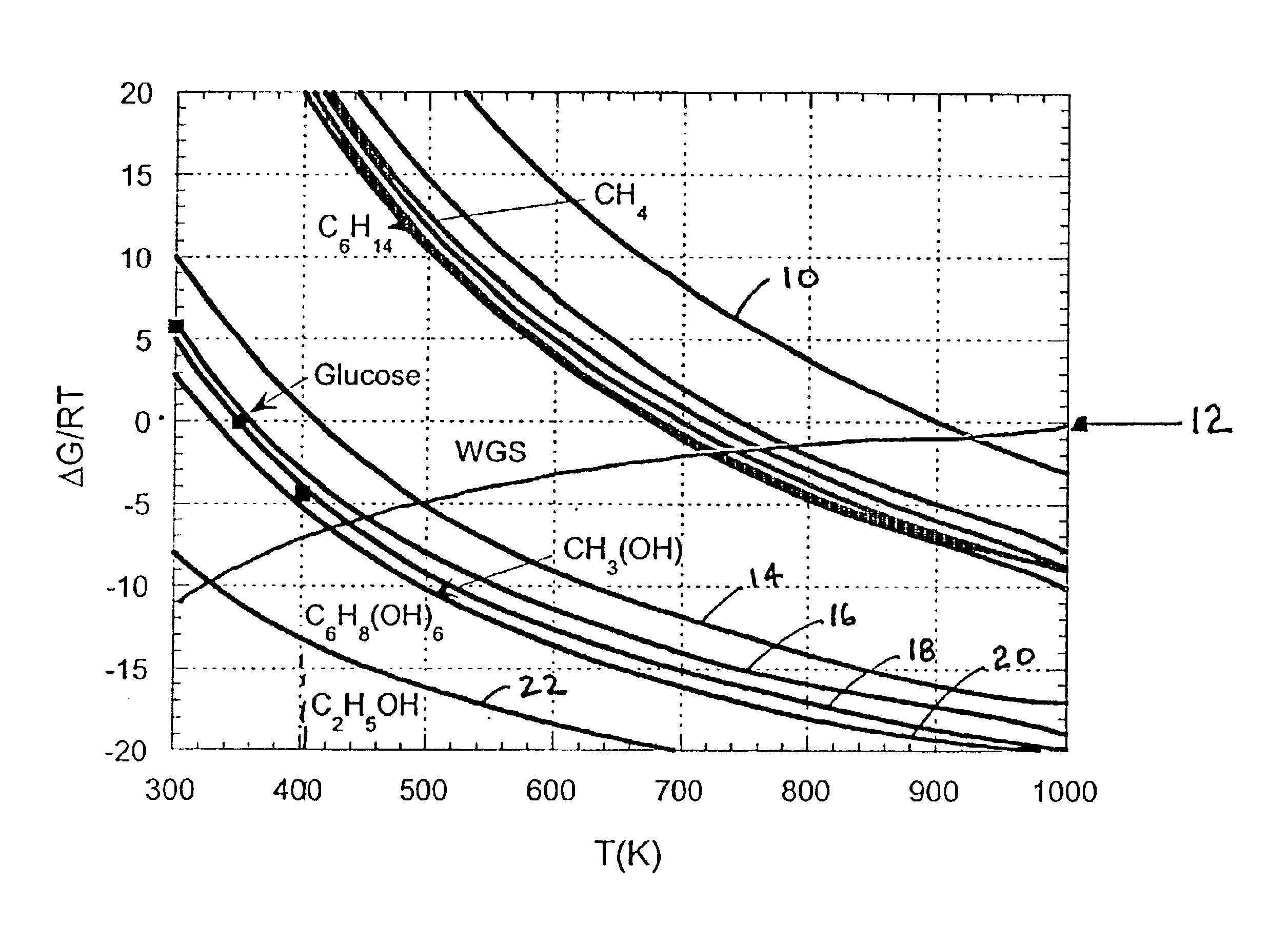
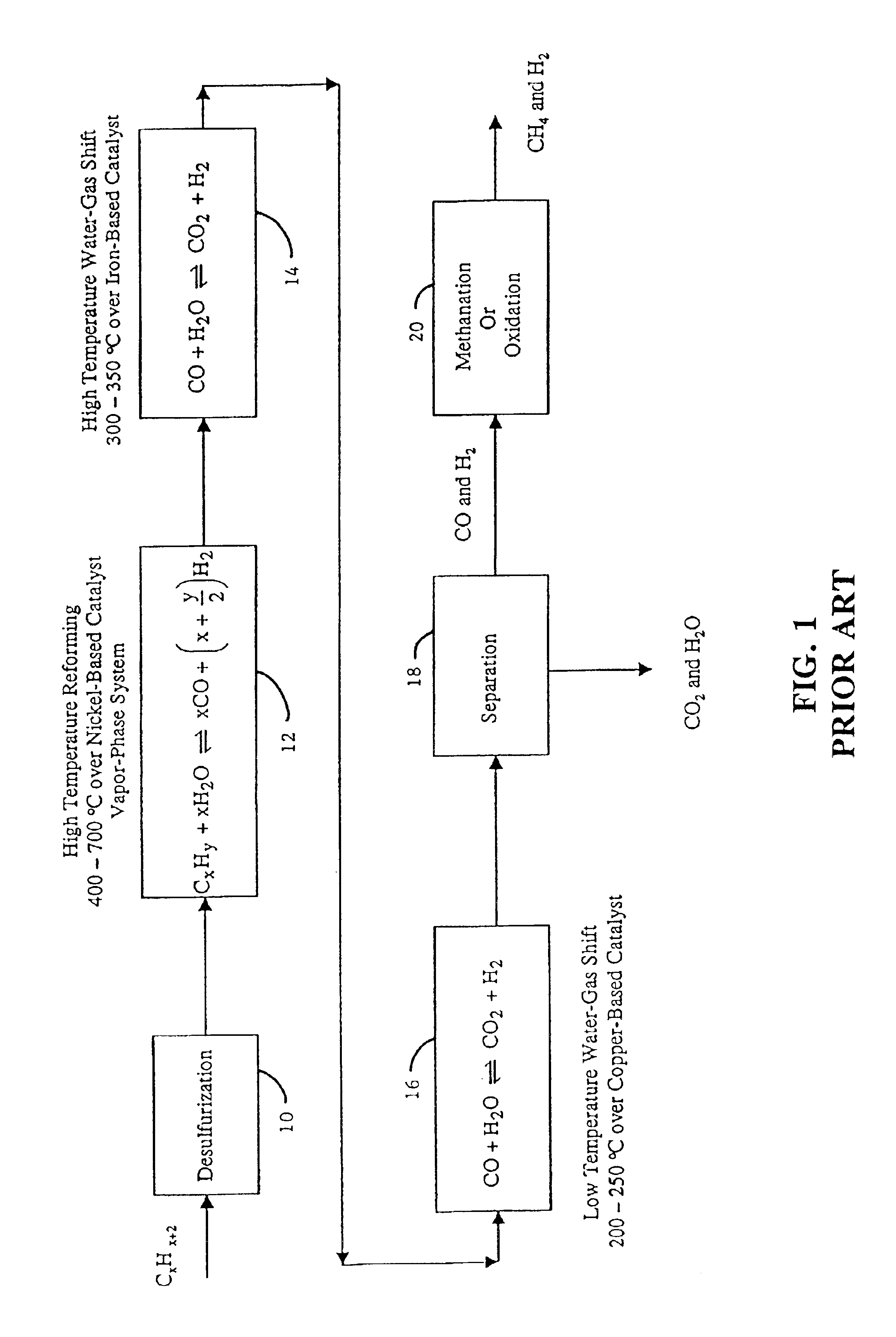
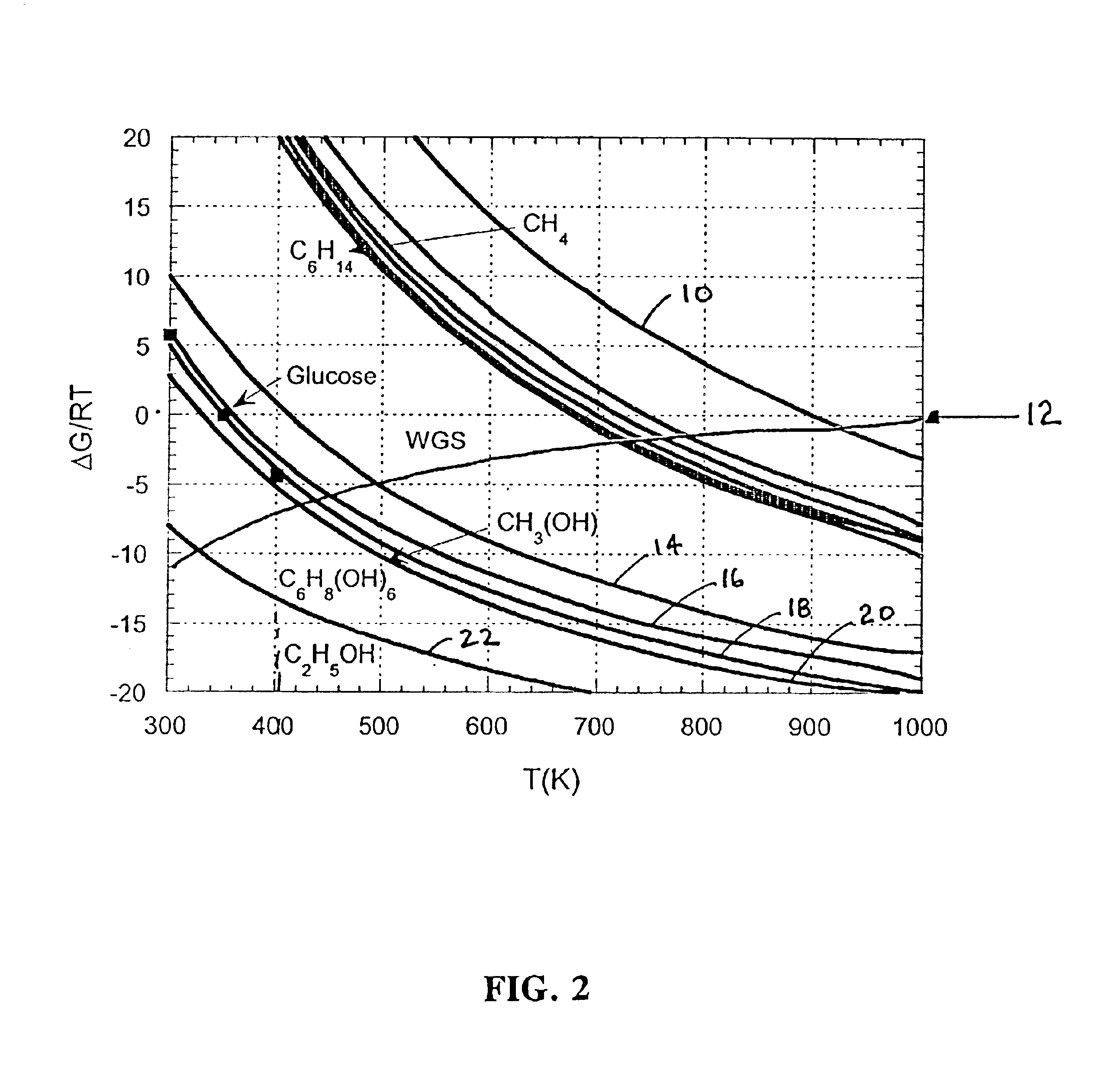
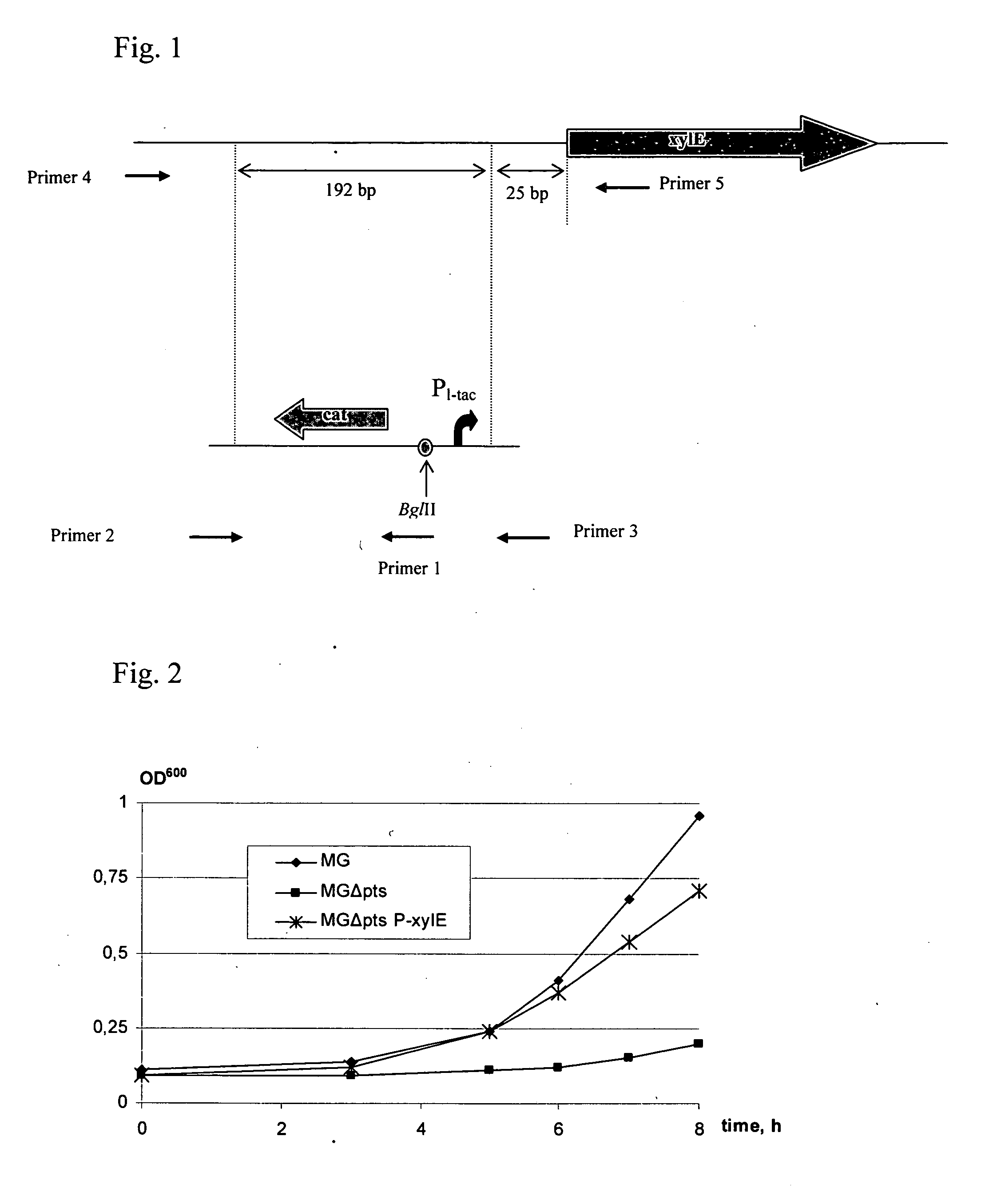
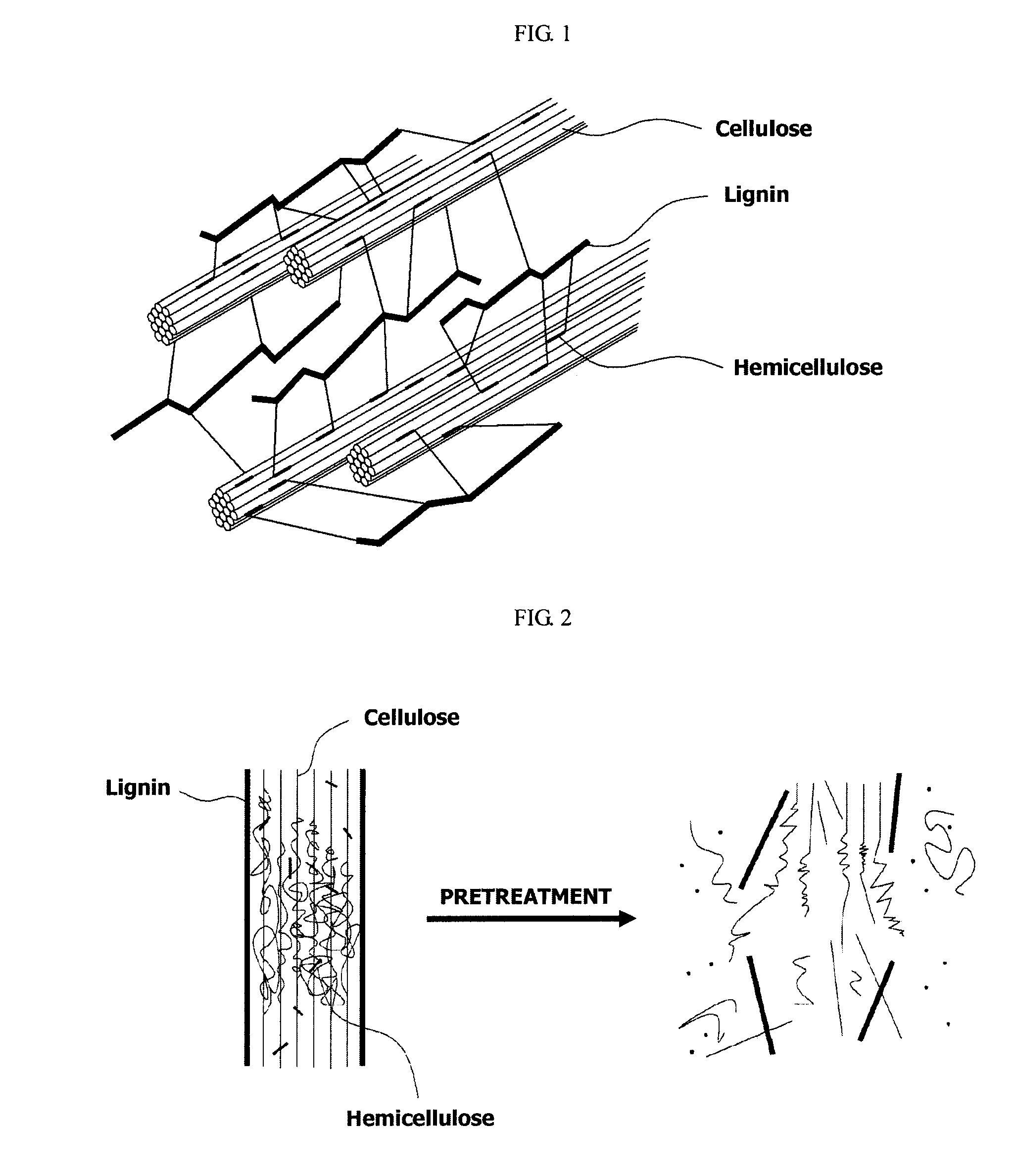
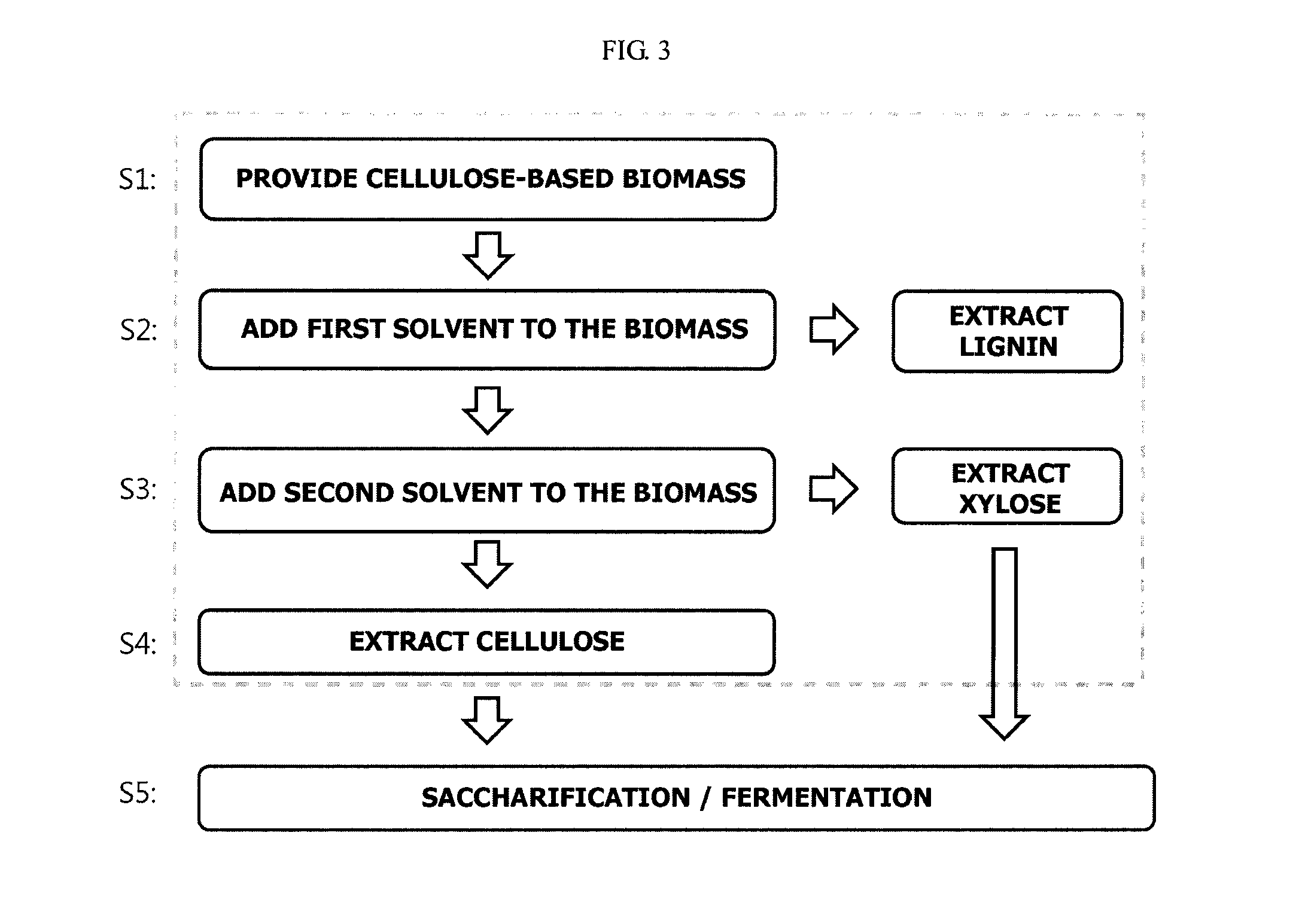
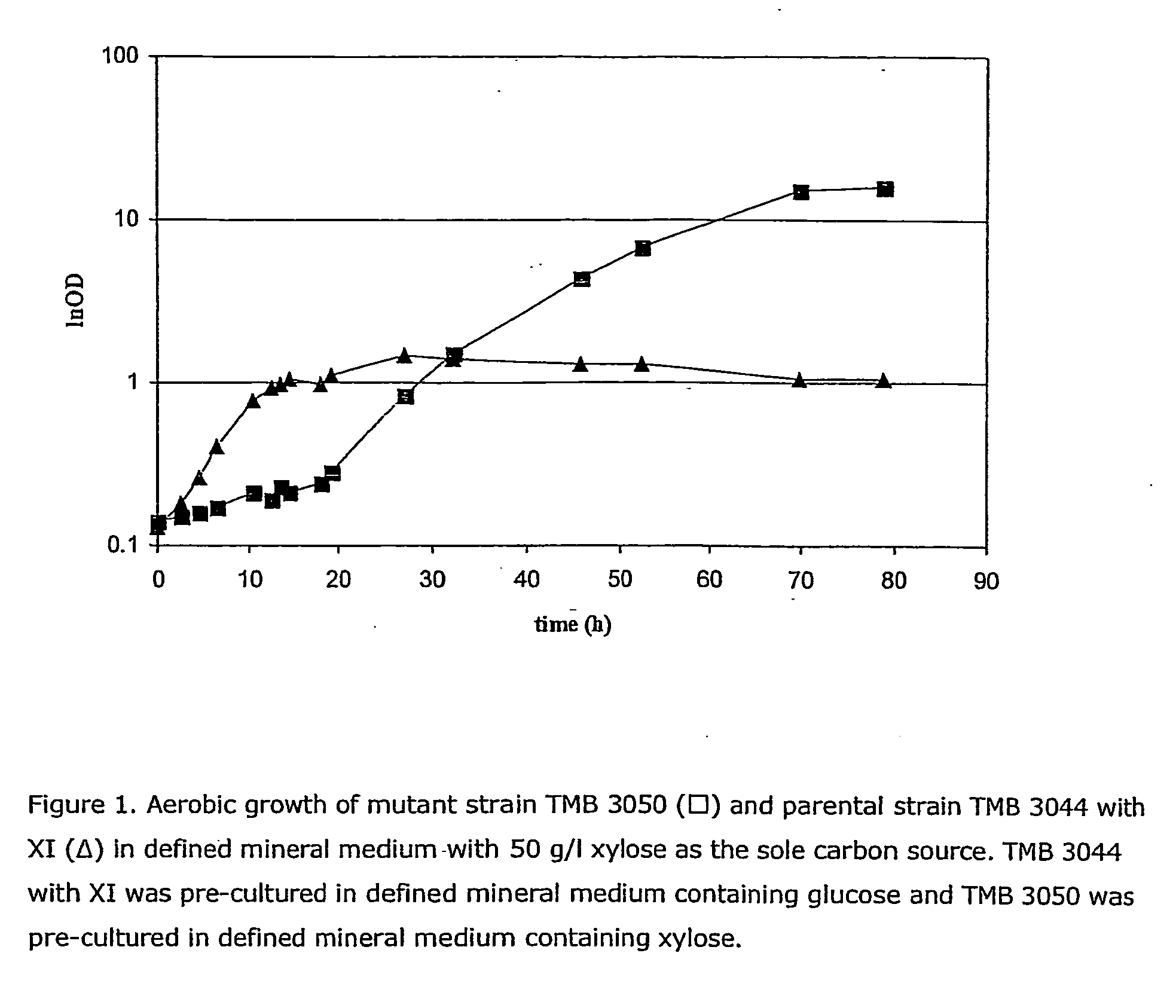
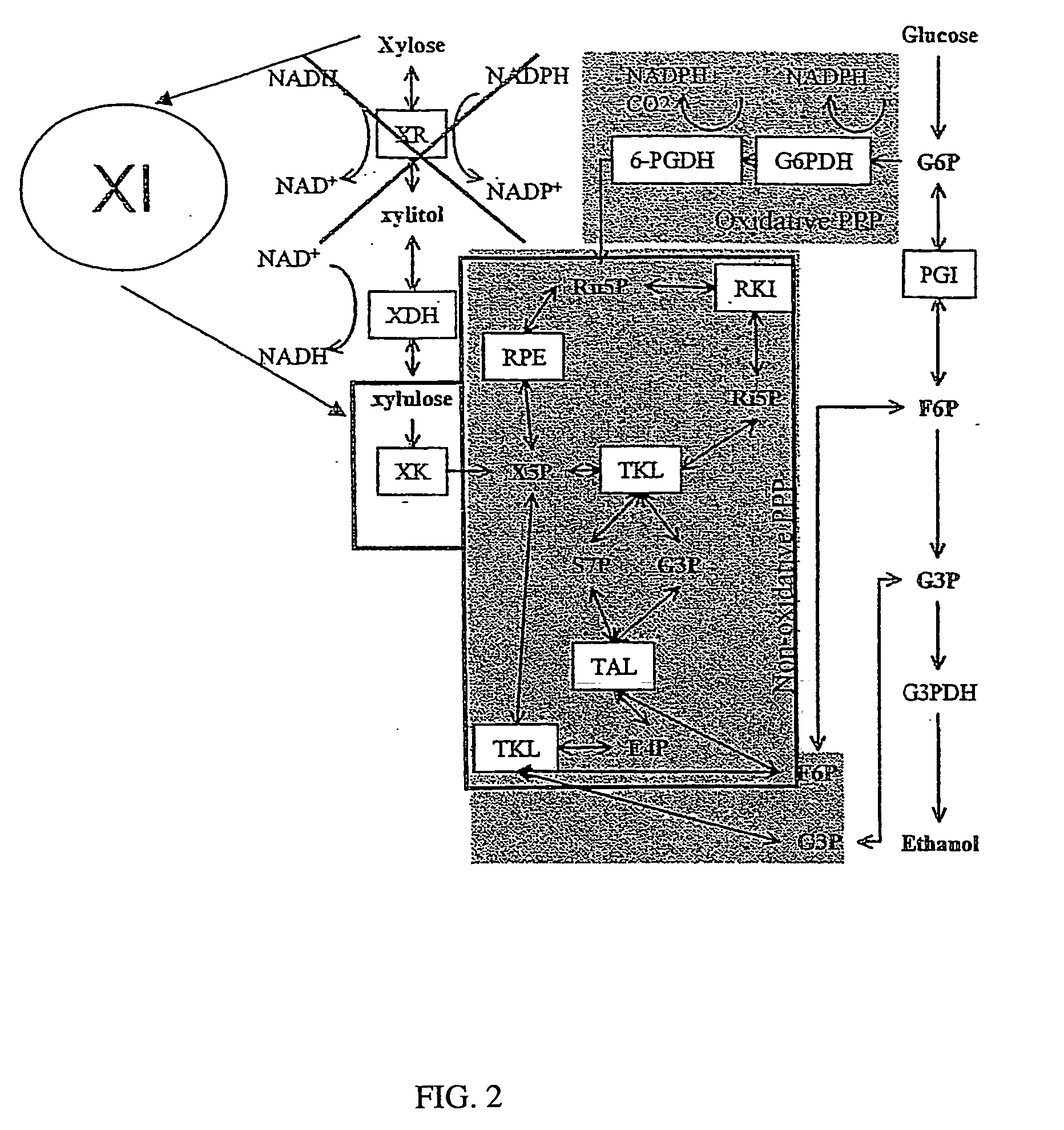
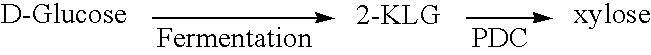Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
82 results about "Xylose-glucose" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Xylose (cf. Greek: ξύλον, xylon, wood) is a sugar first isolated from wood, and named for it. Xylose is classified as a monosaccharide of the aldopentose type, which means that it contains five carbon atoms and includes an aldehyde functional group.
Low-temperature hydrogen production from oxygenated hydrocarbons
InactiveUS6964757B2Reduce riskWeaken energyHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionSteam reformingAlkane
Disclosed is a method of producing hydrogen from oxygenated hydrocarbon reactants, such as methanol, glycerol, sugars (e.g. glucose and xylose), or sugar alcohols (e.g. sorbitol). The method takes place in the condensed liquid phase. The method includes the steps of reacting water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon in the presence of a metal-containing catalyst. The catalyst contains a metal selected from the group consisting of Group VIIIB transitional metals, alloys thereof, and mixtures thereof. The disclosed method can be run at lower temperatures than those used in the conventional steam reforming of alkanes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Method for producing L-amino acids using bacteria of the Enterobacteriaceae family
ActiveUS20060088919A1Improve productivityD-xylose permease is enhancedBacteriaDepsipeptidesL-threonineArginine
There is disclosed a method for producing L-amino acid, for example L-threonine, L-lysine, L-histidine, L-phenylalanine, L-arginine or L-glutamic acid, using a bacterium of the Enterobacteriaceae family, wherein the bacterium has been modified to enhance an activity of D-xylose permease.
Owner:AJINOMOTO CO INC
Method for the production of a fermentation product from a pretreated lignocellulosic feedstock
A method for obtaining a fermentation product from a sugar hydrolysate obtained from a feedstock containing hemicellulose, by (i) removing suspended fiber solids from said sugar hydrolysate to obtain a clarified sugar solution; (ii) fermenting xylose in the clarified sugar solution in a fermentation reaction with yeast to produce a fermentation broth comprising the fermentation product; (iii) separating the yeast from the fermentation broth to produce a yeast slurry; (vi) treating the yeast slurry thus obtained with an oxidant to kill microbial contaminants, thereby an oxidant-treated yeast slurry; (v) re-introducing at least a portion of the oxidant-treated yeast back to step (ii) to increase the concentration of yeast in said fermentation reaction; and (vi) recovering the fermentation product.
