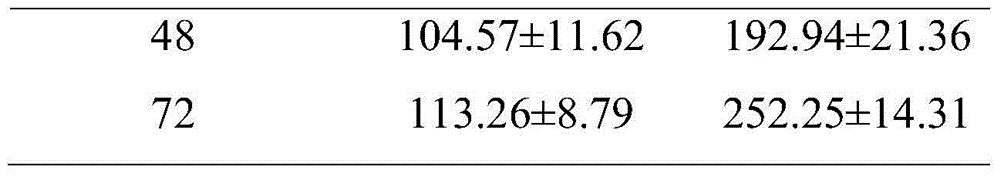Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
65 results about "Pentose phosphate pathway" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
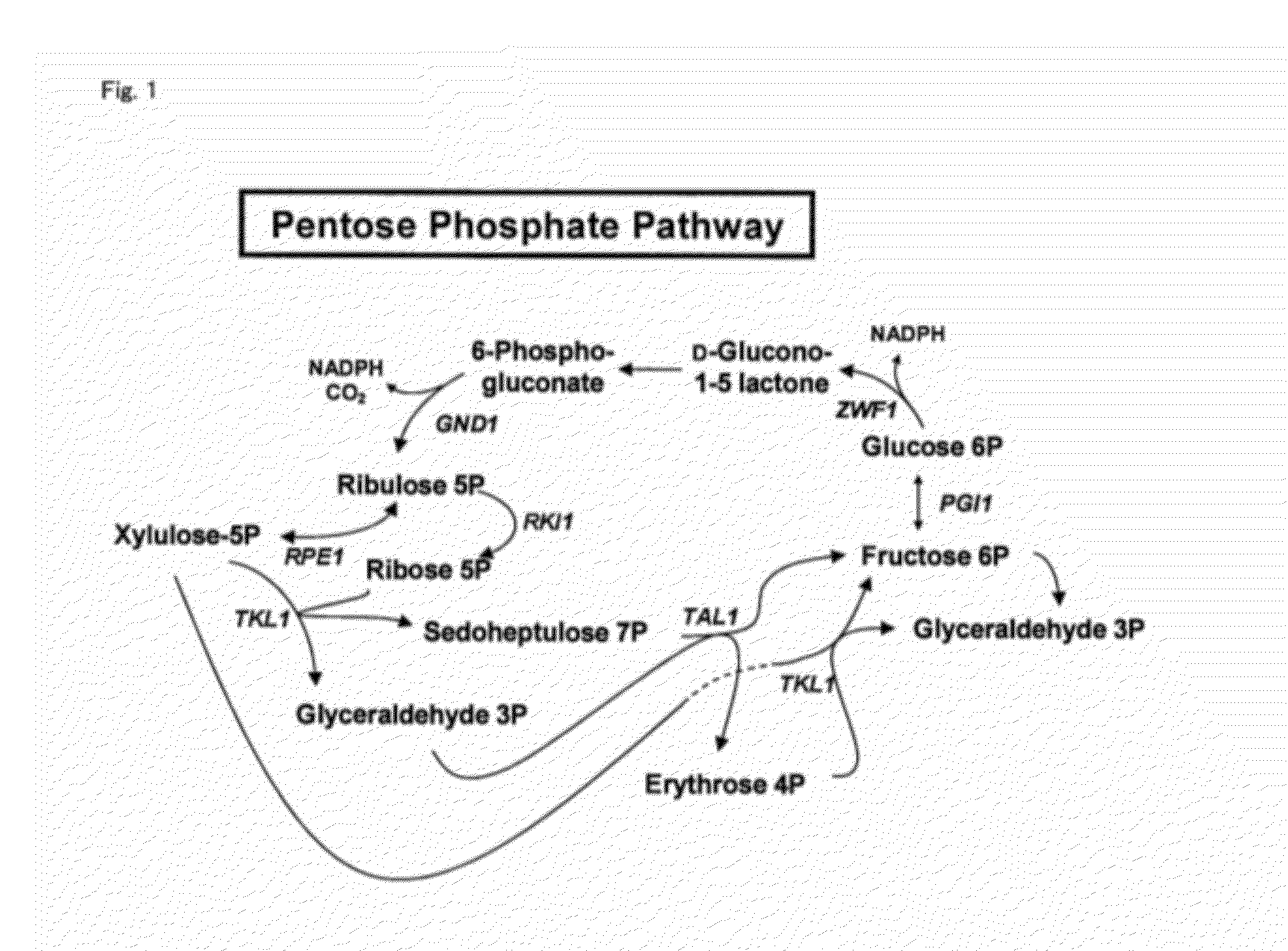
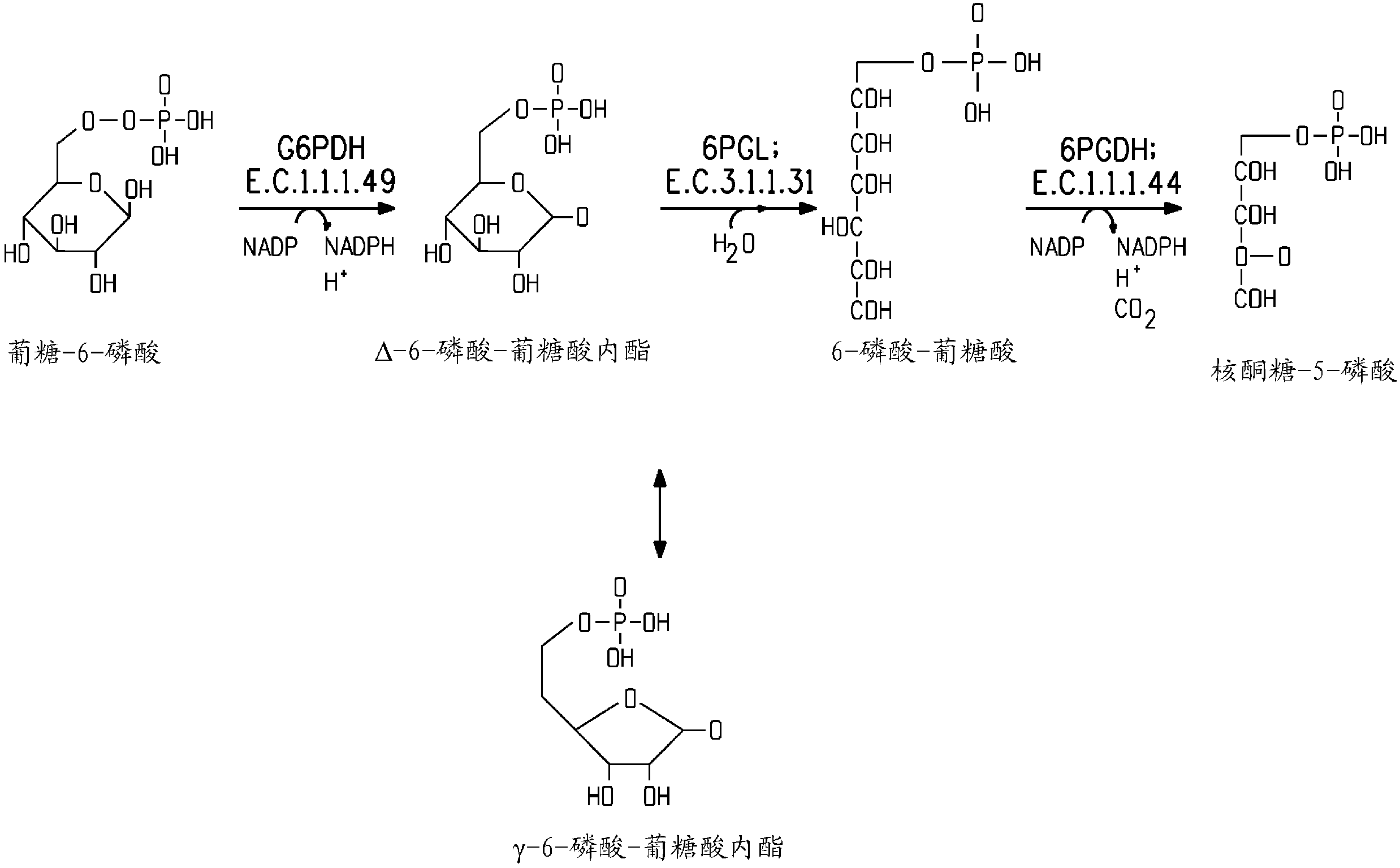
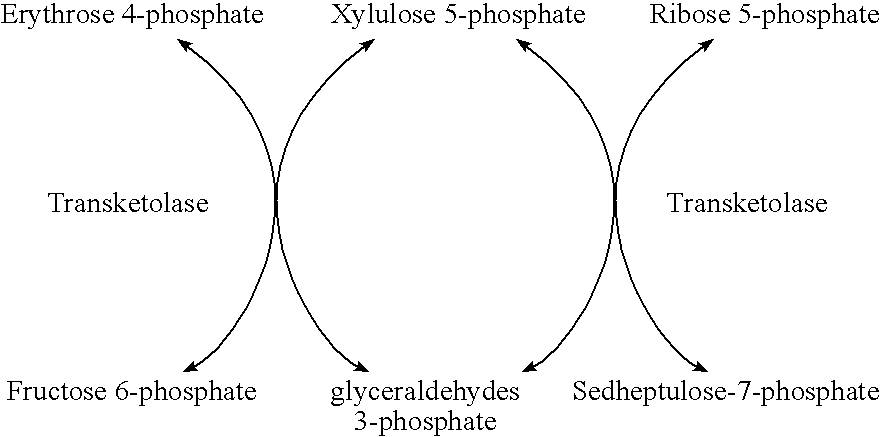
The pentose phosphate pathway (also called the phosphogluconate pathway and the hexose monophosphate shunt) is a metabolic pathway parallel to glycolysis. It generates NADPH and pentoses (5-carbon sugars) as well as ribose 5-phosphate, the last one a precursor for the synthesis of nucleotides. While it does involve oxidation of glucose, its primary role is anabolic rather than catabolic. The pathway is especially important in red blood cells (erythrocytes).
