Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
441 results about "Oral treatment" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Oral treatment is a non-invasive treatment option. It is also convenient option, just swallowing some tablets on regular basis. Some oral treatments for Peyronie's disease are relatively cheap, while others are more expensive.
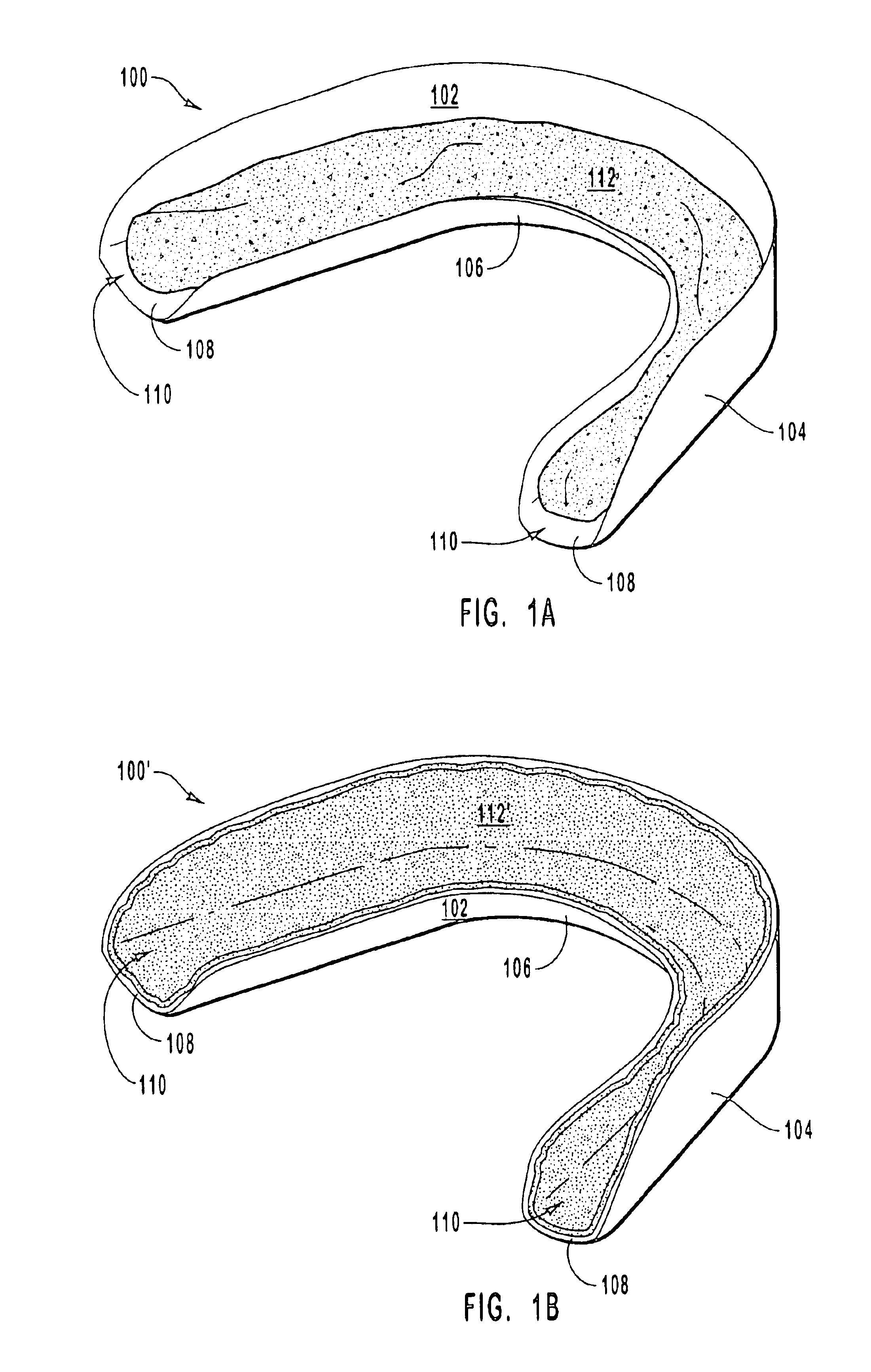
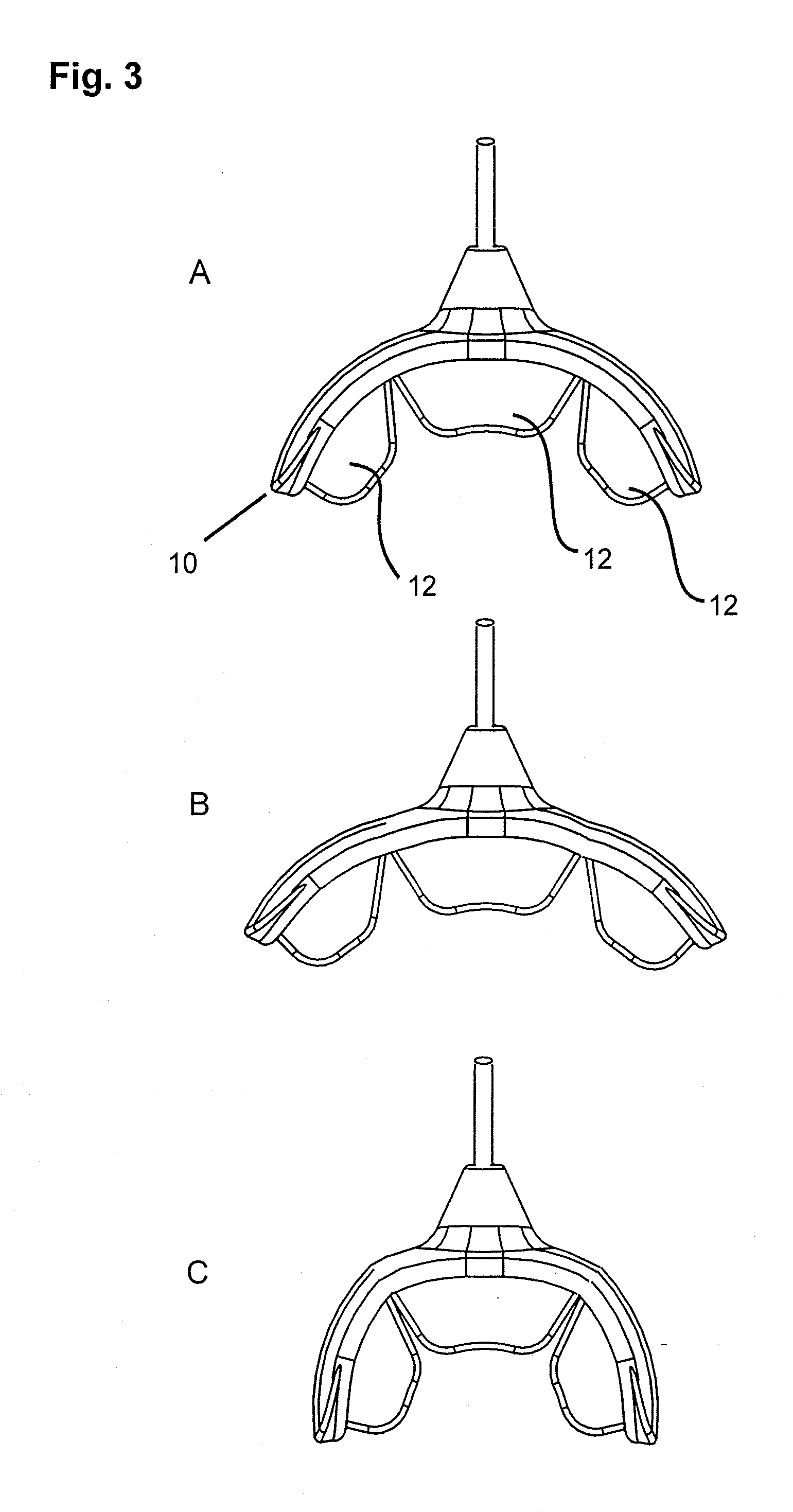
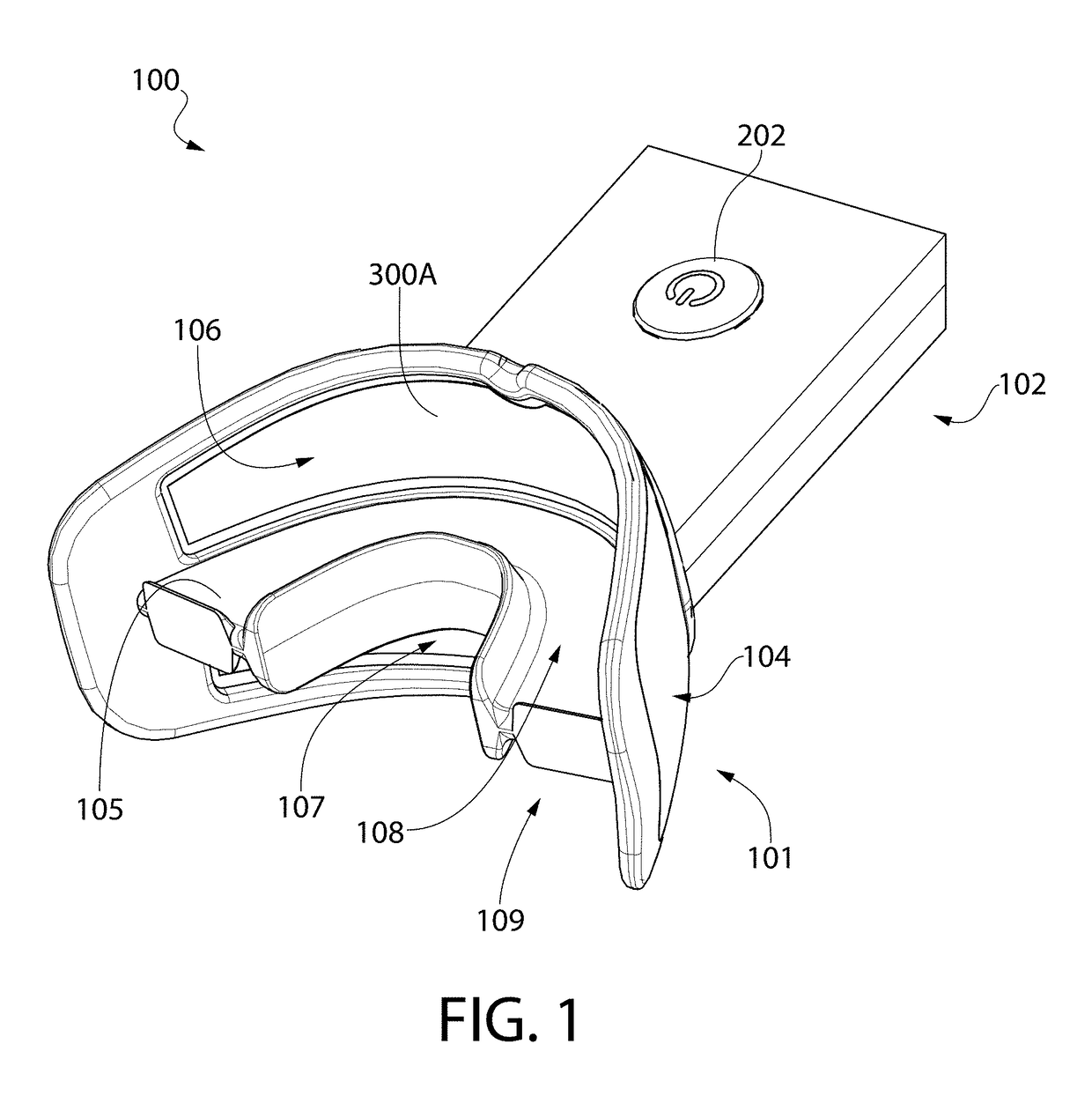
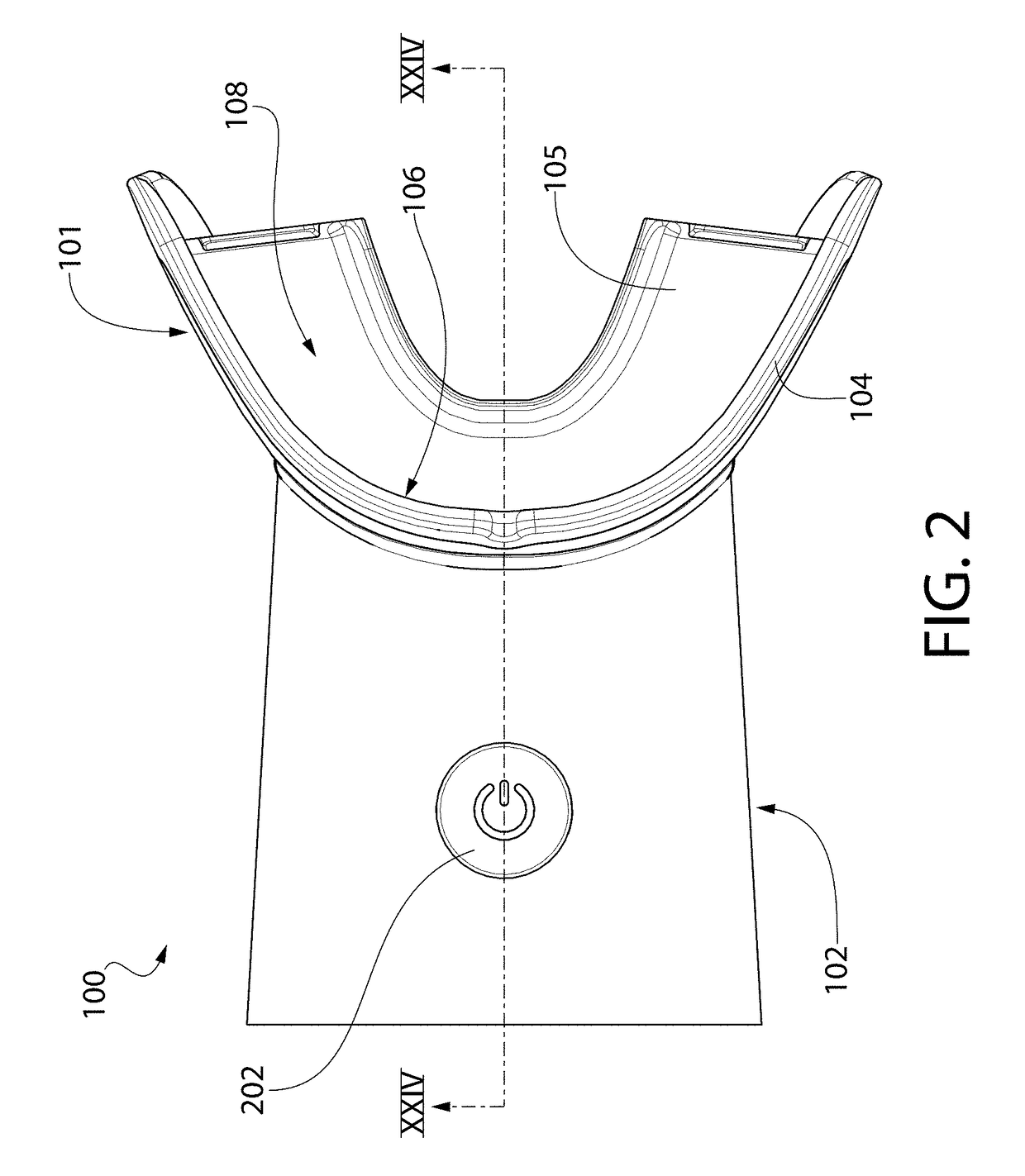
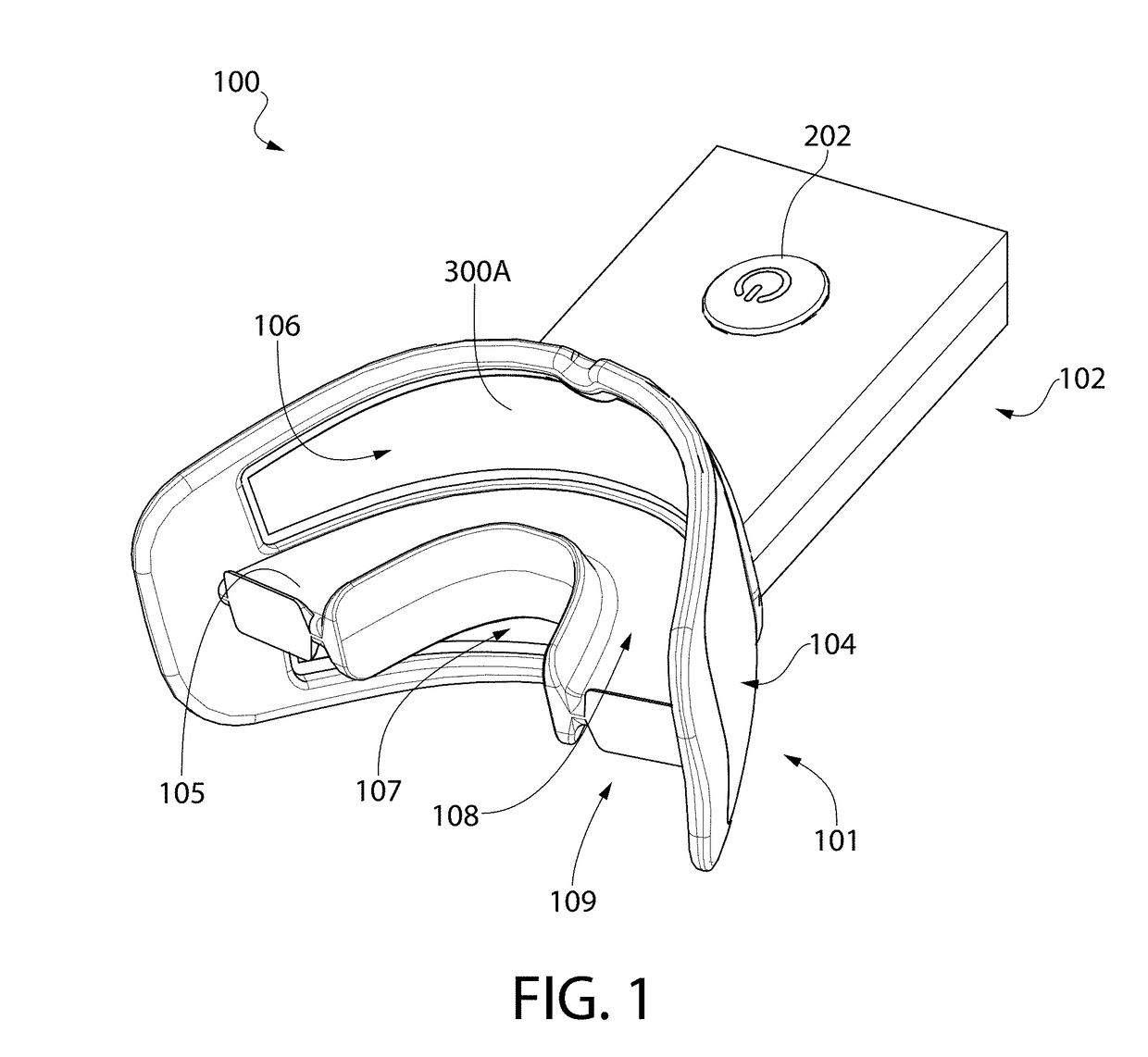
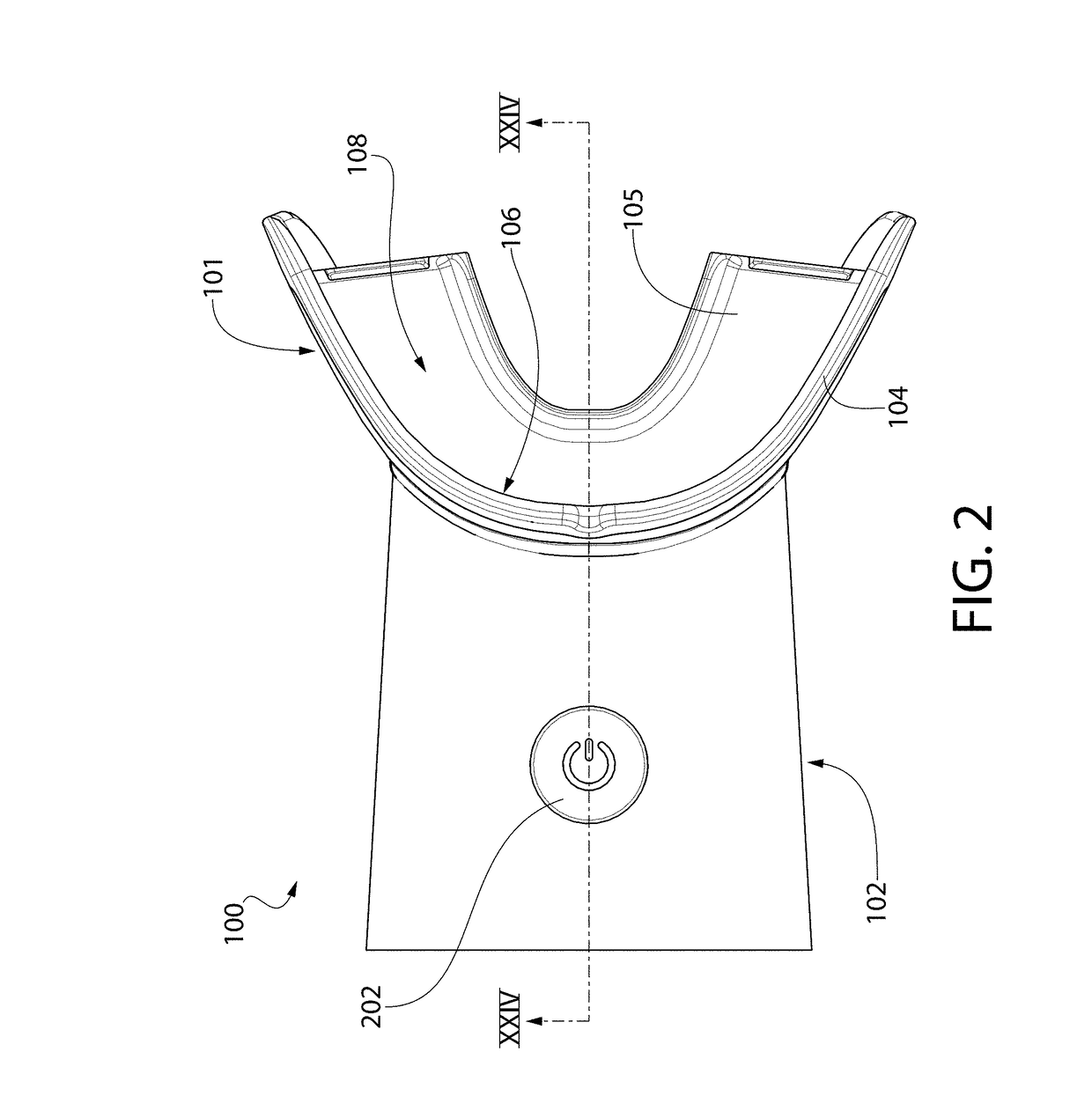
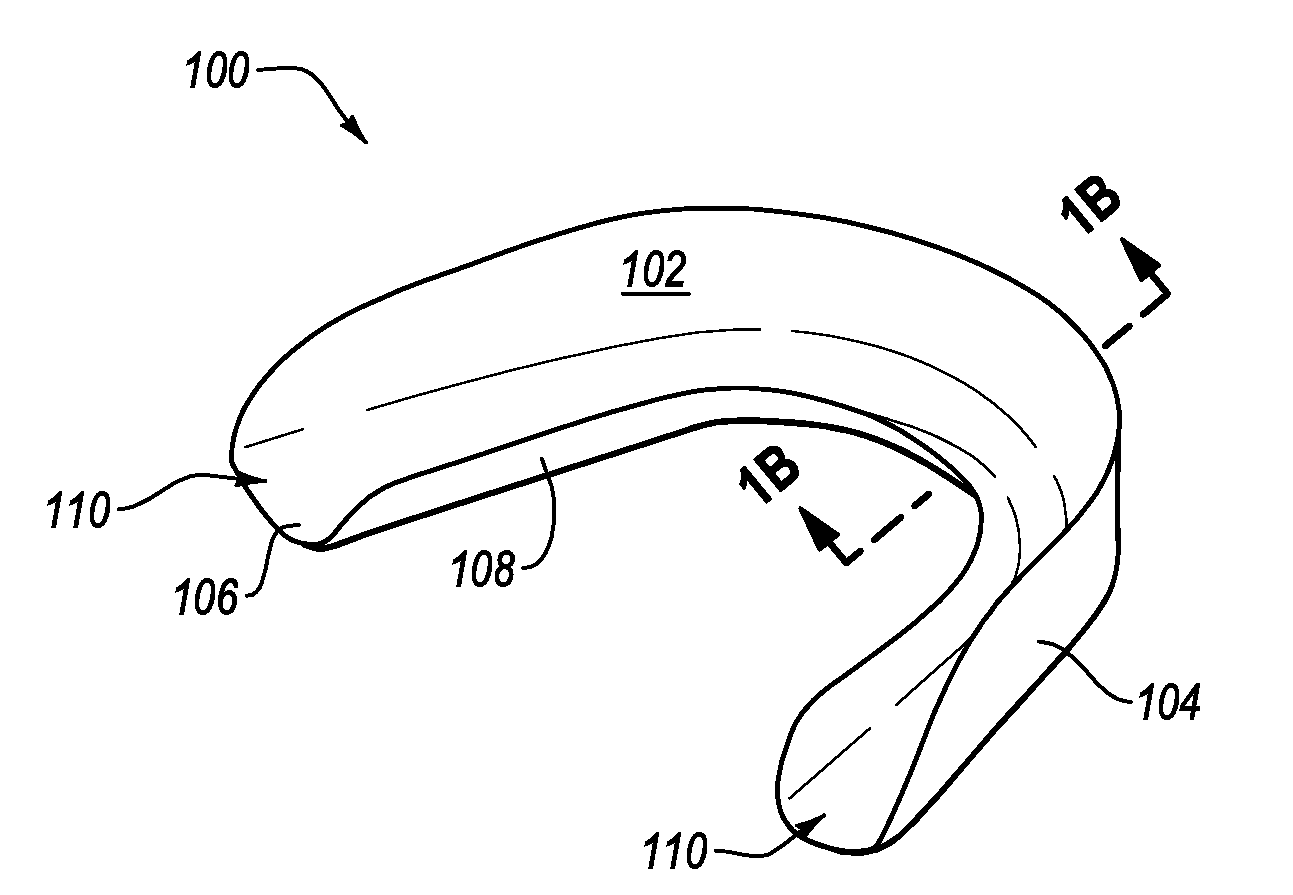
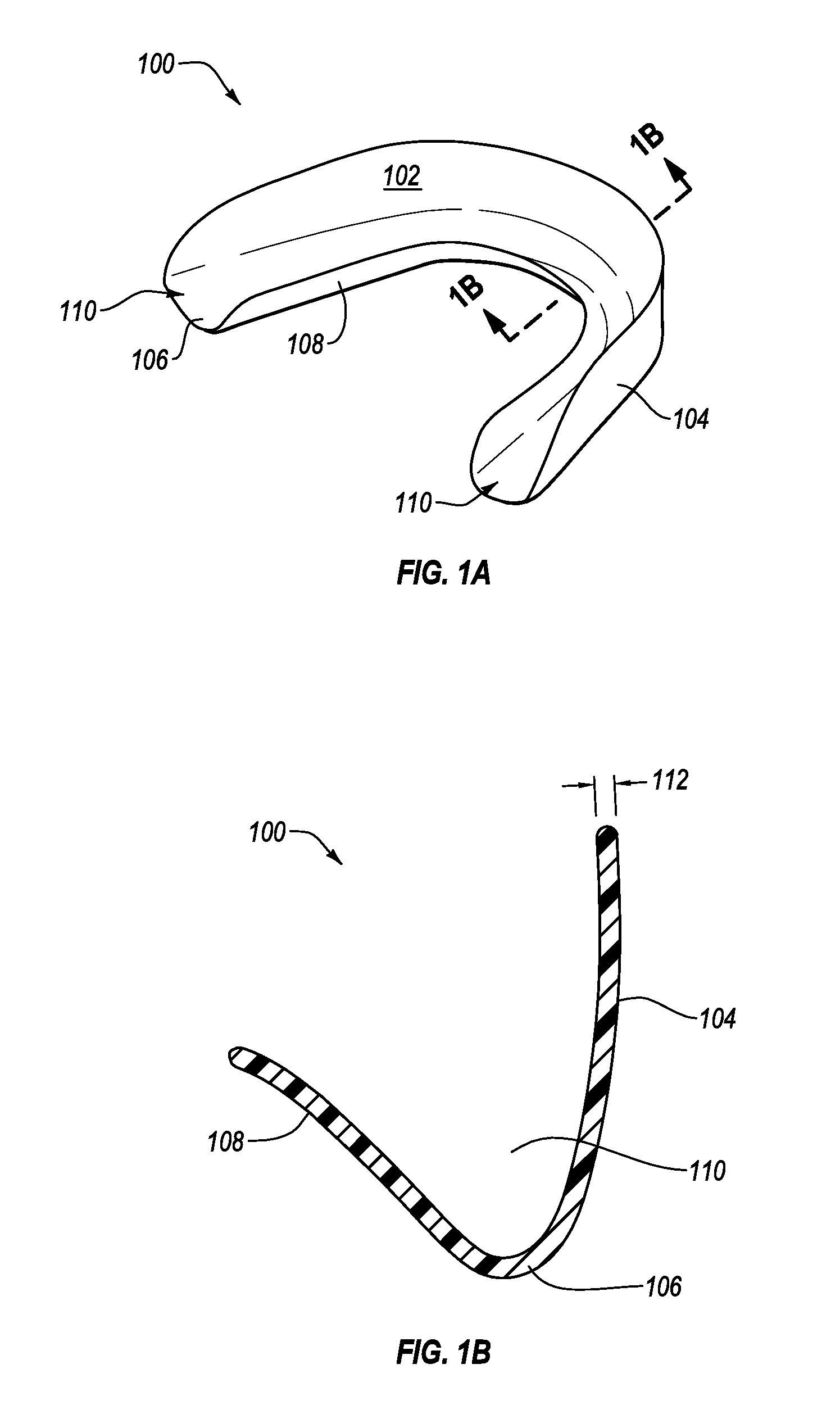
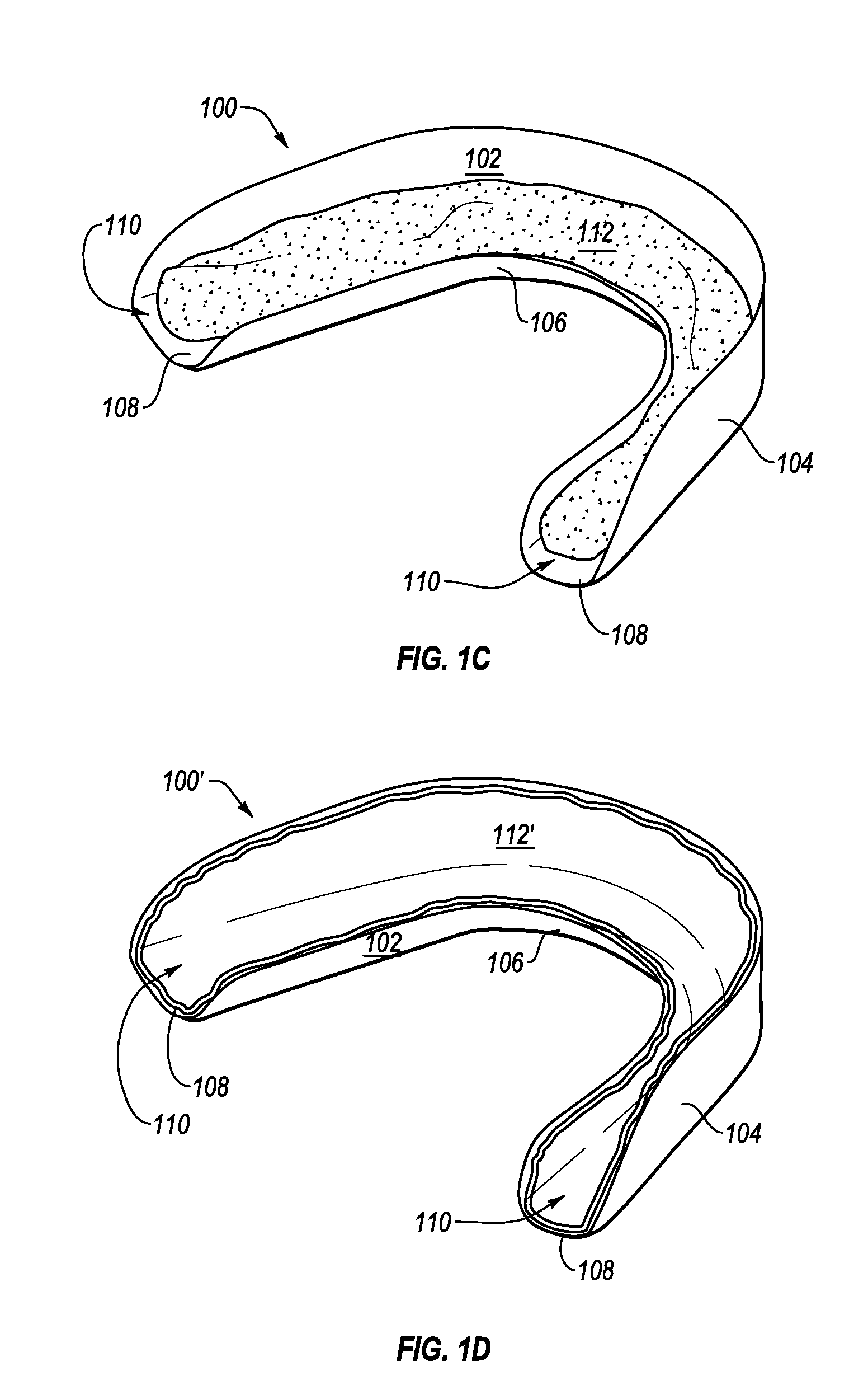
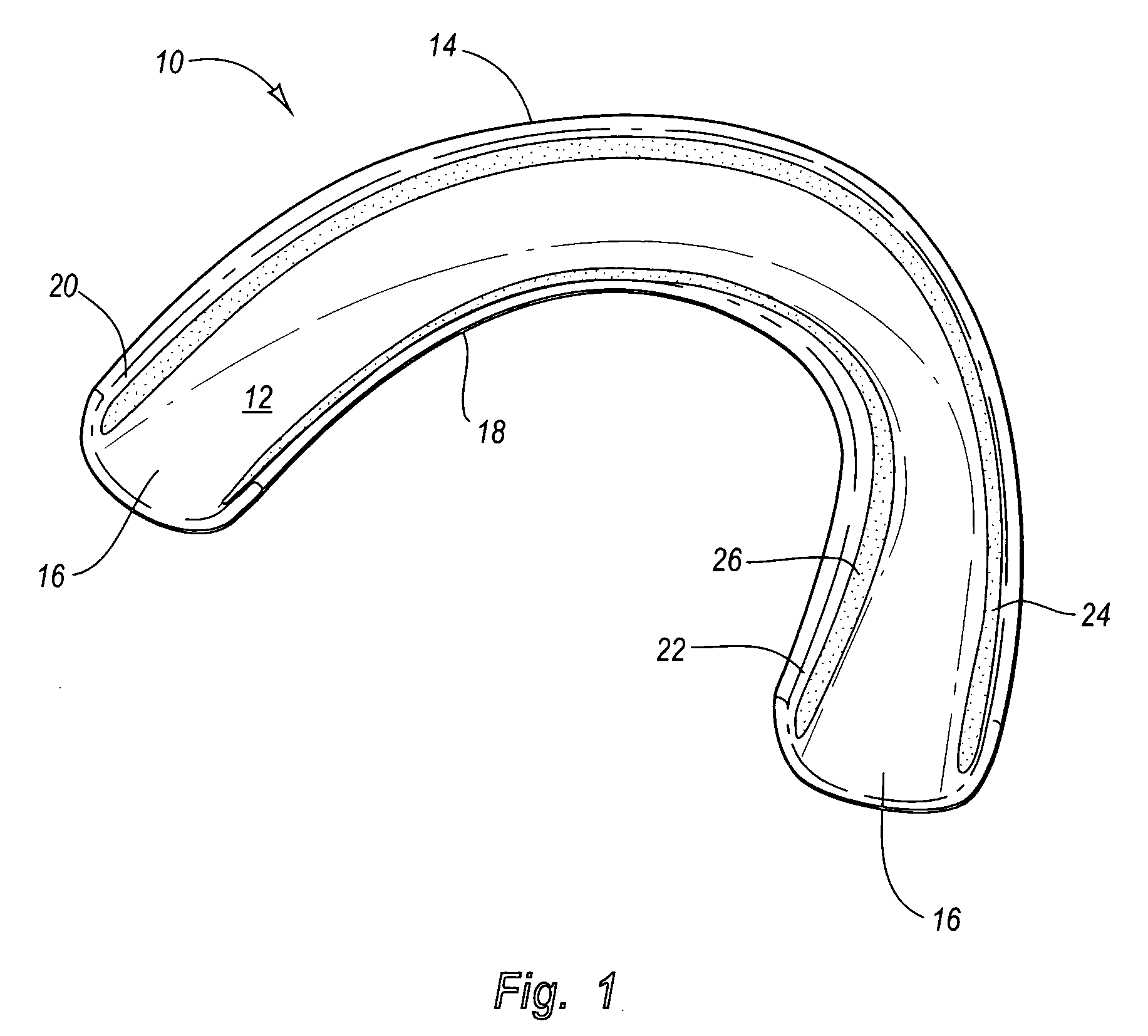
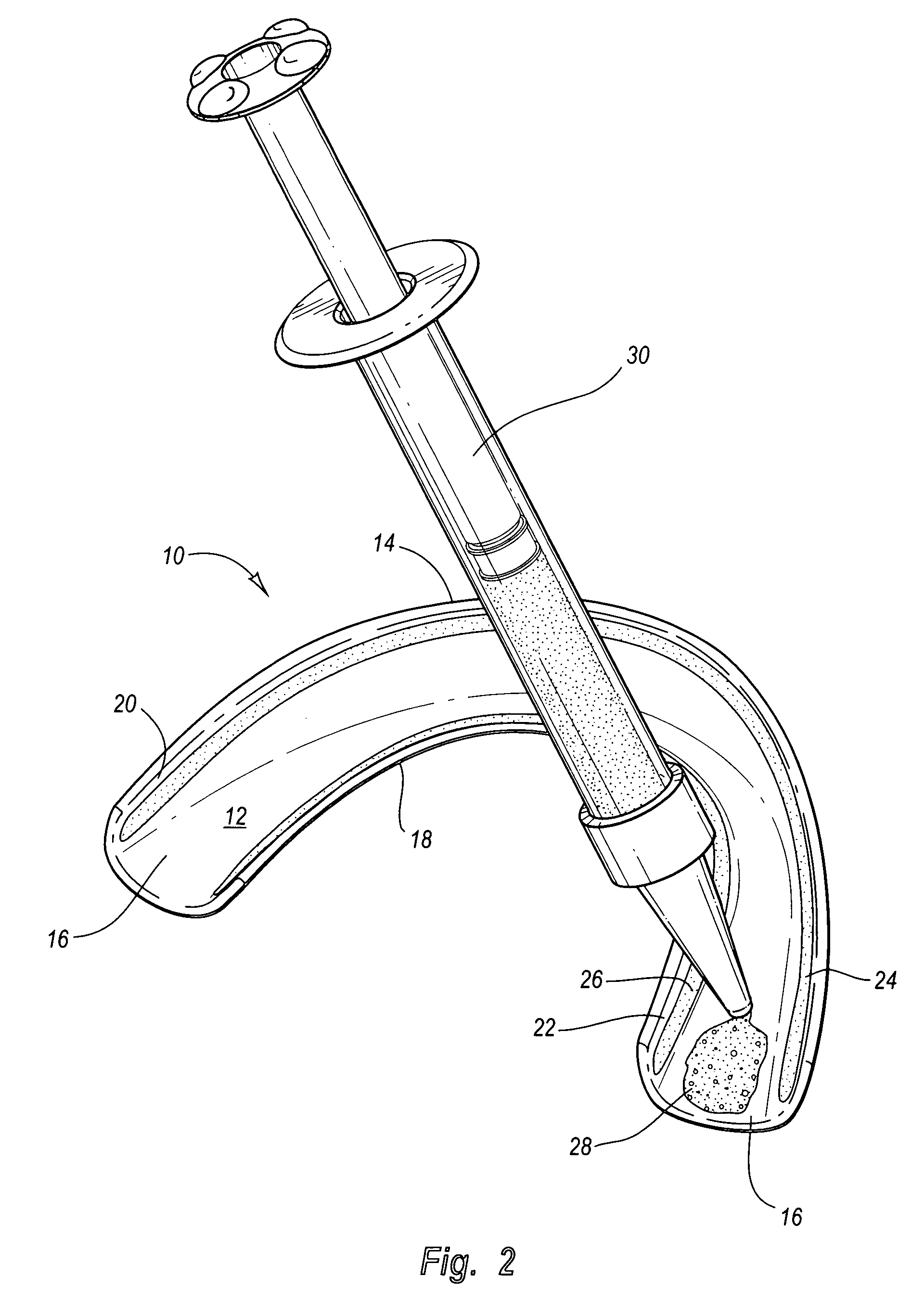
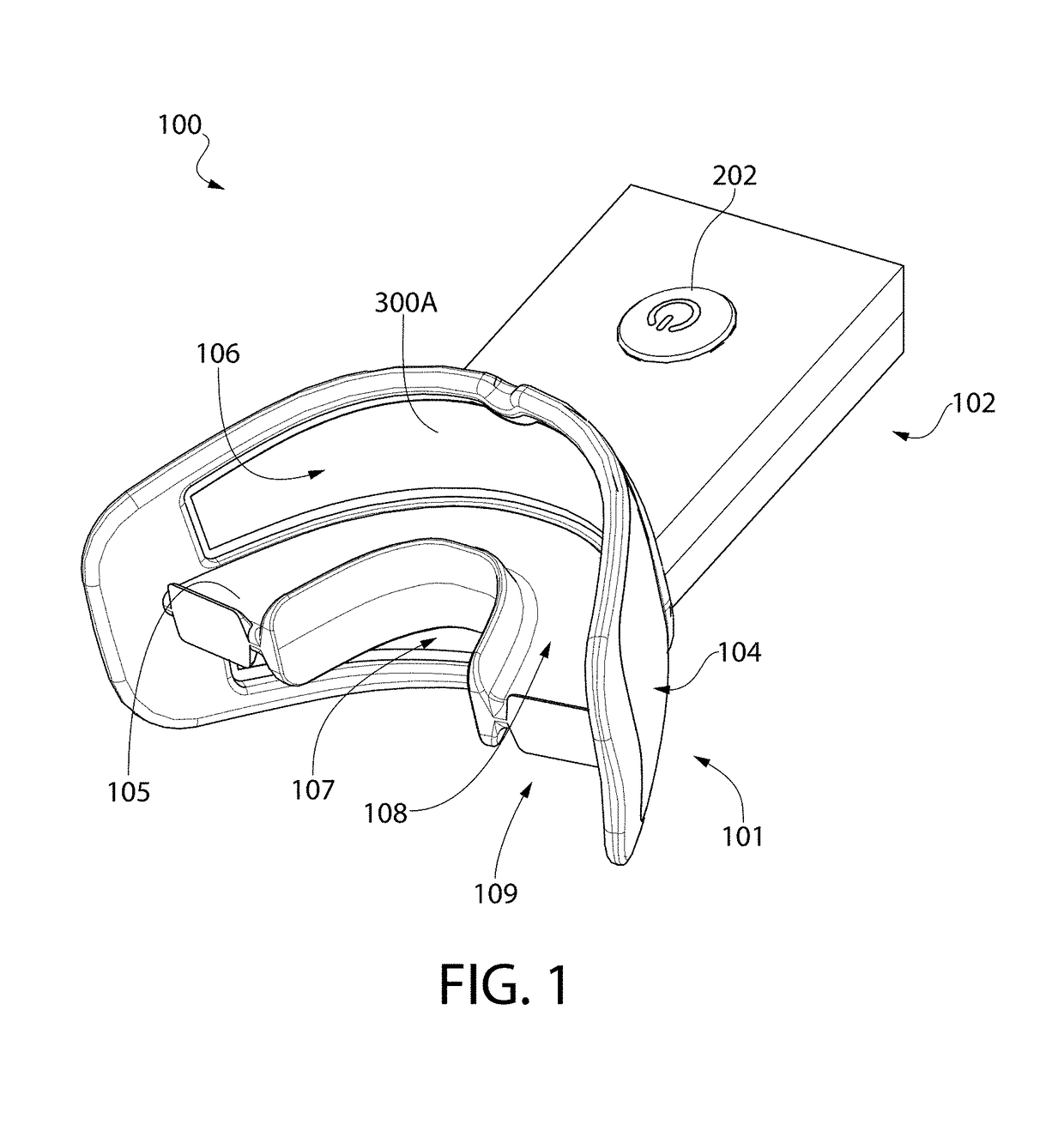
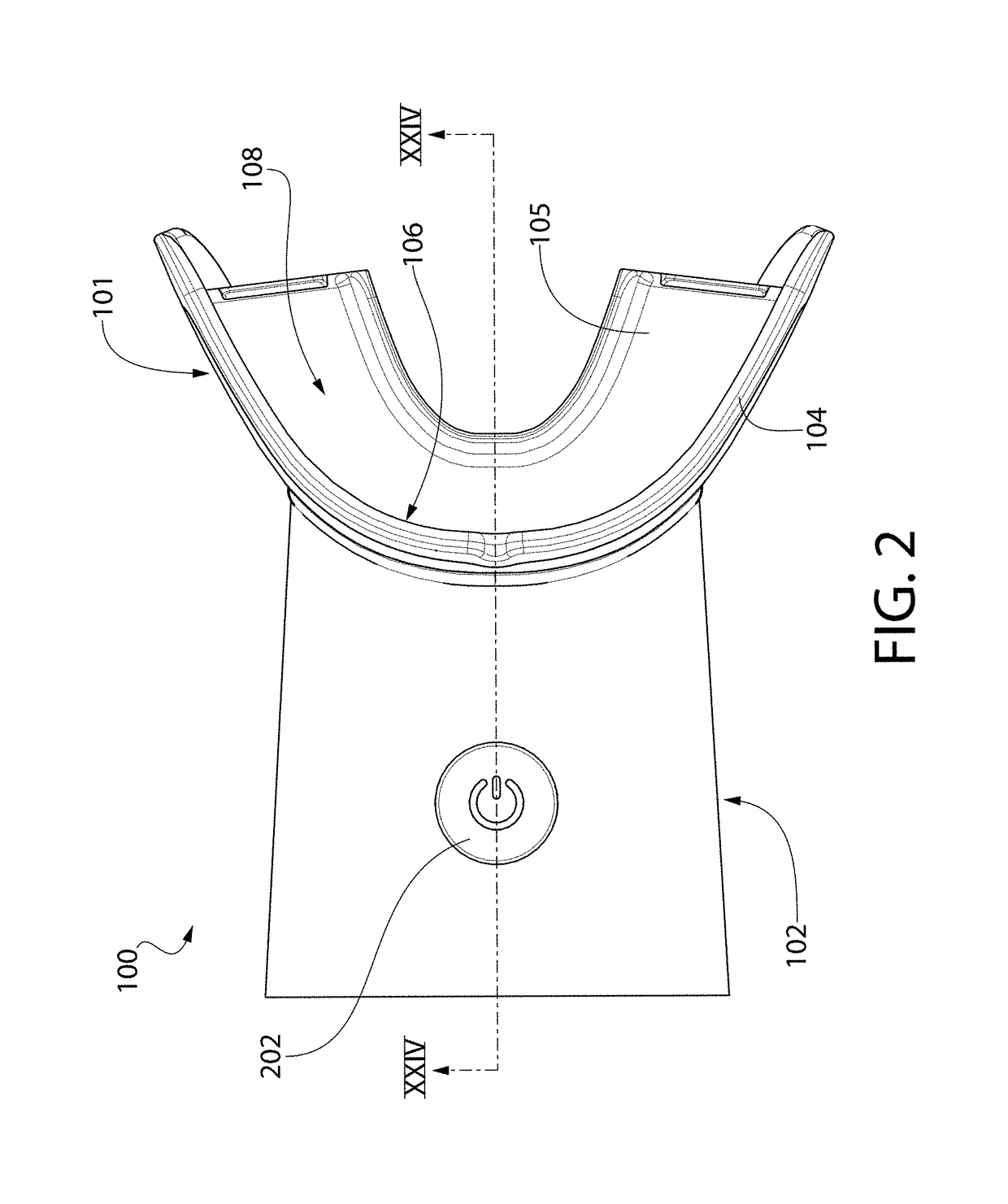
Pre-impregnated disposable dental substance delivery mouthpiece
InactiveUS20030003421A1Increase the patient's comfortPromote healingTeeth fillingCoffinsOral treatmentAdhesive
Disposable dental mouthpiece-strip which has been pre-impregnated with dental substance which can either be placed in the mouth by the user or inserted in the mouth by a dentist for oral treatments, such as teeth whitening treatments, fluoride treatments, or medical treatments, such as the application of anasthetic or antimicrobal / antiseptic treatments. The mouthpiece-strip is made with a foldable structure