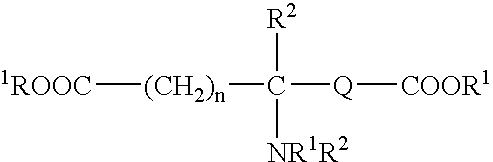
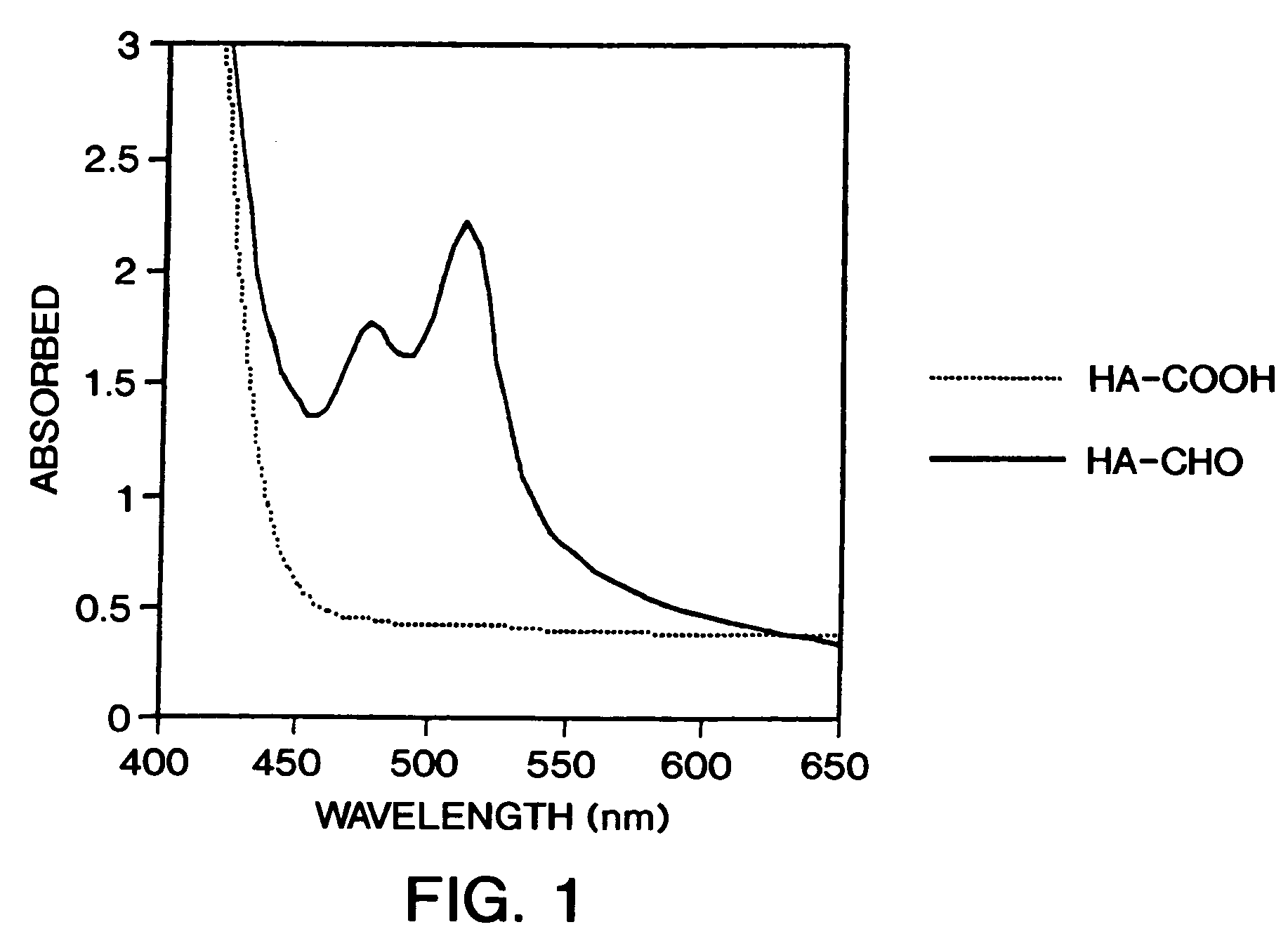
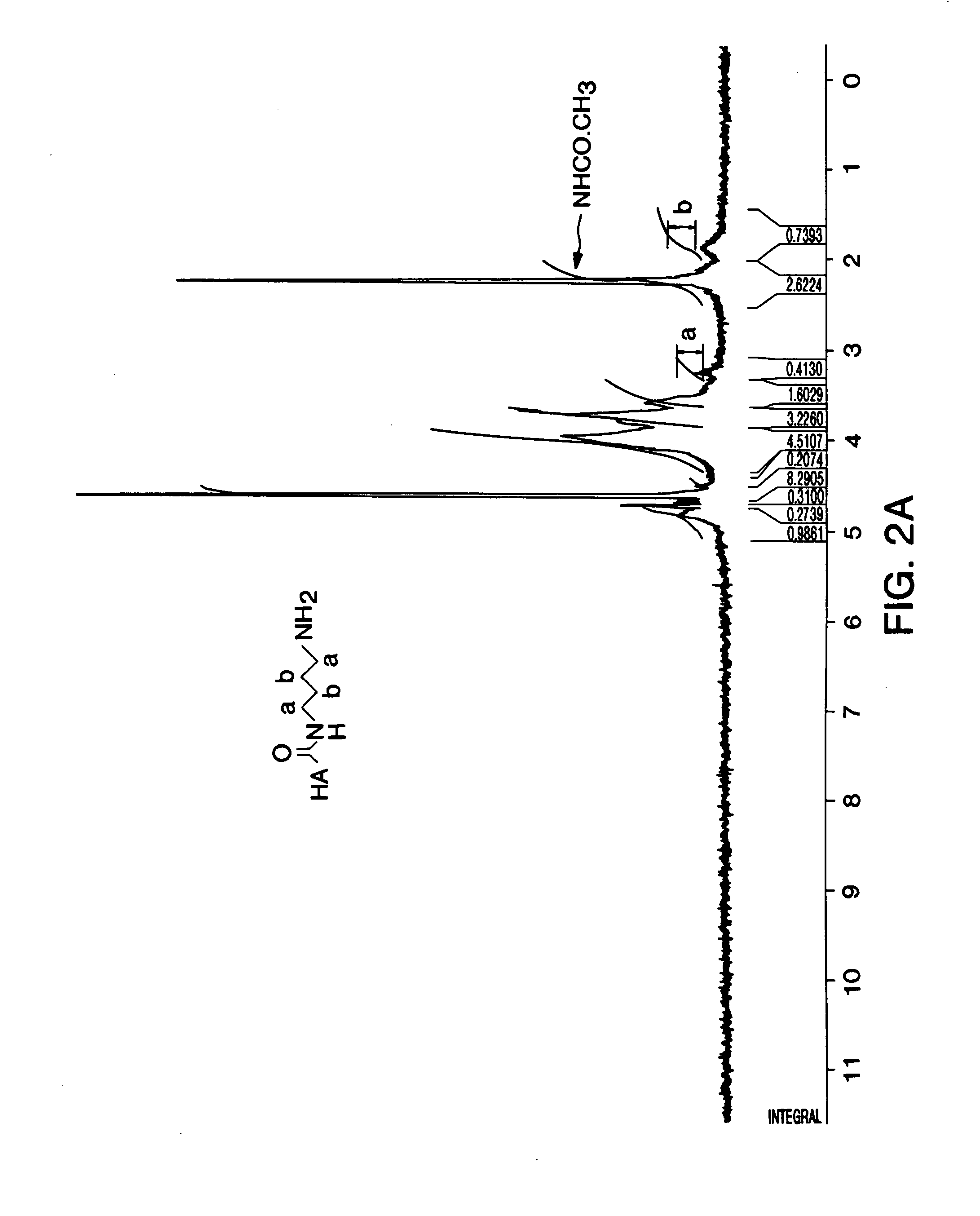
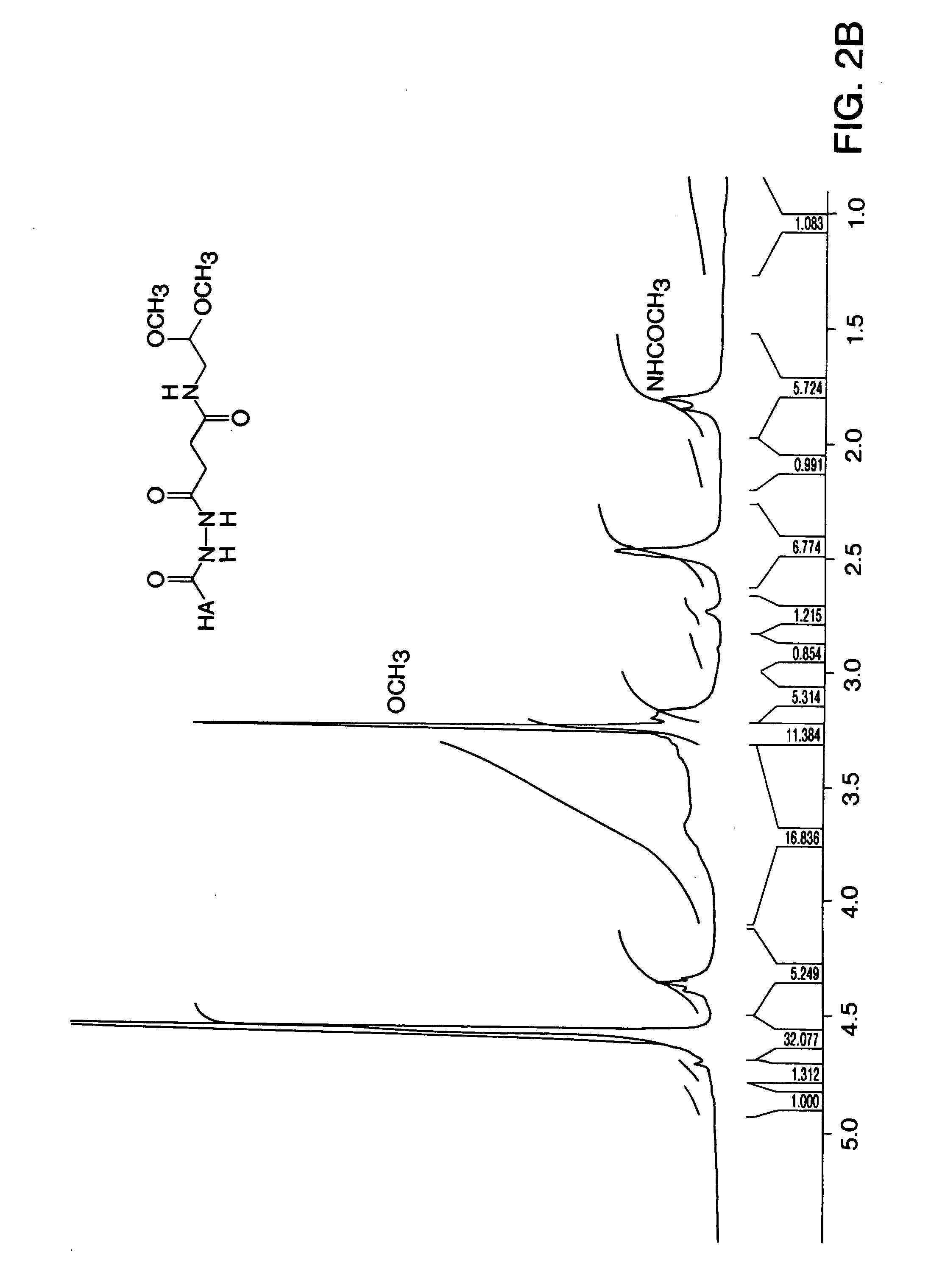
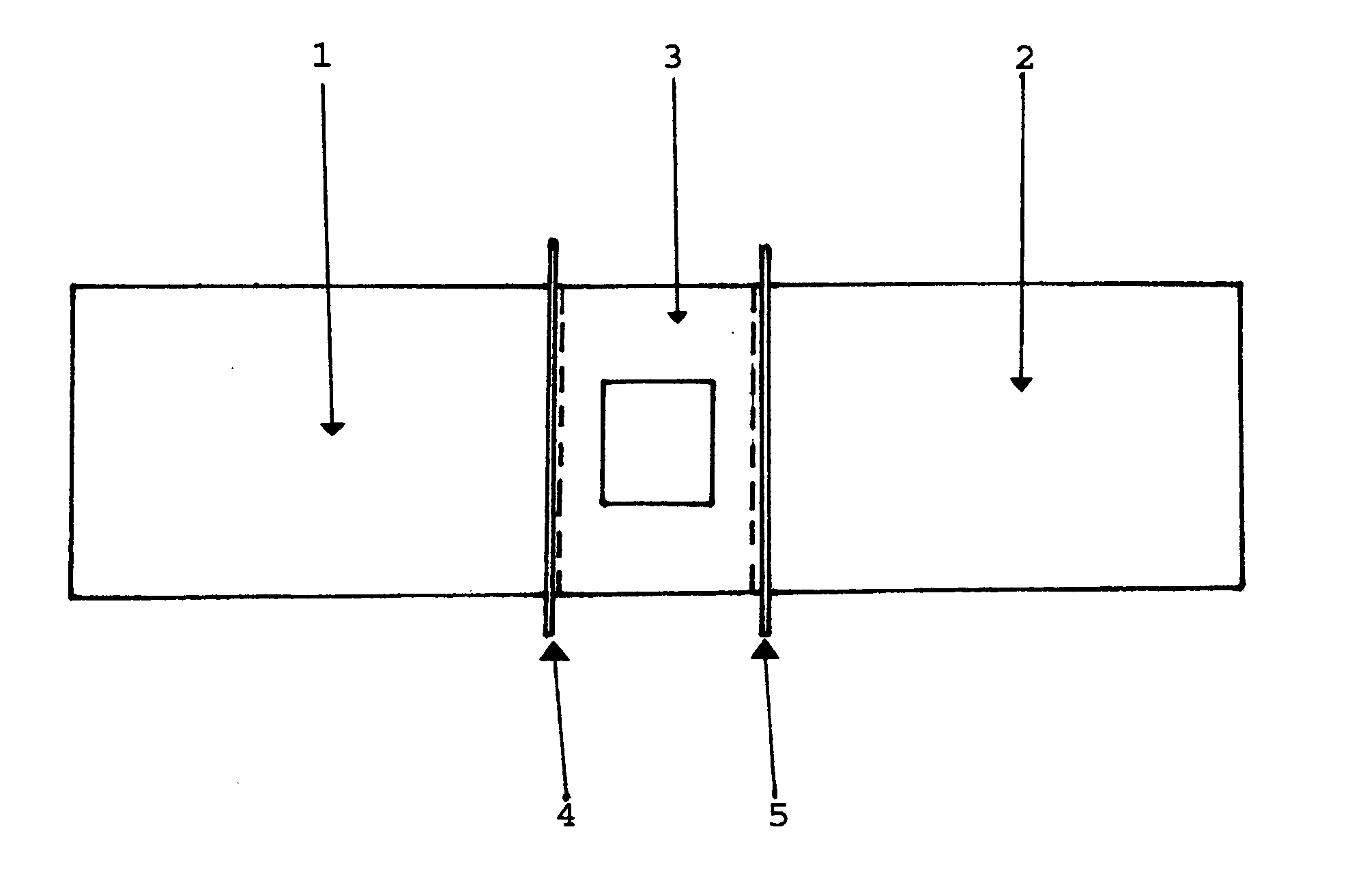
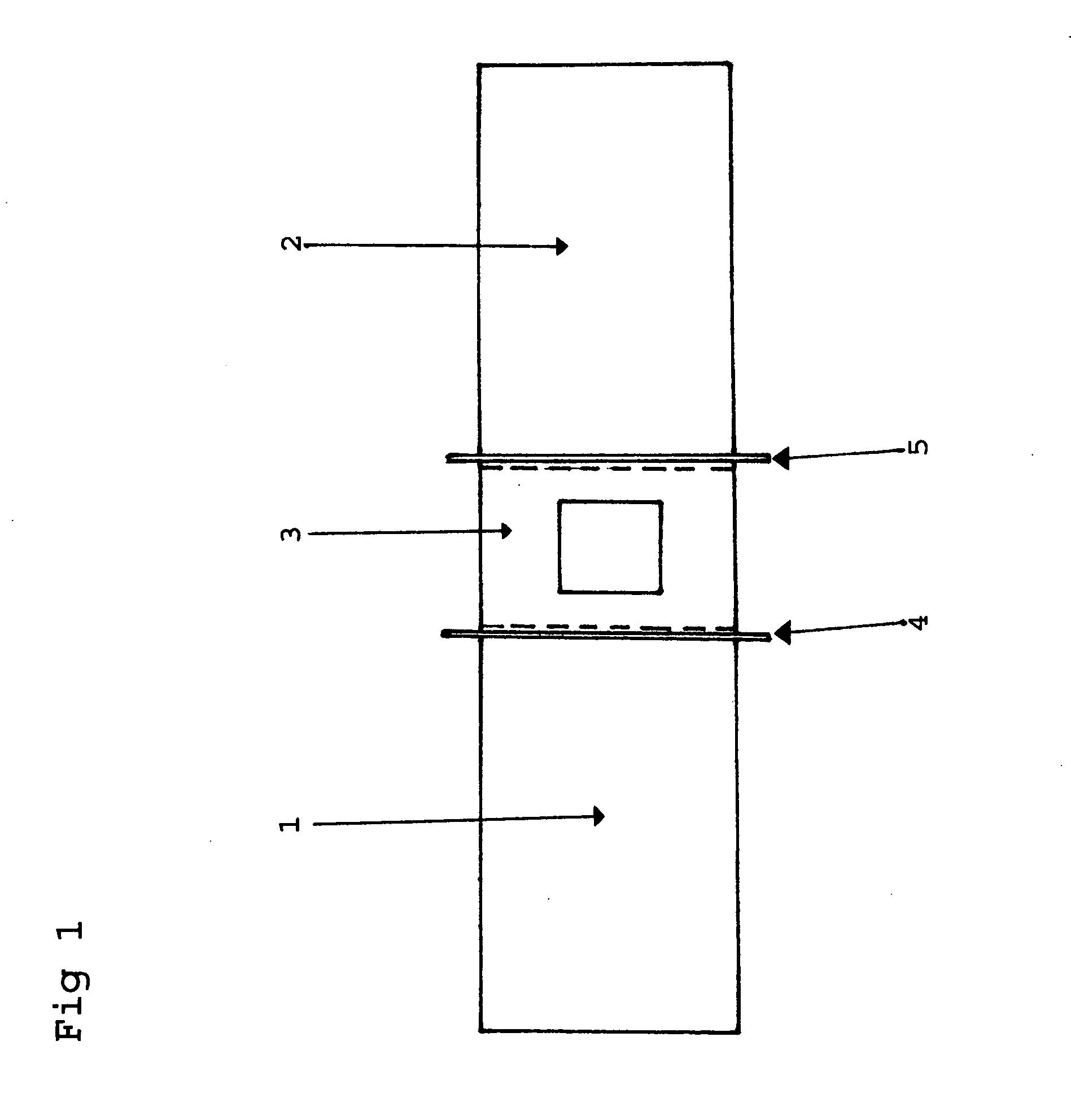
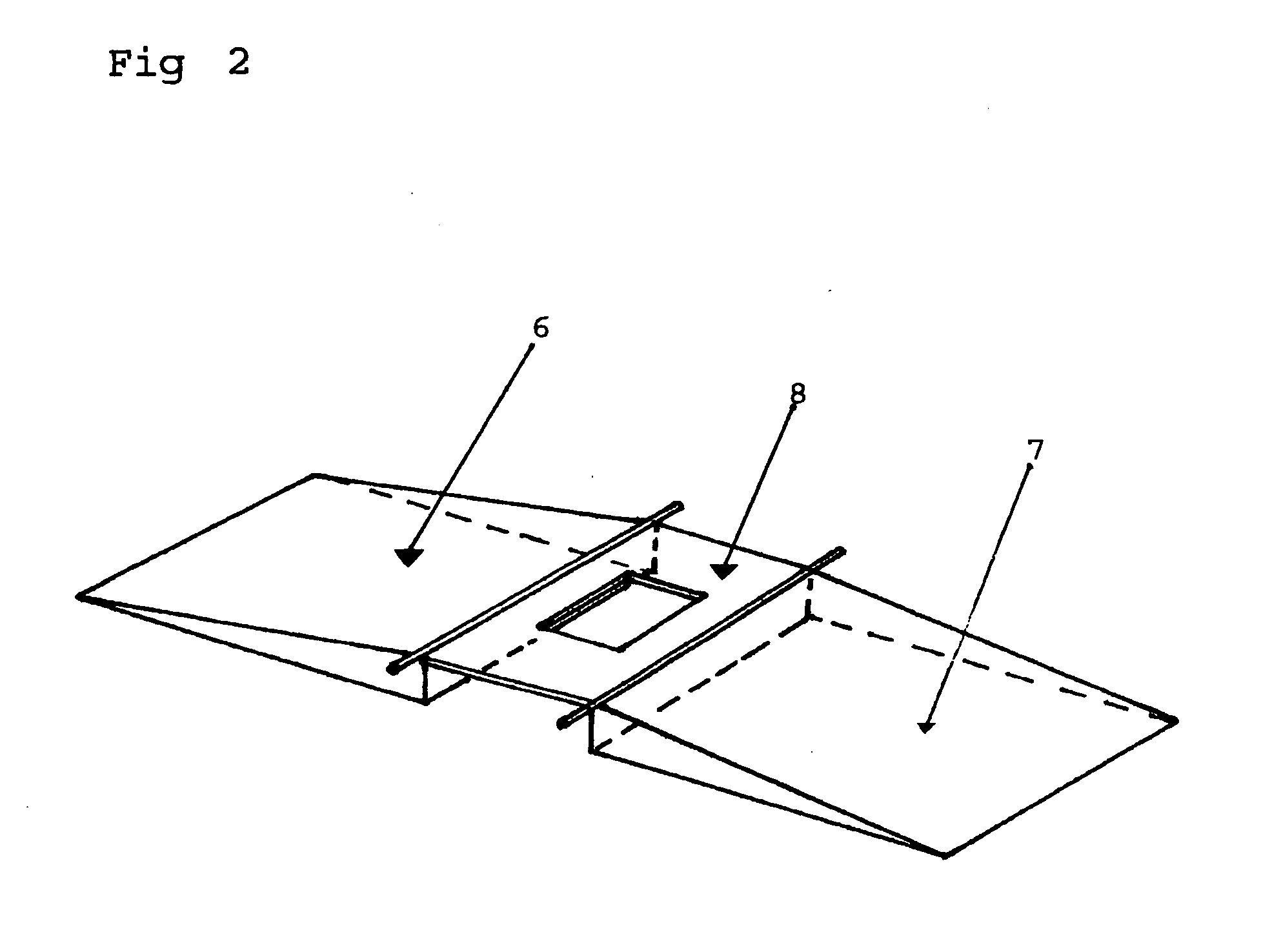
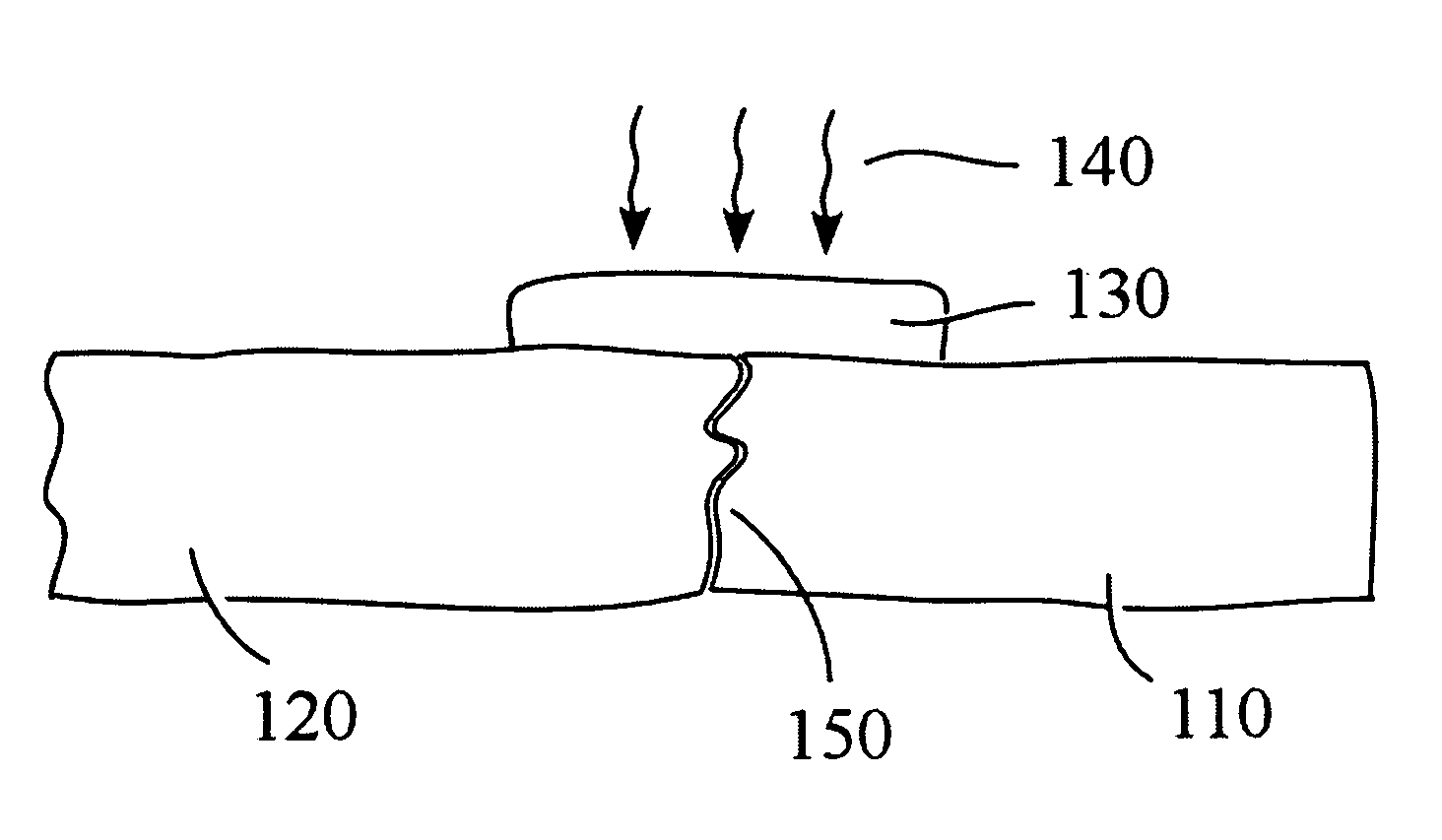
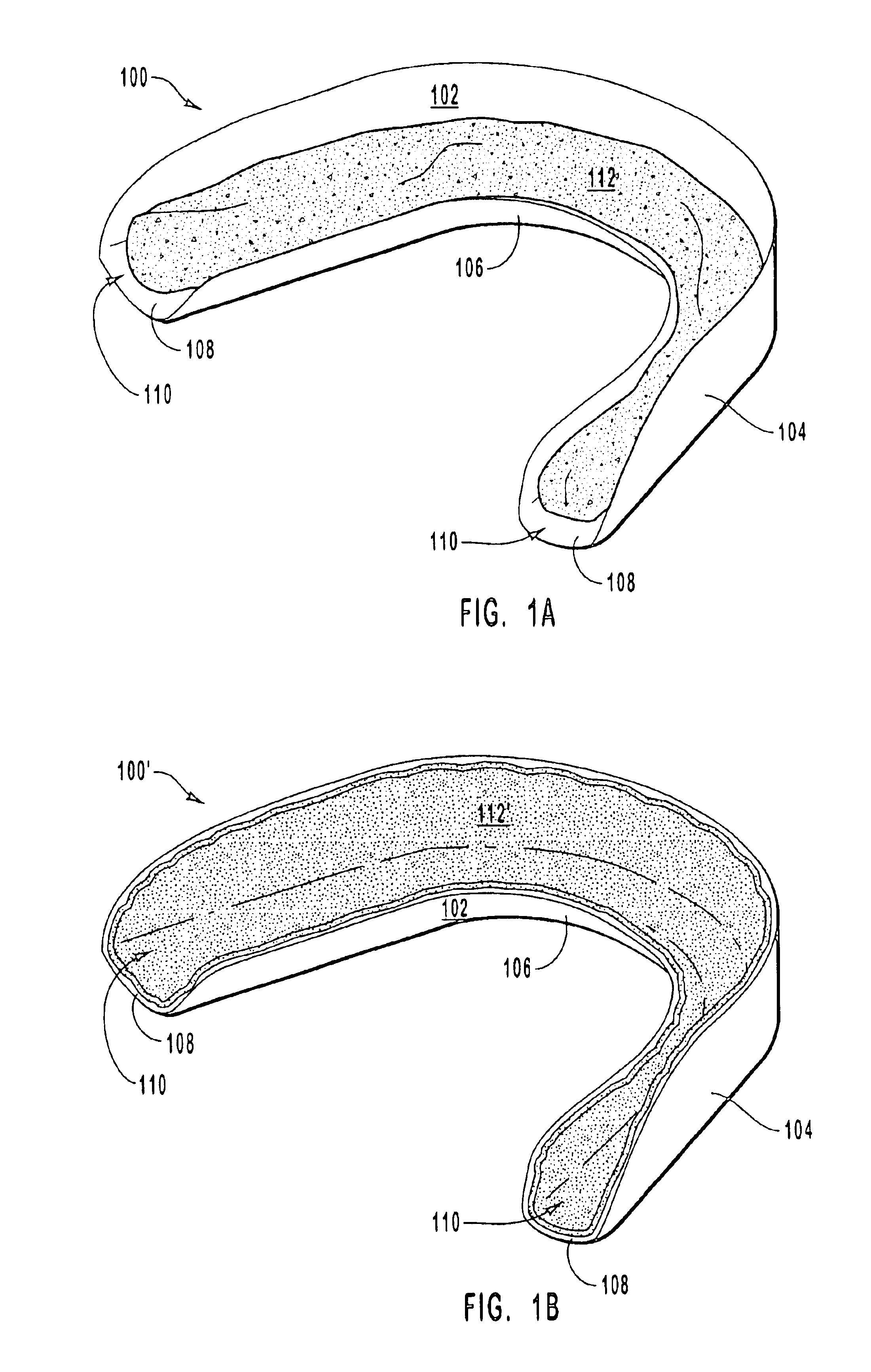
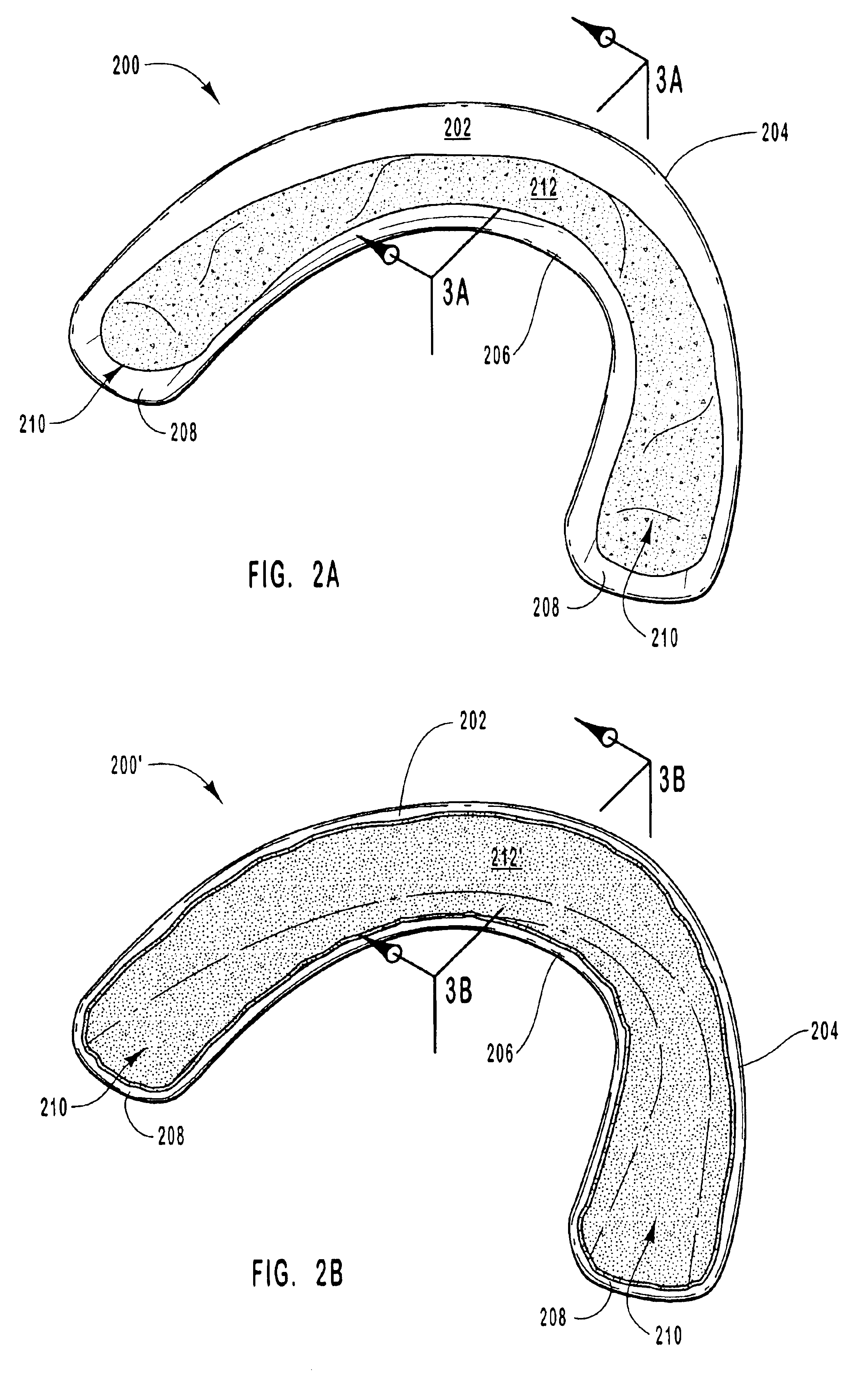
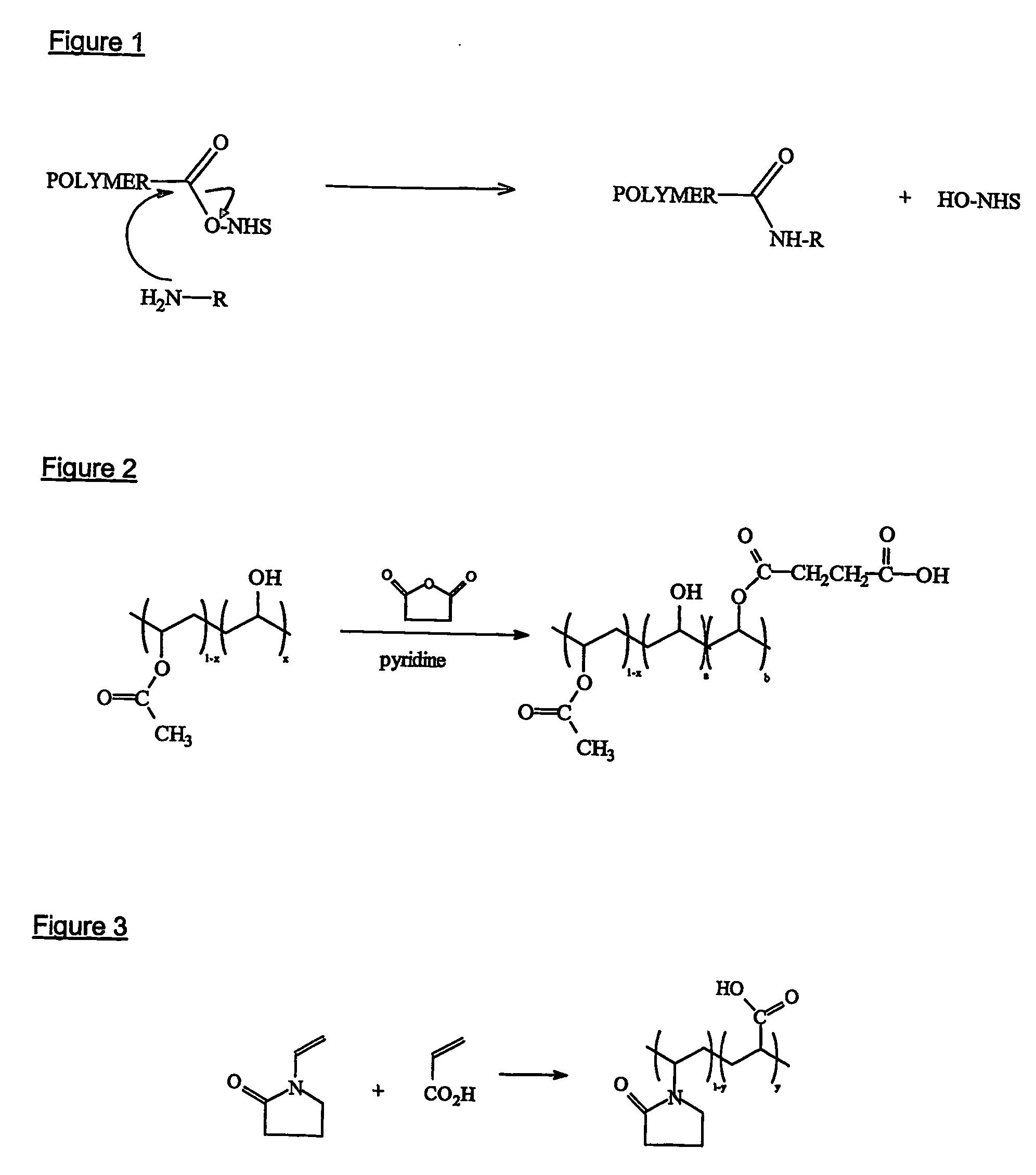
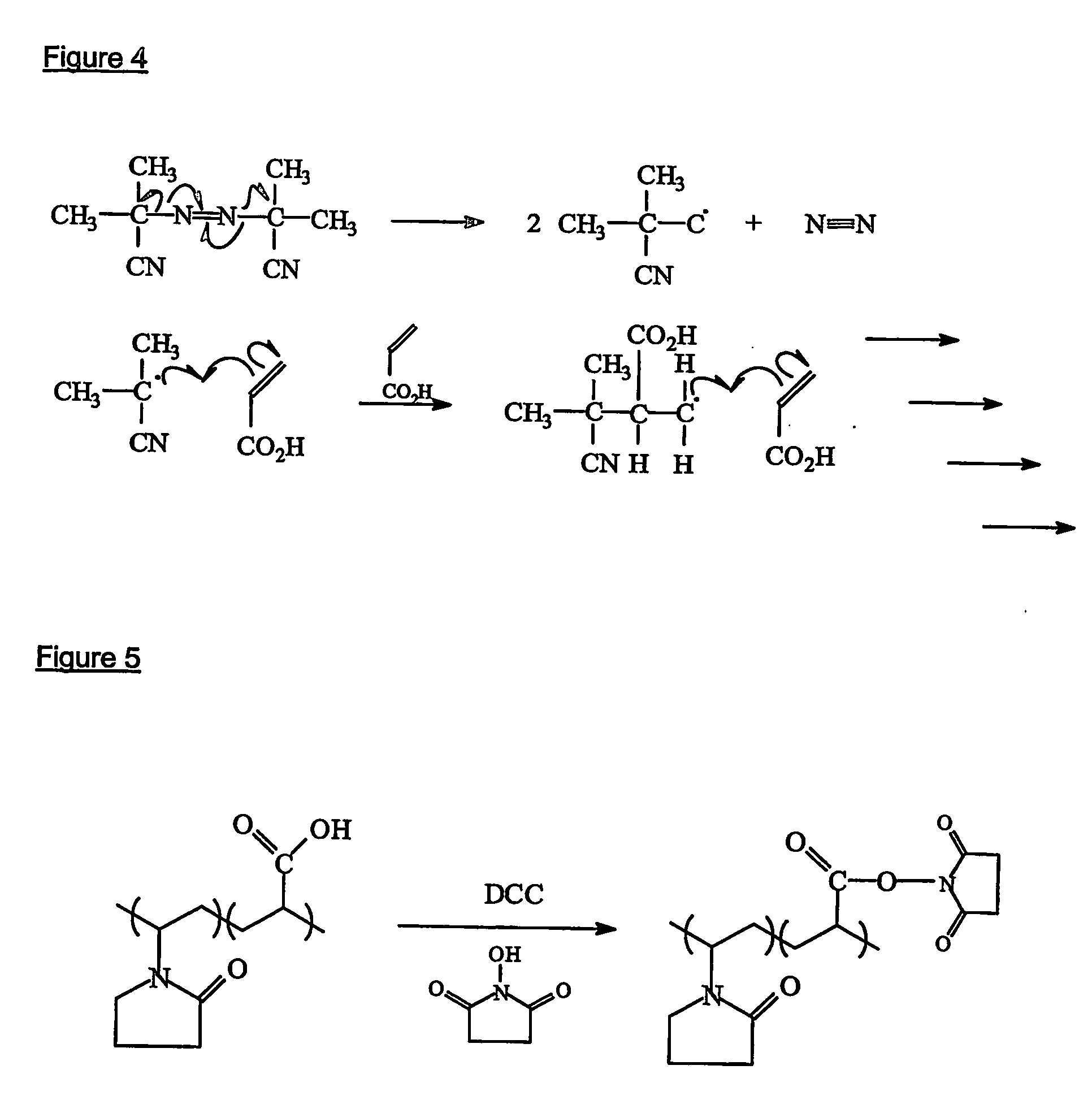
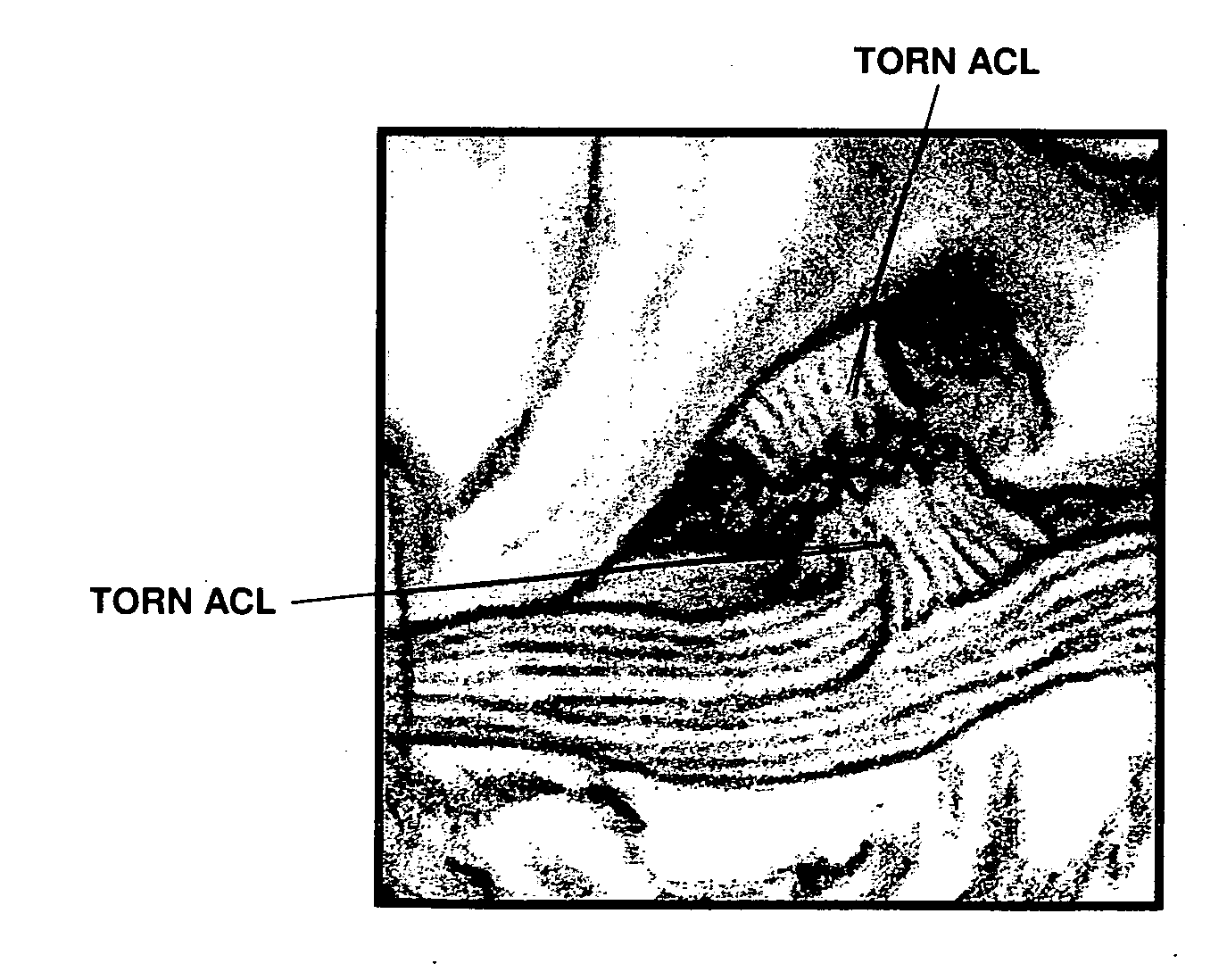
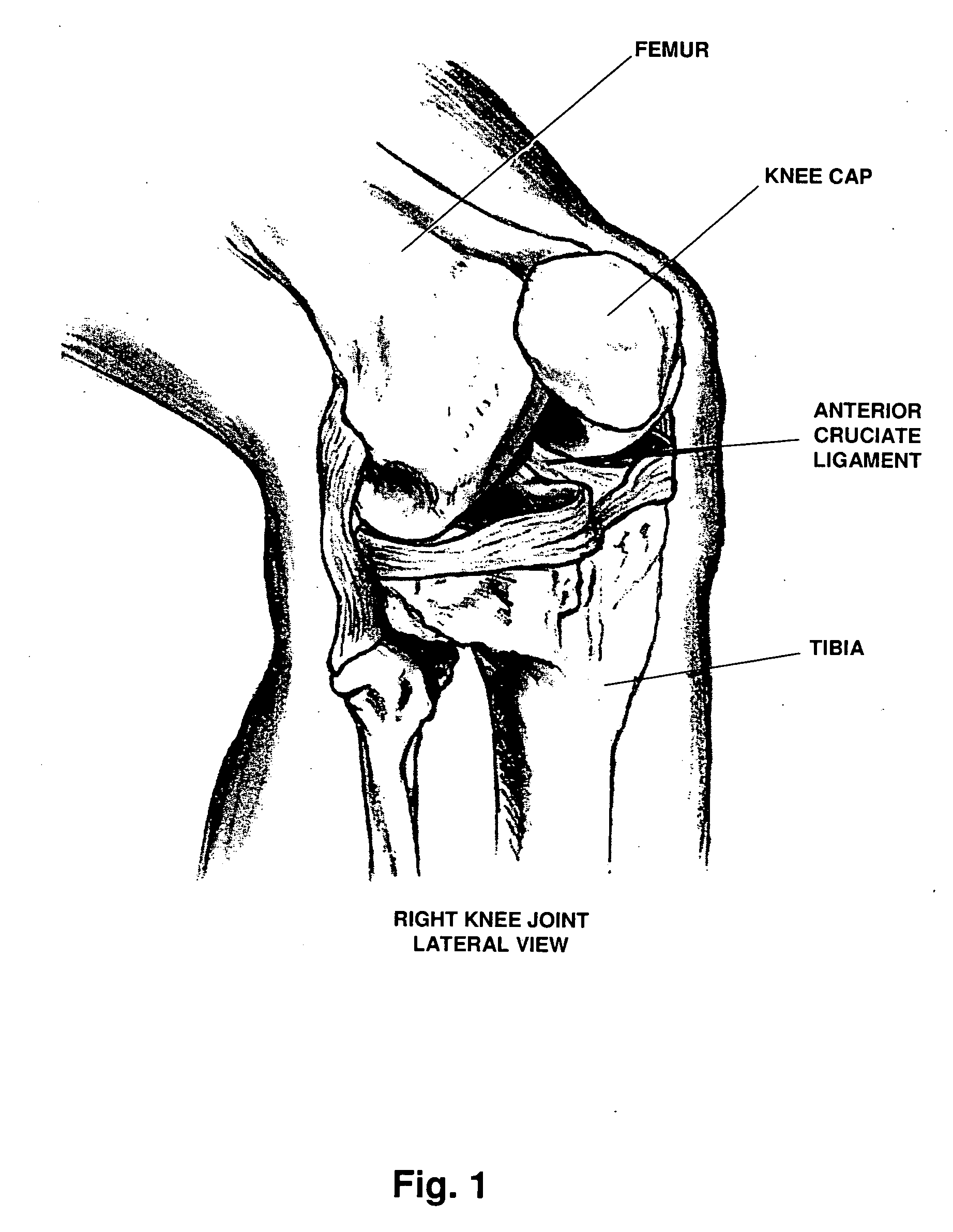
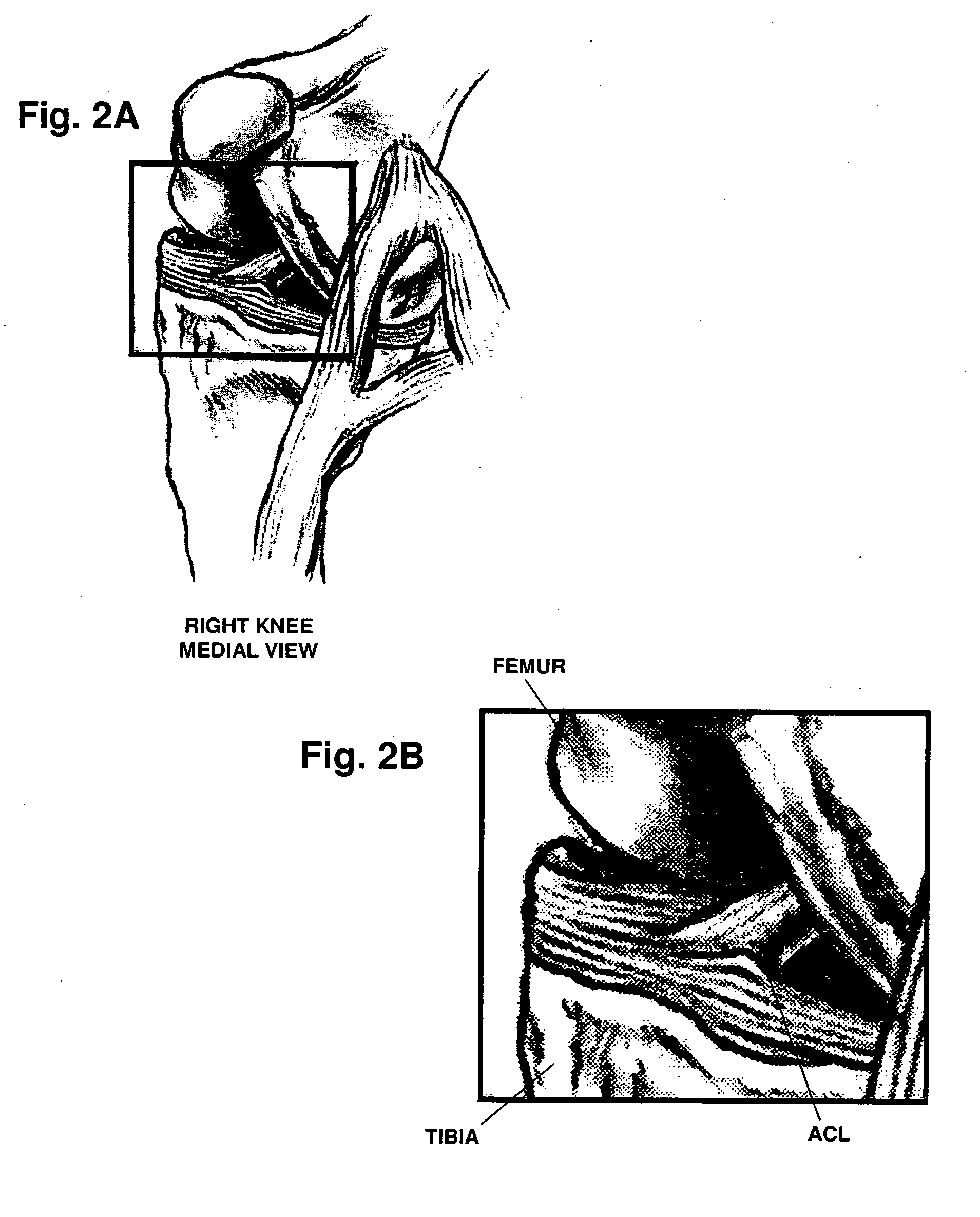
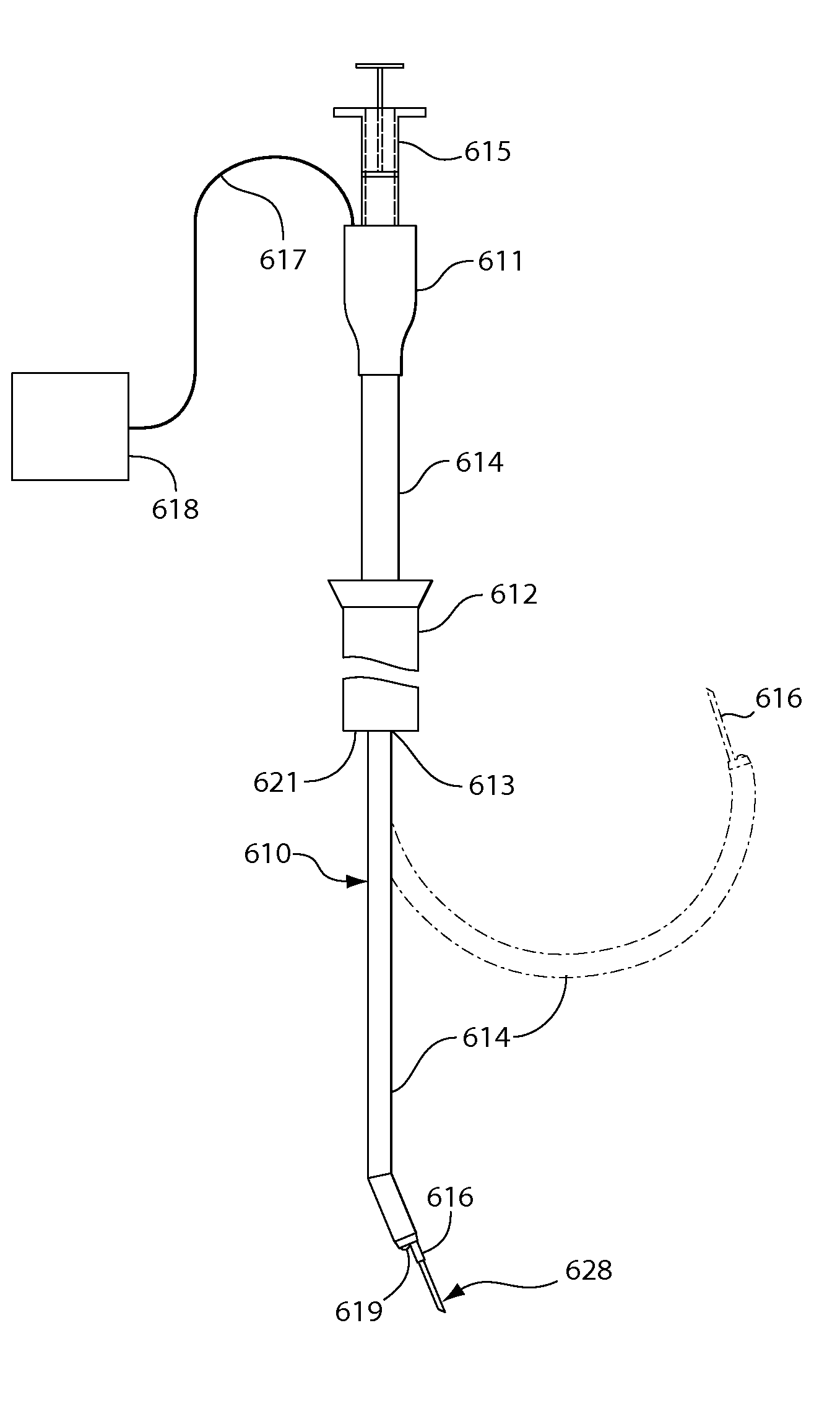
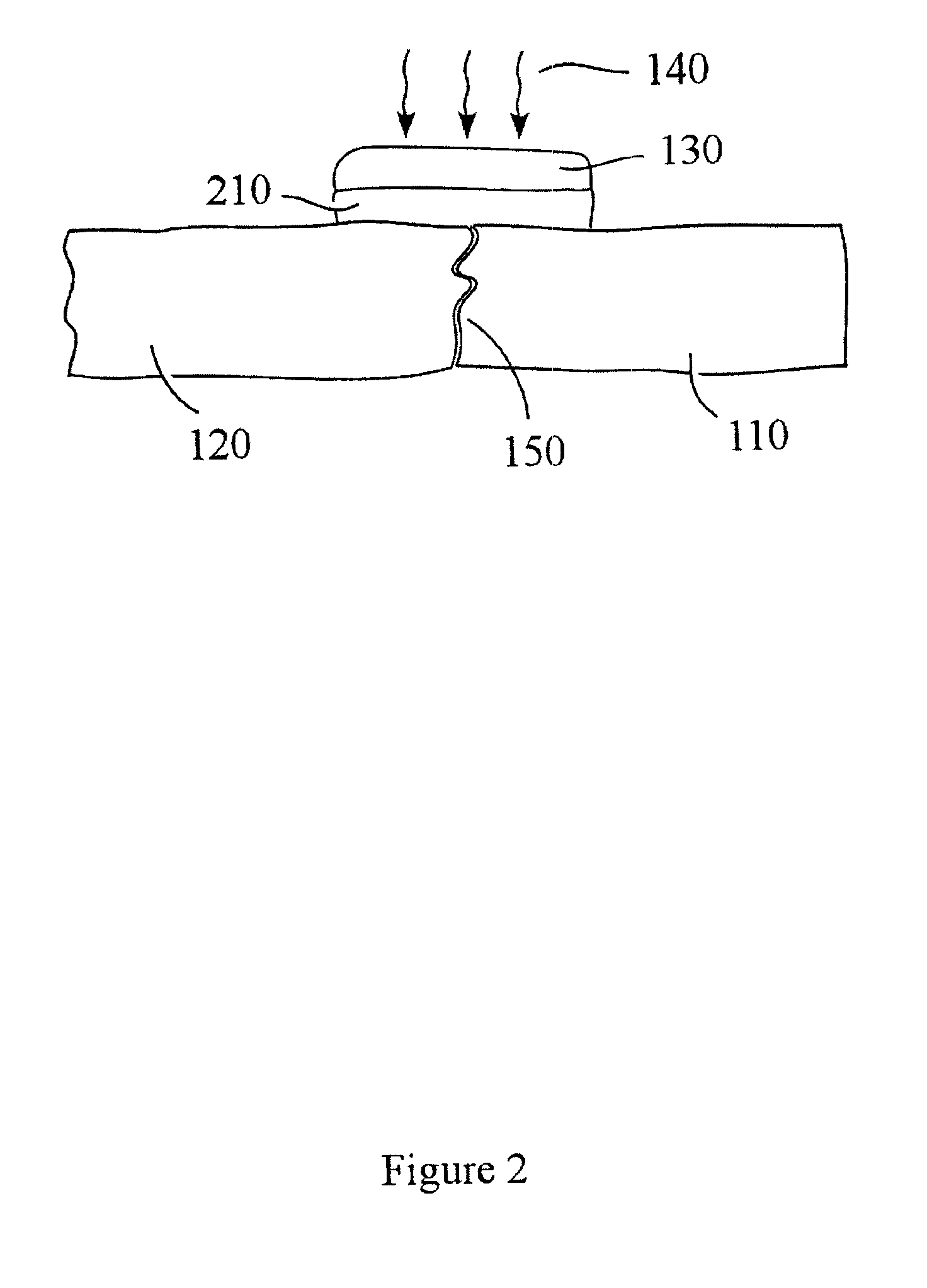
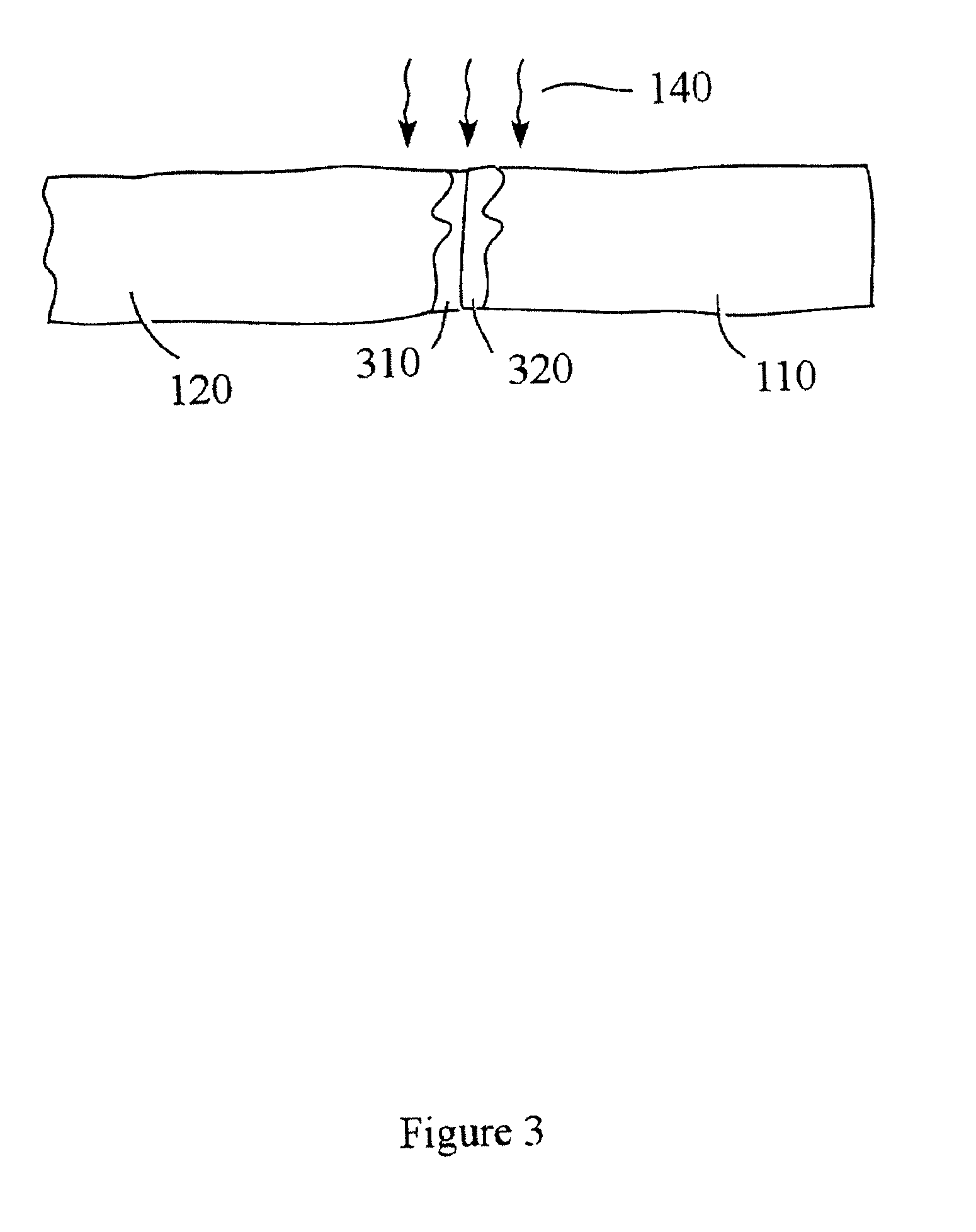
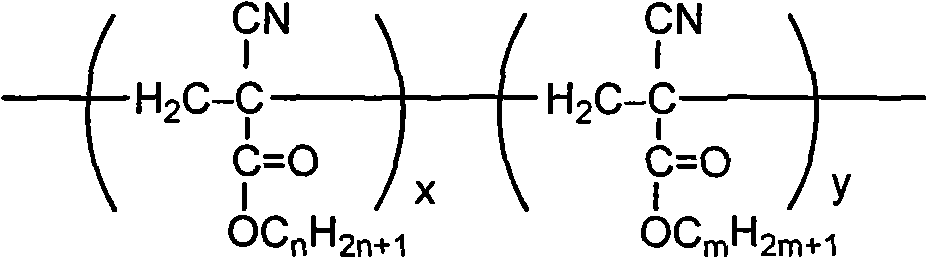Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
288 results about "Tissue adhesives" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Tissue adhesives represent a group of natural and artificial compounds that are currently used for a variety of local applications including hemostasis, wound closure, and fistula repair. The most commonly utilized tissue adhesives in GI endoscopy include cyanoacrylates, fibrin glues, and thrombin.
