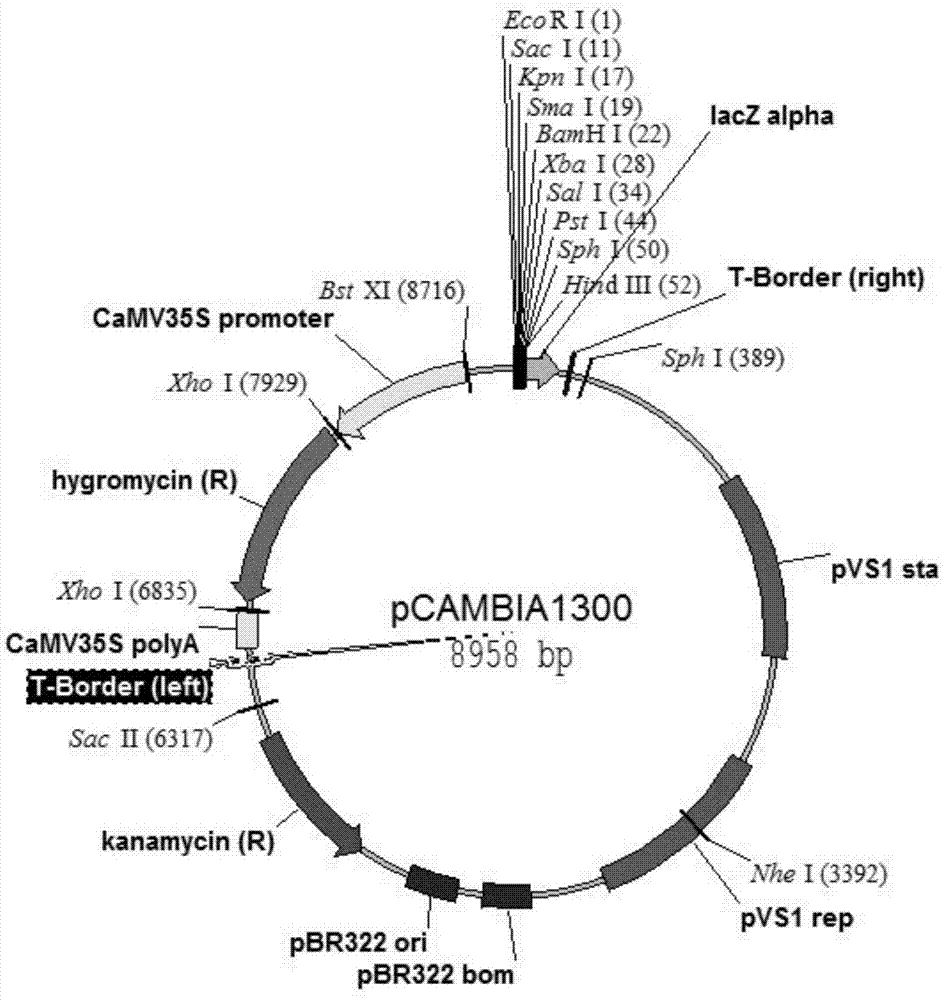
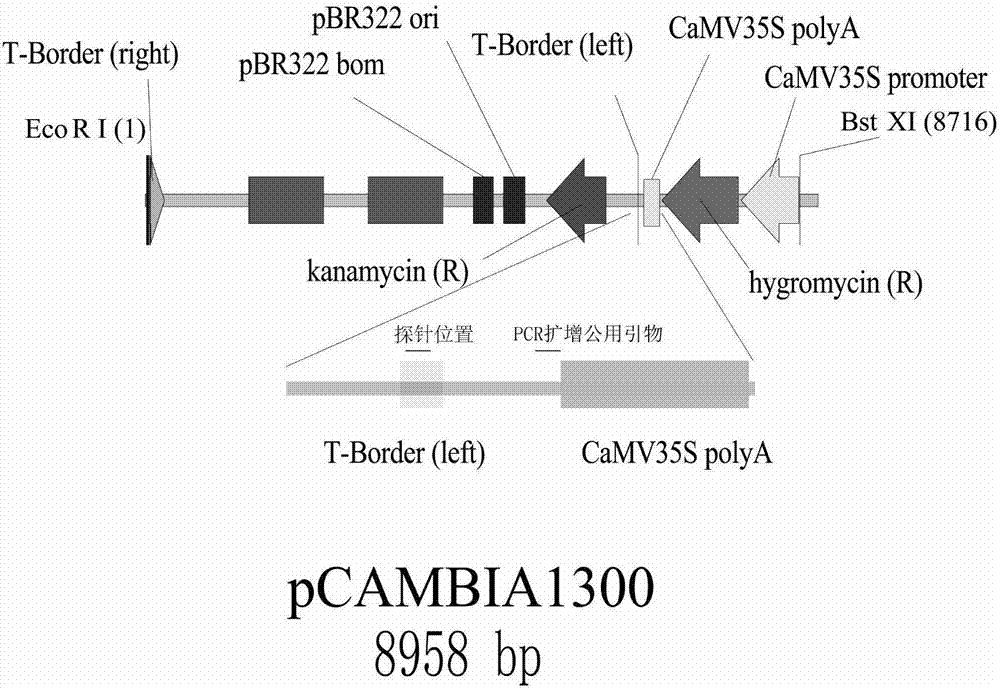
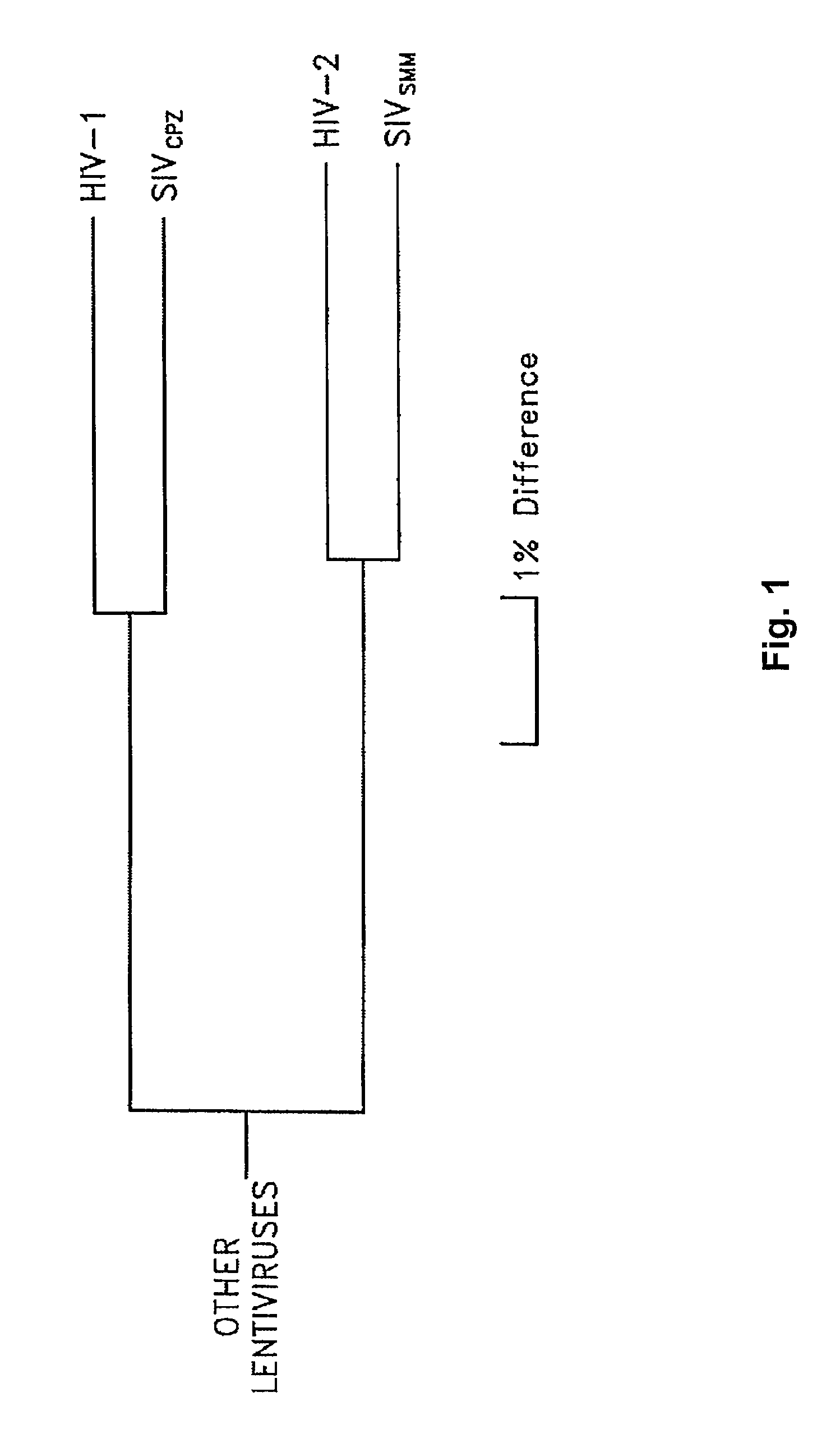
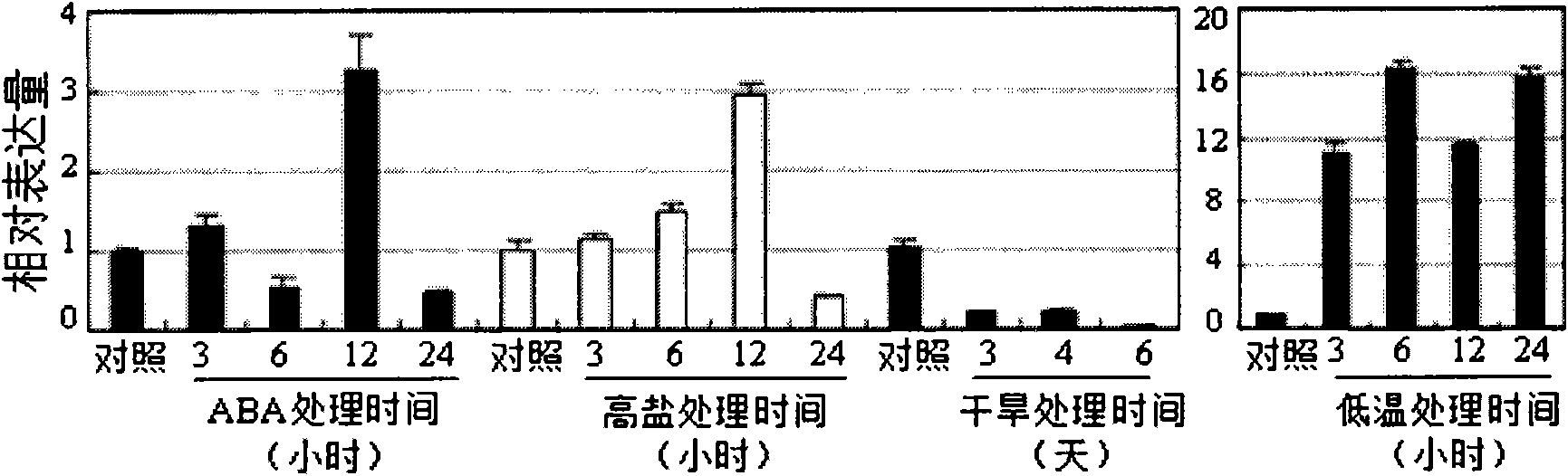
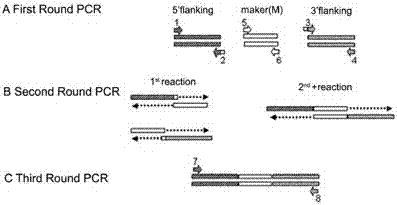
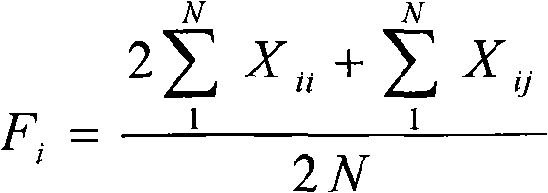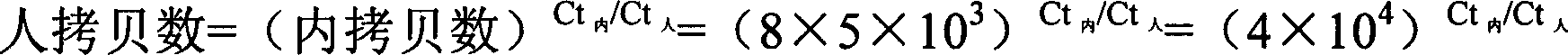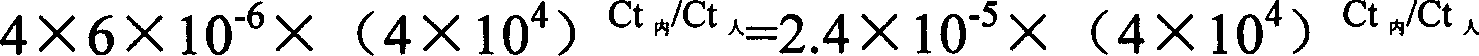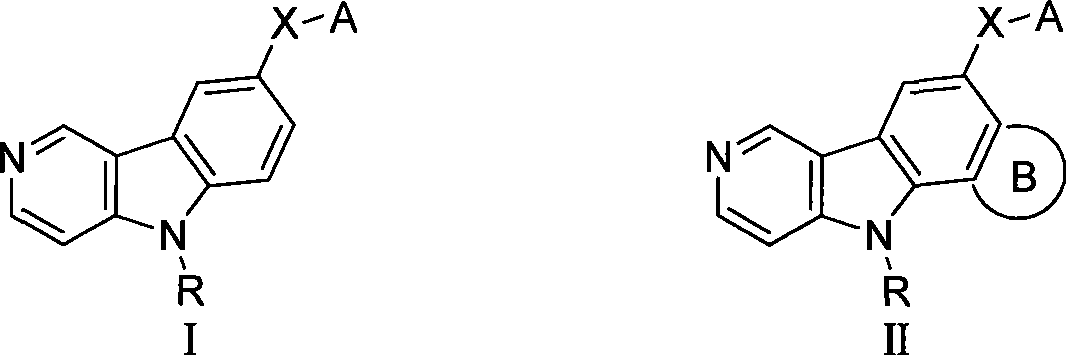Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
135 results about "DNA Intercalation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
DNA Intercalation involves insertion by covalent linkage of a molecule into the double-stranded deoxyribonucleotide polymer between the internal purine and pyrimidine base pairs stacked one on another perpendicular to the double helix axis.
