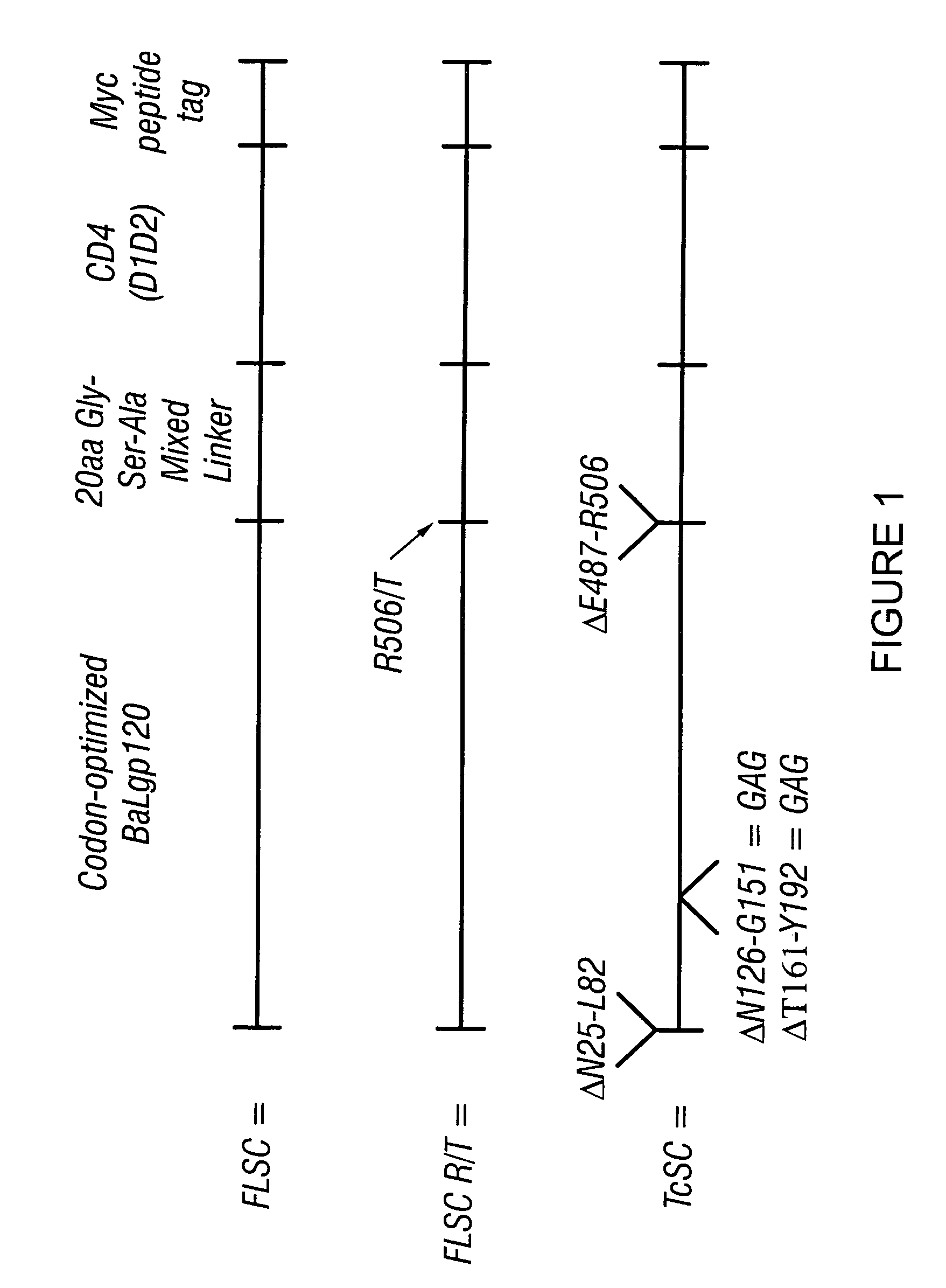