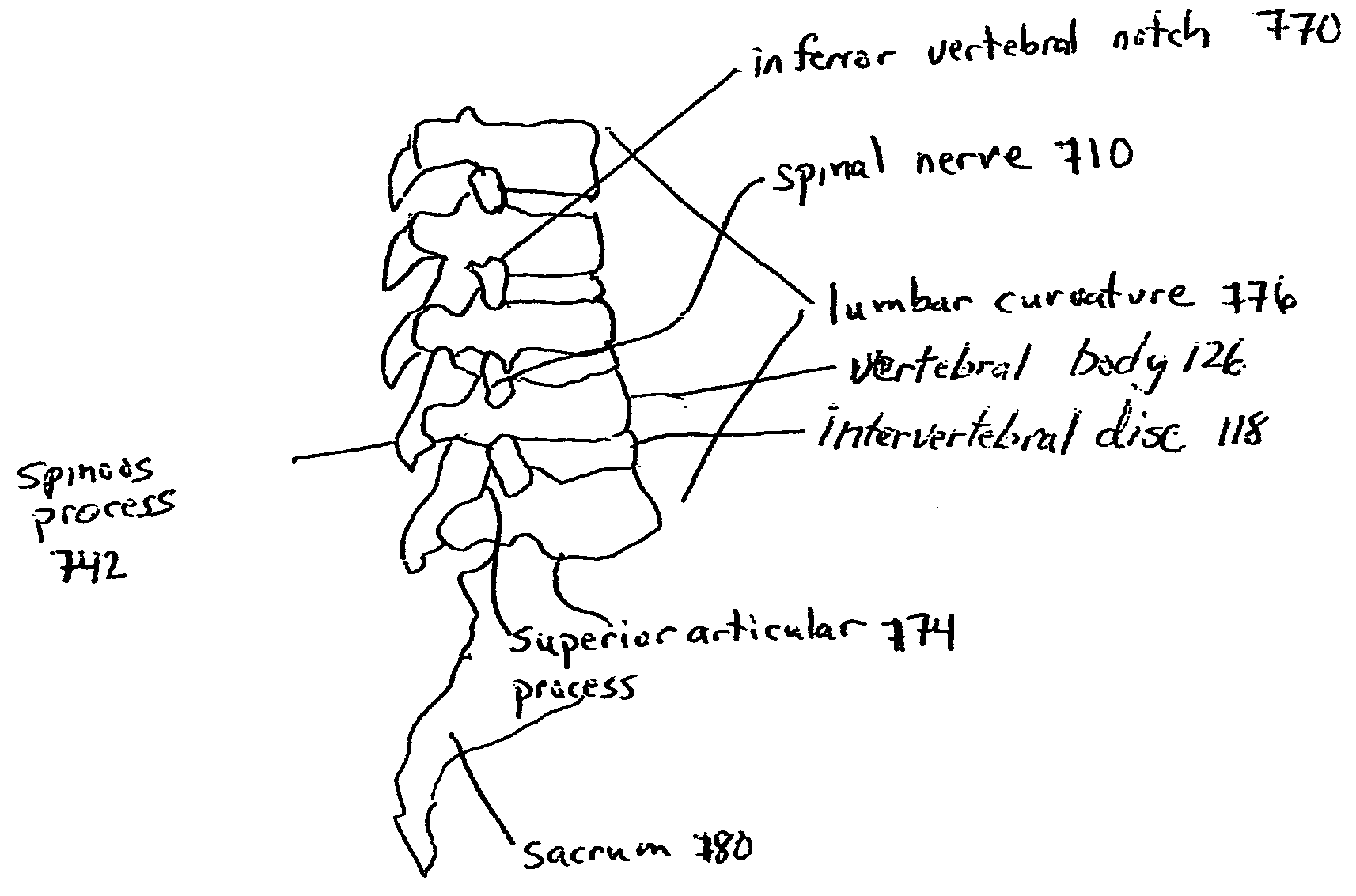
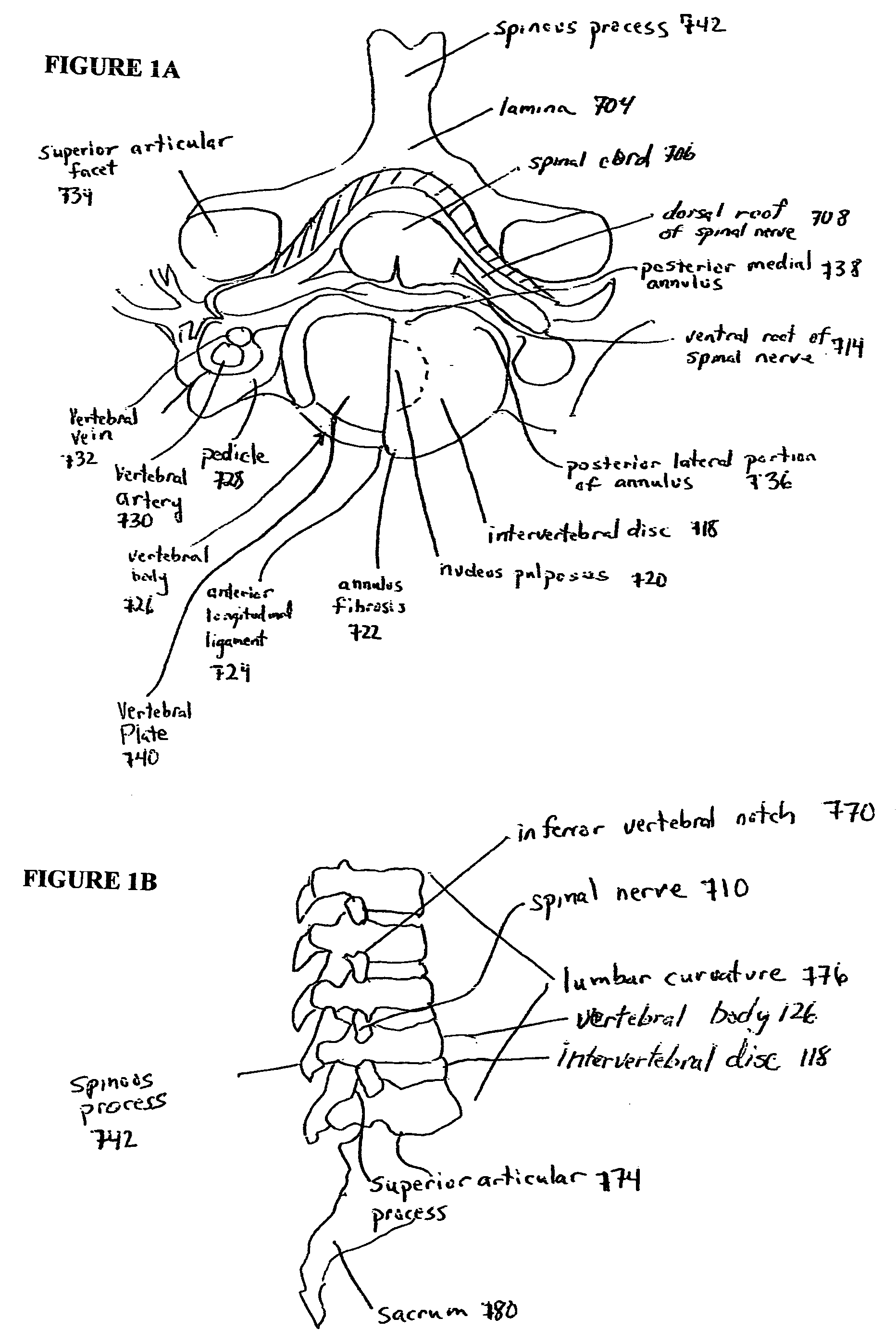
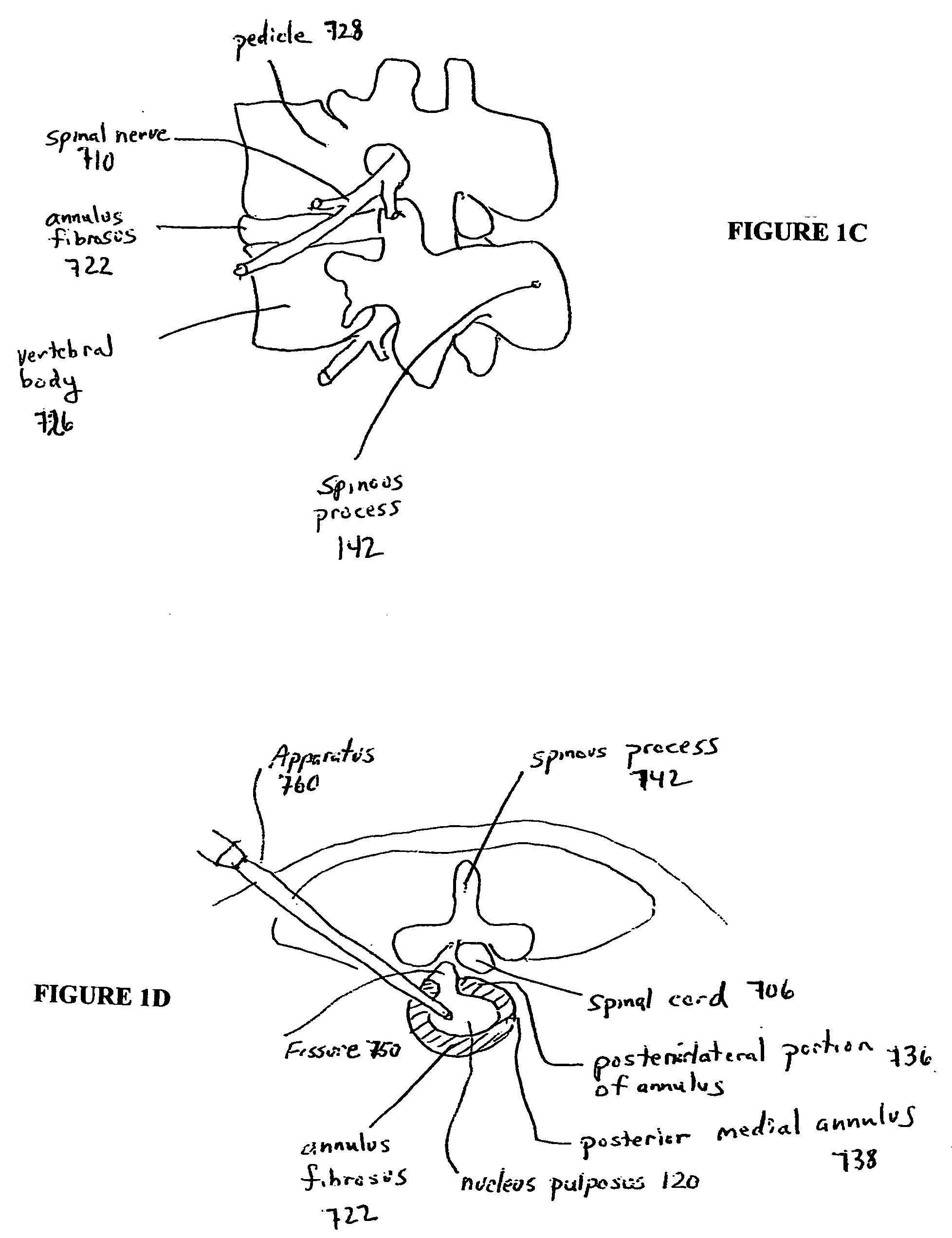
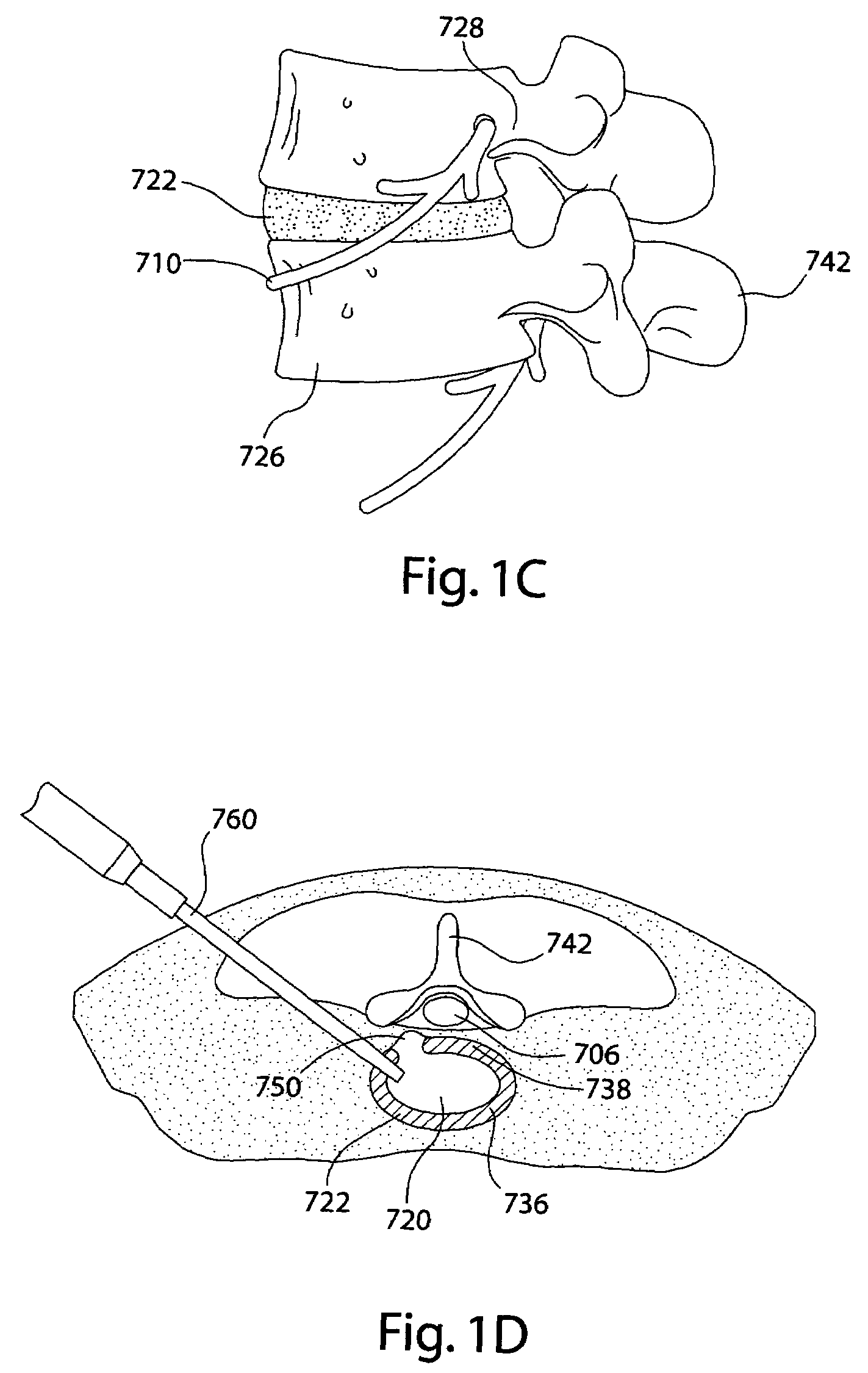
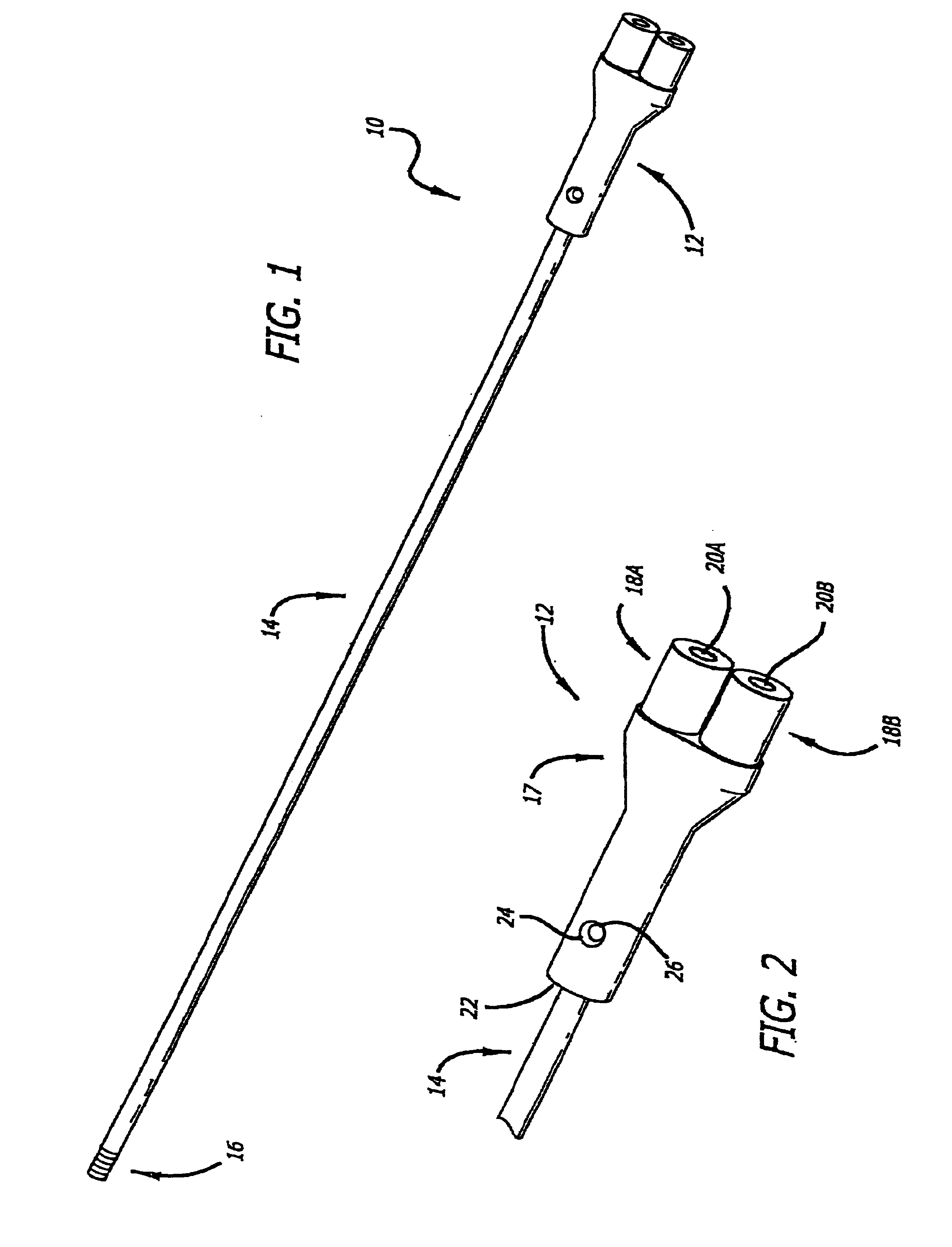
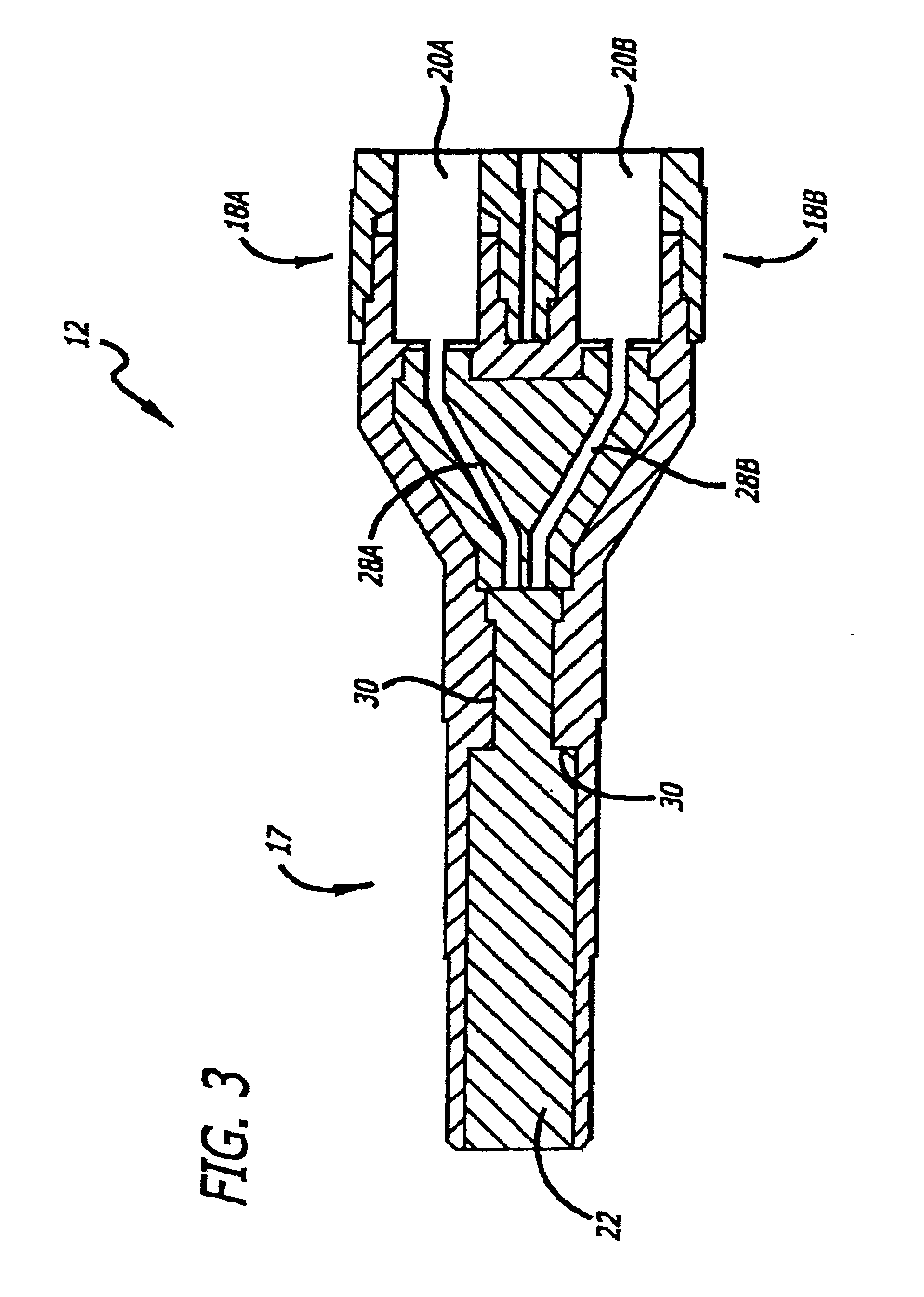
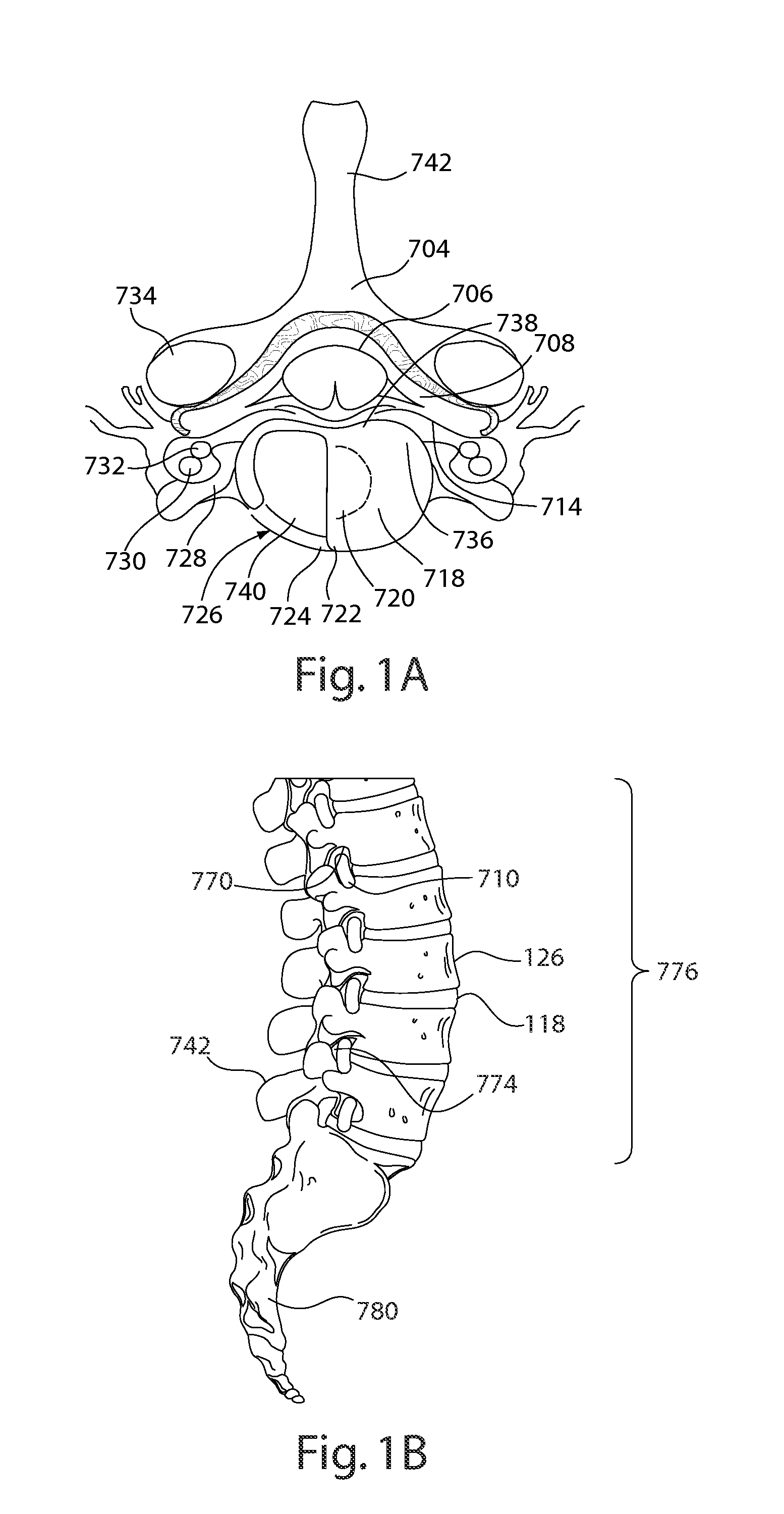
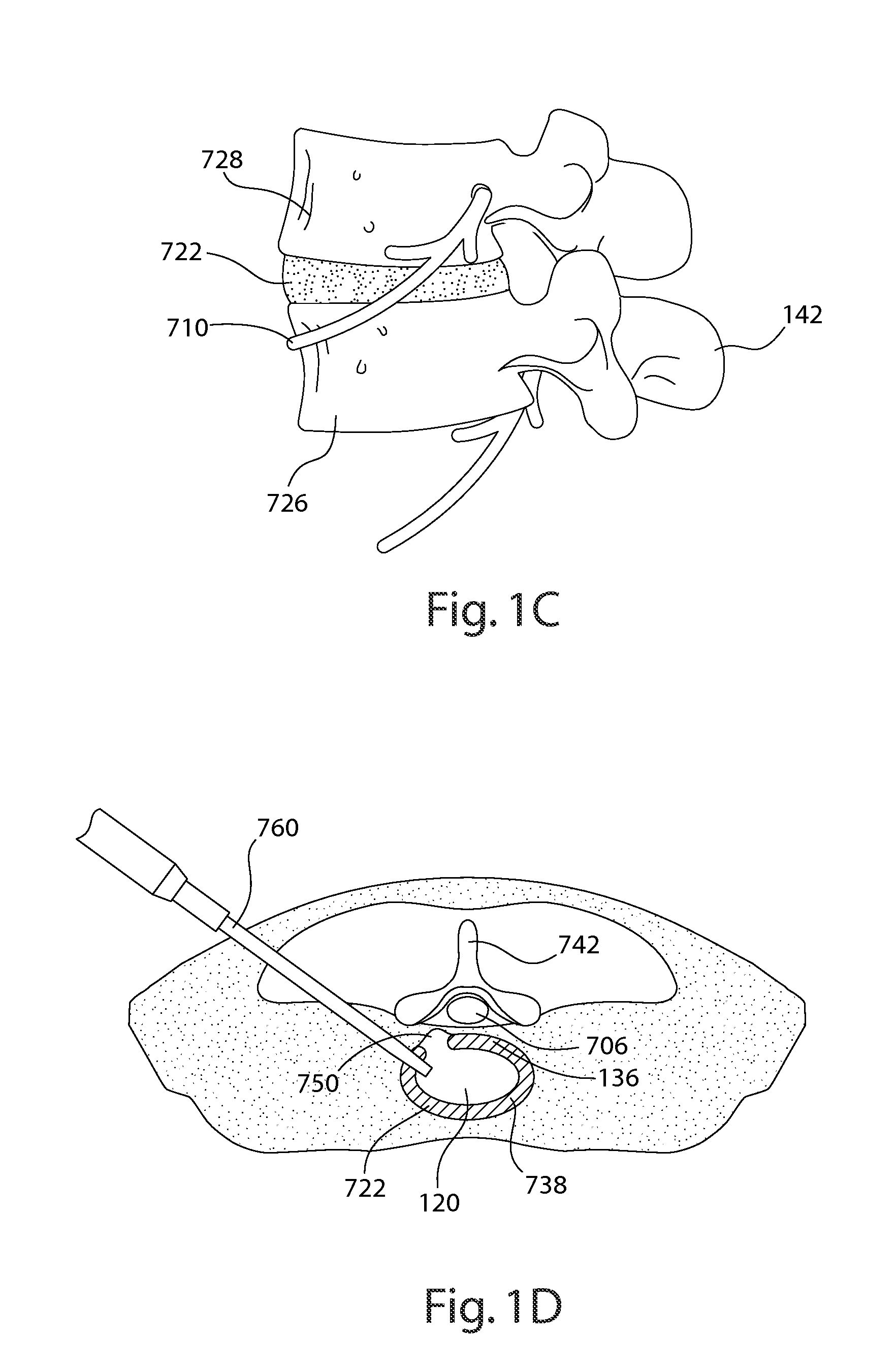
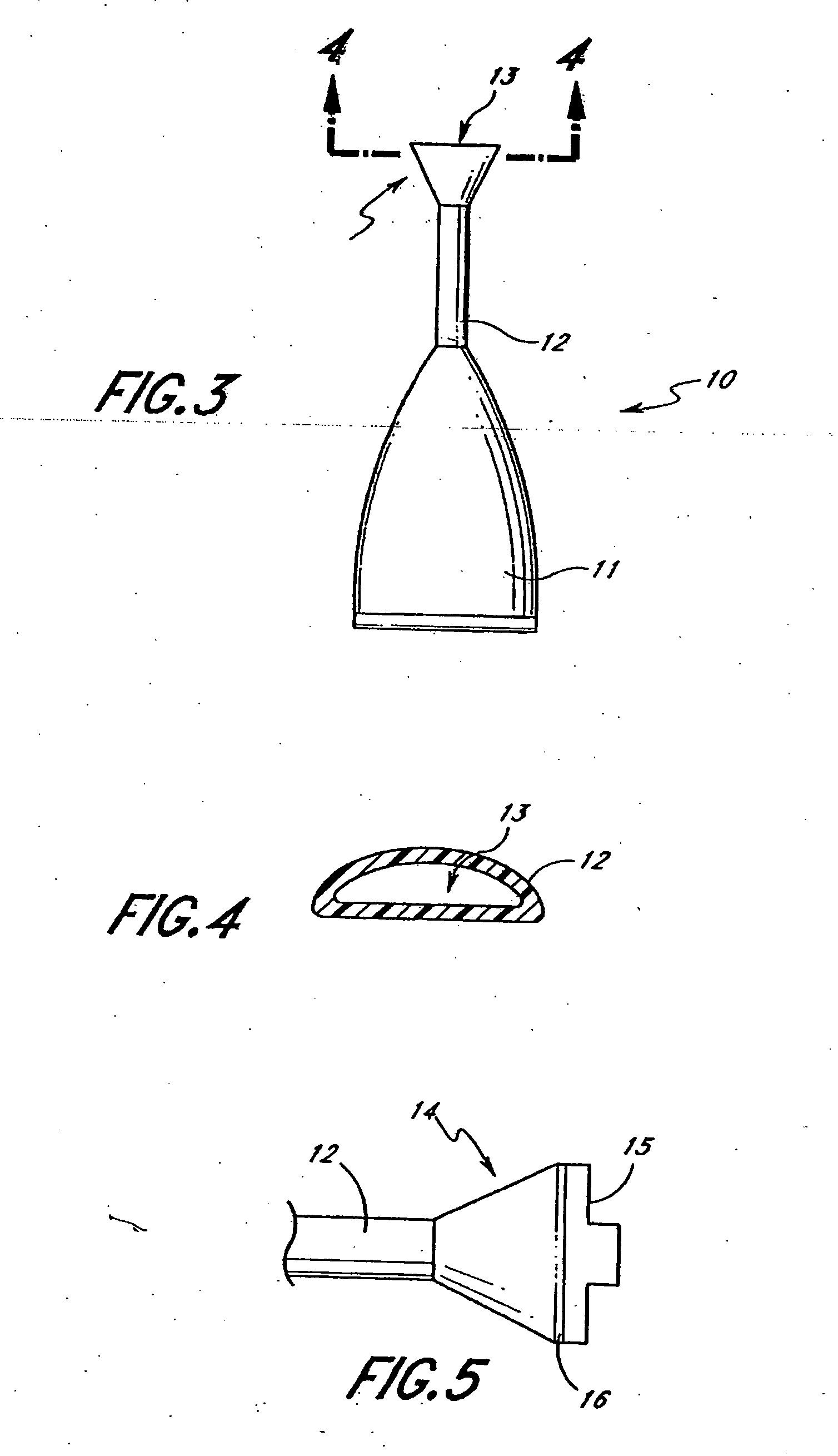
Devices and methods for spine repair
InactiveUS20050070913A1Strengthening intervertebral spaceEasy to operateSurgical furnitureBone implantRepair siteIntervertebral disk
Surgical methods of repairing defects and deficiencies in the spine are disclosed. The methods involve delivering a single part in-situ polymerizing fluid to (i) close a weakened segment or fissure in the annulus fibrosus, (ii) strengthen the annulus, (iii) replace or augment the disc nucleus, or (iv) localize a disc prosthesis. The methods may include placing a delivery conduit adjacent to the repair site and providing a liquid tissue adhesive to bond to and repair a disc defect or deficiency