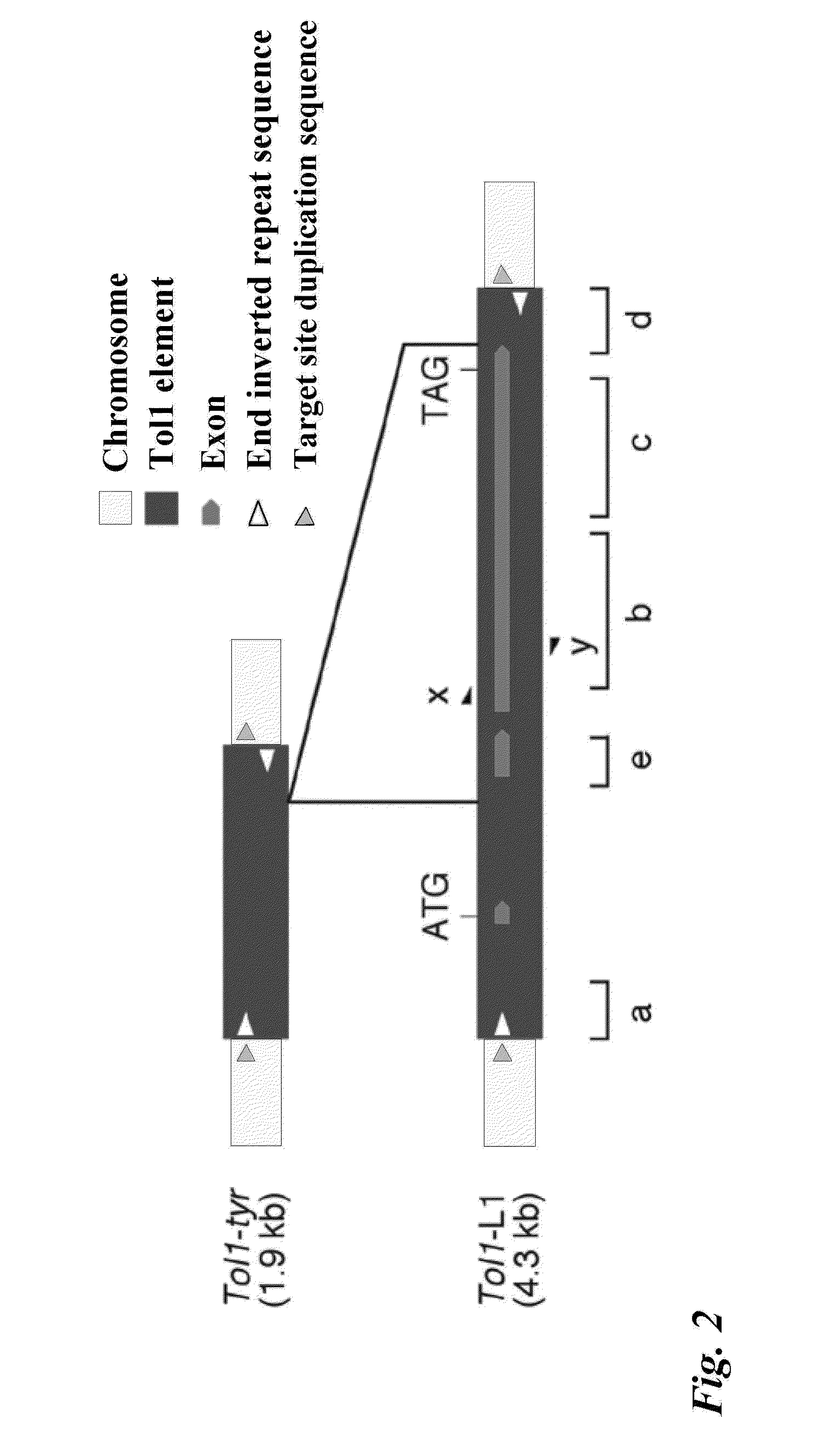
Tol1 factor transposase and DNA introduction system using the same
InactiveUS8598328B2High transposition frequencyEffectively actSugar derivativesHydrolasesGene defectNucleotide
Owner:NAGOYA UNIVERSITY +1
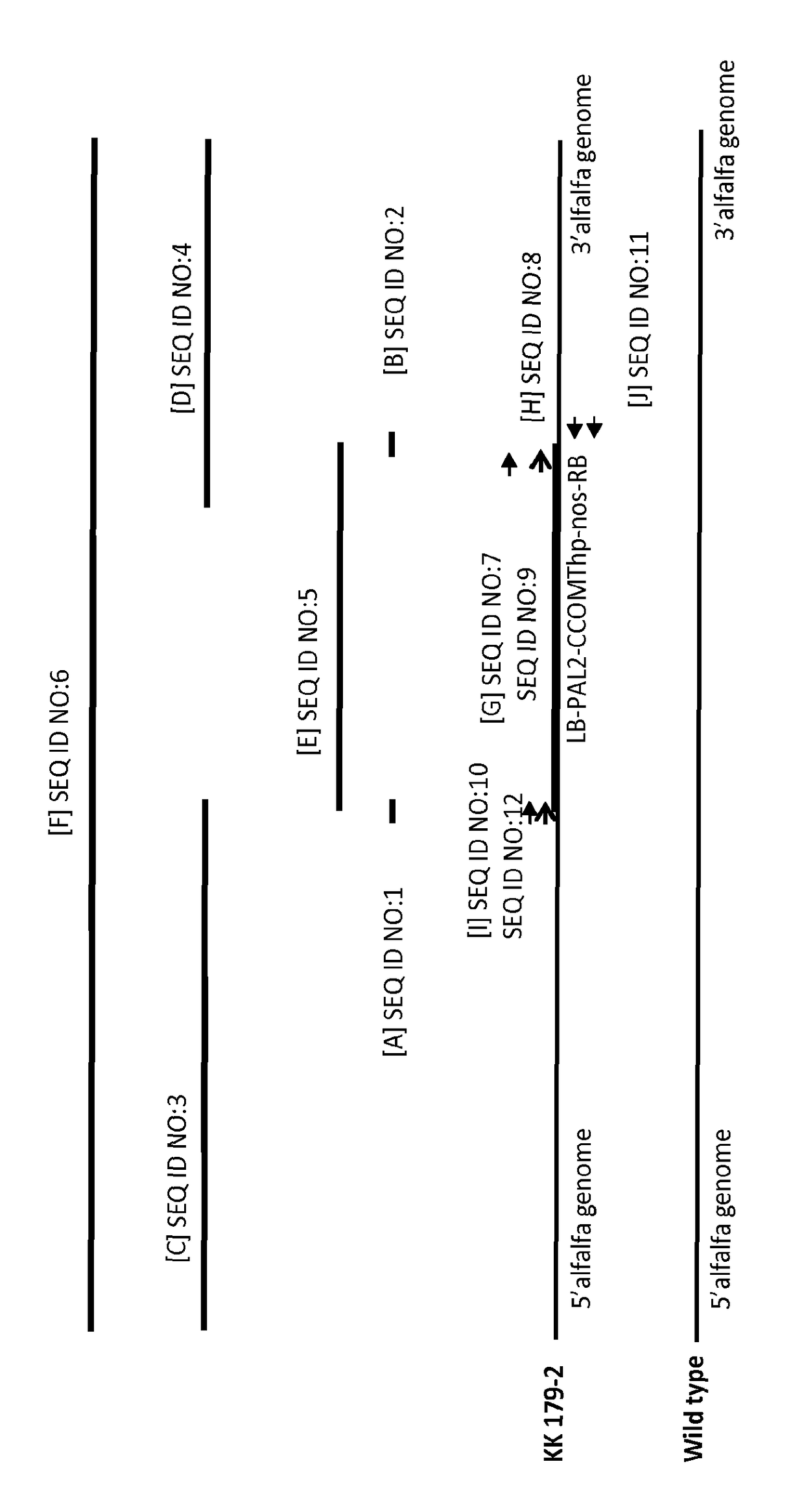
Alfalfa plant and seed corresponding to transgenic event KK 179-2 and methods for detection thereof
The present invention provides a transgenic alfalfa event KK179-2. The invention also provides cells, plant parts, seeds, plants, commodity products related to the event, and DNA molecules that are unique to the event and were created by the insertion of transgenic DNA into the genome of a alfalfa plant. The current invention also provides anti-sense-oriented RNA gene suppression agents in the form of a loop of anti-sense-oriented RNA that is produced in the cells of transgenic alfalfa. In addition, the invention also provides methods for detecting the presence of said alfalfa event nucleotide sequences in a sample, probes and primers for use in detecting nucleotide sequences that are diagnostic for the presence of said alfalfa event.