Medical stent provided with inhibitors of atp synthesis
A stent provided with a composition having at least one type of inhibitor of ATP synthesis, optionally together with at least one inhibitor of the pentose phosphate pathway is disclosed. The medical stent is useful for treating stenosis and preventing restenosis in vascular ducts and for treating cancerous tumors present in ducts, resectioned cavities and scars and any disorder arising from the proliferation of cells in ducts or cavities.
Owner:INTERSTITIAL THERAPEUTICS
Construction of new xylose utilizing saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
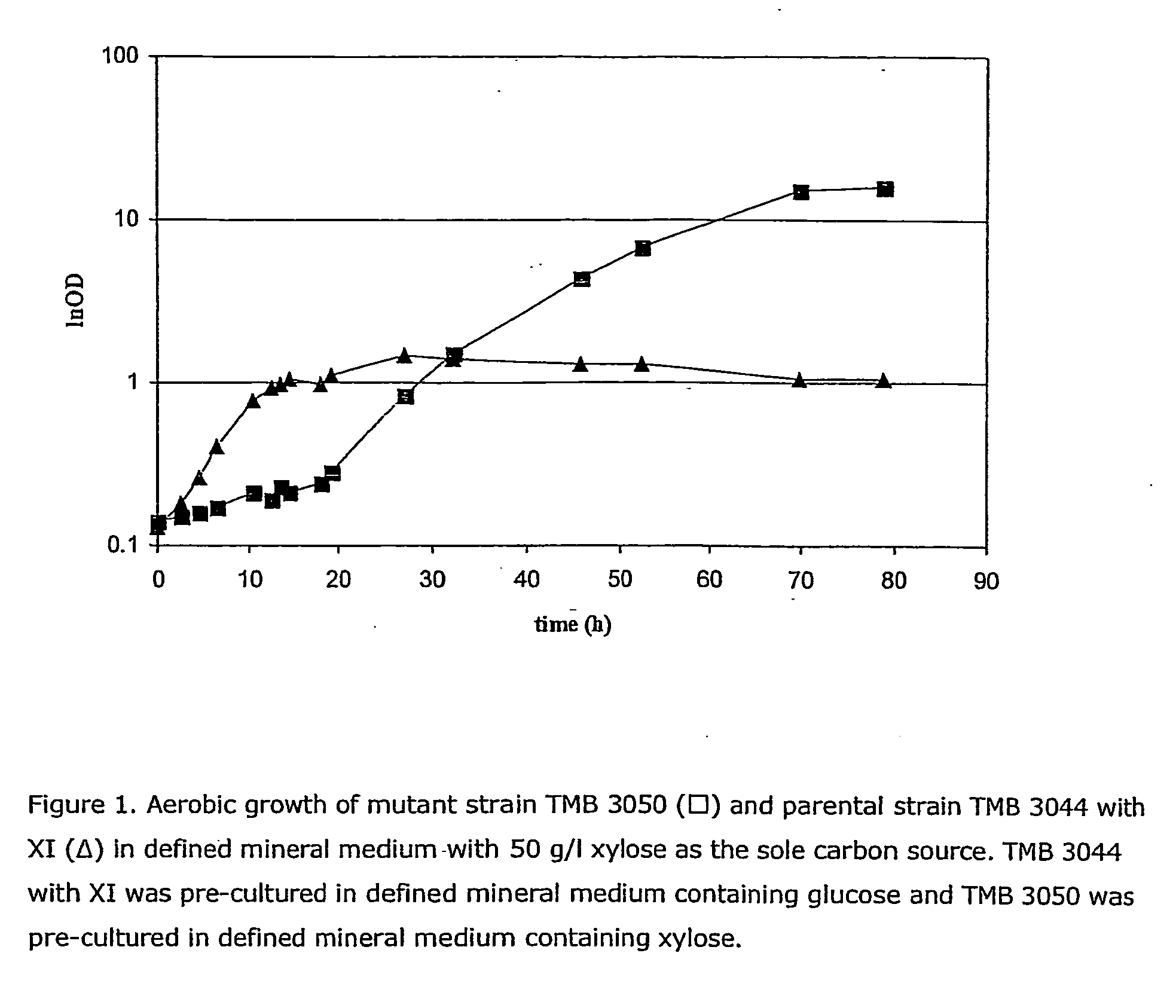
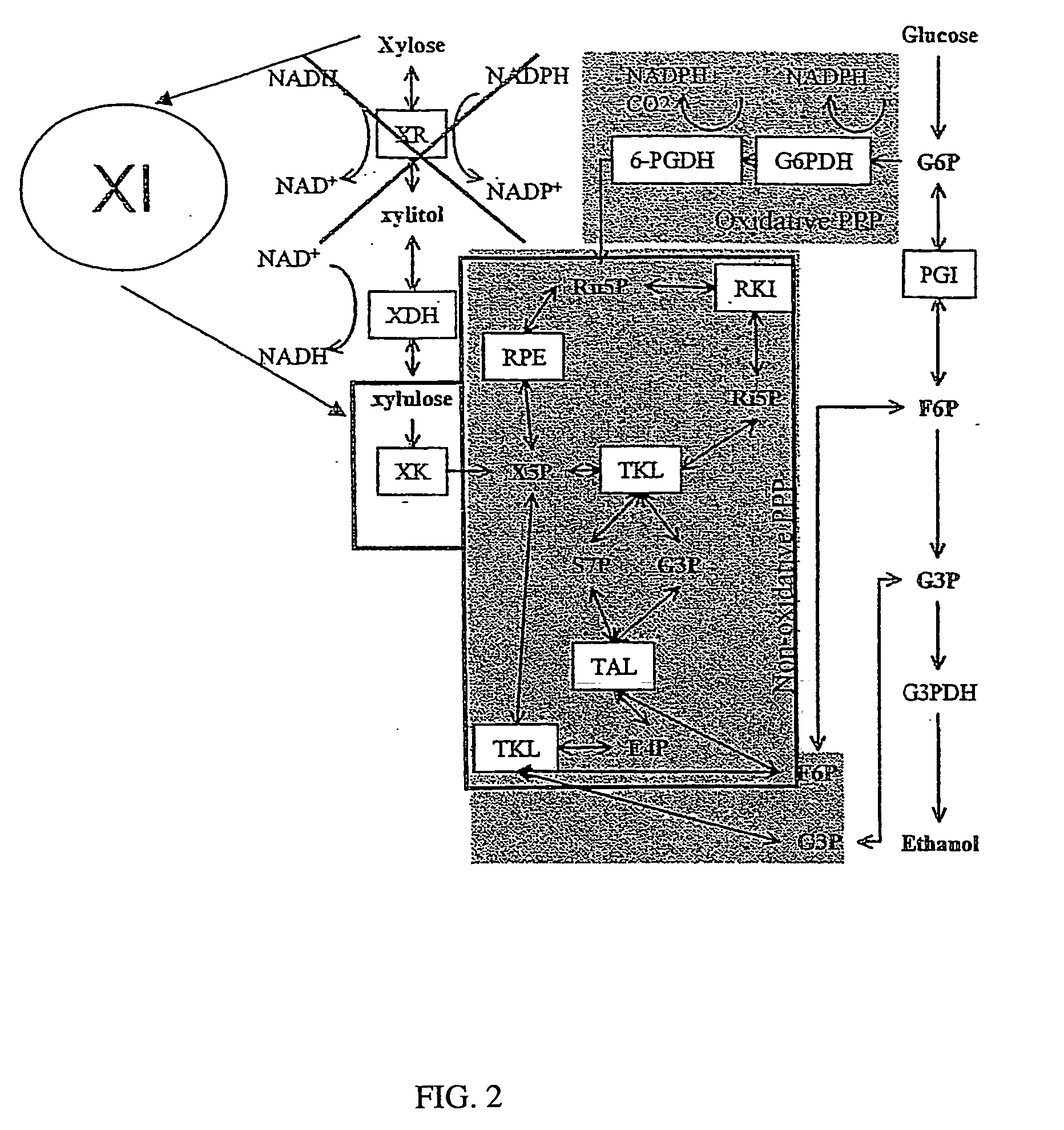
The present invention relates to a novel Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain utilizing xylose for fermenting ethanol expressing xylose isomerase (XI), overexpressing xylulokinase (XK), overexpressing the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), and non-expressing aldose reductase (AR) and being adapted to growth in mineral defined medium with xylose as sole carbon source.
Owner:FORSKARPATENT I SYD AB
Corynebacterium glutamicum and its construction method and application
ActiveCN107227283AIncrease productionAttenuated allosteric regulationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismPhenylalanine
The invention belongs to the field of microorganisms and particularly relates to Corynebacterium glutamicum and its construction method and application. Serine at the 361th site of a gnd gene for coding 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase in the cell of Corynebacterium glutamicum is mutated into phenylalanine. Corynebacterium glutamicum is used for point mutation of the gnd gene in the pentose phosphate pathway so that serine at the 361th site of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase is replaced by phenylalanine and thus allosteric regulation of 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase is reduced, the ability of NADPH regeneration is improved, enough NADPH is supplied for proline synthesis and a proline yield is improved. An experiment result shows that the Corynebacterium glutamicum is an L-proline high-yield strain, effectively accumulates L-proline, improves an L-proline yield and lays the foundation for the industrial production of L-proline.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
A kind of preparation method of cyclic adenosine monophosphate
InactiveCN102268469APromote circulationReduce formationMicroorganismsFermentationTricarboxylic acidArthrobacter sp.