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
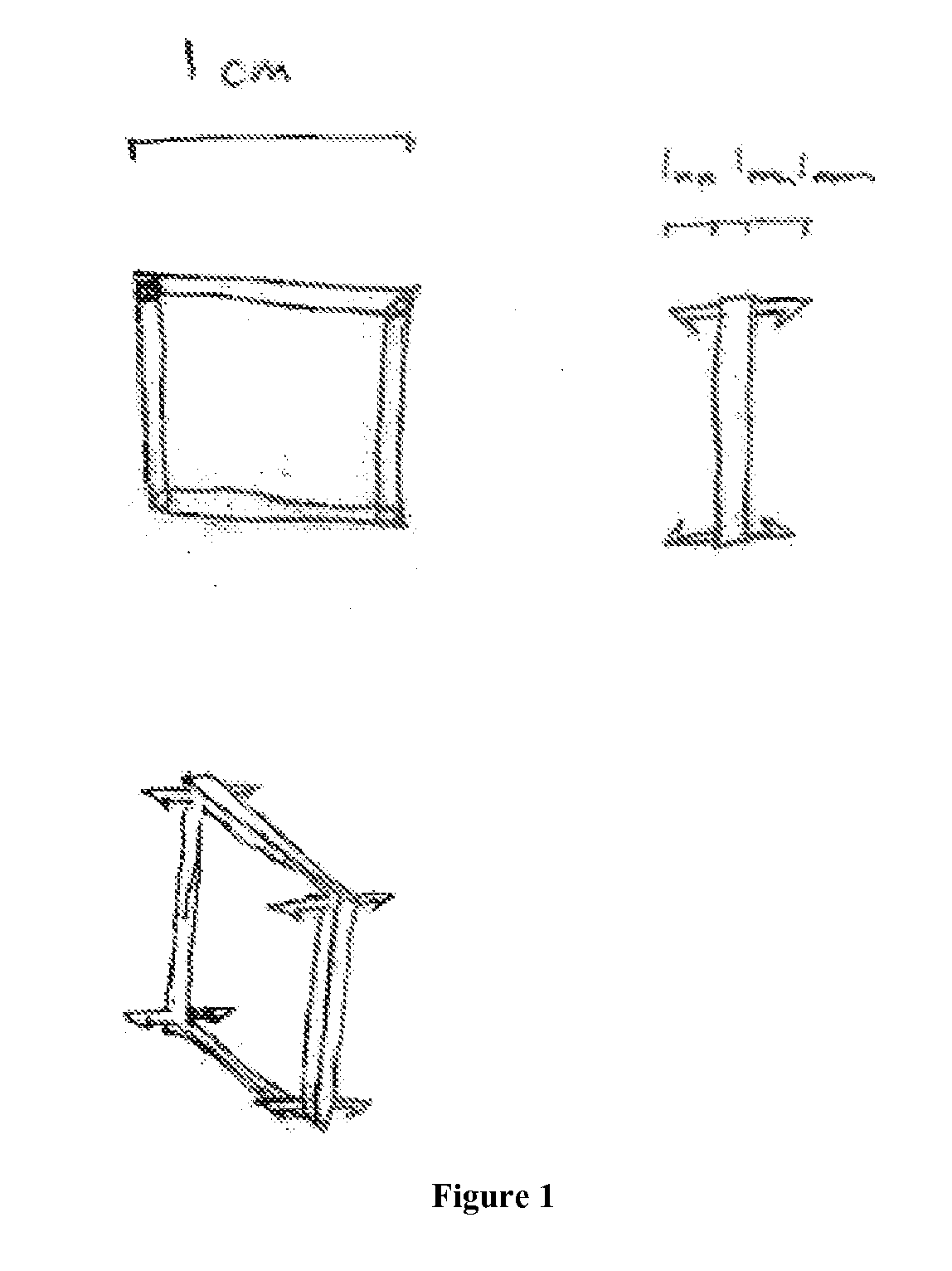
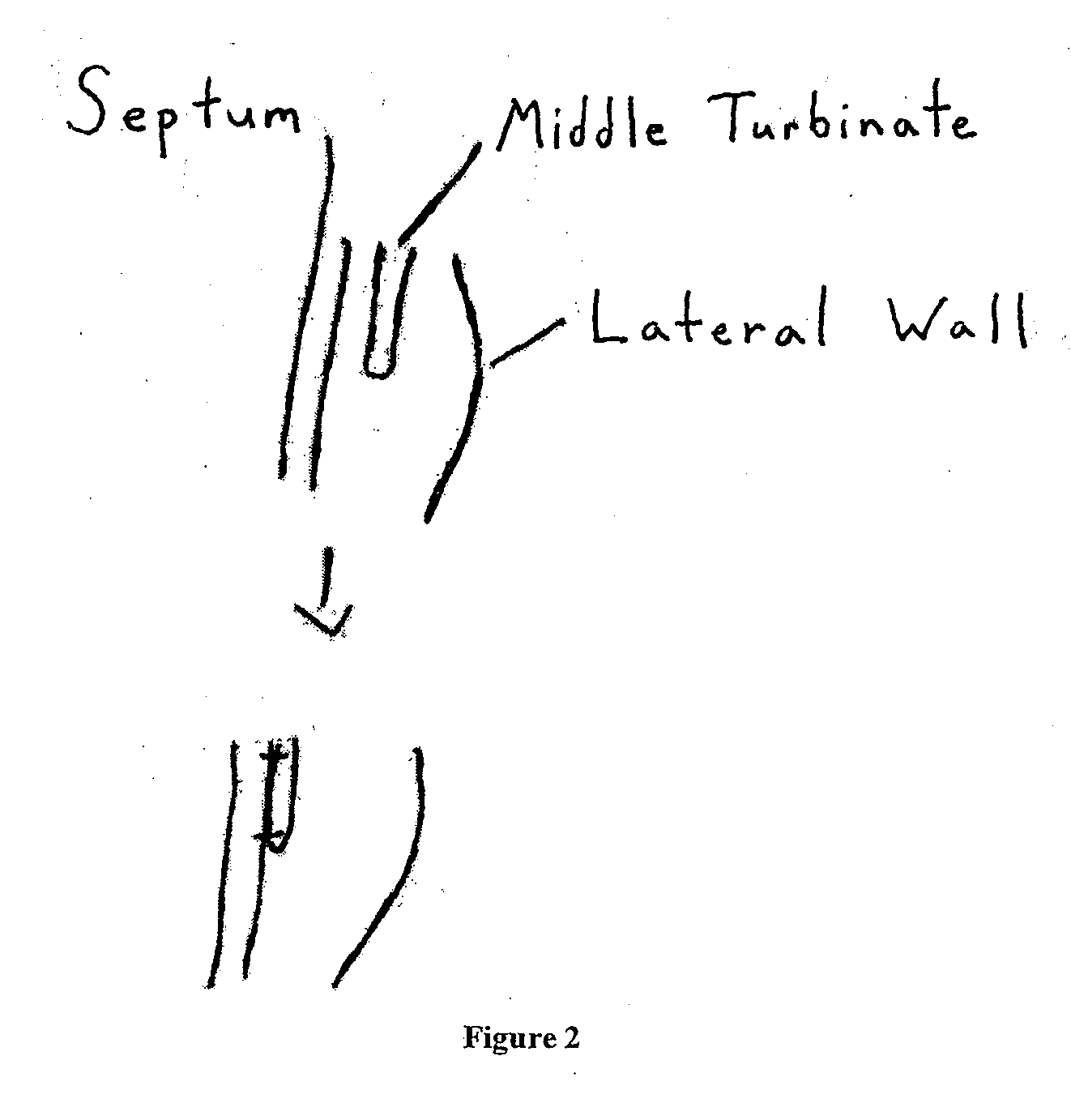
Middle Turbinate Medializer
InactiveUS20070293946A1Avoid stickingRestoring natural anatomySuture equipmentsDiagnosticsPalate muscleMiddle turbinates
Medializing the middle turbinate in the nose has been realized as a solution to the common complication of adhesions following nasal and sinus surgery. The invention provides a system for medializing the middle turbinate by attaching the middle turbinate temporarily to the nasal septum. The attachment is performed using a wafer with means on both sides for attaching the wafer to a mucosal surface. The attachment may also be performed using a tissue adhesive, pins, or other medical devices described herein. The invention also provides a system for attaching the uvula to the nasopharyngeal side of the soft palate. The invention provides a medical device for use in the inventive procedures as well as methods for the procedures and kits for use by a physician.
