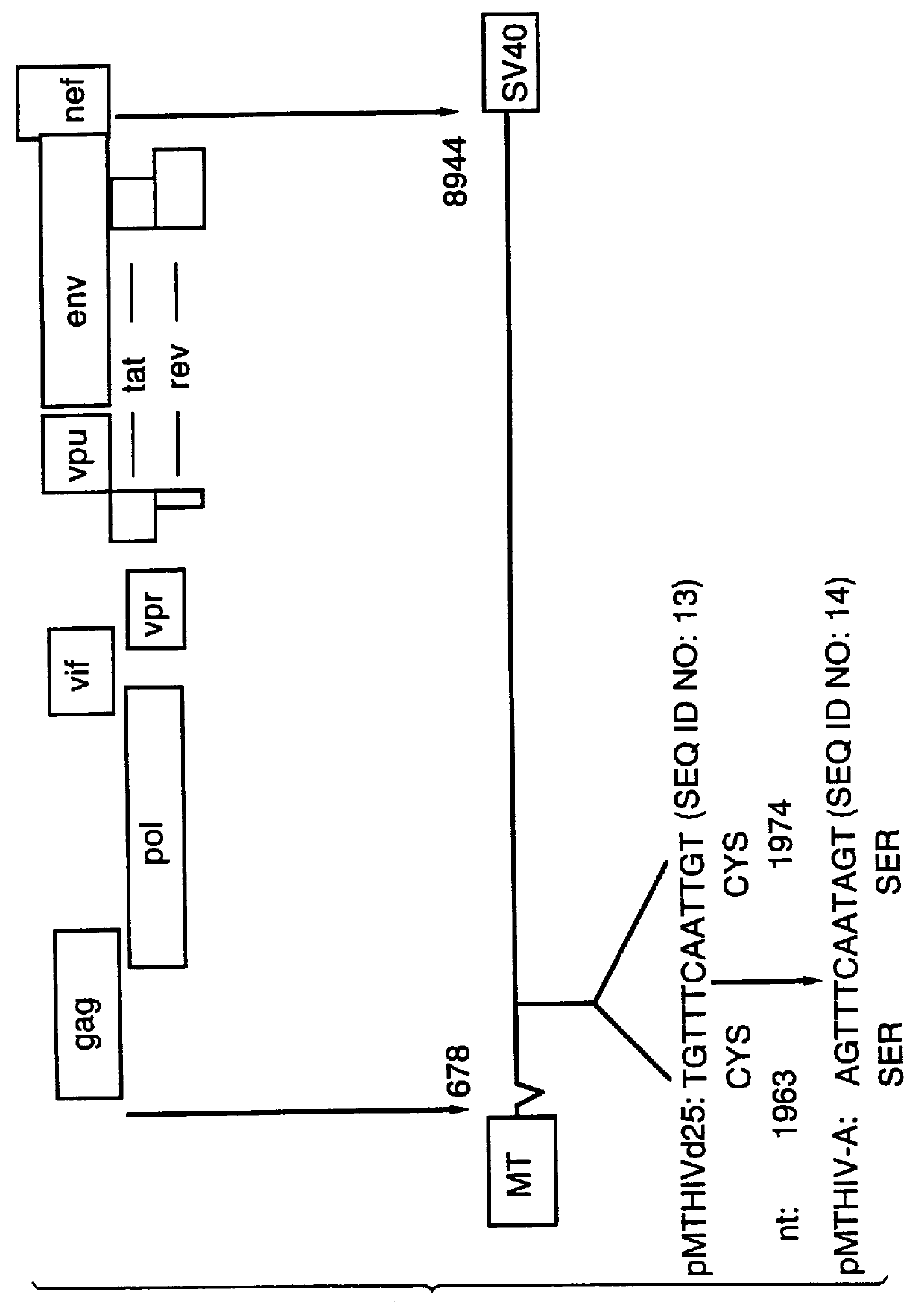
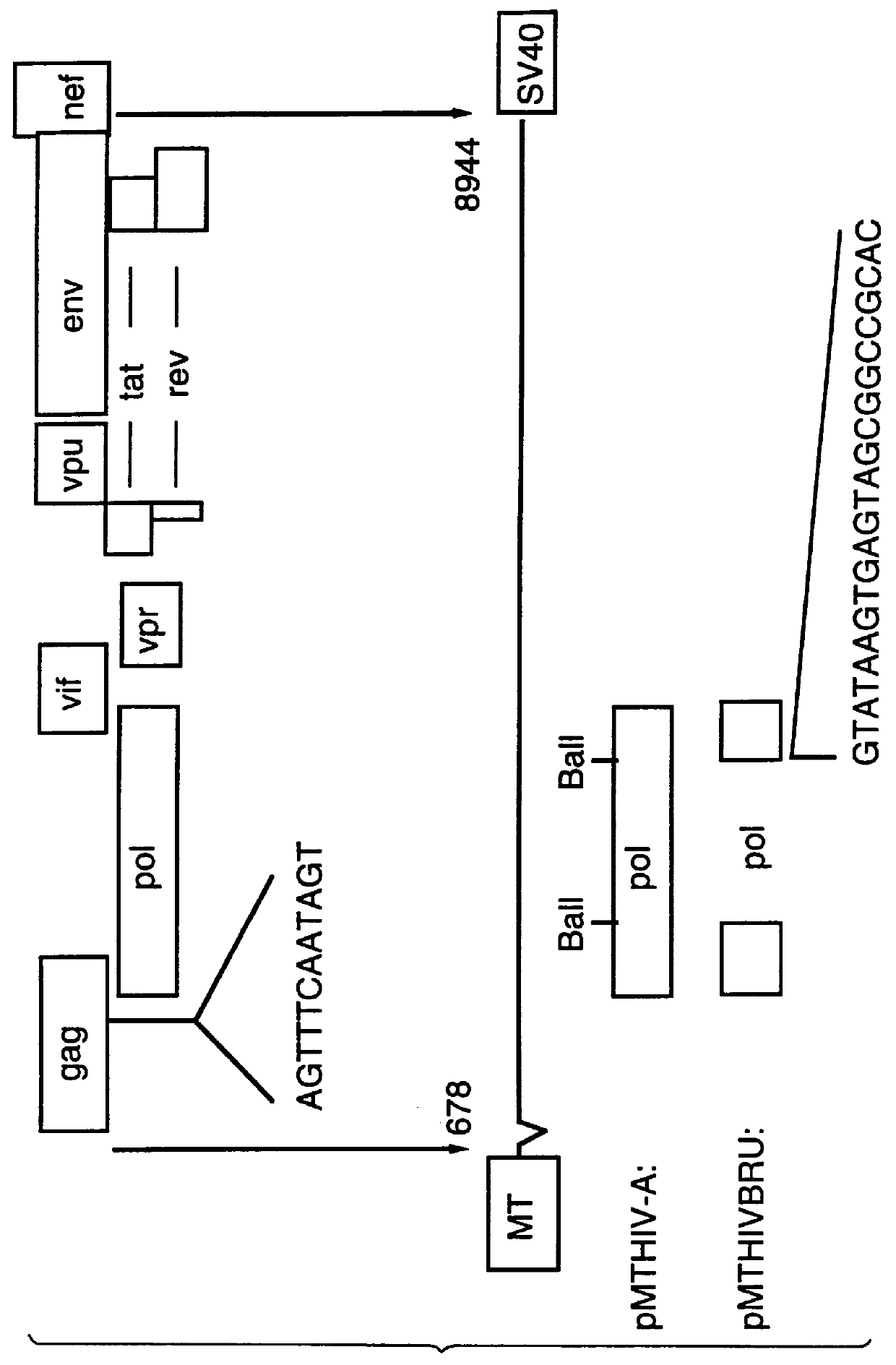
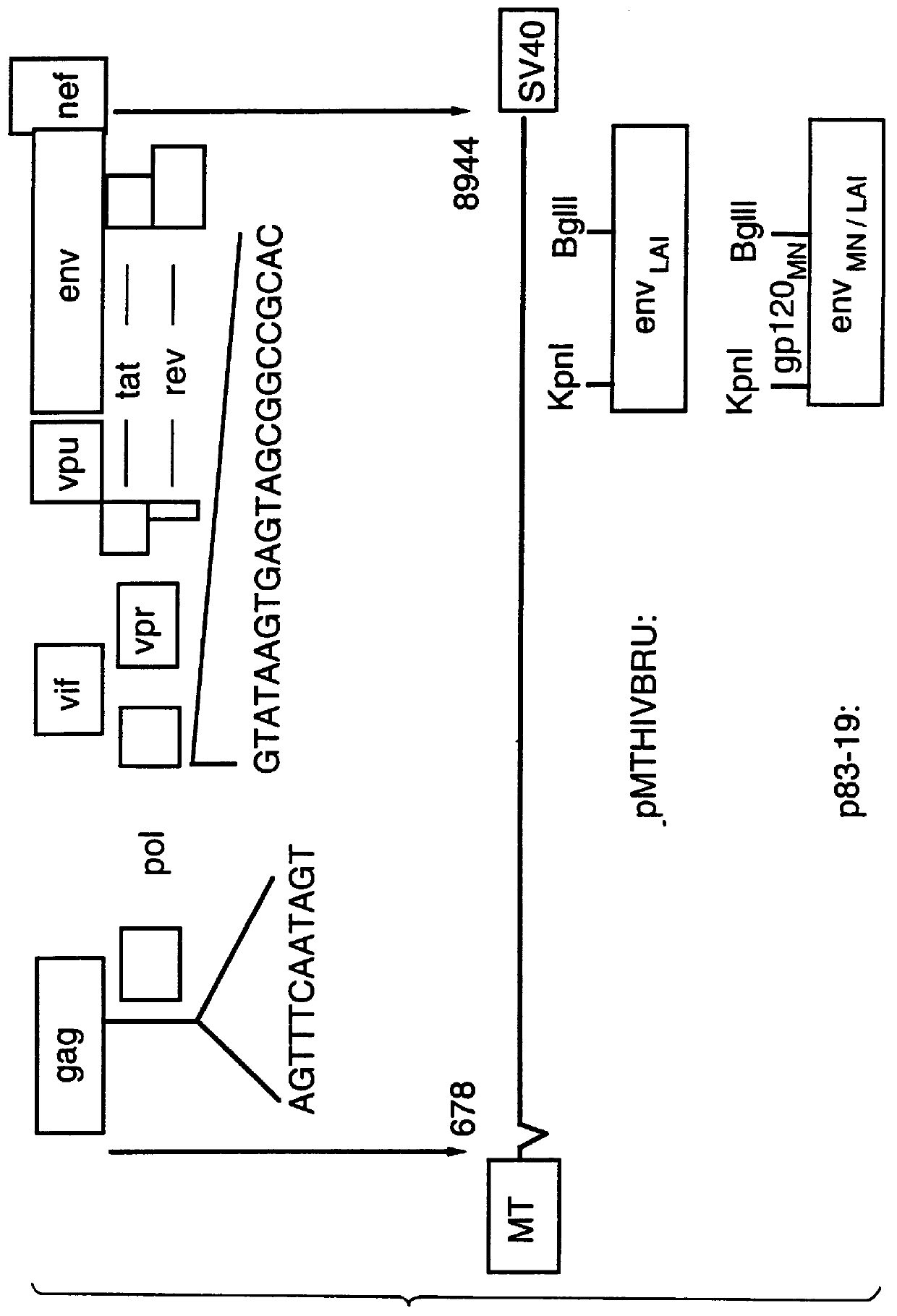
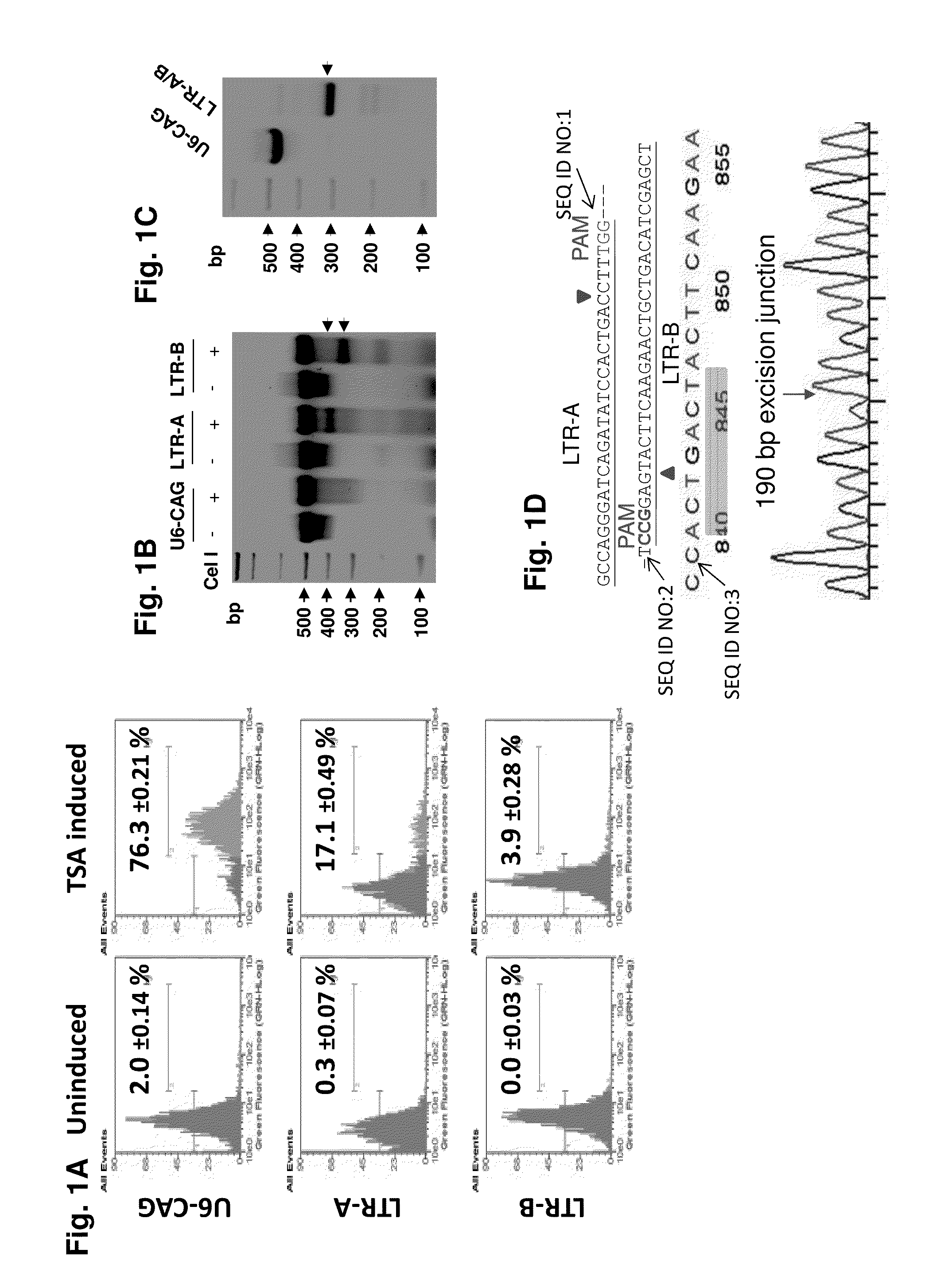
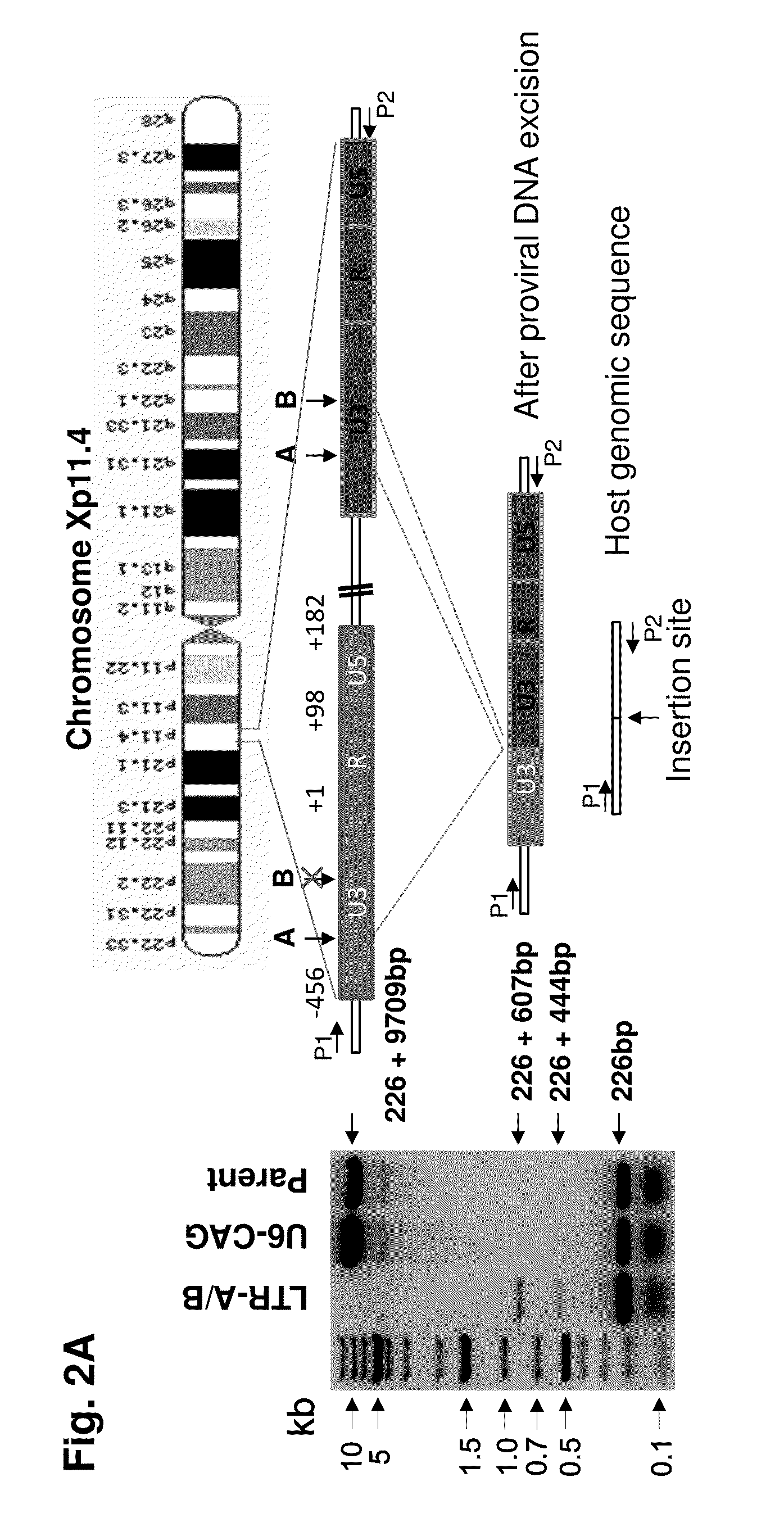
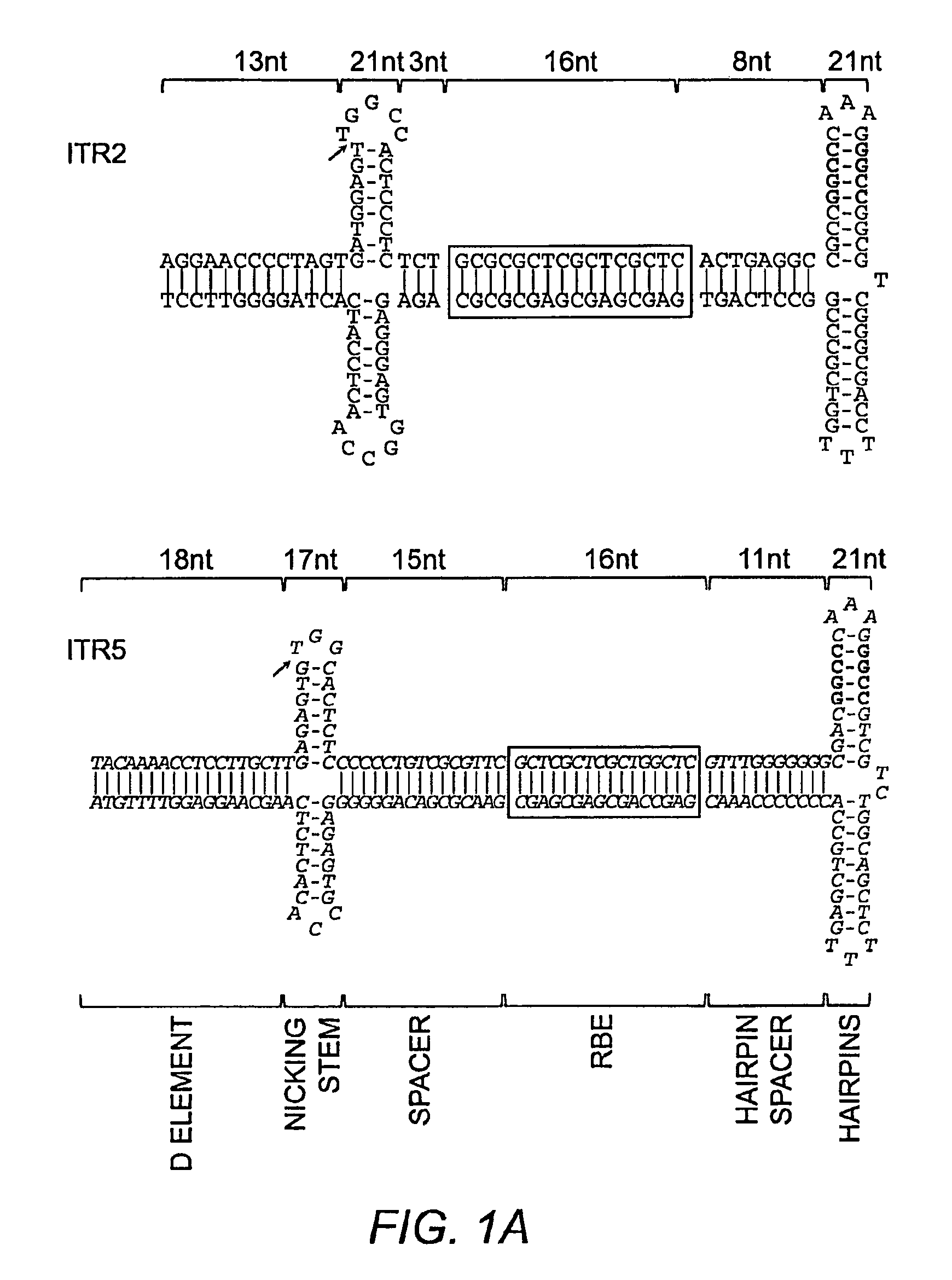
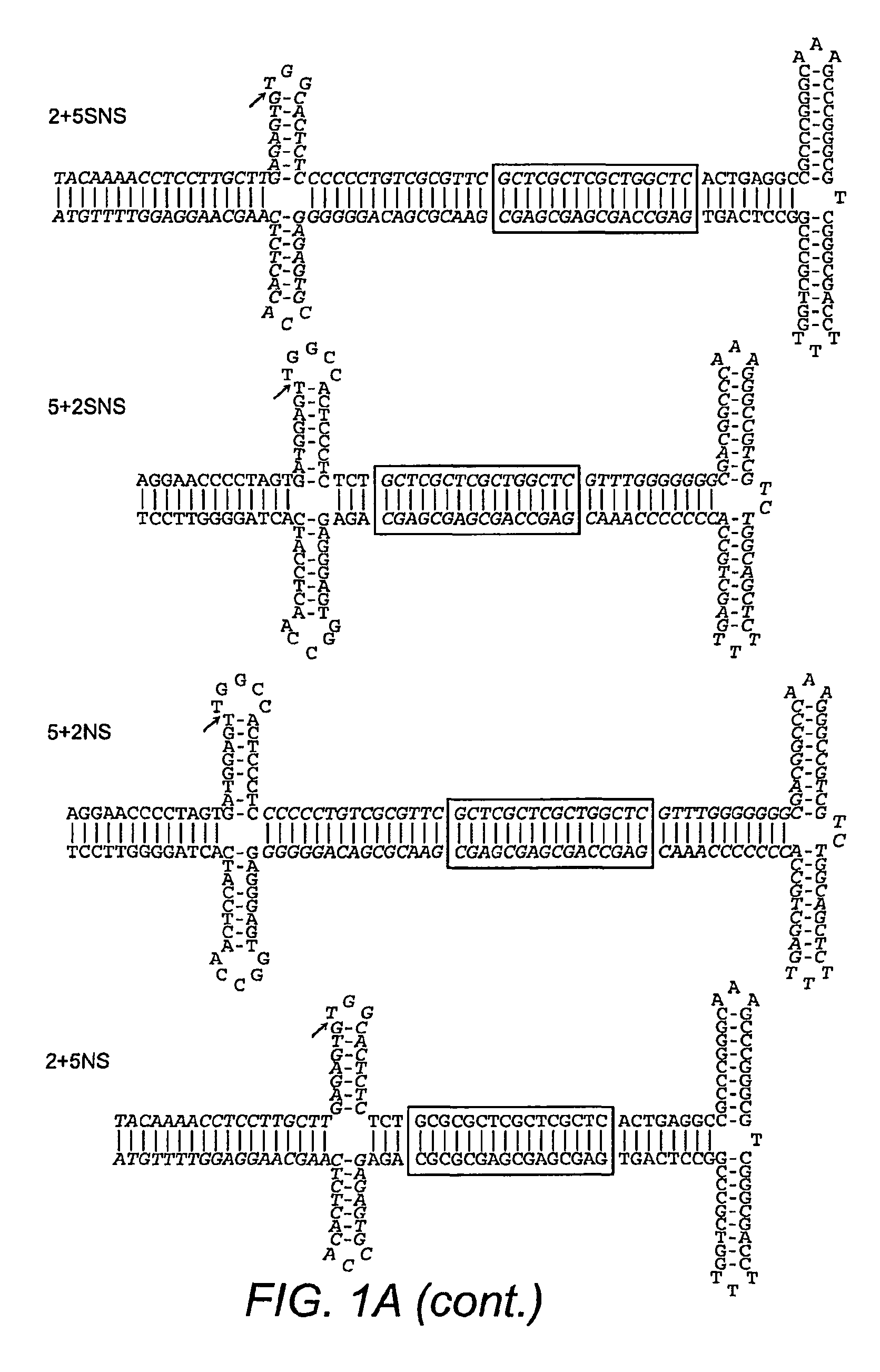
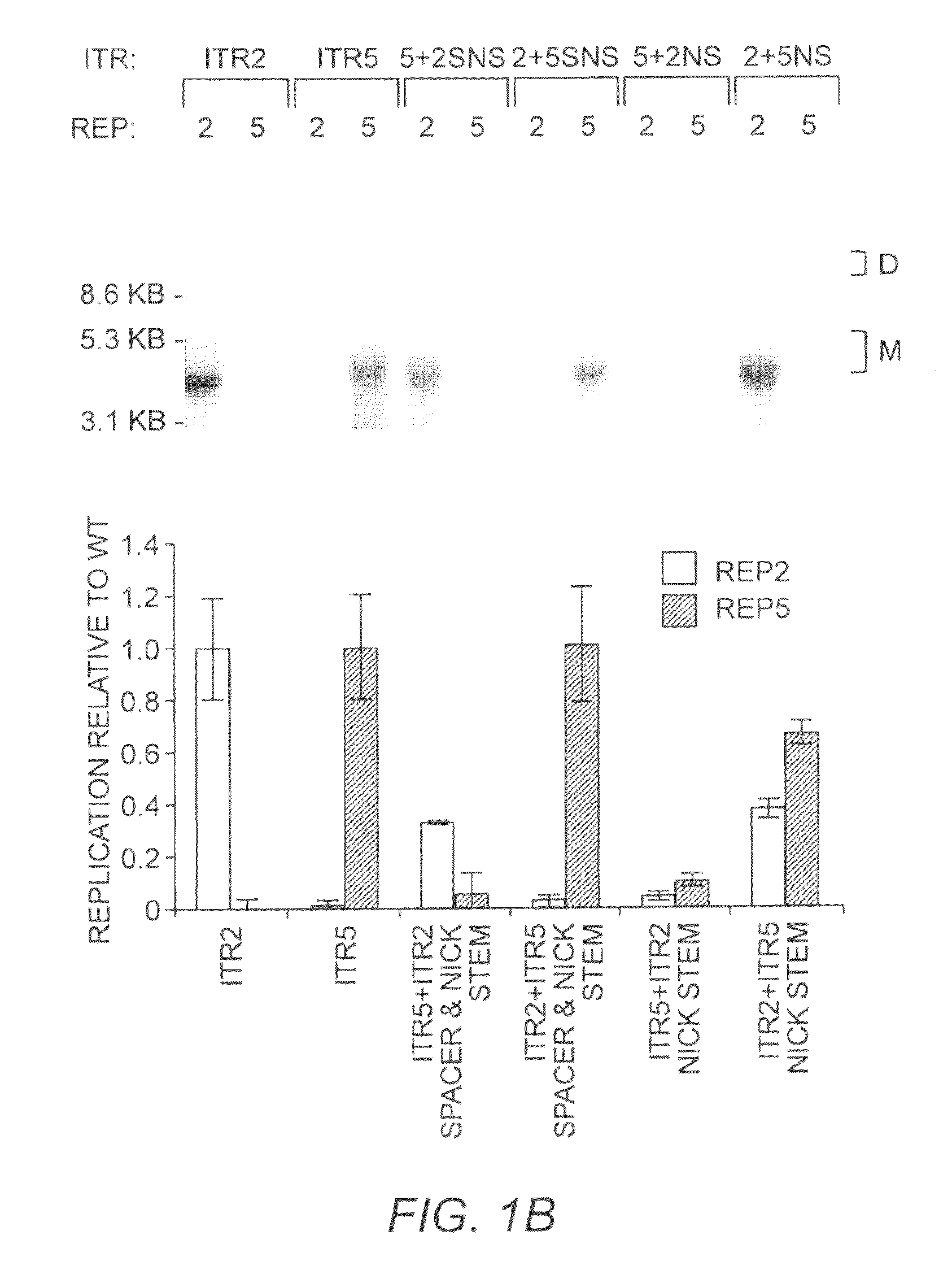
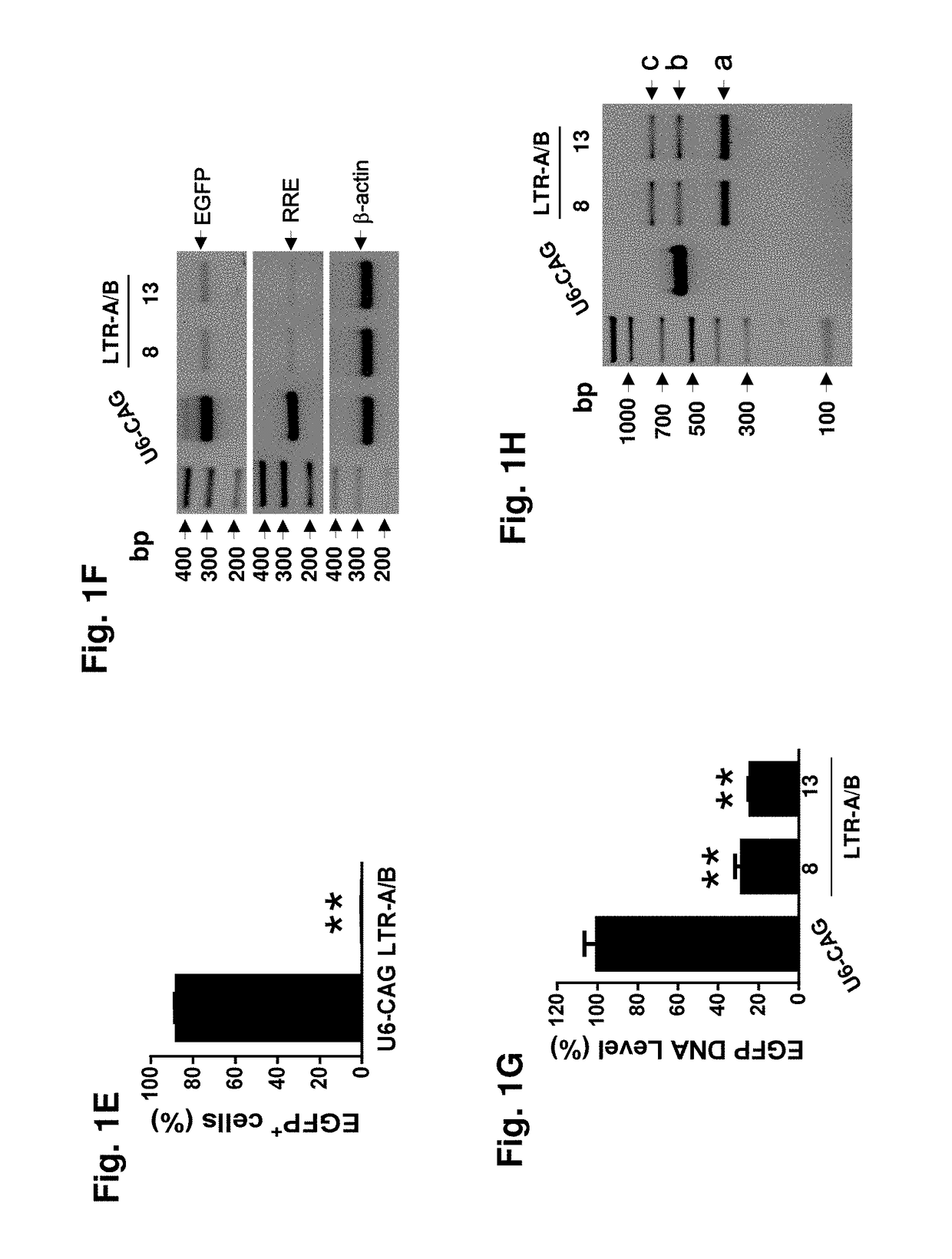
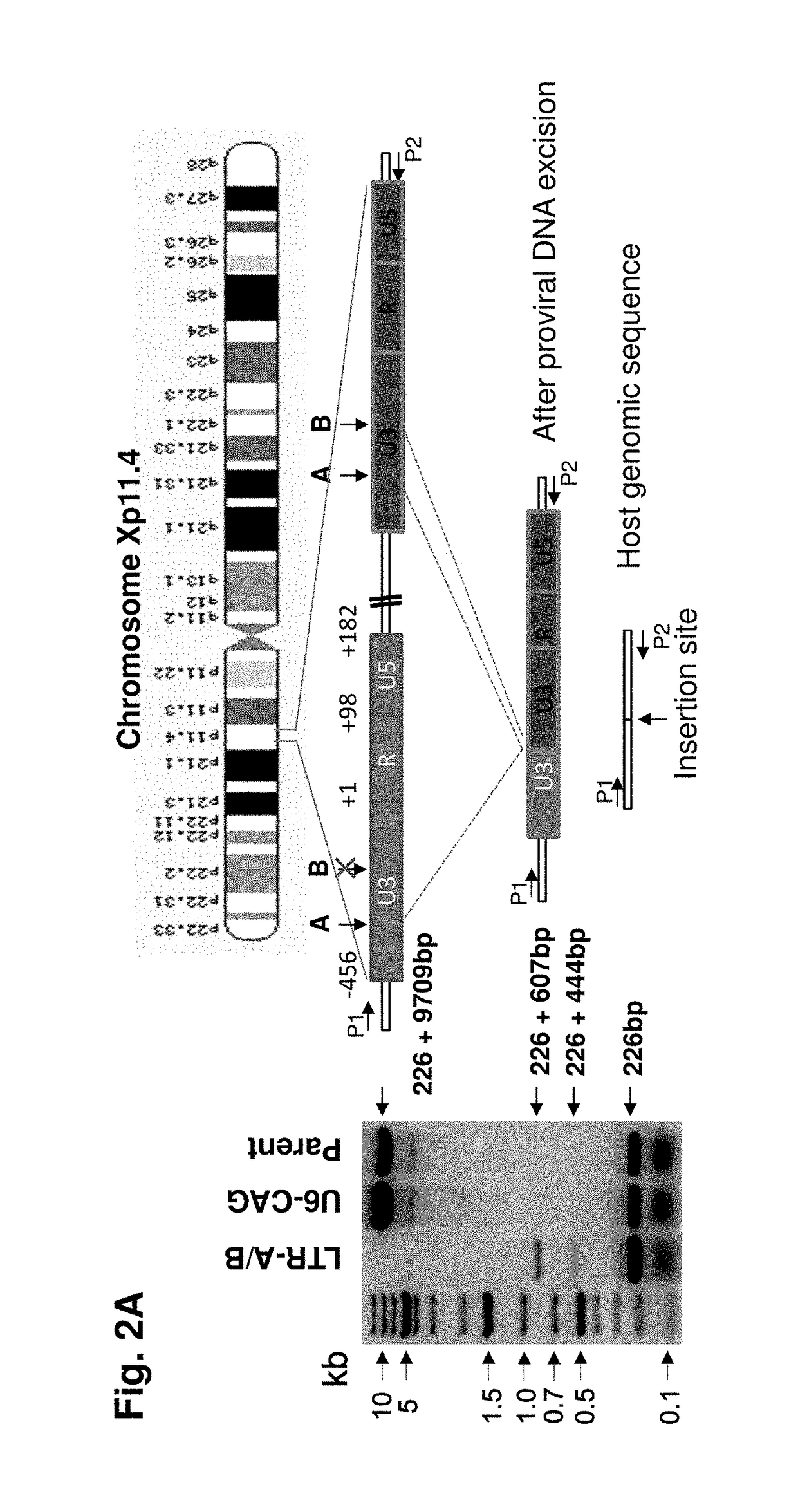
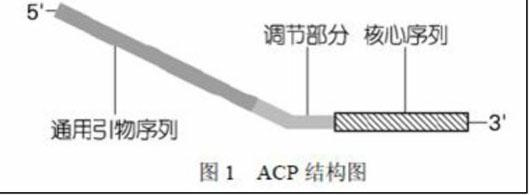
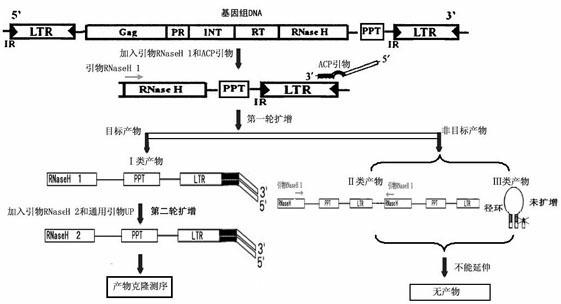
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
55 results about "Long terminal repeat" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
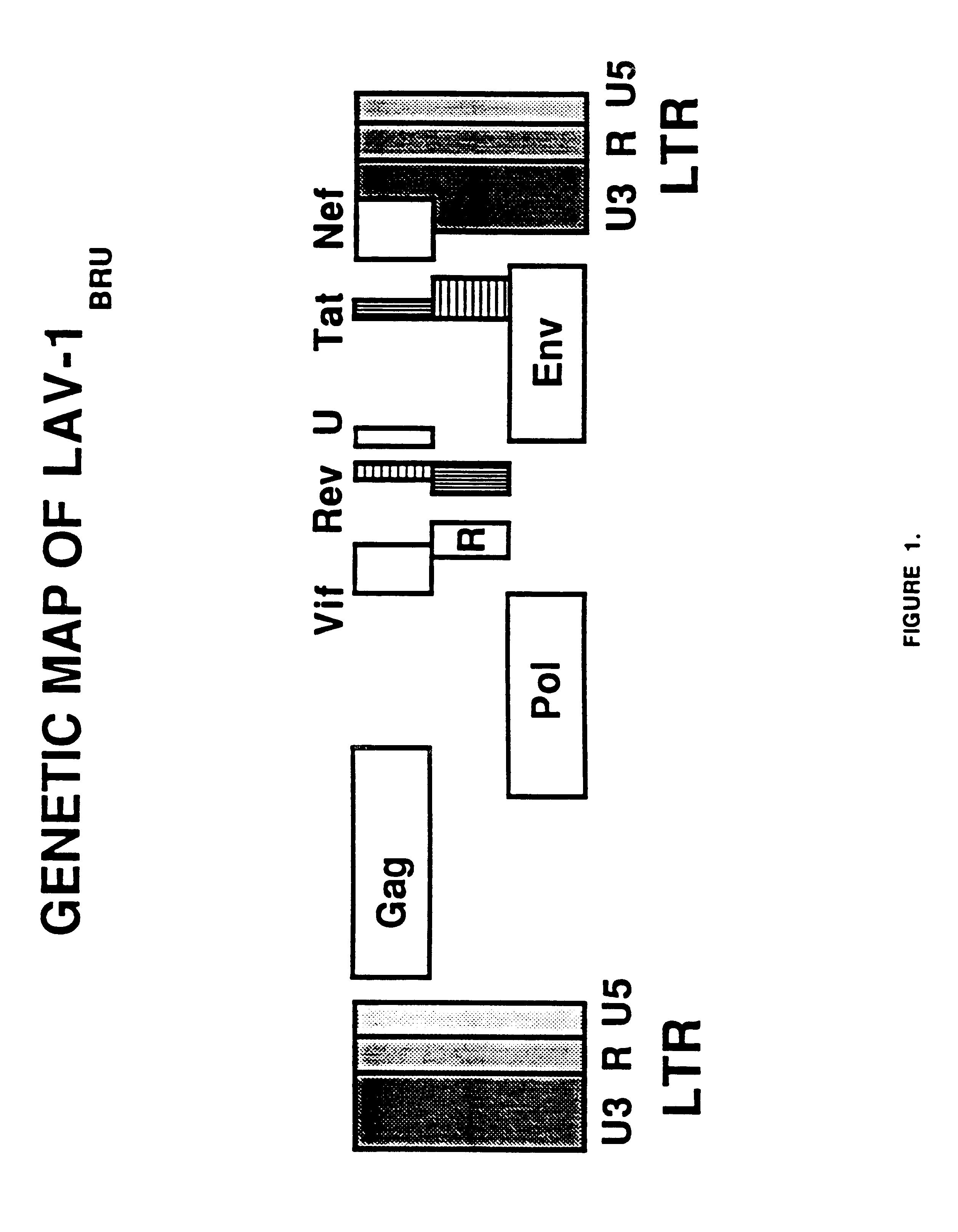
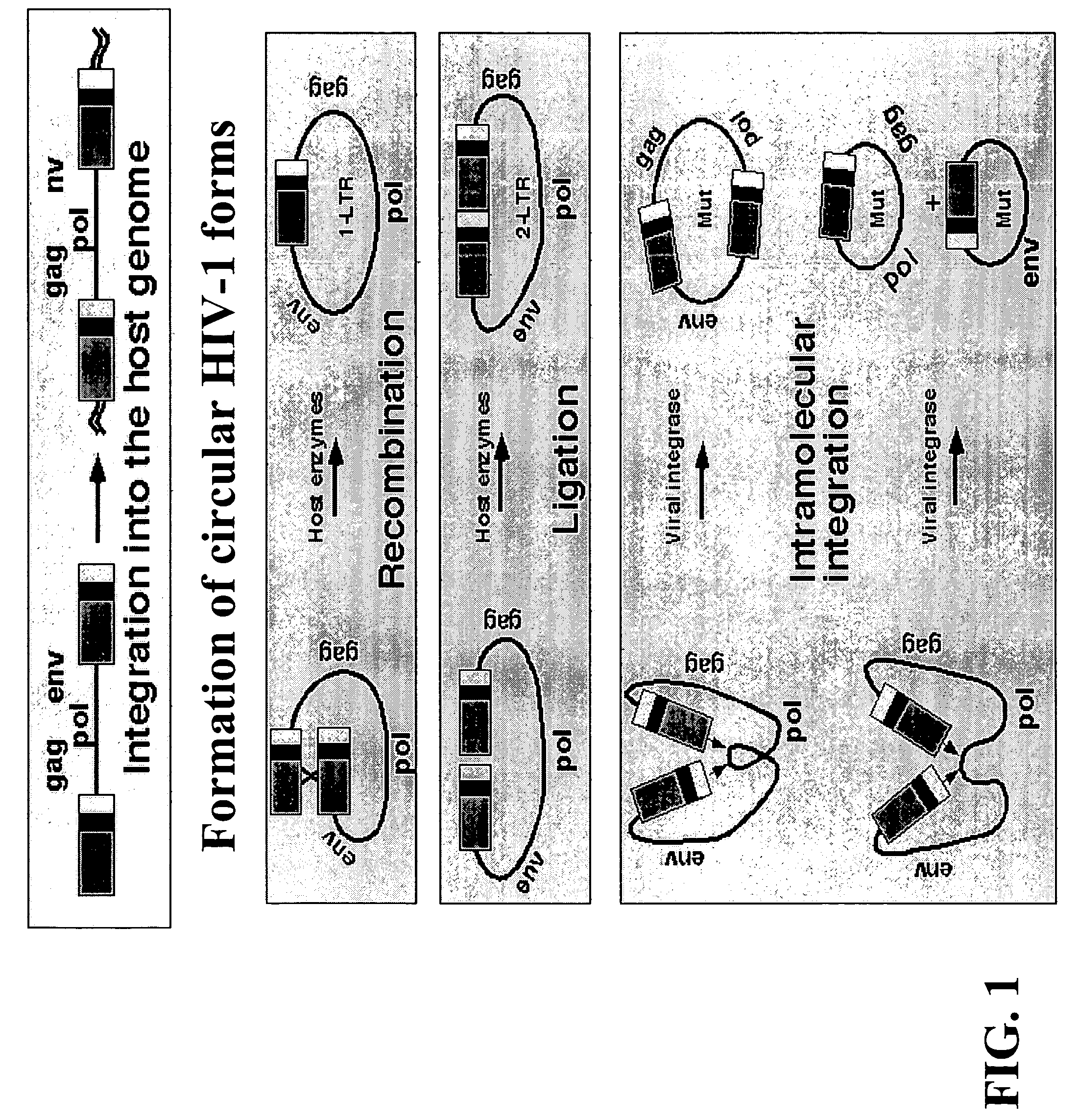
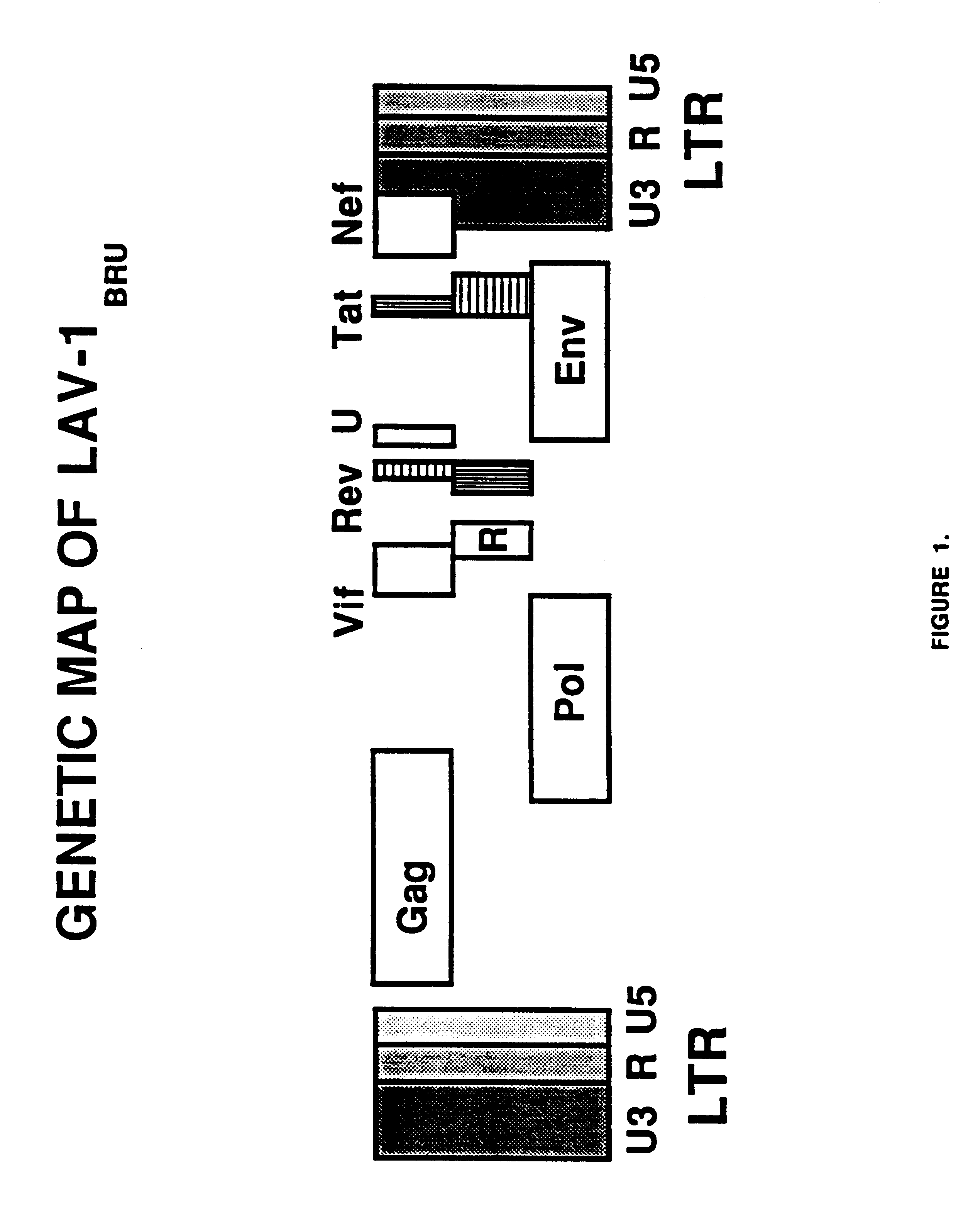
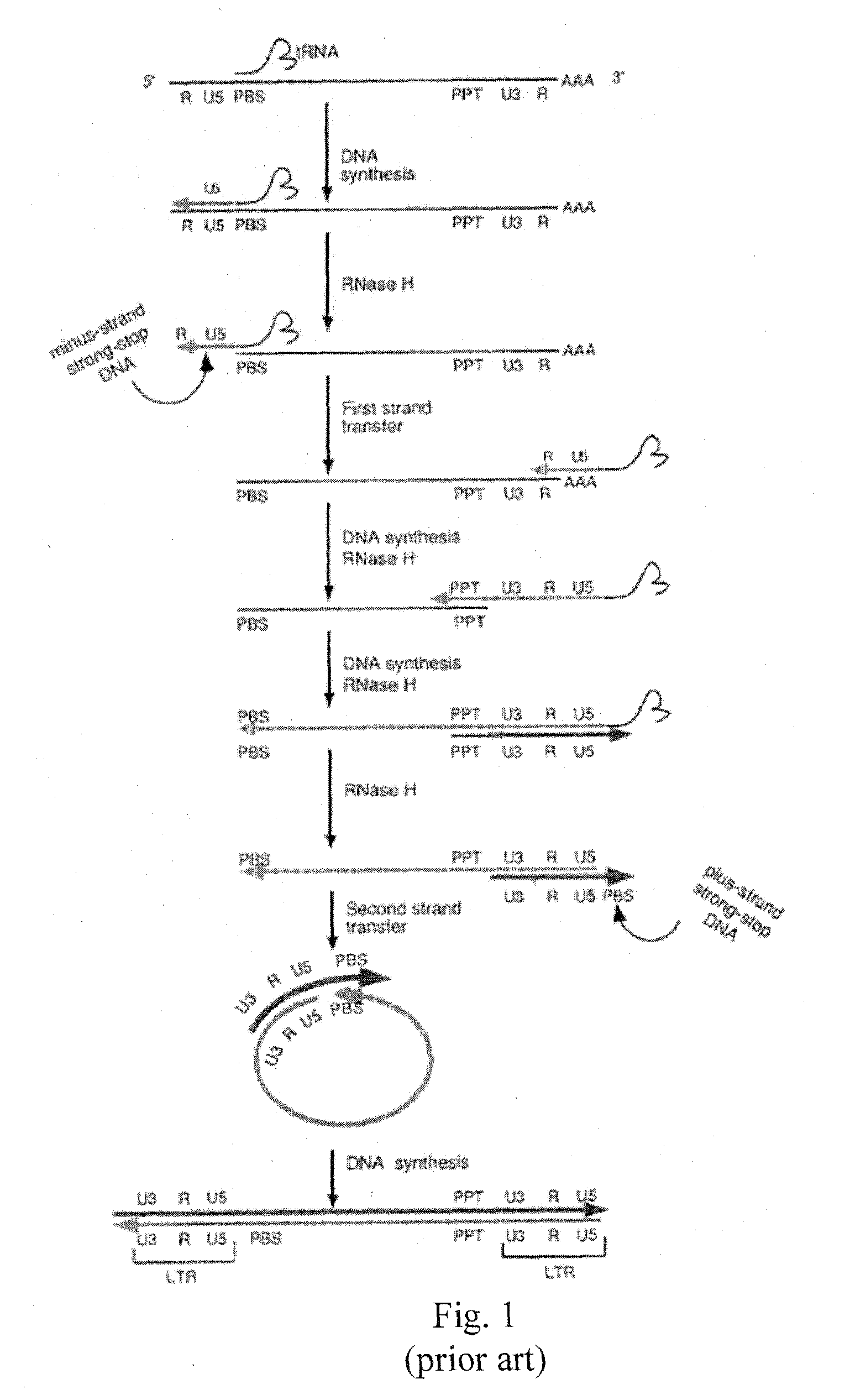
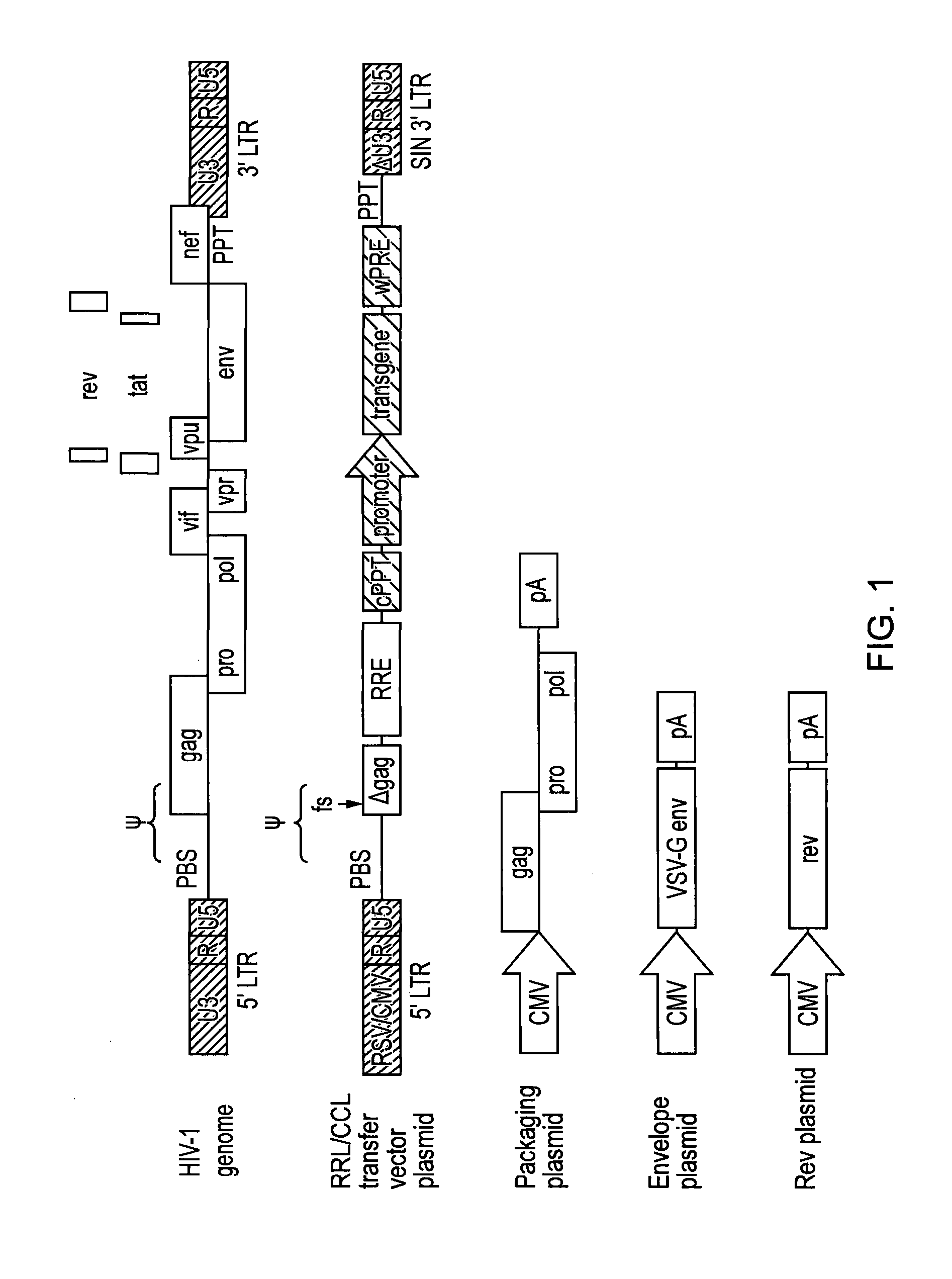
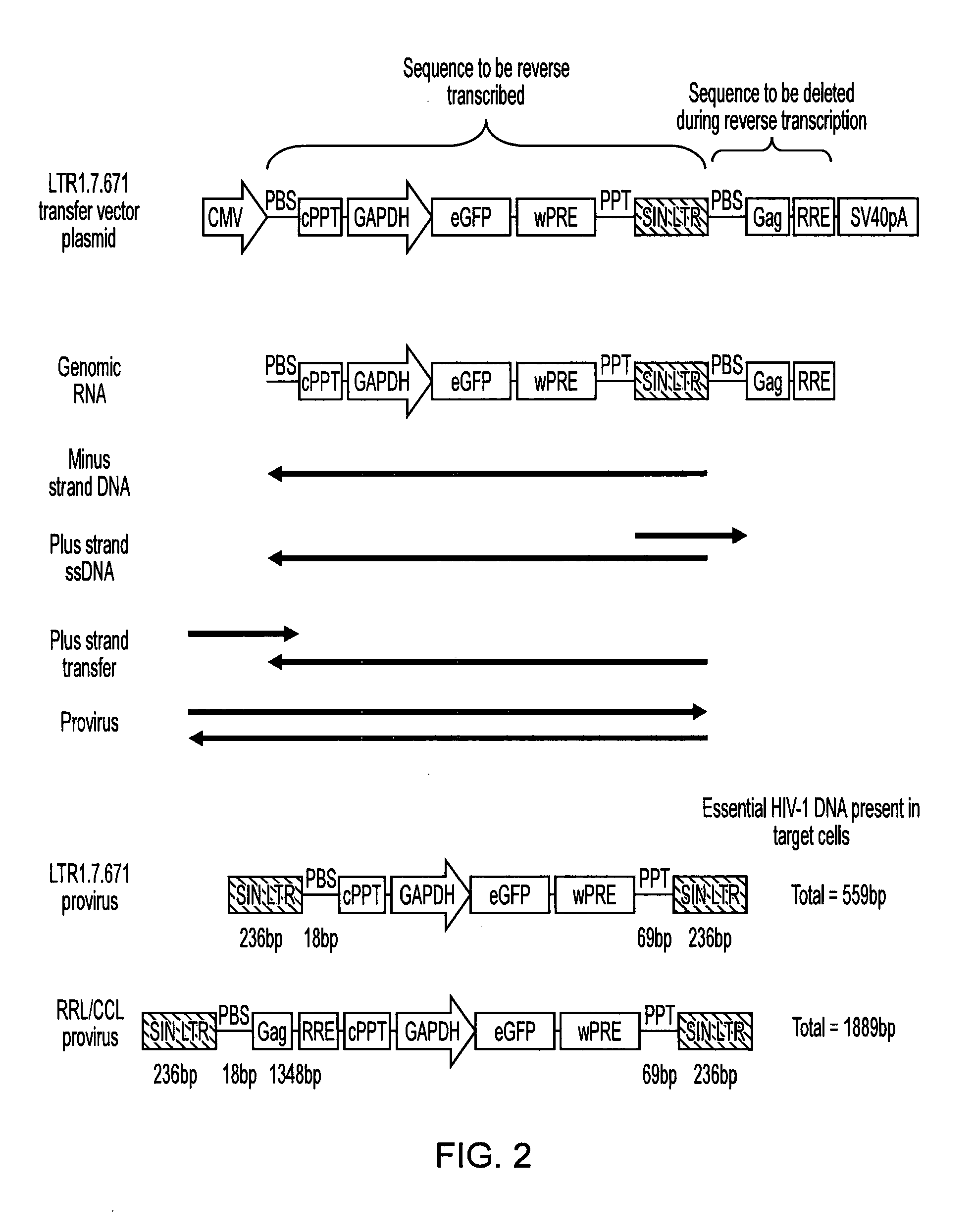
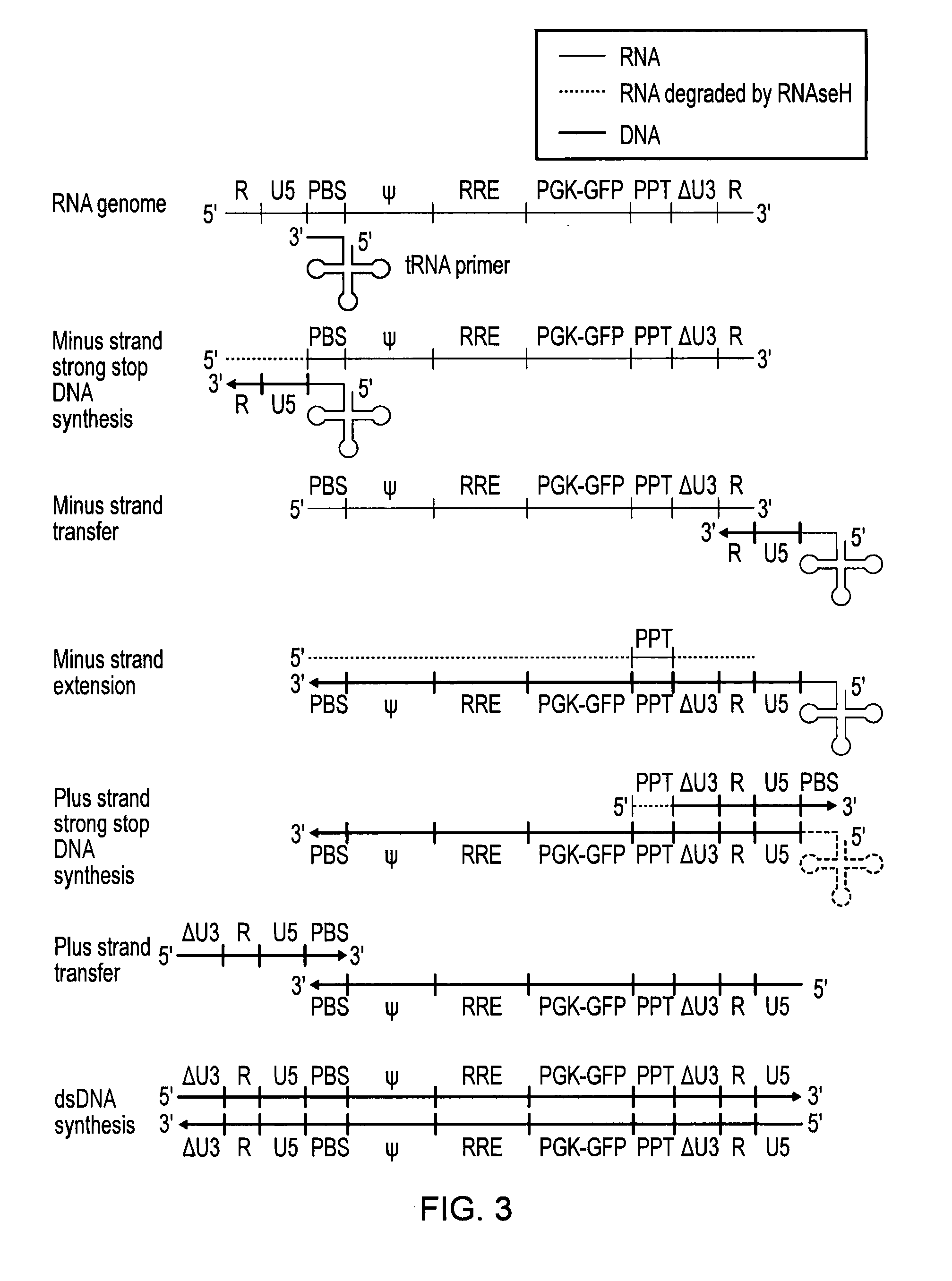
Long terminal repeats (LTRs) are identical sequences of DNA that repeat hundreds or thousands of times found at either end of retrotransposons or proviral DNA formed by reverse transcription of retroviral RNA. They are used by viruses to insert their genetic material into the host genomes.