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC +1
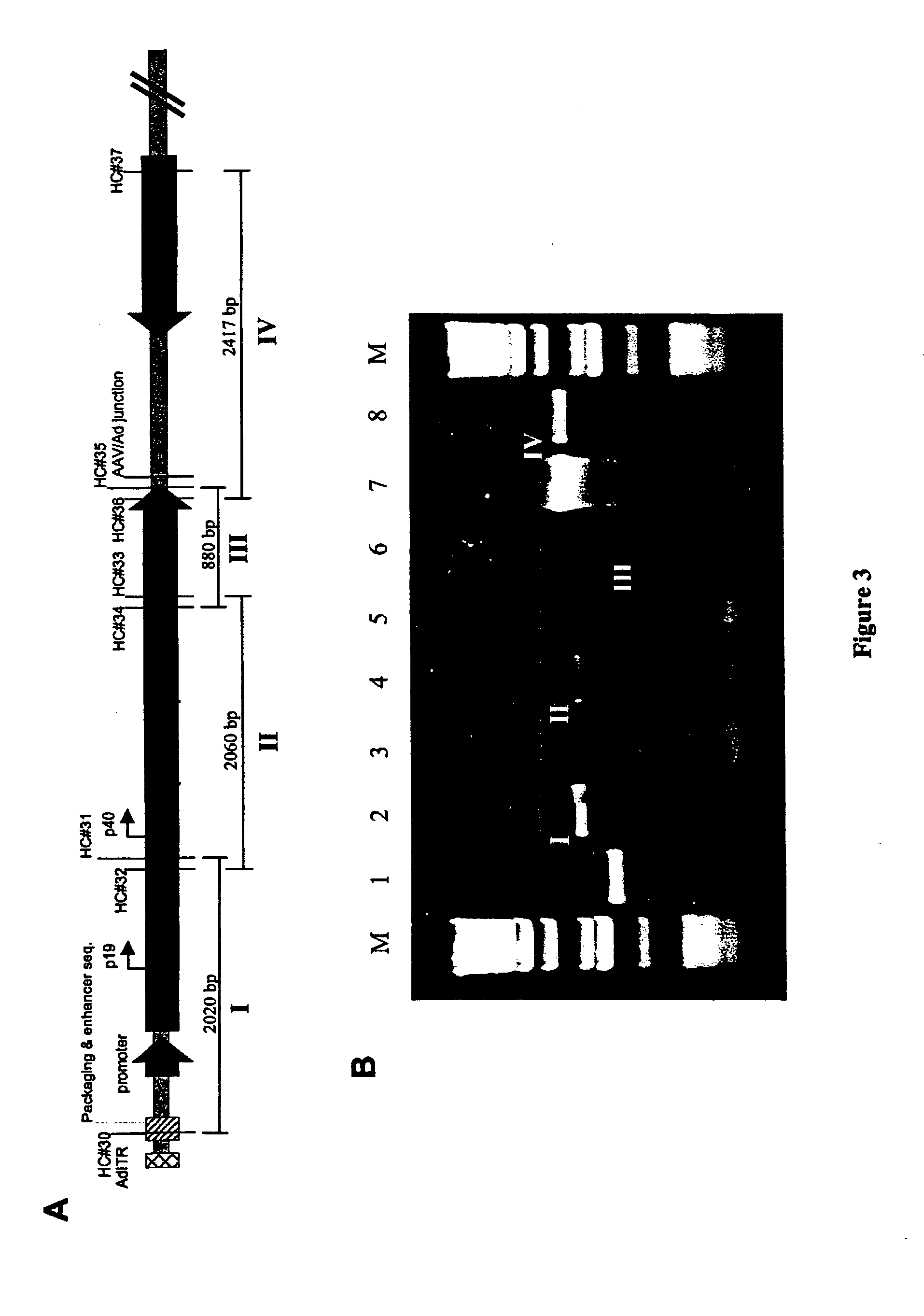
Production of recombinant AAV using adenovirus comprising AAV rep/cap genes
InactiveUS7115391B1High yieldAmenable to large-scale industrial applicationBiocideVectorsMinimal promoterDNA Intercalation
This invention relates to novel adenoviruses useful in the production of high titers of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) comprising a foreign DNA insert and methods of making these adenoviruses. The adenovirus comprises the AAV rep gene in which the p5 promoter is replaced by a minimal promoter or by no promoter. The invention also provides methods of producing high levels of rAAV as a substantially homogenous preparation and composition of rAAV.
Owner:GENOVO
Methods for nucleic acid mapping and identification of fine-structural-variations in nucleic acids
ActiveUS20090325239A1Quick buildEfficient sortingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid mappingA-DNA
A method of juxtaposing sequence tags (GVTs) that are unique positional markers along the length of a population of target nucleic acid molecules is provided, the method comprising: fragmenting the target nucleic acid molecule to form target DNA insert; ligating the target DNA insert to a DNA vector or backbone to create a circular molecule; digesting the target DNA insert endonuclease to cleave the target DNA insert at a distance from each end of the target DNA insert yielding two GVTs comprising terminal sequences of the target DNA insert attached to an undigested linear backbone; recircularizing the linear backbone with the attached GVTs to obtain a circular DNA containing a GVT-pair having two juxtaposed GVTs; and recovering the GVT-pair DNA by nucleic acid amplification or digestion with endonuclease having sites flanking the GVT-pair. Cosmid vectors are provided for creating GVT-pairs of ˜45- to 50-kb separation sequencable by next-generation DNA sequencers.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Targeted genomic rearrangements using site-specific nucleases
The present invention relates to a method for genomic DNA rearrangements, and more particularly, to a method for deletion, duplication, inversion, replacement, or rearrangement of genomic DNA using pairs of site-specific nucleases targeting two or more sites in the genome, a cell in which genomic DNA is deleted, duplicated, inverted, replaced, or rearranged by the same method, and a method for expressing the site-specific nucleases in cells. Further, the present invention relates to a method for inserting synthetic DNA molecules into the genome using site-specific nucleases targeting a pre-determined site in the genome, a cell in which DNA insertion occurs by the same method, and a method for expressing the site-specific nucleases in cells.
Owner:TOOLGEN INC
Polypeptide, novel DNA and novel antibody
InactiveUS7667005B2Effectively useful for prolongation of lifeAging can be suppressedVirusesBacteriaDiseasePremature aging
Owner:SHIRANKAI KYOTO UNIV FACULTY OF MEDICINE ALUMNI ASSOC
Compositions and Methods for Transposon Mutagenesis of Human Embryonic Stem Cells
InactiveUS20100240133A1Increase heightIncreased frequency of transpositionSugar derivativesStable introduction of DNATransposon mutagenesisExogenous DNA
PiggyBac transposons and transposases with enhanced transposition activity in cells are provided. Also provided are associated methods and kits for both introducing exogenous DNA inserts into the genomes of host cells as well as for the removal of the inserts from the host cell genomes. Cells obtained by use of the compositions, methods and kits are also provided.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Targeted DNA insertion in plants
Owner:BASF AGRICULTURAL SOLUTIONS SEED LLC
Bacterial traceless genetic manipulation vector and construction method and application thereof
ActiveCN106676119AAvoid toxicityImprove function and effectBacteriaVector-based foreign material introductionAntibiotic YToxin protein
The invention provides a bacterial traceless genetic manipulation vector. The vector contains a toxin inverse-screening element controlled by an antitoxin switch and an antibiotics resistance gene. The invention also provides a construction method of the vector and a method for application of the vector in bacterial traceless gene knock-out, knock-in, replacement, point mutation and insertion and deletion of large DNA fragments (larger than 194kb). By the utilization of a constitutive promoter for continuous expression of toxin protein and by the utilization of an inducible promoter for inducible expression of antitoxin protein, the toxin inverse-screening element (TCCRAS) controlled by the antitoxin switch is established, and the problem that specificity of existing genetic manipulation systems of gram-positive bacterium is not high, the systems are instable and screening is difficult is solved.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for efficiently and rapidly separating T-DNA insertion site flanking sequence, and uses thereof
InactiveCN107190003AQuick analysisEasy to analyzeMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA preparationMagnetic beadSeparation technology
The invention provides a method for efficiently and rapidly separating a T-DNA insertion site flanking sequence. The method comprises: extracting the genomic DNA of an Agrobacterium-mediated transgenic plant; fragmenting the genomic DNA, carrying out DNA repairing, adding A, linking, carrying out fragment selection by using magnetic beads, carrying out library construction, carrying out hybridization capture on the constructed library and a T-DNA boundary sequence, and carrying out PCR enrichment; and carrying out high-throughput sequencing on the library, and carrying out bioinformatics analysis on the sequenced data so as to obtain the T-DNA insertion site. According to the present invention, the capture is performed with the target DNA, and the low-throughput sequencing is specially performed on the T-DNA boundary sequence; the disadvantages of low throughput, low efficiency and low success rate of the existing flanking sequence separation technology are overcome with the method of the present invention; and with the method of the present invention, the DNA capture and the second-generation sequencing technology are combined, the T-DNA boundary sequence is specially sequenced and the simple analysis is performed to obtain the T-DNA insertion site flanking sequence, and the method has characteristics of high efficiency, economy, and simple analysis.
Owner:武汉天问生物科技有限公司
Recombinant modified vaccinia ankara (MVA) vaccinia virus containing restructured insertion sites
The present invention relates to recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) virus containing restructured sites useful for the integration of heterologous nucleic acid sequences into an intergenic region (IGR) of the virus genome, where the IGR is located between two adjacent, essential open reading frames (ORFs) of the vaccinia virus genome, wherein the adjacent essential ORFs are non-adjacent in a parental MVA virus used to construct the recombinant MVA virus, and to related nucleic acid constructs useful for inserting heterologous DNA into the genome of a vaccinia virus, and further to the use of the disclosed viruses as a medicine or vaccine.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
