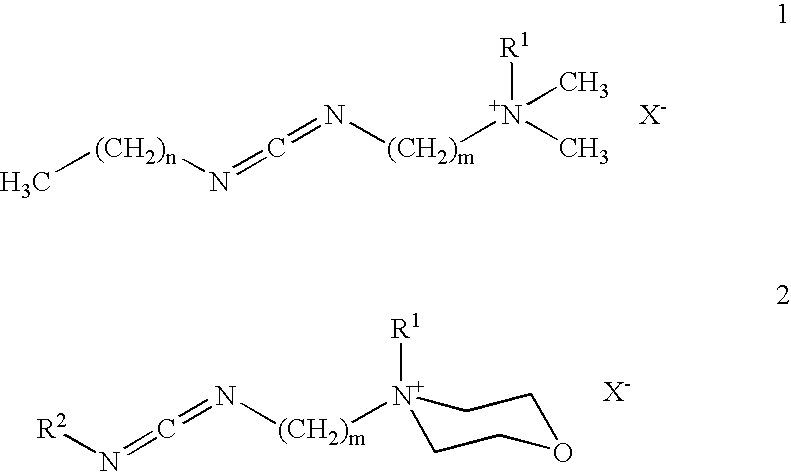
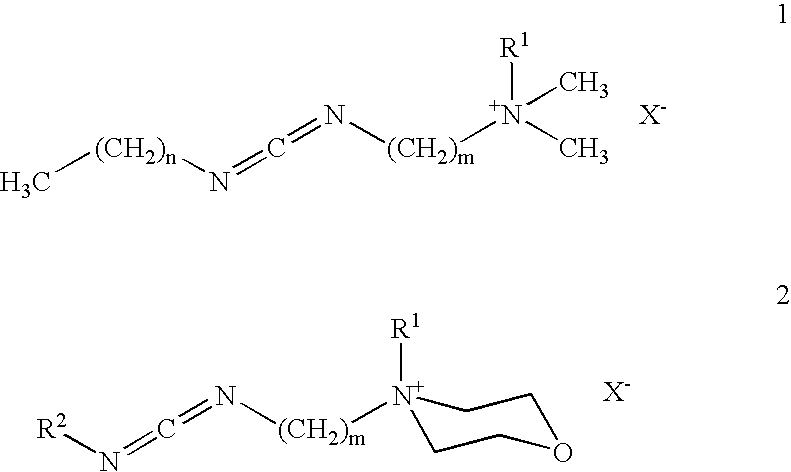
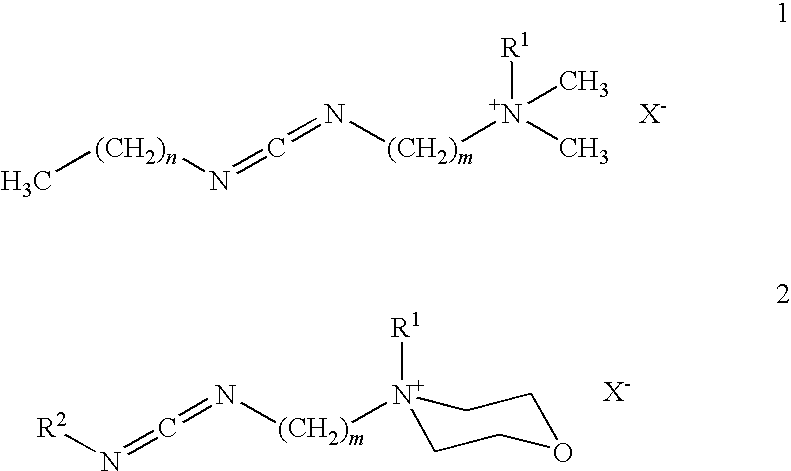
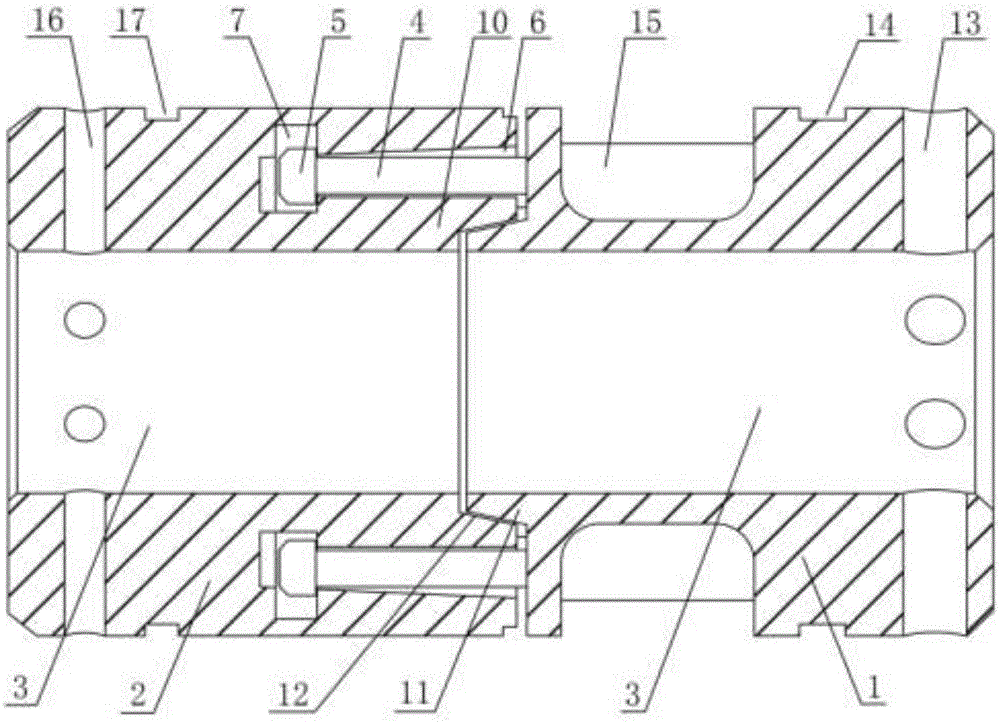
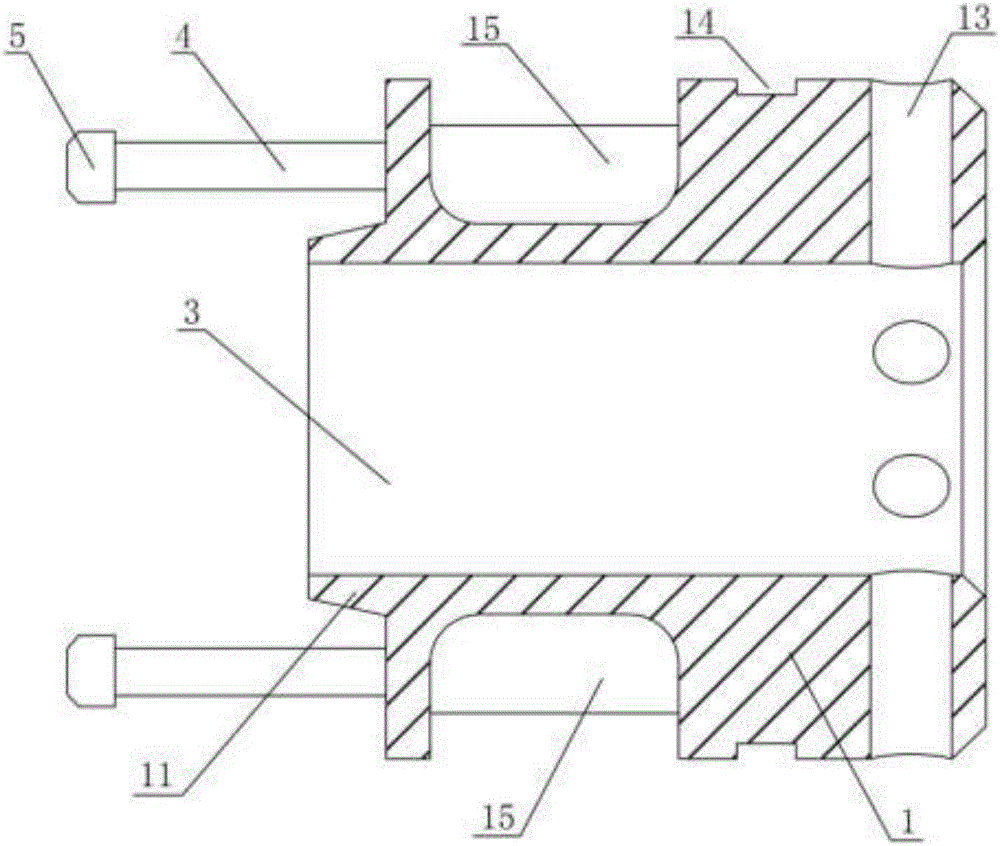
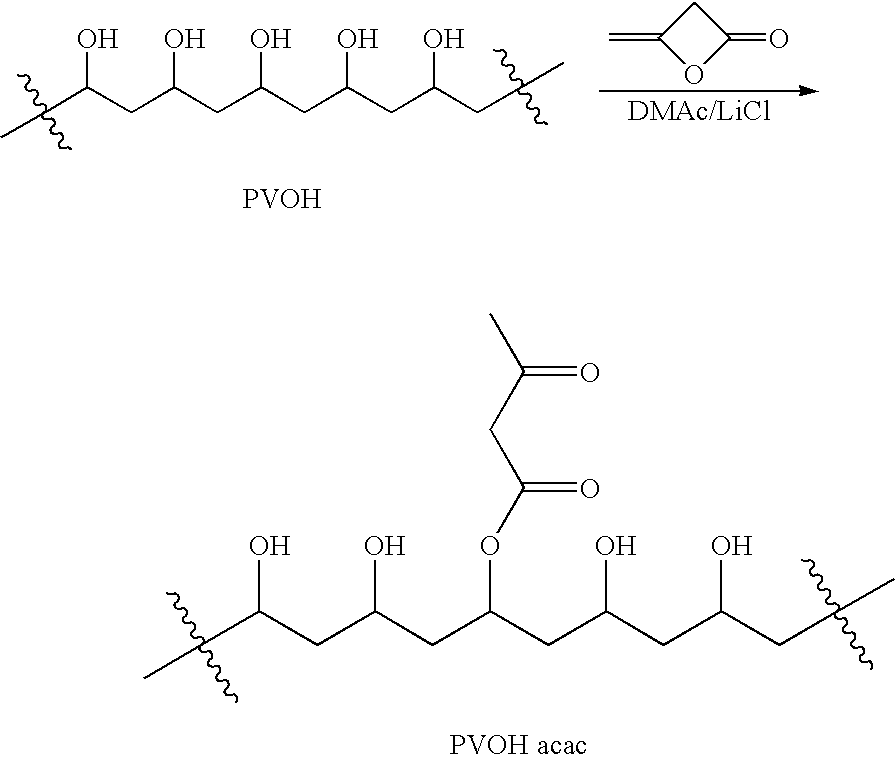
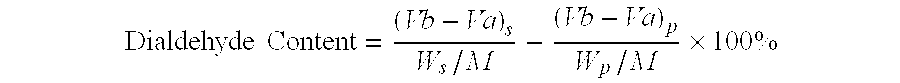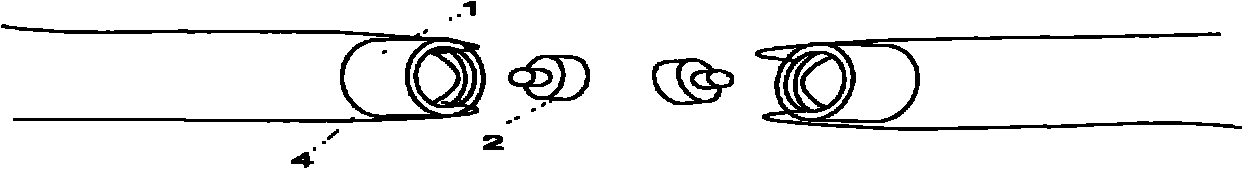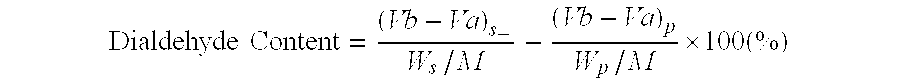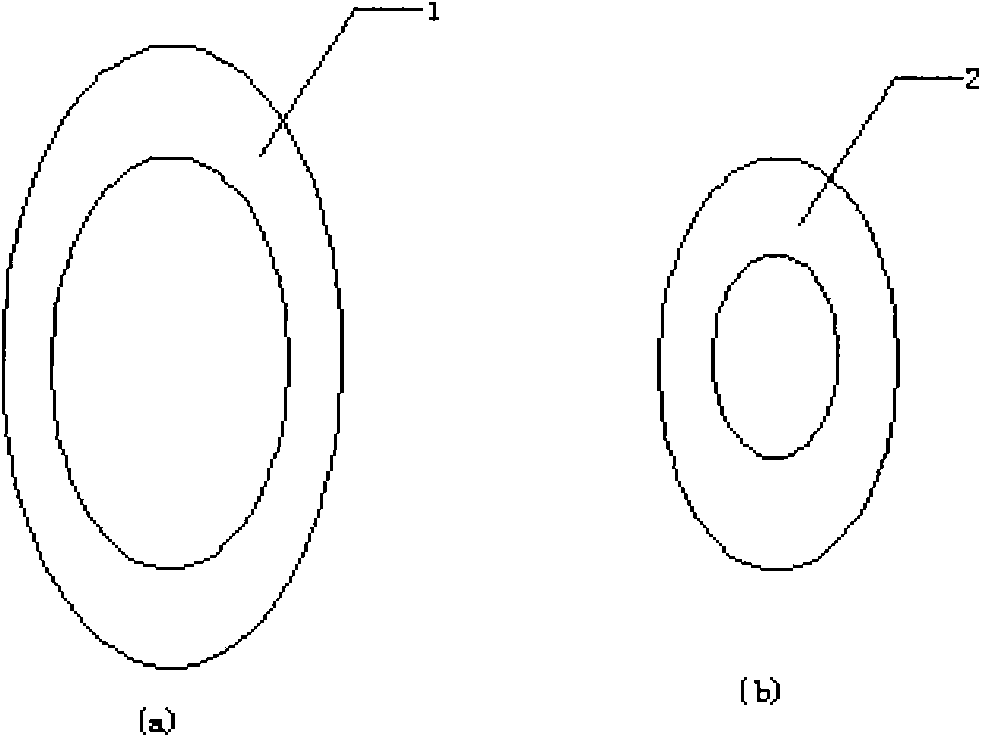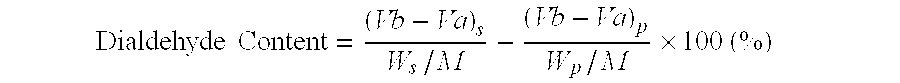Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
69 results about "Intestinal anastomosis" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
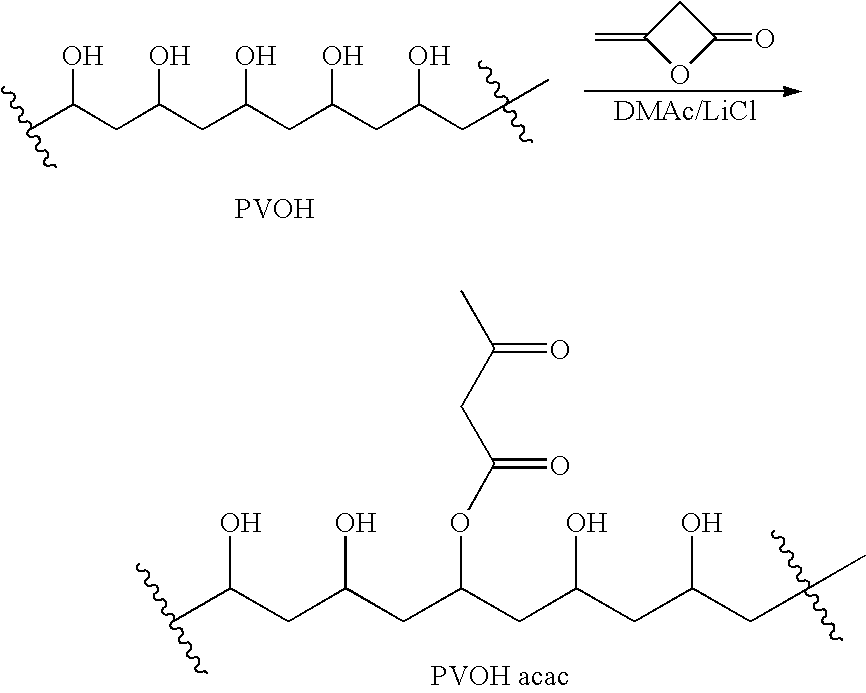
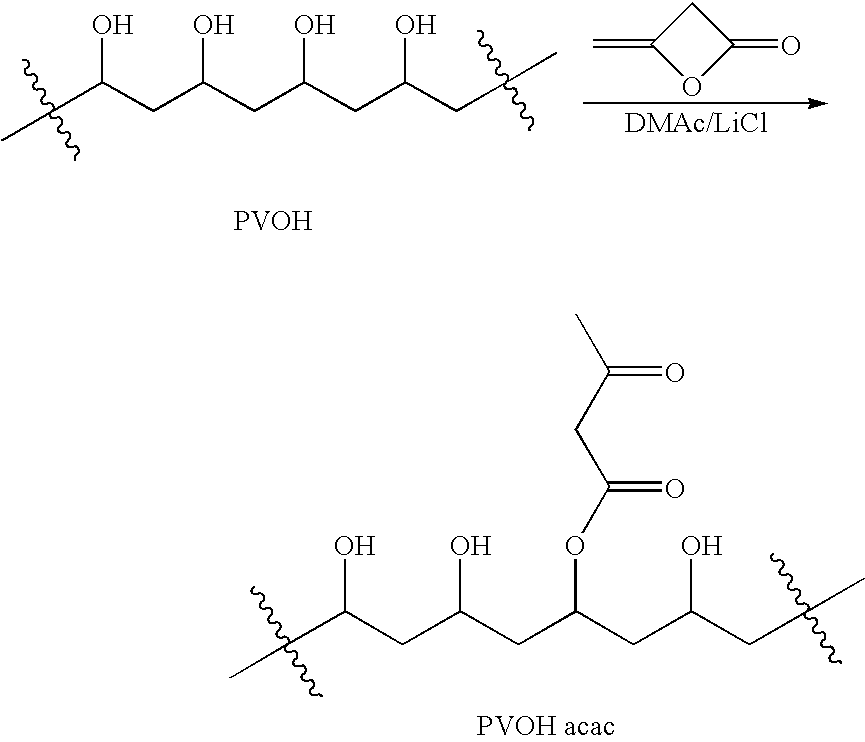
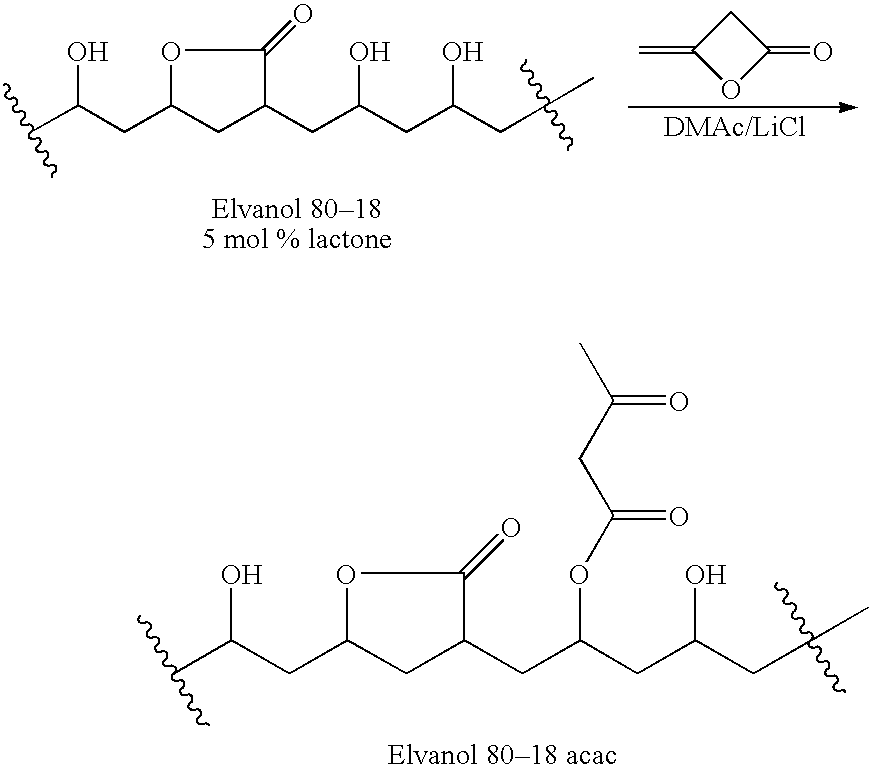
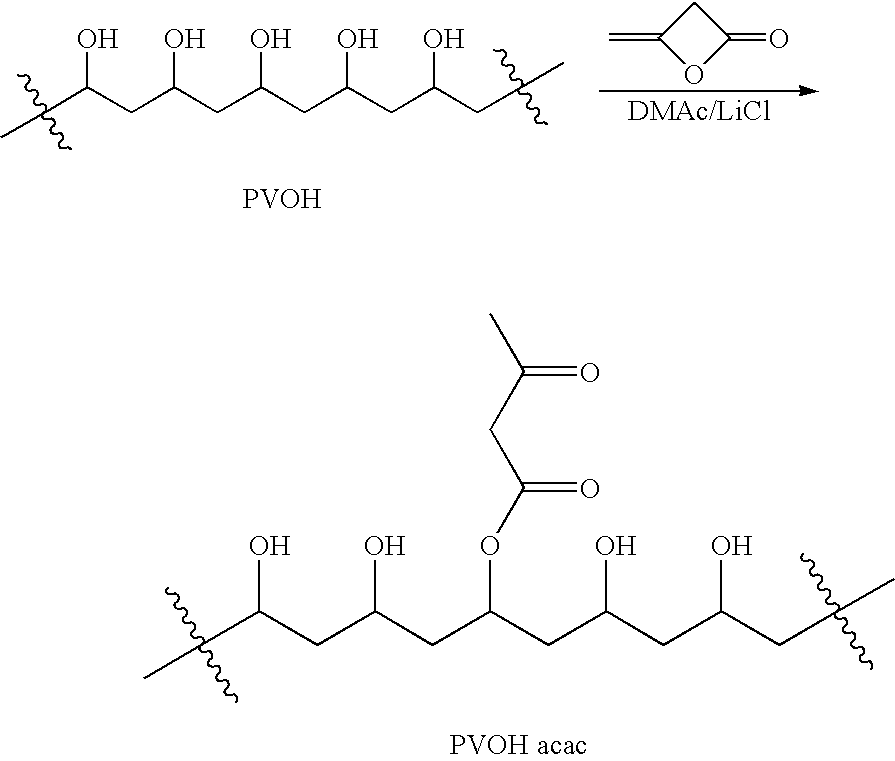
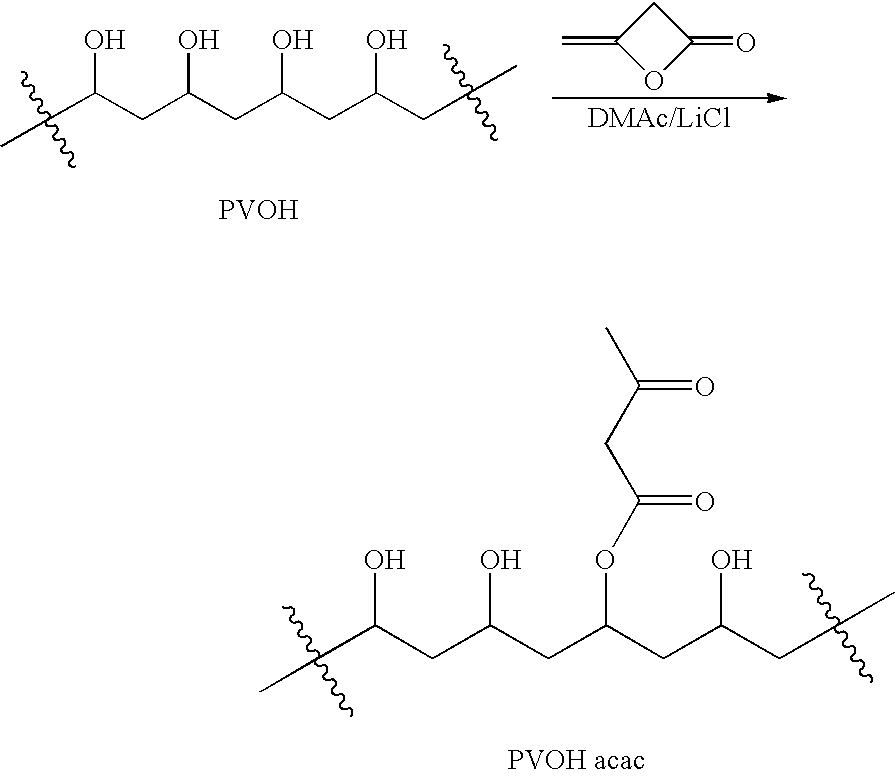
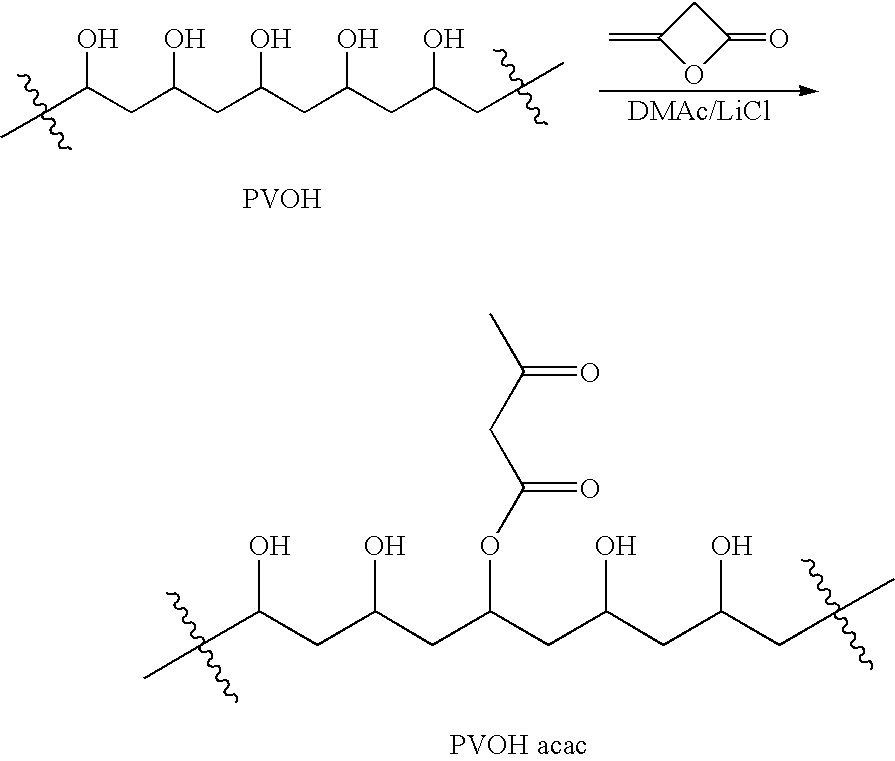
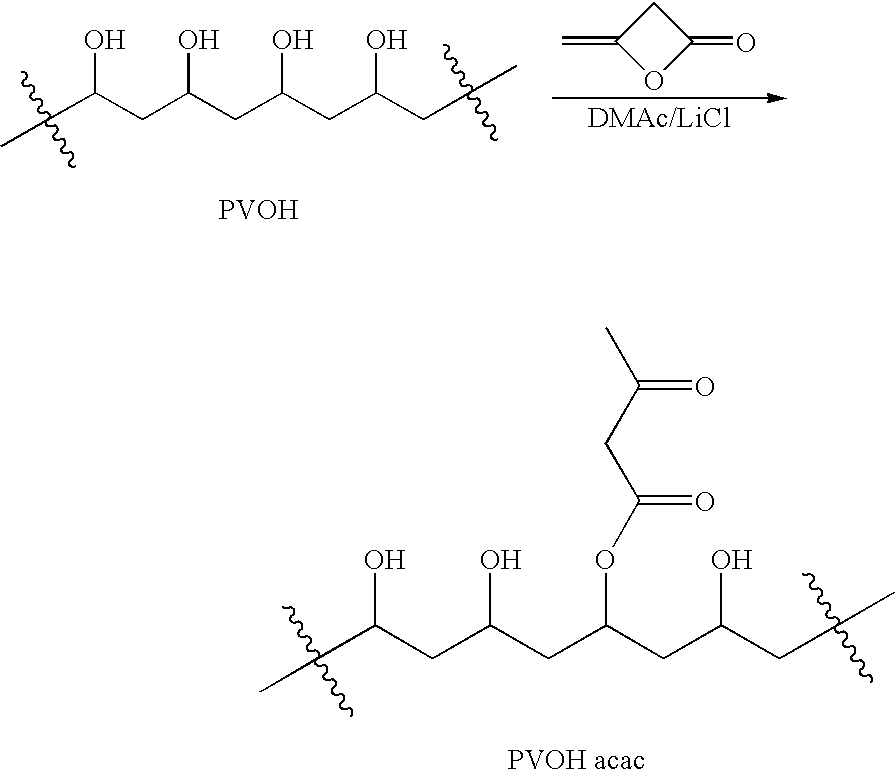
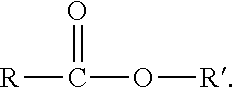
Polymer-based tissue-adhesive form medical use
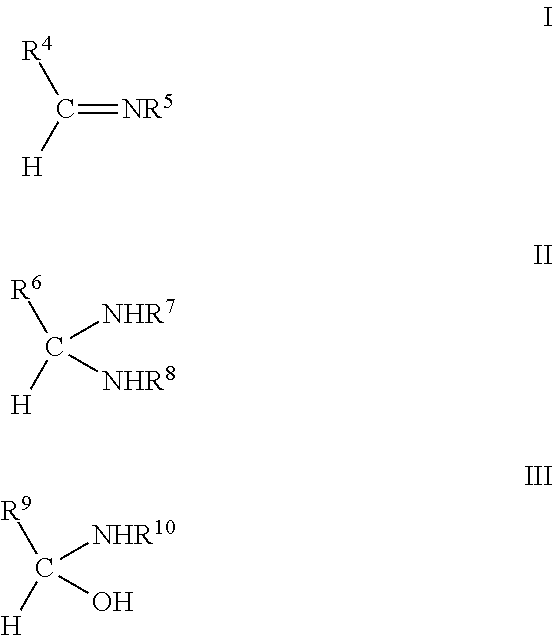
Tissue adhesives formed by reacting poly(hydroxylic) compounds derivatized with acetoacetate groups and / or polyamino compounds derivatized with acetoacetamide groups with an amino-functional crosslinking compound are disclosed. The use of the tissue adhesives for medical and veterinary applications such as topical wound closure; and surgical procedures, such as intestinal anastomosis, vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, and ophthalmic procedures; drug delivery; and anti-adhesive applications are described.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
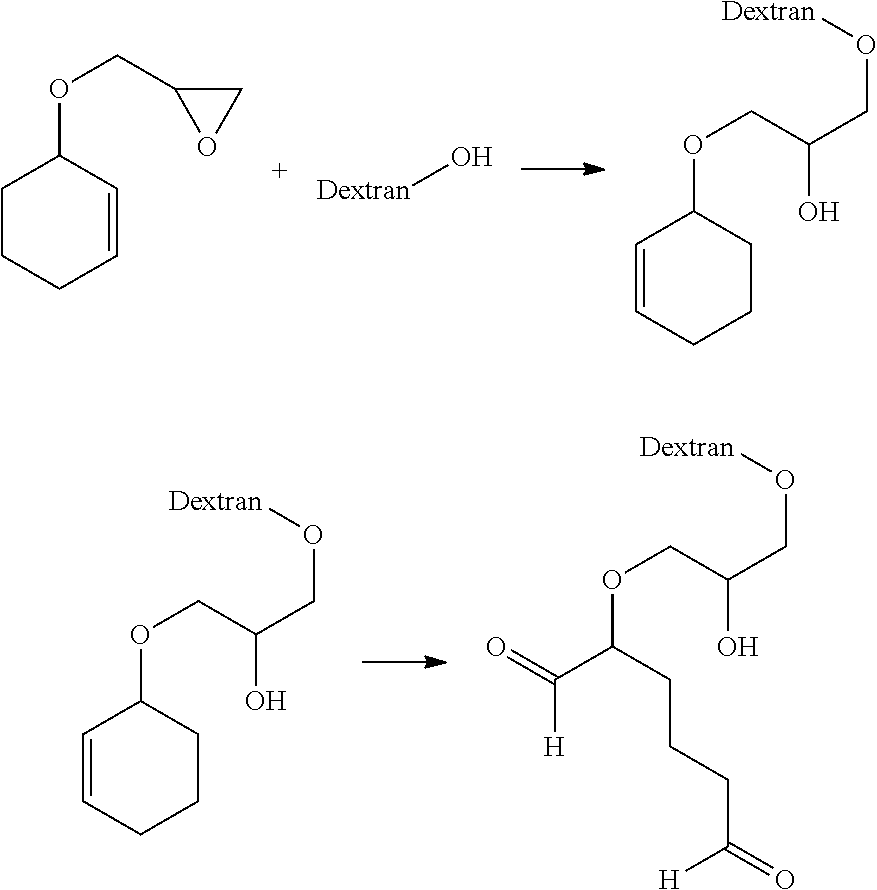
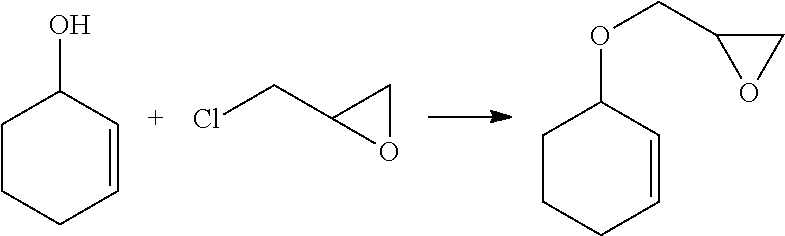
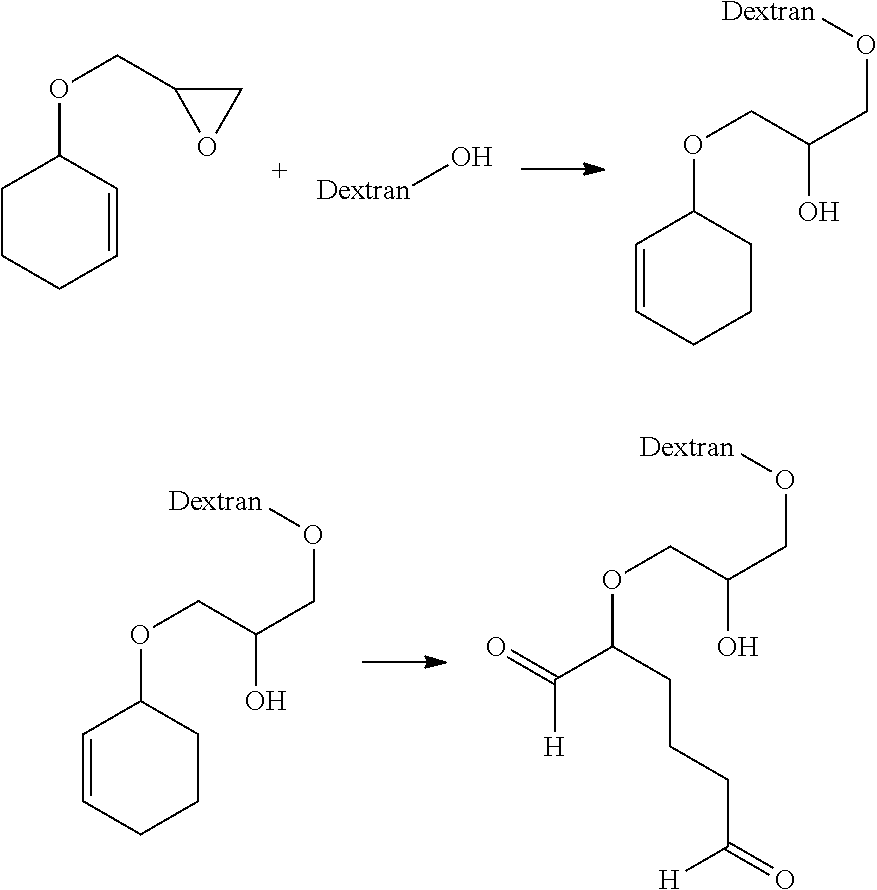
Aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharides
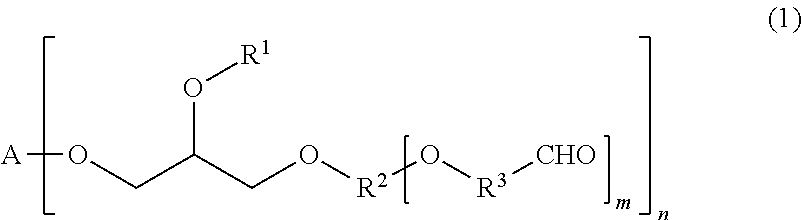
