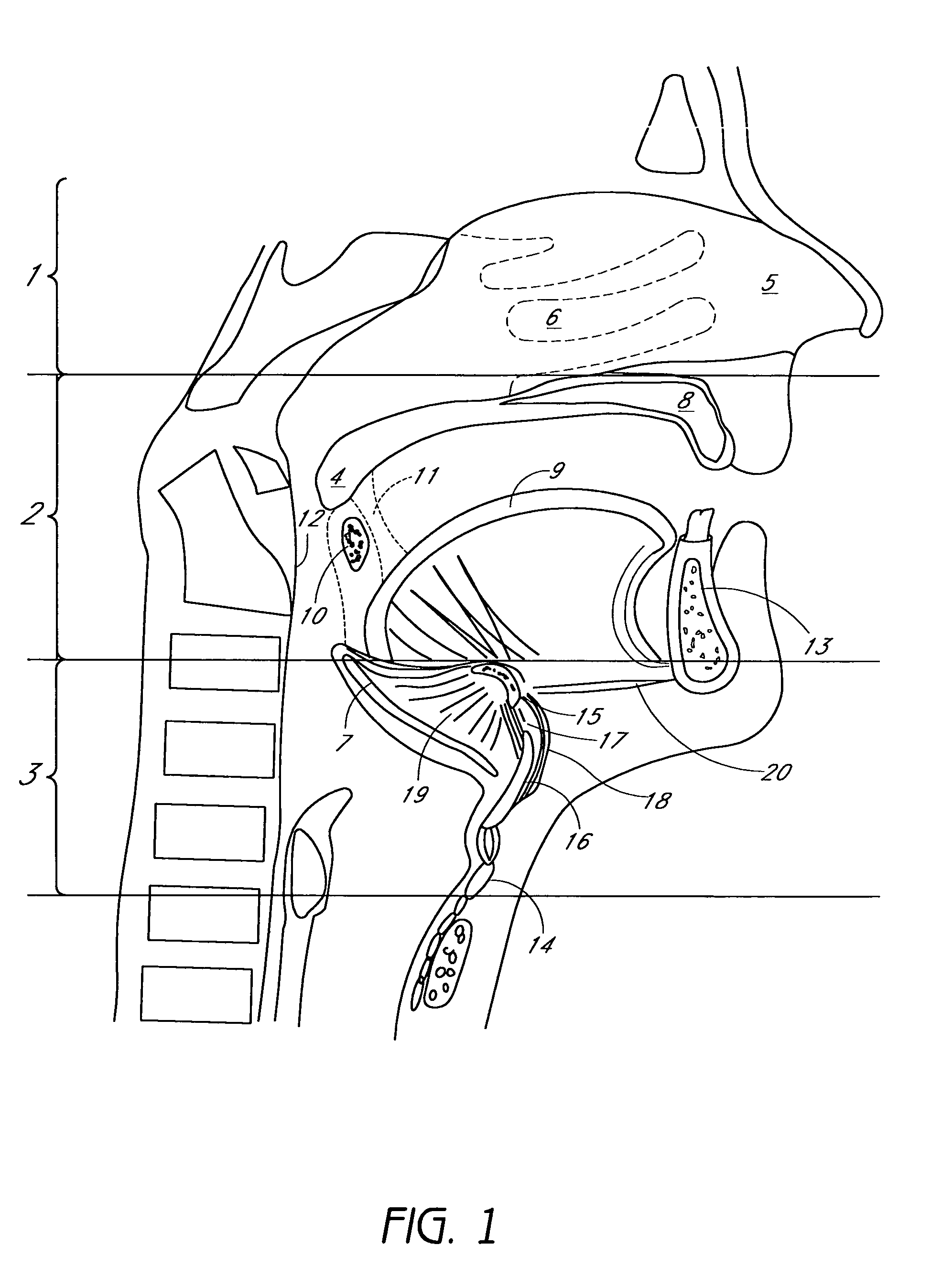
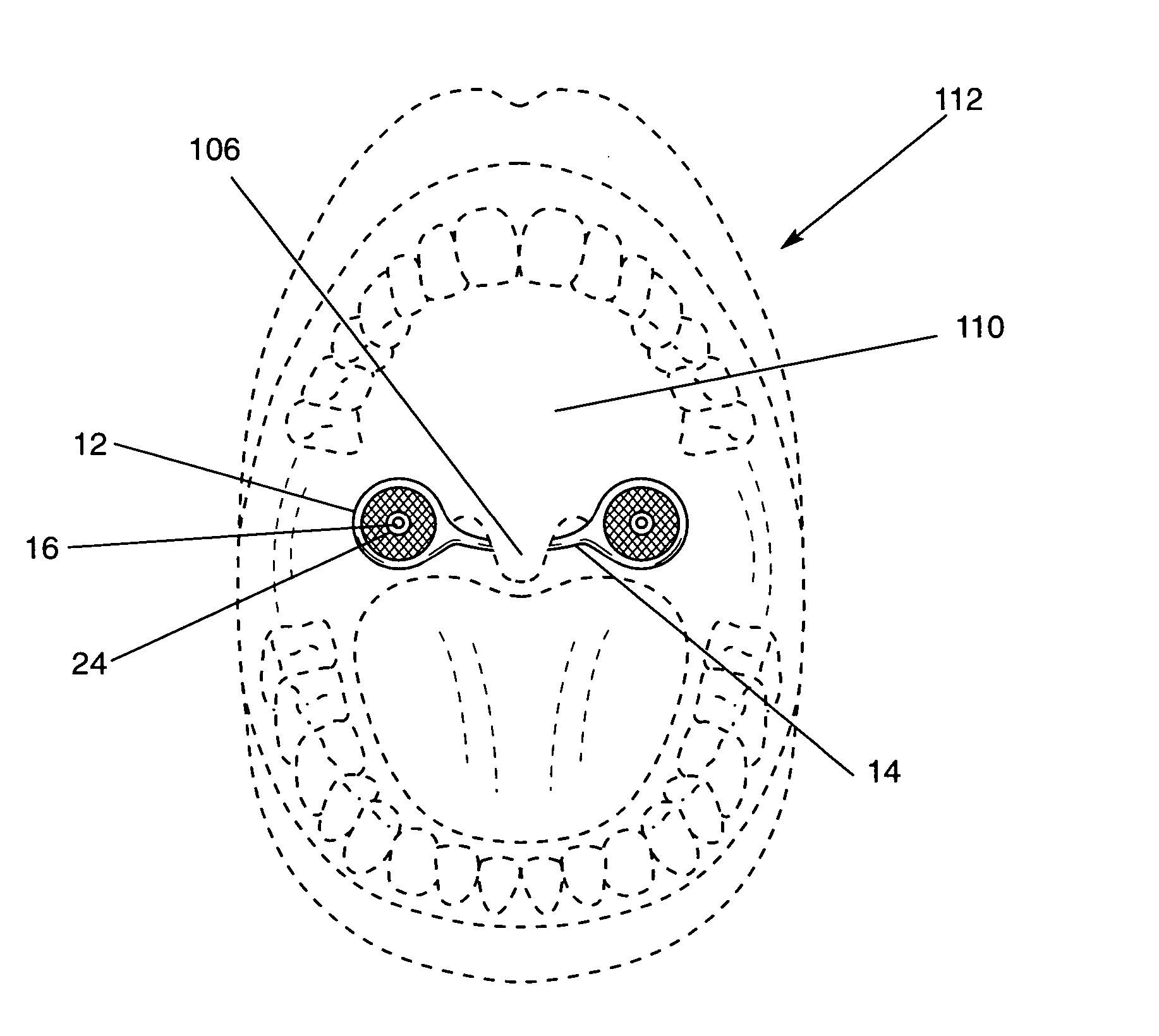
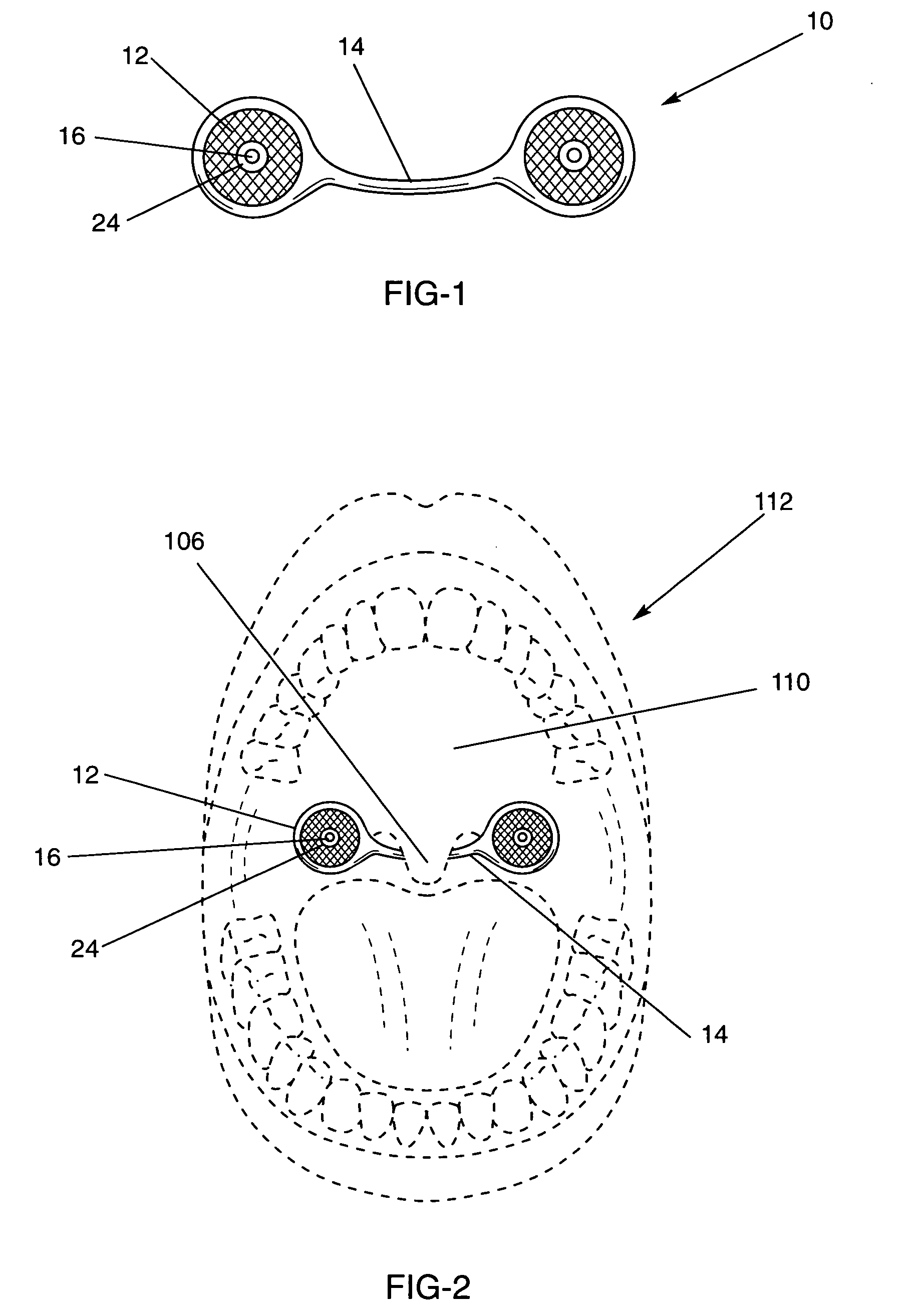
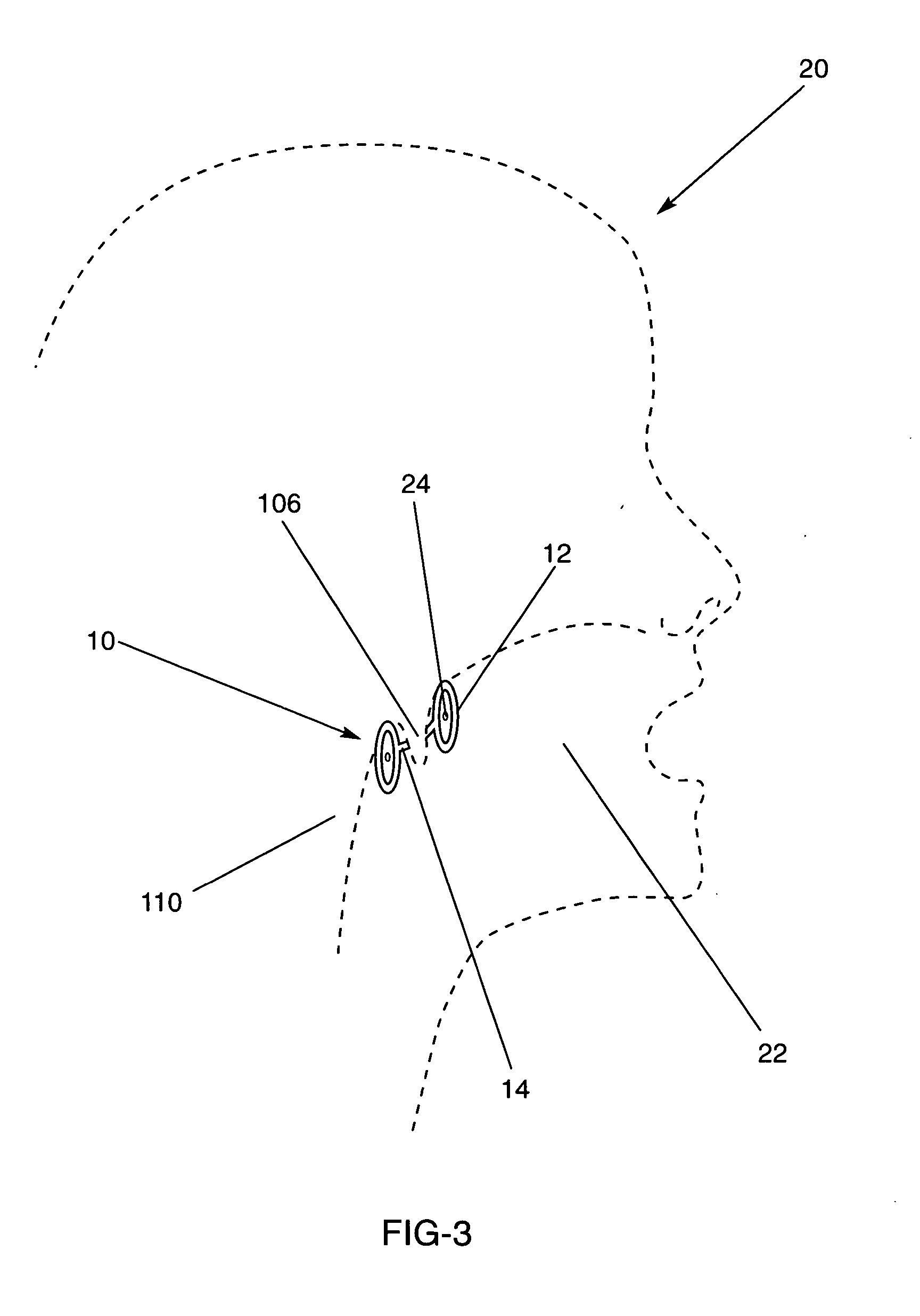
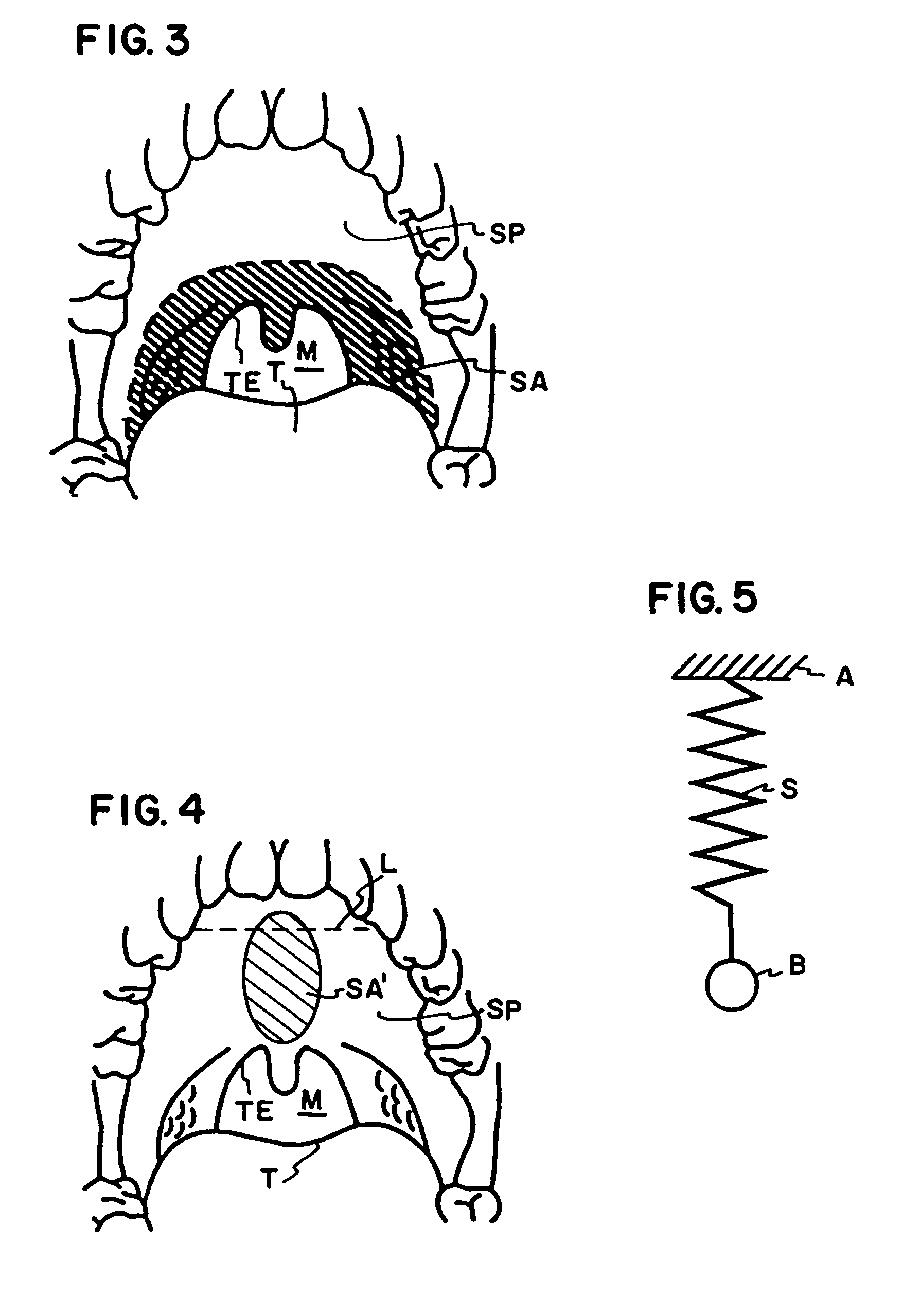
The five muscles of the soft palate play important roles in swallowing and breathing. The muscles are: These muscles are innervated by the pharyngeal plexus via the vagus nerve, with the exception of the tensor veli palatini.
