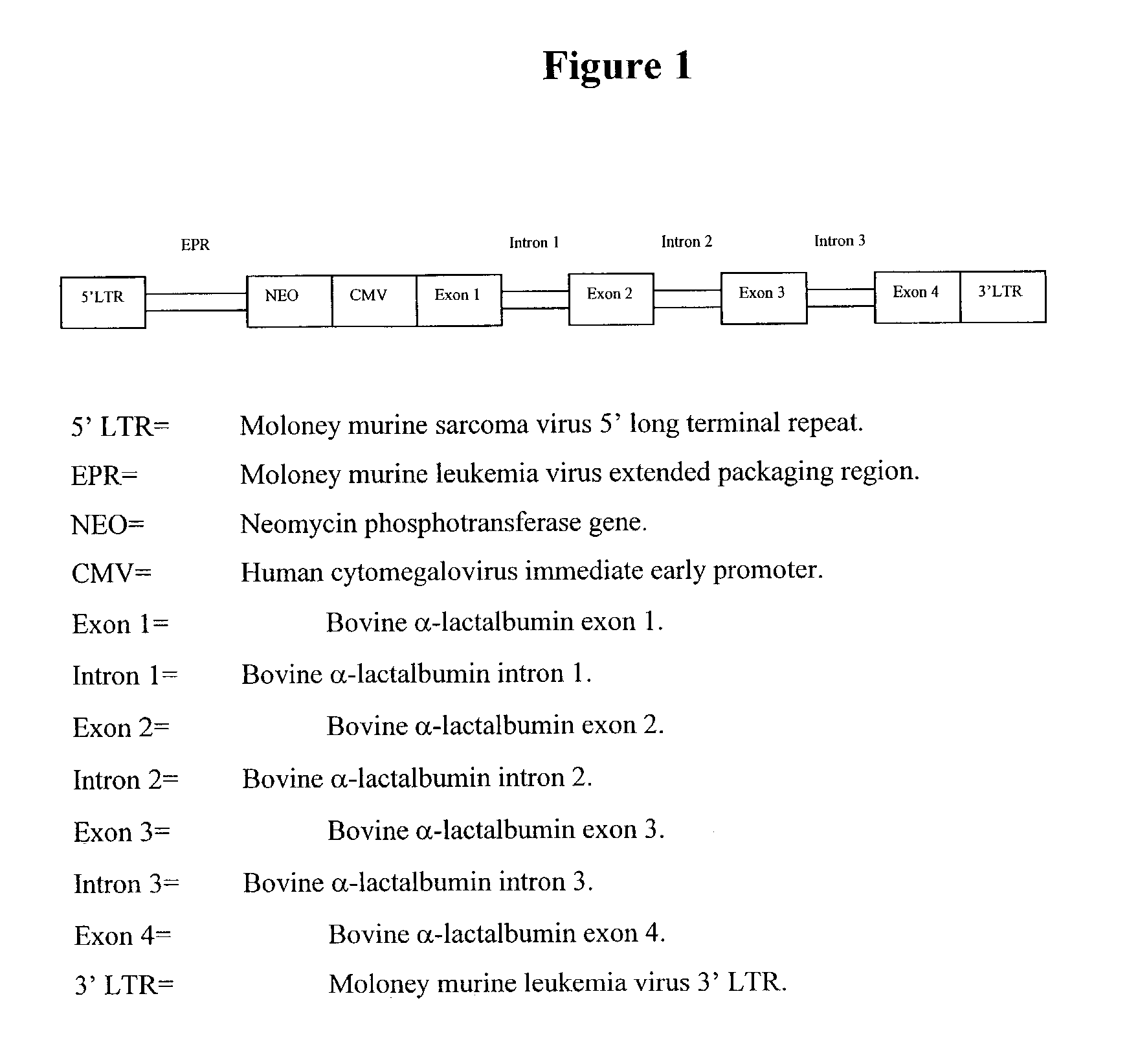
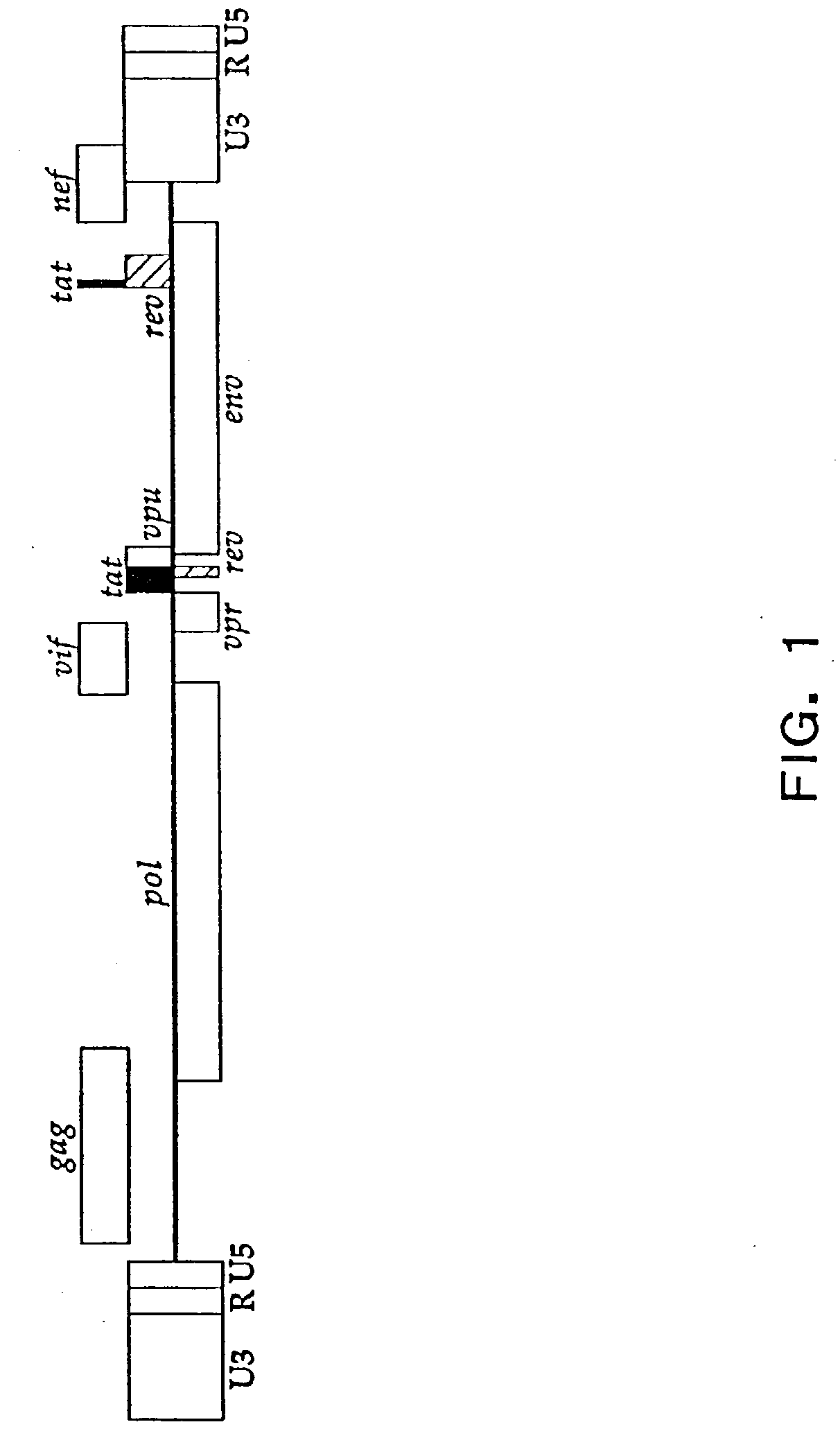
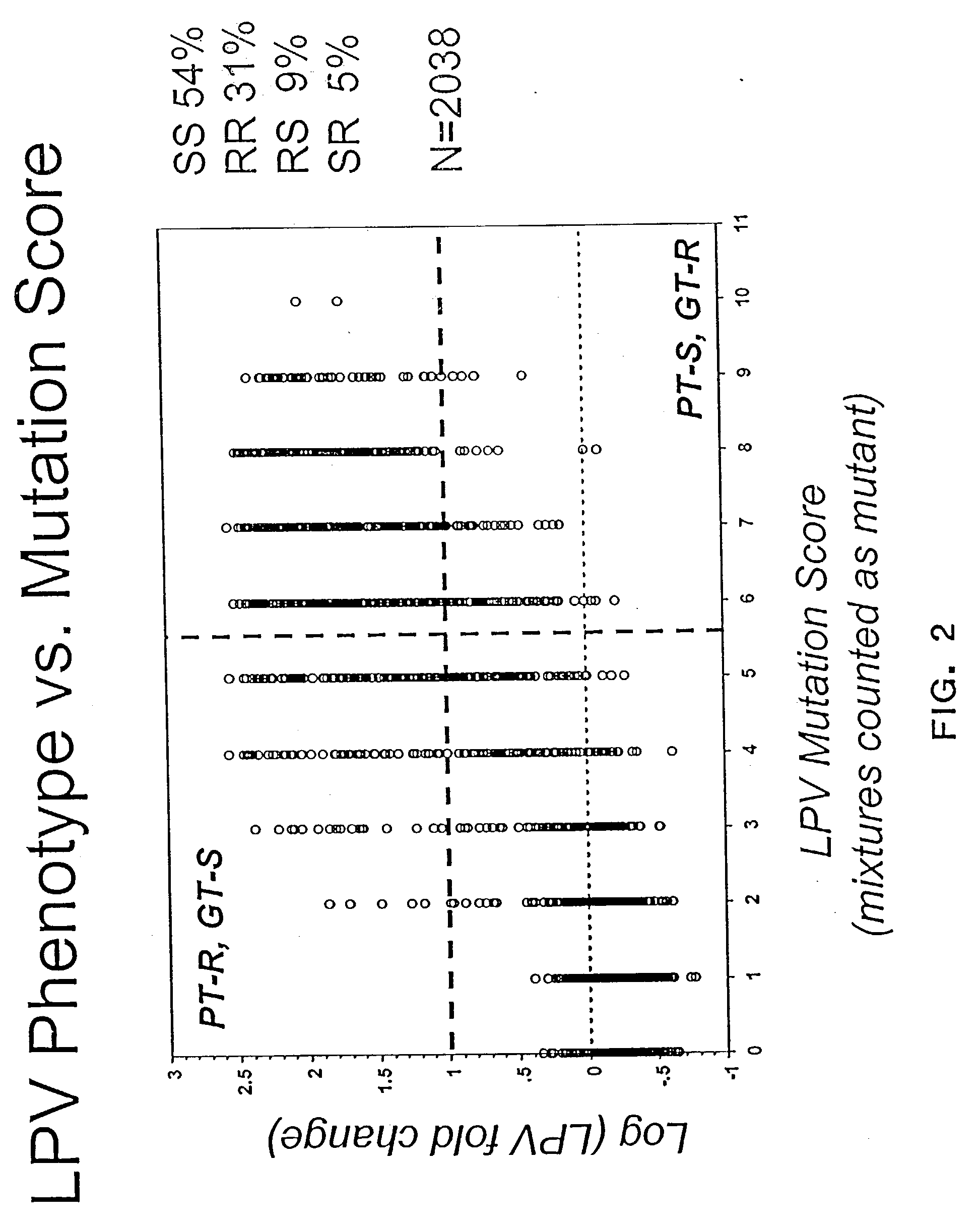
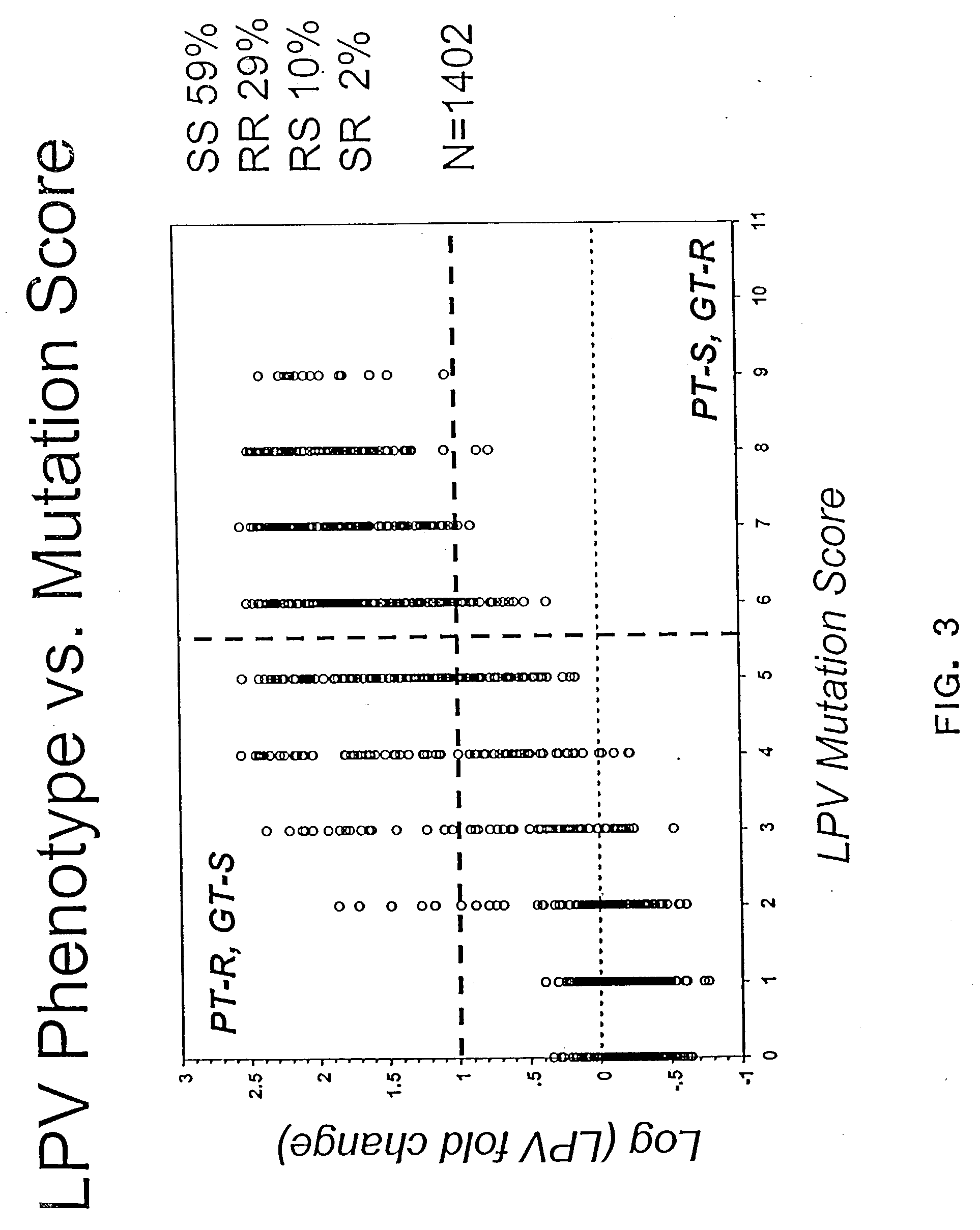
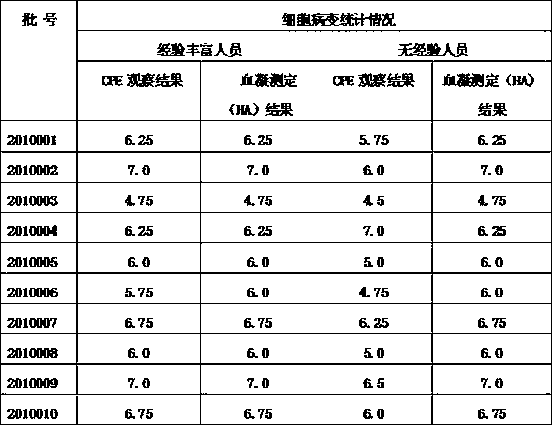
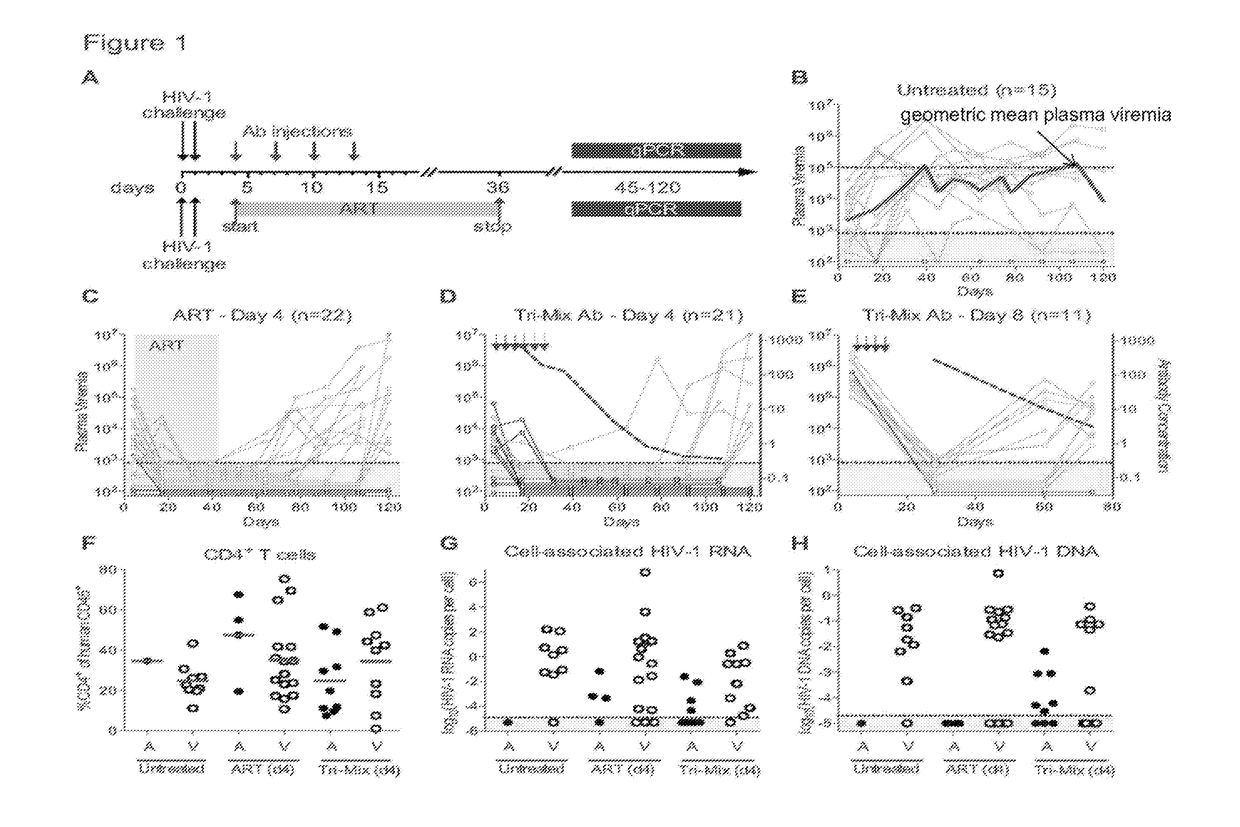
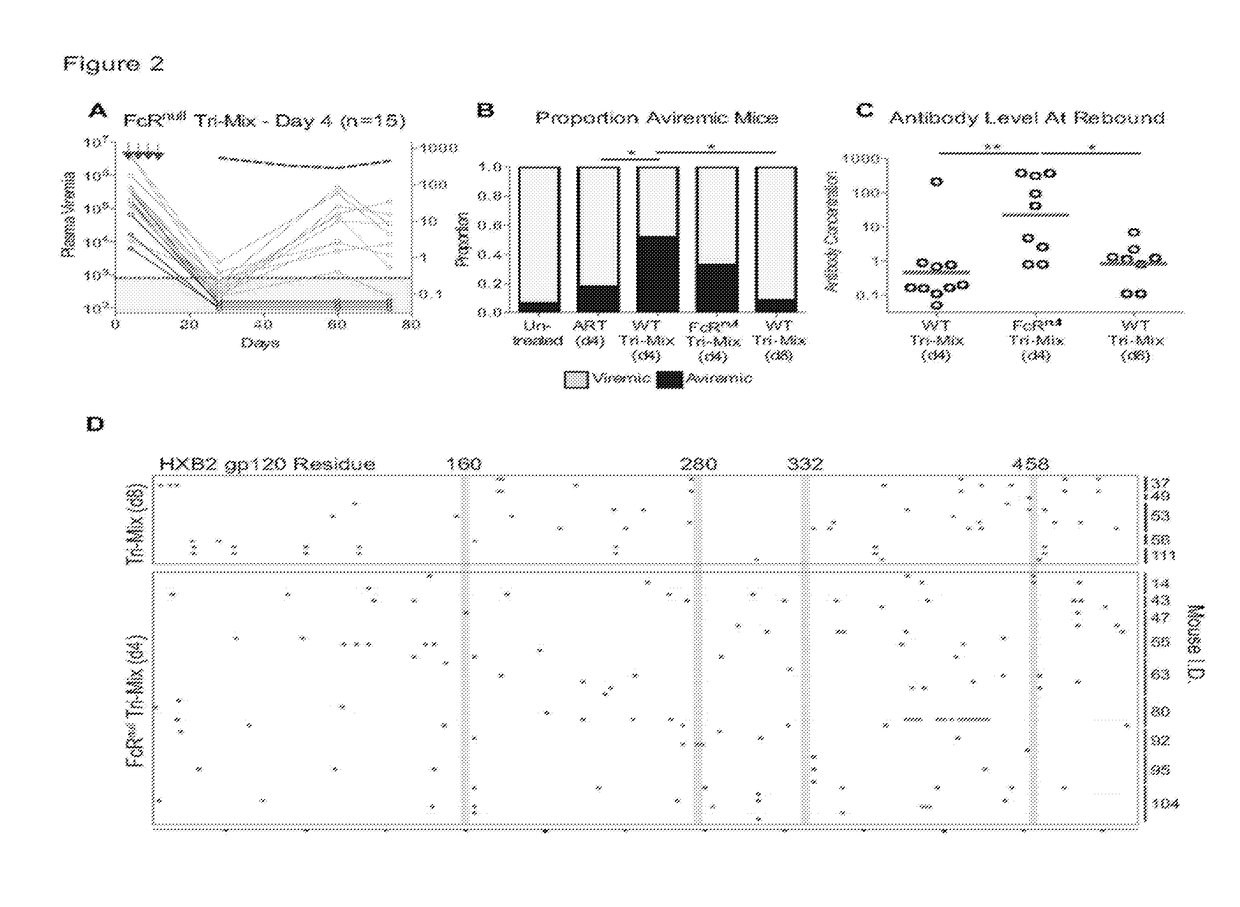
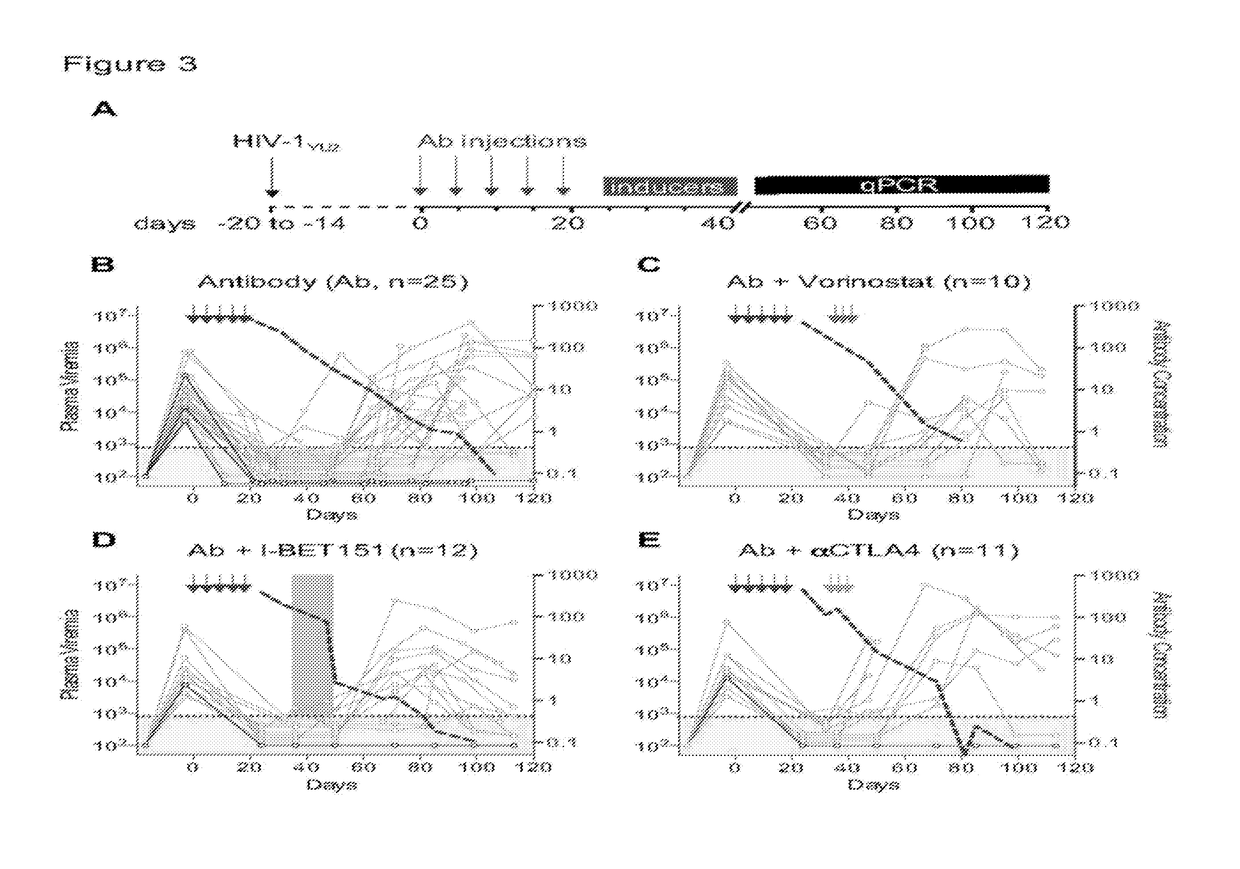
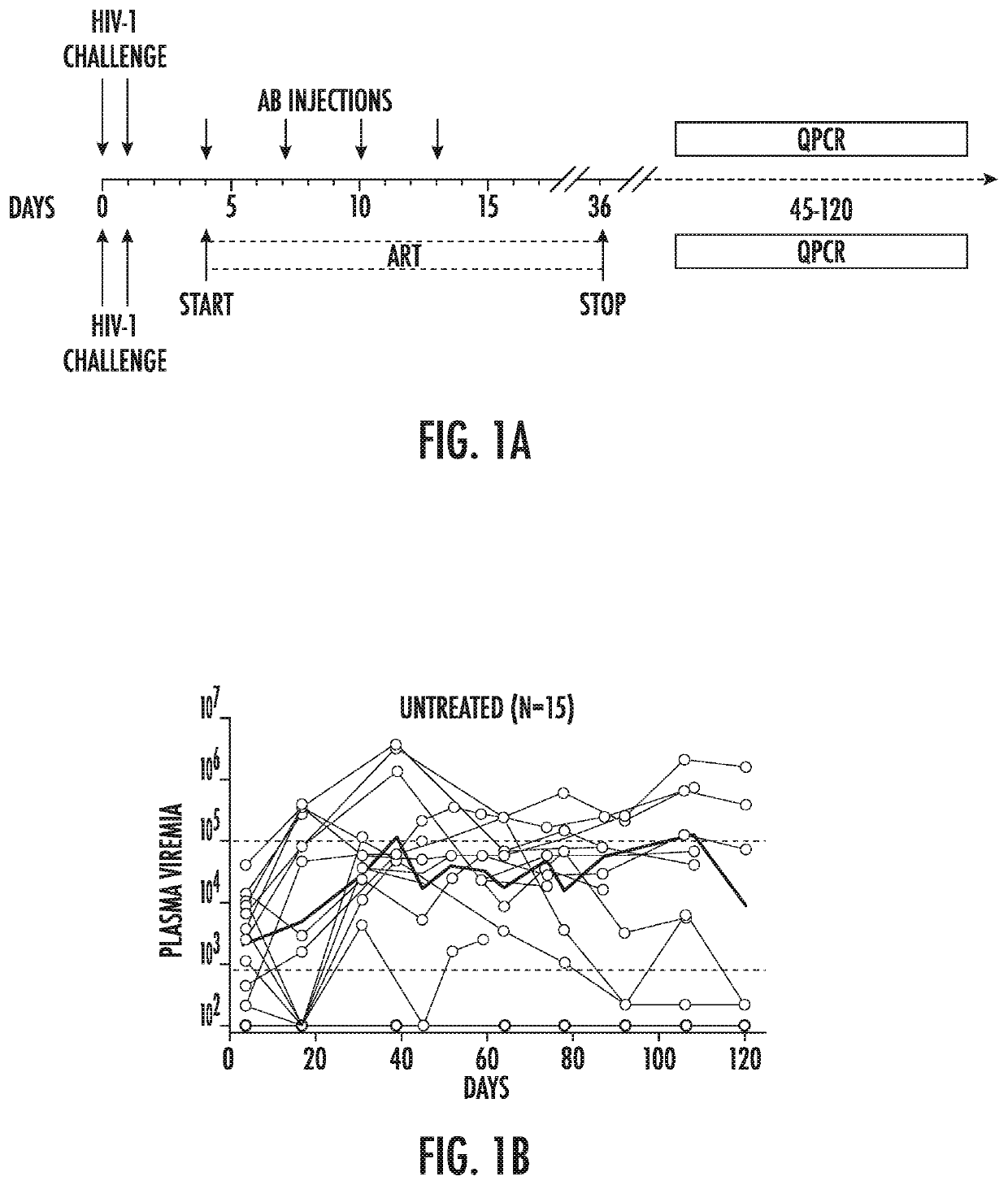
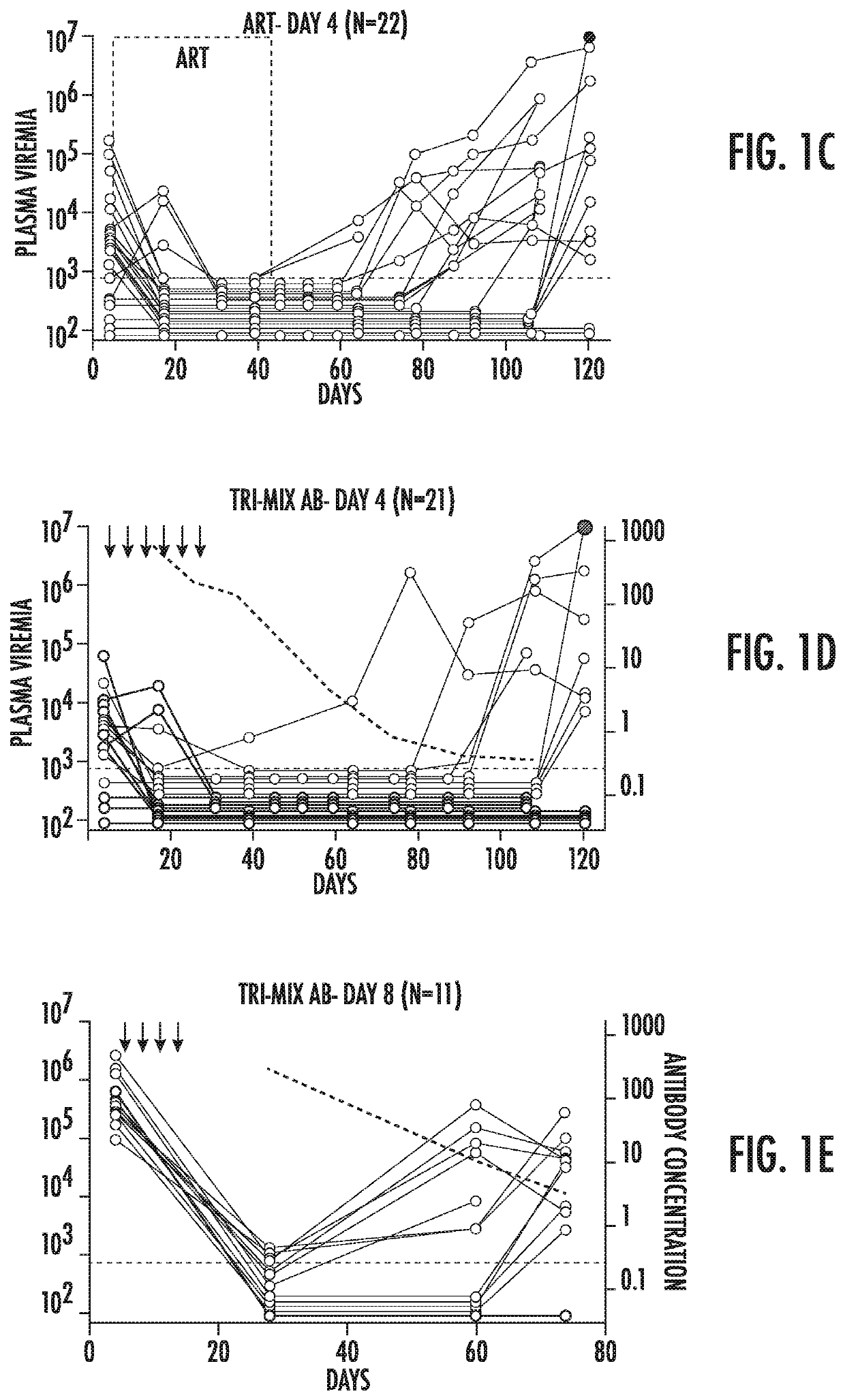
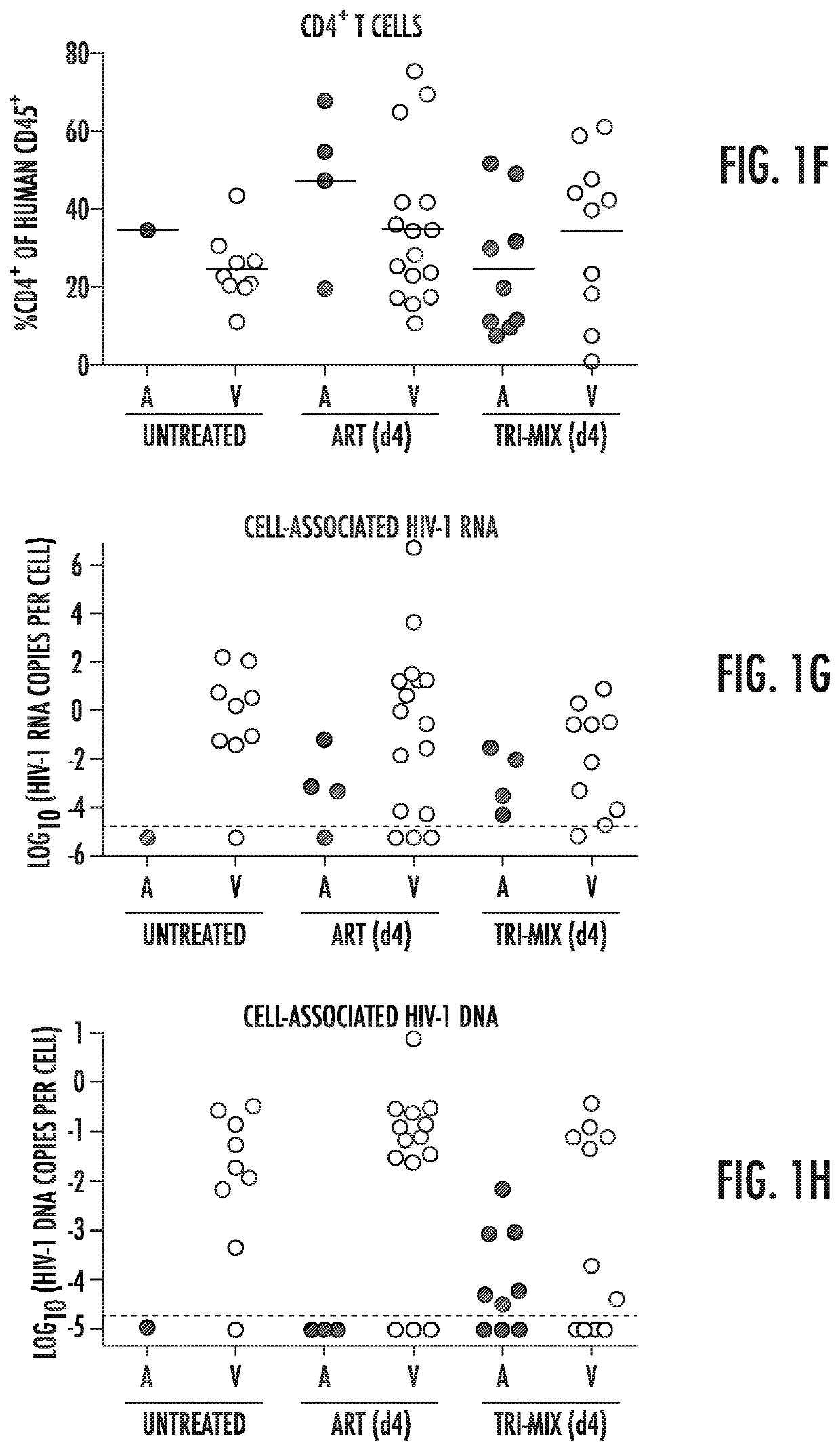
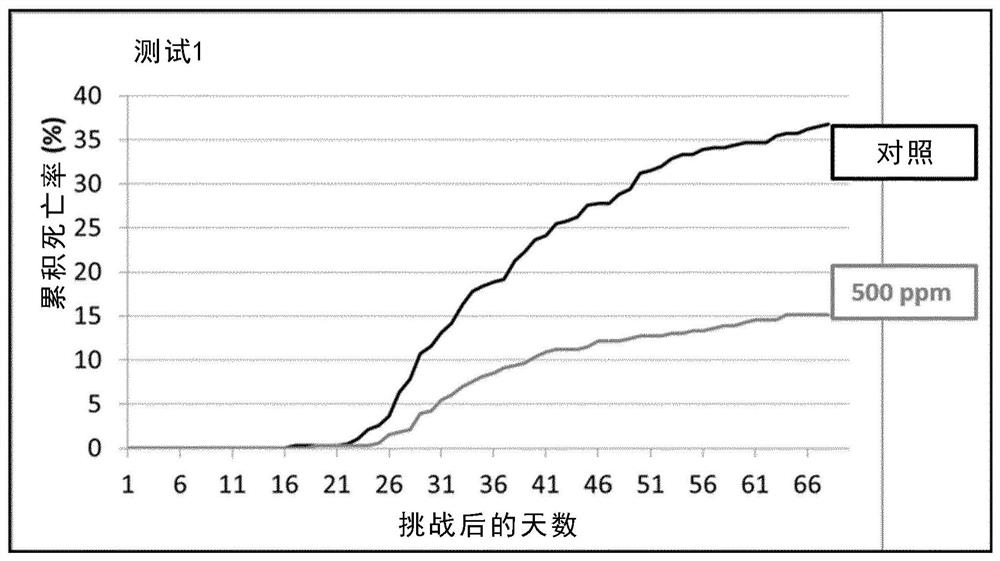
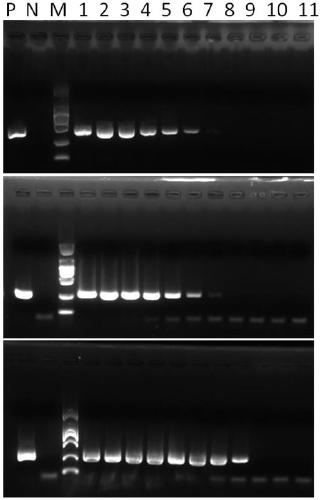
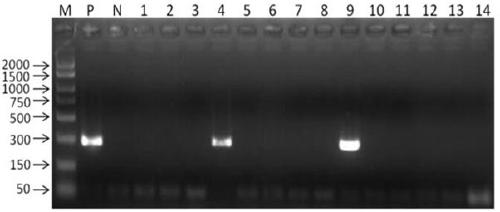
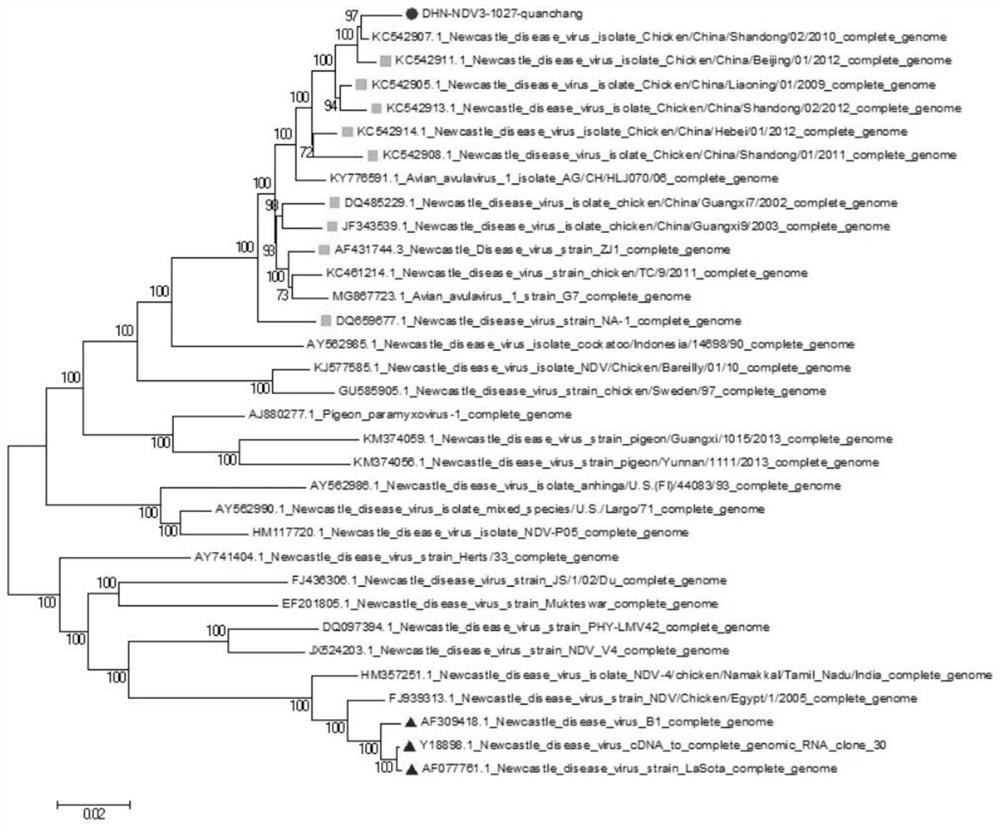