Owner:IOGEN ENERGY CORP
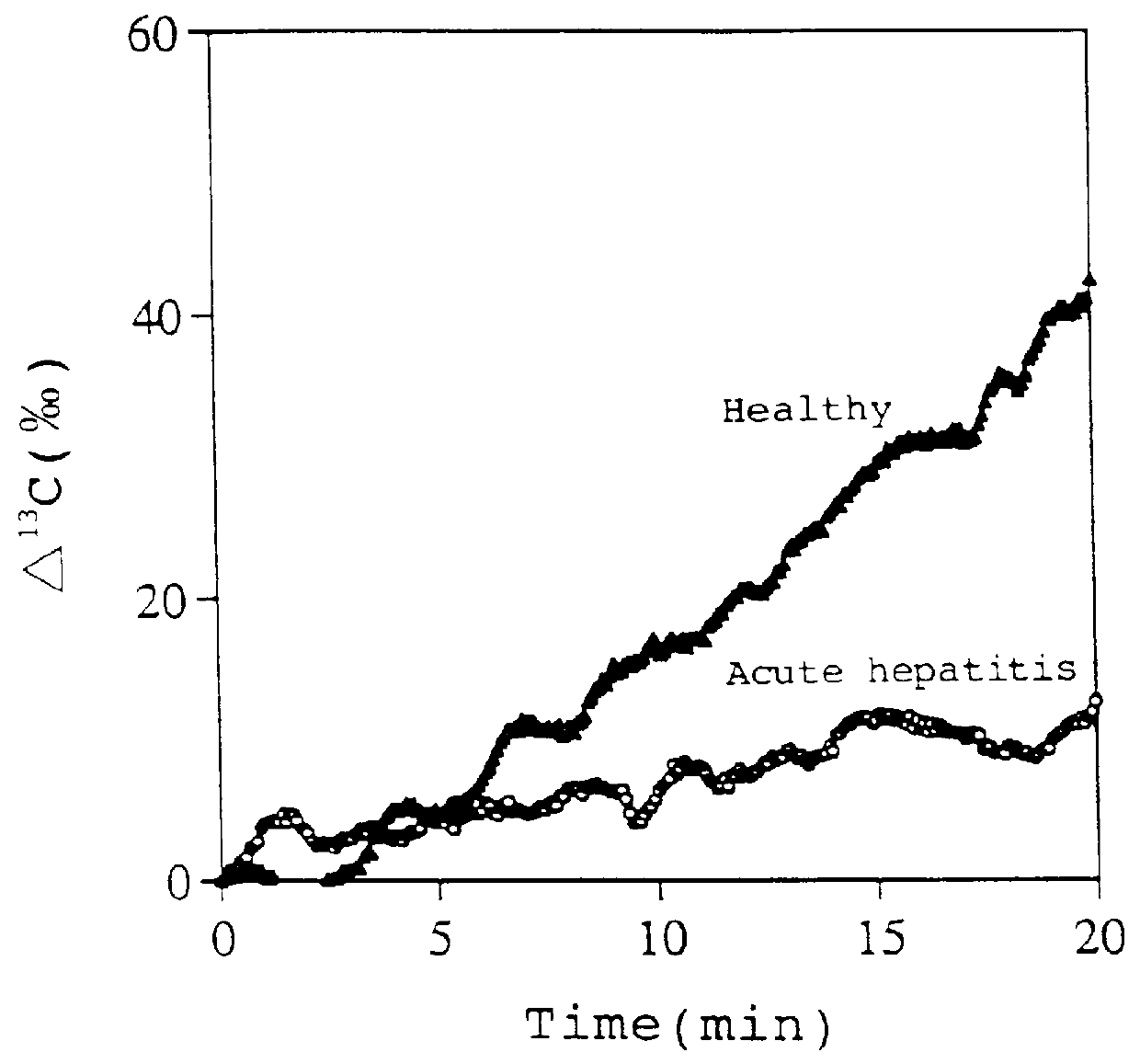
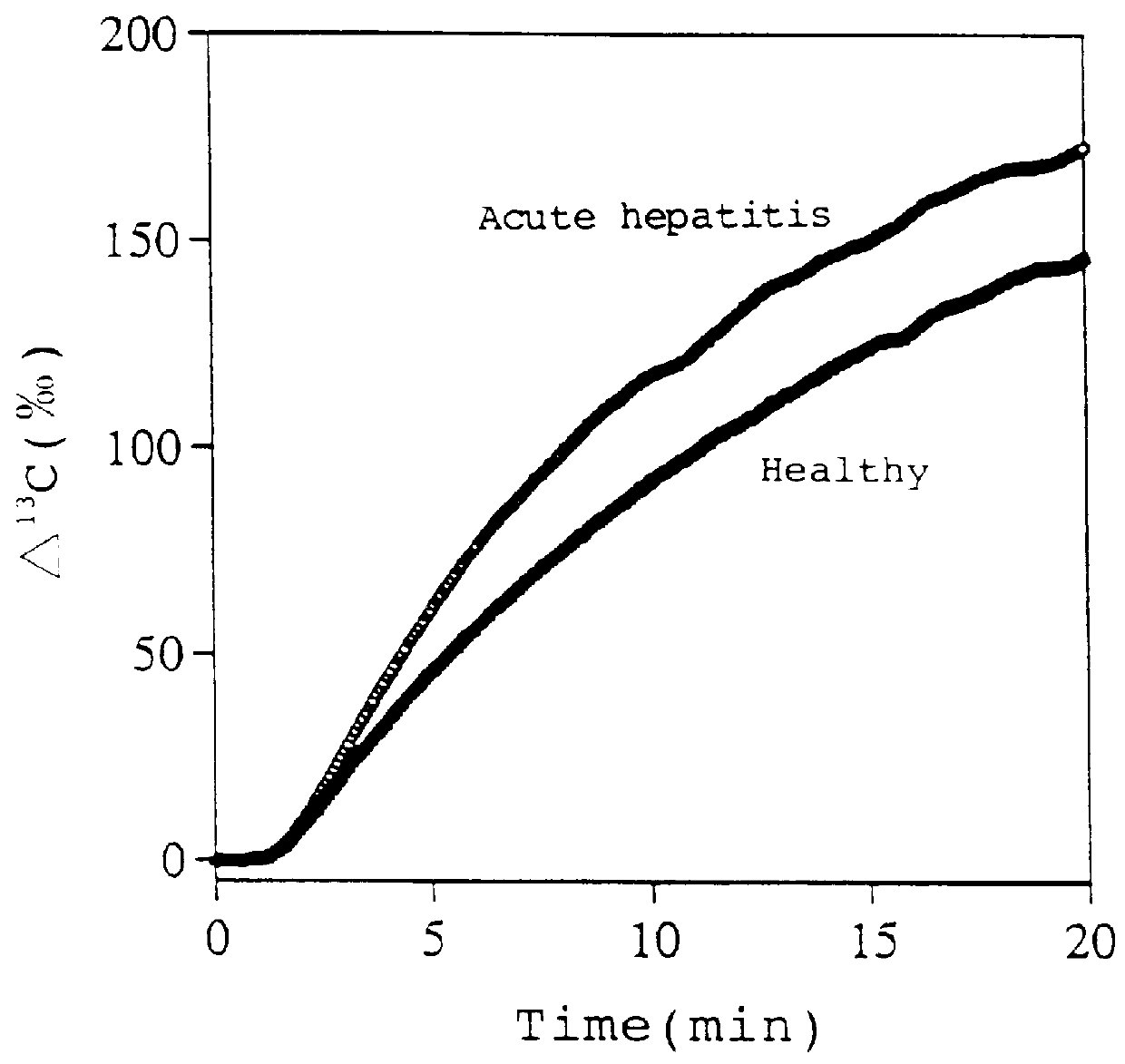
Diagnostic agent for liver function
InactiveUS6071245ALessen the burden on the bodyEasy to useRadioactive preparation carriersRespiratory organ evaluationSide effectGlycerol
The present invention relates to a diagnostic agent for liver function, comprising a compound labelled with 13C at least at one specific position selected from the group consisting of the following (a) to (f): (a) galactose, glucose or xylose labelled with 13C at least at one specific position or a starch composed of glucose units labelled with 13C at least at one specific position; (b) a polar amino acid, heterocyclic amino acid, isoleucine or valine labelled with 13C at least at one specific position; (c) a carboxylic acid constituting the glycolytic pathway or the citric acid cycle, labelled with 13C at least at one specific position; (d) a fatty acid labelled with 13C at least at one specific position; (e) a glyceride labelled with 13C at least at one specific position; and (f) glycerol labelled with 13C at least at one specific position. According to the present invention, a diagnostic agent for liver function which imposes less physical burden on a subject, can give accurate test result immediately, and can be used safely without side effects is provided. The diagnostic agent of the invention is useful for evaluating the liver function of a subject at the time when the test is carried out.
Owner:TOKYO GAS CO LTD
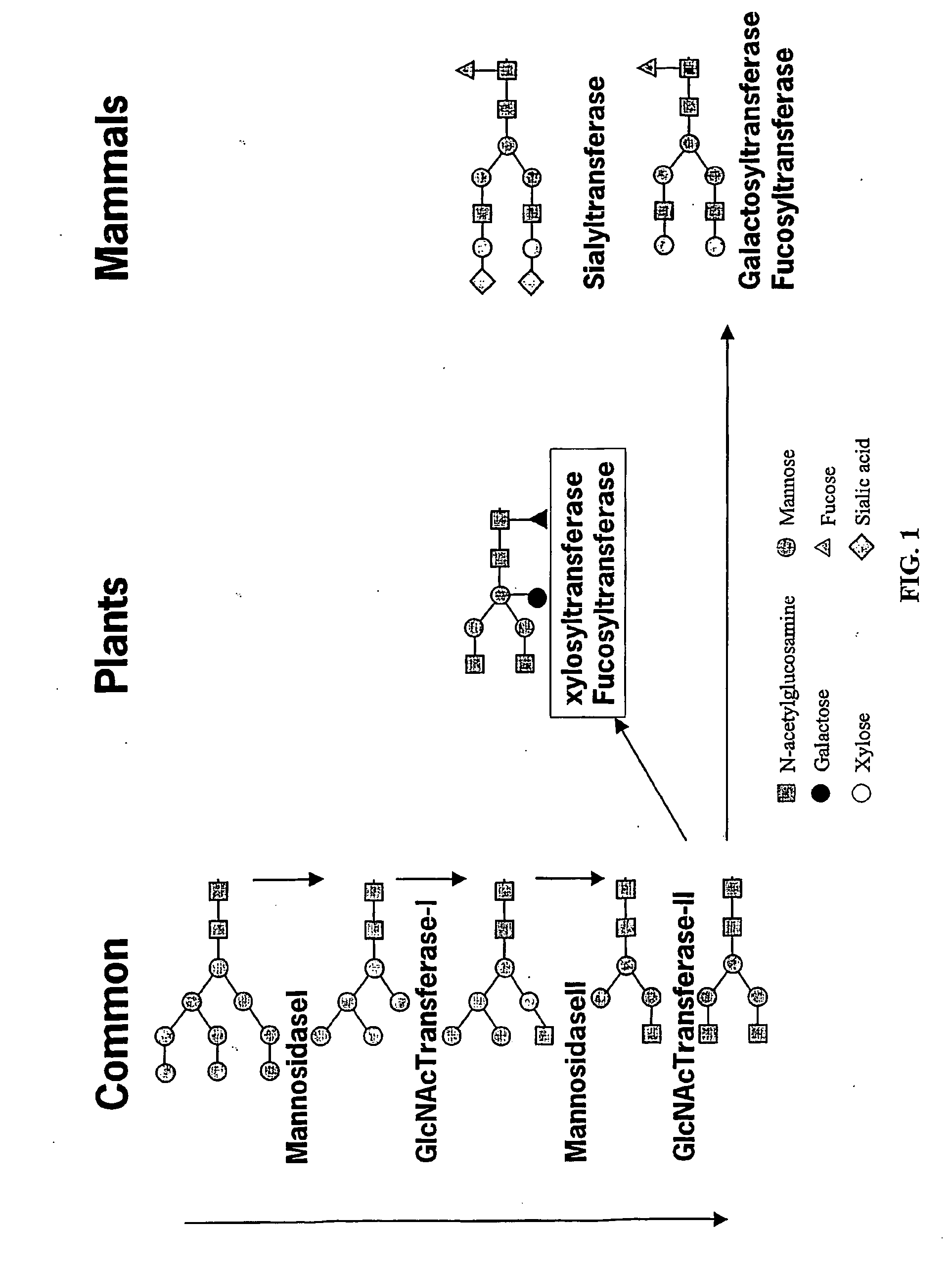
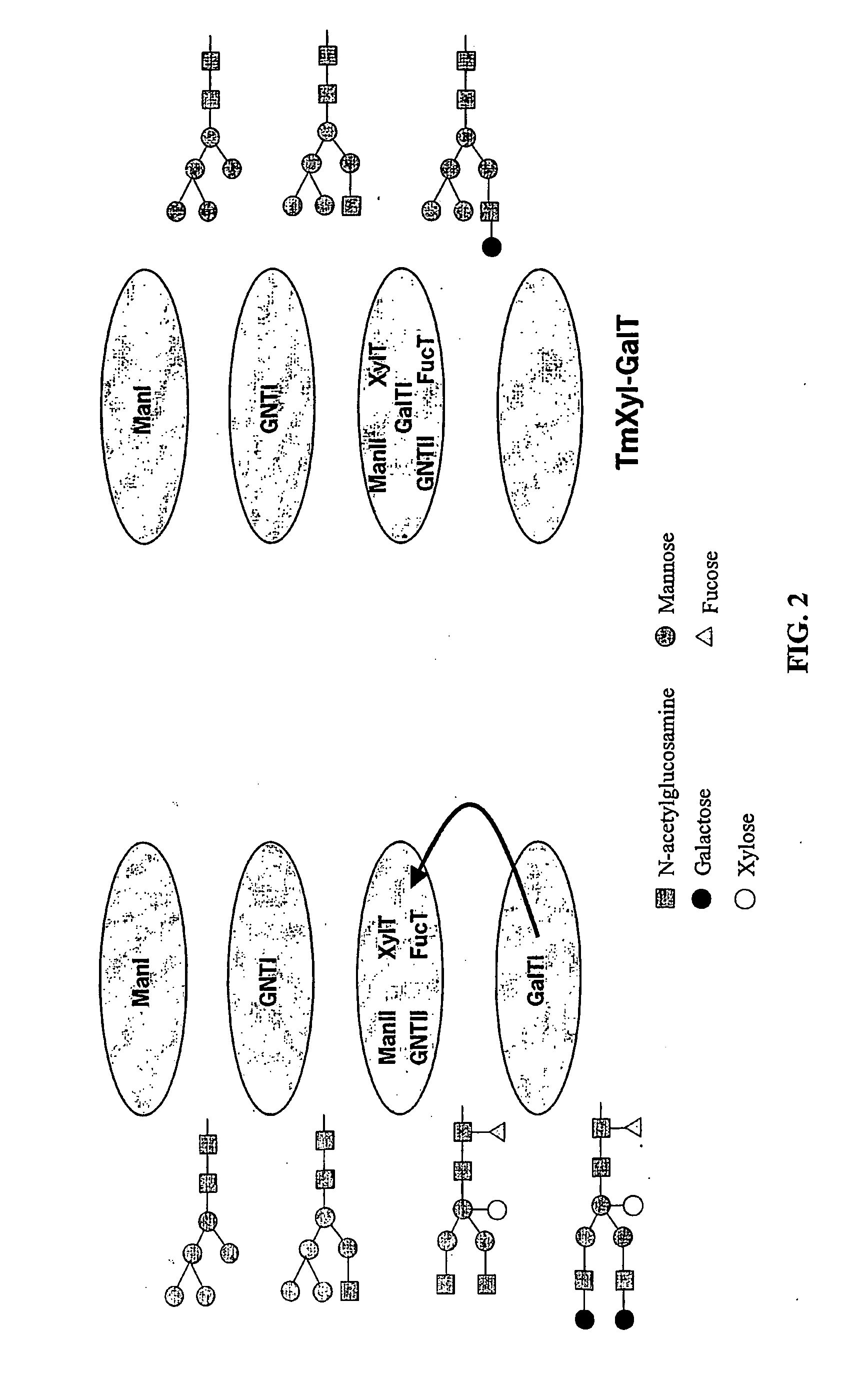
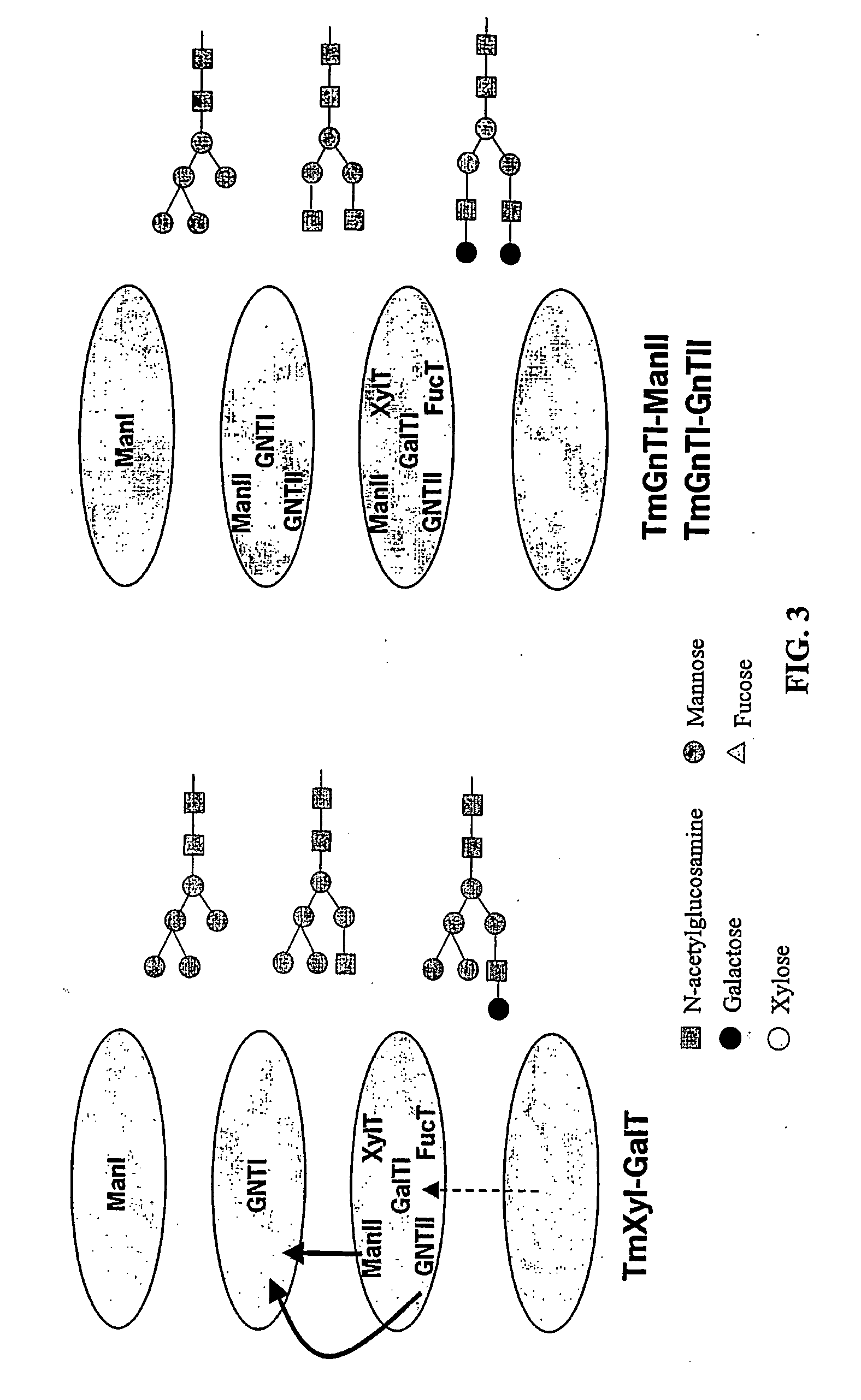
Optimizing glycan processing in plants
InactiveUS20060253928A1Reduce diversityGalactosylation is improvedFungiBacteriaBiological bodyComplex type
The invention is directed to methods for optimizing glycan processing in organisms (and in particular, plants) so that a glycoprotein having complex type bi-antennary glycans and thus 5 containing galactose residues on both arms and which are devoid of (or reduce in) xylose and fucose can be obtained. The invention is further directed to said glycoprotein obtained and host system comprising said protein.