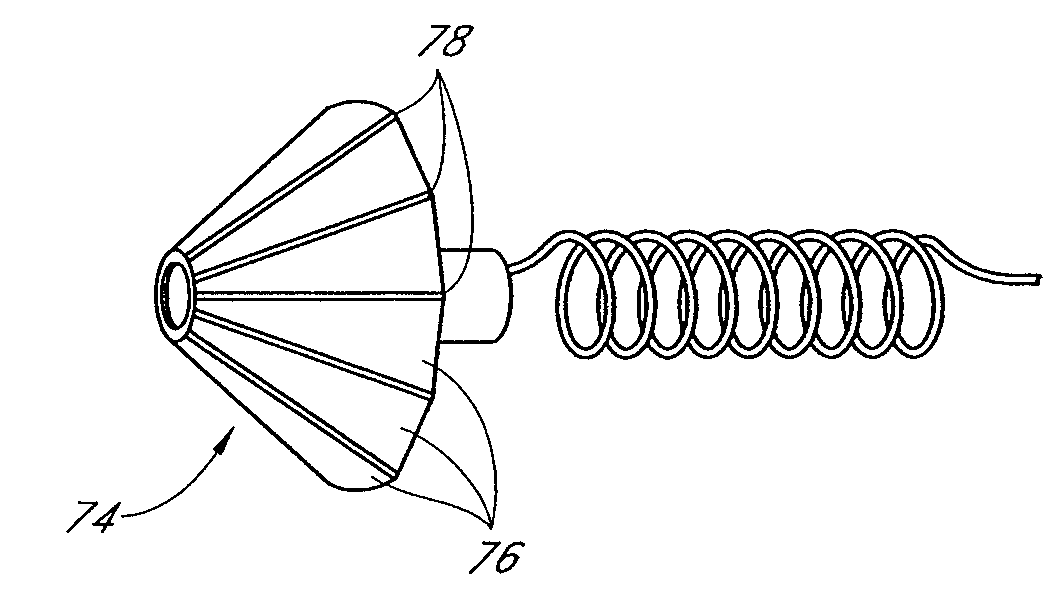
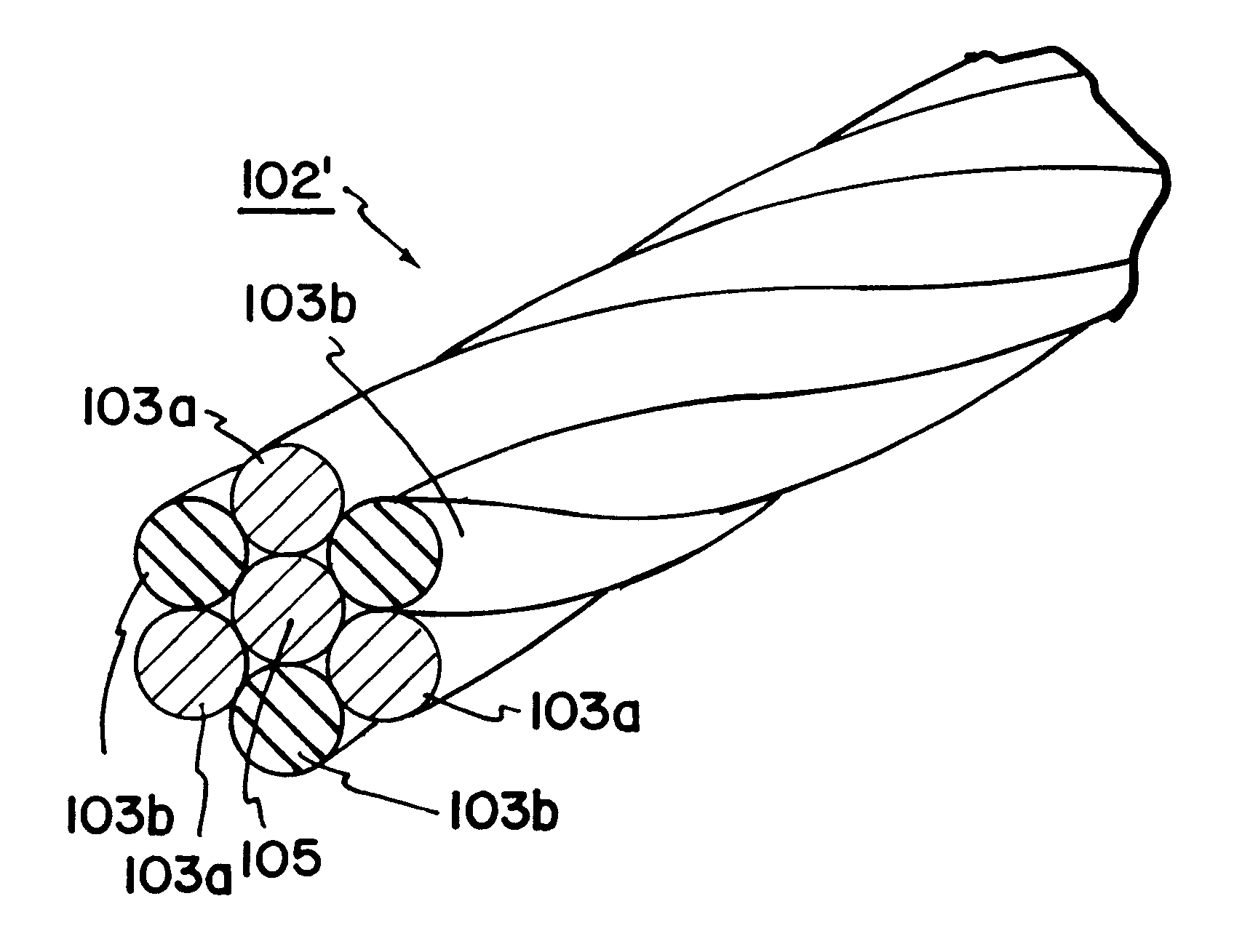
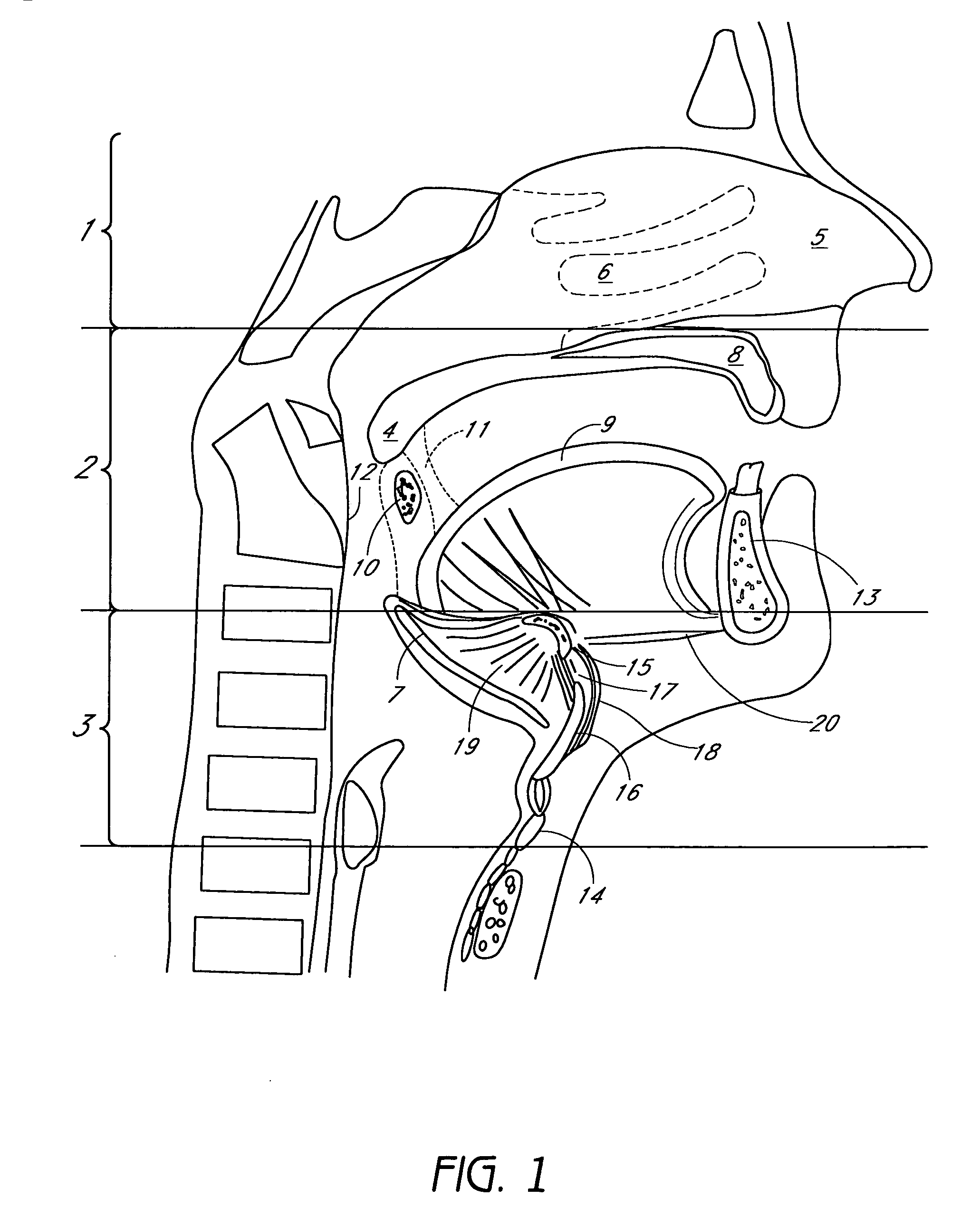
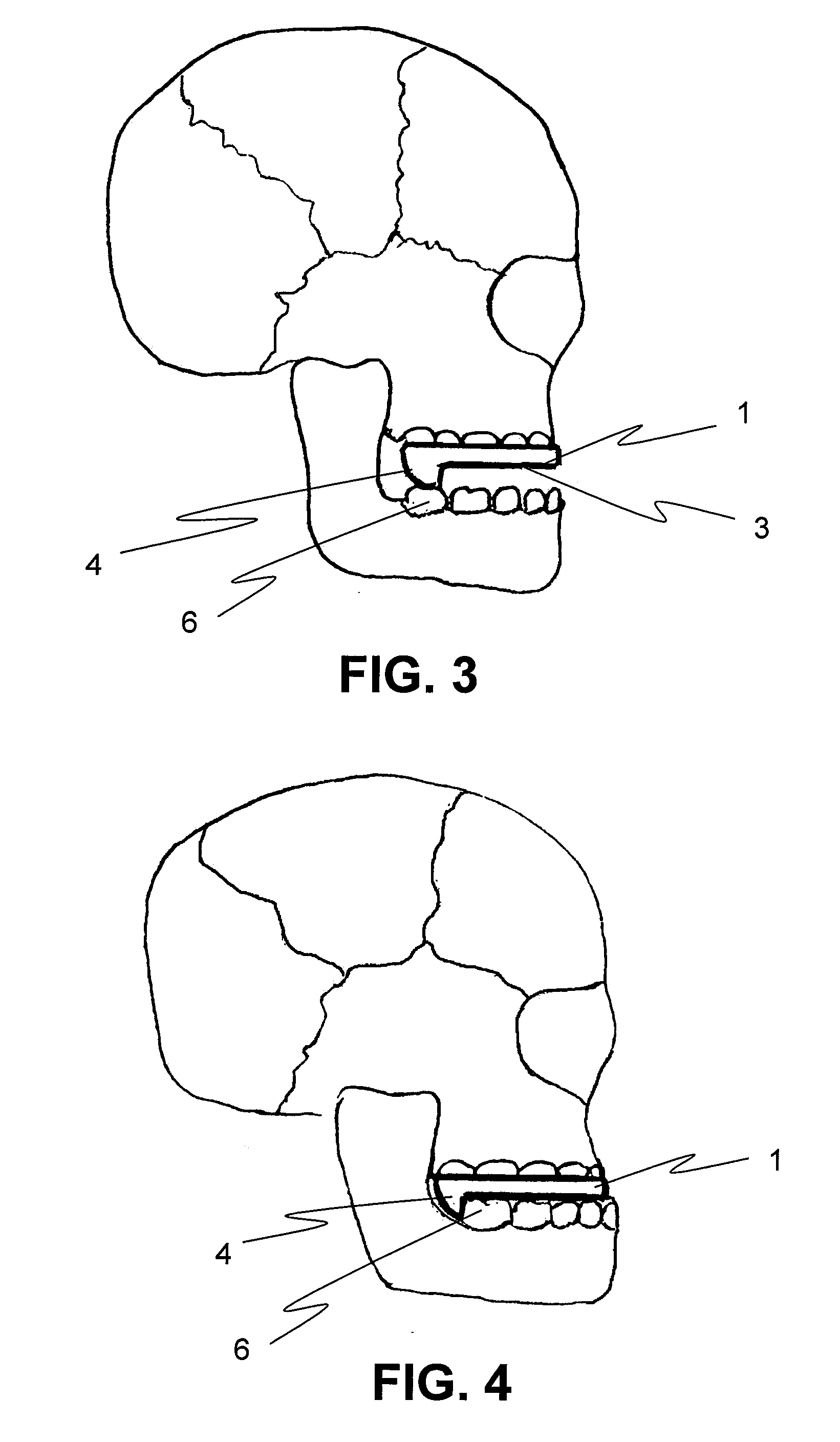
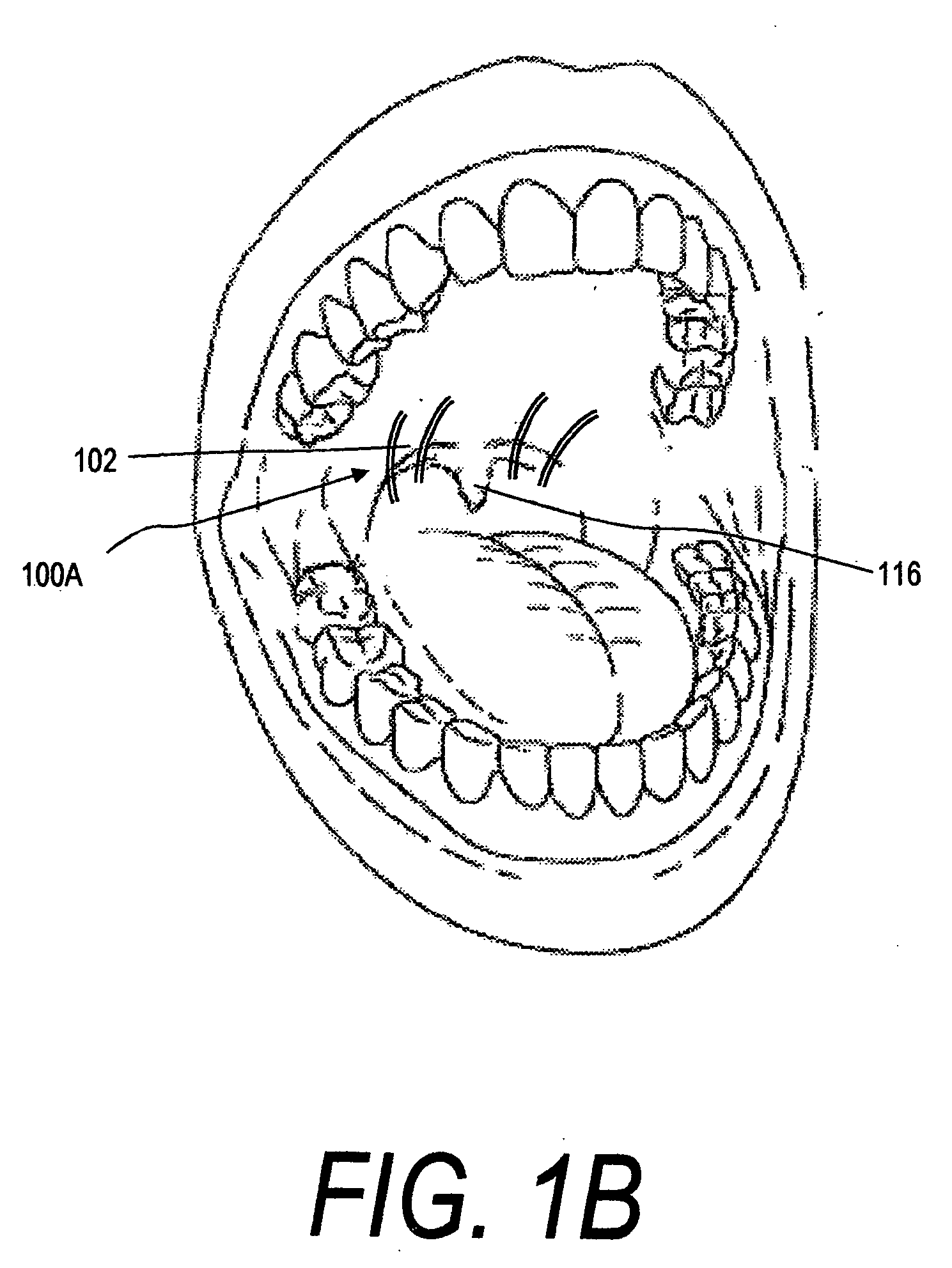
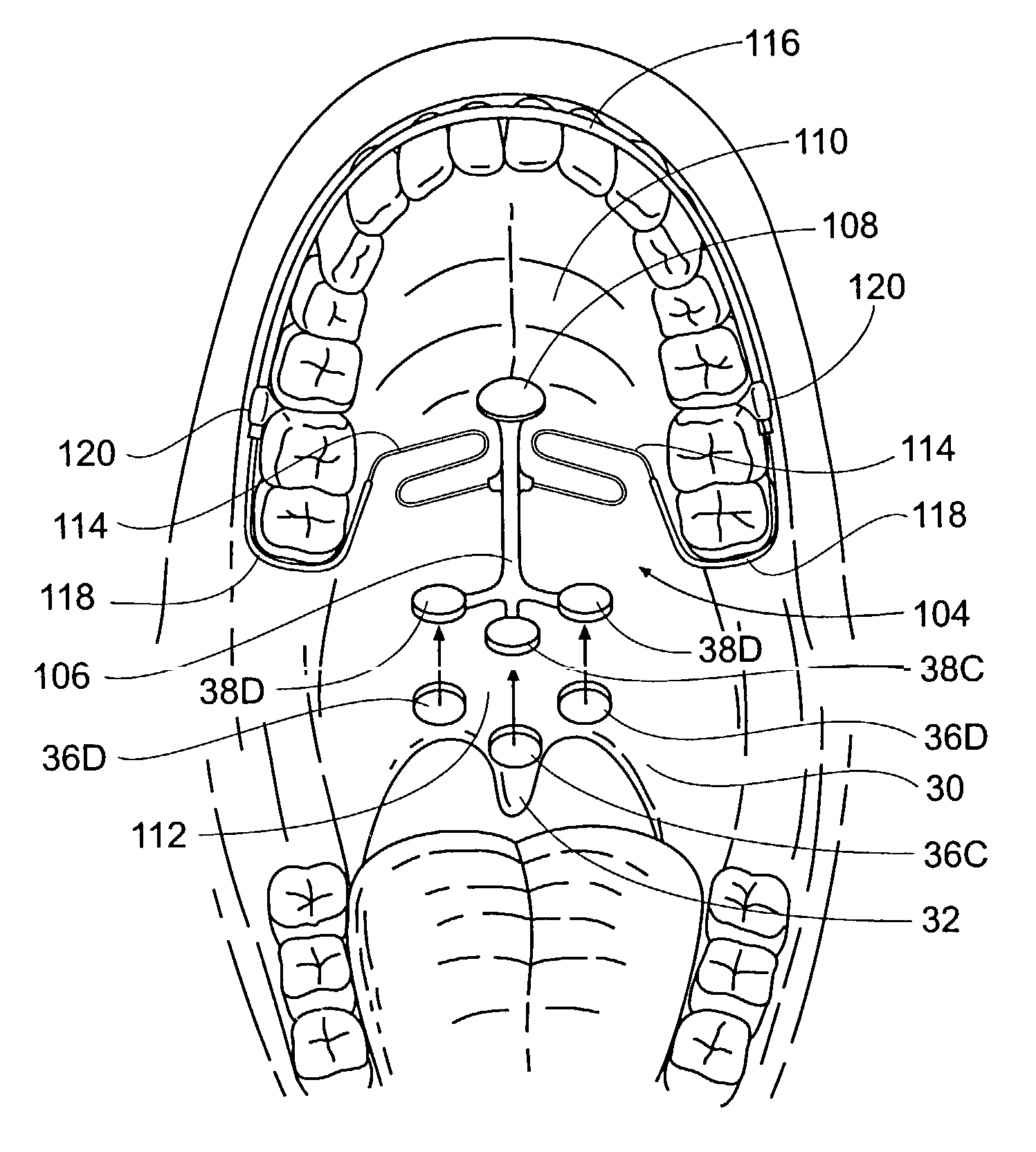
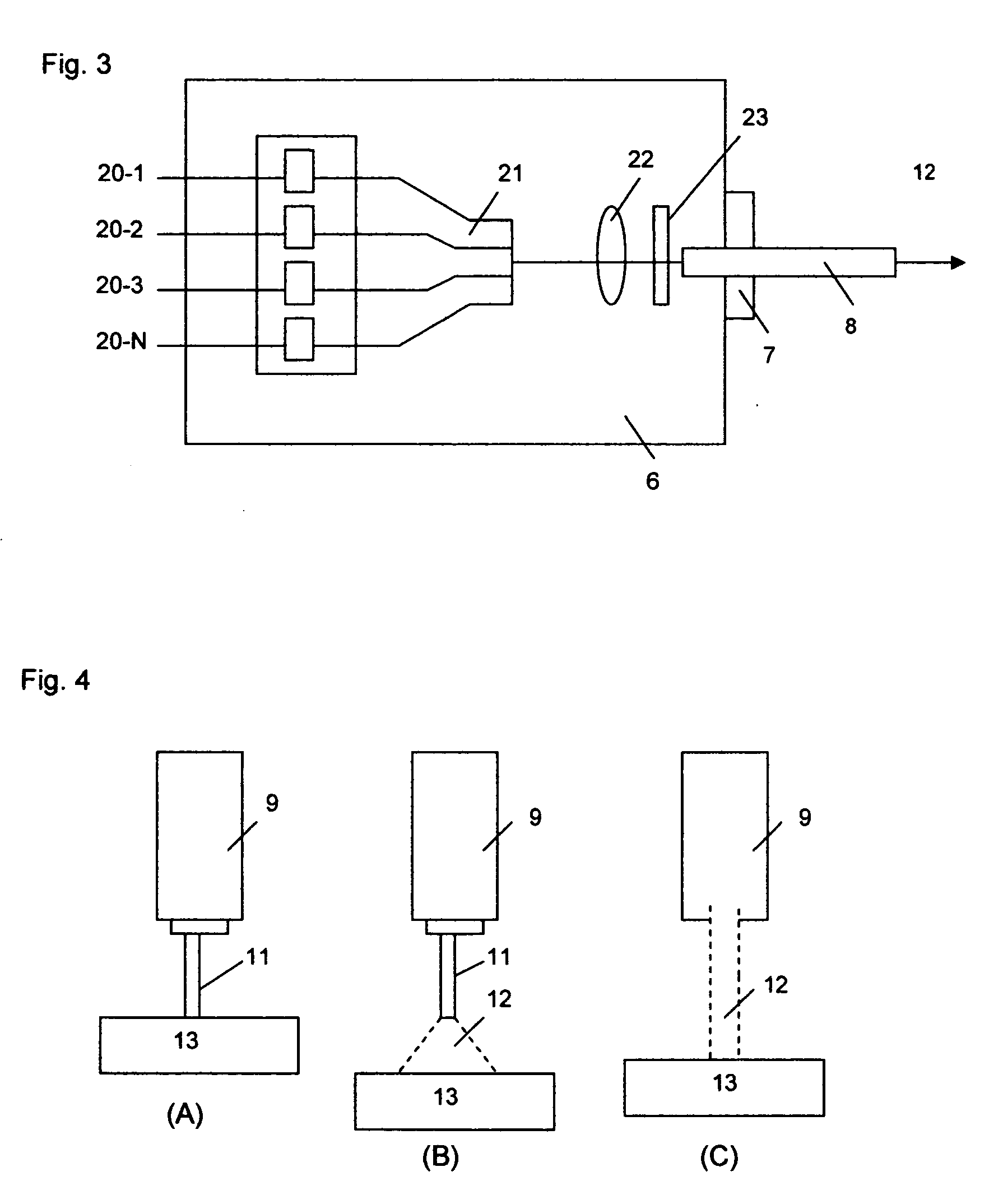
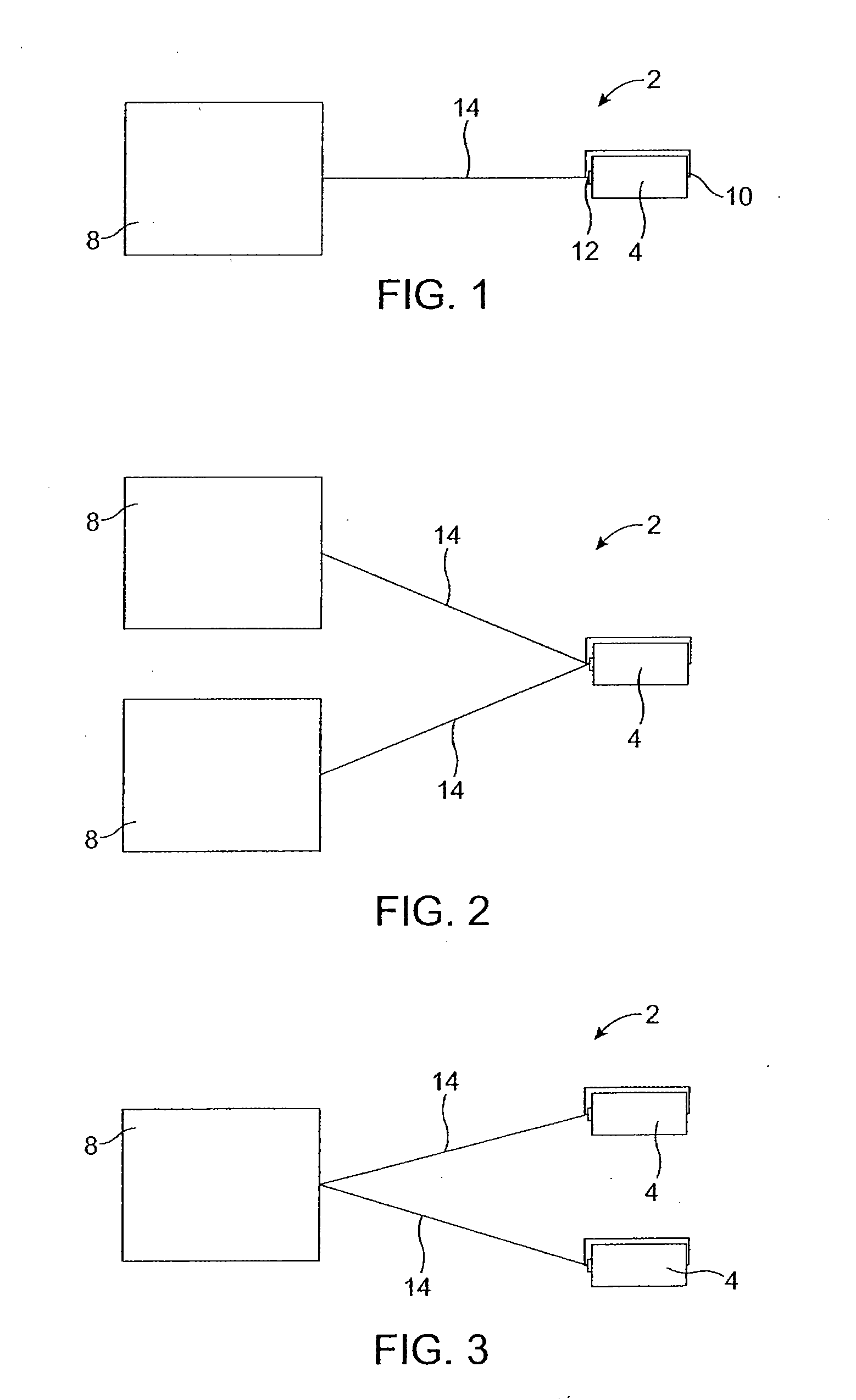
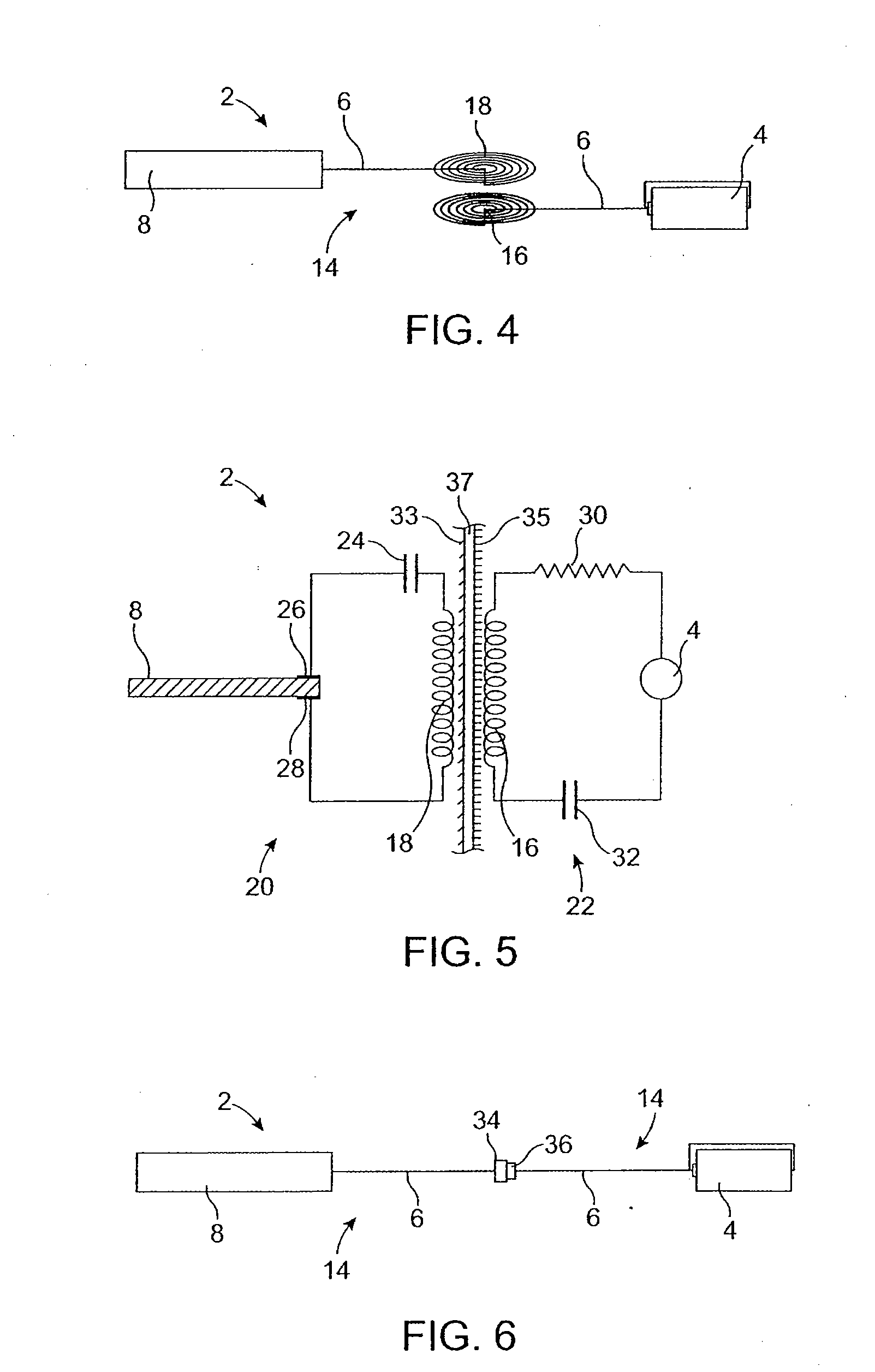
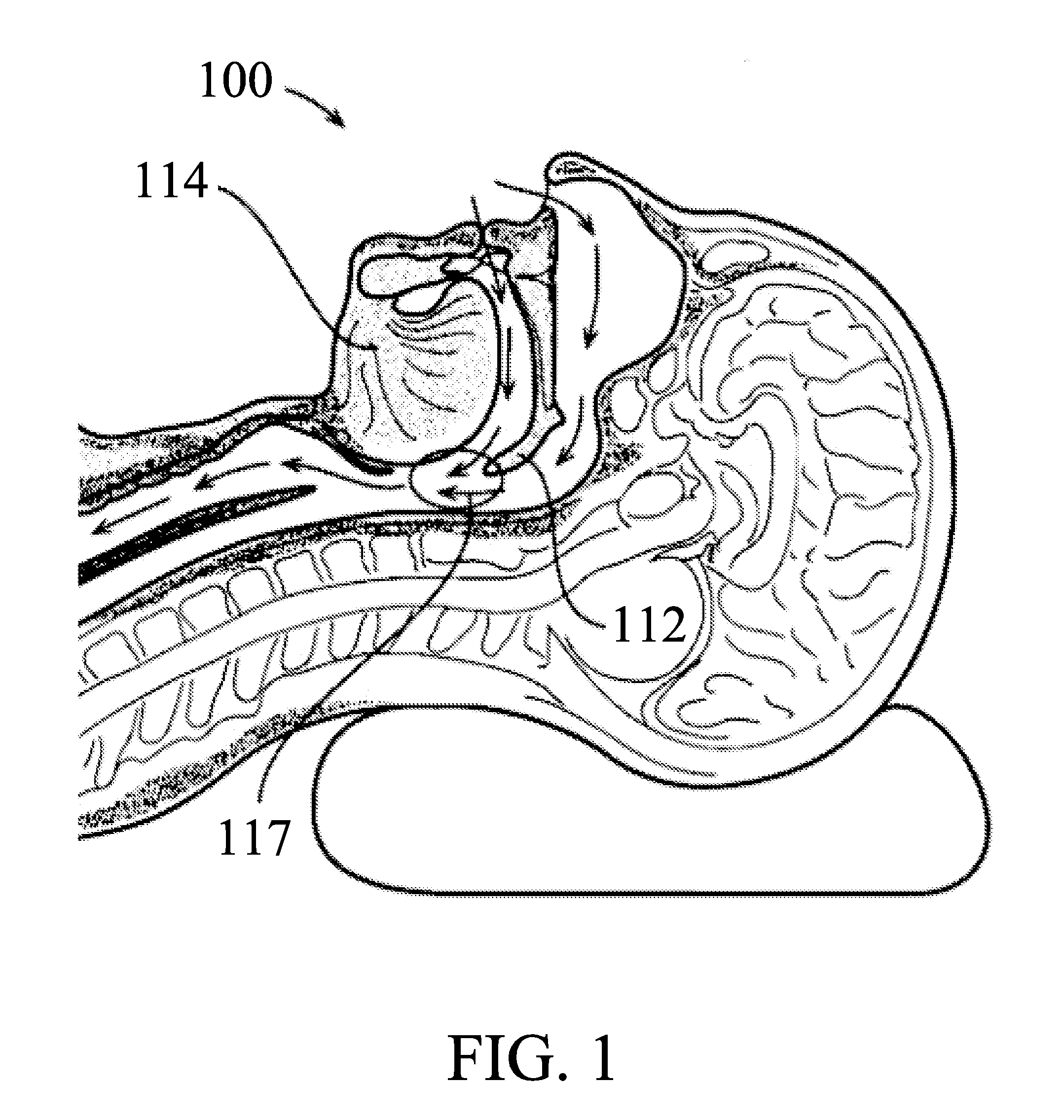
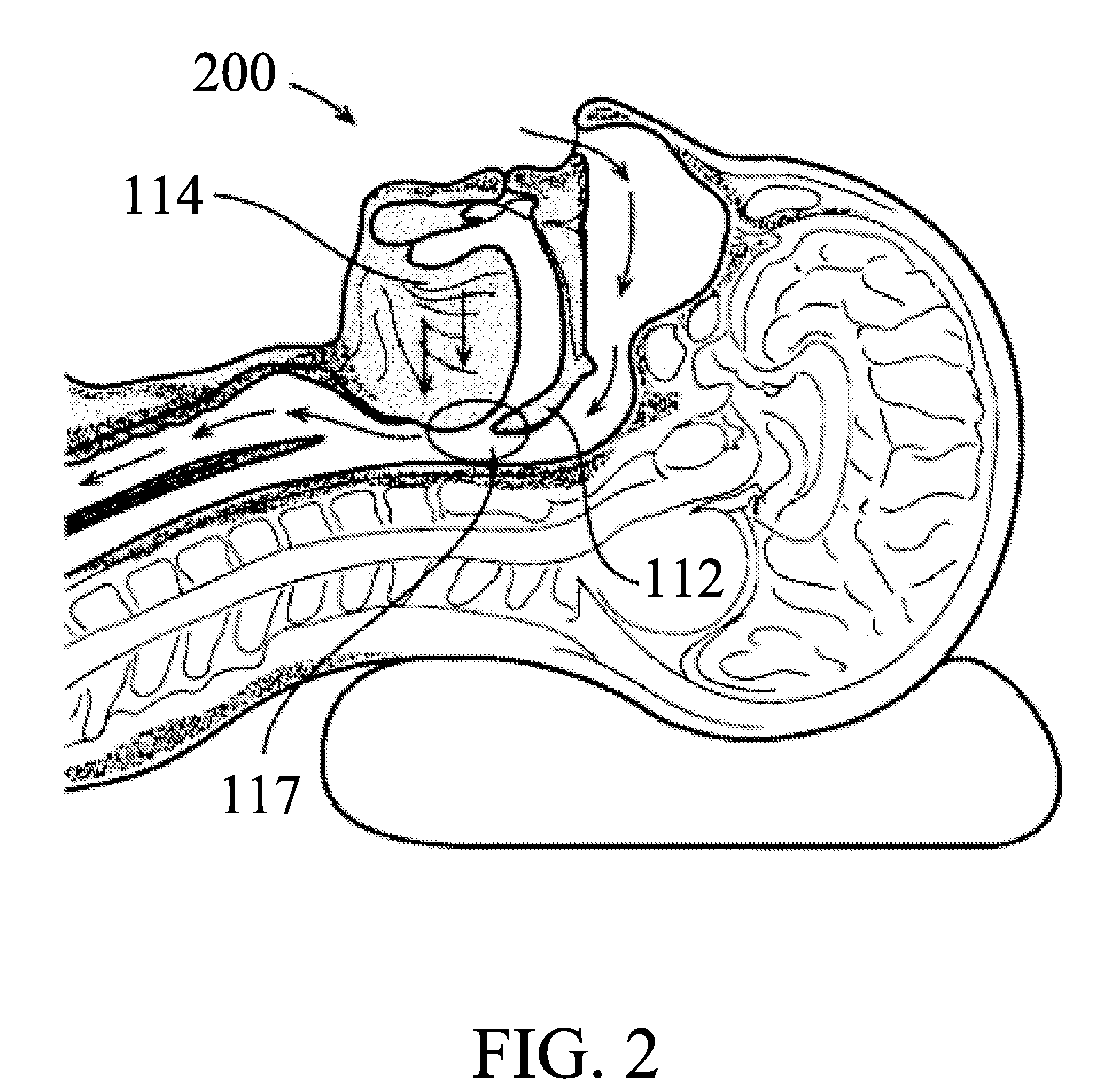
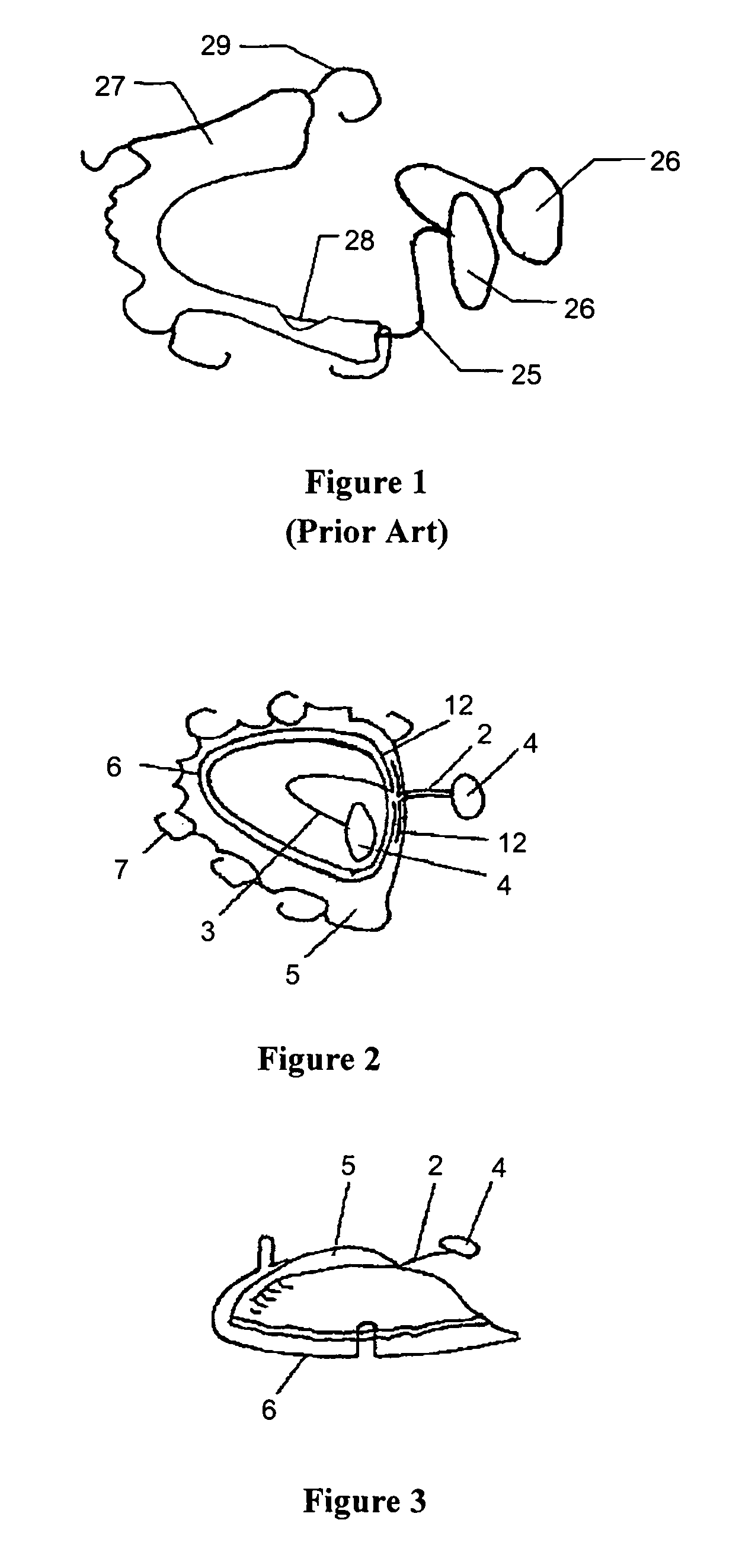
System and method for percutaneous palate remodeling
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating the palatal tissue. An implant is positioned within at least a portion of the soft palate and may be secured to other surrounding, less mobile structures such as the hard palate or the mucosa overlying the hard palate. The implant may be manipulated to displace at least a portion of the soft palate in an anterior or lateral direction, or to alter the tissue tension or compliance of the soft palate.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
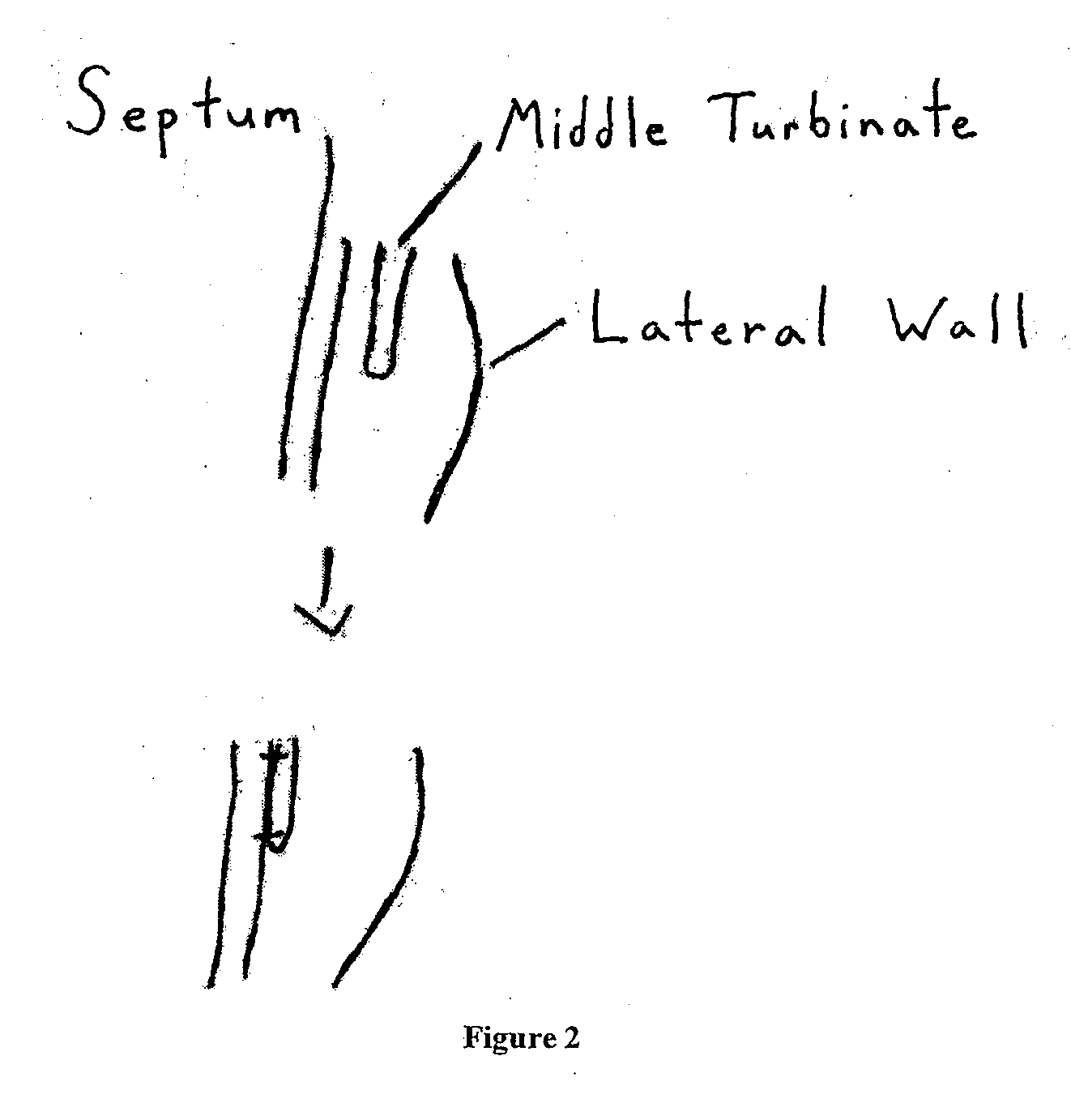
Middle Turbinate Medializer
InactiveUS20070293946A1Avoid stickingRestoring natural anatomySuture equipmentsDiagnosticsPalate muscleMiddle turbinates
Medializing the middle turbinate in the nose has been realized as a solution to the common complication of adhesions following nasal and sinus surgery. The invention provides a system for medializing the middle turbinate by attaching the middle turbinate temporarily to the nasal septum. The attachment is performed using a wafer with means on both sides for attaching the wafer to a mucosal surface. The attachment may also be performed using a tissue adhesive, pins, or other medical devices described herein. The invention also provides a system for attaching the uvula to the nasopharyngeal side of the soft palate. The invention provides a medical device for use in the inventive procedures as well as methods for the procedures and kits for use by a physician.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Tissue anchoring system for percutaneous glossoplasty
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating the tongue. An implant is positioned within at least a portion of the tongue and may be secured to other surrounding structures such as the mandible and / or hyoid bone. In general, the implant is manipulated to displace at least a portion of the posterior tongue in an anterior or lateral direction, or to alter the tissue tension or compliance of the tongue. Methods and devices are also disclosed for manipulating other soft tissue structures, including the soft palate and pharyngeal airway.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Braided palatal implant for snoring treatment
A method and apparatus for treating snoring of a patient includes providing an implant for altering a dynamic response of a soft palate of the patient to airflow past the soft palate. The implant is embedded in the soft palate to alter the dynamic response. The implant has multiple fibers braided along a length of the implant. The braid includes unbonded ends and air-textured yarns.
Owner:PILLAR PALATAL LLC +1
System and method for percutaneous glossoplasty
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating the tongue. An implant is positioned within at least a portion of the tongue and may be secured to other surrounding structures such as the mandible and / or hyoid bone. In general, the implant is manipulated to displace at least a portion of the posterior tongue in an anterior or lateral direction, or to alter the tissue tension or compliance of the tongue. Methods and devices are also disclosed for manipulating other soft tissue structures, including the soft palate and pharyngeal airway.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Mandibular Advancement Mouthpiece, An Intraoccusal Removable Improved Device For Eliminating Or Reducing Snoring