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Provirus" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
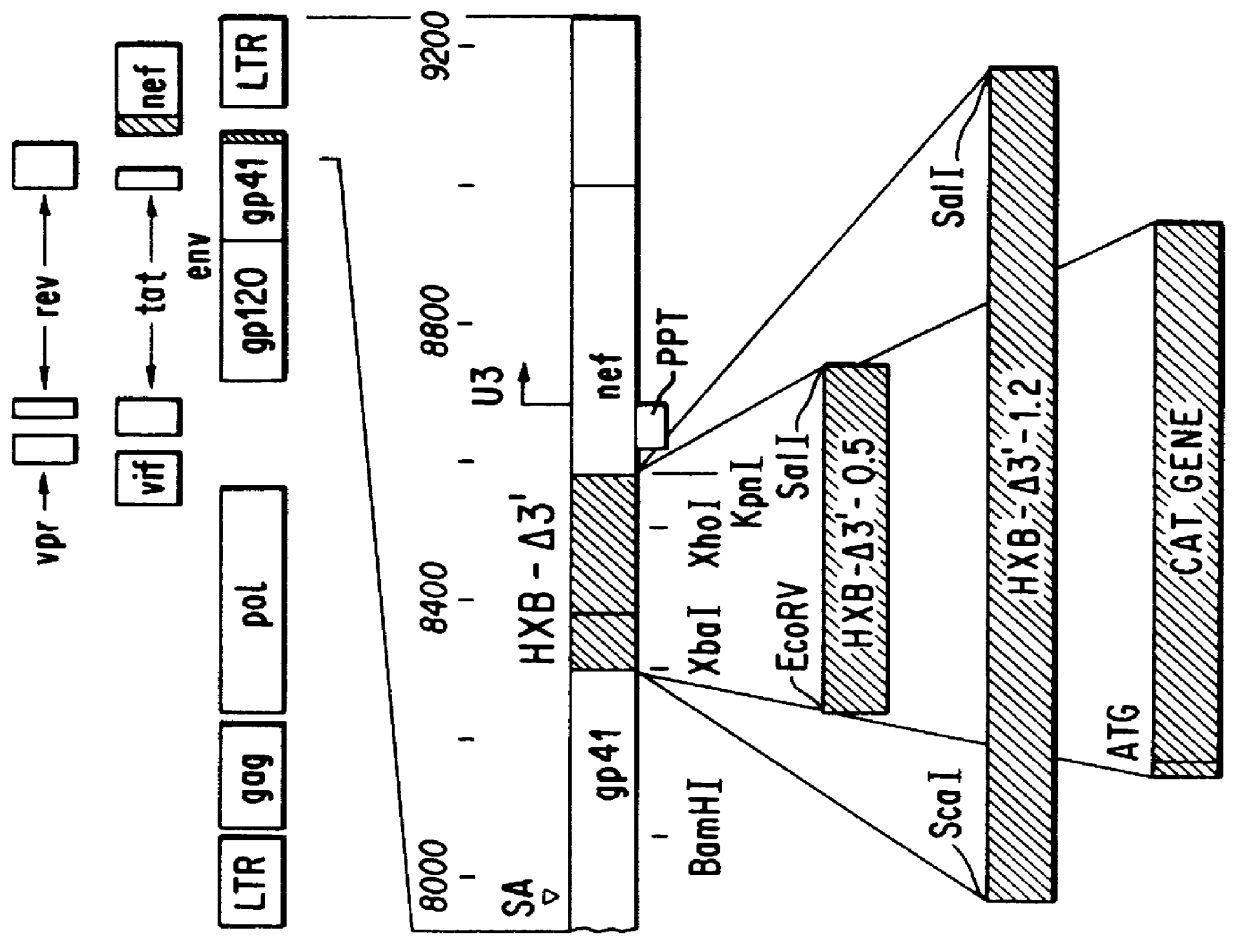
A provirus is a virus genome that is integrated into the DNA of a host cell. In the case of bacterial viruses (bacteriophages), proviruses are often referred to as prophages. This state can be a stage of virus replication, or a state that persists over longer periods of time as either inactive viral infections or an endogenous viral element. In inactive viral infections the virus will not replicate itself except through replication of its host cell. This state can last over many host cell generations.
