Metabolic Engineering yeast using xylose fermentation for producing ethanol
A technology for engineering bacteria and ethanol production, applied in the biological field, can solve the problems of depletion of reduced coenzyme II, accumulation of reduced coenzyme I, low conversion rate and the like
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
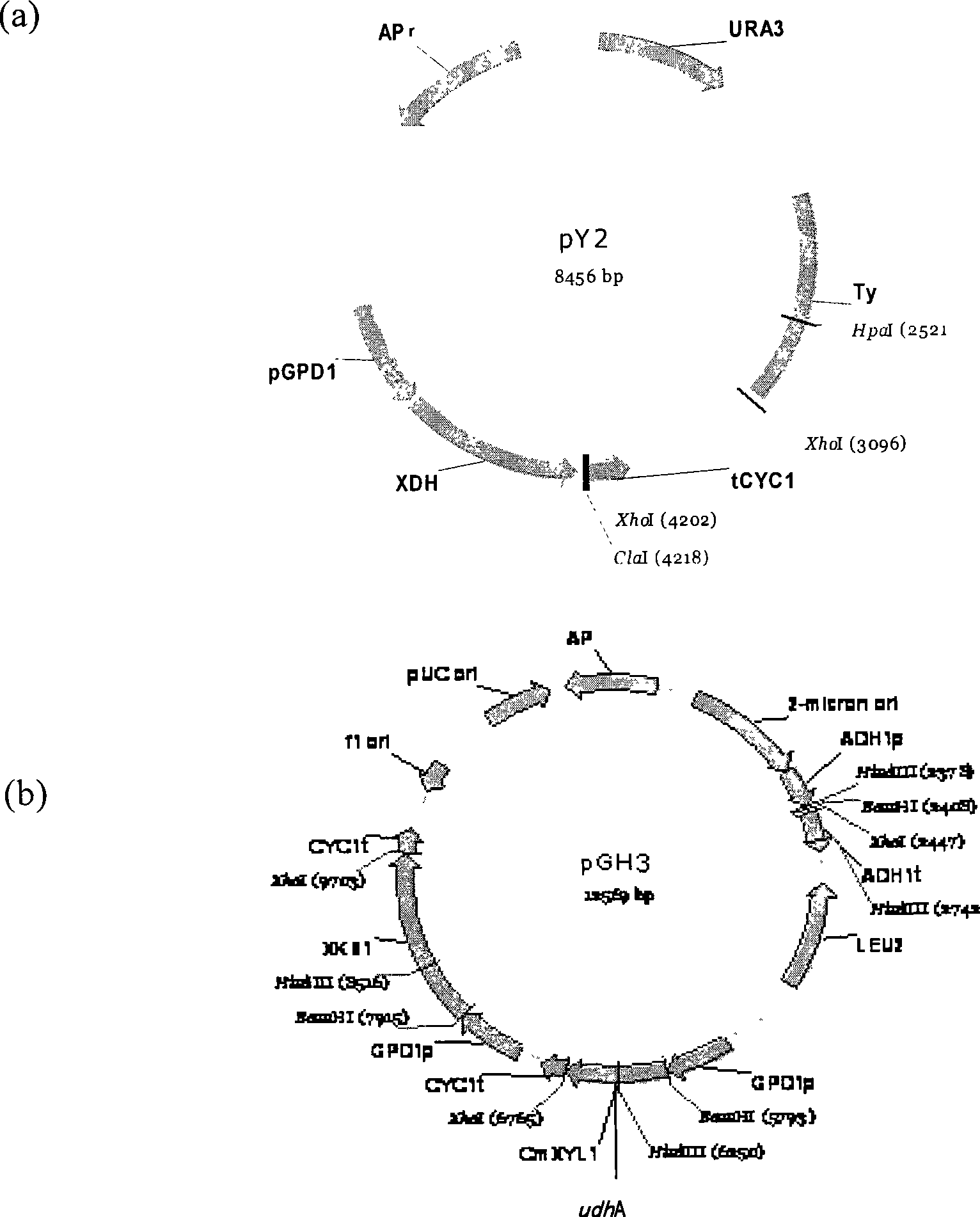
[0014] Example 1 Construction of Saccharomyces cerevisiae (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) E33 engineering bacteria
[0015] Saccharomyces cerevisiae W303-1Bα (Pearce, A.K. et al.: Micobiology 147, 391-401., 2001) was used as the starting strain for constructing engineering bacteria. The strains used in the construction process also include Pichia pastoris CBS 6054 (Wahlbom, C.F. et al.: FEMS Yeast Res 3, 319-26., 2003), Candida maltosa (Candida maltosa) XU316 (C.Guo, etc.: J. Appl. Microb. 101, 139-150, 2006) and Escherichia coli (E. coli) JM109 (Invitrogene). Genomes of yeast Pichia CBS 6054, Saccharomyces cerevisiae W303-1Bα, Candida maltosa XU316 and Escherichia coli JM109 were extracted according to standard methods (Ausubel, F.M., et al.: Current protocols in molecular biology. Wiley, Toronto, 1987) DNA. Using Pichia pastoris CBS 6054 genomic DNA as a template, using primers
[0016] Pxdhs (5′-GCAGGATCCATGACTGCTAACCCTTCCTTG-3′) and
[0017] Pxdha (5′-GCACTCGAGTTACTCAGGG CC...
Embodiment 2
[0030] Example two, xylose reductase and transhydrogenase activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae E33 engineering bacteria
[0031] Recombinant engineering bacteria E33 and starting strain W303-1Bα were inoculated in 5ml of SC medium (0.67%, yeast nitrogen base; 2%, glucose; appropriate amount of essential amino acids (histidine, tryptophan)), cultured (30 ℃, 250rpm shaker culture) overnight. The starting strain W303-1Bα was used as a control. The bacterial cells were collected by centrifugation (5000 rpm, 3 minutes). Cells were lysed by the glass bead method ("Experimental Guide to Yeast Genetics Methods", 87-88), and the protein supernatant was collected by high-speed centrifugation (13000 rpm, 40 minutes). The specific activities of xylose reductase and transhydrogenase in cell extracts were determined according to the assay described by Bruinenberg (Bruinenberg, P.M., et al., J. Gen. Microbiol., 129:953-964, 1983). Only weak coenzyme II-related xylose reductase activity wa...
Embodiment 3
[0032] Embodiment three, Saccharomyces cerevisiae E33 engineered bacteria strain ferments xylose to produce ethanol
[0033] Recombinant engineered bacterial strain E33 is inoculated in 100ml YPD medium (yeast extract 10g l -1 ;Tryptone 20g l -1 ; Glucose 20g l -1 )middle. 30°C, 250rpm shaker culture for 24 hours. The cells were collected by centrifugation (5000 rpm, 5 minutes), and the cells were washed twice with an equal volume of 0.9% physiological saline. Cells were resuspended in 100ml YPX medium (yeast extract 10g l -1 ;Tryptone 20g l -1 ; Xylose 30g l -1 ), cultured on a shaker at 30°C and 100rpm. After 84 hours, the concentration of xylose consumed was 22.2 g l -1 , the concentration of ethanol is 9.0 g l -1 , the yield of xylose to ethanol is 0.405g g -1 , and the conversion rate was 88%.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com