such as a thin strip of wax with a section of porous material (sponge) that holds the treatment dental product (liquid or gel). The mouthpiece-strip is disposable; the amount of time it is worn is determined by the type of dental treatment. The mouthpiece-strip may be adjusted in size by cutting it with scissors. The wax used for the mouthpiece is non-toxic and allows for a perfect adjustment in the mouth by contouring to the teeth during adjustment by the user. To enhance the fit in the mouth, the inner surface of the mouthpiece-strip may contain a thin layer of non-toxic sticky adhesive. The porous (sponge) strip attached to the wax strip is an inert, nontoxic material which is easy to process and inexpensive. It is attached to the wax strip with a non-toxic adhesive.
Owner:BESTENHEIDER THIERRY +1
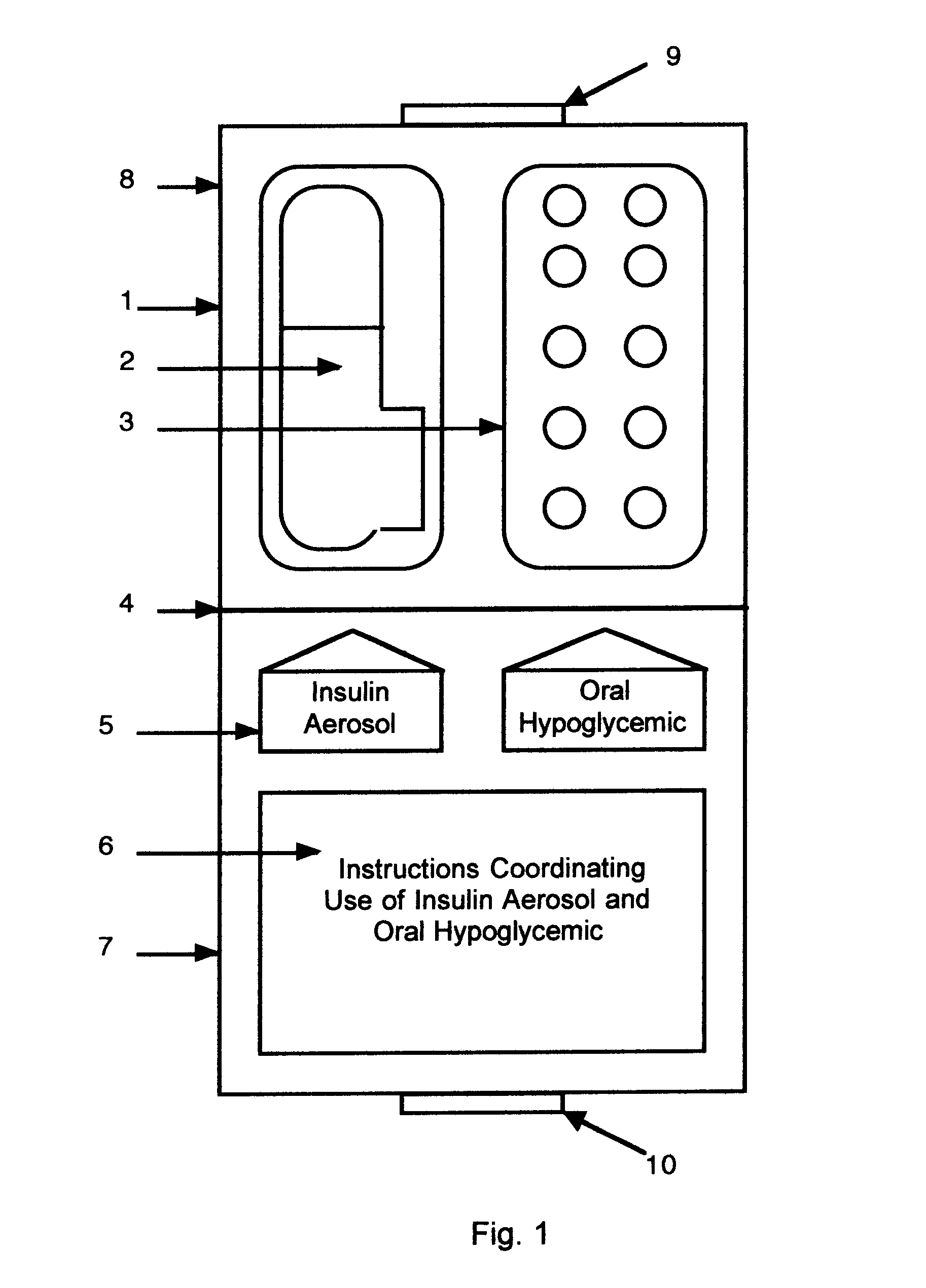
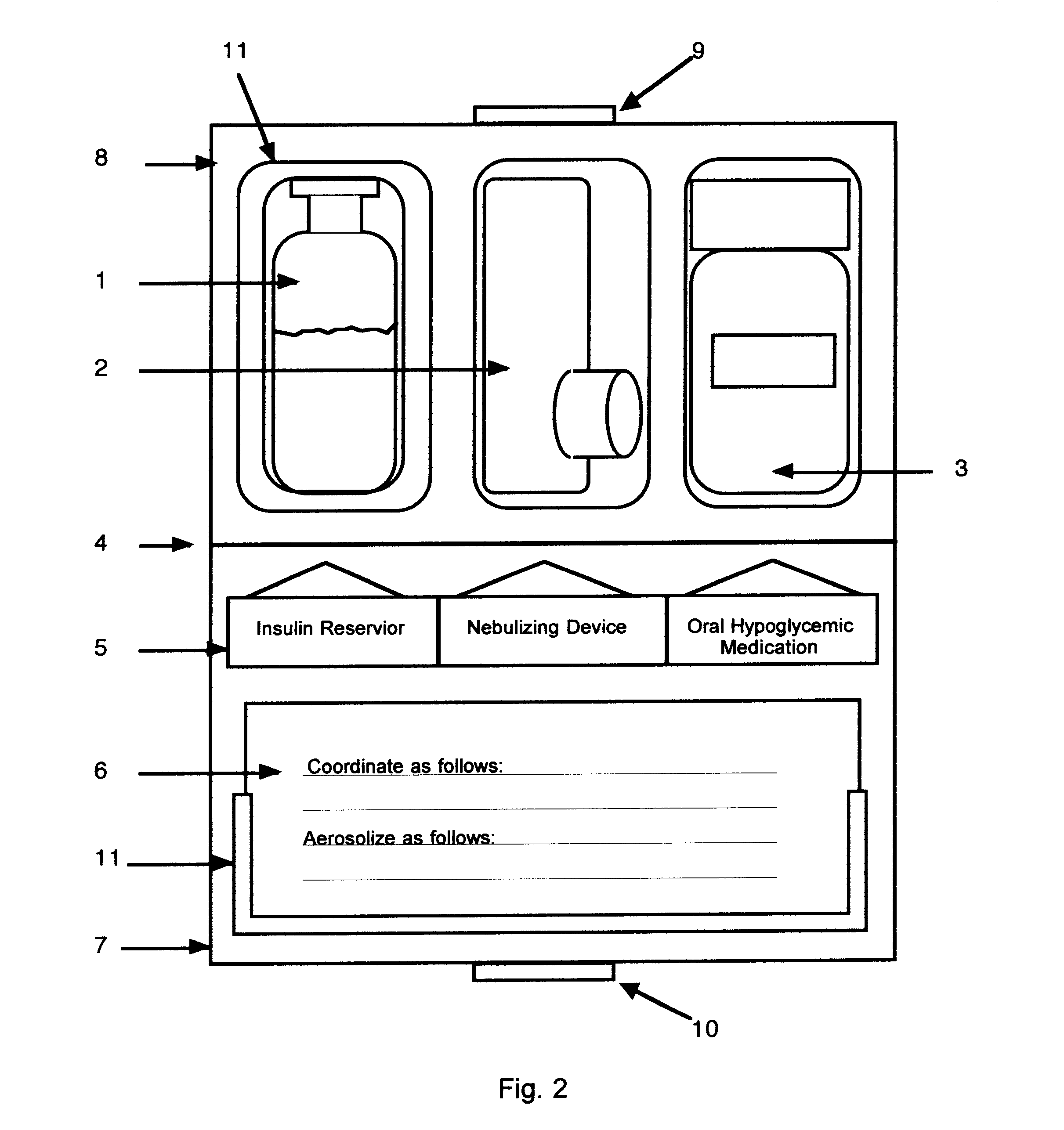
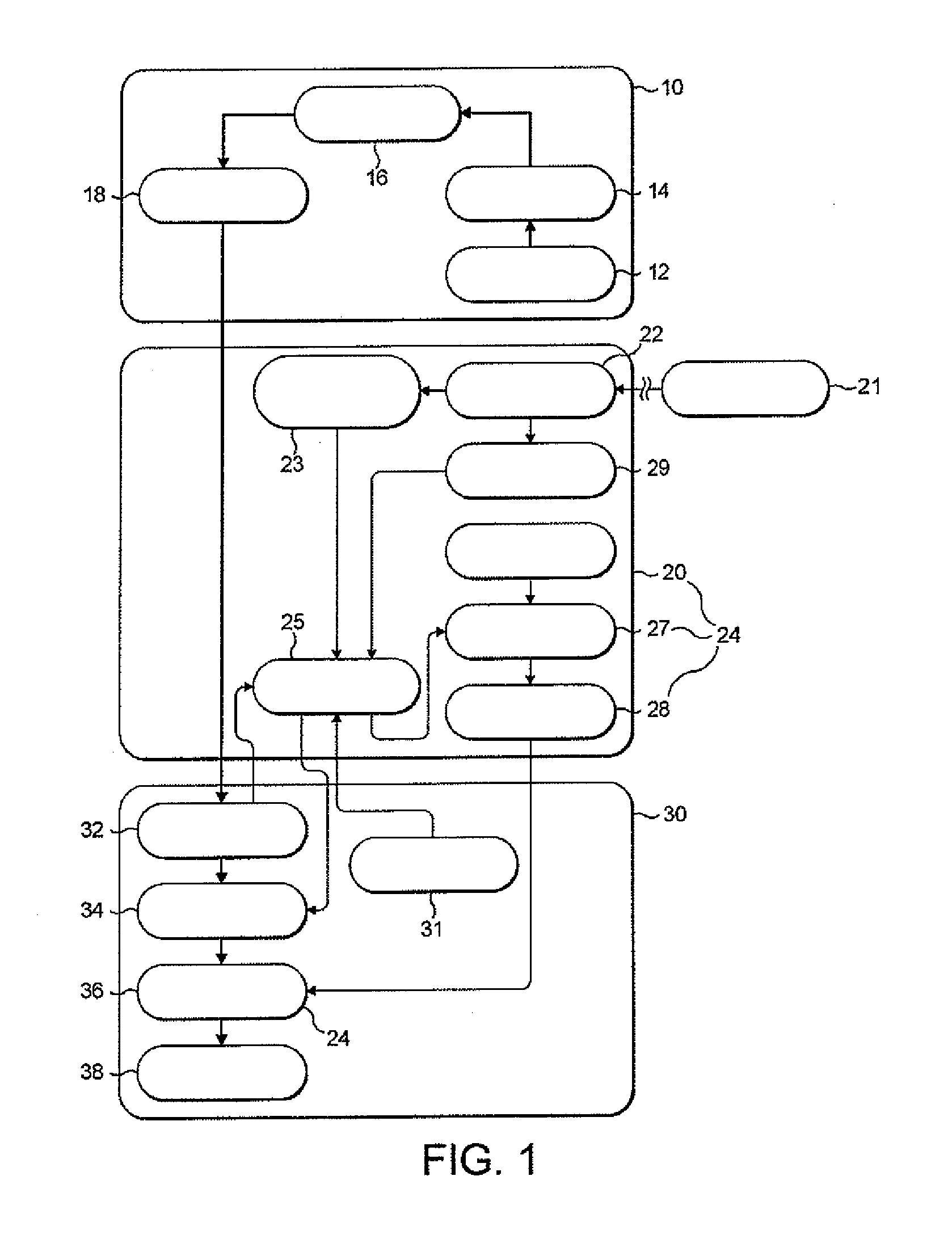
Method and device for facilitating combined aerosol and oral treatments for diabetes mellitus
InactiveUS6187291B1Improve convenienceImprove organizationPowder deliveryAerosol deliveryOral treatmentINSULIN PREPARATIONS
A dispensing container which incorporates an aerosolizable topical insulin preparation, at least one oral hypoglycemic agent, and indicia and instructions for their coordinated use as a single therapeutic regimen for the treatment of diabetes mellitus in a human, and a method for treating diabetes mellitus which employs such a device.