Mammalian viral vectors and their uses
InactiveUS6255071B1Stable episomal maintenanceMaintain relatively stableSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementRetroviral provirusMammal
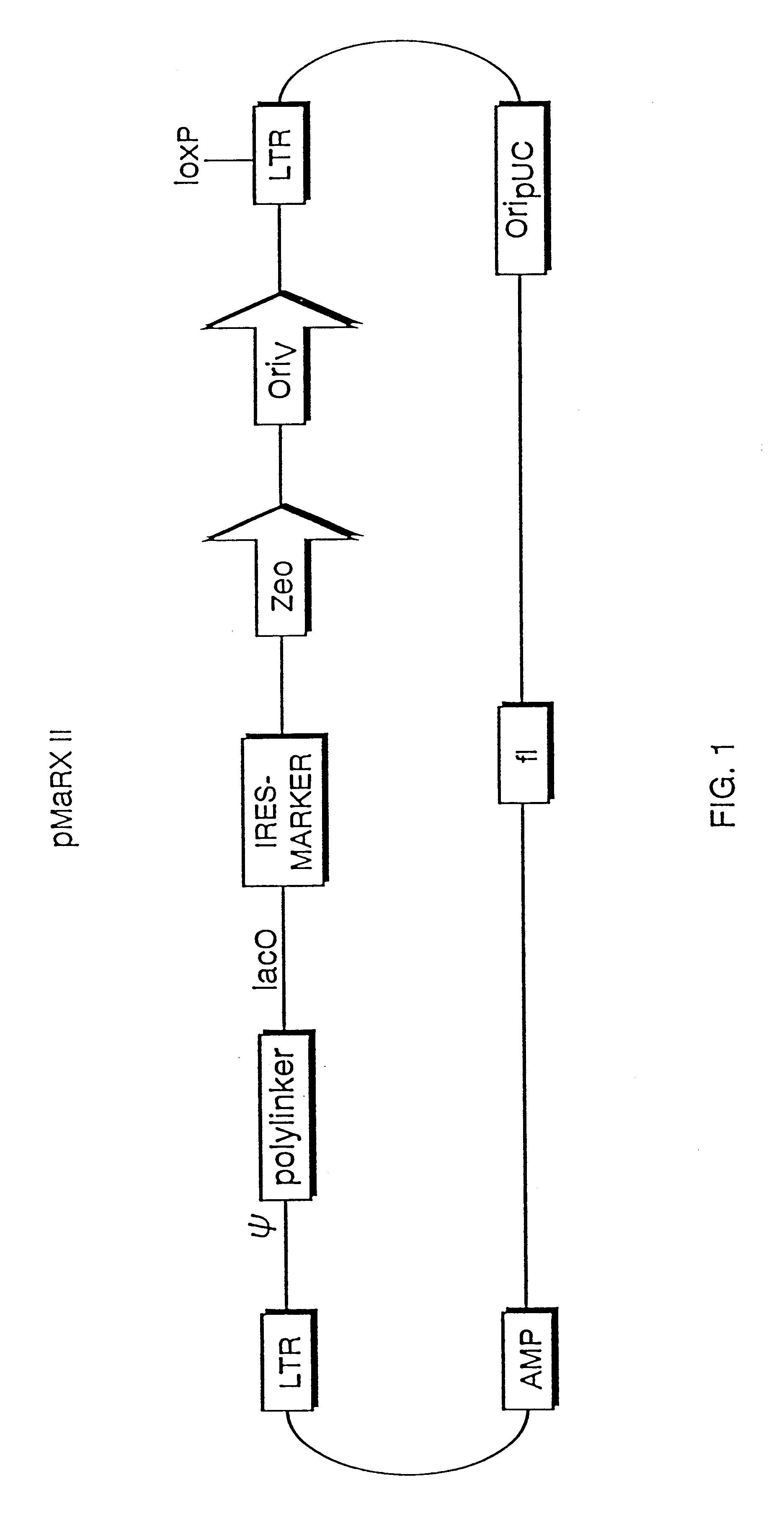
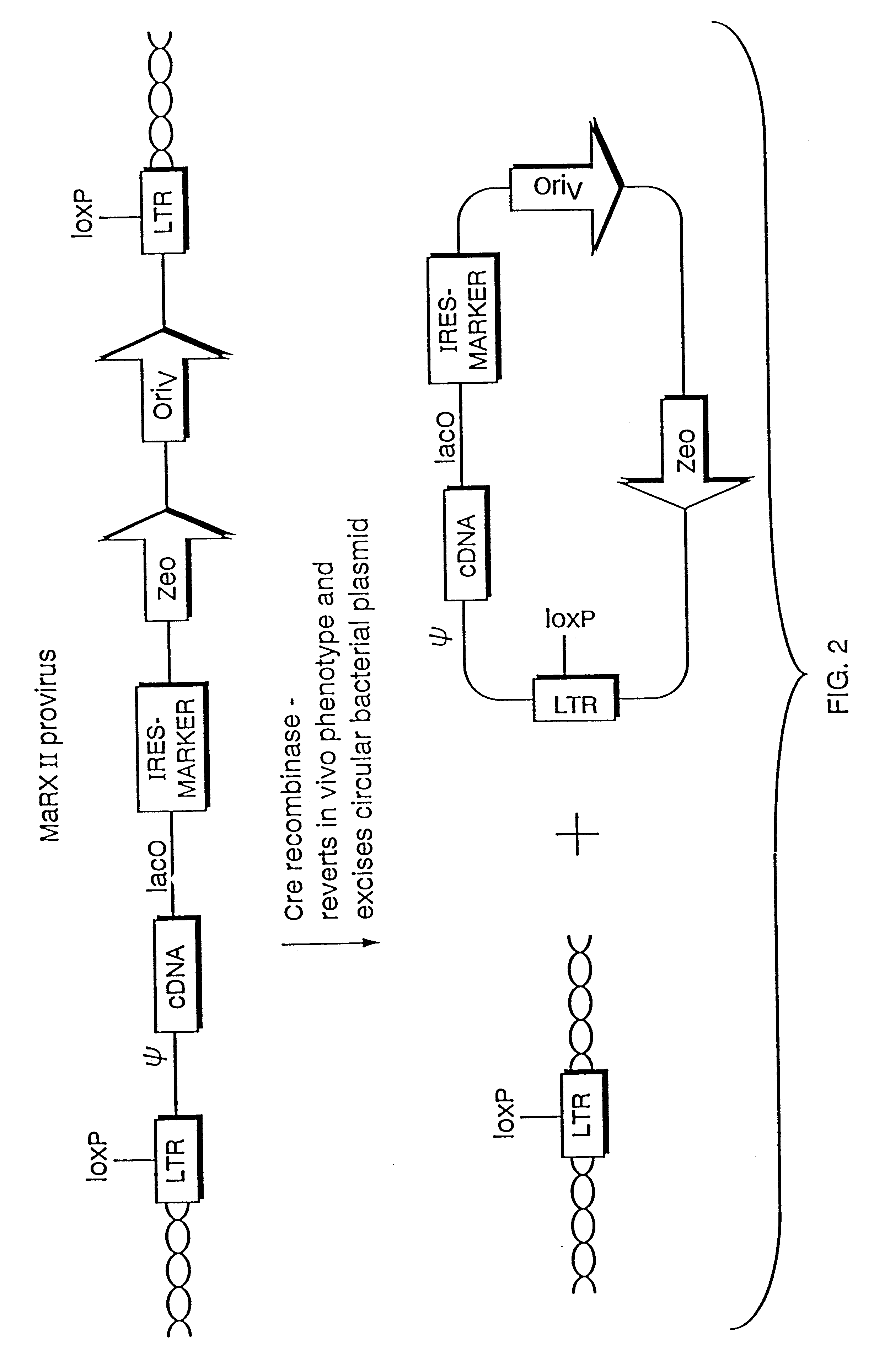
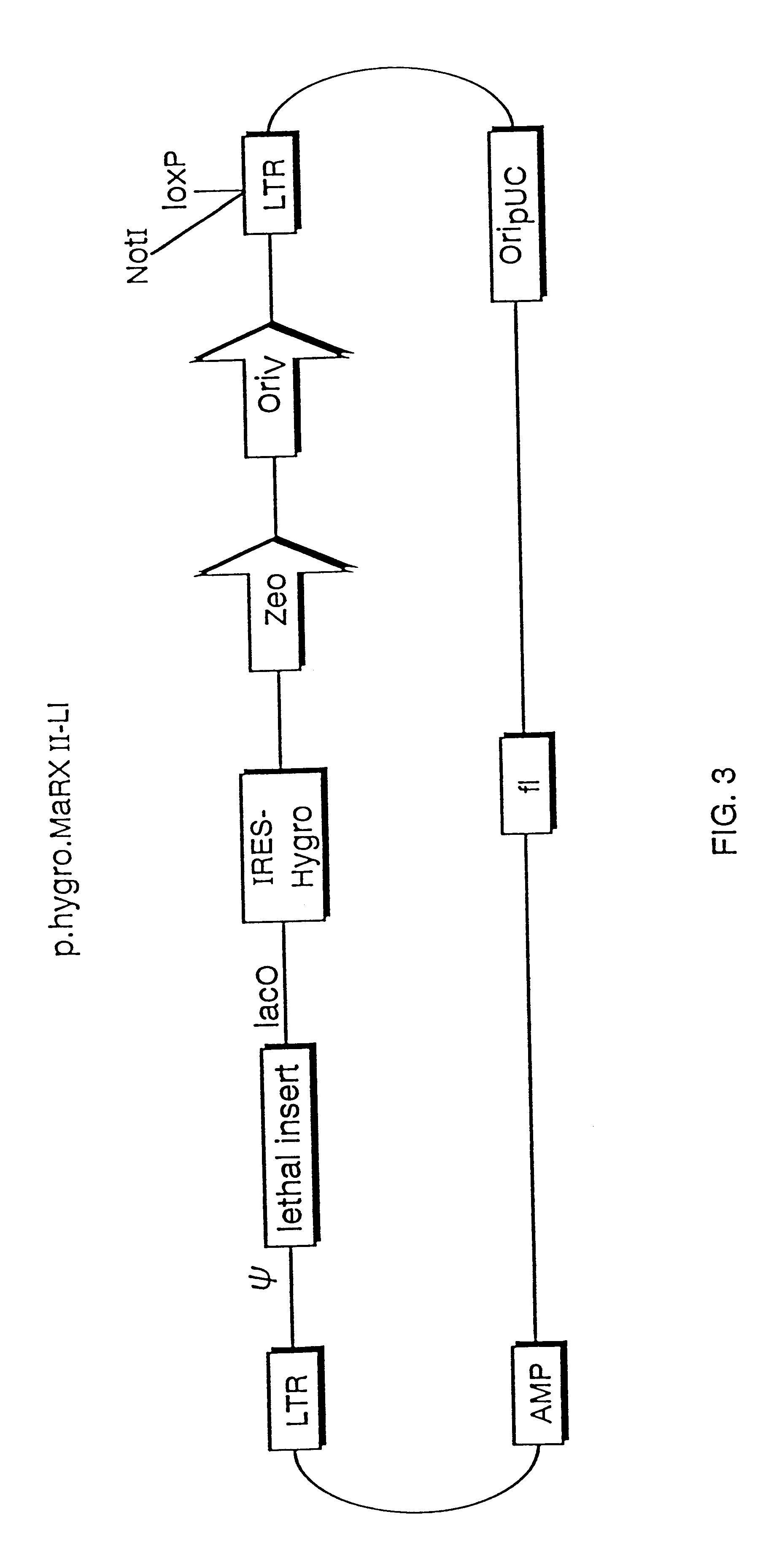
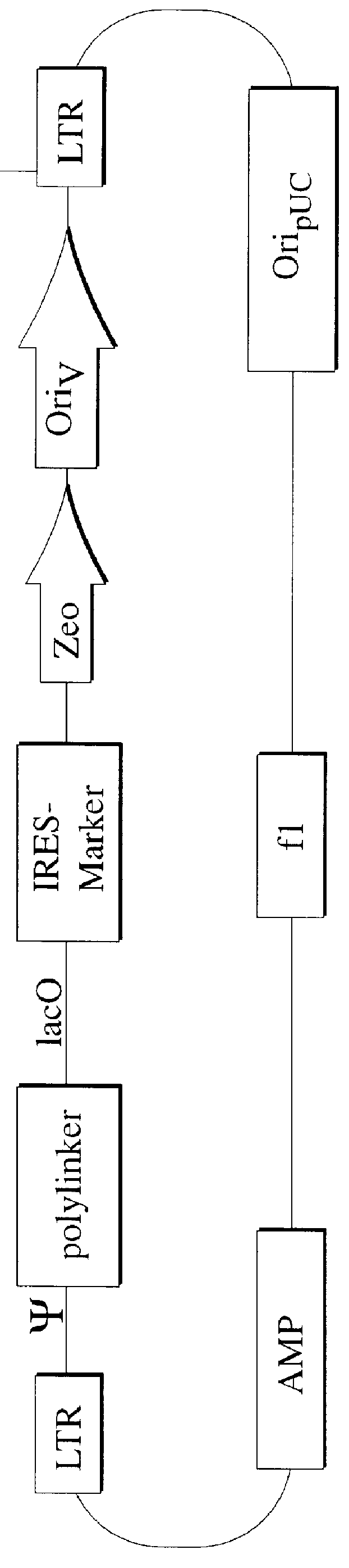
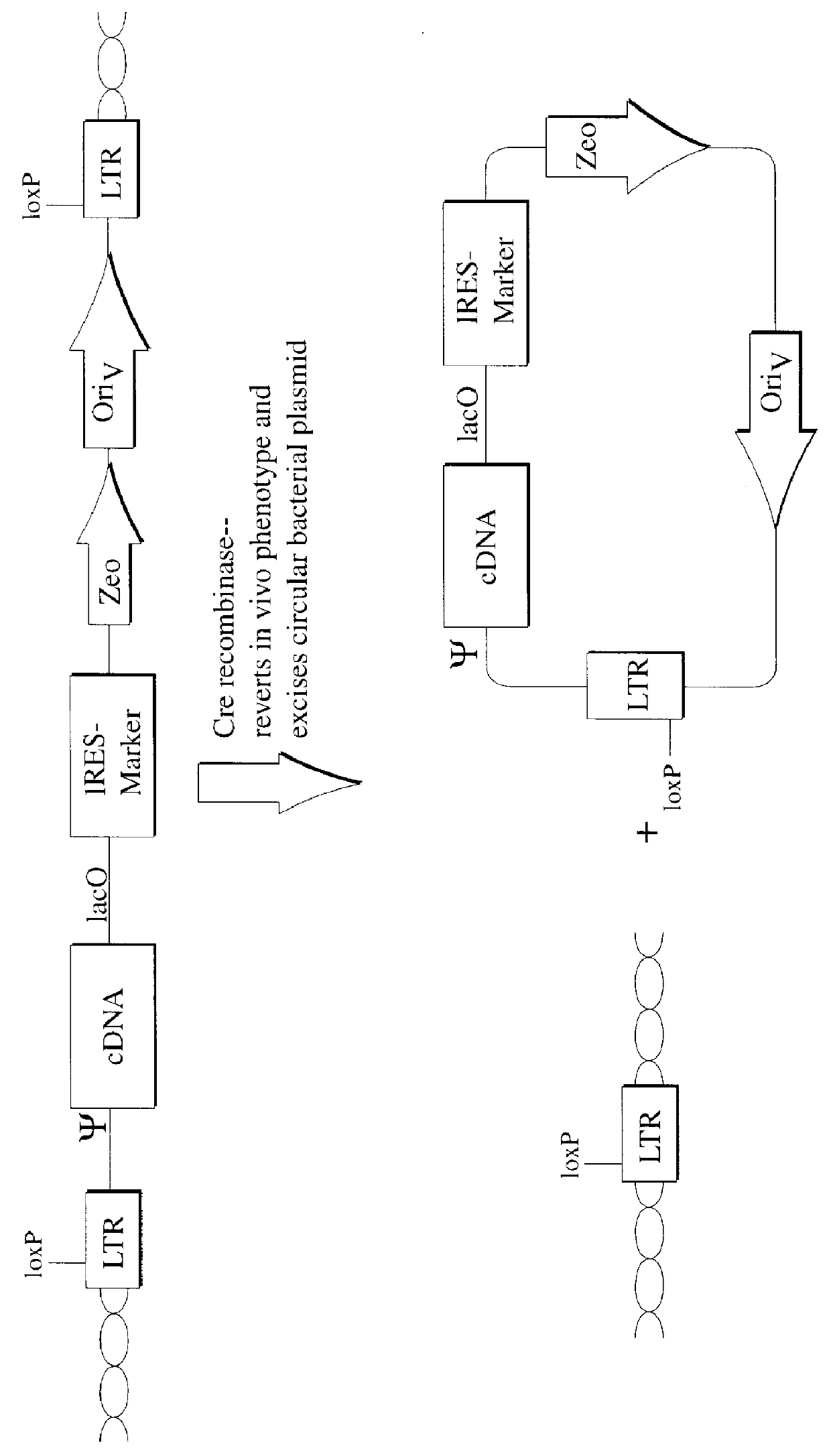
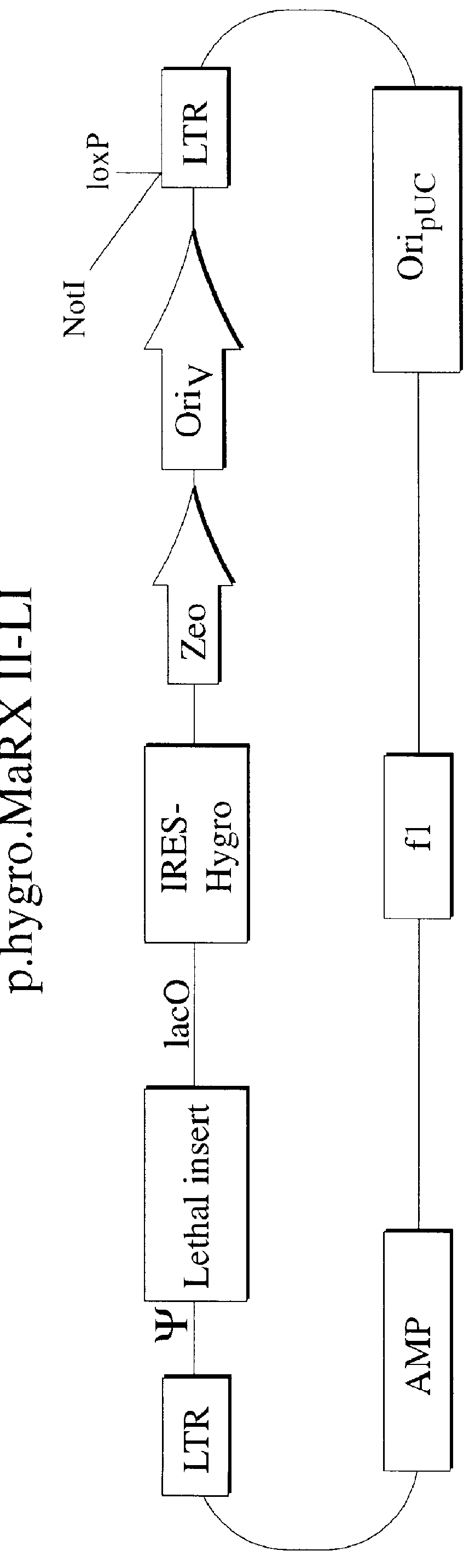
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the elucidation of mammalian gene function. Specifically, the present invention relates to methods and compositions for improved mammalian complementation screening, functional inactivation of specific essential or non-essential mammalian genes, and identification of mammalian genes which are modulated in response to specific stimuli.In particular, the compositions of the present invention include, but are not limited to, replication-deficient retroviral vectors, libraries comprising such vectors, retroviral particles produced by such vectors in conjunction with retroviral packaging cell lines, integrated provirus sequences derived from the retroviral particles of the invention and circularized provirus sequences which have been excised from the integrated provirus sequences of the invention. The compositions of the present invention further include novel retroviral packaging cell lines.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Modified retroviral vectors
The present invention relates to methods and compositions for the elucidation of mammalian gene function. Specifically, the present invention relates to methods and compositions for improved mammalian complementation screening, functional inactivation of specific essential or non-essential mammalian genes, and identification of mammalian genes which are modulated in response to specific stimuli. In particular, the compositions of the present invention include, but are not limited to, replication-deficient retroviral vectors, libraries comprising such vectors, retroviral particles produced by such vectors in conjunction with retroviral packaging cell lines, integrated provirus sequences derived from the retroviral particles of the invention and circularized provirus sequences which have been excised from the integrated provirus sequences of the invention. The compositions of the present invention further include novel retroviral packaging cell lines.
Owner:COLD SPRING HARBOR LAB INC
Vector comprising a replication competent HIV-1 provirus and a heterologous gene
InactiveUS6033902AQuick analysisSmall sizeMicrobiological testing/measurementVirus peptidesHeterologousRetroviral provirus
A vector comprising an HIV segment and a heterologous gene segment, which produces a replication competent and an infective HIV virus is disclosed. When the heterologous gene is a marker gene, the spread of the virus can be observed in both in vitro and in vivo systems. The use of this vector in establishing methods for screening anti-viral compounds is also disclosed.