Novel aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharide compositions are described that are more stable in aqueous solution than oxidized polysaccharides or other types of polysaccharides containing pendant aldehyde groups. The aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharides may be reacted with various amine-containing polymers to form hydrogel tissue adhesives and sealants that may be useful for medical applications such as wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures such as intestinal anastomosis and vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, preventing leakage of fluids such as blood, bile, gastrointestinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid, ophthalmic procedures, drug delivery, and preventing post-surgical adhesions.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Methods for sealing an orifice in tissue using an aldol-crosslinked polymeric hydrogel adhesive
ActiveUS20070048251A1Organic active ingredientsUnsaturated alcohol polymer adhesivesAcetoacetatesVascular anastomosis
Methods for sealing an orifice in tissue in the body of a living animal using an adhesive formed by reacting an oxidized polysaccharide with a poly(hydroxylic) compound derivatized with acetoacetate groups in the presence of a base catalyst are disclosed. Methods for using the adhesive for medical and veterinary applications such as topical wound closure; and surgical procedures, such as intestinal anastomosis, vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, and ophthalmic procedures; and drug delivery are described.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Aldol-crosslinked polymeric hydrogel adhesives
Adhesives formed by reacting an oxidized polysaccharide with a poly(hydroxylic) compound derivatized with acetoacetate groups in the presence of a base catalyst are disclosed. The use of the adhesives for medical and veterinary applications such as topical wound closure; and surgical procedures, such as intestinal anastomosis, vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, and ophthalmic procedures; and drug delivery are described. The adhesive may also be used for industrial and consumer applications.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Oxidized cationic polysaccharide-based polymer tissue adhesive for medical use