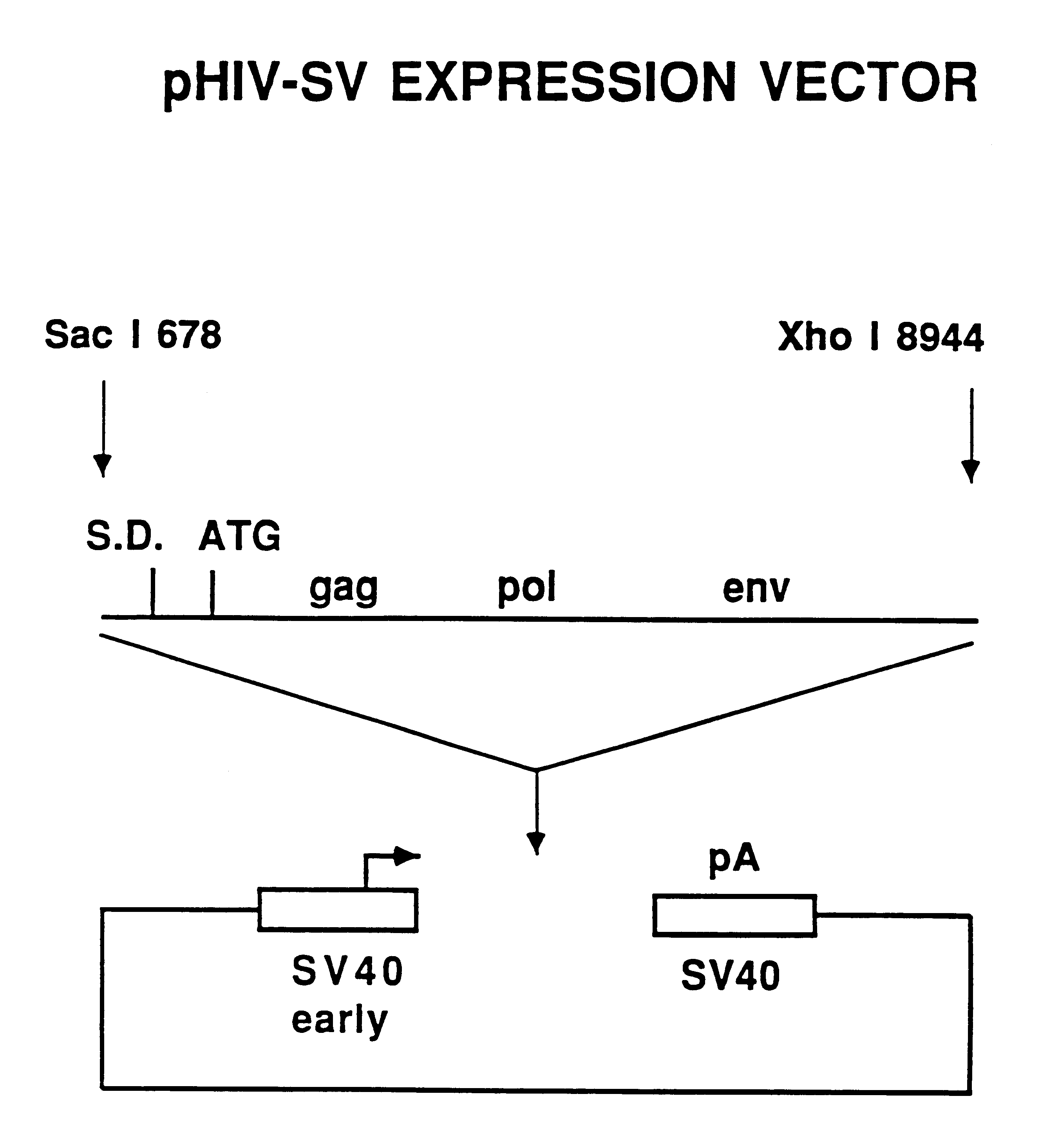
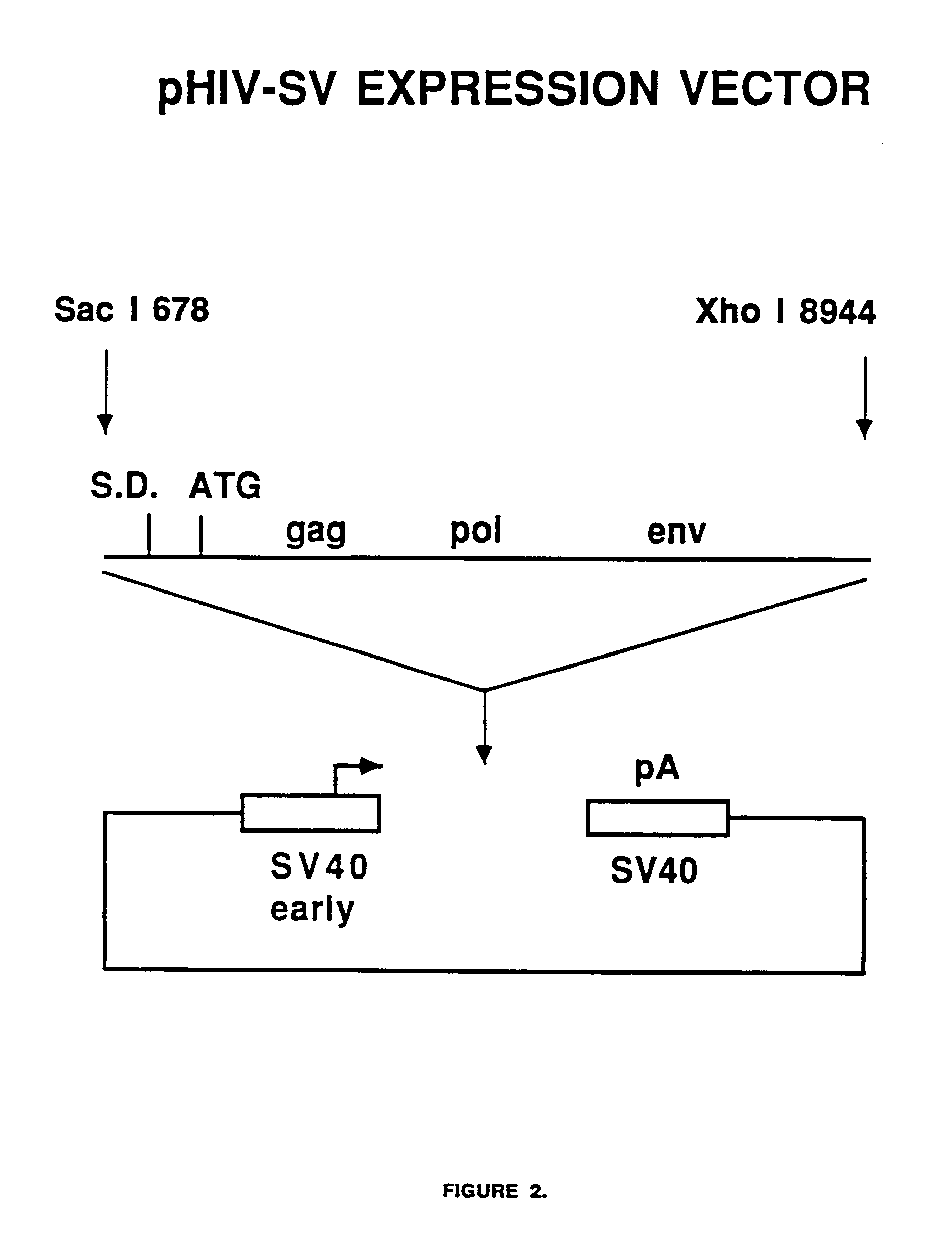
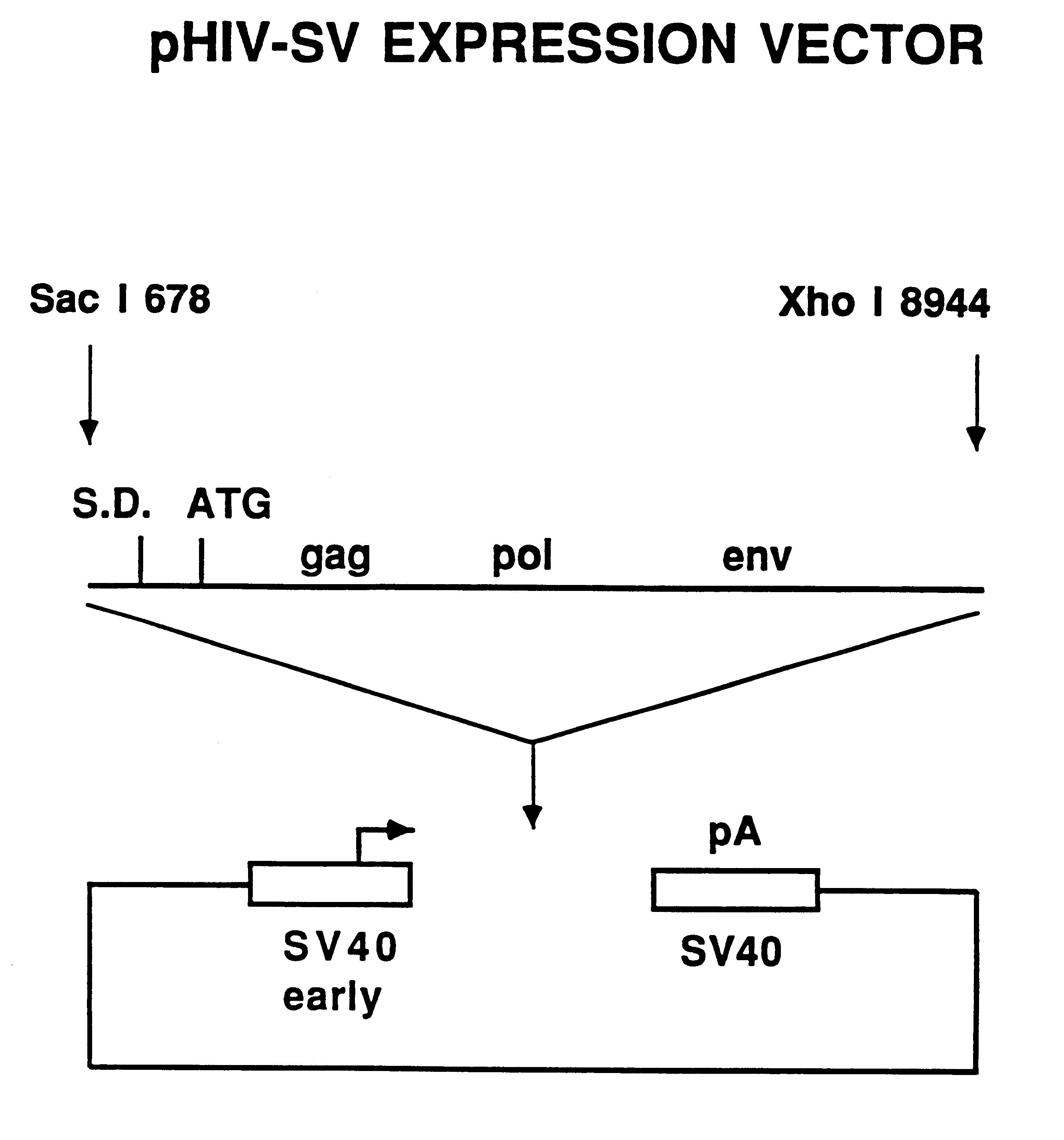
Human immunodeficiency virus type 1 nucleic acids devoid of long terminal repeats capable of encoding for non-infectious, immunogenic, retrovirus-like particles
InactiveUS6080408AImprove efficiencyLow backgroundSugar derivativesViral antigen ingredientsPol genesReverse transcriptase activity
Non-infectious, retrovirus-like particles contain mutations to reduce gag-dependent RNA-packaging of the gag gene product, eliminate reverse transcriptase activity of the pol gene product, eliminate integrase activity of the pol gene product and eliminate RNase H activity of the pol gene product through genetic manipulation of the gag and pol genes. The corresponding nucleic acid molecules are described. The non-infectious, retrovirus-like particles have utility in diagnosis.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
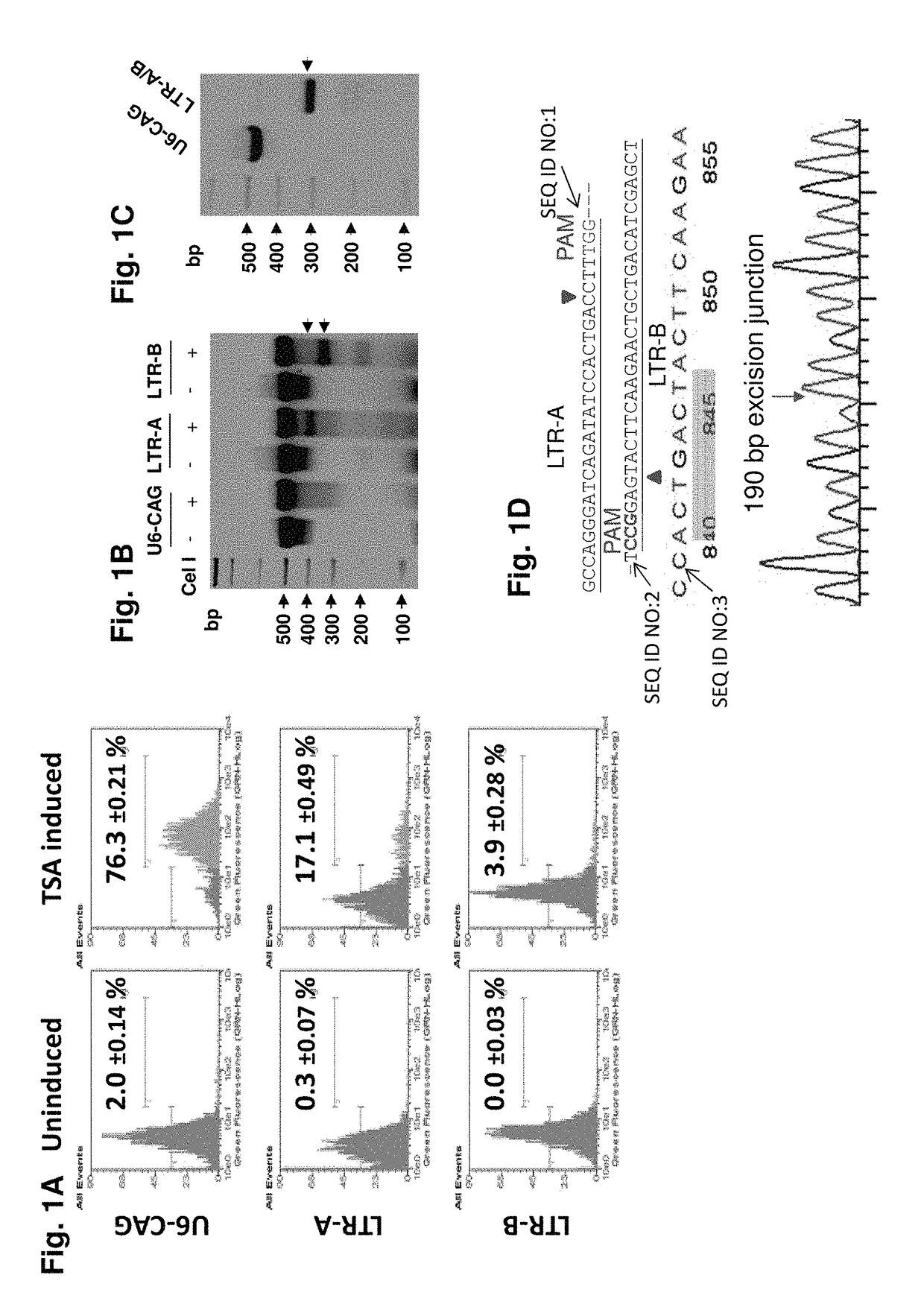
Methods and compositions for rna-guided treatment of HIV infection
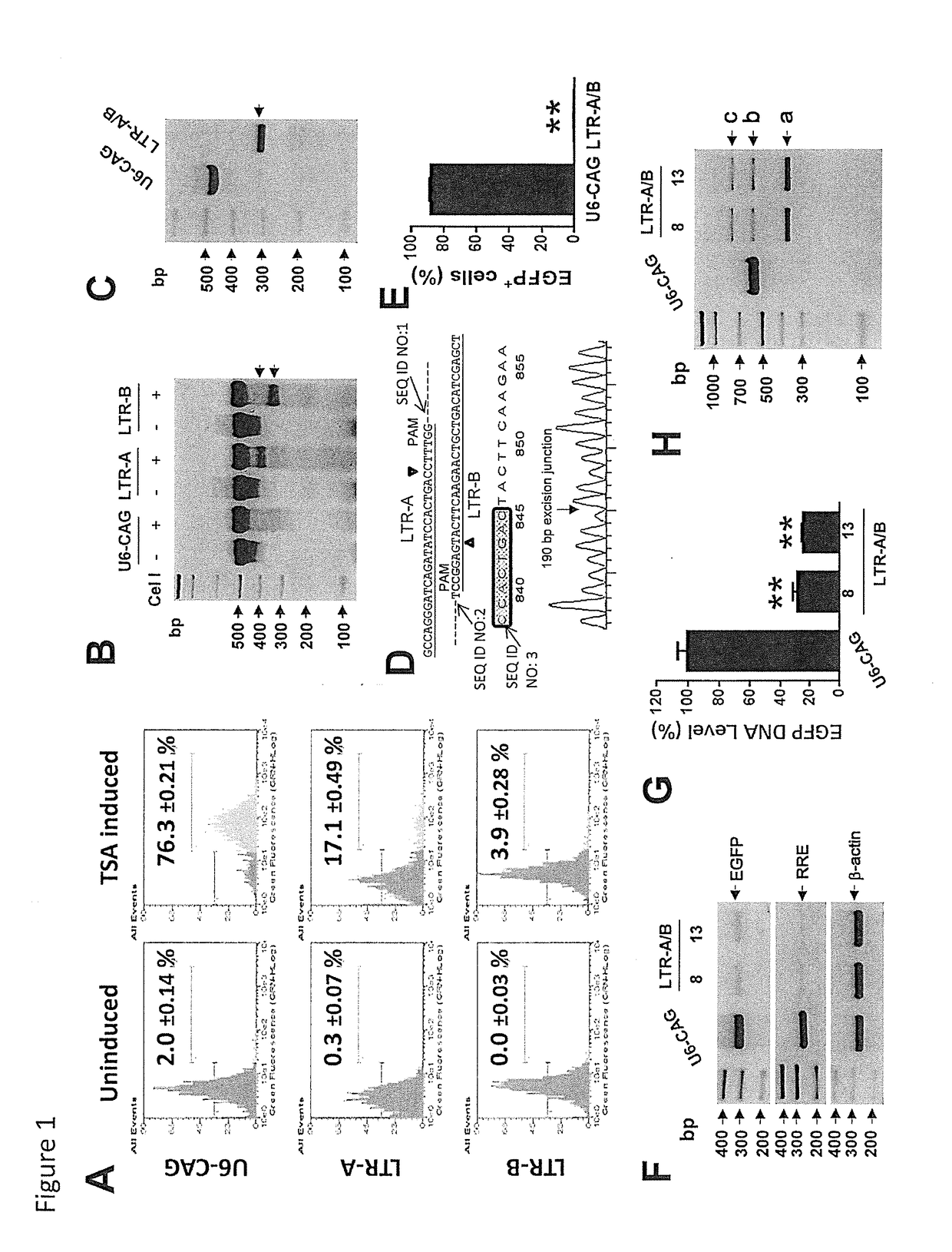
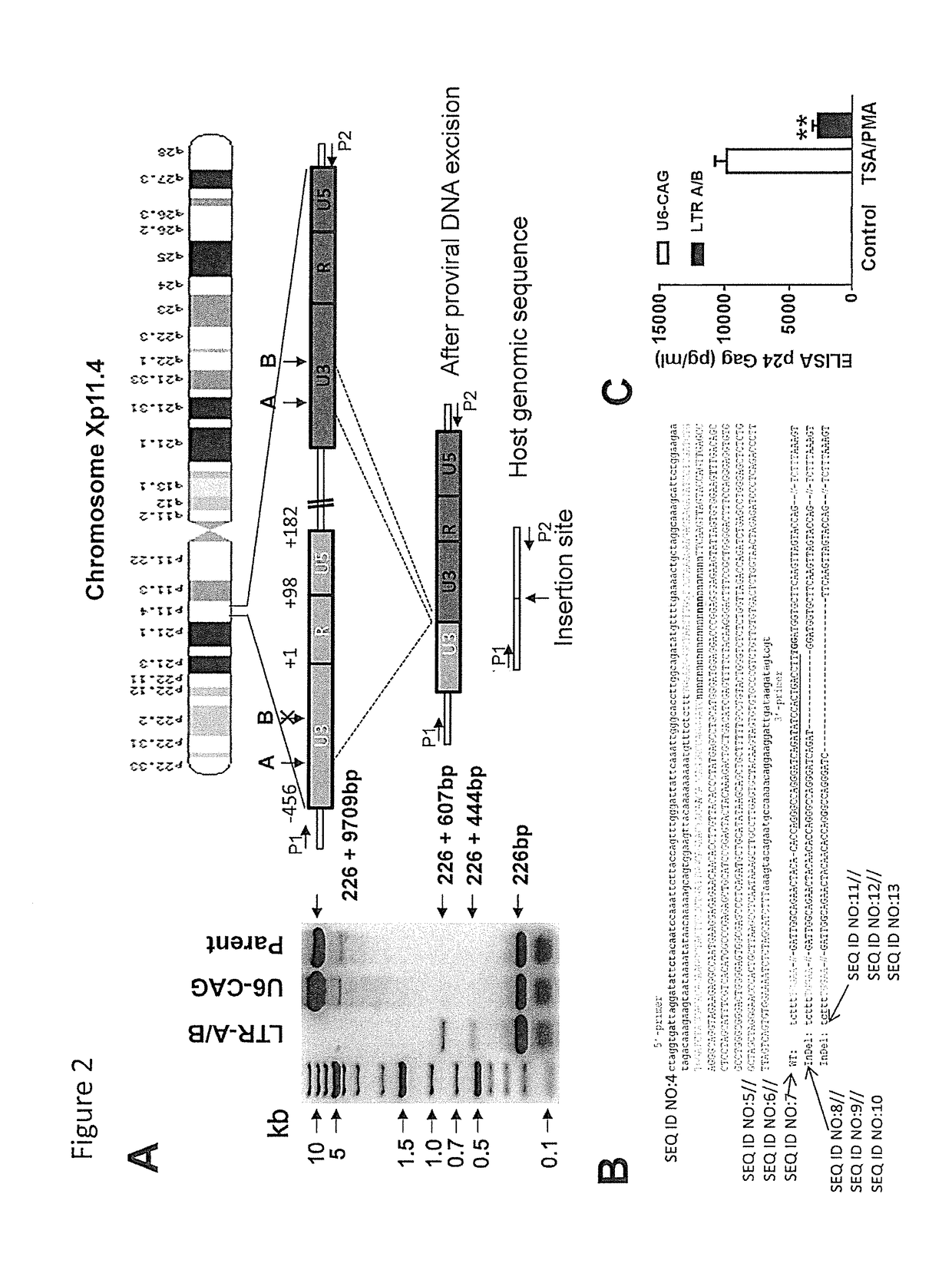
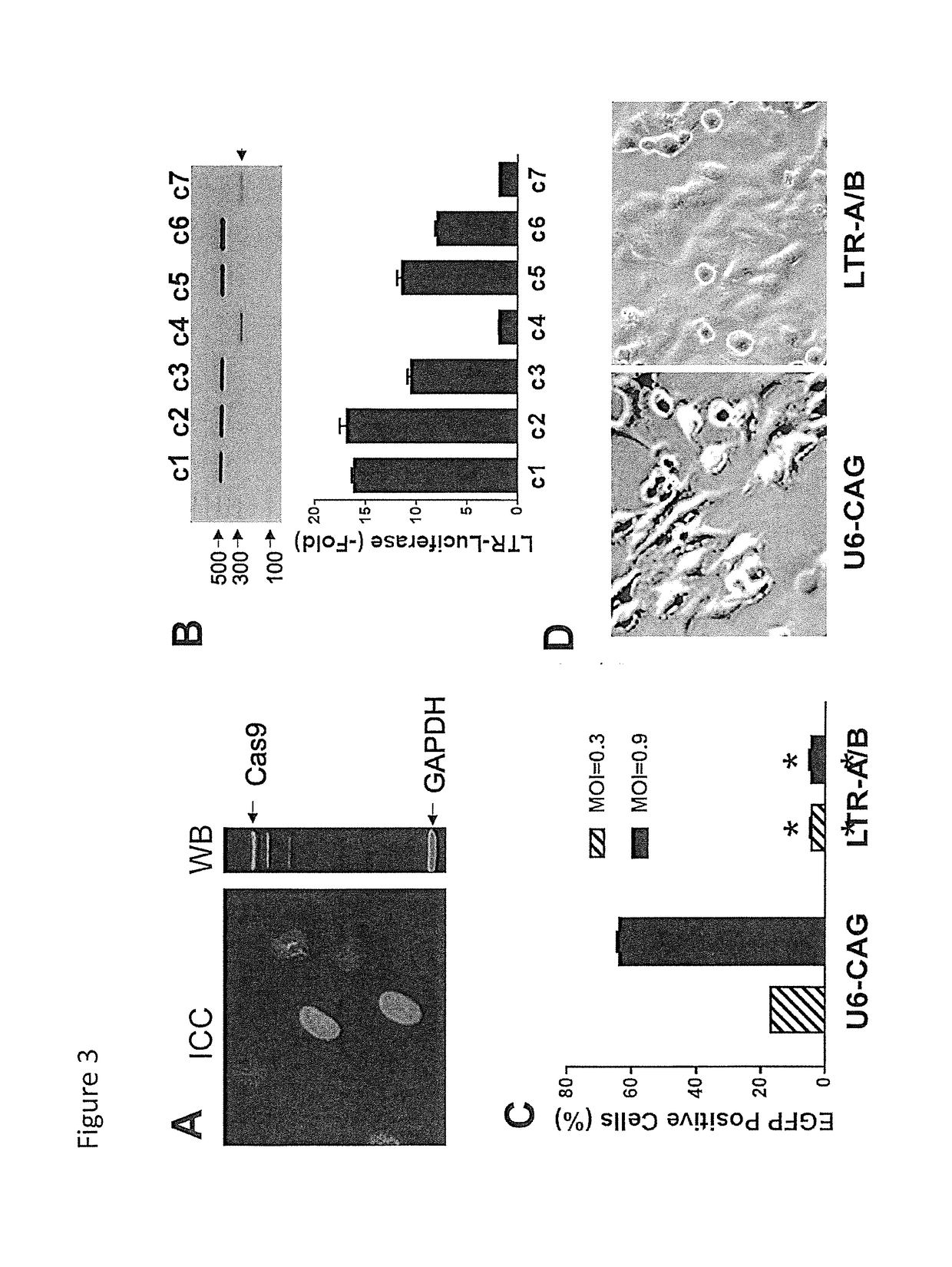
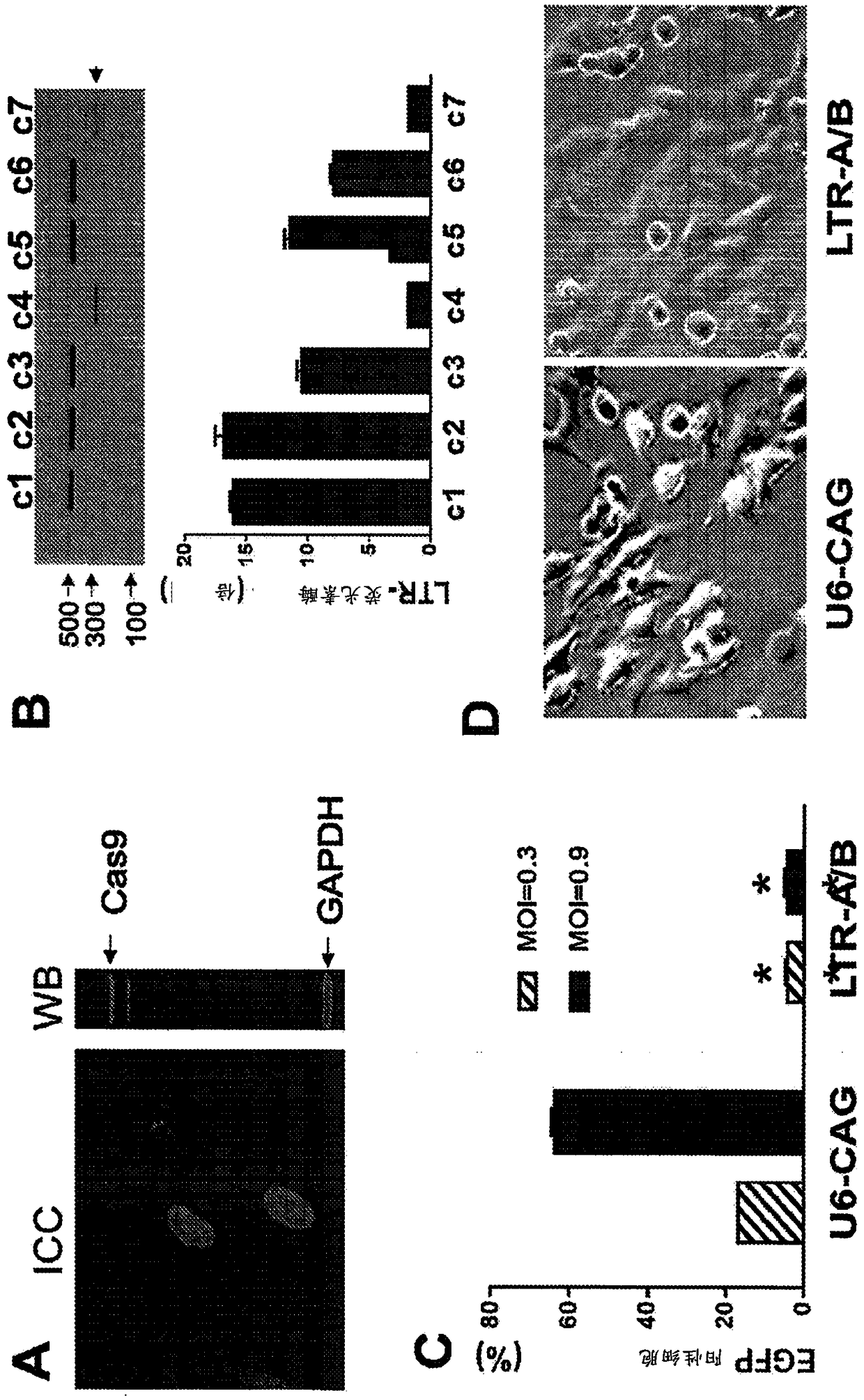
