Control of targeted turnover of key ethylene hormone signaling pathway proteins to modulate ethylene sensitivity in plants
一种乙烯、蛋白的技术,应用在在植物中控制关键乙烯激素信号传导途径蛋白的目标周转率以调节乙烯敏感性领域,能够解决诱导水平低、易位/移动差、植物非毒性诱导剂特异性不够等问题
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
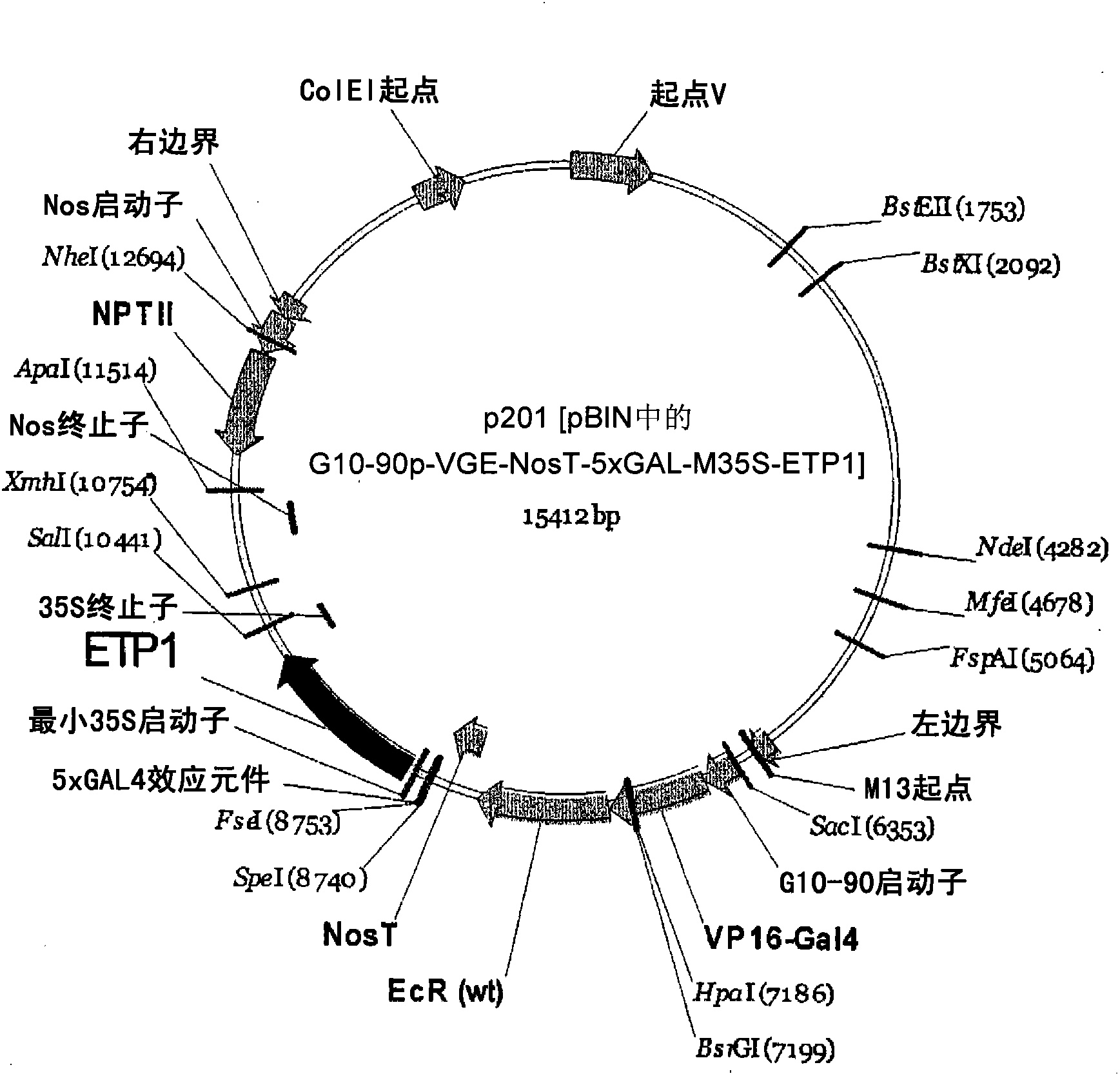
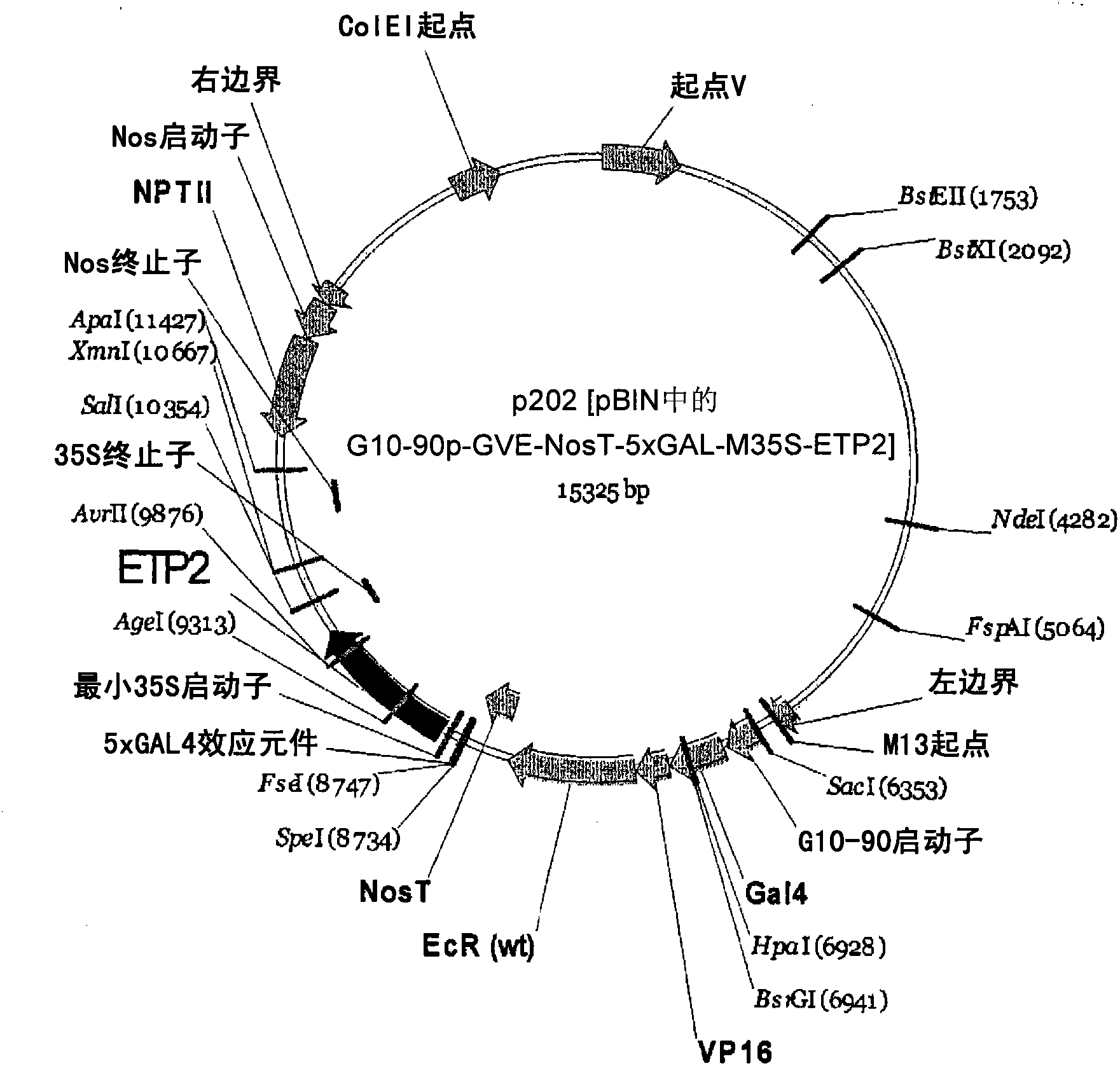
[0110] Example 1: Plasmids
[0111] Activation cassettes of individually cloned gene cassette assemblies include:
[0112] G10-90 constitutive promoter,
[0113] VP16 activation domain,
[0114] GAL4 DNA binding domain, and
[0115] Ecdysone receptor ligand binding domain linked to NOS terminator sequence.
[0116] Similarly, to clone the targeting cassette components individually, the targeting cassette includes:
[0117] an inducible promoter consisting of 5 copies of the GAL4 response element and a minimal 35S promoter, and
[0118] ETP1 gene (GENBANK accession number NM_112874) or ETP2 gene (GENBANK accession number NM_112777) and
[0119] 35S terminator sequence.
[0120] All individual sequences are identified with reference to the nucleotide number of SEQ ID NO: 1 below.
[0121] During the assembly of the activation cassette, the following components fuse in two different orders to form two different activation cassettes:
[0122] VP16 AD to GAL4 LBD to DBD EcR...
