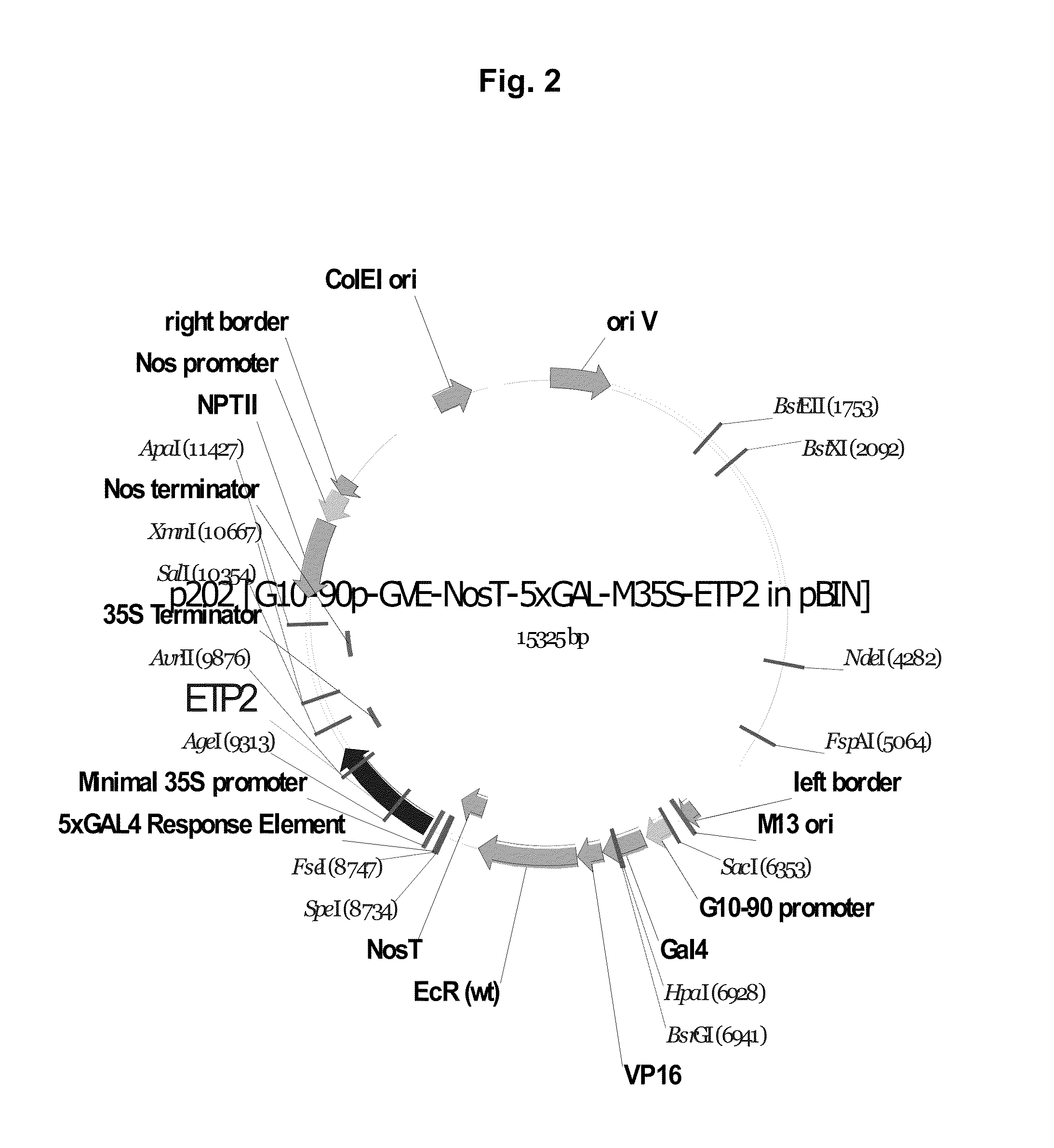
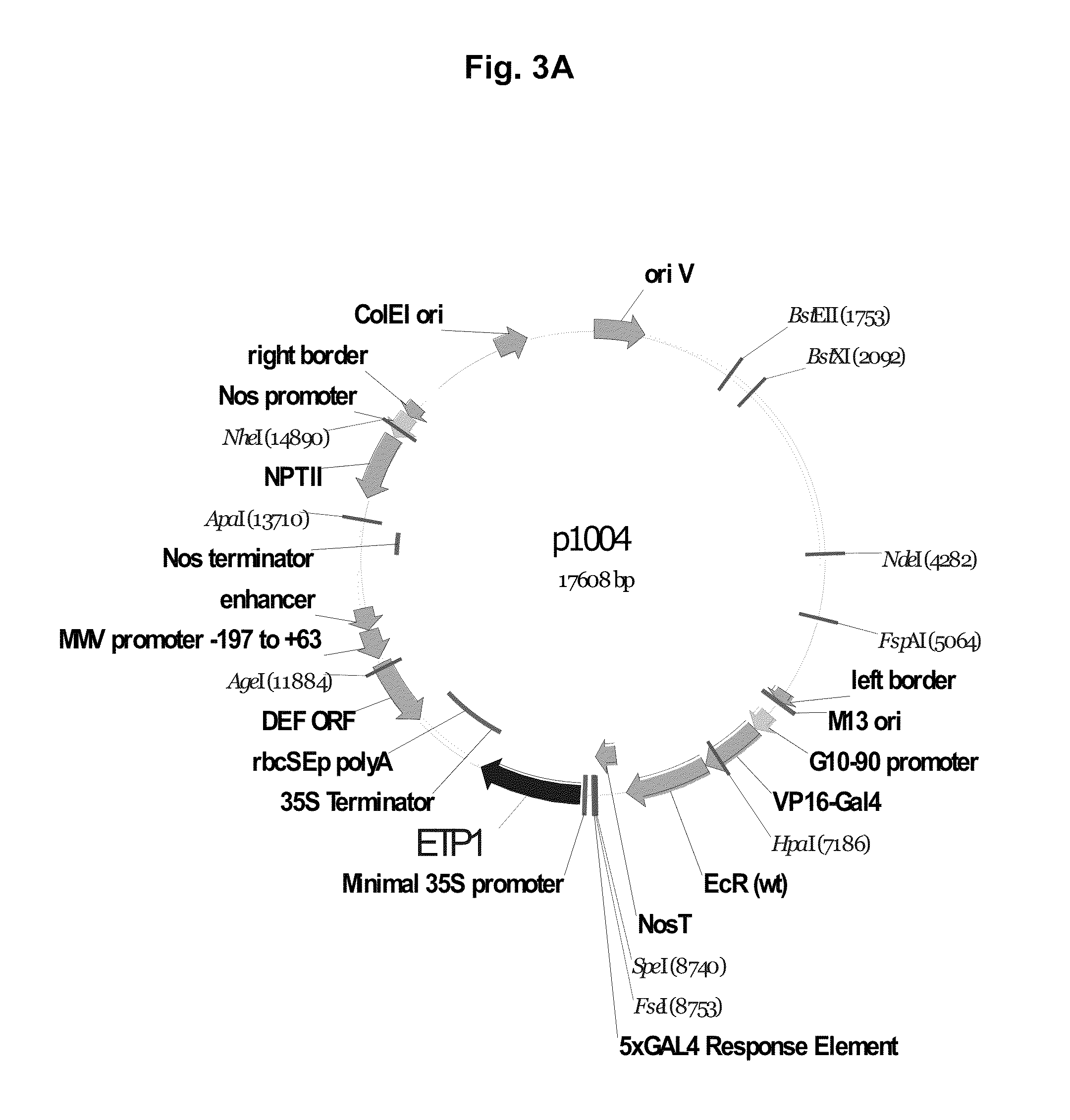
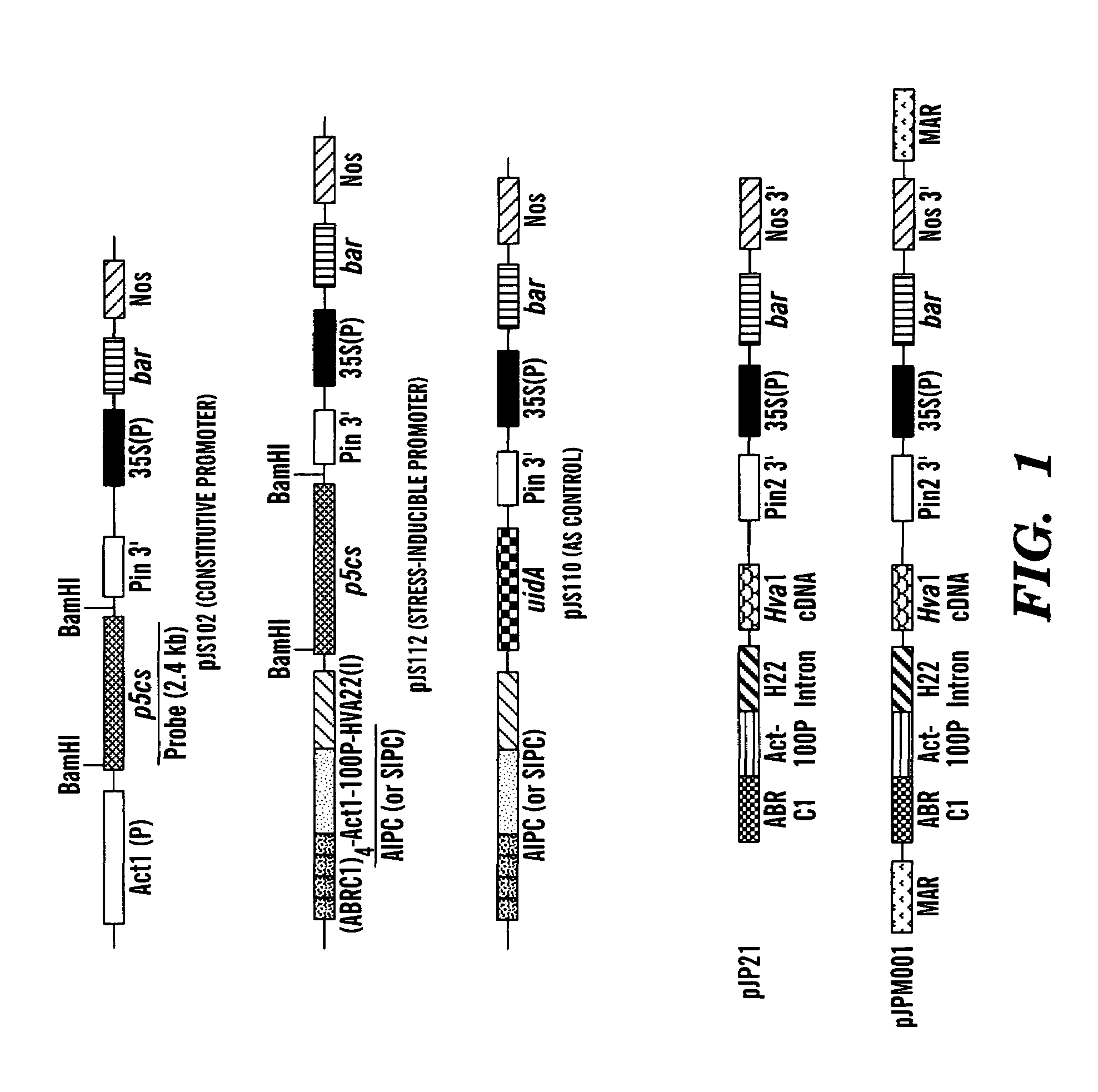
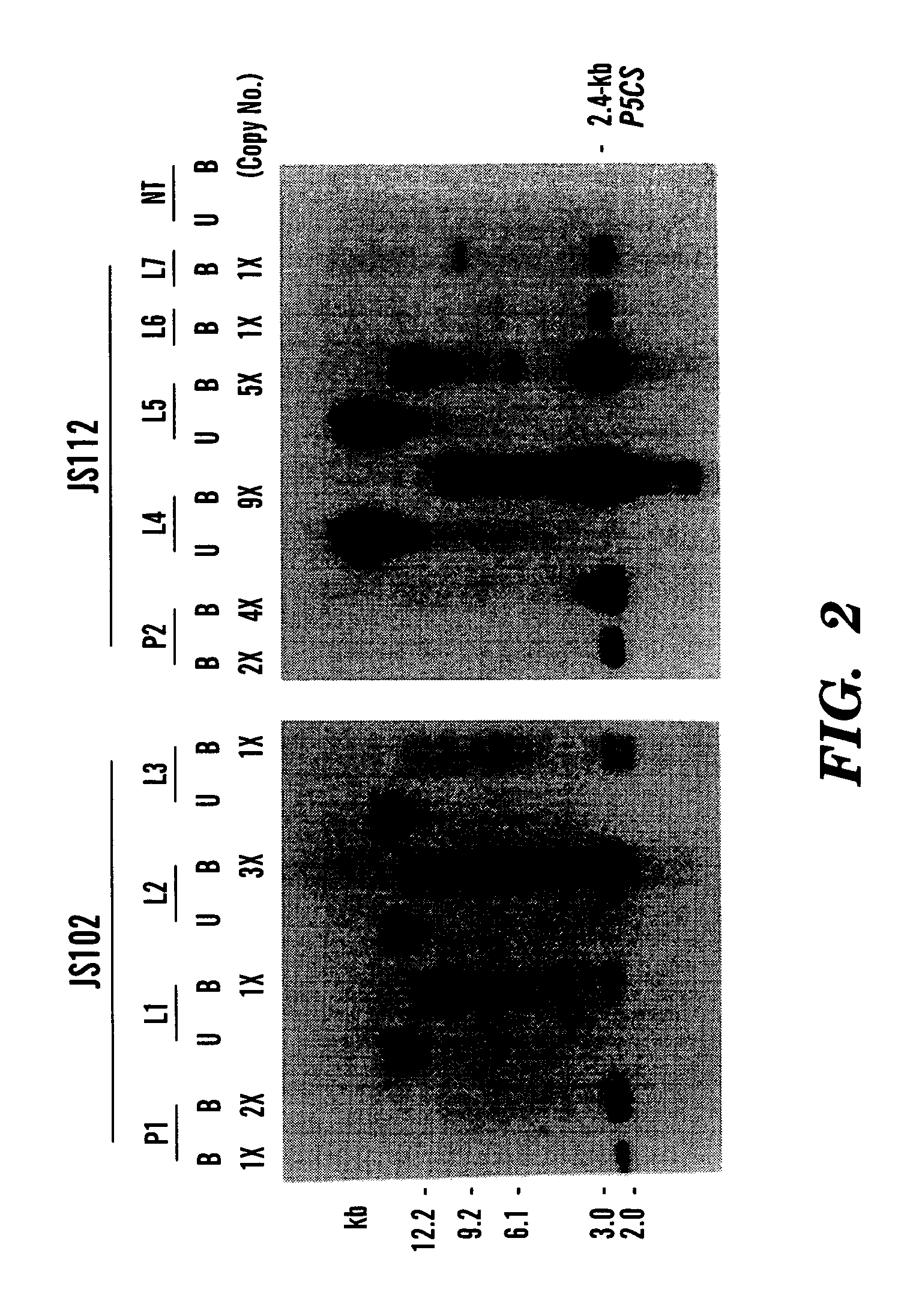
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
62 results about "Minimal promoter" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
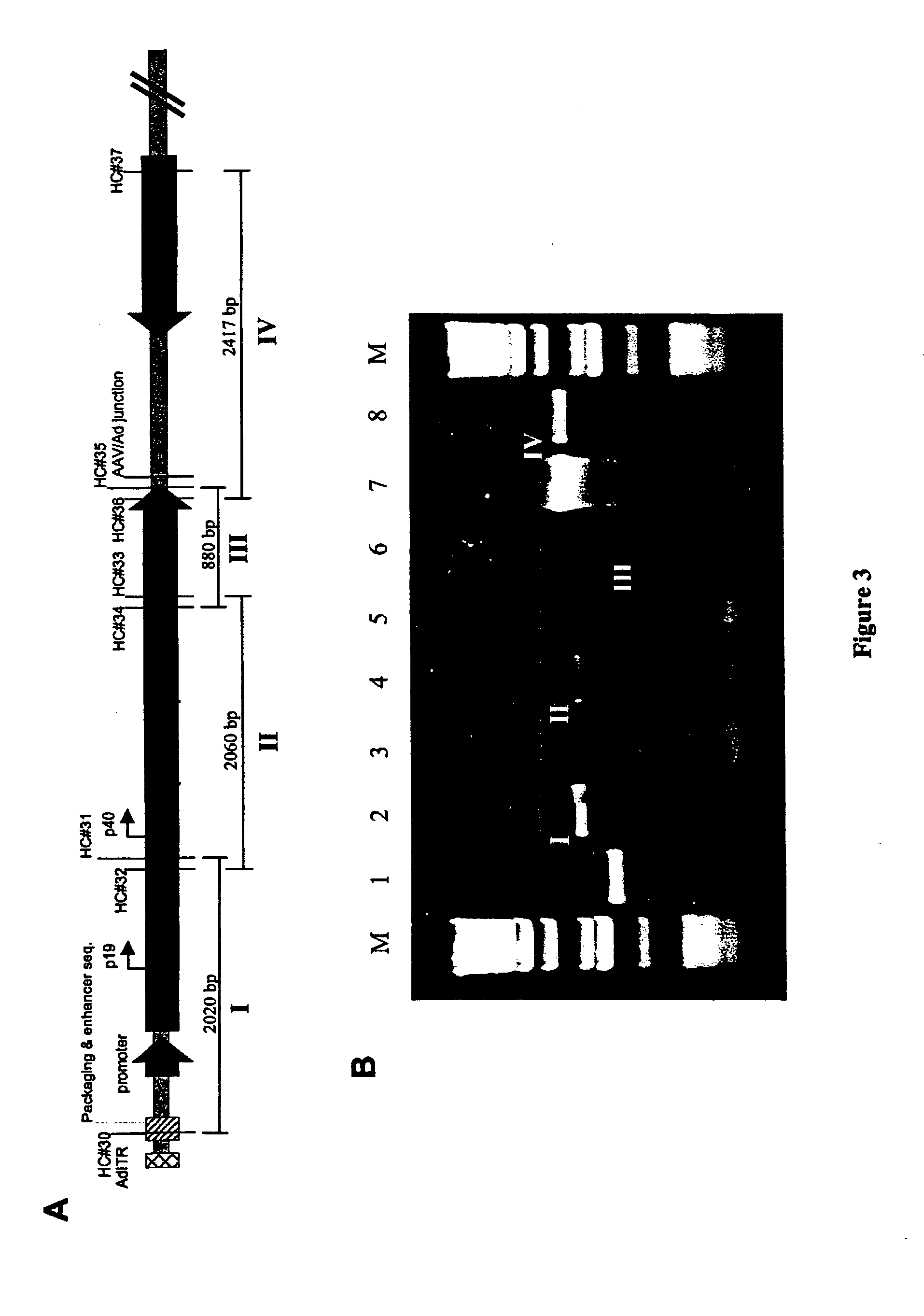
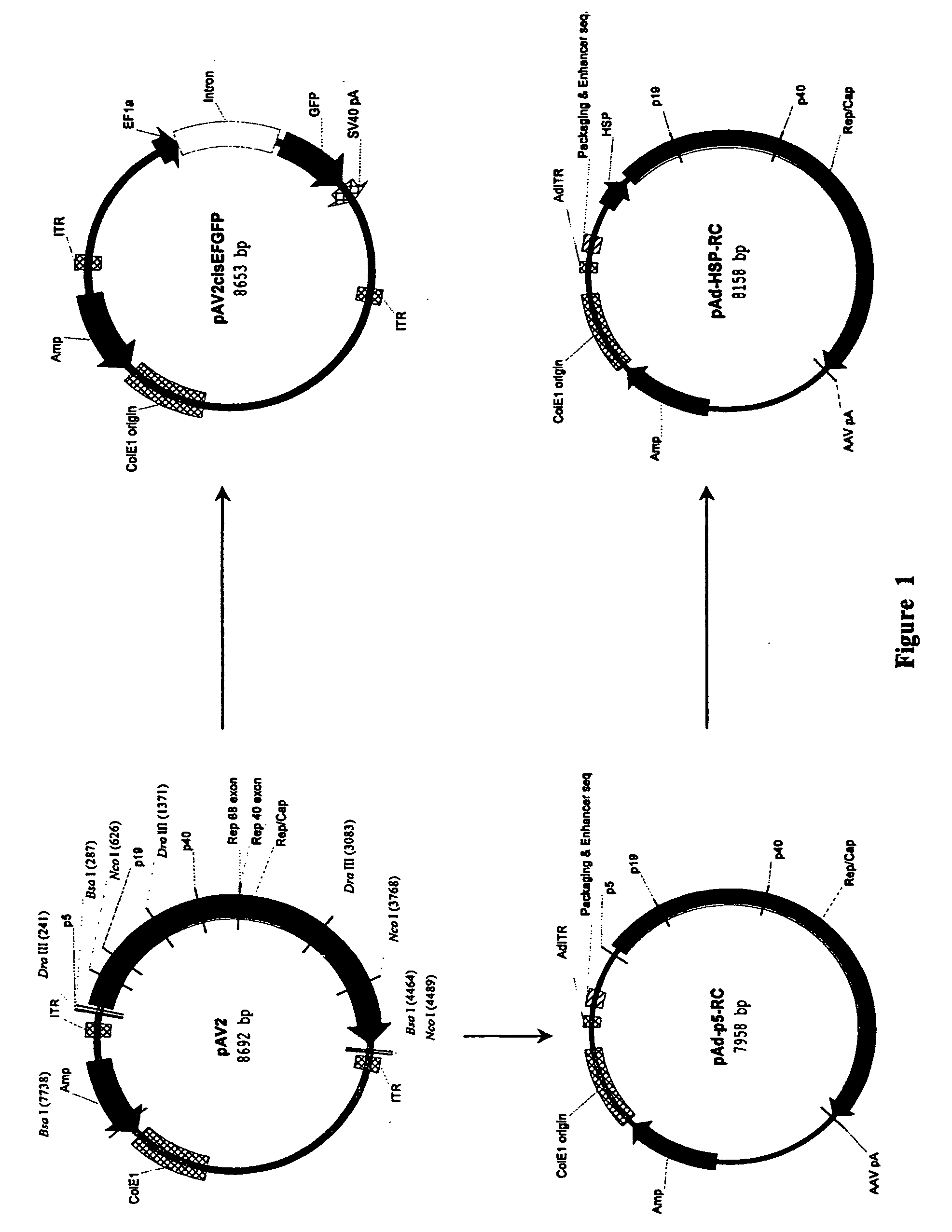
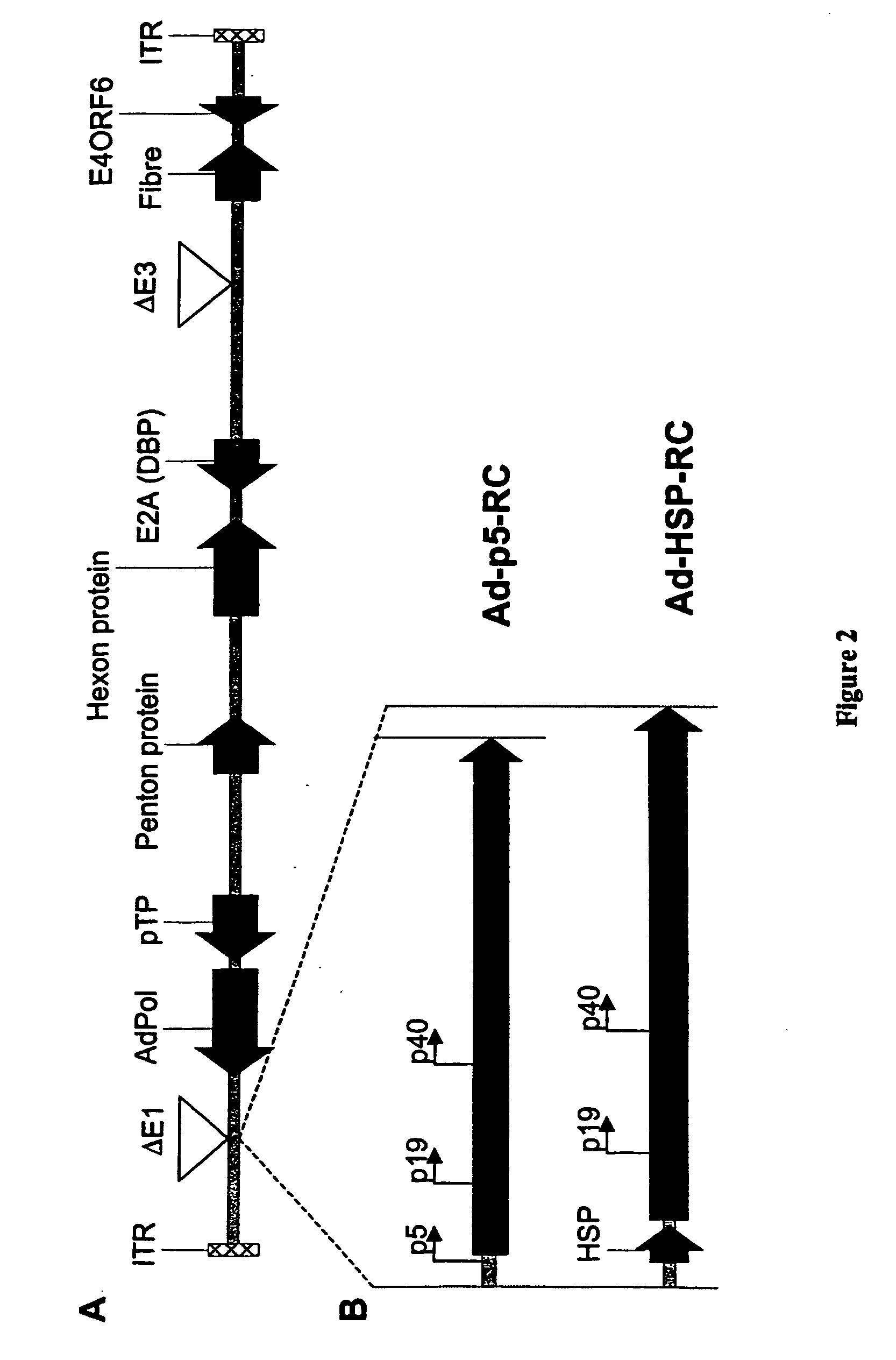
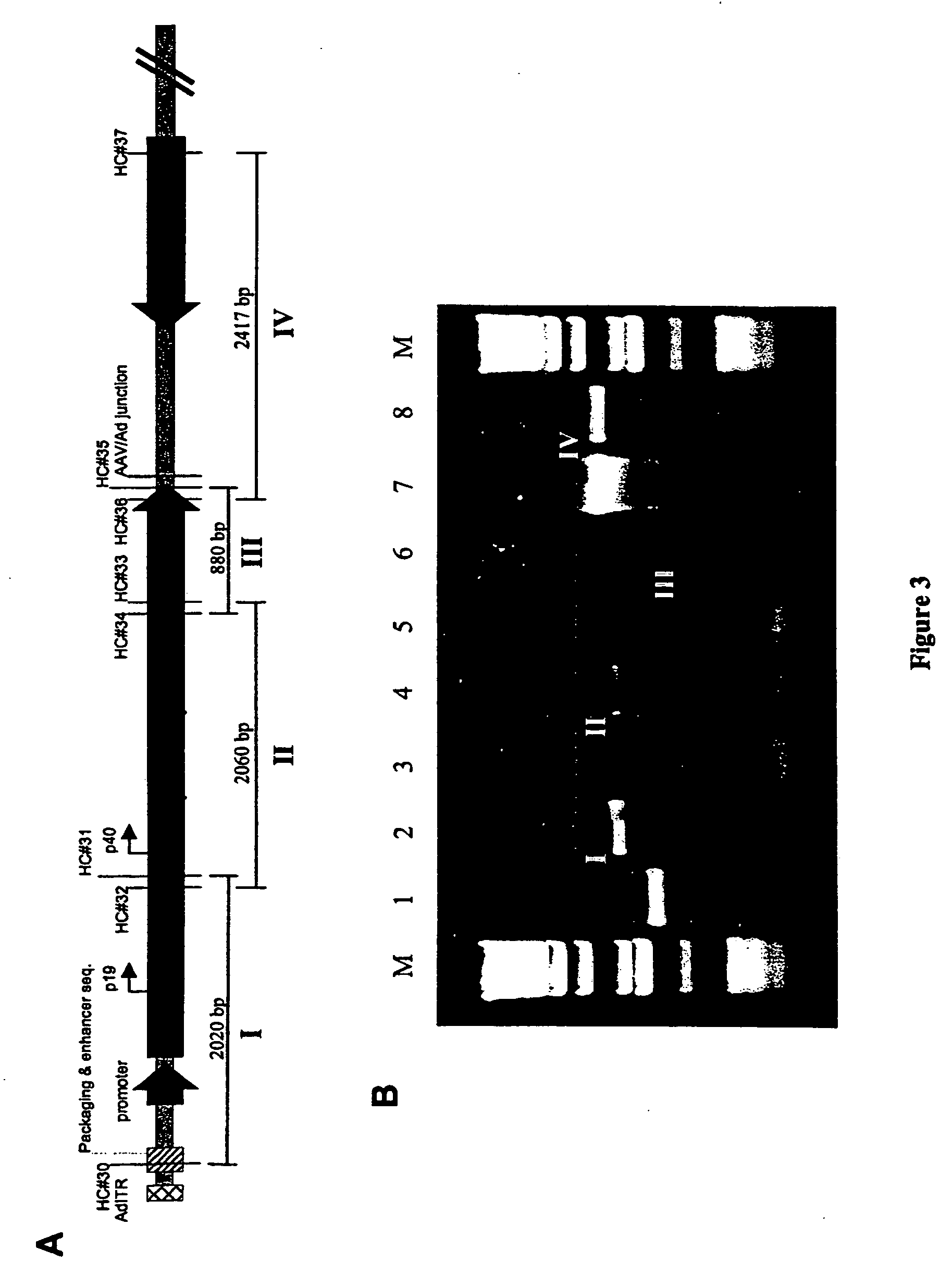
Production of recombinant AAV using adenovirus comprising AAV rep/cap genes
InactiveUS7115391B1High yieldAmenable to large-scale industrial applicationBiocideVectorsMinimal promoterDNA Intercalation
This invention relates to novel adenoviruses useful in the production of high titers of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) comprising a foreign DNA insert and methods of making these adenoviruses. The adenovirus comprises the AAV rep gene in which the p5 promoter is replaced by a minimal promoter or by no promoter. The invention also provides methods of producing high levels of rAAV as a substantially homogenous preparation and composition of rAAV.
Owner:GENOVO
Production of recombinant AAV using adenovirus comprising AAV rep/cap genes