A tissue adhesive formed by reacting an oxidized cationic polysaccharide containing aldehyde groups and amine groups with a multi-arm amine is described. The oxidized cationic polysaccharide-based polymer tissue adhesive may be useful for medical applications including wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures such as intestinal anastomosis and vascular anastomosis, ophthalmic procedures, drug delivery, anti-adhesive applications and as a bulking agent to treat urinary incontinence. Additionally, due to the presence of the positively charged amine groups on the oxidized polysaccharide, the polymer tissue adhesive disclosed herein may promote wound healing and blood coagulation, and may possess antimicrobial properties.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Hydrogel tissue adhesive formed from aminated polysaccharide and aldehyde-functionalized multi-arm polyether
A hydrogel tissue adhesive formed by reacting an aminated polysaccharide with a water-dispersible, aldehyde-functionalized multi-arm polyether is described. The hydrogel tissue adhesive may be useful as a general tissue adhesive and sealant for medical and veterinary applications such as wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures such as intestinal anastomosis and vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, ophthalmic procedures, drug delivery, and to prevent post-surgical adhesions. Additionally, due to the presence of the aminated polysaccharide, the hydrogel tissue adhesive may also promote wound healing and blood coagulation, and provide antimicrobial properties.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Protein-based polymer tissue adhesives for medical use
ActiveUS20060115531A1Avoid stickingPowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsVascular anastomosisTissue repair