A method of inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus by treating the host cell with a composition comprising a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)-associated endonuclease, and two or more different guide RNAs (gRNAs), wherein each of the at least two gRNAs is complementary to a different target nucleic acid sequence in a long terminal repeat (LTR) in the proviral DNA, and inactivating the proviral DNA. A composition for use in inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus including isolated nucleic acid sequences comprising a CRISPR-associated endonuclease and a guide RNA, wherein the guide RNA is complementary to a target sequence in a human immunodeficiency virus.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
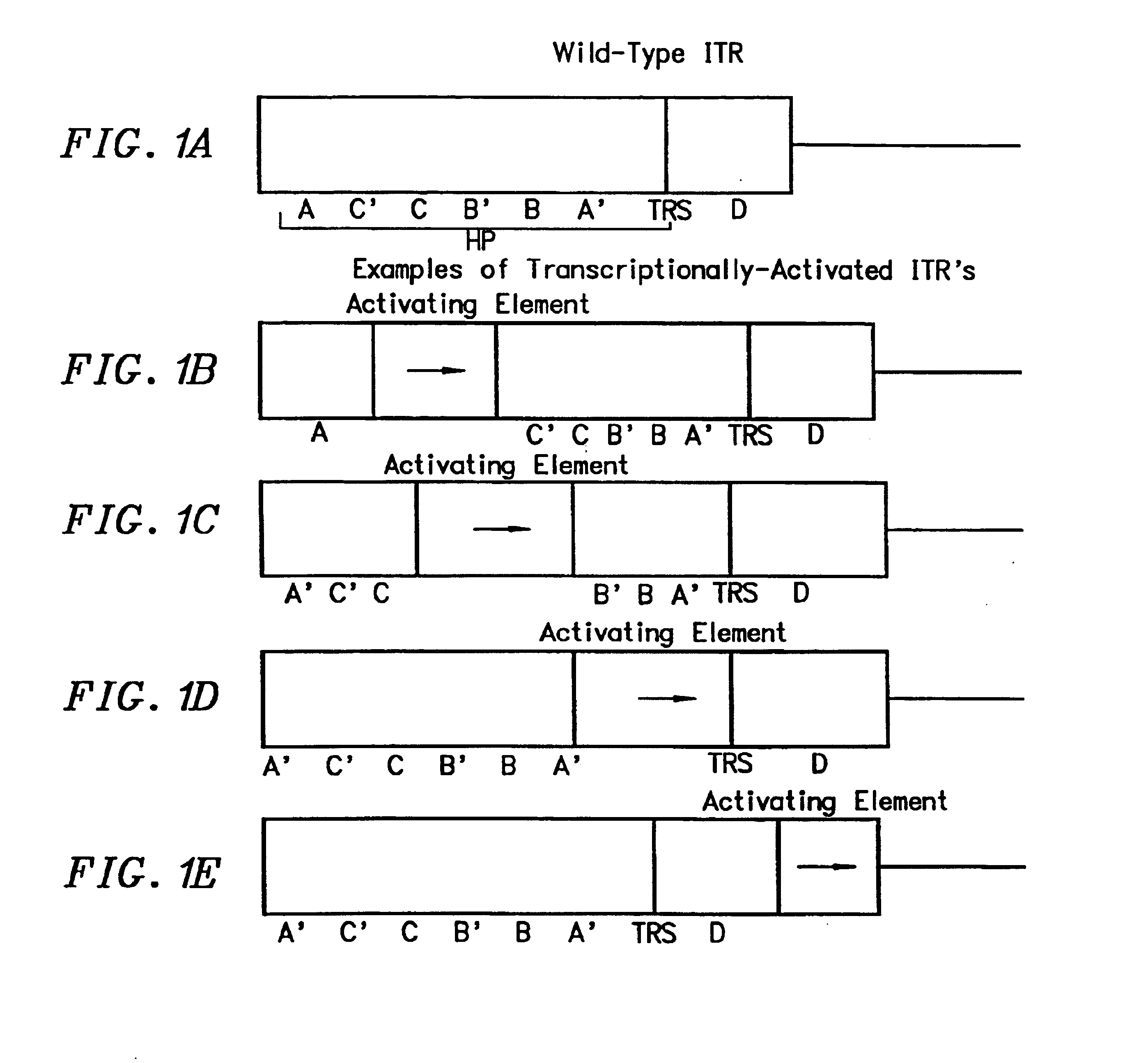
Restrictive inverted terminal repeats for viral vectors
This invention relates to modified parvovirus inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) that do not functionally interact with wild-type large Rep proteins, synthetic Rep proteins that functionally interact with the modified ITRs, and methods of using the same for delivery of nucleic acids to a cell or a subject. The modifications provide a novel Rep-ITR interaction that limits vector mobilization, increasing the safety of viral vectors.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