This invention relates to novel adenoviruses useful in the production of high titers of recombinant adeno-associated virus (rAAV) comprising a foreign DNA inert and methods of making these adenoviruses. The adenovirus comprises the AAV rep gene in which the p5 promoter of rep is replaced by a minimal promoter or by no promoter. The invention also provides methods of producing high levels of rAAV as a substantially homogeneous preparation and compositions of rAAV.
Owner:GENOVO
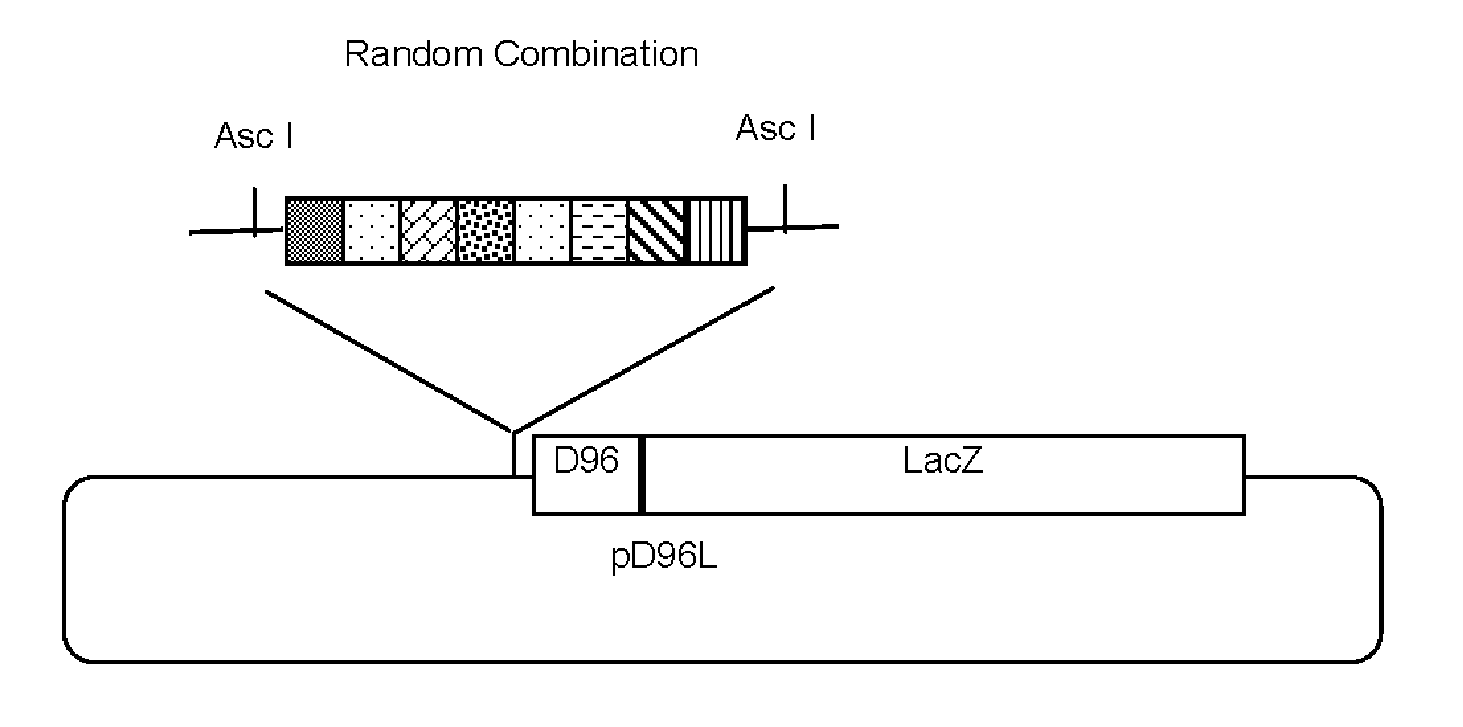
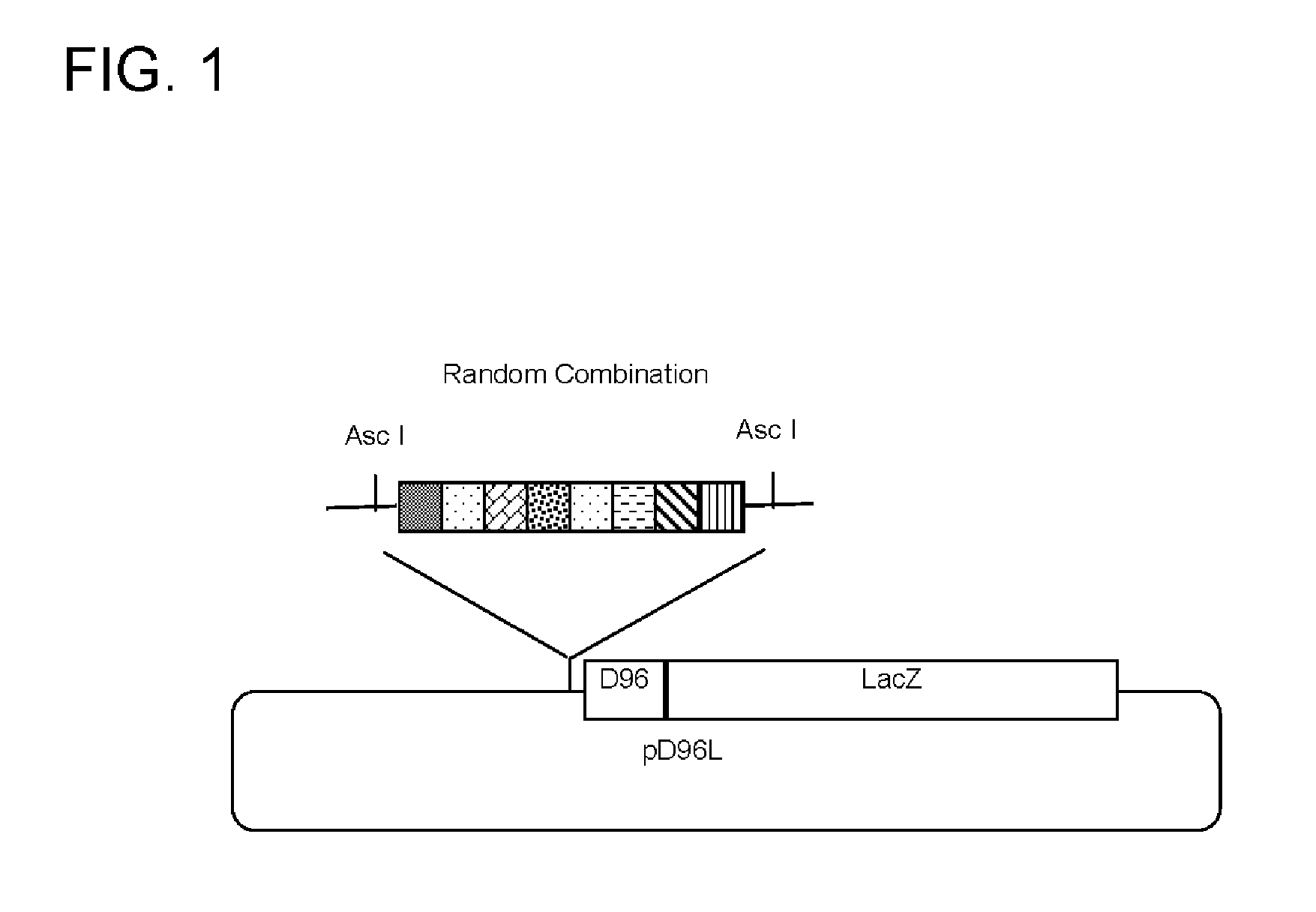
System for producing Synthetic Promoters
ActiveUS20050227246A1Improve efficiencyGood curative effectVectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscription regulatorMinimal promoter
The present application discloses a method for making and selecting a transcription enhancing combined promoter cassette, which includes constructing a library of randomly combined transcription regulatory elements, which comprise double stranded DNA sequence elements that are recognized by transcription regulators; inserting the combined transcription regulatory elements upstream of a minimum promoter followed by a reporter gene in a vector; inserting the vector into a host cell; and then screening for the cells showing enhanced expression of the reporter gene, and identifying the combined promoter cassette in the cell.