Owner:ARTHROCARE
Tissue adhesive sealant
Owner:COVALENT MEDICAL
Functionalized derivatives of hyaluronic acid, formation of hydrogels in situ using same, and methods for making and using same
InactiveUS7196180B2Good physical propertiesSimple structureOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesCross-linkIn situ polymerization
Methods for chemical modification of hyaluronic acid, formation of amine or aldehyde functionalized hyaluronic acid, and the cross-linking thereof to form hydrogels are provided. Functionalized hyaluronic acid hydrogels of this invention can be polymerized in situ, are biodegradable, and can serve as a tissue adhesive, a tissue separator, a drug delivery system, a matrix for cell cultures, and a temporary scaffold for tissue regeneration.
Owner:ORTHOGENE
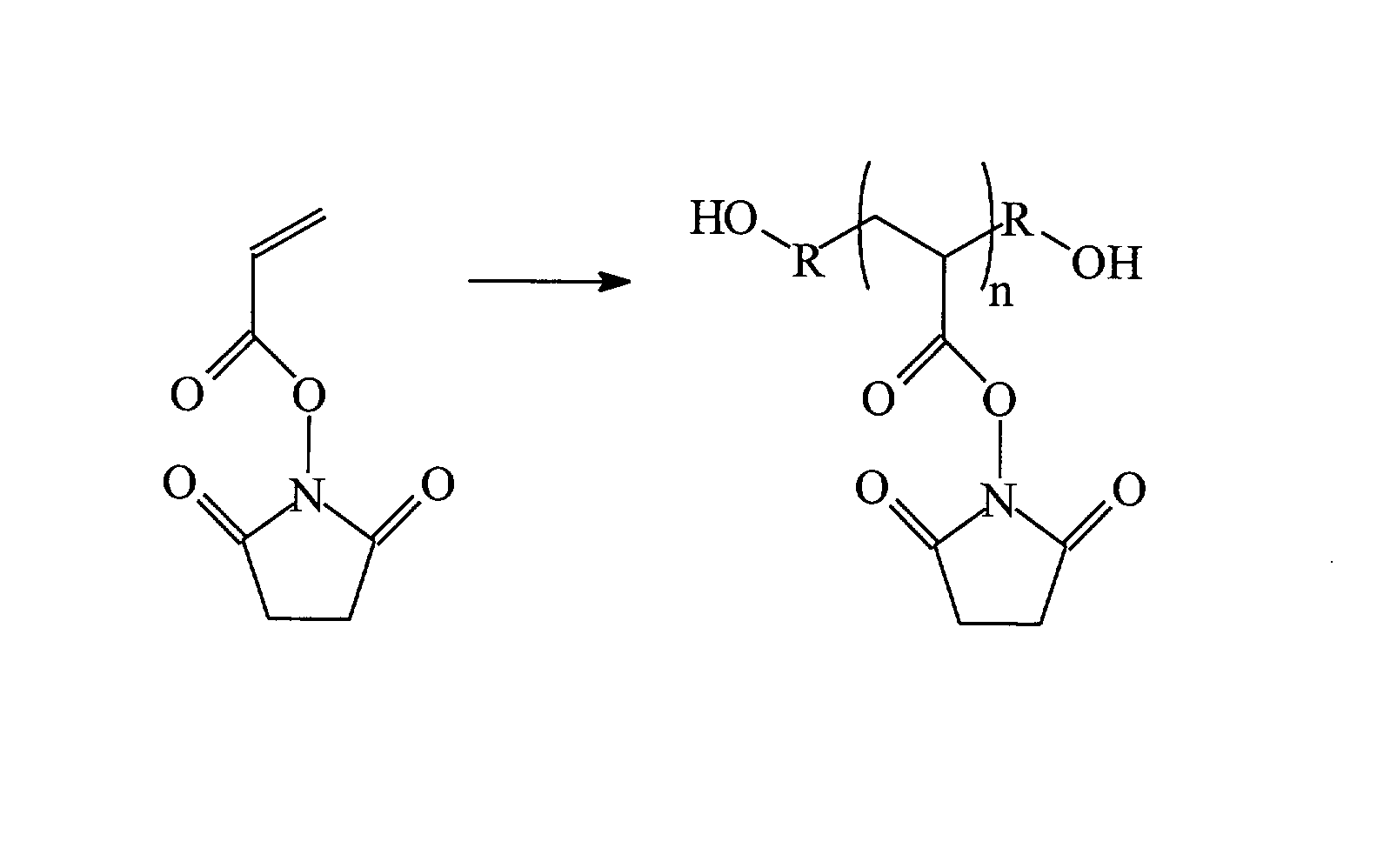
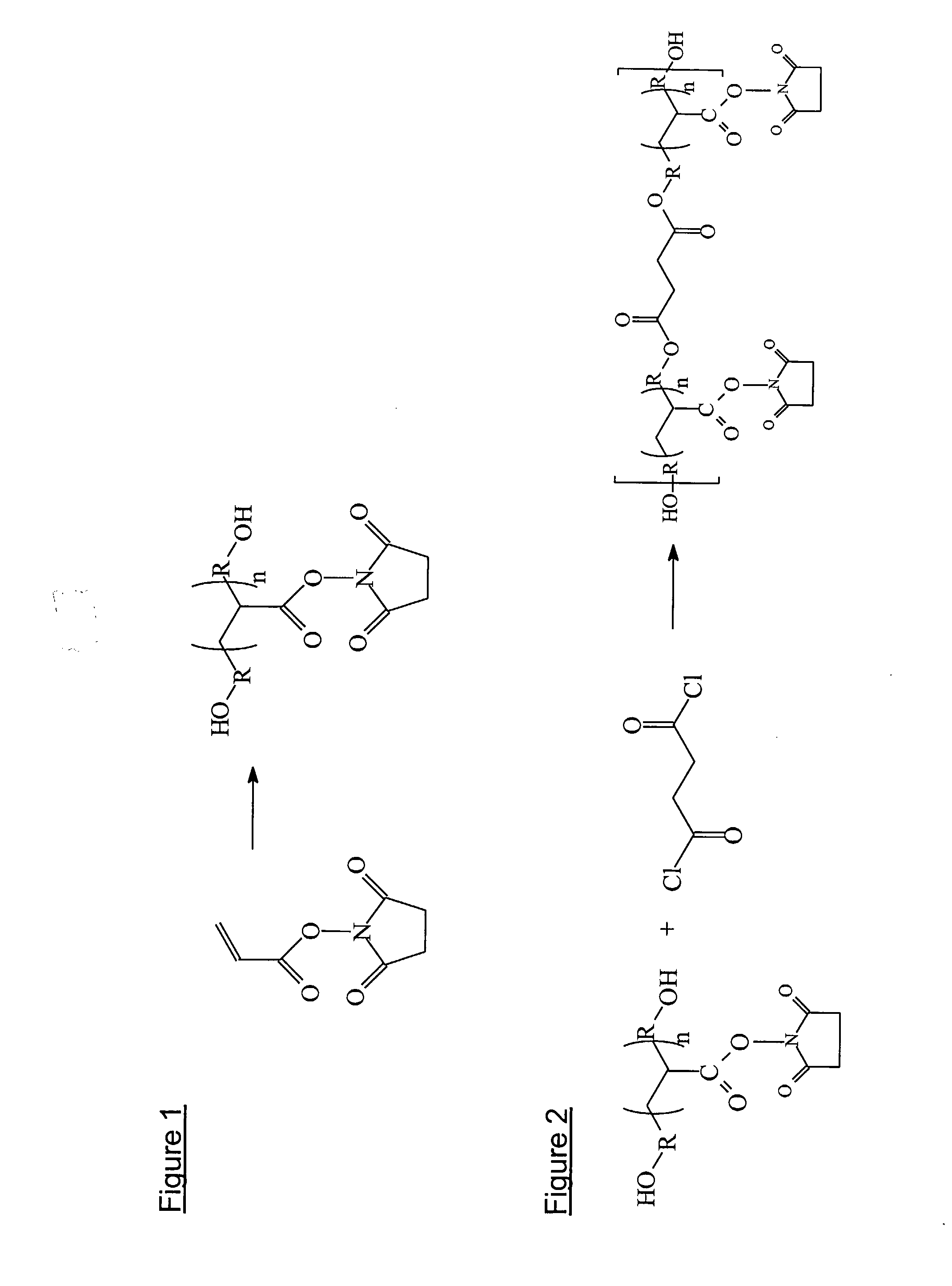
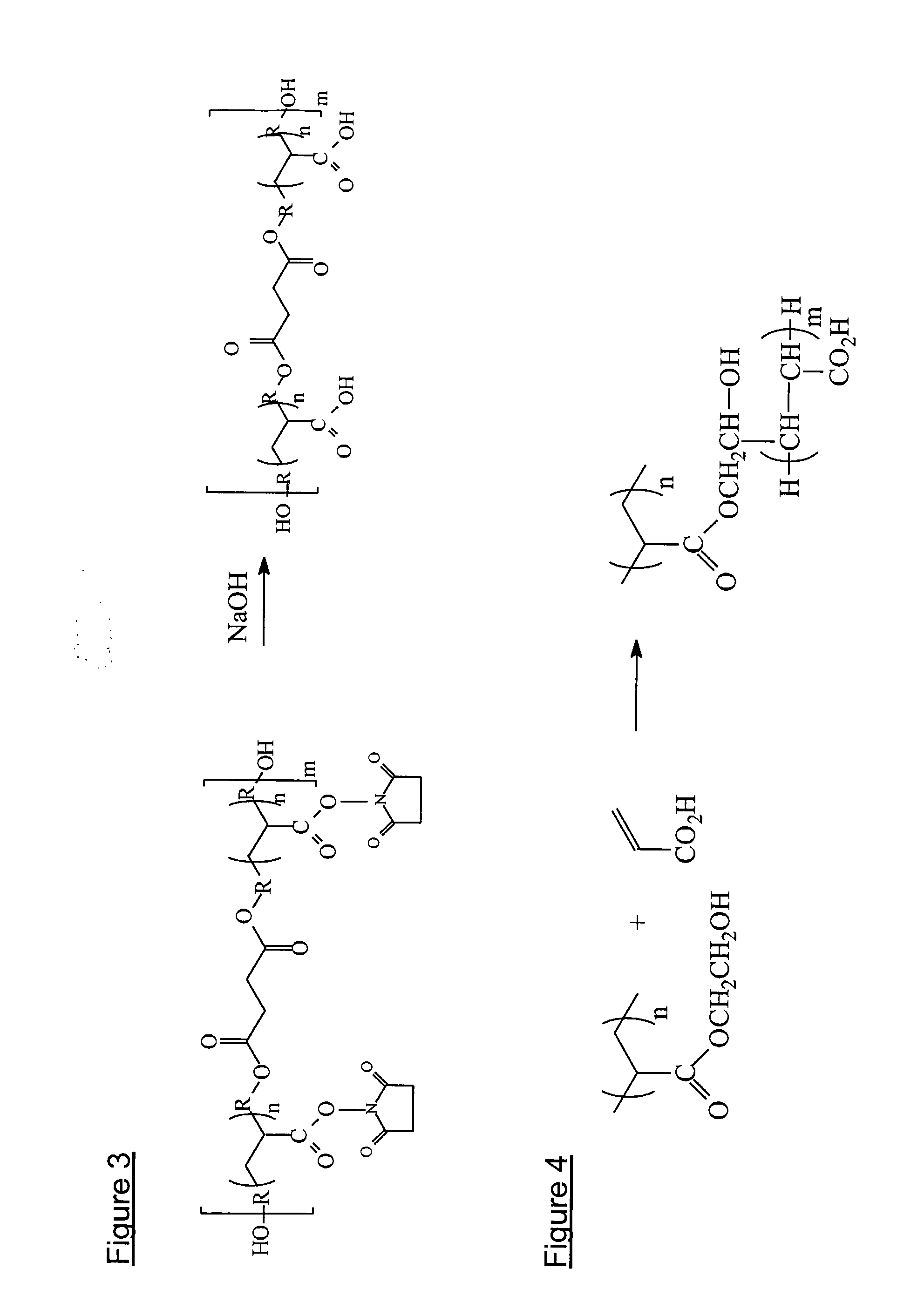
Polymer-based tissue-adhesive form medical use
Tissue adhesives formed by reacting poly(hydroxylic) compounds derivatized with acetoacetate groups and / or polyamino compounds derivatized with acetoacetamide groups with an amino-functional crosslinking compound are disclosed. The use of the tissue adhesives for medical and veterinary applications such as topical wound closure; and surgical procedures, such as intestinal anastomosis, vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, and ophthalmic procedures; drug delivery; and anti-adhesive applications are described.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Devices and methods for spine repair
InactiveUS7632294B2Avoid squeezingMinimally invasiveSurgical furnitureBone implantRepair siteProsthesis
Surgical methods of repairing defects and deficiencies in the spine are disclosed. The methods involve delivering a single part in-situ polymerizing fluid to (i) close a weakened segment or fissure in the annulus fibrosus, (ii) strengthen the annulus, (iii) replace or augment the disc nucleus, or (iv) localize a disc prosthesis. The methods may include placing a delivery conduit adjacent to the repair site and providing a liquid tissue adhesive to bond to and repair a disc defect or deficiency.