The present invention provides a method of preparing cyclic adenosine monophosphate, which includes the use of Arthrobacter sp. as an engineering bacterium, and the addition of precursors, inhibitors of glycolytic pathway and / or activators of tricarboxylic acid cycle into a fermentation medium, so as to acquire the cyclic adenosine monophosphate by fermentation. Further provided is a use of precursors, inhibitors of glycolytic pathway and / or activators of tricarboxylic acid cycle for preparing cyclic adenosine monophosphate by Arthrobacter sp.. The present invention inhibits the excessive glycolysis, increases the flux of pentose phosphate pathway, and enhances the tricarboxylic acid cycle by the addition of precursors, inhibitors of glycolytic pathway and / or activators of tricarboxylic acid cycle, so as to redistribute rationally the metabolic flux of central metabolic pathways, make the carbon flux more efficiently direct to the target product - cyclic adenosine monophosphate, and synthesize cyclic adenosine monophosphate by using carbon source efficiently.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF TECH
Tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof
ActiveCN110699310APromote accumulationIncrease productionBacteriaTransferasesBacilliBiological safety
The invention discloses tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum and application thereof and belongs to the field of bioengineering. Feedback inhibition is relieved through site-directed mutagenesis of Corynebacterium glutamicum aspartokinase gene lysC, and expression of mutational LysC is intensified through promoter replacement. Further, pentose phosphate pathway of host bacteriais further intensified through promoter replacement to meet needs on reducing power NADPH in efficient synthesis of tetrahydropyridine. Finally, tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum