Method for efficiently and rapidly separating T-DNA insertion site flanking sequence, and uses thereof
An insertion site and flanking sequence technology, which is applied in the field of efficient and rapid separation of T-DNA insertion site flanking sequences, can solve the problems of low efficiency, low throughput, low success rate, etc., and achieves the effect of economy and simple analysis.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] Example 1: Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation
[0045] The Agrobacterium-mediated genetic transformation method mainly refers to the method shown in the "Agrobacterium-mediated Genetic Transformation Operation Manual" published by the State Key Laboratory of Crop Genetic Improvement, Huazhong Agricultural University (Lin Yongjun et al., Agrobacterium-mediated Mudanjiang No. 8 high-efficiency Establishment of transgenic system, Acta Crops Sinica, 2002, 28(3): 294-300).
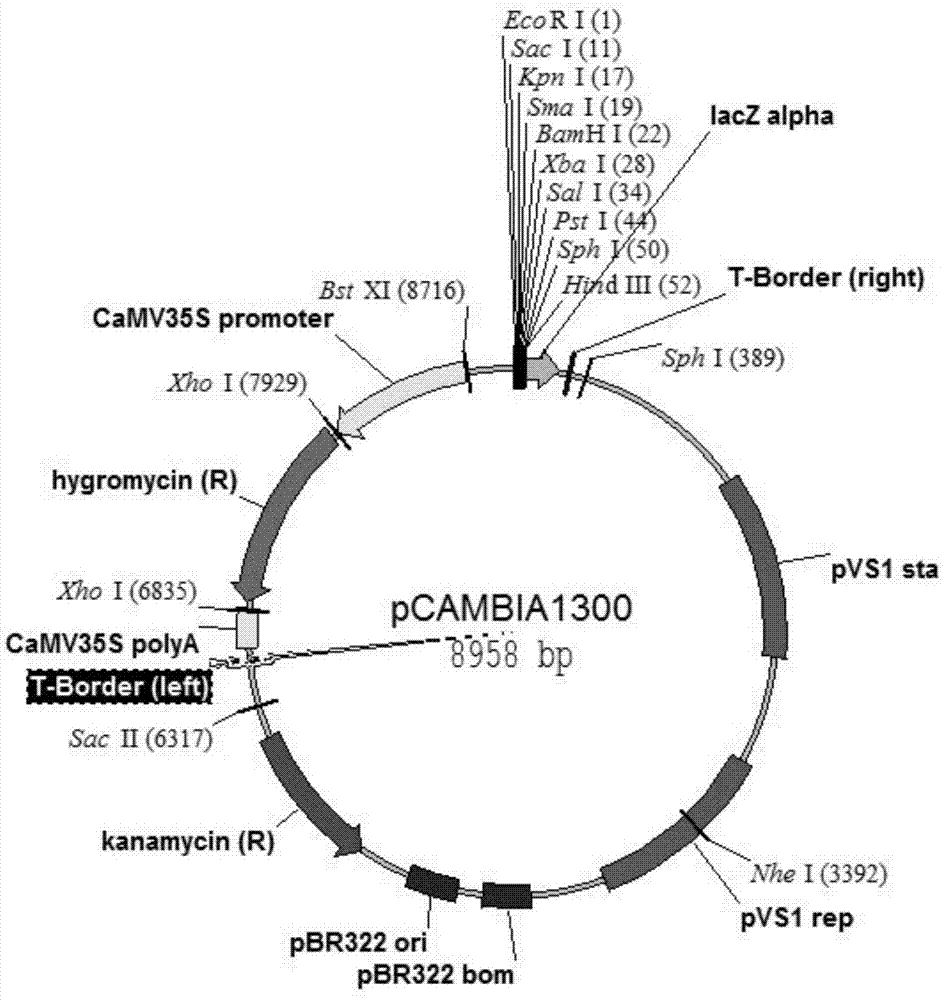
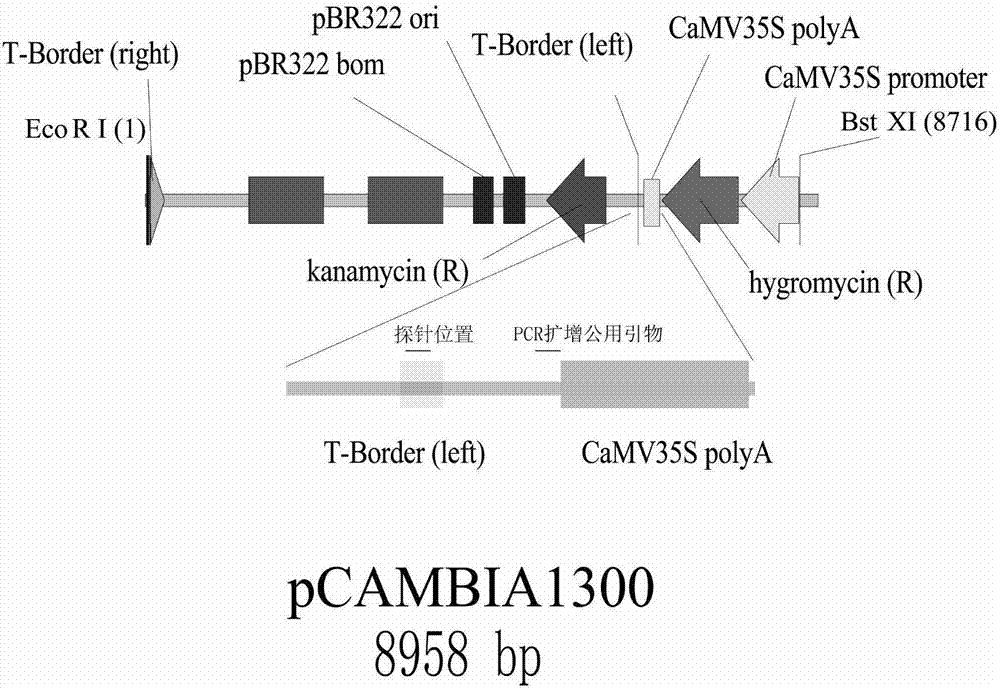
[0046] As shown in Figure 1, the transformation vector is pC1300, the exogenous gene is the hygromycin selection marker gene, pCAMBIA1300 (GenBank No. AF234296.1), and pC1300 is used to electrotransform into Agrobacterium strain EHA105 (purchased from Huazhong Agricultural University) for standby, transformation The recipient is the embryogenic callus induced by mature seeds of rice variety Zhonghua 11. The embryogenic calli were pre-cultured for 3 days, infected with Agrobacterium containing...
Embodiment 2
[0047] Example 2: Extraction of Genomic DNA