Embodiment 2
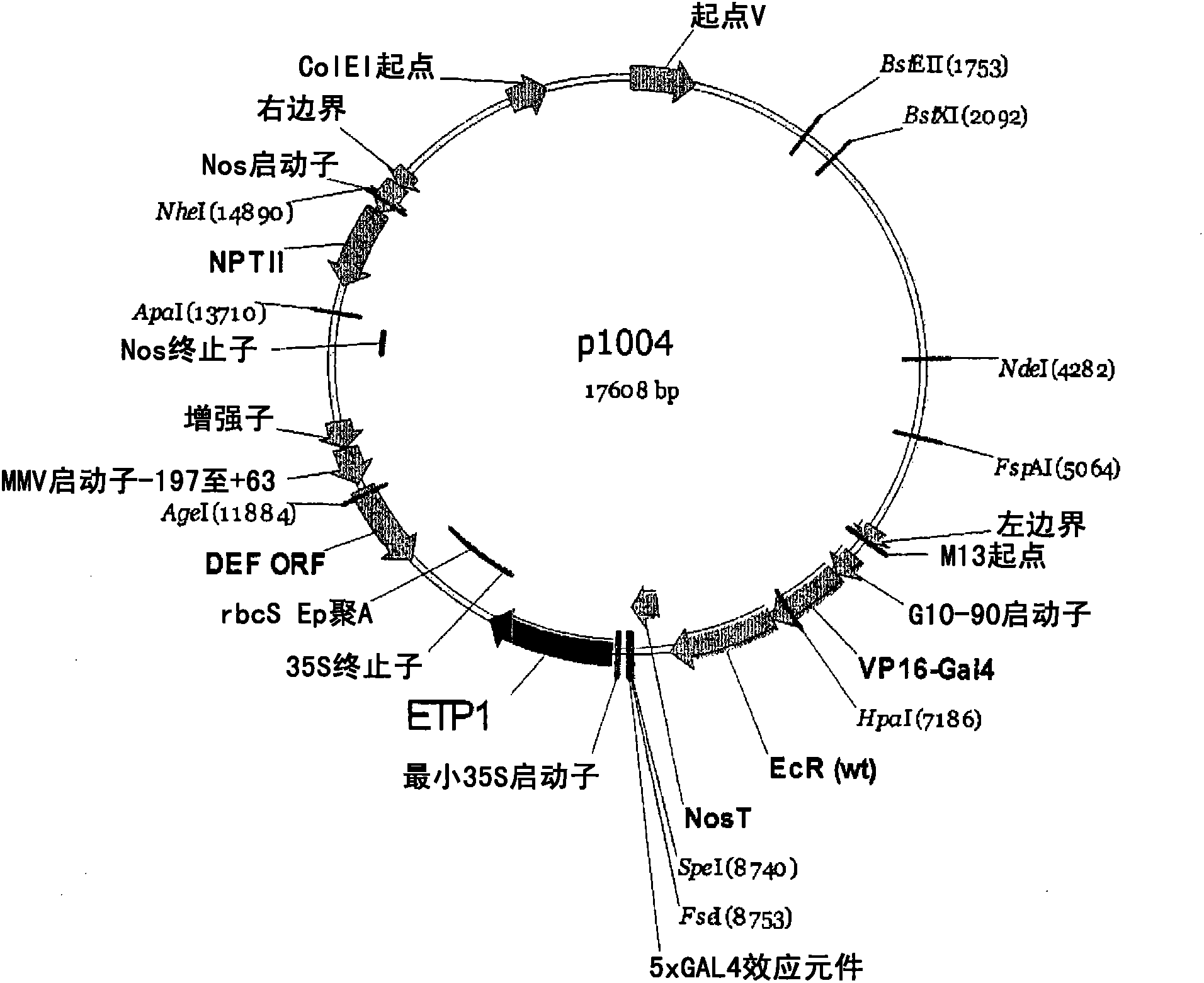
[0133] Embodiment 2: Preparation of transgenic Arabidopsis plants
[0134] Arabidopsis plants were transformed with the Agrobacterium plasmid of Example 1 using standard flower dipping procedures. Seeds were harvested and inoculated on kanamycin-containing medium. Transformed plants were selected for their ability to grow on kanamycin and screened by PCR to verify the presence of the ETP1 or ETP2 gene. Positive transformants were selfed to produce T1 seeds. Seeds were grown on media containing kanamycin to identify transgenic homozygous lines. Homozygous plants were used for the experiment of inducing ethylene insensitivity.
Embodiment 3
[0135] Example 3: Effects of Modulating Ethylene Sensitivity on Growth of Arabidopsis Plants
[0136] Triple reaction assays (modified as described below based on Guzman and Ecker, 1990 cited above) were performed to determine the modulation of ethylene sensitivity in the transformed Arabidopsis plants of Example 2. Wild-type ein2-5 (ethylene-insensitive mutant control) and p1004 or p1005 Arabidopsis transformant seedlings were assayed. The Arabidopsis seeds were sterilized on the surface and soaked in 20 μM inducer, and kept in the dark at 4°C for 4 days. Seeds were inoculated on 0.5X MS containing 1% sucrose and 20 μM inducer, with and without 20 μM ACC (ethylene precursor), and incubated at 21° C. in the dark for 4-8 days. In some experiments, 5 μM AgNO was added to the medium 3 (ethylene inhibitor that induces ethylene insensitivity) served as a control. Responses to ethylene were recorded on the last day. Transgenic plants containing an activation cassette and a targe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com