is obtained by transferring tetrahydropyridine synthetic gene cluster ectABC of P. stutzeri into recombinant bacteria. By recombinant Corynebacterium glutamicum, tetrahydropyridine can be efficiently synthesized by utilizing cheap raw materials like glucose and maize plasm; compared with recombinant Escherichia coli produced strains, tetrahydropyridine high-yield Corynebacterium glutamicum hasbetter bio-safety and is of great significance to industrial production and large-scale application of tetrahydropyridine.
Owner:无锡晶扬生物科技有限公司
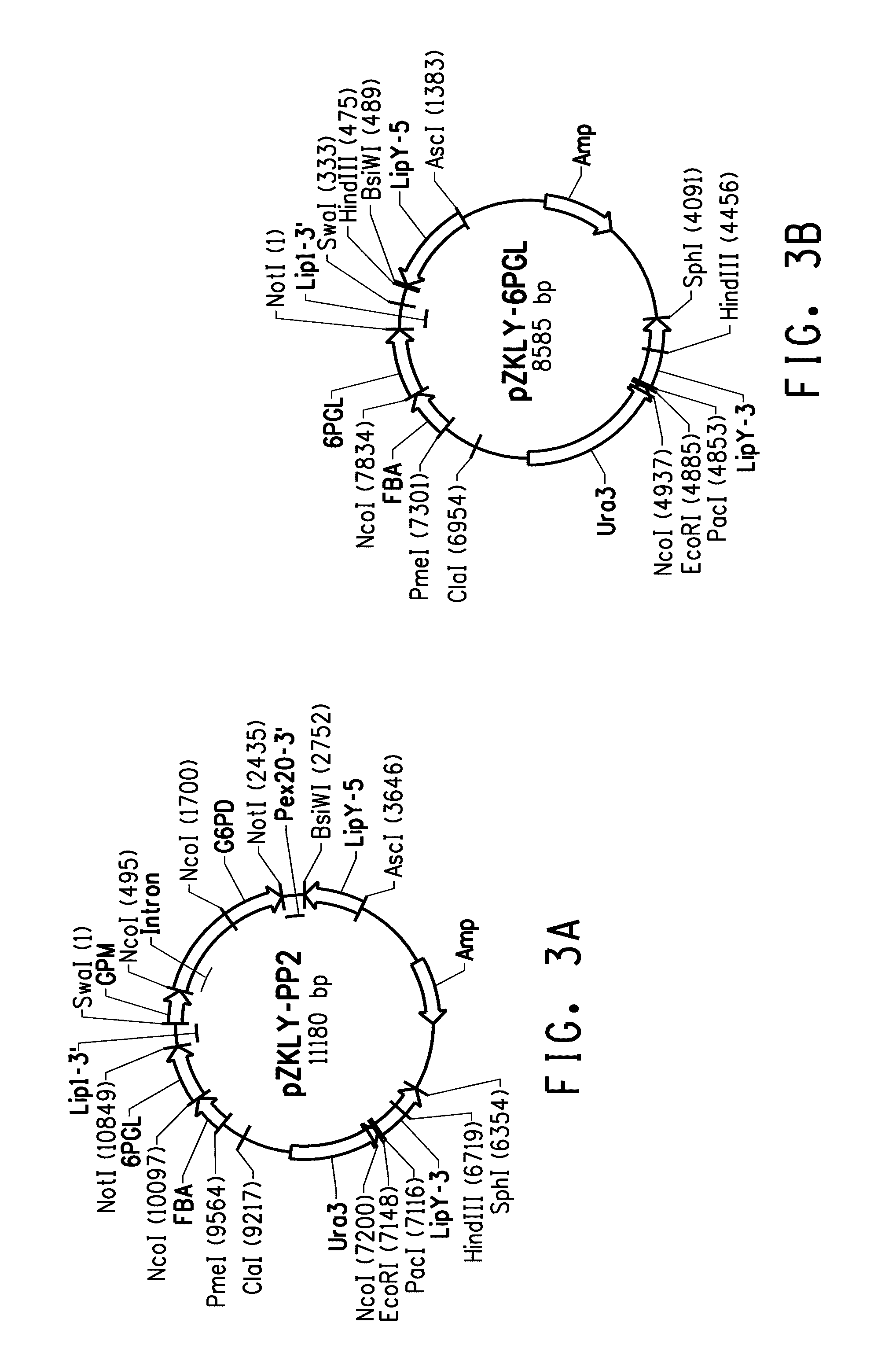
Pentose phosphate pathway upregulation to increase production of non-native products of interest in transgenic microorganisms
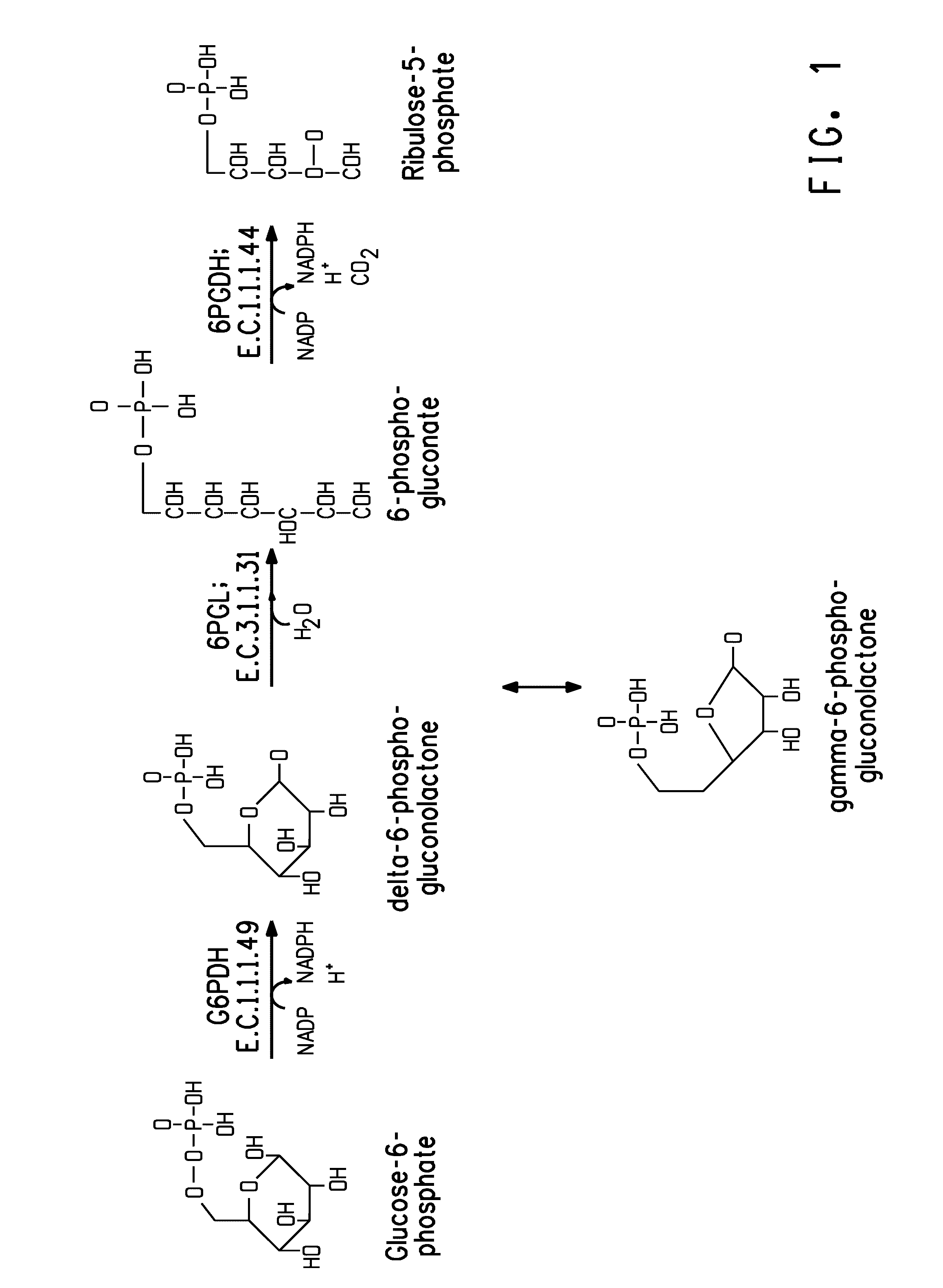
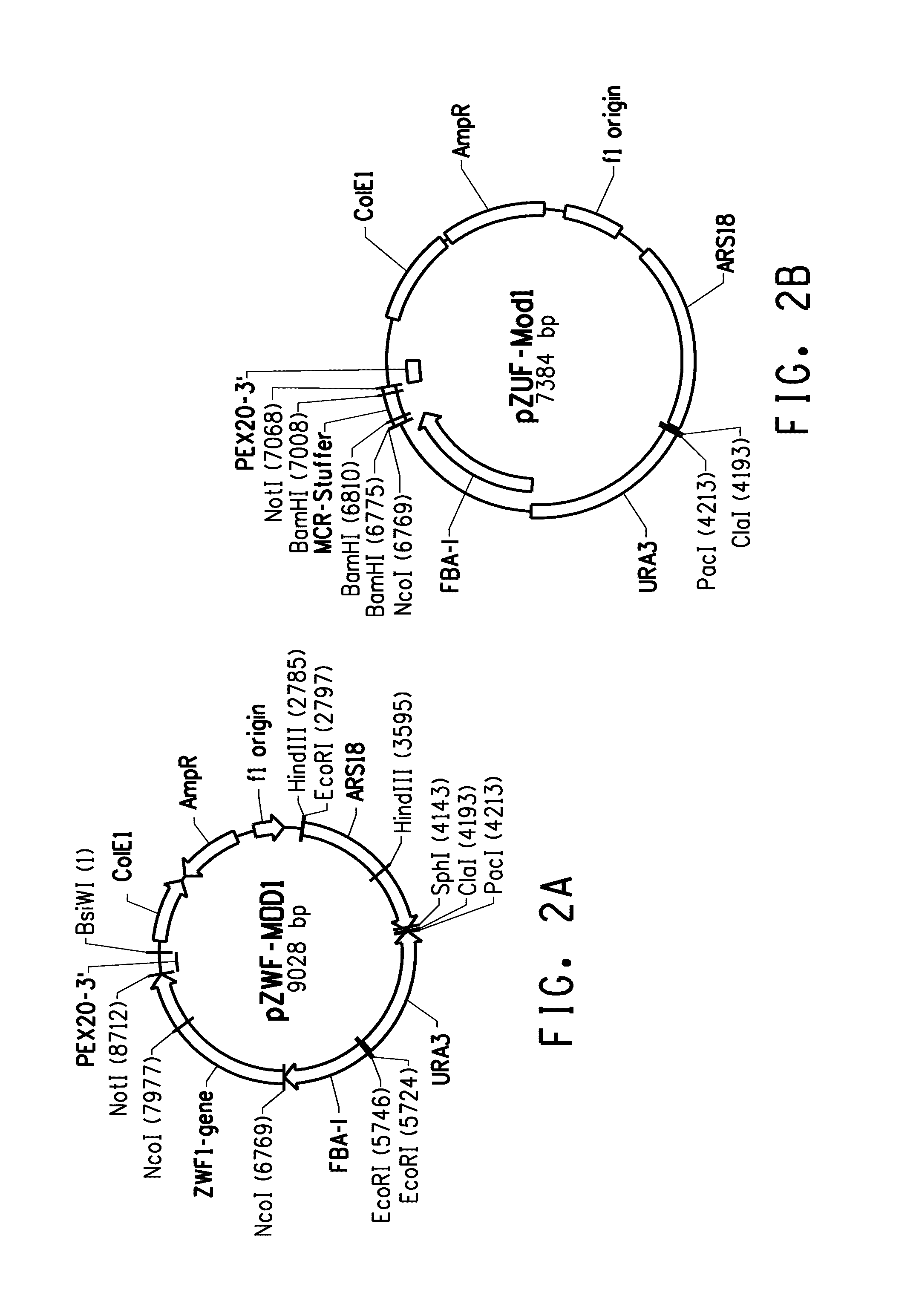
Coordinately regulated over-expression of the genes encoding glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase [“G6PDH”] and 6-phospho-gluconolactonase [“6PGL”] in transgenic strains of the oleaginous yeast, Yarrowia lipolytica, comprising a functional polyunsaturated fatty acid [“PUFA”] biosynthetic pathway, resulted in increased production of PUFAs and increased total lipid content in the Yarrowia cells. This is achieved by increased cellular availability of the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate [“NADPH”], an important reducing equivalent for reductive biosynthetic reactions, within the transgenic microorganism.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Method for promoting synthesis of DHA in schizochytrium limacinum grease
ActiveCN104450809AInhibitory activityPathway metabolic flux reductionMicroorganism based processesFermentationCarboxylic acidBiology
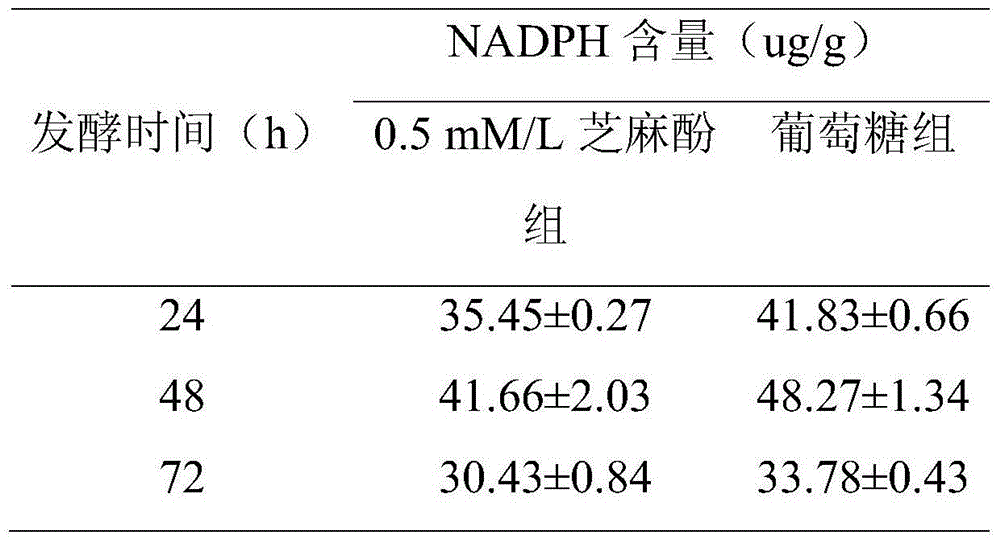
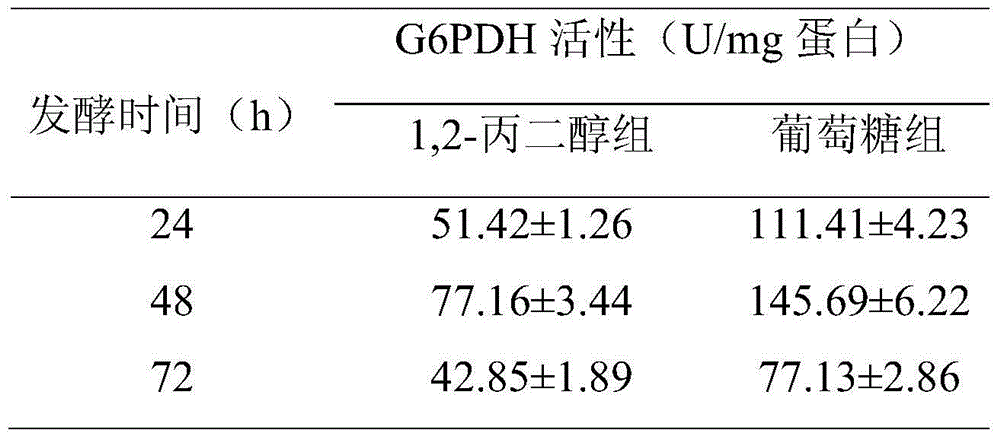
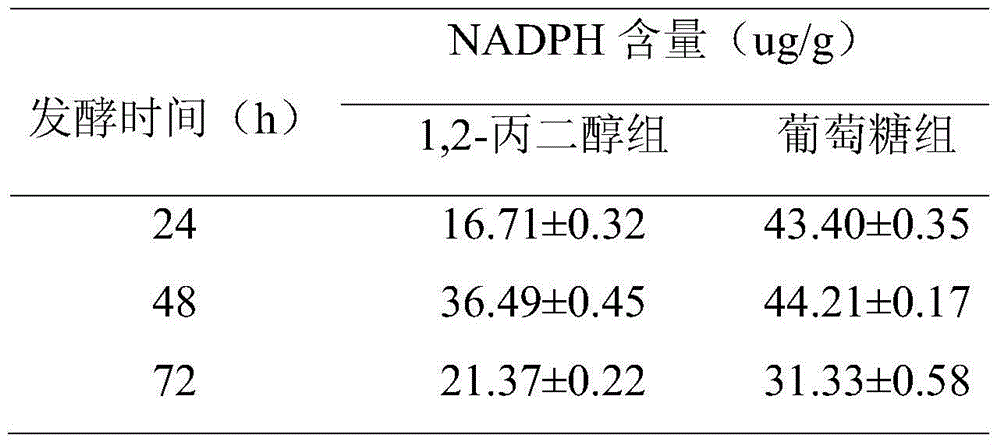
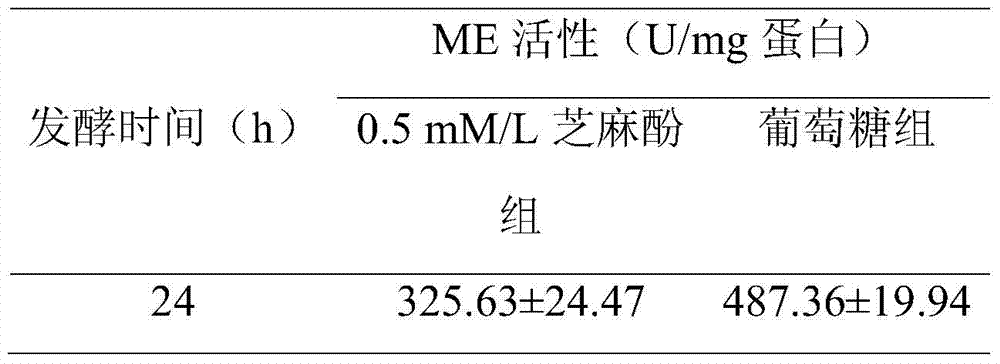