When there is an obstruction to the passage of air through the back of the mouth and nose, the soft palate and the bell collide, producing a vibration called snoring. There are various ways of reducing or eliminating snoring, nasal masks introducing air pressure to the throat (CPAP), surgery of the throat (OPPBA) and devices that are introduced into the mouth to cause a mandibular advancement what increases the oropharyngeal area, improving ventilation, among other solutions. The present invention disclosure an intraocclusal removable device in the form of a “U” that is placed covering all of the upper jaw teeth, wherein two steps, one in each extreme of the lower part of the element, which impede the mandible be closed completely on its normal occlusion, forcing it to produce a forward displacement of the lower jaw.
Owner:HEINE ANDRES
Methods and Devices for Treating Sleep Apnea and Snoring
ActiveUS20070261701A1Minimal invasivenessMinimal safetySuture equipmentsSurgical needlesTongue rootDisease
Embodiments of the invention include methods and devices to prevent or treat upper airway disorders in mammals related to impaired airflow. One aspect of this invention is a tongue retractor (LTR) that indirectly retracts tongue base by its implant site in the frenulum area. This simplifies the insertion, adjustment and maintenance of the device. Another aspect of this invention describes a highly localized and fully implantable LTR that is inserted into the base of tongue to stiffen lax surface mucosa or mechanically couple it to internal tongue structures. Another aspect of this invention is an LTR inserted in or around the pharyngoglossal fold. This site allows retraction and stiffening of tongue base tissue as well as the soft palate and lateral pharyngeal wall.
Owner:LINGUAFLEX INC
Method for adjusting tissue anchors
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating the tongue. An implant is positioned within at least a portion of the tongue and may be secured to other surrounding structures such as the mandible and / or hyoid bone. In general, the implant is manipulated to displace at least a portion of the posterior tongue in an anterior or lateral direction, or to alter the tissue tension or compliance of the tongue. Methods and devices are also disclosed for manipulating other soft tissue structures, including the soft palate and pharyngeal airway.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
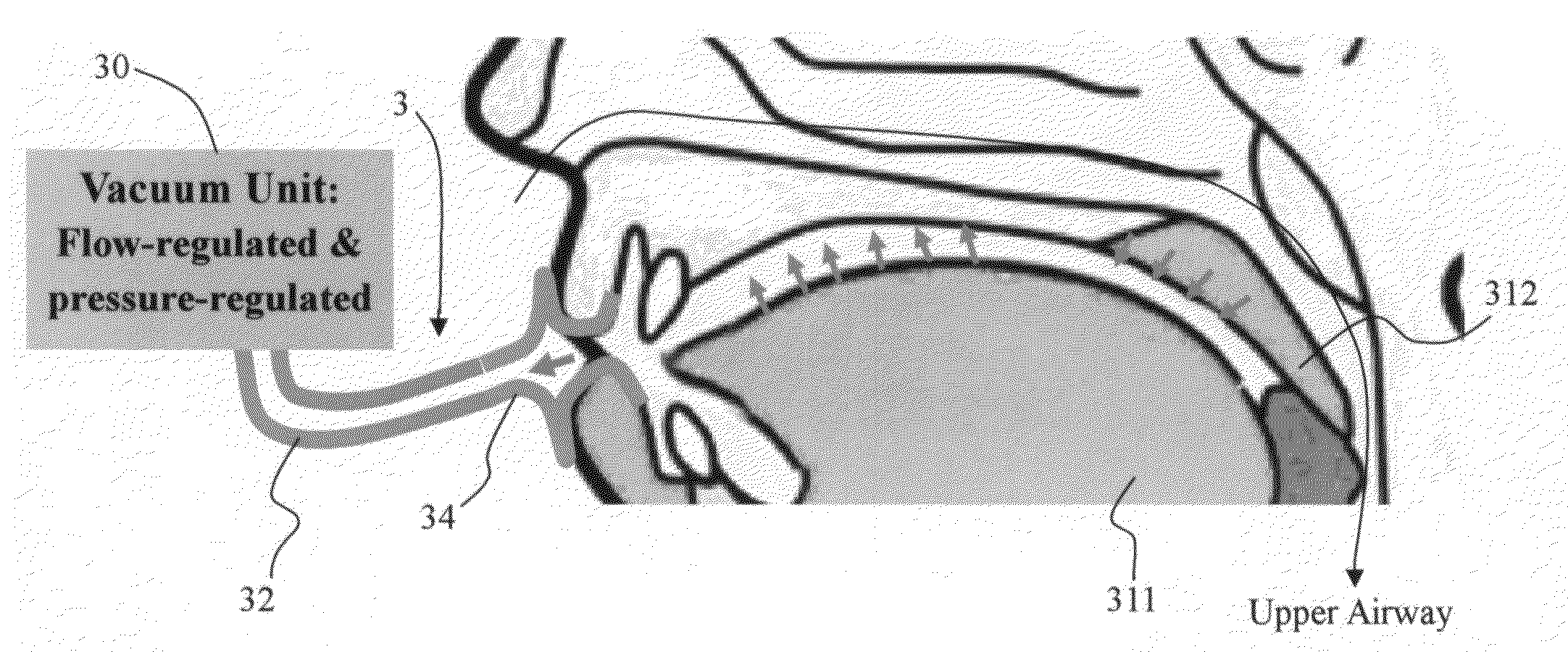
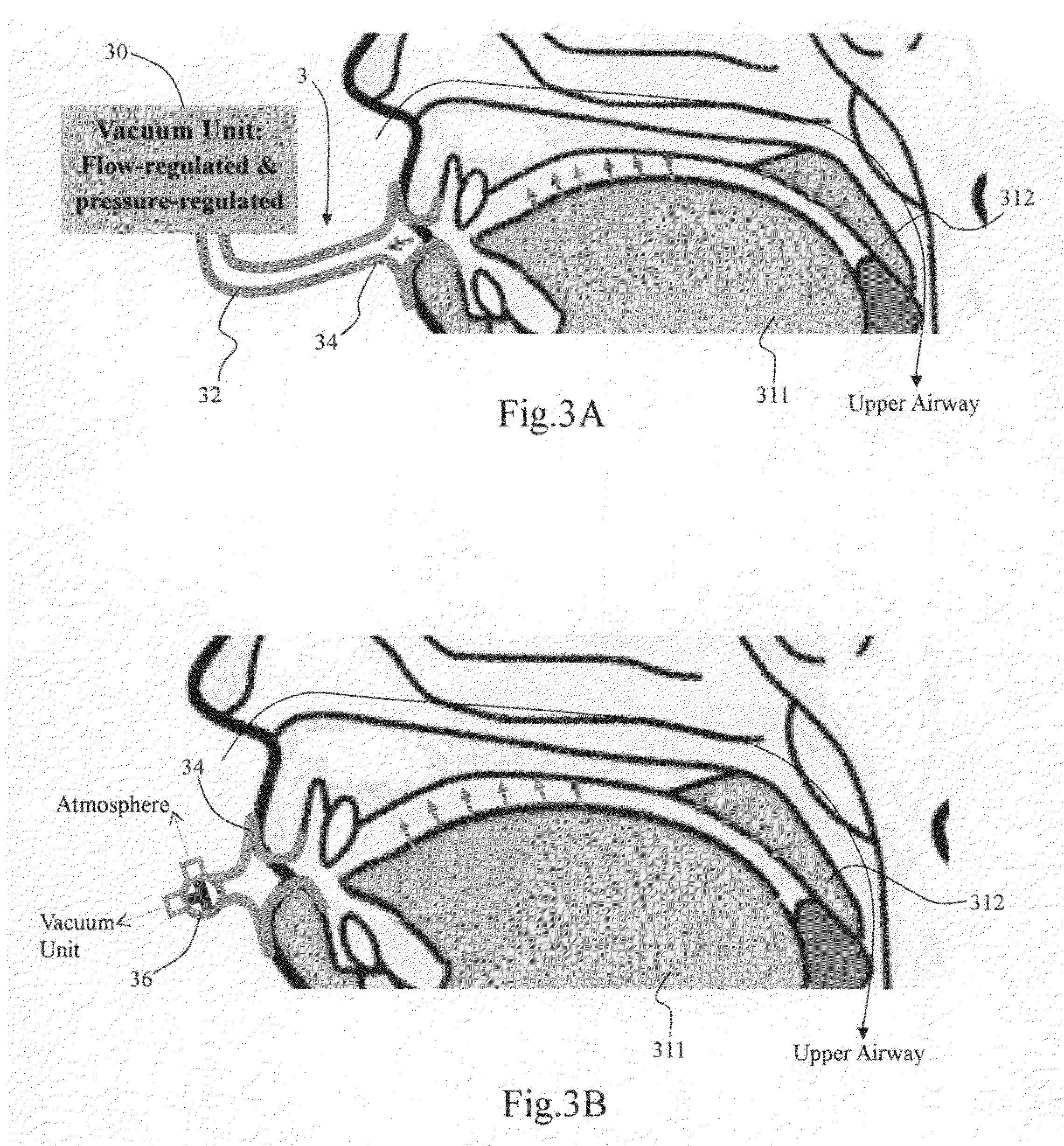
Method and apparatus for treating obstructive sleep apnea by using negative oral pressure to a patient
ActiveUS20070277818A1Improve efficacyImprove complianceRespiratorsBreathing masksNasal cavitySoft palate
The present invention provides a method and apparatus for treating obstructive sleep apnea by using negative oral pressure to a patient. The present apparatus includes a vacuum unit for controlling and maintaining negative pressure of an oral cavity of the patient, a tube with one end thereof connecting to the vacuum unit to suck out air in the oral cavity to generate the negative pressure therein, and a mouthpiece connecting to the other end of the tube and fitting into and sealing the patient's mouth to prevent the oral cavity from air leakage. By using negative pressure in the oral cavity, the patient's soft palate is pulled toward the oral cavity and the patient's tongue is pulled toward an upper palate so as to maintain the patient's nasal air passageway open.