Tissue adhesives formed by crosslinking albumin and / or gelatin with certain polyamines and / or polycarboxylates using a water-soluble carbodiimide are disclosed. The use of the tissue adhesives for medical and veterinary applications such as topical wound closure; and surgical procedures, such as intestinal anastomosis, vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, and ophthalmic procedures; drug delivery; anti-adhesive applications; and as a bulking agent to treat urinary incontinence are described.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
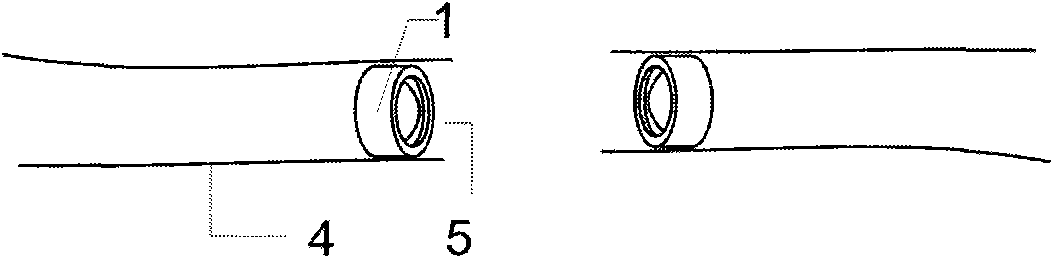
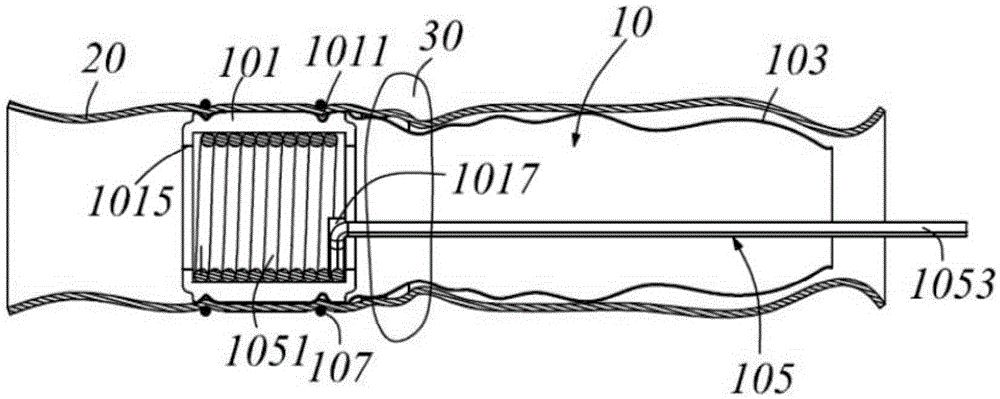
End-to-end intestinal anastomosis magnetic device
The invention relates to an end-to-end intestinal anastomosis magnetic device, consisting of two end anastomosis devices. Each end anastomosis device consists of an annular magnetic ring and a hollow annular tube which is made of a soft magnetic material and has a T-shaped cross section. The magnetic attraction of two auxiliary end anastomosis devices with proper sizes and shapes are utilized to finish wireless suture end-to-end intestinal anastomosis, thereby the defects of a stomach and intestine anastomosis device that the peripheral tissue of an anastomosis wound is easy to rupture, the peripheral tissue of the anastomosis wound easily bleeds, the anastomosis wound is blocked, and the suture is not complete during the end-to-end intestinal anastomosis are avoided, and the two auxiliary end anastomosis devices used during the end-to-end intestinal anastomosis can be discharged out of the body along with excrement, and can not retain in the body to cause inconvenience and discomfort.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Negative pressure intestinal anastomosis protection devices
A device is disclosed that provides for the protection of intestinal anastomosis sites and other body sites from bodily fluids and contaminants. Additionally, the device provides the ability to create negative pressure at the site of the obstruction to ensure that contaminants flow from the visceral compartment into the inner lumen of the bowel. Further, the device provides the sectional forces through natural constrictions of the intestinal muscles through peristaltic action.