AAV vectors
InactiveUS6521225B1Prevent and limit expressionPrevents terminal glycosylation and translationBiocideOrganic active ingredientsLong terminal repeatNucleotide
The present invention is directed to a recombinant adenovirus vector comprising two inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) each of which comprises a D-sequence having (i) from 5 to 15 native nucleotides and (ii) one or more deletions or substitutions therein.
Owner:ADVANCED RES TECH INST +1
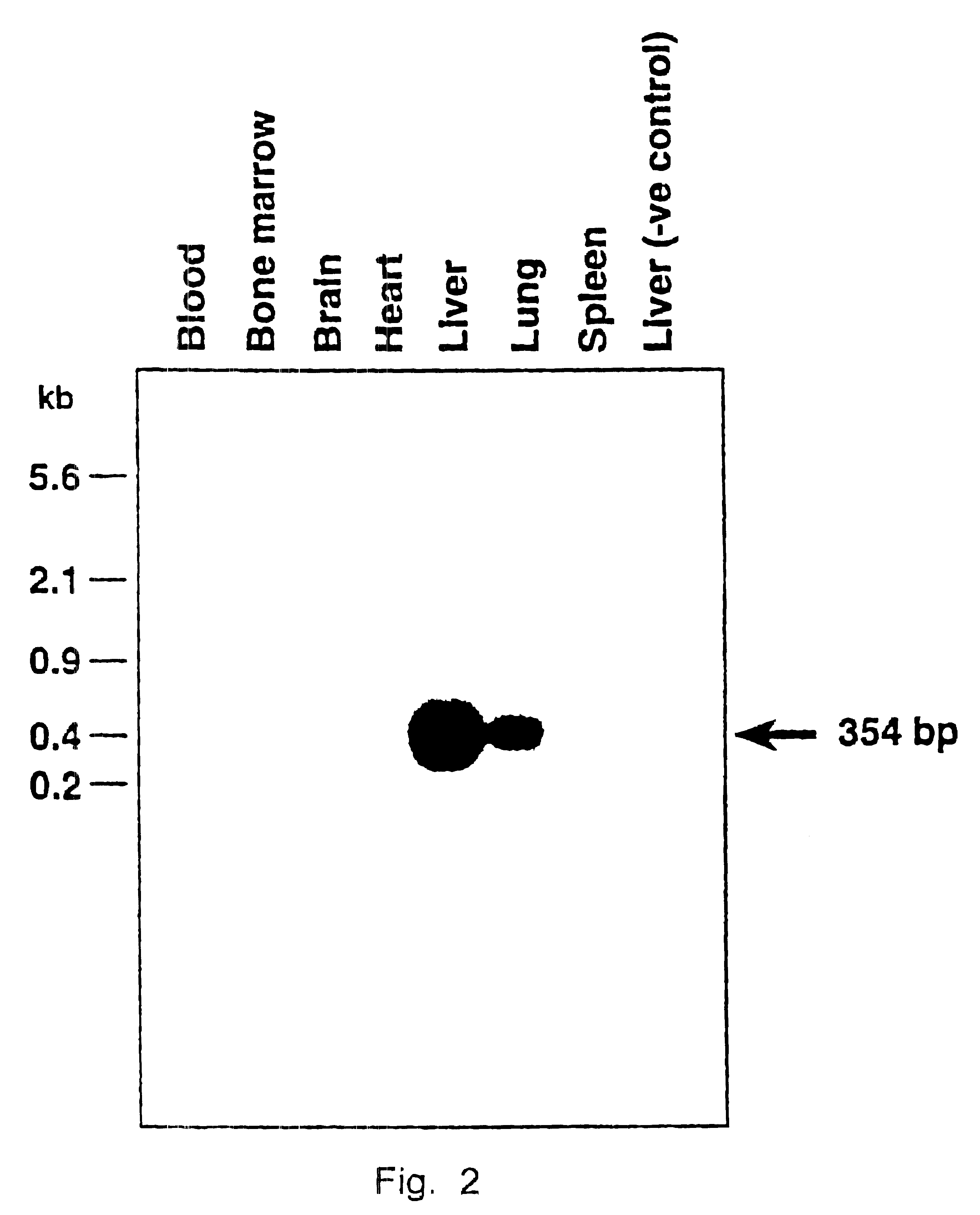
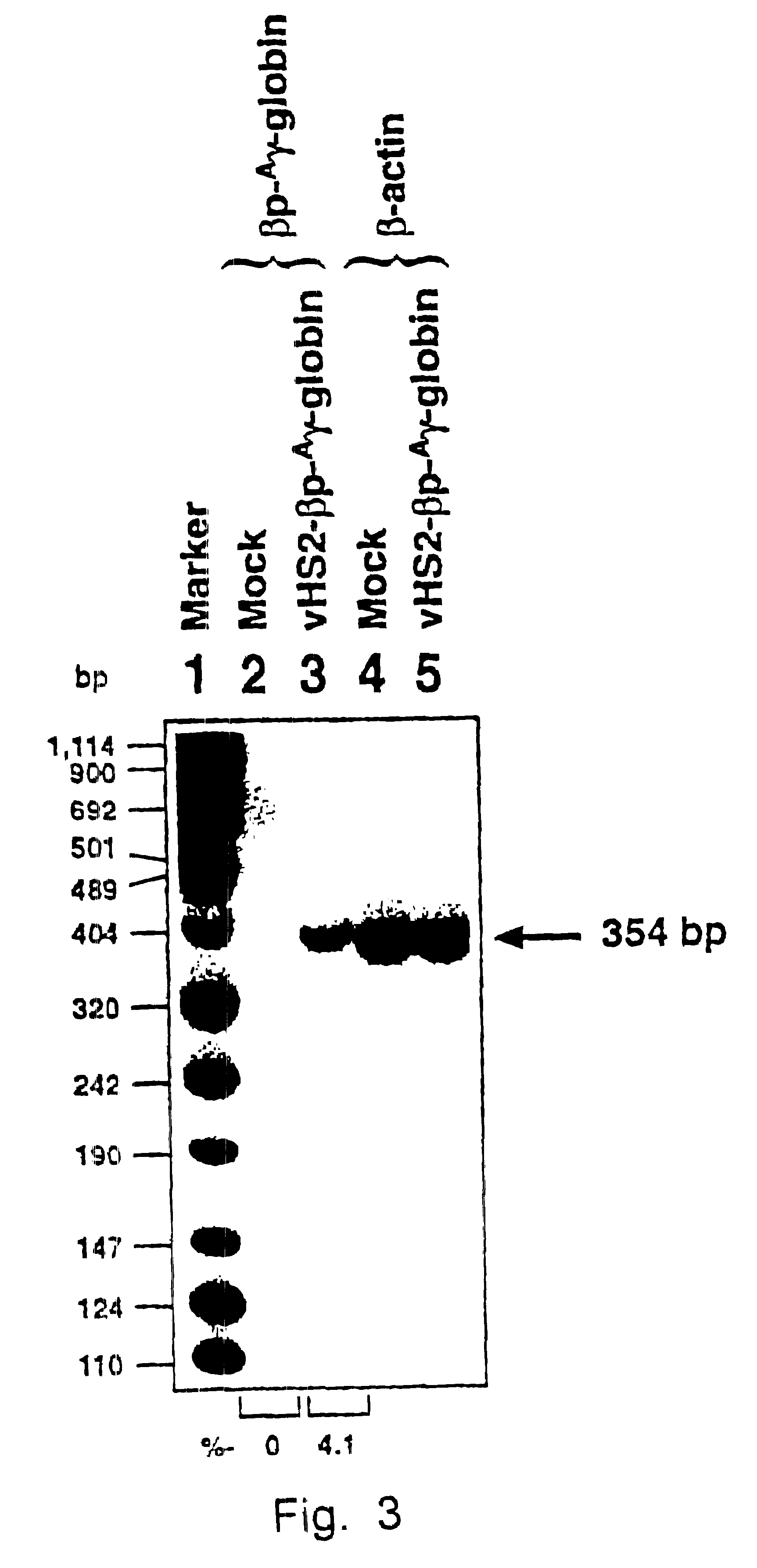
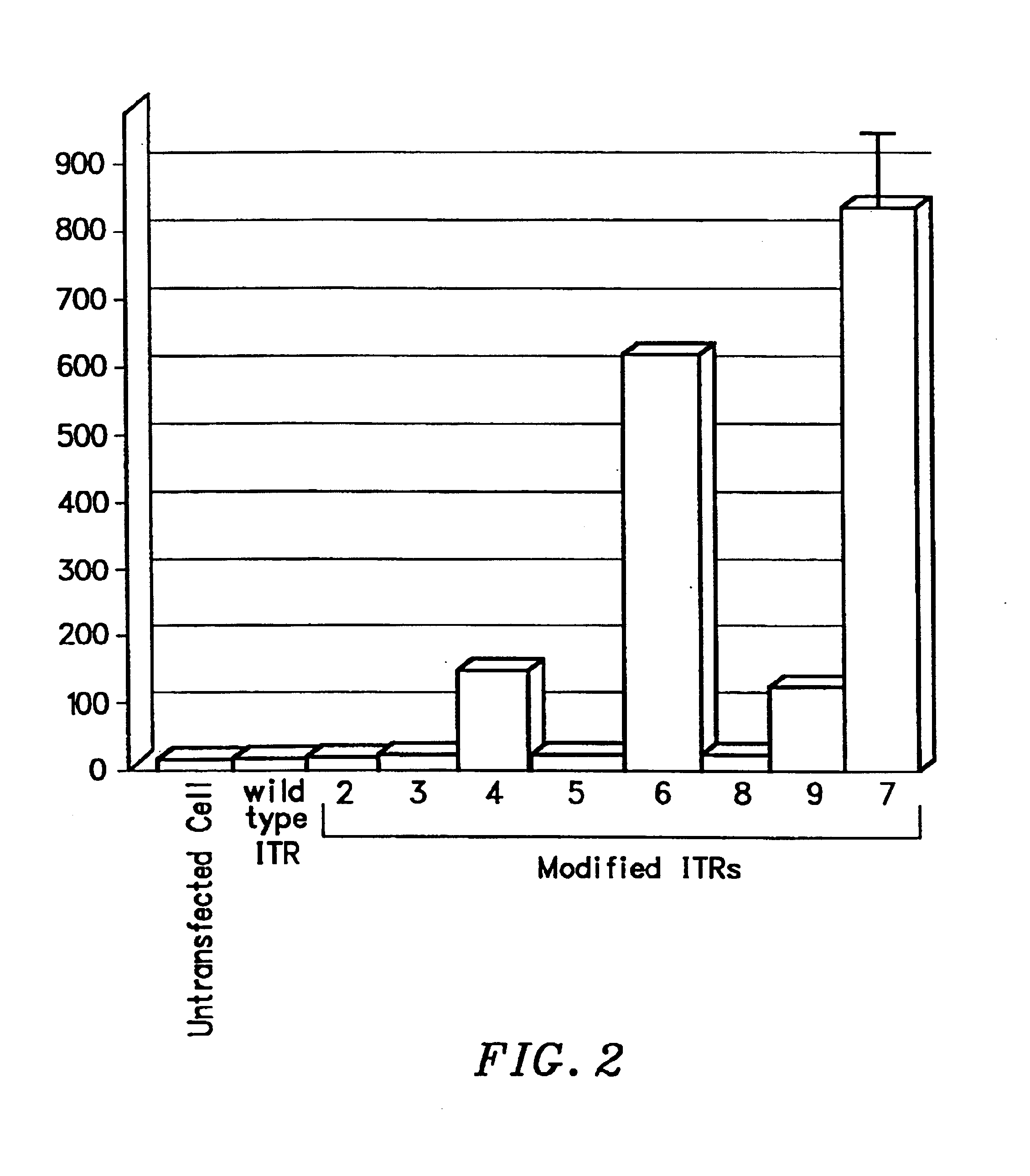
Transcriptionally-activated AAV inverted terminal repeats (ITRs) for use with recombinant AAV vectors
InactiveUS6936466B2Increase transcriptional activityGenetic material ingredientsFermentationLong terminal repeatGenetics
This invention provides transcriptionally-activated AAV ITRs (inverted terminal repeats) which are small and transcriptionally active and uses thereof to optimize the expression of relatively large transgenes packaged in recombinant AAV vectors.