Owner:SOMNICS INC
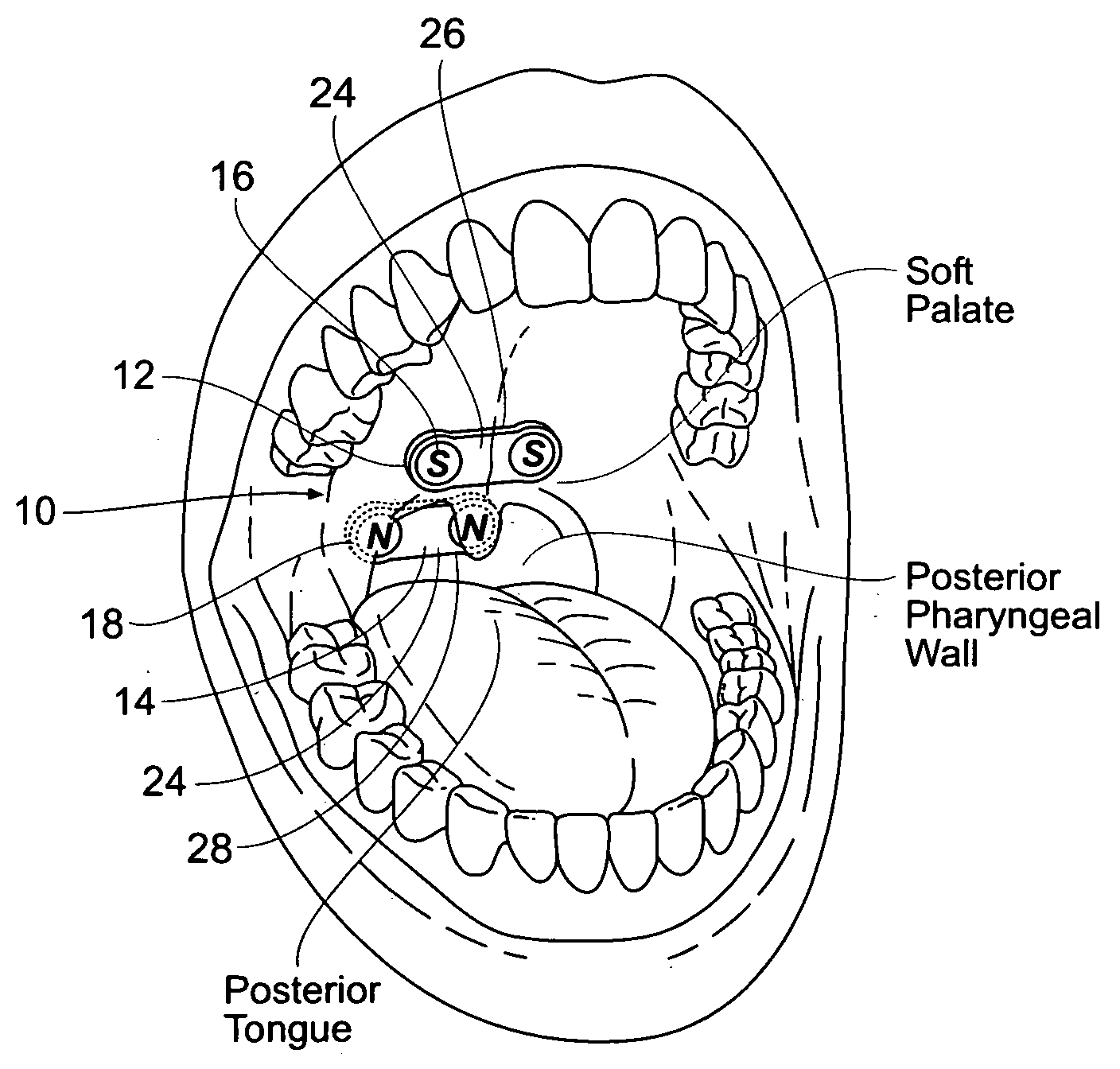
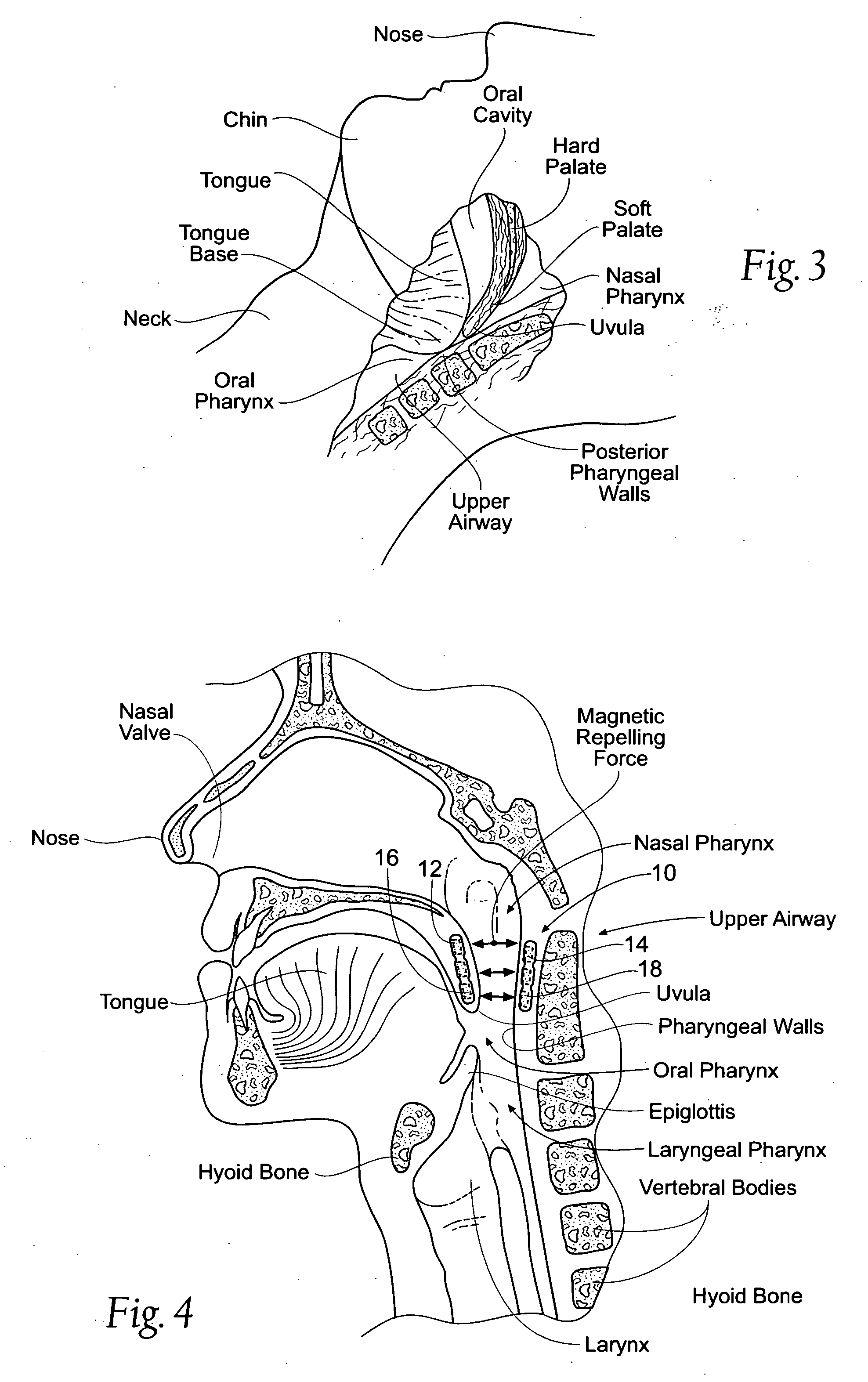
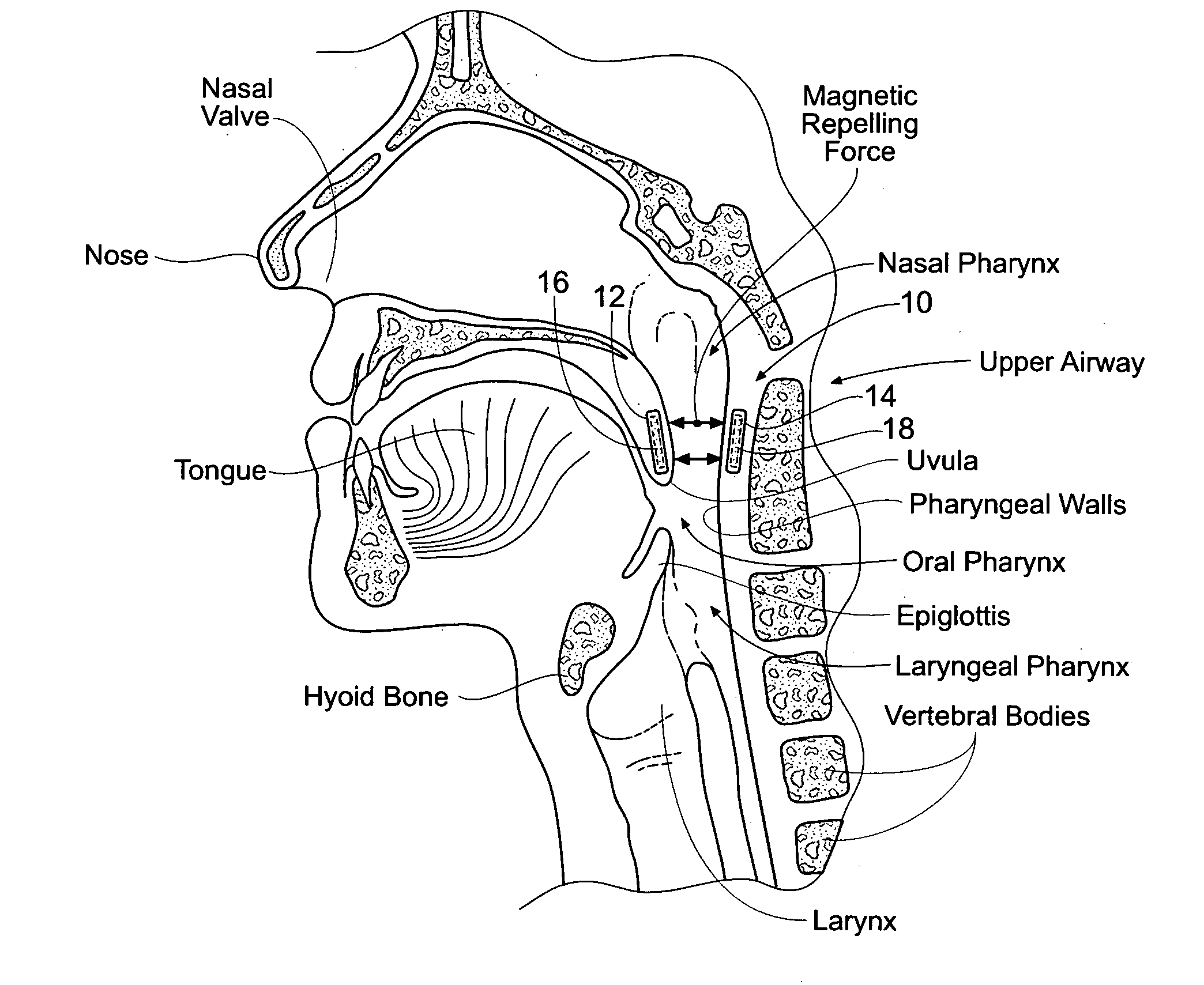
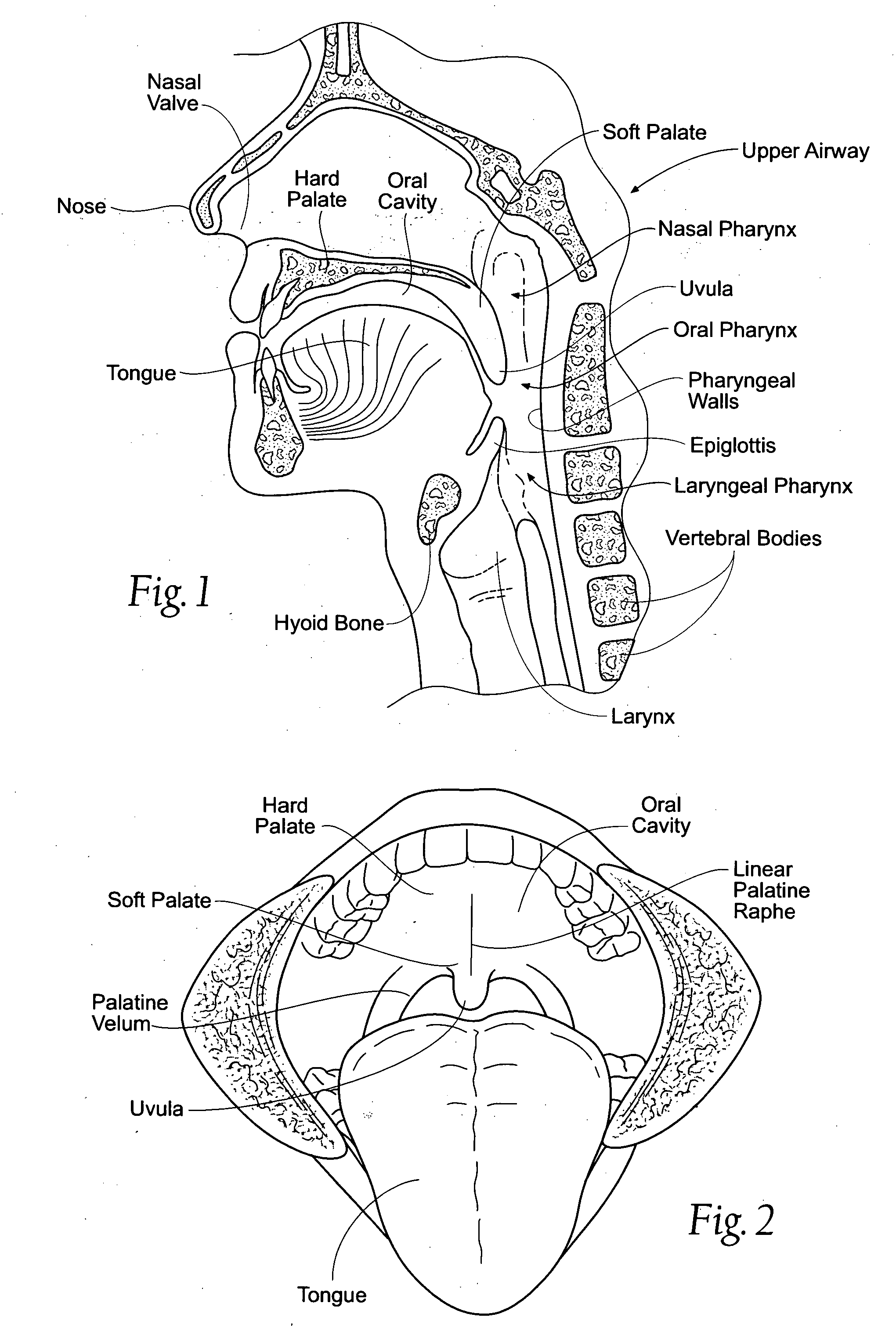
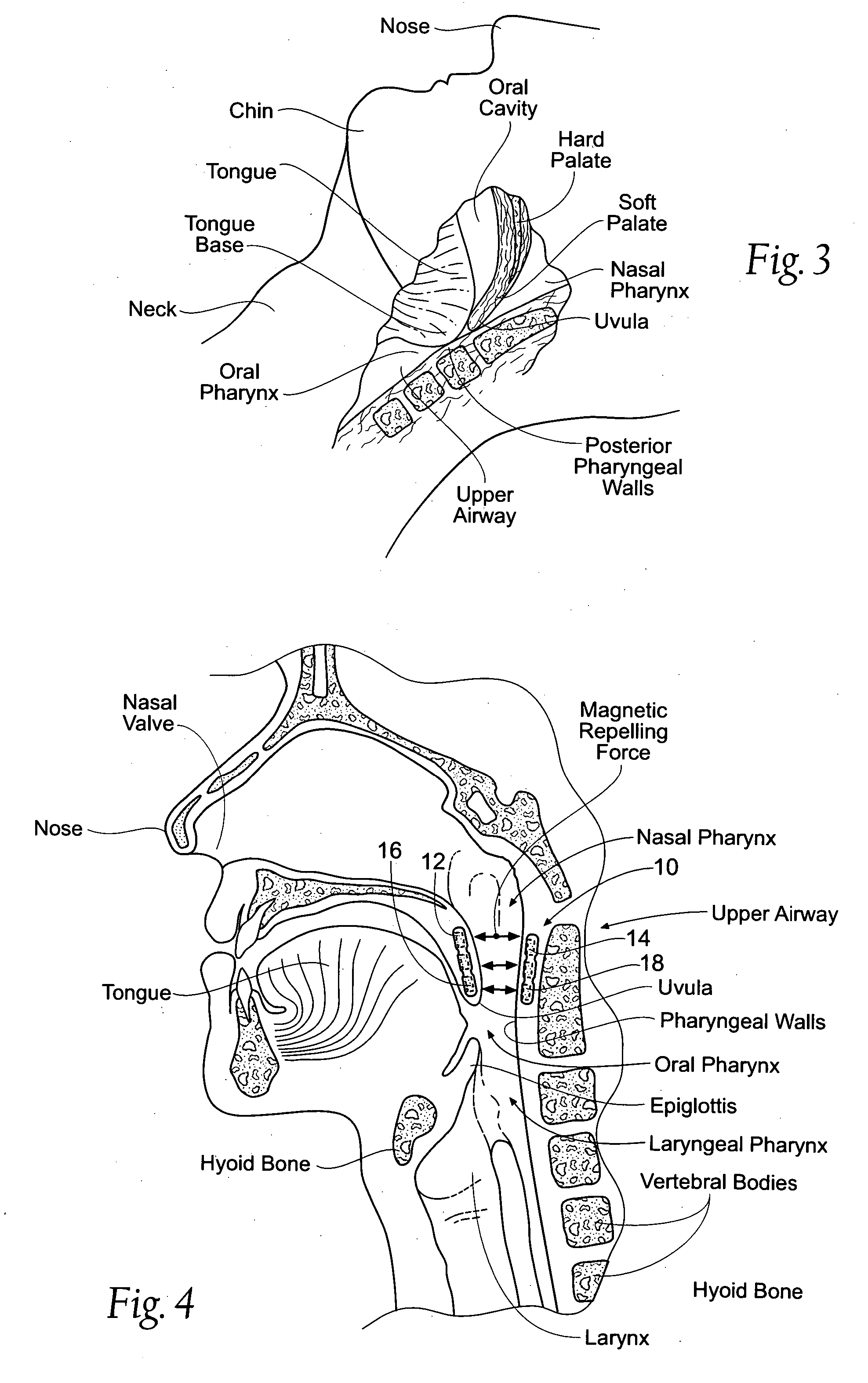
Devices, systems, and methods using magnetic force systems in or on soft palate tissue
InactiveUS20070256693A1Snoring preventionNon-surgical orthopedic devicesMagnetic tension forceMedicine
An implant system places magnetic structures in or on tissue that develop a magnetic repelling force between a soft palate a posterior pharyngeal wall. The magnetic repelling force has a magnitude F-mag, where F-mag=f (F-sep, F-nat), and where F-sep is a force required to separate soft palate tissue from pharyngeal wall tissue during sleep, and F-nat is a force exerted by native muscle on the soft palate during swallowing and / or drinking and / or speech. In another embodiment, a palate implant uses attractive magnetic force to keep the airway open.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Integrated oral appliance for sleep-disordered breathing
ActiveUS20090241969A1Prevent airway closureMovement is lowTeeth fillingSnoring preventionLower dentitionNasal cavity
A custom, sized and fitted, integrated oral appliance is provided to treat breathing obstruction and restriction in the upper airway during sleep. Several novel features are integrated in a single device, which includes mandible repositioning to open the airway, and tongue restraint to prevent airway blockage. This device is comprised of a built-in air conduit to bypass nasal restriction and airway occlusion. In operation, the appliance is positioned in the oral cavity to firmly grip the upper and lower dentition using customized unshaped trays. Appliance positioning advances the mandible to an adjustable predetermined position and simultaneously restrains the tongue using flexible bristles attached to a spring-loaded, tongue-restraint-ac (TRAC) component. A hollow air conduit, built into the TRAC, spans the area between the users' lips and soft palate. It facilitates the flow of self-heated, moisturized air directly to (and from) the oropharynx to bypass airway obstructions and / or nasal restrictions.
Owner:DREAMSCAPE MEDICAL
Elastomeric magnetic nanocomposite biomedical devices
InactiveUS20050267321A1Low flexural modulusIncrease stiffnessElectrotherapyMedical devicesMuscle tissueElastomer
A biomedical device of a smart elastomer, more particularly relating to a class of low modulus elastomers with dispersed, aligned magnetic nanoparticles therein that allow for controlling the flexural modulus of the device and engaged tissue in response to an applied magnetic field. An exemplary embodiment is used for treating obstructive airway syndrome wherein one or more implants including an elastomer magnetic nanocomposite are placed in a patient's soft palate. During sleep, a source of magnetic flux is applied to stiffen the implants to dampen vibrations in tissue which occur in snoring and sleep apnea episodes. The magnetic flux is provided by a permanent magnet or by a magnetic field source coupled to a controller for modulating the stiffness of the implant(s). In similar embodiments, the controlled modulus implants can be used to treat various anatomic structures such as upper airway tissue, oral cavity tissue, gastrointestinal tract tissue, urinary tract tissue, cardiovascular tissue, muscle tissue, penile tissue, sphincters and skin.