Owner:PROMOGEN
BNLEA3-1 promoter
InactiveUS20080244793A1Weakly inducibleSugar derivativesPlant peptidesEscherichia coliNicotiana tabacum
Late embryogenesis abundant (Lea) proteins accumulate in maturing seeds after many of the storage compounds have been synthesized, and they are considered relevant to maturation. We report here the molecular organization and expression of BnLea3-1, a novel Group 3 Lea gene from Brassica napus. BnLea3-1 contains a coding region of 798 bp, sharing 84.4% homology at the amino acid level with Lea76 of B. napus. Two tandem 11-mer repeats are truncated from the coding region of BnLea3-1, compared to the 13 conserved 11-mer repeats of Lea76. Substitutions of consensus residues are found at various positions within the 11-mer repeats. A 1561 bp 5′ flanking promoter fragment of BnLea3-1 fused to E. coli-glucuronidase (GUS) coding region conferred seed-specific GUS expression in stable transgenics of B. napus, tobacco and in transiently-transformed pea. A −137 bp minimal promoter preceding the first transcription start site, identified through progressive deletions from the upstream was sufficient for basal GUS expression in the seeds and in leaves treated with ABA. Deletion studies indicate the presence of enhancing elements located between −137 bp to −742 bp and suppressing elements located between −742 and −1561 bp. BnLea3-1 expression in seeds precedes that of Lea76. Unlike other Group 3 Lea members including HVA1 and Dc3, BnLea3-1 is active in seeds and responsive weakly in vegetative tissues to ABA and methyl jasmonate (MeJA) but not to stress treatments. Possible functions of BnLea3-1 and another member of the Group 3 Lea family BnLea3-2 in embryo development is discussed.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
Constructs for enhancement of gene expression in muscle
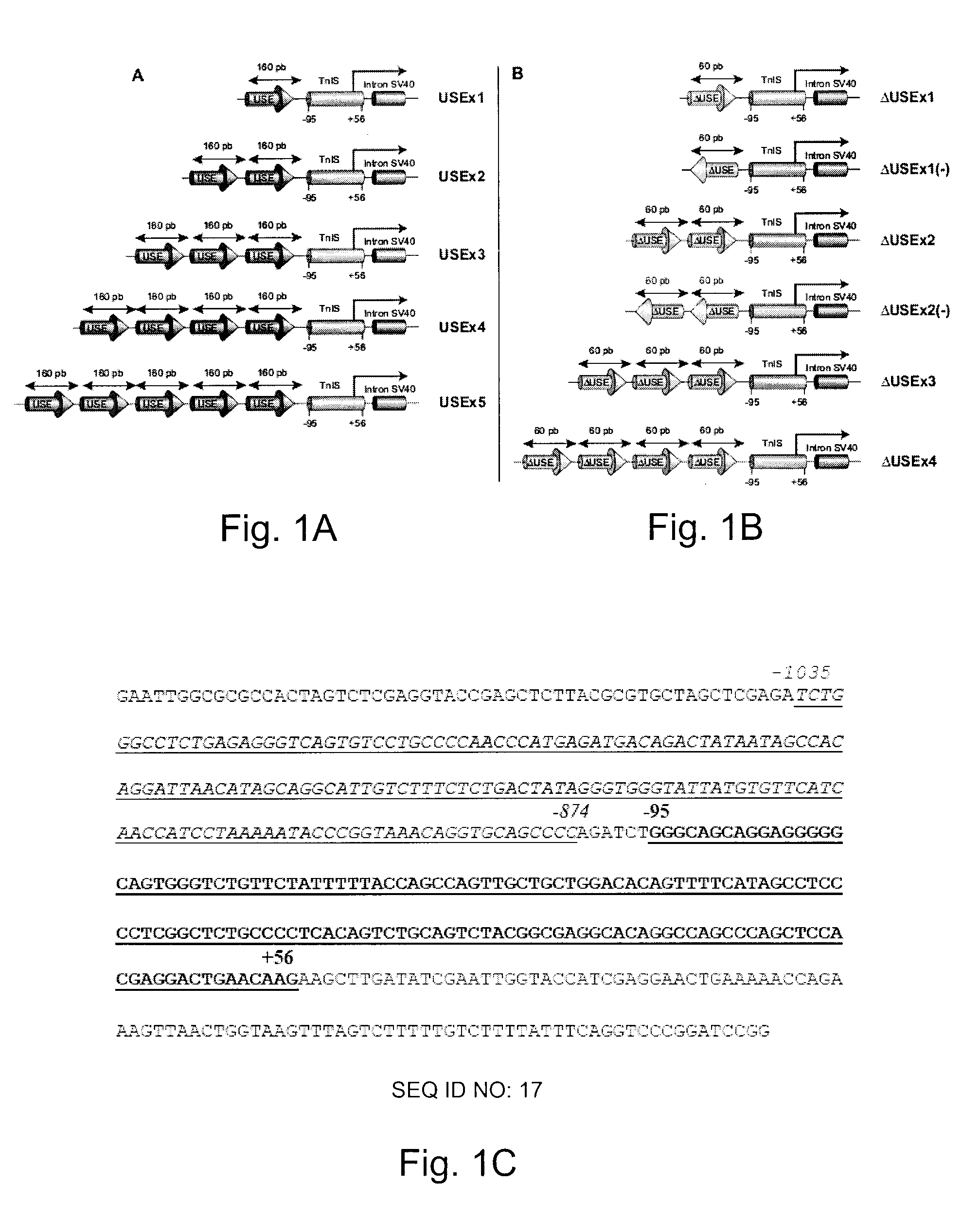
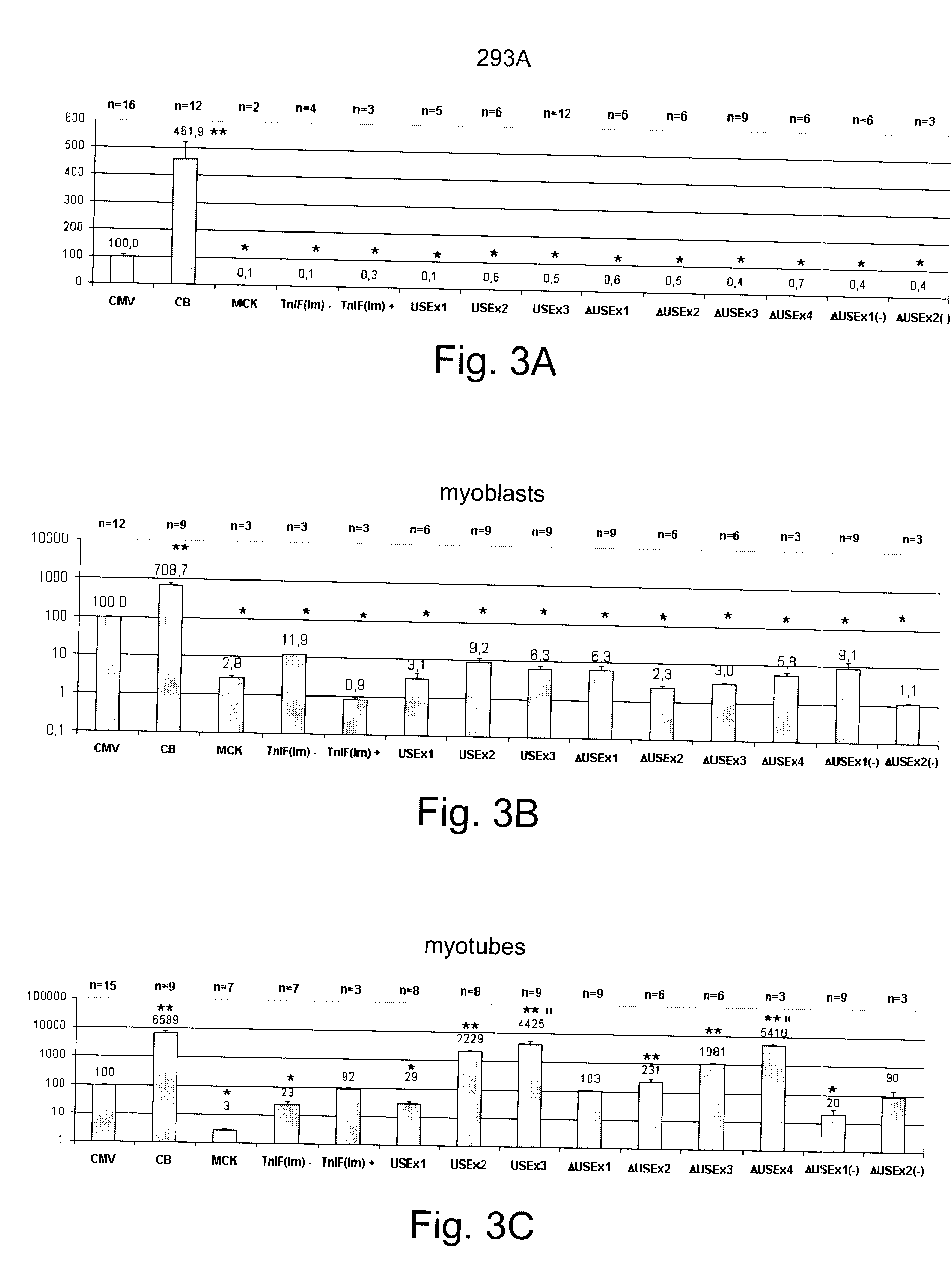
Efficient and muscle-specific gene expression can be obtained with constructs containing two or more copies of USE and / or ΔUSE fused to the minimal promoter of the TnISlow gene. USE is a small (about 160-bp) upstream enhancer of the TnISlow gene that confers slow-twitch muscle fiber specificity. ΔUSE is generated from a 100-bp deletion at the 5′ end of USE. ΔUSE confers expression in slow- and fast-twitch muscle fibers. The strength and relatively small size (less than 600-bp) of these constructs make them useful for gene therapy applications.
Owner:NAT RES COUNCIL OF CANADA
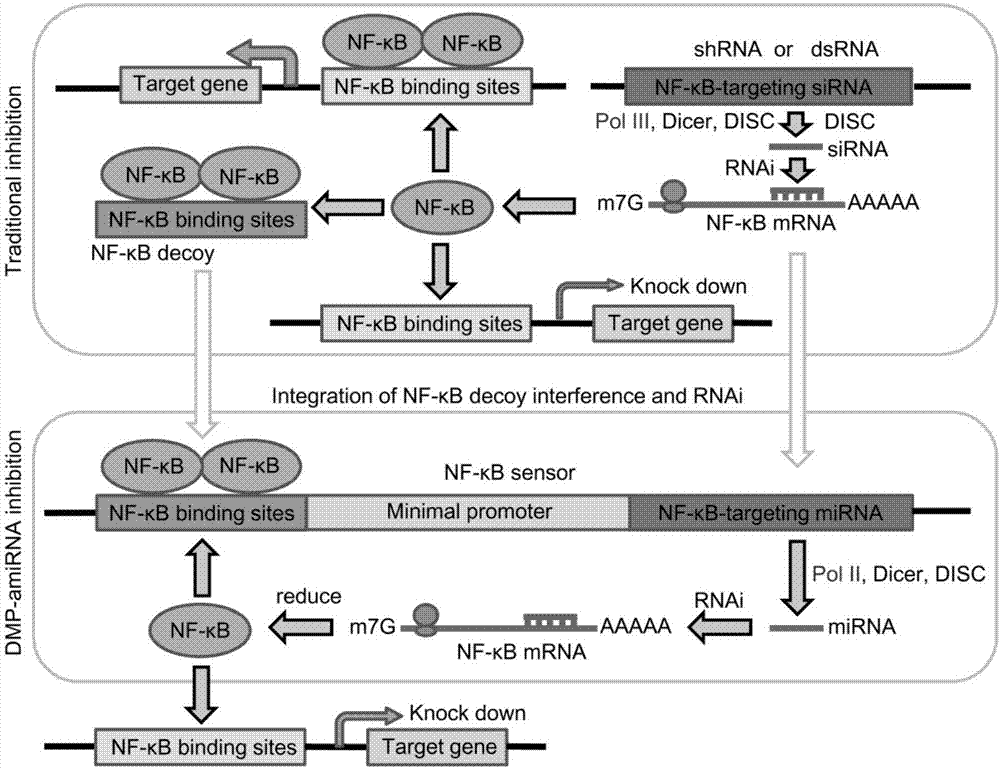
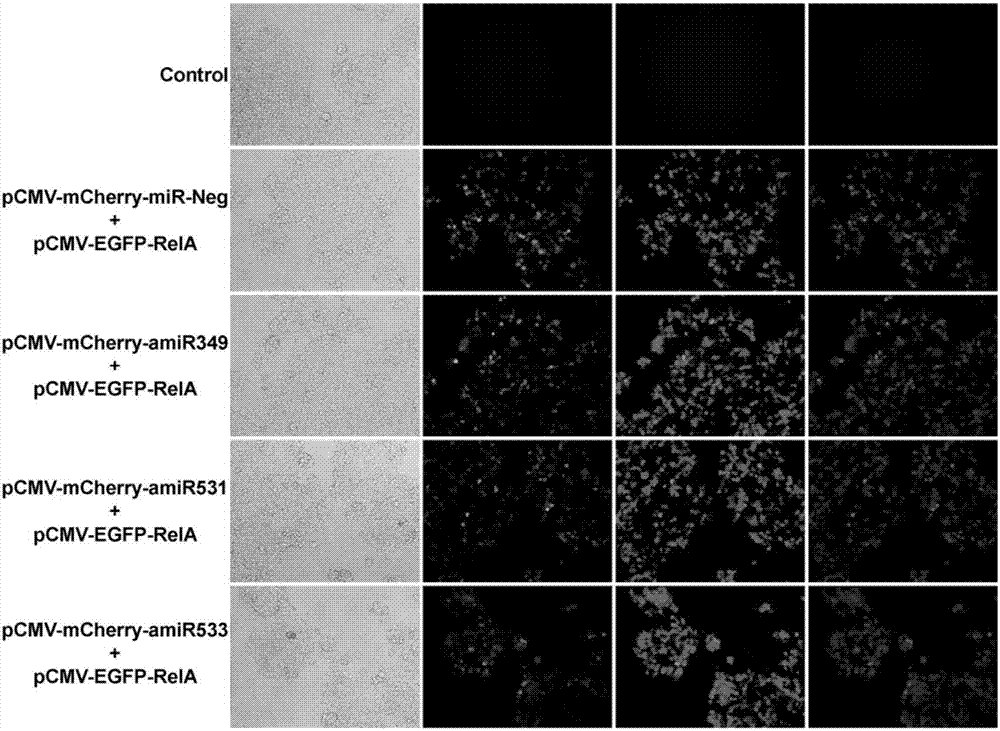
Gene expression vector for adjusting and controlling NF-kB activity in cells as well as regulation and control method and application of gene expression vector
ActiveCN107365785ASimple control methodFast control methodAntipyreticAnalgesicsActivity regulationDisease
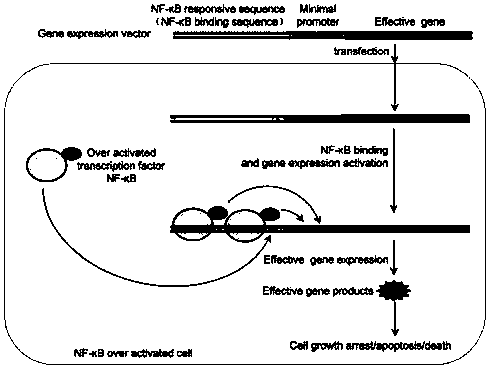
The invention discloses a gene expression vector for adjusting and controlling NF-kB activity in cells as well as a regulation and control method and application of the gene expression vector. The vector comprises two sequence elements, a promoter sequence and an miRNA coding sequence, wherein the promoter sequence is used for adjusting and controlling gene expression, and the miRNA coding sequence is located at the downstream of a promoter; the promoter sequence is formed by a section of NF-kB trapper sequence and a minimal promoter sequence; the miRNA coding sequence is the miRNA coding sequence capable of encoding and targeting NF-kB miRNA. By transfecting the gene expression vector, the NF-kB activity in the overactive cells can be mildly and effectively reduced, and the activity of normal cells is not obviously influenced, so that the side effect is avoided. The regulation and control method of the gene expression vector is simple, rapid and effective; and the gene expression vector is used for preparing an NF-kB activity regulation and control reagent or a drug molecule for treating diseases closely related to NF-kB overactivity and is taken as a novel gene treatment reagent.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Gene expression based on intracellular NF-kappa B activity activation effect gene in NF-kappa B overactivated cells and application
InactiveCN108220336AExpress avoidanceImportant application valueOrganic active ingredientsAntipyreticDiseaseApoptosis
The invention discloses a NF-kappa B specifically activated gene expression vector and application thereof. A gene expression technique is implemented by the NF-kappa B specifically activated gene expression vector. The gene expression vector contains two elements, i.e., a regulatory gene-expressed promoter sequence and a promoter downstream effect gene coding sequence, wherein the promoter sequence consist of a section of NF-kappa B response sequence and a minimal promoter sequence. After the gene expression vector is introduced into NF-kappa B overactivated cells, an effect gene on the vector is expressed under the activation of a sequence-specific transcription factor NF-kappa B, and the effect gene generates influence on cell physiology, such as cell growth inhibition, apoptosis and death. The gene expression technique provided by the invention can be used for treating diseases related to NF-kappa B overactivation, such as inflammation and cancers. The gene expression vector constructed by the invention can be used in the preparation of gene therapy reagents and drugs for treating diseases related to NF-kappa B overactivation.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Methods and compositions for modulating telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) expression
Methods and compositions are provided for modulating, and generally upregulating, the expression of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) by blocking repression of TERT transcription, e.g., by inhibiting binding of repressor factor to a Site C repressor binding site located in the TERT minimal promoter. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications, including the immortalization of cells, the production of reagents for use in life science research, therapeutic applications; therapeutic agent screening applications; and the like. In further describing the subject invention, the methods and compositions of the invention are described first in greater detail, followed by a review of the various applications in which the subject invention finds use.