Owner:TARGETED GENETICS CORPORTION
Constitutive expression of non-infectious HIV-like particles
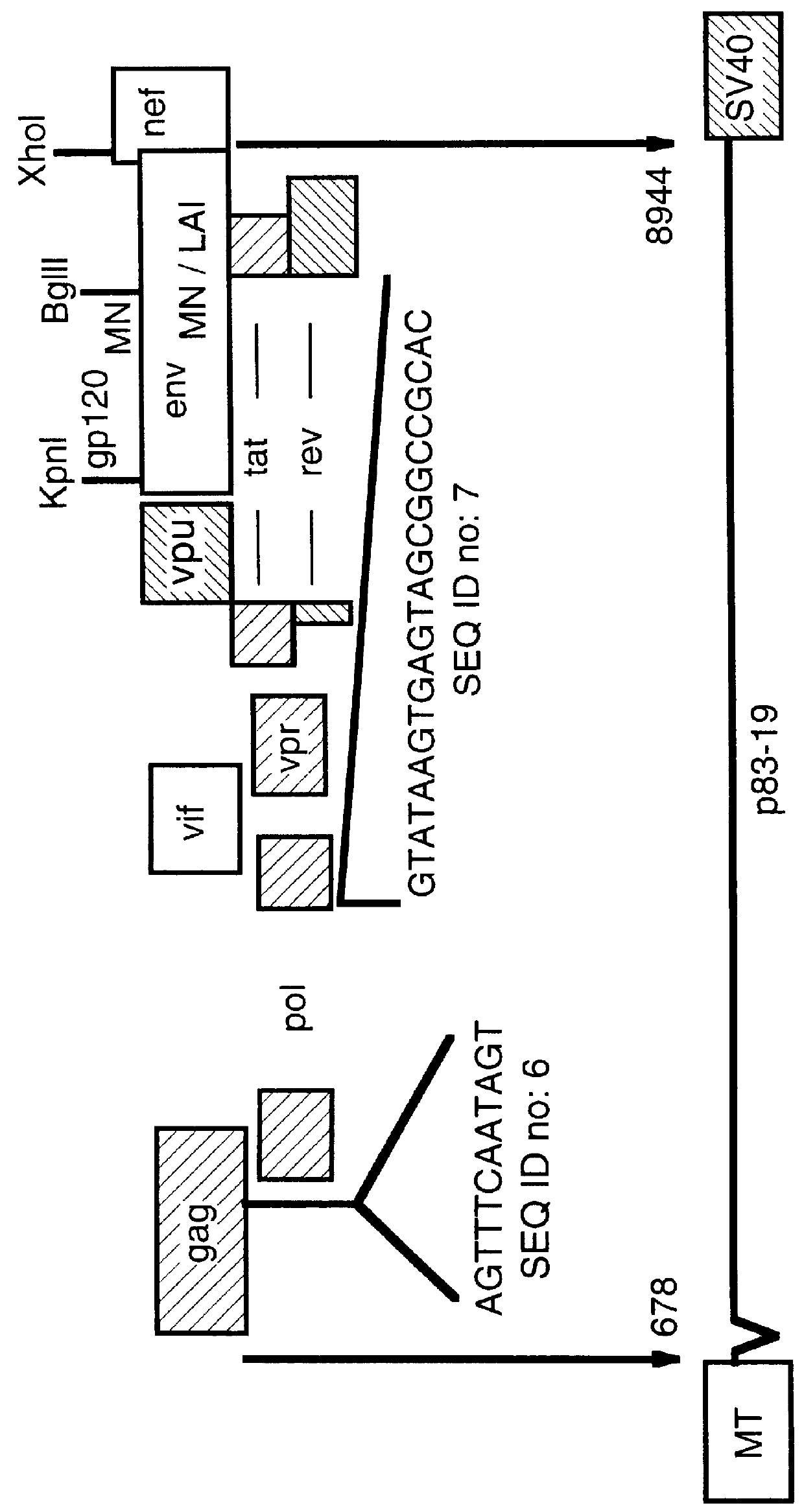
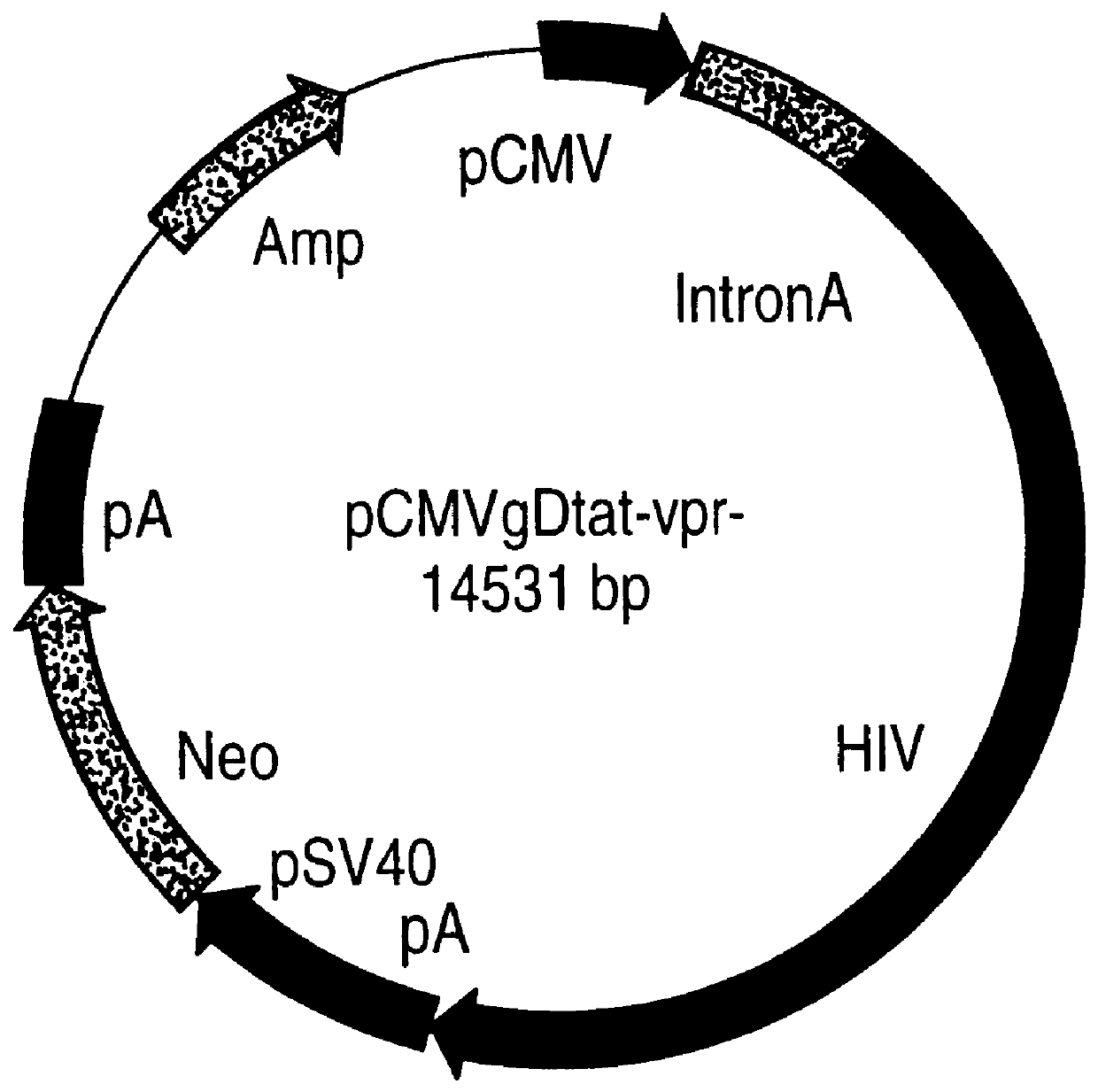
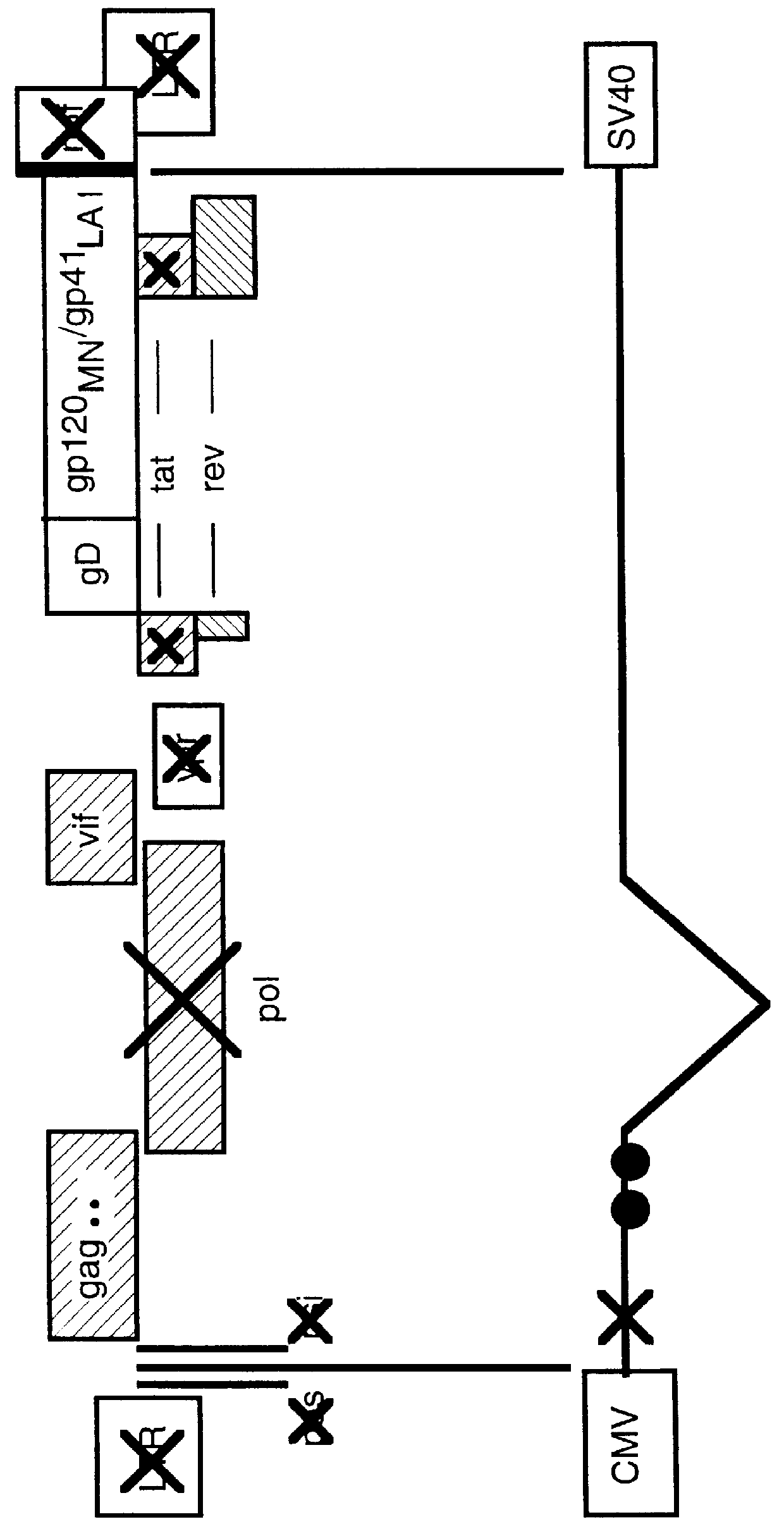
Non-infectious, non-replicating immunogenic HIV-like particles are produced by stable longn-term constitutive expression in mammalian cells by eliminating elements toxic to the mammalian cells. An expression vector contains a nucleic acid molecule comprising a modified HIV genome devoid of long terminal repeats and wherein Tat and vpr sequences are functionally disabled and a constitutive promoter operatively connected to the modified HIV genome for constitutive expression of the modified genome to produce the HIV-like particles.
Owner:CONNAUGHT LAB
Schistosome infectious oncomelania detection kit and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101457258ASuitable for useSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceOncomelaniaBiology
A blood fluke infectious oncomelania detection kit and a detection method thereof belongs to the verminosis transmission medium detecting field. The invention provides a kit and a detection method for detecting blood fluke infectious oncomelania based on a loop-mediated isothermal DNA amplification technology (LAMP). According to the LAMP technology principle, six pairs of specific primers for amplifying a DNA fragment between the 20bp and 231bp of the schistosoma japonicum non-long terminal repeated inverse transcription transposon gene (AF412214) are designed. The LAMP method is constructed for detecting blood fluke gene in the body of the infectious oncomelania and the objective for distinguishing the blood fluke infectious oncomelania from the non-infectious oncomelania is reached. Comparing to the conventional blood fluke infectious oncomelania detection method the method of the invention has advantages of easy and fast operation, sensitive and specific without especial equipment and is suitable for bilharziasis controlling personnel use on site.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF PARASITIC DISEASES
Non-infectious, non-replicating, immunogenic human immunodeficiency virus-like particles
InactiveUS7008784B1Improving immunogenicitySafe preparationNanotechVirus peptidesHeterologousPol genes
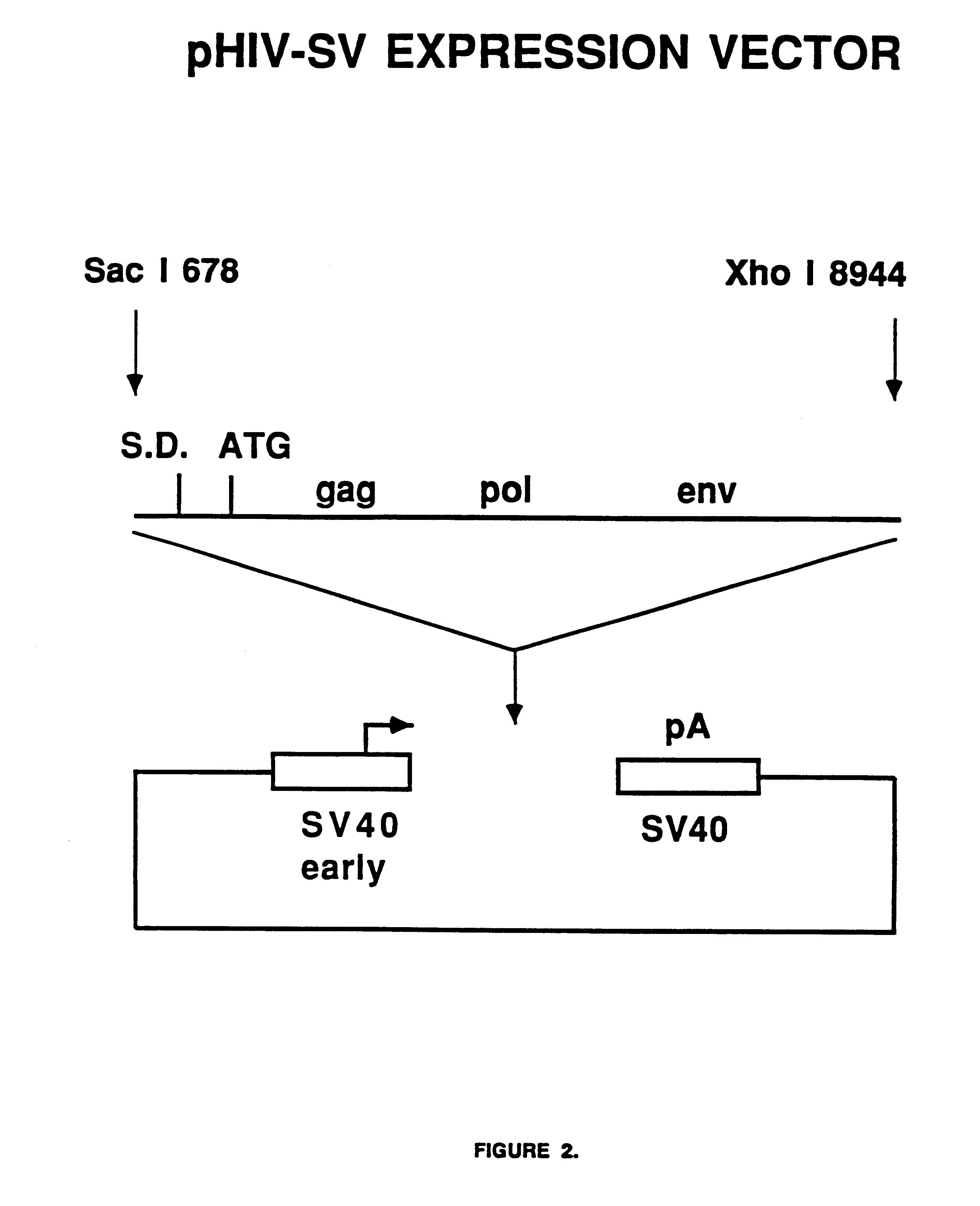
The present invention is directed toward methods for the production of non-infectious, replication-deficient, immunogenic human immunodeficiency virus (HIV)-like particles. These particles are prepared from a recombinant expression vector comprising a heterologous promoter operatively connected to a DNA molecule comprising a modified HIV genome devoid of the long terminal repeat (LTR) regulatory regions but containing at least the gag and pol genes in their natural genomic arrangement. This vector is introduced into mammalian cells to produce the particles of interest. These particles should prove useful in a number of diagnostic, virologic, and immunologic applications.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTEUR LTD
Methods and compositions for RNA-guided treatment of HIV infection
A method of inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus by treating the host cell with a composition comprising a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)-associated endonuclease, and two or more different guide RNAs (gRNAs), wherein each of the at least two gRNAs is complementary to a different target nucleic acid sequence in a long terminal repeat (LTR) in the proviral DNA, and inactivating the proviral DNA. A composition for use in inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus including isolated nucleic acid sequences comprising a CRISPR-associated endonuclease and a guide RNA, wherein the guide RNA is complementary to a target sequence in a human immunodeficiency virus.
Owner:TEMPLE UNIVERSITY
Method for separating long terminal repeats of retrotransposons
InactiveCN102140450AStrong specificityReduce generationMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationLong terminal repeatGenomic clone
The invention discloses a method for separating long terminal repeats of retrotransposons. Genome DNA is taken as a template, an RNaseH1 primer is respectively combined with different annealing control primers for first polymerase chain reaction (PCR) reaction, the first PCR product is diluted to serve as a template, an RNaseH2 primer and a universal primer UP are subjected to secondary PCR reaction amplification, conversion and extraction of plasma DNA are performed, and a sequence is subjected to sequencing to obtain an amino acid sequence of RNaseH enzyme, and proteins are encoded. Compared with the common PCR technology, the method has the advantages that: the operation is simple, long terminal repeat regions of the retrotransposons are easily aligned, and the pertinence is high; compared with a flow type magnetic microbead inverse hybrid method, the method has the advantages of saving hybrid, eluting, screening and other processes, simplifying the flow and having high efficiency;and compared with other separation methods, the method has the advantages of reducing time consumption, quickly obtaining target segments, cloning the long terminal repeats in short time, and reducing false positive rate.
