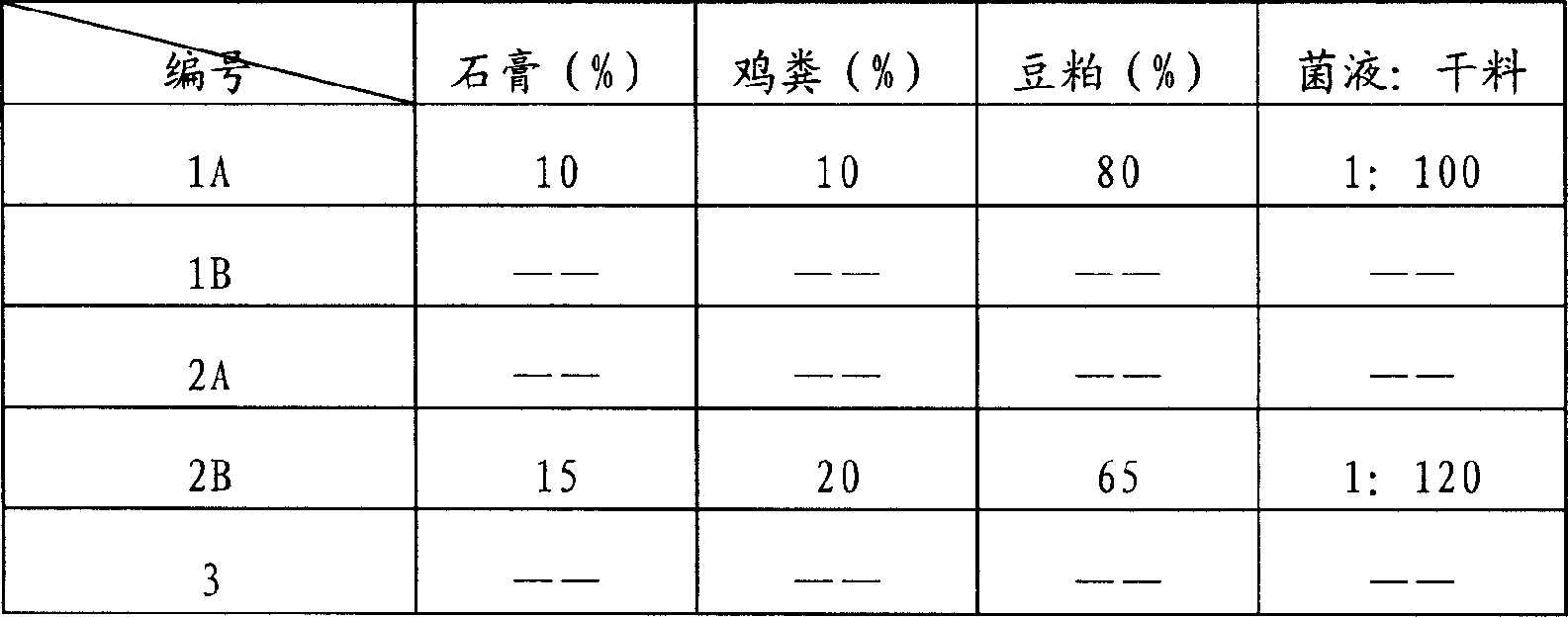
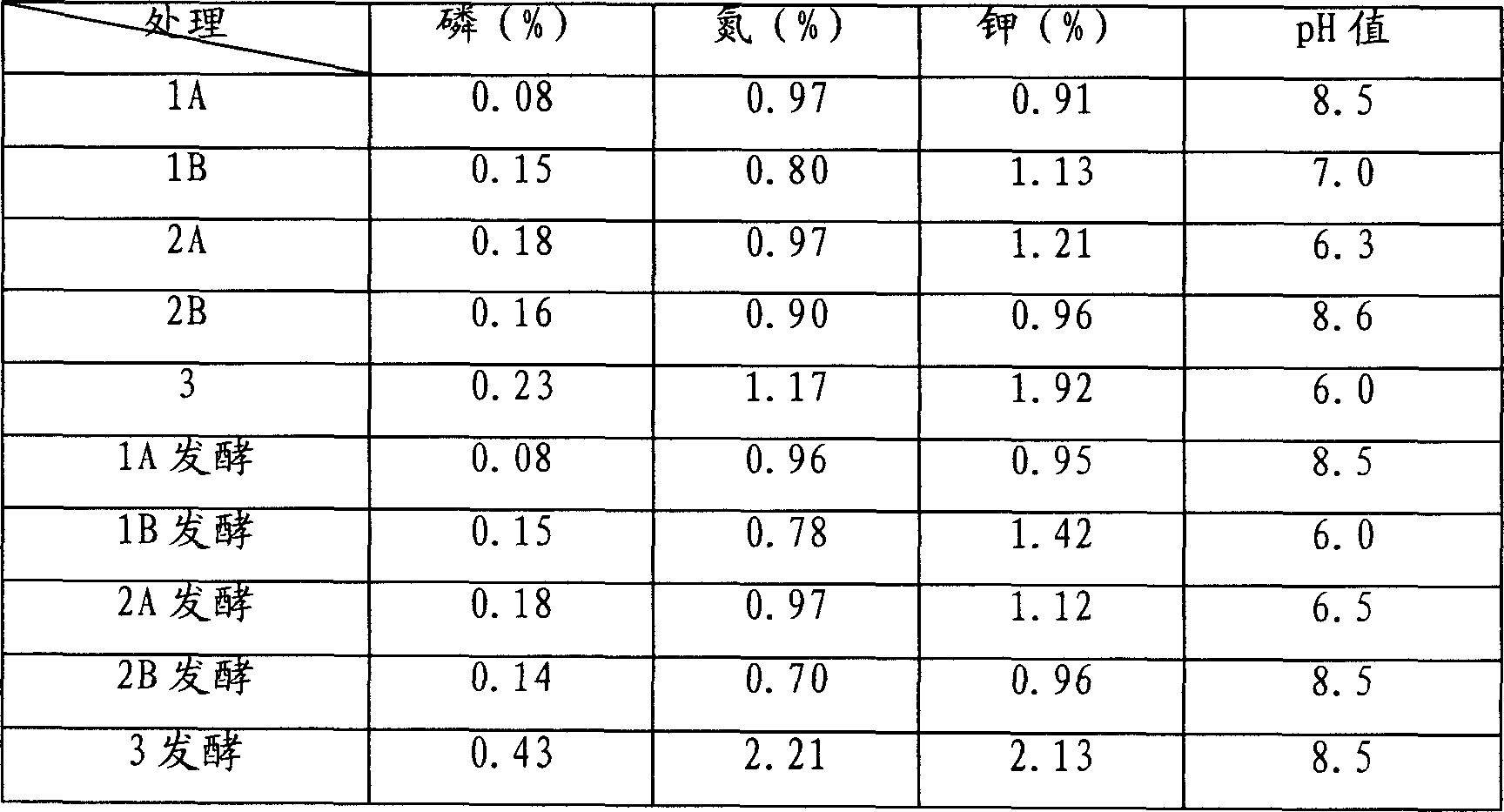
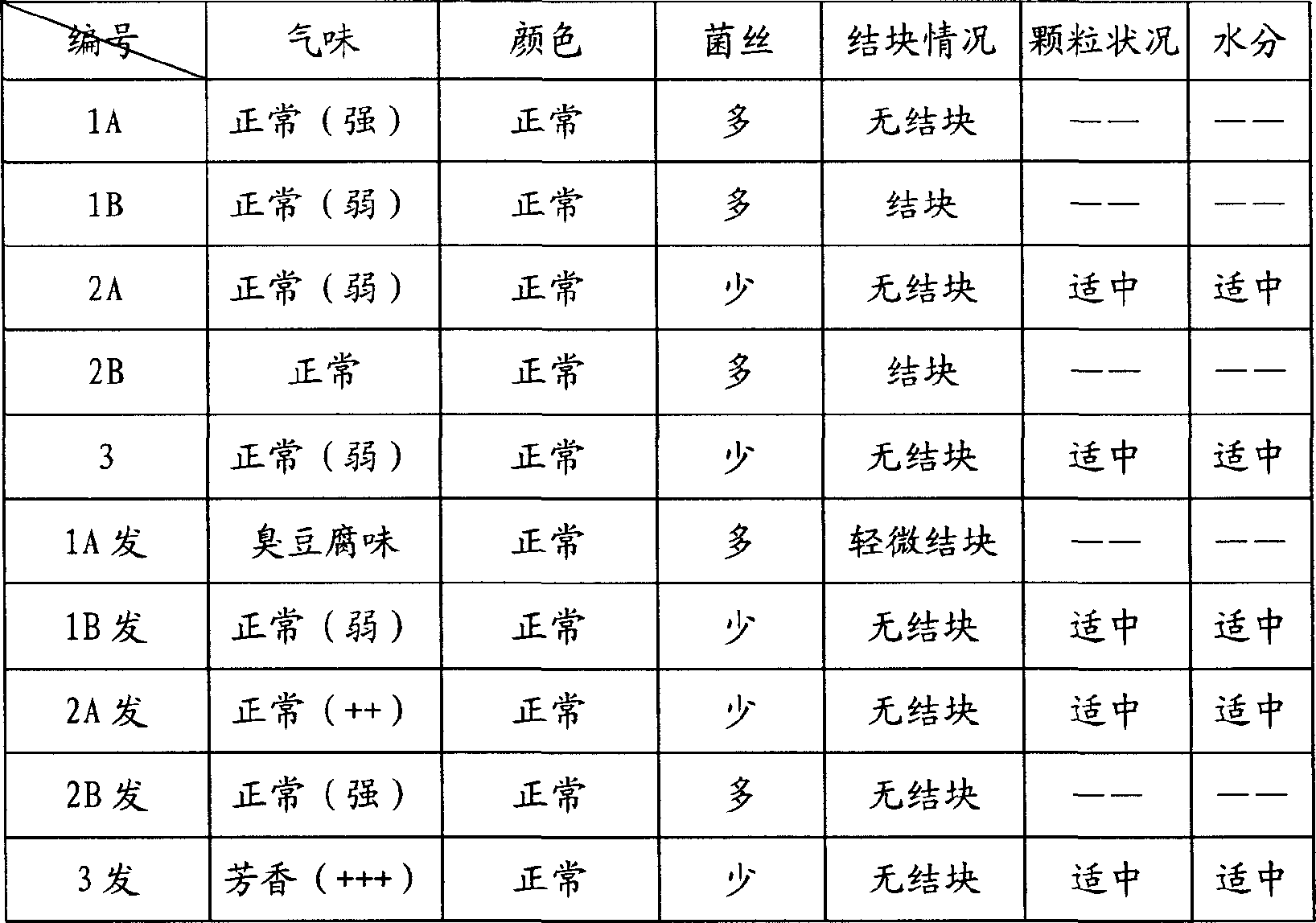
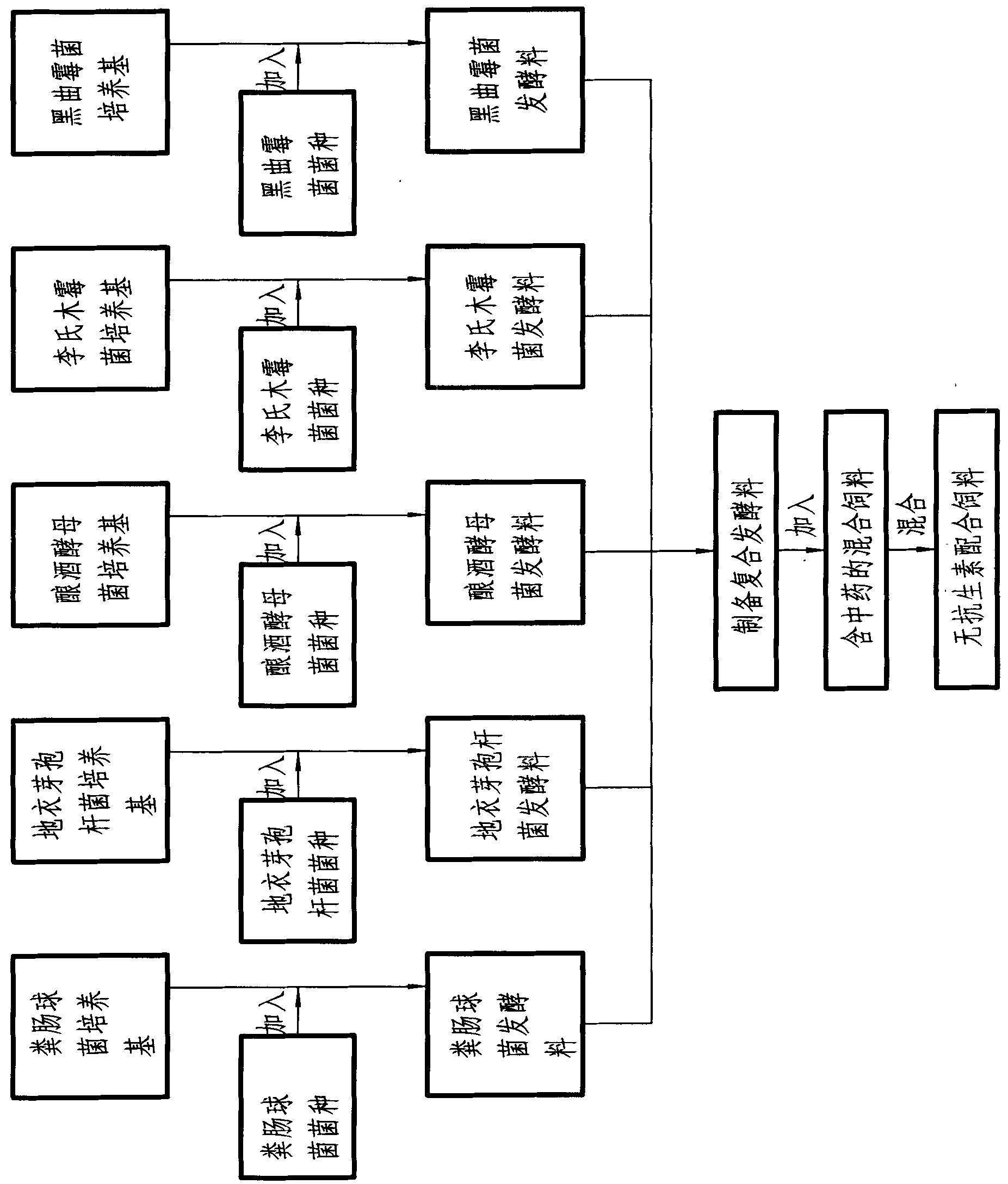
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
603 results about "Trichoderma reesei" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Trichoderma reesei is a mesophilic and filamentous fungus. It is an anamorph of the fungus Hypocrea jecorina. T. reesei can secrete large amounts of cellulolytic enzymes (cellulases and hemicellulases). Microbial cellulases have industrial application in the conversion of cellulose, a major component of plant biomass, into glucose.
Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds, in particular those belonging to the genus Aspergillus
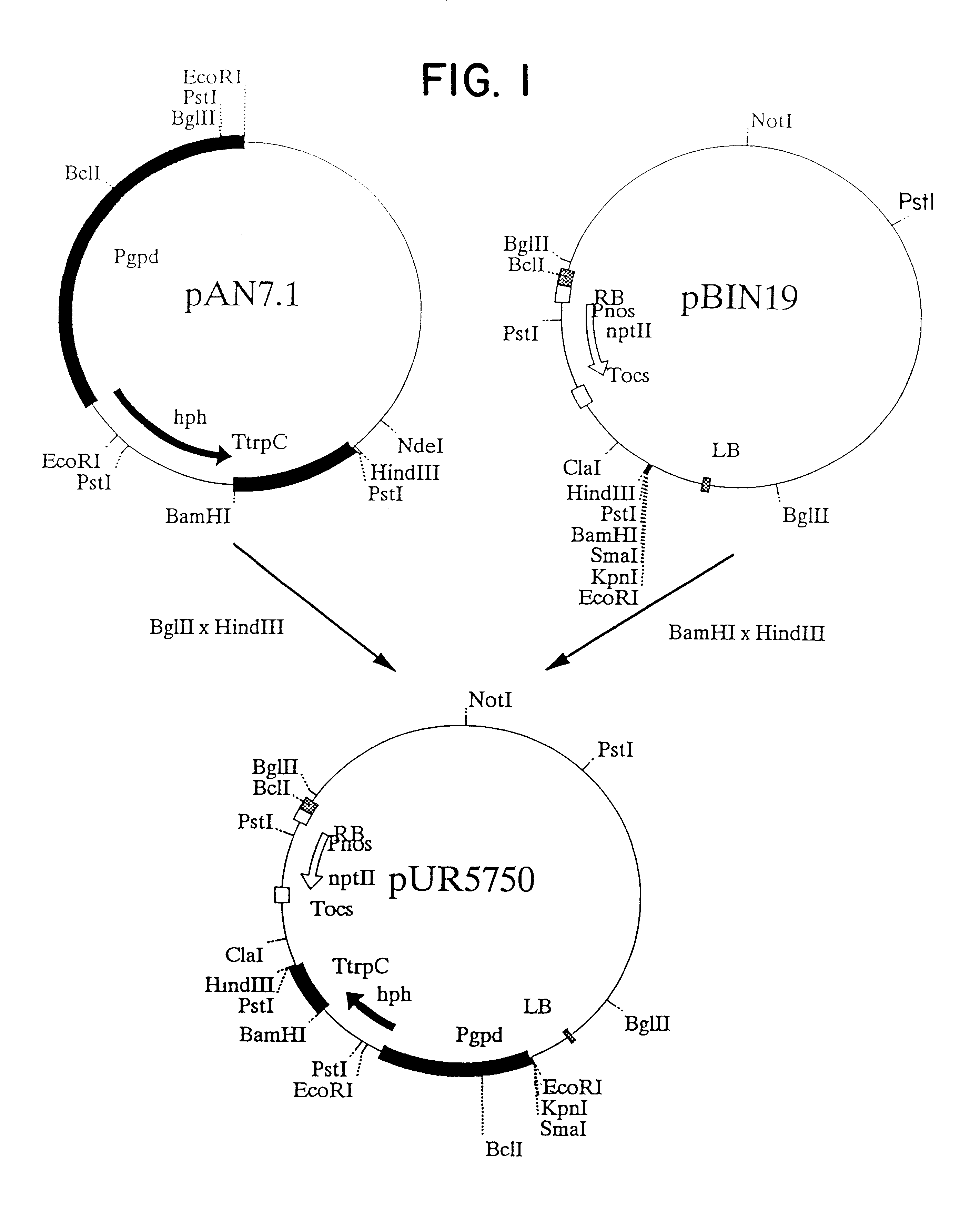
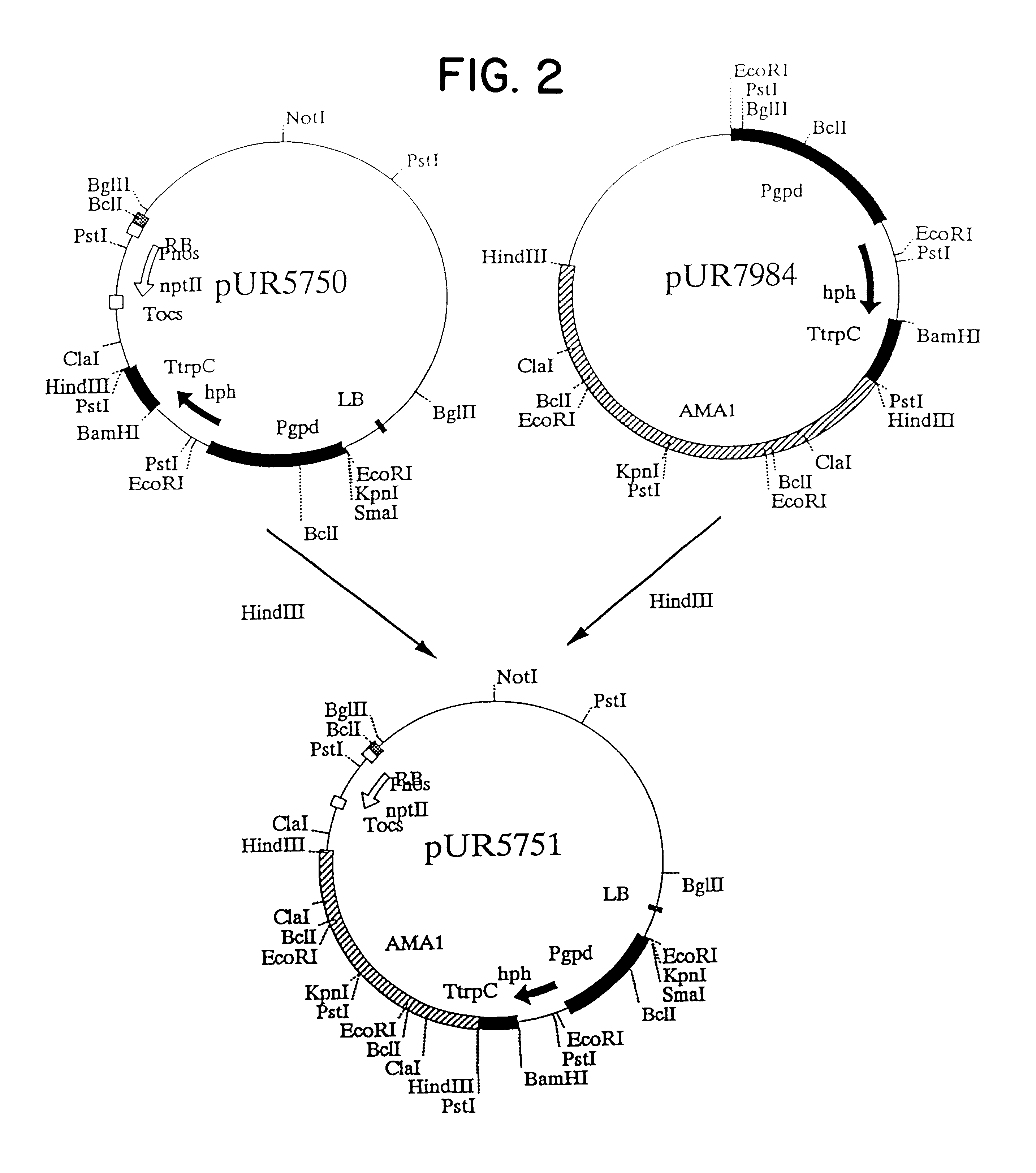
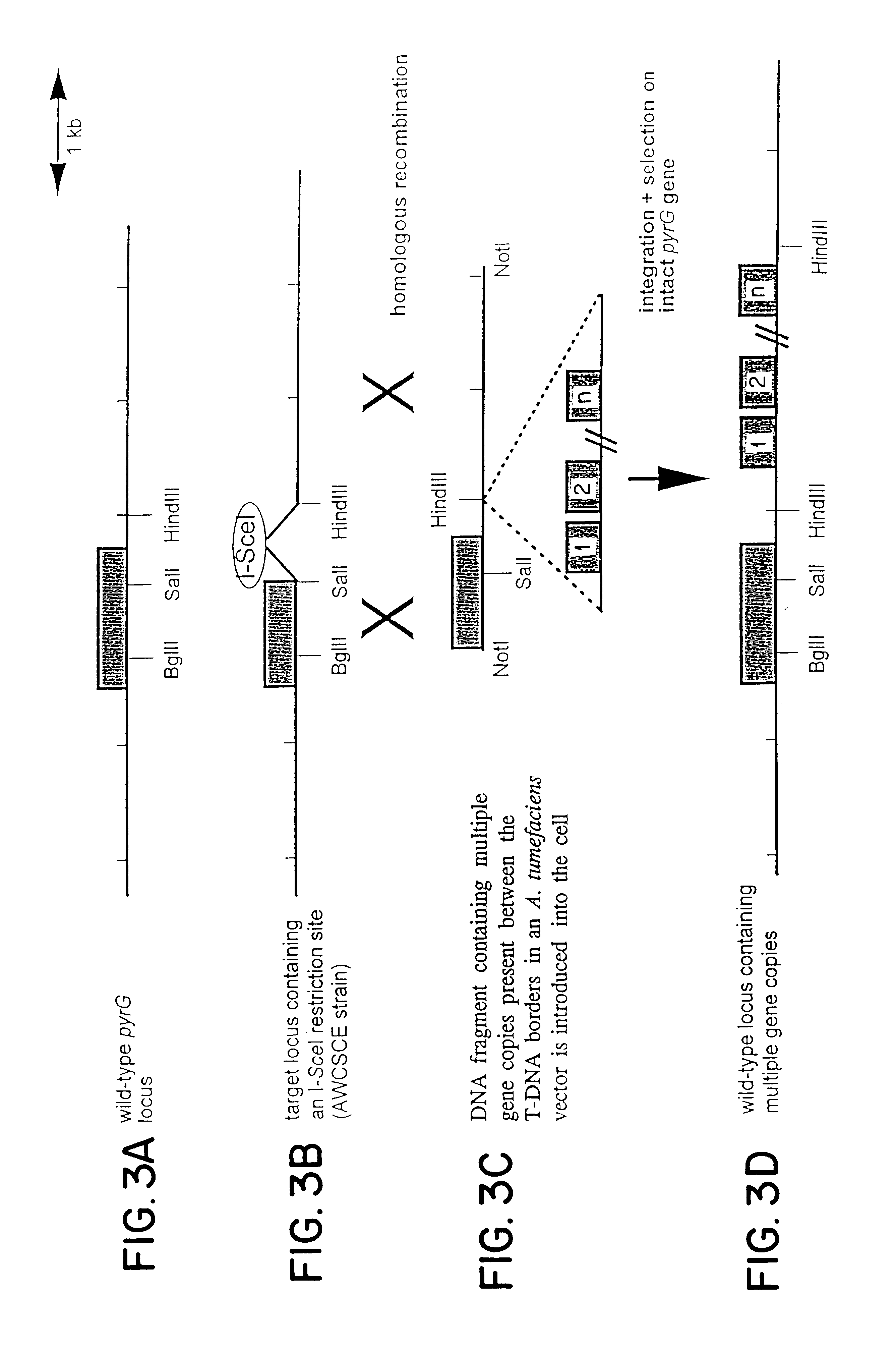
The invention relates to Agrobacterium mediated transformation of moulds comprising species of the fungal sub-divisions Ascomycotina, Basidiomycotina, Deuteromycotina, Mastigomycotina, and Zygomycotina.Examples demonstrate the transformation of Aspergillus awamori (both protoplasts and conidia), Aspergillus nidulans, Aspergillus niger, Colletotrichum gloeosporioides, Fusarium solani pisi, Neurospora crassa, Trichoderma reesei, Pleurotus ostreatus and Agaricus bisporus (all conidia), and Fusarium graminearum (both conidia and rehydrated freeze dried ATCC material).Especially for Aspergillus awamori the transformation frequency is much higher than with conventional mould transformation techniques.It has further been found that not only one expressable gene can be introduced into these moulds, but even multiple copies of such gene, which, moreover, can be targeted e.g. in the chromosomal pyrG locus, as exemplified for A. awamori. These multiple copies can be of a gene encoding a desired, homologous or heterologous, protein.
Owner:UNILEVER PATENT HLDG BV
Microbial straw decomposition additive as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN102382768AAuxiliary Growth-Promoting BenefitsIncrease the ambient temperatureFungiBacteriaSporeMicroorganism
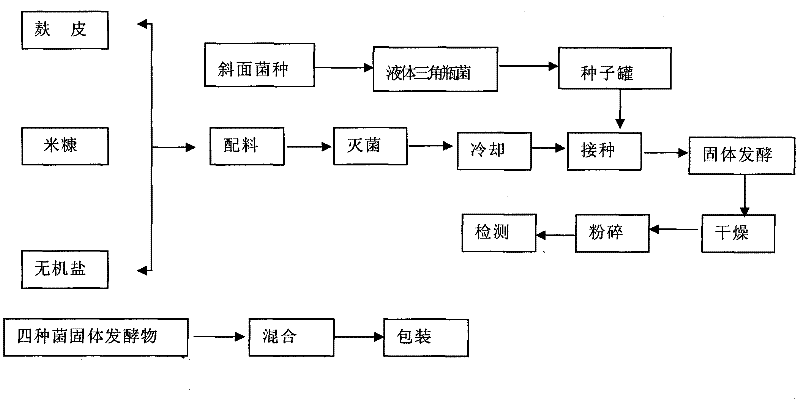
The invention discloses microbial straw decomposition additive, which belongs to the field of straw decomposition additive and is obtained through combining four bacteria: bacillus subtilis, aspergillus niger, trichoderma reesei and saccharomyces cerevisiae. The microbial straw decomposition additive utilizes the temperature rise benefit of the aspergillus niger spore enzyme activity for raising the environment temperature of decomposition, the further temperature rise benefit in the growth process of the bacillus subtilis is cooperated, and the temperature required by the decomposition is ensured, so the decomposition effect of straws is improved. The microbial straw decomposition additive has the obvious temperature rise benefit and can be used for the in-site field returning decomposition of the straws, the straw decomposition can be better accelerated in low-temperature and normal-temperature environment, the bottleneck problem of straw utilization is solved, the straw burning can be effectively reduced, the decomposition work procedure and the labor cost are saved, the fertilizer feeding is reduced, the soil structure is improved, and the planting benefit is improved.
Owner:武汉施瑞福生物技术有限公司
Compound microbial bacterial preparation for degrading crop straw and preparation method and application of compound microbial bacterial preparation
ActiveCN102690755ASolve shipping problemsSolve storage difficultiesBio-organic fraction processingFungiMetabolitePhosphate
The invention relates to a compound microbial bacterial preparation for degrading crop straw and a preparation method and application of the compound microbial bacterial preparation. The compound microbial bacterial preparation is prepared from bacillus subtilis, bacillus cereus, aspergillus niger, aspergillus flavus, trichoderma reesei, trichoderma longibrachiatum, sporotrichum thermophile and phanerochaete chrysosporium through solid fermentation. The compound microbial bacterial preparation can shorten the decomposition time and improve the decomposition efficiency of the crop straw. Microorganisms generate various effective metabolic products with nitrogen fixation and phosphate solubilizing functions and a high disease and pest resistance effect in the fermentation process, so that the compound microbial bacterial preparation is favorable for improving the soil structure and the yield and the quality of crops.
