Lens and associatable flow cell
a flow cell and lens technology, applied in the field of diagnostic equipment components, can solve the problems of deformation or warping of the waveguide portion of the integrally formed or molded biosensor, interfere with the desired analysis, and not reliably seal, so as to increase the performance of the biosensor, improve the coupling efficiency and beam quality, and improve the effect of monitoring coupling efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example i
[0092]A waveguide with integrated lenses, such as that depicted in FIGS. 6 & 7, was injection molded in a clean environment from a transparent, general purpose polystyrene. The waveguide had a length of 38 mm, and a width of 25 mm. The thickness 176 of the planar surface 170 was a consistent 0.5 mm. The ridge or “shelf” had a height of 1.3 mm. The front lens and rear lens had bottom edges co-planar with their respective centers of curvature. The front lens horizontal angle 262 was about 15°. The rear lens horizontal angle 264 was about 19°. The radii of curvature of the front and rear lenses were about 3.2 mm and 1.6 mm respectively. The mean angle θ of the front lens was 21°. The mean angle of the rear lens was about 24°.
example ii
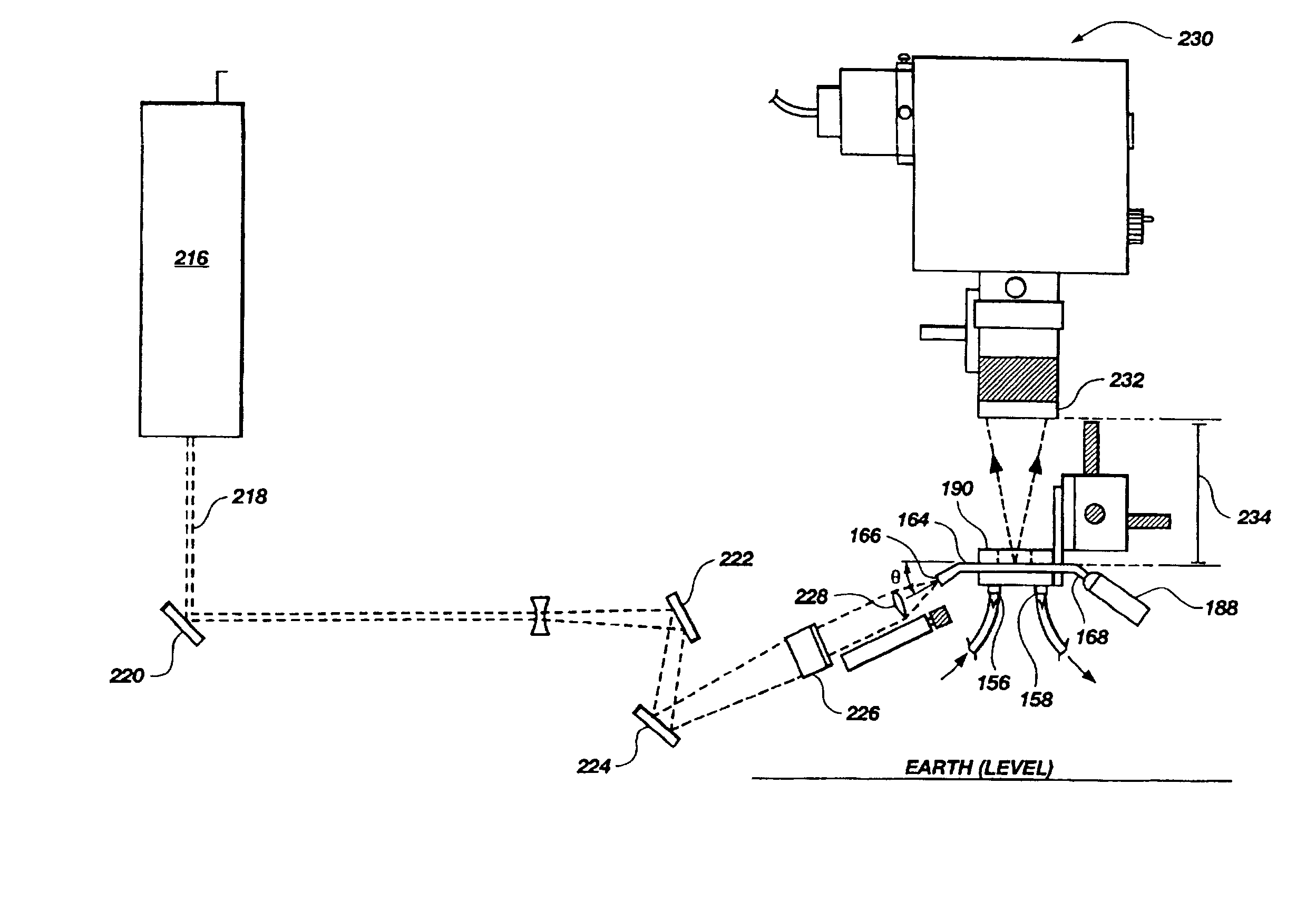
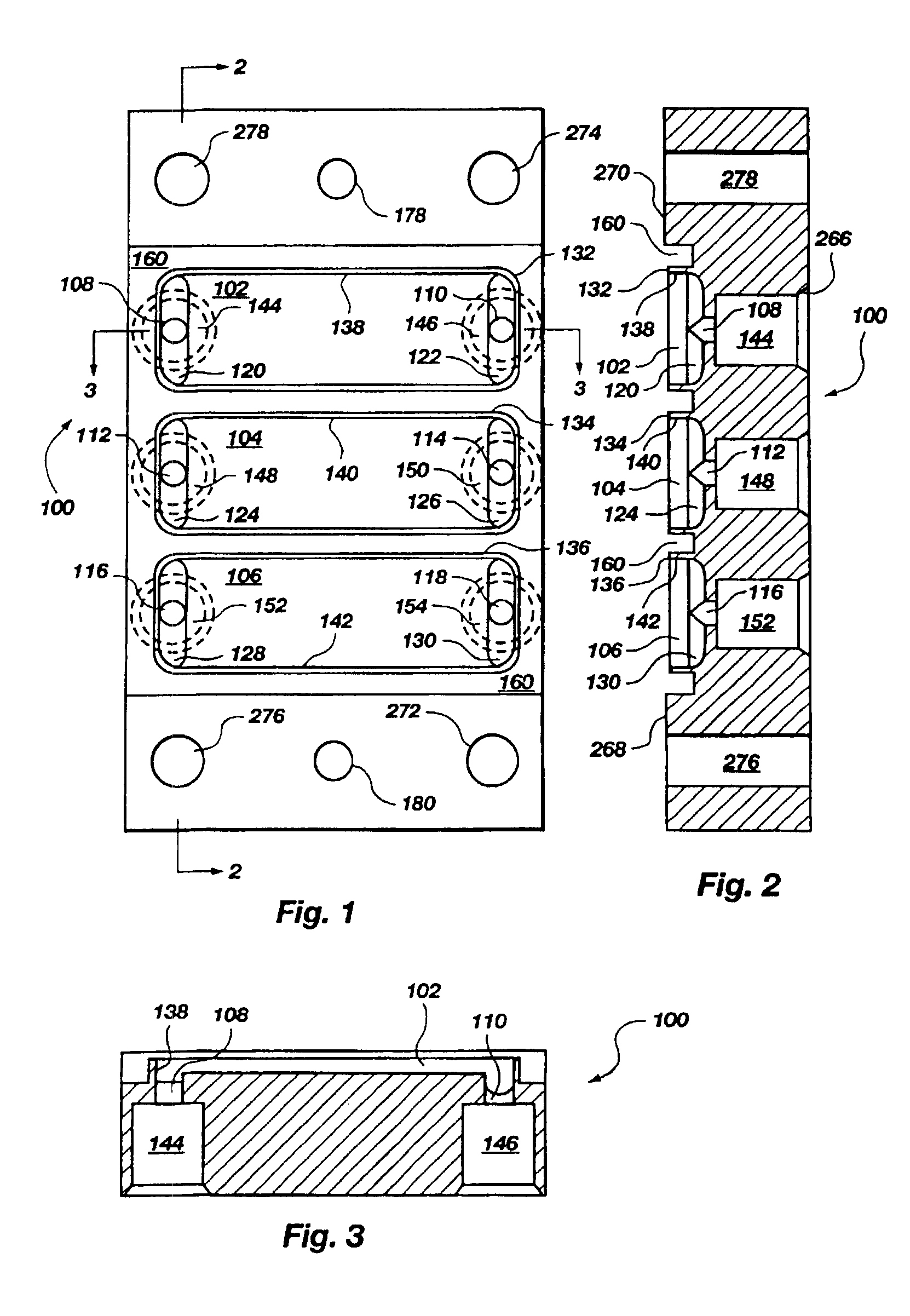
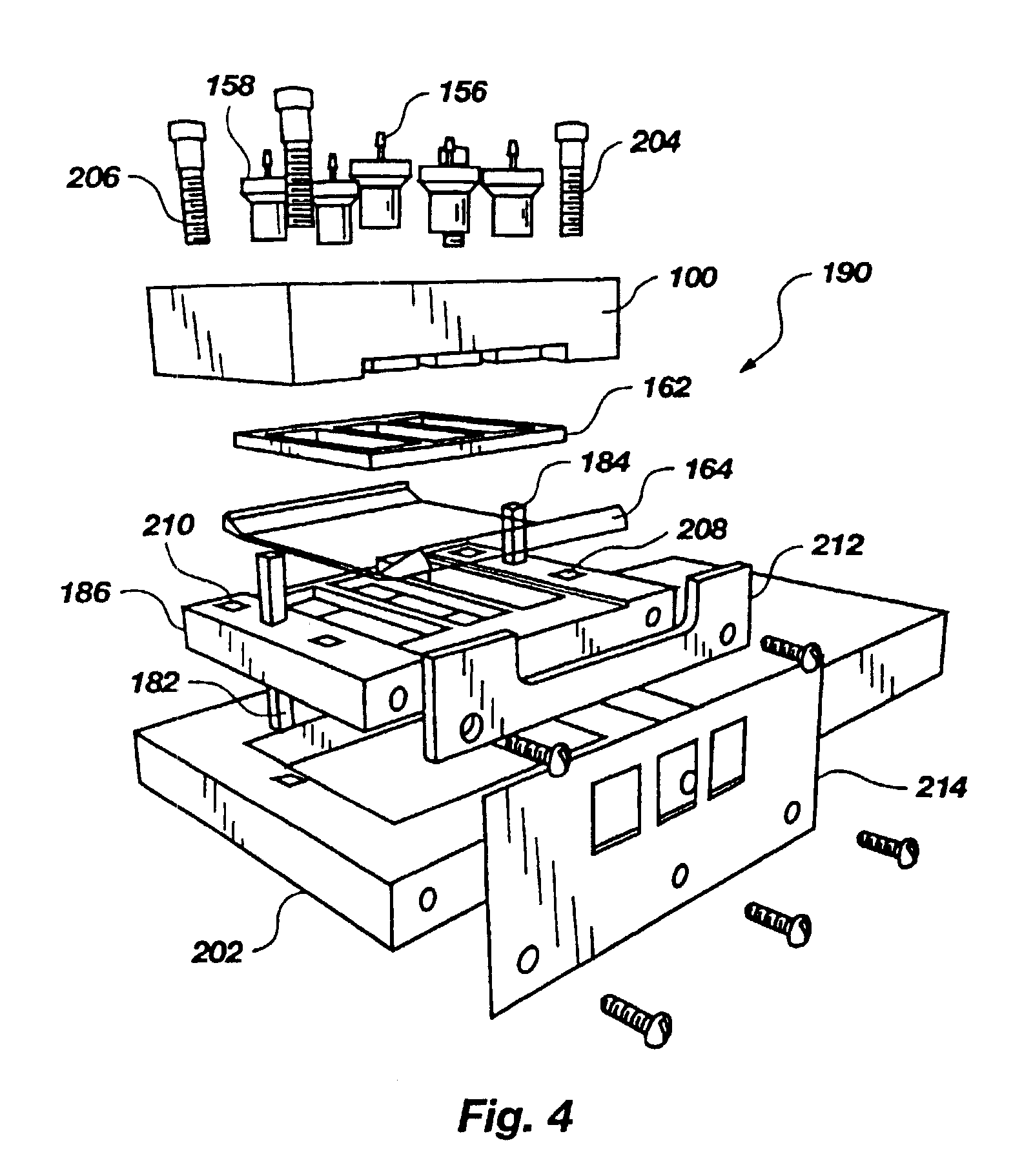
[0093]A flow cell top, such as that depicted in FIGS. 1-3, and 8, was made of hard black anodized 6061-T6 aluminum. It contained three reservoirs each of which had a 0.25 mm (0.010 in.) thick wall surrounding it, a flat floor in middle, two half-capsule shaped recesses at either end 1.6 mm ( 1 / 16 in.) in width, and ports 1.6 mm ( 1 / 16 in.) in diameter running into the center of each recess. The ports opened into a #10-32 (standard thread, not NPT) connector which ran out to the opposite face of the flow cell and was 5.1 mm (0.200 in.) deep. A 90° countersink 266 (FIG. 2) was given at the surface of the port connector (a plastic barbed tubing connector screwed into the port connector and sealed on the countersink). On both sides of the array of reservoirs were two raised platforms which were referred to as lands 268, 270. Each land had three holes running through the thickness of the part. The four #31 clamping holes 272, 274, 276, 278 were formed (i.e. drilled through). The two aper...
example iii
[0094]A gasket 162, such as that depicted in FIGS. 4, 5, and 11, was made as a composite structure laminated from 1.6 mm ( 1 / 16 in.) silicone rubber sheeting and 0.076 mm (0.003 in.) self-adhesive FEP film (total thickness: 1.676 mm (0.066 in.) nominal). Its outer dimensions were about 25 mm (1 in.) by 25.40 mm (1.000 in.) and it had three internal openings which corresponded to the flow cell reservoirs. The gasket was produced using a waterjet cutter and was seated on the flow cell such that the FEP layer faced away from the flow cell surface.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| mean angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| roughness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com