Owner:SIERRA SCIENCES
Methods and compositions for modulating telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) expression
Methods and compositions are provided for modulating, and generally upregulating, the expression of telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) by blocking repression of TERT transcription, e.g., by inhibiting binding of repressor factor to a Site C repressor binding site located in the TERT minimal promoter. The subject methods and compositions find use in a variety of different applications, including the immortalization of cells, the production of reagents for use in life science research, therapeutic applications; therapeutic agent screening applications; and the like. In further describing the subject invention, the methods and compositions of the invention are described first in greater detail, followed by a review of the various applications in which the subject invention finds use.
Owner:SIERRA SCIENCES
Telomerase expression repressor proteins and methods of using the same
Telomerase repressor proteins and nucleic acid compositions encoding the same are provided. The subject repressor proteins bind to a repressor site in the TERT minimal promoter, e.g., a Site C site, and thereby inhibit TERT expression. Also provided are methods of modulating, e.g., inhibiting or enhancing, TERT expression. The subject invention finds use in a variety of different applications, including therapeutic and therapeutic agent screening applications.
Owner:SIERRA SCIENCES
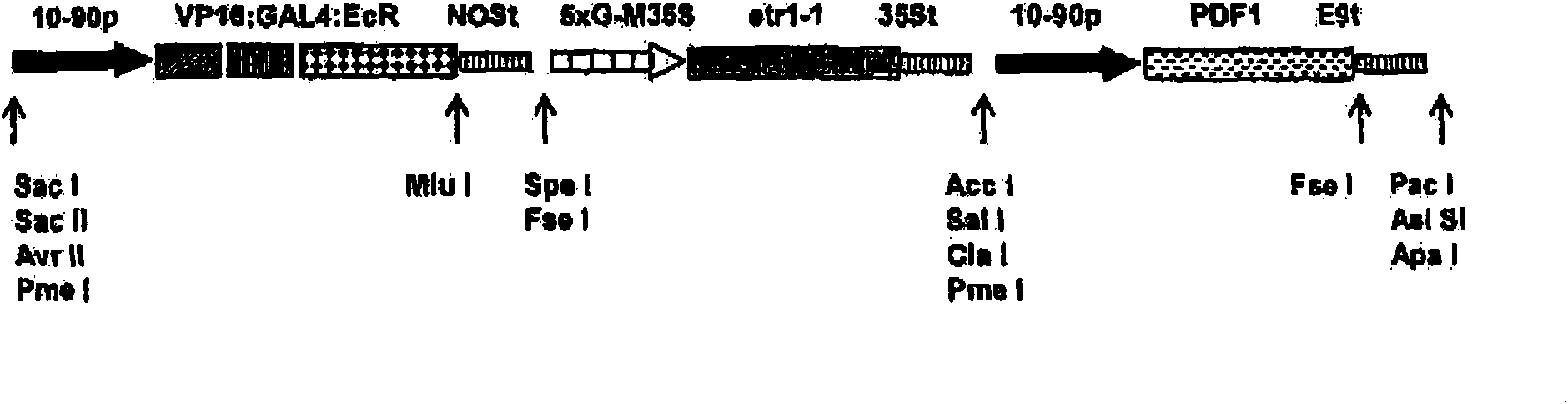
Compositions and methods for the modification of physiological responses in plants
InactiveUS20090077684A1Tight regulationEasy to useSugar derivativesMutant preparationRipeningPlant cell
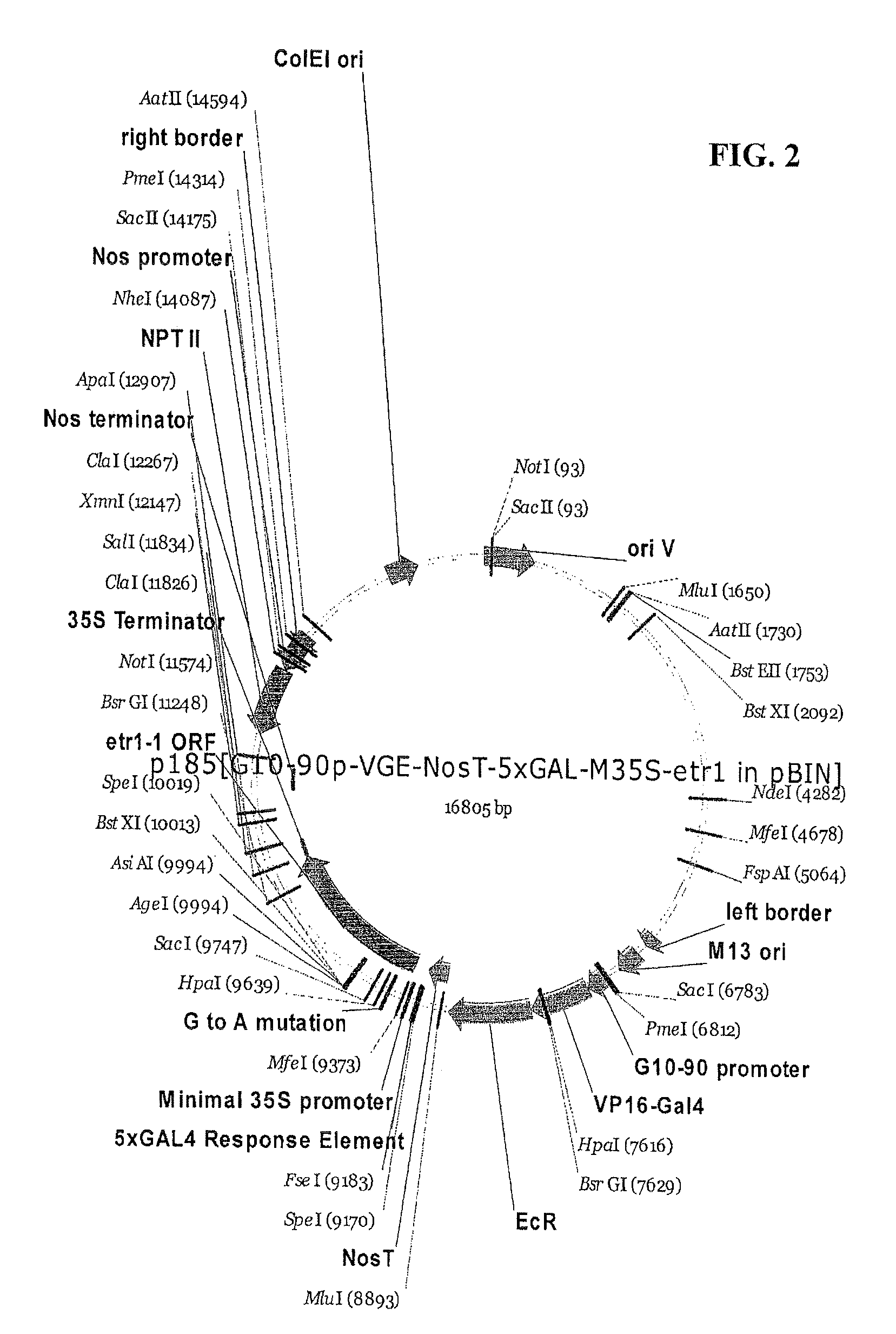
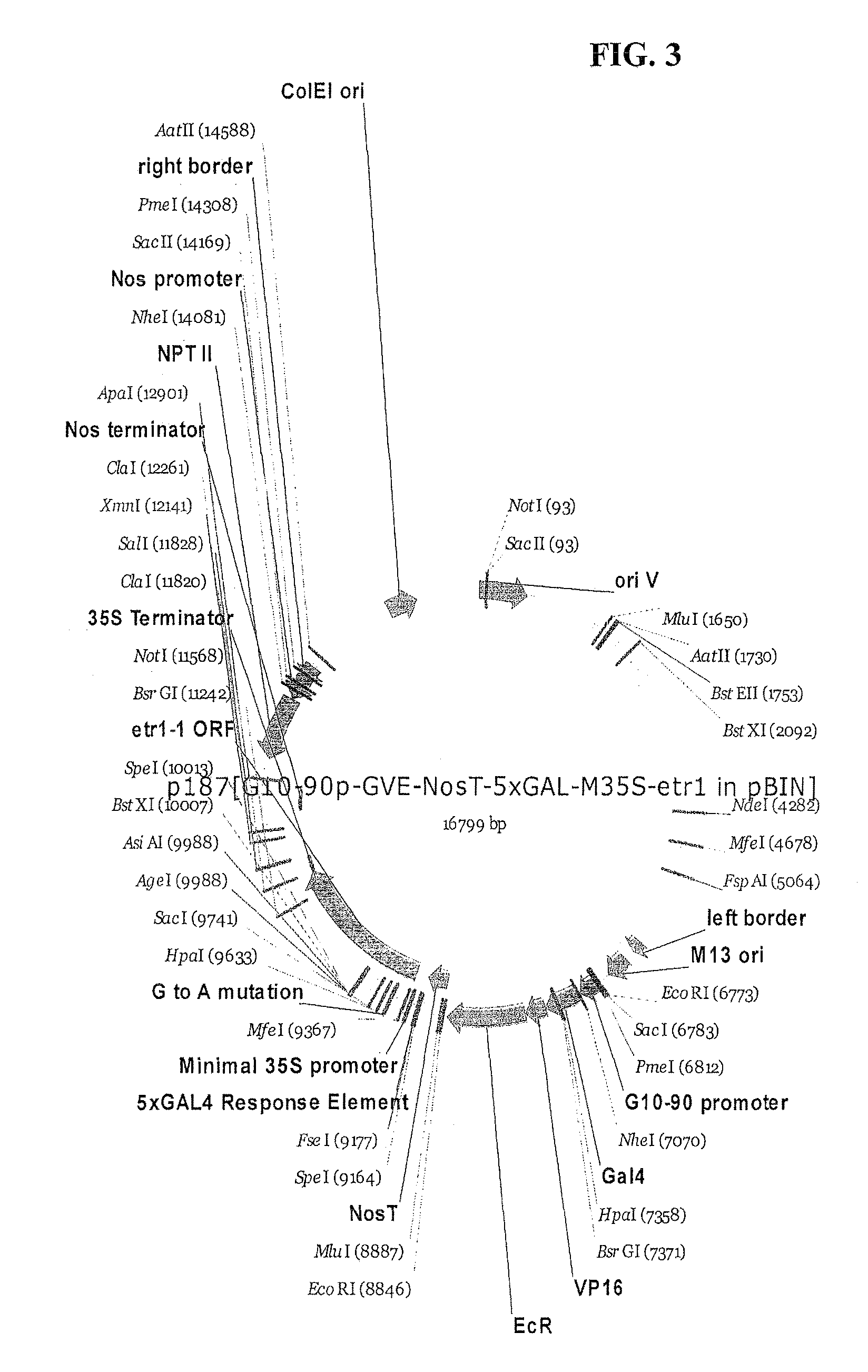
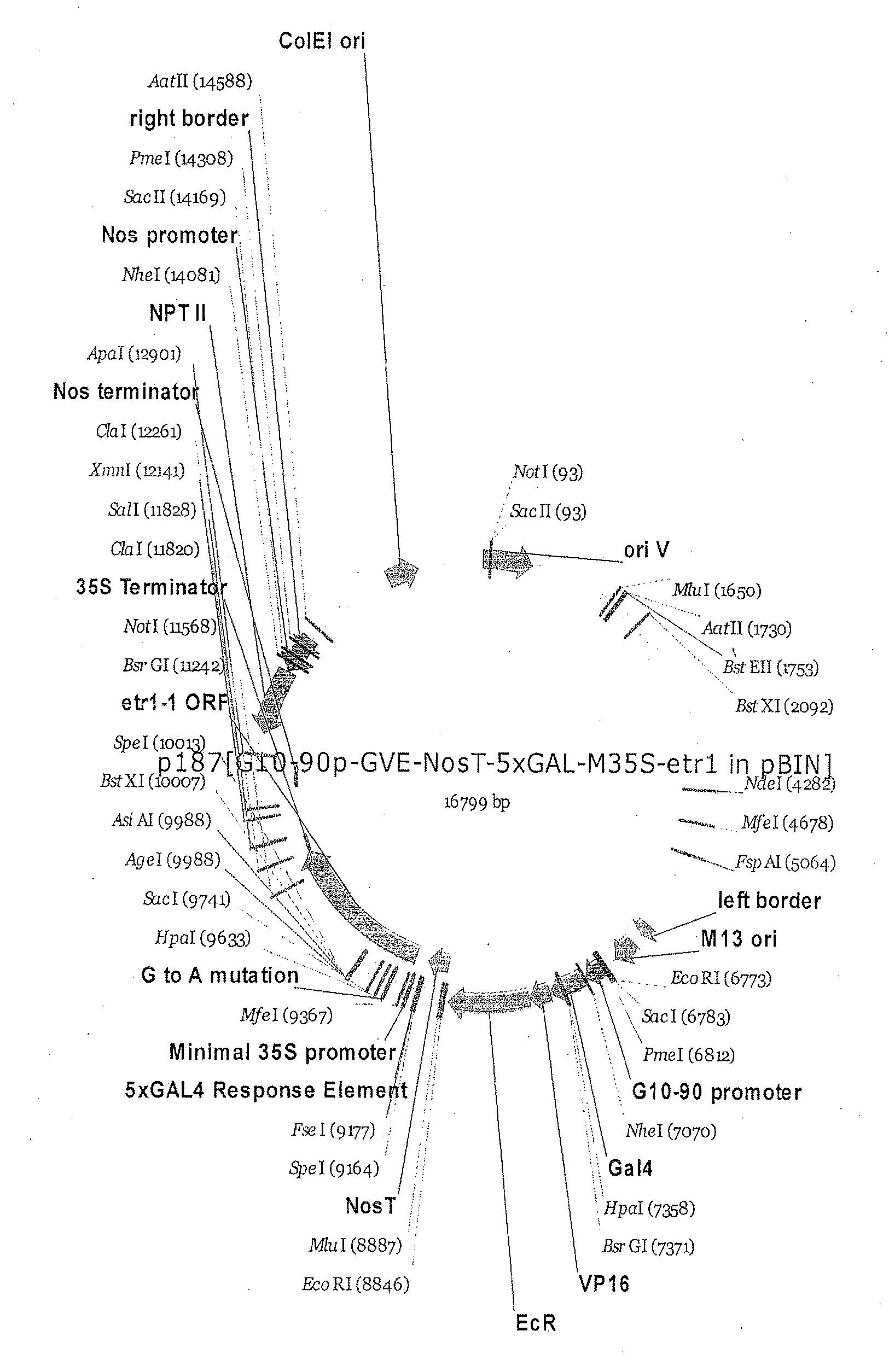
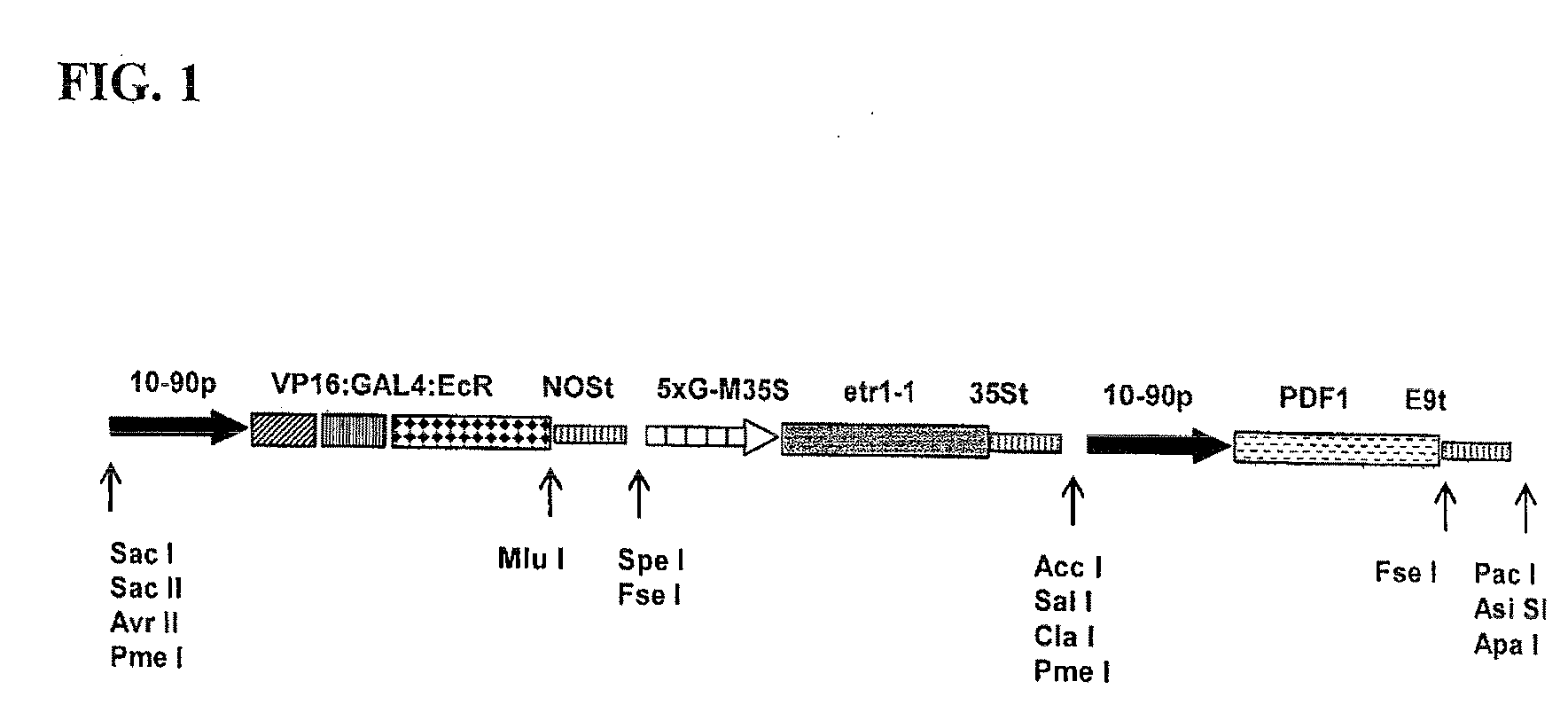
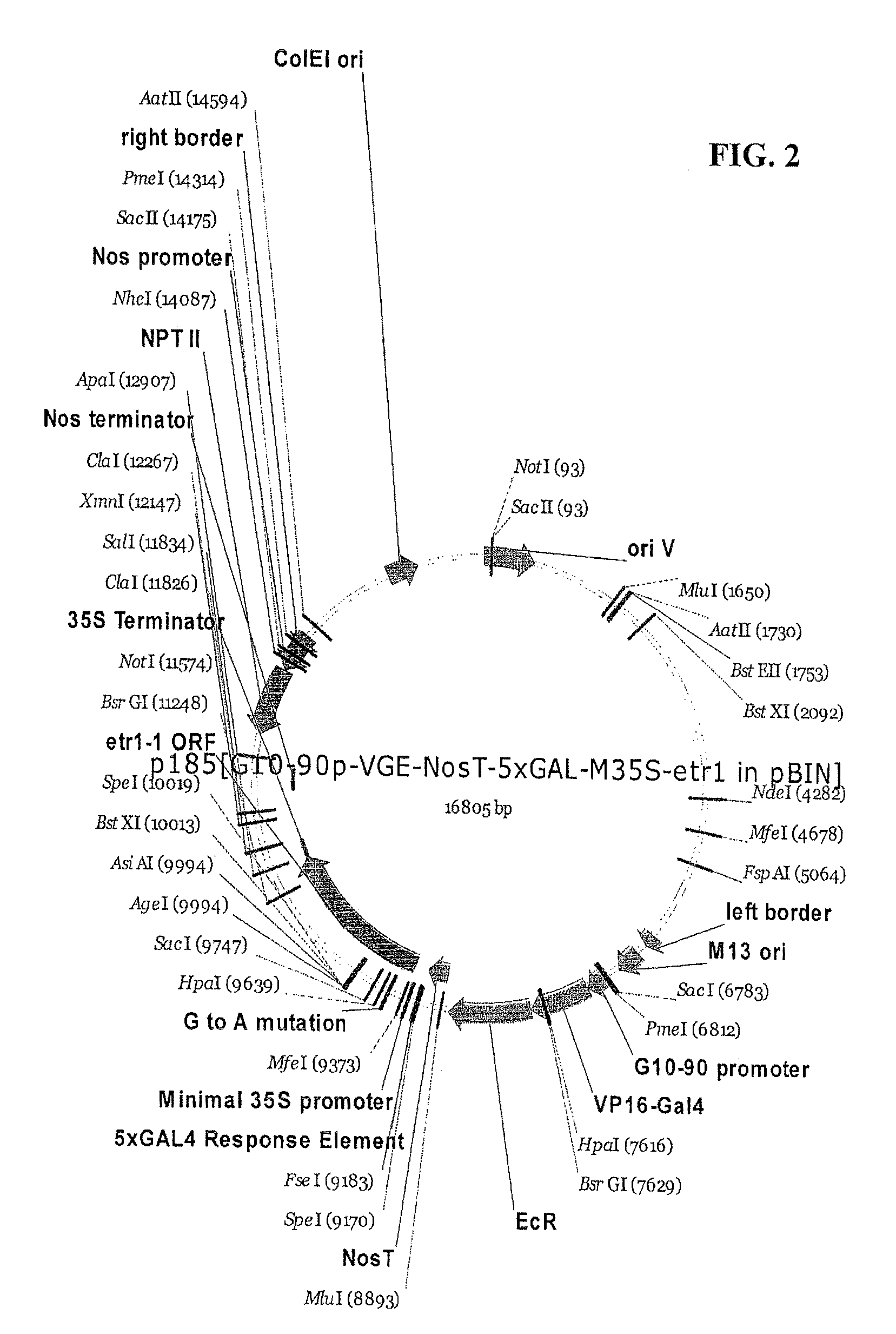
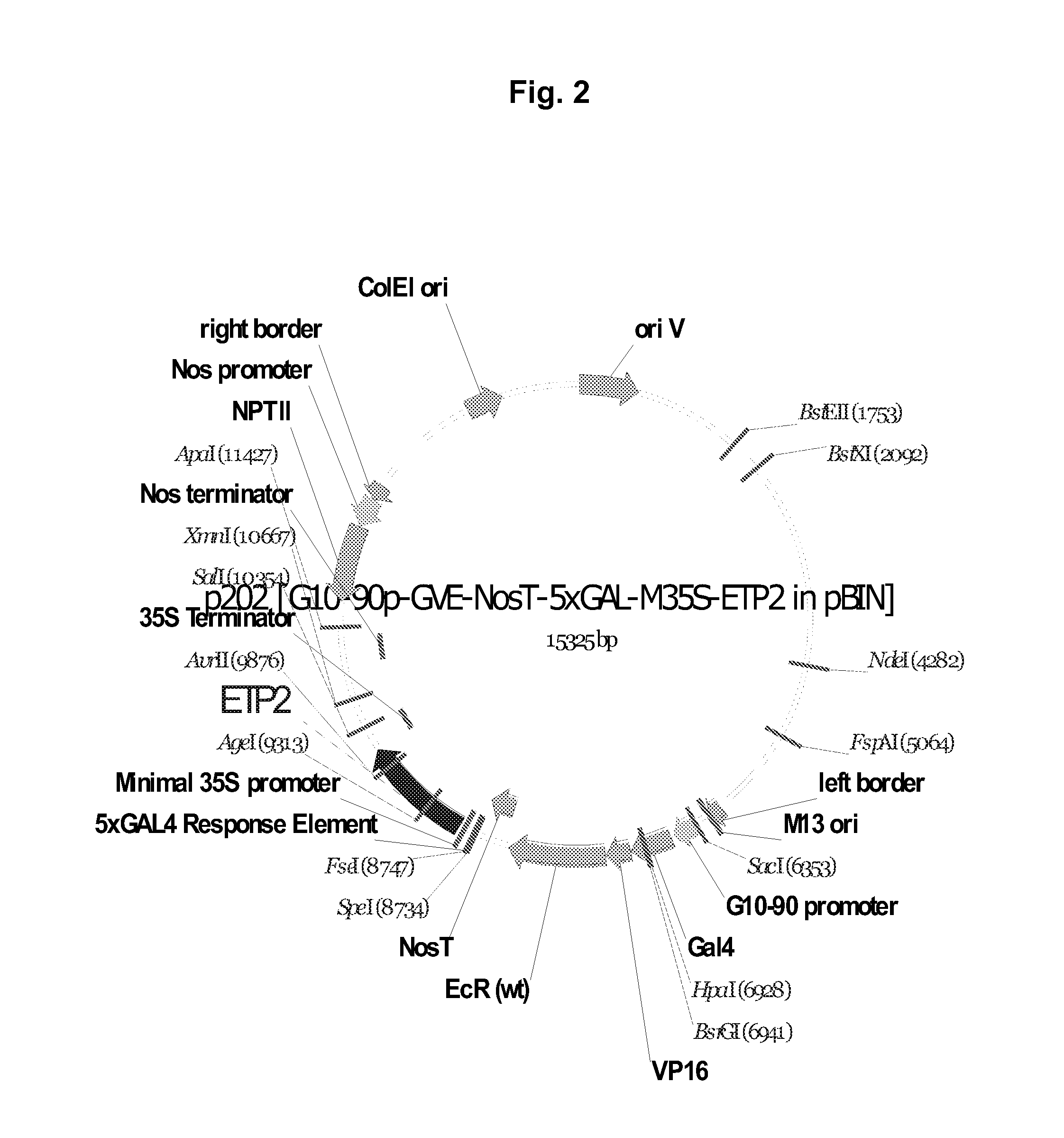
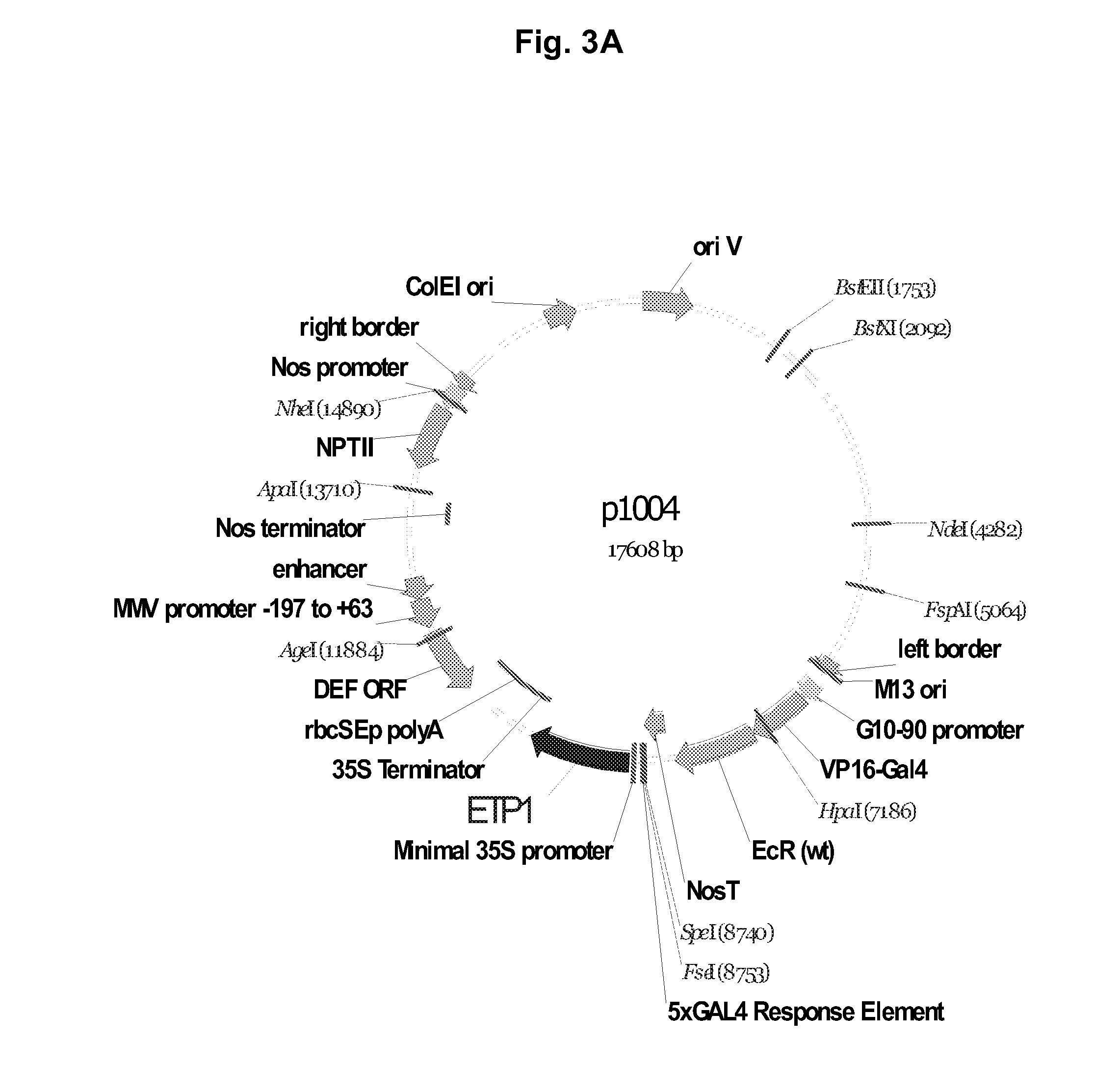
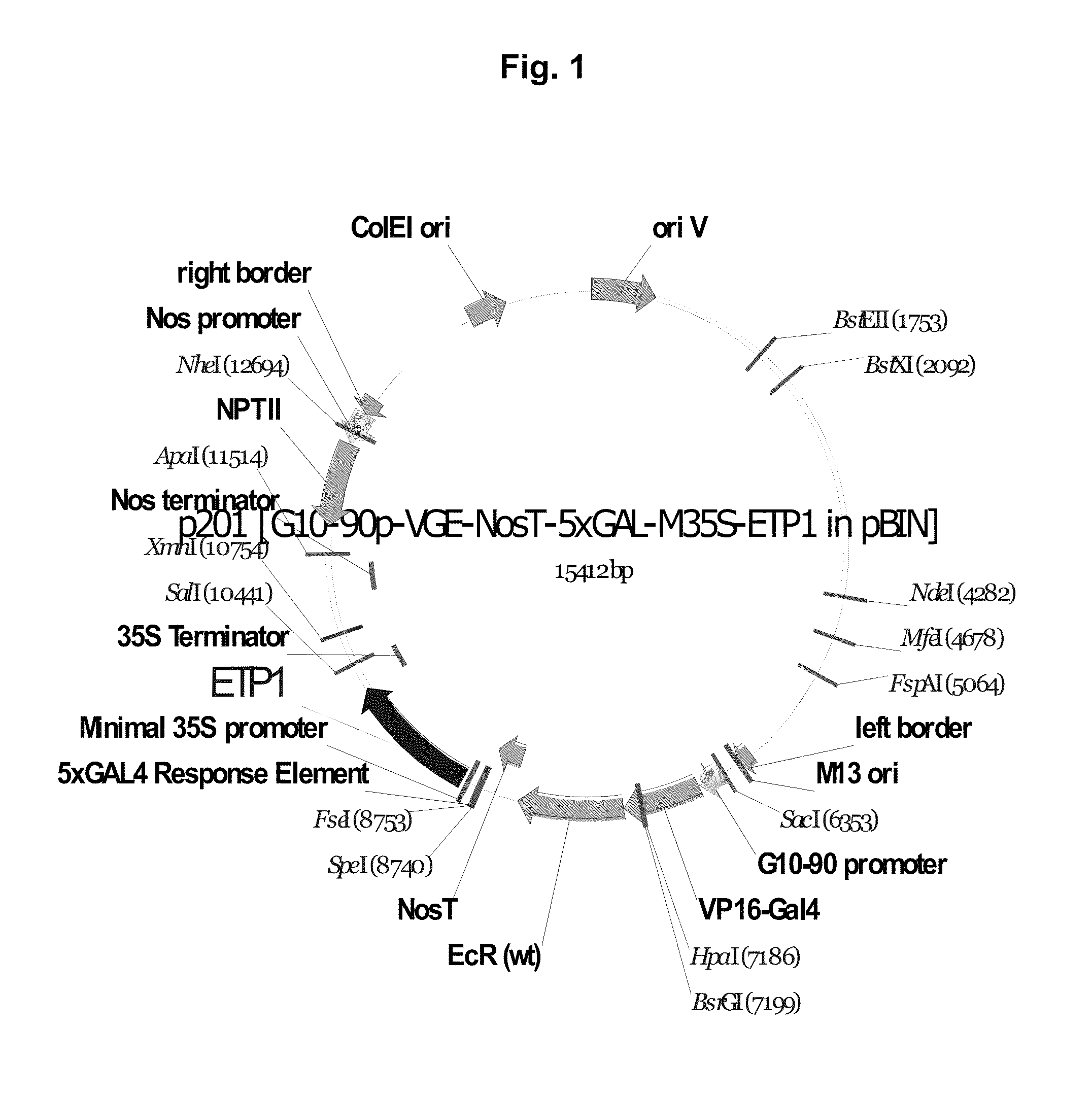
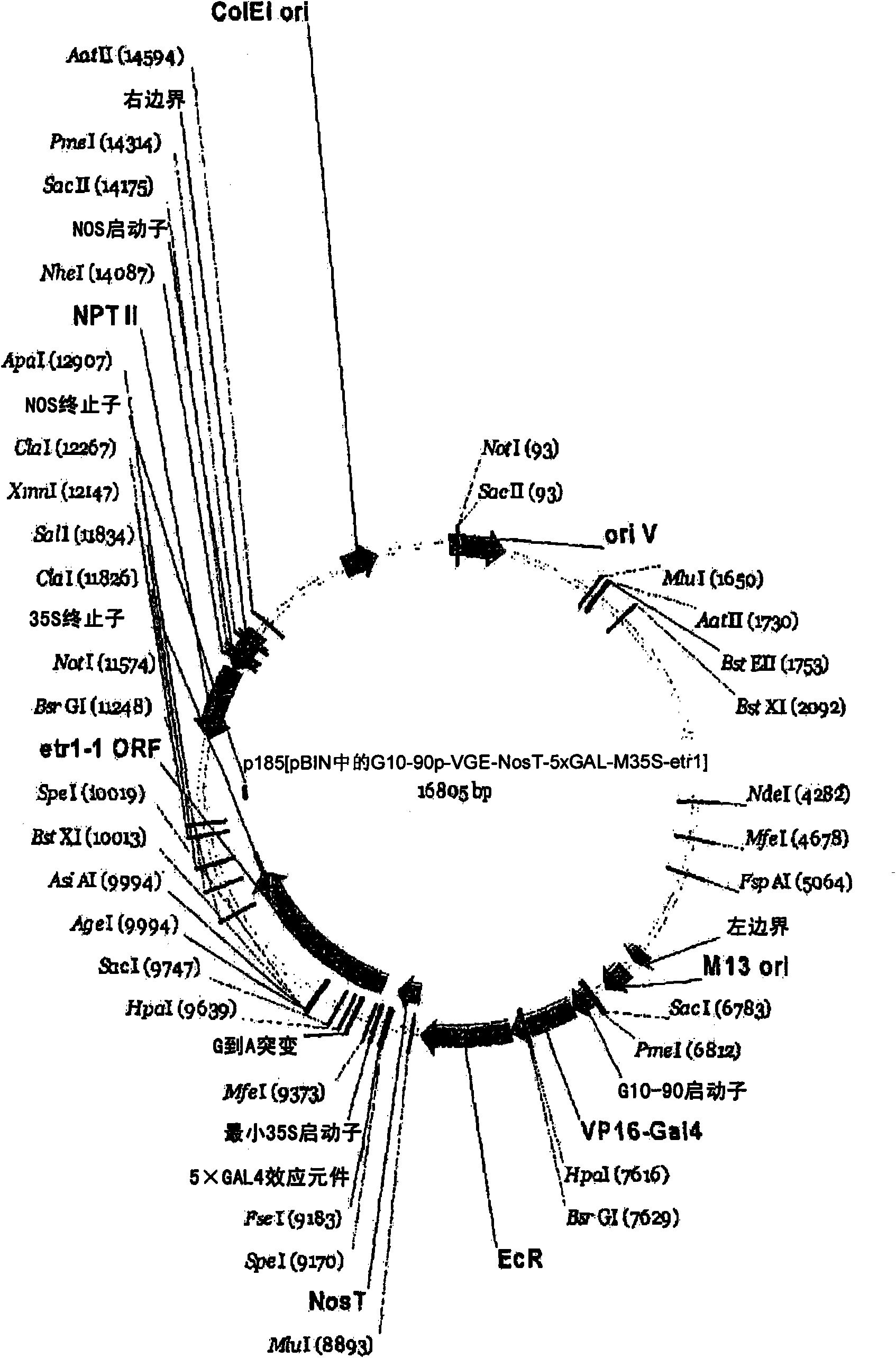
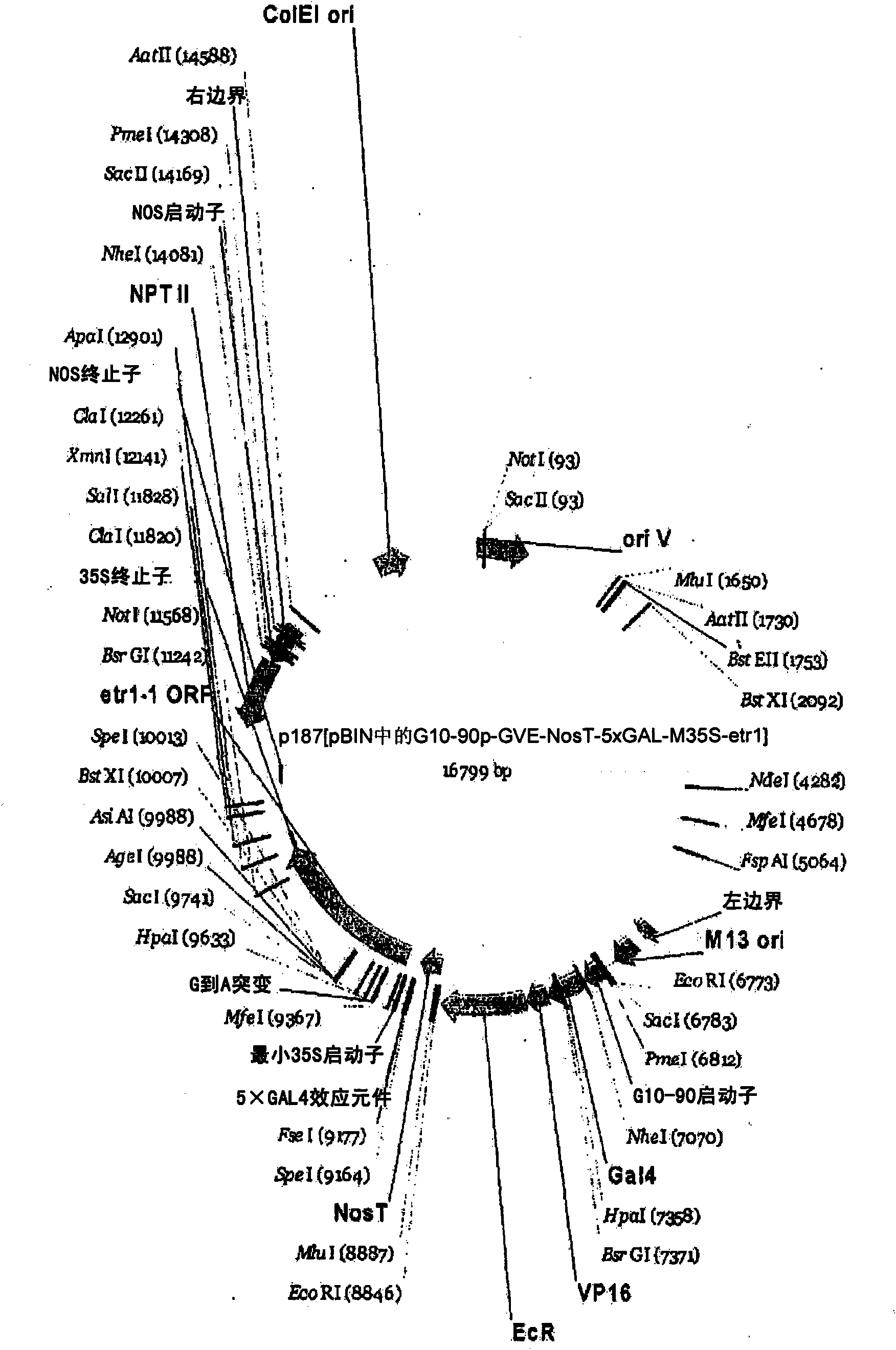
A gene expression system for controllable expression of ethylene response in a plant cell includes an activation cassette comprising a DNA-binding domain that recognizes a response element; an ecdysone receptor ligand binding domain; and an activation domain; and a target cassette comprising an inducible promoter, which comprises, in operative association, the response element and a minimal promoter responsive to the activation domain. The inducible promoter controls the expression of a nucleic acid sequence that encodes a selected protein that modifies sensitivity to ethylene in the plant. Interaction among the components of the activation cassette and target cassette, when in a plant cell, in the presence of an inducing composition, modulates expression of the selected protein and selectively modulates ethylene sensitivity in the plant cell. This modulation in the expression of the protein is controlled by the timing, the concentration and the duration of the application of the inducing composition. Transgenic plant cells, tissues, organs and entire plants are provided, which in the presence of the inducing composition control ethylene sensitivity. Ethylene sensitivity and / or ethylene production in such transgenic plants and tissues may be controlled for purposes of manipulating ripening, flower senescence and other ethylene sensitive functions of the plant.
Owner:AGROFRESH
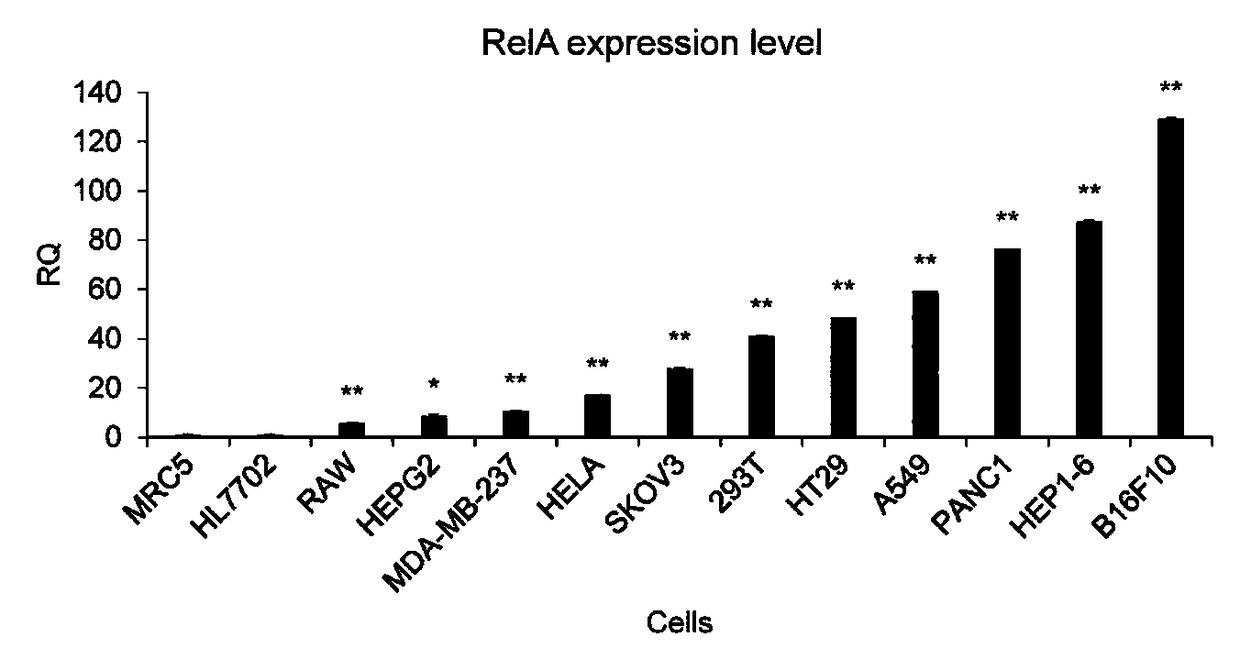