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
Bioabsorbable and biocompatible polyurethanes and polyamides for medical devices
ActiveUS20060188547A1Low toxicitySuture equipmentsOrganic active ingredientsAbsorbable polymersPolyester
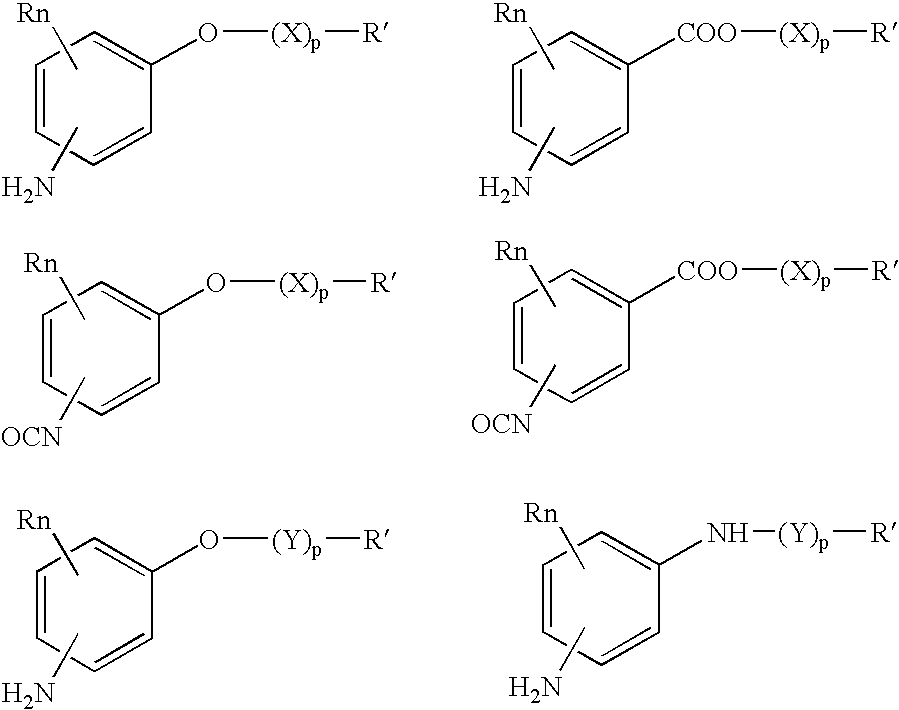
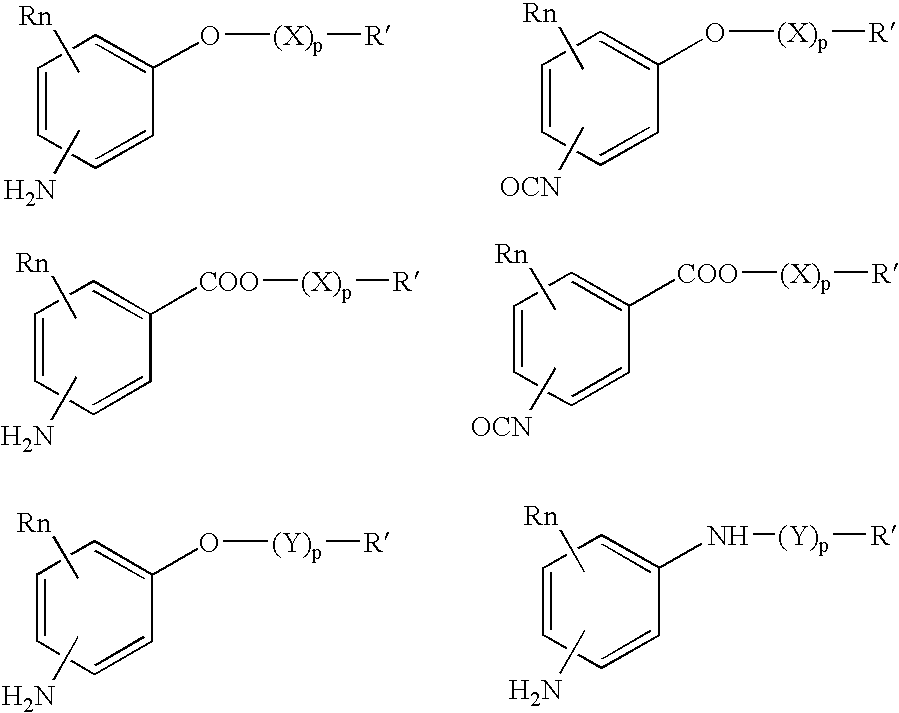
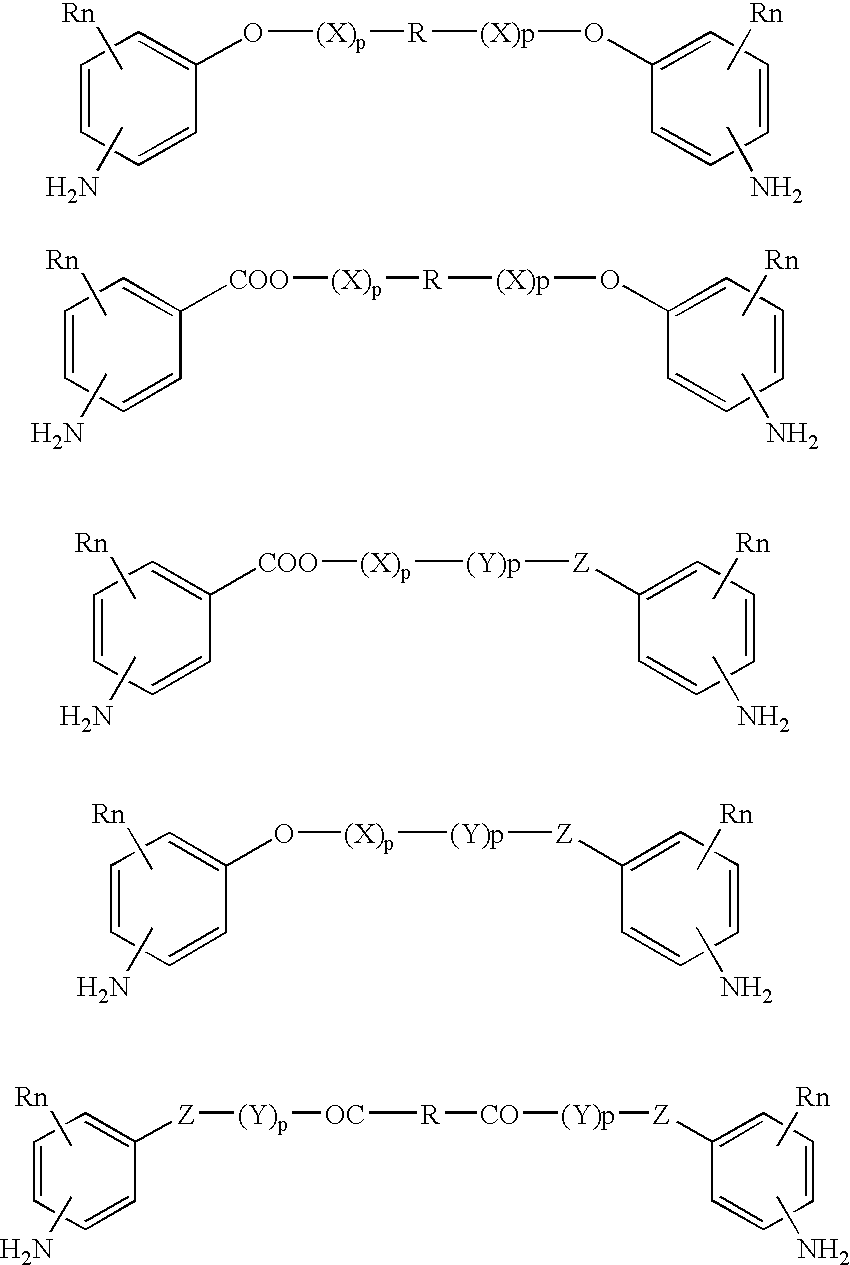
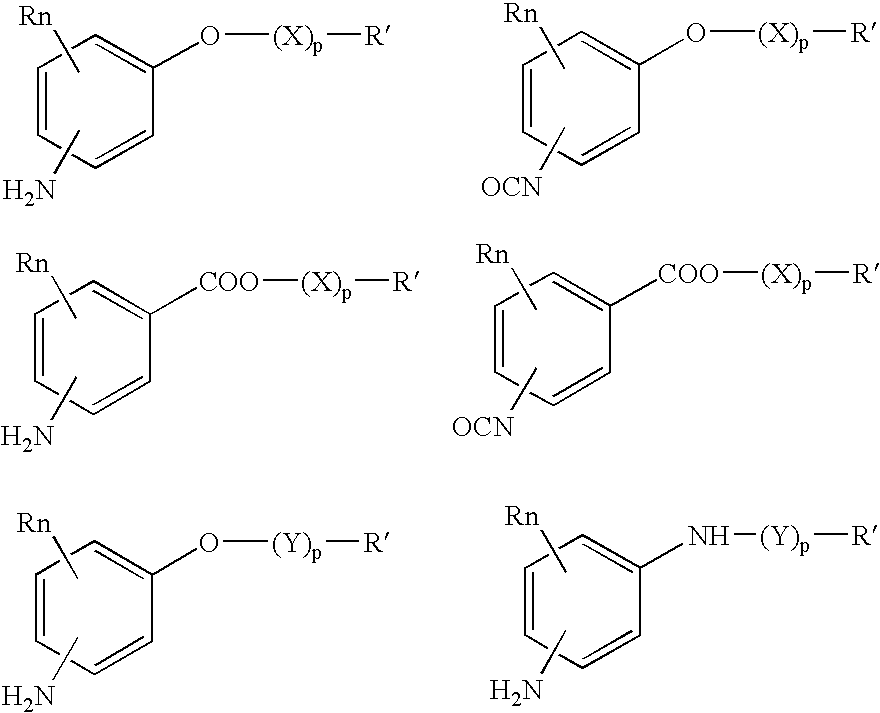
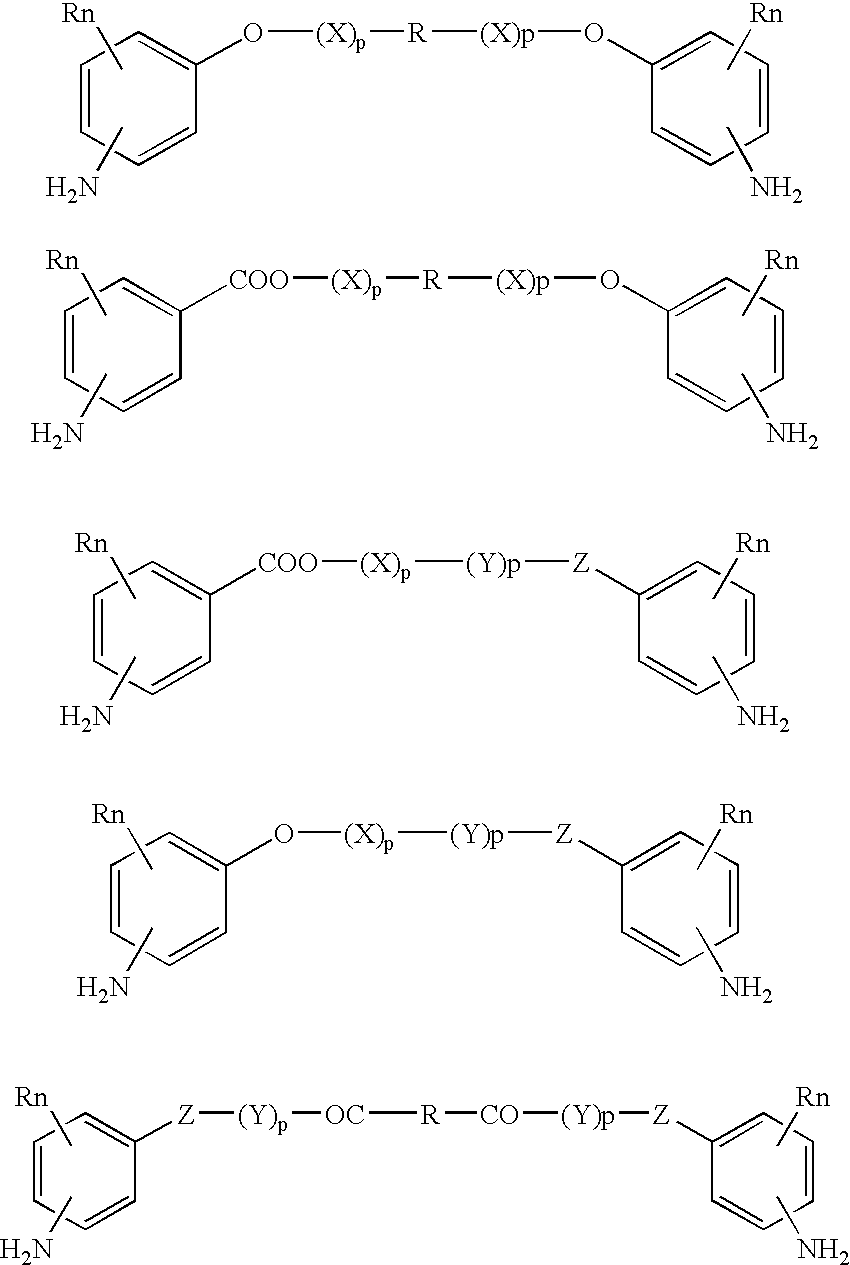
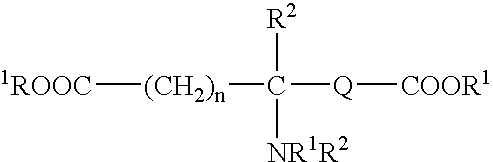
Absorbable polyurethanes, polyamides and polyester urethanes prepared from at least one compound selected from: or the diamines and diisocyanates thereof, wherein each X represents a member independently selected from —CH2COO— (glycolic acid moiety), —CH(CH3)COO— (lactic acid moiety), —CH2CH2OCH2COO— (dioxanone), —CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COO— (caprolactone moiety), —(CH2)yCOO— where y is one of the numbers 2, 3, 4 or 6-24 inclusive, and —(CH2CH2O)z′CH2COO— where z′ is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; each Y represents a member independently selected from —COCH2O— (glycolic ester moiety), —COCH(CH3)O— (lactic ester moiety), —COCH2OCH2CH2O— (dioxanone ester), —COCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2O— (caprolactone ester), —CO(CH2)mO— where m is an integer between 2, 3, 4 or 6-24 inclusive, —COCH2O(CH2CH2O)n— where n is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; R′ is hydrogen, benzyl or an alkyl group, the alkyl group being either straight-chained or branched; p is an integer between 1 and 4, inclusive; and Rn represents one or more members selected from H, alkoxy, benzyloxy, aldehyde, halogen, carboxylic acid and —NO2, which is attached directly to an aromatic ring or attached through an aliphatic chain. Absorbable polymers prepared from these compounds are useful for drug delivery, tissue engineering, tissue adhesives, adhesion prevention and other implantable medical devices.
Owner:BEZWADA BIOMEDICAL LLC
Bioabsorbable and biocompatible polyurethanes and polyamides for medical devices
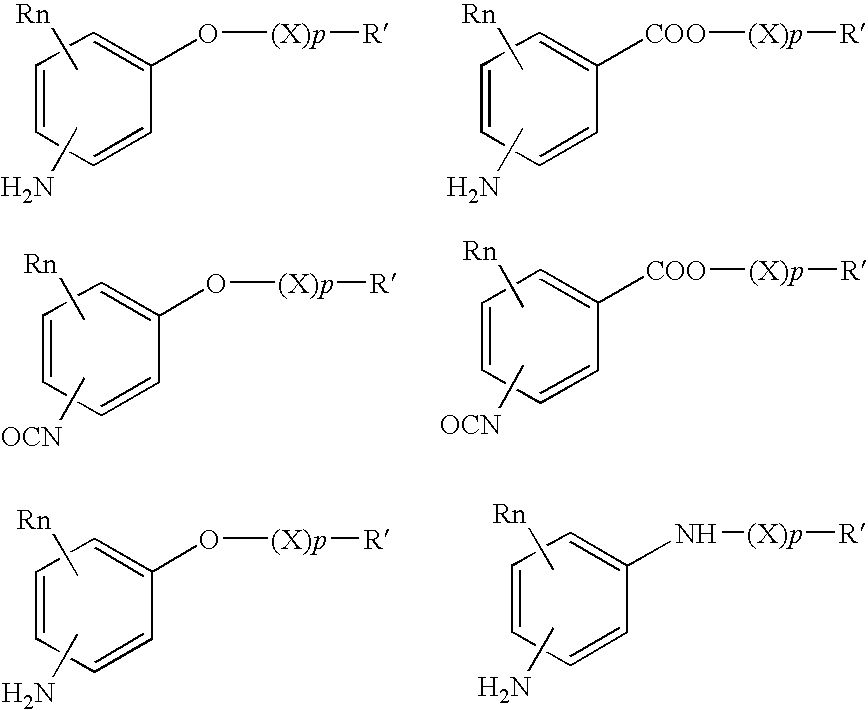
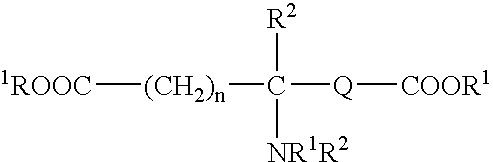
Absorbable polyurethanes, polyamides and polyester urethanes prepared from at least one compound selected from:or the diamines and diisocyanates thereof, wherein each X represents a member independently selected from —CH2COO— (glycolic acid moiety), —CH(CH3)COO— (lactic acid moiety), —CH2CH2OCH2COO— (dioxanone), —CH2CH2CH2CH2CH2COO— (caprolactone moiety), —(CH2)yCOO— where y is one of the numbers 2, 3, 4 or 6-24 inclusive, and —(CH2CH2O)z′CH2COO— where z′ is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; each Y represents a member independently selected from —COCH2O— (glycolic ester moiety), —COCH(CH3)O— (lactic ester moiety), —COCH2OCH2CH2O— (dioxanone ester), —COCH2CH2CH2CH2CH2O— (caprolactone ester), —CO(CH2)mO— where m is an integer between 2, 3, 4 or 6-24 inclusive, —COCH2O(CH2CH2O)n— where n is an integer between 2 and 24, inclusive; R′ is hydrogen, benzyl or an alkyl group, the alkyl group being either straight-chained or branched; p is an integer between 1 and 4, inclusive; and Rn represents one or more members selected from H, alkoxy, benzyloxy, aldehyde, halogen, carboxylic acid and —NO2, which is attached directly to an aromatic ring or attached through an aliphatic chain. Absorbable polymers prepared from these compounds are useful for drug delivery, tissue engineering, tissue adhesives, adhesion prevention and other implantable medical devices.
Owner:BEZWADA BIOMEDICAL LLC
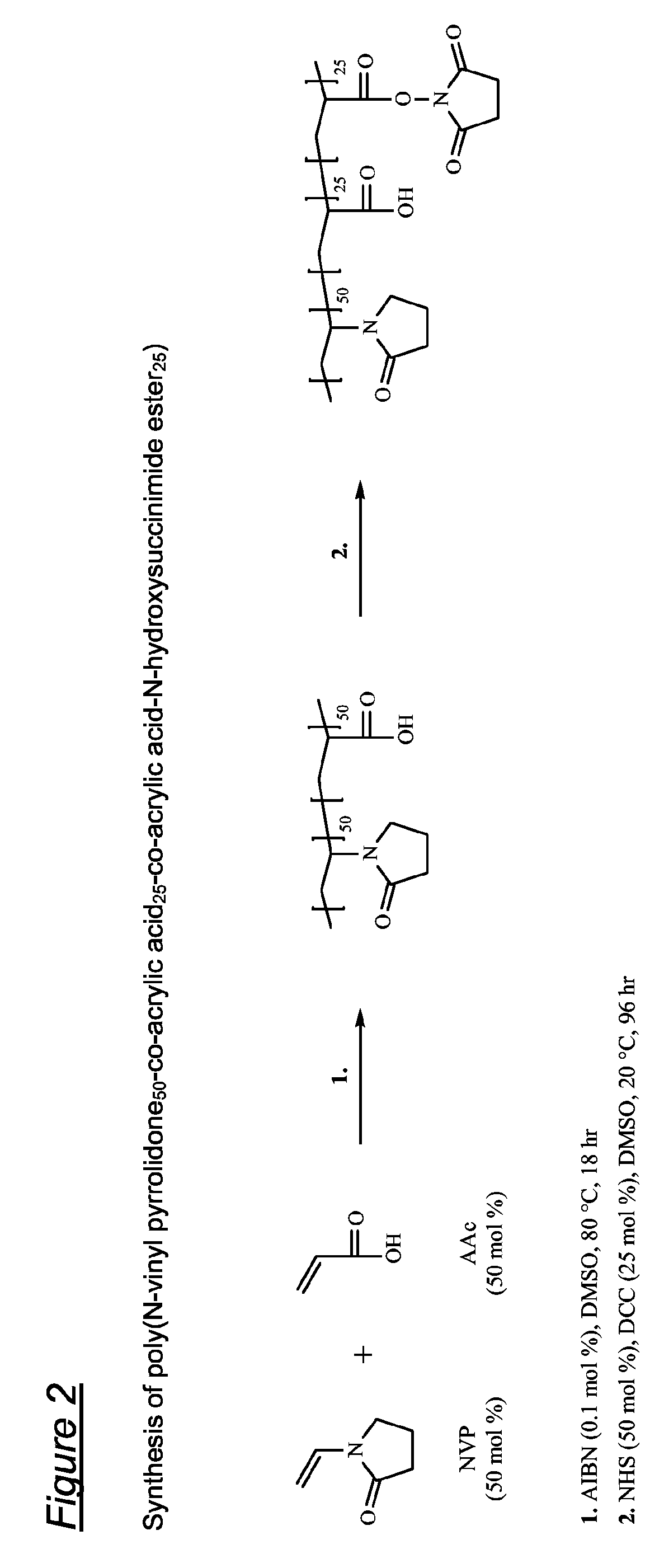
Tissue-adhesive materials
A multi-lamellar tissue-adhesive sheet comprises a structural layer or laminate conjoined to a tissue-contacting layer. The structural layer or laminate comprises one or more synthetic polymers having film-forming properties, and the tissue-contacting layer of material contains tissue-reactive groups. The synthetic polymers having film-forming properties are preferably biodegradable polyesters, and the tissue-reactive groups are most preferably NHS-ester groups.