Owner:HENAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
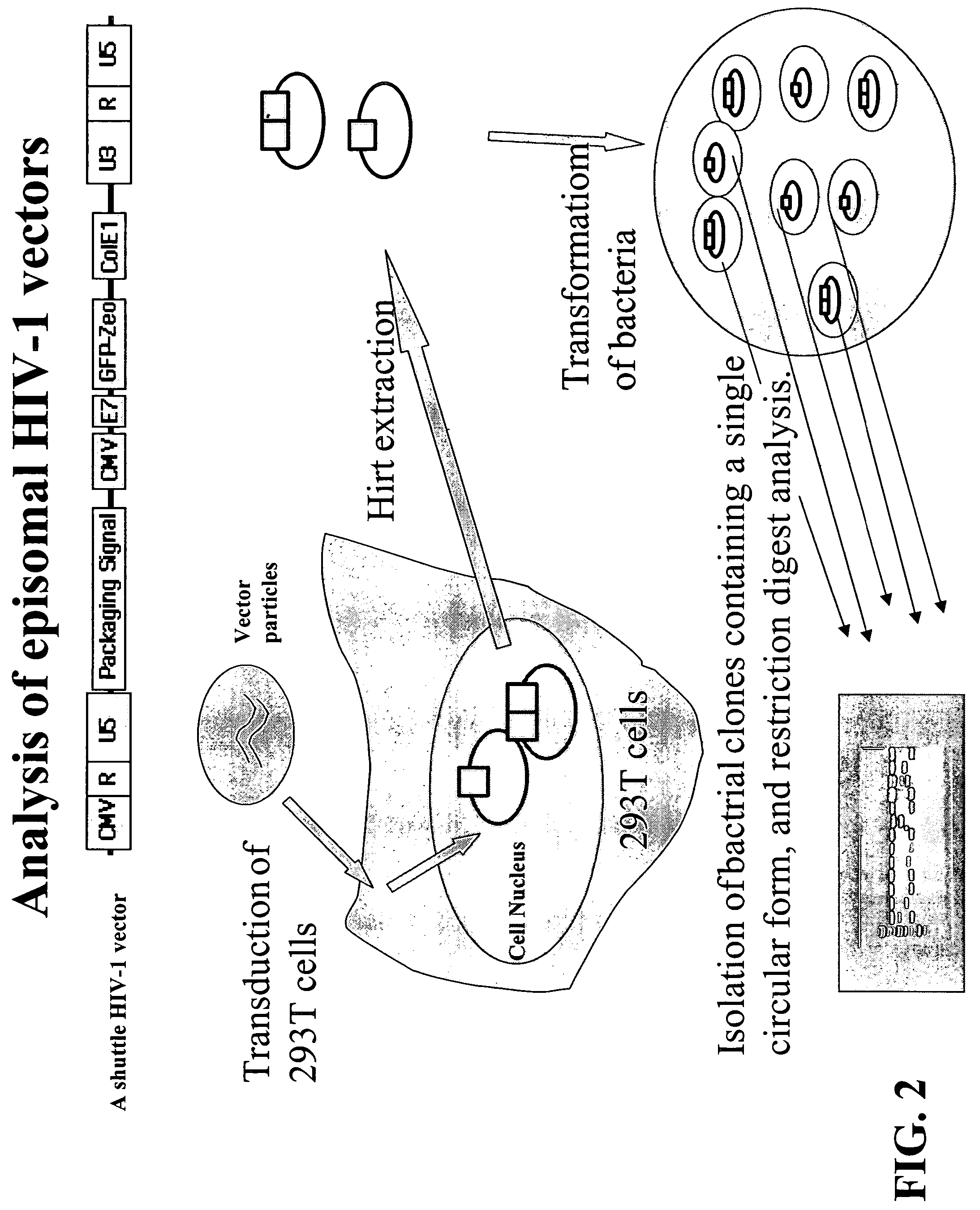
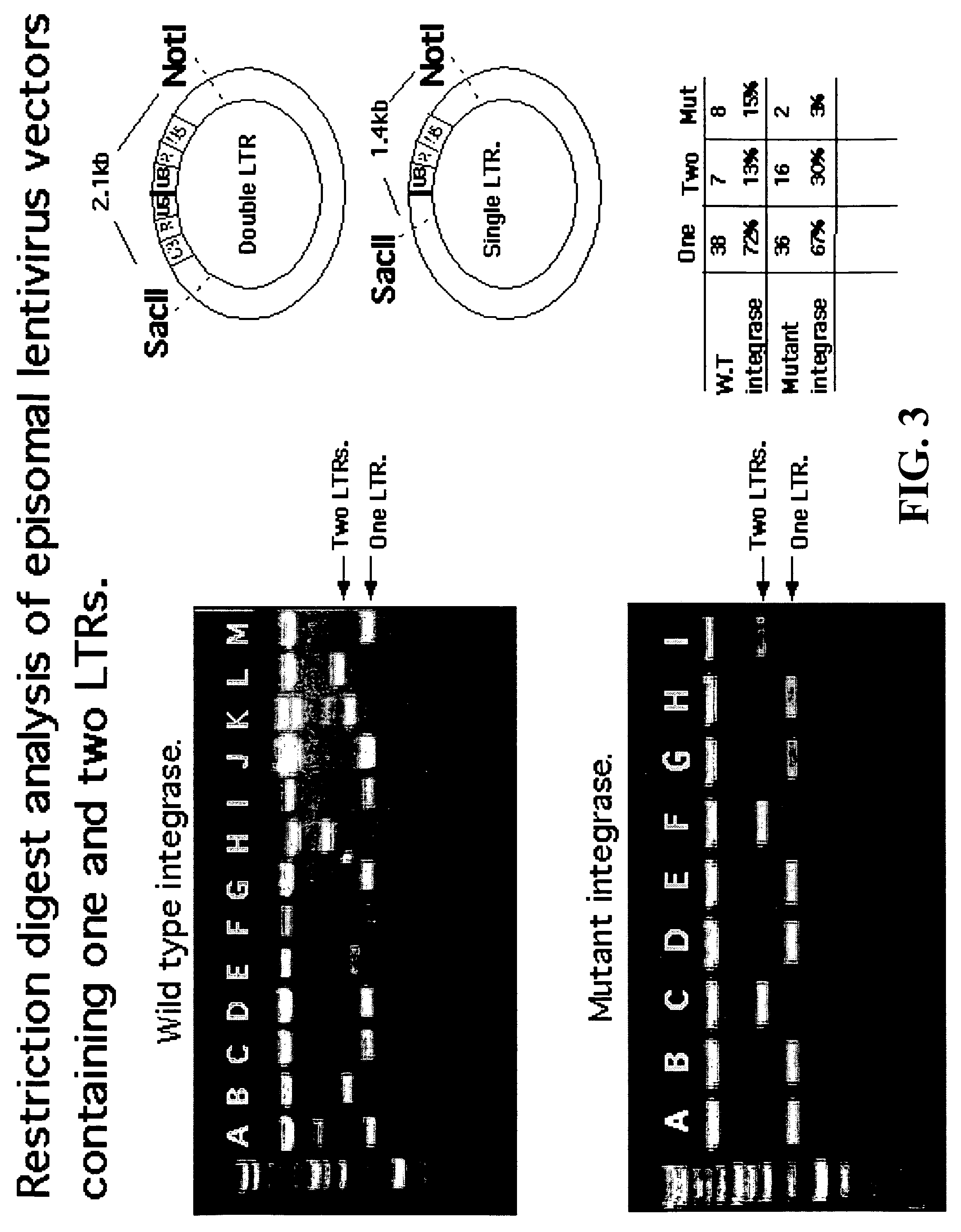
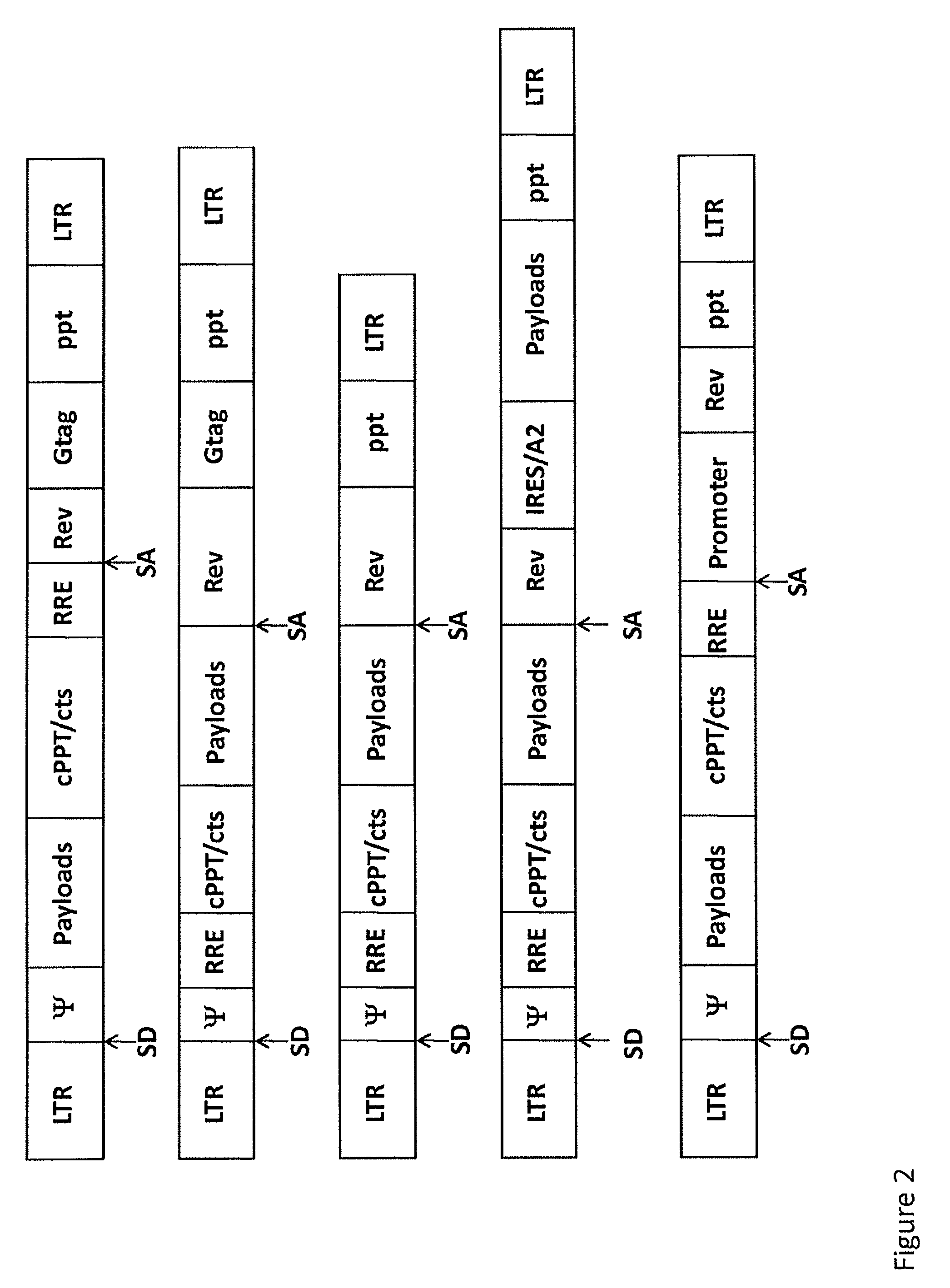
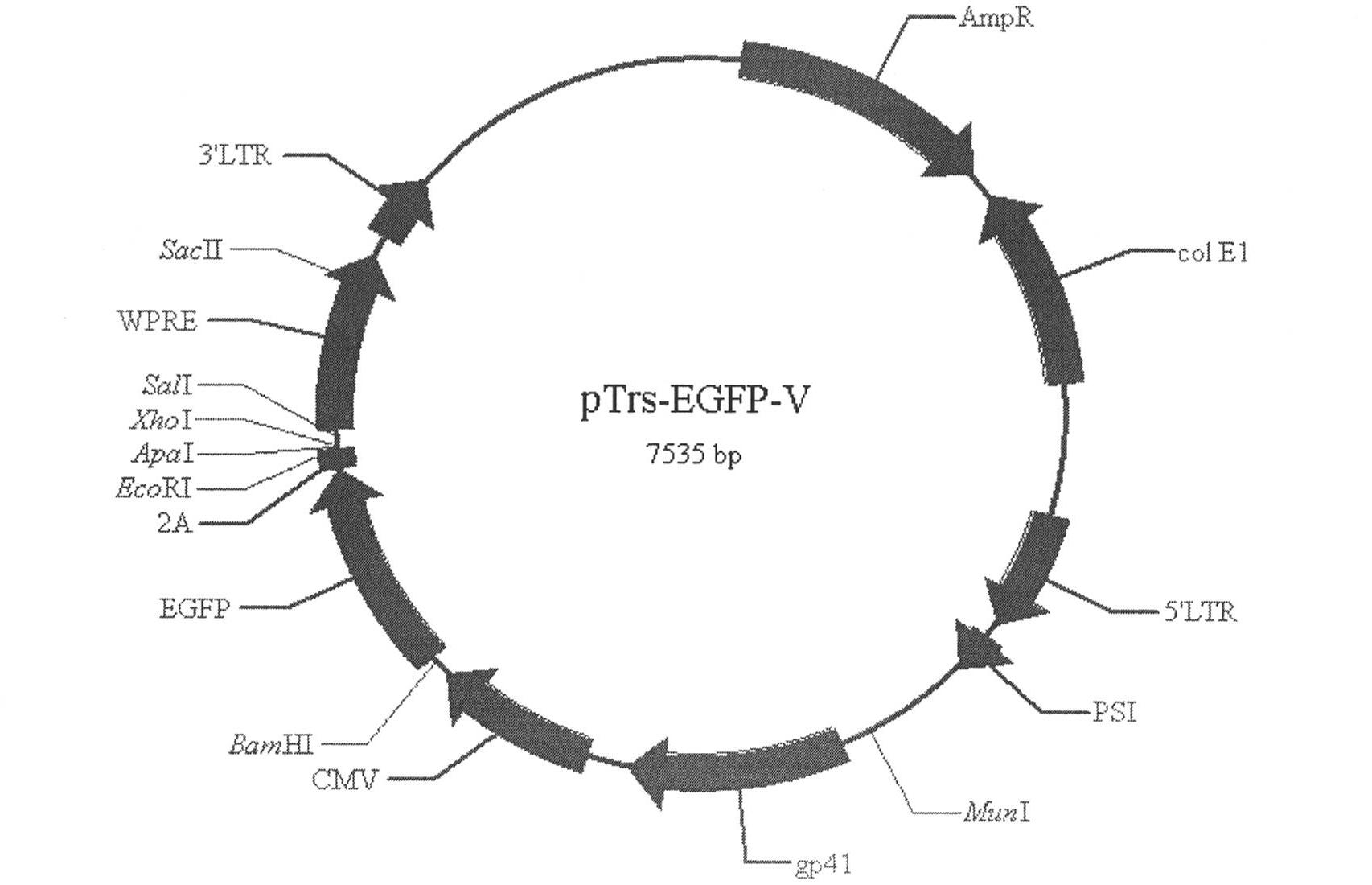
Single LTR lentivirus vector
The present invention provides an isolated nucleic acid comprising a single retroviral LTR, a polypurine tract, a packaging signal, a primer binding site and a rev responsive element. Further provided is an isolated nucleic acid comprising a heterologous nucleotide sequence, a single retroviral long terminal repeat (LTR), a packaging signal, a rev responsive element, a polypurine tract, a eukaryotic promoter, a primer binding site, a bacterial origin of replication and a bacterial selection marker. In addition, the present invention provides an isolated nucleic acid comprising a 5′ retroviral LTR and a 3′ retroviral LTR, a heterologous nucleotide sequence, a packaging signal, a rev responsive element, a polypurine tract, a eukaryotic promoter, a primer binding site, a bacterial origin of replication and a bacterial selection marker cassette, wherein the bacterial origin of replication and bacterial selection marker are located between the two LTRs.
Owner:KAFRI TAL +1
Lentivirus-based immunogenic vectors
InactiveUS20110142880A1Improving immunogenicitySsRNA viruses negative-senseOrganic active ingredientsVaccine deliveryLentivirus
The present invention provides for lentiviral vectors for vaccine delivery comprising a 5′ long terminal repeat (LTR) and a 3′ LTR, an integrated nucleic acid sequence, wherein the integrated nucleic acid sequence is expressed by the 5′ LTR; and a nucleic acid sequence encoding functional REV coding sequence and a rev response element (RRE)-containing sequence, wherein the RRE-containing sequence is located upstream of the REV coding sequence, and wherein transcription of said first nucleic acid sequence and said second nucleic acid sequence is driven by said 5′ LTR. Also provided for are pharmaceutical compositions, methods of making and using the lentiviral vectors of the present invention.
Owner:VIRXSYS
Recombinant J subgroup avian leucosis virus infective cloned plasmids and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101899465AImprove versatilityGood repeatabilityInactivation/attenuationAntiviralsLeucosisEukaryotic plasmids
The invention discloses recombinant J subgroup avian leucosis virus infective cloned plasmids and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: replacing long terminal repetitive sequences of two ends of a provirus gene of a J subgroup avian leucosis virus with long terminal repetitive sequences of two ends of a provirus gene of an E subgroup avian leucosis virus; and inserting the long terminal repetitive sequences of the two ends of the provirus gene of the E subgroup avian leucosis virus into vectors, so that the J subgroup avian leucosis virus infective cloned plasmids are constructed, and the obtained sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The replication capacity and the pathogenicity of recombinant virus strains obtained by transfecting the J subgroup avian leucosis virus infective cloned plasmids are obviously weaker than those of natural J subgroup avian leucosis viruses, but the recombinant virus strains can express structural proteins of the J subgroup avian leucosis viruses, have the antigenicity of the J subgroup avian leucosis viruses and can be identified by a specificity monoclonal antibody JE9 of the J subgroup avian leucosis viruses. The invention provides reference for a material and a method for preparing low-toxicity live vaccines of the J subgroup avian leucosis viruses.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
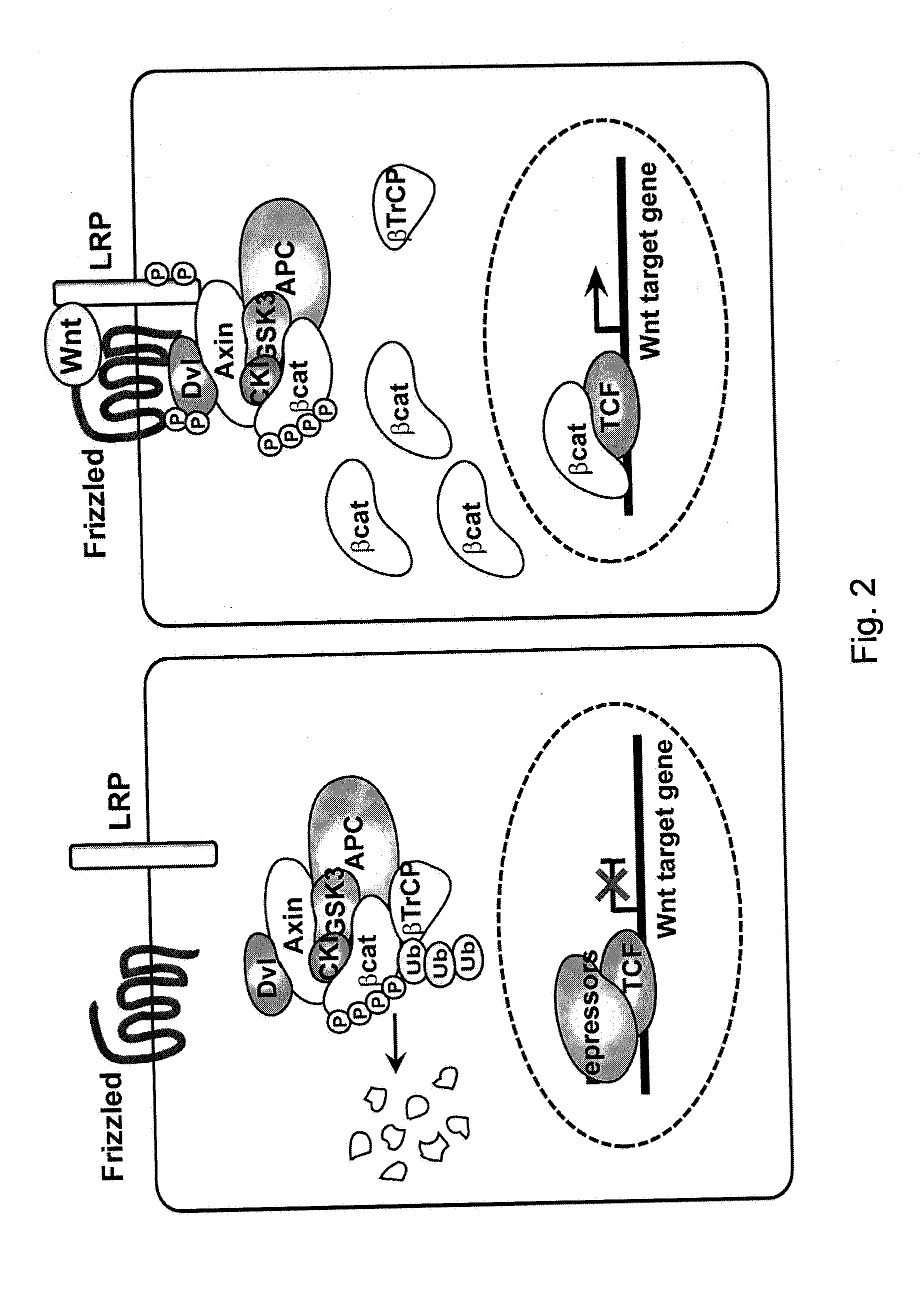
Methods for activating retrovirus in latent infected cells, and compounds for use therein
InactiveUS20150099012A1Increase transcriptionEnhanced signalBiocidePeptide/protein ingredientsInfected cellLong terminal repeat
The present invention relates to a method for increasing retrovirus transcription in an infected eukaryotic cell, comprising increasing Wnt pathway signaling in said cell such that transcription of said retrovirus is increased. Also, the present invention relates to a method of treating a subject infected with a retrovirus, said method comprising administering to said subject an activator of the Wnt pathway in an amount that increased Wnt pathway signaling in resting memory CD4+ T cells of said subject such that the retroviral long terminal repeat (LTR) in said cells is activated or de-repressed.
Owner:ERASMUS UNIV MEDICAL CENT ROTTERDAM ERASMUS MC
Human immunodeficiency virus-1NASBA-ELISA (enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay) detection kit
InactiveCN103540684AGood repeatabilityShort detection time periodMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationImmunodeficiency virusLong terminal repeat
The invention relates to a gene detection kit against human immunodeficiency virus-1 (HIV-1). The gene detection kit comprises a pair of amplification primers, a capture probe, a detection probe, an NASBA (National Association of State Boards of Accountancy) amplification reagent and an NASBA product detection reagent. The gene detection kit provided by the invention designs the primers against the long terminal repeat sequence of the HIV-1, establishes an NASBA fast detection method and is suitable for early diagnosis of HIV-1 infection.
Owner:薛健 +1
Retrovirus-based genomic screening
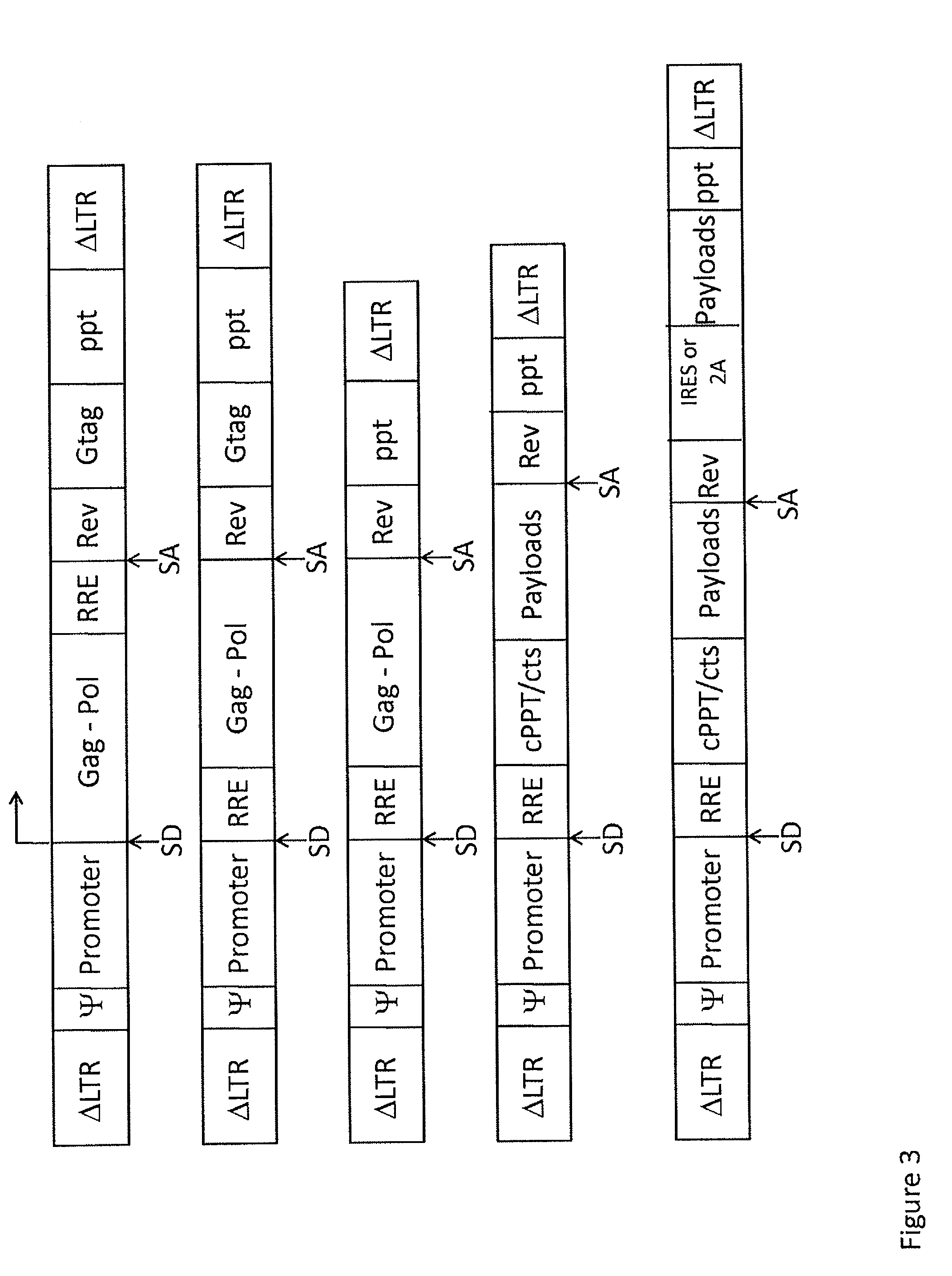
The present invention relates to the expression and screening of genomic DNA sequences encoding uncharacterized genes and proteins. The present invention provides systems utilizing unique features of retroviral replication to analyze uncharacterized genes derived from genomic DNA samples. In preferred embodiments, a segment of genomic DNA is inserted between 5′ and 3′ viral long terminal repeats (LTRs) in a vector (e.g., a plasmid, cosmid, or artificial chromosome vector). The resulting vector (or library of vectors containing a plurality of independent genomic sequences) is then introduced into a retroviral packaging cell. The resulting provirus or proteins expression from the provirus are then analyzed.