Owner:SHADDUCK JOHN H
Systems and methods for moving and/or restraining tissue in the upper respiratory system
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV +1
Injectable snoring implant
A method and apparatus for treating snoring of a patient includes providing an implant for altering a dynamic response of a soft palate of the patient to airflow past the soft palate. The implant is embedded in the soft palate to alter the dynamic response. For example, the implant has a mass, stiffness or dampening sufficient to alter the dynamic response following the implantation without substantially impairing a function of the soft palate to close a nasal passage of the patient during swallowing.
Owner:RESTORE MEDICAL
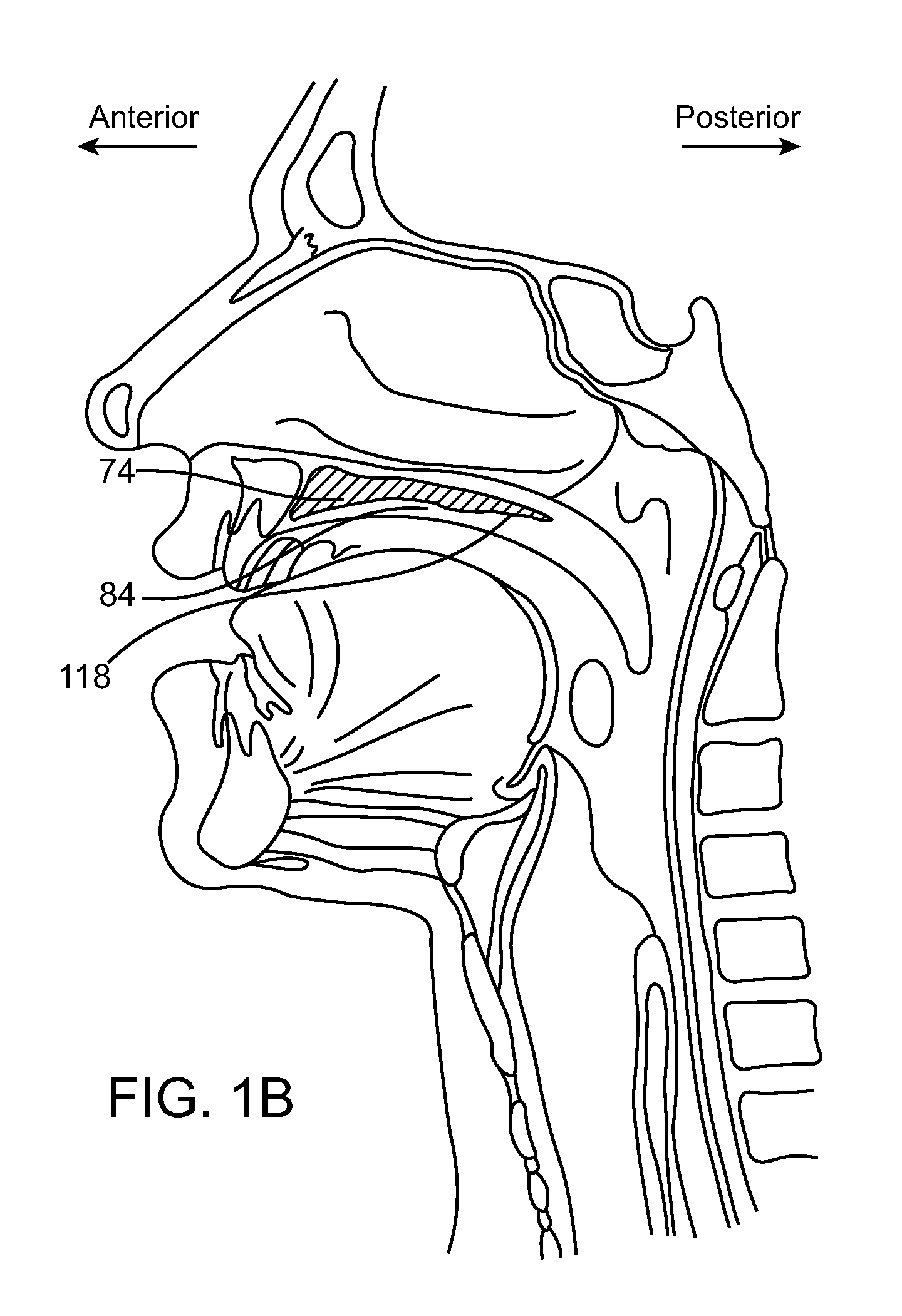
A palate retainer with attached nasopharyngeal airway extender for use in the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea
ActiveUS20110178439A1Minimizes triggering gag reflexPrevent the palate from falling backSurgeryPerson identificationTongue rootRetainer
A medical appliance for the treatment of obstructive sleep apnea in a patient, the appliance comprising: a securing device configured to be removably affixed to the patient's jaw; and a biasing member which is insertable behind the soft palate and / or the base of the patient's tongue, thereby providing for the flow of air in the nasopharyngeal airway; wherein the securing device is connected to the biasing member to allow insertion and / or removal of the biasing member from the nasopharyngeal airway.
Owner:LUMEN DEVICES
Fluid filled implants for treating obstructive sleep apnea
ActiveUS20110100376A1Change flexibilityRigidity be changedRestraining devicesSnoring preventionOropharyngeal airwayPalate muscle
An implant for treating obstructive sleep apnea includes a flexible chamber, a fluid reservoir in fluid communication with the flexible chamber, and a fluid transfer assembly in communication with the fluid reservoir and the flexible chamber for transferring fluid therebetween for selectively modifying the rigidity of the flexible chamber. The flexible chamber is implantable within the soft tissue of an oropharyngeal airway of a patient, such as within the tongue, the soft palate, or the pharyngeal wall. The fluid reservoir and the fluid transfer assembly are implantable within the inframandibular region of the patient. The fluid transfer assembly is selectively engageable by the patient for transferring fluid between the two chambers for modifying the rigidity, flexibility, and / or shape of the flexible chamber with minimal or no change to the volume of the implant.
Owner:ETHICON INC
Gag-less airway for snoring prevention
An oral application for snoring prevention which has a flattened tube with an unobstructed airway and ridges on the inferior surface for pulling the tongue forward out of the path of the airway while the superior surface of the tube follows closely the hard and soft palate. The tube is short and extends in the oral cavity or mouth to a location which will not cause a gag reflex.
Owner:DAGOSTO JOSEPH
Devices, systems and methods for the treatment of sleep apnea
ActiveUS20110226264A1Minimizing the gag reflexFully removedTracheal tubesBronchoscopesTreatment sleepNasopharyngeal airway