Method for identifying indica rice and japonica rice by inserting or deleting molecular marker in rice DNA
InactiveCN101323878ASimple methodImprove accuracyMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationDNA fragmentationAllele
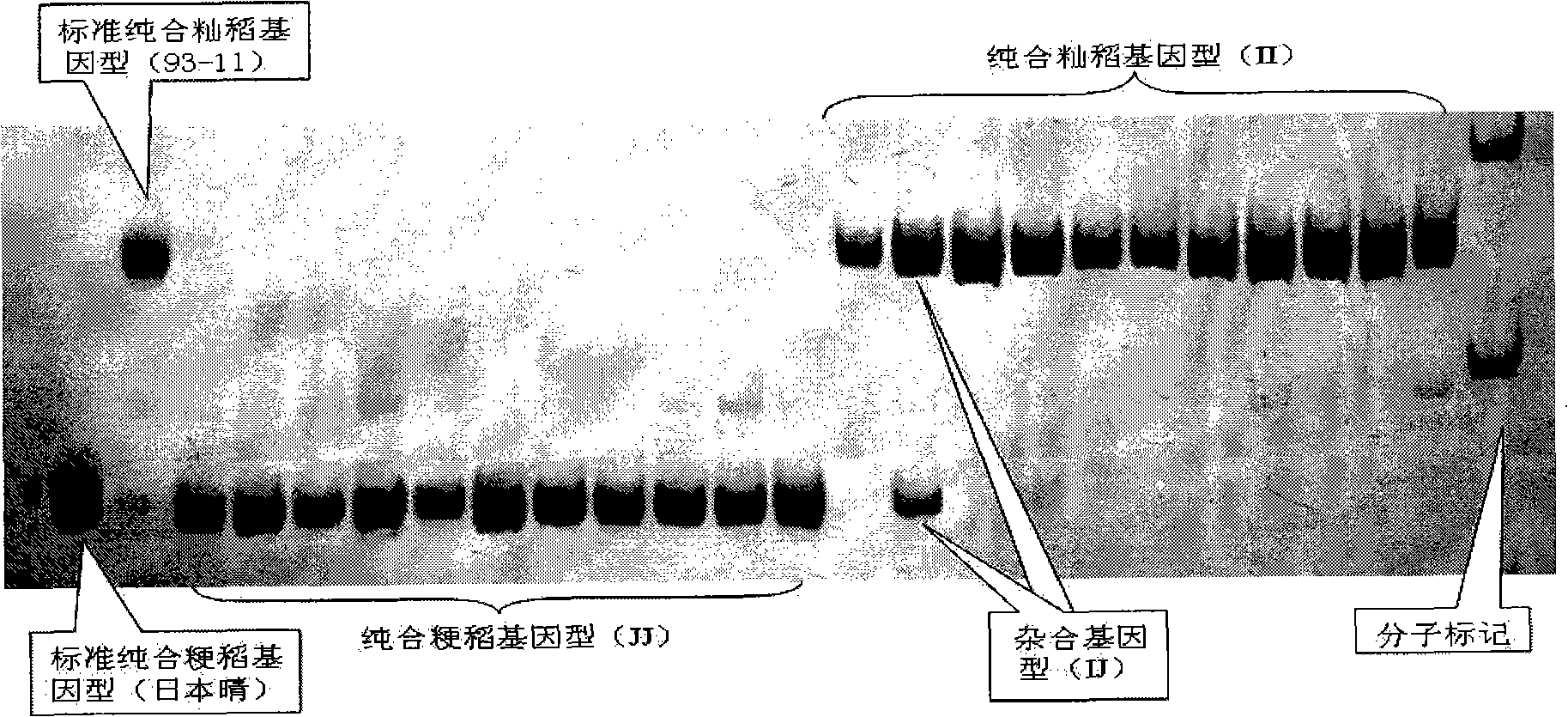
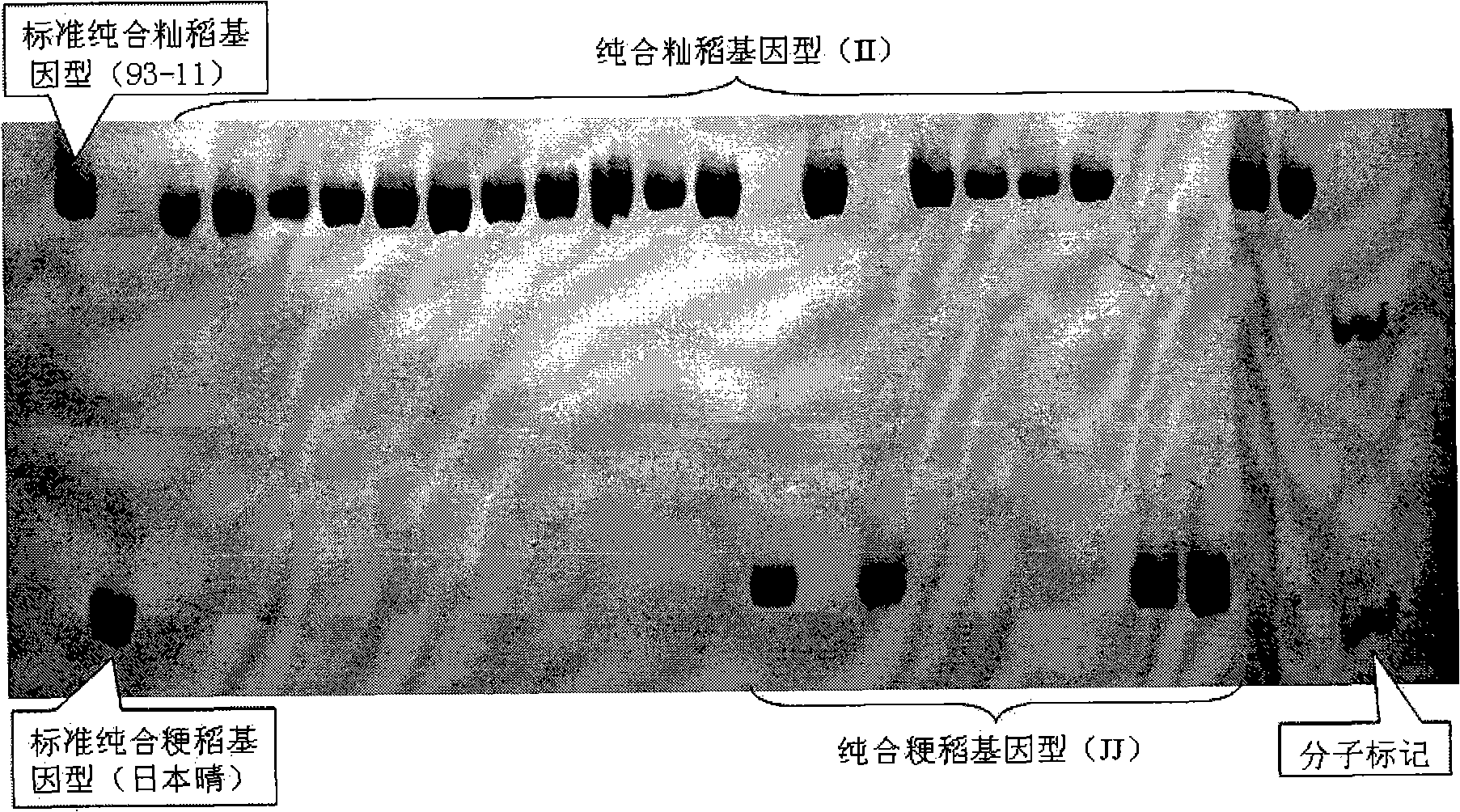
The invention pertains to the technical field of biological discrimination, in particular to a method for discriminating indica rice from japonica rice by utilizing molecular markers of rice DNA insertion or deletion. The method obtains 34 pairs of differential DNA primers designed by InDel differential fragment by making a comparison of whole genome sequence between indica rice cultivar 93-11 and japonica rice cultivar (Nipponbare). The DNA extraction, the amplification and ionophortic separation of DNA fragments and the analysis and calculation of an electrophoretogram of a target rice cultivar are carried out to discriminate indica rice from japonica rice. Precisely speaking, the 34 pairs of InDel primer groups are utilized and analysis and calculation are carried out according to a finger-print obtained on the basis of a polymerase chain reaction and vertical slab gel electrophoresis; the characteristics of indica rice or japonica rice of rice samples detected are worked out according to the average frequency (Fi or Fj) showing on indica rice alleles and japonica rice alleles on 34 InDel locuses. The invention has the advantages of simple, fast and convenient method, few samples for detection and correct discrimination results, thus having good prospect of promotion and application.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Pathogenic related protein VdGRP1 from verticillium dahliae kleb and coded gene thereof
ActiveCN102212121AReduce pathogenicityMicroorganismsMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMutant phenotype
The invention discloses a pathogenic related protein VdGRP1 from verticillium dahliae kleb and a coded gene thereof. The pathogenic related protein is the protein of 1) or 2): 1) the protein consisting of the amino acid sequence shown as sequence 2 in a sequence table; and 2) the protein formed by substituting and / or deleting and / or adding one or more amino acid residues of the amino acid residuesequence shown as sequence 2 in the sequence table, related to pathogenic fungi and derived from 1). A mutant strain vdgrpl of which the pathogenicity is weakened is obtained by screening a verticillium dahliae kleb mutant library mediated by agrobacterium tumefaciens and built through T-DNA insertion technology by the inventor. Southern hybridization proves that the mutant strain is a T-DNA single-insertion mutant. A gene causing mutant phenotype is obtained through TAIL-PCR technology by the inventor. Gene complementation tests prove that the mutation of the gene VdGRP1 weakens the pathogenicity of the strain vdgrpl which means that the gene VdGRP1 is a fungi pathogenic related gene.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Methods for nucleic acid mapping and identification of fine-structural-variations in nucleic acids
ActiveUS8329400B2Quick buildEfficient sortingSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNADigestion
A method of juxtaposing sequence tags (GVTs) that are unique positional markers along the length of a population of target nucleic acid molecules is provided, the method comprising: fragmenting the target nucleic acid molecule to form target DNA insert; ligating the target DNA insert to a DNA vector or backbone to create a circular molecule; digesting the target DNA insert endonuclease to cleave the target DNA insert at a distance from each end of the target DNA insert yielding two GVTs comprising terminal sequences of the target DNA insert attached to an undigested linear backbone; recircularizing the linear backbone with the attached GVTs to obtain a circular DNA containing a GVT-pair having two juxtaposed GVTs; and recovering the GVT-pair DNA by nucleic acid amplification or digestion with endonuclease having sites flanking the GVT-pair. Cosmid vectors are provided for creating GVT-pairs of ˜45- to 50-kb separation sequencable by next-generation DNA sequencers.
Owner:VERSITECH LTD
Application of rice OsWRKY45-1 gene in improving abiotic stress resistance of plants
The invention relates to the technical field of plant gene engineering, in particular to a functional verification of a rice OsWRKY45-1 gene in resisting abiotic stress. A T-DNA insertion technology is used to inhibit OsWRKY45-1 gene expression in the rice varieties. The genetic transformation rice with inhibited OsWRKY45-1 gene expression has obvious enhancement for drought and hypothermal endurance capacity, thereby proving that the OsWRKY45-1 gene is a negative control factor in resisting the abiotic stress for the rice. The invention cultivates plants with drought and hypothermy resistance by inhibiting the OsWRKY45-1 gene.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
Huaman plasma DNA quantitative analyser
InactiveCN1811387AAccurate quantitative detectionOvercoming Extraction EfficiencyMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluorescenceTherapeutic effect
The present invention relates to a quantitative detection analysis method of human plasma DNA level. Said method includes the following steps: selecting artificially-synthetic exogenous DNA series whose extraction efficiency is identical to or similar to that of human plasma DNA, but they are non-homologous, selecting housekeeping gene beta actin as determination gene, inserting artificially-synthetic exogenous DNA into carrier pMD18T and placing it in the bacteria to make culture, making blue and white spot screening, colony PCR identification, enzyme-cutting into linearity, placing the above-mentioned material into plasma, adopting double fluorescent quantitative gene amplification, fluorescent groups are respectively FAM and HEX, extracting known exogenous positive plasmid recovery efficiency, using computation formula to make computation so as to obtain the quantity of plasma DNA.
Owner:潘世扬
Watermelon oxysporum pathogenic FonAGL3 gene as well as deleted DNA fragment, deletion mutant and application thereof
InactiveCN107299105AClear control functionEffectiveness of Good Fusarium Wilt ControlBiocideFungiHygromycin BTreatment effect
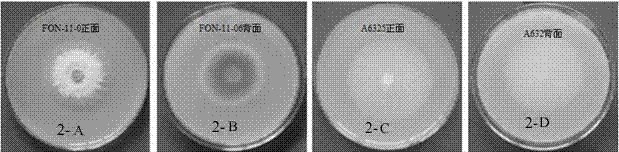
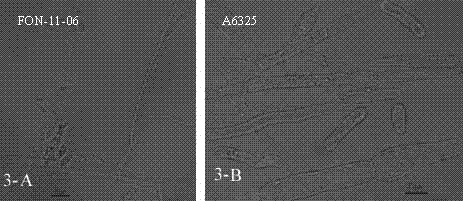
The invention discloses a watermelon oxysporum pathogenic FonAGL3 gene as well as a deleted DNA fragment, a deletion mutant and application thereof, and aims to solve the technical problem of biological prevention and treatment on watermelon oxysporum. A pathogenic gene FonAGL3 derived from watermelon fusarium oxysporum is analyzed and screened by inserting watermelon oxysporum T-DNA into a mutant library, by utilizing the homologous gene replacement principle, DNA fragments of the target gene FonAGL3 are replaced by gene DNA fragments of a resistance gene hygromycin B (HPH), a FonAGL3 gene deletion mutant is obtained by establishing a gene deletion carrier and implementing genetic transformation of a wild strain FON-11-06, and the FonAGL3 mutant bacterium has a good wilt prevention and treatment effect and is environmental-friendly and low in prevention and treatment cost.