Owner:STICHTING DIENST LANBOUWKUNDIG ONDERZOEK
Reduced-carbohydrate and nutritionally-enhanced frozen desserts and other food products
InactiveUS20060286248A1Mitigate laxation effectReduce impactFrozen sweetsConfectioneryTagatoseMaltitol
A reduced carbohydrate ice cream or other frozen dessert product that contains a low-digestible sweetener system and a fermentable fiber material. The a low-digestible sweetener system consists of one or more low-digestible sweeteners having a molecular weight of from about 90 to about 190; and is typically a low molecular weight saccharide or a polyol. Typical low-digestible sweeteners include mannitol, maltitol, sorbitol, lactitol, erythritol, xylitol, isomalt, glycerin, talitol, mannose, tagatose, fructose, arabinose, fucose, lycose, ribose, sorbose, talose, and xylose, and mixtures thereof. The low-digestible sweetener replaces the digestible sugars to provide the appropriate freezing point depression of the product. The level of fermentable fiber is sufficient to mitigate a Taxation effect that can be caused by ingestion of the amount of the low-digestive sweetener. The fermentable fiber can be an inulin, a maltodextrin resistant to human digestion, an oligofructose, a fructooligosaccharide, a high water binding fermentable fiber, and a mixture thereof.
Owner:TECHCOM GRP LLC
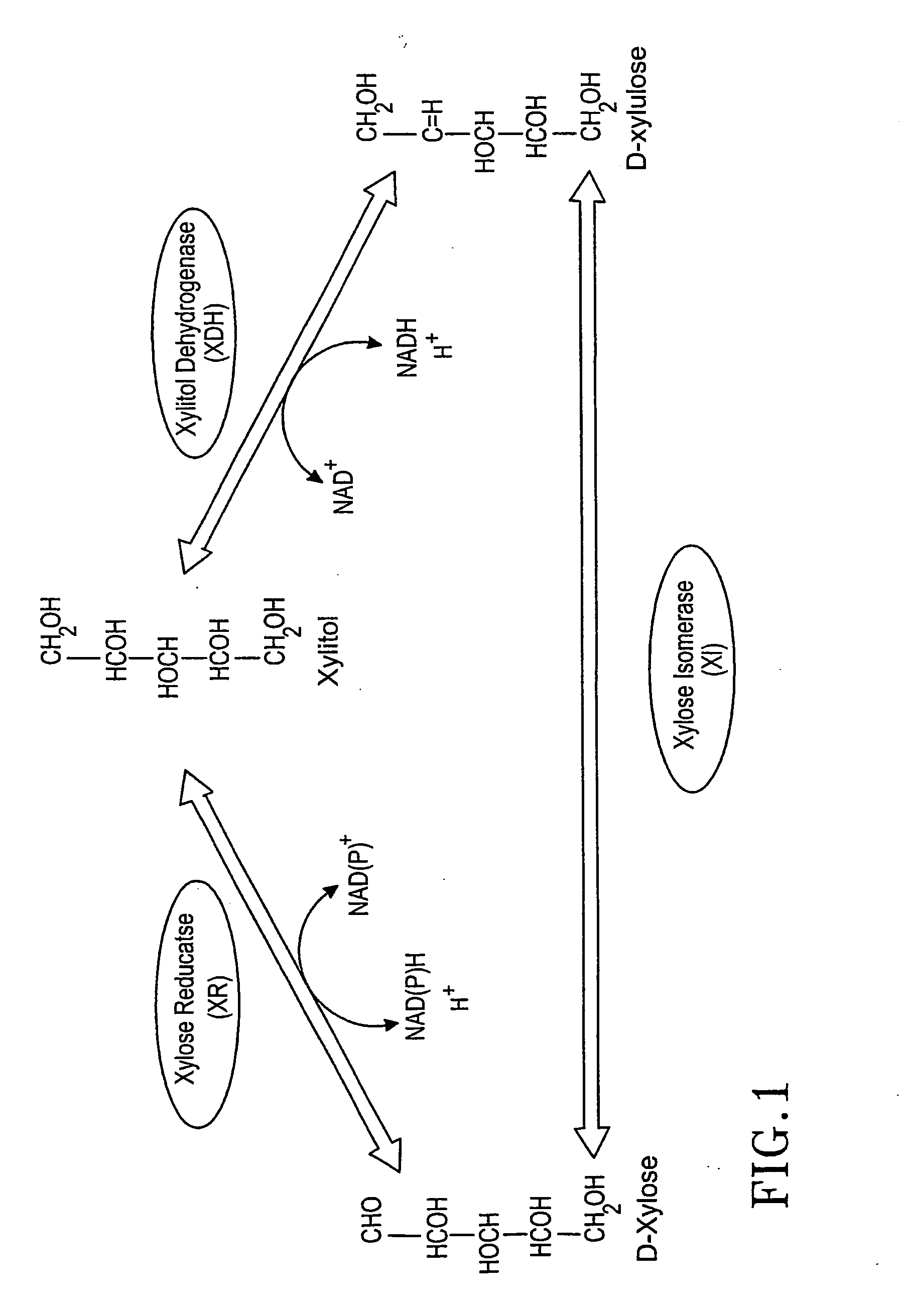
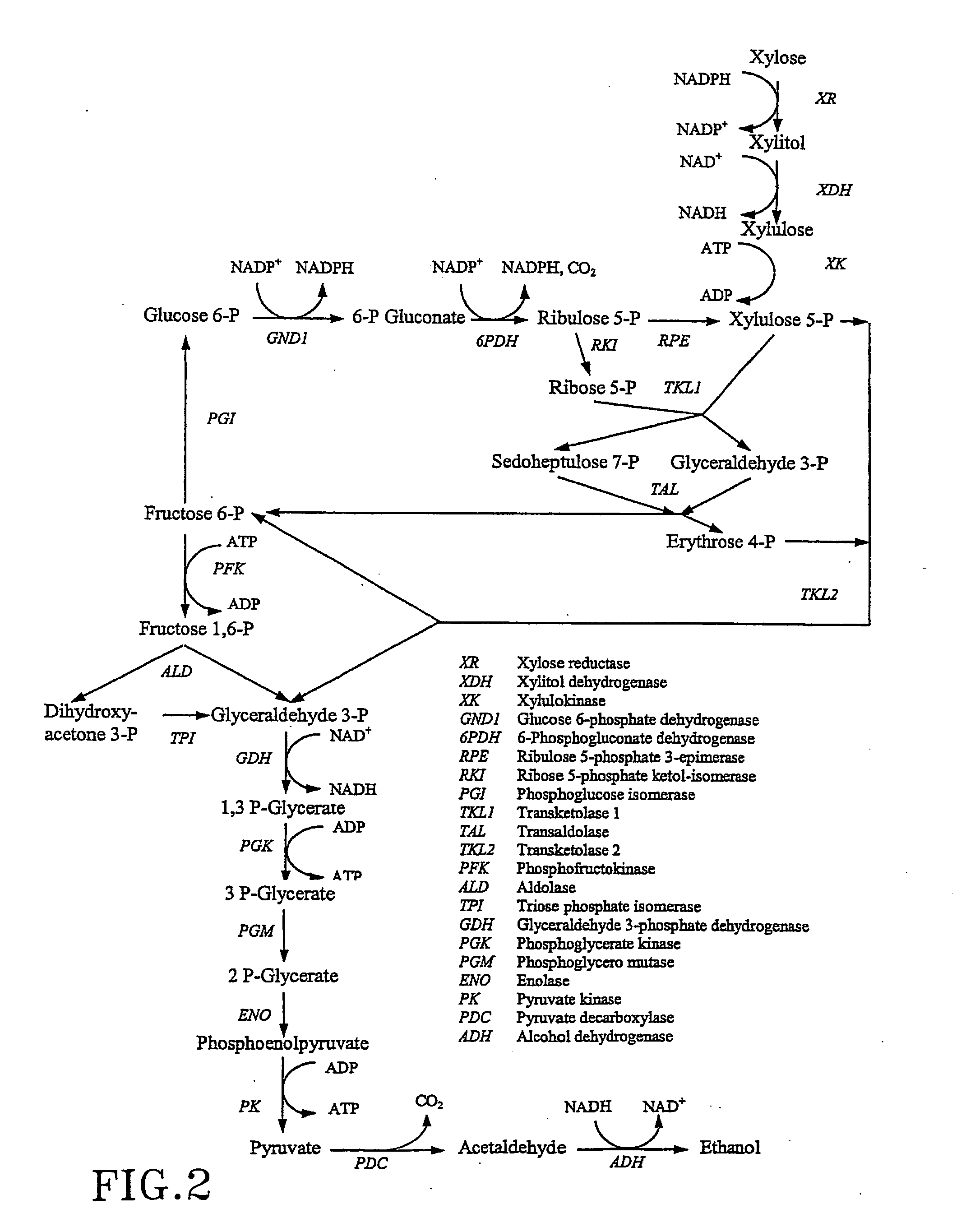
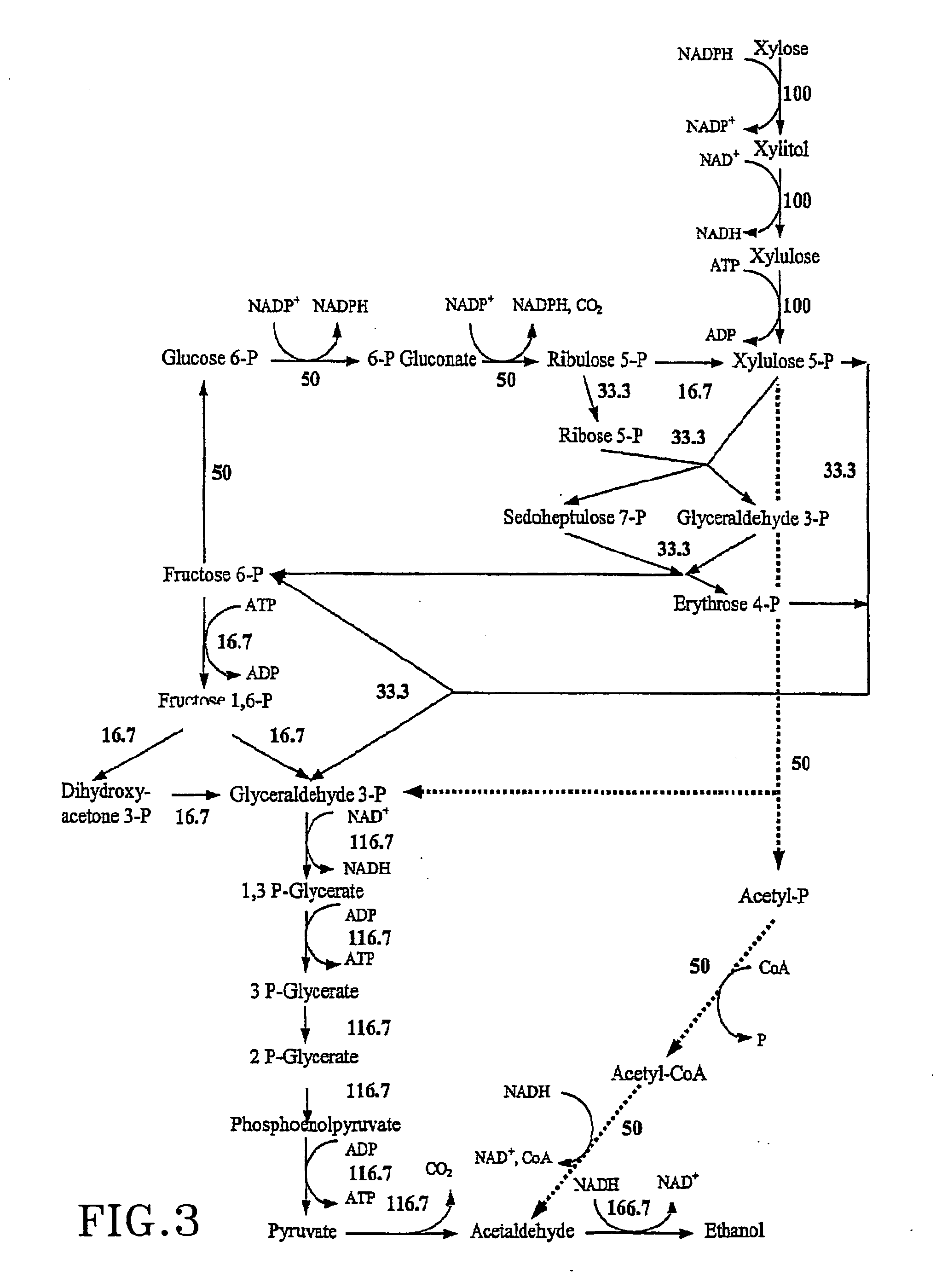
Metabolic engineering for improved xylose utilisation of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
The present invention relates to a method for preparing an ethanol producing, xylose utilizing strain of Saccharomyces cerevisiae comprising genes for overexpression of xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase and xylulokinase, wherein in addition to said genes for production o phosphoacetyltransferase, and acetaldehyde dehydrogenase are introduced and optionally overexpressed.
Owner:SCANDINAVIAN TECH GRP AB
Low-temperature hydrogen production from oxygenated hydrocarbons
InactiveUS20050207971A1Reduce riskHigh energy costHydrogen productionHydrogen/synthetic gas productionAlkaneSteam reforming
Disclosed is a method of producing hydrogen from oxygenated hydrocarbon reactants, such as methanol, glycerol, sugars (e.g. glucose and xylose), or sugar alcohols (e.g. sorbitol). The method takes place in the condensed liquid phase. The method includes the steps of reacting water and a water-soluble oxygenated hydrocarbon in the presence of a metal-containing catalyst. The catalyst contains a metal selected from the group consisting of Group VIIIB transitional metals, alloys thereof, and mixtures thereof. The disclosed method can be run at lower temperatures than those used in the conventional steam reforming of alkanes.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
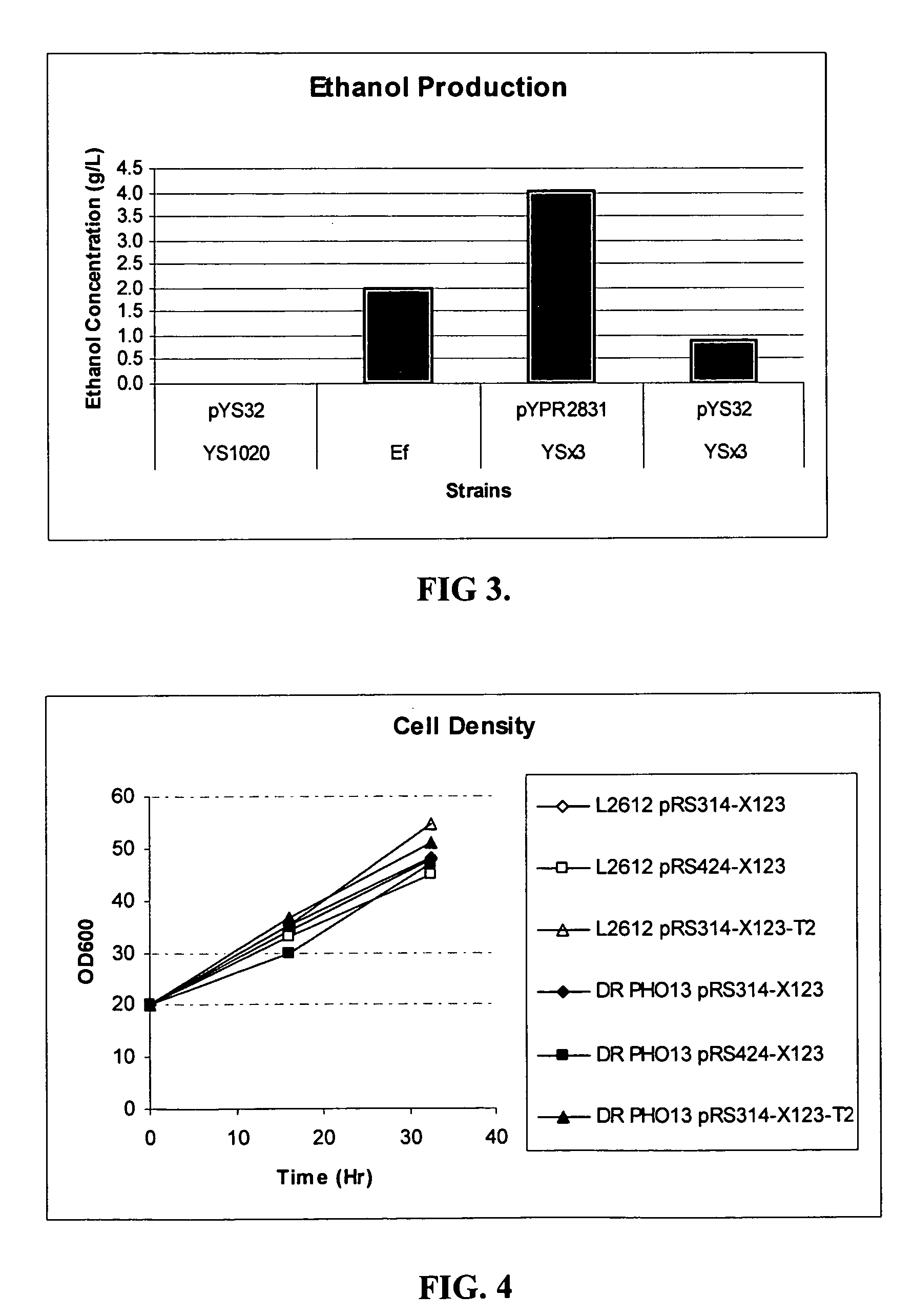
Ethanol production in fermentation of mixed sugars containing xylose
Xylose-utilizing Z. mobilis strains were found to have improved ethanol production when grown in medium containing mixed sugars including xylose if sorbitol or mannitol was included in the medium. The effect was seen in concentrations of mixed sugars where no growth lag period occurs, as well as in higher sugars concentrations.