A medical appliance for the treatment of one or more sleep disorders such as obstructive sleep apnea in a patient, the appliance comprising: a biasing member for inserting behind and exerting a force upon the patient's soft palate or tongue, wherein the biasing member is inserted in a reduced or minimized form and then expanded or firms once in place to exert the force. The appliance may be nasally inserted or be placed through the mouth. In a particular configuration, both the soft palate and tongue are biased to prevent obstruction of the flow of air in the nasopharyngeal airway.
Owner:LUMEN DEVICES
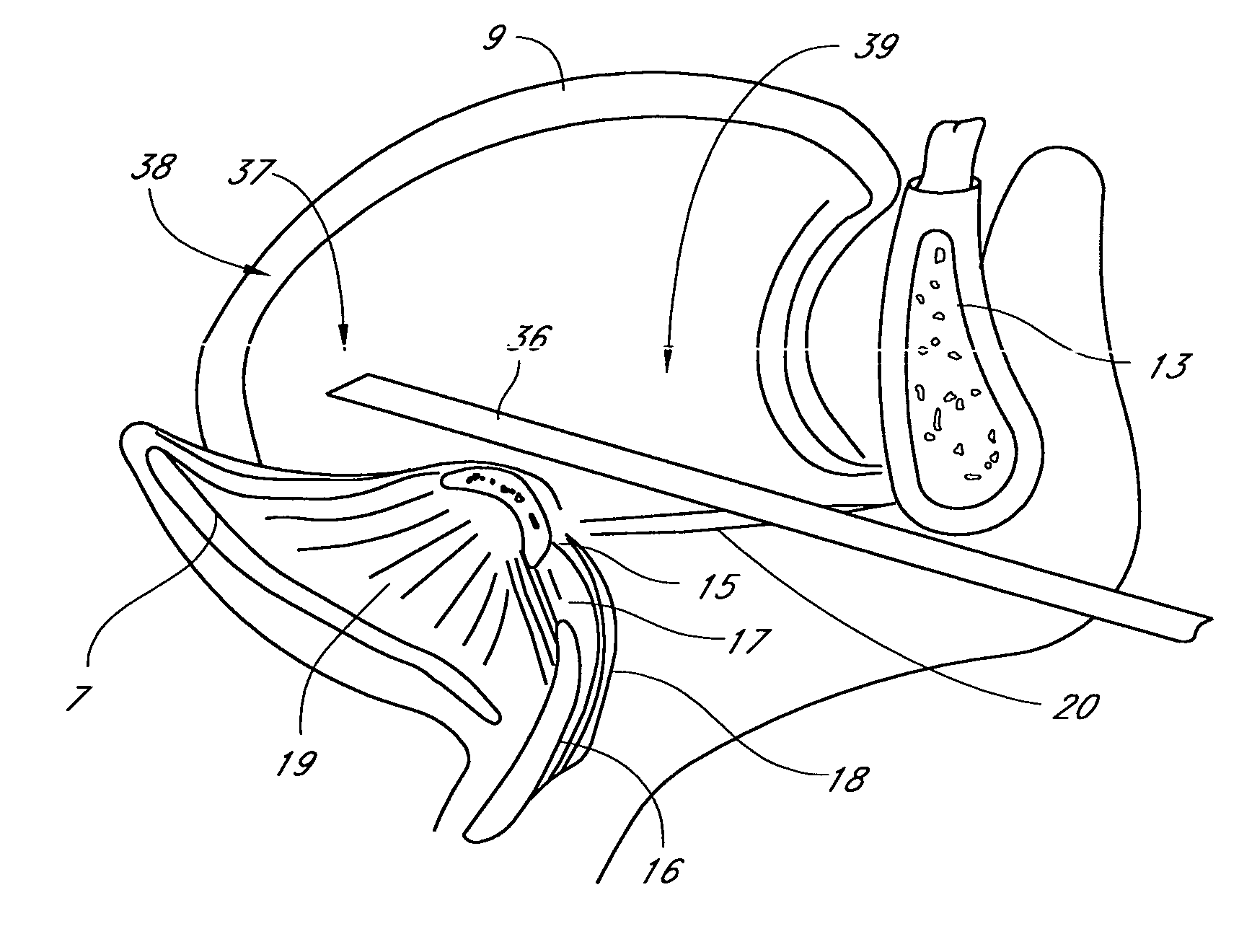
Devices, systems, and methods using magnetic force systems in or on tissue
InactiveUS20070000497A1Maintain separationTeeth fillingSurgeryMagnetic tension forceTherapeutic effect
Systems and methods include magnetic structures for placement in or on tissues in an airway. The magnetic structures carry sources of magnetism, which generate magnetic fields having directions. The magnetic fields interact to provide magnetic forces that provide a desired therapeutic effect, e.g., maintaining separation between the soft palate and / or tongue and the posterior pharyngeal wall. The systems and methods size and configure the directions of the magnetic fields to provide stability, which makes possible the achievement of the desired therapeutic effect in a straightforward and elegant manner.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and method for percutaneous palate remodeling
Methods and devices are disclosed for manipulating the tongue. An implant is positioned within at least a portion of the tongue and may be secured to other surrounding structures such as the mandible and / or hyoid bone. In general, the implant is manipulated to displace at least a portion of the posterior tongue in an anterior or lateral direction, or to alter the tissue tension or compliance of the tongue. Methods and devices are also disclosed for manipulating other soft tissue structures, including the soft palate and pharyngeal airway.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Non-invasive method and system for the treatment of snoring and nasal obstruction
InactiveUS20060276861A1Efficient thermal shrinkage of treated areaSurgical instrument detailsLight therapyHigh power diode laserPalate muscle
Laser for thermal shrinkage of soft tissue of uvula, soft palate, nasal turbinate or tongue base for the treatment of snoring, nasal obstruction or sleep apnea are disclosed. The preferred laser includes infrared laser about 0.7 to 1.85 micron, pulse duration about 100 microsecond to 5 seconds, spot size of about 2 to 5 mm and power of about 2 to 20 W at the treated area. The laser energy is delivered to the treated area by an optical fiber and a hand piece to cause a localized temperature about 65 to 85 degree Celsius for sufficient shrinkage of the treated soft tissues. Optical fiber bundles to produce high-power diode laser output or multi-wavelength are also disclosed.
Owner:NEW VISION
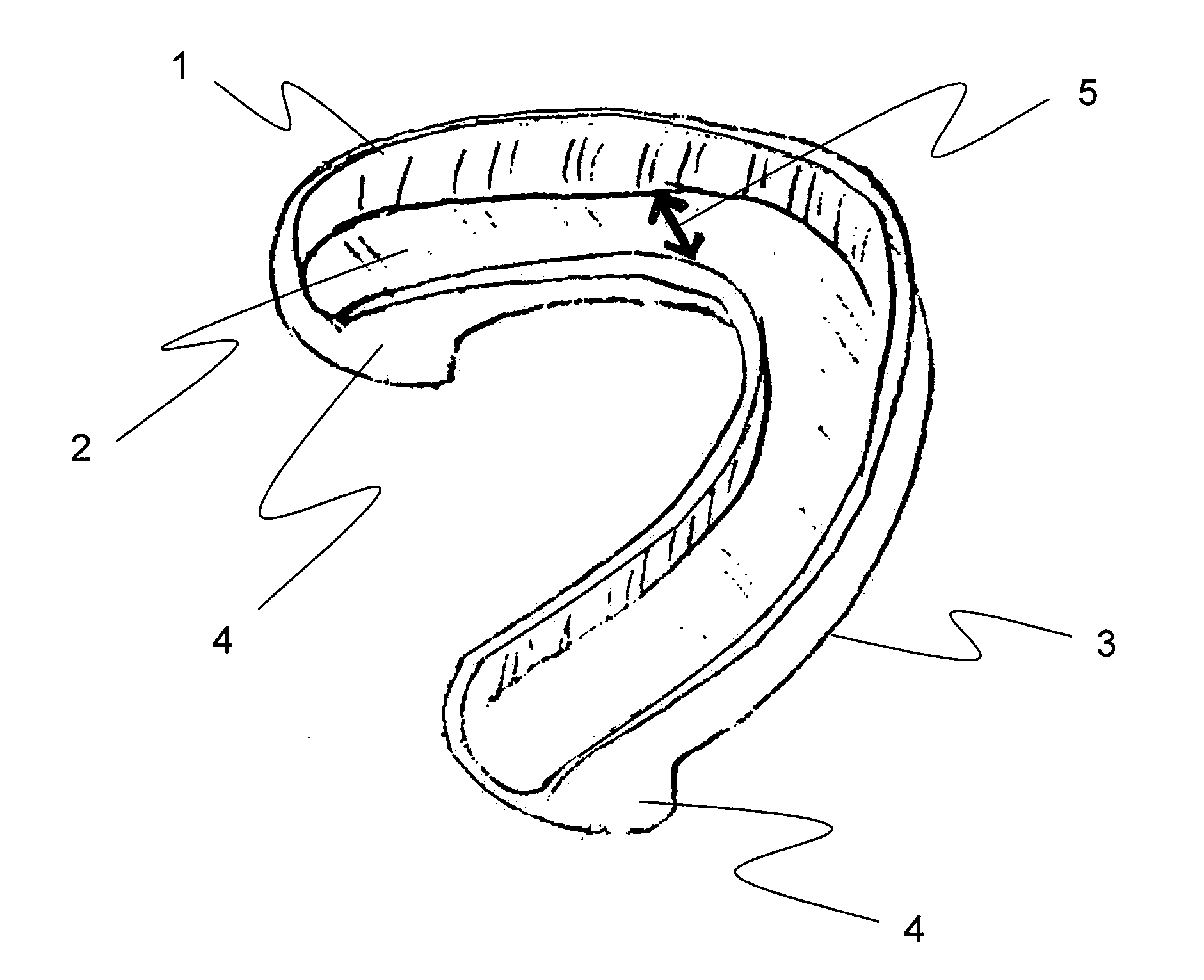
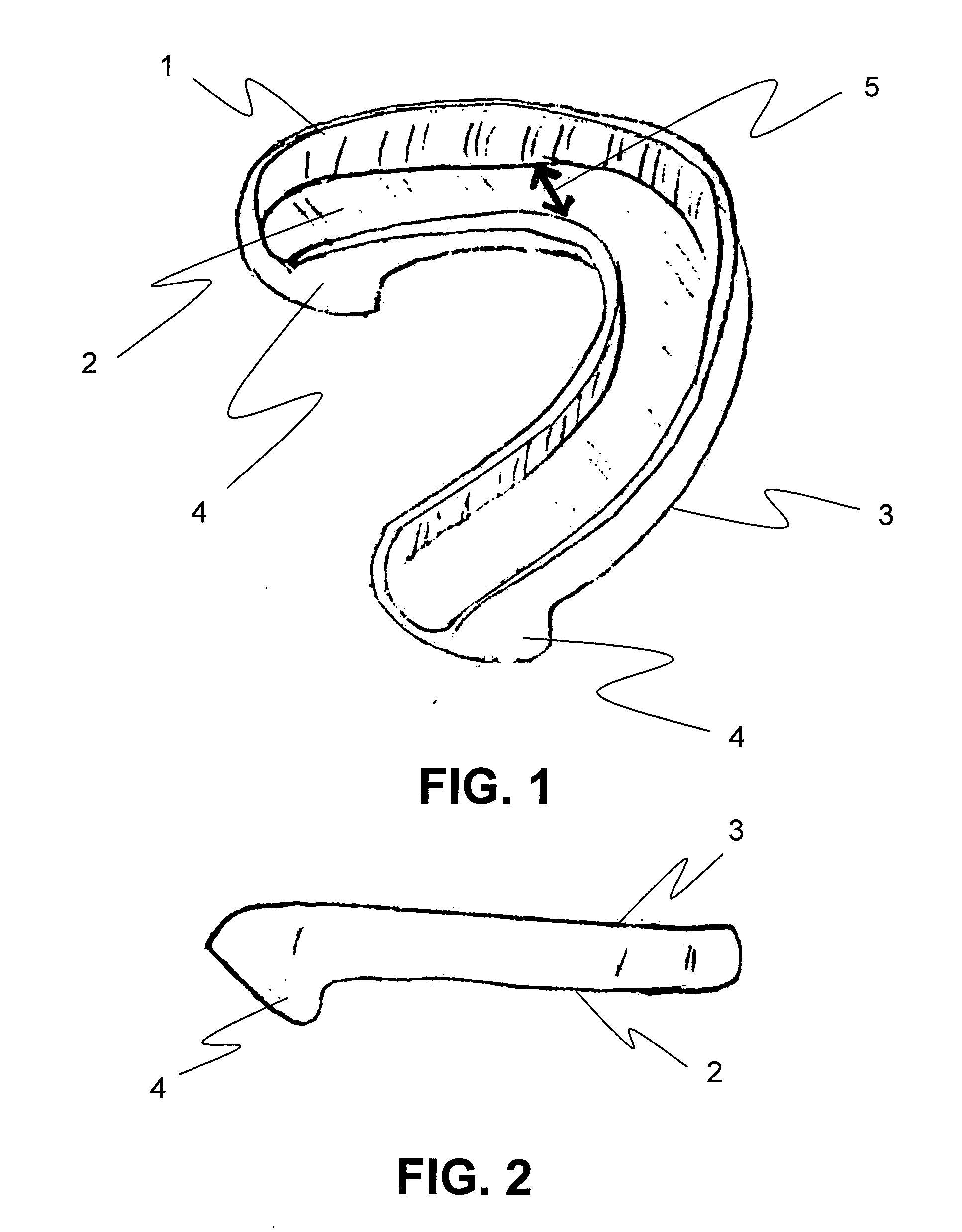
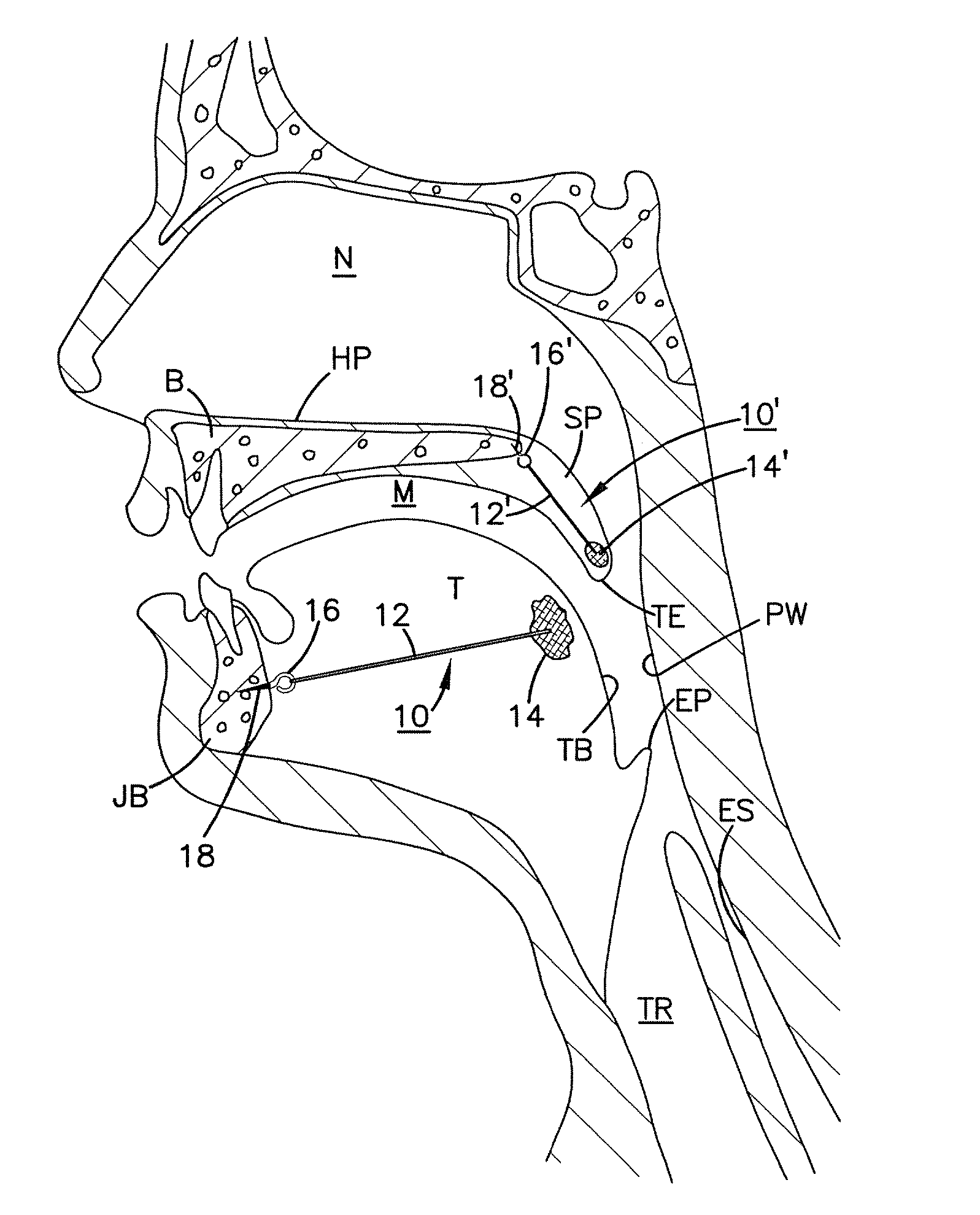
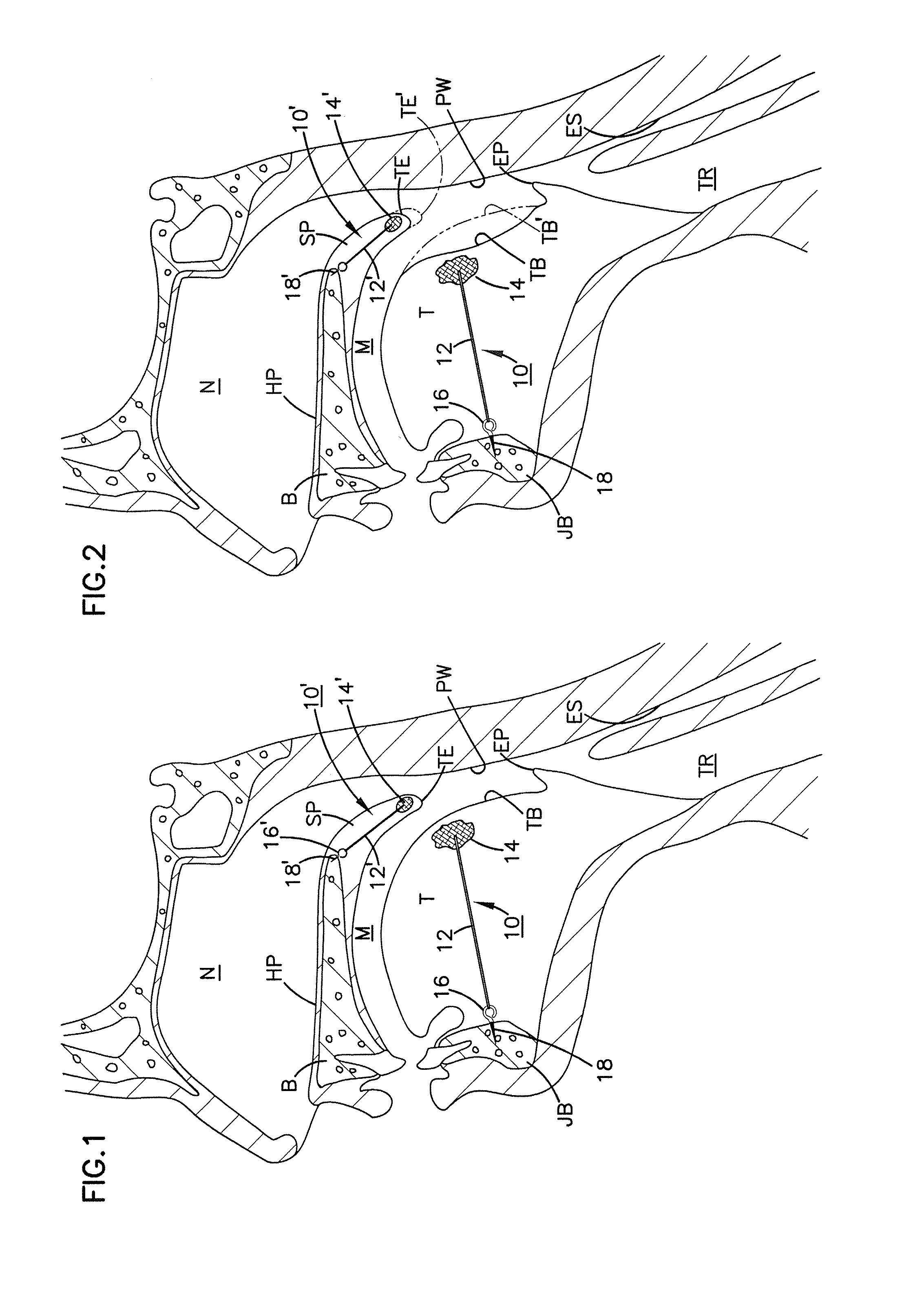
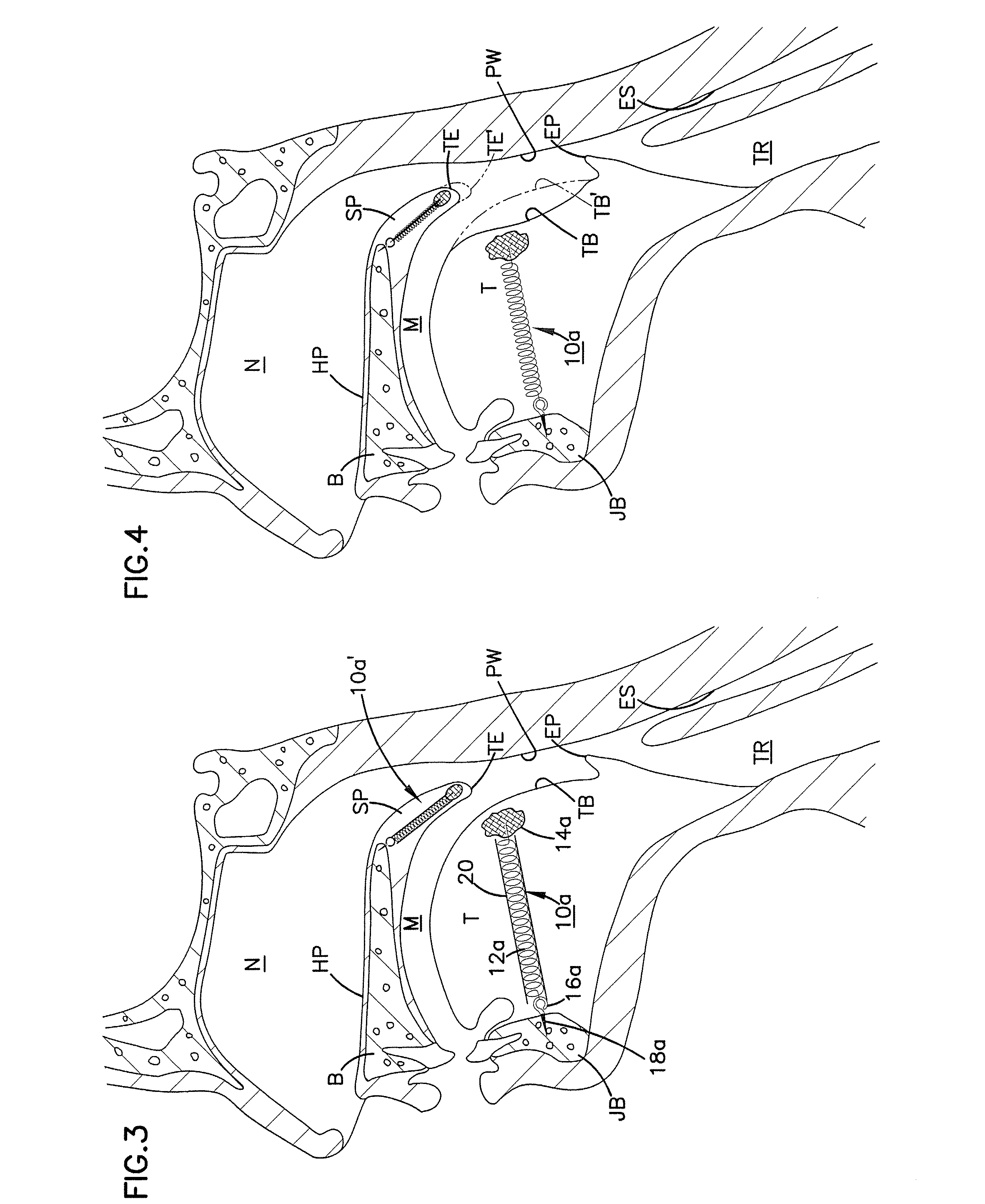
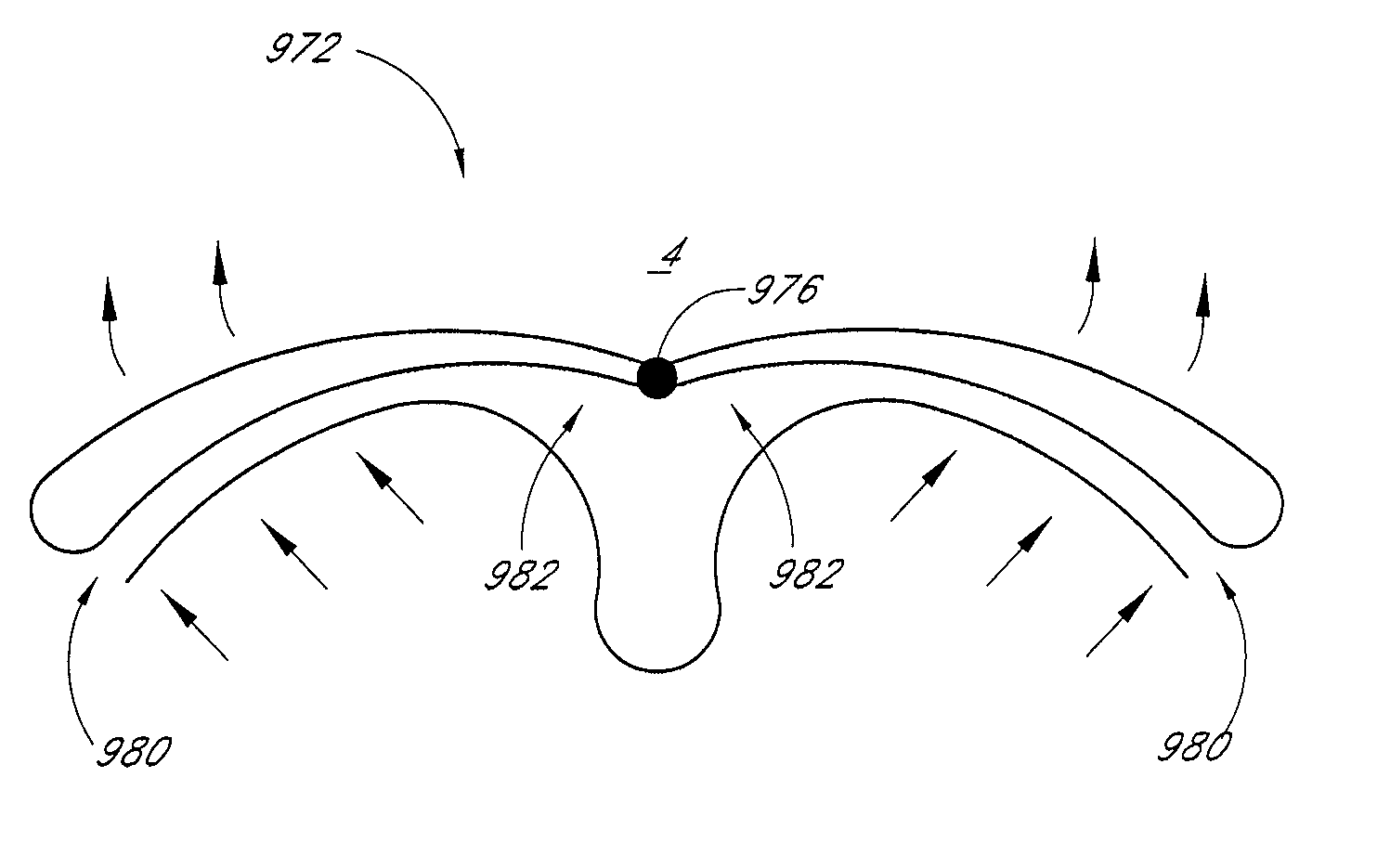
Soft palate implant
An airway condition of a patient is treated by selecting an implant sized to be implanted within a soft palate of the patient. The implant has a tissue-engaging member sized to be implanted within the soft palate near a trailing end of the soft palate to oppose relative movement between the tissue-engaging member and surrounding tissue of the soft palate. The implant further has an elongated tether member with a first end secured to the tissue-engaging member. The implant is placed within the soft palate with the tissue-engaging member implanted within tissue of the soft palate near the trailing end and with the tether member extending from the first end to a second end near a hard palate of the patient. The second end of the tether is secured to the hard palate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