Owner:DANA FARBER CANCER INST INC
Superior molecular vaccine based on self-replicating rna, suicidal dna or naked dna vector, that links antigen with polypeptide that promotes antigen presentation
InactiveUS20050277605A1Great E7-specific T cell-mediated immunityEfficiently presentedSsRNA viruses positive-senseAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsMHC class IDisease
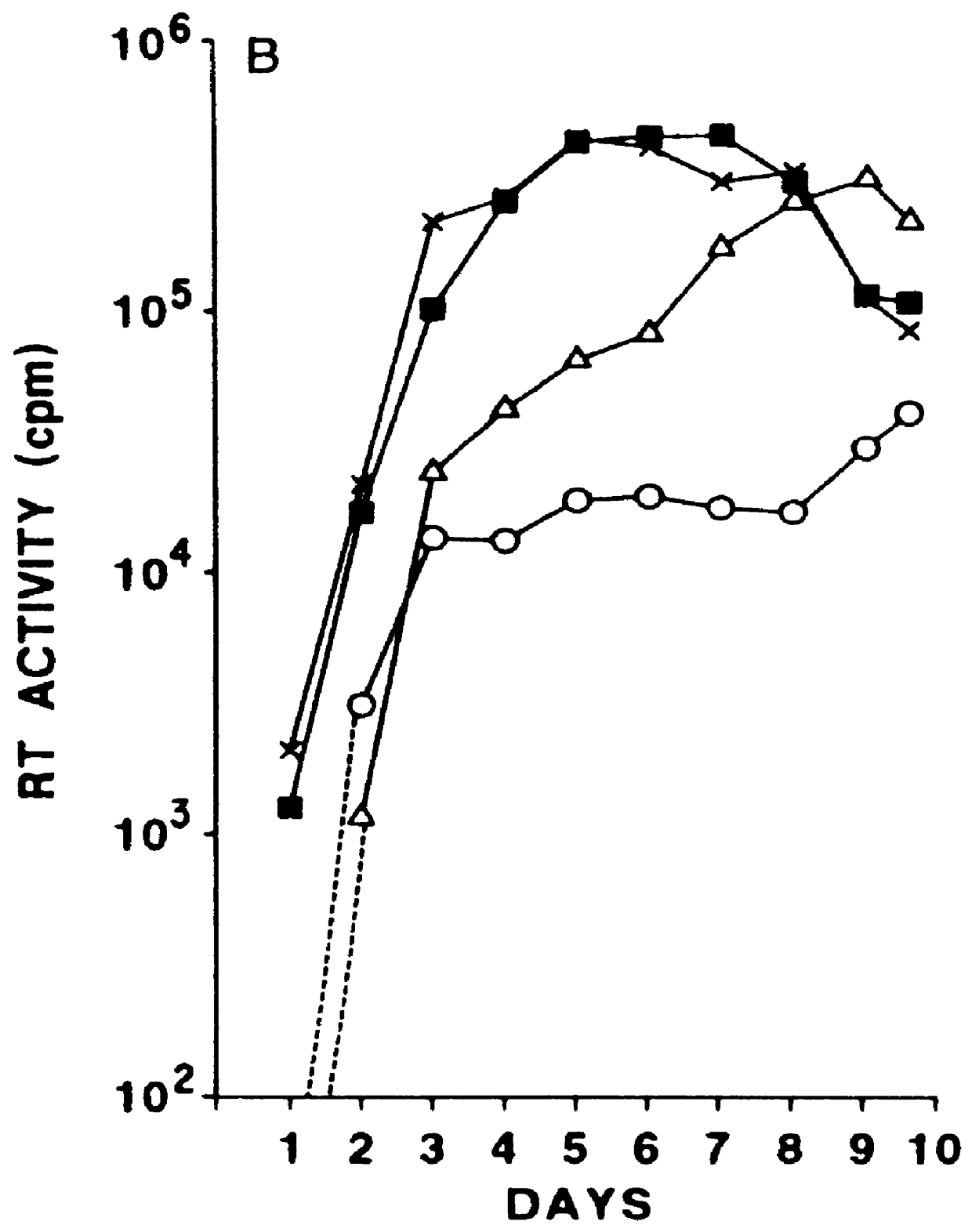
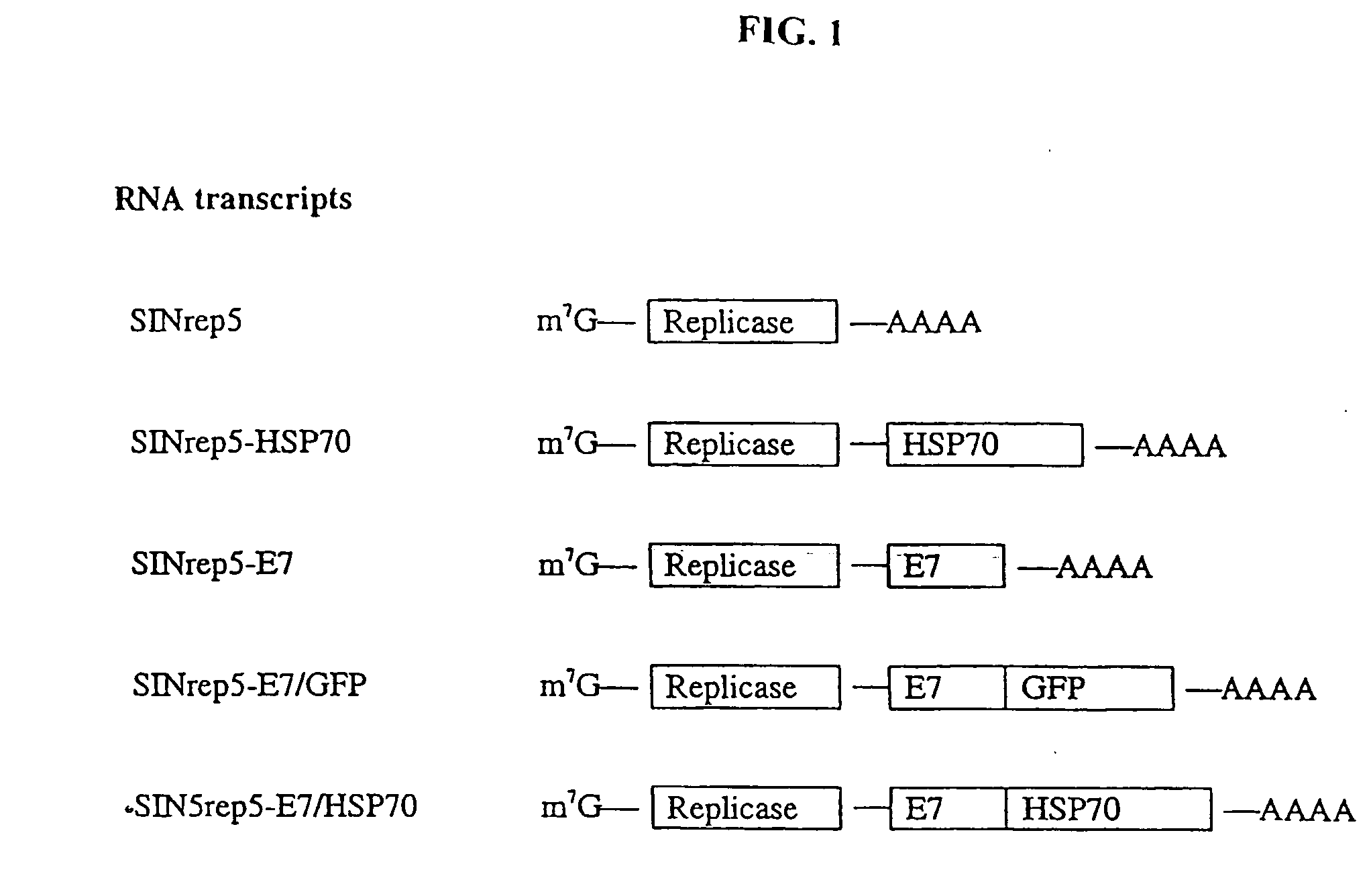
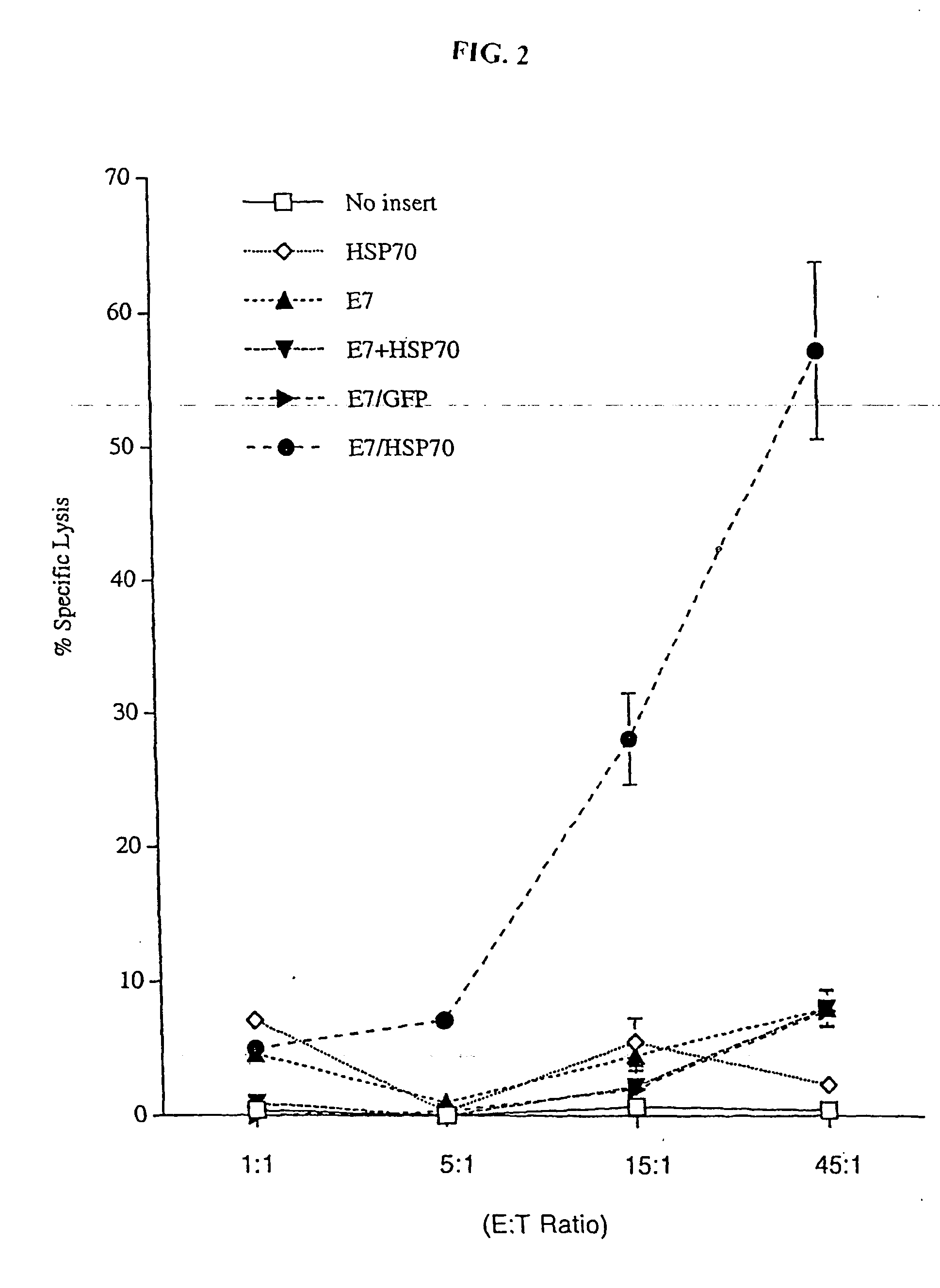
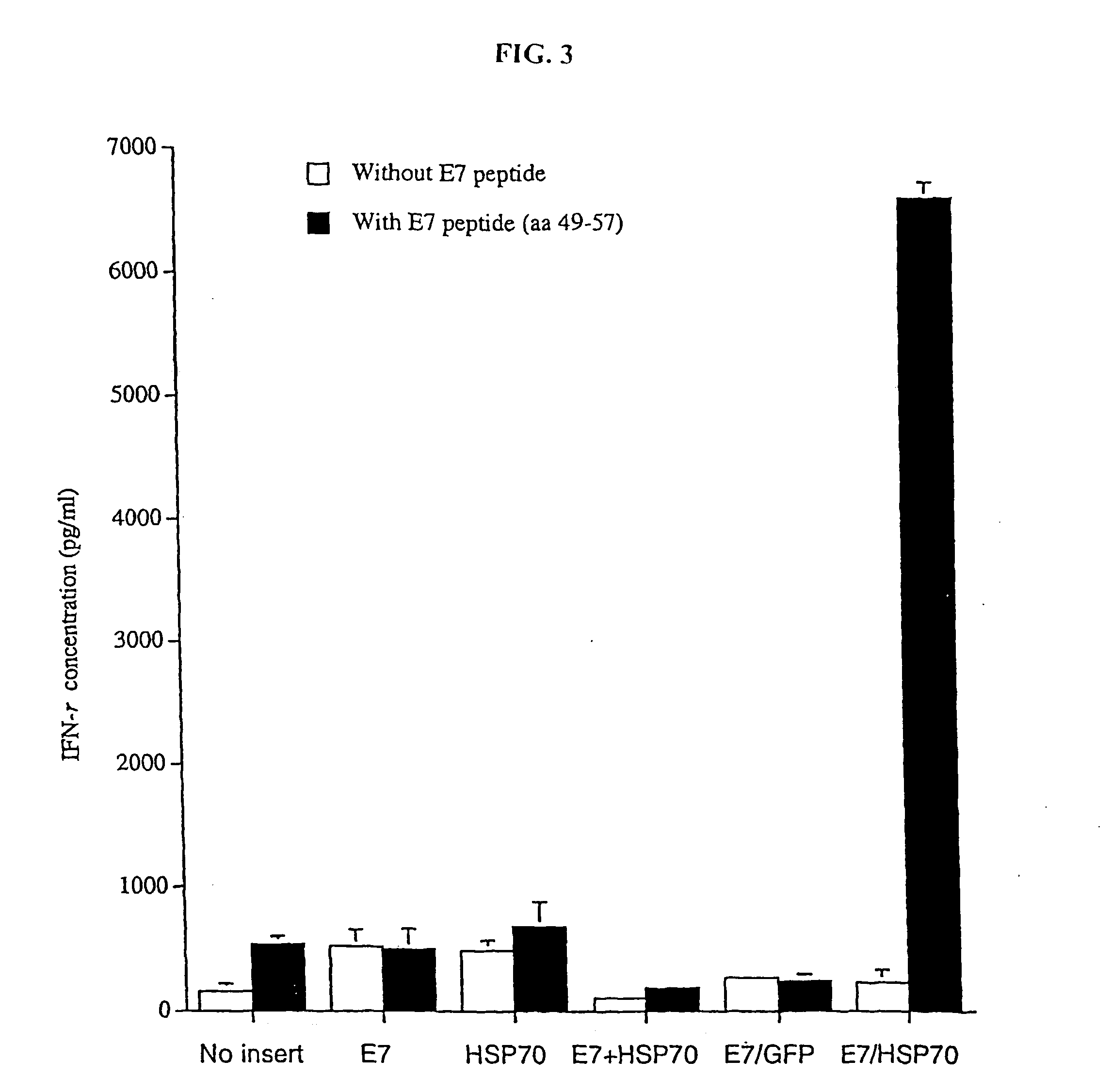
Improved molecular vaccines comprise nucleic acid vectors that encode a fusion polypeptide that includes polypeptide or peptide physically linked to an antigen. The linked polypeptide is one that (a) promotes processing of the expressed fusion polypeptide via the MHC class I pathway and / or (b) promotes development or activity of antigen presenting cells, primarily dendritic cells. These vaccines employ one of several types of nucleic acid vectors, each with its own relative advantages: naked DNA plasmids, self-replicating RNA replicons and suicidal DNA-based on viral RNA replicons. Administration of such a vaccine results in enhance immune responses, primarily those mediated by CD8+ cytotoxic T lymphocytes, directed against the immunizing antigen part of the fusion polypeptide. Such vaccines are useful against tumor antigens, viral antigens and antigens of other pathogenic microorganisms and can be used in the prevention or treatment of diseases that include cancer and infections.
Owner:THE JOHN HOPKINS UNIV SCHOOL OF MEDICINE
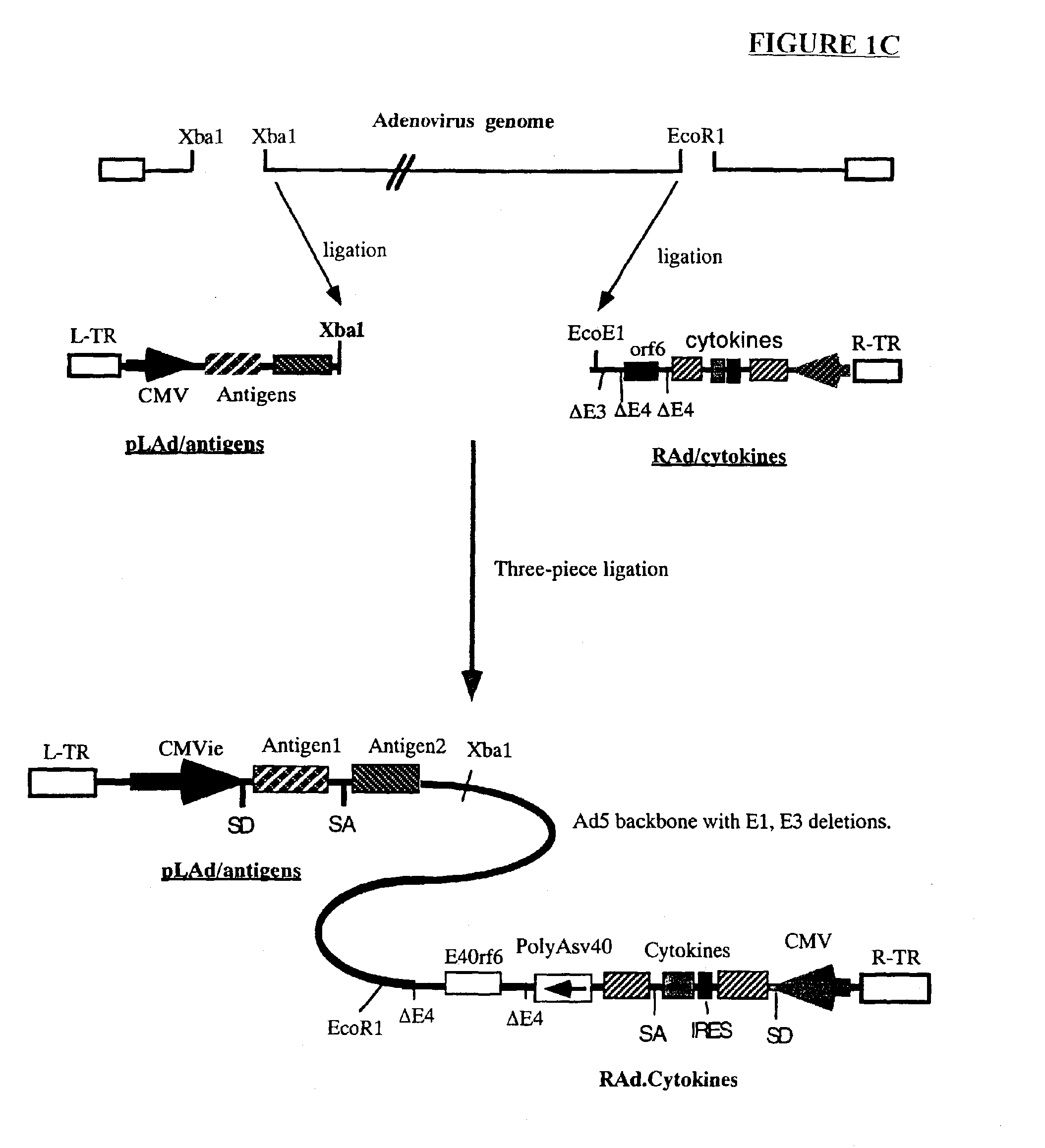
Composition and method for stimulating immune response to pathogen using complex adenoviral vector
InactiveUS6964762B2Improving immunogenicityStrong immune responseSsRNA viruses negative-senseAntibacterial agentsHeterologousProgenitor
Genetic vaccines and methods are provided for enhancing the immunity of a host such as a human to one or more pathogens. In one aspect, a method of enhancing the immunity of a host to a pathogen is provided. The method comprises administering to the host a recombinant virus comprising an antigen sequence that is heterologous to a native progenitor of the recombinant adenovirus and encodes a viral antigen from a pathogenic virus, expression of which is under the transcriptional control of a first promoter; and a cytokine sequence that is heterologous to the native progenitor of the recombinant adenovirus and encodes a cytokine, expression of which is under the transcriptional control of a second promoter. Expression of the antigen and cytokine sequences elicits an immune response directed against the viral antigen upon infection of the host by the recombinant virus. The method can be used for immunizing a host against a wide variety of pathogen viruses, such as HIV, Ebola virus, Marburg virus, hepatitis B virus, hepatitis C virus, influenza virus, human simplex virus, human papilloma virus and respiratory syncytial virus.
Owner:GENPHAR INC
Recombinant retroviral vector
InactiveUS6326195B1Promote vascularizationLower the volumeVirusesPeptide/protein ingredientsProviral dnaBiocompatibility
The invention relates to an implant obtained by assembling in vitro various elements in order to form a neo-organ which is introduced preferably in the peritoneal cavity of the recipient. The implant comprises a biocompatible support intended to the biological anchoring of cells; cells having the capacity of expressing and secreting naturally or after recombination a predetermined compound, for example a compound having a therapeutical interest; and a constituent capable of inducing and / or promoting the geling of said cells. The invention also relates to a kit for the preparation of the implant as well as to a new recombinant retroviral vector comprising a provirus DNA sequence modified in that the genes gag, pol and env have been deleted at least partially so as to obtain a proviral DNA capable of replication. The invention also relates to recombinant cells comprising the new retroviral vector.
Owner:INST PASTEUR
Compositions and methods of use of phorbol esters
Methods and compositions containing a phorbol ester or a derivative of a phorbol ester are provided for the treatment of cytopathic diseases. Cytopathic diseases may be caused by a variety means suchas viral infections like HIV and AIDS, or the development of neoplasms in a mammalian subject. The methods and compositions of the invention are effective for inhibiting de novo HIV infection, upregulating viral expression from latent provirus, inhibiting HIV-induced cytopathic effects, down regulating the HIV receptor, increasing ThI cytokine expression, decreasing Th2 cytokine expression, increasing ERK phosphorylation, inducing apoptosis in malignant cells, inducing remission, maintaining remission, as chemotherapeutic agents, as well as for decreasing symptoms of cytopathic diseases and opportunistic infections that may accompany such diseasesl. Additional compositions and methods are provided which employ a phorbol ester or derivative compound in combination with at least one additional agent such as those used in HAART protocols, therapeutic agents used to treat opportunistic infections due to HIV, or chemotherapeutic agents to yield more effective treatment tools against cytopathic diseases in mammalian subjects.