Owner:河南省农业科学院园艺研究所 +1
Paddy rice gene of synthetase of coded beta - keto acyl coenzyme A
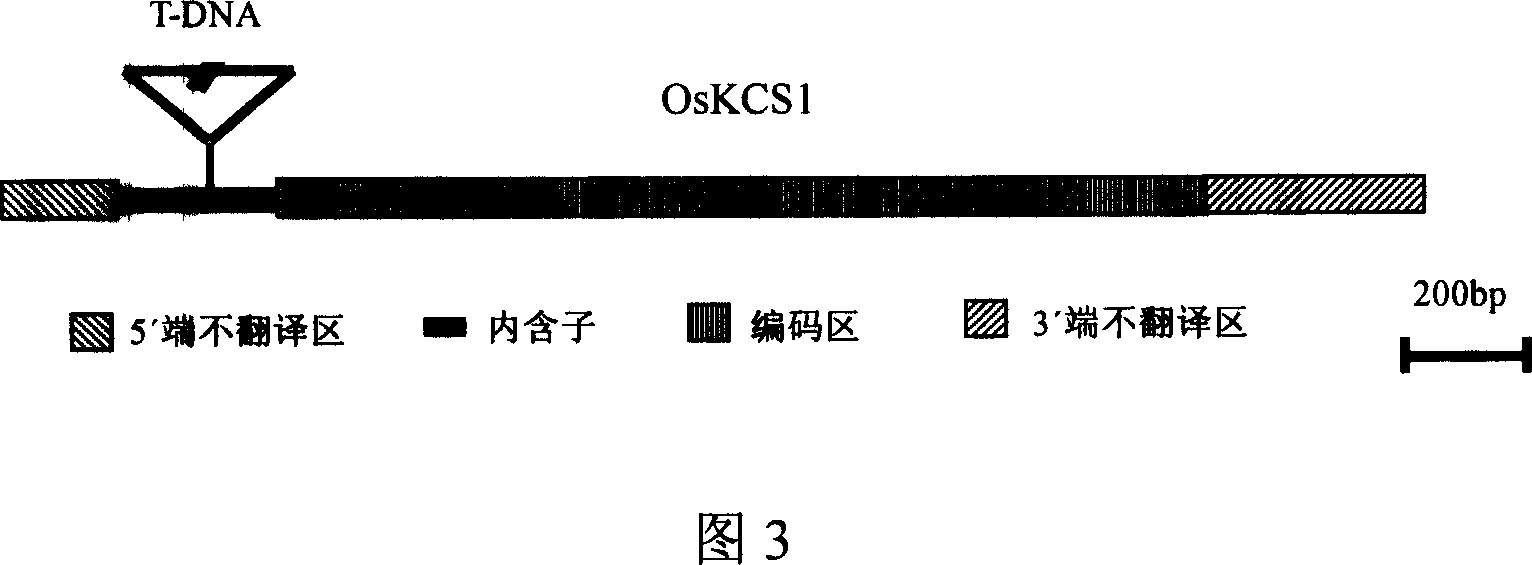
This invention provides a rice gene coding beta-keto co A synthetase, OsKCS1, which comprises 2186bp and 1560bp coding zones at the upstream of the start codon with promoter function, codes 519 amino acid, and contains typical FAE1 CUT1 RppA domain. The function-deficient mutant P1424 obtained by inserting T-DNA into rice OsKCS1 gene has short plants, occasionally curled leaves, and low fruiting rate. Further research shows that the wax at the surfaces of the mutant gas-generating organs is obviously reduced, and the draught resistance is seriously influenced. The expression of OsKCS1 gene in the mutant can recover its wild phenotype, thus can confirm the direction relationship between OsKCS1 gene and synthesis and growth of wax on rice surfaces. The identification of the gene is important to research on synthesis of wax on rice surfaces, and breeding of draught-resistant rice or other monocotyledon crops.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Arabidopis thaliana heat shock transcription factor gene HSFA 2 and coding protein and application thereof
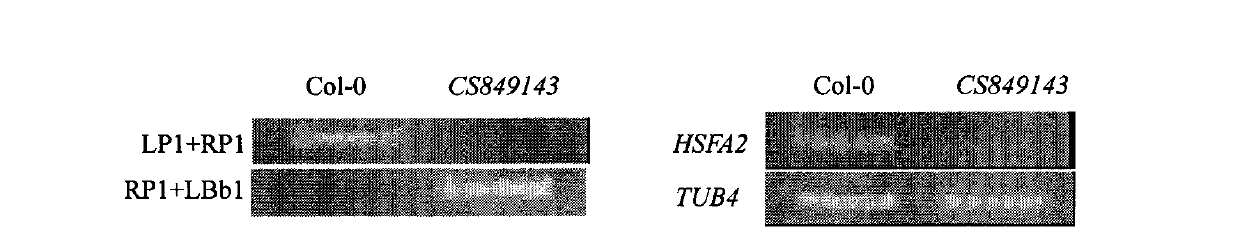
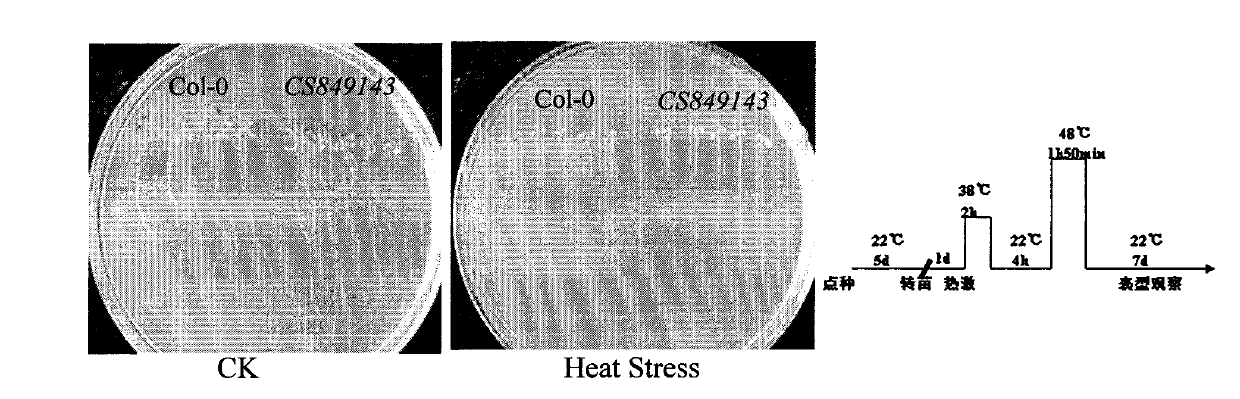
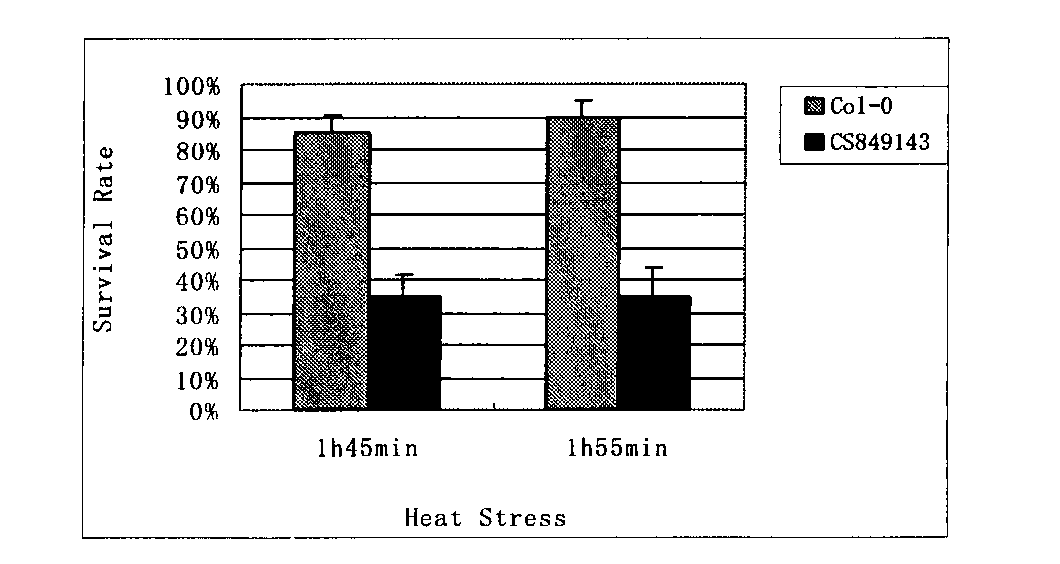
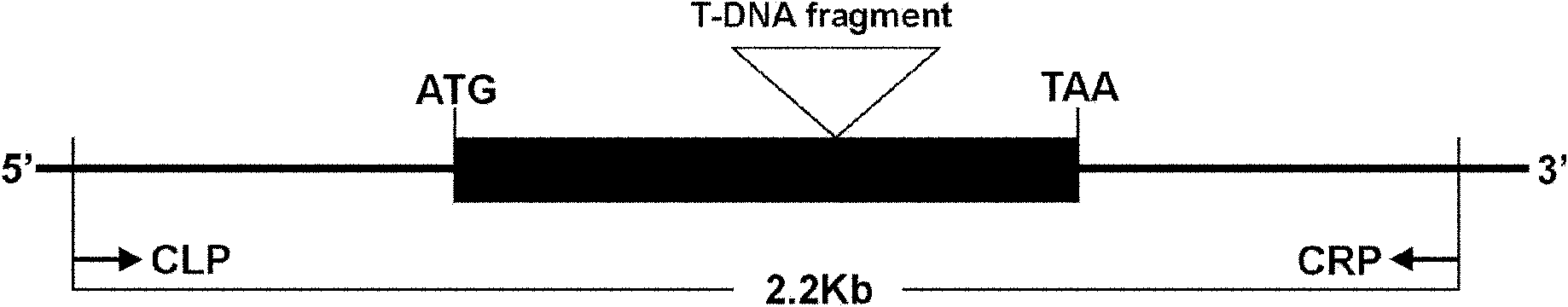
The invention belongs to the field of technology related to plant molecular biology and transgenosis. Concretely, the invention relates to verification of high temperature resistance function of the Arabidopis thaliana heat shock transcription factor gene HSFA 2, and the application of the gene in high temperature resistance plant new species cultivation. According to the invention, a model plant Arabidopis thaliana is used as material, and a HSFA gene T-DNA is inserted into a homozygous mutant lines CSS 849143 for researching high temperature resistance function of the HSFA2 gene in plants. The experiment result displays that the HSFA2 gene knock-out mutant appears a sensitive phenotype with heat shock stress, and survival rate, conductivity and osmotic pressure and other physiological indexes are significantly or highly significantly different from those of the wild type; The invention instructs that the HSFA2 gene plays an important effect in the signal transduction pathway of plant response low nitrogen stress, and predicts that the excessive expression of the gene can improve the heat resistance capability of plant and has a larger economic value in the plant stress-resistance molecular breeding.