Owner:DEZHOU YUANHE AGRI TECH DEVCO
Zymophyte of plant straw feedstuff and its preparation
InactiveCN1663422AOvercoming complexityOvercoming the poor orientation of the fermentation processFood processingAnimal feeding stuffBiotechnologyZymogen
The invention discloses one kind of bread zymogens agents for plants straw especially fit to fermentation of dried and yellow straw contained plant lactobacillus, microzyme, trichoderma reesei, bacillus subtilis, which is preparation by mixing bacterial liquid in proportion after third class general cultivation in solid test tube, liquid triangle bottle and liquid malt wort for all bacterial, and state fermentation cultivation to grow up. All bacterial in this invention are cultivated separately, mixed till the stage of producing bacterial in liquid, which is more suitable to different cultivation conditions of different bacterial and enables every bacterium with the strongest activity.
Owner:单德章
Method for efficiently producing cellulase
InactiveCN101735993AIncrease vitalityPromote formationMicroorganism based processesEnzymesMetaboliteSugar
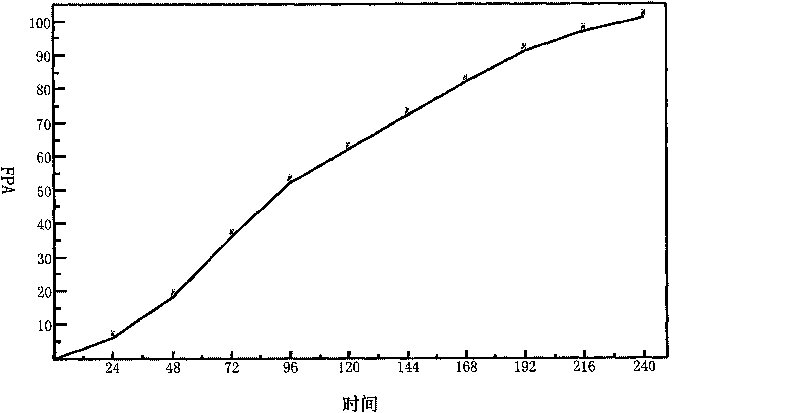
The invention provides a method for producing cellulase, which comprises the following steps of: inoculating Trichoderma reesei to a fermentation medium; fermenting for 60 to 90 hours, and then starting feed-batch culture; feeding a culture medium when a pH value of a fermentation liquor is more than 4.8 in the process of the feed-batch culture; stopping feeding the culture medium when the pH value of the fermentation liquor is less than 4.5; and stopping fermenting when the total fermentation time reaches 192 to 240 hours. The method integrates an insoluble carbon source and a soluble carbon source to collaboratively induce expression of cellulase genes. The method achieves coordinated balance in the process of growing strains and forming a target metabolic product through the feed-batch culture, solves the problems existing in the process for producing the cellulase by merely taking cellulose or soluble sugar as an inducer, effectively improves fermentation level of the cellulase; and the obtained cellulase has high degradation performance to cellulose substrates.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Mannanases
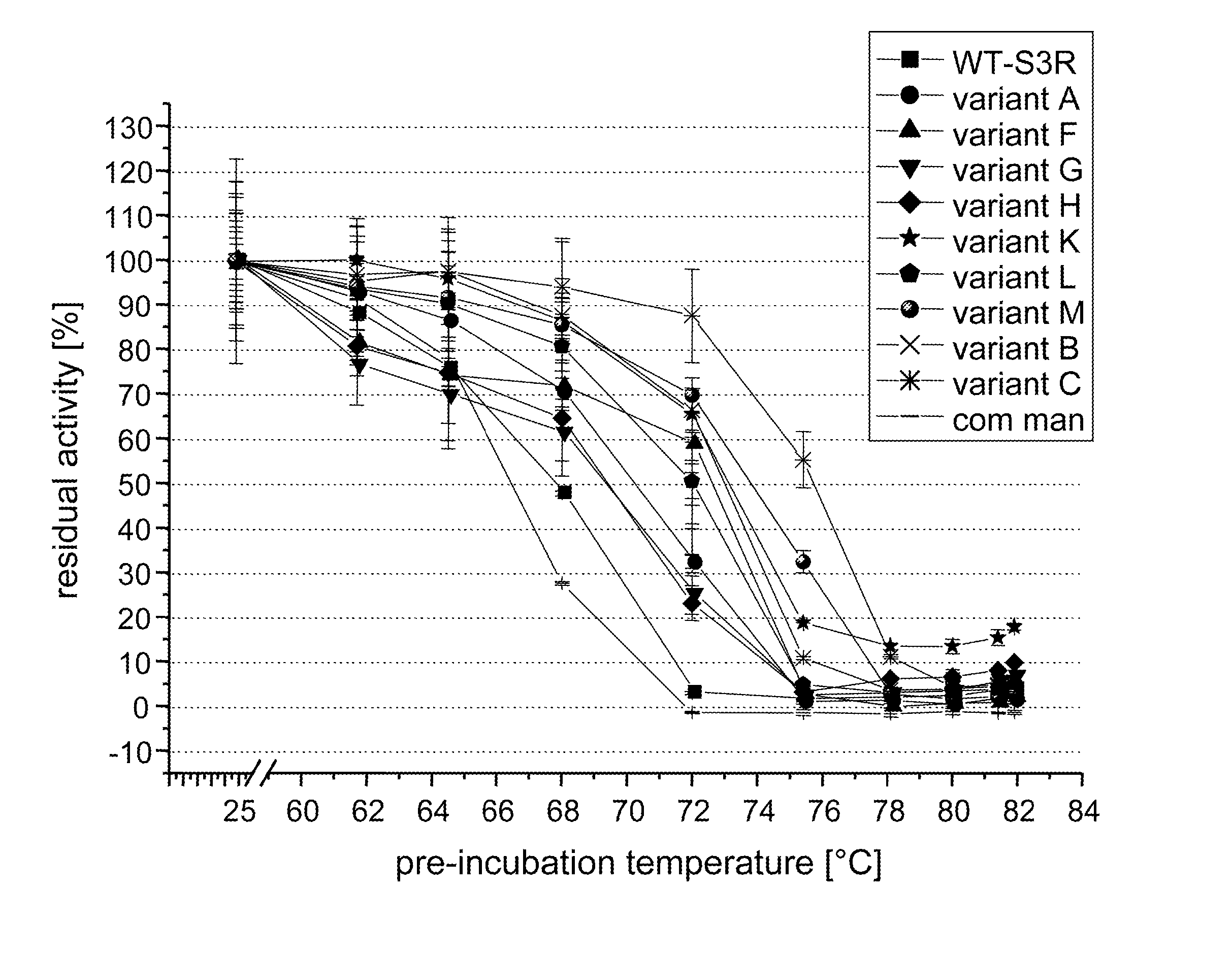
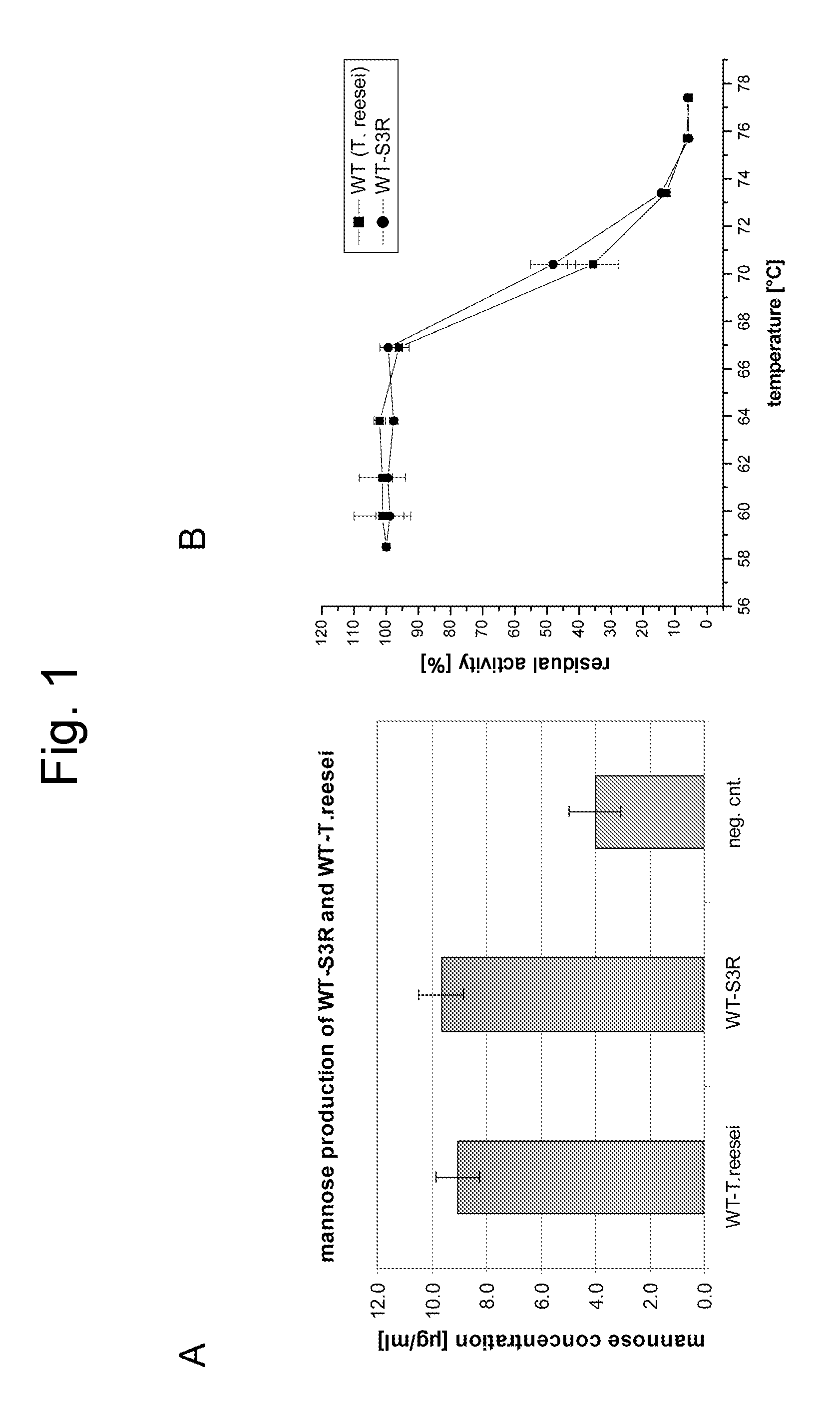
ActiveUS20080064064A1Precise and reproducible enzyme dosagePrevent steppingTissue cultureFlushingBleachWild type
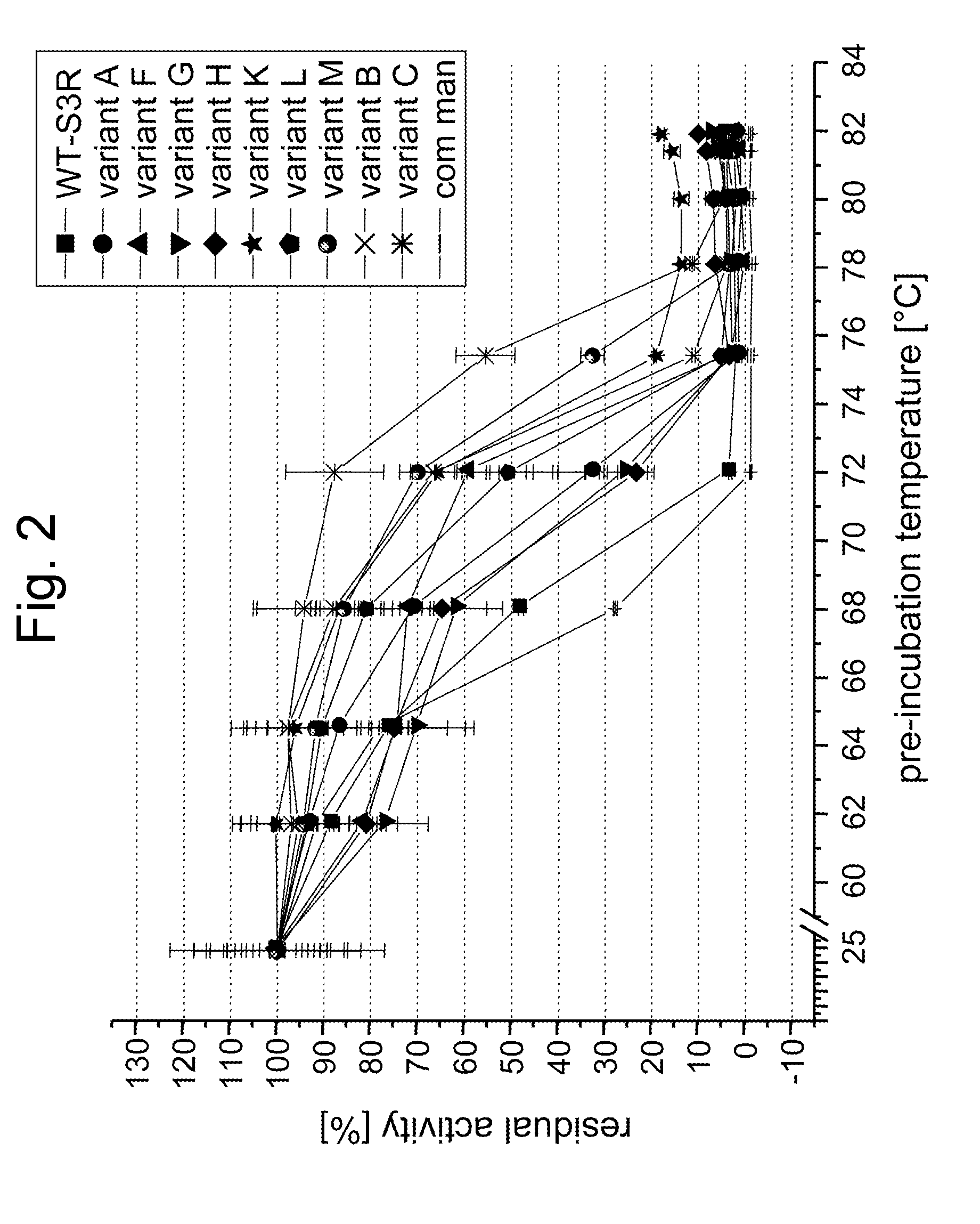
The present invention provides an insertion, deletion and / or substitution mutein of wild-type Trichoderma reesei β-mannanase having enhanced thermostability, proteolytic stability, specific activity and / or stability at low pH, a nucleic acid molecule encoding said mannanase mutein, a composition comprising said mannanase mutein; a method for its preparation, and its use for food and feed processing, for coffee extraction and the processing of coffee waste, as a supplement to food and feed, for enzyme aided bleaching of paper pulps, as bleaching and / or desizing agent in textile industry, for oil and gas well stimulation by hydraulic fracturing, as detergent, for removal of biofilms and in delivery systems, or for the processing of renewable resources intended for the production of biological fuels.