Owner:BIOSUCCESS BIOTECH CO LTD
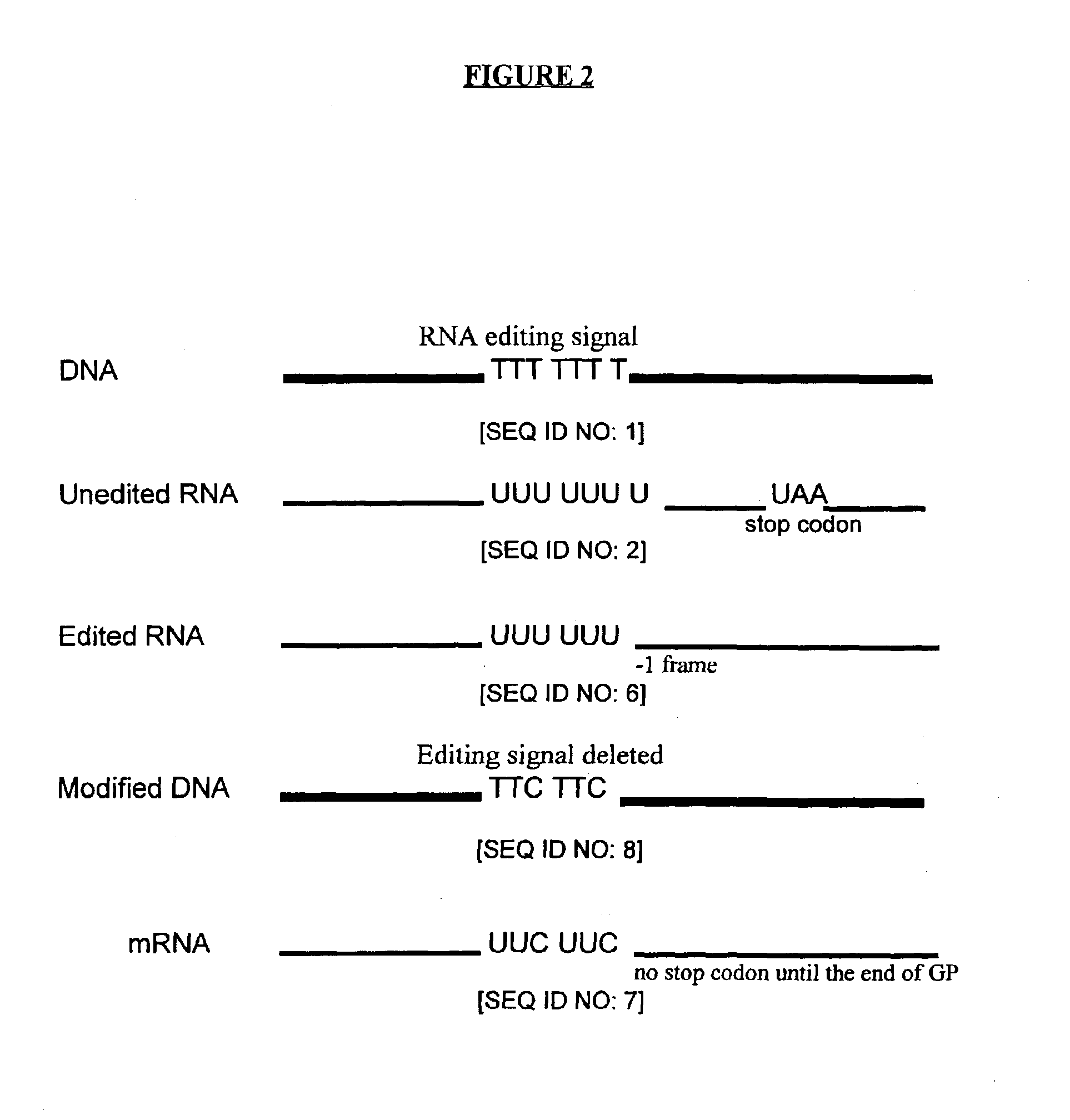
Nucleic acids encoding human immunodeficiency virus type 1 genetic suppressor elements
InactiveUS6426412B1Sugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementExpression LibraryImmunodeficiency virus
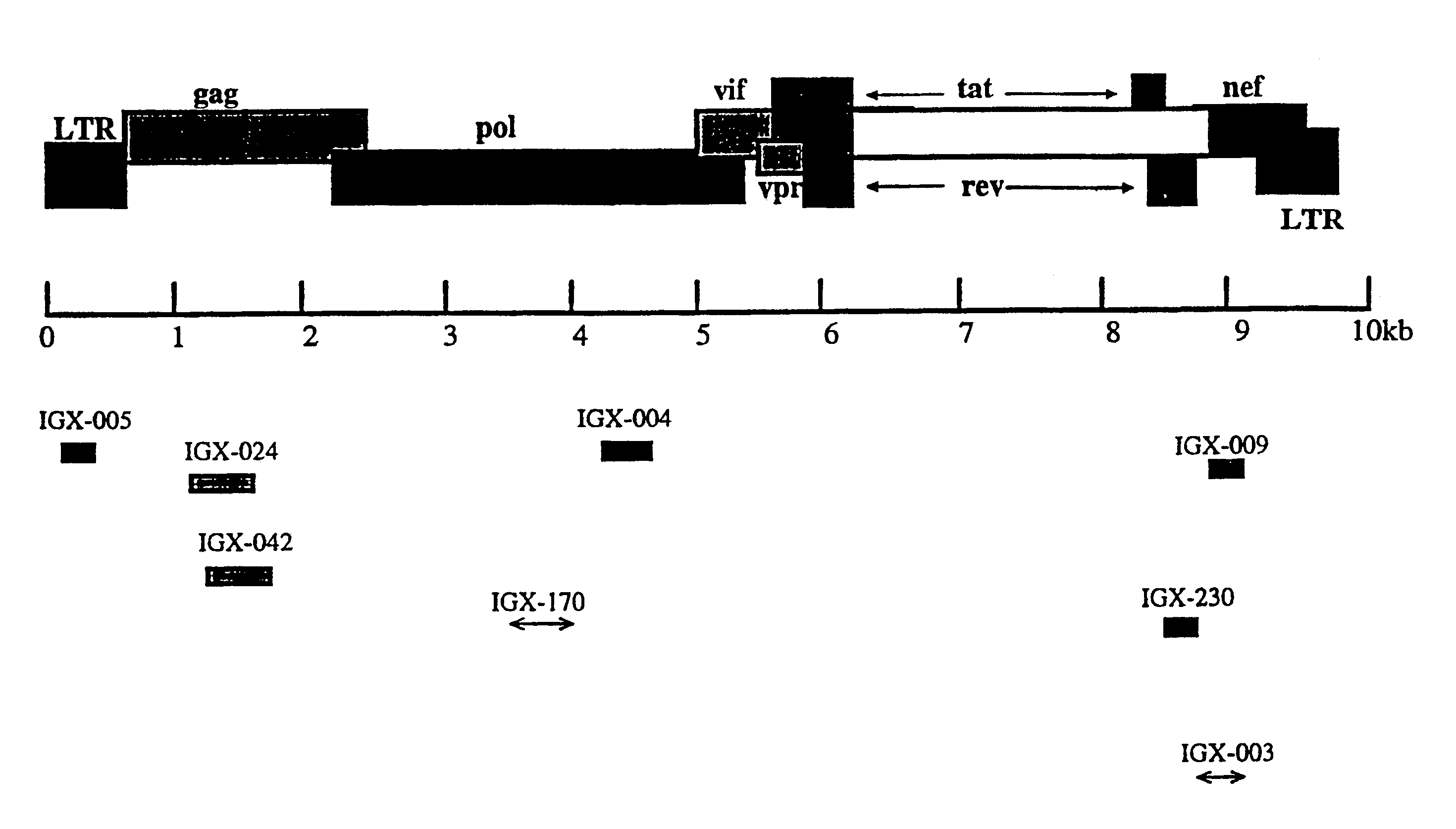
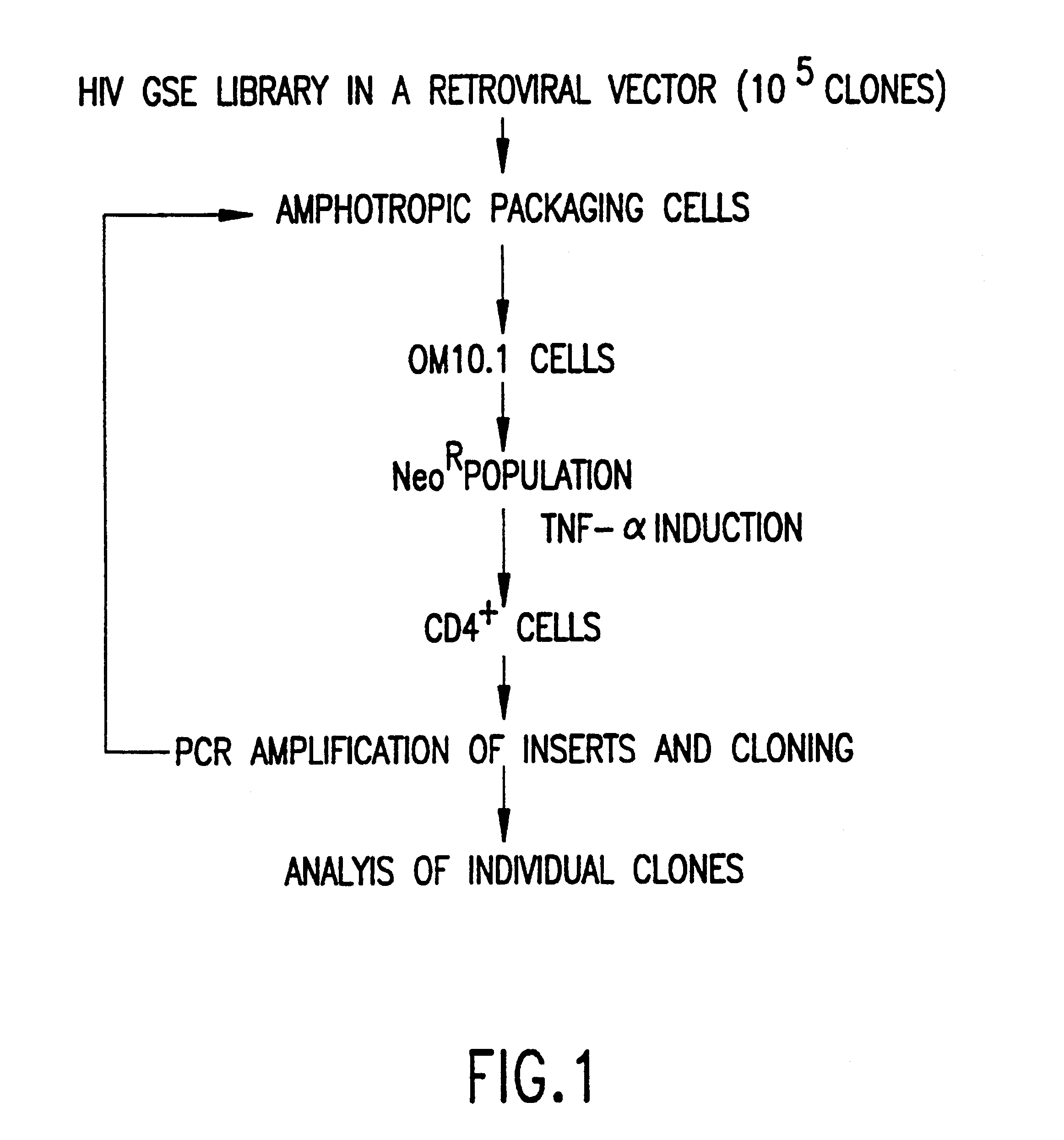
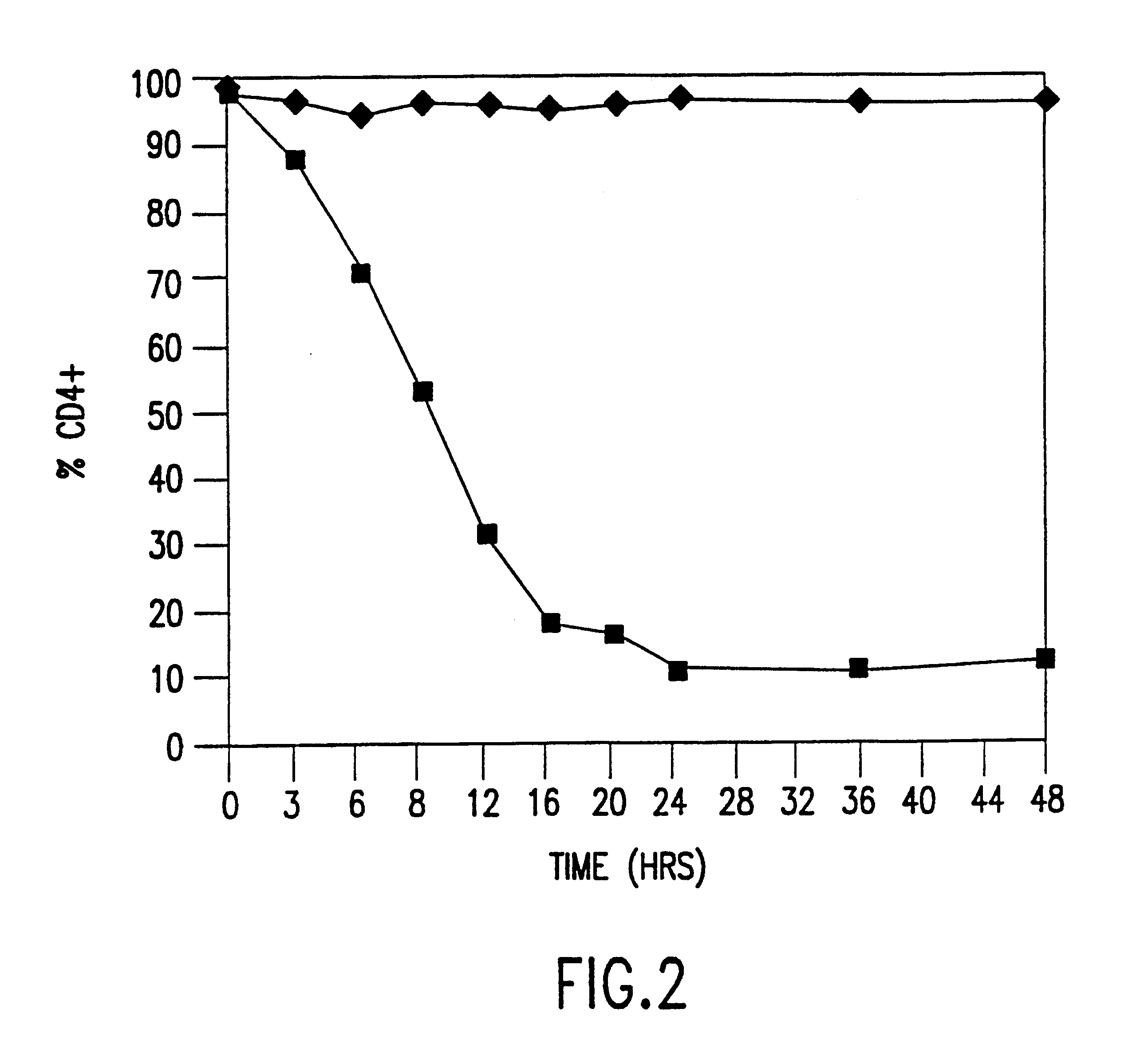
The development of general approaches for the isolation of efficient antivirals is becoming increasingly important. The genetic suppressor element (GSE) technology is an approach based on the functional expression and selection of efficient genetic inhibitors from random fragment libraries derived from a gene or genome of interest. We have applied this technology to isolate potent genetic inhibitors against the human immunodeficiency virus type 1 (HIV-1) The strategy employed involved the following steps: 1) fragmenting the HIV-1 genome into 100-700 base pair (bp) fragments; 2) inserting the fragments into expression vectors to form an expression library; 3) transferring the expression library into a population of cells (e.g., OM10.1) containing an inducible latent HIV-1 provirus; 4) selecting a subpopulation of cells which contain a subset of the expression library enriched for HIV-1 GSE by monitoring the expression of a cellular (e.g., CD4) or viral (e.g., p24) marker associated with HIV infection; 5) recovering the GSE from the selected cell population. The GSEs identified clustered in seven narrowly defined regions of the HIV-1 genome and were found to be functionally active. These elements are potential candidates for the gene therapy of AIDS. The developed approaches can be applied to other viral pathogens, as well as, for the identification of cellular genes supporting the HIV-1 life cycle.
Owner:SUBSIDIARY NO 3 +1
Application of HBcAg (hepatitis B core antigen) virus-like particle serving as cancer therapeutic vaccine carrier
InactiveCN105497886AImprove the level ofViral antigen ingredientsAntineoplastic agentsHepatitis B virus core AntigenEscherichia coli
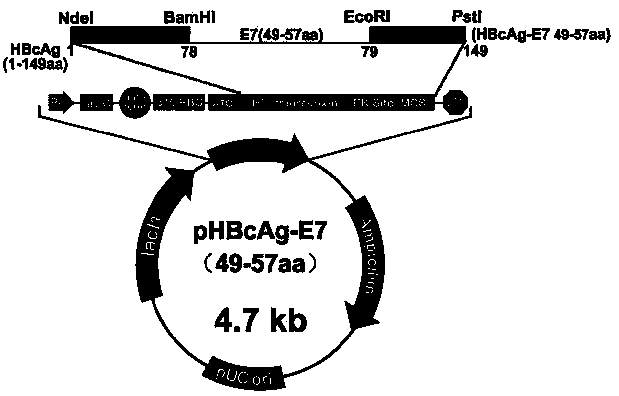
The invention relates to the field of molecular biology and immunology, in particular to an application of an HBcAg (hepatitis B core antigen) virus-like particle serving as a cervical cancer therapeutic vaccine carrier. A preparation method comprises steps as follows: an HPV16 E749-57CTLs epitope peptide fragment is selected, a DNA (deoxyribose nucleic acid ) fragment of the HPV16 E749-57CTLs epitope peptide fragment is inserted between 78 and 79 amino acids of the HBcAg through genetic recombination, an obtained recombinant plasmid pHBcAg-E749-57 is converted into Escherichia coli DH5alpha, and an HBcAg virus-like particle vaccine presenting E749-57 is obtained after induction expression and purification. After a tumor-bearing mouse is immunized with the virus-like particle vaccine, the body of the mouse can be induced to generate a higher HPV16E7 specific cellular immunologic response, and growth of tumors is remarkably inhibited.