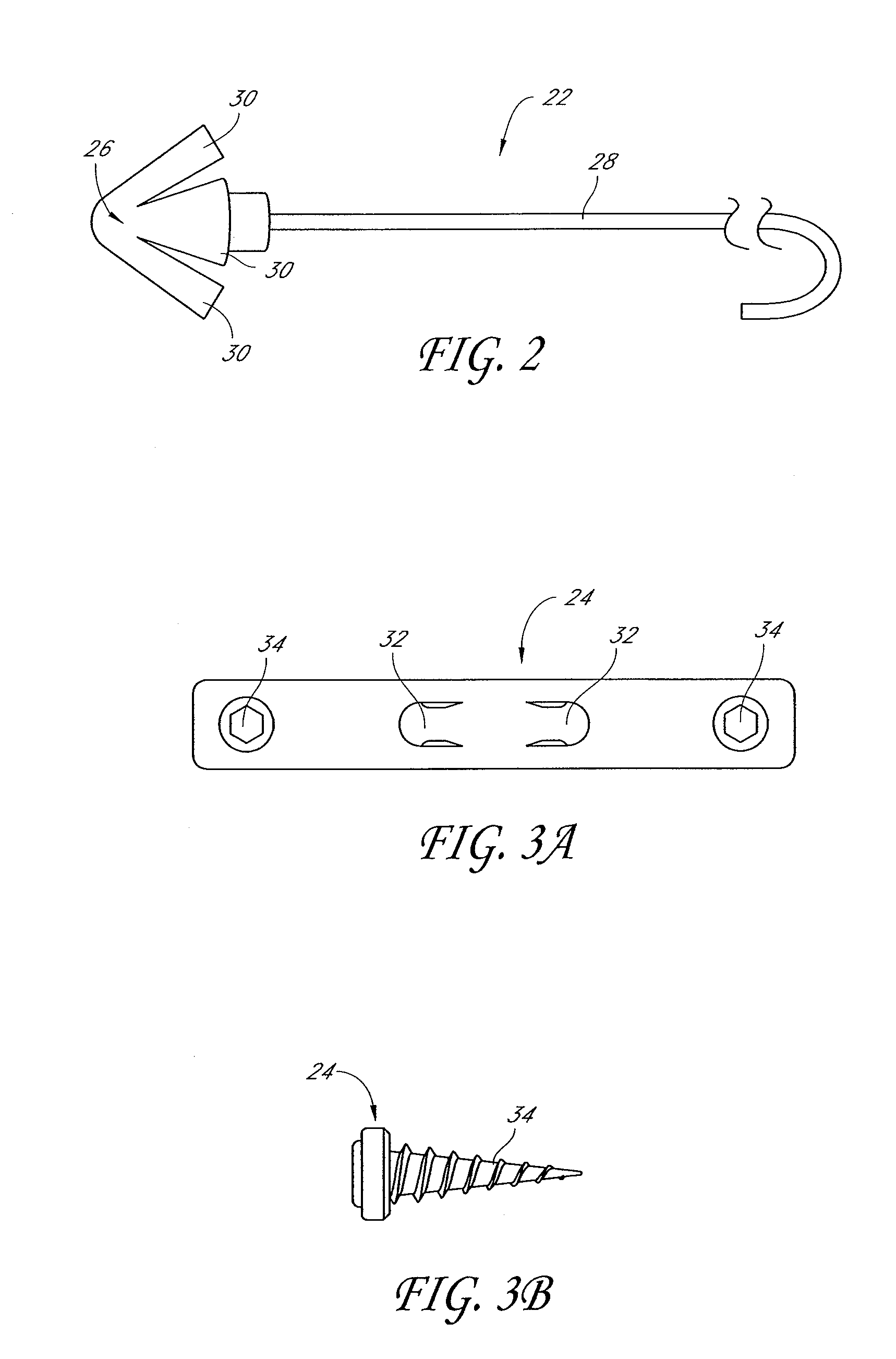
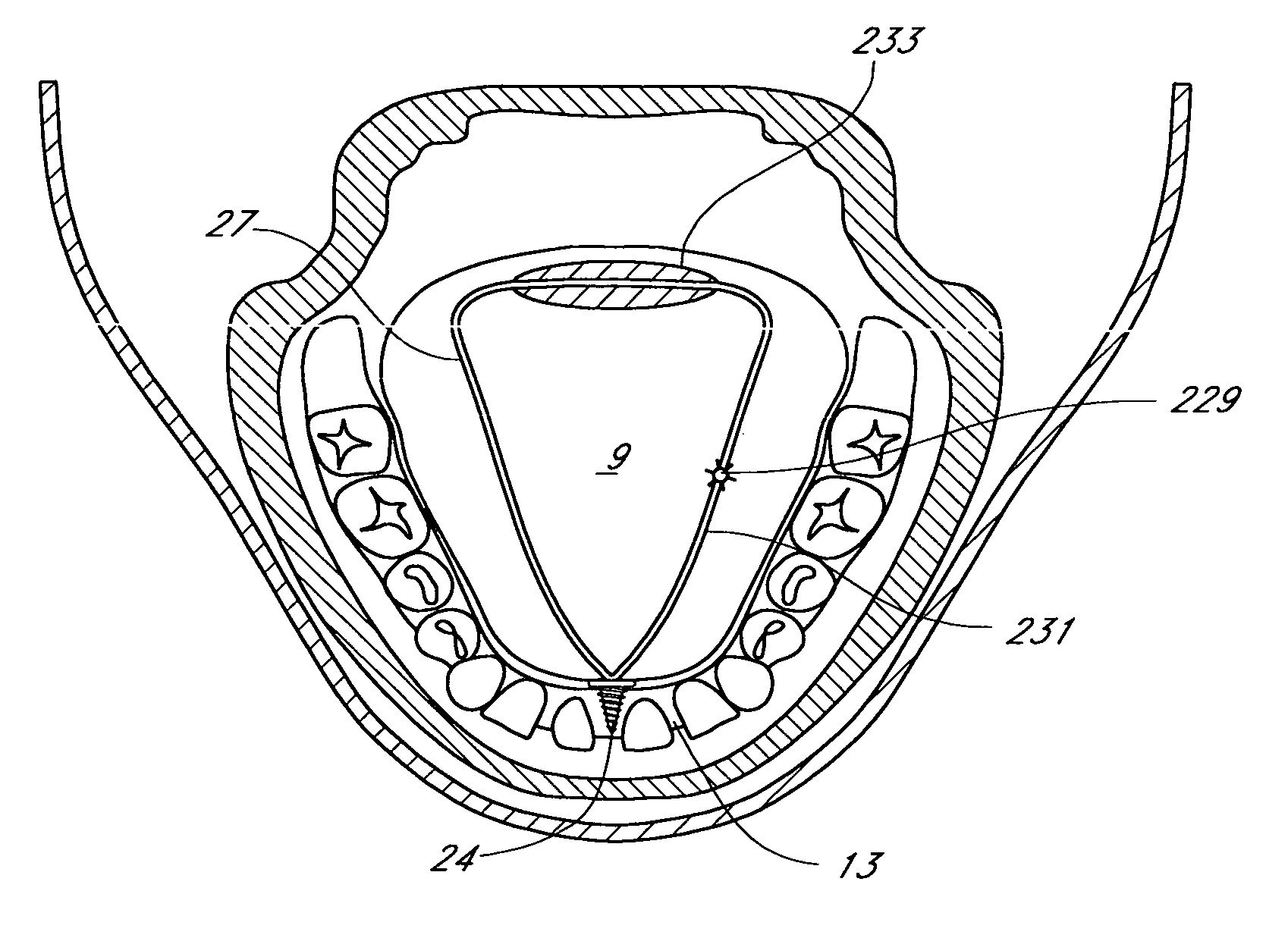
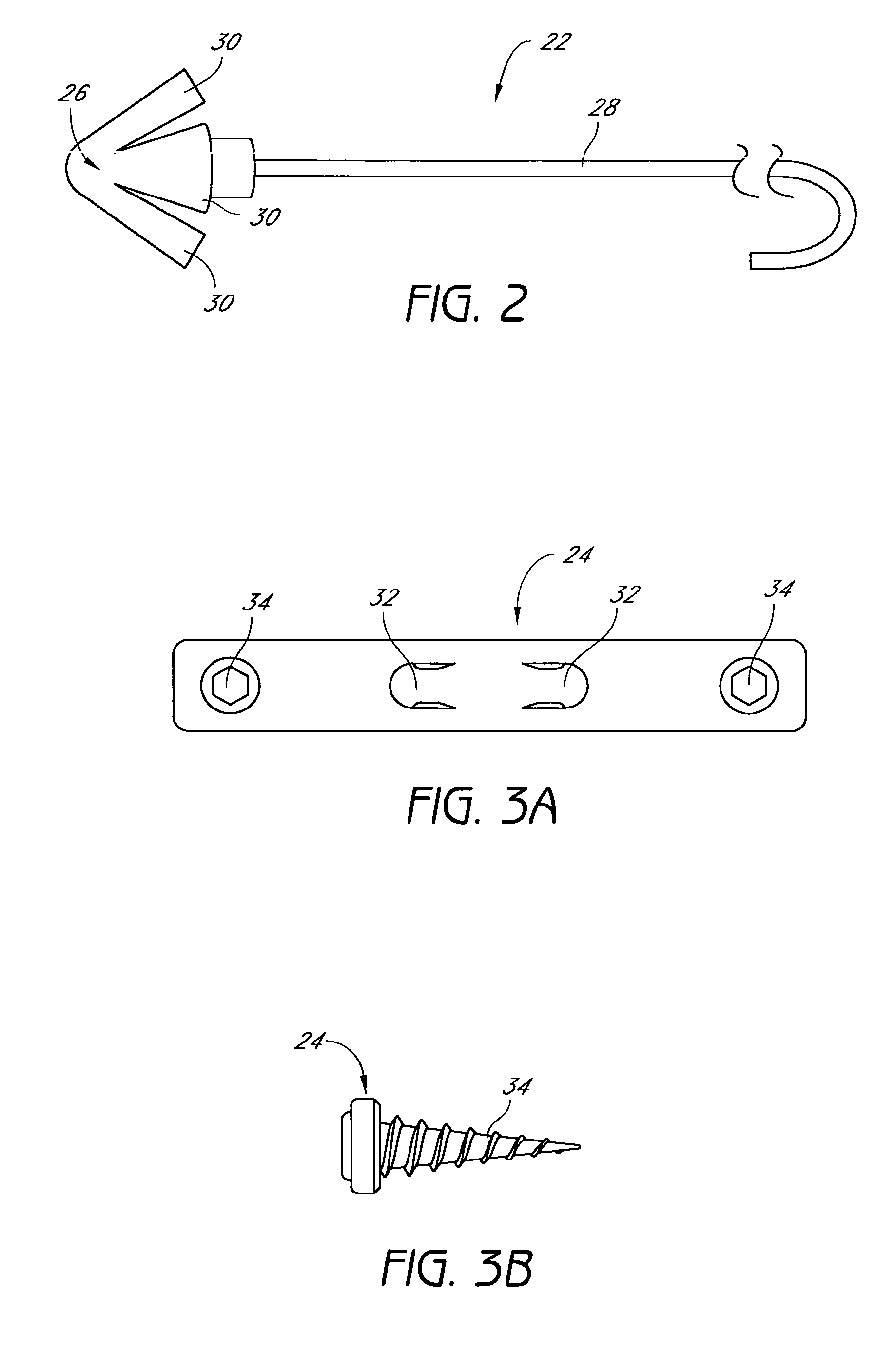
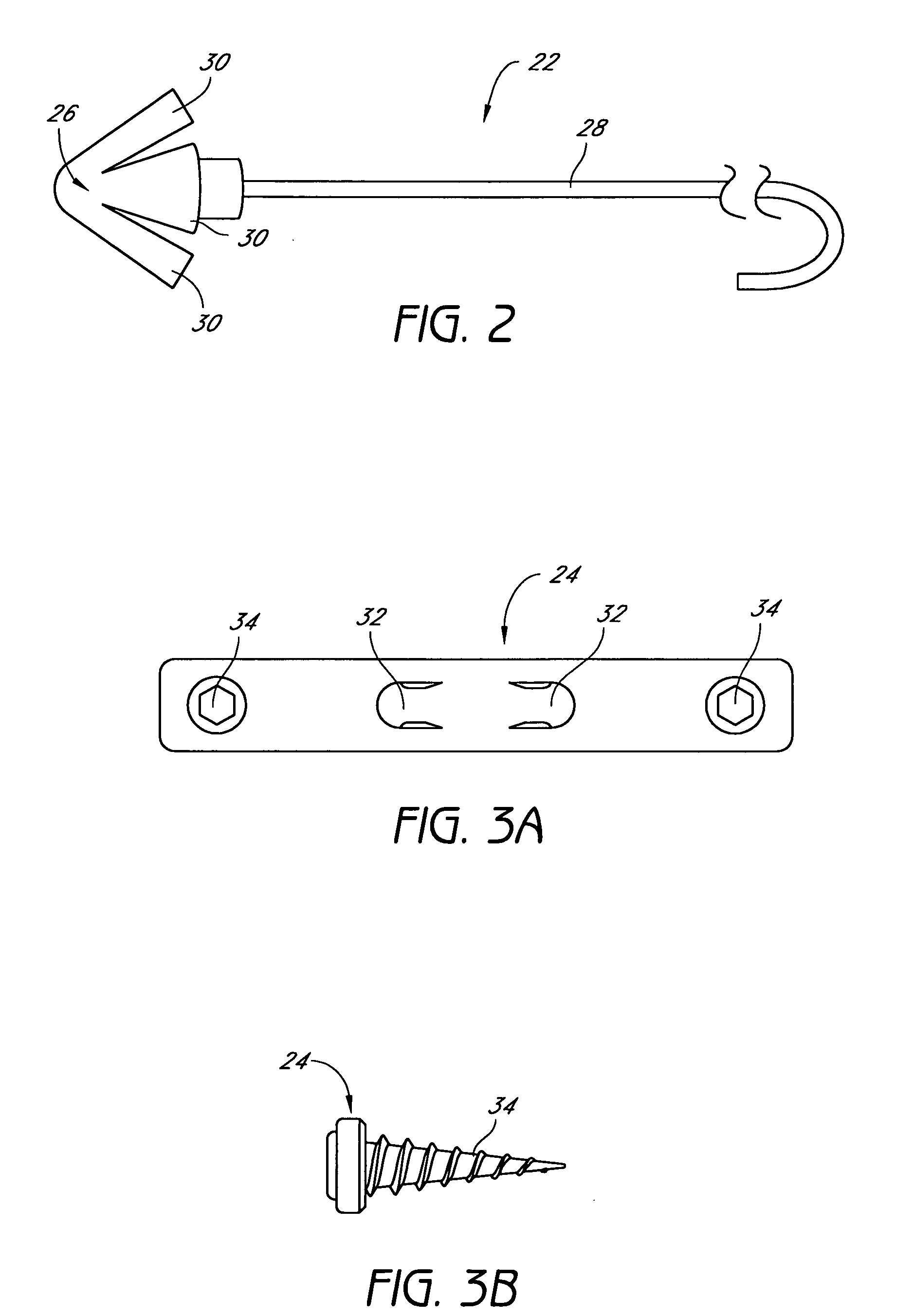
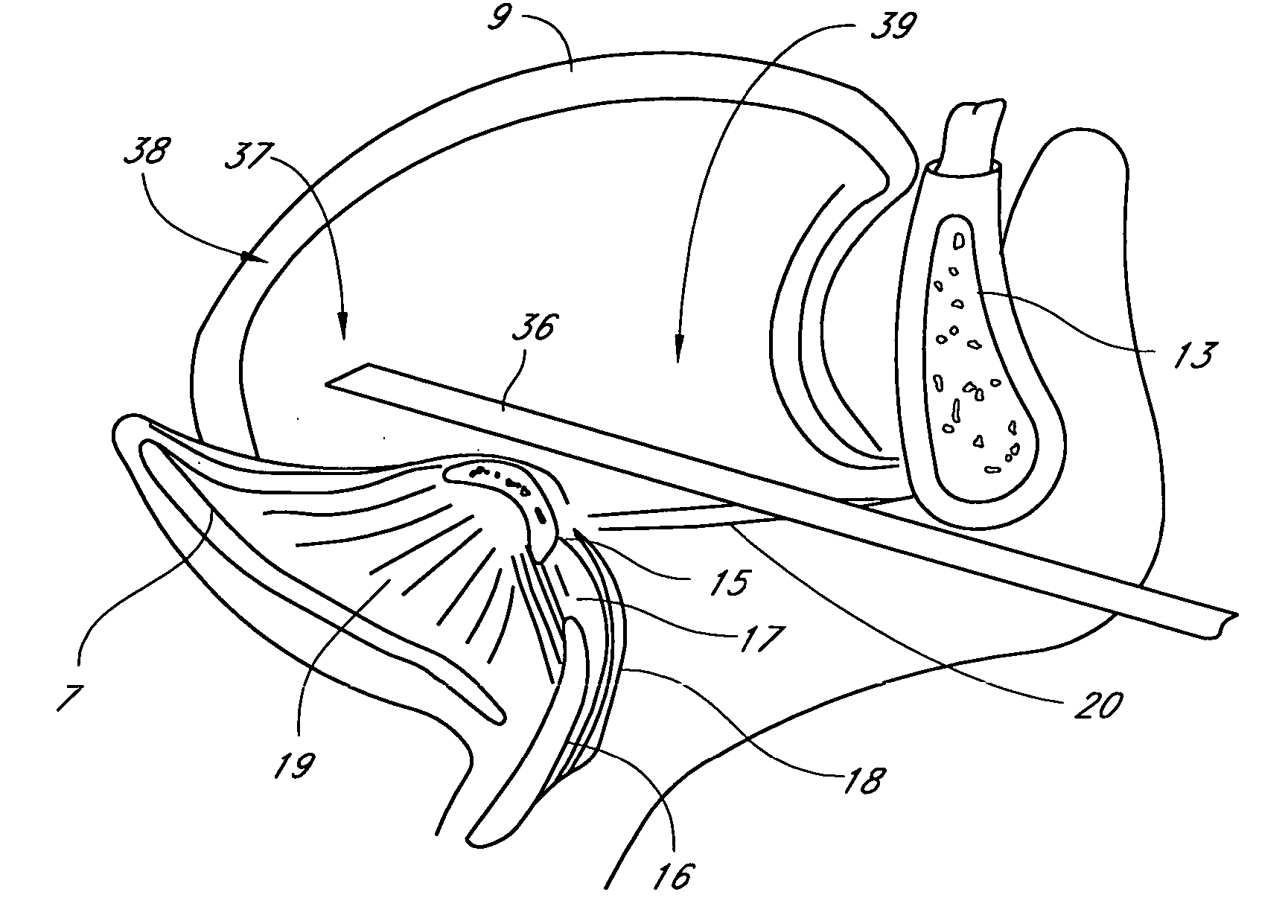
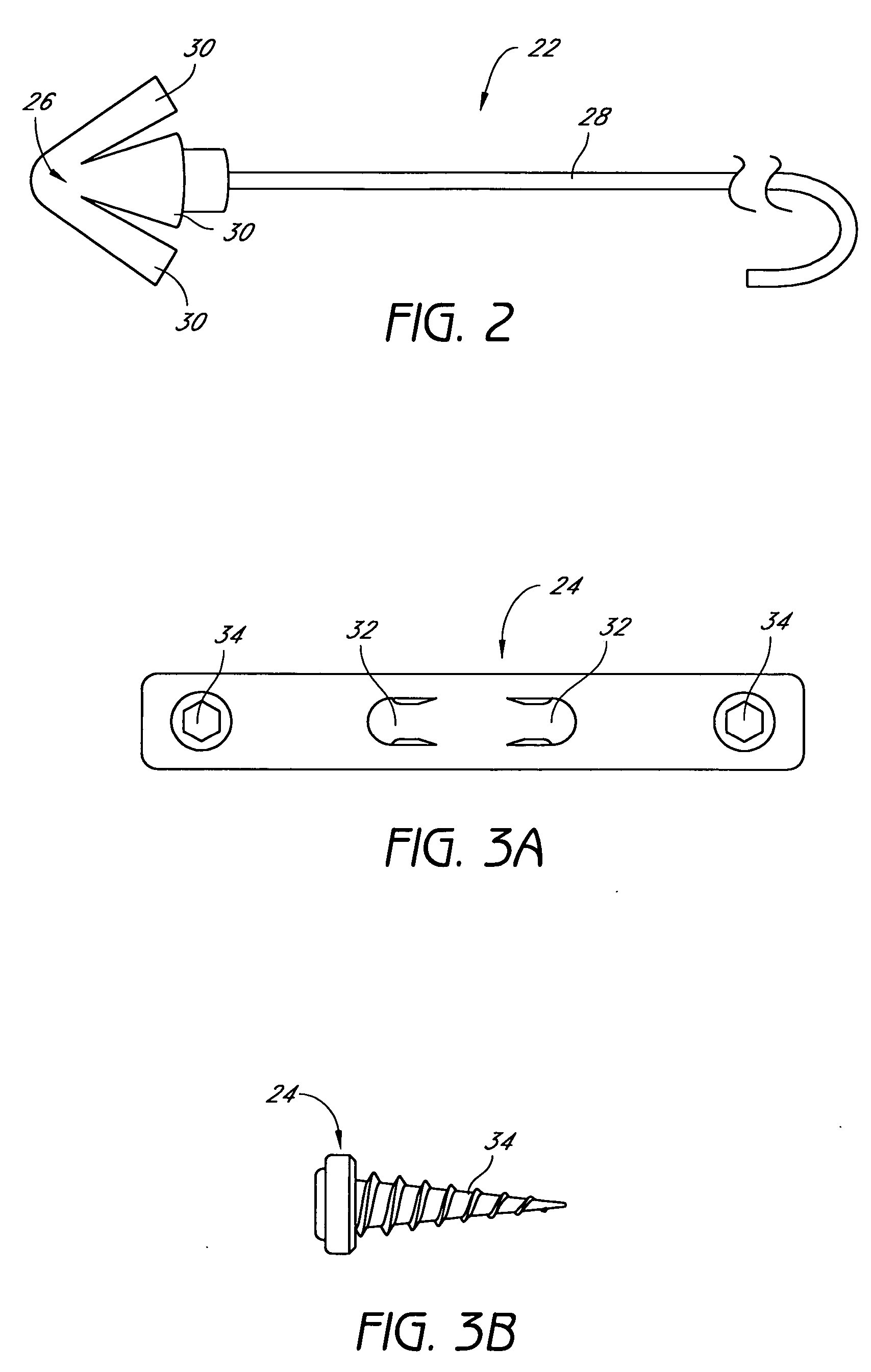
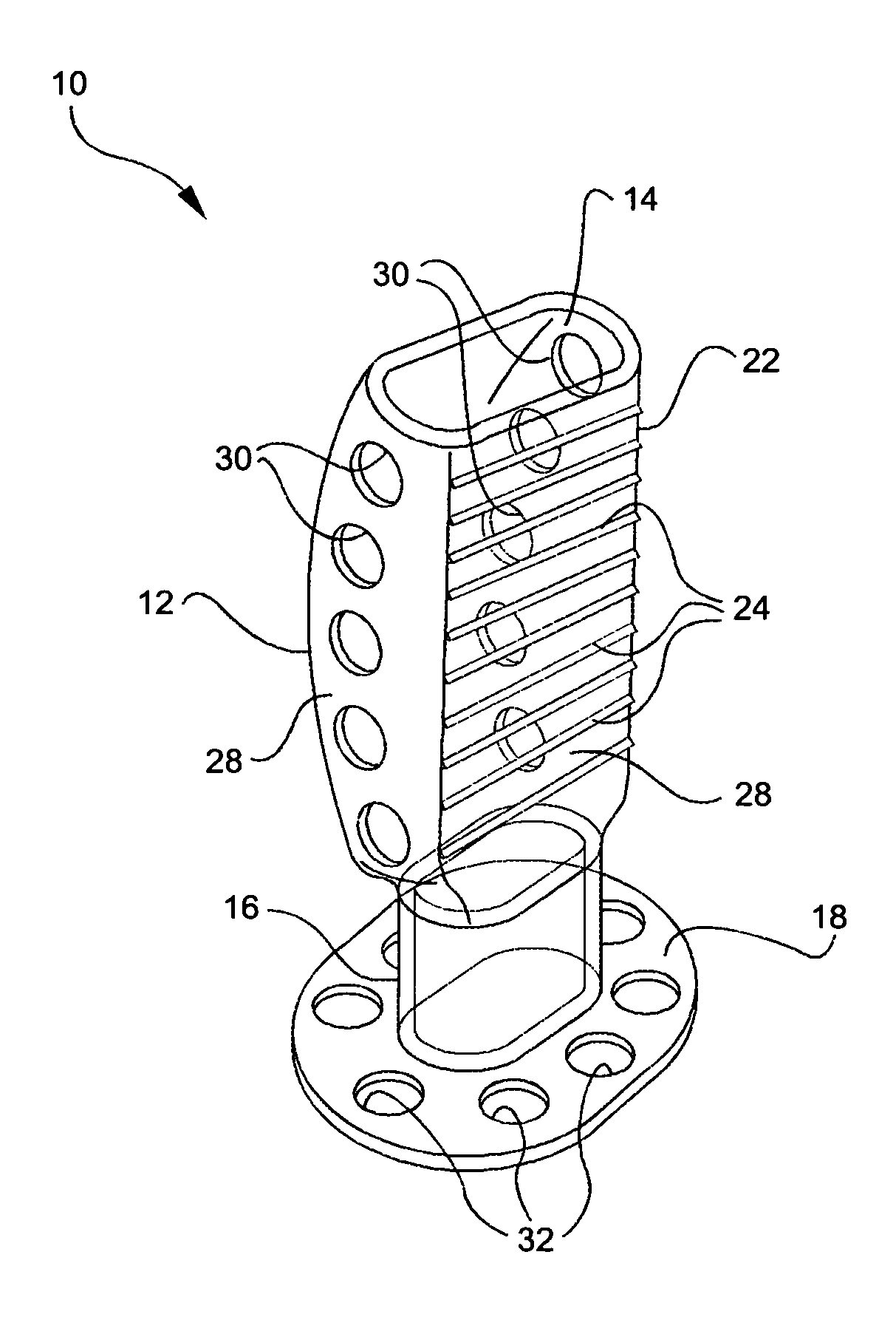
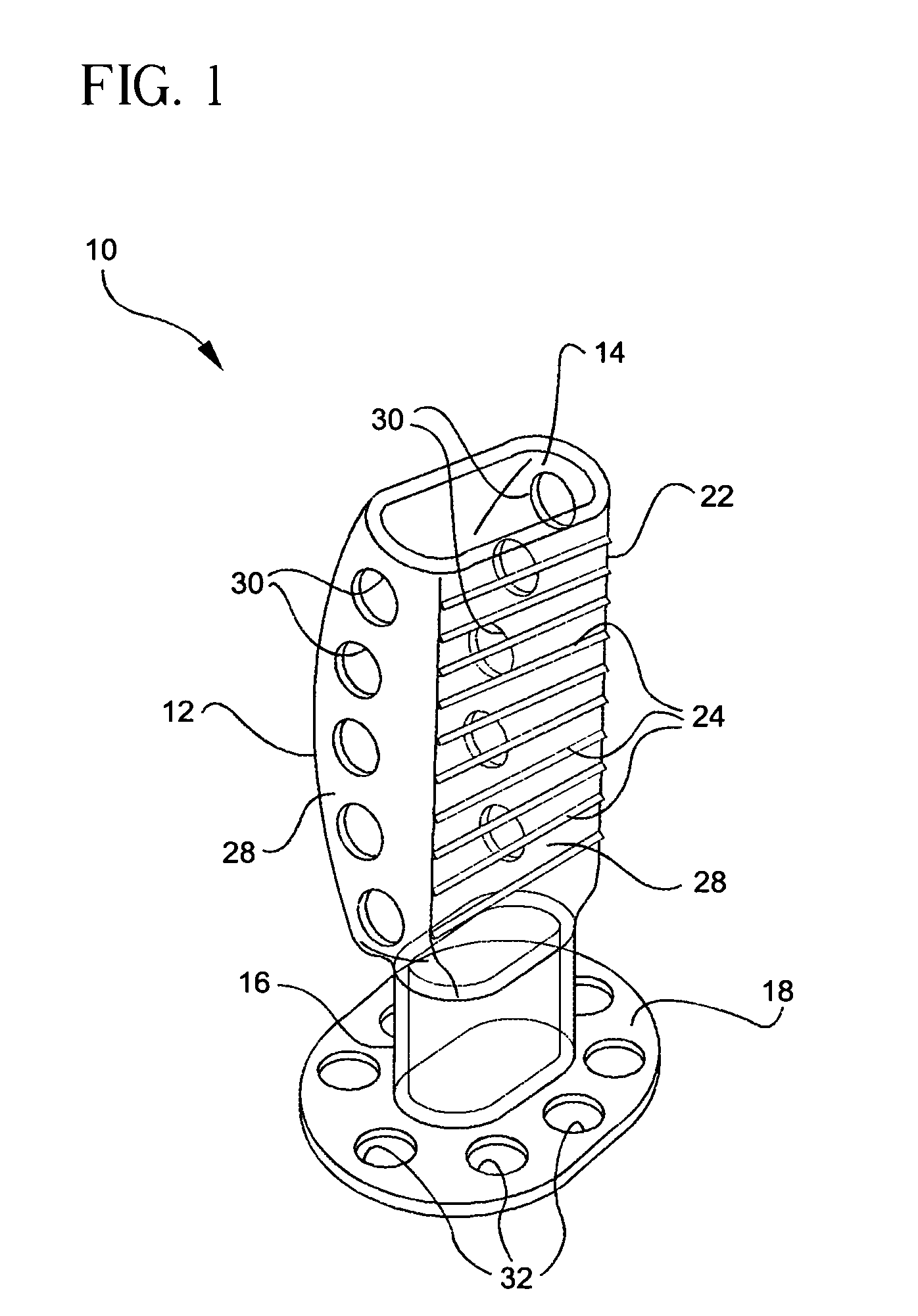
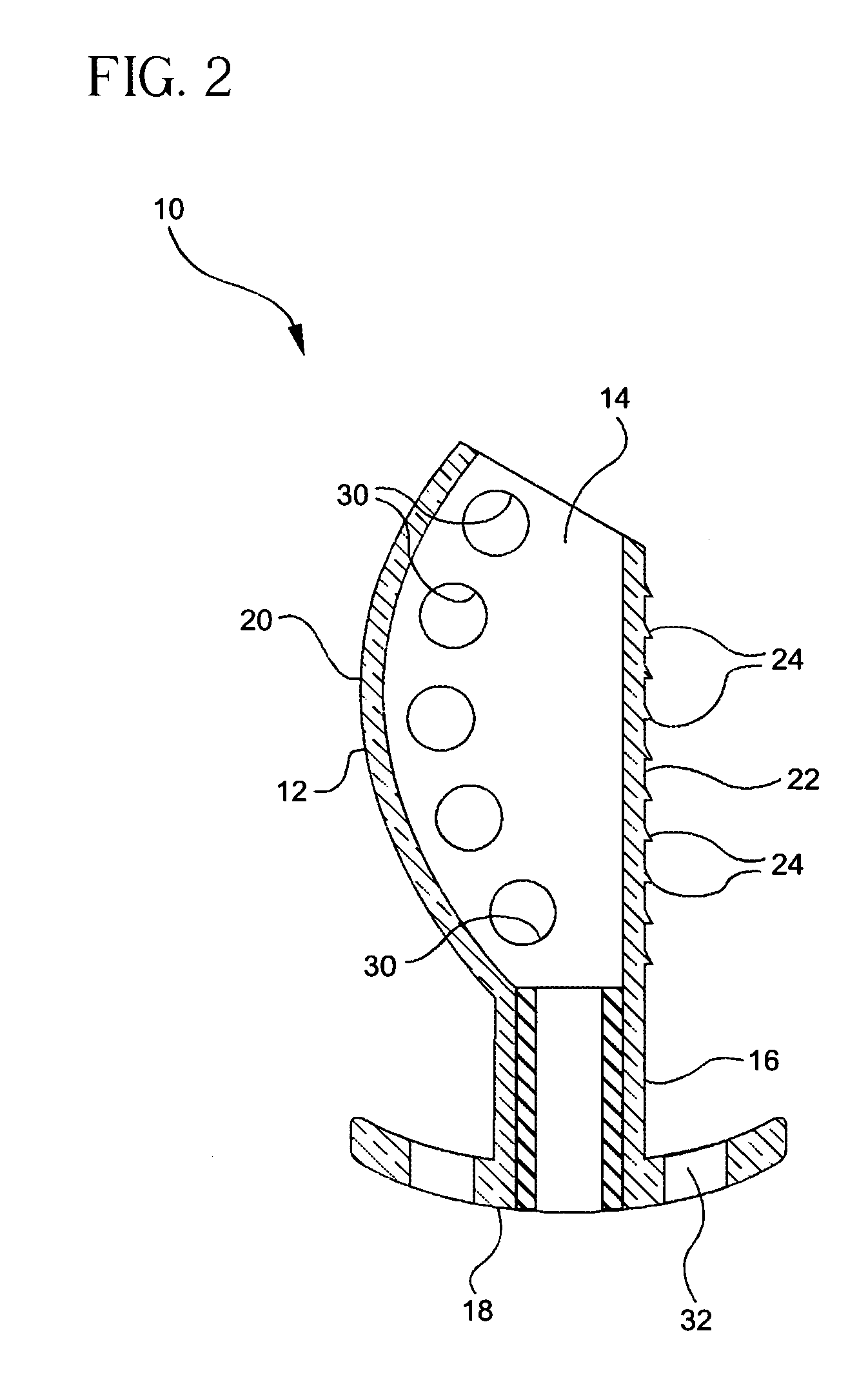
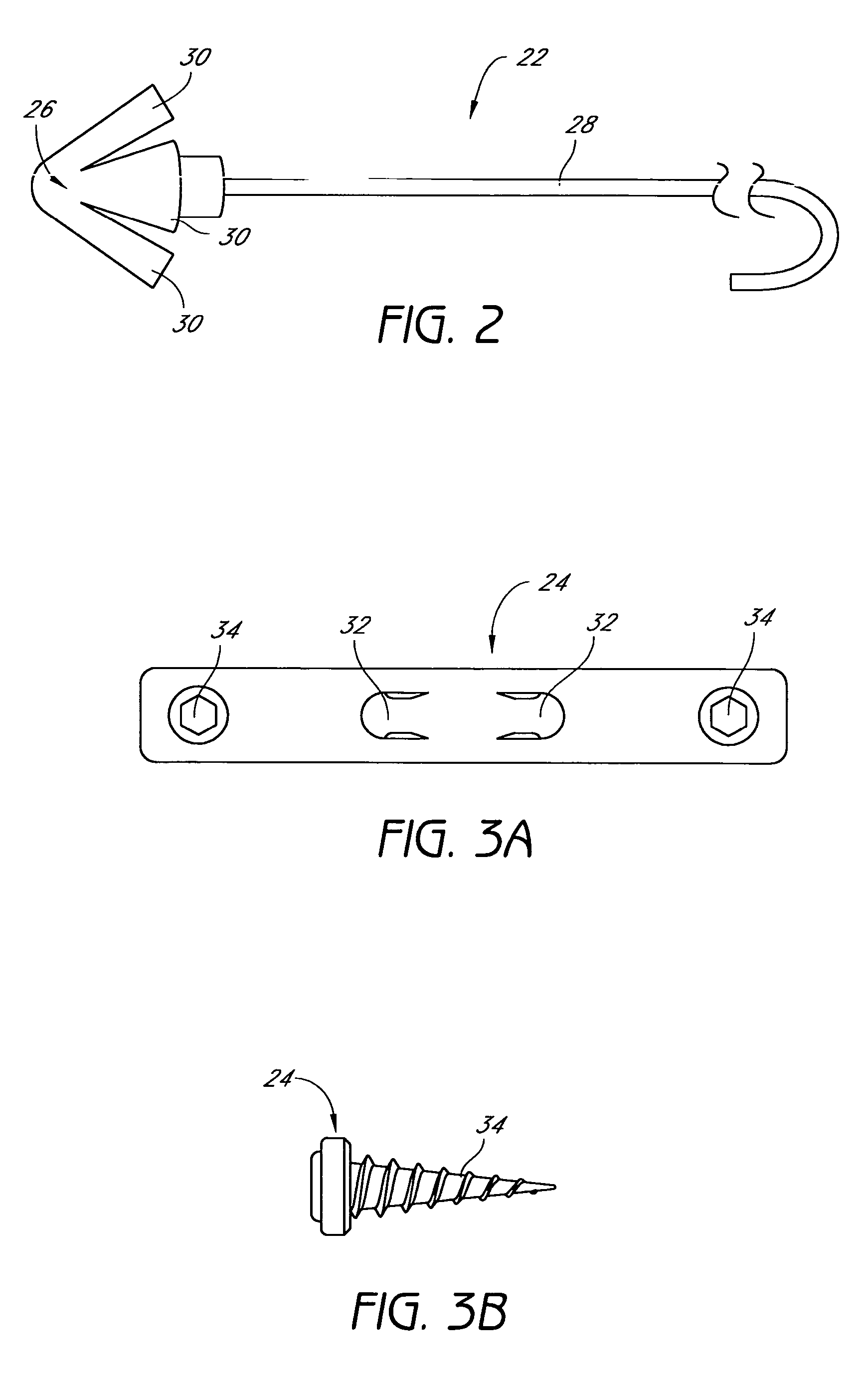
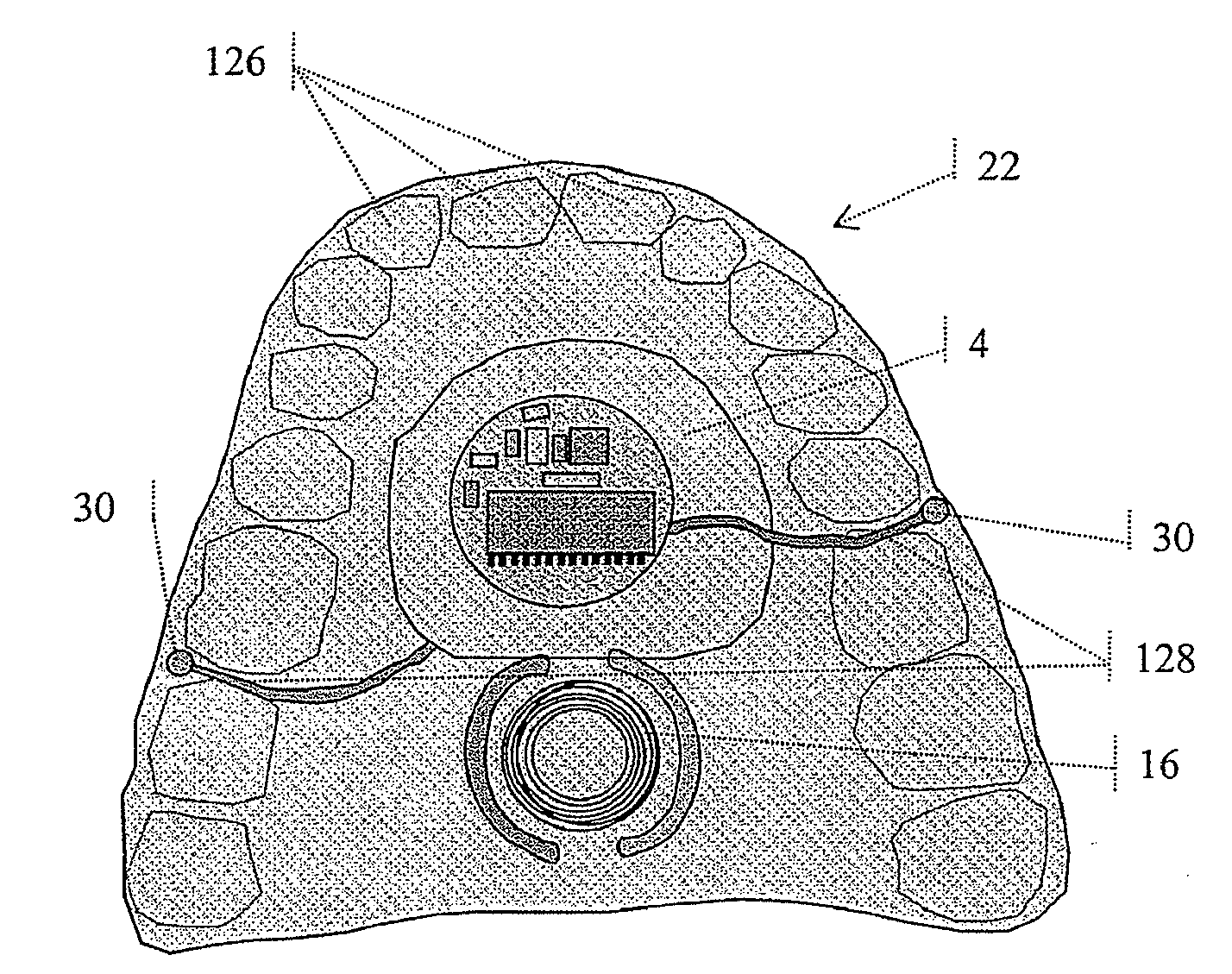
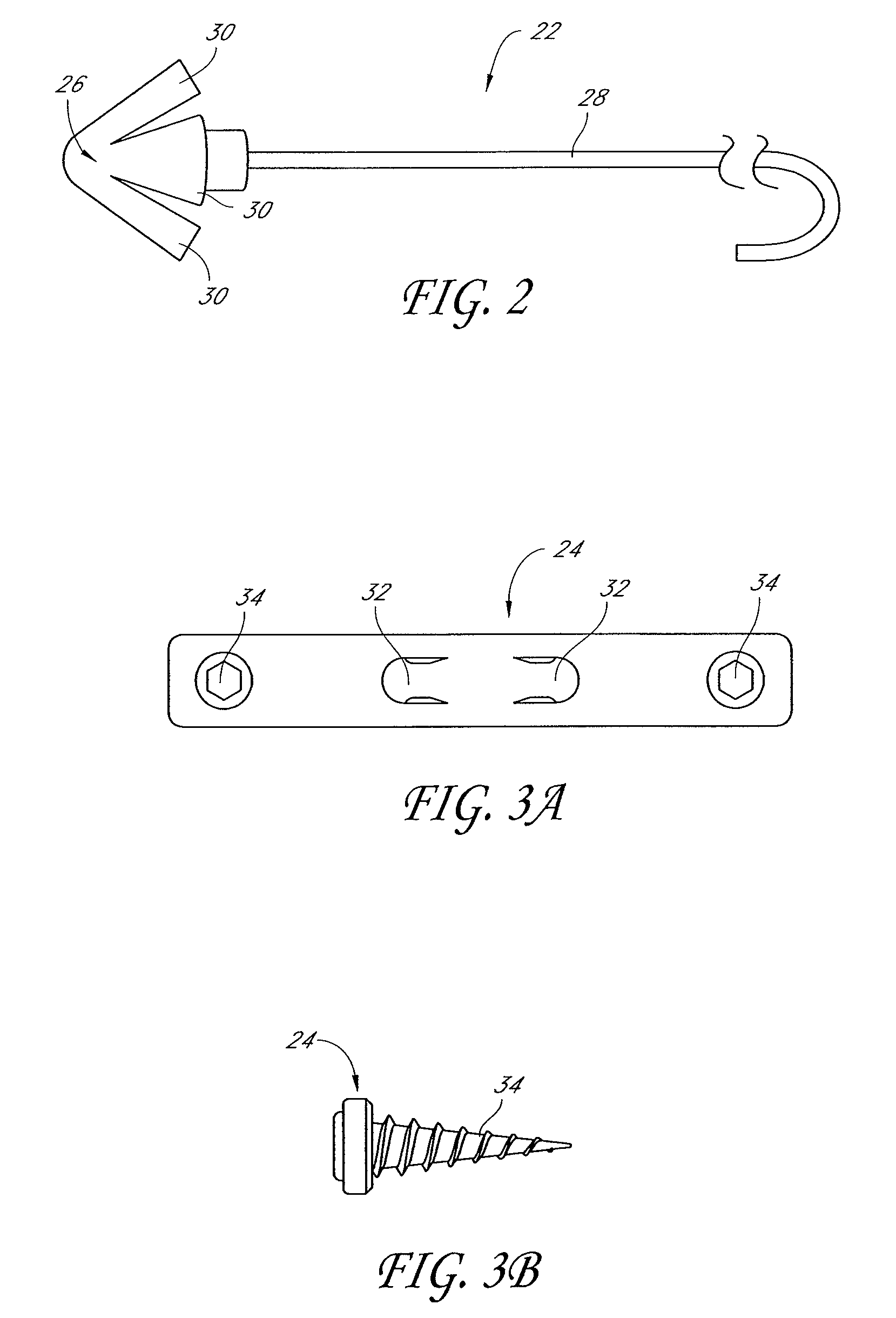
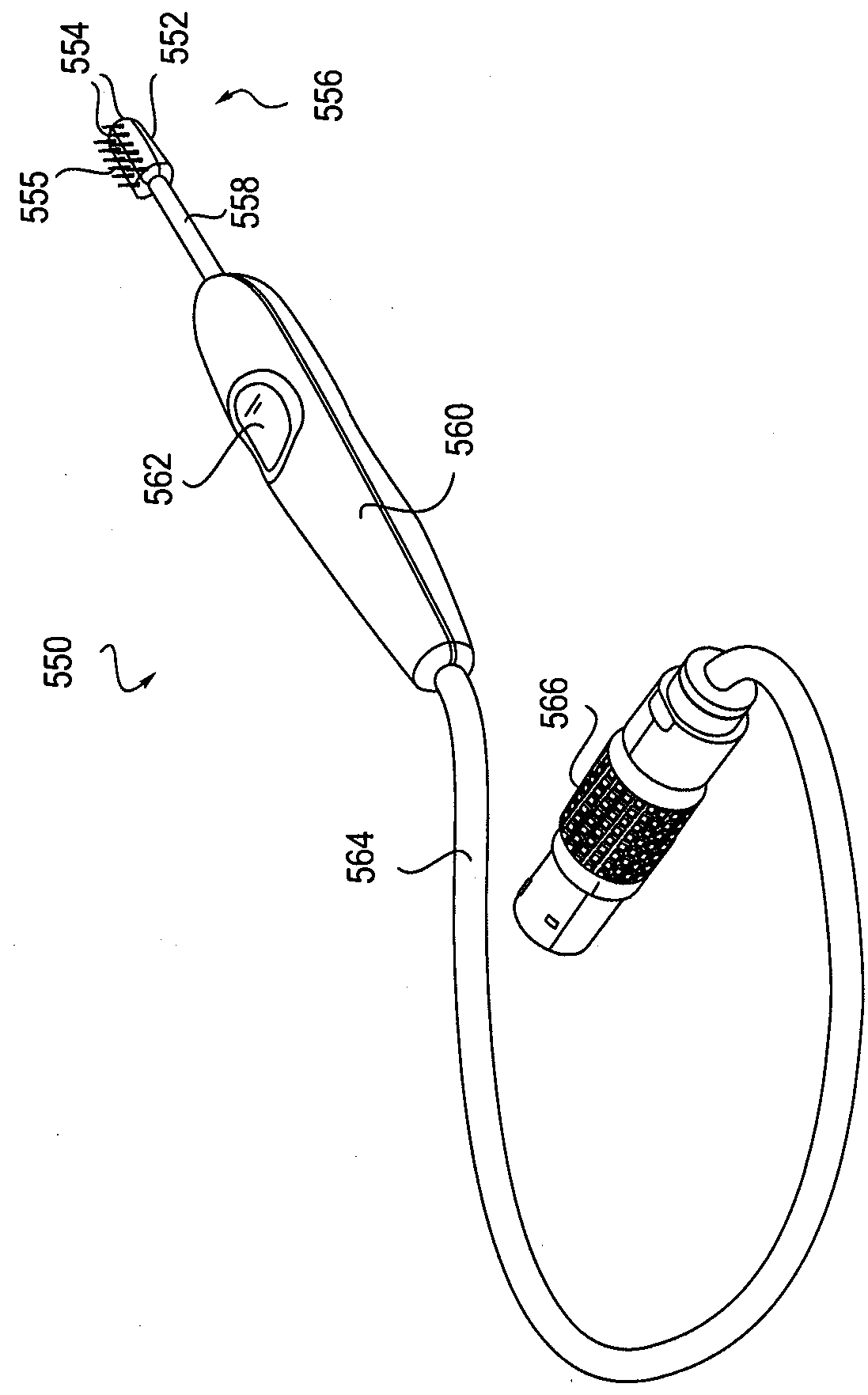
Palatal Implant Fixation Devices and Methods
Devices and methods for securing an implant to the hard palate are disclosed. The device may use a bracket and a retention element, such as a screw or tack, for retaining the device to the hard palate. The device may include a housing and an actuator element for actuating a portion of the soft palate. The method may include securing the retention element into the hard palate.
Owner:MEDTRONIC XOMED INC
System and method for percutaneous palate remodeling
Owner:KONINK PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Soft palate treatment
ActiveUS20180177546A1Prevent and least reduce and snoringPrevent collapse of the soft palateUltrasound therapyHead electrodesObstetricsTreatment sleep
A method of treating a soft palate in a patient to treat sleep apnea, snoring or both may involve advancing a treatment element of a treatment device through the patient's mouth, contacting a tissue-contact surface of the treatment element with the soft palate, delivering energy to the soft palate via one or more energy delivery members on the tissue-contact surface, and removing the treatment element from the mouth.
Owner:AERIN MEDICAL
Anti-snoring apparatus and method
InactiveUS20050279365A1Prevent flutteringConstrict movementBreathing masksSnoring preventionAdhesivePalate muscle
An anti-snoring piercing in the form of specially designed thin mesh-like symmetric structure resembling a pair of wings connected symmetrically by means of a middle bar-like bridge. A middle bar-like bridge is mounted under the uvula while the two symmetric wing parts are placed over the soft palate and pierced on the soft palate in the mouth to provide stiffness to uvula-soft palate assembly and thus prevent snoring. A stiffening member is attached to the uvula by means of at least one piercing post with a backing or with an adhesive. Each of these embodiments stiffens the uvula and prevents snoring.
Owner:ARMIJO DENNIS F +1
Snoring and obstructive sleep apnea prevention and treatment device
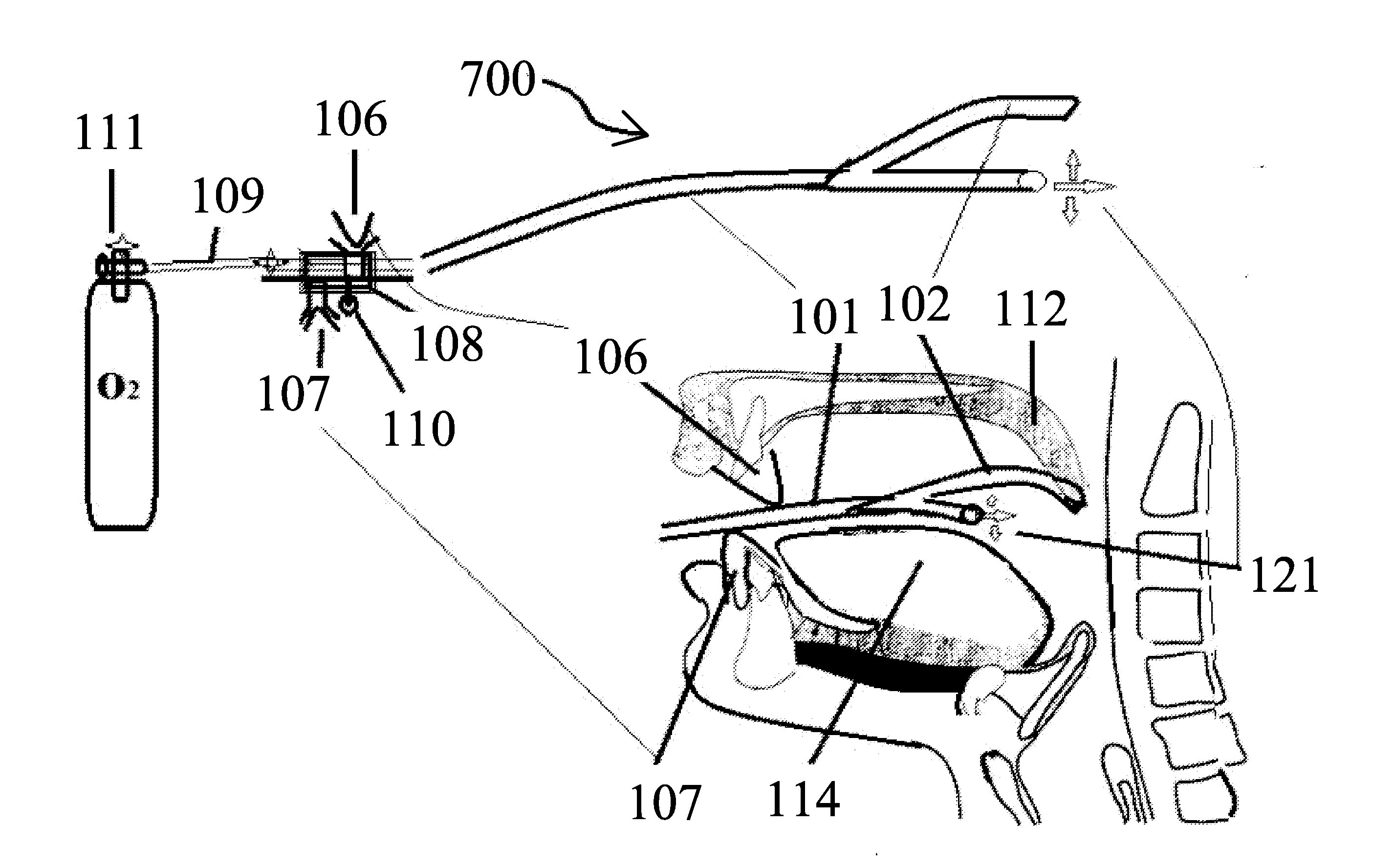
InactiveUS20120234332A1Reduce air turbulencePromotes nasalRespiratorsHead electrodesDiseaseHyoid bone
A anti-snoring and anti-obstructive sleep apnea apparatus has a plate or metal frame tongue shelf splint to prevent the flaccid tongue falling back, a palate shelf splint projection to elevate the soft palate and prevents its vibration, incisors teeth receptacles or pockets sockets for jaw displacer to hold the mandible moved forwards, and to prevent it falling back held between the bite block, catheter-tubing to administer oxygen supplementation from the external source which reduces air turbulence and promotes nasal breathing, a submental suprahyoid muscle stimulator placed below the tongue, and above the mucous membrane. An injection port is provided to administer any therapeutic agents and local anesthetics to reduce the sensitivity of the tongue and oral cavity mucus membrane lining to the foreign objects. This device is used to deliver therapeutic agents to prevent and to treat halitosis and various diseases.