Owner:INST OF CROP SCI CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Anther development control gene and use thereof in realizing male sterility in Arabidopsis thaliana
ActiveCN102140131AAccording to Mendelian inheritanceIn line with the law of inheritancePlant peptidesFermentationNucleotideWild type
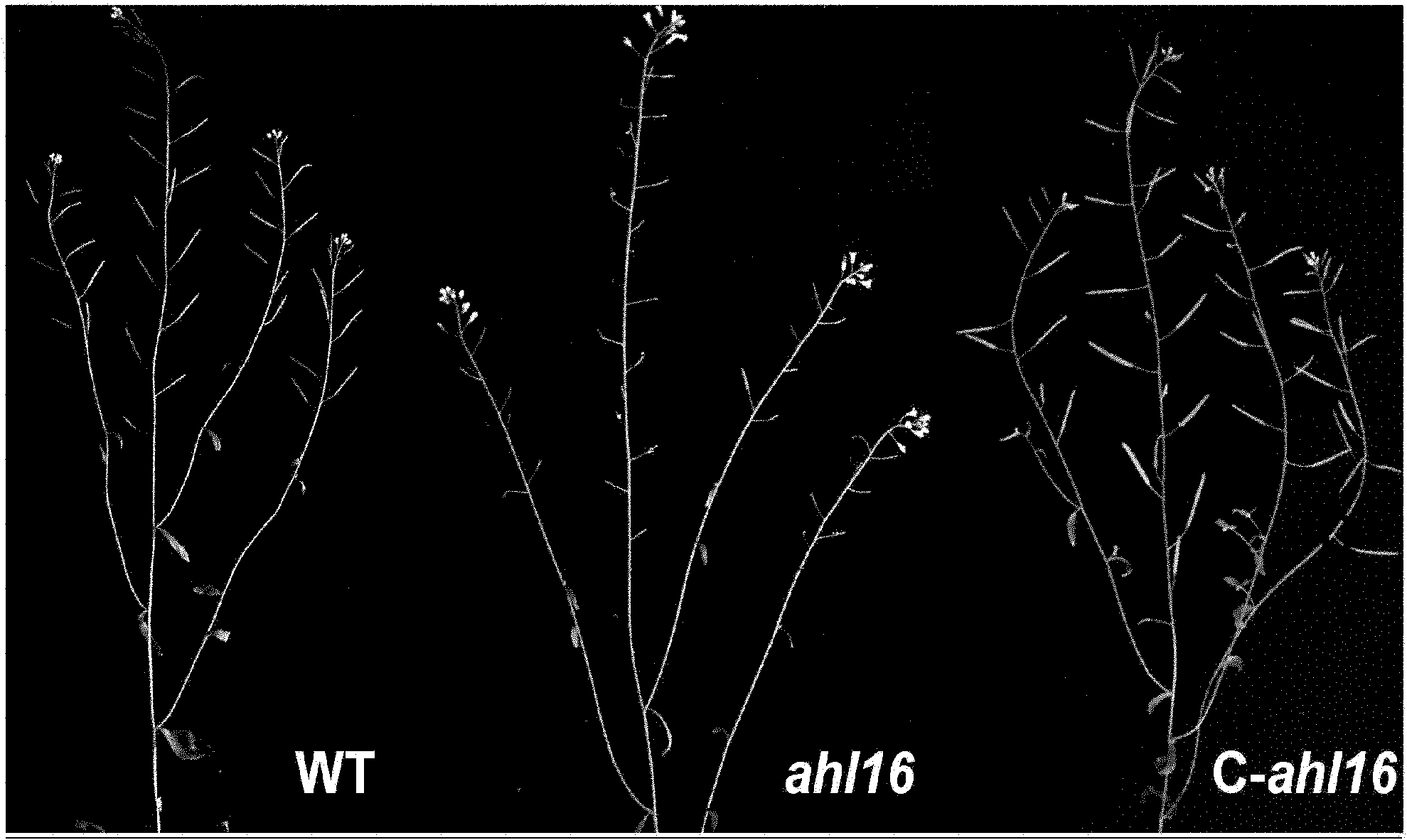
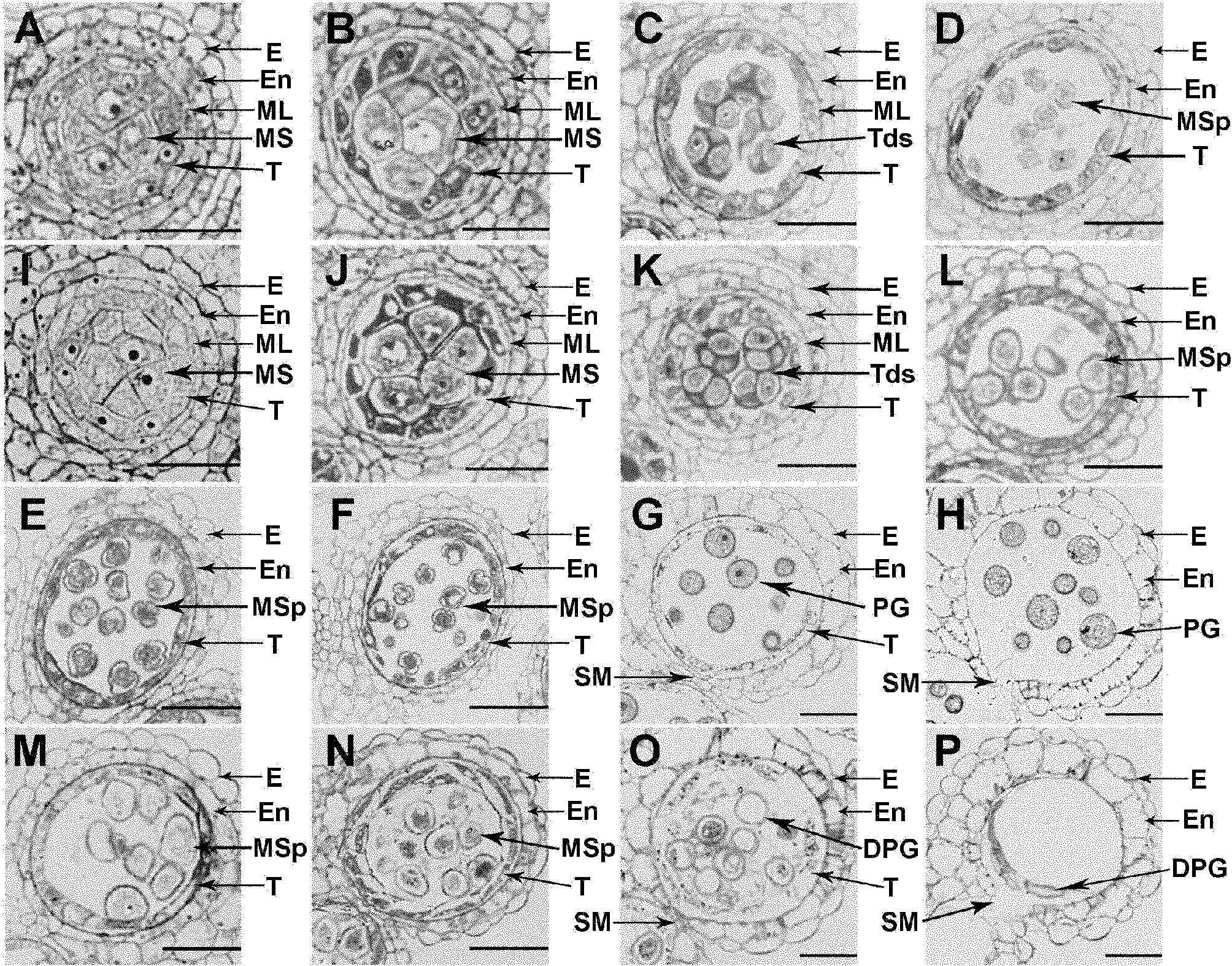
The invention relates to an anther development control gene and use thereof in realizing male sterility in Arabidopsis thaliana. An Arabidopsis thaliana male sterile mutant ahl16 is screened out from T-DNA-inserted mutant population, a gene AHL16 controlling the fertility of Arabidopsis thaliana is cloned and identified, the nucleotide sequence of the gene AHL16 is represented by SEQ ID N0.1, and genetic complement experiments prove that the AHL16 gene in a wild type can restore the male sterile phenotype. Amino acid sequence analysis and subcellular localization experiments indicate that the AHL16 gene codes proteins of an AT-hookmotif nuclear localized protein family and is located in the nucleus. In Arabidopsis thaliana, the mutation of the gene leads to complete male sterility. The gene has a very important application value in aspects of explanation of influences of the growth of the inner layers of the outer walls of microspores and the structures of the inner walls on the fertility of plants and improvement on yield by hybrid seed production.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Fused protein, gene therefor, recombinant vector, recombinant virus, and its use
InactiveUS7348422B2Enhanced infection prevention activityEasy to identifyAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesA-DNAMycoplasma gallisepticum
A DNA coding for a fusion protein comprising a polypeptide having the antigenicity of Mycoplasma gallisepticum and a polypeptide derived from Herpesvirus outer membrane protein, in which the polypeptide derived from the outer membrane protein has been ligated with the polypeptide having the antigenicity of Mycoplasma gallisepticum at the N terminus thereof, is prepared. The DNA is inserted into a region non-essential to growth of Avipox virus and the resulting recombinant Avipox virus is provided as a more potent recombinant virus as an anti-Mycoplasma vaccine.
Owner:ZEON CORP
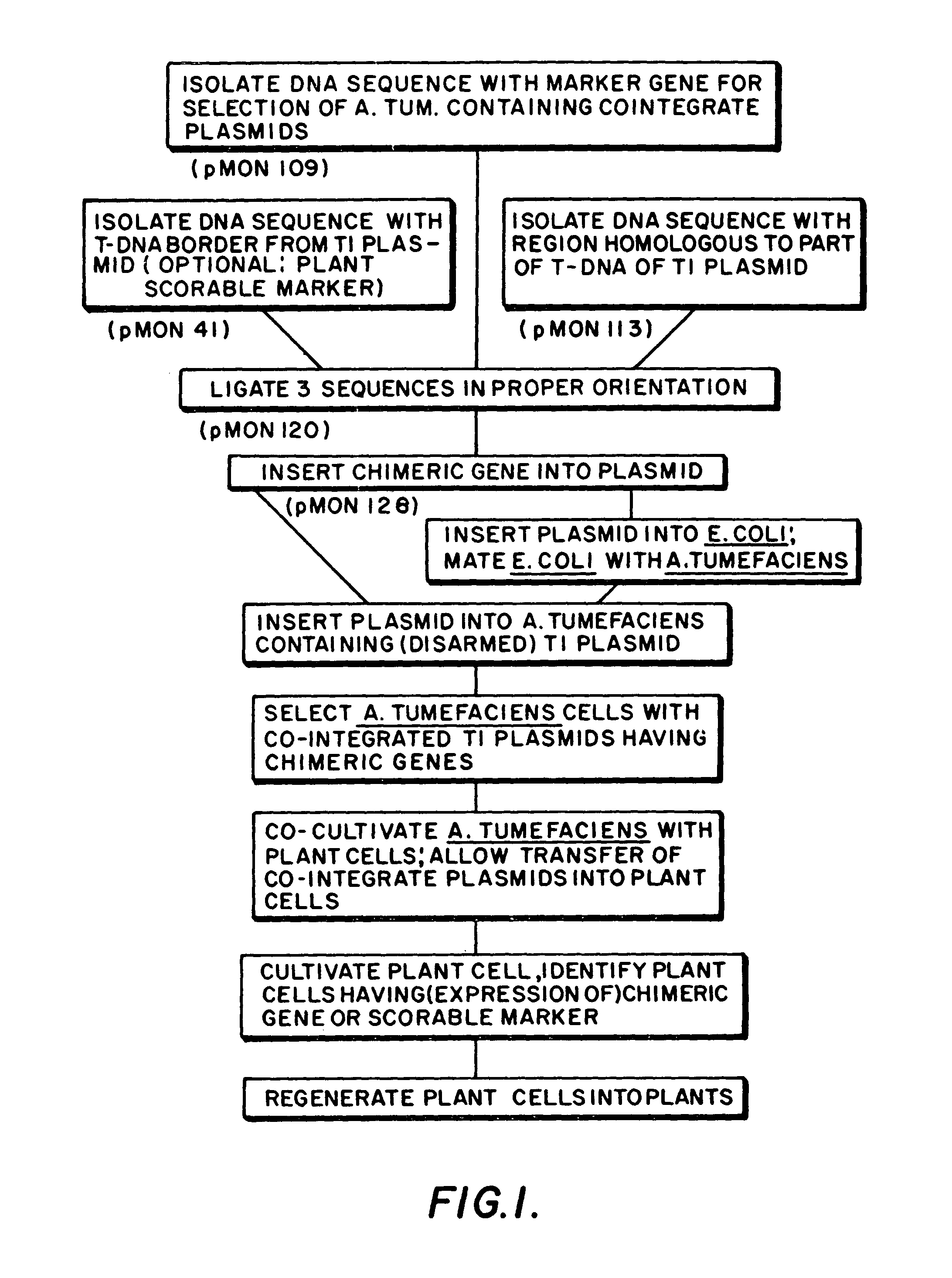
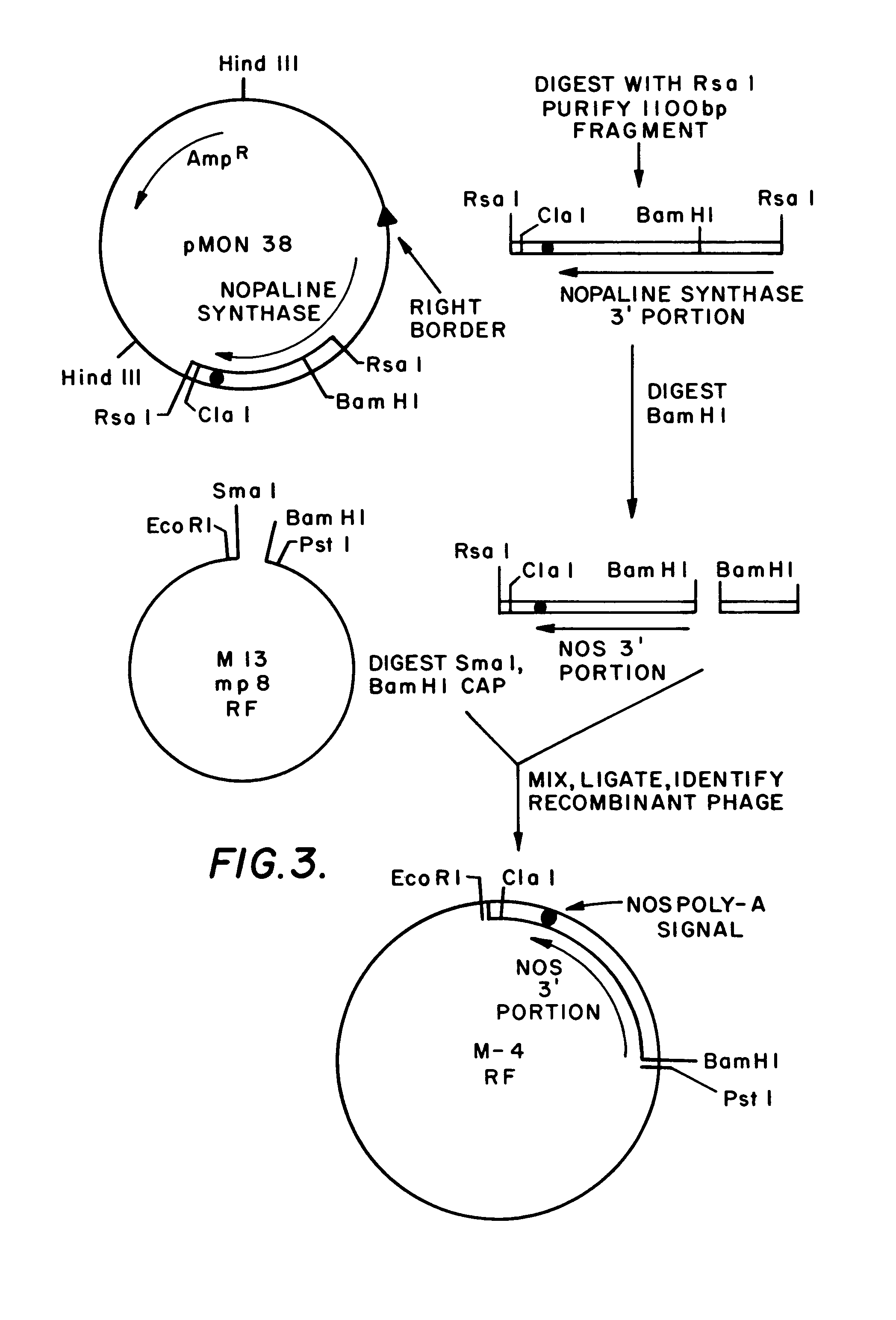
Plasmids for transforming plant cells
Owner:MONSANTO TECH LLC
Rice blast bacterium nontoxic gene Avr-Pib and application
InactiveCN101240282AAvoid infectionFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionAgricultural scienceNon toxicity
A rice blast bacterium innocuity gene Avr-Pib is obtained by separation and appraising in T-DNA insertion mutation. The out-knocking mutant of the gene can cause susceptibility of rice breed variety containing Pib disease-resistant gene. The out-knocking mutant and field susceptibility individual plant can recover non-toxicity by function complementation experiment and the breed variety is disease-resistant. The gene can be used as molecule target of newly pesticides and paddy rice disease-resistant genetic engineering.
Owner:FUJIAN AGRI & FORESTRY UNIV
Method for cloning rice auxin induced protein gene
InactiveCN101492671AHigh homologySimple implementation stepsFermentationPlant genotype modificationMutantDNA Intercalation