Owner:SUSTAINABLE TECH CORP +1
Method and apparatus for fractionating lignocellulose-based biomass
ActiveUS20100203605A1Improve processing efficiencyEnhanced interactionPressurized chemical processBiological substance pretreatmentsCelluloseLignin degradation
A method and apparatus for fractionating a lignocellulose-based biomass are provided. The method includes providing a lignocellulose-based biomass, extracting lignin from the biomass by adding a first solvent capable of dissolving the lignin, extracting xylose by adding a second solvent capable of dissolving hemicellulose to the biomass treated with the first solvent, and extracting the cellulose remaining in the biomass. In this method, a continuous process can be performed instead of a low efficiency batch-type process and components of the biomass can be obtained at high yield.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Catalytic cracking method for sugar and sugar alcohol
InactiveCN101613253AReduce tensionLow costOrganic compound preparationHydroxy compound preparationAlcohol sugarsPropanediol
The invention relates to a method for preparing low-carbon alcohol through the catalytic cracking of sugar and sugar alcohol, which comprises the steps: under the action of an Ni-based catalyst, taking polycarbon sugar such as glucose, fruit sugar, xylose, sorbierite, mannite and xylitol, and water solution of various carbon sugar and sugar alcohol as raw materials, and cracking the raw materials into low-carbon alcohol of C3 or below C3 (particularly glycol and 1,2-propanediol) in a high selectivity mode through hydrogenation and dehydration processes. The conversion rate of the raw materials reaches over 95 percent. The yield of the glycol and the 1,2-propanediol in the low-carbon alcohol reaches over 50 percent. The method has the advantages of high efficiency, mild conditions, and high selectivity of the low-carbon alcohol.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
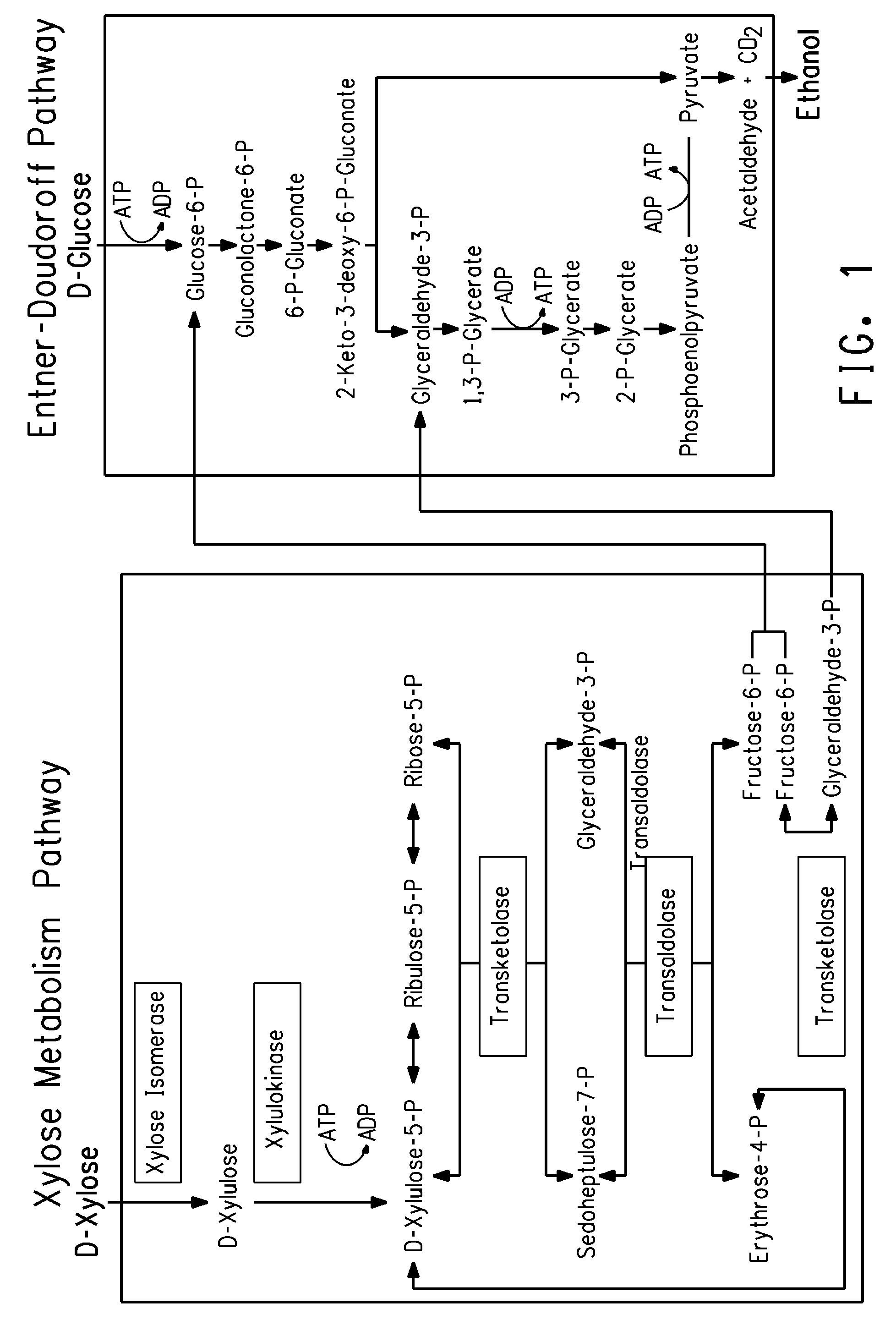
Construction of new xylose utilizing saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
The present invention relates to a novel Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain utilizing xylose for fermenting ethanol expressing xylose isomerase (XI), overexpressing xylulokinase (XK), overexpressing the pentose phosphate pathway (PPP), and non-expressing aldose reductase (AR) and being adapted to growth in mineral defined medium with xylose as sole carbon source.
Owner:FORSKARPATENT I SYD AB
Novel process for preparing xylitol
ActiveCN101823939AIncrease contentImprove qualityIon-exchange process apparatusOrganic compound preparationChromatographic separationDistillation
The invention relates to a novel process for preparing xylitol, which belongs to the technical field of functional sugar alcohol production. Pre-treatment, hydrolysis, neutralization, decoloring, ion exchange, evaporation and concentration and chromatography are carried out to corncob or bagasse and other agricultural waste which contains hemicellulose, high-content xylose solution is collected and distillated, and then continuously hydrogenated, so that the xylose solution is converted into xylitol solution, and finally a xylitol crystal is obtained through refining, concentration, crystallization, centrifugation and drying; the process comprises: corncob-> pre-treatment->hydrolysis->neutralization and decoloring->ion exchange->evaporation and concentration->chromatography->high-content xylose solution collection and distillation-> hydrogenatio->refining->concentration->crystallization->centrifugation->drying->finished crystal xylitol product obtaining. The novel process for preparing xylitol saves a xylose crystallization procedure and a conversion process xylose crystal into sugar, shortens a production procedure, adopts a chromatography technology to improve the content of thexylose solution, facilitates the obtaining of high-content xylitol solution after hydrogenation can prepare the high-grade xylitol product, adopts a continuous hydrogenation process, improves the hydrogenation efficiency, reduces the labor intensity of a worker, and saves the production cost.
Owner:FUTASTE PHARM CO LTD
Method for separating xylose from lignocelluloses rich in xylan, in particular wood
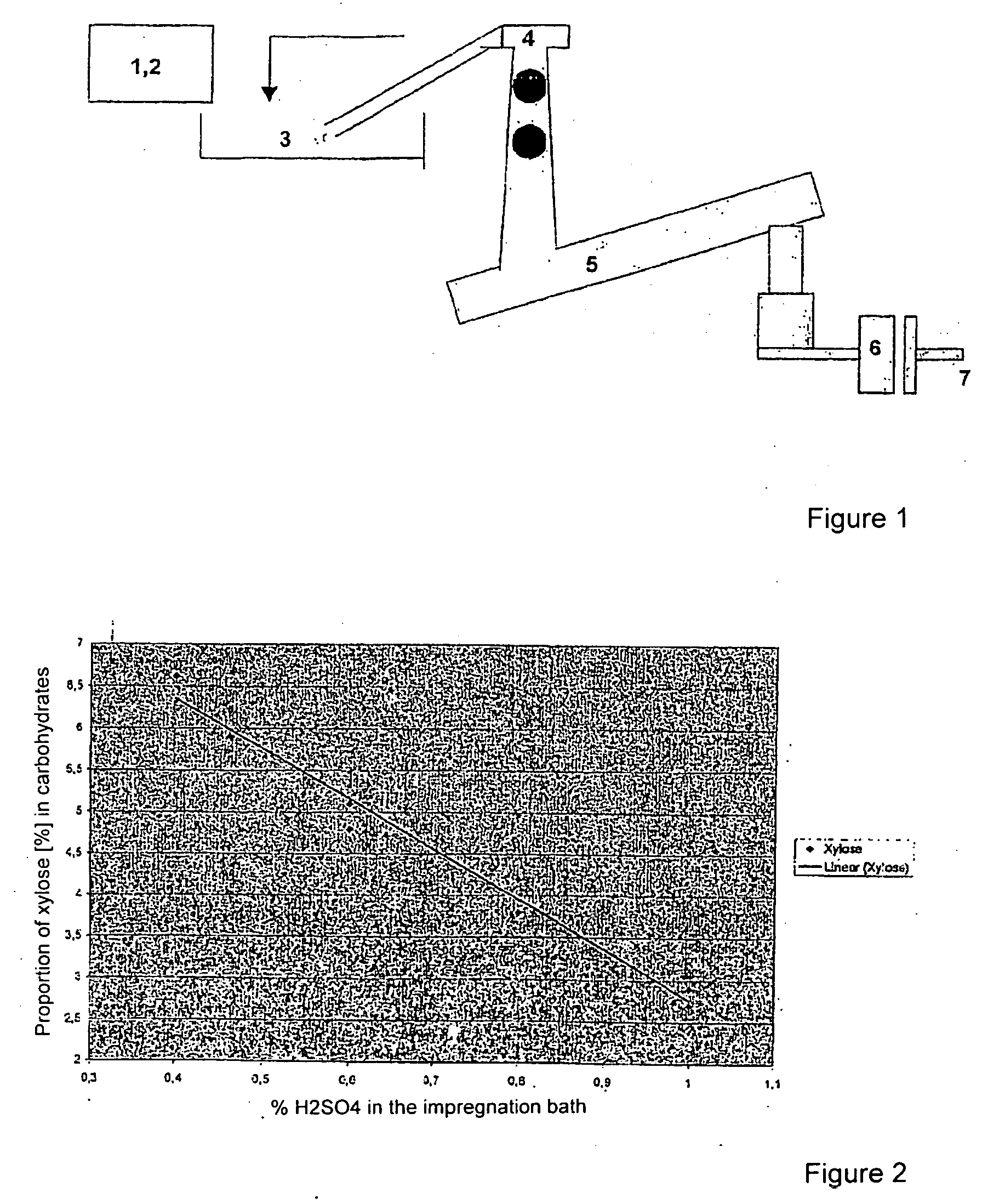
InactiveUS20050065336A1Many solutionsHigh cellulose yieldSugar derivativesXylose productionXylanPre treatment
The invention is directed to a method for separating xylose from lignocelluloses rich in xylan, particularly wood, and for obtaining pulp, characterized by the following steps: (1) pretreating wood chips through mechanical destruction of the original structure; (2) impregnating the obtained wood mass with diluted mineral acid; (3) carrying out prehydrolysis of the obtained wood mass modified by the process under the influence of steam at an elevated temperature to hydrolyze the obtained hemicelluloses; and (4) removing the hemicelluloses from the residual pulp by washing, filtering and / or centrifuging while obtaining an aqueous solution rich in xylose. The combination of method steps according to the invention makes it possible to achieve high α-cellulose contents with very low proportions of xylose, that is, highly pure chemical pulp qualities, while at the same time enabling a virtually quantitative separation of the valuable xylose.