Owner:INST OF MEDICAL BIOLOGY CHINESE ACAD OF MEDICAL SCI
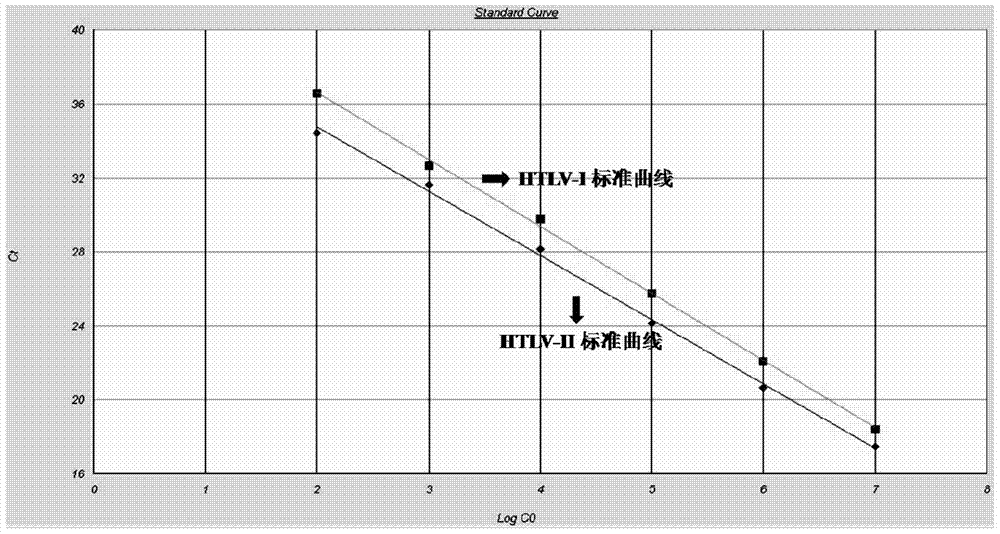
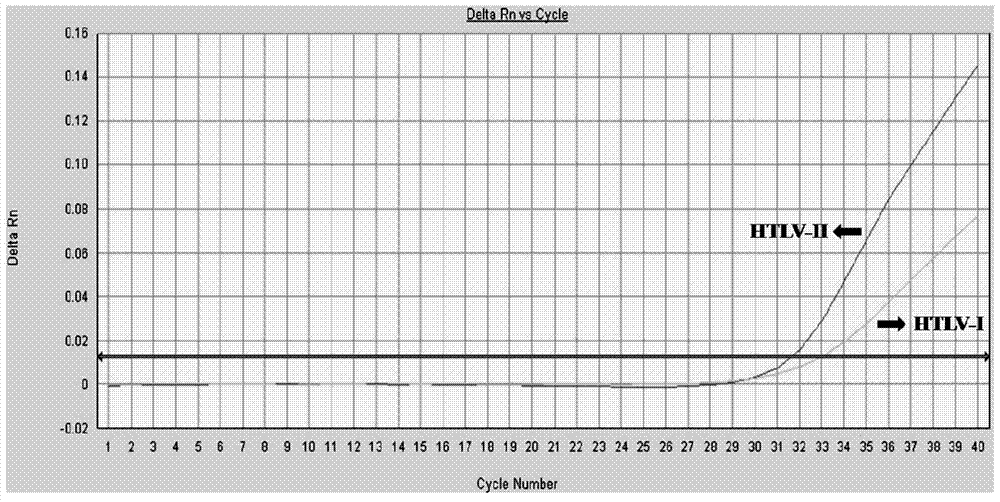
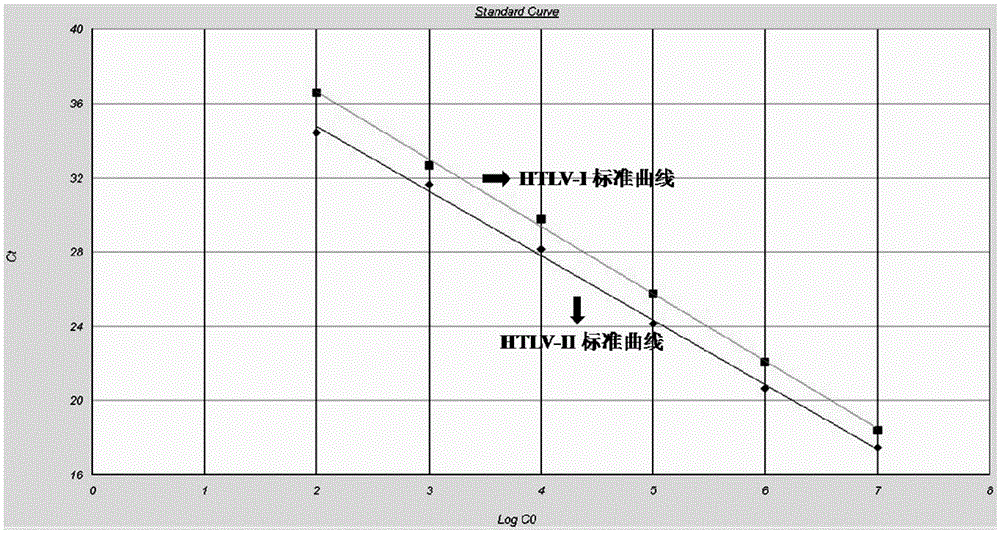
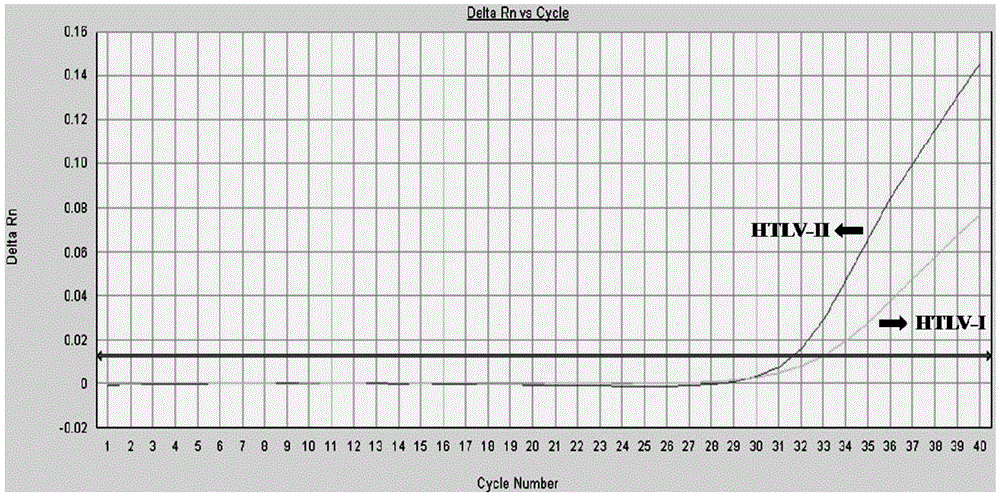
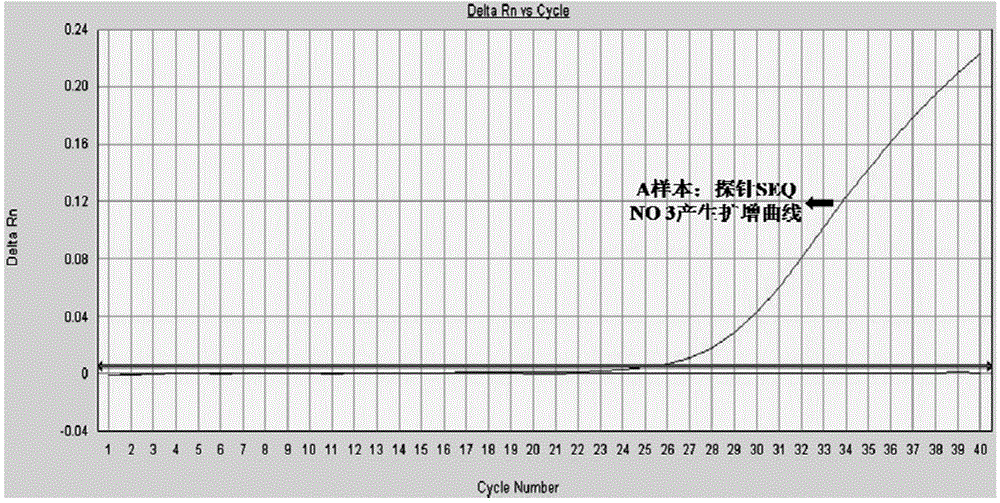
Primer and method for detecting HTLV (human T-lymphotropic virus)-I and HTLV-II proviruses in same pipe
ActiveCN103898239AHelp monitorLimit transmissionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationCarrying capacityRetroviral provirus
The invention provides a primer and a method for detecting HTLV (human T-lymphotropic virus)-I and HTLV-II proviruses. The primer comprises a specific primer and a probe for detecting an HTLV-I provirus and a specific primer and a probe for detecting an HTLV-II provirus, the two primers and the two probes are added in the same PCR (polymerase chain reaction) pipe according to a reasonable concentration ratio, and a sample is detected by means of optimized Real-time PCR reaction conditions. The detection method can be used for detecting whether HTLV infection exists before serological changes, thereby greatly shortening the window phase; meanwhile, compared with a conventional serological detection method, the detection method has the advantages of short detection period, high specificity, high accuracy, high sensitivity, little dependence on the conditions, low pollution risk and the like. The detection result is beneficial to monitor the change of the carrying capacity of the HTLV provirus of a patient and limit the propagation of the HTLV virus.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADICON CLINICAL LAB LNC
Recombinant J subgroup avian leucosis virus infective cloned plasmids and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101899465AImprove versatilityGood repeatabilityInactivation/attenuationAntiviralsLeucosisEukaryotic plasmids
The invention discloses recombinant J subgroup avian leucosis virus infective cloned plasmids and a preparation method and application thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps of: replacing long terminal repetitive sequences of two ends of a provirus gene of a J subgroup avian leucosis virus with long terminal repetitive sequences of two ends of a provirus gene of an E subgroup avian leucosis virus; and inserting the long terminal repetitive sequences of the two ends of the provirus gene of the E subgroup avian leucosis virus into vectors, so that the J subgroup avian leucosis virus infective cloned plasmids are constructed, and the obtained sequence is shown as SEQ ID NO:1. The replication capacity and the pathogenicity of recombinant virus strains obtained by transfecting the J subgroup avian leucosis virus infective cloned plasmids are obviously weaker than those of natural J subgroup avian leucosis viruses, but the recombinant virus strains can express structural proteins of the J subgroup avian leucosis viruses, have the antigenicity of the J subgroup avian leucosis viruses and can be identified by a specificity monoclonal antibody JE9 of the J subgroup avian leucosis viruses. The invention provides reference for a material and a method for preparing low-toxicity live vaccines of the J subgroup avian leucosis viruses.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA AGRI UNIV
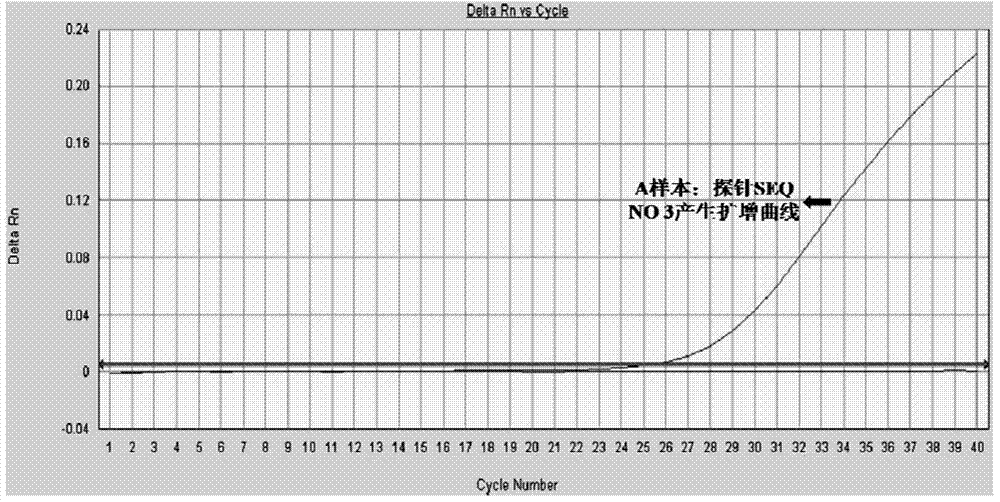
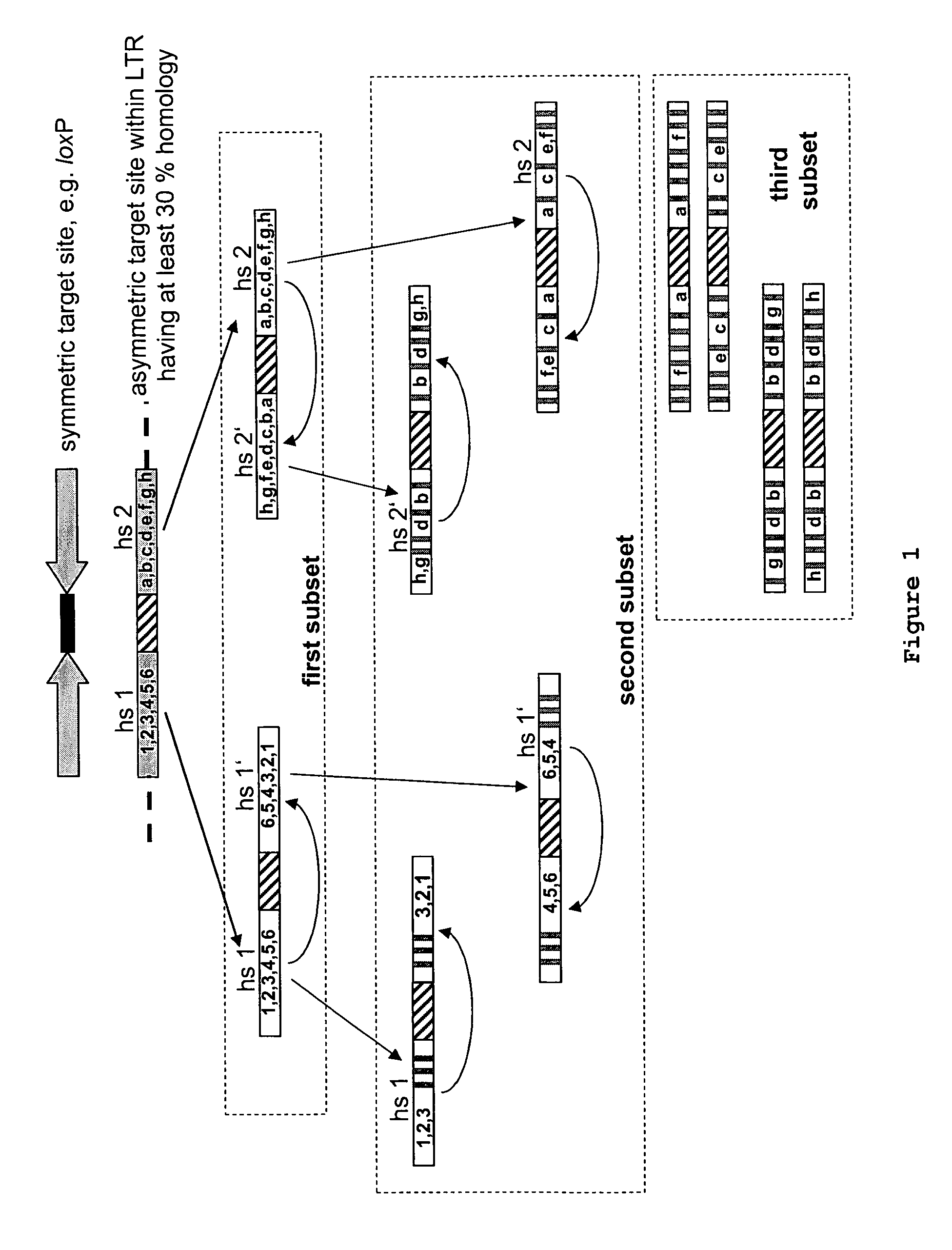
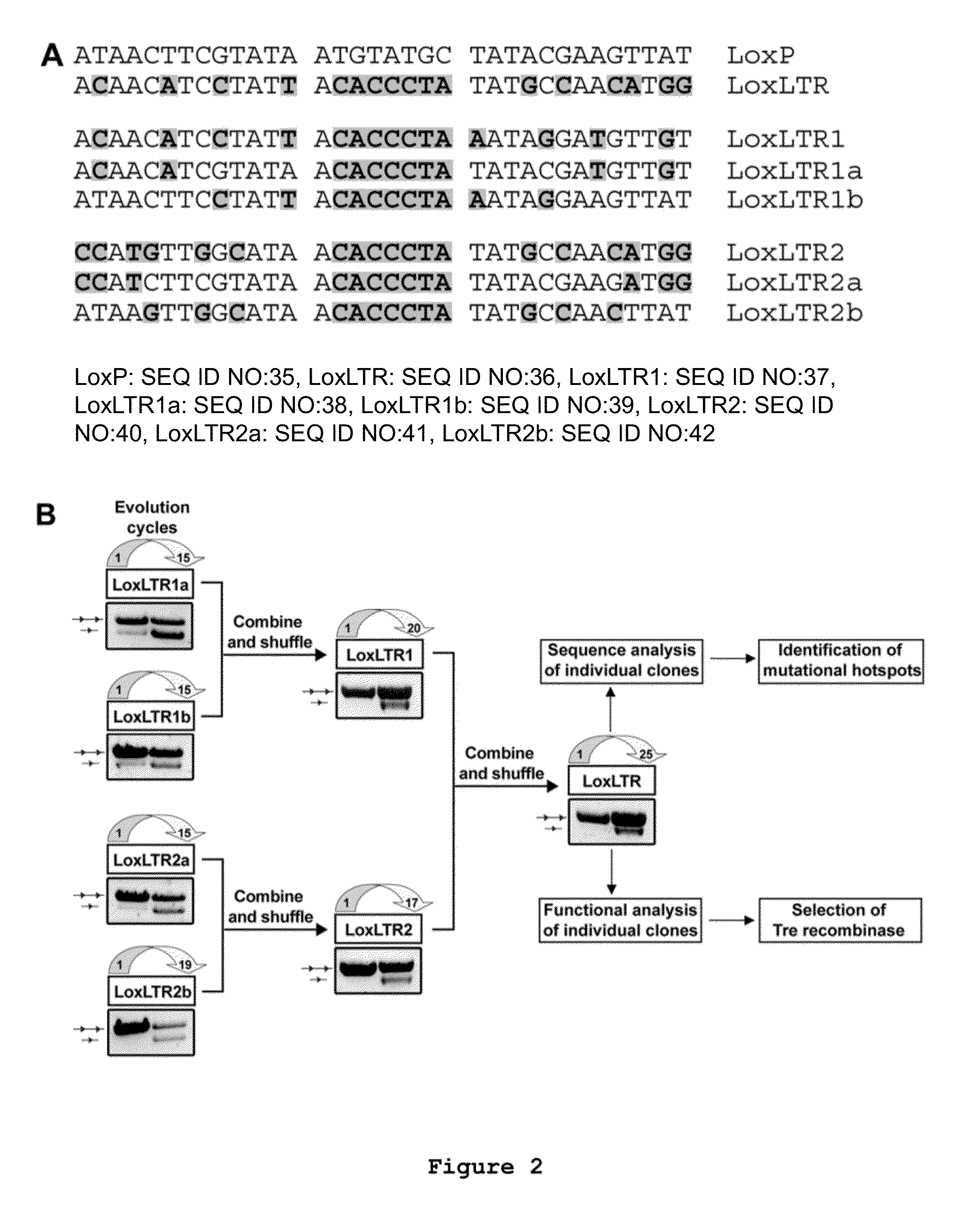
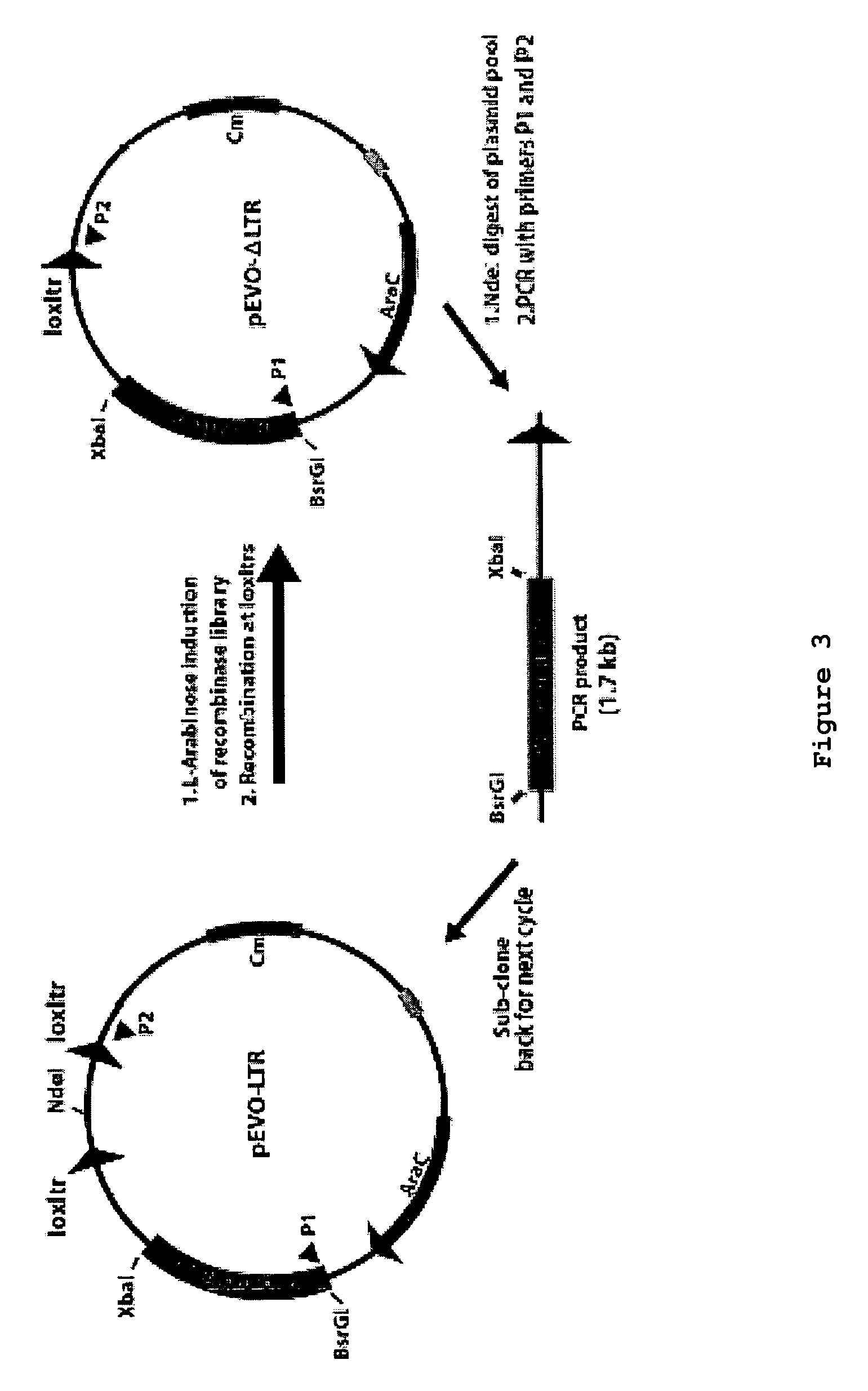
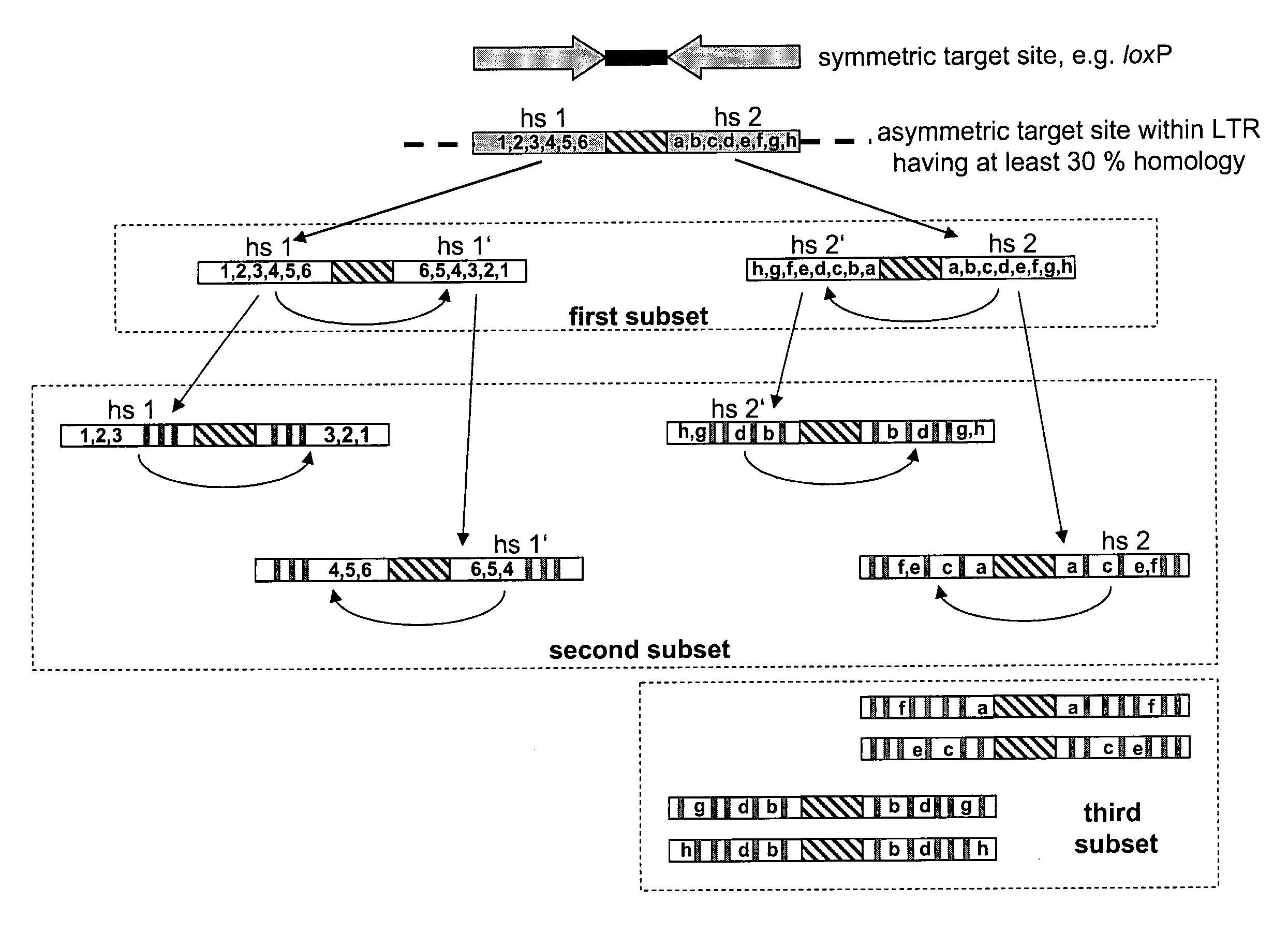
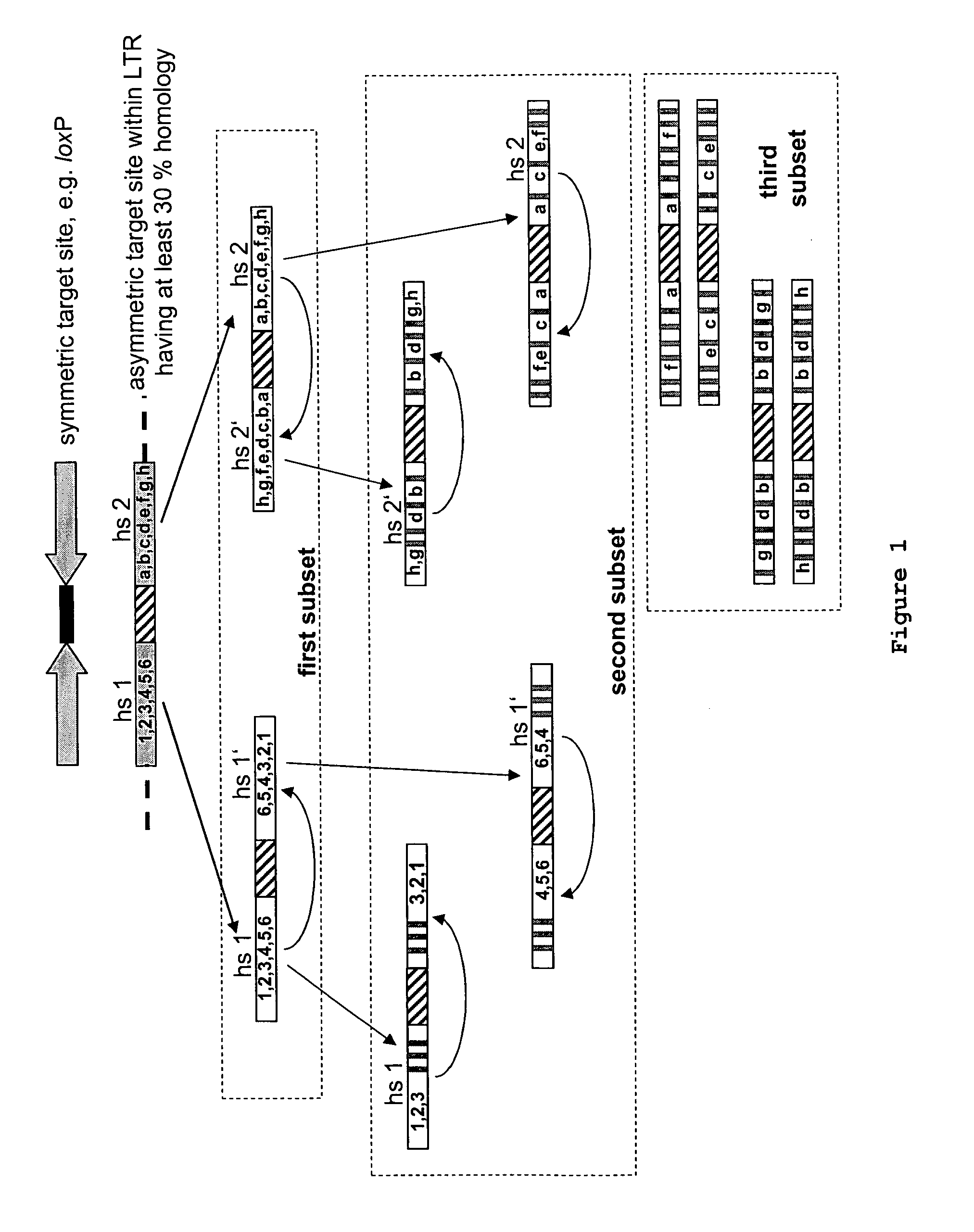
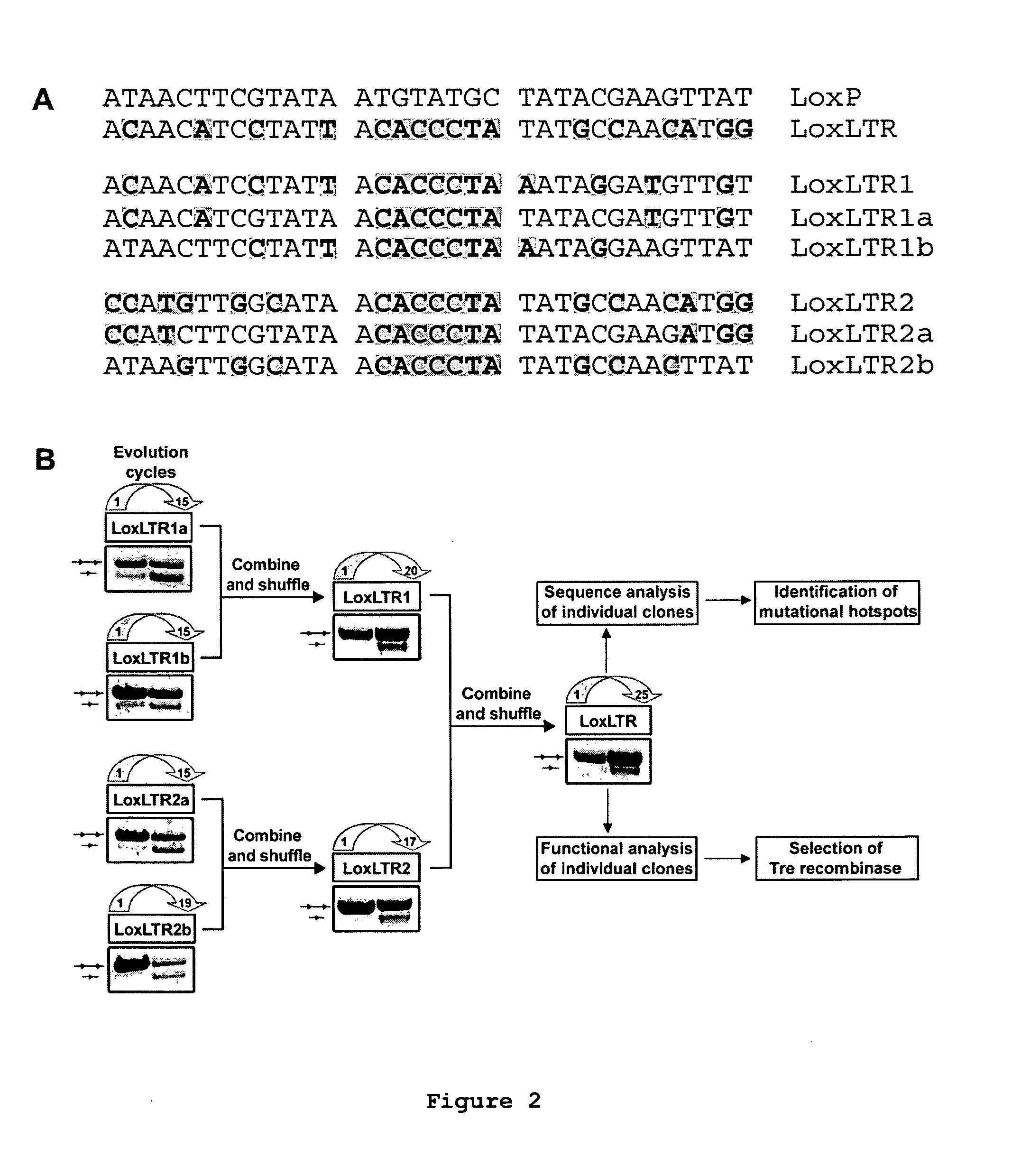
Use of tailored recombinases for the treatment of retroviral infections
The present invention is directed to a method for preparing an expression vector encoding a tailored recombinase, wherein said tailored recombinase recombines asymmetric target sites within the LTR of proviral DNA of a retrovirus inserted into the genome of a host cell and is useful as means for excising the provirus from the genome of the host cell. The present invention further relates to an in vitro-method of optimising the treatment of a retroviral infection of a subject and to the use of tailored recombinases for the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions for reducing the viral load in a subjected infected by a retrovirus.
Owner:DRESDEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +2
Fluorescence quantitative PCR technology for extracting and amplifying hepatitis B virus nucleic acid by 'one tube method'
InactiveCN101302560ASolve pollutionQuick and accurate quantificationMicrobiological testing/measurementForward primerFluorescence