Cancer cell specific effect gene expression vector started by NF-KB and expression product and application thereof
ActiveCN108410893ARevolutionizing the principles of immunotherapyInnovation principleVectorsViral antigen ingredientsAntigenCancer cell
The invention discloses a cancer cell specific effect gene expression vector started by NF-KB and an expression product and an application thereof. The gene expression vector contains two sequence elements which are a promoter sequence for regulating gene expression and an effect gene coding sequence at the downstream of the promoter sequence. The promoter sequence is formed by a section of a NF-KB response sequence and a minimum promoter sequence. While the gene expression vector is guided into a cancer cell, the sequence specificity transcription factor NF-KB in the cell can activate the vector, and an effect gene on the vector is expressed. The effect gene expression product is a polypeptide or a protein of cell surface, the polypeptide or the protein of the cell surface not only can beused as a new antigen substance for exciting an in-vivo immune system to attack the cancer cell, and developing the efficacy of tumor immunity treatment, but also can be used as a cancer cell artificial mark for tumor imaging, diagnosis, cell separation and the like.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
Control of targeted turnover of key ethylene hormone signaling pathway proteins to modulate ethylene sensitivity in plants
A gene expression system for controllable expression of ethylene response in a plant cell includes an activation cassette comprising a DNA-binding domain that recognizes a response element; an ecdysone receptor ligand binding domain; and an activation domain; and a target cassette comprising an inducible promoter, which comprises, in operative association, the response element and a minimal promoter responsive to the activation domain. The inducible promoter controls the expression of a nucleic acid sequence that encodes a selected regulatory protein that modifies sensitivity to ethylene of certain signal proteins in the plant. Interaction among the components of the activation cassette and target cassette, when in a plant cell, in the presence of an inducing composition, increases expression of the selected regulatory protein, and in turn decreases expression and accumulation of the signal protein in the plant, thereby and decreasing ethylene sensitivity in the plant cell. This increase in the expression of the regulatory protein, particularly in the presence of ethylene, is controlled by the timing, the concentration and the duration of the application of the inducing composition. Transgenic plant cells, tissues, organs and entire plants are provided, which in the presence of the inducing composition control ethylene sensitivity. Ethylene sensitivity and / or ethylene production in such transgenic plants and tissues may be controlled for purposes of manipulating ripening, flower senescence and other ethylene sensitive functions of the plant.
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
Telomerase expression repressor proteins and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20090239219A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTelomeraseMinimal promoter
Telomerase repressor proteins and nucleic acid compositions encoding the same are provided. The subject repressor proteins bind to a repressor site in the TERT minimal promoter, e.g., a Site C site, and thereby inhibit TERT expression. Also provided are methods of modulating, e.g., inhibiting or enhancing, TERT expression. The subject invention finds use in a variety of different applications, including therapeutic and therapeutic agent screening applications.