Owner:RHODIA ACETOW AG
Zymomonas with improved ethanol production in medium containing concentrated sugars and acetate
Owner:ALLIANCE FOR SUSTAINABLE ENERGY +1
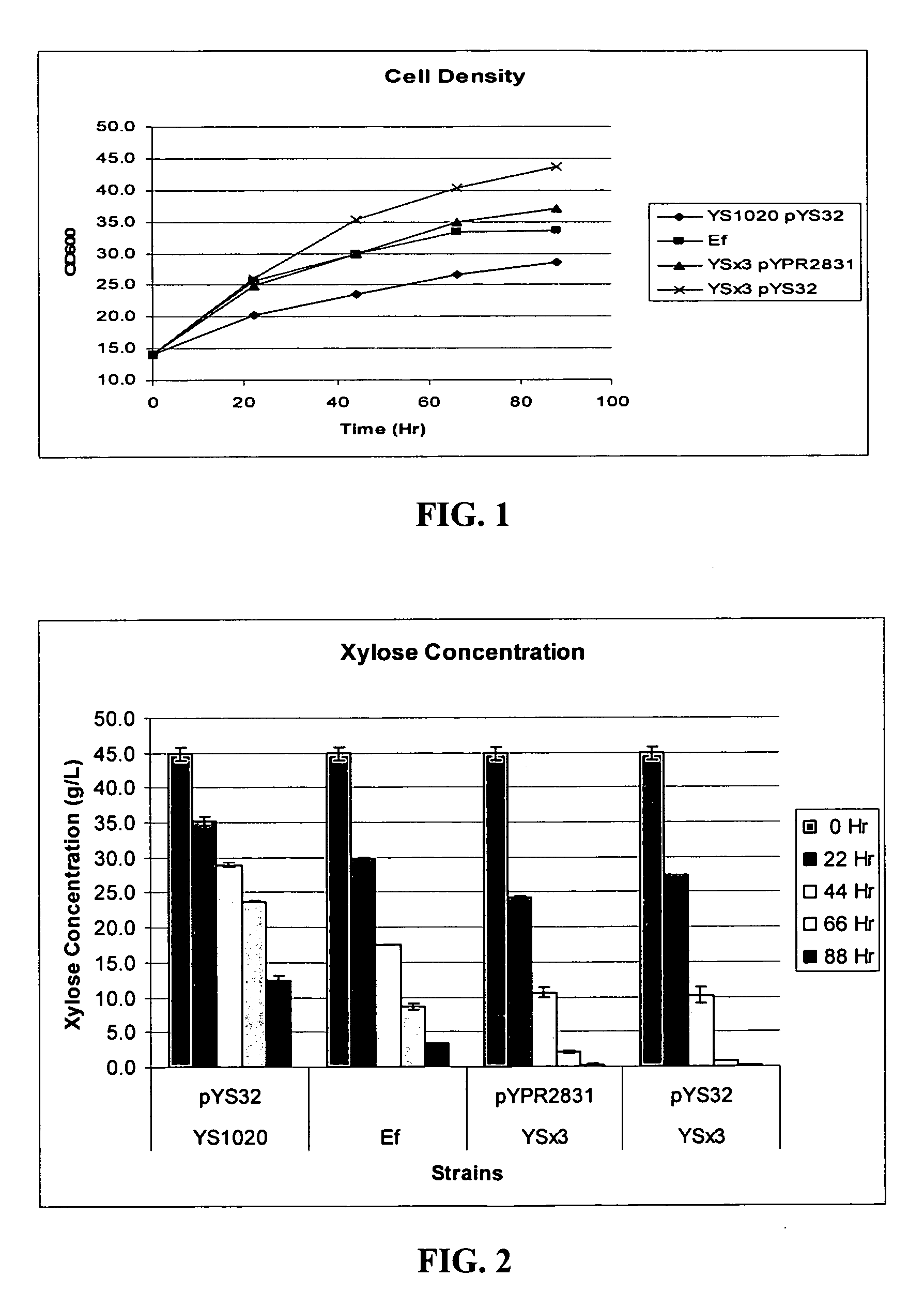
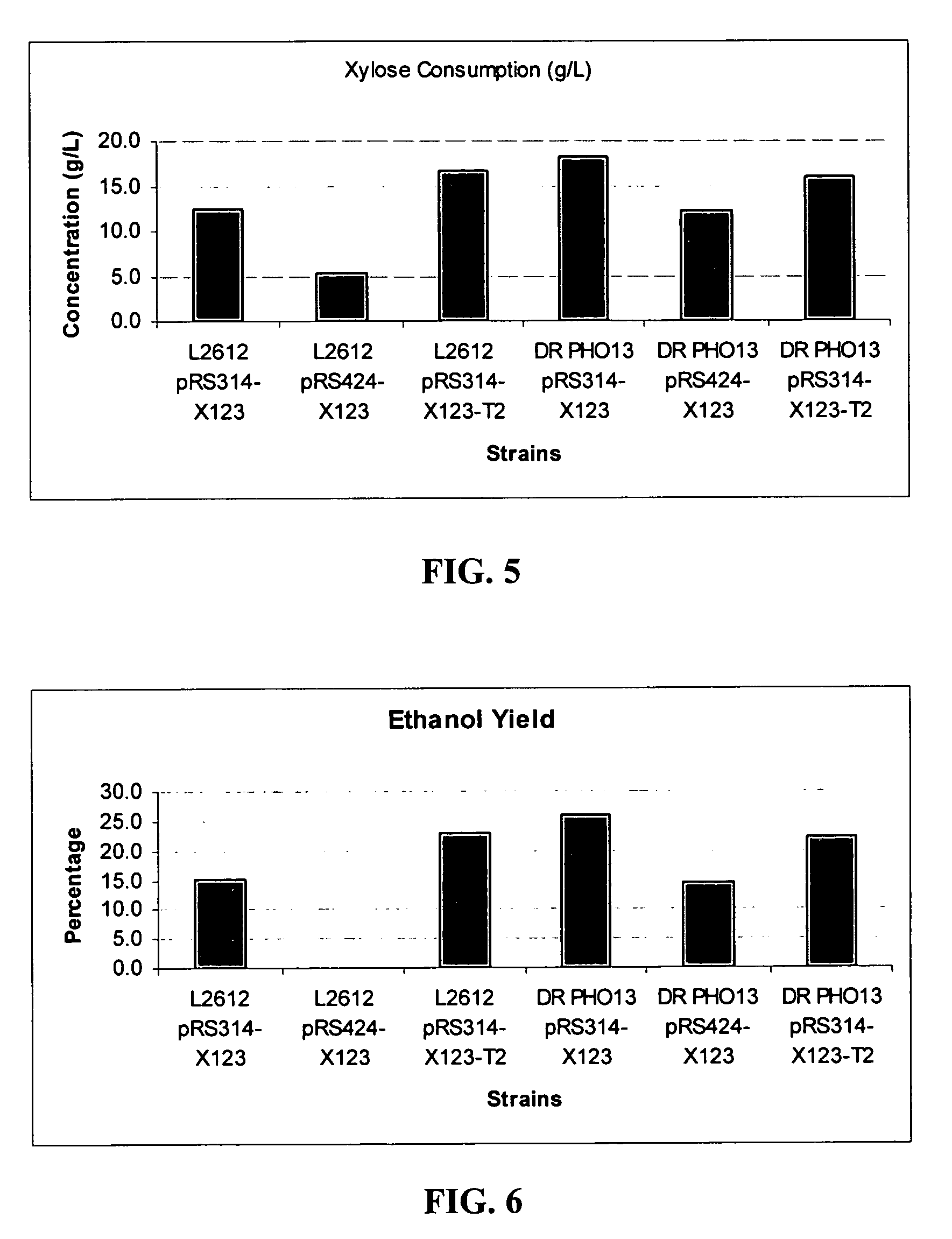
Xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains
Disclosed are xylose-fermenting recombinant yeast strains expressing xylose reductase, xylitol dehydrogenase, and xylulokinase and having reduced expression of PHO13 or a PHO13 ortholog, as well as methods of fermenting xylose to obtain ethanol using the recombinant yeast strains.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND +1
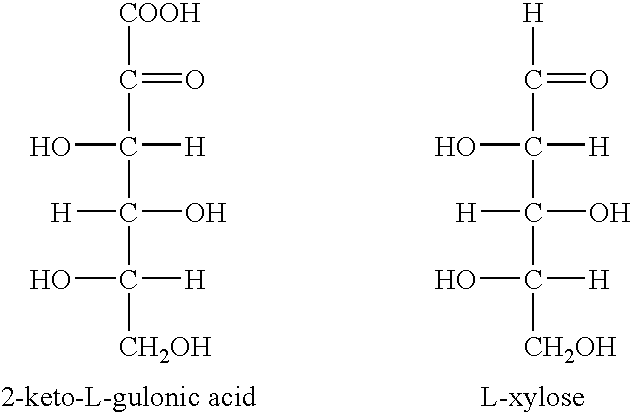
Enzymatic decarboxylation of 2-keto-L-gulonic acid to produce xylose
ActiveUS20050239174A1Increase valuePrepared cost-effectivelyMicrobiological testing/measurementBiofuelsIn vivo2-keto-L-gulonic acid
The invention is drawn to the enzymatic decarboxylation of 2-keto-L-gulonic acid (2-KLG) to produce xylose. The invention is also drawn to a method to detect xylose in vitro or in vivo (intracellularly), which employs an L-xylose dehydrogenase.
Owner:ARCHER DANIELS MIDLAND CO
Sugar compositions
Owner:VIRDIA
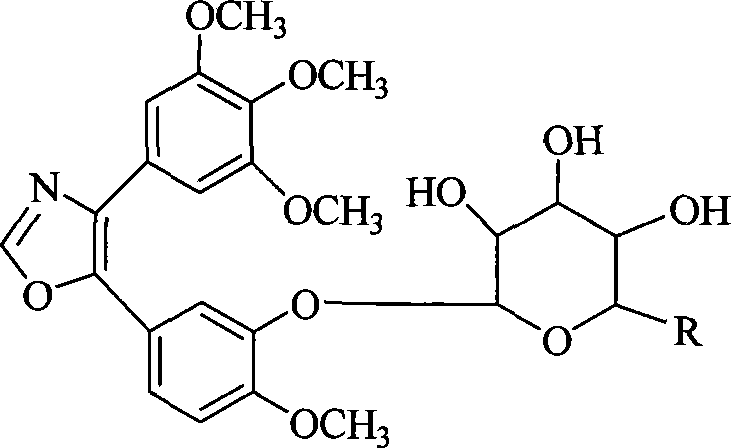
1,2-glycoside transderivative of oxazole compounds and preparation method thereof
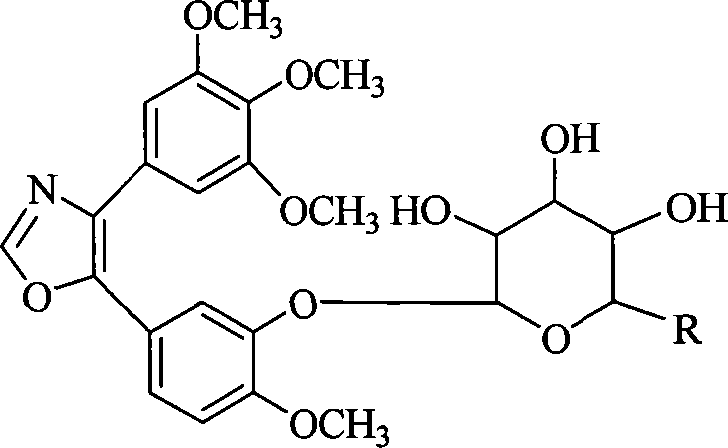
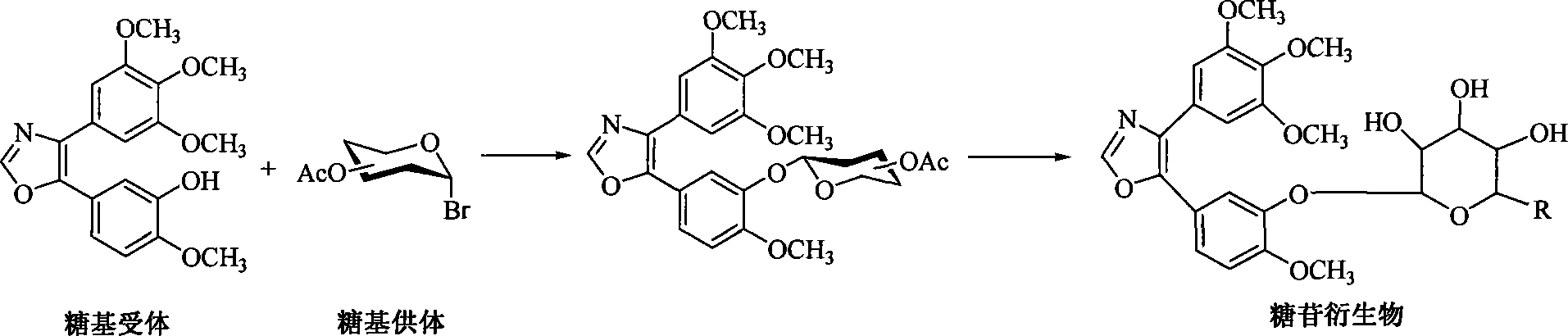
InactiveCN101230079AImprove bioavailabilityImprove targeted tumor vasculatureOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSolubilitySodium methoxide
The invention discloses 1, 2-anti form glucoside derivative of oxazole compound. During the preparation, 4-(3, 4, 5-trimethoxy phenyl)-5-(3-hydroxyl-4-methoxy phenyl oxazole is used as the acceptor of glycosyl, bromo sugar of D-glucose, D-galactose, L-arabinose, D-xylose, L-fucose or lactose with full acetyl protection, or trichlorine imine ester of L-rhamnose or D-mannose with full acetyl protection is adopted as the donator of glycosyl, glycosylation is performed with the catalysis of alkali and tetrabutyl ammonium bromide or lewis acid, to obtain glucoside derivative containing acetyl protecting group; and then the acetyl protecting group is removed by utilizing methyl alcohol and sodium methoxide, to obtain 1,2 anti-form glucoside derivative of oxazole compound. The preparation method is simple, highly effective and universal, the route is short, the water-solubility of the product is good, the bioavailability is high, thereby the glucoside derivative can be applied as antineoplastic medicine inhibiting microtubule assembly and selectively targeting tumor blood vessels.
Owner:OCEAN UNIV OF CHINA
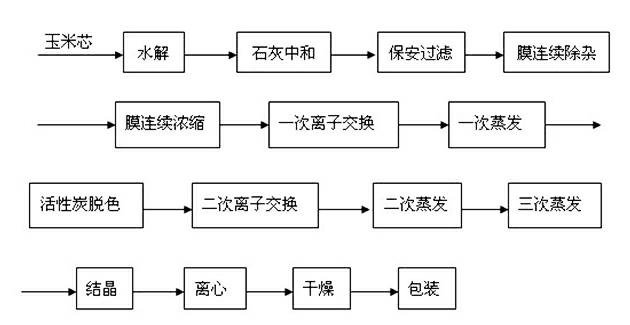
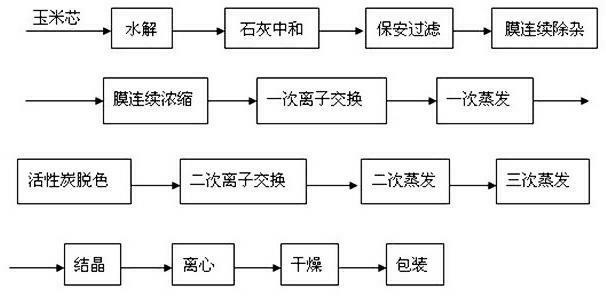
Efficient and energy-saving xylose producing process
The invention discloses an efficient and energy-saving xylose producing process, which comprises the following steps of: A, corncob hydrolysis; B, lime neutralization; C, cartridge filtration; D, continuous membrane decontamination; E, continuous membrane concentration; F, primary ion exchange; G, primary evaporation; H, activated carbon decoloration; I, secondary ion exchange; J, secondary evaporation; K, third-time evaporation; L, crystallization; M, centrifugation; N, drying; and O, finished product packaging. The process disclosed by the invention has the beneficial effects that impurities and pigment are removed by membrane separation and concentration, the usage amount of activated carbon is reduced, steam consumption is reduced, the pollution load of ion exchange resin is reduced, the regeneration period of the ion exchange resin is prolonged, the discharge of waste water of the producing process is reduced, the production efficiency is improved, and the production cost is reduced, so that the sustainable development ability of an enterprise is promoted.
Owner:上海诚洲科技中心(有限合伙)
Method for producing aromatic aldehyde by degrading lignin separated and coupled from cellulose component
InactiveCN102603504ARealize full component utilizationHigh purityOrganic compound preparationPulping with inorganic basesLiquid glucoseAlcohol sugars
The invention provides a method for producing aromatic aldehyde by degrading lignin separated and coupled from a cellulose component. The method comprises the following steps: 1) performing pretreatment on a lignocellulose raw material through a diluted acid method to remove more than 80% of hemicellulose and obtain acid hydrolysis residue; 2) based on a perovskite type composite oxide as a catalyst and the acid hydrolysis residue obtained in the step 1) as the raw material, performing lignin wet-process oxidation reaction under alkaline conditions to degrade the lignin and further produce an aromatic aldehyde type compound, and performing solid-liquid separation after reaction to finally obtain the cellulose with the purity of not less than 80%. In the method provided by the invention, after the pretreatment is performed on the lignocellulose raw material through the diluted acid method, the obtained liquid glucose can be used for preparing xylose, xylitol, arabinose and other sugar alcohol products; and the lignin wet-process oxidation reaction is further performed on the acid hydrolysis residue under the alkaline conditions to obtain the high-purity cellulose and the aromatic aldehyde type compound so as to realize the all-component utilization of the lignocellulose raw material and have economic and social benefits.
