Application of arabidopsis gene SPOC1 in regulating and controlling flowering stages of plants
A technology of Arabidopsis and genes, applied in the field of molecular biology, can solve the problems of key regulatory factors of target genes and unclear molecular regulatory mechanisms
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0018] Embodiment 1, T-NDA insertion mutant homozygous screening
[0019] 1. Obtain sterile vaccine
[0020] Seeds of wild-type Arabidopsis thaliana and SPOC1 gene T-DNA insertion mutant (SALK_099124C) were purchased from ABRC (Arabidopsis Biological Resource Center). The full-length gene coding (CDS) sequence of the SPOC1 gene is shown in SEQ ID No:1.
[0021] Arabidopsis thaliana seeds were sterilized with 1% NaClO solution (V / V) for 8 minutes, washed with sterile Tween water for 1 minute after shaking for 1 minute, dried and sown on 1 / 2 MS medium. After being placed at 4°C for 3 days, the light culture was placed in a light incubator (16h light / 8h dark, 22°C). After 10 days of light culture, the seedlings were moved into the soil to continue culturing.
[0022] 2. Arabidopsis plant DNA extraction
[0023] (1) Take 2 leaves and place them in a 1.5ml EP tube, add 800μl of DNA extraction solution;
[0024] (2) Water bath at 60°C for 1 hour, and mix by inverting every 10 mi...
Embodiment 2
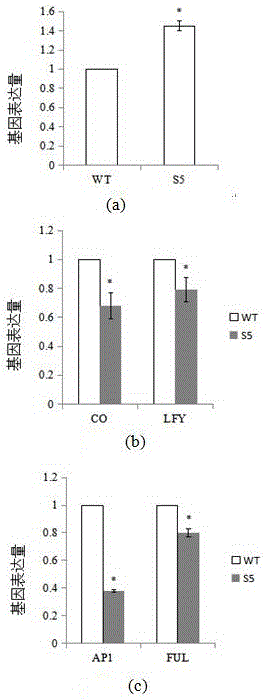
[0046] Example 2. SPOC1 (AT5G25520) expression analysis in spoc1 mutants
[0047] 1. Extraction of Arabidopsis total RNA
[0048] (1) Take 2 pieces of rosette leaves of Arabidopsis thaliana and put them into a pre-cooled mortar, add liquid nitrogen and quickly grind them into a uniform powder. During the grinding process, ensure that the material is immersed in liquid nitrogen;
[0049] (2) After the liquid nitrogen volatilizes, quickly transfer the material to a pre-cooled 1.5ml RNase-free centrifuge tube, add 1ml TRIZOL solution for every 50-100mg tissue material, mix well, and place it at room temperature for 5min, then 12000rpm, 4℃ Centrifuge for 10 minutes;
[0050] (3) Take 800 μl of the supernatant to a new 1.5ml RNase-free centrifuge tube, add 0.2ml of chloroform, oscillate for 15sec to mix well, leave at room temperature for 5min, centrifuge at 12000rpm, 4℃ for 15min;
[0051] (4) Take 450 μl of supernatant, add an equal volume of isopropanol, mix well, and place a...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Embodiment 3.spoc1 mutants compare with wild type flowering time
[0073] 1. Obtain sterile vaccine
[0074] Arabidopsis thaliana seeds were sterilized with 1% NaClO solution (V / V) for 8 minutes, washed with sterile Tween water for 1 minute after shaking for 1 minute, dried and sown on 1 / 2 MS medium. After being placed at 4°C for 3 days, the light culture was placed in a light incubator (16h light / 8h dark, 22°C). After 10 days of light culture, the seedlings were moved into the soil to continue culturing.
[0075] 2. Statistical analysis of flowering time and number of rosette leaves
[0076] 40 Arabidopsis wild-type plants and 40 spoc1 mutant plants with normal growth were selected, and the days of plant growth and the number of rosette leaves when the first flower of the plants opened were counted.
[0077] Statistical results such as image 3 As shown, the flowering time of the spoc1 mutant was later than that of the wild type, and the number of rosette leaves was...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com