Owner:ANDREWS WILLIAM H +4
Control of targeted turnover of key ethylene hormone signaling pathway proteins to modulate ethylene sensitivity in plants
A gene expression system for controllable expression of ethylene response in a plant cell includes an activation cassette comprising a DNA-binding domain that recognizes a response element; an ecdysone receptor ligand binding domain; and an activation domain; and a target cassette comprising an inducible promoter, which comprises, in operative association, the response element and a minimal promoter responsive to the activation domain. The inducible promoter controls the expression of a nucleic acid sequence that encodes a selected regulatory protein that modifies sensitivity to ethylene of certain signal proteins in the plant. Interaction among the components of the activation cassette and target cassette, when in a plant cell, in the presence of an inducing composition, increases expression of the selected regulatory protein, and in turn decreases expression and accumulation of the signal protein in the plant, thereby and decreasing ethylene sensitivity in the plant cell. This increase in the expression of the regulatory protein, particularly in the presence of ethylene, is controlled by the timing, the concentration and the duration of the application of the inducing composition. Transgenic plant cells, tissues, organs and entire plants are provided, which in the presence of the inducing composition control ethylene sensitivity. Ethylene sensitivity and / or ethylene production in such transgenic plants and tissues may be controlled for purposes of manipulating ripening, flower senescence and other ethylene sensitive functions of the plant.
Owner:AGROFRESH
Telomerase expression repressor proteins and methods of using the same
Telomerase repressor proteins and nucleic acid compositions encoding the same are provided. The subject repressor proteins bind to a repressor site in the TERT minimal promoter, e.g., a Site C site, and thereby inhibit TERT expression. Also provided are methods of modulating, e.g., inhibiting or enhancing, TERT expression. The subject invention finds use in a variety of different applications, including therapeutic and therapeutic agent screening applications.
Owner:SIERRA SCIENCES
Mutagenicity test method using mammalian cells
InactiveUS20140308675A1High sensitivityAccurately reflect mutagenicityMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisP53 bindingMinimal promoter
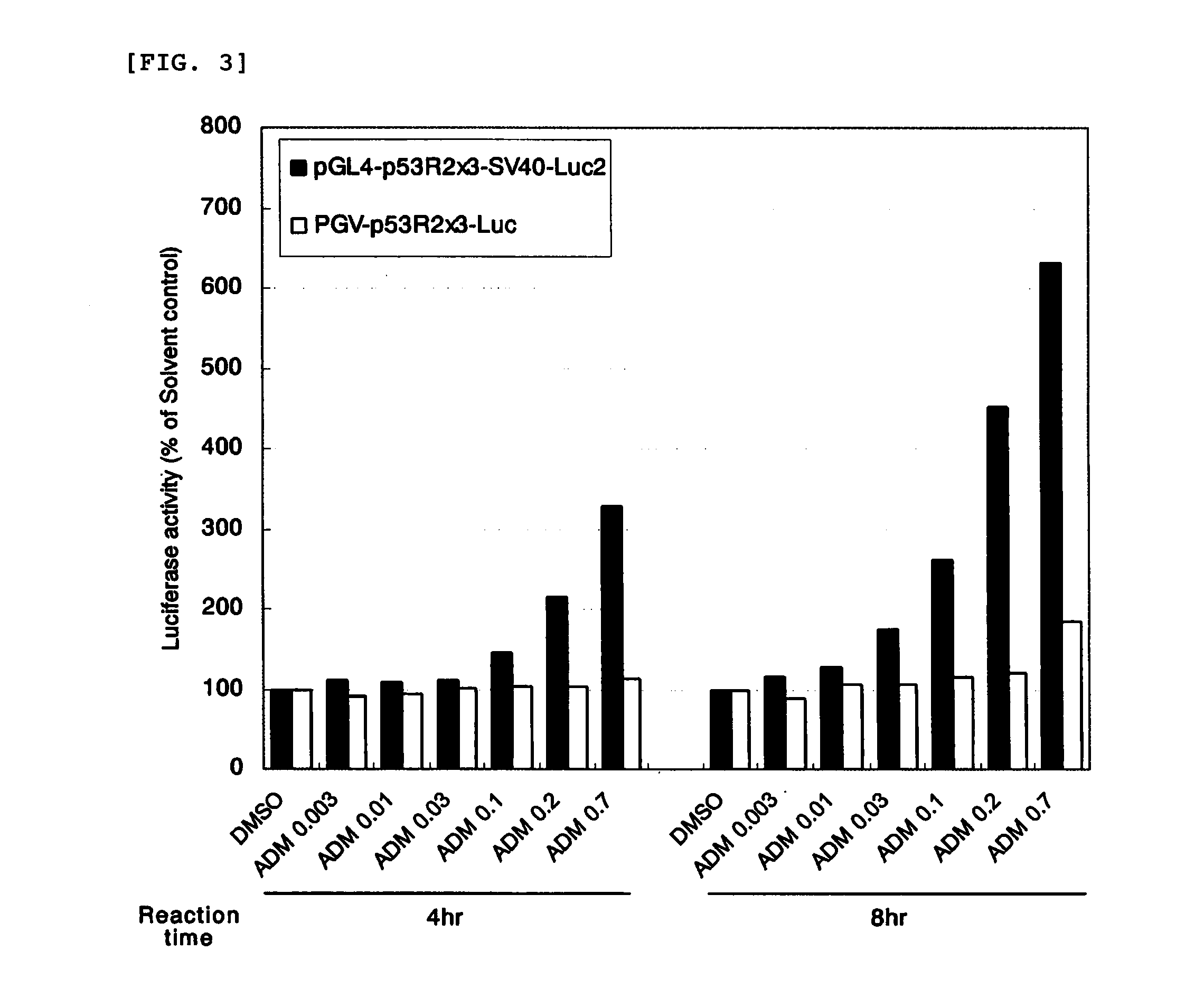
Provided is a test method that allows mutagenicity on a mammal including a human to be confirmed accurately and simply in a short time. Specifically, provided is a mutagenicity test method, including the steps of: (1) culturing a transformant of a mammalian cell harboring a recombinant vector including a p53 binding sequence, a minimal promoter that can function in the mammalian cell, and a reporter gene linked so that the gene can be expressed by the minimal promoter, in the presence of a test substance for a predetermined time; and (2) assessing whether or not the test substance affects an expression amount of the reporter gene in the transformant by comparing an expression amount of the reporter gene in the transformant cultured in the step (1) to an expression amount of the reporter gene in the transformant free of contact with the test substance.