Owner:BASF AG
Method for producing organic fertilizer from municipal dry branch/fallen leaf waste and application thereof
ActiveCN104387136AImprove fertilityImprove water retentionBio-organic fraction processingAlkali orthophosphate fertiliserPhosphatePotassium
The invention provides a method for producing an organic fertilizer from municipal dry branch / fallen leaf waste and application thereof. The method comprises the following steps: collecting branches, fallen leaves and other municipal greening wastes, and mixing Aspergillus niger, Saccharomyces cerevisiae, Bacillus subtilis and Trichoderma reesei to obtain a composite microbial inoculant; adding bran coat, chaff powder or peanut hull meal, the composite microbial inoculant, urea and potassium dihydrogen phosphate, thoroughly mixing, piling into a 1.5-2m-high cone, and controlling the water content at 60-70%; carrying out hide lifting on the pile in the composting process, and fermenting for 20-30 days; and carrying out aerobic and anaerobic fermentation on the dry branch / fallen leaf waste by using the microbial inoculant to obtain the organic fertilizer. The preparation technique is simple; and the prepared organic fertilizer can improve the soil and reduce the environmental pollution caused by the waste.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
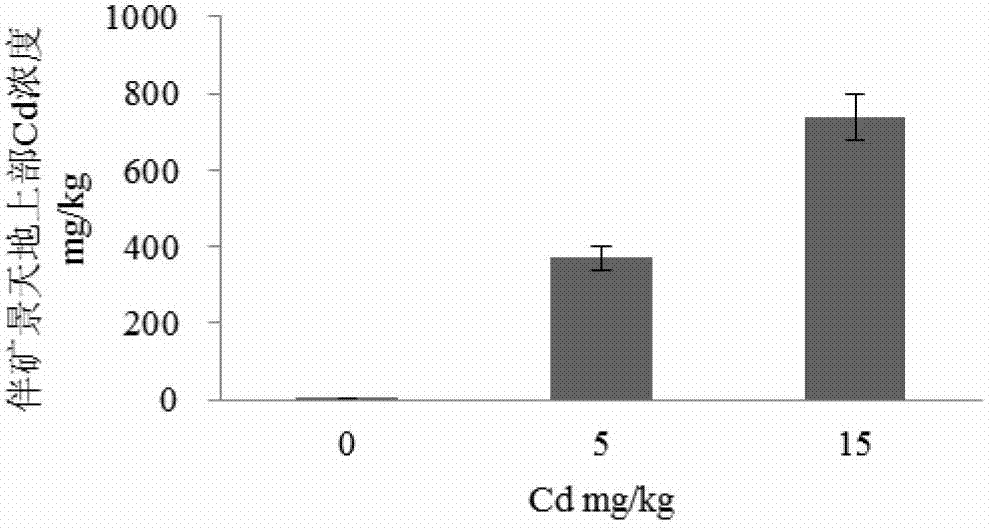
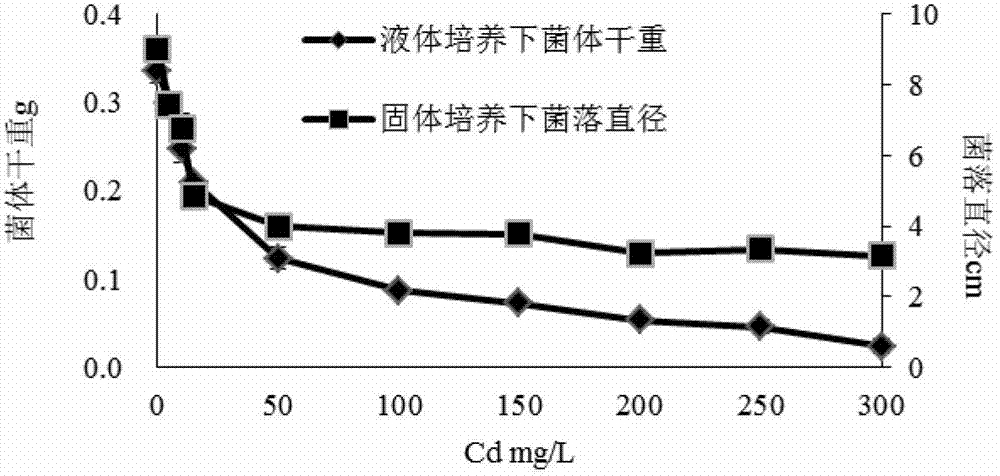
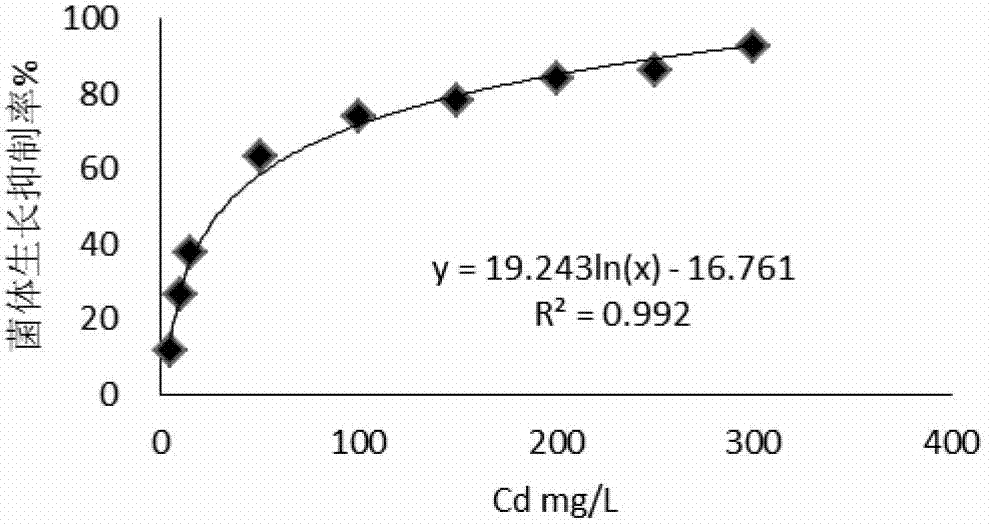
Application of trichoderma reesei and sedum plumbizincicola in remediation of cadmium-polluted farmland soil
ActiveCN103191914AImprove micro-ecological environmentImprove repair efficiencyContaminated soil reclamationEcological environmentTrichoderma reesei
The invention provides the application of trichoderma reesei and sedum plumbizincicola in the remediation of cadmium-polluted farmland soil. The application comprises the following steps of: cutting sedum plumbizincicola seedlings with about 10cm of plant height into soil to be remedied, applying trichoderma reesei FS10-C fermentation liquor or microbial preparation to the rhizosphere of the plant, keeping the soil water content to be 70%wt of the maximum field capacity in the process of remediation, and scissoring the plant along the surface of soil after the plant grows for 60-150 days to complete one remediation process. According to the application, the plant remediation efficiency of the cadmium-polluted farmland soil can be improved; and the sedum plumbizincicola plant remediation efficiency can be improved according to the trichoderma preparation, the biomass of the soil microorganism can be enhanced, the micro-ecological environment of the soil can be improved, and the application is good in ecological efficiency, and suitable for the remediation of the cadmium-polluted farmland soil.
Owner:INST OF SOIL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
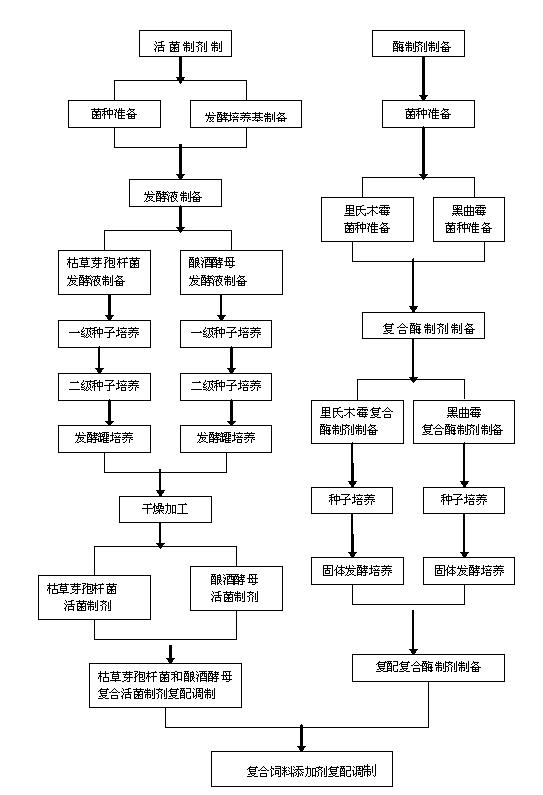
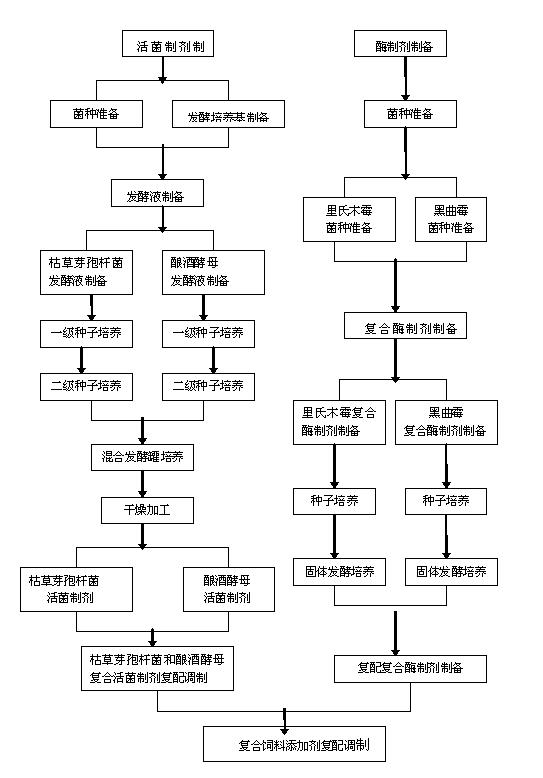
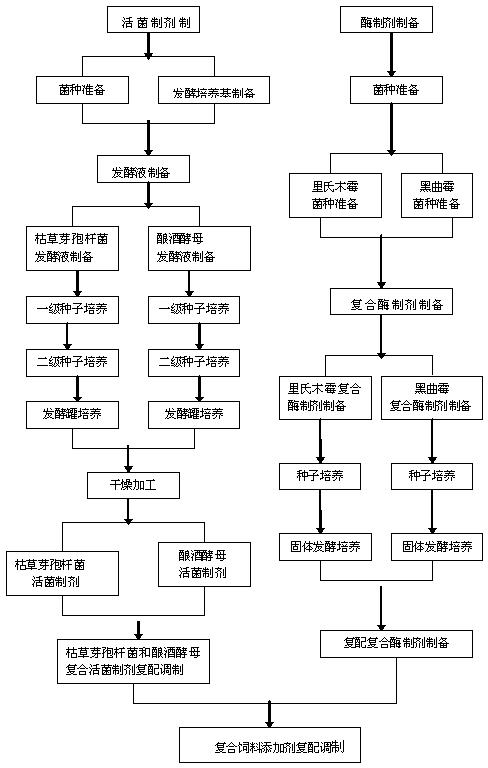
Bio-enzyme and microorganism containing compound feed additive and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN102599351AImprove feed utilizationIncrease production capacityAnimal feeding stuffAmylaseTrichoderma reesei
The invention discloses a bio-enzyme and microorganism containing compound feed additive and a preparation process thereof, which solve the problems of high production cost and less viable count of beneficial microorganisms in the prior art. The bio-enzyme and microorganism containing compound feed additive is characterized in that the additive is prepared by compounding a viable organism preparation (prepared by carrying out liquid fermentation and low-temperature drying on bacillus subtilis and brewer's yeast) with an enzyme preparation (prepared by carrying out solid fermentation and drying on trichoderma reesei and Aspergillus niger); and the viable count of beneficial microorganisms in each gram of the product is greater than 8*10<9> cfu / g, the cellulase activity (refer to the quantity of cellulose degraded by each gram of the product per minute) is greater than 500 mg, the alpha-amylase activity (refer to the quantity of starch hydrolyzed by each gram of the product per minute) is greater than 3000 mg, and the protease activity (refer to the mount of an amino acid generated by caseins hydrolyzed by each gram of the product per minute) is greater than 400 mg. The bio-enzyme and microorganism containing compound feed additive disclosed by the invention has the advantages that: the feed utilization rate of livestock can be improved in a short term, the intestinal digestive flora of livestock is improved and balanced, the breeding cost is reduced, and the feed conversion rate and the animal production performance are improved; and meanwhile, the additive is simple in preparation process, low in production cost, and suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:LIAONING SHENNONG BIOLOGICAL ENG
Saline-alkali land improving and fertilizing agent and its preparation method
InactiveCN1631857AImprove physical and chemical propertiesGood dispersionOrganic fertilisersFertilizer mixturesMicroorganismLactobacillaceae
Disclosed are a fertilizer for advancing alkaline land and its preparing method, comprising of microbe compound bacterium solution and dry matter and their mess ratio is 1:80-150, the microbe compound bacterium solution is formed by plant lactobacillaceae, distillers yeast . The invention is made by completely using organic substance to fermen, which can adyance alkaline land as wellas be fertilizer for green organic agricultural products.
Owner:牛发国
Enzyme-bacterium duplex straw decomposing agent and its preparation and application methods
InactiveCN105368744AIncreased degradation rateEasy to separateBio-organic fraction processingFungiMicrobial agentTrichoderma reesei
The invention discloses an enzyme-bacterium duplex straw decomposing agent and its preparation and application methods. The decomposing agent is made by mixing a composite microbial agent and a composite enzyme agent in a weight ratio of 3-4:1. The composite microbial agent includes Trichoderma viride, Aspergillus niger, Aspergillus oryzae, Brevibacillus laterosporus and a fused Saccharomyces cerevisiae, having a weight ratio of (1-2):(1-2):(1-2):(2-3):(2-3). The composite enzyme agent includes cellulase produced by the fermentation of Trichoderma reesei, hemicellulase produced by the fermentation of Bacillus subtilis, and ligninase produced by the fermentation of Pleurotus ostreatus, having a weight ratio of (1-2):(1-2):(1-2). The decomposing agent has a double straw degrading function, allowing more efficient and more thorough biological degradation, increasing the straw degrading speed to a higher extent and shortening degrading time, and can fully decompose crop straw to fields within about a week, without affecting the planting and transplanting of next-stubble crops.
Owner:甘肃明德伟业生物科技有限公司
Straw-decomposing inoculant
InactiveCN103725631ASpeed up the ripening processHigh activityFungiBacteriaPotassiumOrganic content
The invention discloses a straw-decomposing inoculant which comprises the following active components: bacillus subtilis, aspergillus niger, trichoderma viride, phanerochaete chrysosporimn and geobacillus stearothermophilus. In the straw-decomposing inoculant, the total content of effective viable bacteria is (1-2)* 10<8> / ml. With adoption of the straw-decomposing inoculant, the fertilizer prepared from straws can be rapidly degraded, and the normal compost fermentation is performed in advance for at least 15 days. When the straw organic fertilizer prepared from the straw-decomposing inoculant is used as the base fertilizer, alkali-hydrolyzale nitrogen, rapid available phosphorus, potassium and organic contents in the soil are higher than that in the soil in which straws are directly utilized and no fertilizer is applied, and the urease activity and cellulase activity in the soil are obviously higher than that in the soil in which straws are directly utilized and no fertilizer is applied.