Owner:CATALENT USA WOODSTOCK INC +3
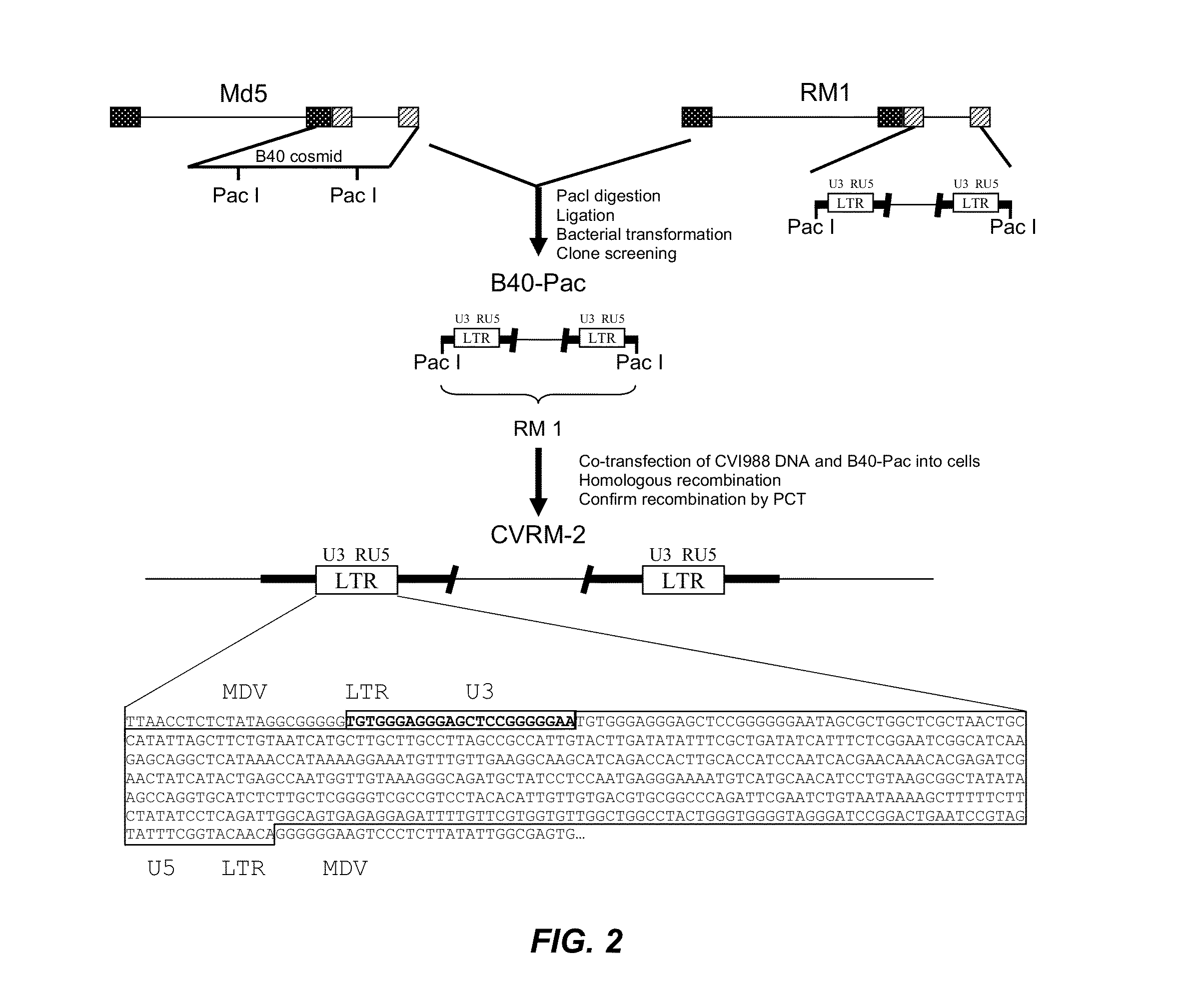
Modified Mareks Disease Virus, and Vaccines Made Therefrom
InactiveUS20130251737A1Improve viabilityIncrease productivityAnimal cellsVectorsMareks disease virusDNA construct
The present invention provides an effective vaccine for Marek's disease, which may be prepared using a recombinant Marek's Disease Virus (MDV), strain CVI988, having been transformed with a foreign DNA construct that includes a long terminal repeat sequence of a reticuloendotheliosis virus. This safe viral agent elicits a highly protective immune response in a chicken against virulent MDV challenge without causing a significant degree of pathogenicity. Suitable formulations of the vaccine for use in chickens include an effective immunization dosage of this novel viral agent, along with a pharmaceutically acceptable carrier or diluent.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM ANIMAL HEALTH USA INC
A conserved region of the hiv-1 genome and uses thereof
InactiveUS20100285464A1Highly suitableSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementLong terminal repeatGenetics
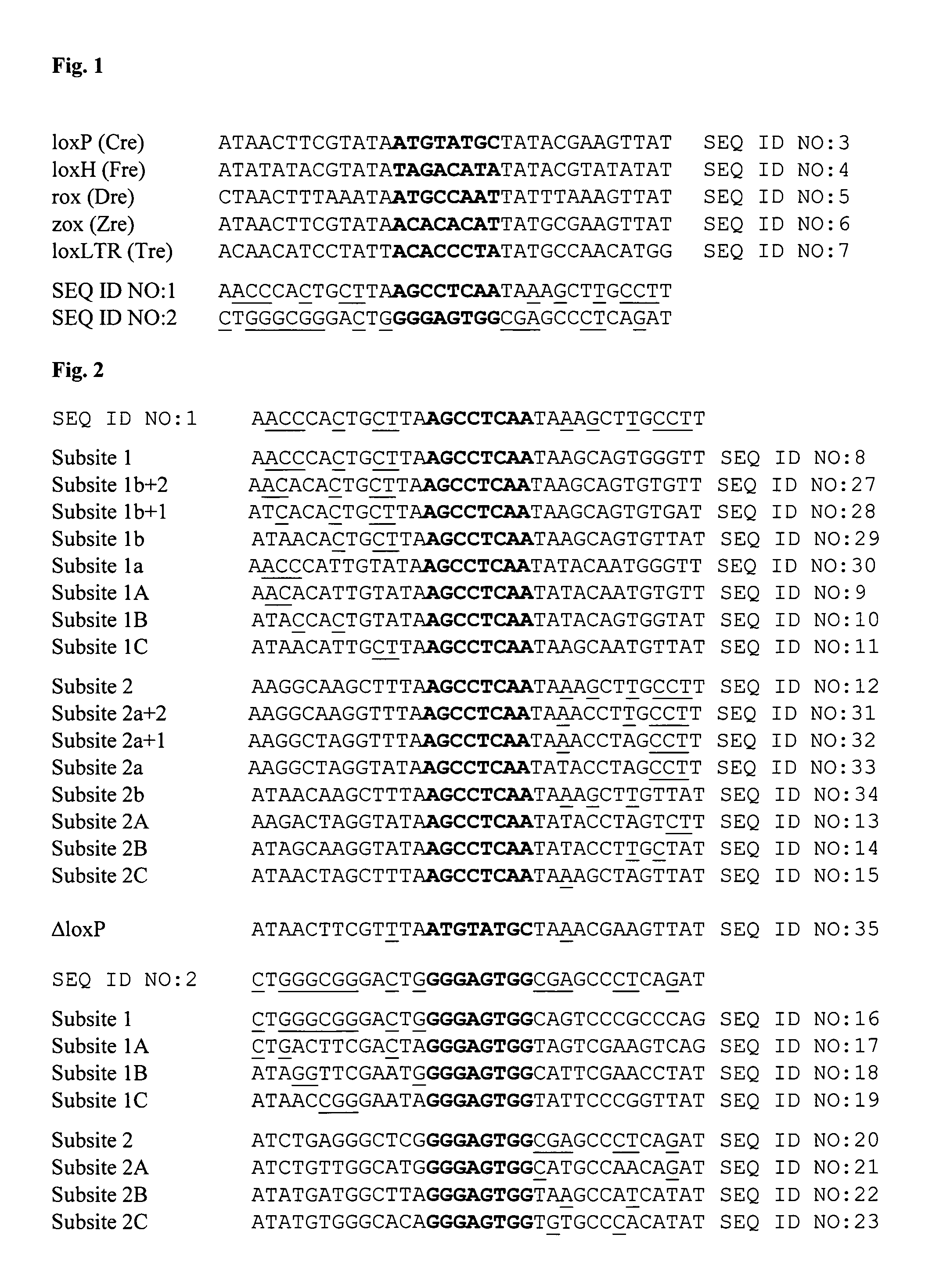
The present invention discloses sequences having a structure and sequence homology to lox-P recombinase target site corresponding to a highly conserved region within the Long Terminal Repeats (LTR) of HIV and to the use thereof for the identification of recombinase enzymes useful in treating HIV-1.
Owner:RECOGENE +1
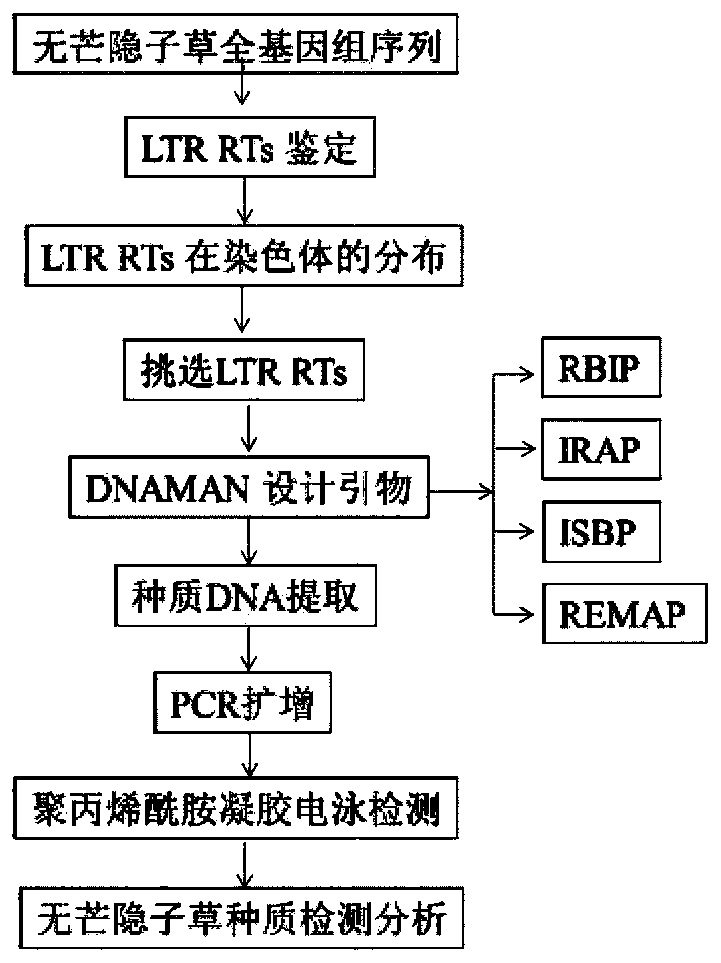
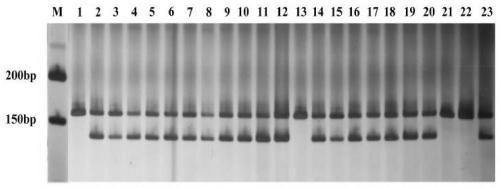
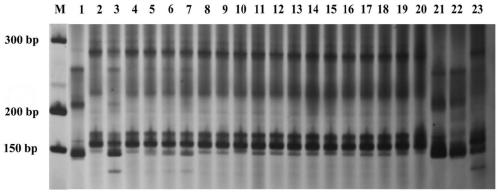
Cleistogenes songorica LTR-RT molecular marker primer and application in cleistogenes songorica germplasm identification
ActiveCN110373492AHigh sensitivityHigh precisionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationBiotechnologyAgricultural science
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and particularly relates to a cleistogenes songorica LTR-RT (long-terminal repeat retrotransposons) molecular marker primer and application incleistogenes songorica germplasm identification. Specifically, 80 pairs of primer pairs and 23 kinds of cleistogenes songorica germplasm are used for distinguishing. According to the identification method, comparison and identification of the cleistogenes songorica germplasm can be completed within 4 hours by using few primer combinations, the advantages of being accurate, efficient, quick, low incost, convenient to operate and the like are achieved, and the sensitivity and accuracy are relatively high.
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY
High-infection quasi-influenza virus preparation as well as special coding sequence and application thereof
InactiveCN102234635AHigh physiological propertiesConsistent antigenicityMicrobiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesHighly pathogenicViral Membrane Proteins
The invention particularly relates to a high-infection quasi-influenza virus system which is mainly characterized in that carriers of LTR(Long Terminal Repeat) containing HIV(Human Immunodeficiency Virus)-1, promoters, gag-pol and other elements and high-infection influenza virus membrane protein expression plasmids are subjected to co-transfection and packaging to form quasi-influenza viruses which have infection characteristics and antigenicity of high-infection influenza virus membrane protein. The system is used as a convenient and safe platform for researches on the physiological characteristics of highly pathogenic influenza virus membrane protein and researches on neutralizing antibodies. The system is used as an efficient gene introduction carrier, a target gene can be inserted into a gene-containing system reconstructed through packaging signals of the HIV-1, and the target gene can be introduced into various cells through quasi-virus infection according to retrovirus integration rules. After the cells are infected by quasi-viruses, reporter genes are integrated and expressed through gag-pol protein of the HIV-1, and the inhibition to the gag-pol function by medicaments can be reflected through the expression of the reporter genes, thus the system can be used as an evaluation platform for gag-pol medicaments.
Owner:中国疾病预防控制中心病毒病预防控制所
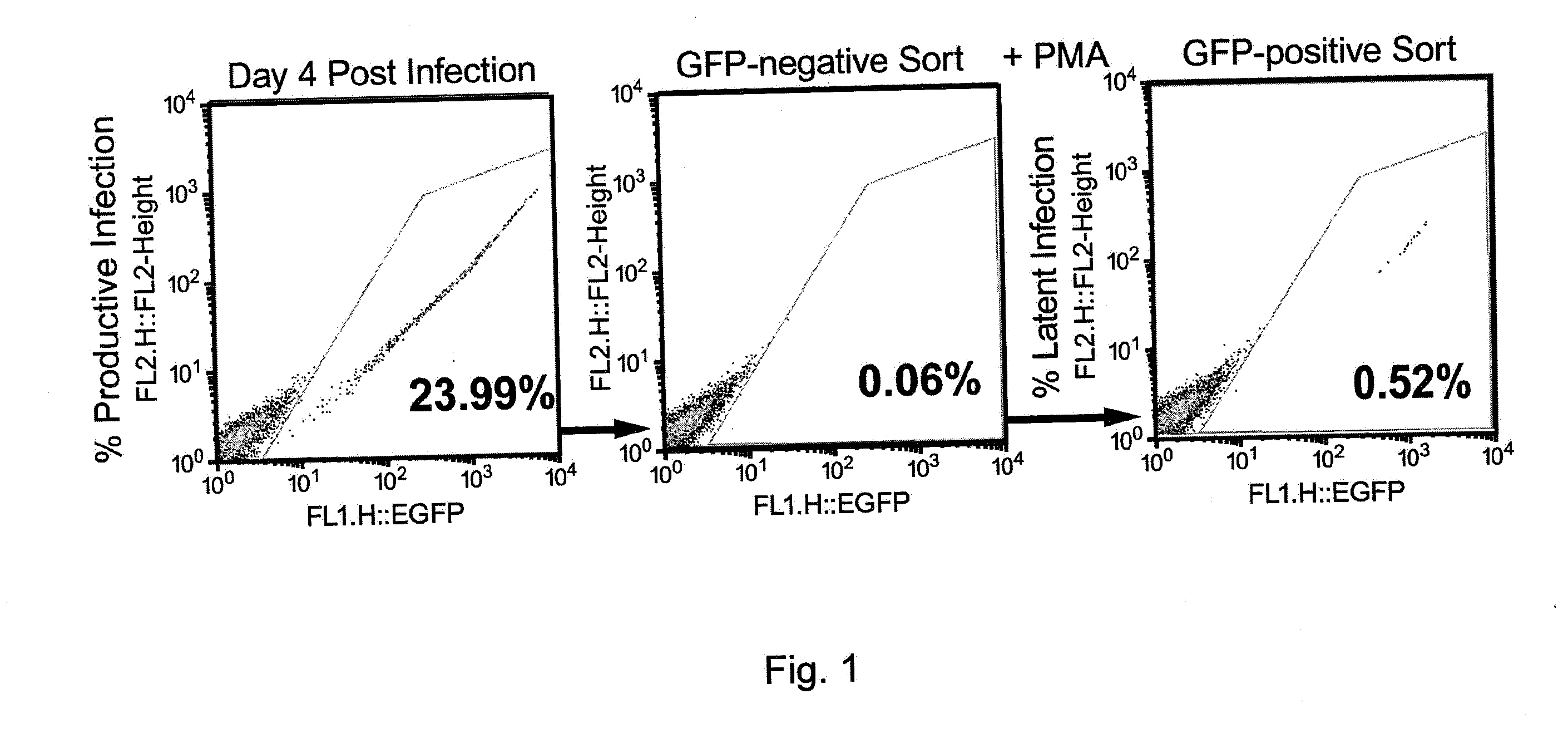
Compositions and methods for identifying latently infected cells
ActiveUS20160186210A1Lower Level RequirementsBiocideMammal material medical ingredientsImmunodeficiency virusNucleotide
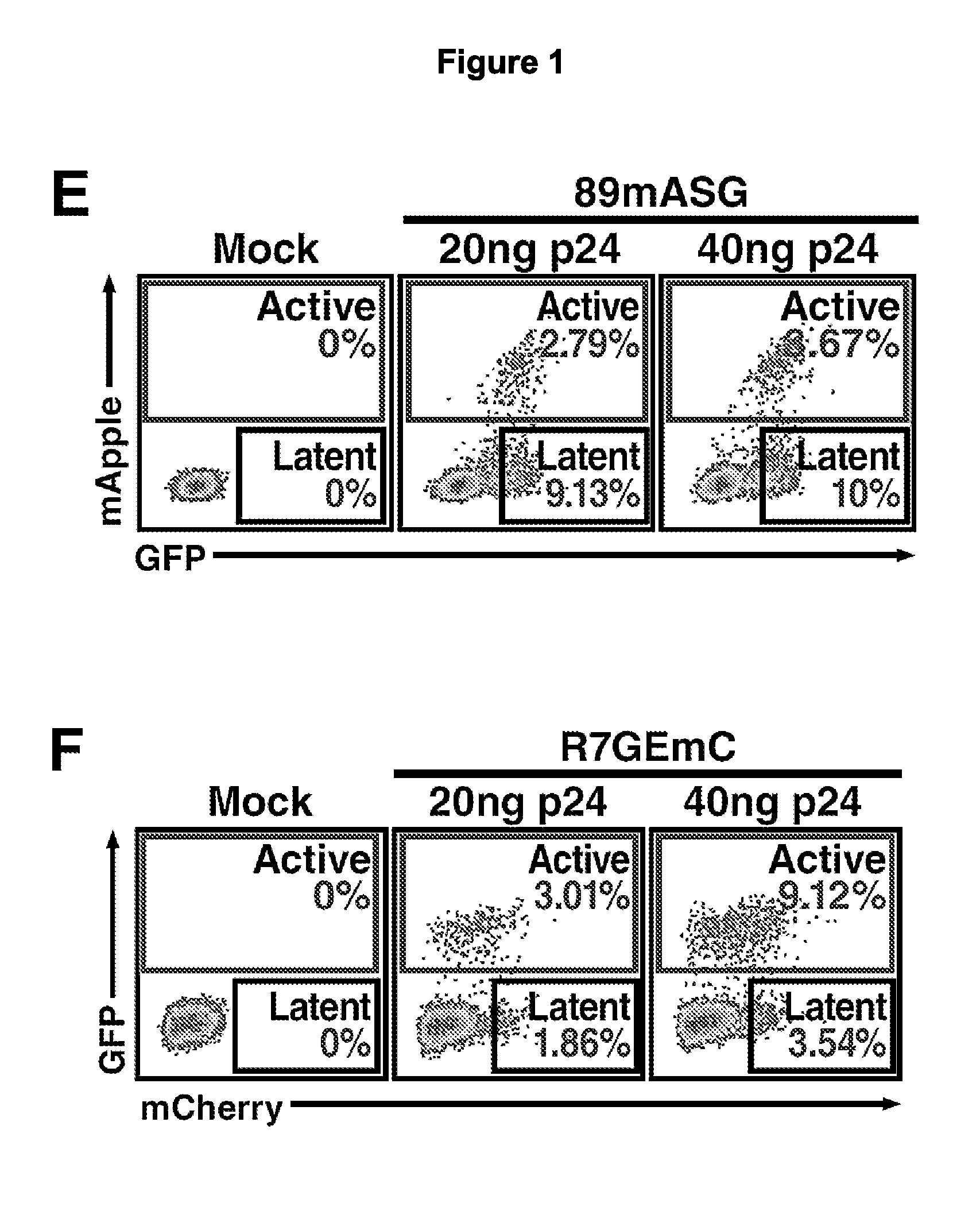
The present disclosure provides for recombinant nucleic acids, and cells and virions comprising the recombinant nucleic acids, that can be used to identify, isolate, and / or purify cells latently infected with immunodeficiency virus. A subject recombinant nucleic acid includes (a) a first nucleotide sequence encoding a first reporter polypeptide that produces a first detectable signal, where the first nucleotide sequence is operably linked to an immunodeficiency virus promoter and is translated as an early gene; and (b) a second nucleotide sequence encoding a second reporter polypeptide that produces a second detectable signal that is distinguishable from the first detectable signal, where the second nucleotide sequence is operably linked to a non-immunodeficiency virus promoter. In some aspects, the first and second nucleotide sequences are both positioned between a shared 5′ long terminal repeat (LTR) and a shared 3′ LTR. Also provided are related methods.
Owner:THE J DAVID GLADSTONE INST A TESTAMENTARY TRUST ESTABLISHED UNDER THE WILL OF J DAVID GLADS
Schistosome infectious oncomelania detection kit and detection method thereof
InactiveCN101457258BSuitable for useSimple and fast operationMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceOncomelaniaA-DNA
A blood fluke infectious oncomelania detection kit and a detection method thereof belongs to the verminosis transmission medium detecting field. The invention provides a kit and a detection method for detecting blood fluke infectious oncomelania based on a loop-mediated isothermal DNA amplification technology (LAMP). According to the LAMP technology principle, six pairs of specific primers for amplifying a DNA fragment between the 20bp and 231bp of the schistosoma japonicum non-long terminal repeated inverse transcription transposon gene (AF412214) are designed. The LAMP method is constructedfor detecting blood fluke gene in the body of the infectious oncomelania and the objective for distinguishing the blood fluke infectious oncomelania from the non-infectious oncomelania is reached. Comparing to the conventional blood fluke infectious oncomelania detection method the method of the invention has advantages of easy and fast operation, sensitive and specific without especial equipmentand is suitable for bilharziasis controlling personnel use on site.
Owner:JIANGSU INST OF PARASITIC DISEASES
Methods and compositions for rna-guided treatment of HIV infection
A method of inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus by treating the host cell with a composition comprising a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)-associated endonuclease, and two or more different guide RNAs (gRNAs), wherein each of the at least two gRNAs is complementary to a different target nucleic acid sequence in a long terminal repeat (LTR) in the proviral DNA, and inactivating the proviral DNA. A composition for use in inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus including isolated nucleic acid sequences comprising a CRISPR-associated endonuclease and a guide RNA, wherein the guide RNA is complementary to a target sequence in a human immunodeficiency virus.
Owner:EXCISION BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC +1
Nucleic acids containing modified human immunodeficiency virus genomes devoid of long terminal repeats encoding non-infectious, replication-deficient, immunogenic retrovirus-like particles
InactiveUS6291227B1Improve the level ofHigh level of particleNanotechVirus peptidesMammalRetroviral infection
An immunogenic retrovirus-like particle which is non-infectious and non-replicating and which is useful as a candidate vaccine component against retroviral infections, including AIDS and ATLL, is produced by genetic engineering. A DNA molecule comprising a retroviral genome devoid of long terminal repeats is incorporated into an expression vector, which is introduced into mammalian cells for expression of the retrovirus-like particle.
Owner:AVENTIS PASTUER LTD
Methods and compositions for rna-guided treatment of HIV infection
A method of inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus by treating the host cell with a composition comprising a Clustered Regularly Interspaced Short Palindromic Repeat (CRISPR)-associated endonuclease, and two or more different guide RNAs (gRNAs), wherein each of the at least two gRNAs is complementary to a different target nucleic acid sequence in a long terminal repeat (LTR) in the proviral DNA, and inactivating the proviral DNA. A composition for use in inactivating a proviral DNA integrated into the genome of a host cell latently infected with a retrovirus including isolated nucleic acid sequences comprising a CRISPR-associated endonuclease and a guide RNA, wherein the guide RNA is complementary to a target sequence in ahuman immunodeficiency virus.
Owner:EXCISION BIOTHERAPEUTICS INC +1
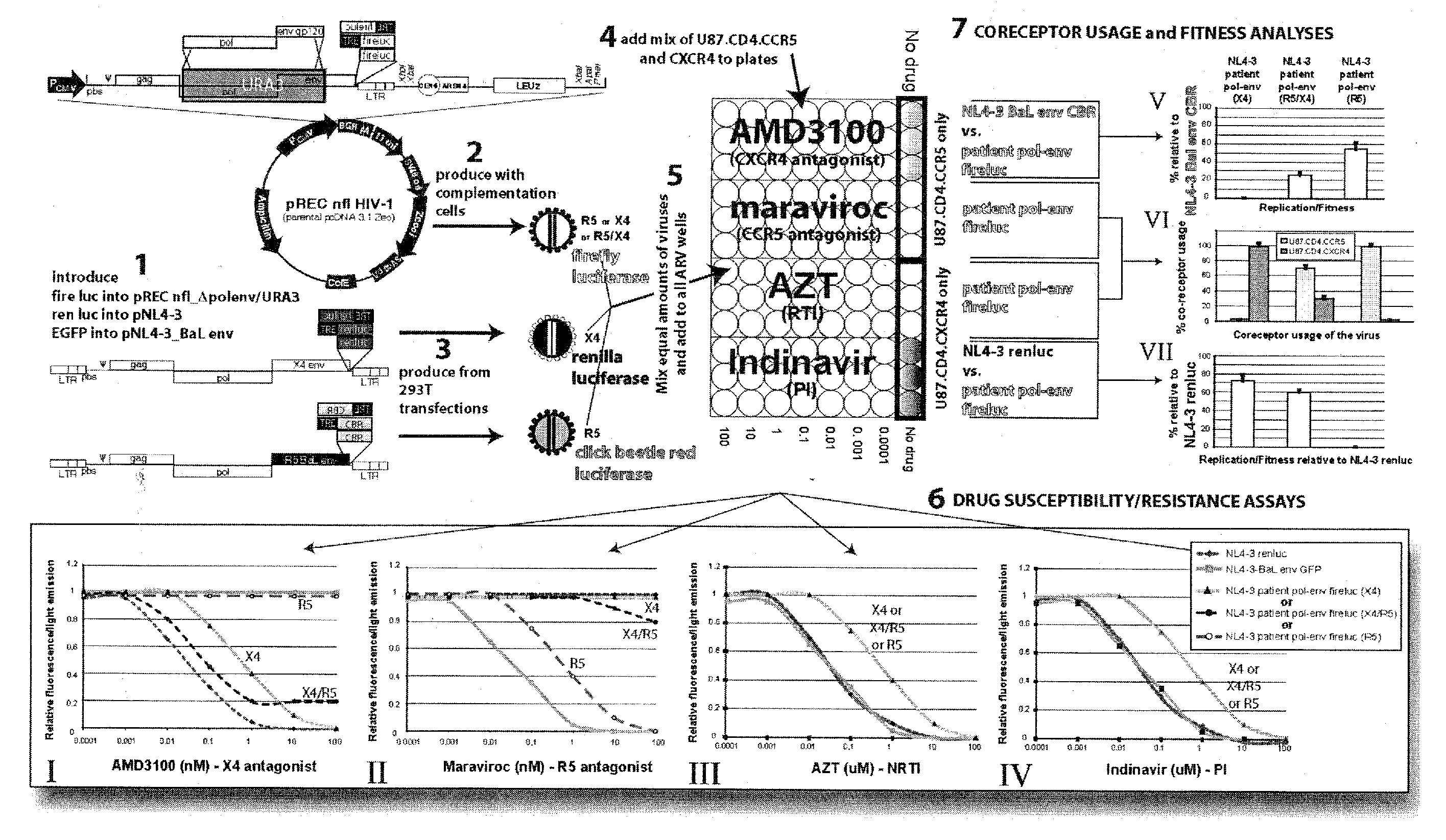
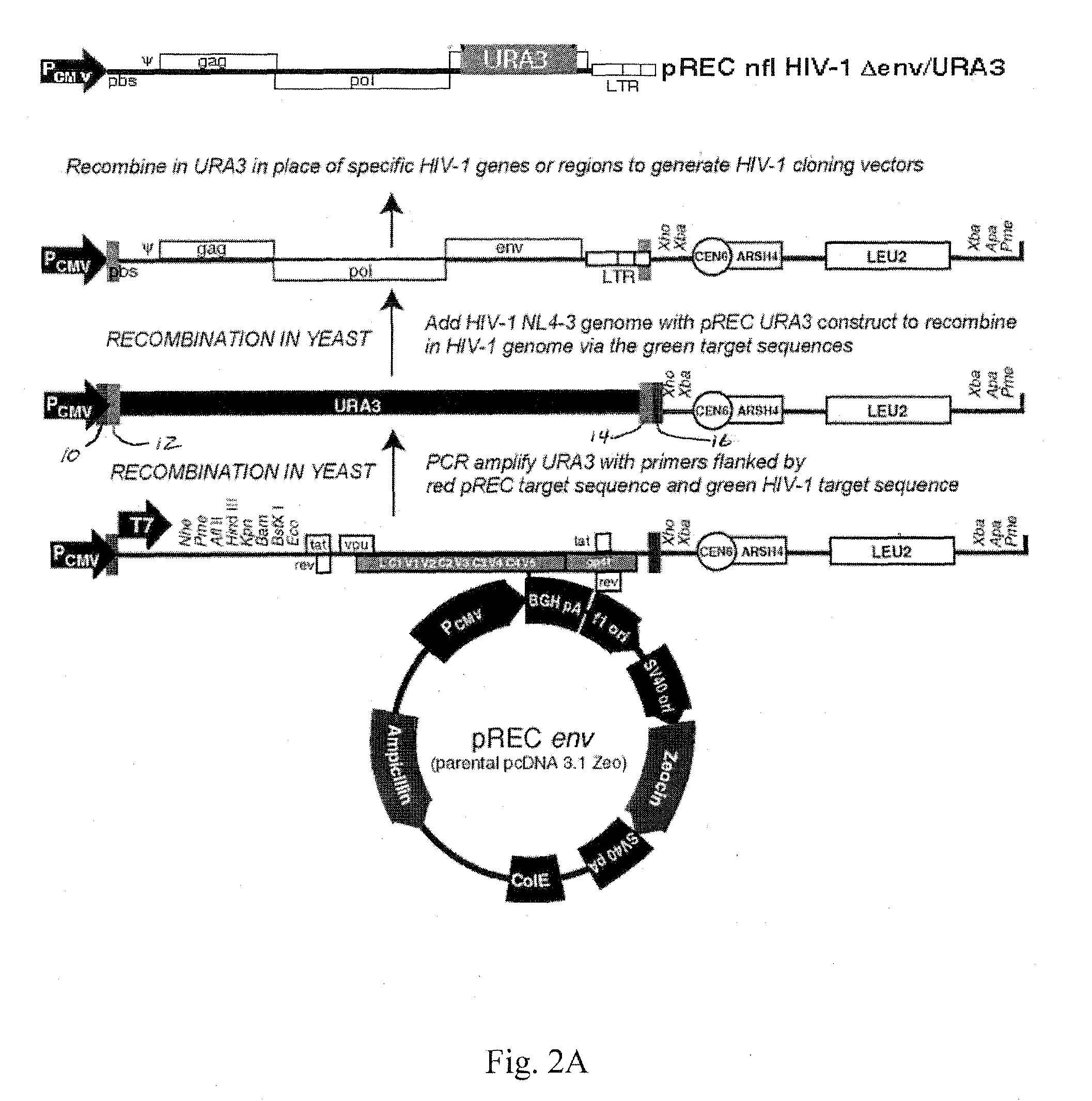
Method for screening HIV drug sensitivity
A method for monitoring ARV resistance, to determine viral fitness, and to forecast possible drug failure utilizes two nucleic acid sequences. One nucleic acid includes a retroviral nucleic acid devoid of at least a majority of the sequence for one of the two long terminal repeat regions. A second nucleic acid, includes a retroviral nucleic acid sequence devoid of the sequences encoding an envelope gene and the second long terminal repeat region of the retrovirus. The method allows the rapid cloning of an amplicon into an HIV-1 genome vector through recombination / gap repair in organisms such as yeast. The vectors can be directly passed to a mammalian cell line which has been specifically engineered to produce replication competent HIV-1 particles. The susceptibility of an isolate to any of several ARVs, i.e. PRIs, NRTIs, NNRTIs, T20, as well as entry and integrase inhibitors in developmentlclinical trials, may be tested.