Owner:TISSUEMED LTD
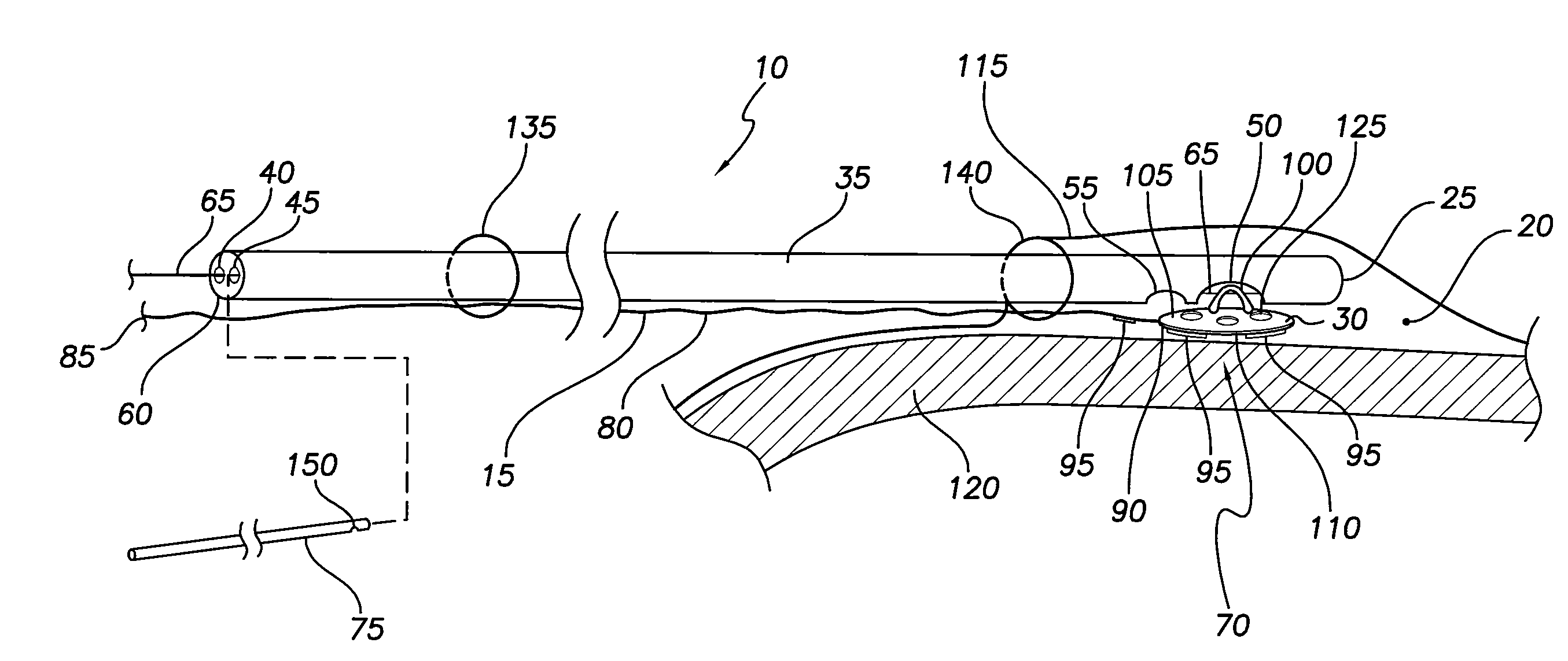
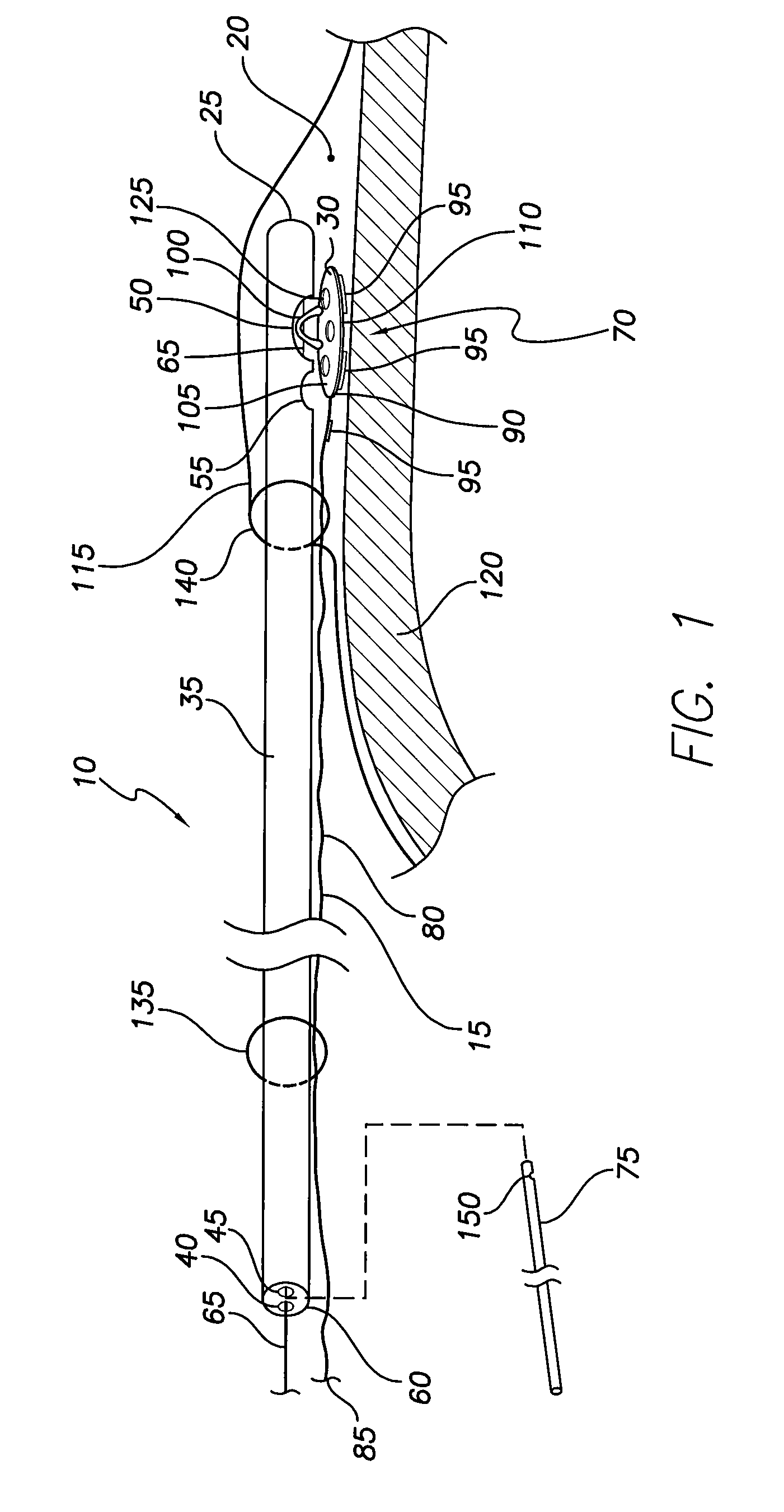
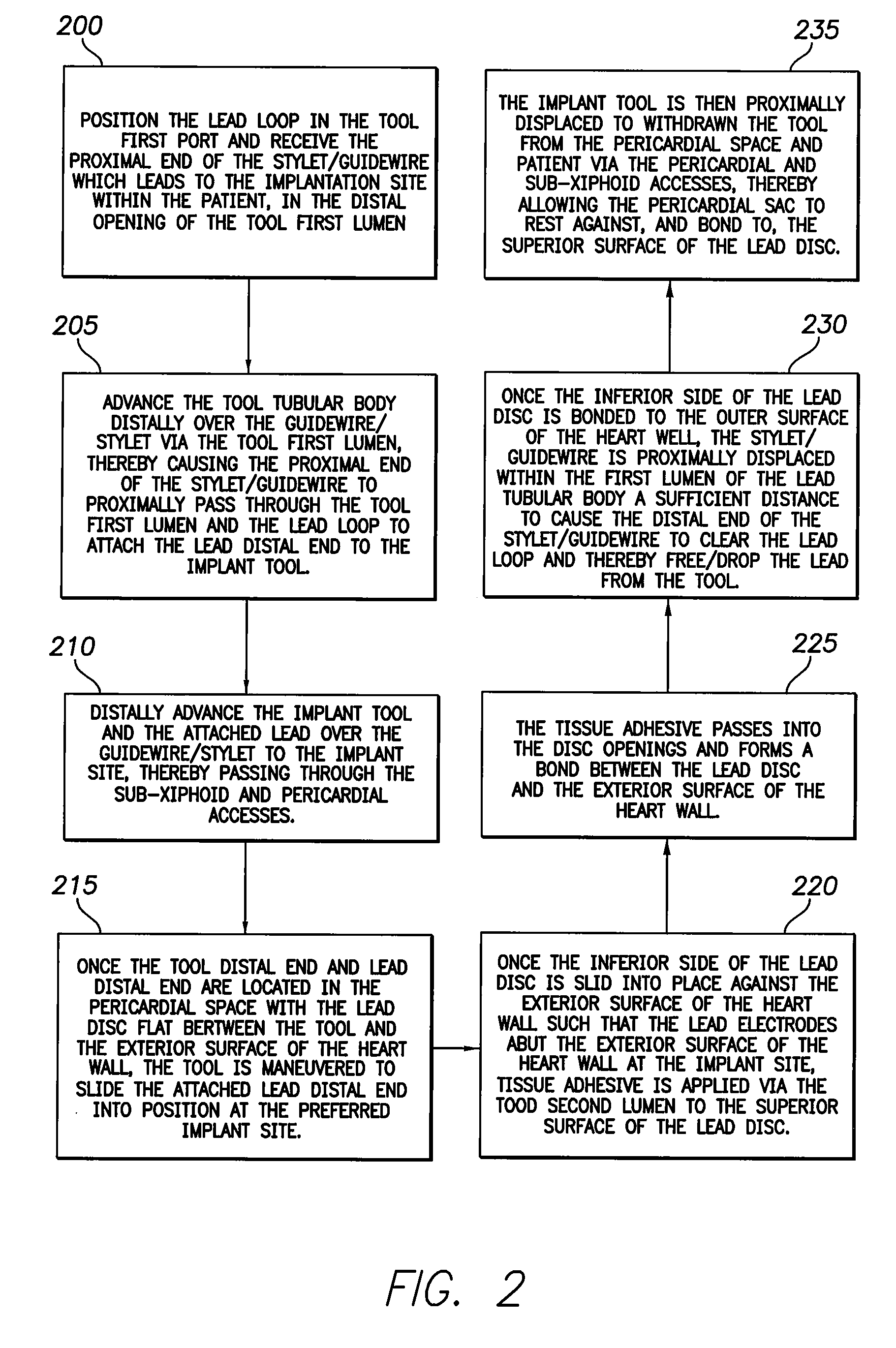
System and method for lead implantation in a pericardial space
A system for pericardial lead implantation is disclosed herein. The system includes an implantation tool and a stimulation lead. The implantation tool includes a tubular body, a first lumen, a second lumen, a stylet or guidewire, a first port, and a second port. The first and second lumens longitudinally extend through tubular body. The first port is in communication with the first lumen, and the second port is in communication with the second lumen. The stylet or guidewire is longitudinally displaceable in the first lumen and across the first port. A tissue adhesive is selectively administrable through the second port via the second lumen. The stimulation lead includes a distal end and an engagement feature. Placing the engagement feature in the first port and causing the stylet or guidewire to displace in a first direction across the first port causes the lead to attach to the implantation tool. Displacing the stylet or guidewire in a second direction opposite the first direction allows the lead to detach from the implantation tool.
Owner:PACESETTER INC
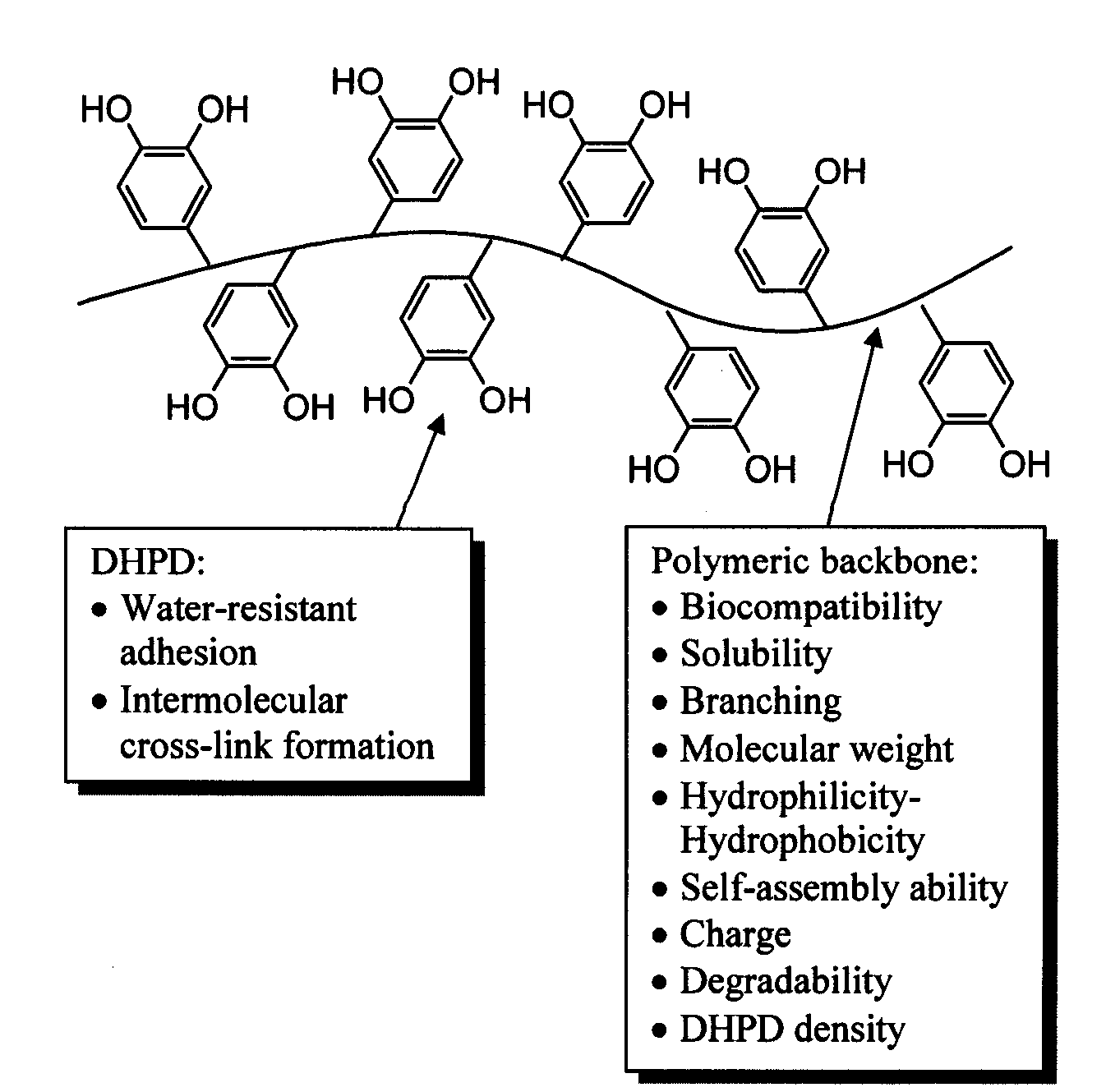
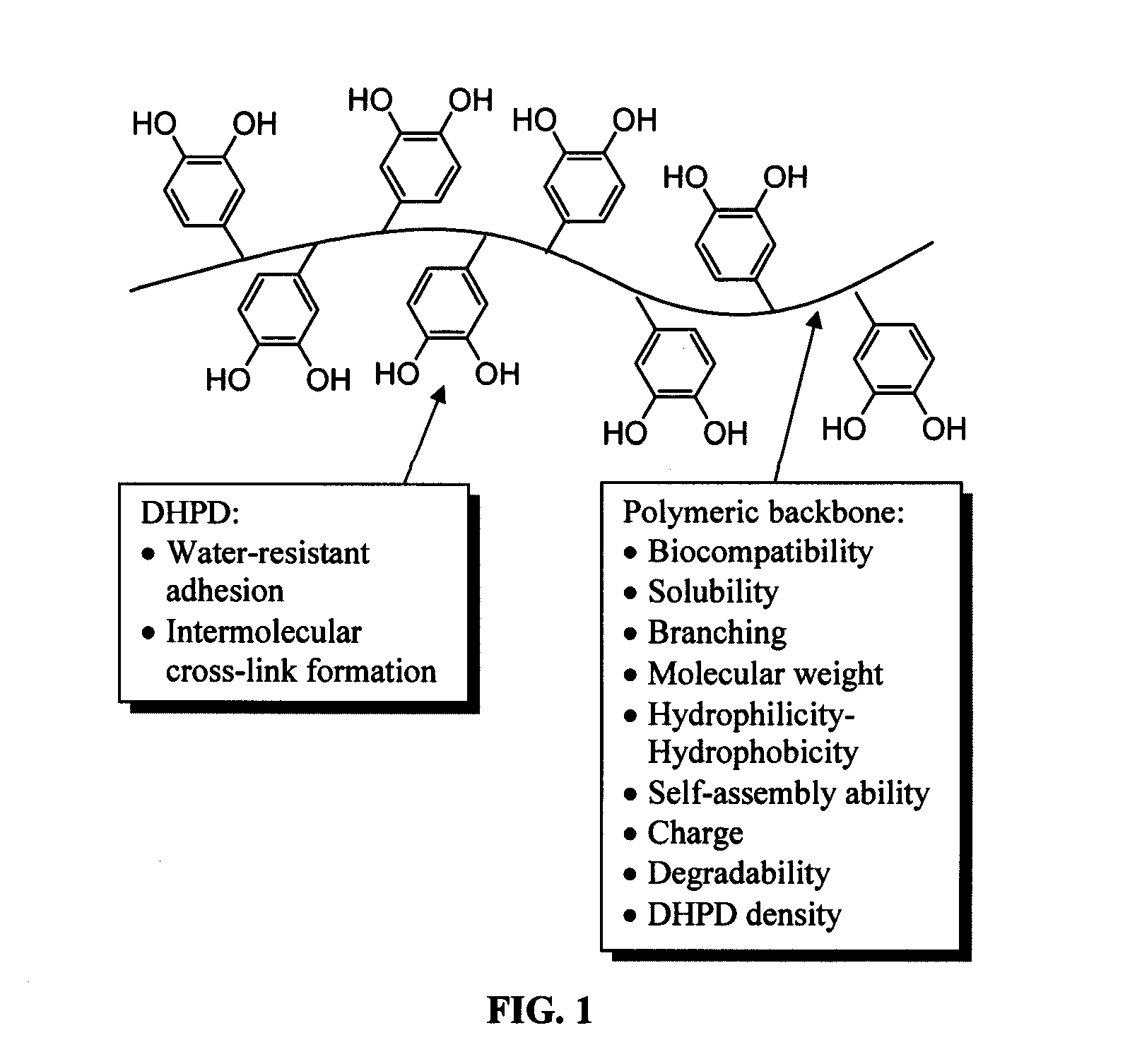
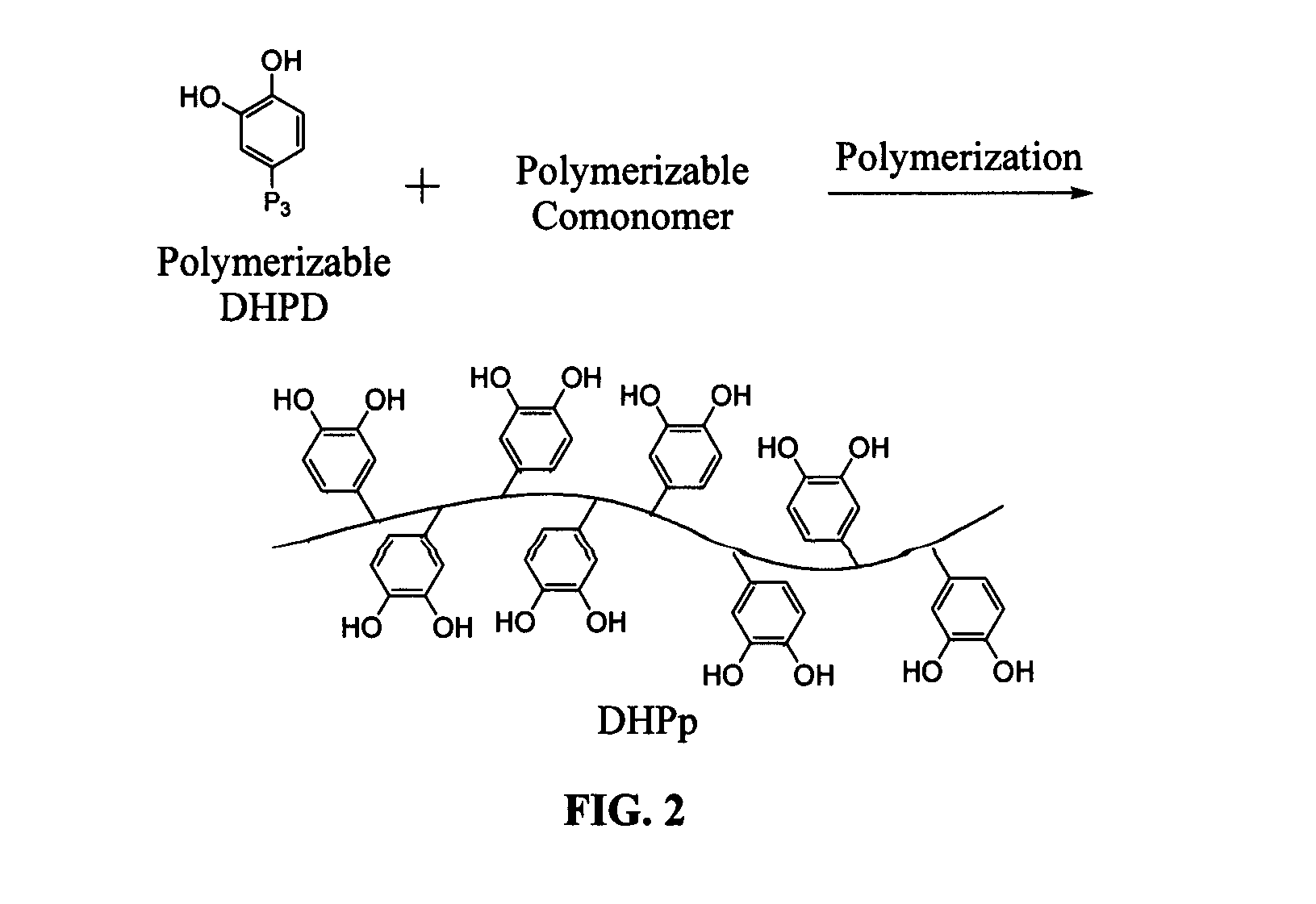
Biomimetic compounds and synthetic methods therefor
Synthesis methods for creating polymeric compounds comprising dihydroxyphenyl derivatives (DHPD), or DHPp i.e. polymers modified with DHPD, with desired surface active effects are described. The polymer backbone of DHPp has structural or performance features that can be tailored to control physical properties of DHPp, allowing it to be useful for different applications i.e. tissue adhesives or sealants, adhesion promoting coatings, and antifouling coatings.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
Collagen type I and type III compositions for use as an adhesive and sealant
InactiveUS20030032143A1Reduce riskInherently hemostatic propertiesFibrinogenSurgical adhesivesWound healingCollagen i
Polymerized type I and / or III collagen based compositions for medical use as adhesives and sealants and preparation thereof are described. Prior to polymerization, the collagen monomers are prepared recombinantly whereby chemical modifications of the collagen are not needed to form such monomers. The type I and / or III collagen compositions are useful as medical adhesives for bonding soft tissues or in a sealant film for a variety of medical uses. In a further aspect of the present invention, the polymerized type I and / or III collagen composition includes agents which induce wound healing or provide for additional beneficial characteristics desired in a tissue adhesive and sealant.
Owner:NEFF THOMAS B +1
Composite tissue adhesive
InactiveUS6939364B1Precise temperature controlShorten treatment timeSurgical instrument detailsSurgical veterinaryThermal energyHigh concentration
Consistent with the present invention, tissue adhesive compositions and an associated laser exposure system are provided for bonding or sealing biological tissues. The compositions are comprised of chemically derivatized soluble collagen which is formulated to concentrations ranging from 300 mg / ml (30%) to 800 mg / ml (80%) collagen protein. In particular, Type I collagen, for example, is first prepared by extraction from bovine or porcine hide and purified. The collagen preparations are then chemically derivatized with sulfhydryl reagents to improve cohesive strength and with secondary derivatizing agents, such as carboxyl groups, to improve the adhesive strength of the solder to the tissue. The compositions are then formed into viscous solutions, gels or solid films, which when exposed to energy generated from an infrared laser, for example, undergo thermally induced phase transitions. Solid or semi-solid protein compositions become less viscous enabling the high concentration protein to penetrate the interstices of treated biological tissue or to fill voids in tissue. As thermal energy is released into the surrounding environment, the protein compositions again become solid or semi-solid, adhering to the treated tissue or tissue space.
Owner:CONVERSION ENERGY ENTERPRISES
Denaturated starch absorbable hemostatic material and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN101121041AHigh viscosityImprove water absorption speedSurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismMedicineBlood plasma
An absorbable modified starch hemostatic material and preparation thereof, wherein the hemostatic material is etherified starch, or a mixture of one or more etherified starches, crosslinked starches. The modified starch has a molecular weight of 15,000 - 10,000,000, a particle size of 10 - 1000µm, and a water absorption rate of 1 - 100. The biocompatible hemostatic material can directly effect on the wound with blood, concentrate the blood quickly to congulate blood; moreover, the gelatiniform mixture formed with blood has high viscosity, which can plug damaged tissue and blood vessel. The biocompatible hemostatic material is easy to swell in the water and easy to be washed so that the residue can be reduced; it is stable, not easy to decompose, and has long shelf life and storage advantage. The biocompatible hemostatic material can also be used as absorbable surgical antisticking material, promoting tissue healing material, surgical sealant and wound no-joint tissue adhesive.
Owner:美国淀粉医疗公司
Oral treatment devices that include a thin, flexible barrier layer and an endoskeleton treatment or adhesive composition
InactiveUS6860736B2Prevent, minimize or lessen their diffusion into the user's mouthPlace stableTeeth fillingCoffinsOral treatmentDentistry
Oral treatment devices include a barrier layer and an oral treatment composition, and optionally an auxiliary adhesive composition, that acts as an endoskeleton so as to at least partially contribute to maintaining the barrier layer in the shape of a dental tray, or in a tray-like configuration, prior to use. The barrier layer protects the oral treatment and / or adhesive composition from saliva or moisture during use. The treatment and / or auxiliary adhesive compositions can have a consistency ranging from a sticky, viscous gel or a solid. They preferably include a tissue adhesion agent comprising a hydrophilic polymer.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
Tissue-adhesive formulations
InactiveUS20060105026A1Efficient use ofGood initial adhesionSurgical adhesivesAbsorbent padsParticulatesMedicine
A tissue-adhesive formulation consists of a naturally occurring or synthetic polymerisable and / or cross-linkable material in particulate form, the polymerisable and / or cross-linkable material being in admixture with particulate material comprising tissue-reactive functional groups. The formulation may be used in the preparation of a tissue-adhesive sheet, by applying the formulation to at least one side of a core of a naturally occurring or synthetic polymeric material.
Owner:TISSUEMED LTD
Cyanoacrylate-capped heterochain polymers and tissue adhesives and sealants therefrom
The present invention is directed toward cyanoacrylate-based tissue adhesive or sealant compositions comprising cyanoacrylate-capped heterochain polymers, such as those comprising one or more oxyalkylene, alkylene carbonate, and ester-units derived from cyclic lactones. Such compositions can be radiochemically sterilized and used in repairing internal organs or tissue blocking body conduits.