Owner:DALIAN SANKE BIO ENG
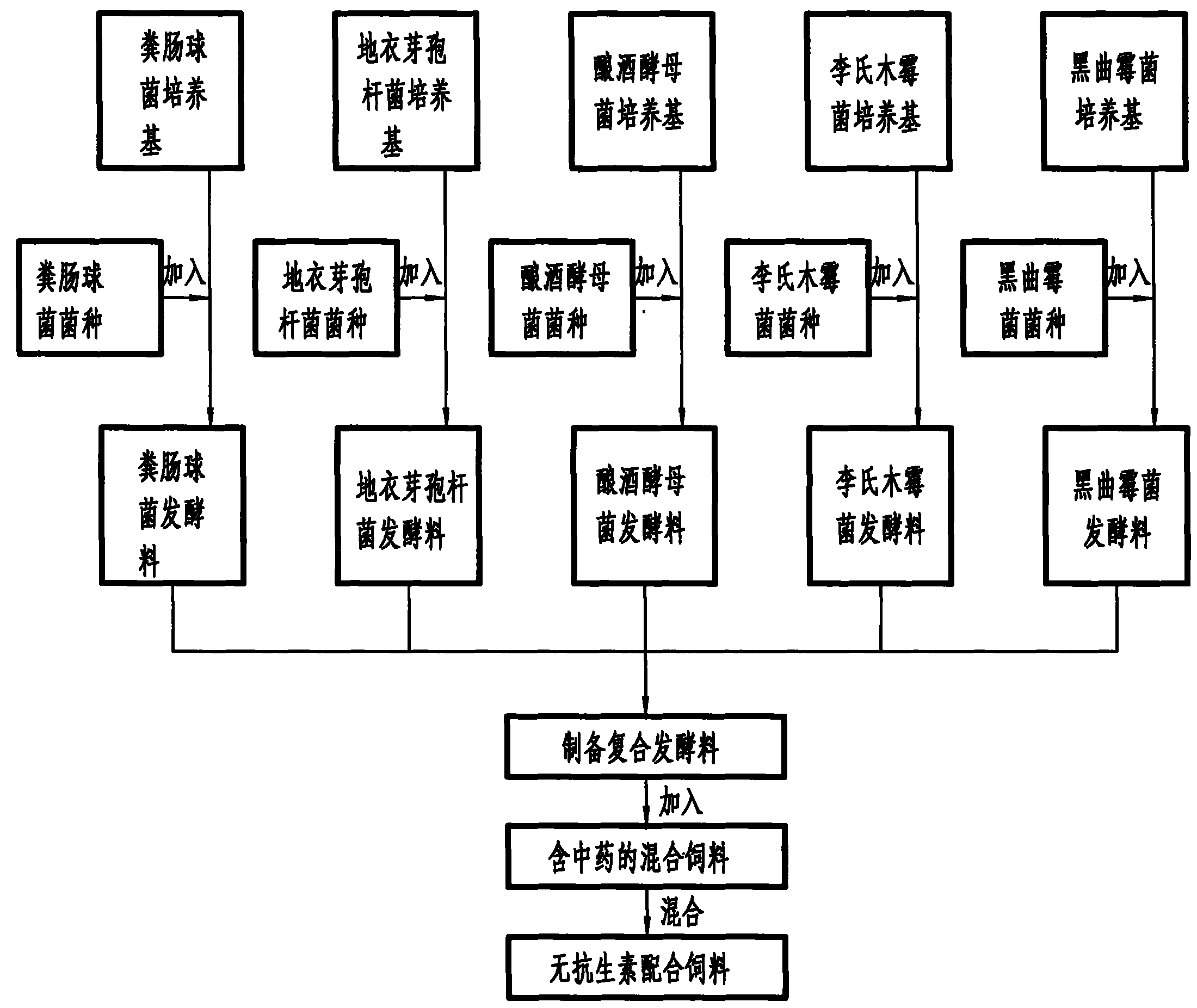
Antibiotic-free mixed feedstuff and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102318735ANo pollution in the processNo drug resistanceFood processingAnimal feeding stuffTrichoderma reeseiAspergillus niger
The invention provides an antibiotic-free mixed feedstuff and a preparation method thereof. The invention belongs to the field of animal feedstuffs. According to the invention, a mixed feedstuff containing Chinese herbal medicines is mixed with a mixed fermentation material containing various probiotics according to a certain proportion, such that the feedstuff provided by the invention is obtained. The mixed feedstuff containing Chinese herbal medicines comprises half-dried ginkgo leaves or ginkgo leaf extraction residues, Japanese honeysuckle stems, balloon flower root, soybean meal, peanutmeal, corn powder, wheat flour, calcium hydrogen phosphate, common salt, composite microelement, mulvital, and selenium-enriched yeast. The mixed fermentation material containing various probiotics comprises an enterococcus faecalis fermentation material, a bacillus licheniformis fermentation material, a saacharomyces cereisiae fermentation material, a Trichoderma reesei fermentation material, and an aspergillus niger fermentation material, which are mixed according to a certain proportion. Microbe strains are processed through targeted acclimatization, and are cultivated by using a solid fermentation medium, such that the mixed fermentation material is obtained. The antibiotic-free mixed feedstuff provided by the invention assists in promoting growth, and brings no toxic or side-effect. The feedstuff causes no antibiotic residue, no pollution, and no drug resistance. With the mixed fermentation the utilization rate of the feedstuff can be improved, healthy growth of live stocks can be promoted, and meat qualities of the live stocks can be improved.
Owner:SHANDONG YONGCHUNTANG GRP
Method for preparing bean slags soluble food fibers by zymolysis method
The present invention provides a method for preparing bean dregs soluble dietary fiber by zymotechnics. Firstly, to dry the fresh bean dregs at the temperature of 60 to 80 DEG C for 12 to 14 hours, then to comminute until passing 40 mesh sieve, and to confect into ferment culture medium according to the ratio of 1 : 20 to 25 of bean dregs : water, and regulating the pH value to 4 to 4.5, then to disinfect at the temperature of 121 DEG C for 15 to 20 min to obtain liquid; to inoculate leeb wood mildew into the culture medium according to the 3 to 4 percent of the liquid volume ratio, then to shake bed culture at the speed of 140 to 160 r / min for 3 to 4d at the temperature of 28 to 30 DEG C. After sterilization, filtering and concentrating, to obtain deposit by non-water ethanol deposition, then to dry the deposit in vacuum to produce finished product. The present invention condition is geniality, equipment is simple, enzyme specificity is high, and can improve activity component amount maximum, has no pollution to circumstance, the SDF content in the bean dregs is increased greatly.
Owner:NORTHEAST AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Isolated polypeptide having arabinofuranosidase activity
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Composite aroma-producing microorganism as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103992975AIncrease the content of aroma substancesPromote accumulationTobacco preparationFungiMicroorganismMicrobiology
The invention discloses a composite aroma-producing microorganism as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The composite aroma-producing microorganism is formed by compounding bacillus subtilis, trichoderma reesei, aspergillus niger and hansenula polymorpha at a wet thallus mass ratio of 5:2:1:1. The composite aroma-producing microorganism disclosed by the invention can be used for preparing a filter material for a cigarette filter and greatly improving the aroma and taste of the cigarettes, and has good application value in the cigarette processing production.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AOJIAN PERFUME
Trichoderma reesei strain capable of producing cellulase with high yield through space mutation
InactiveCN104328057AGenetically stableIncreased filter paper enzyme activityFungiMicroorganism based processesMicroorganismBiotechnology
The invention provides a trichoderma reesei strain capable of producing cellulase with high yield through space mutation, belonging to the technical field of microorganism mutation. According to the invention, trichoderma reesei Rw-X1 strain is preferably selected to be carried by Shenzhou IX to be subjected to space mutation and trichoderma reesei TG-C521 strain capable of producing cellulase with high yield can be carefully screened and cultured; the strain is collected in China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on August 25, 2014 and has a collection Number of CGMCCNo.9537. According to the invention, the genetic character of the strain is changed by virtue of a special environment so that a strain with normal distributed mutation and stable genetic transformation can be screened out preferably; and the strain is used for producing cellulose and the filter paper activity of the strain is 25.83-34.49% higher than that of the trichoderma reesei Rw-X1 strain; the strain is friendly to the environment and is free of pollution, thus having a wide industrial application prospect.
Owner:河南天冠纤维乙醇有限公司
Fermentation inducement preparation method for ramee degumming composite enzyme
The invention relates to a process for preparation of fermentation and induction of ramie degumming compound enzyme, which includes the steps of (1) induction preparation of ramie degumming compound enzyme system of trichoderma reesei, (2) determination of the activity of cellulose, xylanase and pectinase and (3) the processing of ramie by crude enzyme liquid which is obtained by fermentation. The invention can obtain the higher enzyme activity, is better qualified to the compound enzyme system of the ramie degumming, and is low in costs, simple and convenient in operation and easy in industrial production.
Owner:DONGHUA UNIV
Recombinant vector and recombinant bacterium of Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1, and expression of Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1 in recombinant bacterium
InactiveCN102220369AEfficient productionIncrease productionFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyPichia pastoris
The invention discloses a recombinant vector and recombinant bacterium of Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1, and expression of the Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1 in the recombinant bacterium. The recombinant vector containing the Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1 is constructed by the following steps: (1) carrying out PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification on the Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene BGL1, and connecting to a TA vector; and (2) constructing the Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase gene to a pichia pastoris expression vector. The recombinant bacterium disclosed by the invention can effectively express the target protein Trichoderma reesei beta-glucosaccharase BGL1. The invention overcomes the defect that a great deal of beta-glucosaccharase can not be purified from Trichoderma reesei in the prior art. Lots of waste lignocellulose exists in the natural world. The method provided by the invention can increase the yield of beta-glucosaccharase, and has very important meanings in enhancing degradation efficiency of cellulose, efficiently producing energy from waste cellulose and solving the problem of energy crisis at present.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
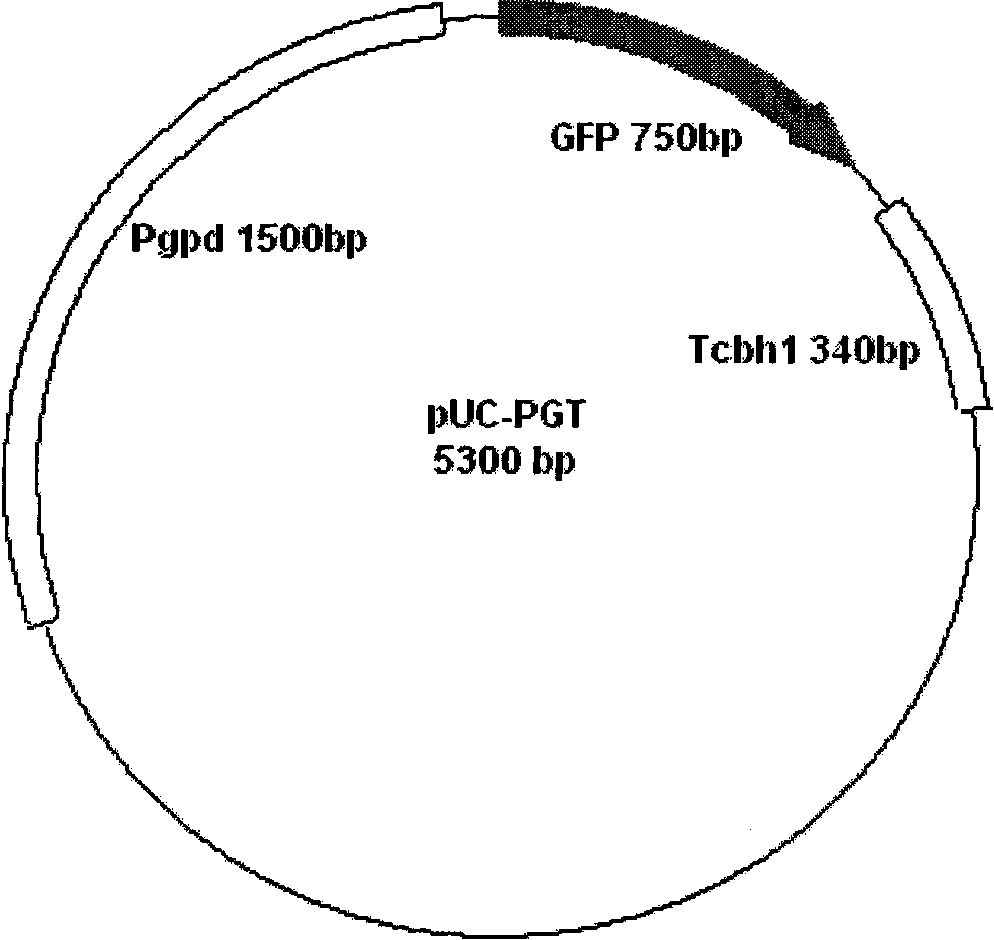
Trichoderma reesei expression cassette, recombinant strain and application thereof
InactiveCN101560513AHigh expressionAvoid it happening againFungiAnimal feeding stuffPaper manufacturingGlyceraldehyde
The invention discloses a Trichoderma reesei expression cassette, a recombinant strain and application thereof. The expression cassette includes Trichoderma reesei glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase promoter, foreign target genes and Trichoderma reesei CBHI terminator. The expression cassette of the invention adopts the technical scheme that the sequence of the Trichoderma reesei glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase gene promoter and the sequence of the Trichoderma reesei CBHI terminator form a constitutive promoter, genes of animals, vegetables or epiphyte can be expressed without induction, expression products can be properly modified, the efficient synthesis and exudation capability of the Trichoderma reesei can be utilized for high protein expression, and overmuch foreign proteins can be prevented from being generated in the expression products. The recombinant strain of the invention can efficiently express cellulose-free xylanase which has important using value in the paper manufacturing industry.