Owner:NISSIN YORK
Control of targeted turnover of key ethylene hormone signaling pathway proteins to modulate ethylene sensitivity in plants
A gene expression system for controllable expression of ethylene response in a plant cell includes an activation cassette comprising a DNA-binding domain that recognizes a response element; an ecdysone receptor ligand binding domain; and an activation domain; and a target cassette comprising an inducible promoter, which comprises, in operative association, the response element and a minimal promoter responsive to the activation domain. The inducible promoter controls the expression of a nucleic acid sequence that encodes a selected regulatory protein that modifies sensitivity to ethylene of certain signal proteins in the plant. Interaction among the components of the activation cassette and target cassette, when in a plant cell, in the presence of an inducing composition, increases expression of the selected regulatory protein, and in turn decreases expression and accumulation of the signal protein in the plant, thereby and decreasing ethylene sensitivity in the plant cell. This increase in the expression of the regulatory protein, particularly in the presence of ethylene, is controlled by the timing, the concentration and the duration of the application of the inducing composition. Transgenic plant cells, tissues, organs and entire plants are provided, which in the presence of the inducing composition control ethylene sensitivity. Ethylene sensitivity and / or ethylene production in such transgenic plants and tissues may be controlled for purposes of manipulating ripening, flower senescence and other ethylene sensitive functions of the plant.
Owner:AGROFRESH
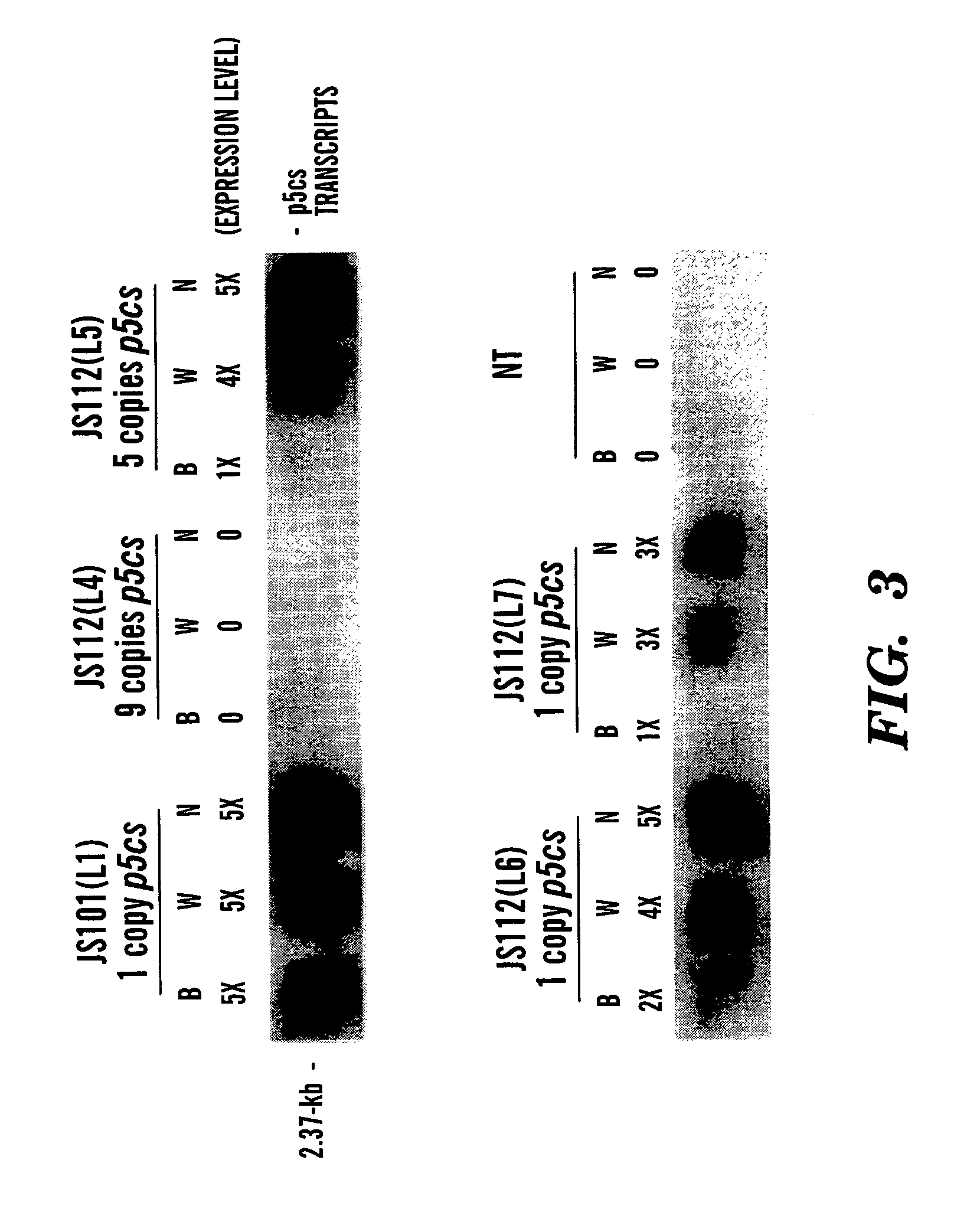
Method of making water stress or salt stress tolerant transgenic cereal plants
InactiveUS6951971B1Improve toleranceImprove the level ofOther foreign material introduction processesFermentationIncreased toleranceMinimal promoter
The present invention relates to a method for conferring tolerance to salt stress and drought stress in a monocot plant including transforming the monocot plant with an expression cassette comprising at least one ABRC unit, a minimal promoter, and a DNA molecule that increases tolerance to salt stress and drought stress in plants, wherein the at least one ABRC unit, the minimal promoter, and a DNA molecule are operably linked together to permit expression of the DNA molecule. The present invention also relates to a transgenic monocot plant transformed with a DNA molecule that increases tolerance to salt stress and drought stress operably linked to at least one ABRC unit and a minimal promoter.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC +1
System for producing synthetic promoters
ActiveUS7063947B2Improve efficiencyGood curative effectVectorsMicrobiological testing/measurementTranscription regulatorTranscriptional Regulatory Elements
The present application discloses a method for making and selecting a transcription enhancing combined promoter cassette, which includes constructing a library of randomly combined transcription regulatory elements, which comprise double stranded DNA sequence elements that are recognized by transcription regulators; inserting the combined transcription regulatory elements upstream of a minimum promoter followed by a reporter gene in a vector; inserting the vector into a host cell; and then screening for the cells showing enhanced expression of the reporter gene, and identifying the combined promoter cassette in the cell.
Owner:PROMOGEN
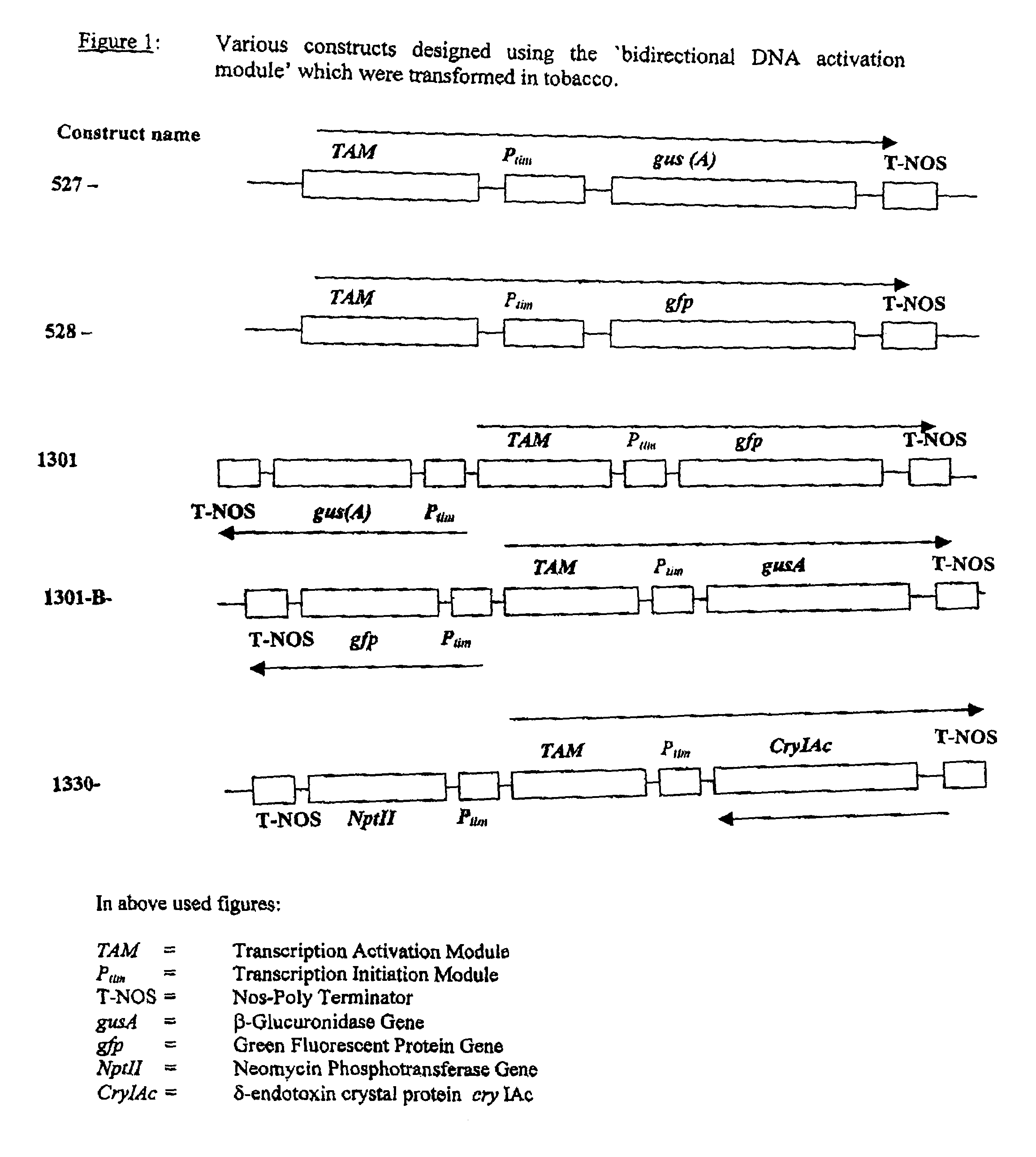
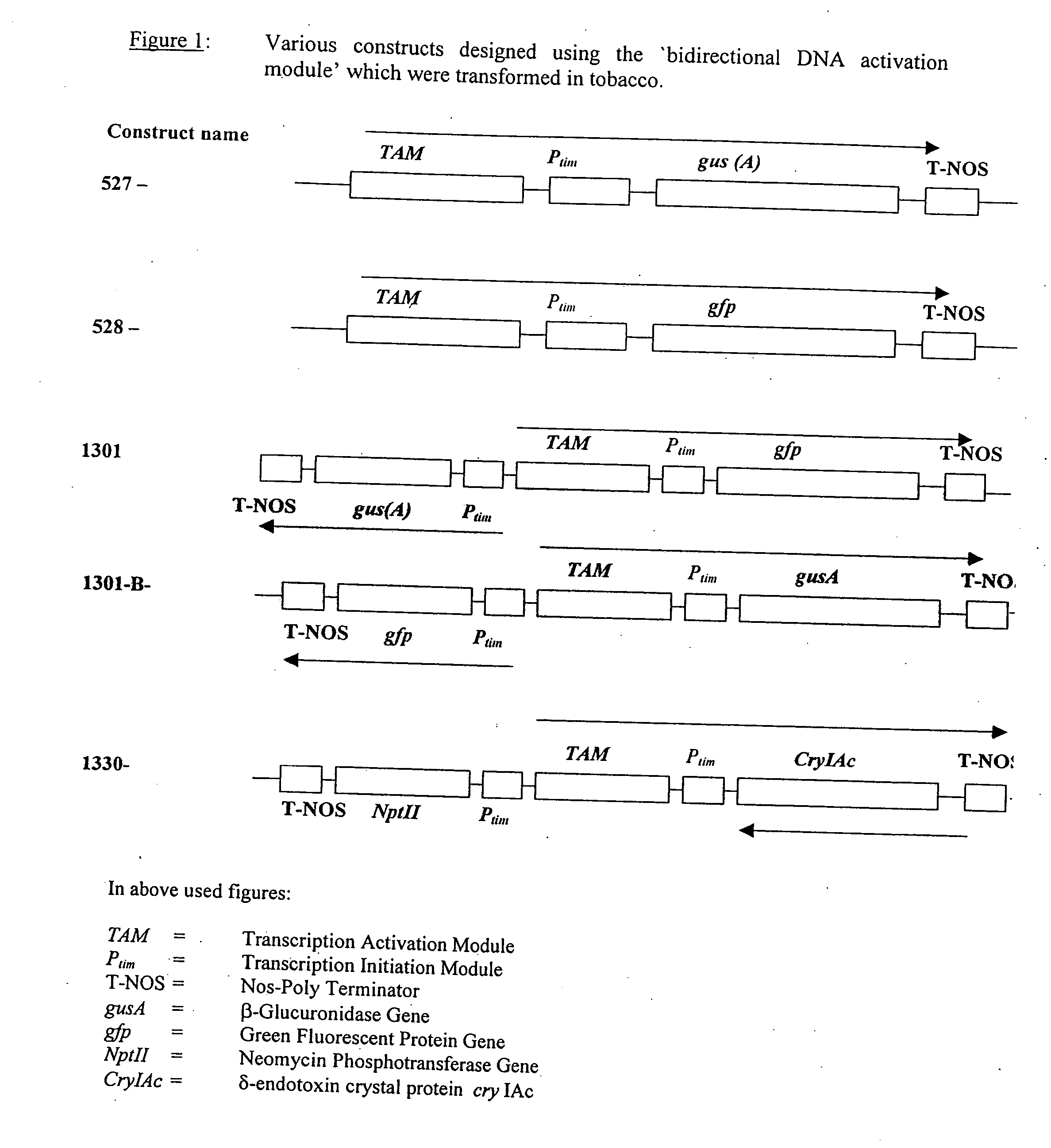
Artificial bidirectional promoter for activation of gene expression
InactiveUS7235652B2Sugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesTranscription initiationHigh level expression
A bidirectional module for activation of gene expression and regulation of transcription in both directions is disclosed. The bidirectional module comprises multiple cis regulatory DNA sequence elements, strategically arranged to give a ‘Transcription Activating Module’ that achieves high level expression from a ‘Transcription Initiation Module’. The latter functions like a minimal promoter. The former activates transcription simultaneously in both the directions from the latter and also responds to several transcription inducing, external stimuli in both the directions. Since it is an artificially designed bidirectional transcription module, it has no equivalent DNA sequence in plant genome. This reduces the chances of the genes from being silenced by homology based mechanisms. A bidirectional promoter module as this, can therefore be used to develop efficient vectors for genetic engineering in plants.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Compositions and methods for the modification of physiological responses in plants
InactiveCN101848990AVector-based foreign material introductionPlant cellsBiotechnologyResponse element
Owner:ROHM & HAAS CO
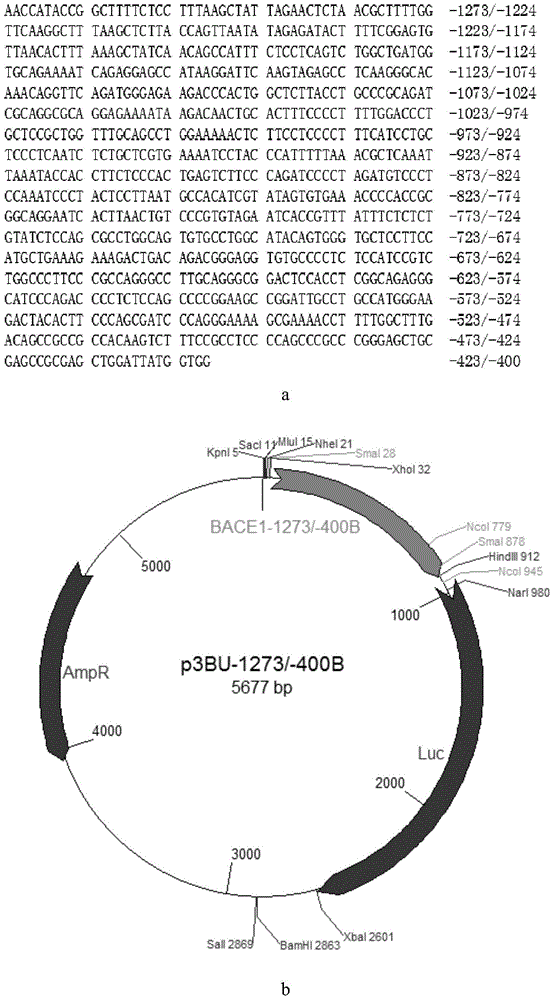
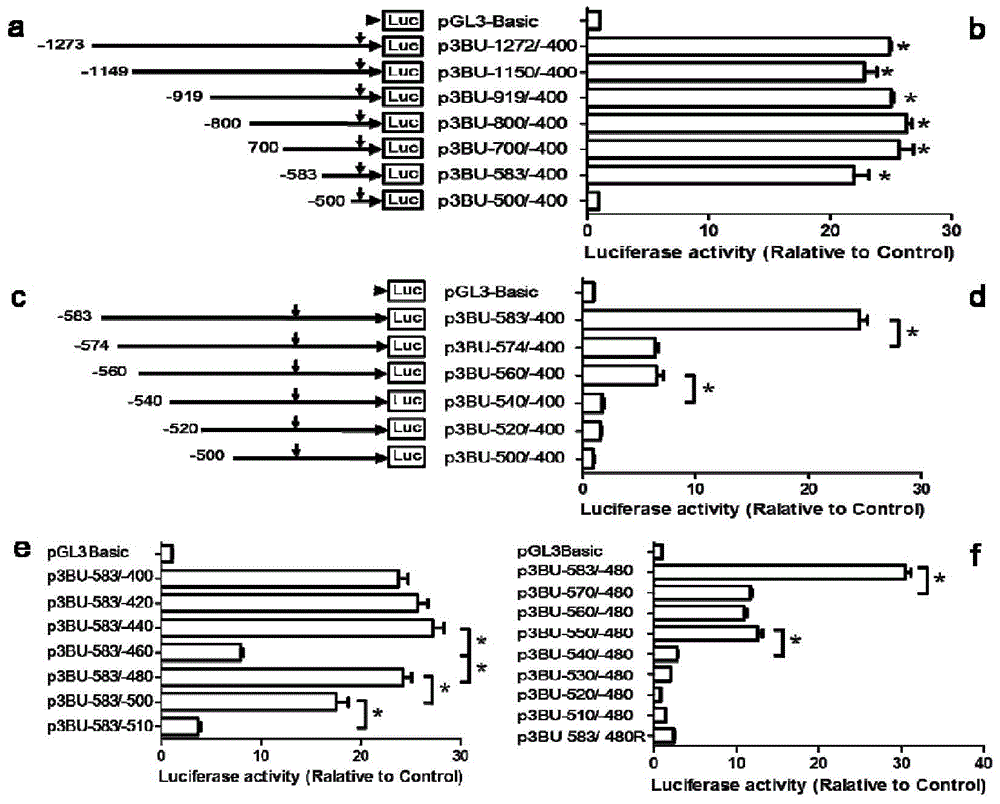
Transcriptional promoter for human BACE1 gene as well as main cis-acting elements and application of transcriptional promoter
ActiveCN104357448AUnderstand the mechanisms of transcriptional regulationNervous disorderMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseCis-regulatory element
The invention provides a transcriptional promoter for the human BACE1 gene as well as a core promoter region and cis-acting elements of the transcriptional promoter. According to the invention, the smallest promoter region defining the high-level transcription of the human BACE1 gene and the core promoter region defining basal transcription of the human BACE1 gene are firstly confirmed, and the two cis-acting elements capable of enhancing gene transcription are confirmed, the structure of the BACE1 gene promoter core region playing a key function on the transcription of the BACE1 gene is disclosed, and a transcription regulatory mechanism of the BACE1 gene and influence, found through the transcription regulatory mechanism, on the transcription and expression of the BACE1 gene are understood more deeply. Effective action target spots are provided for preventing, diagnosing and treating AD and other diseases.