Owner:ANHUI BBCA FERMENTATION TECH ENG RES
System and method for treating biomass
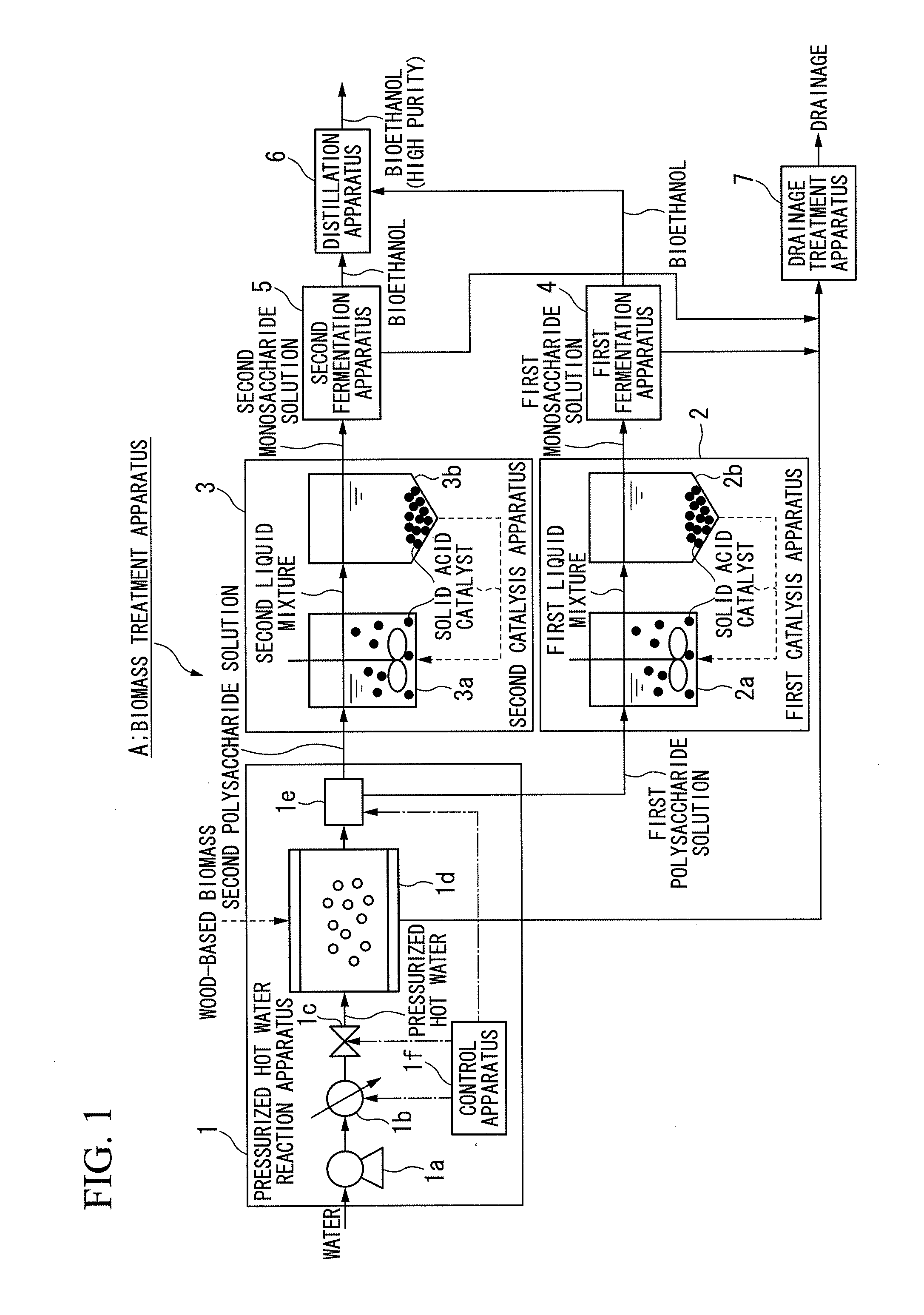
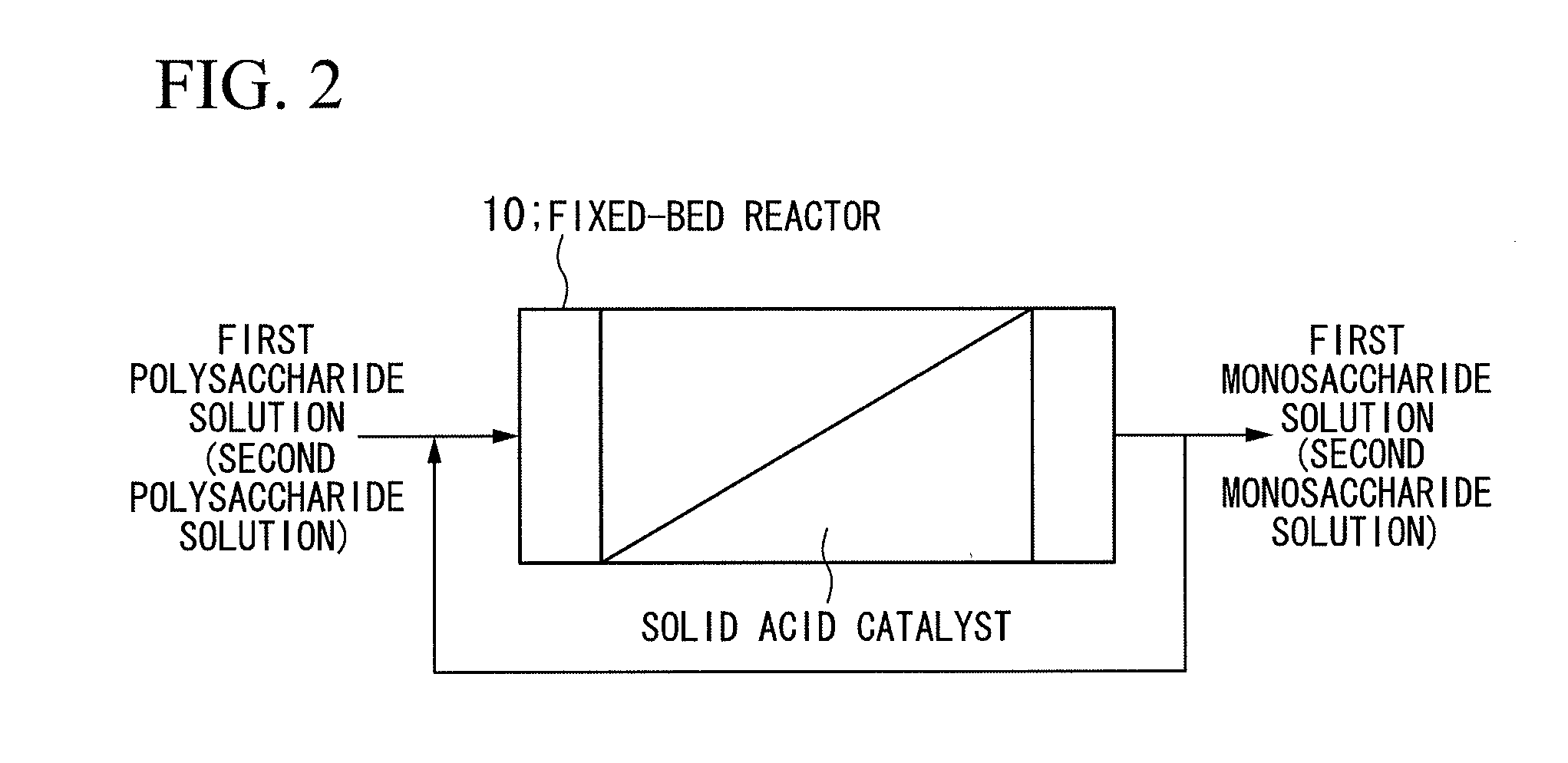
InactiveUS20120232264A1Reduce the amount of solutionIncrease productionBiological substance pretreatmentsSugar derivativesFiberDecomposition
A biomass treatment apparatus (A) is constituted by a pressurized hot water reaction apparatus (1) in which pressurized hot water is used, biomass is hydrolyzed under first reaction conditions that provide for decomposition of hemicellulose so as to generate a first polysaccharide solution including xylooligosaccharides, and then the biomass is hydrolyzed under second reaction conditions that provide for decomposition of cellulose to generate a second polysaccharide solution including cellooligosaccharides, a first catalysis apparatus (2) in which the first polysaccharide solution that flows out from the pressurized hot water reaction apparatus (1) is hydrolyzed using a solid acid catalyst so as to generate a first monosaccharide solution including xylose, and a second catalysis apparatus (3) in which the second polysaccharide solution that flows out from the pressurized hot water reaction apparatus (1) is hydrolyzed using a solid acid catalyst so as to generate a second monosaccharide solution including glucose.
Owner:IHI CORP +1
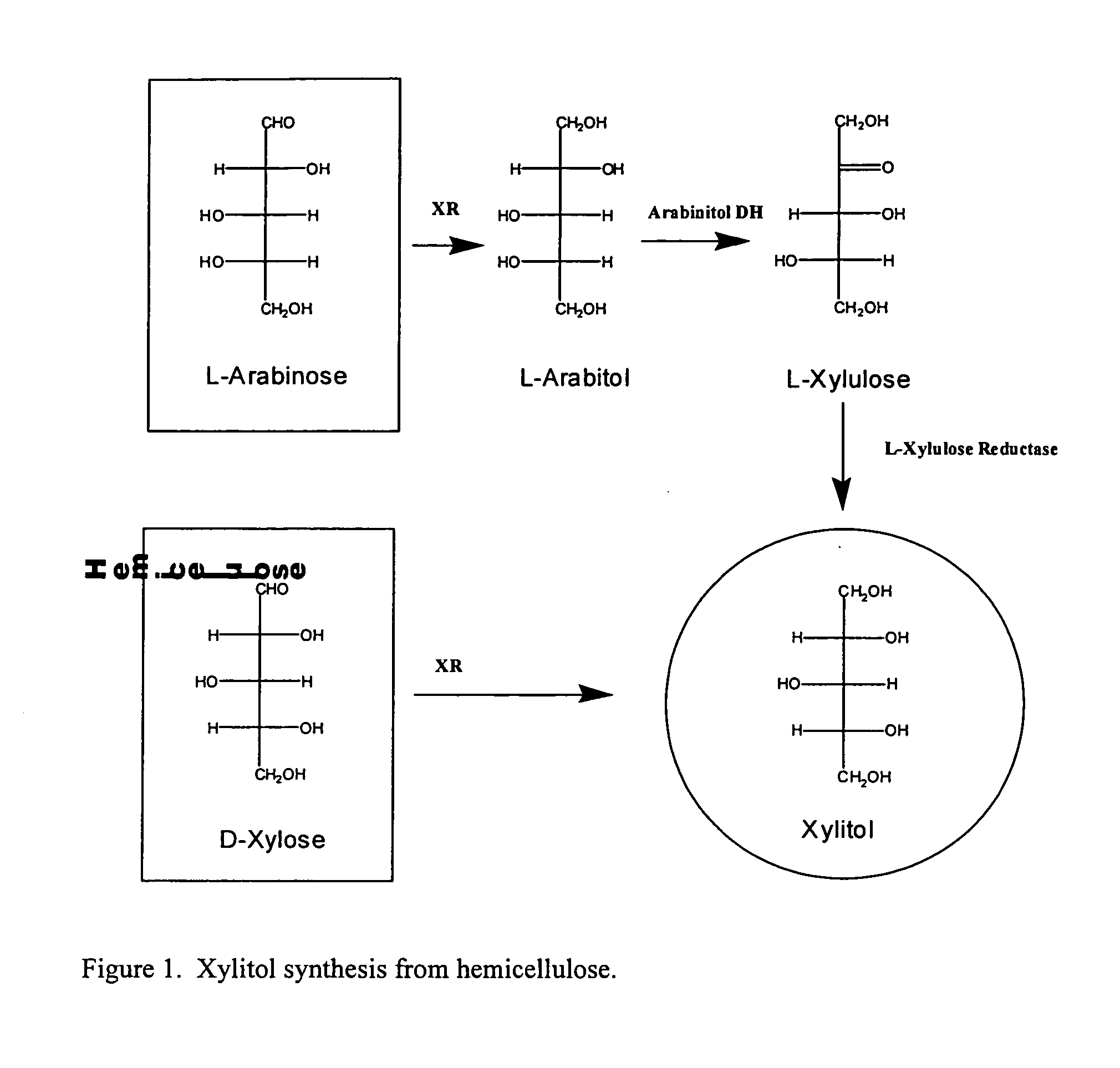
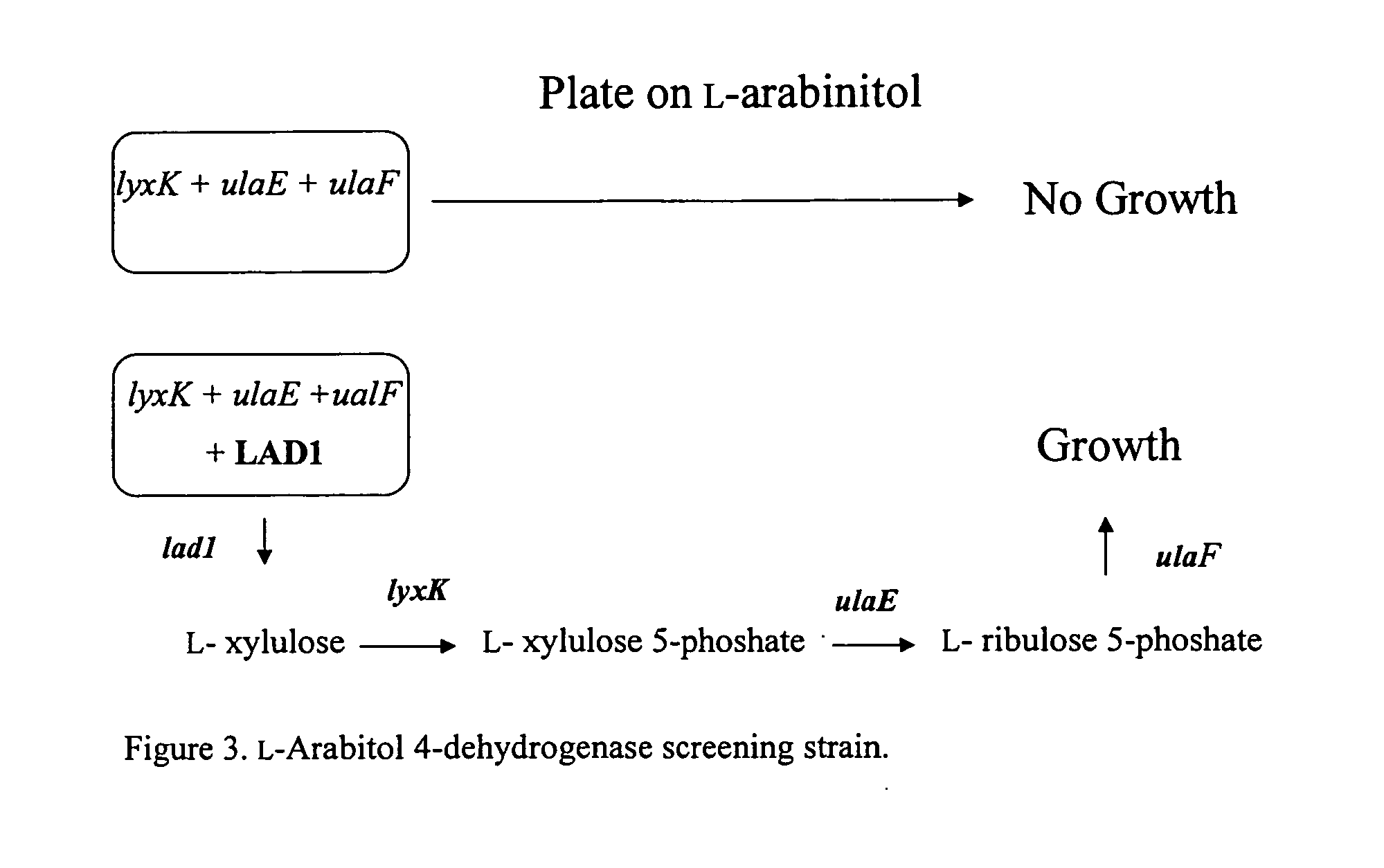
Methods for production of xylitol in microorganisms
The invention provides biosynthetic routes to xylitol production that do not require pure D-xylose for synthesis and that can utilize inexpensive substrates such as hemicellulose hydrolysates.
Owner:BIOTECH RES & DEV +1
Method for making furfuraldehyde using xylose mother liquor as material
The present invention belongs to the field of furfural preparing technology. The process of preparing furfural from xylose mother liquid as material includes adopting titania acidified with acetic acid, phosphoric acid, sulfuric acid or hydrochloric acid or zirconia acidified with sulfuric acid as catalyst, adopting sodium chloride, potassium chloride, zinc chloride, multiple superphosphate, sodium sulfate, potassium sulfate or sodium acetate as co-catalyst, adding xylose mother liquid, water, catalyst and co-catalyst in certain weight proportion inside dewatering reactor, reacting at 120-260 deg.c and 0.1-5.0 MPa, condensing produced vapor to obtain water solution of furfural, and evaporating water to obtain furfural. The present invention has the advantages of simple technological process and high furfural yield.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Crystallization of sugars
The invention relates to removing crystallization inhibitors from a solution comprising one or more reducing sugars by nanofiltration, hydrolysis and / or chromatography. The reducing sugars are typically selected from fructose and xylose.
Owner:DANISCO SWEETENERS
Modified carbon nitride photocatalyst, preparation method thereof, and method for synthesizing xylosic acid by photocatalytic oxidation of xylose
ActiveCN108927198AIncrease valueUniversalOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationNon toxicitySolvent
The invention belongs to the technical fields of catalysts and xylosic acid, and discloses a modified carbon nitride photocatalyst, a preparation method thereof, and a method for synthesizing xylosicacid by photocatalytic oxidation of xylose. The preparation method of the photocatalyst comprises the following steps: (1) uniformly mixing a nitrogen-containing organic matter precursor with a low-melting point chlorine-containing salt compound in a solvent, and removing the solvent to obtain a solid product; and (2) performing calcining, acid treatment, washing and drying on the solid product toobtain the modified carbon nitride photocatalyst. The modified carbon nitride photocatalyst is used for photocatalytic oxidation of xylose to synthesize xylosic acid. The method for synthesizing xylosic acid is characterized in that the photocatalytic oxidation of the xylose is carried out in an alkaline solution under an illuminating condition in the presence of the modified carbon nitride photocatalyst to obtain the xylosic acid. The photocatalyst has the advantages of good thermal stability, high catalytic activity and good recyclability. The method for successfully synthesizing xylosic acid by photocatalytic oxidation of xylose through using the photocatalyst has the advantages of good safety, non-toxicity, quick effect, low energy consumption, high yield of the xylosic acid, and easiness in realizing industrial production.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Antiproliferative Compositions Comprising Aryl Substituted Xylopyranoside Derivatives
InactiveUS20080027023A1Synergistic effectOrganic active ingredientsBiocideAbnormal tissue growthAryl
Novel xylose based glycoside compounds that have xylose linked O-, S- or C-glycosidically to an aglycone containing several aromatic rings, and compositions that comprise the novel xylose based glycosides and non-xylose-based anti-tumor agents, pharmaceuticals or dietary supplements. The compounds or compositions are administered to treat proliferative diseases, including various forms of cancer.
Owner:GLUCOGENE MEDICAL HFM
Glycosidase inhibitors and methods of synthesizing same
Methods for synthesizing Salacinol, its stereoisomers, and analogues, homologues and other derivatives thereof potentially useful as glycosidase inhibitors are described. In some embodiments the compounds of the invention may have the general formula (I) or (II): The synthetic schemes may comprise reacting a cyclic sulfate with a 5-membered ring sugar containing a heteroatom (X). The heteroatom preferably comprises sulfur, selenium, or nitrogen. The cyclic sulfate and ring sugar reagents may be readily prepared from carbohydrate precursors, such as D-glucose, L-glucose, D-xylose and L-xylose. The target compounds are prepared by opening of the cyclic sulfates by nucleophilic attack of the heteroatoms on the 5-membered ring sugars. The resulting heterocyclic compounds have a stable, inner salt structure comprising a heteroatom cation and a sulfate anion. The synthetic schemes yield various stereoisomers of the target compounds in moderate to good yields with limited side-reactions. Chain-extended analogues of Salacinol are also described.