Owner:SHANTHA TOTADA R
Airway stiffening implant
A method and apparatus for treating snoring of a patient includes providing an implant for altering a dynamic response of a soft palate of the patient to airflow past the soft palate. The implant is embedded in the soft palate to alter the dynamic response. For example, the implant has a mass, stiffness or dampening sufficient to alter the dynamic response following the implantation without substantially impairing a function of the soft palate to close a nasal passage of the patient during swallowing.
Owner:PILLAR PALATAL LLC +1
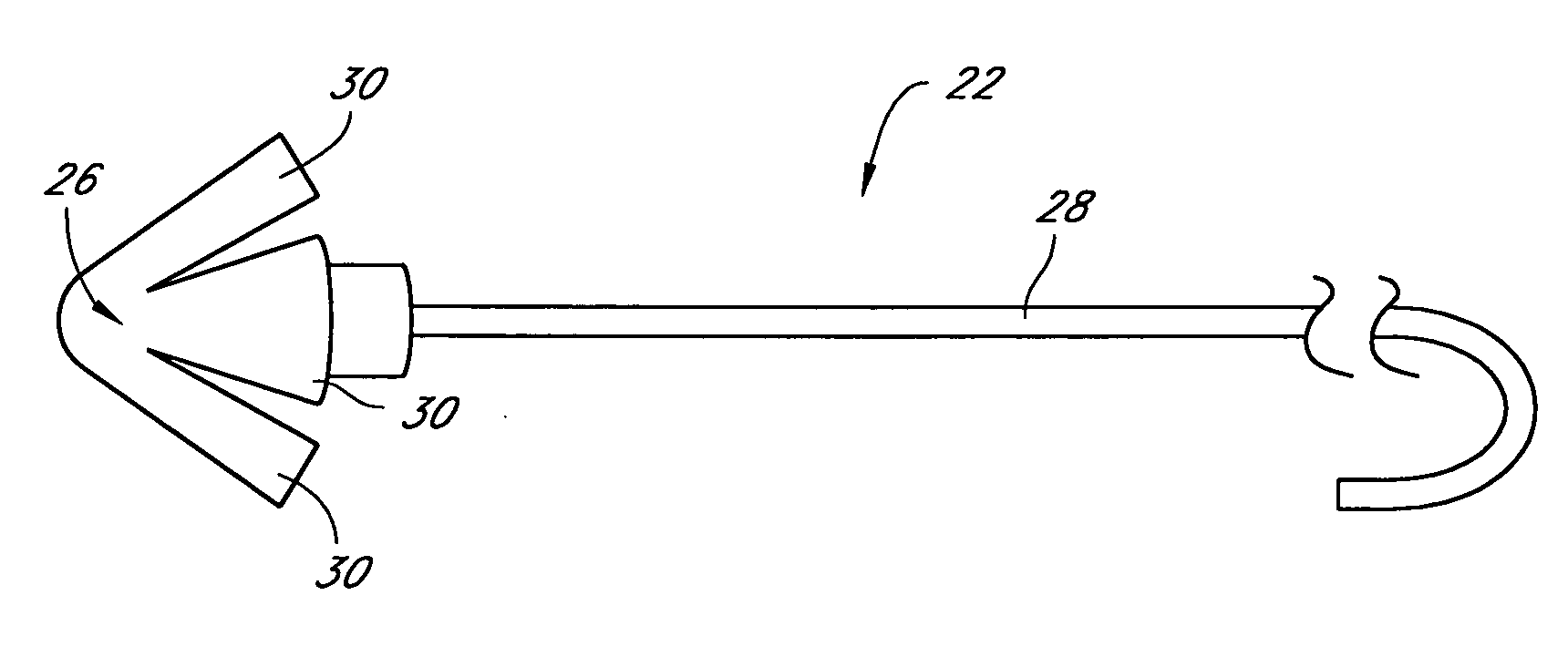
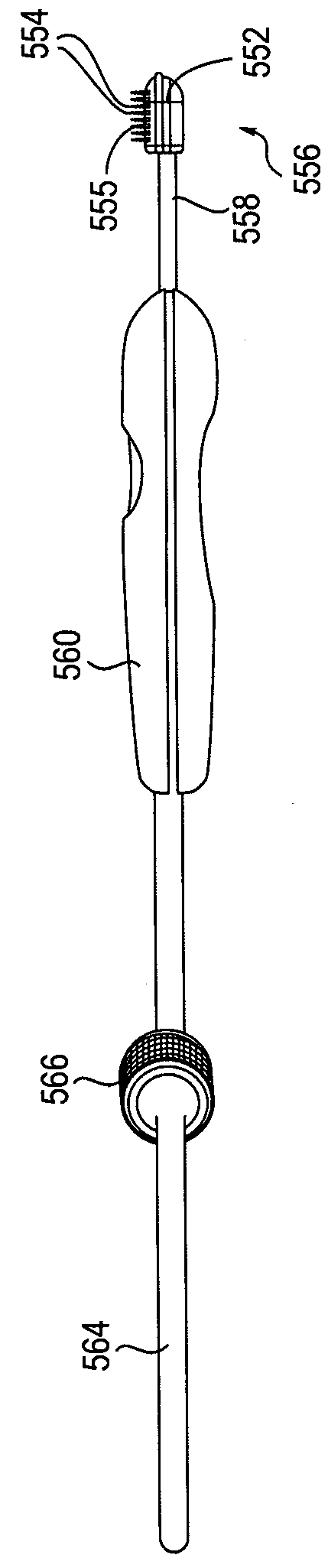
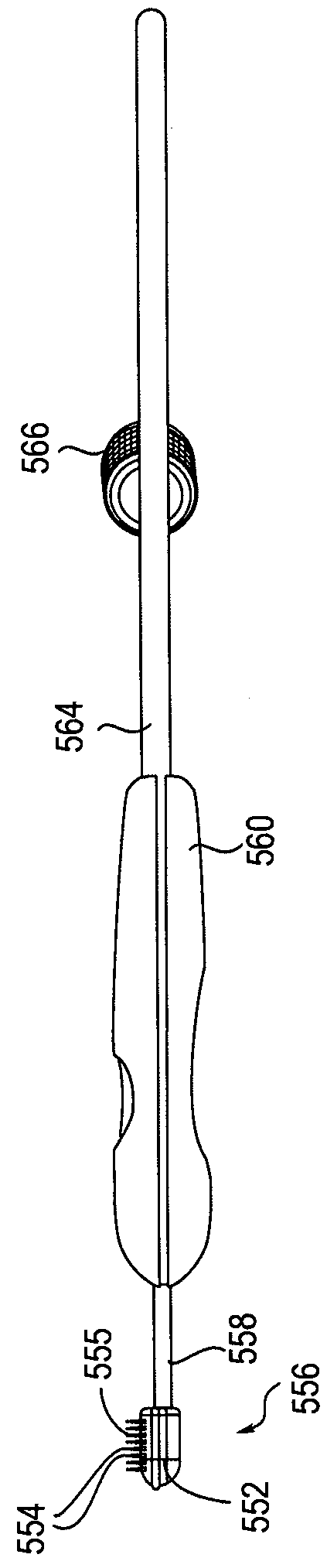
Delivery tools for sleep disorders treatment implant and methods of implantation
InactiveUS7980248B2Easy accessPrevent excessive extension of the bladeIncision instrumentsSnoring preventionRight hard palateSleep Disorder Therapy
Methods and tools are disclosed for inserting an implant device that treats snoring and apnea of a patient by altering the position of a soft palate. Methods and tools can make an incision in patient's soft and hard palate to create a cavity that can house the implant. The tools can have visually observable markings that can be aligned with the incision, thus controlling the depth of the cavity. A needle having an incision edge can be used to make an incision in patient's soft palate. The needle can be bent into a suitable longitudinal shape to allow easier access and visualization of the process. A blade that makes the cavity in the tissue can be housed inside a channel in the needle. The tools may have stoppers to prevent excessive extension and retraction of the blade thus preventing an excessive cavity depth. Some tools may also house the implant device, which may be implanted after the cavity is formed.
Owner:PAVAD MEDICAL
Removable tongue position corrective anti-snoring and anti-suffocating device
InactiveUS7770582B2Without causing discomfort and nausea of peripheral tissueRaise up the palatine and uvulaStammering correctionTeeth fillingEngineeringPalate muscle
A comfortable and viable and removable device of channel-type tongue position correction for anti-snoring. The device is made of wire or band material, including a fixer, an upper and nether force-components which are connected with the fixer. The device is mostly applied on upper jaw. The force end of the upper force-component is designed to be suitable to the soft palate palatine velum, and acts to raise up the soft palate palatine velum and uvula upward / upward and backward suitably. The force end of the nether force-component is designed to be suitable to the normal configuration of the corpora linguae (anterior tongue), and acts on the portion in front of the sensitive position of the hind half of the corpora linguae (anterior tongue) to press the big tongue downward / downward and forward. Thus, depending on the co-action of the upper and nether force-components, the blocked respiratory tract could be expanded to prevent snore and remit sleep apnoea syndrome.
Owner:SHANGHAI GUANG REN ANTI SNORING HEALTH CENT
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com