Owner:ETHICON INC
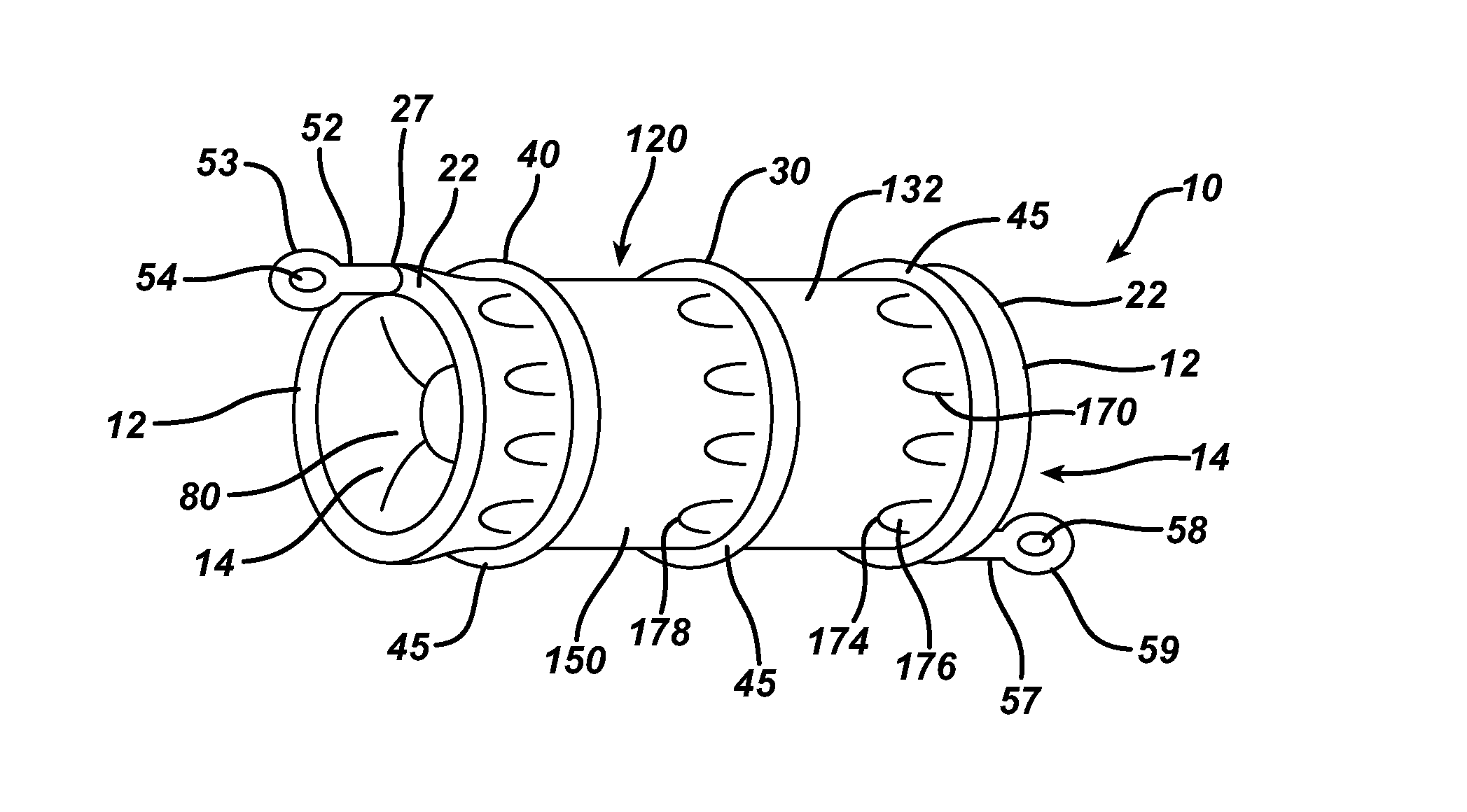
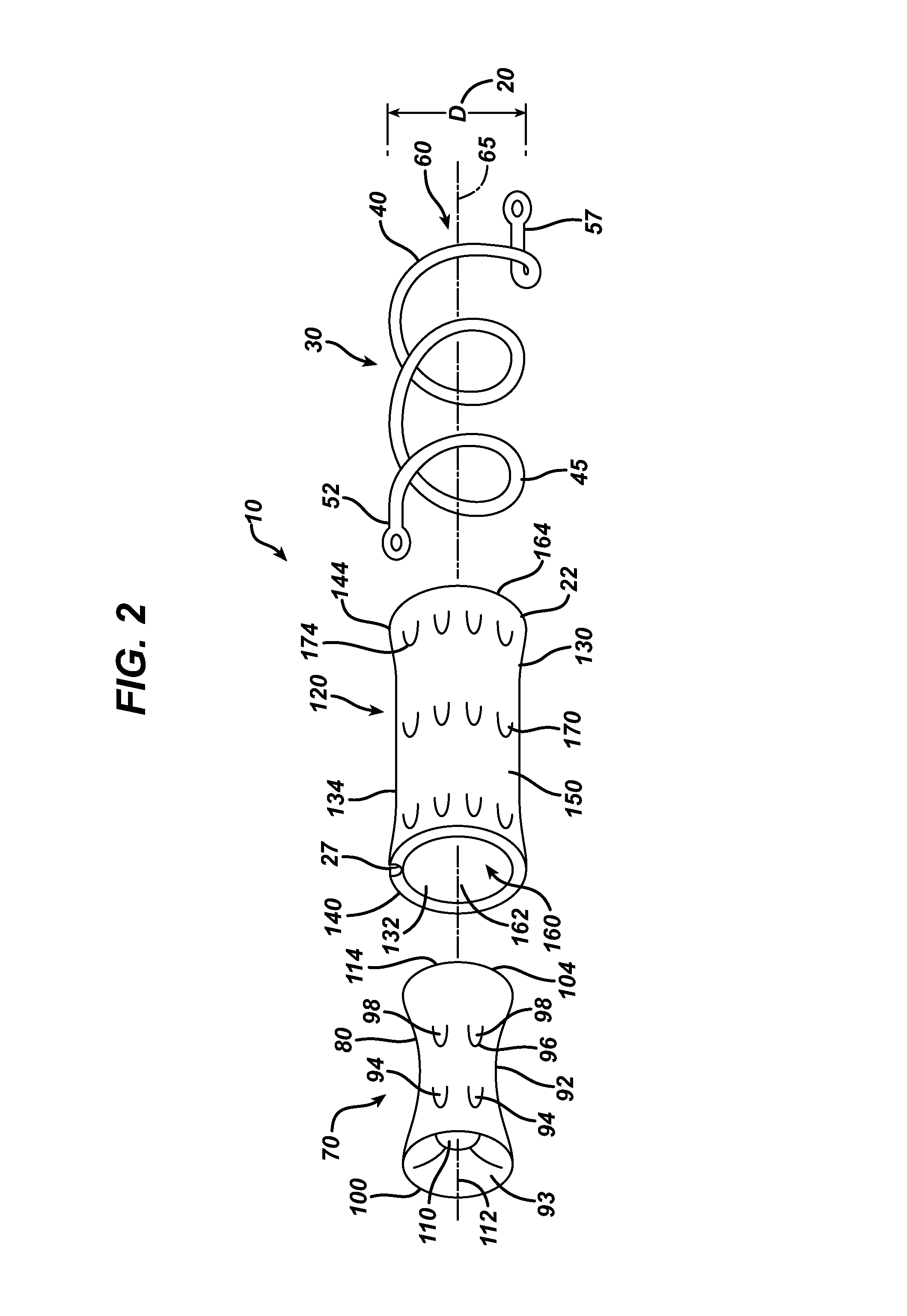
Directional disintegrating traceable intestinal anastomosis stent
ActiveCN105078535AReduce stenosisPrecise design methodSurgical staplesInsertion stentControllability
The invention discloses a directional disintegrating traceable intestinal anastomosis stent, which comprises a through tube which is made from a human-acceptable and degradable material, wherein the middle of the through tube is of a tubular structure, and two ends are gradually expanded to form trumpet-shaped openings; bunch grooves or convex rings for tying intestinal broken ends are arranged on the joints of the tubular middle of the trumpet-shaped opening; a creeping anastomosis section for the intestinal broken ends on two sides is arranged in the middle of the through tube; annular grooves in circumferential direction are marked in the middle and in two ends of the through tube; and barium sulfate is contained in material. The stent can gradually break according to a pre-designed scheme, so as to enhance the supporting capacity thereof, to reduce the occurrence of leakage or stenosis of anastomosis and additionally to enhance controllability over a stent splitting process, and the stent can improve foreseeability when designing; and the stent can be developed through X radiography.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Polysaccharide-based polymer tissue adhesive for medical use
ActiveUS8431114B2Avoid stickingSurgical adhesivesEther/acetal active ingredientsVascular anastomosisOcular operation
Tissue adhesives formed by reacting an oxidized polysaccharide with a water-dispersible multi-arm polyether amine, wherein at least three of the arms are terminated by primary amine groups, are disclosed. The use of the tissue adhesives for medical and veterinary applications such as topical wound closure; and surgical procedures, such as intestinal anastomosis, vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, and ophthalmic procedures; drug delivery; anti-adhesive applications; and as a bulking agent to treat urinary incontinence are described.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharides
Novel aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharide compositions are described that are more stable in aqueous solution than oxidized polysaccharides or other types of polysaccharides containing pendant aldehyde groups. The aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharides may be reacted with various amine-containing polymers to form hydrogel tissue adhesives and sealants that may be useful for medical applications such as wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures such as intestinal anastomosis and vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, preventing leakage of fluids such as blood, bile, gastrointestinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid, ophthalmic procedures, drug delivery, and preventing post-surgical adhesions.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
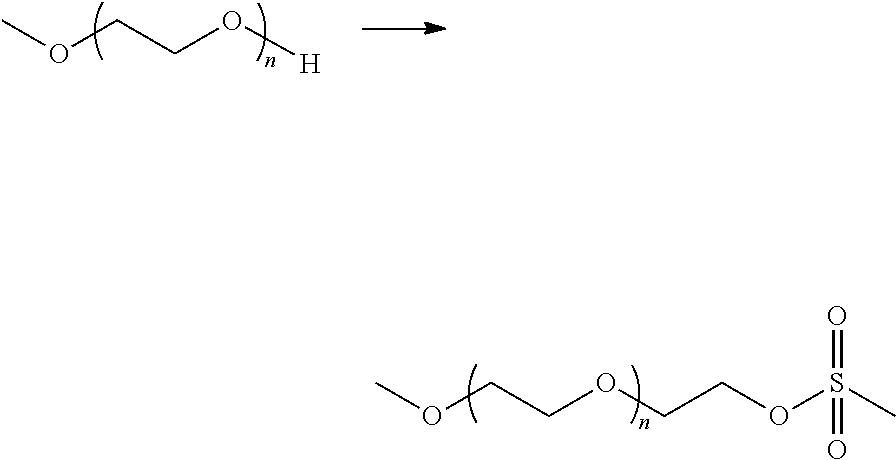
Method of dissolving an oxidized polysaccharide in an aqueous solution
InactiveUS20120094955A1High dissolution rateOrganic active ingredientsBiocideVascular anastomosisTissue repair
A method of dissolving an oxidized polysaccharide in an aqueous solution using an oligomer additive is described. The resulting aqueous solution of the oxidized polysaccharide may be used in combination with an aqueous solution comprising an amine-containing component to prepare hydrogel tissue adhesives and sealants for medical and veterinary applications, such as wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures such as intestinal anastomosis and vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, ophthalmic procedures, drug delivery, and to prevent post-surgical adhesions.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Negative pressure intestinal anastomosis protection devices
Owner:ETHICON INC
Oxidized cationic polysaccharide-based polymer tissue adhesive for medical use
A tissue adhesive formed by reacting an oxidized cationic polysaccharide containing aldehyde groups and amine groups with a multi-arm amine is described. The oxidized cationic polysaccharide-based polymer tissue adhesive may be useful for medical applications including wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures such as intestinal anastomosis and vascular anastomosis, ophthalmic procedures, drug delivery, anti-adhesive applications and as a bulking agent to treat urinary incontinence. Additionally, due to the presence of the positively charged amine groups on the oxidized polysaccharide, the polymer tissue adhesive disclosed herein may promote wound healing and blood coagulation, and may possess antimicrobial properties.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Invagination type glue ring lock catch fixed intestines fitting ring
The invention relates to a telescopic lock catch fastened intestinal anastomosis ring, belonging to a anastomosis device, in particular to a telescopic lock catch fastened intestinal anastomosis ring of the intestinal operation after the total stomach removal, providing a telescopic lock catch fastened intestinal anastomosis ring without intestinal anastomotic leakage, anastomotic stenosis and foreign body residue at the anastomotic and with few reflux, smooth passing of the holding substance and low medical service cost. The invention comprises an elastic ring, an inner ring and an external ring; wherein, a plurality of an annular inner grooves are arranged at the bottom of the inner ring, a clasp is arranged at the inner side of the inner ring; a plurality of annular outer grooves are arranged at the bottom of the external ring, the barb arranged at the inner side of the bottom of the external ring and the annular clasp forms a lock catch.