Owner:SIMON FRASER UNIVERSITY
Xylose production and purification process
ActiveCN101824054AReduce manufacturing costReach crystallizationIon-exchange column/bed processesSugar derivativesIon exchangeEvaporation
The invention relates to a xylose production and purification process which belongs to the technical field of functional sugar production, and comprises the following steps that: (1) ion exchange is carried out to destaining solution in xylose production through an ion exchange column filled with gel-type anion exchange resin; (2) xylose solution after treatment in step (1) is beaten into a series column which comprises gel-type cation exchange resin and macroporous anion exchange resin; (3) the xylose solution after treatment in step (2) passes through a mixed bed exchange column which comprises anion and cation exchange resin; and (4) after treatment, a crystal xylose product is obtained through evaporation, concentration, centrifugation and drying procedures. The xylose production and purification process changes a traditional two-step purification into one-step purification, changes traditional step evaporation and concentration into centralized evaporation and concentration, simultaneously removes a one-step activated carbon decoloring procedure, simplifies the process, shortens the production cycle, reduces the production cost of xylose, adopts a mixed bed technology, ensures that the pH value of the exchange fluid to be 6.5 to 7.0, has lighter color after evaporation and concentration, and fully meets the requirements of xylose crystallization and separation.
Owner:鹤岗市经纬糖醇有限公司
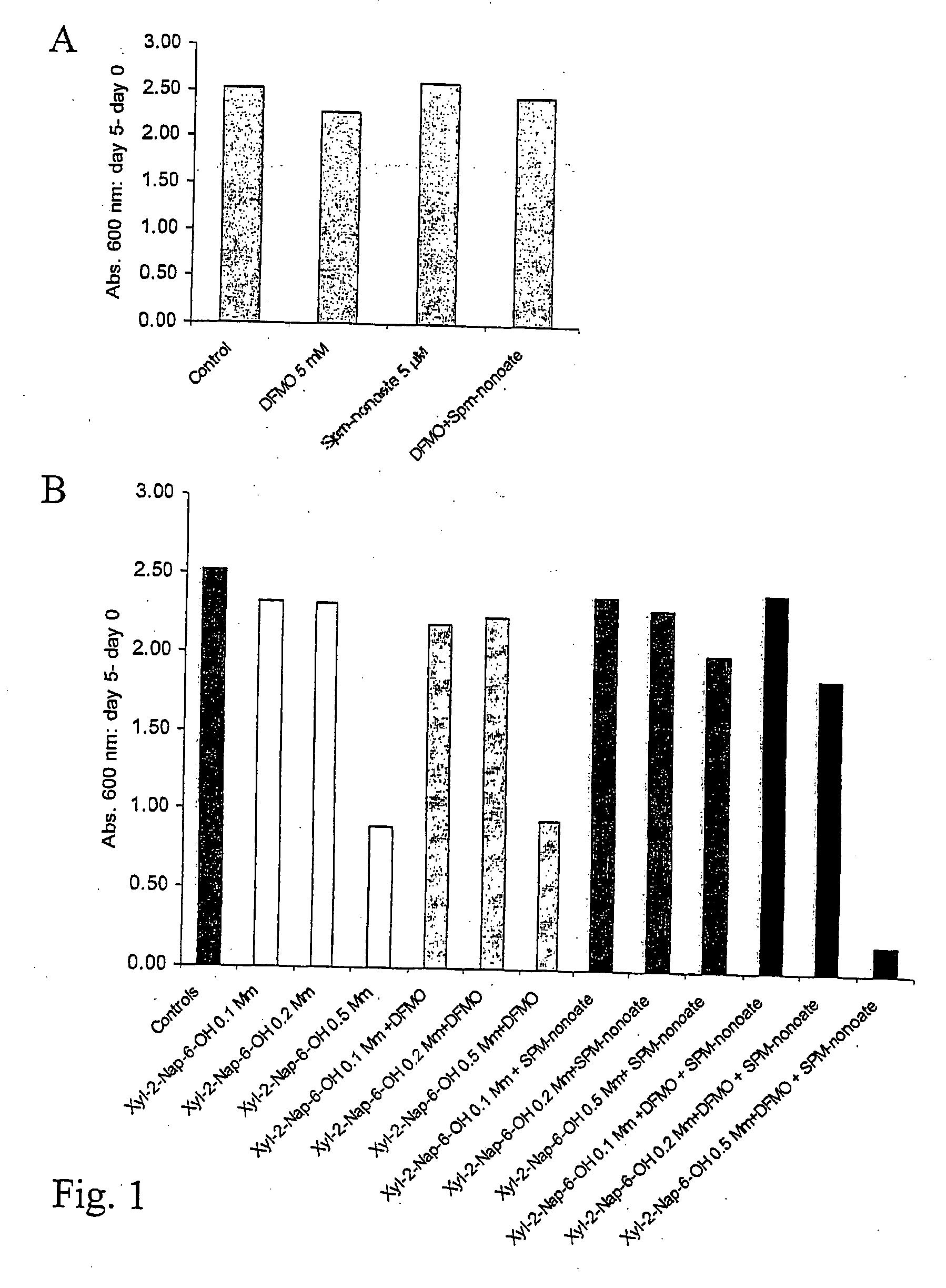
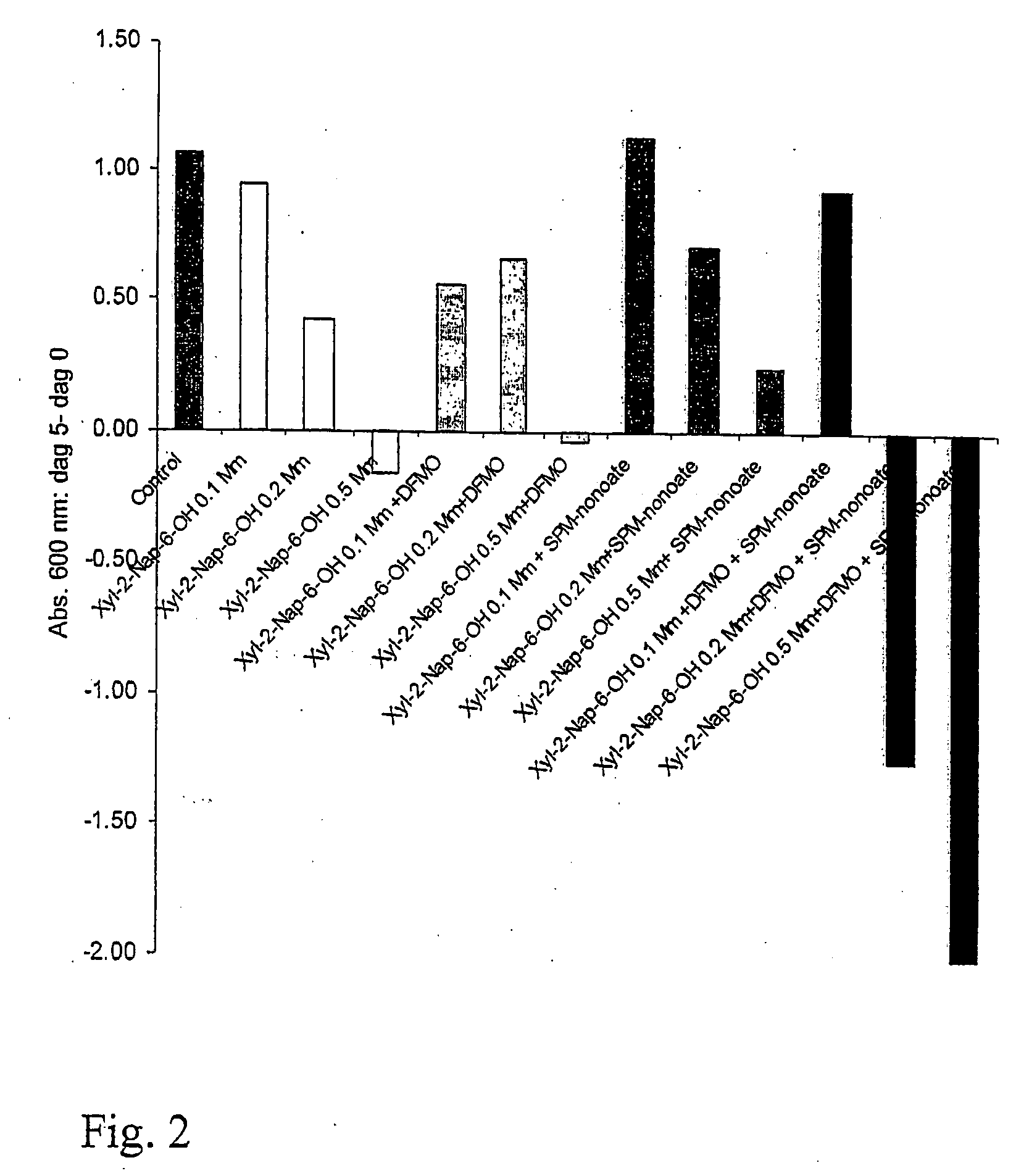
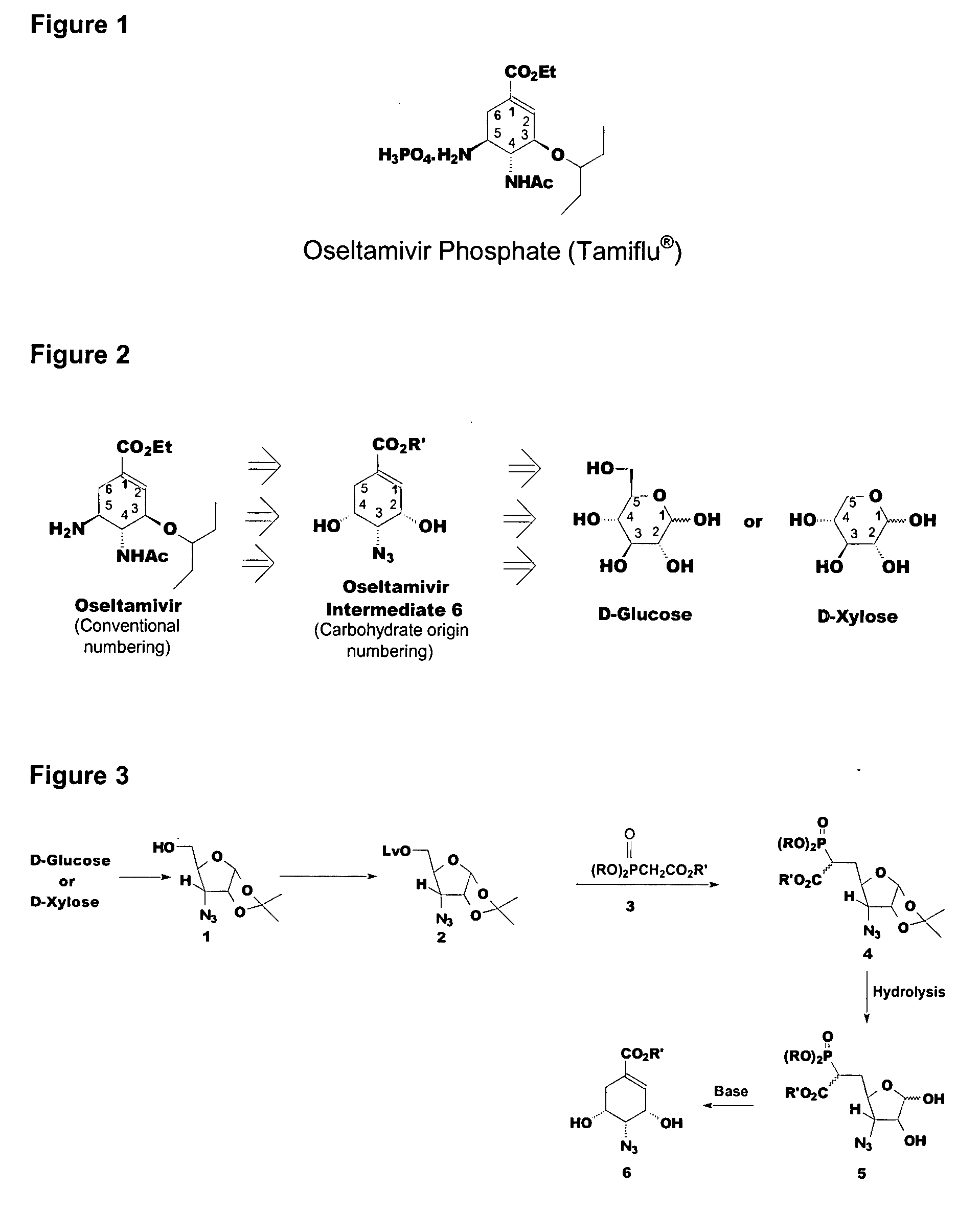
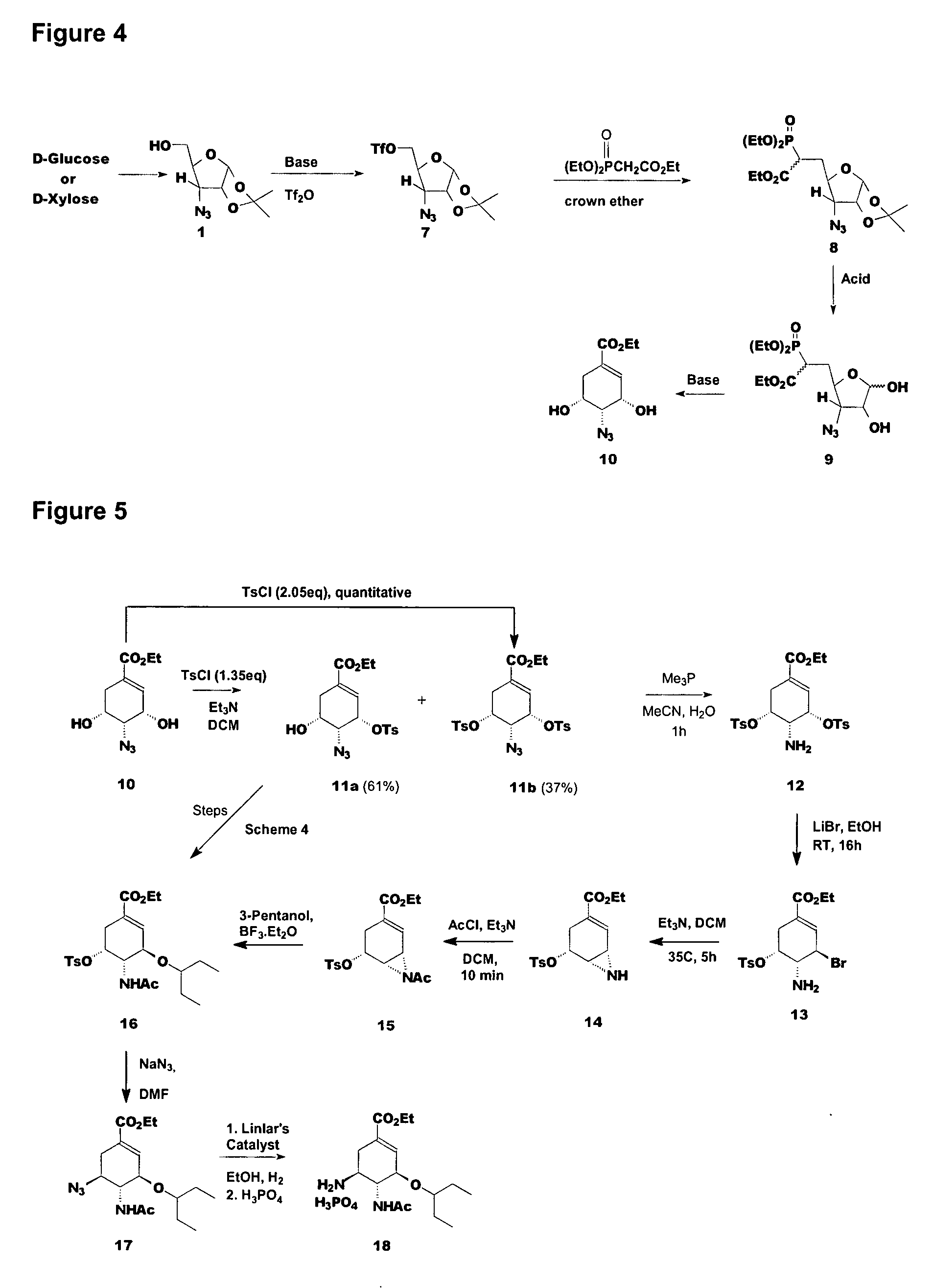
Preparation of oseltamivir phosphate (Tamiflu) and intermediates starting from D-glucose or D-xylose
InactiveUS20080009639A1Marginally expensiveSilicon organic compoundsOrganic compound preparationGlucose polymersD-Glucose
Novel processes for the preparation of the anti-viral agent, Oseltamivir Phosphate and novel intermediates prepared in such processes. The novel processes use as starting materials D-glucose or D-xylose in the preparation of Oseltamivir Phosphate.
Owner:APOTEX PHARMACHEN INC
Popular searches
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com