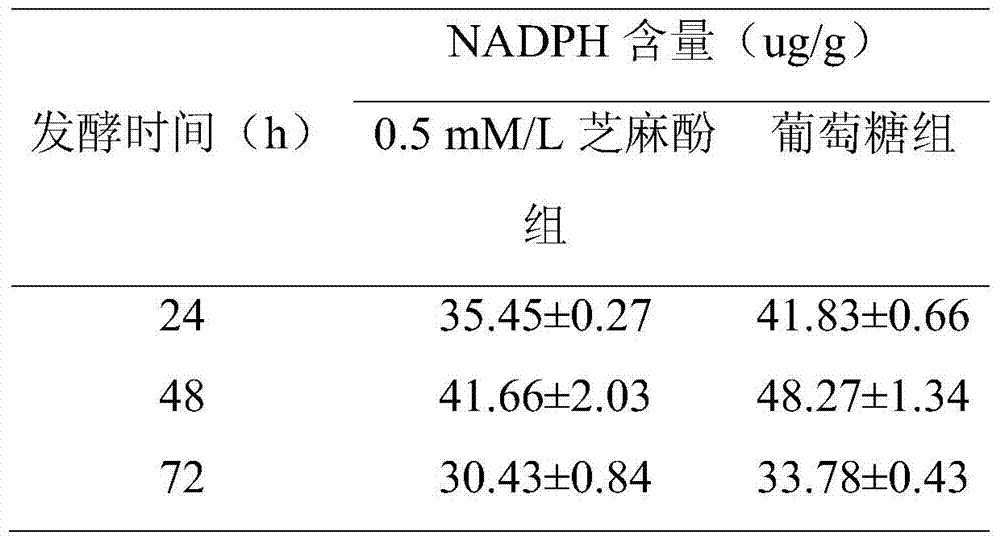
The invention relates to a method for promoting synthesis of DHA in schizochytrium limacinum grease, and particularly relates to a method for prompting synthesis of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in schizochytrium limacinum grease. The method is characterized in that the activity of malic enzyme in a tricarboxylic acid transport system is inhibited by adding an exogenous control factor, so that the content of the NADPH in the schizochytrium limacinum can be greatly reduced, the synthesis of a great amount of DHA can be promoted, and the exogenous control factor is sesamol. According to the method, a fermentable carbon source also can be selected to reduce metabolic flux of a pentose phosphate pathway in the bacteria, so that the content of NADPH in the schizochytrium limacinum can be greatly reduced, the synthesis of a great amount of DHA can be promoted, and the largest content of the DHA in the grease of final bacteria can reach 55.3 percent. The method is simple, easy, obvious in effect, capable of greatly increasing the content of DHA in the bacteria grease and is likely to realize the industrialized application.
Owner:WUHAN HUASHITE IND BIOTECH DEV
Process for production of ethanol from biomass
InactiveUS20120282664A1Efficient productionAvoid competitionTransferasesBiofuelsMetabolic enzymesGene
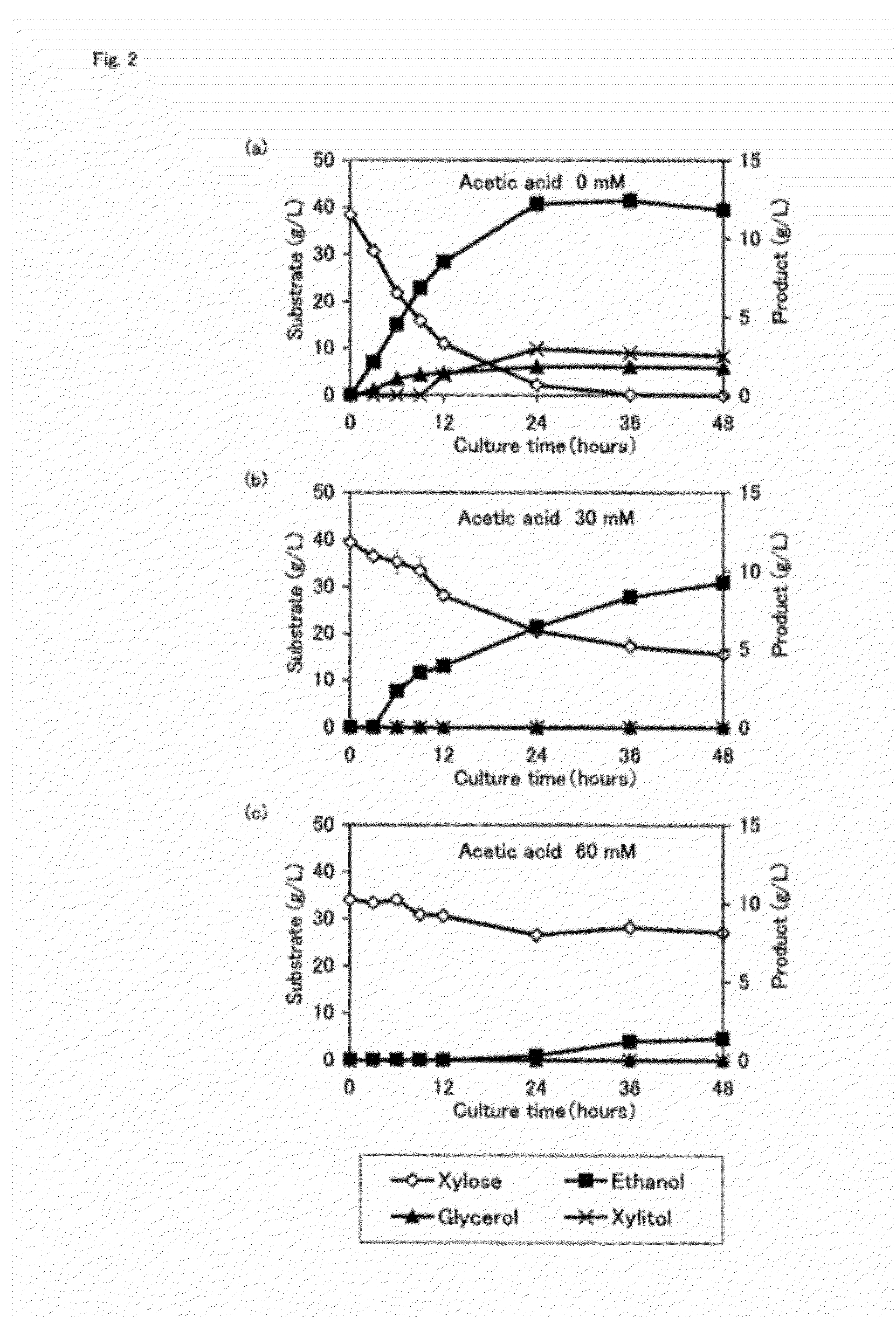
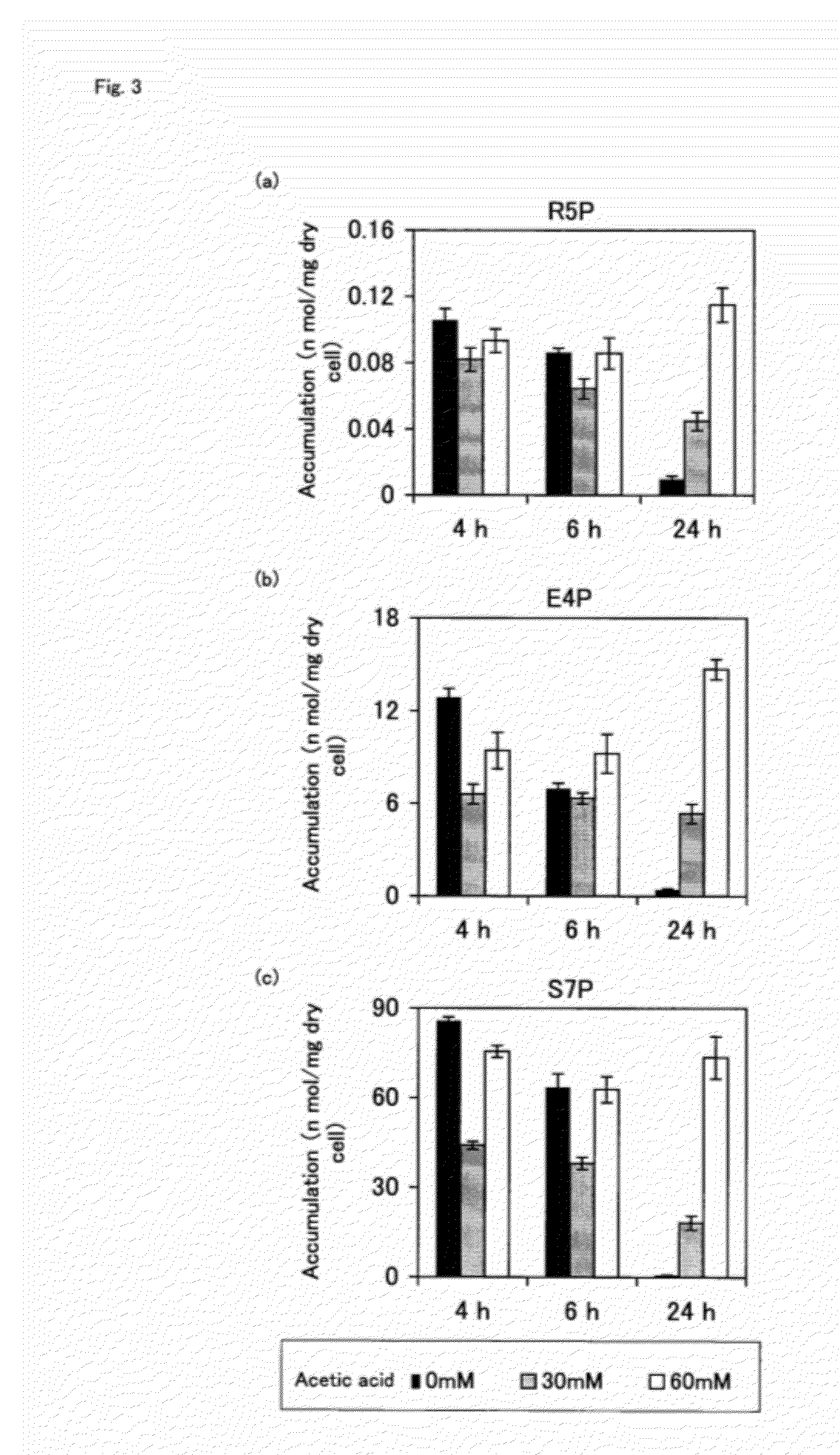
An object of the present invention is to provide a method for producing ethanol efficiently even in the presence of a fermentation inhibitor in a saccharified biomass. The present invention provides a method for producing ethanol from biomass, comprising: culturing a transformed xylose-utilizing yeast to overexpress the gene for at least one pentose phosphate pathway metabolic enzyme, with a saccharified biomass.