Owner:刘忠臣
Novel intestinal anastomosis ring
PendingCN109480943AAvoid narrow situationsPromote healingSurgical staplesIntestinal structureForeign body
The invention relates to the technical field of medical instruments, in particular to a novel intestinal anastomosis ring. The anastomosis ring comprises a ring, a nail body, a connecting ring and a supporting frame. The ring is provided with a hole, the nail body passes through the hole in the ring and is connected with the ring, the nail body is fixed on the connecting ring, and the supporting frame is fixed at the lower end of the connecting ring. The novel intestinal anastomosis ring is made of a degradable material, a nail body punching fixing mode is adopted, and the supporting frame isdesigned at the rear end of the nail body, which not only can avoid residual in the body which causes a patient to have a foreign body irritating feeling, promotes the healing of a affected part and reduces the medical cost, but also has a better fixing anastomosis effect and can also effectively avoid the narrowing of stomas.
Owner:JIANGSU QIANJING MEDICAL EQUIP
Medical intestinal anastomosis ring made of degradable magnesium alloy
InactiveCN102793951AGuaranteed stabilityInhibition of abnormal excitability of nervesSurgeryCoatingsIntestinal wallsMetal nail
The invention discloses a medical intestinal anastomosis ring made of a degradable magnesium alloy, and relates to the field of medical apparatus and instruments and the medical intestinal anastomosis ring is used for solving the problem that the existing intestinal anastomosis material is not degradable. The medical intestinal anastomosis ring is made of a degradable magnesium alloy, and a poly lactic-co-glycolic acid copolymer coating or modified chitosan coating is coated on the surface medical intestinal anastomosis ring. Mg<2+> in the degradable product of the medical intestinal anastomosis ring is the second important positive ion in human cells and is harmless to a human body. The medical intestinal anastomosis ring is in contact type anastomosis, avoids damage to intestinal wall by suture or metal nails, cause less tissue wounds, is minium in the tissue necrosiss degree of the whole anastomosis stomas, can be degradable after being implanted in a human body for 2-3 weeks, and has no permanent foreign body reaction, thus effectively reducing scars at the anastomosis stomas, thereby having low stenosis incidence rate of the anastomosis stomas.
Owner:HARBIN MEDICAL UNIVERSITY +1
Magnetic device for side-to-side intestinal anastomosis
The invention discloses a magnetic device for side-to-side intestinal anastomosis. The magnetic device comprises a magnetic ring set, wherein the magnetic ring set consists of two pairs of annular magnetic rings with thickness ranging from 2 to 4mm; and each pair of magnetic rings consists of a first magnetic ring and a second magnetic ring. By performing the side-to-side intestinal anastomosis of seamless seaming by using the magnetic attraction of the two pairs of magnetic rings with both proper thickness and shape, the device prevents the defects of easy dehiscence and easy bleeding of perienchyma of the anastomotic stoma produced by a gastrointestinal stapler in the side-to-side intestinal anastomosis, obstruction of the anastomotic stoma and incomplete seaming; and because the two pairs of magnetic rings used in the side-to-side intestinal anastomosis can be removed from the body along with excrement after a certain period, the magnetic rings cannot be remained in human body to cause inconvenience and discomfort.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Intestinal anastomotic stoma protecting device
The invention discloses an intestinal anastomotic stoma protecting device which is used for supplying protection to the rectum after intestinal anastomosis surgery. The intestinal anastomotic stoma protecting device comprises a hollow elastic support part, a shielding cover which is connected with the elastic support part and provided with openings at the two ends and a traction part detachably connected with the elastic support part; when the intestinal anastomotic stoma protecting device is in the state of protecting an anastomotic stoma, the elastic support part is arranged at the far end of the anastomotic stoma, the shielding cover circumferentially shields the anastomotic stoma in the intestine, and the near end of the traction part penetrates through the shielding cover to be exposed out of a human body. According to the intestinal anastomotic stoma protecting device, the anastomotic stoma can be effectively protected and prevented from being polluted by excreta; in addition, after the physiological tissue of the anastomotic stoma grows well, the intestinal anastomotic stoma protecting device can be directly taken out without needing secondary surgery, convenience and rapidness are achieved, and secondary hurt cannot be caused to a patient.
Owner:TOUCHSTONE INTERNATIONAL MEDICAL SCIENCE CO LTD
Aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharides
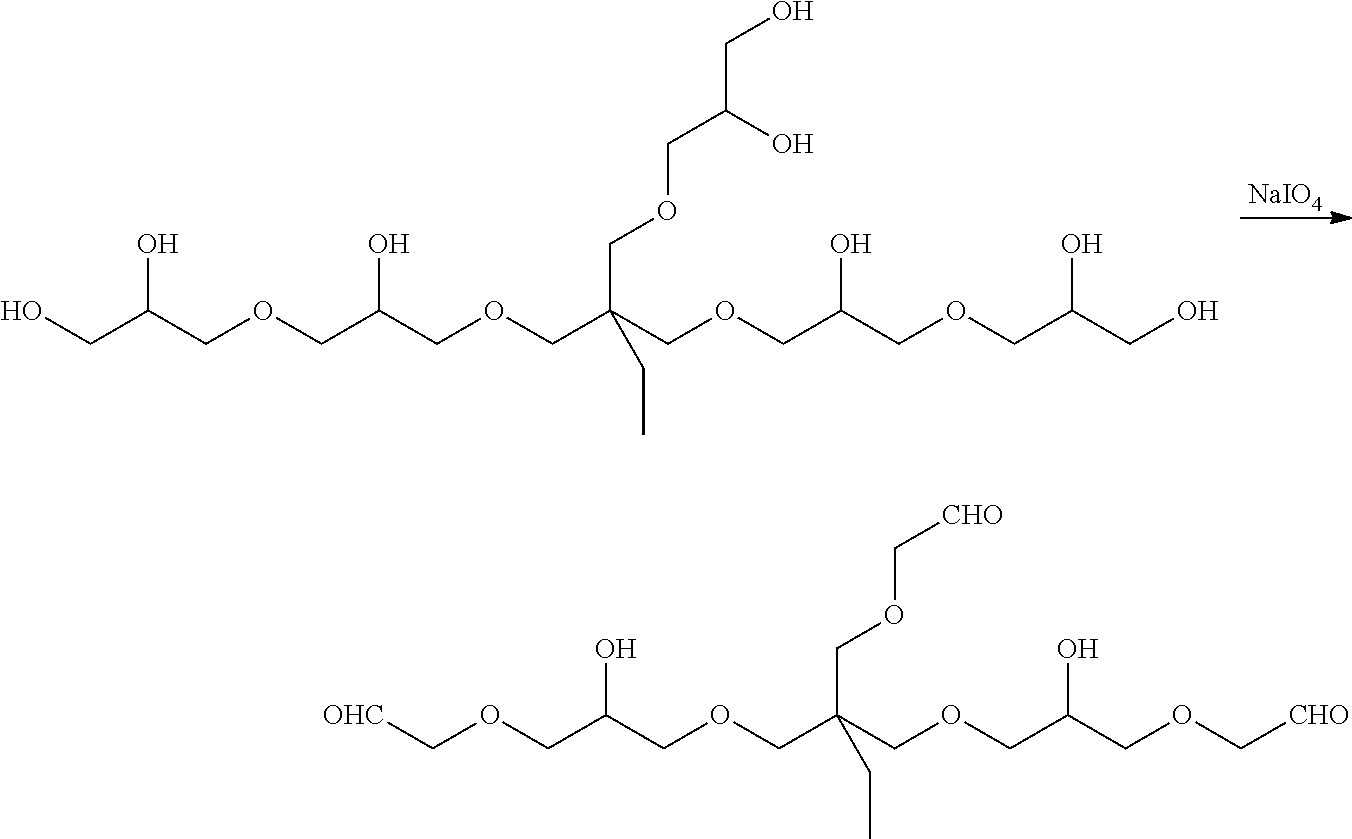
Novel aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharide compositions containing pendant dialdehyde groups are described that are more stable in aqueous solution than oxidized polysaccharides. The aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharides may be reacted with various amine-containing polymers to form hydrogel tissue adhesives and sealants that may be useful for medical applications such as wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures such as intestinal anastomosis and vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, preventing leakage of fluids such as blood, bile, gastrointestinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid, ophthalmic procedures, drug delivery, and preventing post-surgical adhesions.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharides
Novel aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharide compositions containing pendant dialdehyde groups are described that are more stable in aqueous solution than oxidized polysaccharides. The aldehyde-functionalized polysaccharides may be reacted with various amine-containing polymers to form hydrogel tissue adhesives and sealants that may be useful for medical applications such as wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures such as intestinal anastomosis and vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, preventing leakage of fluids such as blood, bile, gastrointestinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid, ophthalmic procedures, drug delivery, and preventing post-surgical adhesions.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Tissue adhesive and sealant comprising polyglycerol aldehyde
A tissue adhesives and sealant formed by reacting a polyglycerol aldehyde with a water-dispersible, multi-arm amine is described. The tissue adhesive and sealant may be useful for medical and veterinary applications, including, but not limited to, wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures such as intestinal anastomosis and vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, preventing leakage of fluids such as blood, bile, gastrointestinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid, ophthalmic procedures, drug delivery, and to prevent post-surgical adhesions.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Polymer-based tissue-adhesive form medical use
Tissue adhesives formed by reacting poly(hydroxylic) compounds derivatized with acetoacetate groups and / or polyamino compounds derivatized with acetoacetamide groups with an amino-functional crosslinking compound are disclosed.The use of the tissue adhesives for medical and veterinary applications such as topical wound closure; and surgical procedures, such as intestinal anastomosis, vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, and ophthalmic procedures; drug delivery; and anti-adhesive applications are described.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Protein-based polymer tissue adhesives for medical use
Tissue adhesives formed by crosslinking albumin and / or gelatin with certain polyamines and / or polycarboxylates using a water-soluble carbodiimide are disclosed. The use of the tissue adhesives for medical and veterinary applications such as topical wound closure; and surgical procedures, such as intestinal anastomosis, vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, and ophthalmic procedures; drug delivery; anti-adhesive applications; and as a bulking agent to treat urinary incontinence are described.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
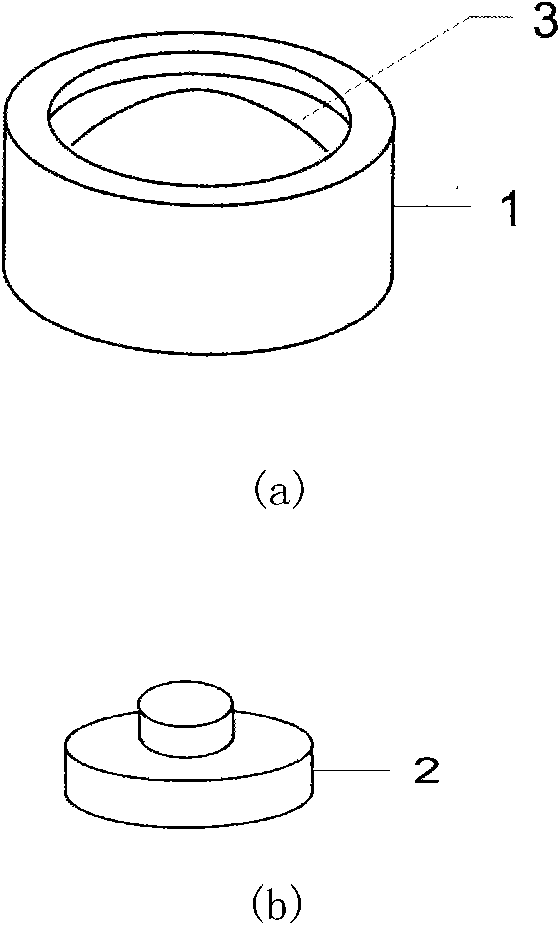
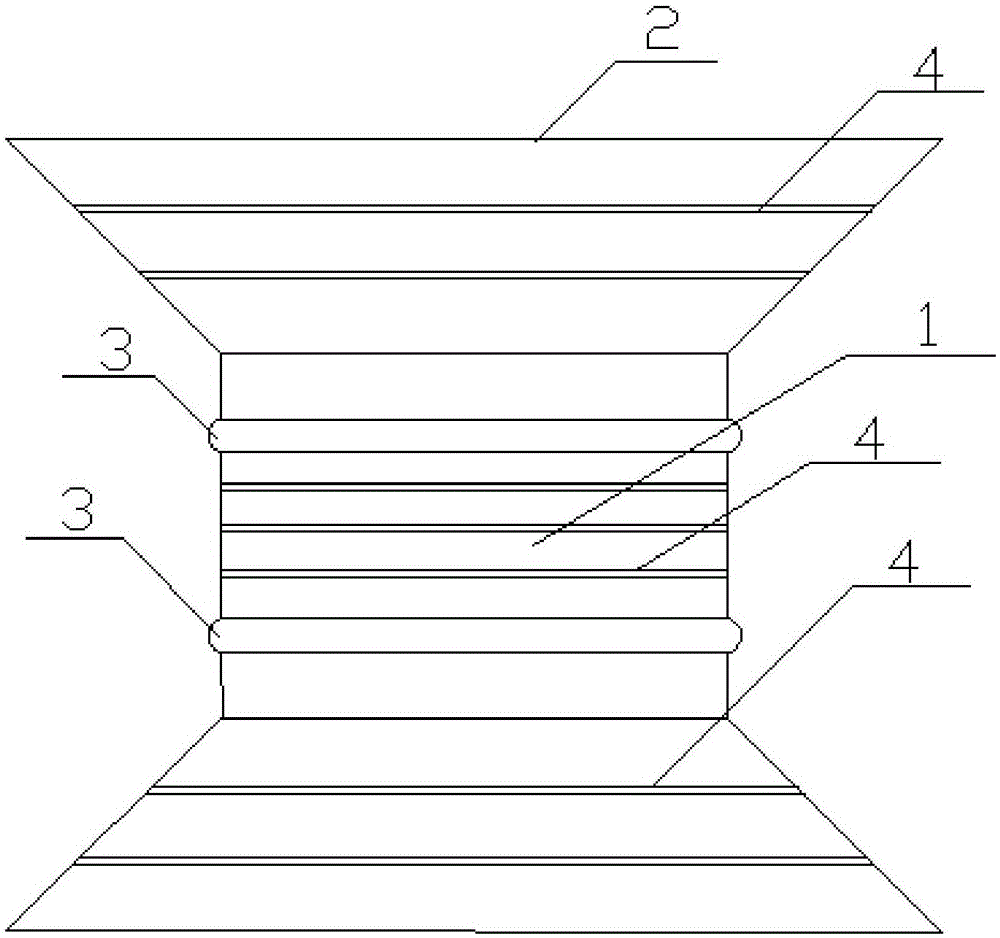
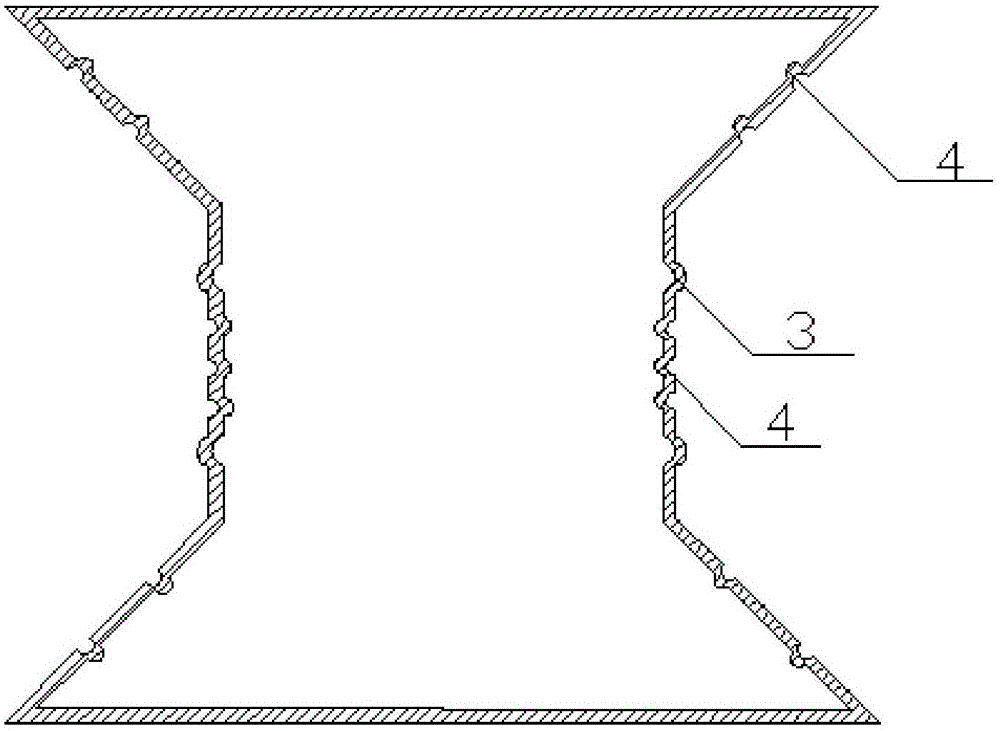
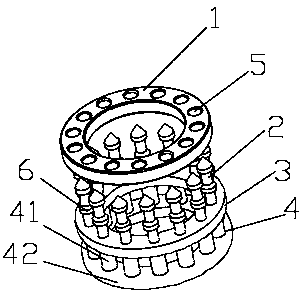
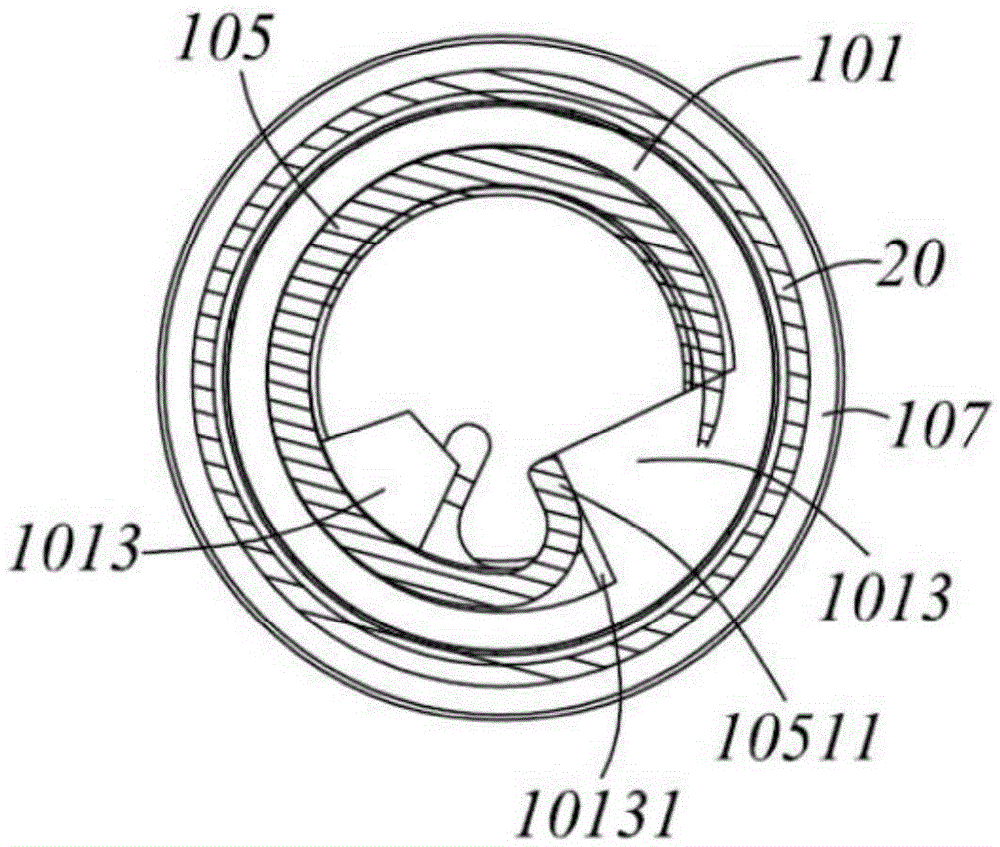
Intestinal anastomosis ring
PendingCN106419987ALow costGood biocompatibilitySurgical staplesIntestinal anastomosisGeneral surgery
The invention discloses an intestinal anastomosis ring. The intestinal anastomosis ring comprises a first half ring (1) and a second half ring (2) which are mutually anastomotic. The inner ring of each of the first half ring (1) and the second half ring (2) is an intestinal channel (3). One end of the first half ring (1) is provided with an elastic guide sleeve (4). The end of the elastic guide sleeve (4) is provided with a reverse lock head (5) with the thickness being larger than the thickness of the body part of the elastic guide sleeve (4). One end of the second half ring (2) is provided with an axial anastomosis ring groove (6) matched with the elastic guide sleeve (4). A reverse lock groove (7) matched with the reverse lock head (5) is formed in the bottom of the axial anastomosis ring groove (6). The first half ring (1) and the second half ring (2) are connected with each other in a clamped manner through the reverse lock head (5) and the reverse lock groove (7) so as to form the intestinal anastomosis ring. The intestinal anastomosis ring is simple to operate, stable and reliable in connection and few in used materials.