[0048] Take embodiment 1 and randomly select 4 strains of T 0 Generation of transgenic rice, 2g of young leaves per plant, after grinding with liquid nitrogen, add 2ml 80°C 1.5×CTAB (15g CTAB; 75ml 1M Tris-HCl, pH 8.0; 30ml 0.5M EDTA, pH 8.0; 61.4g NaCl; Set volume to 1L, stir and dissolve with a stirrer for 2h); 65°C water bath for 30min; add 2ml of chloroform / isoamyl alcohol (24:1) and slowly invert up and down for 15min until the lower liquid phase turns dark green; centrifuge at 3000r / min for 15min at room temperature; take Put the supernatant in a new 10ml centrifuge tube, add 200μl 10% CTAB and 2ml chloroform / isoamyl alcohol (24:1) slowly upside down for about 15min; centrifuge at 3000r / min for 15min at room temperature; take 1.5ml supernatant, add 4ml 1% CTAB, after mixing, pick out the precipitate with a pipette tip and dissolve it in 1ml 1M NaCl (plus 1μl RNase). Add 3ml of frozen absolute ethanol to precipitate the DNA,...
Embodiment 3
[0049] Example 3: DNA library construction
[0050] DNA purification: take 1 μg DNA (prepared in Example 2) and dissolve it in 50 μl ddH 2 After being neutralized in O, it was crushed to a size of 300-500 bp by an ultrasonic crusher. Add 0.5X magnetic beads (Beckman, http: / / www.beckmancoulter.cn / ), mix well and place at room temperature for 15 minutes; use a magnetic stand (invitrogen, http: / / www.thermofisher.com / cn / zh / home. html) Adsorb the magnetic beads, transfer the supernatant to a new centrifuge tube, add 0.5X magnetic beads again, mix well and place at room temperature for 15 minutes; absorb the magnetic beads with a magnetic stand, discard the supernatant, add 200 μl 80% ethanol, and wash for 2 all over. After drying, add 10 μl ddH 2 O dissolved DNA, set aside.
[0051] DNA repair, addition of A and ligation: DNA repair and addition of A use the kit (E7546S) from NEB (http: / / www.neb-china.com / ) company, see the instructions for the operation steps. After the react...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com