Owner:WEINSTEIN ROBERT E +1
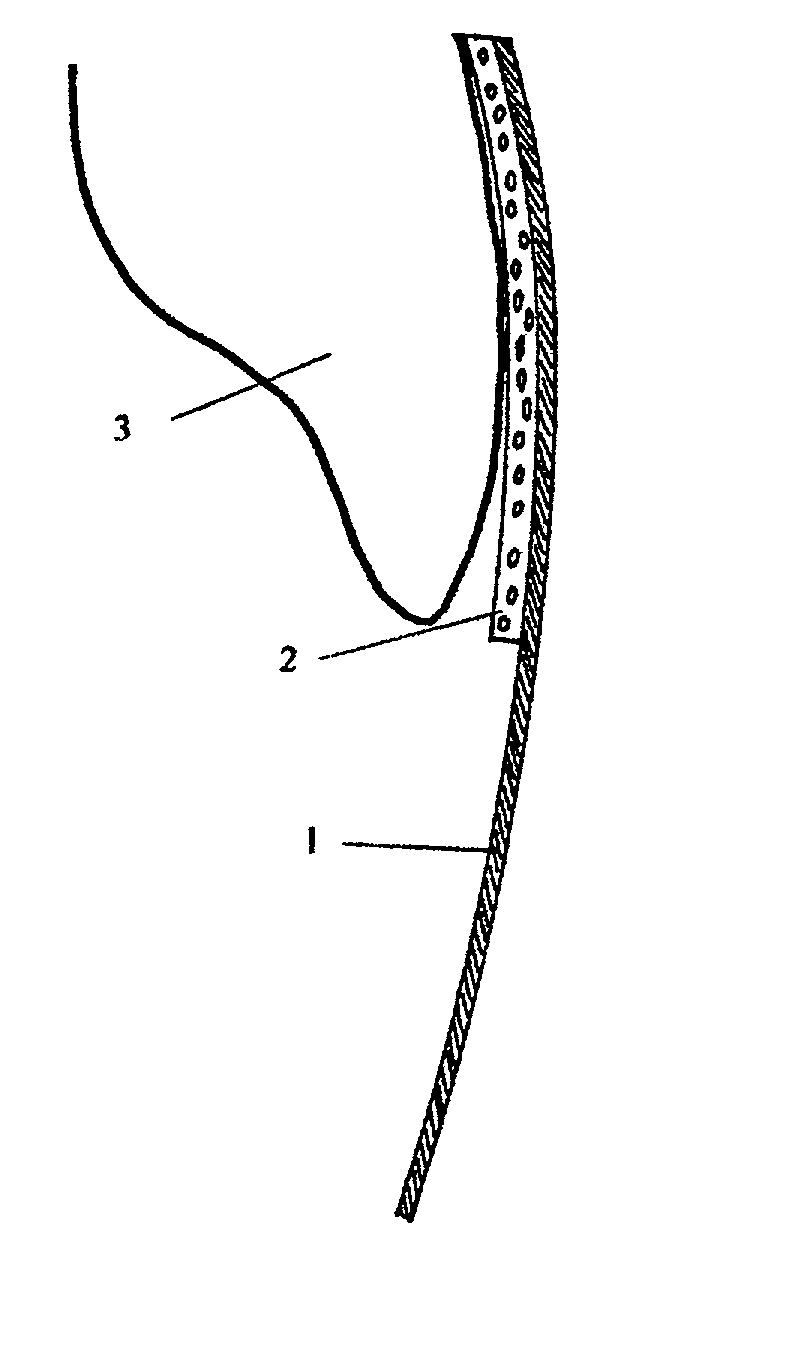
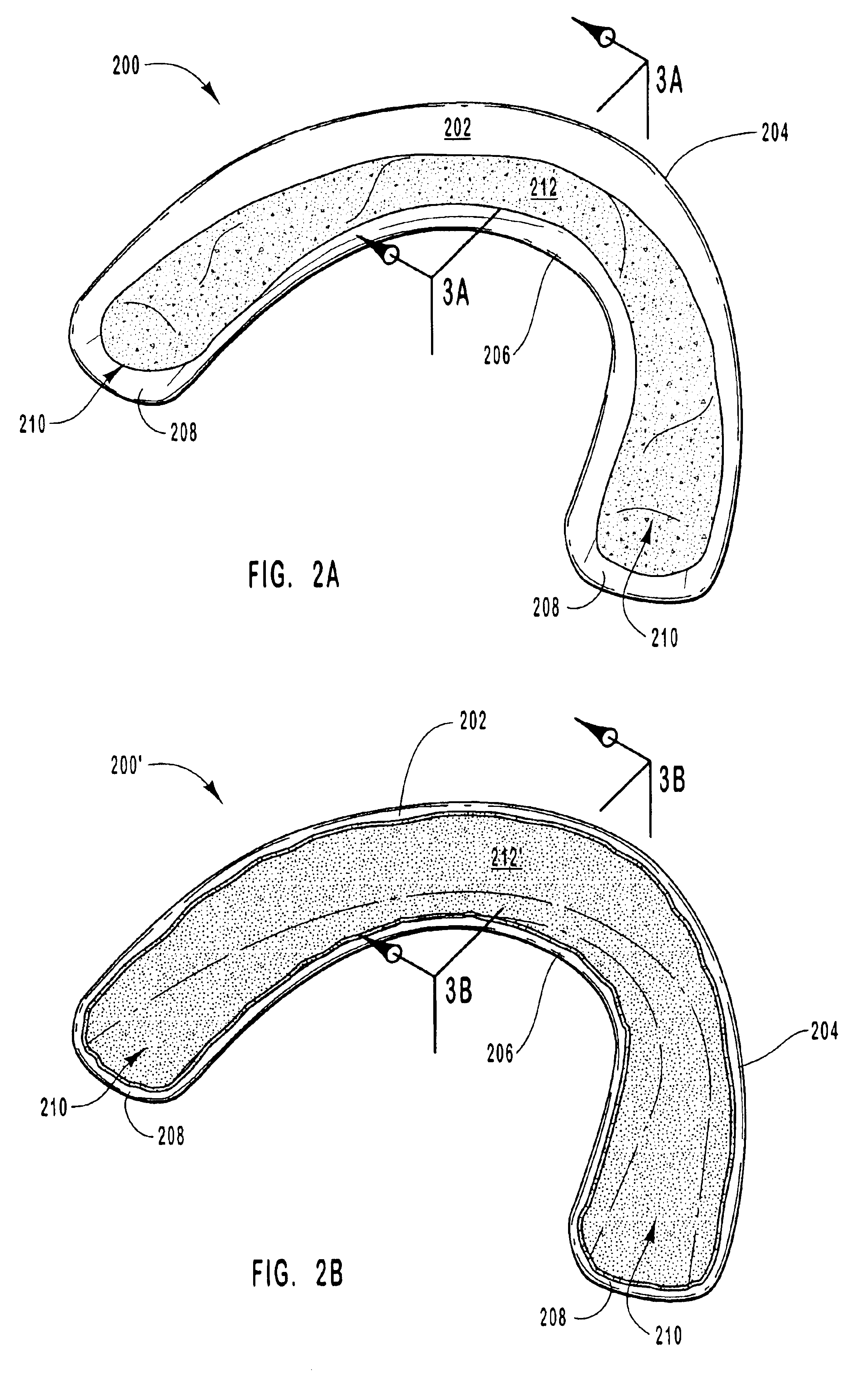
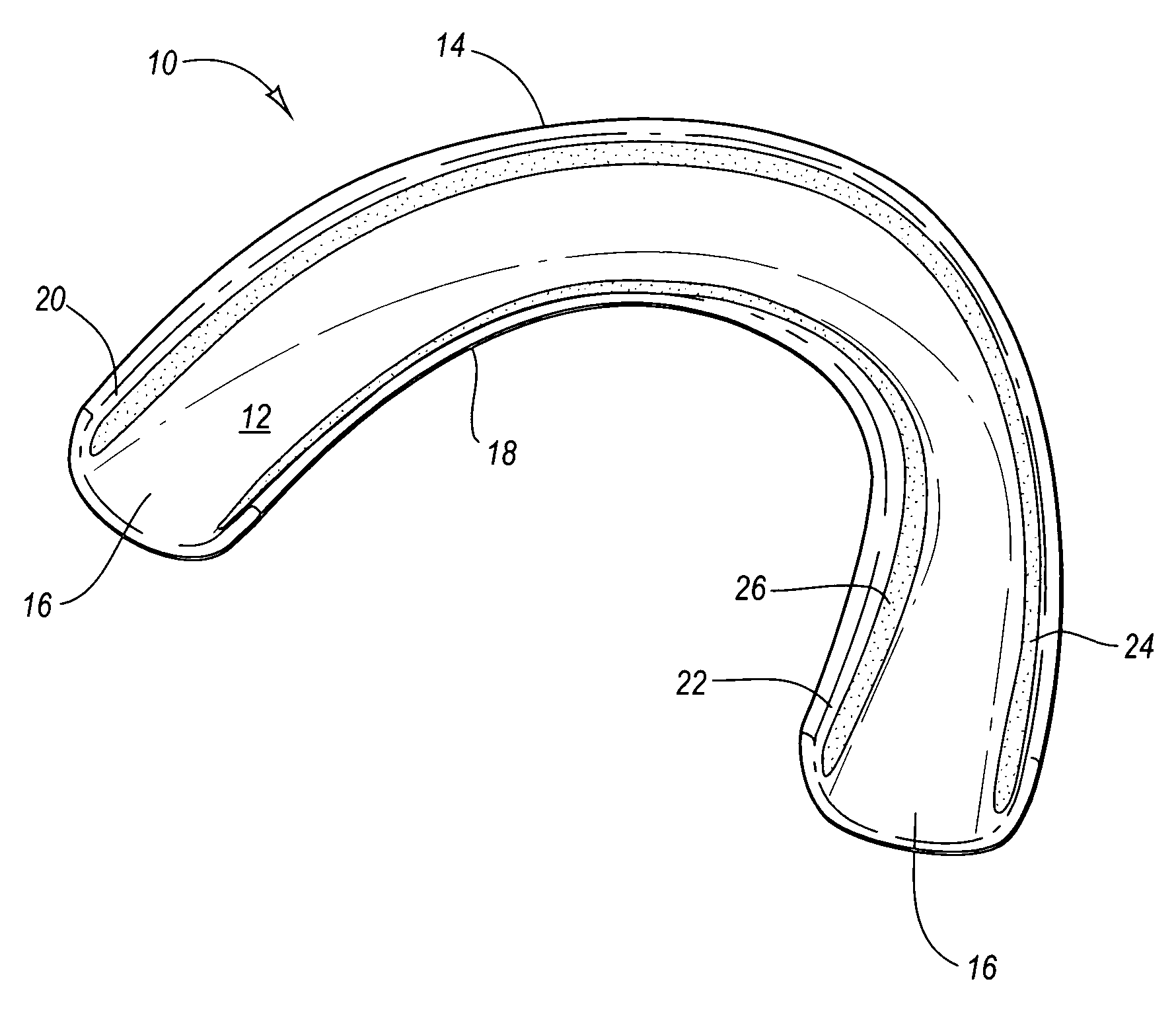
Oral treatment devices that include a thin, flexible barrier layer and an endoskeleton treatment or adhesive composition
InactiveUS6860736B2Prevent, minimize or lessen their diffusion into the user's mouthPlace stableTeeth fillingCoffinsOral treatmentDentistry
Oral treatment devices include a barrier layer and an oral treatment composition, and optionally an auxiliary adhesive composition, that acts as an endoskeleton so as to at least partially contribute to maintaining the barrier layer in the shape of a dental tray, or in a tray-like configuration, prior to use. The barrier layer protects the oral treatment and / or adhesive composition from saliva or moisture during use. The treatment and / or auxiliary adhesive compositions can have a consistency ranging from a sticky, viscous gel or a solid. They preferably include a tissue adhesion agent comprising a hydrophilic polymer.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
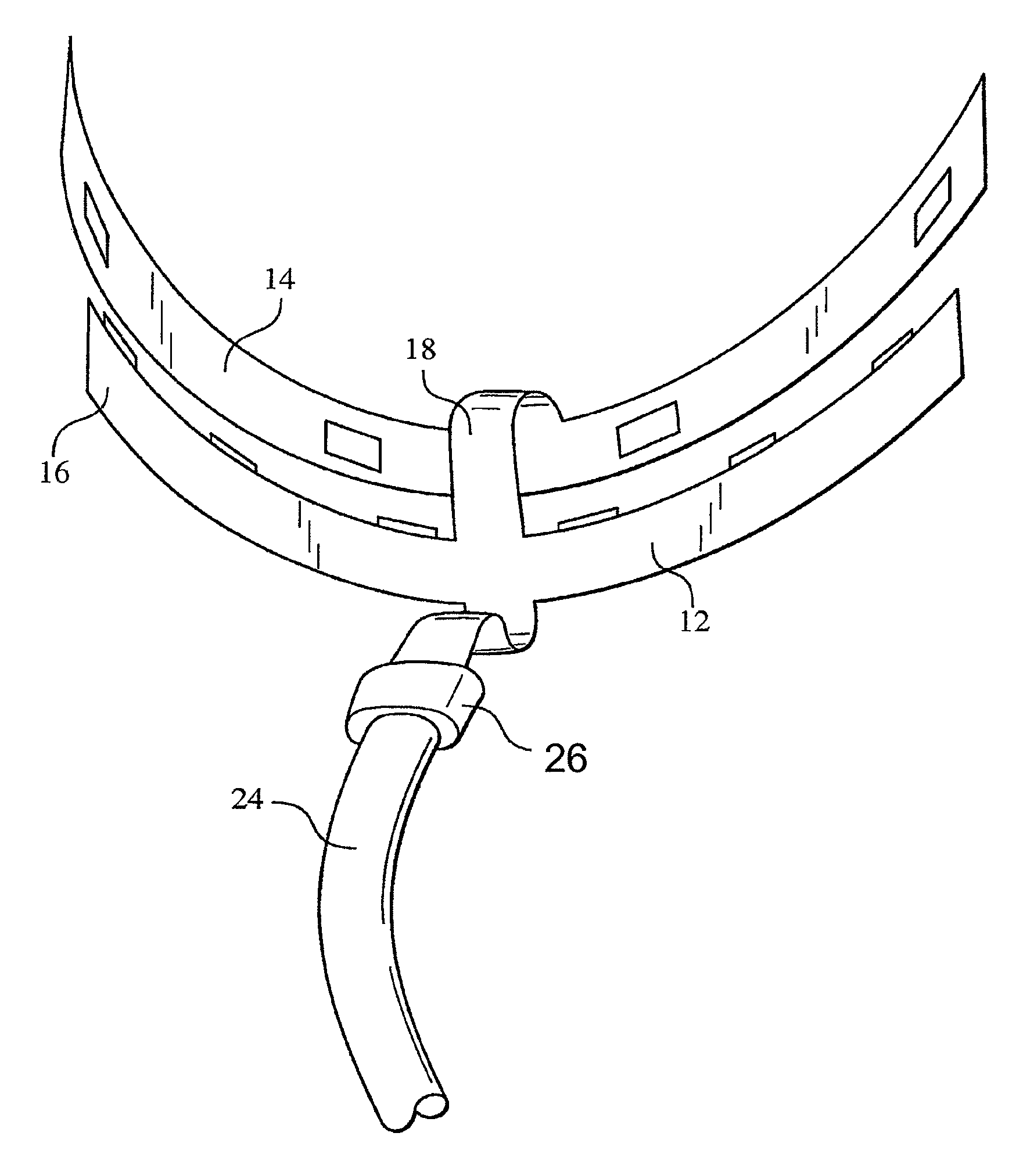
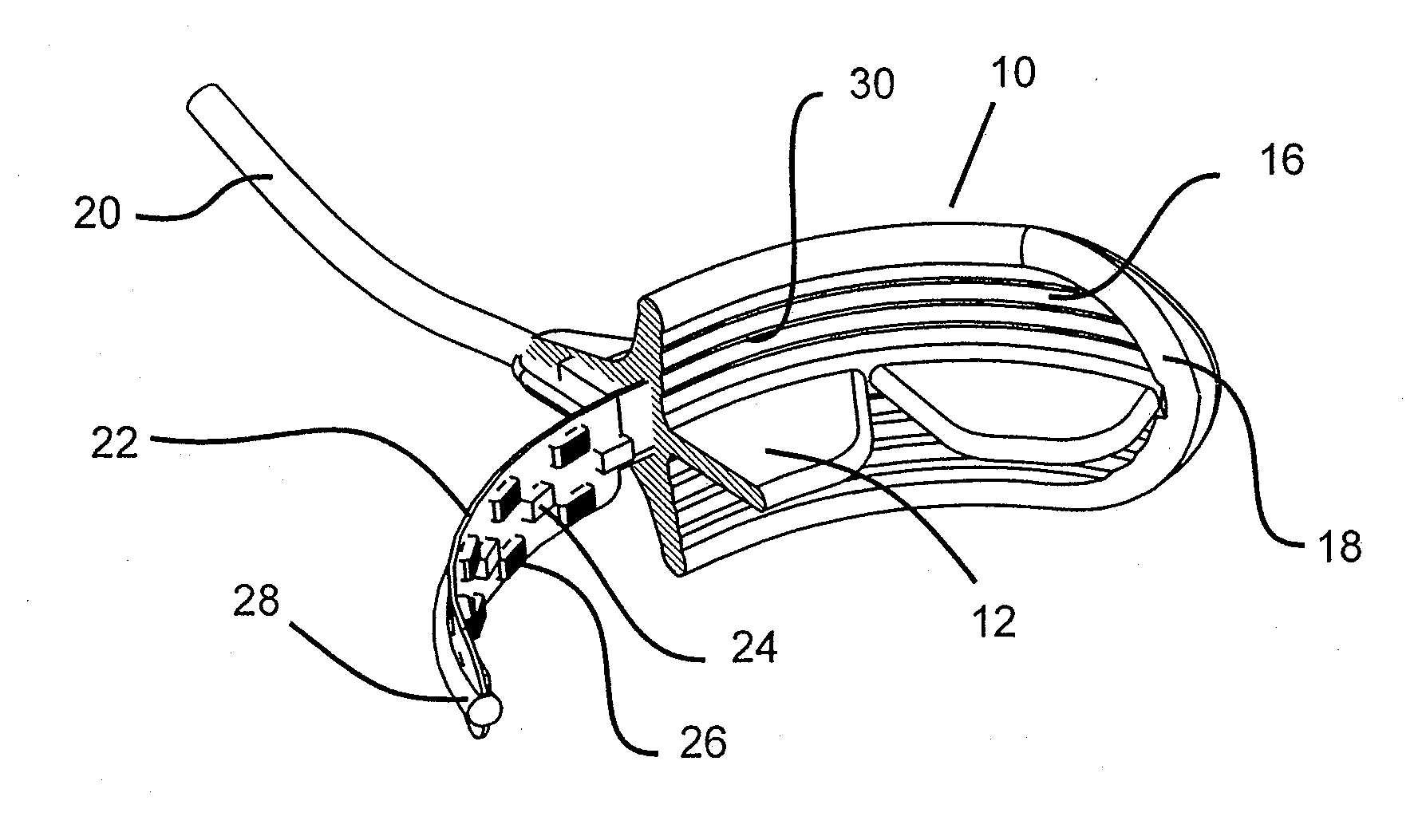
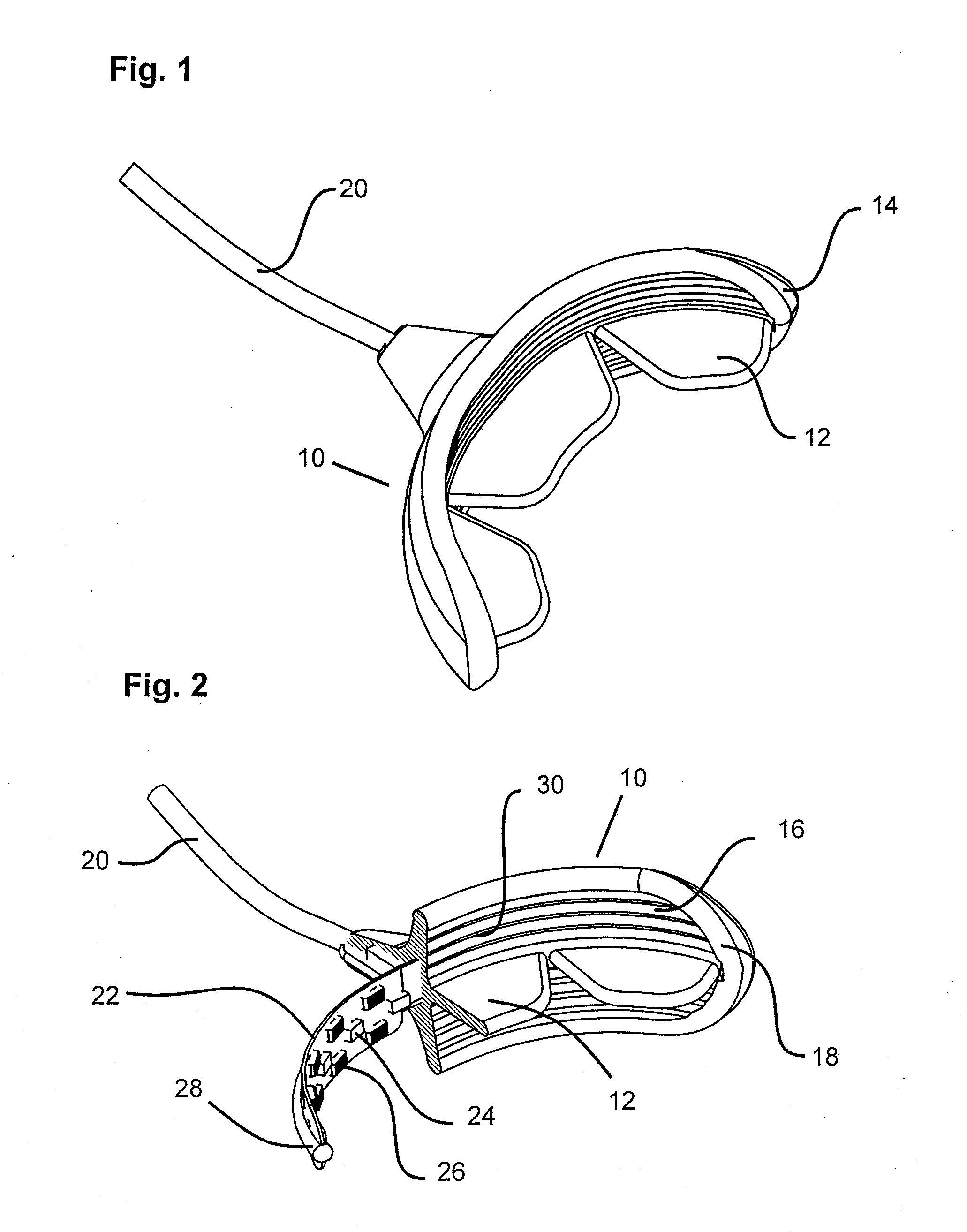
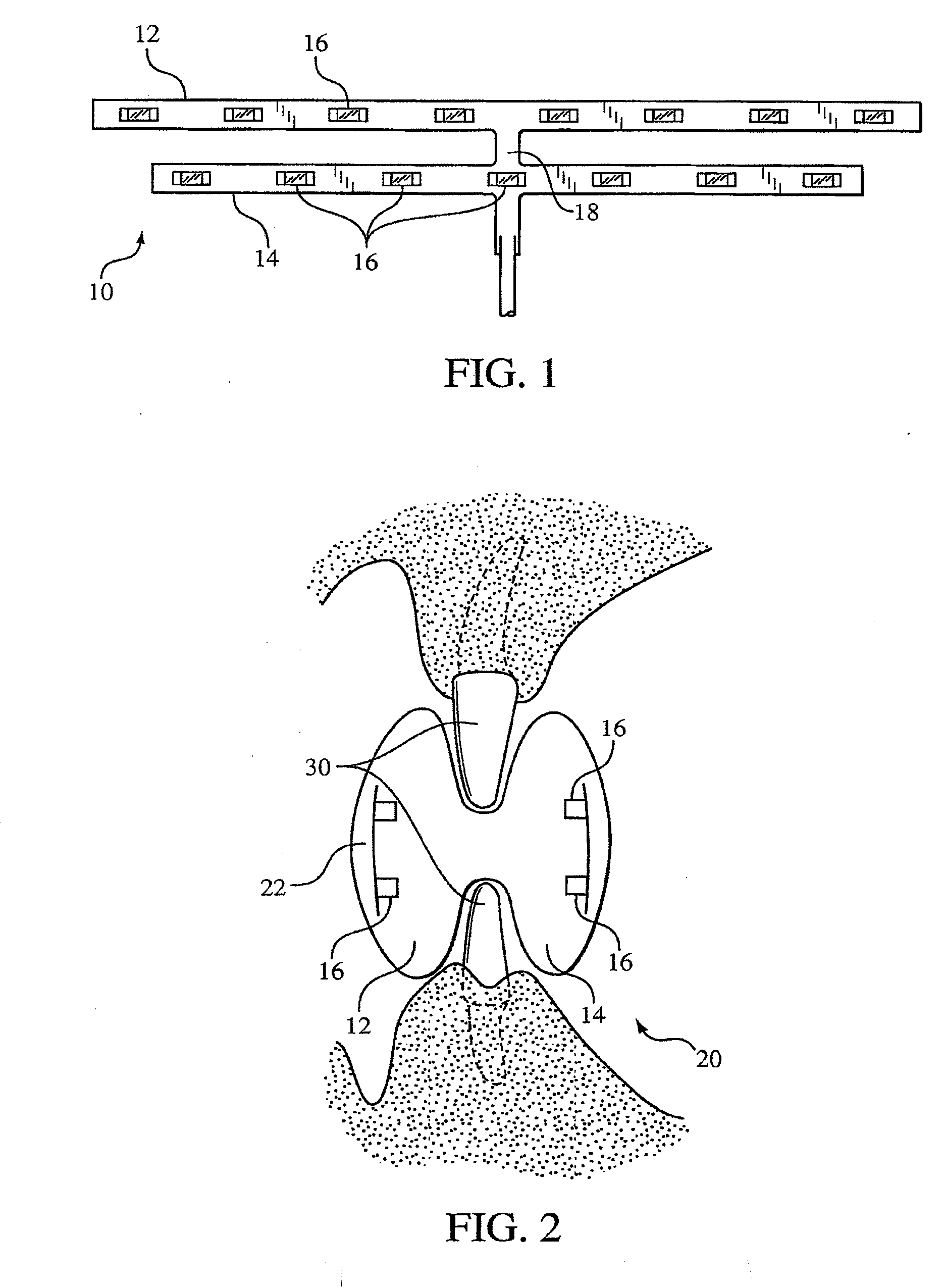
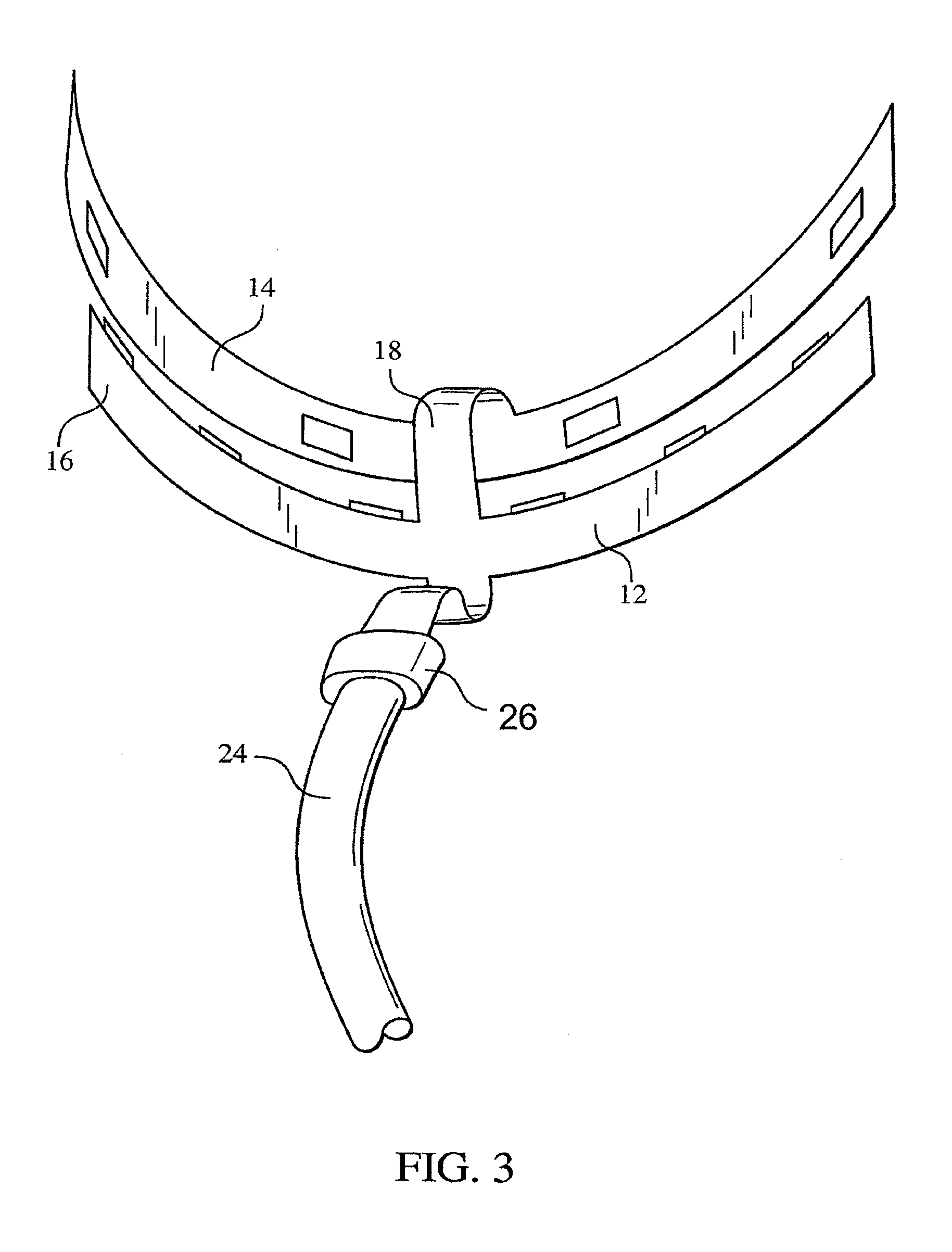
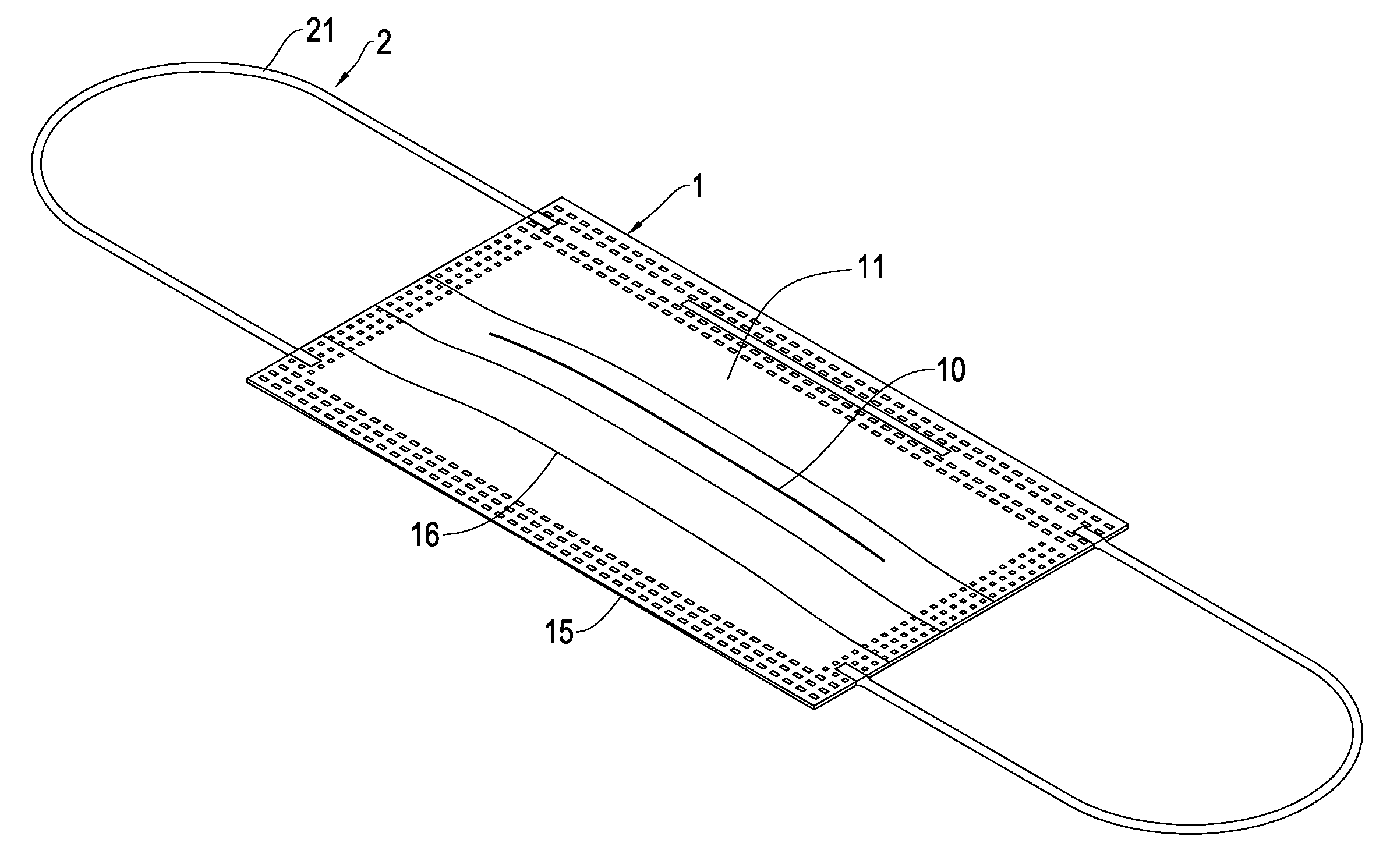
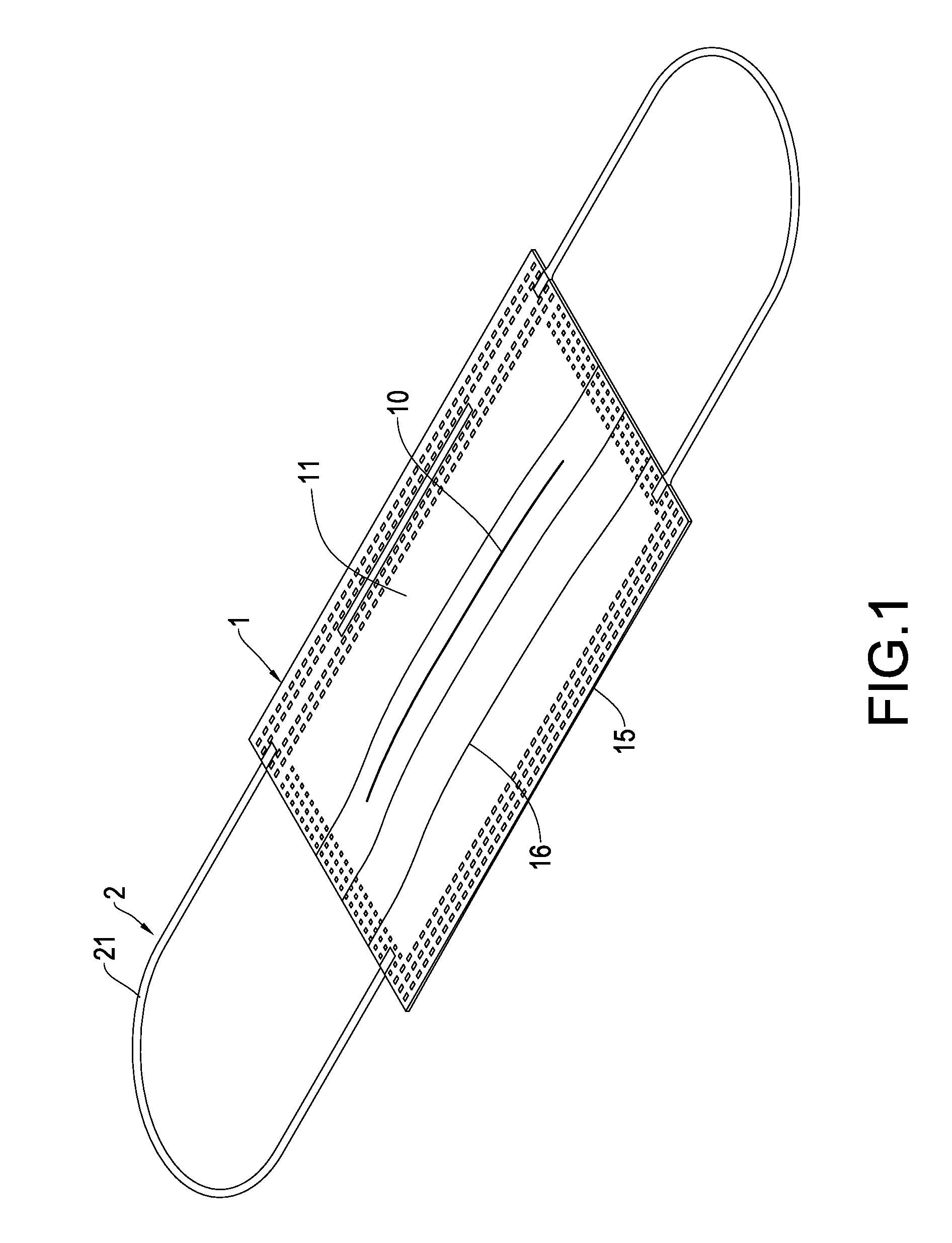
Methods for effecting oral treatment of teeth or gums
ActiveUS8215954B2Improve reaction speedSafe and effective and convenientTeeth fillingDental toolsOral treatmentFlexible circuits
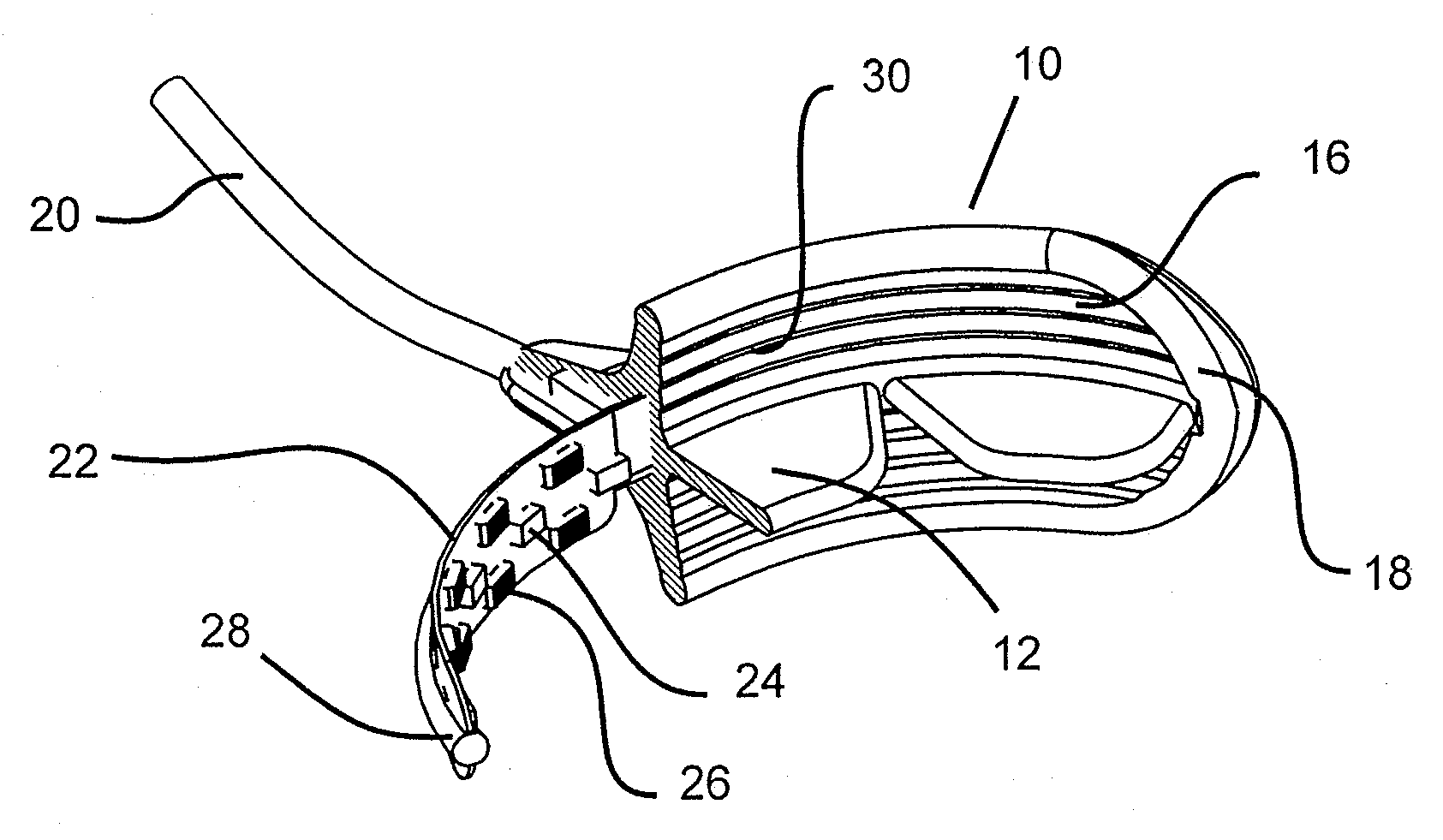
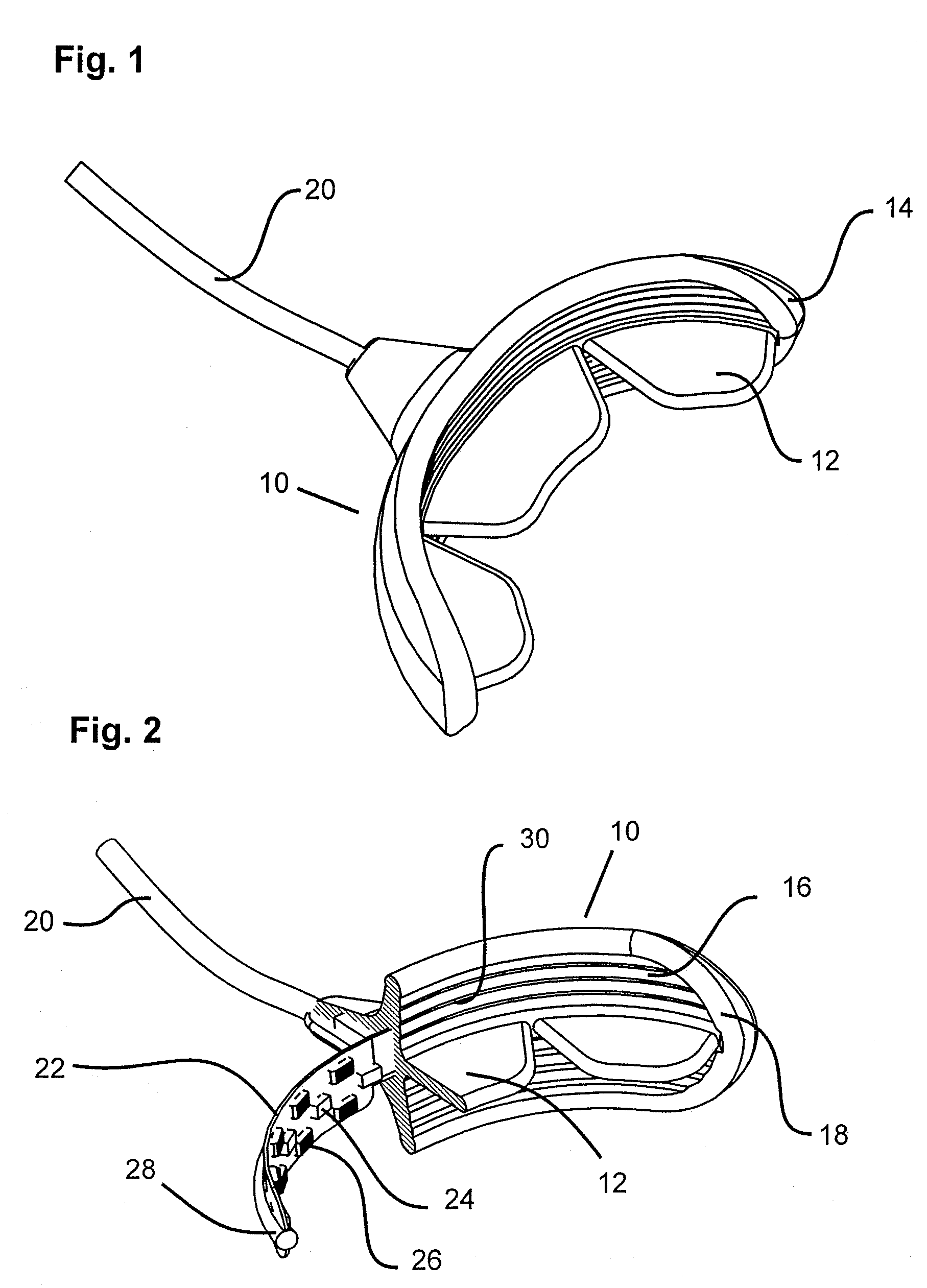
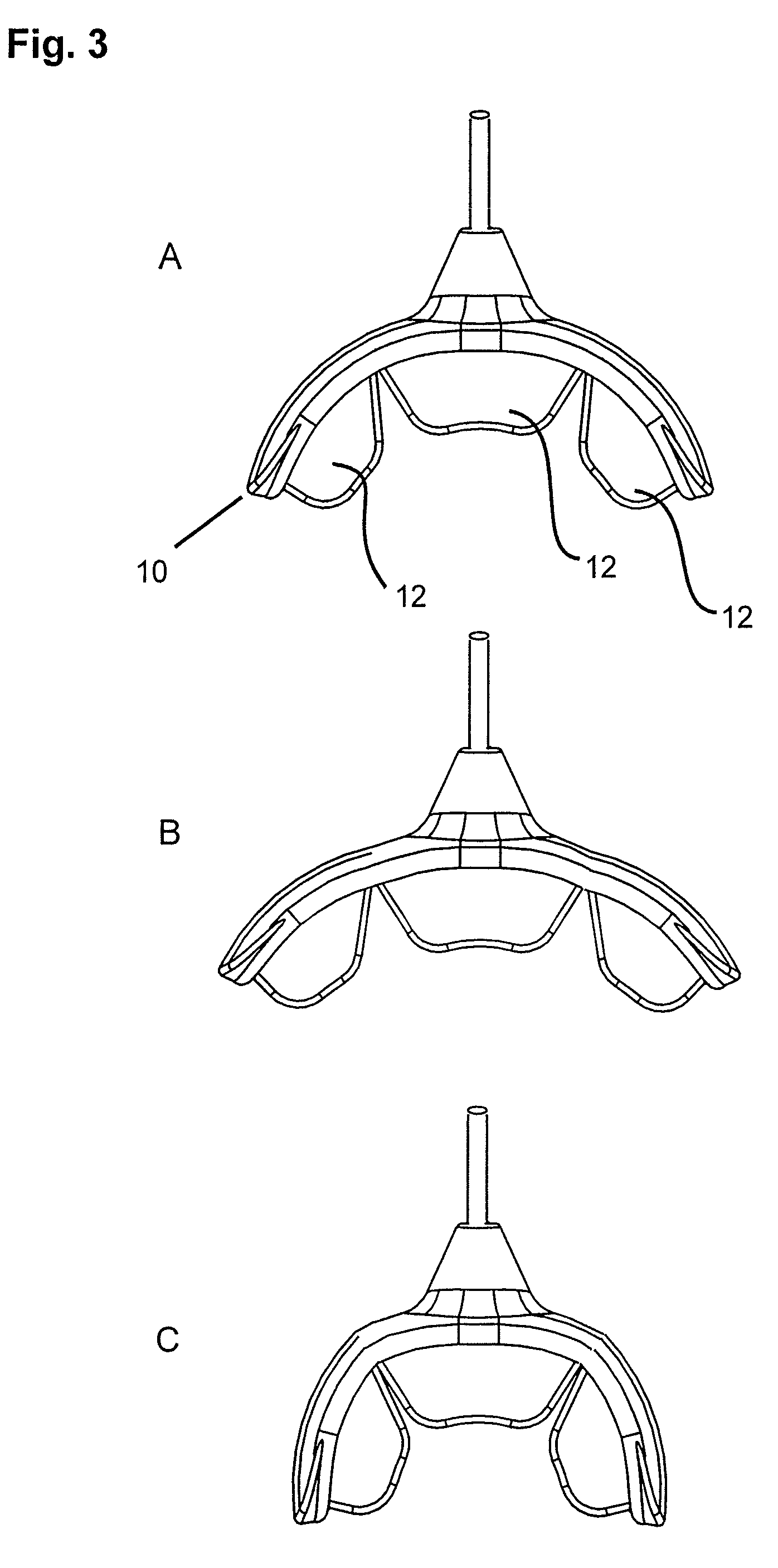