Owner:CHILDRENS HOSPITAL OF CHONGQING MEDICAL UNIV
Methods and compositions for modulating telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) expression
Nucleic acid compositions comprising a region and a TERT minimal promoter activator binding site that acts to activate transcription of the telomerase reverse transcriptase (TERT) coding sequence, as well as vectors and constructs including the same, are provided. Also provided are methods of modulating, e.g., inhibiting, the TERT transcription activation activity of the subject TERT activator binding site regions in order to regulate, e.g., repress, telomerase expression, which methods find use in a variety of different applications, including the therapeutic applications and the like. In addition, methods of screening for agents that modulate the TERT transcription activating activity of the subject TERT activator sites are provided. The subject invention finds use in, among other applications, the regulation of TERT expression.
Owner:SIERRA SCIENCES
Telomerase expression repressor proteins and methods of using the same
InactiveUS20050176629A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsTelomeraseMinimal promoter
Telomerase repressor proteins and nucleic acid compositions encoding the same are provided. The subject repressor proteins bind to a repressor site in the TERT minimal promoter, e.g., a Site C site, and thereby inhibit TERT expression. Also provided are methods of modulating, e.g., inhibiting or enhancing, TERT expression. The subject invention finds use in a variety of different applications, including therapeutic and therapeutic agent screening applications.
Owner:SIERRA SCIENCES
Minimum promoter for enhancing activity and expression of exogenous protein in bacteria
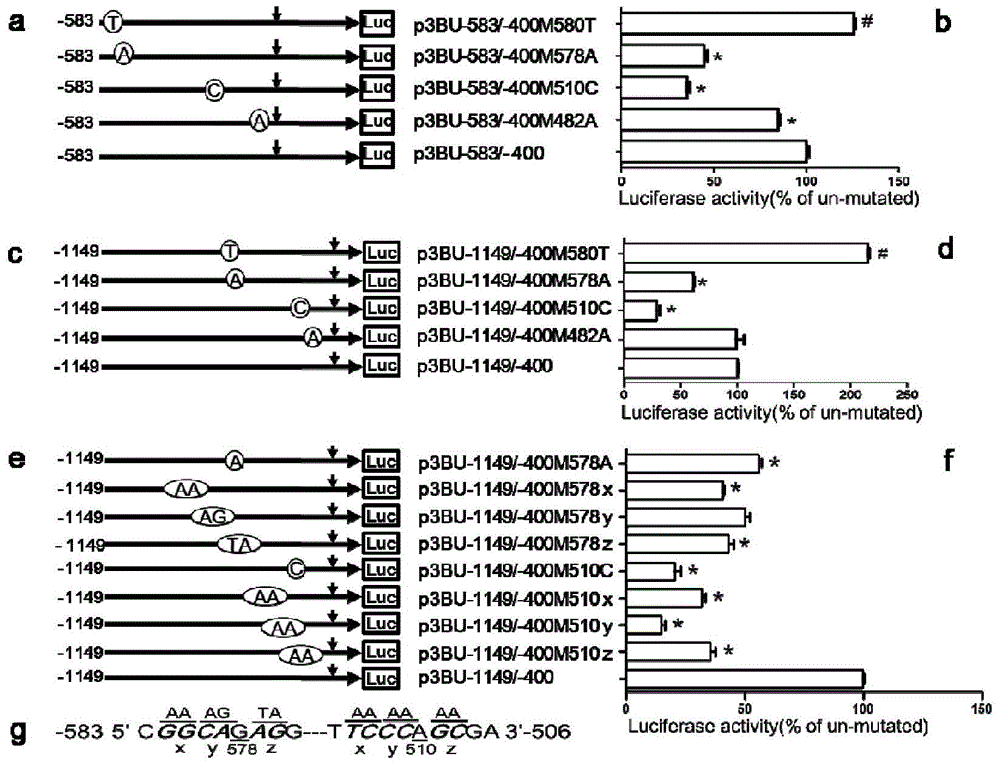
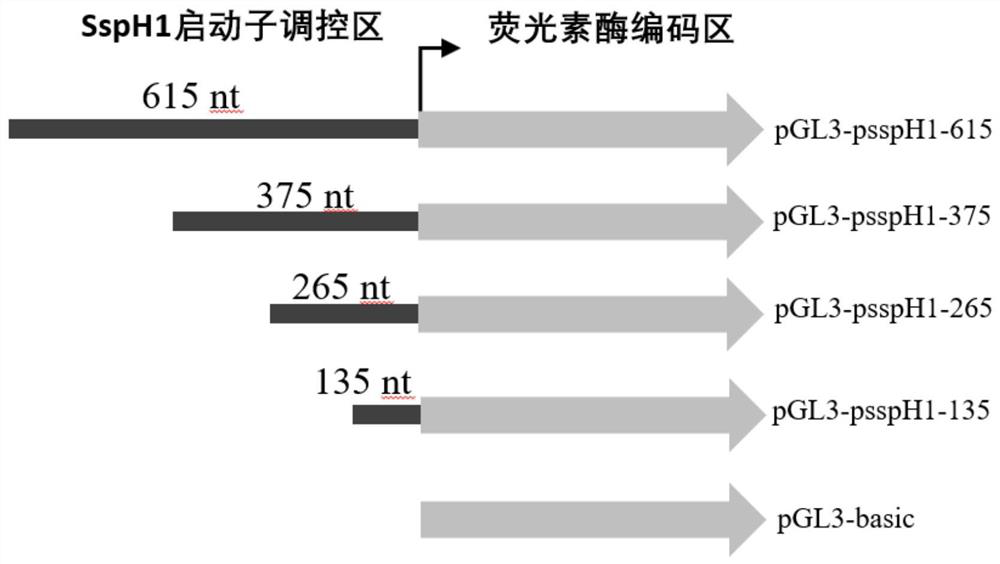
ActiveCN113549621AEnhance expressionHigh activityMicrobiological testing/measurementPeptidesEscherichia coliTyphimurium strain
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, and discloses a minimum promoter for enhancing activity and expression of exogenous protein in bacteria. According to the minimum promoter, the minimum promoter capable of enhancing the activity and the expression of the exogenous protein in the bacteria is screened in a deletion mutation manner, and the minimum promoter is 265 nucleotides on the upstream of a gene coding region of salmonella enteric subspecies enteric chlamydia mouse typhimurium strain RM13672SspH1, and the nucleotide sequence of the minimum promoter is represented by SEQ.ID.NO: 1. The obtained minimum promoter for enhancing the activity and expression of the exogenous protein in the bacteria still keeps activity in escherichia coli, is a promoter with general activity, has the potential to be applied to other different types of prokaryotic bacteria, and can be used as a tool for improving the protein yield and the protein activity in the industry or scientific research, and scientific research, biological medicine industrial production and preparation of anti-infectious disease vaccines are facilitated.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
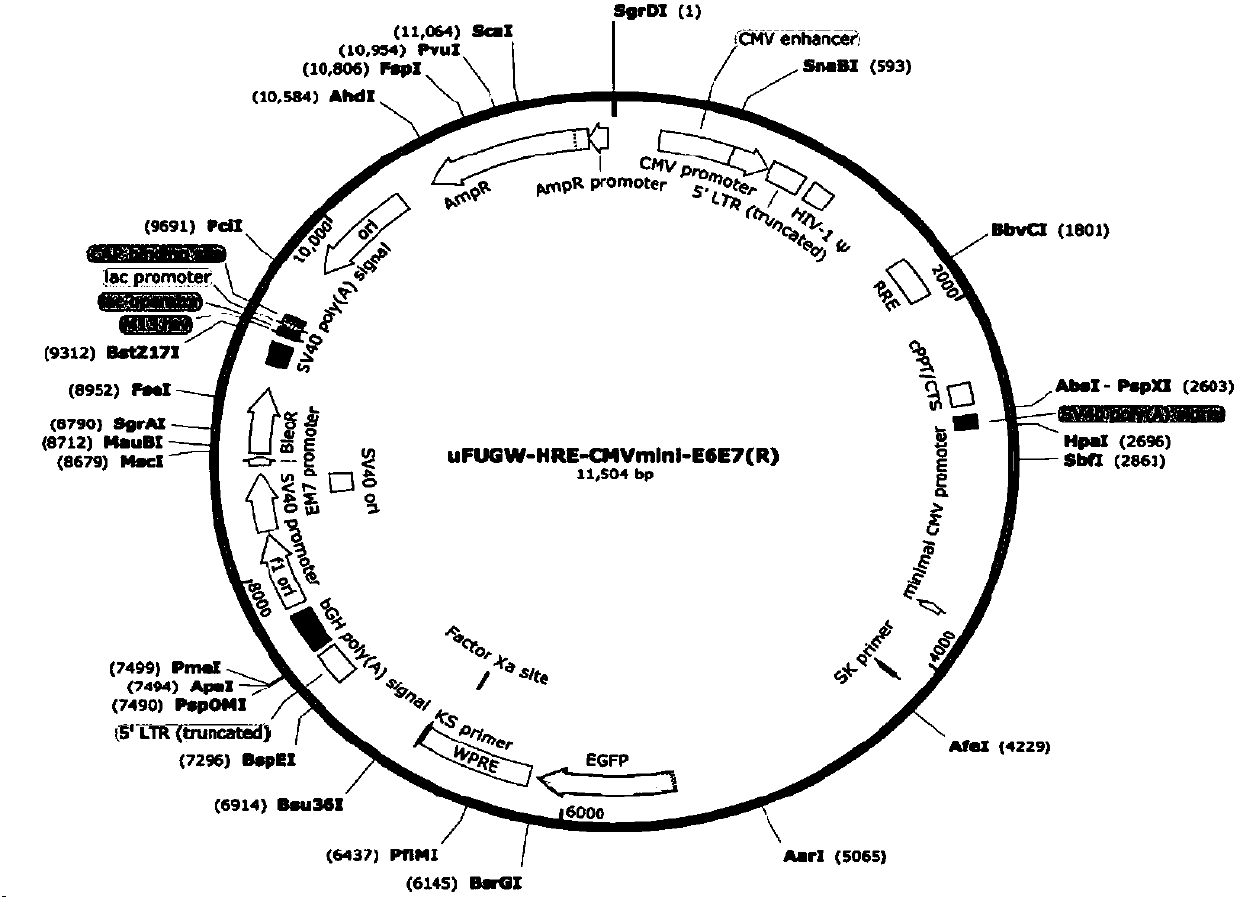
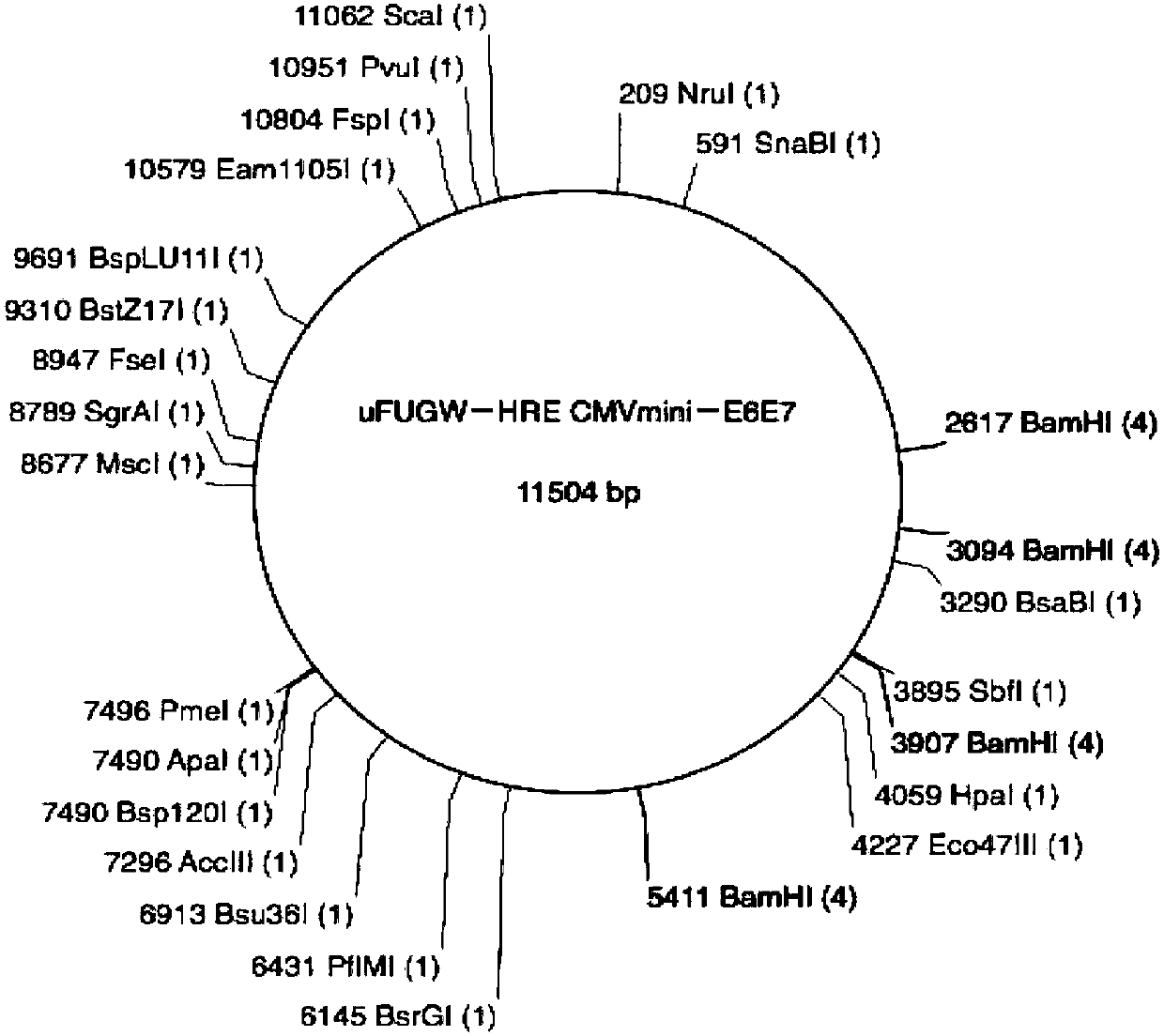
Lentiviral expression vector for inducing HPV16 E6/E7 gene expression under hypoxia conditions
ActiveCN107630039APromote differentiationAvoid immunogenic reactionsBlood/immune system cellsFermentationVirus typeRed blood cell
The invention discloses a lentiviral expression vector for inducing HPV16 E6 / E7 gene expression under hypoxia conditions. The lentiviral expression vector contains a hypoxia response element, a CMV-minimum promoter and a HPV16 E6 / E7 gene. The lentiviral expression vector can induce directional differentiation of hematopoietic stem cells into immortalized erythroid progenitor cells under the hypoxia conditions and the immortalized erythroid progenitor cells can differentiate into mature erythrocytes under normal oxygen supplying conditions. The erythrocytes induced by the vector has deformability and a oxygen bonding and release capability similar to those of the normal mature erythrocytes and has oxygen content of hemoglobin of 28+ / -2mmHg. The diameter of the erythrocyte injected into a mouse for 10min to 24h is decreased and the erythrocyte has a mature erythrocyte form in 24h and has good adaptability of existence in the body.
Owner:长春力太生物技术有限公司
Artificial bidirectional promoter for activation of gene expression
InactiveUS20070028323A1Improve expression levelSugar derivativesOther foreign material introduction processesTranscription initiationHigh level expression
A bidirectional module for activation of gene expression and regulation of transcription in both directions is disclosed. The bidirectional module comprises multiple cis regulatory DNA sequence elements, strategically arranged to give a ‘Transcription Activating Module’ that achieves high level expression from a ‘Transcription Initiation Module’. The latter functions like a minimal promoter. The former activates transcription simultaneously in both the directions from the latter and also responds to several transcription inducing, external stimuli in both the directions. Since it is an artificially designed bidirectional transcription module, it has no equivalent DNA sequence in plant genome. This reduces the chances of the genes from being silenced by homology based mechanisms. A bidirectional promoter module as this, can therefore be used to develop efficient vectors for genetic engineering in plants.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com