Owner:KOBE UNIV
A strain producing L-tryptophan and use thereof
The present invention relates to a strain producing L-tryptophan and use thereof in fermentation. Specifically, the L-tryptophan producing capability of the strain is greatly improved through attenuating or blocking an oxidation stage of a pentose phosphate pathway of engineering bacteria (such as Escherichia coli or Corynebacterium glutamicum) with a genetic engineering method.
Owner:MEIHUA BIOTECH LANGFANG CO LTD
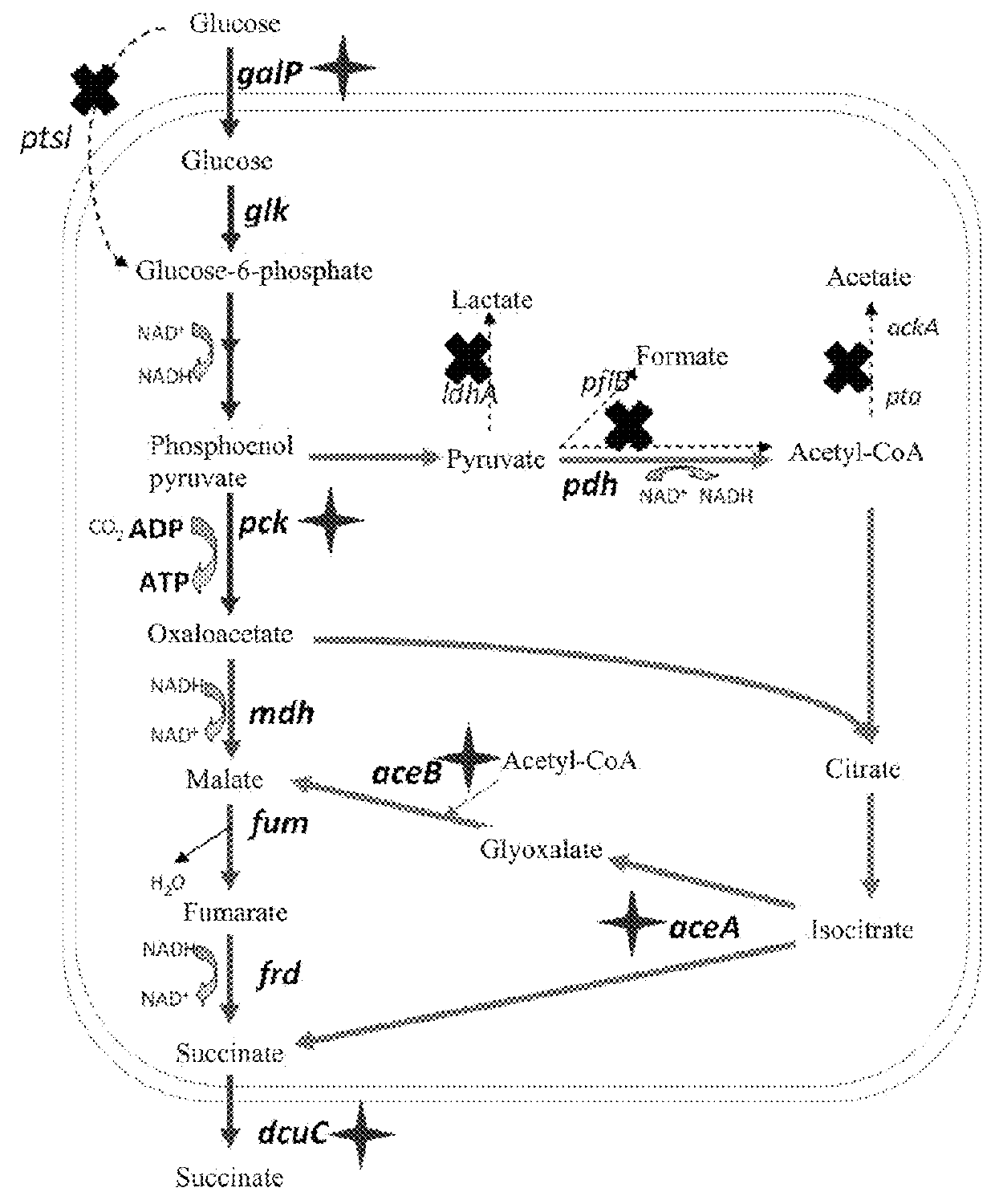
Recombinant escherichia coli for producing succinic acid and application thereof
The invention relates to the field of producing succinate by E. coli fermentation. Specifically, the invention provides an engineered recombinant E. coli for producing succinate, wherein said E. coli contains one or more of the following modifications: a) enhanced activity of the protein(s) encoded by the gene(s) involved in pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), b) enhanced activity of the protein encoded by sthA gene, and optionally c) mutant lpdA gene. The invention also relates to use of the engineered recombinant E. coli for producing succinate, and a method of using the engineered recombinant E. coli for producing succinate.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Pentose phosphate pathway upregulation to increase production of non-native products of interest in transgenic microorganisms
Coordinately regulated over-expression of the genes encoding glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase ["G6PDH"] and 6-phospho-gluconolactonase ["6PGL"] in transgenic strains of the oleaginous yeast, Yarrowia lipolytica, comprising a functional polyunsaturated fatty acid ["PUFA"] biosynthetic pathway, resulted in increased production of PUFAs and increased total lipid content in the Yarrowia cells. This is achieved by increased cellular availability of the reduced form of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate ["NADPH"], an important reducing equivalent for reductive biosynthetic reactions, within the transgenic microorganism.
Owner:EI DU PONT DE NEMOURS & CO
Biohydrogen production by an artificial enzymatic pathway
The present invention comprises an in vitro enzymatic process that effectively converts renewable polysaccharides into high yields of hydrogen at mild conditions, using only enzymes and water. The process comprises a number of enzymes: (1) phosphorylases, (2) phosphoglucomutases, (3) hydrogenases, and (4) enzymes involved in the pentose-phosphate pathway. Preferred embodiments of the process produce only hydrogen and carbon dioxide as net products, translating into an inexpensive method of generating hydrogen in very large quantities from low-cost feedstocks.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC +1
Method for preventing or treating obesity by modulating the activities of the pentose phosphate patway
Method for preventing or treating overweight or obesity, the method comprising administering to a patient in need thereof an antagonist that inhibits gene expression or activity of an enzyme that is involved or related to the pentose phosphate pathway. Preferably, the enzyme is a transketolase, and the antagonist is an antibody, an antisense molecule, an siRNA molecule, a molecule for forming a triplex nucleic acid molecule with the enzyme-encoding polynucleotide. Also disclosed are pharmaceutical compositions comprising the same, and method for screening a substance that inhibits gene expression of a PPP enzyme or its function.
Owner:MINKON BIOTECH
Method of Producing Methionine in Corynebacteria by Over-Expressing Enzymes of the Pentose Phosphate Pathway
InactiveUS20120288901A1High activityReduce the amount of solutionBacteriaOxidoreductasesCorynebacterium amycolatumEnzyme
The present invention relates to a method of producing methionine in Coryneform bacteria in which enzymes of the pentose phosphate pathway are over-expressed. The present invention also relates to Coryneform bacteria for producing methionine in which at least two enzymes of the pentose phosphate pathway are over-expressed.