A method for effecting an oral treatment of teeth and / or gums using an intra-oral device that has a mouthpiece in which is embedded a flexible circuit board and arrays of spaced apart lamps. The mouthpiece has a curvature. The lamps may be light emitting diodes that generate electromagnetic radiation, preferably in the white and blue light spectrum and the infrared and ultraviolet light spectrum. The arrays are positioned to expose the facial and lingual sides of the teeth and / or gums for effecting the treatment when the mouthpiece is positioned to fit upper and lower rows of teeth within accommodating recesses. The flexible circuit board is flexed to exhibit a curvature that follows a curvature of the mouthpiece. Treatments include whitening teeth, desensitizing teeth, and treating gums to prevent periodontal disease.
Owner:GLO SCI INC
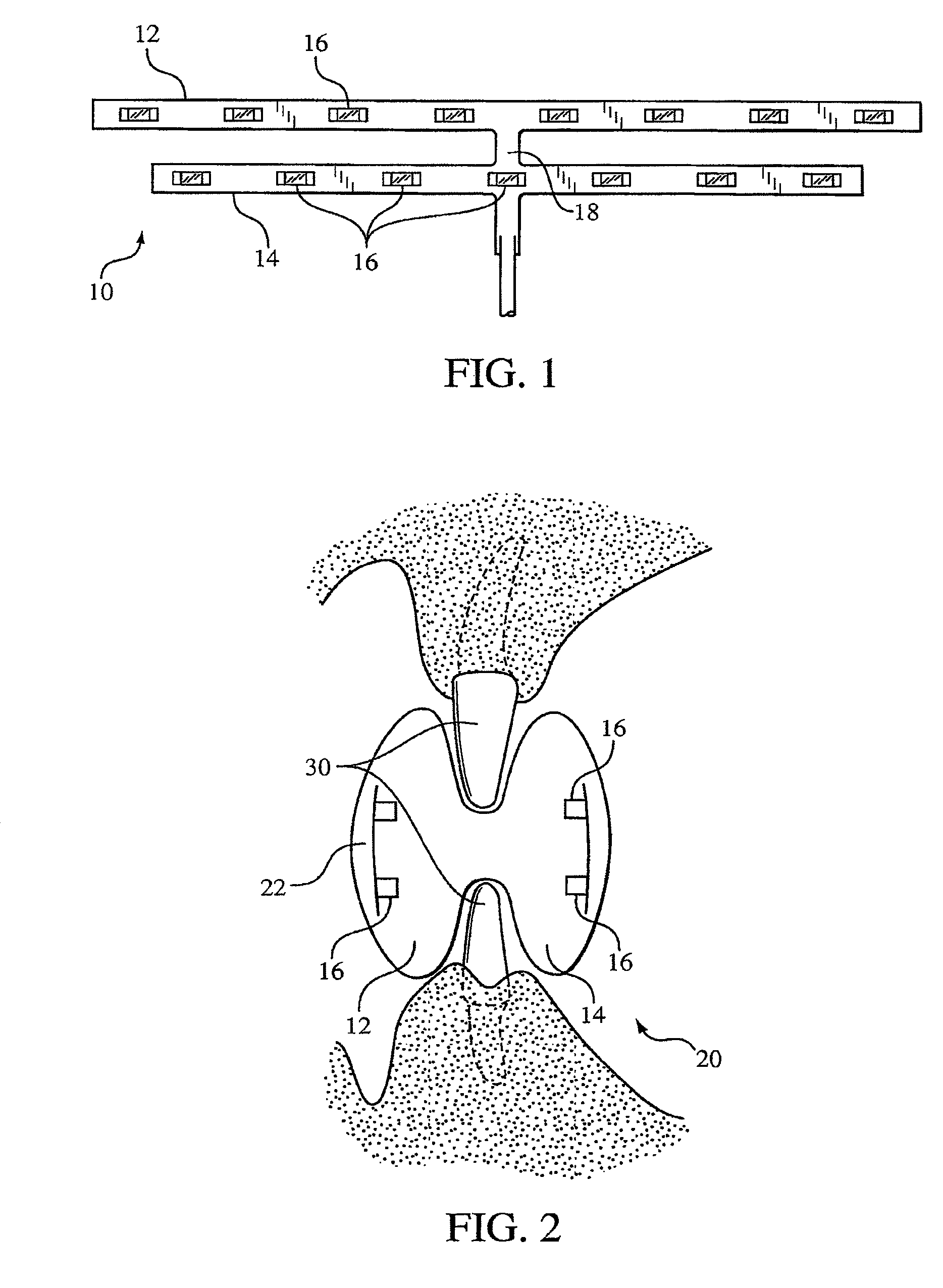
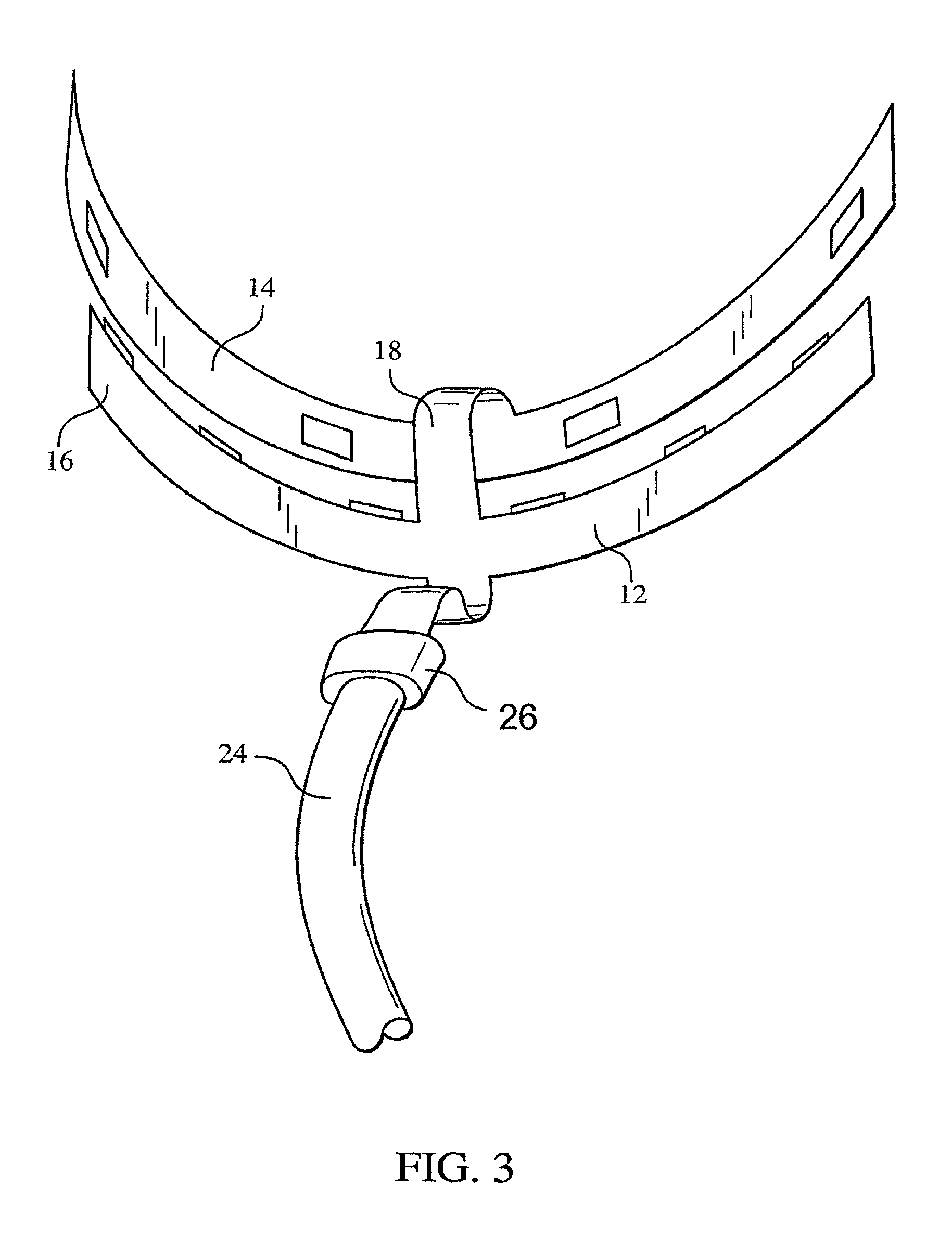
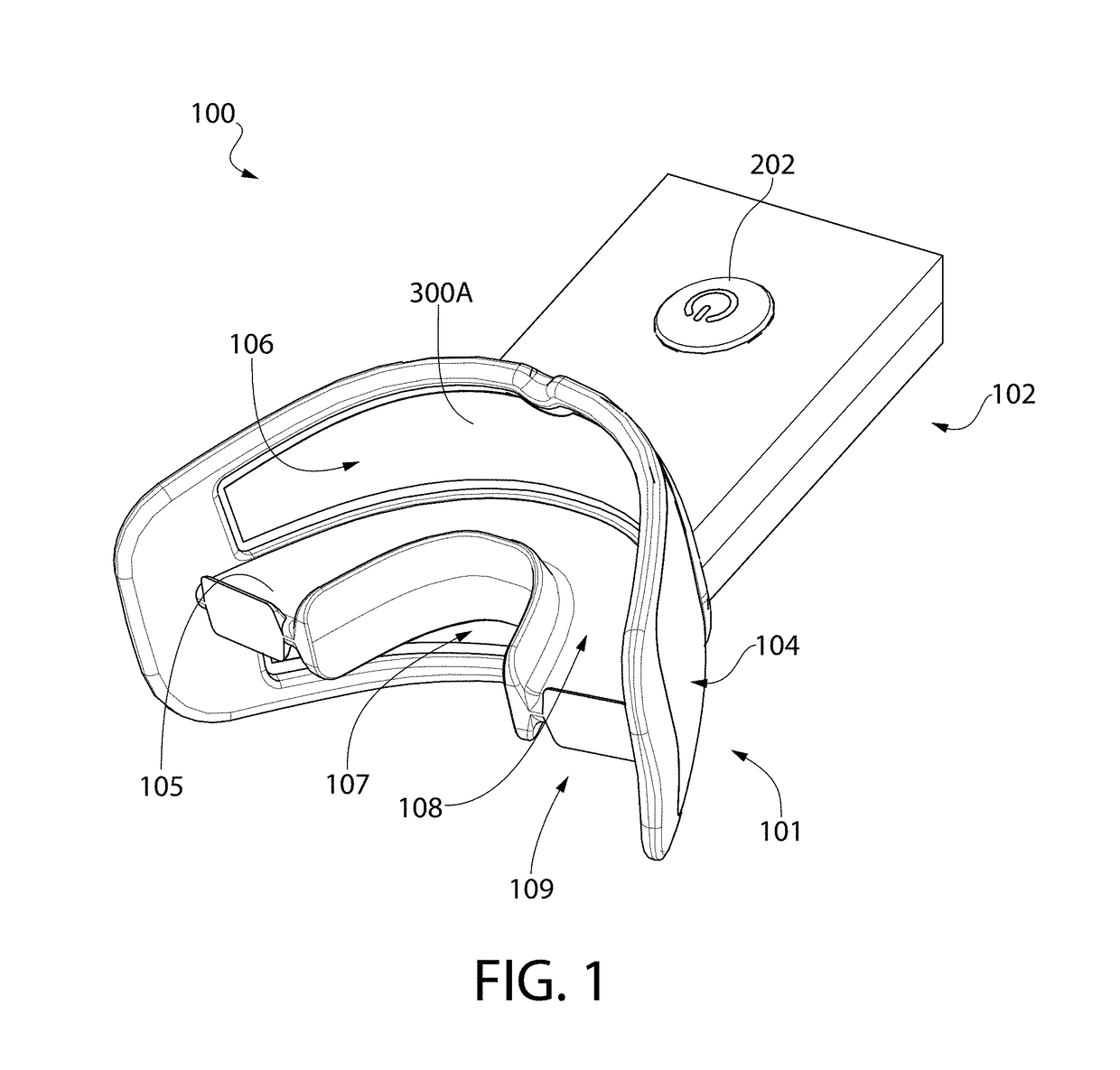
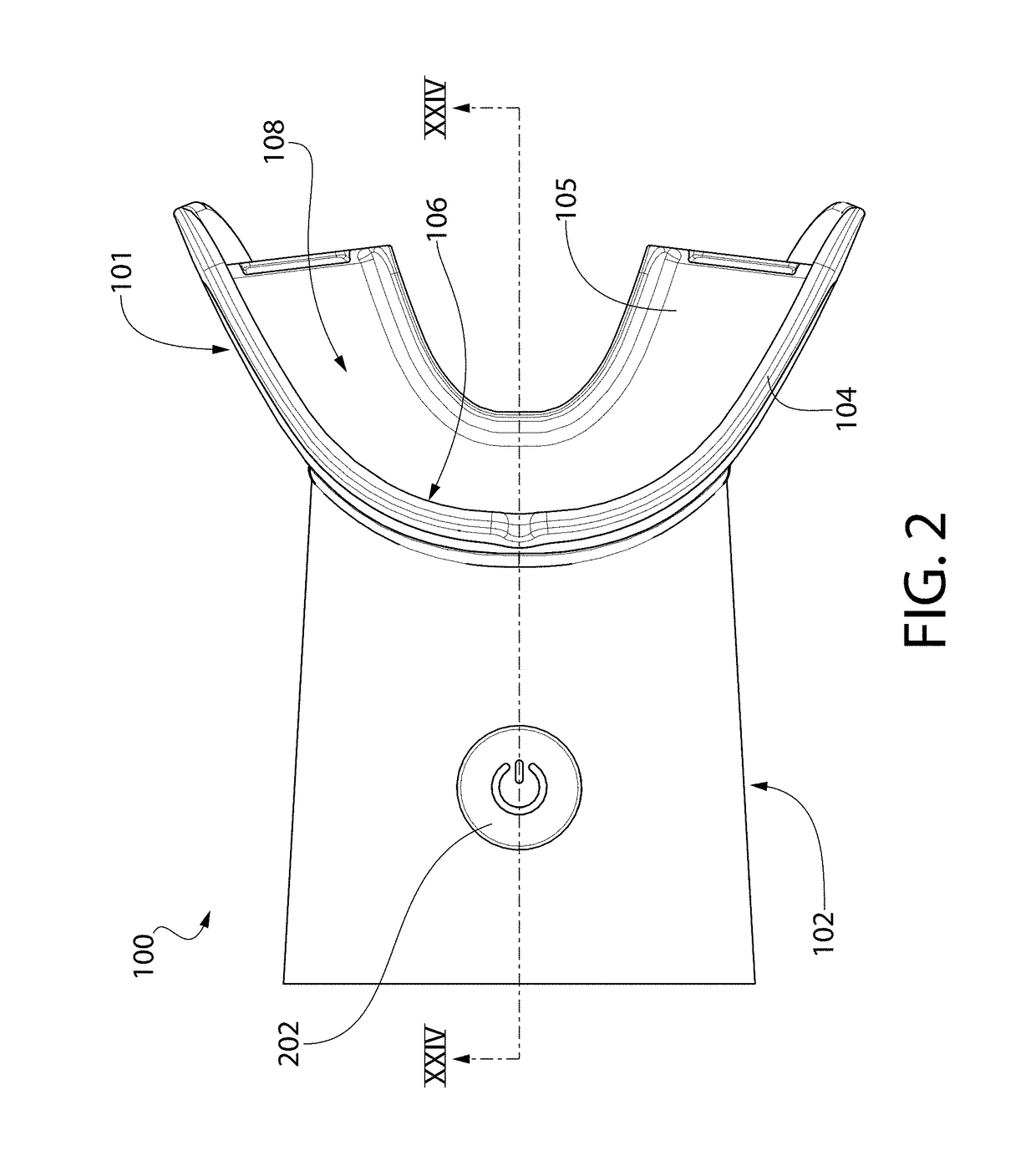
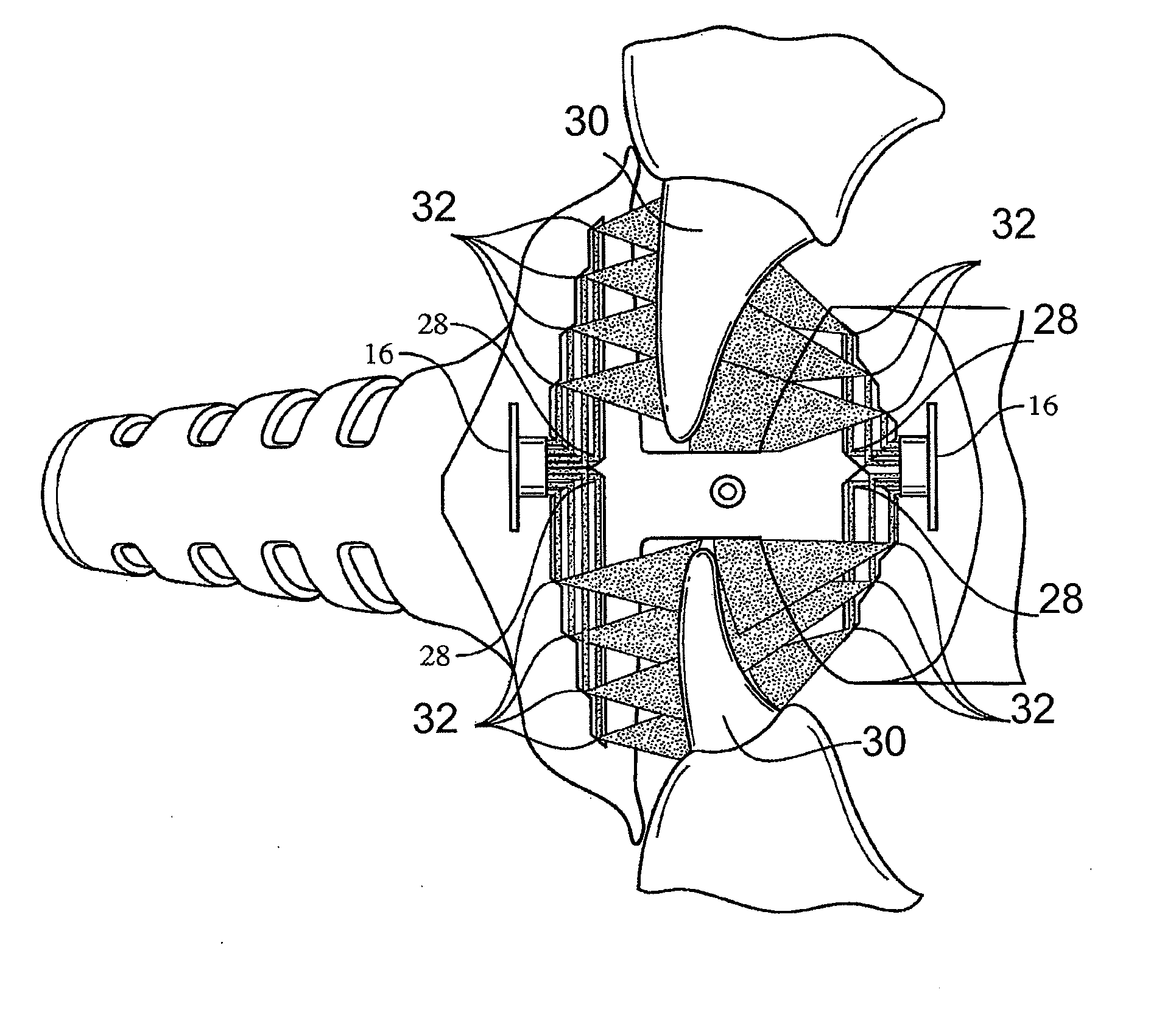
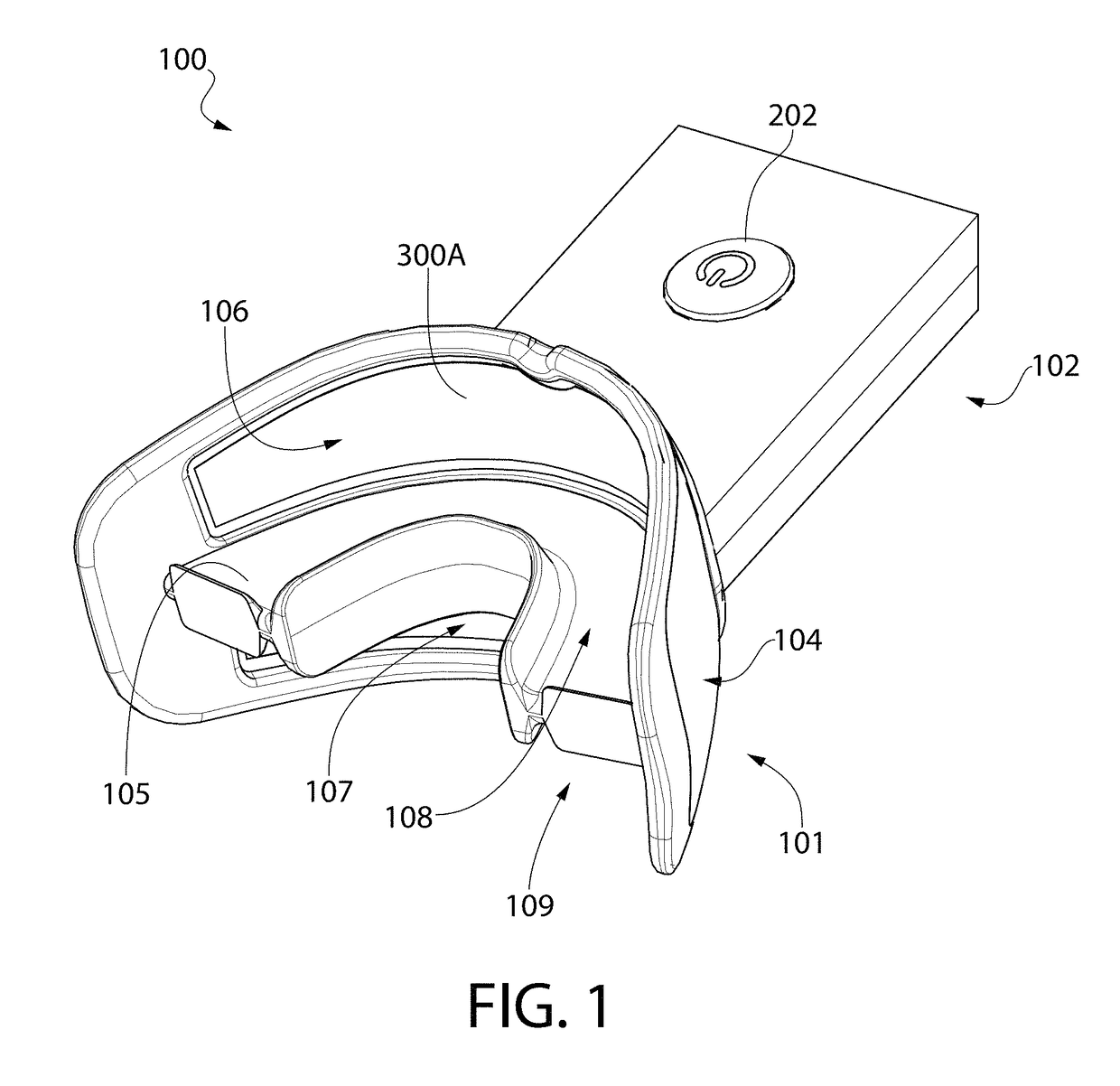
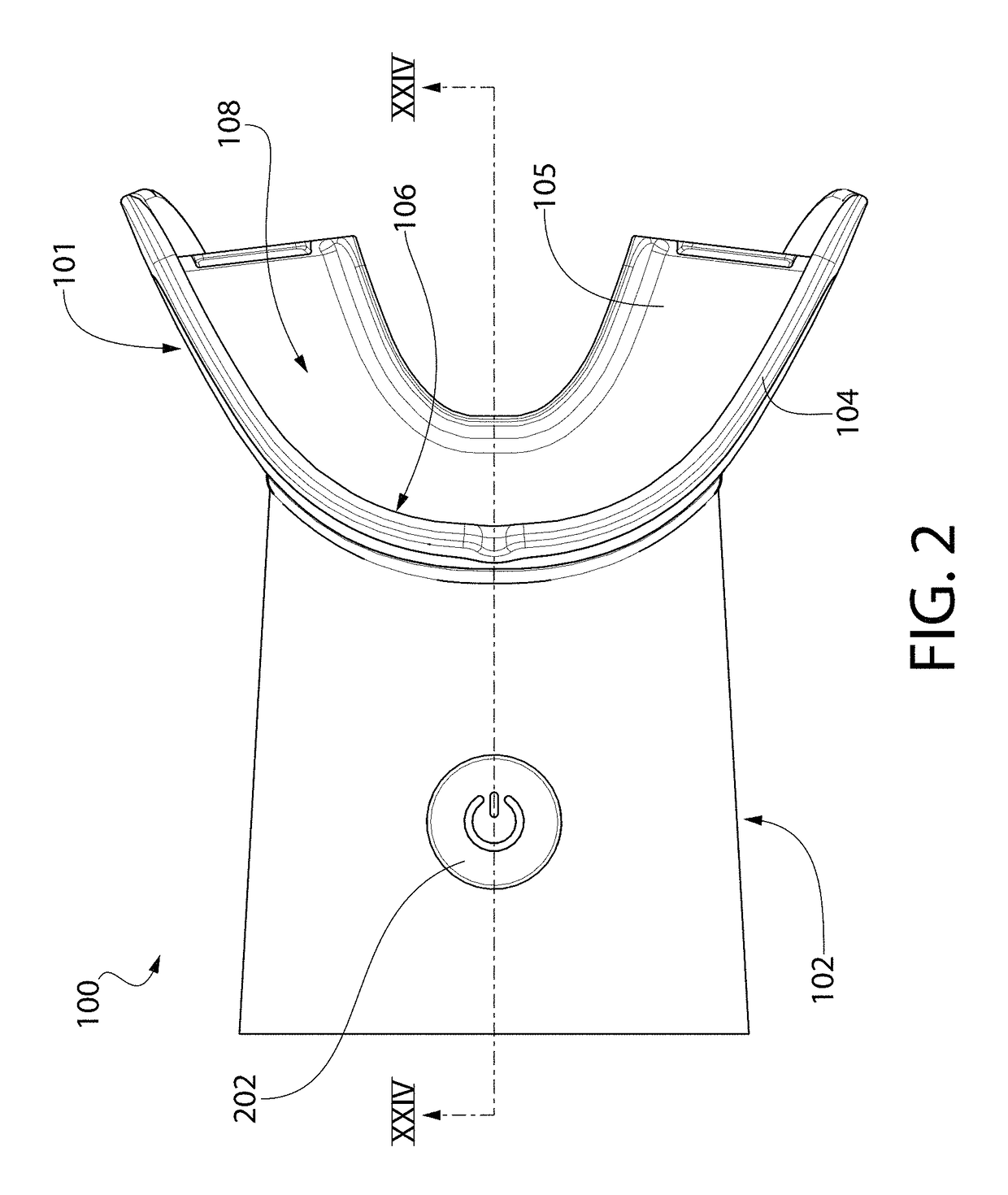
Mouthpiece that adjusts to user arch sizes and seals from oxygen exposure and methods for effecting an oral treatment
ActiveUS8371853B2Improve reaction speedSafe and effective and convenient and economicalTeeth fillingDental toolsOral treatmentRespirator
A mouthpiece that adjusts manually in the mouth and seals the treatment area. It includes light emitters and heat generators. Textured bands guide and direct light to diffuse evenly. A seal bead seals the gum above the teeth. For whitening, a whitening gel is first applied to the user's teeth, the mouthpiece is then positioned in the user's mouth, and the seal bead seals against the user's gums. Then, the light emitter(s) and heat generator(s) are activated to effect the whitening while causing an increase in the temperature enabling the user to mold the mouthpiece to their mouth.
