Method for identifying infection resistance of peanuts to aspergillus flavus and application thereof
An identification method and a technology for Aspergillus flavus, applied in the agricultural field, can solve the problems of unfavorable rapid identification, large operation errors, and high detection costs, and achieve the effects of avoiding mold growth and contaminating results, reliable results, and high detection costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] A kind of identification method of peanut to the infection resistance of Aspergillus flavus, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0040] Step 1, after Aspergillus flavus As3.2890 is activated on a slant, the spores of Aspergillus flavus are eluted with an acetic acid solution with a volume fraction of 5%, and prepared into a suspension of Aspergillus flavus spores for future use. The preferred concentration of Aspergillus flavus spores is 10 5 a / ml;
[0041] Step 2, select healthy peanut seeds, shell and peel, then crush them into powder, pass through a 40-mesh sieve, soak the obtained peanut powder in ethanol with a volume fraction of 75% for 3 minutes, use for disinfection and sterilization, and then aseptic Rinse with water, and finally drain the water to obtain a seed sample and set aside;
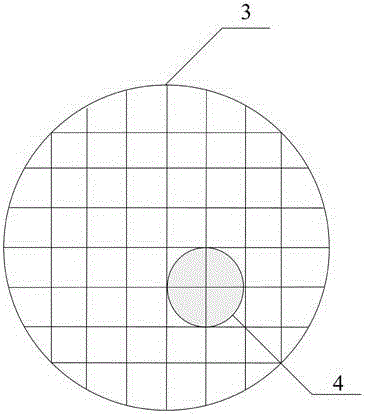
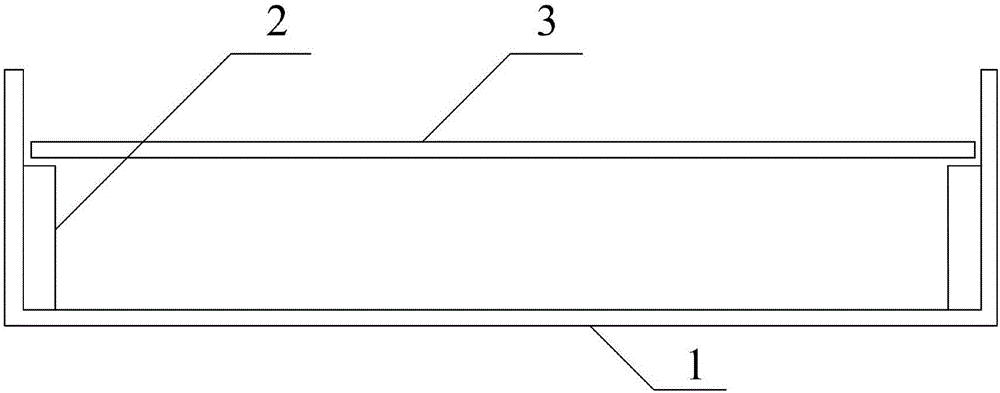
[0042] Step 3, making the culture device according to the following structure: the structure of the culture device is as follows Figure 1-2 As shown, a petri dish 1 ...
Embodiment 2
[0064] A kind of identification method of peanut to the infection resistance of Aspergillus flavus, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0065] Step 1, after Aspergillus flavus As3.4408 is activated on a slant, the spores of Aspergillus flavus are eluted with an acetic acid solution with a volume fraction of 5%, and prepared into a suspension of Aspergillus flavus spores for future use. The preferred concentration of Aspergillus flavus spores is 10 5 a / ml;
[0066] Step 2, select healthy peanut seeds, shell and peel, then crush them into powder, pass through a 40-mesh sieve, soak the obtained peanut powder in ethanol with a volume fraction of 75% for 5 minutes, use for disinfection and sterilization, and then aseptic Rinse with water, and finally drain the water to obtain a seed sample and set aside;
[0067] Step 3, making the culture device according to the following structure: the structure of the culture device is as follows Figure 1-2 As shown, a petri dish 1 ...
Embodiment 3
[0086] A kind of identification method of peanut to the infection resistance of Aspergillus flavus, specifically comprises the following steps:
[0087] Step 1, after Aspergillus flavus As3.4408 is activated on a slant, the spores of Aspergillus flavus are eluted with an acetic acid solution with a volume fraction of 5%, and prepared into a suspension of Aspergillus flavus spores for future use. The preferred concentration of Aspergillus flavus spores is 10 5 a / ml;
[0088] Step 2, select healthy peanut seeds, shell and peel, then crush them into powder, pass through a 40-mesh sieve, soak the obtained peanut powder in ethanol with a volume fraction of 75% for 5 minutes, use for disinfection and sterilization, and then aseptic Rinse with water, and finally drain the water to obtain a seed sample and set aside;
[0089] Step 3, making the culture device according to the following structure: the structure of the culture device is as follows Figure 1-2 As shown, a petri dish 1 is...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com