The invention discloses a trace nucleic acid releasing agent. The releasing agent realizes that hepatitis B virus nucleic acid extraction and fluorescent augmentation are directly performed in the same tube, radically solves the problems of nucleic acid loss and pollution caused by a multi-step nucleic acid extraction method, and is applicable to the fluorescent PCR detection of a whole blood sample for the first time; the releasing agent adopts quantificational provirus serum as a quantificational standard and realizes the whole process monitoring of the standard to the sample; the releasing agent adopts double pairs of forward primers and reverse primers and a probe decorated by forward fluorescence and reverse fluorescence to perform fluorescent PCR augmentation, further to improve the sensitivity and the augmentation efficiency of the releasing agent; blue promoting fluorescer is introduced to ensure that prepared PCR operating liquid is light blue, and has the functions of steady fluorescent signals, strengthened augmentation efficiency and so on, without affecting the fluorescent detection; the releasing agent sets two temperature gradient programs, adopts a rear-section fluorescence acquisition method, is convenient to analyze and improves the service life of an instrument; compared with the prior method, the technology has revolutionary innovation.
Owner:王海滨
Retrovirus-based genomic screening
The present invention relates to the expression and screening of genomic DNA sequences encoding uncharacterized genes and proteins. The present invention provides systems utilizing unique features of retroviral replication to analyze uncharacterized genes derived from genomic DNA samples. In preferred embodiments, a segment of genomic DNA is inserted between 5′ and 3′ viral long terminal repeats (LTRs) in a vector (e.g., a plasmid, cosmid, or artificial chromosome vector). The resulting vector (or library of vectors containing a plurality of independent genomic sequences) is then introduced into a retroviral packaging cell. The resulting provirus or proteins expression from the provirus are then analyzed.
Owner:CATALENT USA WOODSTOCK INC +3
Compositions and methods for determining the susceptibility of a pathogenic virus to protease inhibitors
InactiveUS20040224307A1Improve the quality of lifeIncreases noMicrobiological testing/measurementAntibody medical ingredientsSide effectRegimen
The present invention provides an approach for developing an algorithm for determining the effectiveness of anti-viral drugs based on a comprehensive analysis of paired phenotypic and genotypic data guided by phenotypic clinical cut-offs. In one aspect, the algorithm allows one to provide a patient with effective treatment. It helps predict whether an infected individual will respond to treatment with an anti-viral compound, thereby allowing an effective treatment regimen to be designed without subjecting the patient to unnecessary side effects. Also, by avoiding the administration of ineffective drugs, considerable time and money is saved.
Owner:MONOGRAM BIOSCIENCES
Expression vector for targeted inhibition of HIV-1 provirus expression as well as preparation method and application of expression vector
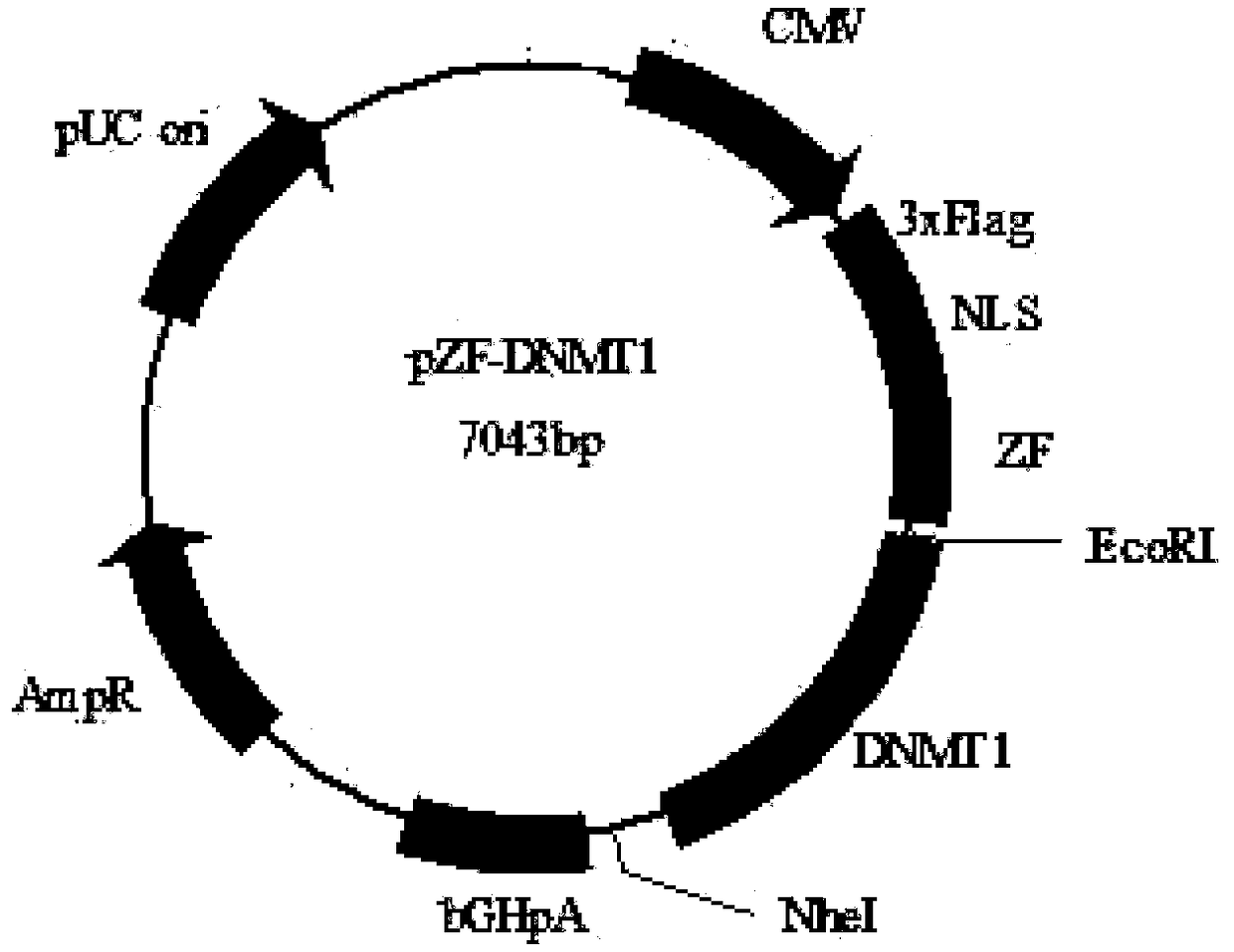
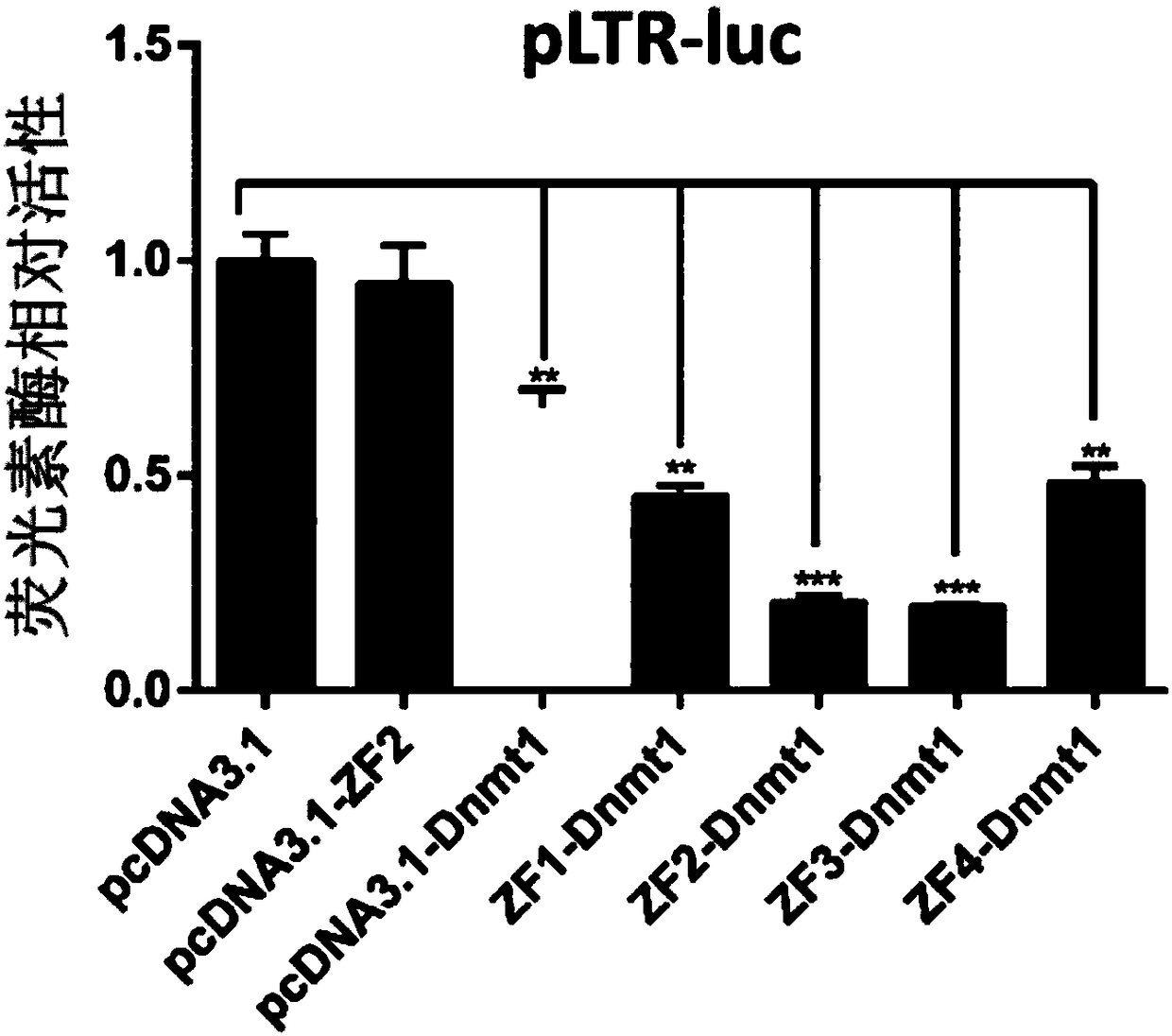
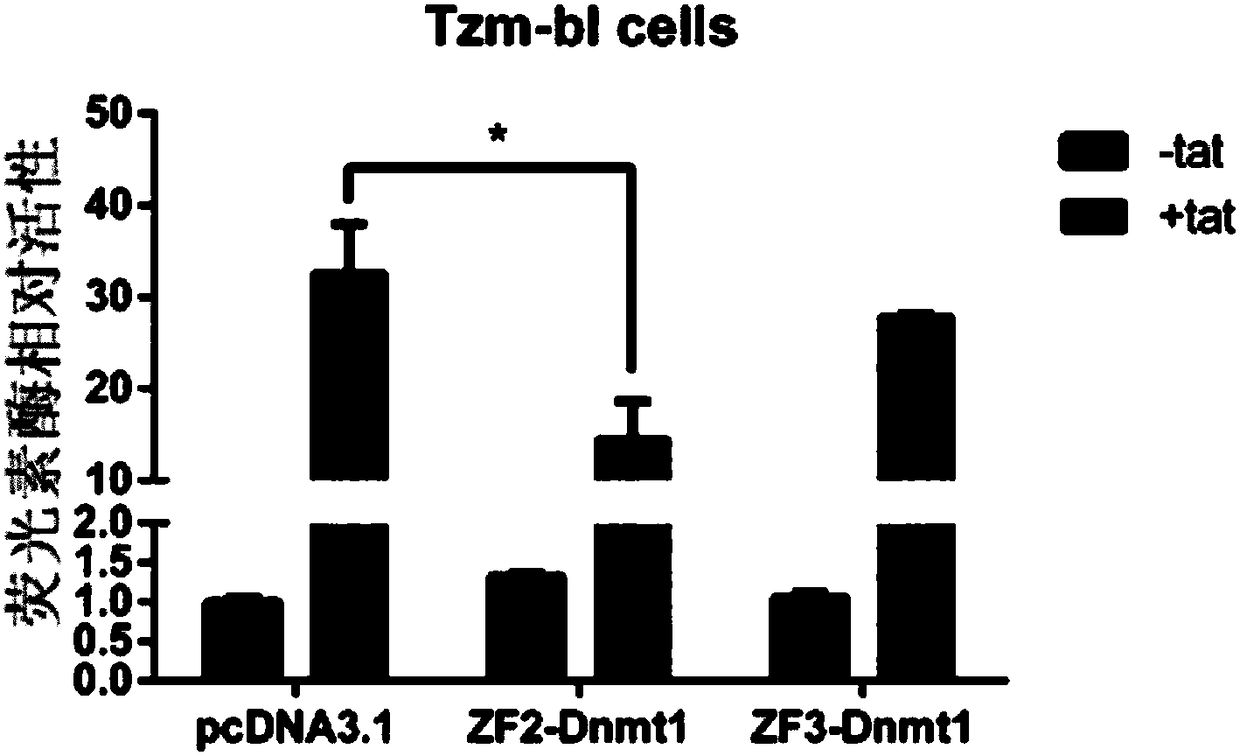
ActiveCN108103094AInhibition of replicationSafeFusion with DNA-binding domainTransferasesRetroviral provirusHiv disease
The invention belongs to the field of gene therapy and relates to preparation and an application of an expression vector for targeted inhibition of HIV-1 provirus expression by use of embedded DNA methyltransferase adopting a zinc finger structure. The expression vector carrying the DNA methyltransferase adopting the zinc finger structure is proved to be able to inhibit silence of HIV-1 provirus expression in HIV-1 infection and latent infection cell models, the vector can effectively inhibit virus replication in virus infected cells and latent infected cells for 15-40 days or above. Besides,provirus expression silence caused by the expression vector carrying the embedded methyltransferase adopting the zinc finger structure can be inhered among cell generations and has certain safety in cells. A new idea is provided for curing AIDS.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Use of tailored recombinases for the treatment of retroviral infections
ActiveUS20100172881A1Reduce viral loadTime consumingOrganic active ingredientsAnimal cellsProviral dnaRetroviral provirus
The present invention is directed to a method for preparing an expression vector encoding a tailored recombinase, wherein said tailored recombinase recombines asymmetric target sites within the LTR of proviral DNA of a retrovirus inserted into the genome of a host cell and is useful as means for excising the provirus from the genome of the host cell. The present invention further relates to an in vitro-method of optimising the treatment of a retroviral infection of a subject and to the use of tailored recombinases for the preparation of pharmaceutical compositions for reducing the viral load in a subjected infected by a retrovirus.
Owner:DRESDEN UNIVERSITY OF TECHNOLOGY +2
Method for detecting SARS coronavirus
InactiveUS7399588B2High sensitivityEliminate needSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleotideOligonucleotide Primer
This invention provides: a method for detecting SARS pathogenic viruses with high sensitivity and rapidity for diagnosing severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS); an oligonucleotide primer that can specifically hybridize with any nucleotide sequence constructed based on the nucleotide sequence of RNA polymerase of the SARS coronavirus; a method for nucleic acid amplification using such primer; a method for diagnosing infection with the SARS coronavirus via detection of nucleic acid amplification; and a kit for diagnosing SARS.