Owner:EVONIK DEGUSSA GMBH
Method for improving yield of arginine by utilizing corynebacterium glutamicum and corynebacterium crenatum
InactiveCN105018515AReduced transcript levelsIncrease supplyMicroorganism based processesFermentationArginineCarboxylic acid
The invention discloses corynebacterium glutamicum and corynebacterium crenatum, as well as a method for improving the yield of arginine by utilizing corynebacterium glutamicum and corynebacterium crenatum. According to the method, dtsR1 genes of corynebacterium glutamicum and corynebacterium crenatum are knocked out; then the transcriptional level of alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase complex (oxoglutarate dehydrogenase complex, ODHC) regulated by the dtsR1 genes is greatly lowered, and alpha-ketoglutaric acid flows to arginine; meanwhile, Tween-80, oleic acid or a mixture of Tween-80 and oleic acid is added to a fermentation medium, so as to make up for nutrition loss caused by loss of the dtsR1 genes, and at the early logarithmic growth stage during the fermentation culturing, Tween-40 is added to induce the transcription level of the genes in the pentose phosphate pathway to be greatly improved. Thus, sufficient NADPH is provided for the synthesis of arginine, and other complicated molecular breeding methods for improving supply of NADPH and other accumulation methods for improving content of alpha-ketoglutaric acid in the tricarboxylic acid cycle pathway are eliminated.
Owner:JIANGXI NORMAL UNIV
Method for increasing content of docosahexaenoic acid in schizochytrium limacinum grease
ActiveCN104480152APathway metabolic flux declinePathway metabolic flux reductionMicroorganism based processesFermentationTricarboxylic acidCarboxylic acid
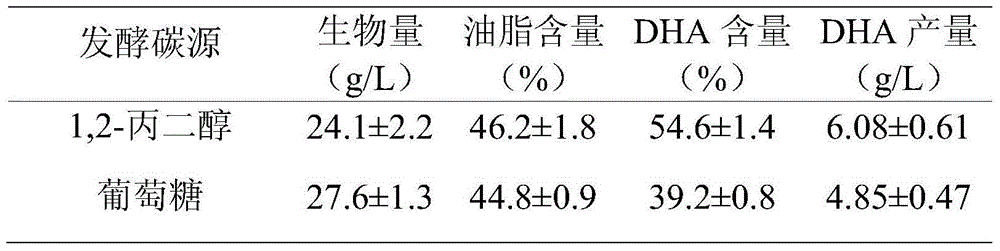
The invention relates to a method for increasing content of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in schizochytrium limacinum grease. The method is characterized by comprising the following steps: lowering metabolic flux of a pentose phosphate pathway in thallus by selecting a fermentable carbon source, and lowering the metabolic flux of the pentose phosphate pathway in thallus by further adding an exogenous regulation factor; inhibiting the activity of malic enzyme in a tricarboxylic acid transfer system to greatly lower the content of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate (NADPH) in the schizochytrium limacinum thaluus, promote the large-scale synthesis of DHA and enable the content of DHA in the grease of the obtained thallus to be as high as 55.3%, wherein the fermentation carbon source is 1,2-propylene glycol or any one or a mixture of 1,2-propylene glycol and acetate, the exogenous regulation factor is preferably sesamol which is added after filtering and degerming when a fermentation culture medium is sterilized, and the addition amount of the sesamol is 0.5-3.0mM / L. The method disclosed by the invention is simple and easy to perform, obvious in effect, capable of greatly increasing the content of DHA in the thallus grease and easy for industrial application.
Owner:WUHAN HUASHITE IND BIOTECH DEV +1
Recombinant yeast cell
The present invention describes a recombinant yeast cell functionally expressing one or more heterologous nucleic acid sequences encoding for ribulose-1,5-phosphate carboxylase / oxygenase (EC4.1.1.39; Rubisco), and optionally one or more molecular chaperones for Rubisco, and one or more phosphoribulokinase (EC2.7.1.19; PRK), wherein one or more genes of the non-oxidative branch of the pentose phosphate pathway are overexpressed and / or wherein said yeast cell comprises a deletion or disruption of a glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase (GPD) gene.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV
Method for quantitative determination of regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate
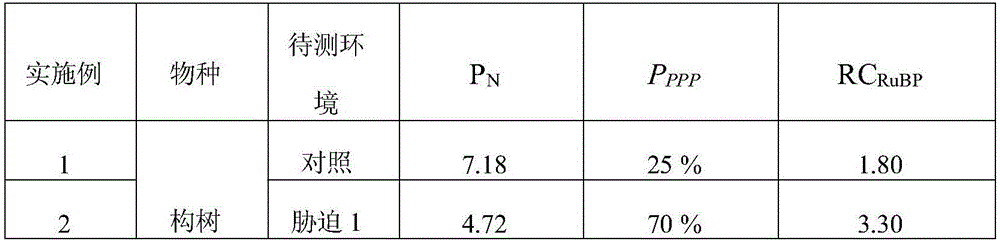
ActiveCN106092944AComparableStable and reliable share of glycolytic pathwayColor/spectral properties measurementsNon destructiveQuantitative determination
The invention discloses a method for quantitative determination of regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate. The method comprises the following steps: selecting the second, the third and the fourth completely spread leaves, performing non-destructive determination on apparent photosynthesis rate, taking a mean value of three leaves to represent the apparent photosynthesis rate PN of the plant; then taking the leave which has measured apparent photosynthesis rate, shearing the leave and fully mixing the leave, taking 0.1 g of the material for enzyme liquid extraction; respectively determining the phosphofructokinase vitality and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase enzyme vitality expressed by the change value at unit volume and unit time in the extracted enzyme liquid, calculating phosphopentose pathway proportion in the glycometabolism according to a formula, and then multiplying by the apparent photosynthesis rate of the plant leave to obtain the regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate. The method can realize rapid quantitative determination of the regeneration capability of 1,5-ribulose diphosphate, and has the advantages of less step, simple calculation, and comparability and reliability of the determination result.
Owner:INST OF GEOCHEM CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Construction method of synthetic path for generating glutamic acid by utilizing xylose in corynebacterium glutamicum
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and discloses a construction method of a synthetic path for generating glutamic acid by utilizing xylose in corynebacterium glutamicum. The construction method comprises the following steps of (1) expressing heterogenous pentose transport protein in the corynebacterium glutamicum; (2) expressing heterogenous xylose isomerase and xylulokinasein the corynebacterium glutamicum; (3) generating alpha-ketoglutarate from generated 5-xylulosephosphate through a phosphopentose pathway and a glycolysis pathway, and carrying out weakened expressionon alpha-ketoglutarate dehydrogenase, so that more alpha-ketoglutarate flows to the synthesis of glutamic acid; and (4) modifying glutamic acid secretory protein to ensure that the corynebacterium glutamicum does not respond to external biotin pressure any more, and continuously secreting the glutamic acid out of cells. According to the constructed synthetic path from the xylose to the glutamic acid, the corynebacterium glutamicum can utilize the xylose to produce the glutamic acid in a conventional synthetic culture medium, and the synthesis from the xylose to the glutamic acid can also be conducted in a high-biotin environment such as lignocellulose.
Owner:EAST CHINA UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Combined anticancer drug sensitivity-determining marker
ActiveUS20150038522A1High therapeutic effectPromote anti-cancer agent sensitivityBiocideMass spectrometric analysisAnticarcinogen6-phosphogluconic acid
To provide an anti-cancer agent sensitivity determination marker, which marker can determine whether or not the patient has a therapeutic response to the anti-cancer agent, and novel cancer therapeutic means employing the marker.The anti-cancer agent sensitivity determination marker, the anti-cancer agent including oxaliplatin or a salt thereof and fluorouracil or a salt thereof, contains one or more substances selected from among an amino-acid-metabolism-related substance, a nucleic-acid-metabolism-related substance, a substance in the pentose phosphate pathway, a substance in the glycolytic pathway, a substance in the TCA cycle, a polyamine-metabolism-related substance, 7,8-dihydrobiopterin, 6-phosphogluconic acid, butyric acid, triethanolamine, 1-methylnicotinamide, NADH, NAD+, and a substance involved in the metabolism of any of these substances.