Owner:GLO SCI INC
Oral treatment device
An oral treatment device that emits light onto surfaces of a user's teeth. In one aspect, the oral treatment device includes an intraoral mouthpiece comprising: a lamp support surface; and a lamp. When the lamp is mounted to the lamp support surface, a first contact surface of the lamp contacts a first contact surface of a first electrical contact element of the lamp support surface; and (2) a second contact surface of the lamp contacts a second contact surface of a second electrical contact element of the lamp support surface.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Mouthpiece that adjusts to user arch sizes and seals from oxygen exposure and methods for effecting an oral treatment
ActiveUS20110104633A1Promote healingImprove reaction speedTeeth fillingDental toolsDiseaseOral treatment
A mouthpiece that adjusts manually to accommodate a broad range of different size sets of upper and lower teeth in the mouth and yet seals the treatment area from oxygen exposure. The mouthpiece includes one or more light emitters and one or more heat generators. A series of parallel texture bands are provided to guide and direct the light from the light emitters to diffuse generally evenly onto teeth to be treated. The seal arises from an inner surface of the mouthpiece tilting inwardly so that a seal bead seals in the vicinity of the gum above the teeth to be treated. Method for effecting an oral treatment such as whitening or desensitizing teeth or treating gum disease. For whitening, a whitening gel is applied to the user's teeth, the mouthpiece is then positioned in the user's mouth such that a bite surface is between upper and lower arches, a main body is between a front surface of the teeth and an inner surface of the user's lips, and a seal bead is against the user's gums. Then, the light emitter(s) and heat generator(s) are activated to effect the whitening while causing an increase in the temperature of the main body thereby enabling the user to mold the main body and conform its shape to their mouth.
Owner:GLO SCI INC
Methods for effecting oral treatment of teeth or gums
ActiveUS20110104631A1Improve reaction speedSafe and effective and convenientTeeth fillingDental toolsOral treatmentFlexible circuits
A method for effecting an oral treatment of teeth and / or gums using an intra-oral device that has a mouthpiece in which is embedded a flexible circuit board and arrays of spaced apart lamps. The mouthpiece has a curvature. The lamps may be light emitting diodes that generate electromagnetic radiation, preferably in the white and blue light spectrum and the infrared and ultraviolet light spectrum. The arrays are positioned to expose the facial and lingual sides of the teeth and / or gums for effecting the treatment when the mouthpiece is positioned to fit upper and lower rows of teeth within accommodating recesses. The flexible circuit board is flexed to exhibit a curvature that follows a curvature of the mouthpiece. Treatments include whitening teeth, desensitizing teeth, and treating gums to prevent periodontal disease.
Owner:JBL RADICAL INNOVATIONS LLC
Mouthpiece and methods for effecting an oral treatment
A mouthpiece that adjusts manually to accommodate a broad range of different size sets of upper and lower teeth in the mouth and yet seals the treatment area from oxygen exposure. The mouthpiece includes light emitting diodes and heat generating resistors all arranged in an array. A series of parallel texture bands are provides to guide and direct the light from the LEDs to diffuse generally evenly onto teeth to be treated. The seal arises from an inner surface of the mouthpiece tilting inwardly so that a seal bead seals in the vicinity of the gum above the teeth to be treated.
Owner:乔纳森·B·列文
Chinese medicine prescription orally taken for curing constipation
The invention discloses a traditional Chinese medicine prescription for oral administration for treating constipation, which belongs to the field of traditional Chinese medicines. This kind of traditional Chinese medicine prescription for oral treatment of constipation, the raw materials of active ingredients are made into the following weights: 10 grams of raw Atractylodes macrocephala, 10 grams of raw white peony root, 20 grams of raw licorice, 6 grams of raw rhubarb, 20 grams of angelica, 12 grams of raw land, Hemp seed 15 grams, Cistanche 12 grams, Ophiopogon japonicus 10 grams, Astragalus 20 grams, Tangerine peel 10 grams, Codonopsis 10 grams, Citrus aurantium 10 grams. Decoction in water, one dose a day, one dose divided into two doses. Ten days is a course of treatment. The medicine of the present invention has the effects of nourishing qi, nourishing blood, moistening intestines and defecating. During the course of treatment for constipation treatment, the effect is remarkable.
Owner:杨海新
Oral treatment device
An oral treatment device that emits light onto surfaces of a user's teeth. In one aspect, the oral treatment device includes an intraoral mouthpiece. The mouthpiece may comprise a lamp support structure comprising a lamp support surface; first and second lamps, each of the first and second lamps comprising a plurality of light emitters that generate light which is emitted from a rear surface of the lamp; each of the first and second lamps mounted to the lamp support surface, thereby forming a lamp assembly, each of the first and second lamps operably coupled to a control circuit having a power source; and a lamp retaining component coupled to the lamp support structure, a lower portion of the first lamp and an upper portion of the second lamp retained between the lamp retaining component and the lamp support surface of the lamp support structure.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Medical oral treatment face mask and method for using the same
InactiveUS20140076334A1Improve breathabilityBreathe smoothly and comfortablyEar treatmentDentistryOral treatmentIsolation layer
A medical oral treatment face mask includes a mask body and a band set. The mask body includes a water-repellent layer, an isolation layer and a water-absorbent layer. The isolation layer, which along with the water-repellent layer has a corresponding opening. The water-absorbent layer is arranged between the water-repellent layer and the isolation layer. The band set is fixed on two sides of the mask body.
Owner:CENT HEALTHCARE TECH
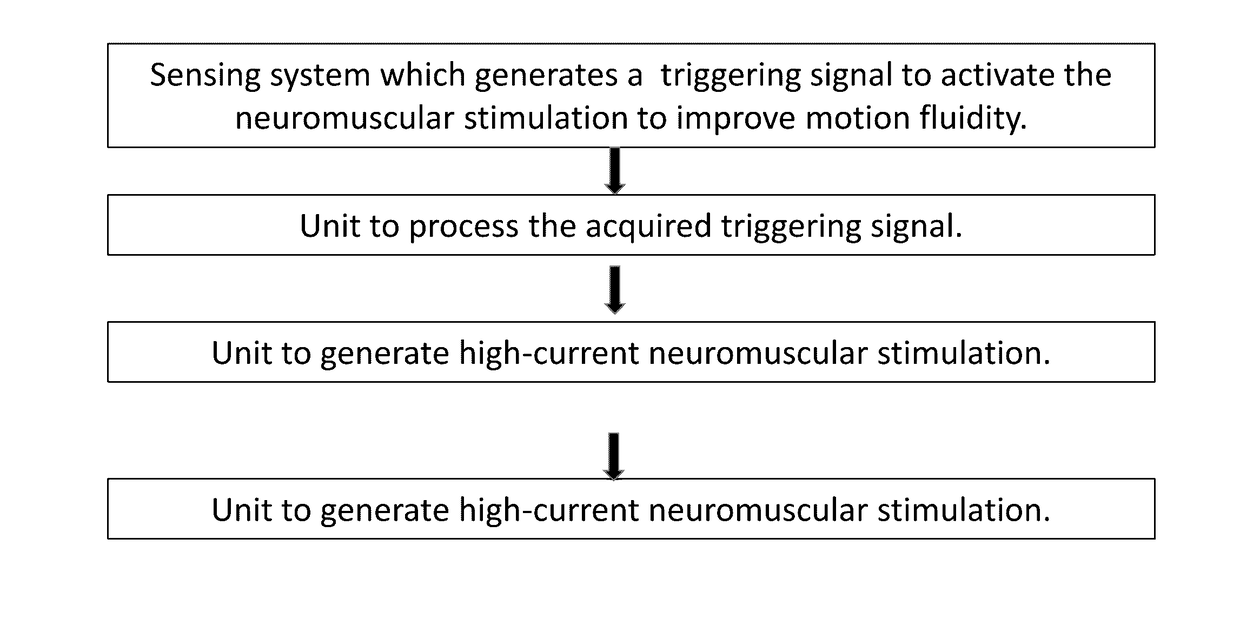
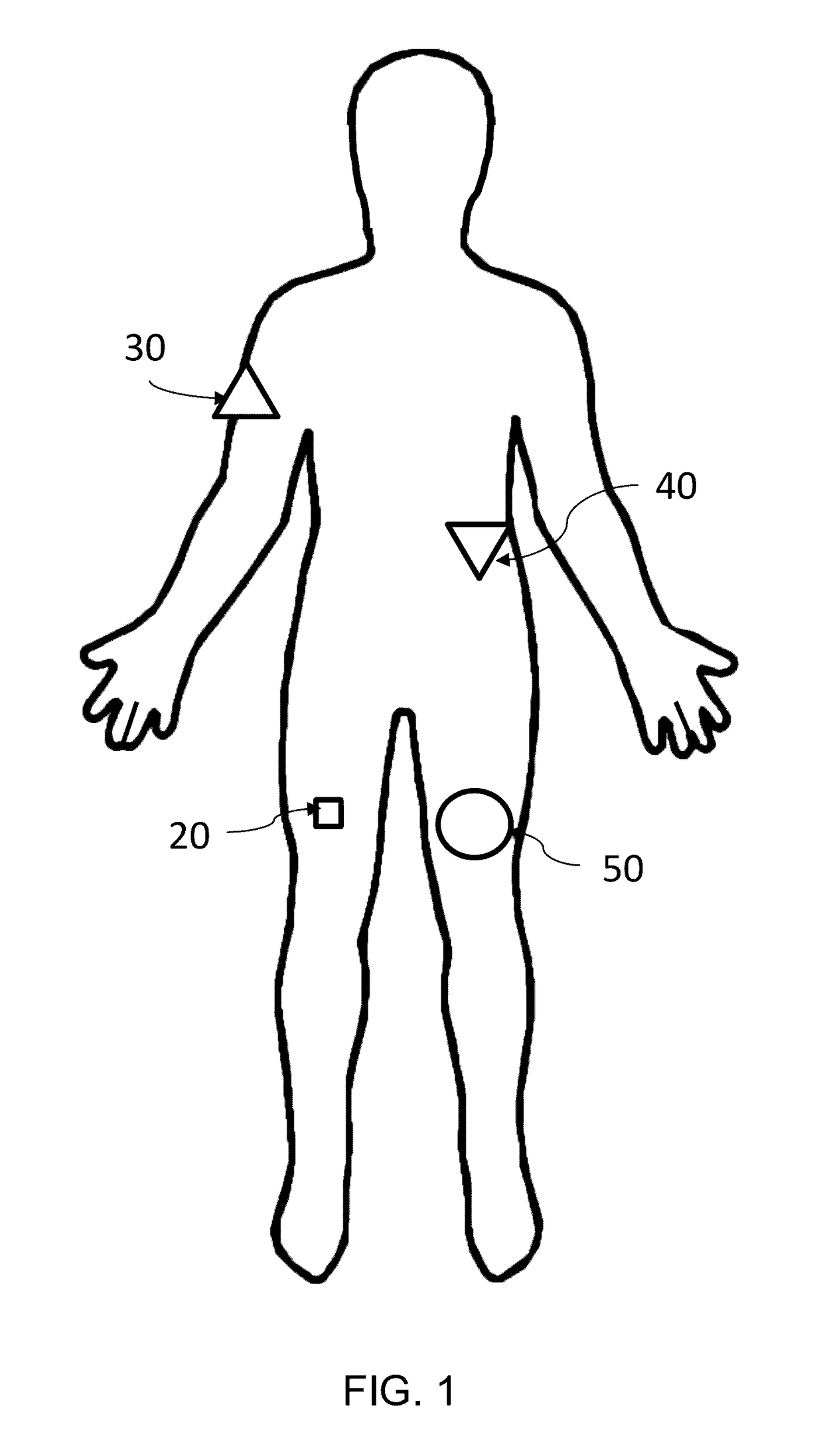
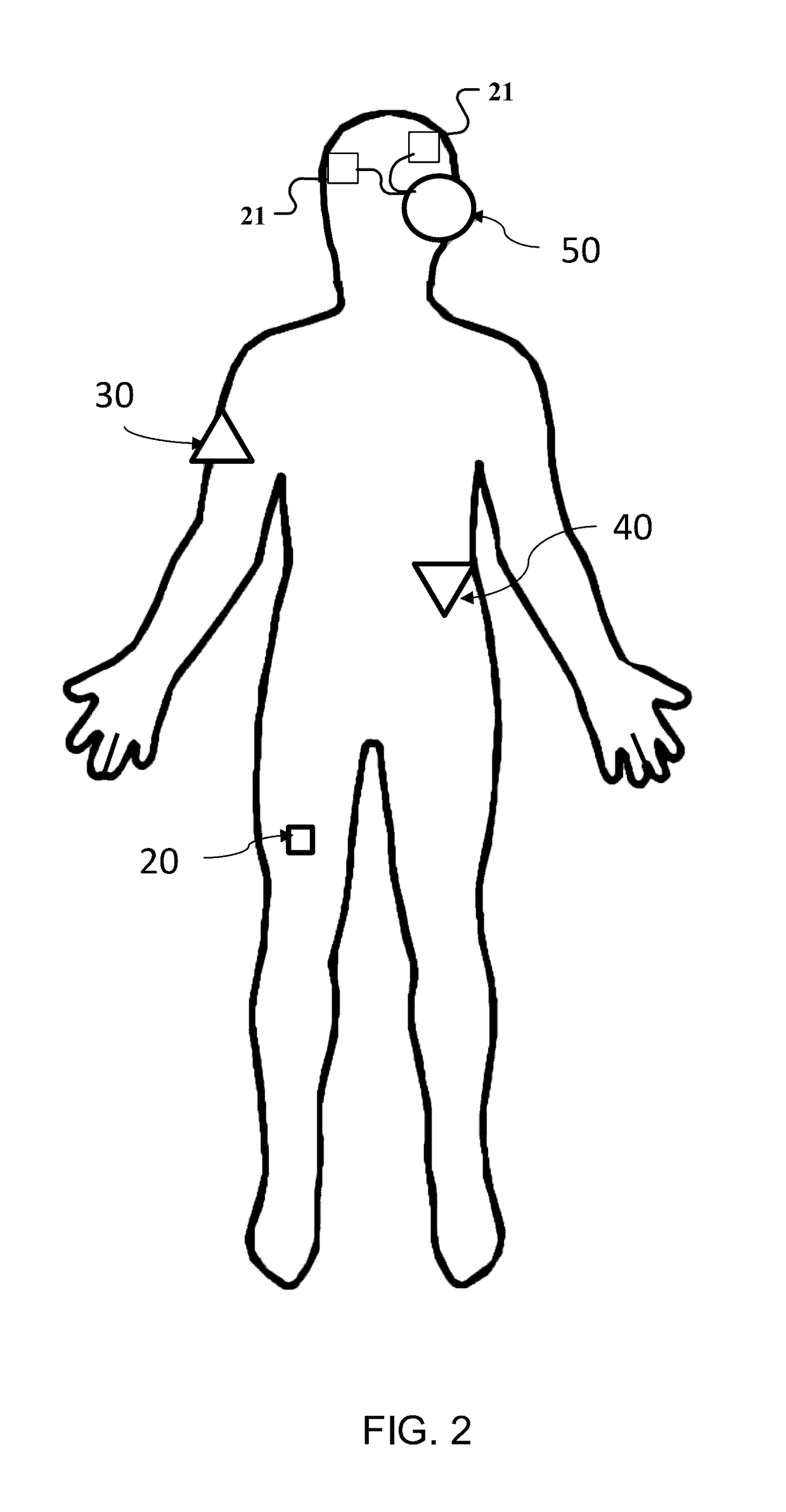
Electrical stimulation device for improving fluidity of motion
ActiveUS20170165481A1The process is simple and effectiveImpaired movementHead electrodesExternal electrodesDiseaseElectricity
The present invention will provide a device in which a movement-impairing episode, such as freezing of gait, is overcome by electrically monitoring and stimulating the individual as soon as the episode is anticipated. The device will be simple and effective when used by individuals suffering from diseases such as Parkinson's Disease without the side effects of oral treatments. This is accomplished through a signal sensing unit, a signal processing unit, a signal generating unit, and an actuation unit.
Owner:KAFANTARIS THEOLOGOS G +1
Oral treatment device
An oral treatment device that emits light onto surfaces of a user's teeth. In one aspect, the oral treatment device includes an intraoral mouthpiece. The mouthpiece comprises: a first light emitting surface configured to emit light onto a user's maxillary teeth, the first light emitting surface having a concave curvature; a second light emitting surface configured to emit light onto a user's mandibular teeth, the second light emitting surface having a concave curvature; the first and second light emitting surface located on opposite sides of a horizontal reference plane; the first light emitting surface inclined so that a first acute angle is formed between with the first light emitting surface and the horizontal reference plane; and the second light emitting surface inclined so that a second acute angle is formed between with the second light emitting surface and the horizontal reference plane.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
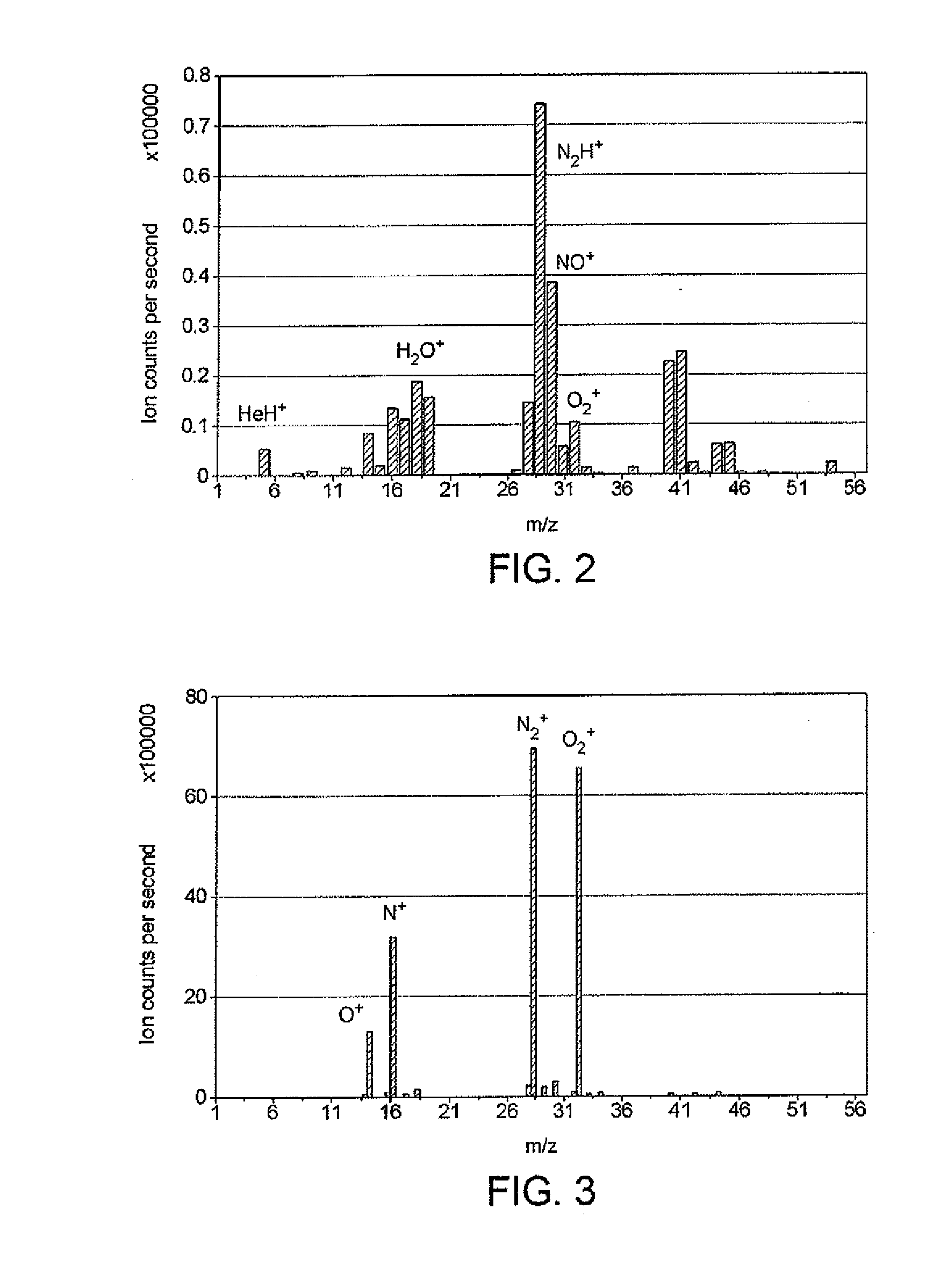
Gas treatment methods
InactiveUS20120094250A1Reduce in quantityHigh ionisation energyGum massageTeeth fillingOral treatmentNoble gas
A method of oral treatment comprises passing a flow of a gas mixture from a pressure vessel containing the gas mixture through a generator of non-thermal plasma; applying a partially ionising electrical potential to the flow of the gas mixture in the plasma generator, and thereby forming a non-thermal gaseous plasma in the gas mixture, and causing the flow of the gas mixture downstream of the plasma generator to perform the oral treatment. The gas mixture comprises (a) a noble gas selected from helium and argon and mixtures thereof, and (b) an additive gas selected from water vapour, air, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, nitrous oxide and nitric oxide and mixtures of any two or more thereof. The additive gas forms up to 1% by volume of the gas mixture. The oral treatment may be the cosmetic whitening of teeth, the non-clinical cleaning of teeth or the in situ cleaning of orthodontic braces, amongst others.