The invention relates to a method for using rice auxin to induce protein genes to be cloned, which is characterized in that the implementation steps comprise: (1) the preparation of a rice transformation receptor; (2) the genetic transformation of the rice; (3) the screening of kanamycin-resistant callus tissue and the regeneration of plants; (4) the screening of the mutant of a T-DNA inserted progenies; (5) Tail-PCR; (6) the comparison and analysis of sequences on the Internet. In the invention, a rice mutant with a short plant height is obtained when carrying out rice functional genome research by using T-DNA label method; the lateral neighboring sequences of the mutant are researched by using TAIL-PCR technology; meanwhile, the position where the mutant T-DNA inserts the rice genome is arranged on the No. 4 chromosome of the rice by the comparison on the databases of NCBI and TIGR on the Internet; moreover, the rice BAC clone (OSJNBa0084K01) of the position is found out. The T-DNA is inserted between the two genes of the clone by analyzing the clone. Known functional genes with a very high homology with BAC cloning code amino acid sequence are forecasted by the sequence comparison on the Internet.
Owner:TIANJIN AGRICULTURE COLLEGE
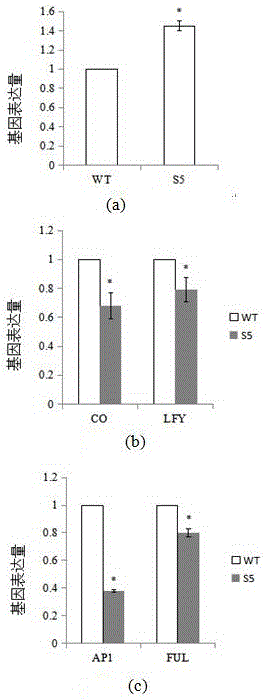
Application of arabidopsis gene SPOC1 in regulating and controlling flowering stages of plants
The invention discloses application of an arabidopsis gene SPOC1 in regulating and controlling flowering stages of plants. The application is implemented as follows: screening out T-DNA of the arabidopsis gene SPOC1, inserting the arabidopsis gene SPOC1 into a mutant homozygote plant; and comparing the flowering time and rosette leaf quantity of the mutant homozygote plant with those of a wild-type plant growing under same conditions so as to discover that the knockout of the SPOC1 gene causes expression changes of flowering relevant genes CO, RGL2, FUL, LFY and AP1 in the arabidopsis plants, and the flowering stage of the mutant homozygote plant is later than that of the wild-type plant. The technical scheme provided by the invention has great significance in regulating and controlling flowering stages of plants.
Owner:QINGDAO AGRI UNIV
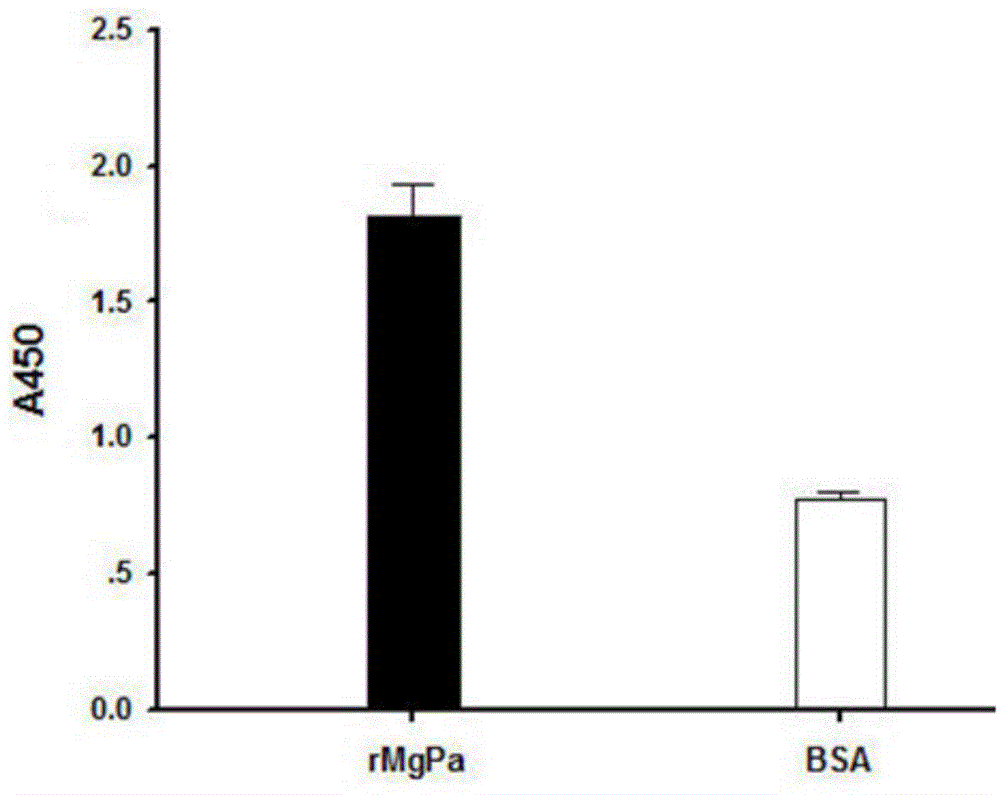
Polypeptide available for specific binding to mycoplasma genitalium adhesin protein MgPa and application thereof
InactiveCN104829693AGood effectAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDNA IntercalationAmino acid
Owner:NANHUA UNIV
Recombinant modified vaccinia ankara (MVA) vaccinia virus containing restructured insertion sites
ActiveUS20120263750A1Viral antigen ingredientsVirus peptidesModified vaccinia AnkaraOpen reading frame
The present invention relates to recombinant modified vaccinia Ankara (MVA) virus containing restructured sites useful for the integration of heterologous nucleic acid sequences into an intergenic region (IGR) of the virus genome, where the IGR is located between two adjacent, essential open reading frames (ORFs) of the vaccinia virus genome, wherein the adjacent essential ORFs are non-adjacent in a parental MVA virus used to construct the recombinant MVA virus, and to related nucleic acid constructs useful for inserting heterologous DNA into the genome of a vaccinia virus, and further to the use of the disclosed viruses as a medicine or vaccine.