Owner:POLY MED
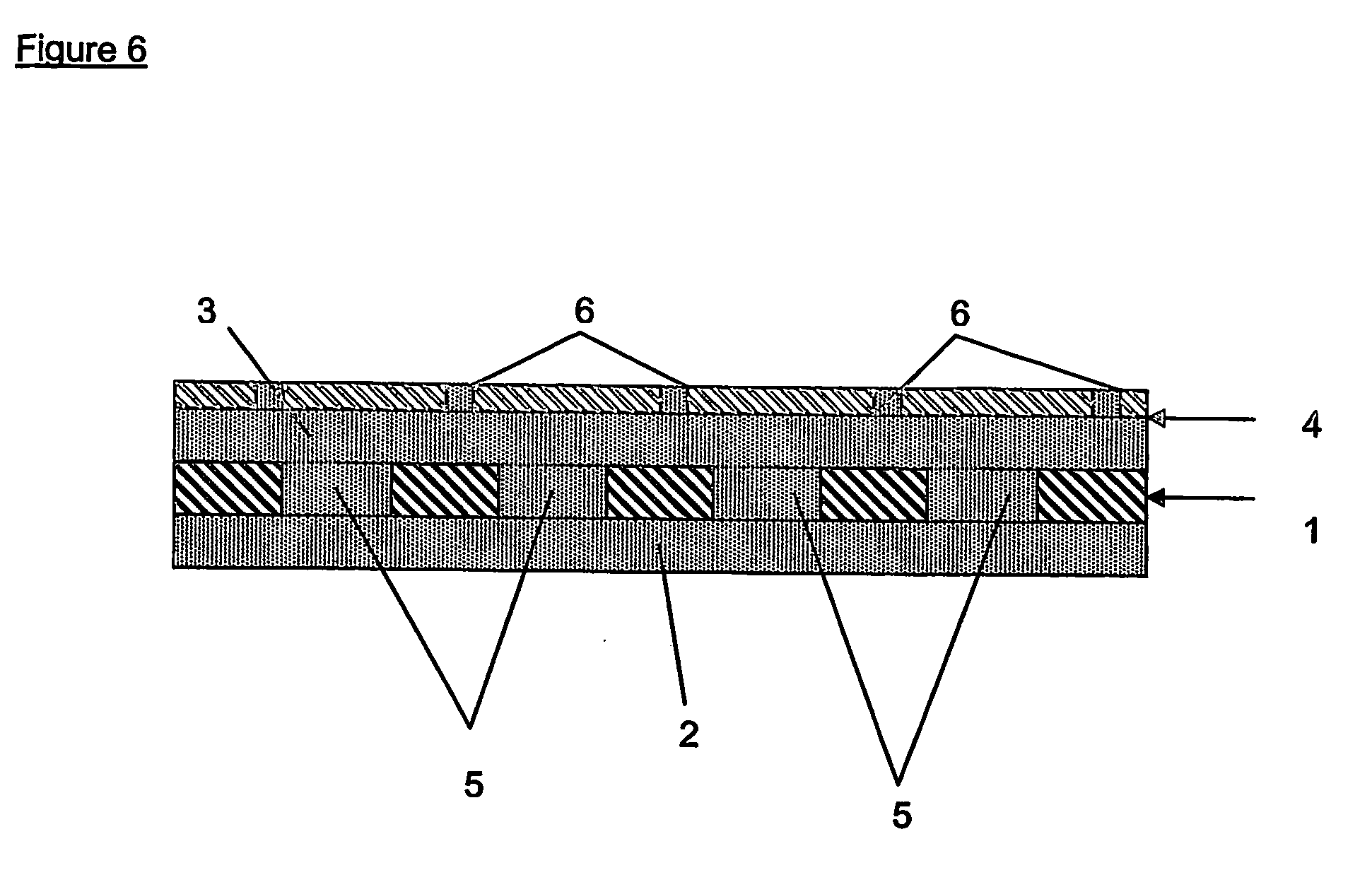
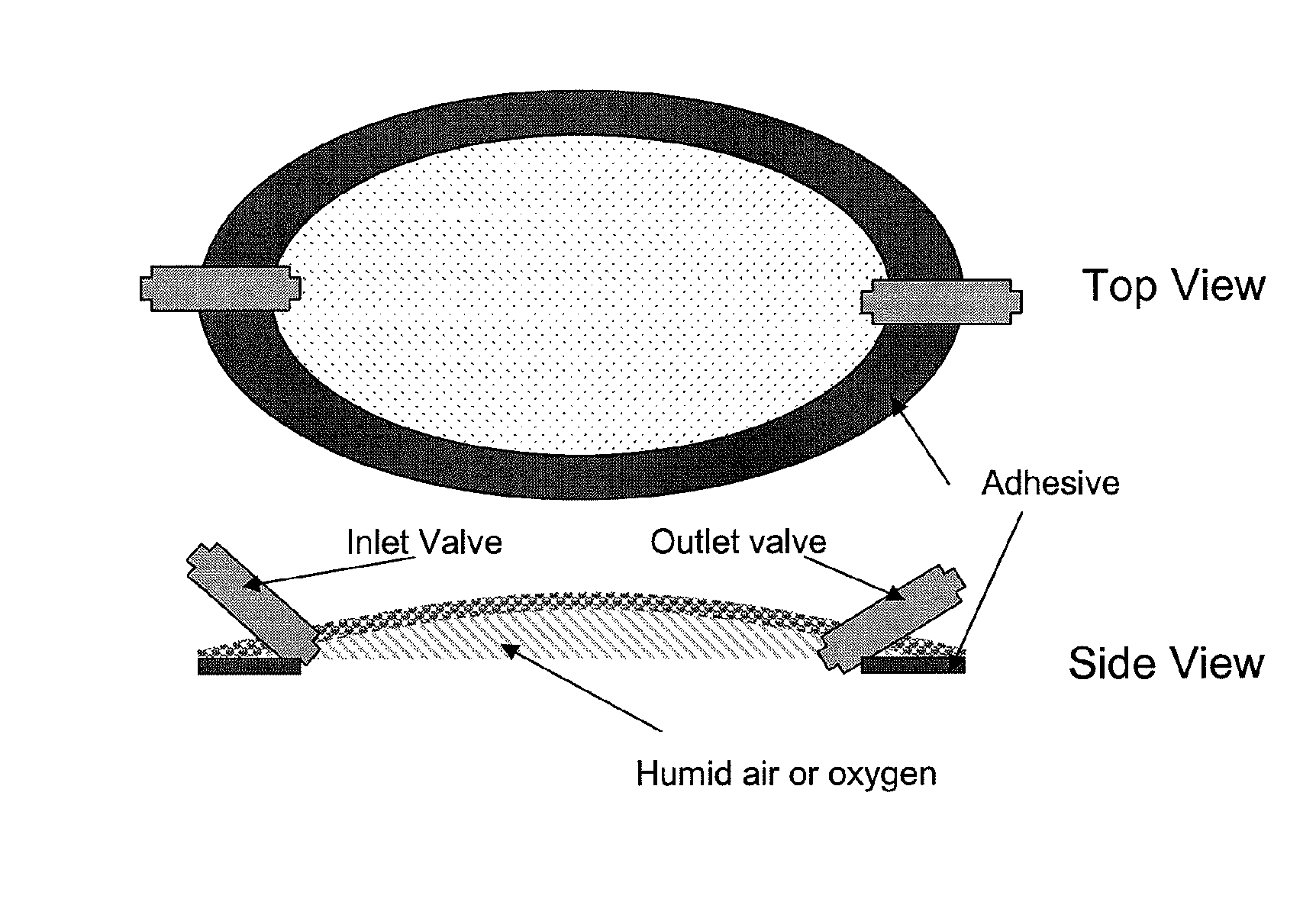
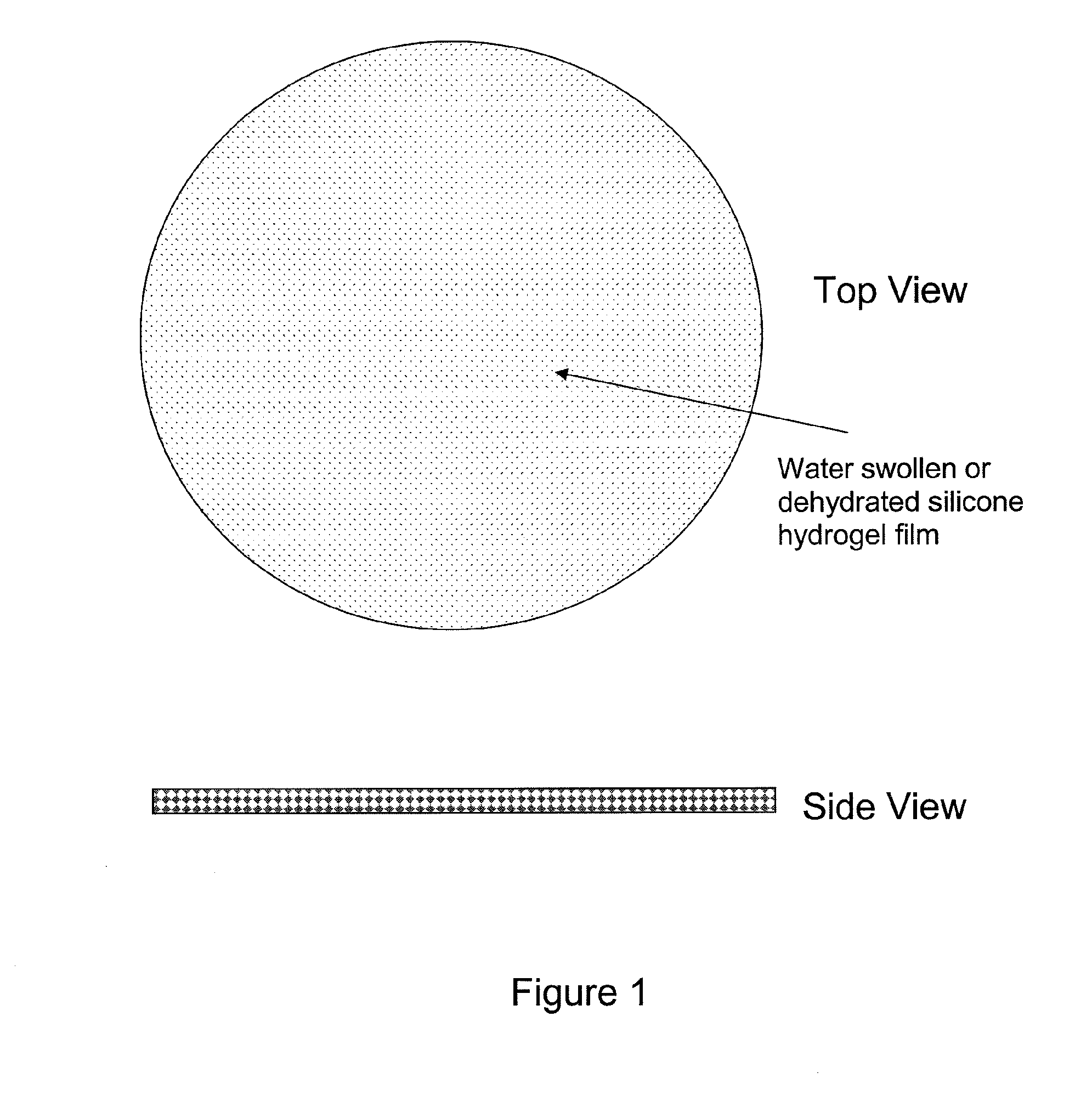
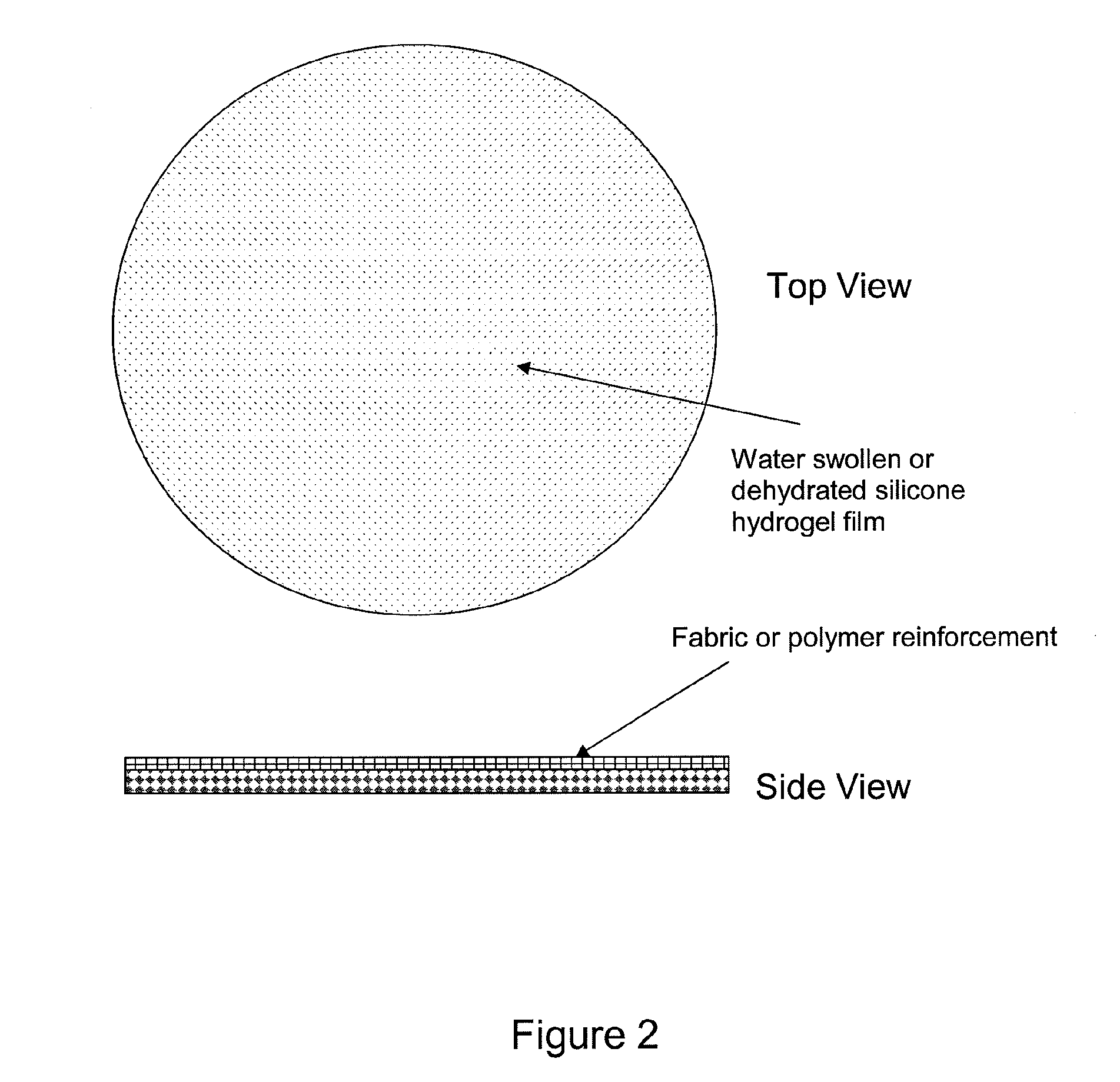
Silicone hydrogels for tissue adhesives and tissue dressing applications
InactiveUS20110086077A1Provide strengthFacilitated releaseBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsWound dressingSilanes
A silicone hydrogel formulation may contains random and / or block copolymers or oligomers or macromers. The silicone copolymer is copolymerized or blended with other polymers or monomers or macromers to obtain final formulation. The silicone hydrogel may contain crosslinking groups to provide a complete or partially crosslinked final structure. The silicone hydrogel formulation may be pre-formed as a film or other structure, or it may be polymerized during application as in the case of an adhesive formulation. A wound dressing comprising a silicone hydrogel formed as a film, either prior to application to a wound or in situ on a wound, which film has gas permeability, moisture permeability, and high water content, wherein said silicone hydrogel is formed from a polymerizable silicone such as a difunctional polydimethylsiloxane methacrylate and crosslinking agents such as N,N-dimethyllacrylamide (DMA), 2-hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA), and trimethylsiloxy silane (TRIS).
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Tissue-Adhesive Materials
This invention related to a tissue-adhesive sheet comprising a homogeneous, preformed and cross-linked matrix formed from one or more polymers, and having at least one surface that, in use, is exposed, at least one of said one or more polymers being a synthetic polymer and having appendant functional groups of a first form, cross-linking of said matrix being via a proportion of said functional groups of the first form, and the remainder of said functional groups of the first form being free. The sheet is particularly useful as a tissue adhesive and sealant, and is intended for topical application to internal and external surfaces of the body for therapeutic reasons. The invention further relates to sheets comprising a scaffold material, three-dimensional articles formed from similar material to that of the sheet and to implantable medical devices coated with such material.
Owner:TISSUEMED LTD
Laparoscopic spray device and method of use
InactiveUS6921381B2Efficient deliveryPrevent backflowLiquid surface applicatorsMedical devicesSurgical siteEngineering
A laparoscopic spray device for selectively applying a multiple component material dispensed from a multiple component material applicator to a surgical site in vivo is disclosed. The device comprises an interface member capable of engaging a multiple component applicator, a body having at least two lumens therein, and a detachable spray tip in fluid communication with the body. The detachable spray tip includes a mixing chamber having at least one flexible mixing member positioned therein which is capable of creating a turbulent flow within a mixing chamber. In addition, the at least one mixing member prevents a back flow of material from the mixing chamber to the at least two lumens. The present invention is particularly useful in remotely applying multiple component tissue adhesives to an internal incision.
Owner:BAXTER INT INC +1
Biocompatibility modified starch sponges
ActiveCN101455857AFlexibleActive bleeding is easily controlledAbsorbent padsBandagesFreeze-dryingBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to biocompatible modified starch sponge and use of the biocompatible modified starch sponge as a hemostatic material, an anti-adhesion material, a material for promoting tissue healing, a surgical sealant or a wound tissue adhesive. Modified starch is one or a combination of more than one among pre-gelatinized starch, acid modified starch, dextrin, oxidized starch, esterified starch, etherified starch, crosslinked starch, grafted starch and composite modified starch. The sponge is prepared by vacuum freeze drying of the modified starch and other biocompatible hemostatic material, coagulant, plasticizer and so on. The biocompatible modified starch sponge has the advantages that the biocompatible modified starch sponge has flexible form and good biocompatibility, can be directly acted on bloody wound surfaces, avoids the conditions of hypersusceptibility, infection and difficult healing of wounds caused by adoption of hemostatic materials such as animal source / human source collagens, obviously improves the water absorption speed, has larger viscosity, forms a zymoplastic mixture which has good adhesion, calks broken tissues and blood vessels, and is used for hemostasis of active hemorrhage.
Owner:BEIJING UNIVERSAL LIKANG TECH CO LTD
Method for repair and reconstruction of ruptured ligaments or tendons and for treatment of ligament and tendon injuries
A method and a means for repair and reconstruction of ruptured ligaments and tendons by in vivo or ex vivo repair and reconstruction surgical procedures. The method comprises providing a biodegradable sleeve placed around the frayed edges of an injured ligament or tendon for protecting the ligament or tendon injury with a protective shield. A composition comprising a biodegradable tissue adhesive applied on top of, around and / or between the frayed edges of the injured ligament.
Owner:HISTOGENICS
Devices and methods for spine repair
InactiveUS20080221628A1Avoid squeezingMinimally invasiveSurgical furnitureDiagnosticsRepair siteProsthesis
Surgical methods of repairing defects and deficiencies in the spine are disclosed. The methods involve delivering a single part in-situ polymerizing fluid to (i) close a weakened segment or fissure in the annulus fibrosus, (ii) strengthen the annulus, (iii) replace or augment the disc nucleus, or (iv) localize a disc prosthesis. The methods may include placing a delivery conduit adjacent to the repair site and providing a liquid tissue adhesive to bond to and repair a disc defect or deficiency
Owner:PROMETHEAN SURGICAL DEVICES
Biodegradable stent composite material and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN102008751AGood mechanical propertiesPromote degradationSuture equipmentsSurgical adhesivesBiocompatibility TestingAlloy
The invention relates to a biodegradable stent composite material and a preparation method thereof. The degradable material has a multi-gradient composite structure, and comprises a matrix made of a medical metal or an alloy thereof, a chemical coupling layer attached to the surface of the matrix, a high polymer transition layer attached to the surface of the chemical coupling layer and a degradable high polymer functional layer fixed on the surface of the high polymer transition layer. The stent composite material has high mechanical property, degradation property and biocompatibility, also can absorb and carry needed therapeutic medicaments, and meets the requirement on clinical treatment. The degradable composite material can be used as stent materials of esophagi, biliary ducts, intestinal tracts, urethrae, tracheae and other non-vessel lumens and blood vessels, and also can be used for manufacturing artificial bones, bone nails, bone connectors, bone sutures, anchors for suture, intervertebral discs, hemostatic clamps, hemostatic forceps, hemostatic plates, hemostatic screws, tissue adhesives, sealants and other medical devices and products.
Owner:清北高科(北京)科技有限公司
Biomimetic compounds and synthetic methods therefor
Synthesis methods for creating polymeric compounds comprising dihydroxyphenyl derivatives (DHPD), or DHPp i.e. polymers modified with DHPD, with desired surface active effects are described. The polymer backbone of DHPp has structural or performance features that can be tailored to control physical properties of DHPp, allowing it to be useful for different applications i.e. tissue adhesives or sealants, adhesion promoting coatings, and antifouling coatings.
Owner:KENSEY NASH CORP
Fibrous tissue sealant and method of using same
Disclosed herein is a fibrous tissue sealant in the form of an anhydrous fibrous sheet comprising a first component which is a fibrous polymer containing electrophilic or nucleophilic groups and a second component capable of crosslinking the first component when the sheet is exposed to an aqueous medium, thereby forming a crosslinked hydrogel that is adhesive to biological tissue. The fibrous tissue sealant may be useful as a general tissue adhesive for medical and veterinary applications such as wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures, tissue repair, and to prevent post-surgical adhesions. The fibrous tissue sealant may be particularly suitable for use as a hemostatic sealant to stanch bleeding from surgical or traumatic wounds.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Controlled viscosity tissue adhesive
InactiveUS20050245966A1Simple and effective methodSimple and effective and compositionSurgical adhesivesAbsorbent padsCyanoacrylatePlasticizer
Disclosed are methods and compositions for closing and sealing a wound, laceration, incision, or other percutaneous opening using an adhesive. In one preferred embodiment, the sides of the percutaneous opening are brought together in apposition and the adhesive is applied topically over the apposed opening and the skin adjacent thereto. Adhesives used in the methods of the preferred embodiments exhibit sufficient viscosity to substantially prevent flow of the adhesive into the percutaneous opening. Adhesives may also be used in surgical applications, as a covering for a trauma to the outer surface of the skin, or as a secondary means of closure in combination with other means of closure, including staples and sutures. In a preferred embodiment, the adhesive is a adhesive comprising cyanoacrylate monomer, cyanoacrylate polymer, and a plasticizer.
Owner:CLAST TRADING LTD CLAST +1
Tissue adhesive sealant
A tissue adhesive sealant includes a cross-linkable protein in a solution that when combined with a cross-linking agent solution including an aldehyde and amino acid containing species reactive with the aldehyde cross-links to form a seal. The sealant is well suited for bonding tissue alone or in combination with a patch. The ratio between the aldehyde and the amino acid containing species is between 20:1 and 1:1 on an aldehyde moiety:amino acid or peptide subunit molar basis. Particularly strong seals are formed when the protein and cross-linking agent are present in a molar ratio of between 15:1 and 1:1.
Owner:COVALENT MEDICAL
Light energized tissue adhesive
InactiveUS6875427B1Lower requirementPrecise temperature controlBiocideSurgical adhesivesHigh concentrationThermal energy
Consistent with the present invention, tissue adhesive compositions and an associated laser exposure system are provided for bonding or sealing biological tissues. The compositions are comprised of chemically derivatized soluble collagen which is formulated to concentrations ranging from 300 mg / ml (30%) to 800 mg / ml (80%) collagen protein. In particular, Type I collagen, for example, is first prepared by extraction from bovine or porcine hide and purified. The collagen preparations are then chemically derivatized with sulfhydryl reagents to improve cohesive strength and with secondary derivatizing agents, such as carboxyl groups, to improve the adhesive strength of the solder to the tissue. The compositions are then formed into viscous solutions, gels or solid films, which when exposed to energy generated from an infrared laser, for example, undergo thermally induced phase transitions. Solid or semi-solid protein compositions become less viscous enabling the high concentration protein to penetrate the interstices of treated biological tissue or to fill voids in tissue. As thermal energy is released into the surrounding environment, the protein compositions again become solid or semi-solid, adhering to the treated tissue or tissue space.
Owner:CONVERSION ENERGY ENTERPRISES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com