Owner:LINDE AG
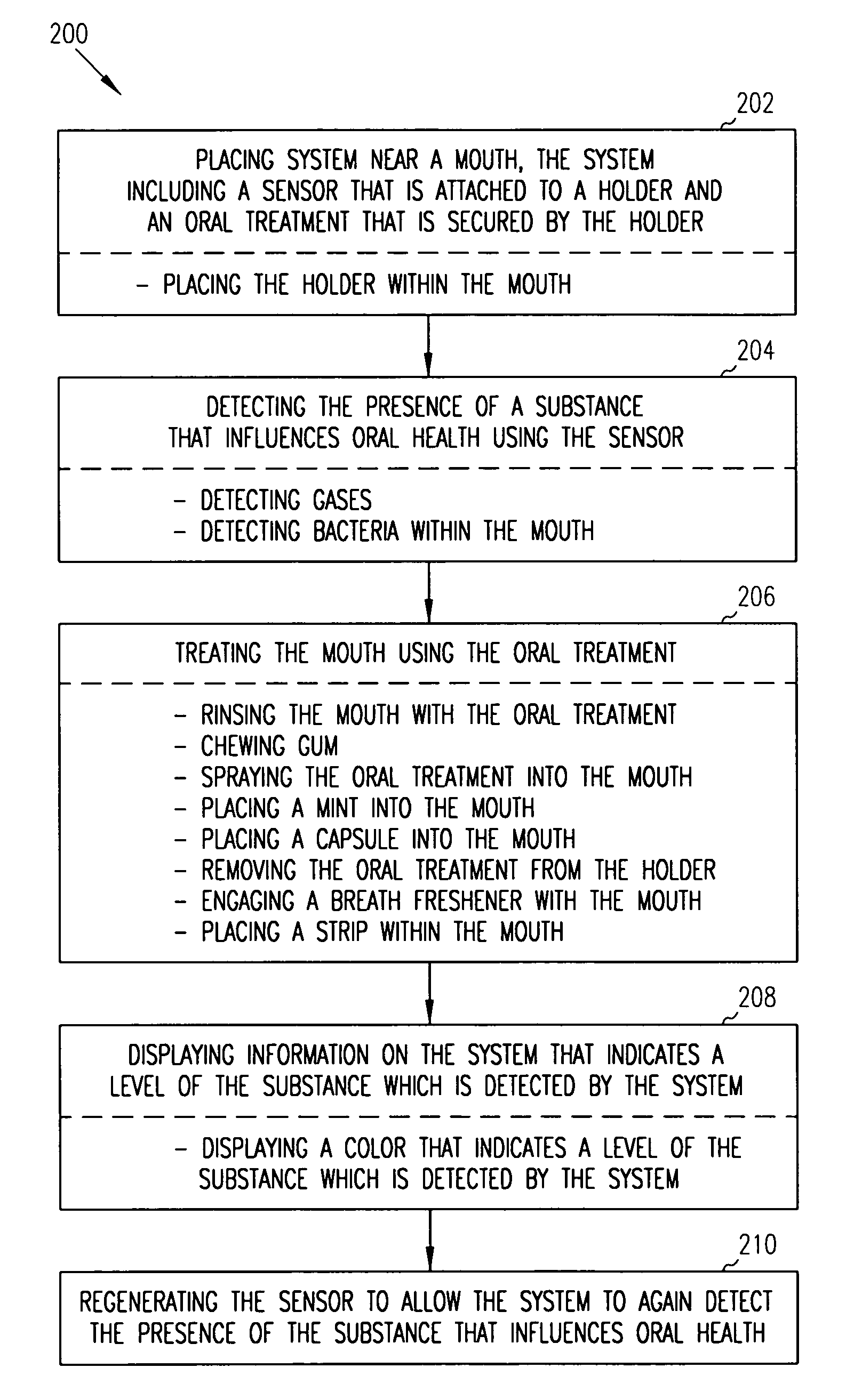
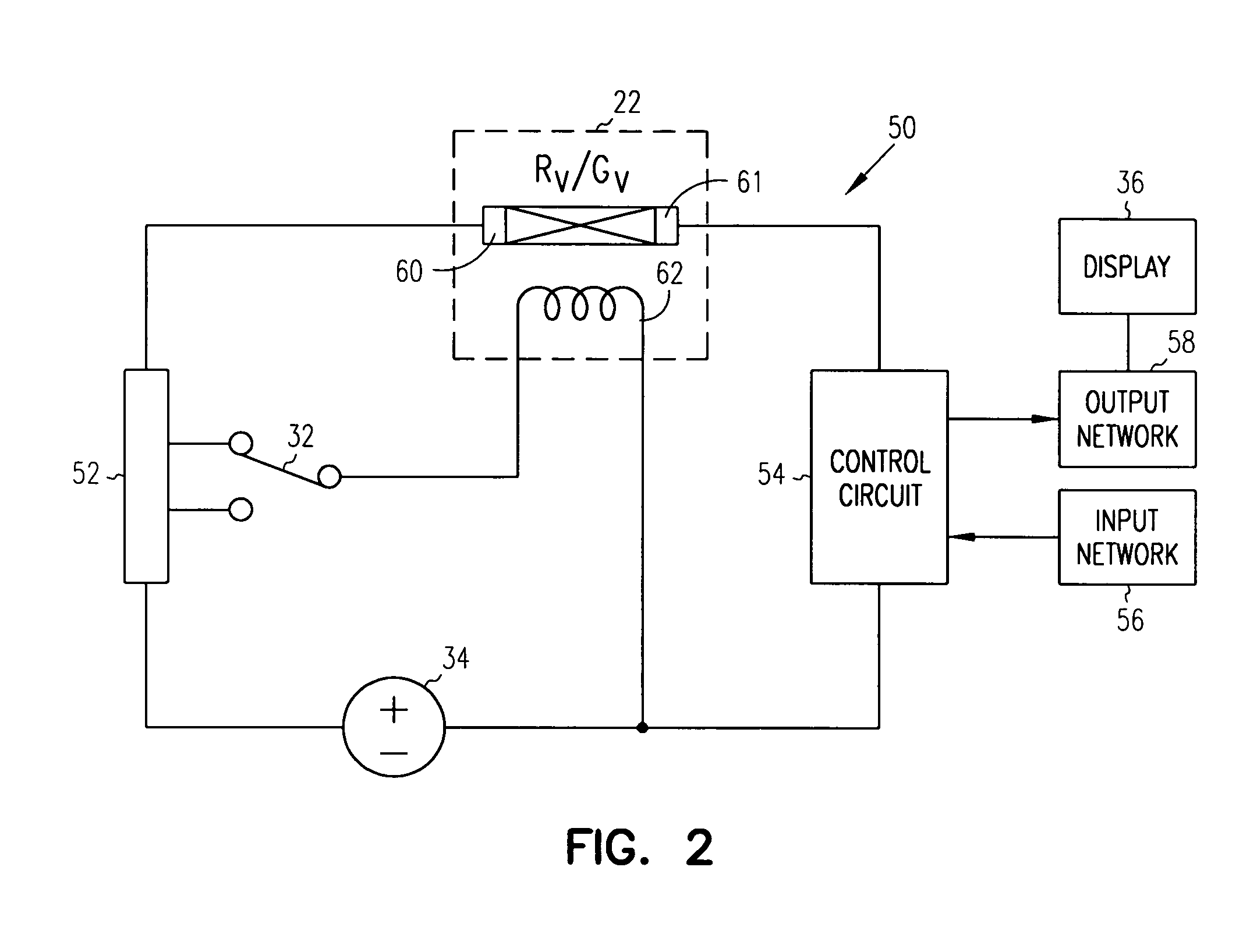
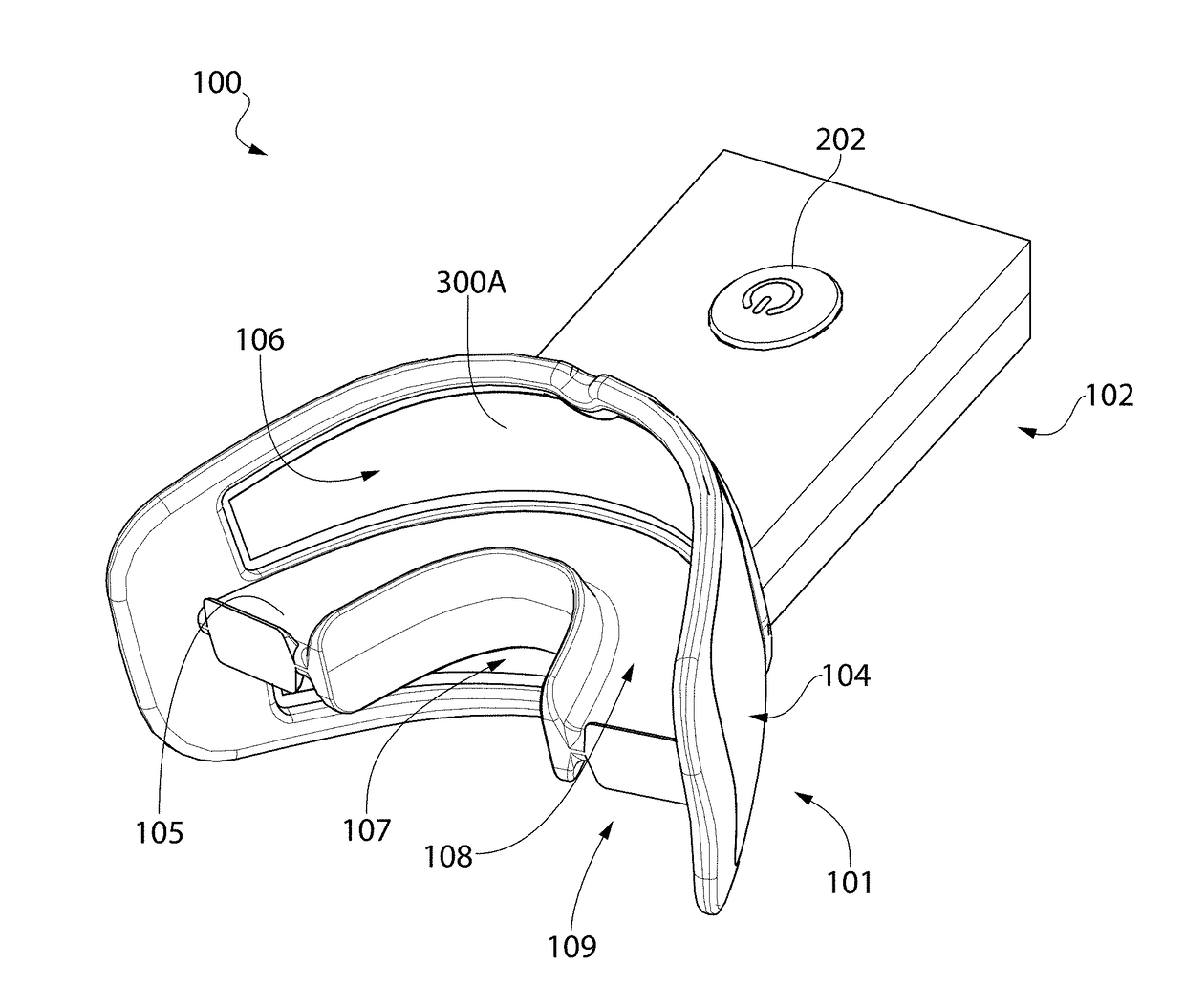
System and method for promoting oral health
The present invention provides a low-cost system and method for detecting substances within a mouth that influence oral health. The system and method also treat the mouth when certain substances are detected within the mouth. In some forms, the system includes a holder, a sensor that is attached to the holder and an oral treatment that is secured by the holder. The sensor detects a substance that influences oral health when the system is placed near a mouth. The oral treatment engages the mouth to treat the mouth when the substance is detected within the mouth. The method includes placing the system near a mouth and detecting the presence of a substance that influences oral health using the sensor. The method further includes treating the mouth using the oral treatment.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
Oral treatment device
An oral treatment device that emits light onto surfaces of a user's teeth. In one aspect, the oral treatment device includes an intraoral mouthpiece. The mouthpiece comprises a lamp support structure comprising a lamp support surface and is formed of a first material. A flexible lamp is mounted to the lamp support surface so that a light emitting surface of the flexible lamp assumes a concave curvature, thereby forming a lamp assembly. A guard component is overmolded to the lamp assembly. The guard component is formed of an elastomeric material having a hardness that is less than a hardness of the first material. In one embodiment, the oral treatment device may be a teeth whitening device.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Wax-based compositions, articles made therefrom, and methods of manufacture and use
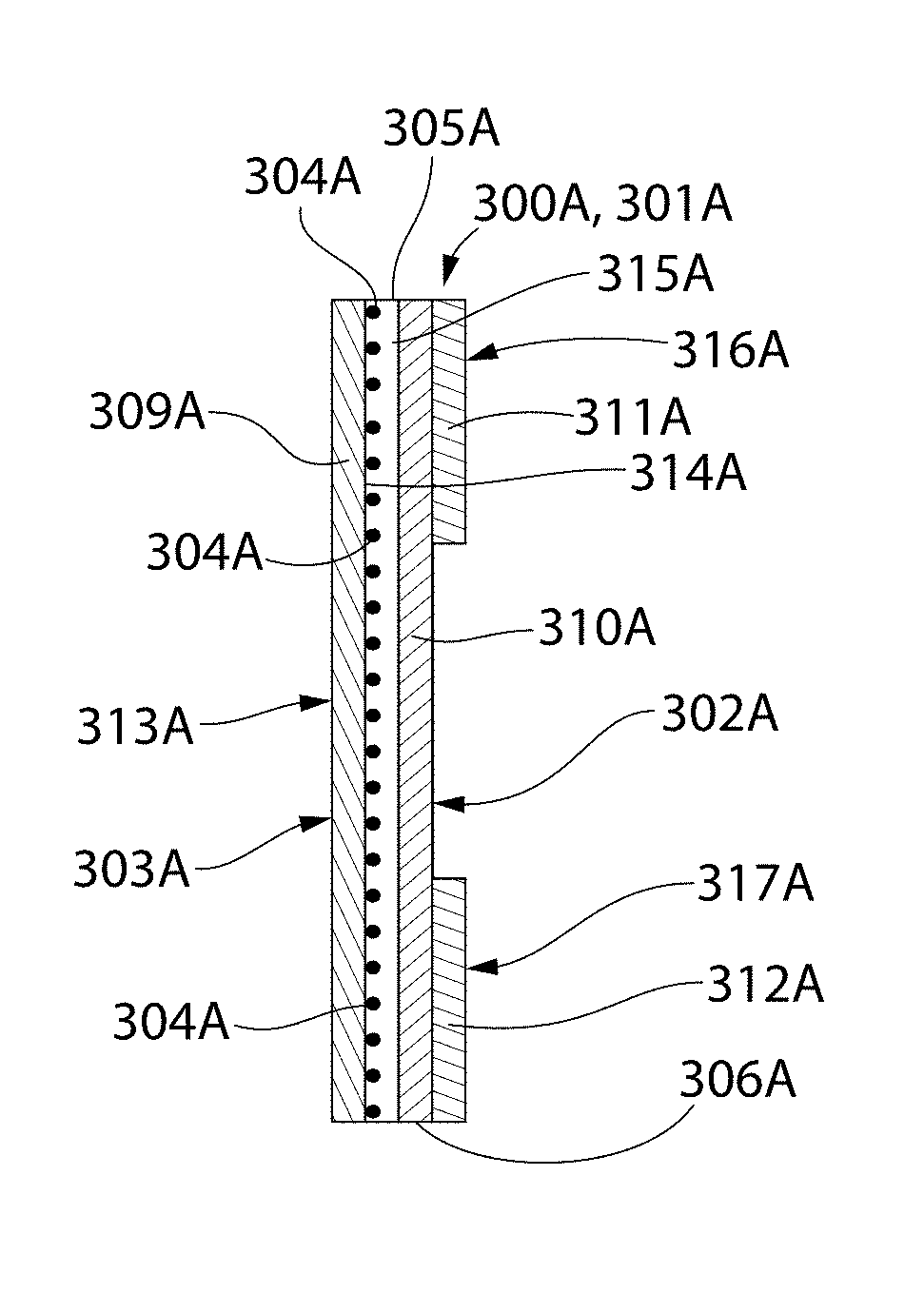
Oral treatment devices formed from wax-based compositions that are thermally stable when formed into a three-dimensional shape to a temperature of at least 45° C. and plastically deformable at room temperature (25° C.). The wax-based compositions include a wax fraction homogeneously blended with a polymer fraction. The wax fraction includes at least one wax. The polymer fraction includes at least one polymer selected such that, when the wax and polymer are homogeneously blended together, they yield a wax-based composition having the desired properties of thermal stability and plastic deformability. Oral treatment devices are dimensionally stable to a temperature of at least 40° C. without external support and can be plastically deformed in a user's mouth to become at least partially customized to the size and shape of user's unique dentition and / or an appliance in a user's mouth.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
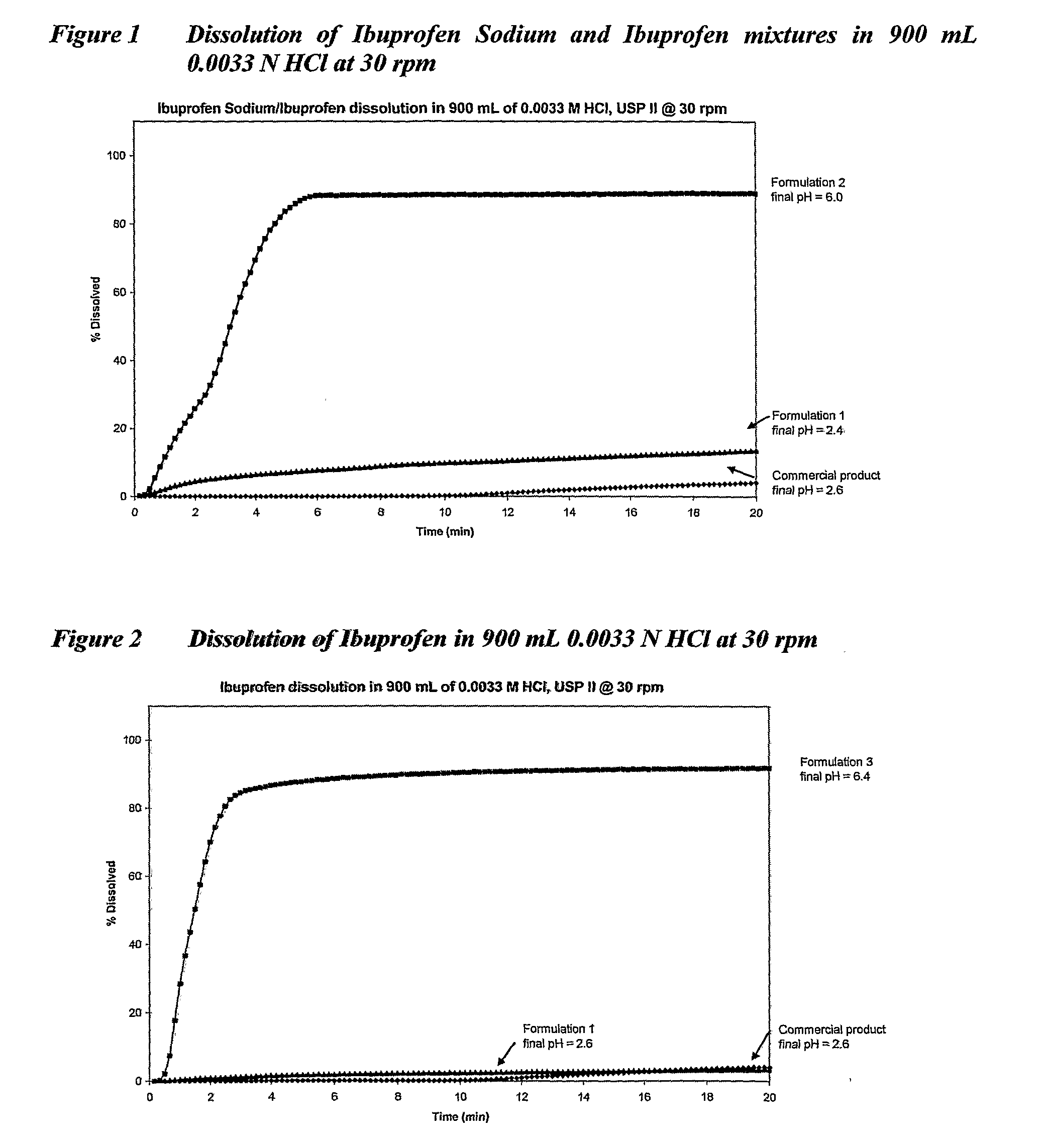
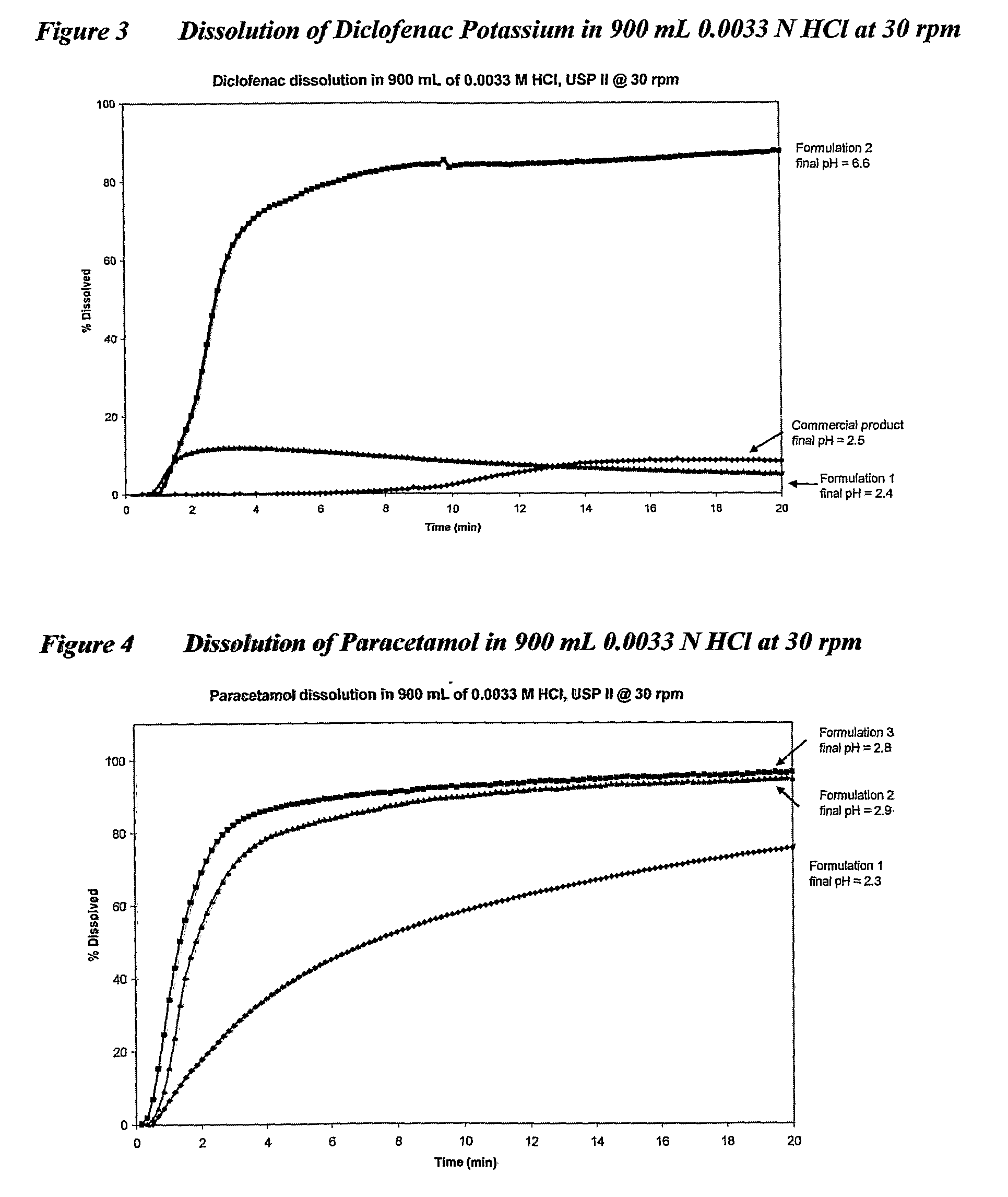
Oral Therapeutic Compound Delivery System
ActiveUS20090311327A1High dissolution rateGood moisture absorptionBiocidePowder deliveryOral treatmentPharmacology
The present, invention provides an oral delivery system for a therapeutic compound that is an acid, a salt of an acid or an unionized compound or a proactive form thereof with pharmacological, physiological or biochemical activity. The present invention particularly provides a swallow formulation comprising a therapeutic compound that is an acid, a salt of an acid or an unionized compound or a proactive form thereof which facilitates the rapid delivery of the therapeutic compound to the circulatory system.
Owner:JOHNSON & JOHNSON CONSUMER COPANIES
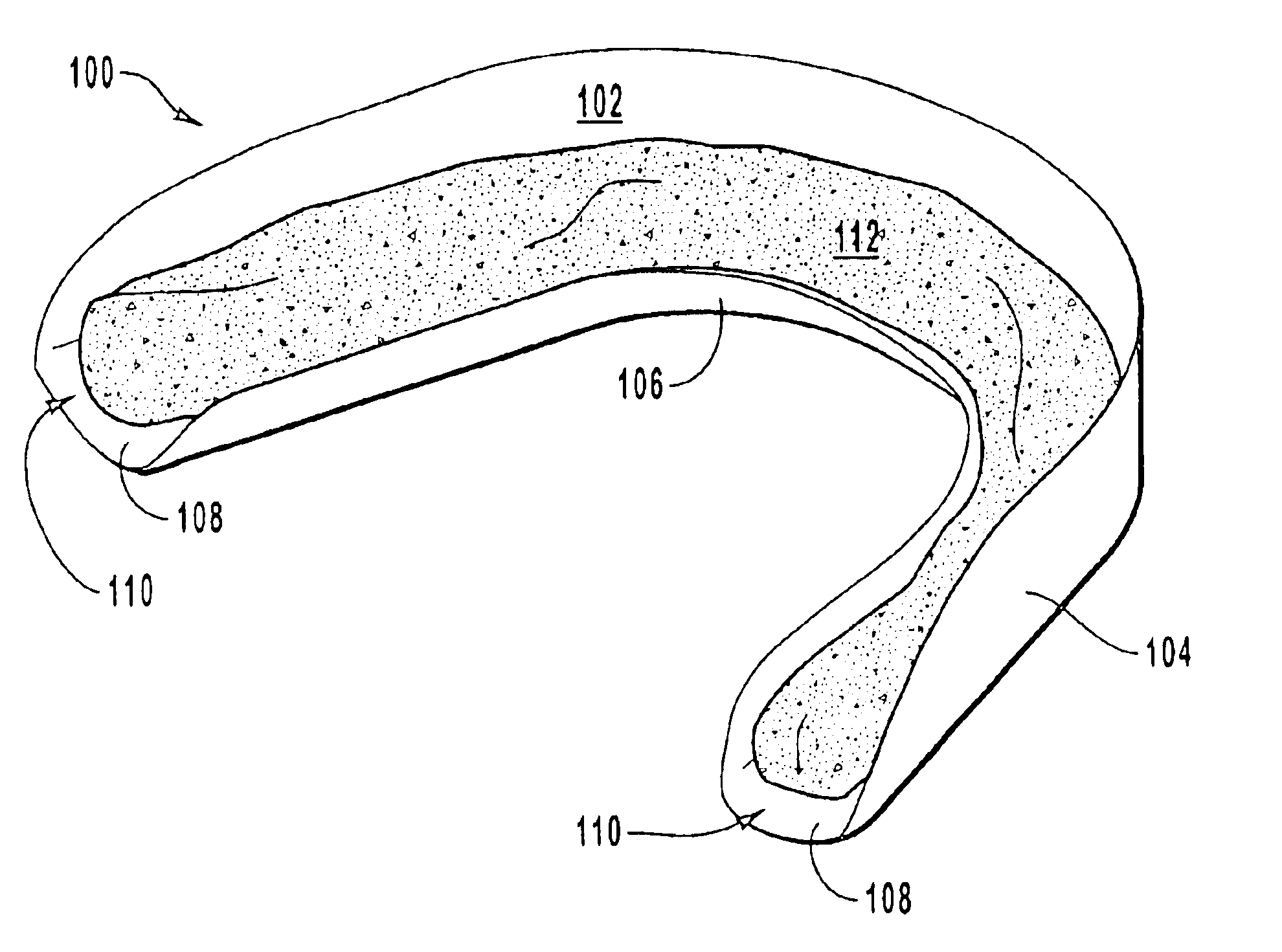
Treatment devices for providing oral treatments and kits and methods that utilize such treatment devices
InactiveUS20060029908A1Inhibited DiffusionPrevents and minimizes and lessens diffusionTeeth fillingTeeth cappingOral treatmentProtection sex
Treatment devices in the shape of a dental tray, strip or patch include a barrier layer and a protective adhesive composition. Treatment kits include one or more treatment devices and one or more treatment compositions that are initially separate from the treatment devices. The treatment compositions may be contained within a syringe (e.g., a unit dose syringe) for ease of delivery. The treatment composition is dispensed from the syringe onto the barrier layer and then placed over a person's teeth and / or gums. The protective adhesive composition, in combination with the barrier layer, at least partially confines the treatment composition to a desired location within the person's mouth during use. The barrier layer protects the treatment and protective adhesive compositions from saliva or moisture found in the person's mouth.
Owner:ULTRADENT PROD INC
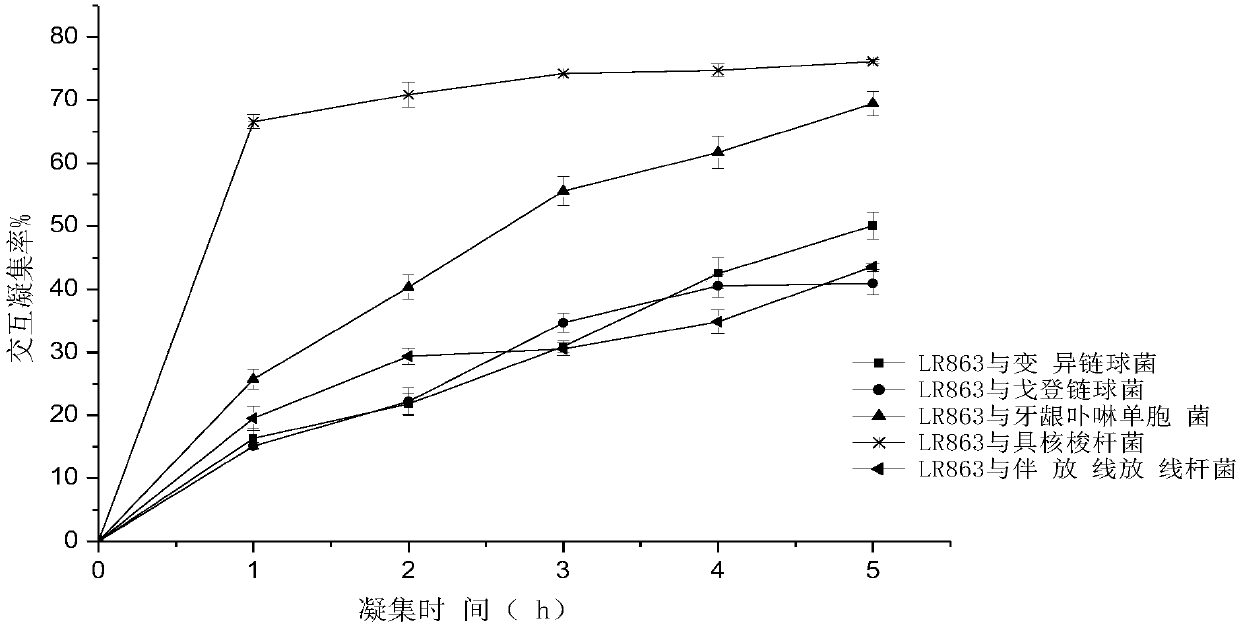
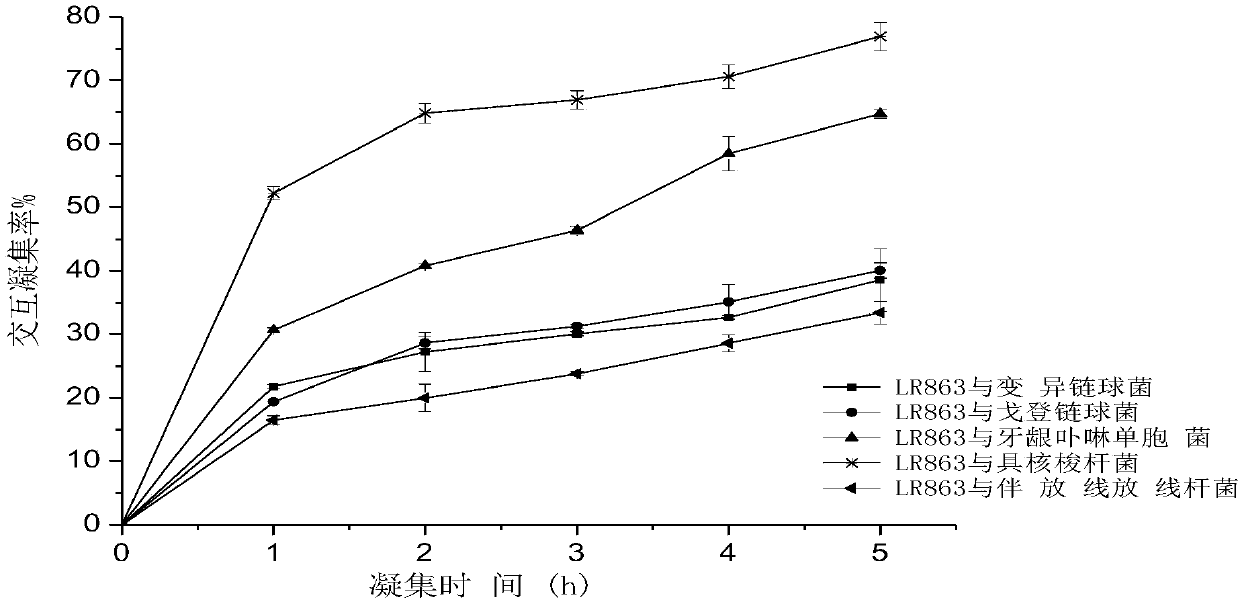
Lactobacillus rhamnosus, lactobacillus rhamnosus preparation and application thereof
ActiveCN108048347AStrong agglutination abilityReduce in quantityBacteriaDigestive systemOral diseaseDisease
The invention discloses lactobacillus rhamnosus. A strain (lactobacillus rhamnosus) LR863 is preserved in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center (CGMCC) and the preservation number isCGMCC No. 14410. The lactobacillus rhamnosus disclosed by the invention has remarkable bacterium-inhibition and sterilization effects on oral pathogenic microorganisms including streptococcus mutans,streptococcus gordonii, porphyromonas gingivalis, fusobacterium nucleatum, actinobacillus actinomycetemcomitans and the like, and has the effects of reducing formation of dental plaque and reducing occurrence and development of oral diseases including tooth decay, periodontitis and the like. A lactobacillus rhamnosus preparation disclosed by the invention can comprise viable bacterium thalli of the lactobacillus rhamnosus, dead bacterium thalli of the lactobacillus rhamnosus, metabolic products of the lactobacillus rhamnosus and intracellular extract, is an oral probiotics preparation which has wide application and a remarkable effect, and can be widely used as an additive of liquid-state foods, solid-state foods, colloidal foods, oral hygiene products and oral treatment drugs.