Owner:CENT SOUTH UNIV
Aldol-crosslinked polymeric hydrogel adhesives
Adhesives formed by reacting an oxidized polysaccharide with a poly(hydroxylic) compound derivatized with acetoacetate groups in the presence of a base catalyst are disclosed. The use of the adhesives for medical and veterinary applications such as topical wound closure; and surgical procedures, such as intestinal anastomosis, vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, and ophthalmic procedures; and drug delivery are described. The adhesive may also be used for industrial and consumer applications.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
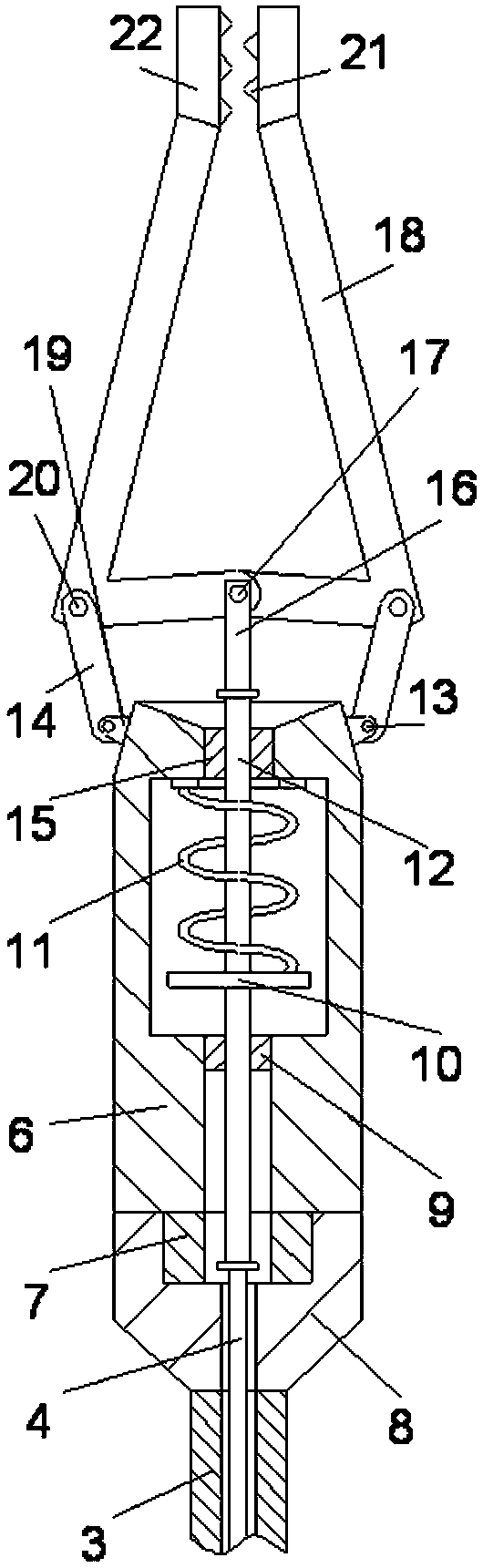
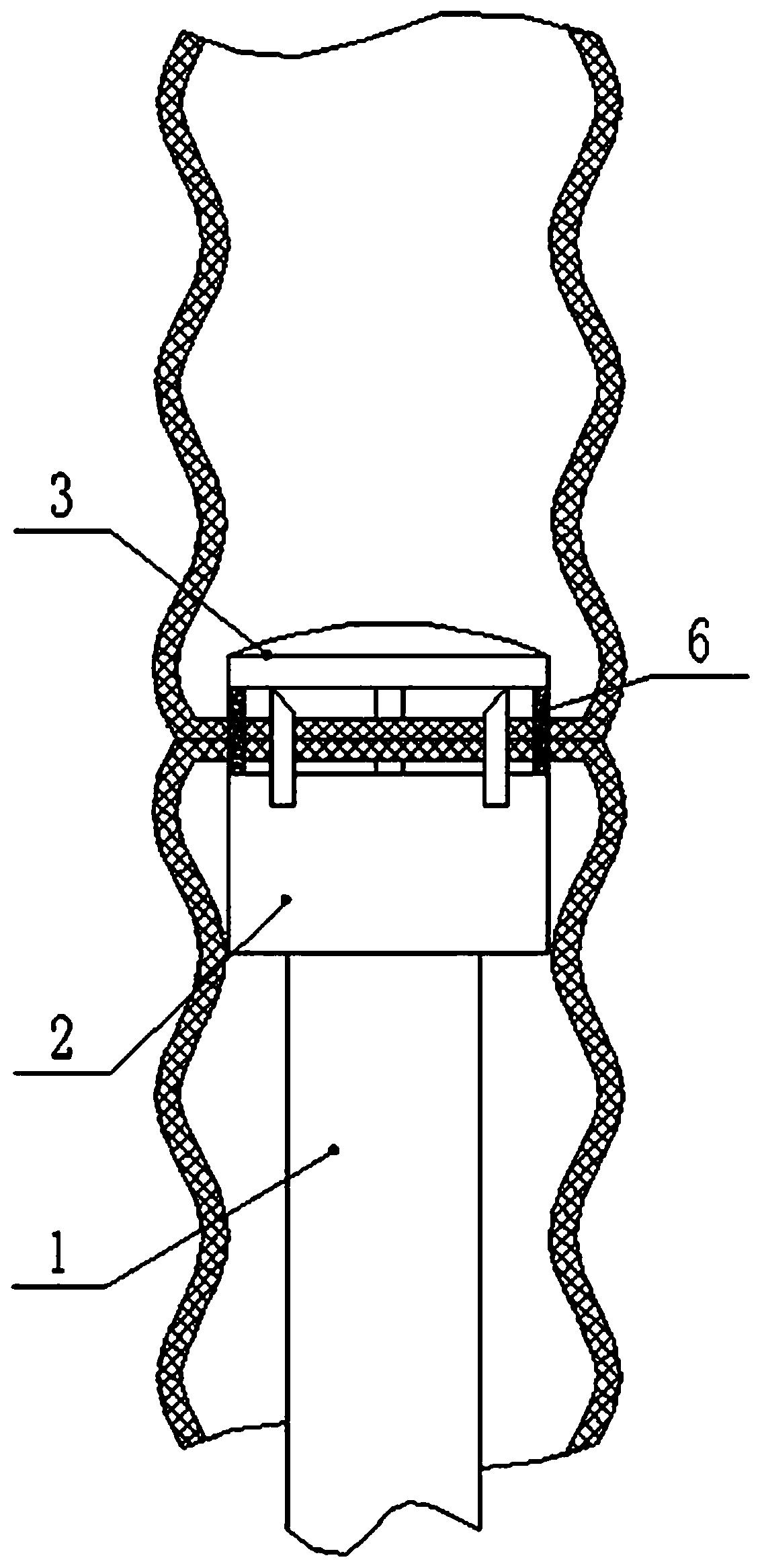
Intestinal anastomosis machine for infants
The invention discloses an intestinal anastomosis machine for infants. The intestinal anastomosis machine comprises an operating device and an auxiliary device, wherein the operating device comprisesa grasping handle, a wire passing pipe and a motion head; a hydraulic cylinder is mounted at the lower part of the inner side of the grasping handle; keys are mounted at the upper part of the front side of the grasping handle; an electricity connector is mounted at the bottom end of the grasping handle; the wire passing pipe is fixedly mounted at the top end of the grasping handle; a threaded seatis fixedly mounted at the top end of the wire passing pipe; the motion head is rotatably connected to the upper part of the threaded seat; and a pull rope is fixedly mounted at the top end of the hydraulic cylinder. The intestinal anastomosis machine disclosed by the invention is reasonable in structural design and ideal in matching effects; during operation, the situation that the fixation of the end surface is not firm, so that deflection and malposition are generated can be avoided; when the intestinal anastomosis machine is applied to a tiny intestine, the sewing operation is convenient to perform through arranged auxiliary equipment, and the surgery effect is better; compared with a rotation closing manner, the intestinal anastomosis machine disclosed by the invention is stable in clamping, and the situation that an intestine body slides from the open end can be avoided; and the technique of the intestinal anastomosis machine is subsidized by the 2017 National Natural Science Foundation of China (81770512) and 2018 "Sanming Project "(SZSM201812055) of Shenzhen city National Health and Family planning Commission.
Owner:SHENZHEN CHILDRENS HOSPITAL
Tissue adhesive and sealant comprising polyglycerol aldehyde
A tissue adhesives and sealant formed by reacting a polyglycerol aldehyde with a water-dispersible, multi-arm amine is described. The tissue adhesive and sealant may be useful for medical and veterinary applications, including, but not limited to, wound closure, supplementing or replacing sutures or staples in internal surgical procedures such as intestinal anastomosis and vascular anastomosis, tissue repair, preventing leakage of fluids such as blood, bile, gastrointestinal fluid and cerebrospinal fluid, ophthalmic procedures, drug delivery, and to prevent post-surgical adhesions.
Owner:ACTAMAX SURGICAL MATERIALS
Novel disposable leakage-proof tubular anastomat
PendingCN111493962AReduce incidenceReduce consumptionSurgical staplesIntestinal wallsIntestine obstruction
The invention discloses a novel disposable leakage-proof tubular anastomat, which comprises an annular knife arranged in a knife body assembly and a nail propping seat connected with the knife body assembly, and is characterized by further comprising an annular gasket concentrically arranged in the knife body assembly and the nail propping seat; wherein the cutter body assembly is provided with two groups of annular cutters comprising an outer-ring annular cutter and an inner-ring annular cutter; the tip of the outer-ring annular cutter is in contact with the outer contour surface of the annular gasket, and the inner-ring annular cutter penetrates through the inner ring of the annular gasket. The intestinal anastomat has the advantages that the redundant intestinal wall of the anastomoticnear-end intestinal canal droops, the anastomotic stoma is protected, the anastomotic stoma cannot crack due to too high pressure in the intestinal cavity, anastomotic stoma leakage is avoided, and the intestinal anastomotic near-end intestinal canal is suitable for intestinal anastomosis under the condition of intestinal obstruction. Operation risks can be reduced, medical resource consumption isreduced, and the risk of enterostomy of a patient is reduced.
Owner:闫兆鹏
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com