Owner:邢苗 +1
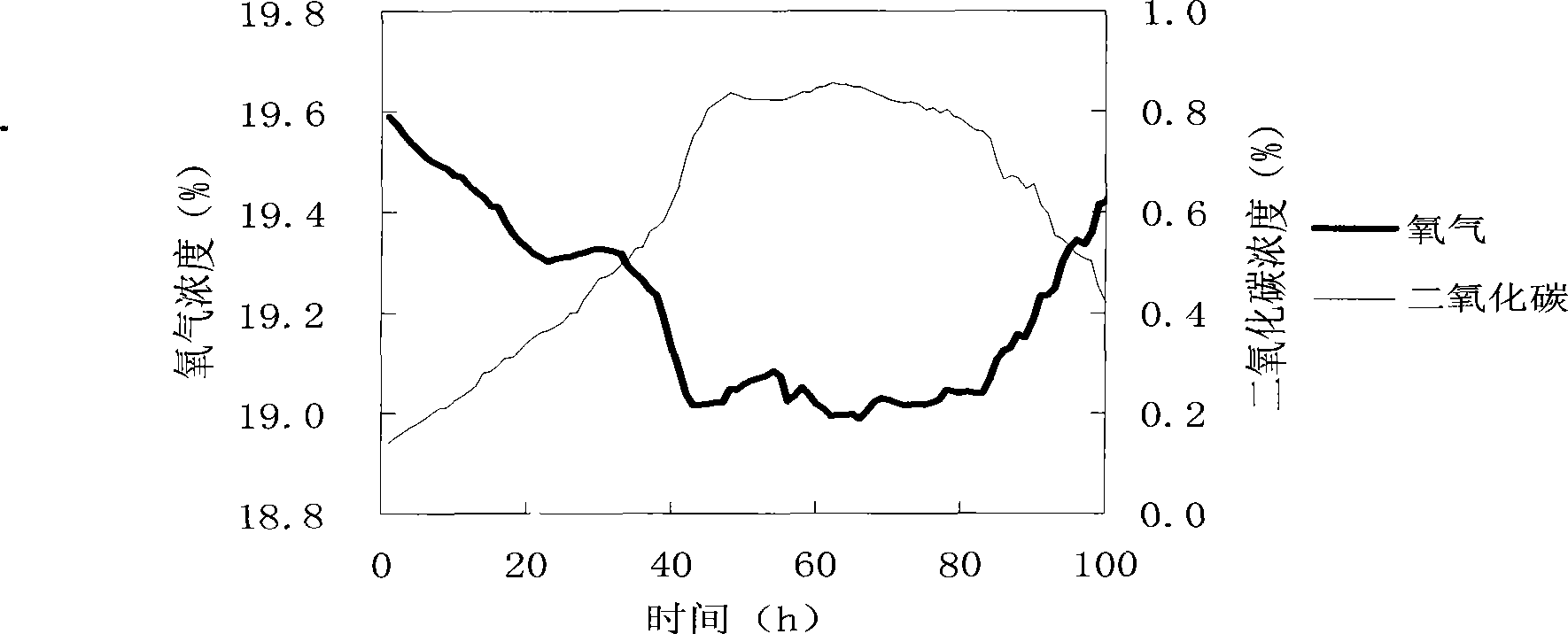
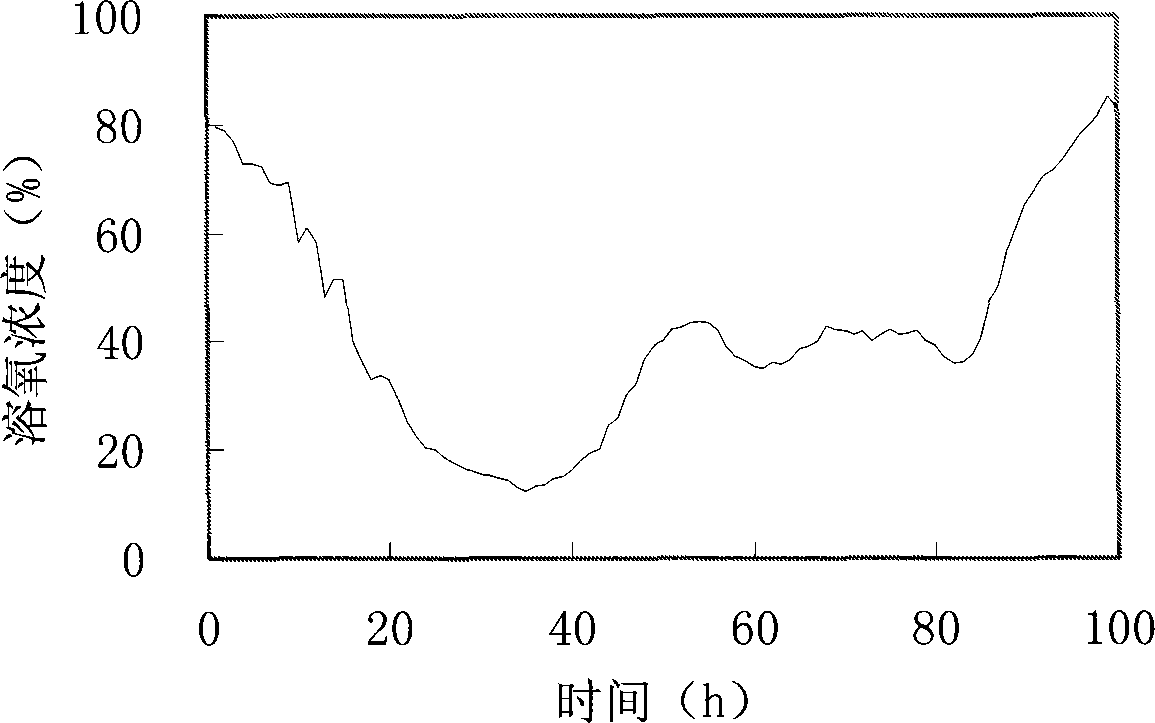
Trichoderma reesei cultivation method for improving yield of cellulase
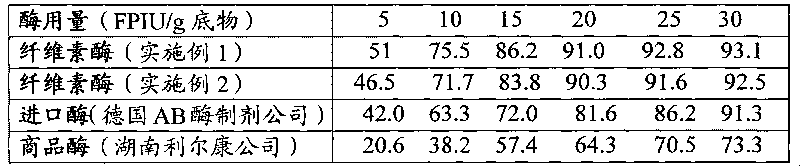
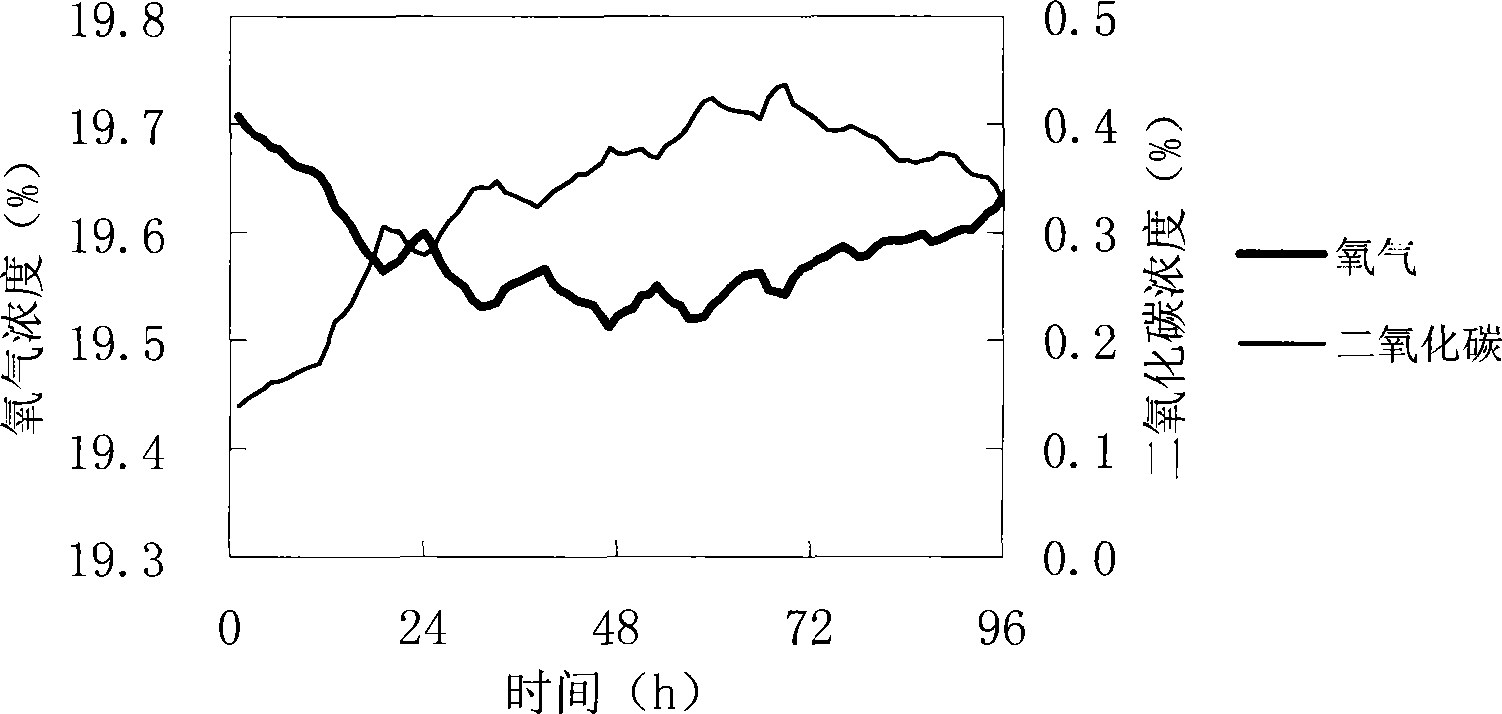
ActiveCN101250485AIncreased filter paper enzyme activityEnzyme production time shortenedFungiMicroorganism based processesFilter paperOxygen
The invention relates to a method for controlling the dissolved oxygen concentration of solution through adopting ventilation quantity regulation to increase the productivity of trichoderma reesei cellulase. The method is characterized in that the ventilation quantity is regulated in the enzyme production process to control the dissolved oxygen concentration in a main enzyme production stage to be 20%-30%, which not only enables the dissolved oxygen concentration of enzyme production liquid to be no lower than the critical concentration, but also lowers the carbon dioxide concentration in tail gas, and the method is beneficial for thalli to grow. Compared with the method for producing enzyme with fixed ventilation quantity, with the method of the invention for producing the enzyme, the filter paper enzyme activity can be increased by 30%, and the enzyme producing time can be shortened by 14%.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP
Lipase and engineering strain of recombinant expression thereof
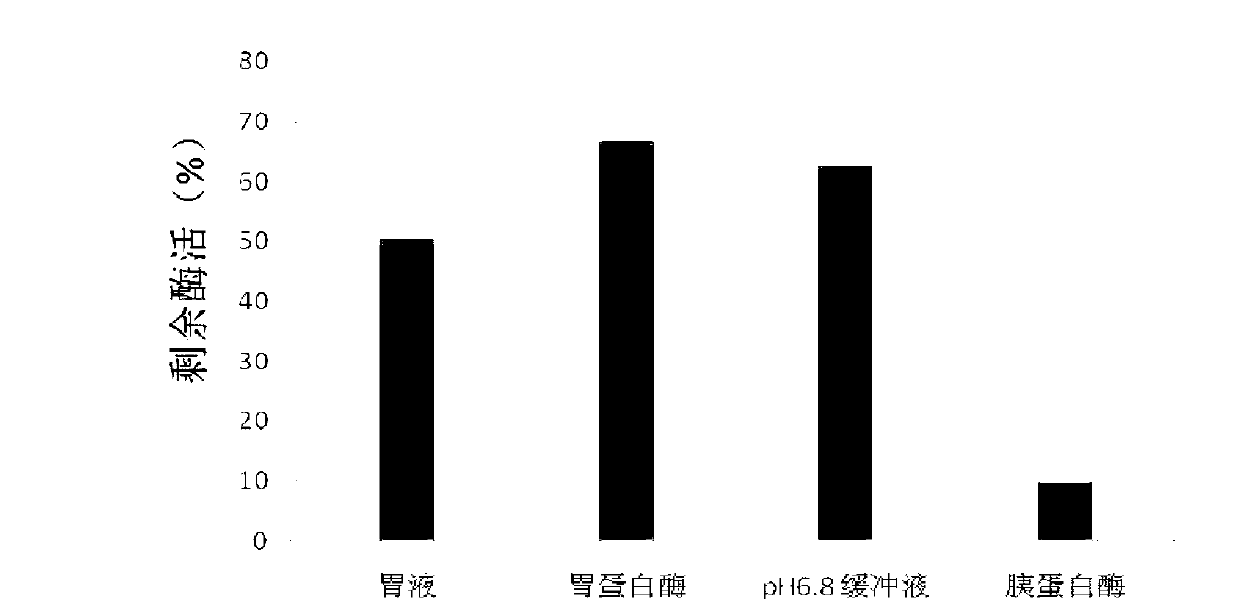
The invention provides an engineering strain of recombinant expression lipase. Lipase gene obtained by cloning in Aspergillus niger is transferred into Trichoderma reesei, so that Trichoderma reesei engineering strain can be constructed and has the preservation number of China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC) No.: M2012483. The recombinant expression lipase has the optimal action pH of 5.0 and the optimal action temperature of 30 DEG C, and the tolerance of the recombinant expression lipase to gastric juice, pepsase and artificial intestinal juice can be enhanced. The lipase remarkably improves the utilization rate of oil matter in feed, thus remarkably reducing the addition of oil in the feed and reducing the cost of the feed.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP
Trichoderma reesei capable of producing cellulase in high yield and application of trichoderma reesei
ActiveCN104328056AMany branchesLow viscosityFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyInduced mutation
The invention provides a trichoderma reesei mutant strain VLKDN-1. The preservation number of the stain VLKDN-1 is CCTCC NO:M 2014506. A trichoderma reesei mutant strain capable of producing cellulase in high yield is obtained by adopting an ultraviolet-induced mutation technology combined with shake flask selection. Compared with a starting strain, the enzyme activity of the fermentation supernatant of mutant strain trichoderma reesei VLKDN-1 is increased by 235%, the content of protein is increased by 157%, the colonial morphology of the mutant strain is obviously smaller than that of the starting strain; the hyphae are shorter than that of the starting strain; the branches are more than that of the starting strain. The viscosity of a fermentation strain solution is remarkably reduced by virtue of the characteristics of short hyphae and more branches of the small colonial morphology of the mutant strain in the production process; the purposes of reducing the stirring rate and improving the dissolved oxygen are achieved; the production cost is reduced; the trichoderma reesei mutant strain VLKDN-1 is wide in application prospect.