Owner:河北一然生物科技股份有限公司
Oral Therapeutic Compound Delivery System
InactiveUS20080287456A1Promote absorptionGood moisture absorptionBiocideSenses disorderOral treatmentPharmacology
The present invention relates generally to therapeutic formulations. More particularly, this present invention provides an oral delivery system for a therapeutic compound that is a base, a salt of a base or an amphoteric compound or a salt of a amphoteric compound with pharmacological, physiological or biochemical activity or a proactive form thereof. The present invention even more particularly provides a swallow formulation comprising a therapeutic compound that is a base, a salt of a base, an amphoteric compound or a salt of an amphoteric compound which facilitates the rapid delivery of the therapeutic compound to the circulatory system.
Owner:IMAGINOT PTY LTD
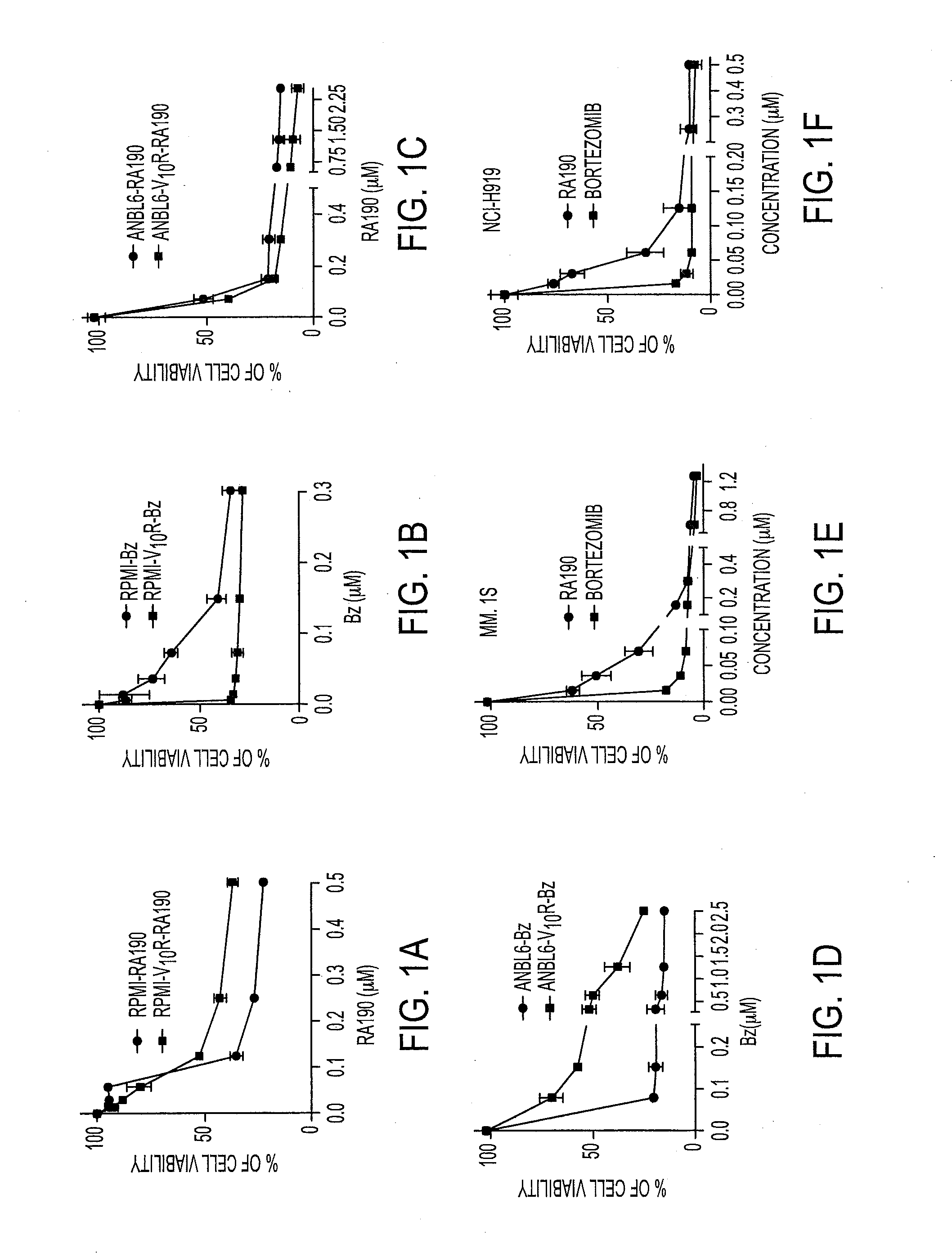
Novel bis-Benzylidine Piperidone Proteasome Inhibitor with Anticancer Activity
ActiveUS20160106725A1Reduced potencyReducing potencyBiocideOrganic chemistryHuman papillomavirus19S regulatory particle
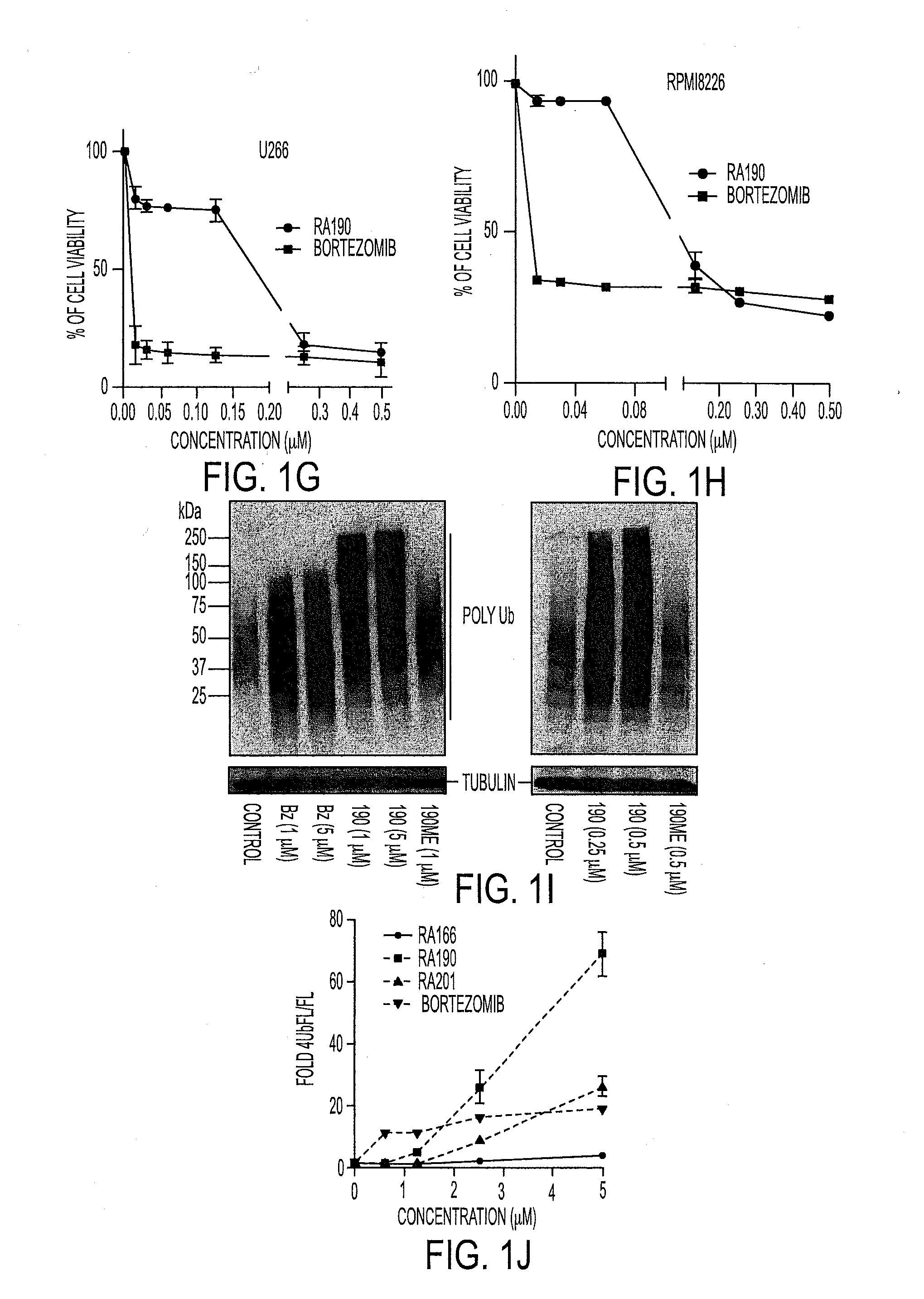
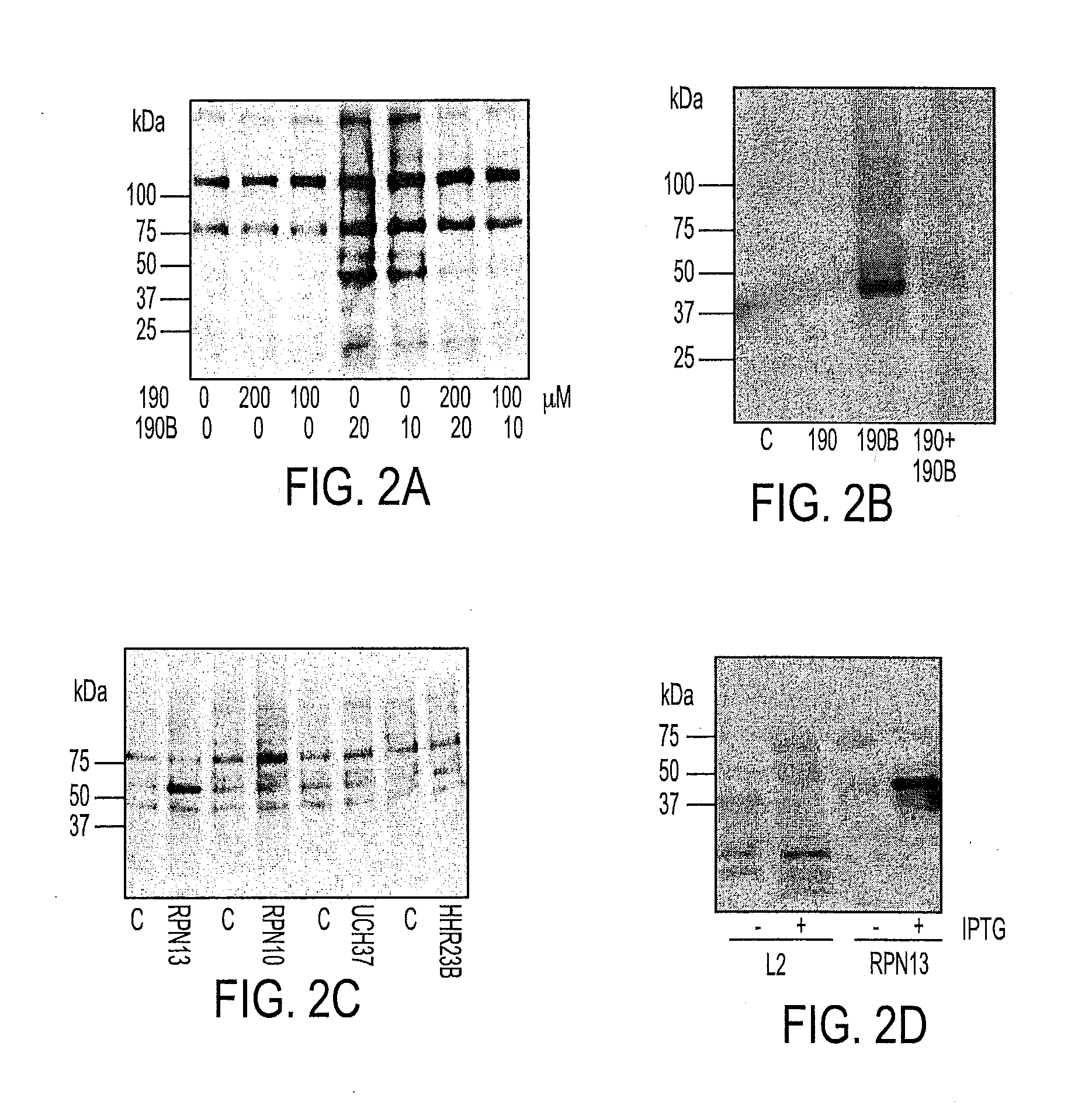
We describe a bis-benzylidine piperidone, RA190, which covalently binds to the ubiquitin receptor RPN13 (ADRM1) in the 19S regulatory particle and inhibits proteasome function, triggering rapid accumulation of polyubiquitinated proteins. Multiple myeloma lines, even those resistant to bortezomib, were sensitive to RA190 via ER stress-related apoptosis. RA190 stabilized targets of human papillomavirus (HPV) E6 oncoprotein, and preferentially killed HPV-transformed cells. After p.o. or i.p. dosing of mice, RA190 distributed to plasma and major organs excepting brain, and potently inhibited proteasome function in skin and muscle. RA190 administration i.p. profoundly reduced growth of multiple myeloma and ovarian cancer xenografts, and oral RA190 treatment retarded HPV+ syngeneic mouse tumor growth, without impacting spontaneous HPV-specific CD8+ T cell responses, suggesting its therapeutic potential. The bis-benzylidine piperidone RA190 is a new orally-available proteasome inhibitor. Multiple myeloma, cervical and ovarian cancers are particularly sensitive to RA190.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
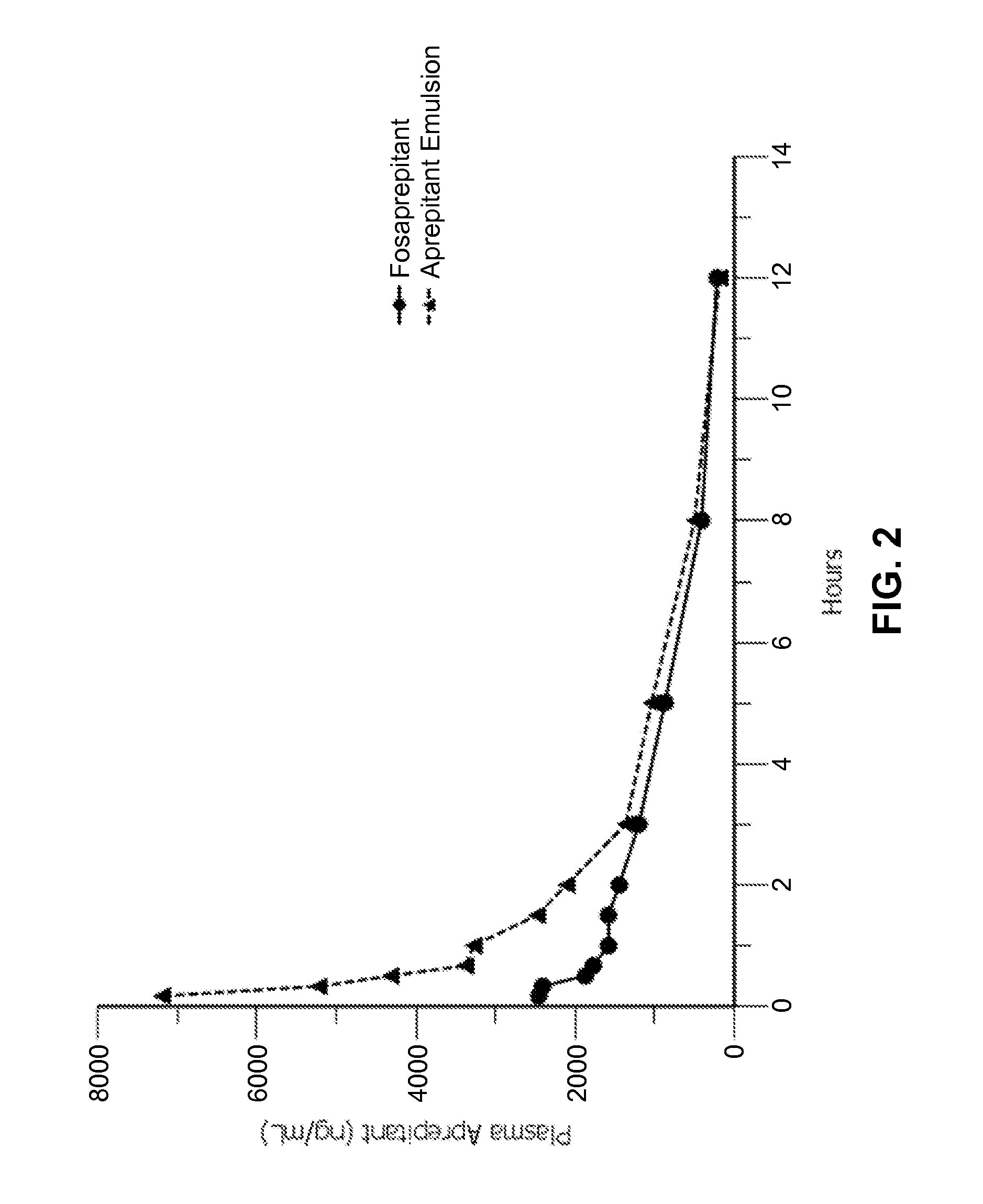
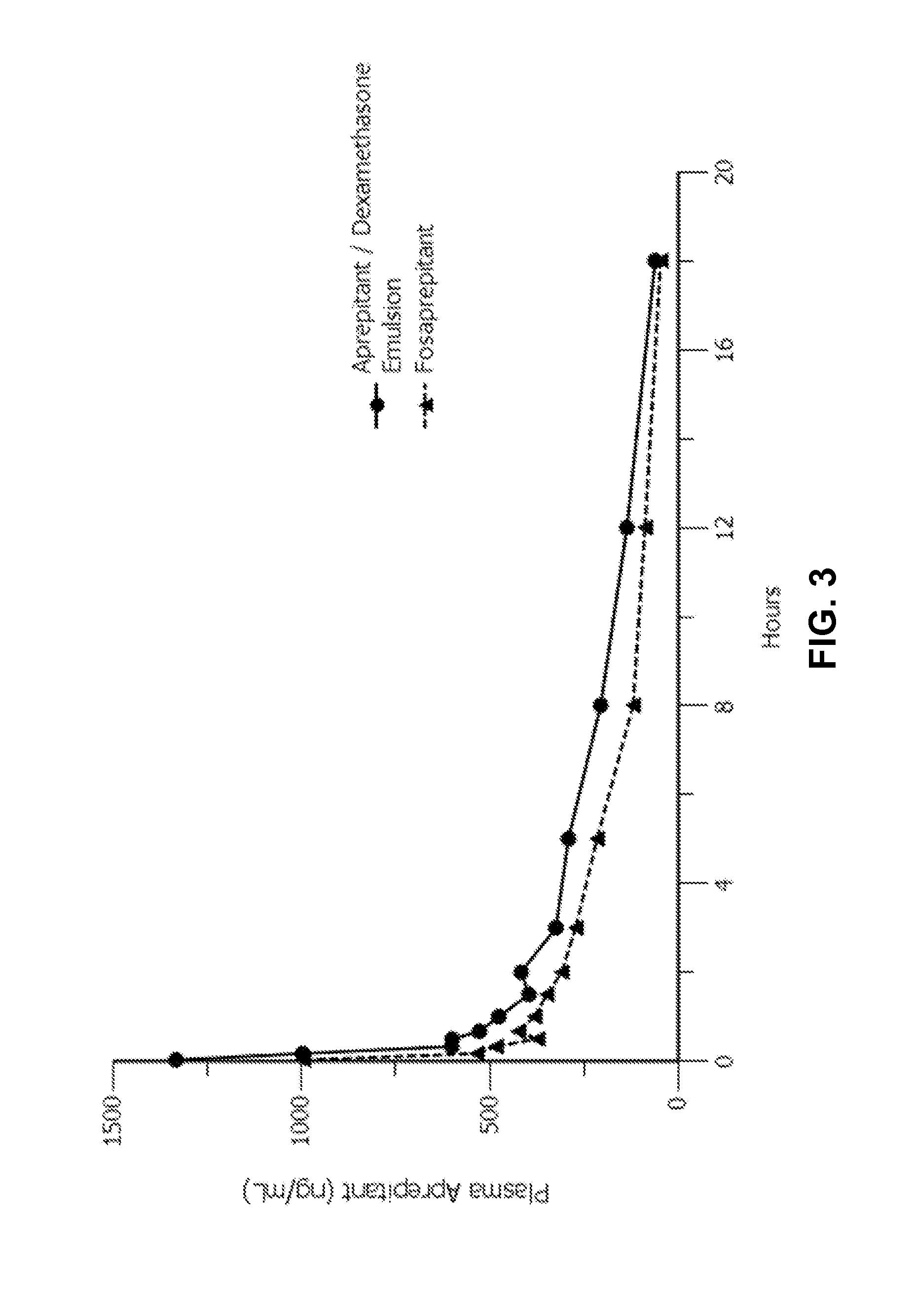
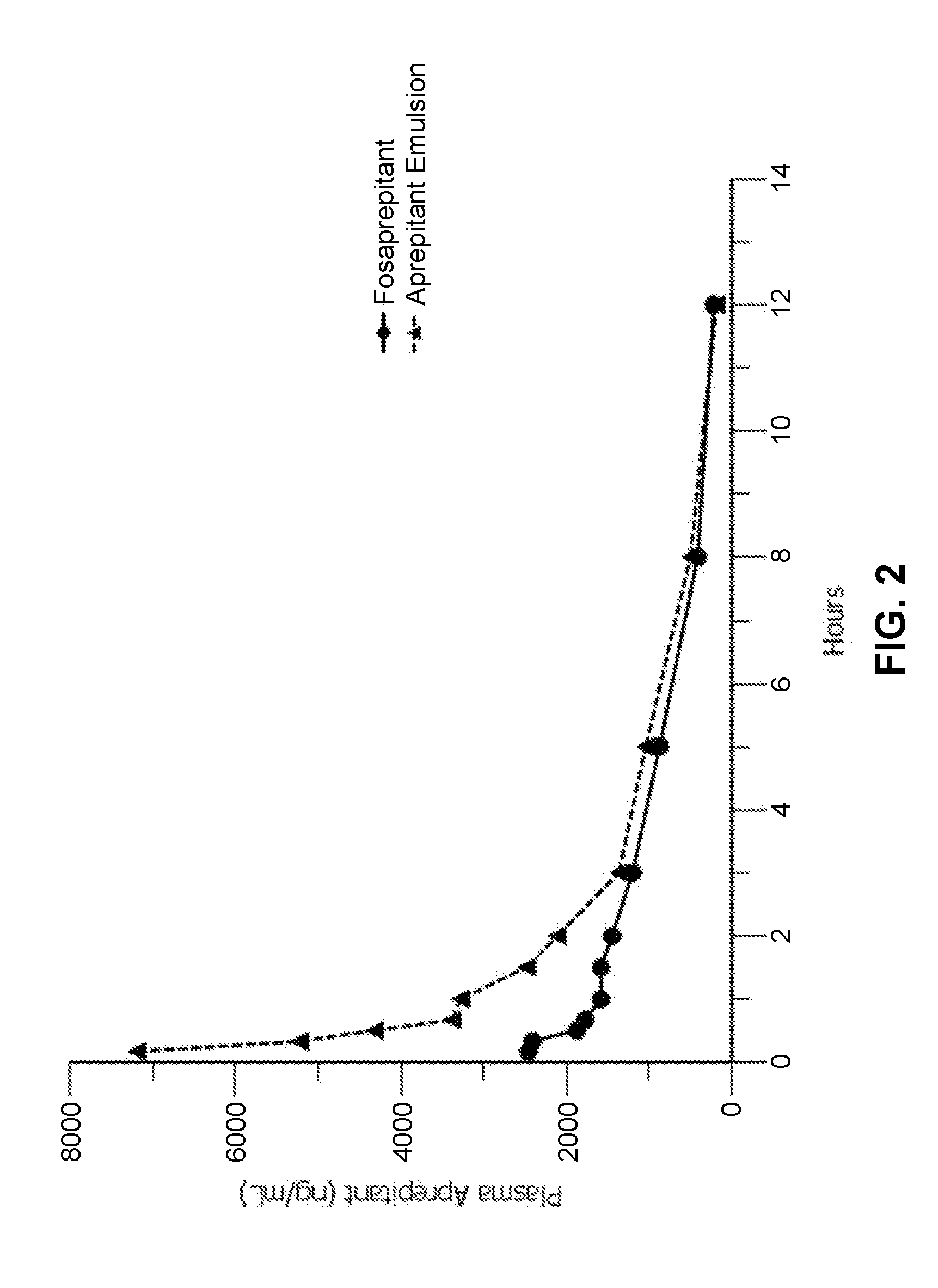
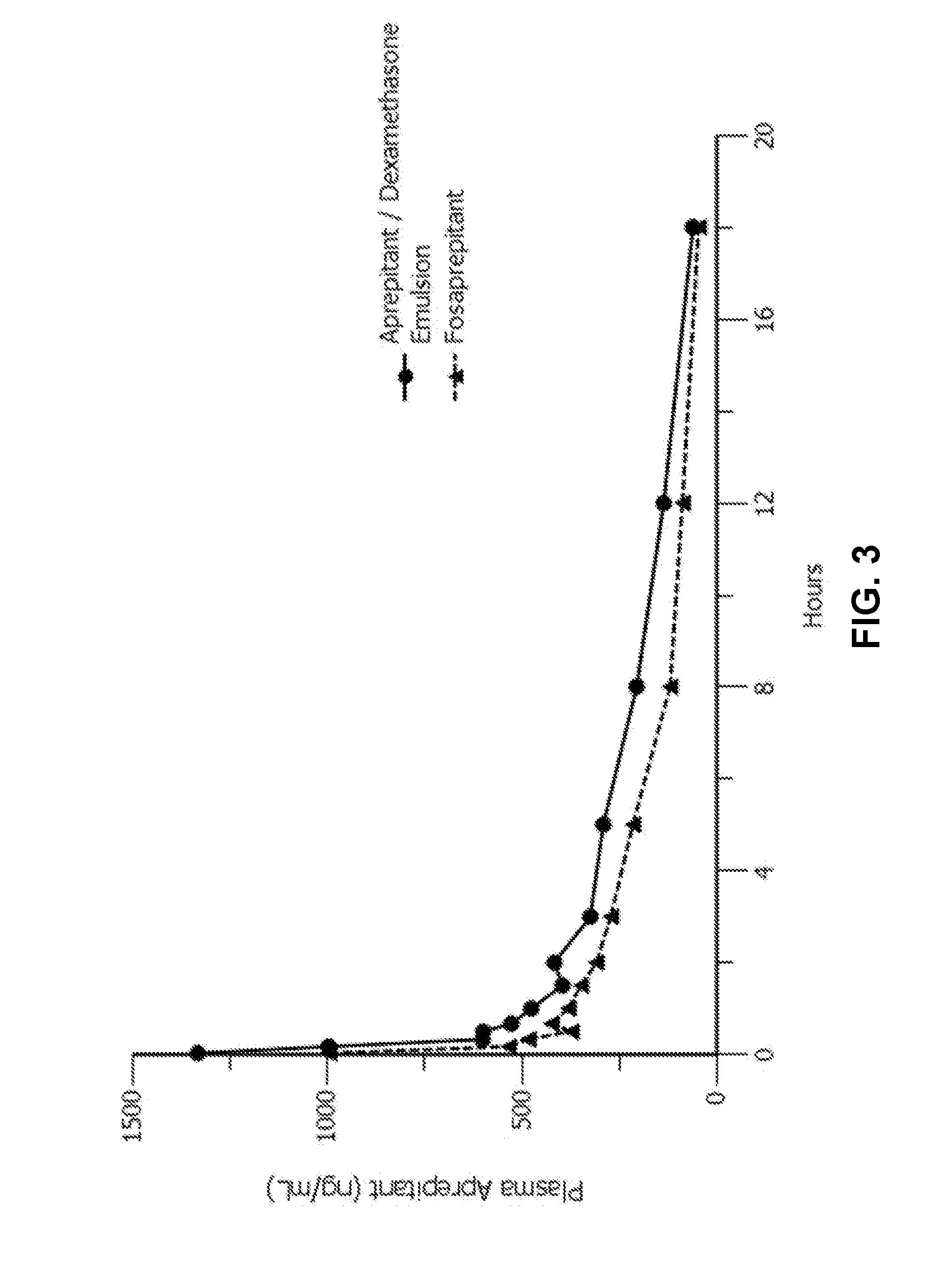
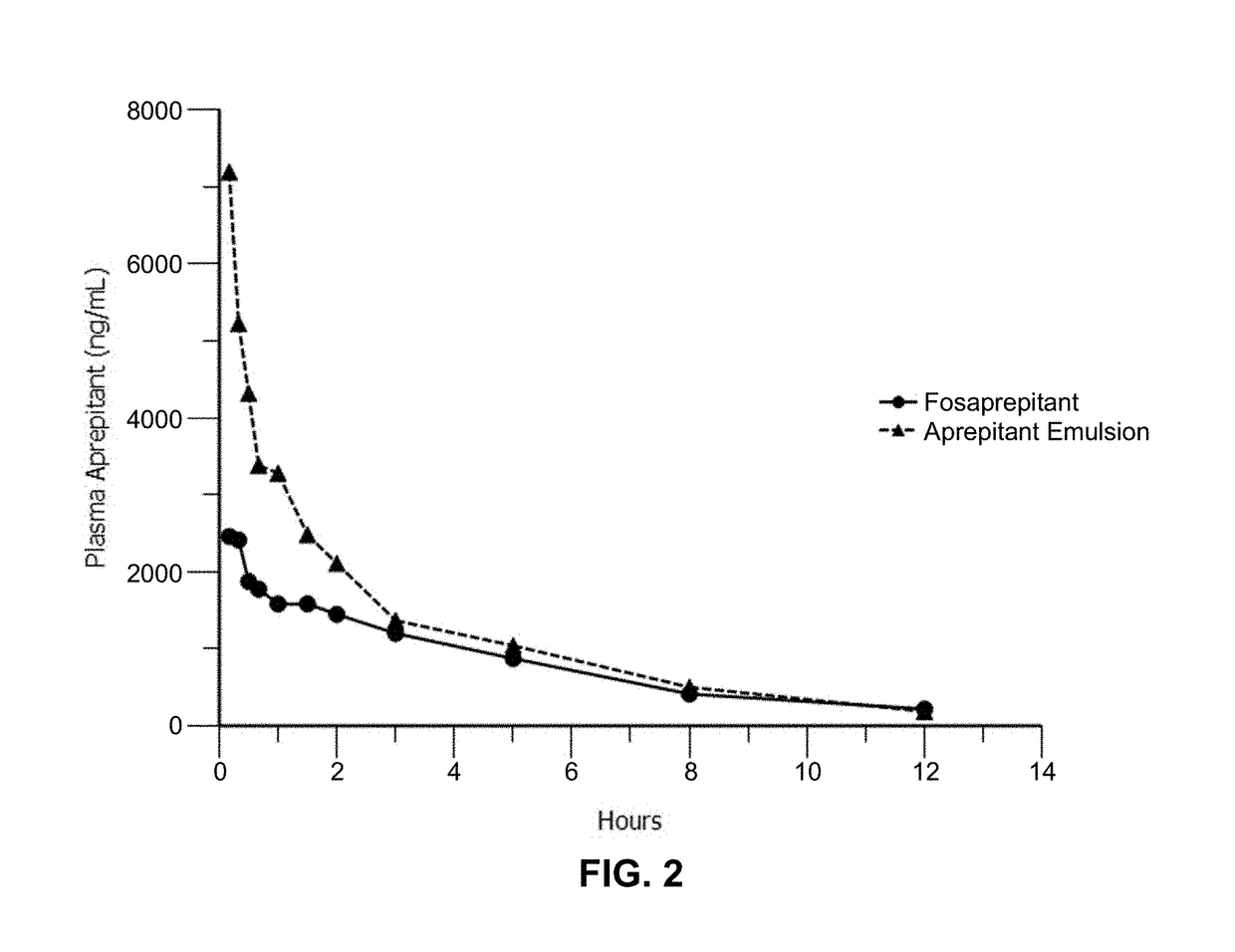
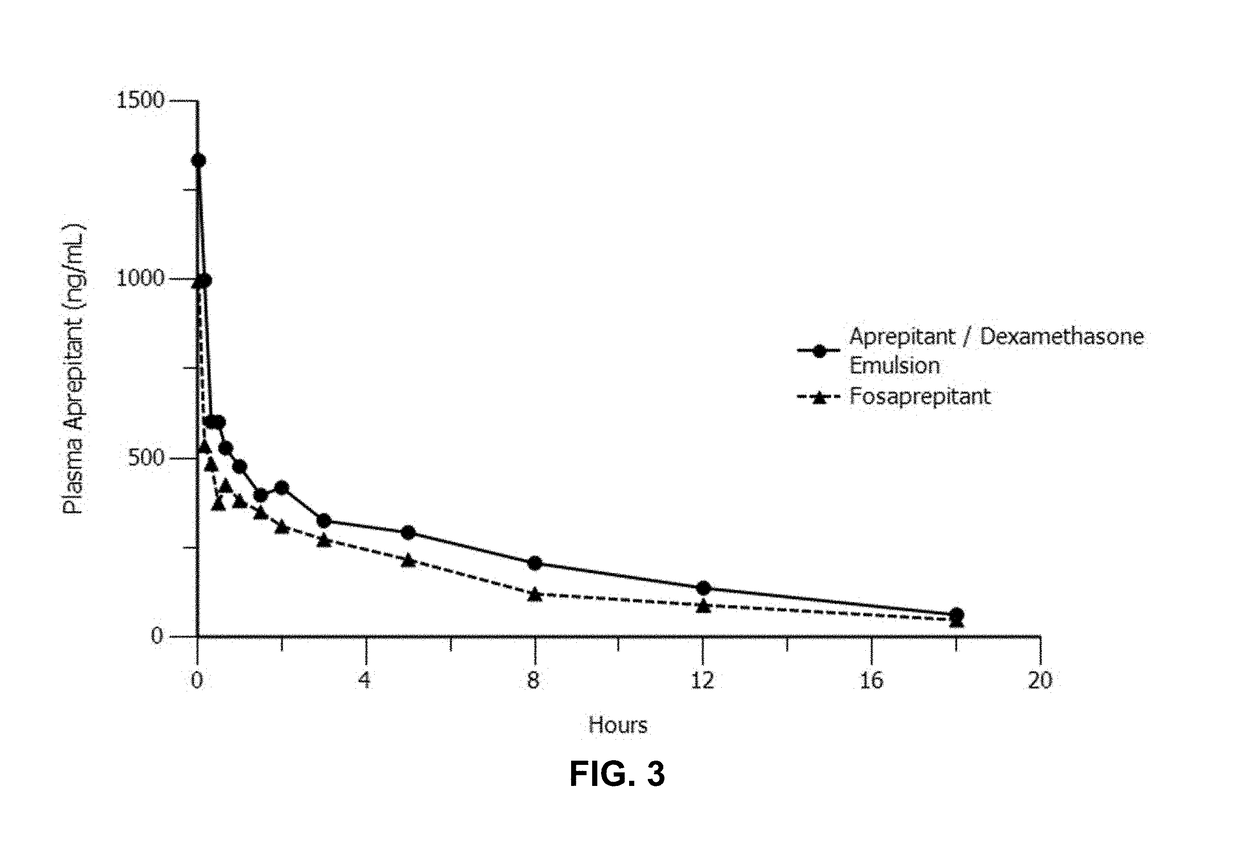
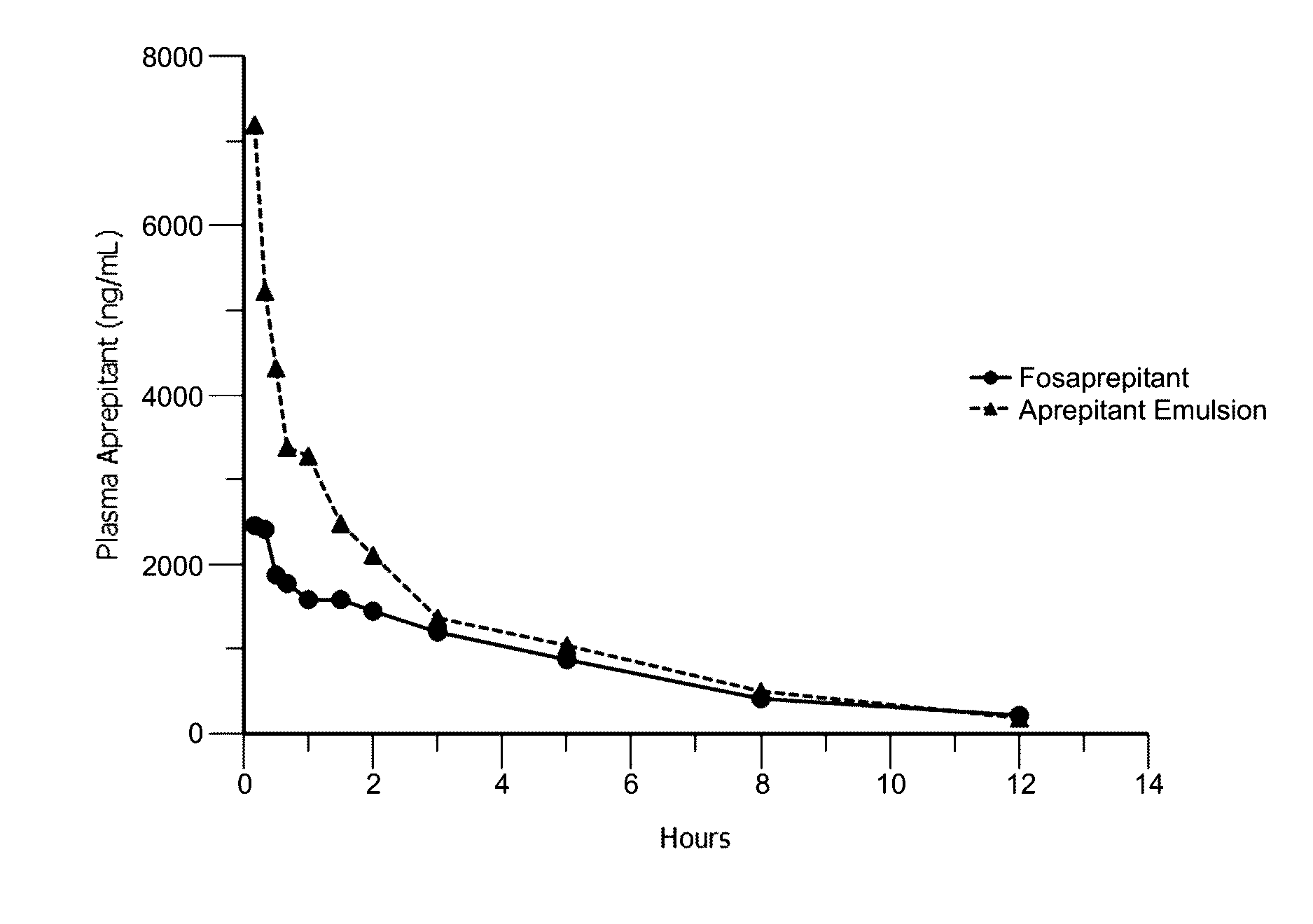
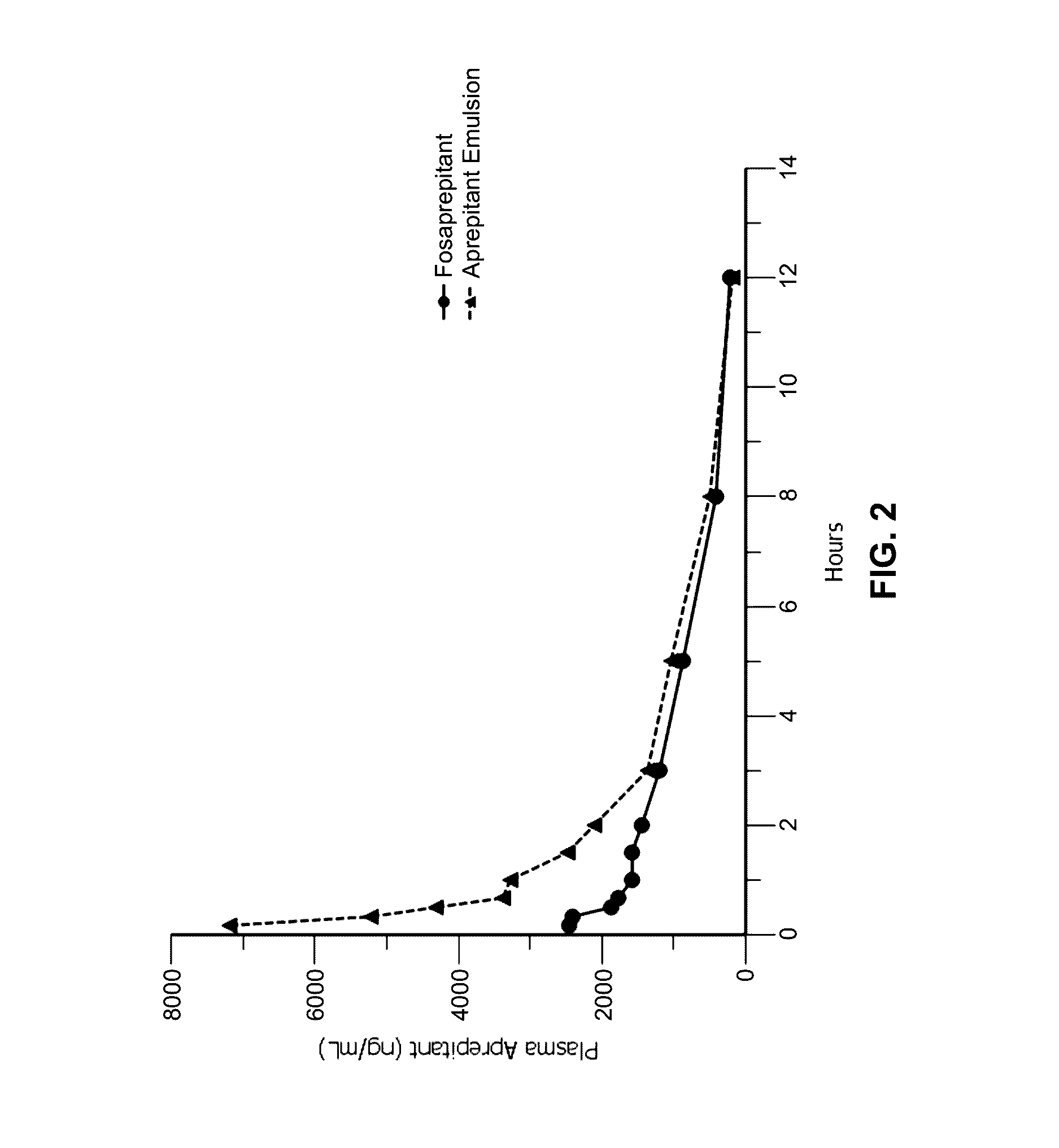
Emulsion formulations of aprepitant
ActiveUS20160082013A1Organic active ingredientsDigestive systemOral treatmentPharmaceutical formulation
Disclosed herein are novel pharmaceutical formulations of aprepitant suitable for parenteral administration including intravenous administration. Also included are formulations including both aprepitant and dexamethasone sodium phosphate. The pharmaceutical formulations are stable oil-in-water emulsions for non-oral treatment of emesis and are particularly useful for treatment of subjects undergoing highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy.
Owner:HERON THERAPEUTICS
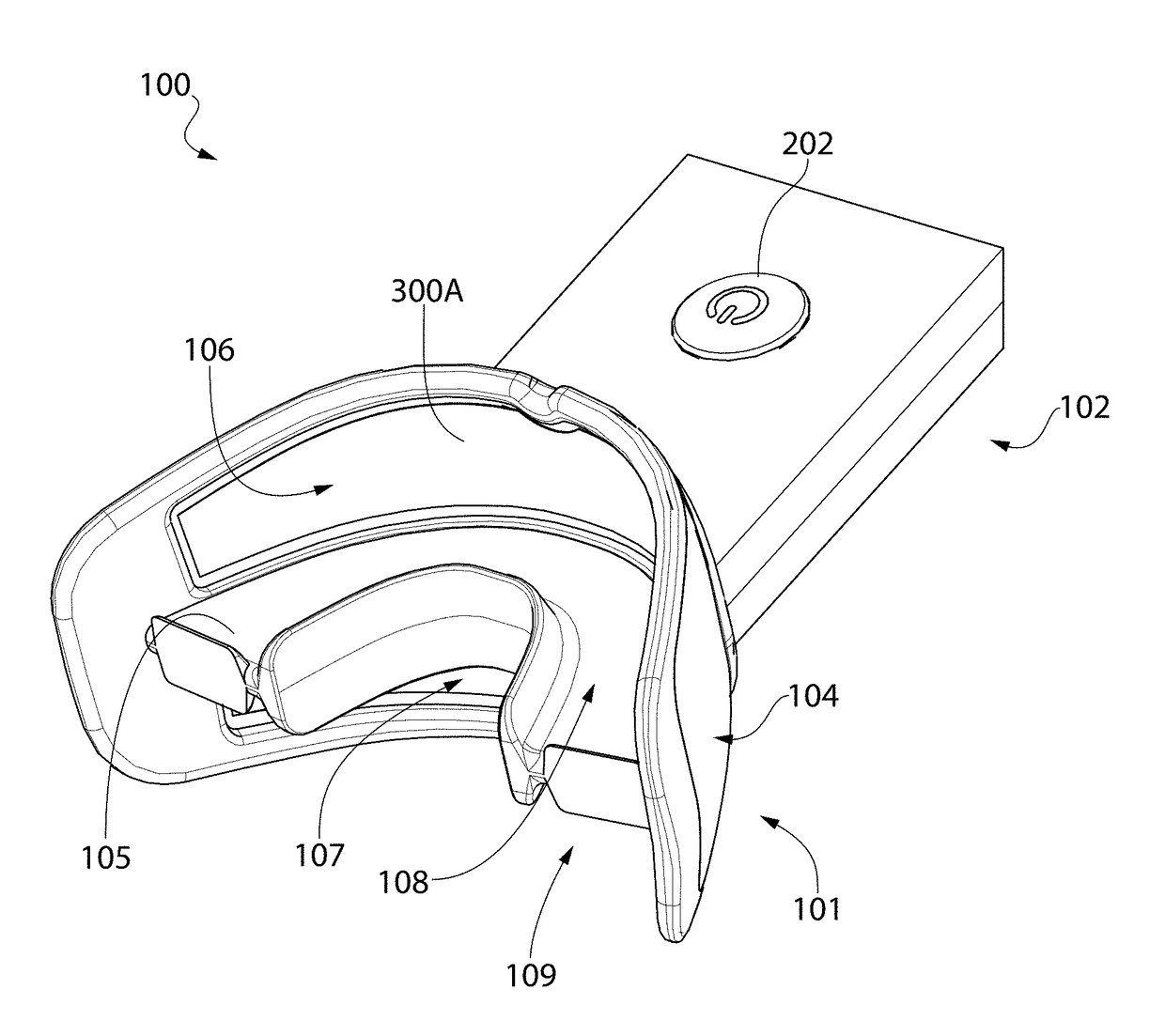
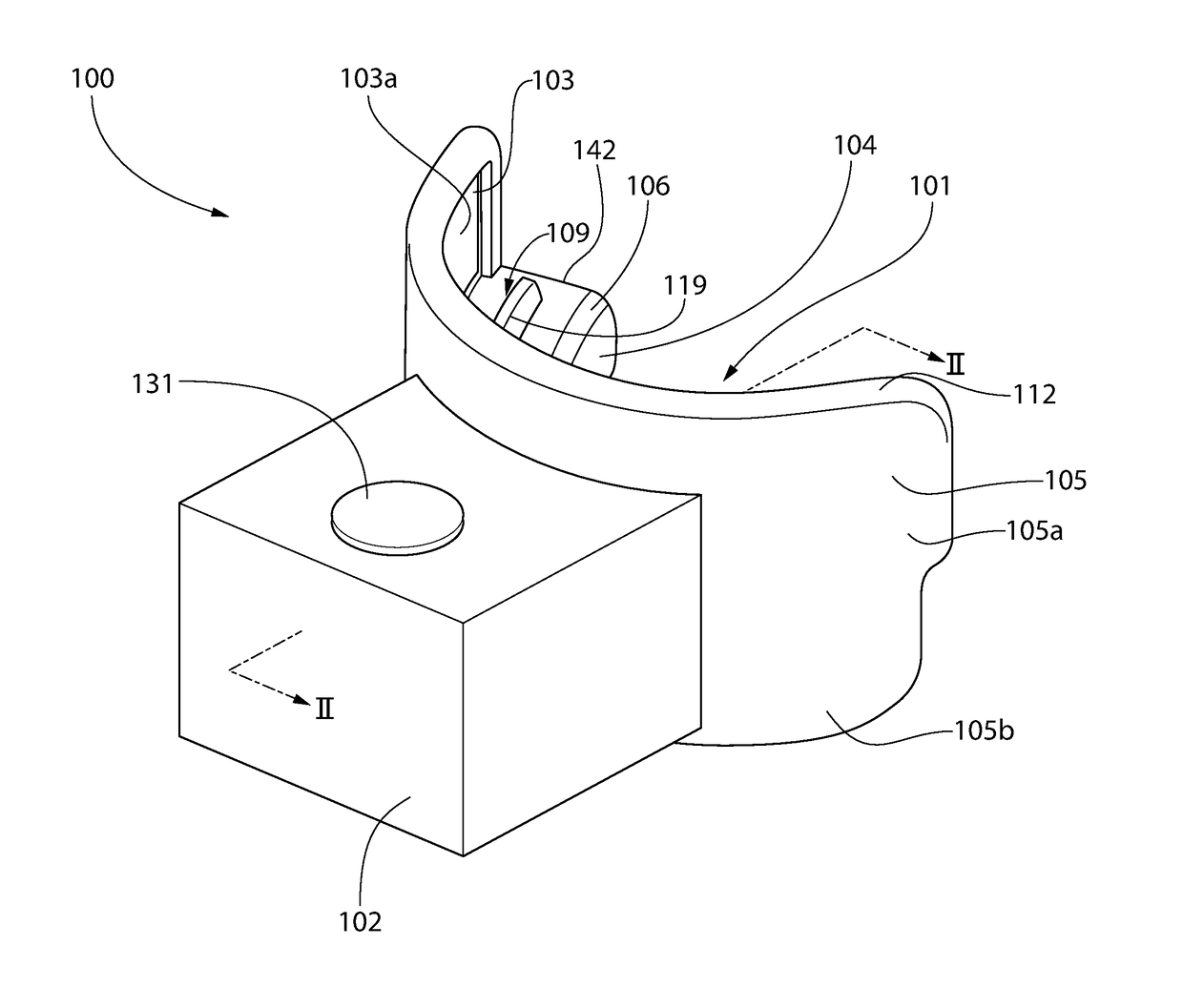
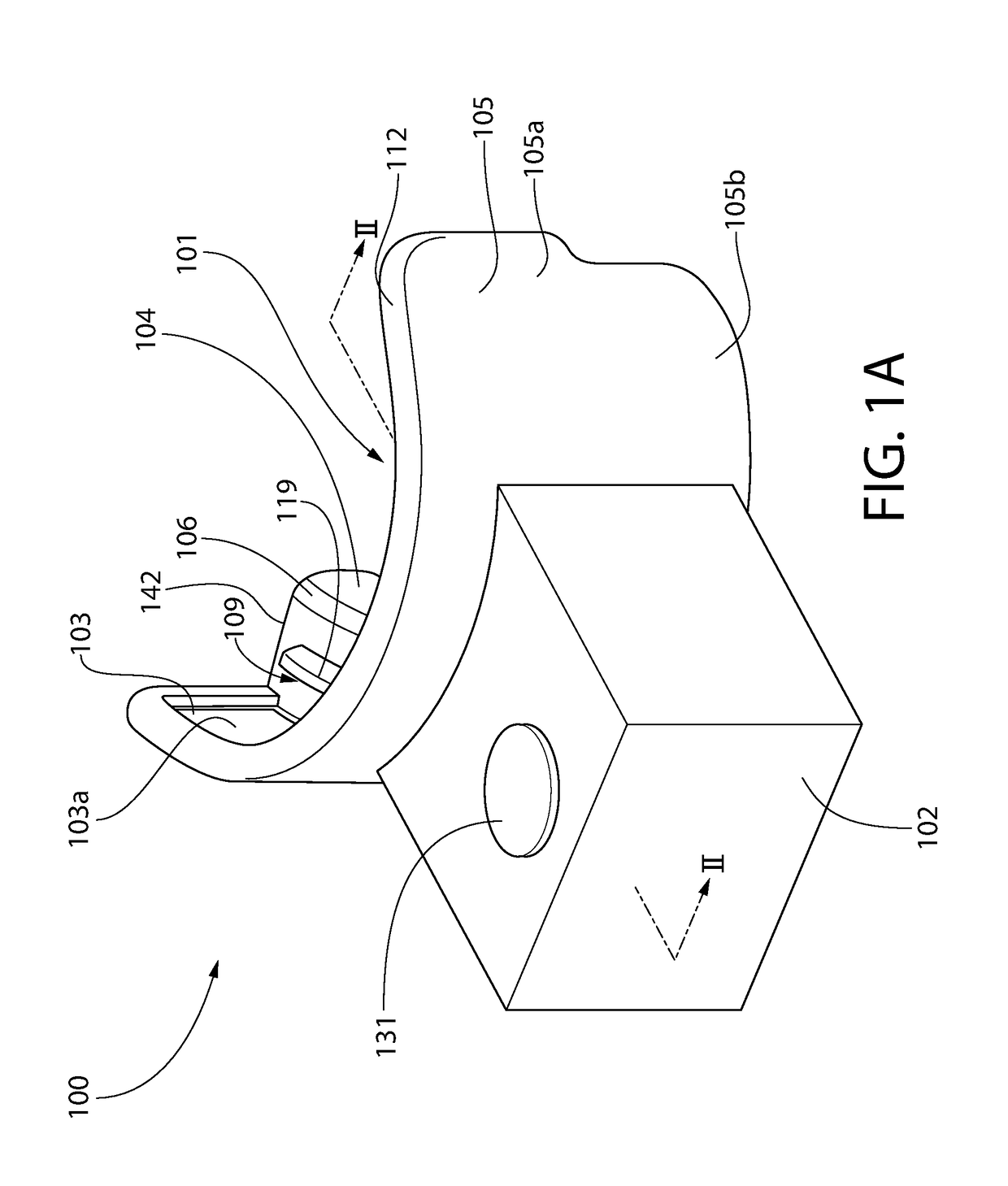
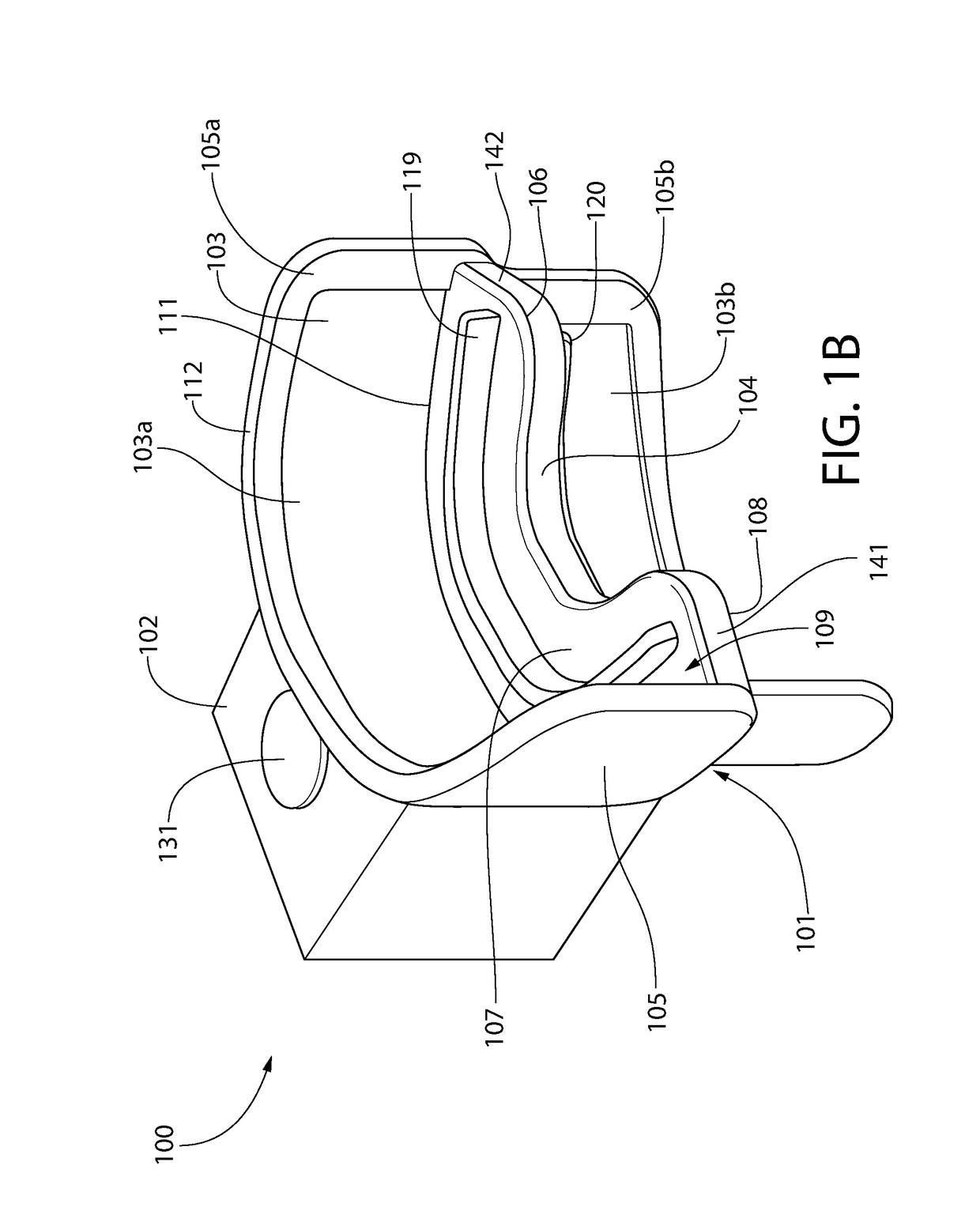
Oral treatment device
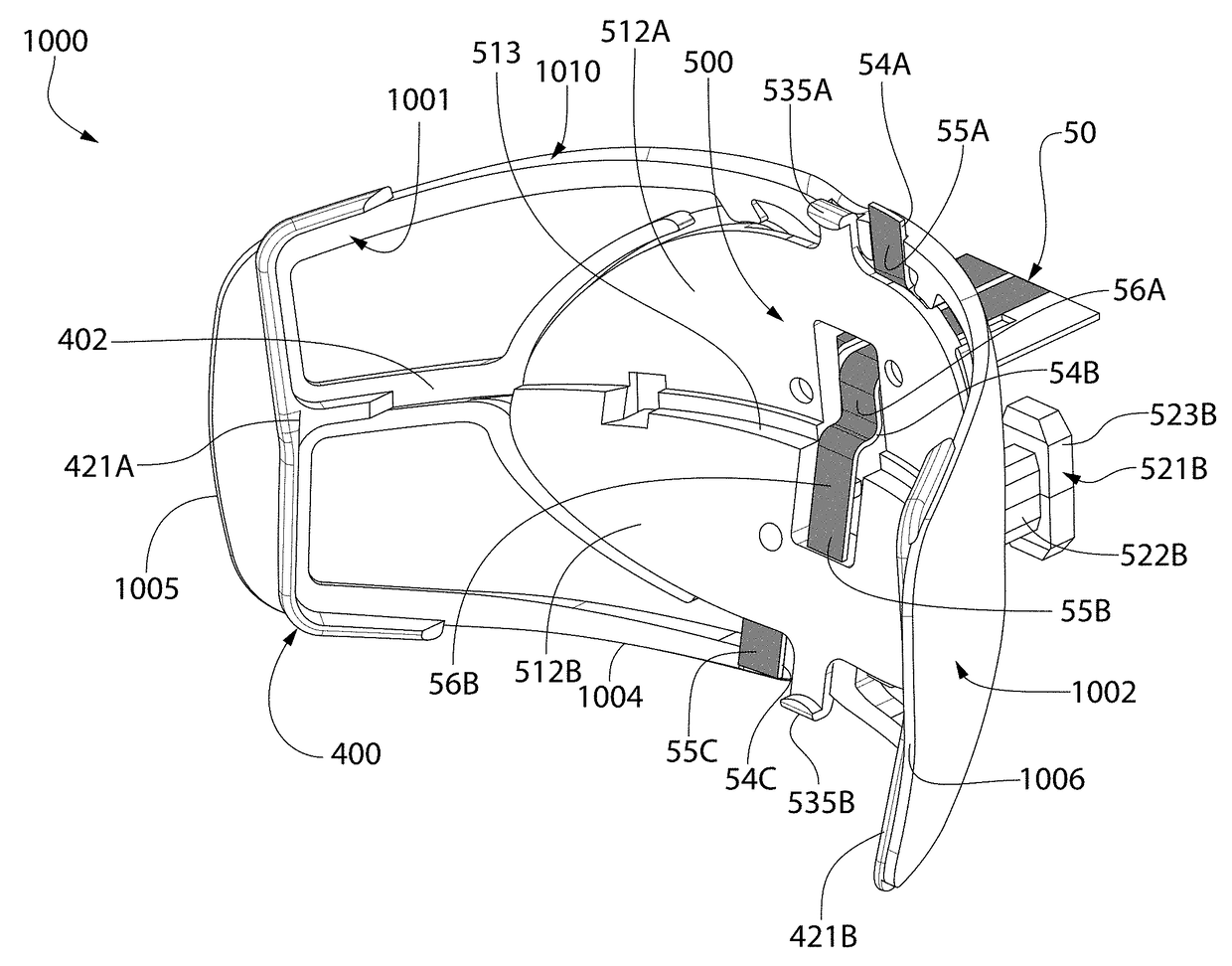
ActiveUS20170173353A1Improve fitLight therapyLip/mouth protectorsOral treatmentElectromagnetic radiation