Owner:EIKEN KAGAKU
Method of promoting an immune response with a bispecific antibody
InactiveUS20060177454A1Peptide/protein ingredientsImmunoglobulins against virusesFungal antigenCancer antigen
A method of inducing an immune response in a patient is provided. The method involves administration of bispecific molecules capable of recognizing and binding FcγRIII and a second antigen. The second antigen may be a cancer antigen, a viral antigen, a fungal antigen, a bacterial antigen or a toxin. The second antigen may or may not be present at the time the method of the invention is performed.
Owner:RING DAVID B
Human recombinant herpes simplex virus for producing slow virus vector
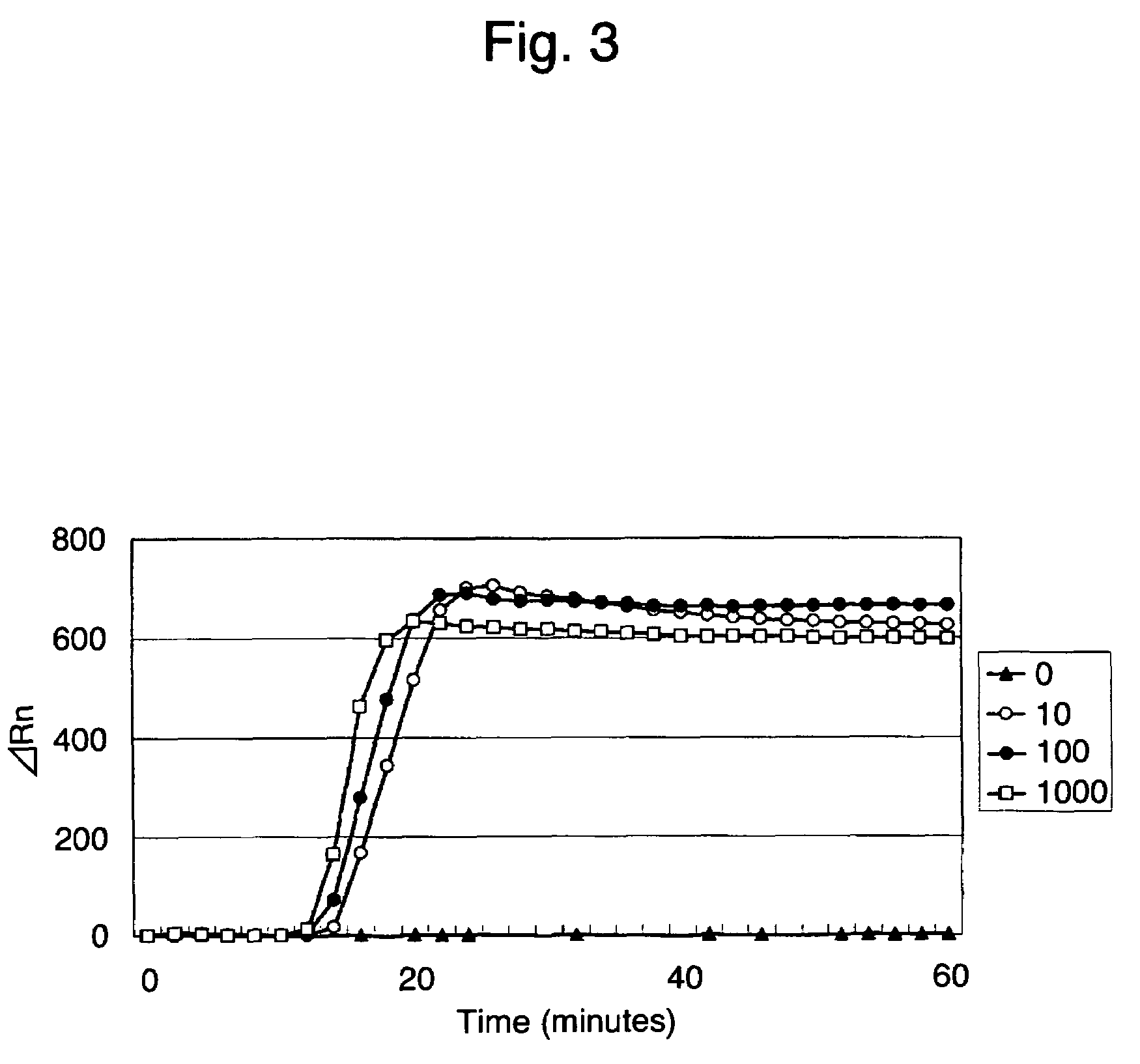
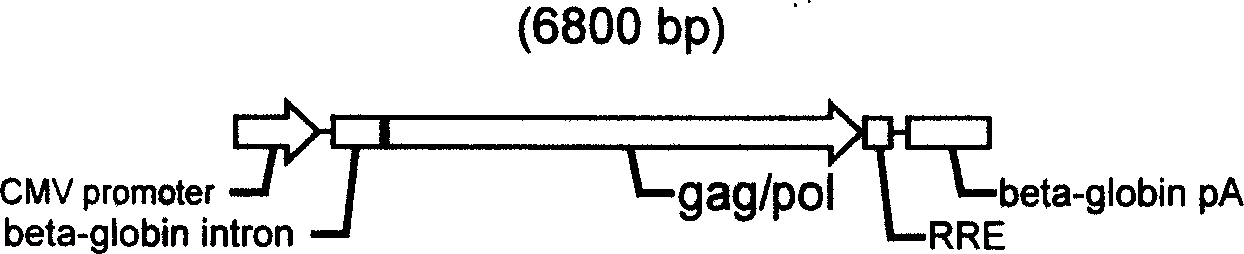
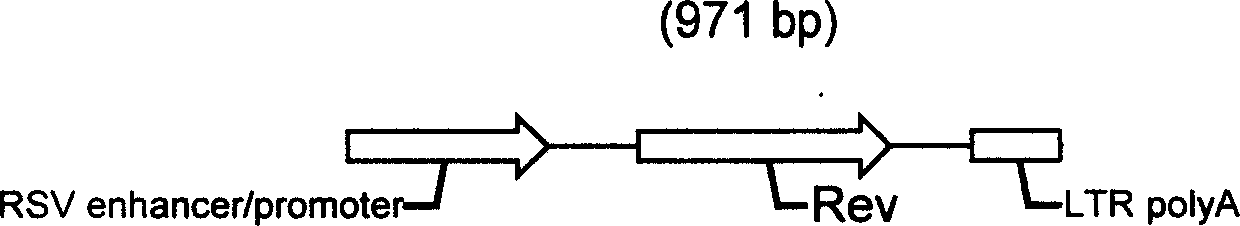
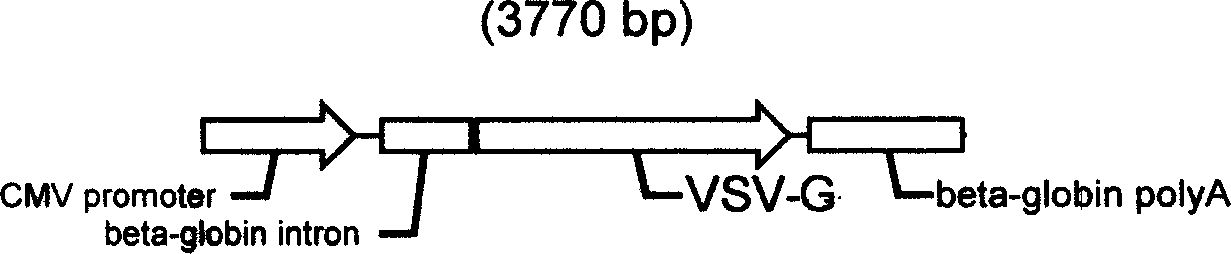
The present invention describes one kind of recombinant human herpes simplex virus-1, named HSV1-Lenti-helper virus, and its genome has inserted various trans protein expressing cassettes, such as gag, pol, VSV-G, Rev, etc. needed for packing slow virus carrier. Infecting carrier cell strain with the recombinant HSV virus can express gag, pol, VSV-G, Rev and other protein in high level, and thiscan save slow virus carrier genome existing in provirus form in the carrier cell strain chromosome to pack slow virus carrier. By means of affinity chromatography, ion adsorption chromatography, hyperfiltration separation or other method, the slow virus carrier may be separated from HSV to reach the aim of purification. The method features the virus infection mode, rather than plasmid transfection mode, in producing slow virus carrier with high carrier titer, low cost and adaptability for large-scale production.
Owner:AGTC GENE TECH CO LTD
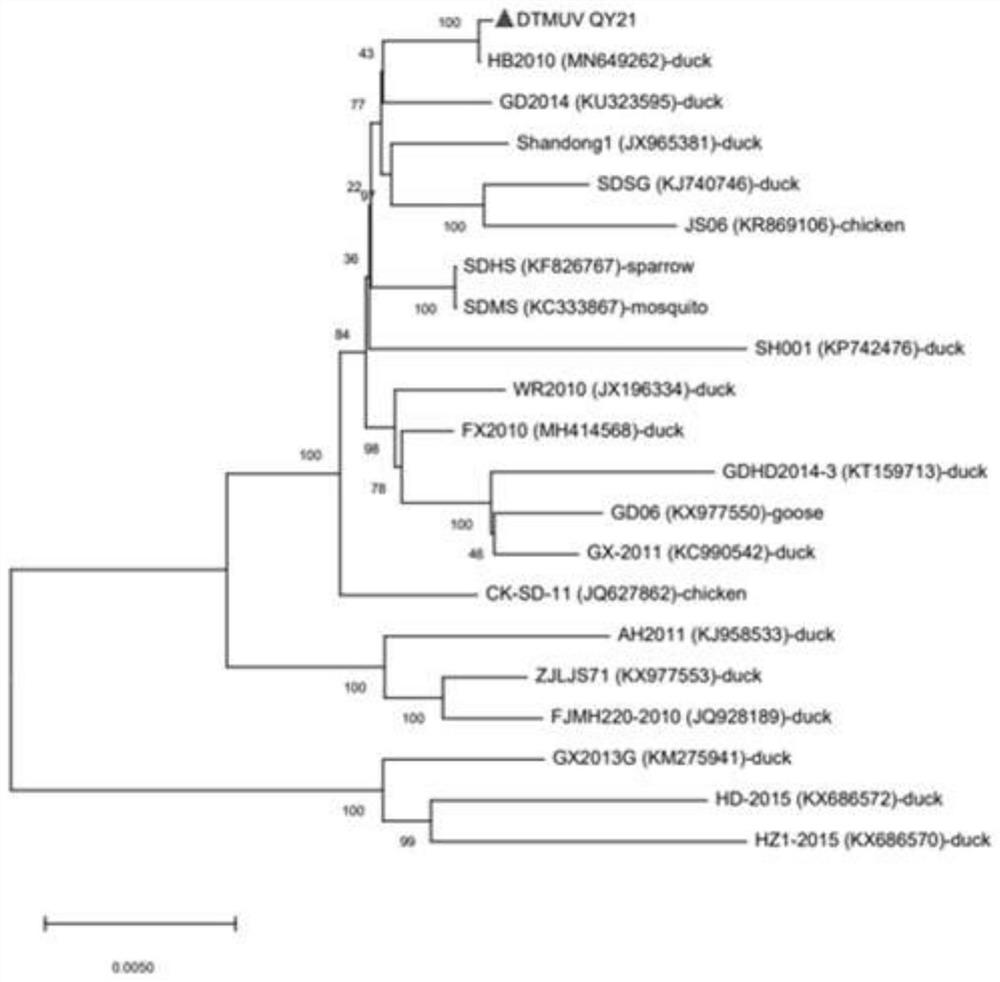
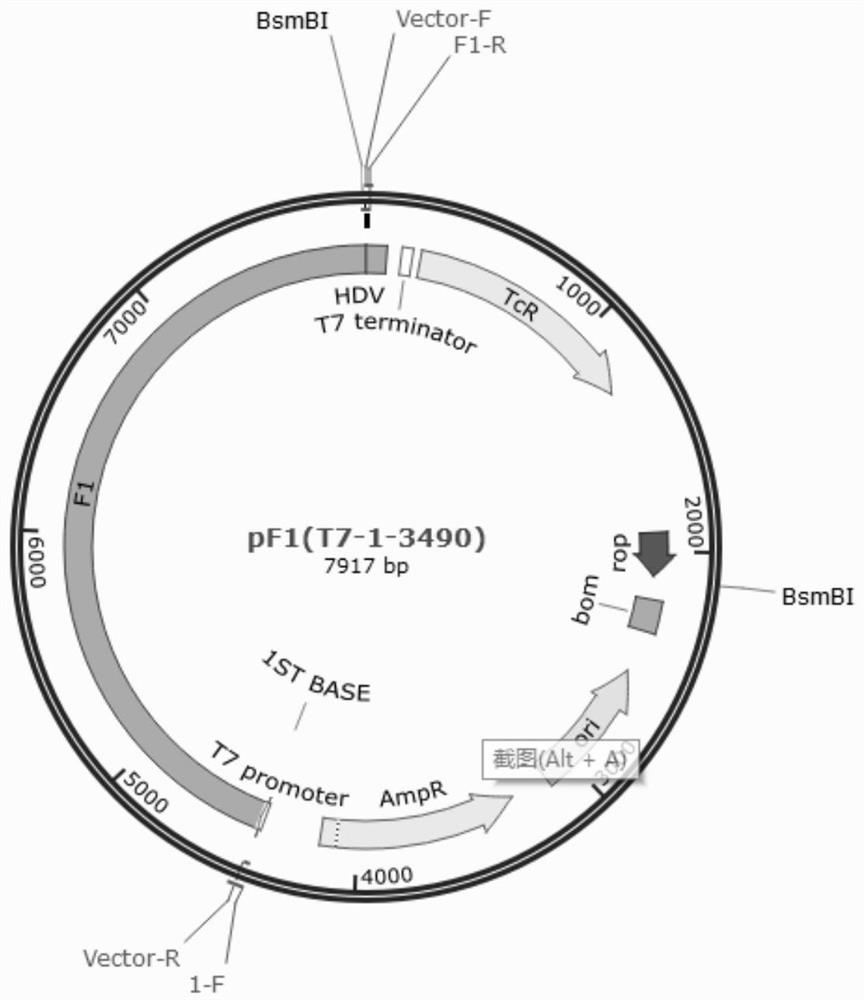
Preparation method of duck tembusu virus infectious cDNA and preparation method of recombinant virus rDTMV-QY21
PendingCN114196683ANo mutationFirmly connectedSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesTembusu virusComplementary deoxyribonucleic acid
The invention belongs to the field of veterinary products, and discloses a preparation method of duck tembusu virus infectious cDNA (complementary deoxyribonucleic acid), which comprises the following steps: step 1, constructing subgenome plasmids, the subgenome plasmids are plasmids pF1, pF2, pF3 and pF4, and the plasmids pF1, pF2, pF3 and pF4 respectively contain target fragments F1, F2, F3 and F4; 2, obtaining target fragments: obtaining the target fragments f1, f2, f3 and f4 for in-vitro connection from the plasmids pF1, pF2, pF3 and pF4; and step 3, connecting target fragments f1, f2, f3 and f4 in vitro to obtain the duck tembusu virus infectious cDNA. The method can successfully clone the recombinant virus which is completely the same as the original virus strain and has no mutation.
Owner:岭南现代农业科学与技术广东省实验室肇庆分中心 +1
Determining method of content of antigen virus of inactivated vaccine of recombinant bird flu cellgen
ActiveCN102703602AReduce mistakesOperational benchmarks are reliableMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesCanine kidneyWater baths
The invention provides a novel determining method of the content of antigen virus of an inactivated vaccine of a recombinant bird flu H5N1 cellgen. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) preparation of MDCK (madin darby canine kidney), wherein 1.5ml of MDCK frozen cell with density of 2.0*10<6> is extracted and put in a water bath at a temperature of 37 DEG C, 10 to 15ml of cell culturefluid is added to culture for 72 hours, the cell is digested with 0.25 percent EDTA (ethylene diamine tetraacetic acid)-pancreatin, the cell nutrient fluid is diluted into MDCK cell suspension of 4.0*10<5>, the MDCK cell suspension is spread to a 96-mesh cell plate in a cell density of 40,000 per pore (0.1ml per pore), the cell plate is put in a CO2 culture case at a temperature of 37 DEG C and humidity of 5 percent to culture for 24 hours to form a compact monolayer for later use; and (2) inoculation of a recombinant bird flu H5N1 antigen, wherein recombinant bird flu H5N1 cellgen antigens in different batches are extracted and respectively added into the compact monolayer with 100mu l in each pore, and 100mu l of cell maintenance fluid is added to culture for four days, and a TCID50 (50% tissue culture infection dose) value is calculated by the number of cytopathic pores in a Reed-Muench method. The method is applicable to a cellgen vaccine for detecting the virus content by an erythrocyte agglutination test, which means that different viruses use corresponding sensitive cells.
Owner:吉林冠界生物技术有限公司
Combination of Broadly Neutralizing HIV Antibodies and Viral Inducers
ActiveUS20170210786A1Avoid the build processSmall sizeImmunoglobulins against virusesAntibody ingredientsRetroviral provirusInducer
The present invention relates to methods and agents for preventing the establishment of HIV-1 latent reservoirs or for reducing the size of the reservoirs. Specifically, the disclosure provides methods and agents for preventing the establishment of HIV-1 latent reservoirs or for reducing the size of the reservoirs, the methods comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of an isolated anti-HIV antibody, and administering to the subject two or more viral transcription inducers in effective amounts to induce transcription of an HIV provirus in the cells. Further provided are antibodies and viral transcription inducers used in the methods.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
Novel coronavirus vaccine as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111920945AIncrease production capacityHigh biosecuritySsRNA viruses positive-senseViral antigen ingredientsBiotechnologyCoronavirus vaccination
The invention relates to a coronavirus vaccine as well as a preparation method and an application thereof. The coronavirus vaccine comprises a nano-carrier and coronavirus coated in the nano-carrier,wherein the nano-carrier comprises chitosan and / or a chitosan derivative. The preparation method of the coronavirus vaccine comprises the following steps: mixing coronavirus with the carrier, and thenmixing with weak acid to form nanoparticles, namely the coronavirus vaccine. According to the invention, the coronaantigen virus is creatively coated in chitosan and / or the chitosan derivative to finish a sterilization procedure in a physical mode, so that compared with a traditional chemical sterilization mode, the production effect of the vaccine is improved, the production cost is saved, and the risk of other diseases caused by mutation and reversion of the coronaantigen virus is reduced; in addition, due to the biocompatibility and biodegradability of the chitosan or the derivative thereof, the vaccine has very good biological safety.
Owner:李伟宏 +3
Combination of broadly neutralizing HIV antibodies and viral inducers
ActiveUS10676521B2Small sizeAvoid the build processImmunoglobulins against virusesAntibody ingredientsAntiendomysial antibodiesNeutralising antibody
The present invention relates to methods and agents for preventing the establishment of HIV-1 latent reservoirs or for reducing the size of the reservoirs. Specifically, the disclosure provides methods and agents for preventing the establishment of HIV-1 latent reservoirs or for reducing the size of the reservoirs, the methods comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of an isolated anti-HIV antibody, and administering to the subject two or more viral transcription inducers in effective amounts to induce transcription of an HIV provirus in the cells. Further provided are antibodies and viral transcription inducers used in the methods.
Owner:THE ROCKEFELLER UNIV
A kind of primer and method for detecting htlv-i and htlv-ii provirus in one tube
ActiveCN103898239BHelp monitorLimit transmissionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationConcentration ratioBiology
The invention provides a primer and a method for detecting HTLV (human T-lymphotropic virus)-I and HTLV-II proviruses. The primer comprises a specific primer and a probe for detecting an HTLV-I provirus and a specific primer and a probe for detecting an HTLV-II provirus, the two primers and the two probes are added in the same PCR (polymerase chain reaction) pipe according to a reasonable concentration ratio, and a sample is detected by means of optimized Real-time PCR reaction conditions. The detection method can be used for detecting whether HTLV infection exists before serological changes, thereby greatly shortening the window phase; meanwhile, compared with a conventional serological detection method, the detection method has the advantages of short detection period, high specificity, high accuracy, high sensitivity, little dependence on the conditions, low pollution risk and the like. The detection result is beneficial to monitor the change of the carrying capacity of the HTLV provirus of a patient and limit the propagation of the HTLV virus.
Owner:SHANGHAI ADICON CLINICAL LAB LNC
Use of alpha lipoic acid as a feed additive for aquatic animals
PendingCN112118743AOrganic active ingredientsClimate change adaptationWeight gainingFeed conversion ratio
The present invention relates to the use of alpha lipoic acid as feed additive for aquatic animals including fish and shrimp, especially for cold water fish as for example salmon, bream, bass and forwarm water fish as for example carp, tilapia, catfish. More particular, this invention relates to the use of alpha lipoic acid for the improvement of the feed conversion ratio and / or daily weight gainin fish, for reducing mortality by regulating the micro flora of the gut and / or by protecting the animal against infections caused by pathogenic viruses.
Owner:DSM IP ASSETS BV +1
Treatment of mosaic viruses and bacterial infections of plants
ActiveCN111163639AImprove the effect of prevention and controlImprove adhesionBiocideDisinfectantsBiotechnologyMicroorganism
Compositions and methods are provided for treating certain plant pathogens using microbe-based products. In particular, the subject invention relates to treatment of plant pathogenic viruses, including mosaic virus, as well as plant pathogenic bacteria, using beneficial microbes and / or their growth by-products. In certain embodiments, the growth by-products are biosurfactants.
Owner:LOCUS AGRI IP CO LLC
Quick detecting method of bovine leukemia virus
InactiveCN109182602AQuick checkEasy to collectMicrobiological testing/measurementRetroviral provirusEpidemiologic survey
Owner:SHANDONG VOCATIONAL ANIMAL SCI & VETERINARY COLLEGE
A method for infectious recombination cloning against type II type VII epidemic ndv strain dhn3
ActiveCN110592108BNo mutationFirmly connectedSsRNA viruses negative-senseVirus peptidesGenome wide expressionVirus
The invention belongs to the technical field of veterinary biological products, and discloses a recombinant cloning method for the type II type VII popular NDV strain DHN3. The target fragments are NP gene, P gene and L gene respectively; Step 2: construct the DHN3 whole genome expression vector; recombine the DHN3 whole genome obtained by artificial recombination into the vector plasmid to obtain the whole genome expression vector; the sequence of the DHN3 whole genome is in sequence List SEQ ID NO 1; Step 3: co-transfect BHK-21 cells with three kinds of helper plasmids and DHN3 whole genome expression vector to obtain virus liquid containing recombinant virus rDHN3; NP gene is located in the sequence list SEQ ID NO: 1 at 1-1591nt; P gene is located at 1925-3109nt in SEQ ID NO: 1 of the sequence listing; L gene is located at 8166-15192nt in SEQ ID NO:1 of the sequence listing. This method can successfully clone a recombinant virus with the same original strain and no mutation.
Owner:ZHAOQING INST OF BIOTECHNOLOGY CO LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com