Owner:KEIO UNIV +1
Method for improving cellulase expression capability of trichoderma reesei by regulating and controlling cell metabolism
ActiveCN114107359AHigh protein expressionHigh activityMicroorganism based processesOxidoreductasesEnzyme GeneMicrobiology
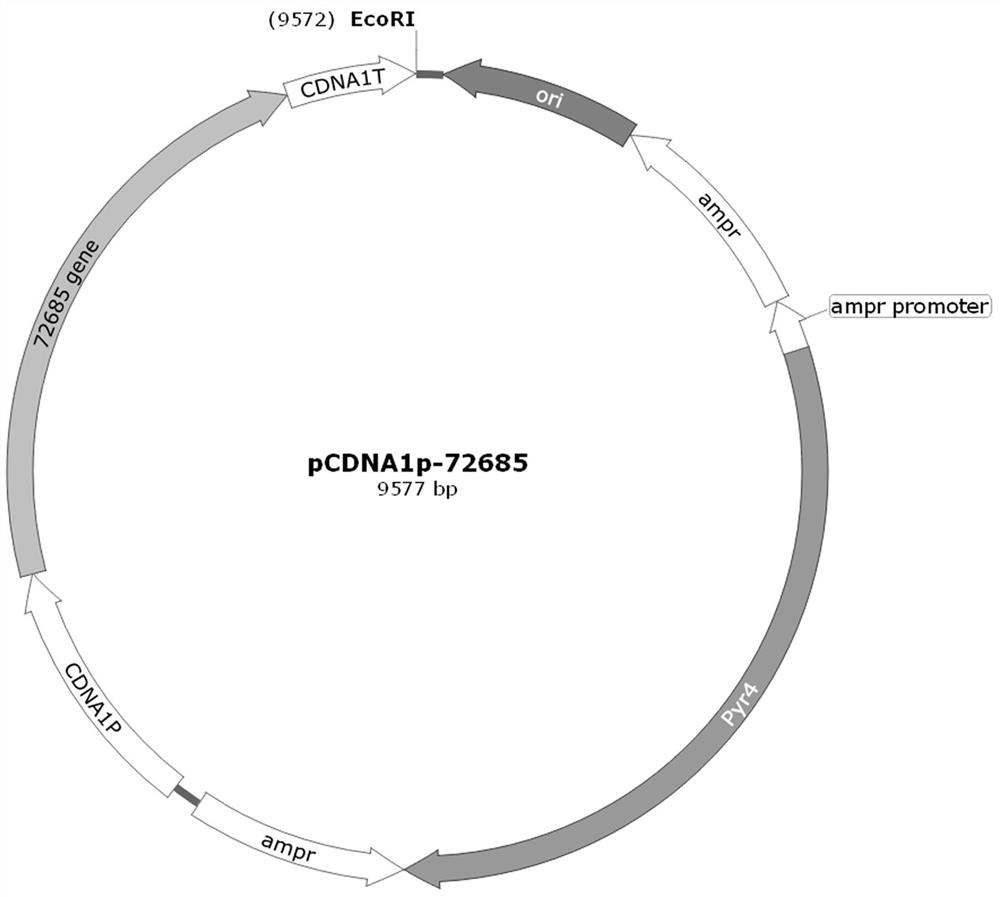
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to a method for improving cellulase expression capacity of trichoderma reesei by regulating cell metabolism. The 6-phosphogluconate dehydrogenase gene 72685 of a pentose phosphate pathway of trichoderma reesei is subjected to overexpression, overexpression plasmids of the gene are constructed, and the overexpression plasmids are used for converting the trichoderma reesei, so that the protein expression quantity and the cellulase activity of the trichoderma reesei are improved.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Xylose isomerase and xylitol dehydrogenase combination for xylose fermentation to ethanol and B. fragilis xylose isomerase
Disclosed herein is a newly discovered problem and solution for engineering S. cerevisiae to ferment xylose to make ethanol utilizing xylose isomerase to convert xylose to xylulose for entry, via xylulokinase, into the pentose phosphate pathway. The problem is that when grown on a media containing xylose xylitol tends to accumulate in the cell despite the absence of xylose reductase activity in S. cerevisiae. Xylitol inhibits the activity of xylose isomerases. One solution described is to simultaneously express an exogenous xylitol dehydrogenase along with the exogenous xylose isomerase while optionally also overexpressing xylulokinase in the absence of expression of a xylose reductase. Another solution is a xylose isomerase from Bacteroides fragilis which is less inhibited by xylitol than other xylose isomerases, exemplified by E. coli xylose isomerase. Expression of the Bacteroides fragilis xylose isomerase may be used alone, or in combination with expression of a xylitol dehydrogenase and optionally over expression of xylulokinase to improve ethanol production from xylose.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
XYLOSE ISOMERASE AND XYLITOL DEHYDROGENASE COMBINATION FOR XYLOSE FERMENTATION TO ETHANOL AND B. fragilis XYLOSE ISOMERASE
ActiveUS20140017768A1Less inhibitedEase of productionMicroorganismsBiofuelsEscherichia coliXylose fermentation
Disclosed herein is a newly discovered problem and solution for engineering S. cerevisiae to ferment xylose to make ethanol utilizing xylose isomerase to convert xylose to xylulose for entry, via xylulokinase, into the pentose phosphate pathway. When grown on a media containing xylose xylitol tends to accumulate in the cell despite the absence of xylose reductase activity in S. cerevisiae. Xylitol inhibits the activity of xylose isomerases. One solution described is to simultaneously express an exogenous xylitol dehydrogenase along with the exogenous xylose isomerase while optionally also overexpressing xylulokinase in the absence of expression of a xylose reductase. Another solution is a xylose isomerase from Bacteroides fragilis which is less inhibited by xylitol than other xylose isomerases, exemplified by E. coli xylose isomerase. Expression of the Bacteroides fragilis xylose isomerase may be used alone, or in combination with expression of axylitol dehydrogenase and optionally over expression of xylulokinase to improve ethanol production from xylose.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
A method for promoting the synthesis of DHA in Schizochytrium oil
ActiveCN104450809BInhibitory activityPathway metabolic flux reductionMicroorganism based processesFermentationSchizochytriumCarboxylic acid
The invention relates to a method for promoting synthesis of DHA in schizochytrium limacinum grease, and particularly relates to a method for prompting synthesis of docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) in schizochytrium limacinum grease. The method is characterized in that the activity of malic enzyme in a tricarboxylic acid transport system is inhibited by adding an exogenous control factor, so that the content of the NADPH in the schizochytrium limacinum can be greatly reduced, the synthesis of a great amount of DHA can be promoted, and the exogenous control factor is sesamol. According to the method, a fermentable carbon source also can be selected to reduce metabolic flux of a pentose phosphate pathway in the bacteria, so that the content of NADPH in the schizochytrium limacinum can be greatly reduced, the synthesis of a great amount of DHA can be promoted, and the largest content of the DHA in the grease of final bacteria can reach 55.3 percent. The method is simple, easy, obvious in effect, capable of greatly increasing the content of DHA in the bacteria grease and is likely to realize the industrialized application.
Owner:WUHAN HUASHITE IND BIOTECH DEV
Method and application of overexpressing zwf2 gene to increase daptomycin production
InactiveCN102286497AIncrease productionReduce manufacturing costBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEscherichia coliPrimary metabolism
The present invention provides a method for overexpressing the zwf2 gene to increase the yield of daptomycin and its application, and clones a key enzyme 6-phosphate glucose dehydrogenase gene (zwf2) in the primary metabolic pentose phosphate pathway, using Escherichia coli-Streptomyces Shuttle plasmid expression vector construction of recombinant plasmids. The recombinant plasmid was introduced into Escherichia coli ET12567, ET12567 was co-cultured with Streptomyces roseospora, and Streptomyces roseospora was transformed by the combined transfer method, and then the transformants were screened by apramycin resistance, and the genetically engineered bacteria were further verified by PCR , thereby constructing the genetically engineered strain HP-2. The Streptomyces roseospora genetically engineered bacterium HP-2 constructed by the present invention has an 18% higher output than the starting strain, and the output of daptomycin is as high as 700mg / L, which can be directly used in the industrialized production of daptomycin, which can improve Yield reduces cost.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Recombinant Escherichia coli for producing succinate acid and application thereof
ActiveUS10006063B2Achieve technical effectsHigh expressionBacteriaBiofuelsEscherichia coliRecombinant escherichia coli
The invention relates to the field of producing succinate by E. coli fermentation. Specifically, the invention provides an engineered recombinant E. coli for producing succinate, wherein said E. coli contains one or more of the following modifications: a) enhanced activity of the protein(s) encoded by the gene(s) involved in pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), b) enhanced activity of the protein encoded by sthA gene, and optionally c) mutant lpdA gene. The invention also relates to use of the engineered recombinant E. coli for producing succinate, and a method of using the engineered recombinant E. coli for producing succinate.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Process for generating male sterile plants
The invention is directed to a process for the generation of male sterility in plants comprising the steps of (a) transforming a plant cell with DNA sequences that selectively inhibit the expression of essential metabolic compounds and (b) regenerating plants from said plant cells. Cells impaired in the biosynthesis of basic metabolic compounds undergo starvation and eventually die. Such pathways include amino acid biosynthesis, nucleic acid biosynthesis and other biosynthetic pathways such as citric acid cycle, pentose phosphate pathway, fatty acid metabolism, vitamin biosynthesis that will render the cell inactive due to nutrient depletion, if one or more enzymes or proteins involved in this pathway would become inactive by using inhibitory DNA constructs.
Owner:HOECHST SCHERING AGREVO GMBH +1
Mixture of rare ginsenoside and application of mixture
ActiveCN108578702ASignificant synergistic anticancer effectImprove anti-tumor effectOrganic active ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsPhosphateIsrapafant
The invention discloses a mixture of rare ginsenoside and application of the mixture. The mixture of rare ginsenoside comprises rare ginsenoside and a pentose metabolic pathway inhibitor. A rare ginsenoside monomer promotes ubiquitination and degradation of HIF-1alpha (hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha) through proteasome; the content of the HIF-1alpha in a tumor cell is lowered, theoretically, tumor glycometabolism pathways including pentose-phosphate pathways can be inhibited, and thus the anti-tumor effect is achieved. According to the mixture of rare ginsenoside and the application of the mixture, it is innovatively achieved that the rare ginsenoside monomer and a pentose-phosphate pathway inhibitor 6-amidogen nicotinamide (6-AN) are jointly applied in vitro to act on a hepatoma cell line (HepG2), and the rare ginsenoside monomer and the pentose-phosphate pathway inhibitor 6-amidogen nicotinamide (6-AN) have an obvious synergistic anticancer effect. Therefore, rare ginsenoside and atumor glycometabolism pathway inhibitor which have the effect of regulating glycometabolism pathways are jointly applied to strengthening the anti-tumor effect of the mixture, and the mixture is usedfor therapy of malignant tumors and has a wide application prospect.
Owner:SHENZHEN YINUO BIOPHARM CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com