Owner:US DEPT OF HEALTH & HUMAN SERVICES
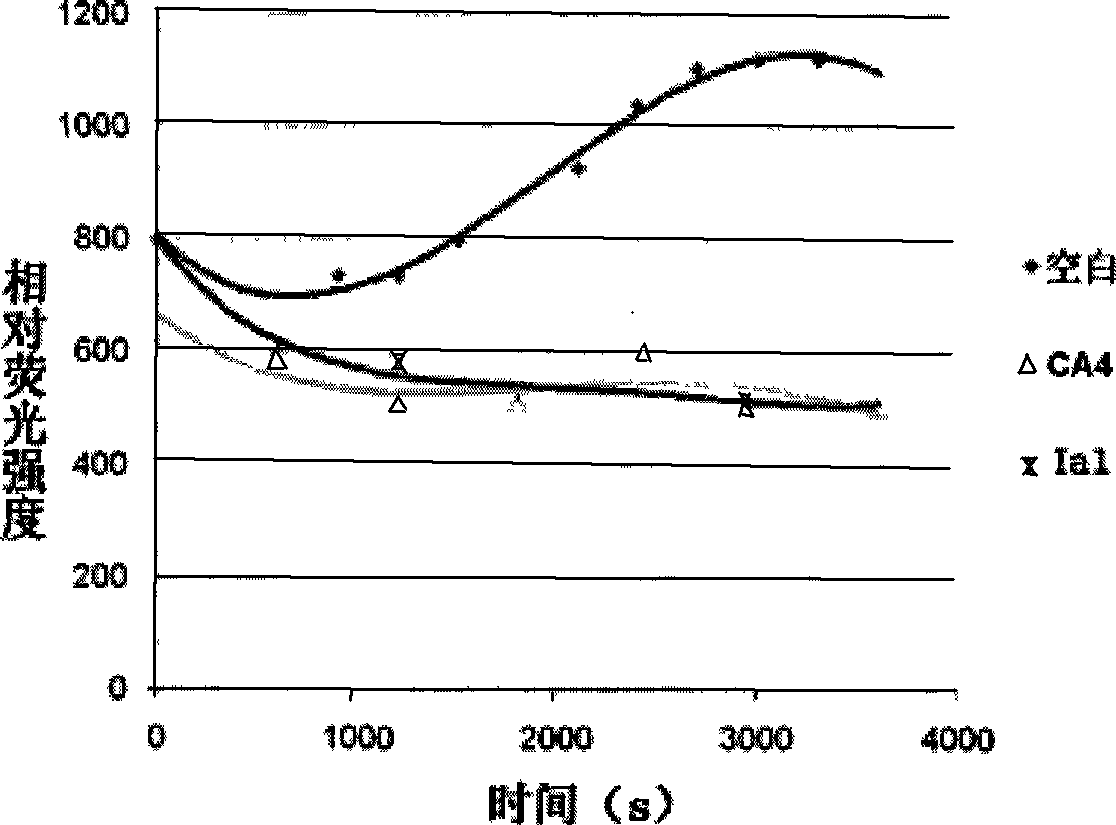
Gamma-carbolines derivates as well as preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101423517AWide variety of sourcesReasonable designOrganic active ingredientsOrganic chemistryPositive controlSide chain
The invention provides a gamma-carboline derivative, which is obtained by using gamma-carboline with antineoplastic activity as a lead compound, and introducing different lateral chains, aromatic rings, aromatic heterocycles or heterocycles to the sixth position of the gamma-carboline. Pharmacological active screening test shows that the compound has in-vitro antihyperplasia function on tumor cells; partial compound has obvious anti-tumor activity; the value of IC50 reaches mu M grade to show cytotoxicity similar to positive control polyenic taxusol; and significant microtubulin polymerization retardation activity and DNA intercalation function are presented in primary activity mechanism research; therefore, the compound is expected to be a new antineoplastic reagent with double functions of micromolecular microtubulin and DNA. The gamma-carboline derivative has the advantages of reasonable design, wide source of raw materials, easy preparation, mild reaction condition, simple operation and practicality. The structural formula of the compound is shown as the above.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
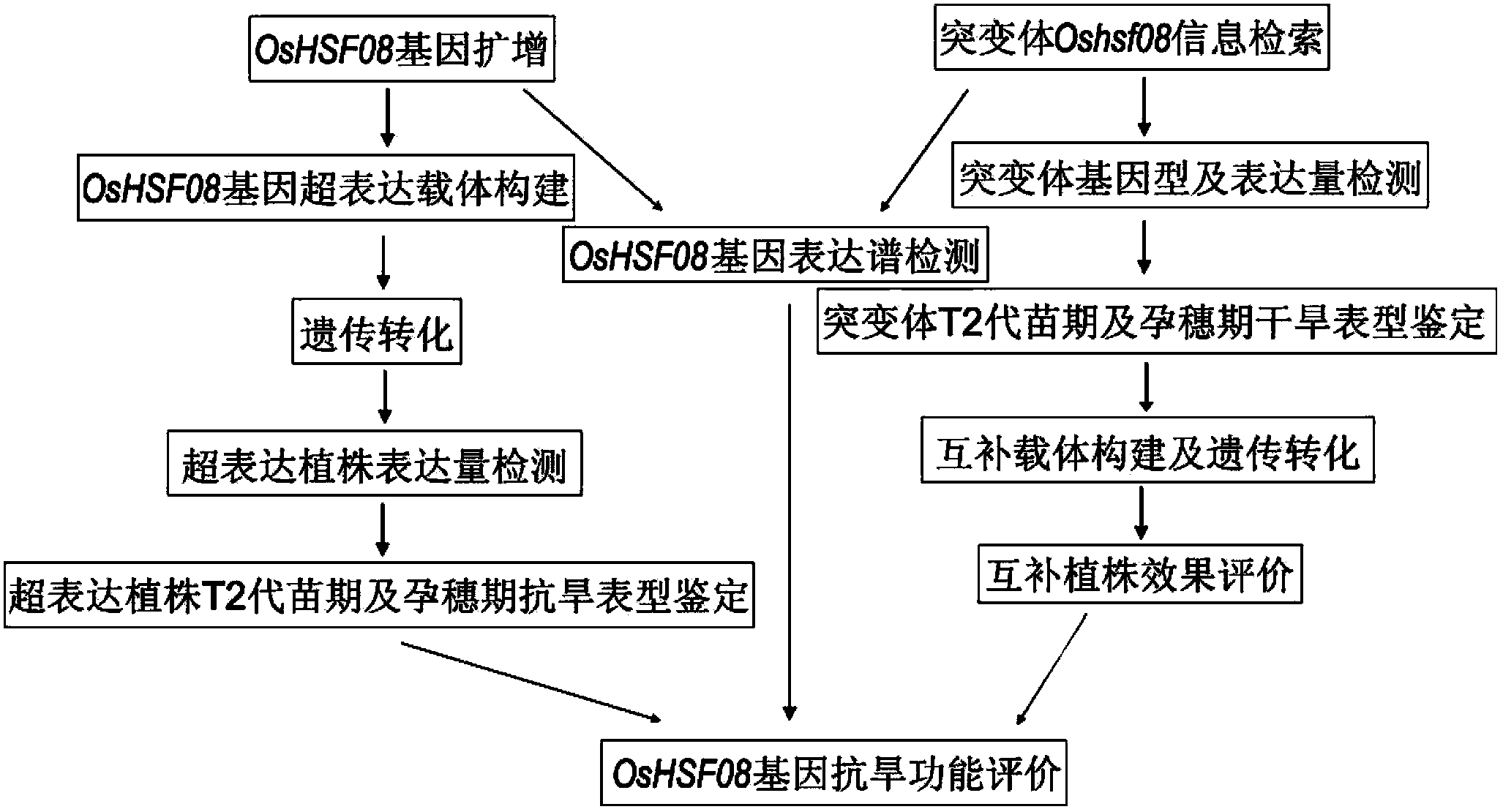
Application of OsHSF08 gene in controlling rice drought resistance
The invention belongs to the technical field of rice genetic engineering, and in particular relates to gene OsHSF08 capable of remarkably increasing drought resistance during seeding stage and booting stage, which is obtained through screening, separating, cloning and functional verification. The gene OsHSF08 capable of controlling rice drought resistance character is obtained through cloning by screening insertion of T-DNA into rice mutant library, and has nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 1; and the coded protein has nucleotide sequence shown in SEQ ID No: 2. Coseparation detection shows that the mutant is tightly linked with drought sensitivity phenotype, and the over-expression of OsHSF08 gene in rice can remarkably increase the drought resistance of the genetically modified rice, so that new function and new application approach of the gene are proven.
Owner:HUAZHONG AGRI UNIV
System and Method For the Heterologous Expression of Polyketide Synthase Gene Clusters
ActiveUS20100184038A1Sufficient quantityEfficient productionBacteriaMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousEscherichia coli
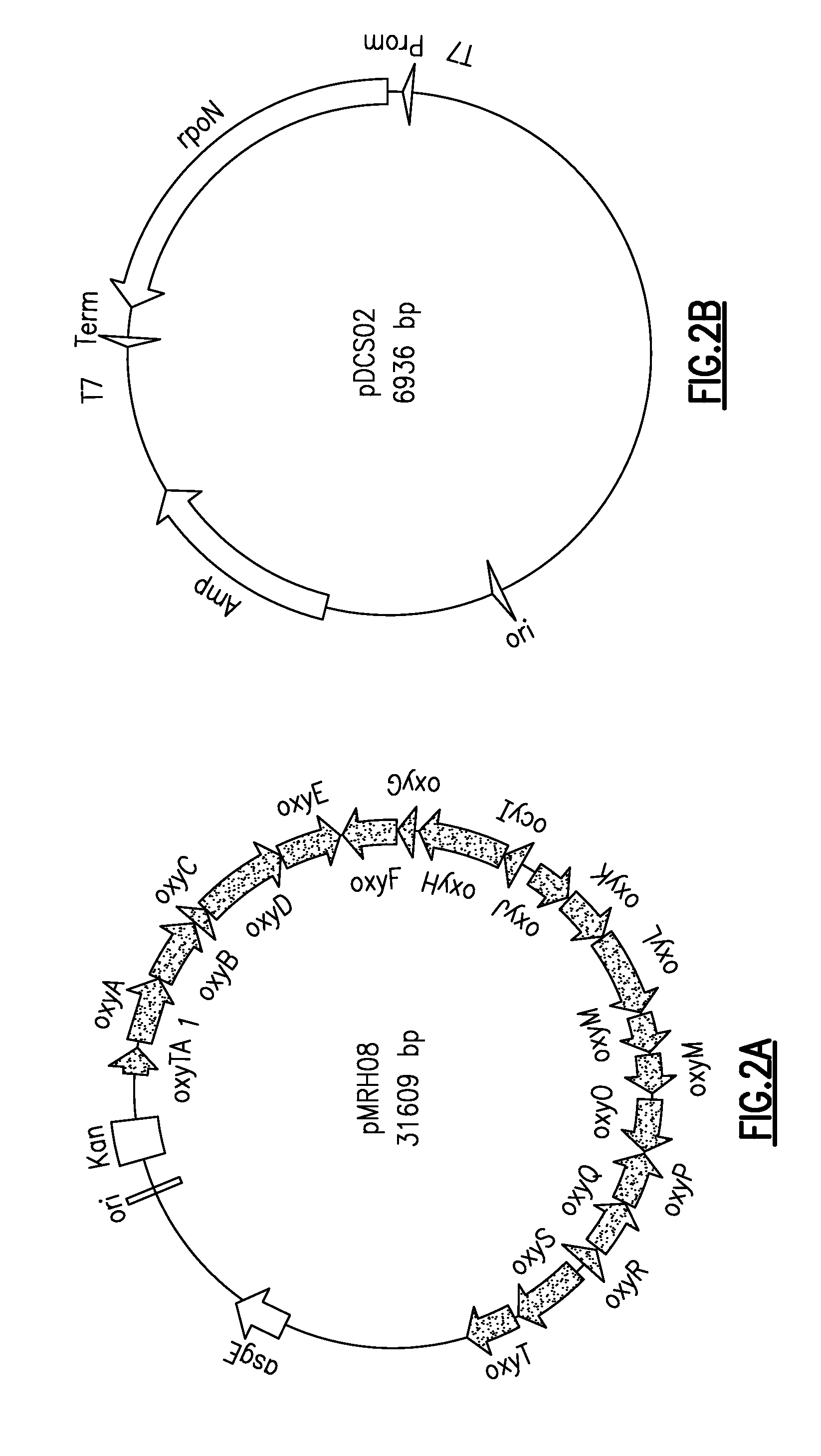
A system and method for heterologous expression of polyketide biosynthetic pathways from streptomycetes hosts in Escherichia coli for the production and discovery of secondary metabolites. Genomic DNA from Streptomyces rimosus encoding the oxytetracycline biosynthetic pathway is inserted into the genome of the surrogate host Myxococcus xanthus. The M. xanthus transcriptional machinery recognizes and uses the streptomycetes promoter regions to express the biosynthetic enzymes. Co-expression in E. coli of S. rimosus oxytetracycline biosythensis enzymes and M. xanthus σ54, a key piece of the M. xanthus transcriptional machinery, enables E. coli to recognize and use the promoters from the S. rimosus oxytetracycline biosynthetic pathway, facilitating production of oxytetracycline.
Owner:SYRACUSE UNIVERSITY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com