An oral treatment device that includes a mouthpiece and an electromagnetic radiation source. In one aspect, the oral treatment device includes a mouthpiece comprising a curved wall having a concave inner surface and a bite platform extending from the concave inner surface of the curved wall to a distal end, the distal end of the bite platform extending continuously in a non-interrupted manner from a first end of the bite platform to a second end of the bite platform; an electromagnetic radiation source configured to emit electromagnetic radiation from the curved wall; and wherein the bite platform comprises a collapsible region such that the mouthpiece is alterable between: (1) a biased state in which the curved wall has a first curvature; and (2) a flexed state in which the curved wall has a second curvature that is different than the first curvature.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Oral treatment device
An oral treatment device that emits light onto a user's teeth. The oral treatment device includes an intraoral mouthpiece comprising: a lamp comprising: a flexible sheet body having a front surface and a rear surface; and a plurality of light emitting diodes embedded within the flexible sheet body that generate light which is emitted from the rear surface of the flexible sheet body. The flexible sheet body comprises: a flexible lens plate formed of a biocompatible material. The plurality of light emitting diodes are printed to the front surface of the flexible lens plate, the rear surface of the flexible lens plate forming the rear surface of the flexible sheet body. The rear surface of the flexible sheet body of the lamp having a concave curvature and being exposed so as to form a light emitting surface of the mouthpiece.
Owner:COLGATE PALMOLIVE CO
Emulsion formulations of aprepitant
Disclosed herein are novel pharmaceutical formulations of aprepitant suitable for parenteral administration including intravenous administration. Also included are formulations including both aprepitant and dexamethasone sodium phosphate. The pharmaceutical formulations are stable oil-in-water emulsions for non-oral treatment of emesis and are particularly useful for treatment of subjects undergoing highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy.
Owner:HERON THERAPEUTICS
Emulsion formulations of an nk-1 receptor antagonist and uses thereof
Disclosed herein are novel pharmaceutical formulations of a neurokinin-1 (NK-1) receptor antagonist suitable for parenteral administration including intravenous administration. Also included are formulations including both the NK-1 receptor antagonist and dexamethasone sodium phosphate. The pharmaceutical formulations are stable oil-in-water emulsions for non-oral treatment of emesis and are particularly useful for treatment of subjects undergoing highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy.
Owner:HERON THERAPEUTICS
Emulsion formulations of aprepitant
Disclosed herein are novel pharmaceutical formulations of aprepitant suitable for parenteral administration including intravenous administration. Also included are formulations including both aprepitant and dexamethasone sodium phosphate. The pharmaceutical formulations are stable oil-in-water emulsions for non-oral treatment of emesis and are particularly useful for treatment of subjects undergoing highly emetogenic cancer chemotherapy.
Owner:HERON THERAPEUTICS
Compositions of (-)-17-(cyclobutylmethyl)morphinan-3,14-diol
ActiveUS9364430B2Increase rangeSlow onsetOrganic active ingredientsGranular deliveryModified Release Dosage FormMorphinan
The present invention is directed to oral, therapeutically effective modified release pharmaceutical compositions of (−)-17-(cyclobutylmethyl)morphinan-3,14-diol and it pharmaceutically acceptable salts and the use thereof, including delayed onset and extended release dosage forms. The present invention is also directed at modified release dosage forms of oral (−)-17-(cyclobutylmethyl)morphinan-3,14-diol which provide robust efficacy and reduced potential for abuse and misuse.
Owner:RELMADA THERAPEUTICS
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com