Owner:QINGDAO VLAND BIOTECH GRP +1
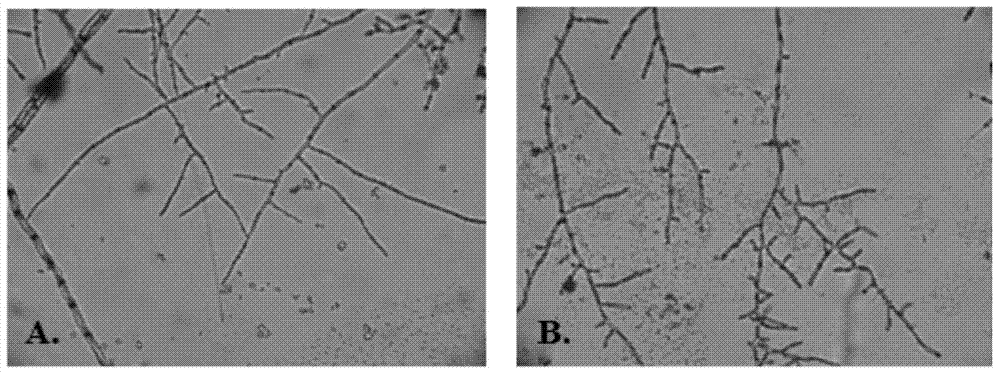
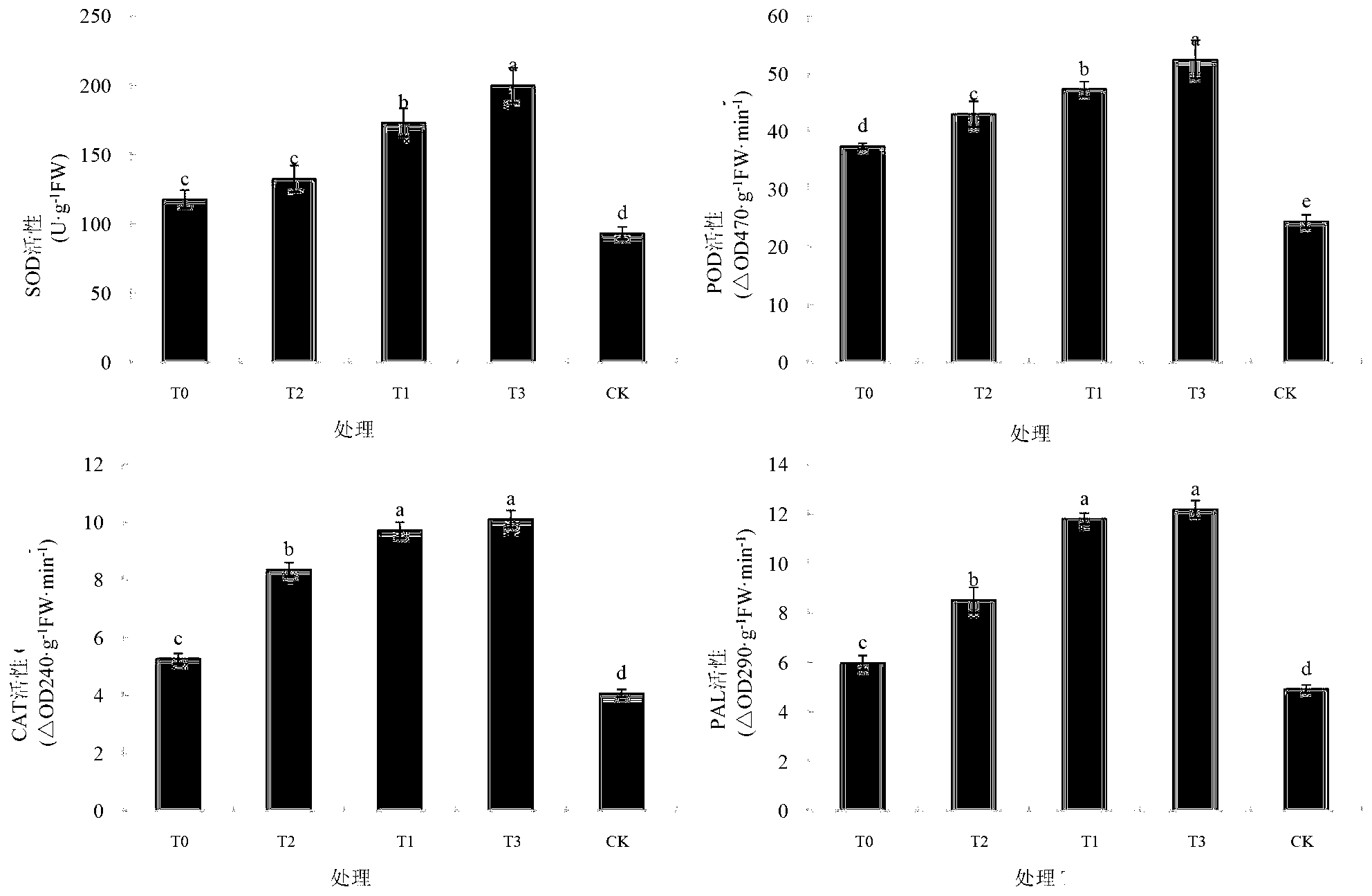
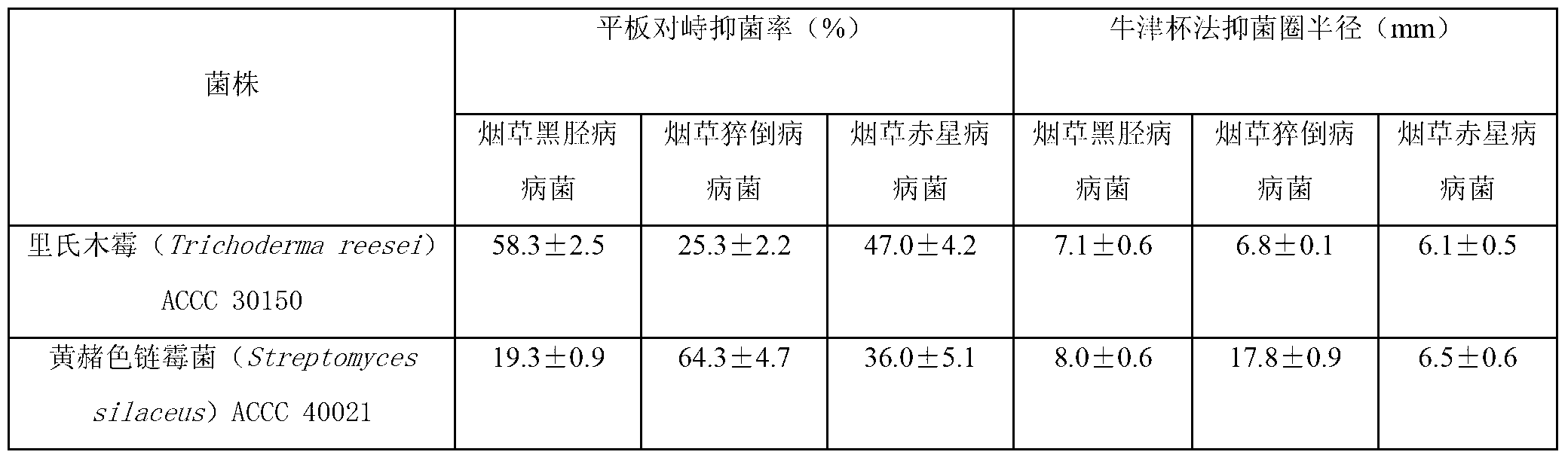
Composite microbial fertilizer bactericide for disease prevention and growth promotion of tobacco and application thereof
The invention discloses a composite microbial fertilizer bactericide for disease prevention and growth promotion of tobacco and an application thereof. The bactericide can be used for promoting tobacco growth and / or preventing tobacco disease, and comprises active components namely Trichoderma ressei ACCC 30150 and Streptomyces silaceus ACCC 40021. The bactericide is environment-friendly, can inhibit dug resistance development of a disease pathogen, is favor of popularization of green food and organic agriculture, is low in cost and non-pollution, and safe to tobacco crops. By introducing antagonistic microbe in soil, through biological control, fungus and bacterial diseases can be effectively prevented, environment is effectively improved, agroecological system balance is maintained, and a foundation for sustainable development of tobacco can be laid.
Owner:INST OF AGRI RESOURCES & REGIONAL PLANNING CHINESE ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Novel trichoderma genes
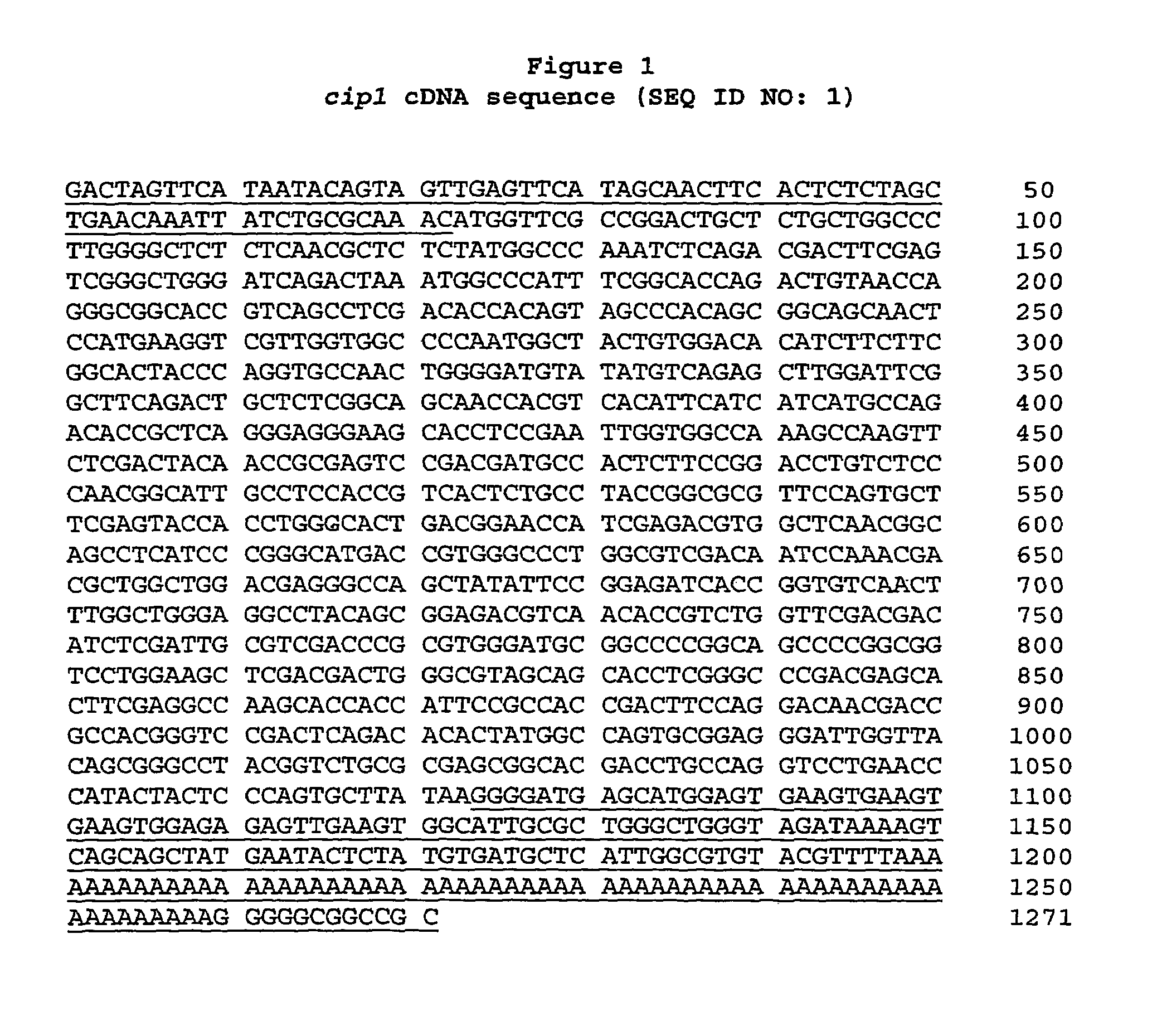
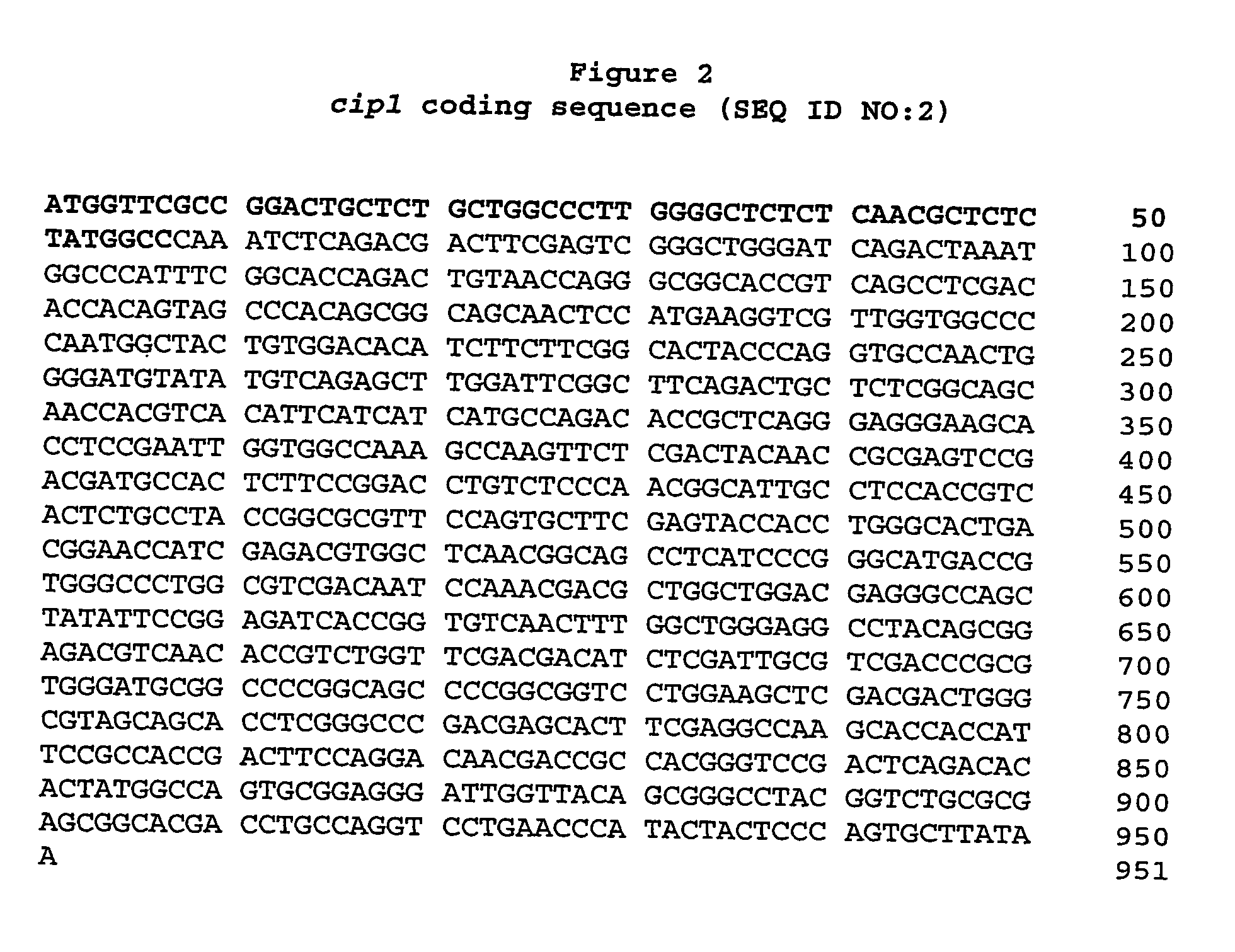
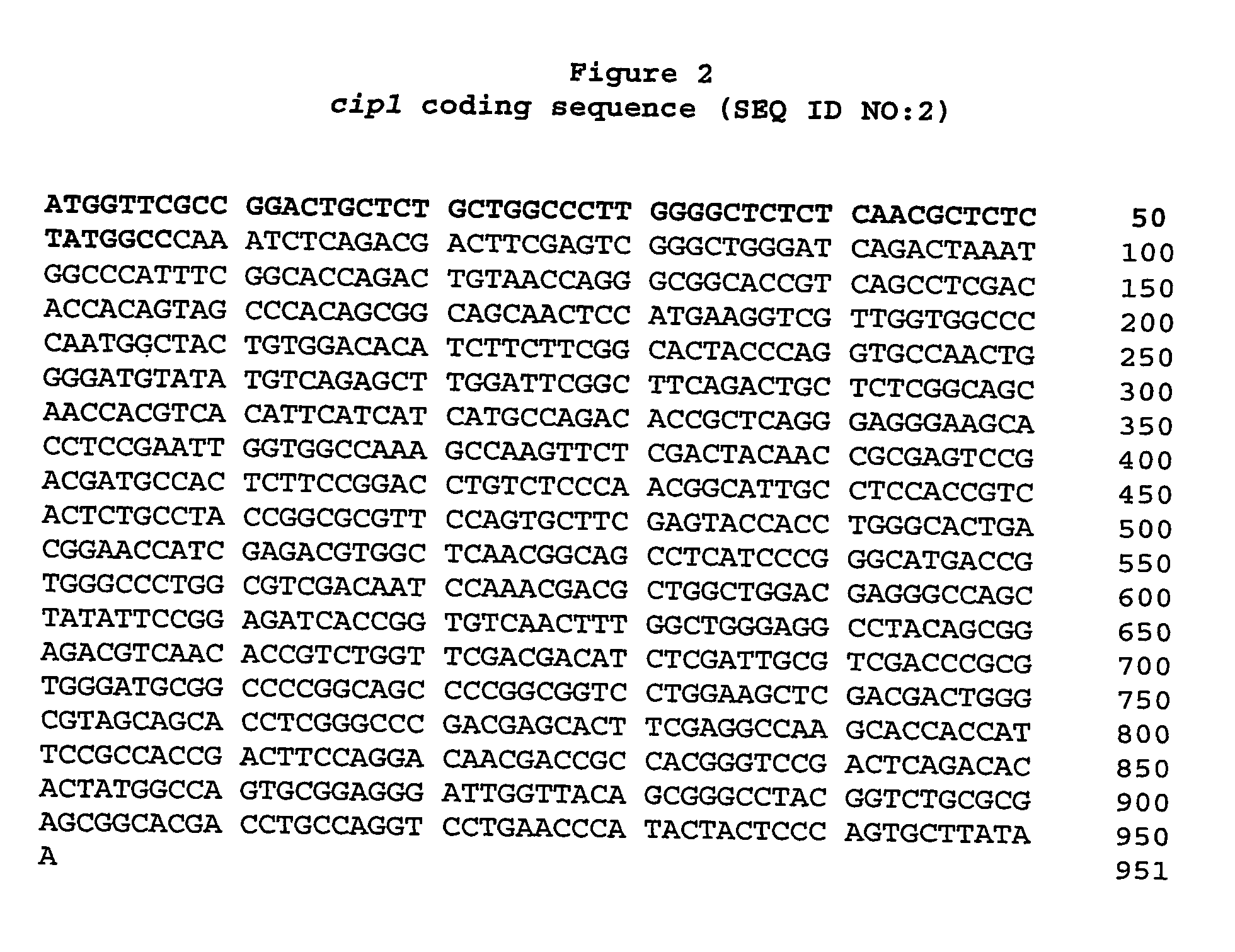
Described herein are novel gene sequences isolated from Trichoderma reesei. Two genes encoding proteins comprising a cellulose binding domain, one encoding an arabionfuranosidase and one encoding an acetylxylanesterase are described. The sequences, CIP1 and CIP2, contain a cellulose binding domain. These proteins are especially useful in the textile and detergent industry and in pulp and paper industry.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Aroma-enhancing puffed tobacco stem particles and preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN103989246AAvoid the problem of excessive burnt smellFully fixedTobacco treatmentTobacco smoke filtersMicroorganismMicrobial inoculation
The invention discloses aroma-enhancing puffed tobacco stem particles and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method of the aroma-enhancing puffed tobacco stem particles comprises the steps that a micropore structure is formed in each tobacco stem, and the tobacco stems are dried and smashed after being fixed and formed to form particles; the tobacco stem particles are inoculated with a compound aroma-generating microorganism, fermental cultivation and drying are carried out on the tobacco stem particles and the compound aroma-generating microorganism, and then the aroma-enhancing puffed tobacco stem particles can be obtained. The compound aroma-generating microorganism is formed by compounding bacillus subtilis, Trichoderma reesei, Aspergillus niger and Hansenula polymorpha according to the wet-cell mass ratio of 5:2:1:1. According to the aroma-enhancing puffed tobacco stem particles and the preparation method and application thereof, the tobacco stems serve as raw materials to be processed to obtain the puffed tobacco stem particles, then the compound aroma-generating microorganism is added, and serving as a filter material of a filter tip, the finally-obtained aroma-enhancing puffed tobacco stem particles have the advantages of being high in filter efficiency, strong in adsorption capacity, free of offensive odors and consistent with tobacco in aroma and have good application prospect.
Owner:GUANGZHOU AOJIAN PERFUME
Method for improving submerged fermentation level of trichoderma reesei cellulase liquid
InactiveCN102229920AIncrease the level of submerged fermentationProlong growth periodMicroorganism based processesEnzymesBiotechnologySpore