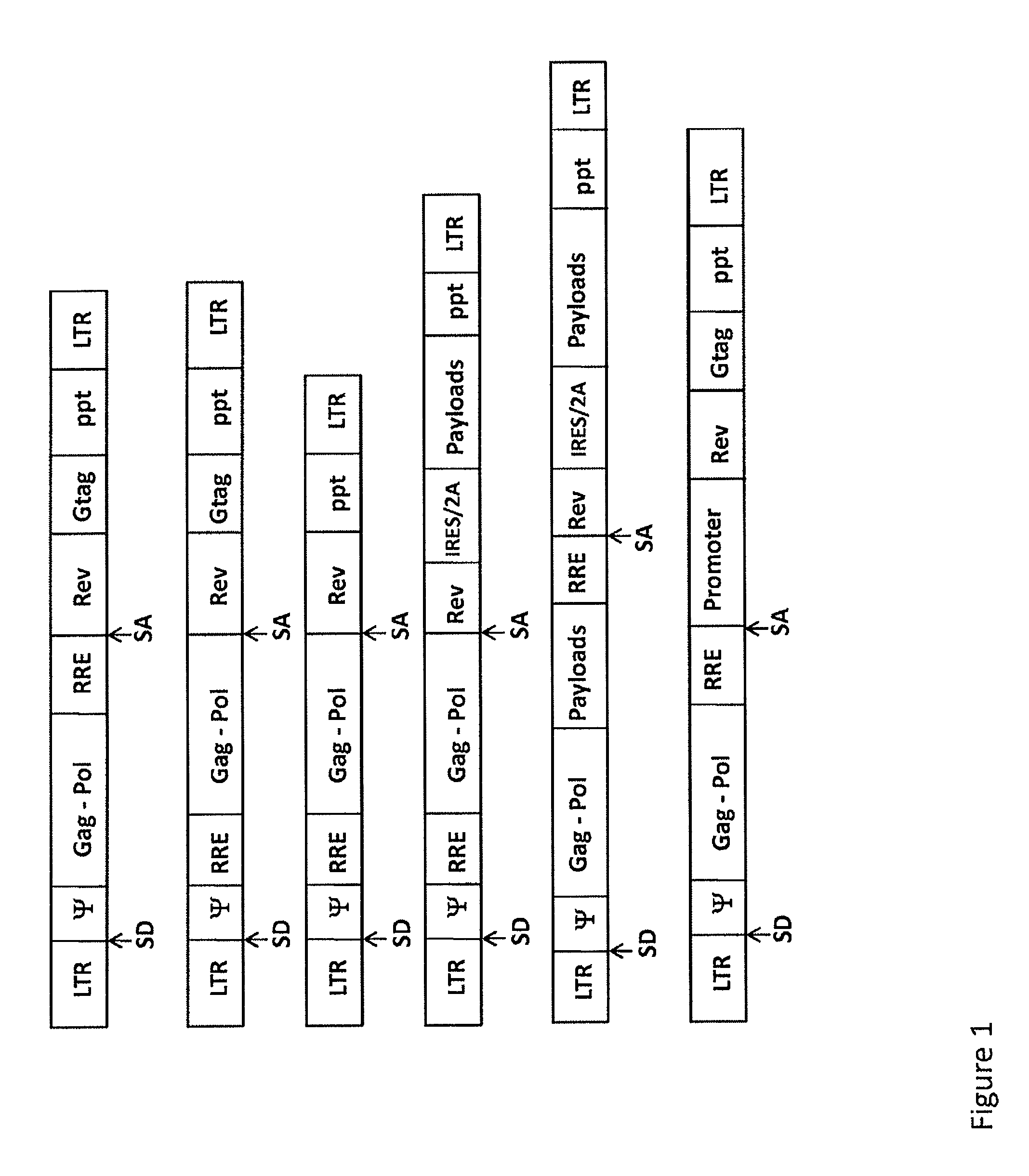
Retroviral vectors
ActiveUS20160230191A1Minimise ci elementReduce disadvantagesVectorsDrug compositionsBinding siteReverse transcriptase
There is disclosed a retroviral vector comprising a primer binding site, a long terminal repeat and an RNA packaging sequence, wherein the RNA packaging sequence is located 3′ of the long terminal repeat and no long terminal repeat is located 3′ of the RNA packaging sequence such that reverse transcription initiated at the primer binding site does not lead to reverse transcription of the RNA packaging sequence into vector DNA in a target cell. Also described is a host cell, a virion, a pharmaceutical composition, a method and uses including or involving the vector described above. Further, a cell or transgenic animal produced by using the vector is also described.
Owner:UCL BUSINESS PLC
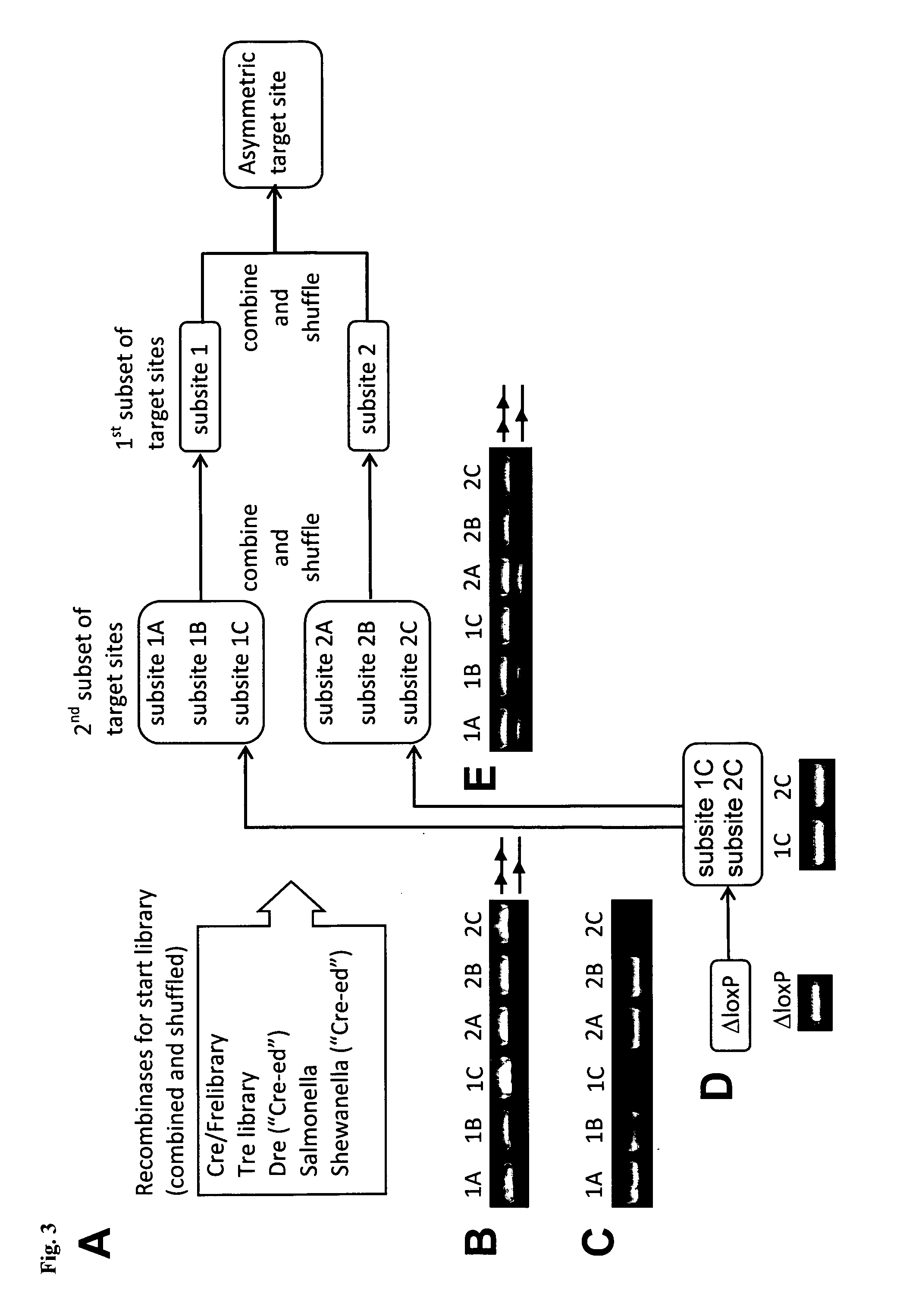
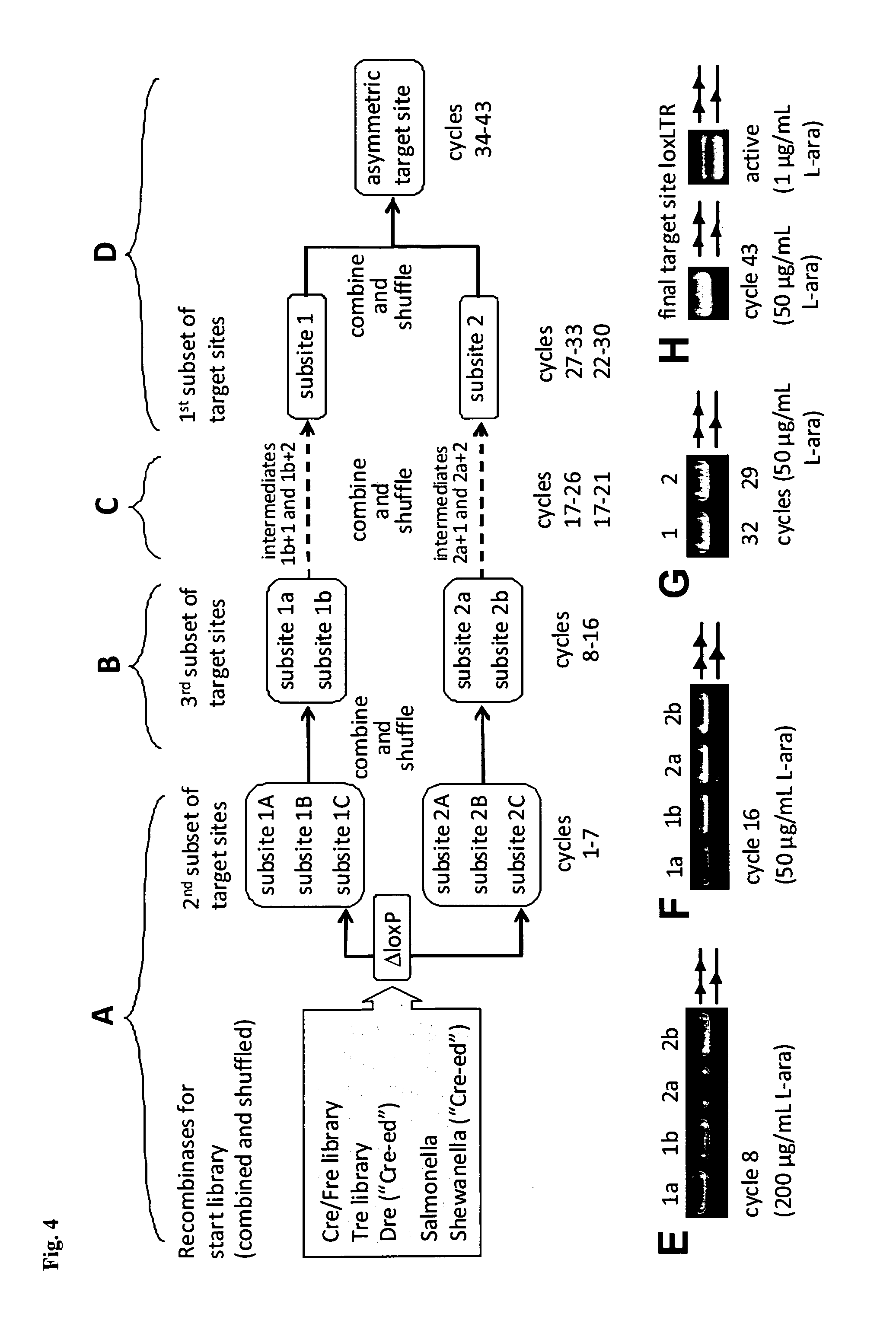
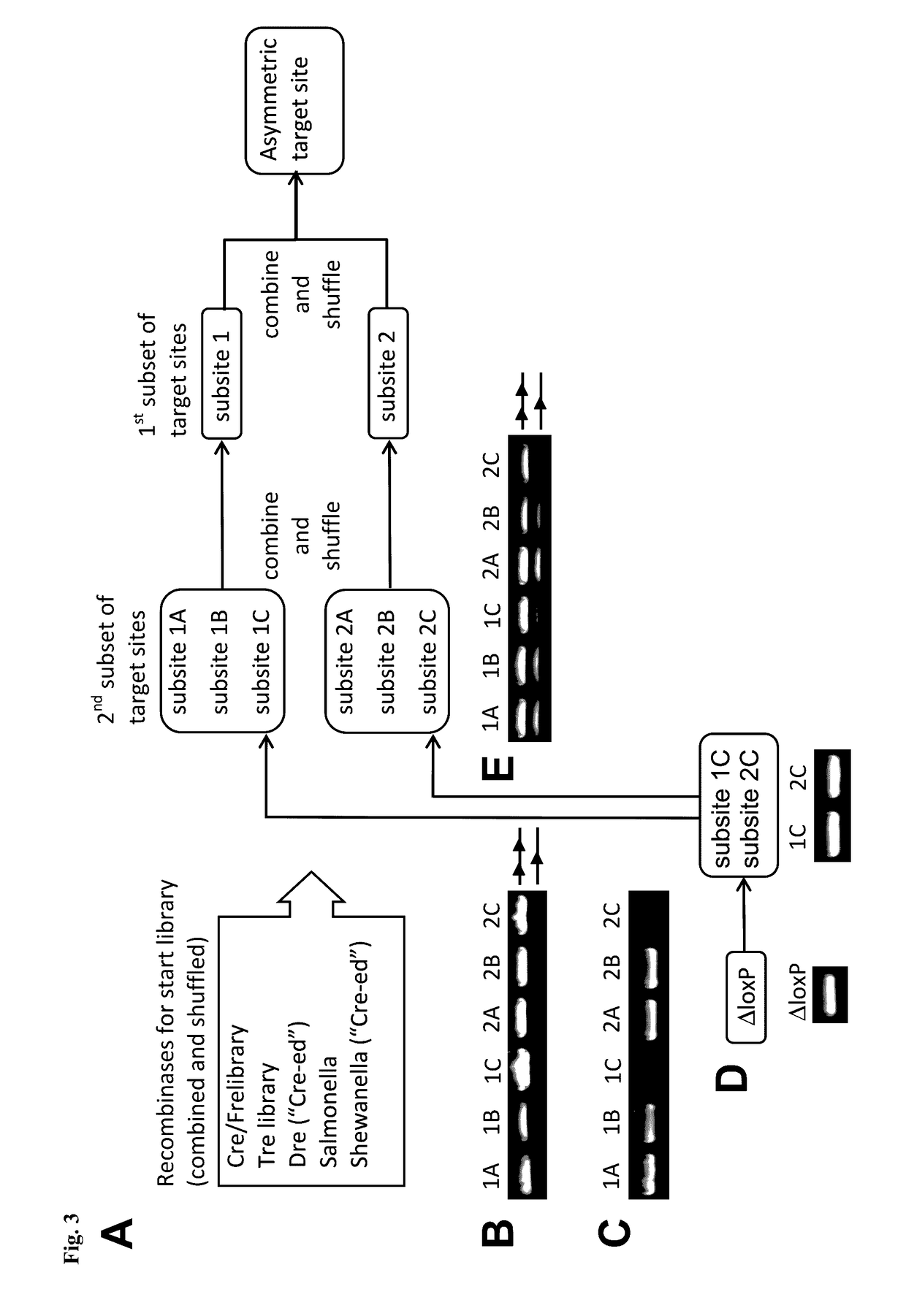
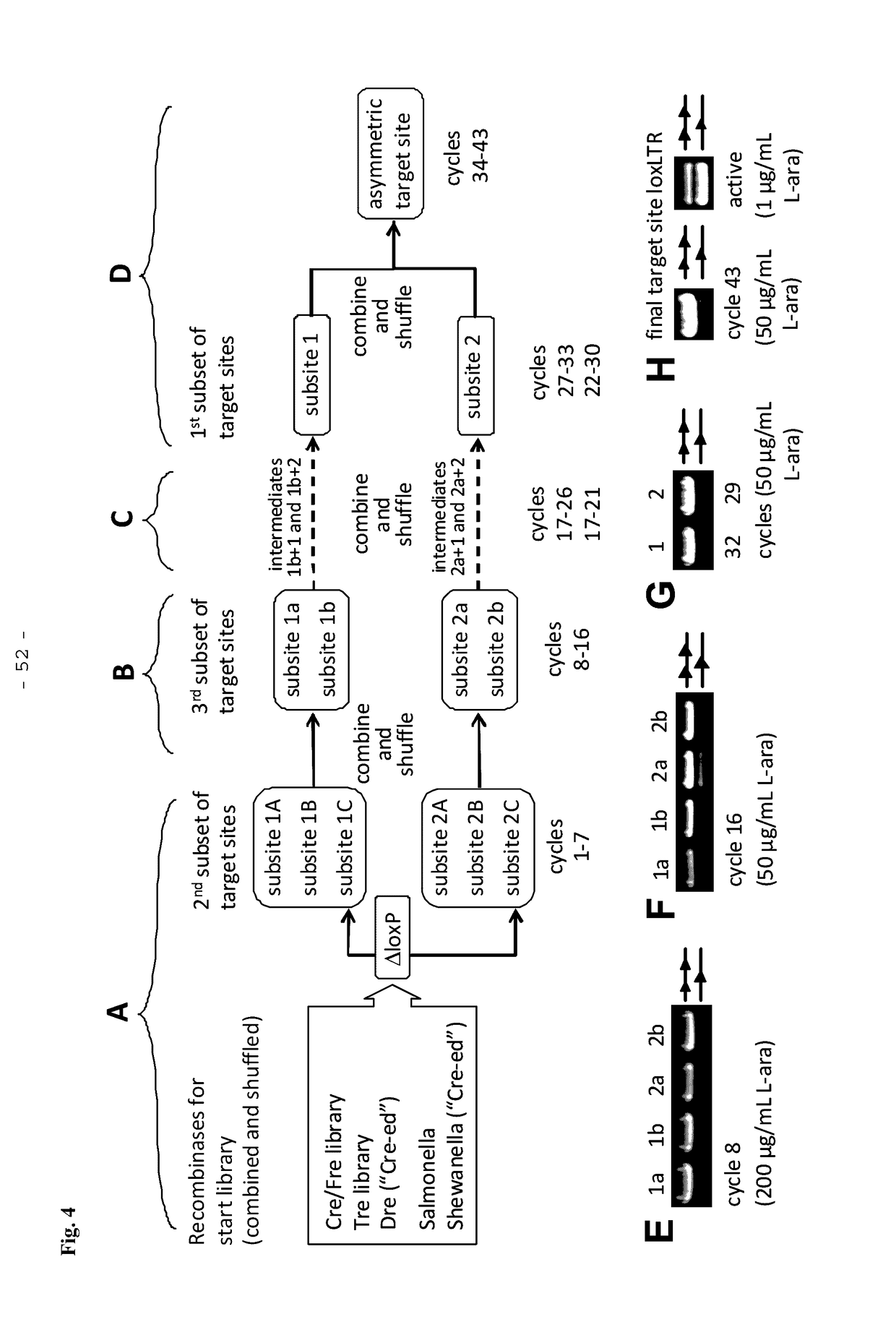
Tailored recombinase for recombining asymmetric target sites in a plurality of retrovirus strains
InactiveUS20130164271A1Simple definitionReduce poolingBiocideBacteriaProviral dnaLong terminal repeat
The present invention relates to a method for preparing an expression vector encoding a tailored recombinase, which tailored recombinase is capable of recombining asymmetric target sequences within the long terminal repeat (LTR) of proviral DNA of a plurality of retrovirus strains inserted into the genome of a host cell, as well as to the obtained expression vector, cells transfected with this, expressed recombinase and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the expression vector, cells and / or recombinase. Pharmaceutical compositions are useful, e.g., in treatment and / or prevention of retrovirus infection. In particular, asymmetric target sequences present in a plurality of HIV strains are disclosed, as well as tailored recombinases capable of combining these sequences (Tre 3.0 and 4.0) and expression vectors encoding them.
Owner:HEINRICH PETTE INST LEIBNIZ INST FUR EXPERIMENTELLE VIROLOGIE STIFTUNG BURGERLICHEN RECHTS +1
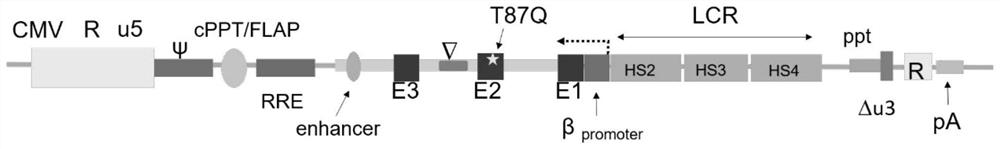
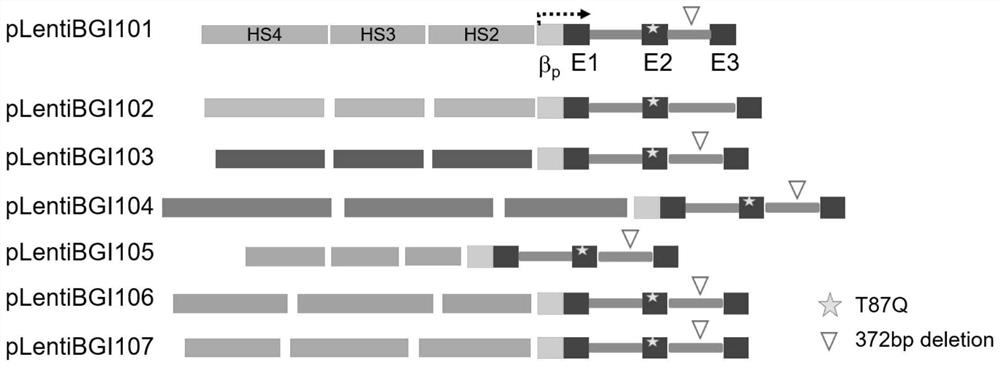
Recombinant lentivirus vector for treating beta-globulin afunction, preparation method and application
ActiveCN113046392AReduce usageImprove gene transfer efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsBeta thalassemiaSickle cell anemia
The application discloses a recombinant lentivirus vector for treating beta-globulin afunction, a preparation method and application. A gene element of the recombinant lentivirus vector disclosed by the application is composed of a left side lentivirus long terminal repeat, a lentivirus counter-response element, a center poly-purine sequence, a gene locus regulating and controlling sequence of a beta-globulin gene, a beta-globulin gene, of which 87-th threonine is mutated into glutamine, and a right side lentivirus long terminal repeat which are connected in order. According to the recombinant lentivirus vector disclosed by the application, through optimizing and improving the gene element, the gene transduction efficiency is increased, and the beta-globulin gene can be efficiently expressed during erythroid differentiation of hemopoietic stem cells, so that the consumption of viruses can be effectively lowered, and the treatment cost is reduced while the safety is improved. The recombinant lentivirus vector disclosed by the application provides a novel treatment tool and scheme for beta-thalassemia and sickle cell anemia caused by the beta-globulin afunction.
Owner:深圳市禾沐基因生物技术有限责任公司
Tailored recombinase for recombining asymmetric target sites in a plurality of retrovirus strains
ActiveUS20170130212A1Simple definitionReduce poolingHydrolasesPeptide/protein ingredientsProviral dnaLong terminal repeat
The present invention relates to a method for preparing an expression vector encoding a tailored recombinase, which tailored recombinase is capable of recombining asymmetric target sequences within the long terminal repeat (LTR) of proviral DNA of a plurality of retrovirus strains inserted into the genome of a host cell, as well as to the obtained expression vector, cells transfected with this, expressed recombinase and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the expression vector, cells and / or recombinase. Pharmaceutical compositions are useful, e.g., in treatment and / or prevention of retrovirus infection. In particular, asymmetric target sequences present in a plurality of HIV strains are disclosed, as well as tailored recombinases capable of combining these sequences (Tre 3.0 and 4.0) and expression vectors encoding them.
Owner:LEIBNIZ-INST FUR VIROLOGIE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com