The invention provides a method for improving a submerged fermentation level of trichoderma reesei cellulase liquid. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps of: first-grade seed culturing: preparing a spore suspension solution from activated trichoderma reesei CICC 13052 bacterial strain on a PDA (Potato-Dextrose-Agar) slant culture medium and inoculating the spore suspension solution into a fresh seed culture medium according to the inoculating amount of 3% to be cultured; and fermenting and culturing: inoculating the first-grade seeds in a logarithm growing periodinto a fresh fermenting culture medium to be cultured and controlling the pH values and dissolved oxygen in a pot of the fermenting process by sections to maintain the pH values and dissolved oxygen of the different periods at the different levels, and carrying out feed supplement and controlled culturing. By utilizing the method provided by the invention, the liquid is fermented for 168 hours; the enzyme activity of the fermenting liquid is measured by utilizing an international standard method which is recommended by the IUPAC (International Union of Pure and Applied Chemistry); and the enzyme activity of filter paper is 14.2 IU / mL and is improved by 67.1% compared with the interval fermenting enzyme activity level (8.5 IU / mL) before the process is optimized.
Owner:TIANJIN INST OF IND BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF SCI
Preparation method of straw decomposition agent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a straw decomposition agent. The straw decomposition agent is prepared by using bacillus subtilis, aspergillus oryzae, lactobacillus plantarum, trichoderma reesei and saccharomyces cerevisiae as preparation strains, carrying out activation and primary and secondary culture on the strains respectively to obtain various strain solutions with bacterial count of 106-108 / ml and mixing the strain solutions according to a certain proportion. The straw decomposition agent has the beneficial effects that the straw decomposition agent can be used for quickly degrading straws to prepare fertilizers and ensures that the straw decomposition time is at least 15 days ahead of the normal composting fermentation time; organic straw fertilizers prepared by the preparation method are used as base fertilizers, so that the contents of available nitrogen, rapidly available phosphorus, potassium and organic matters in soil are higher than those of available nitrogen, rapidly available phosphorus, potassium and organic matters in the soil in which straws are directly used and fertilizers are not applied; the urease activity and cellulase activity of the soil are obviously improved compared with those of the soil in which straws are directly used and fertilizers are not applied.
Owner:DALIAN SANKE BIO ENG
Wood pulp treatment
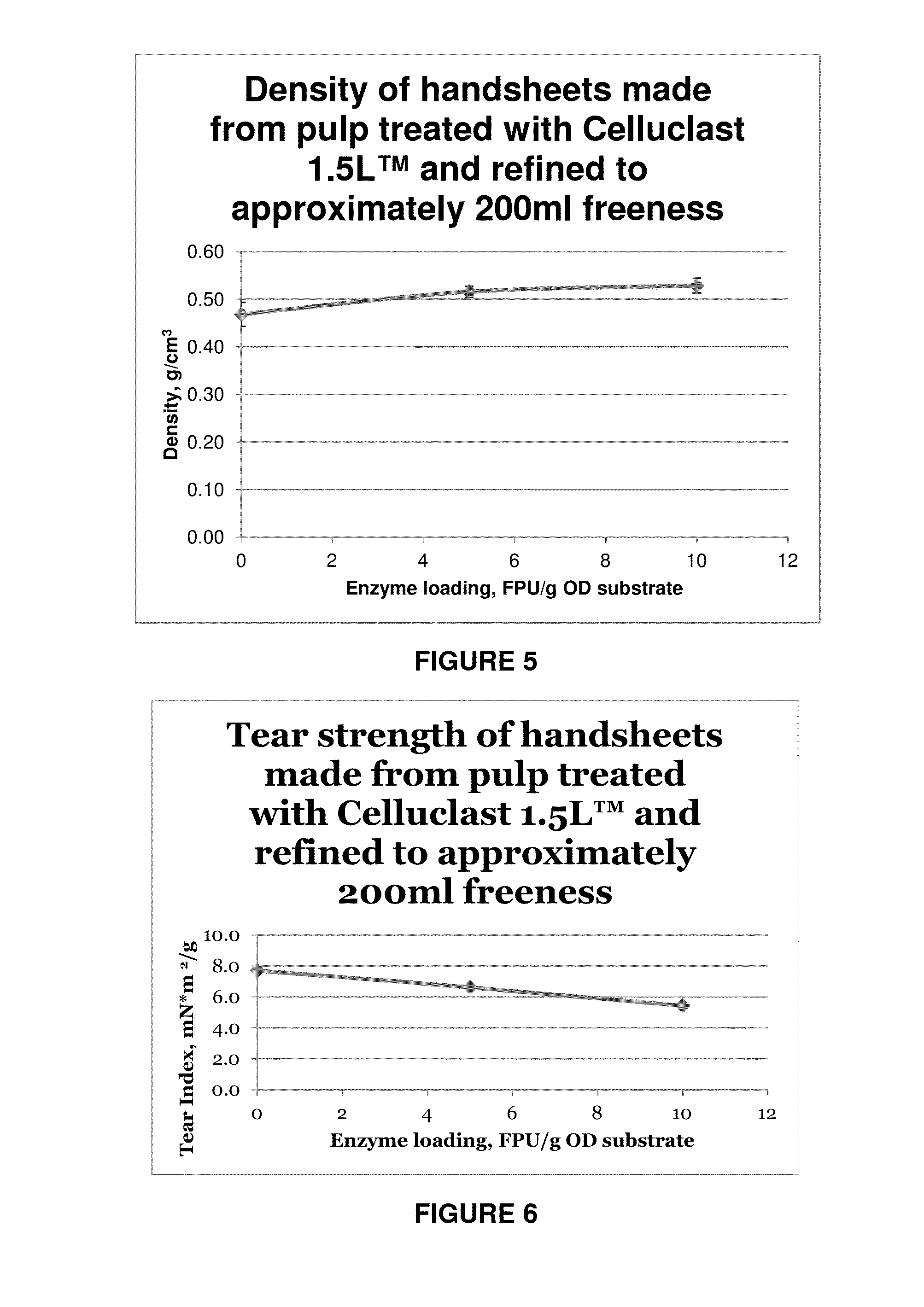
InactiveUS20140209259A1Lower energy requirementsMaintain tensile strengthPulp properties modificationFibrous raw materialsGlycanMannanase activity
A process using a multicomponent enzyme preparation to treat screened once refined pulps and reduces the specific energy consumption and / or increasing production while maintaining or increasing handsheet physical properties. The enzyme preparation has a major endoglucanase activity, a significant mannanase activity and a relatively small cellobiohydrolase activity. This enzyme mixture is prepared from a genetically modified strain of Trichoderma reseii.
Owner:UNIVERSITY OF NEW BRUNSWICK
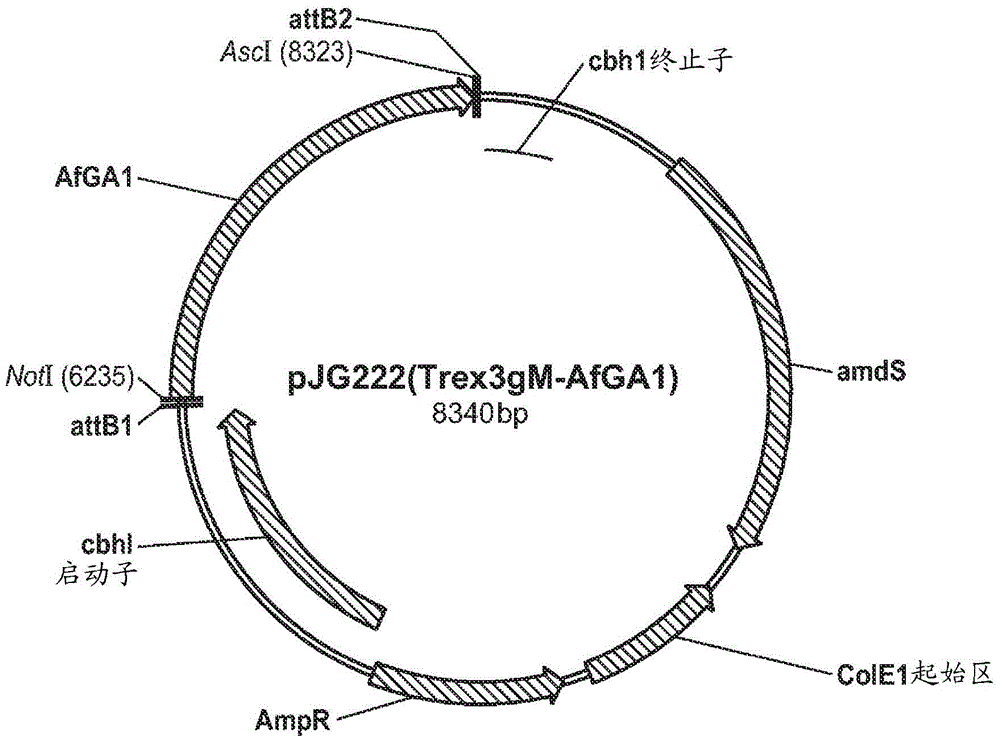
Trichoderma reesei host cells expressing a glucoamylase from aspergillus fumigatus and methods of use thereof
Fungal glucoamylases from Aspergillus fumigatus - expressed in Trichoderma reesei host cells (AfGATR) are provided. Trichoderma reesei host cells express AfGATRs at higher, or at least comparable, levels to natively expressed AfGA Aspergillus fumigatus. AfGATRs, including AfGA1TR and AfGA2TR, exhibit high activity at elevated temperatures and at low pH, so AfGATRs can be used efficiently in a process of saccharification in the presence of alpha-amylase, such as Aspergillus kawachii alpha-amylase (AkAA). AfGATRs advantageously catalyze starch saccharification to an oligosaccharide composition significantly enriched in DP1 (i.e., glucose) compared to the products of saccharification catalyzed by Aspergillus niger glucoamylase (AnGA) or native AfGA expressed in Aspergillus fumigatus. AfGATRs such as AfGA1TR, AfGA2TR or a variant thereof can be used at a lower dosage than AnGA and natively expressed AfGAs to produce comparable levels of glucose.
Owner:DANISCO US INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com