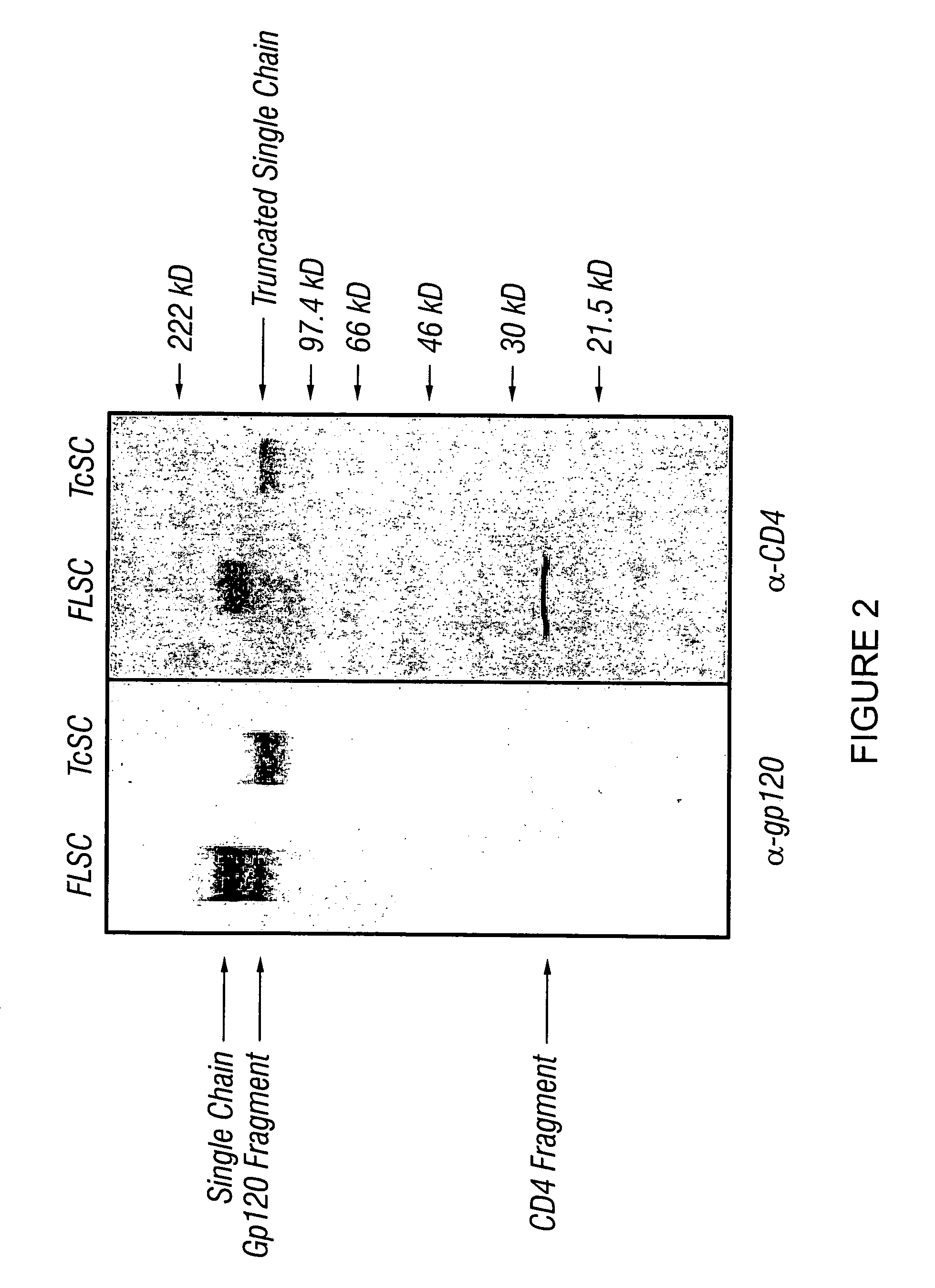
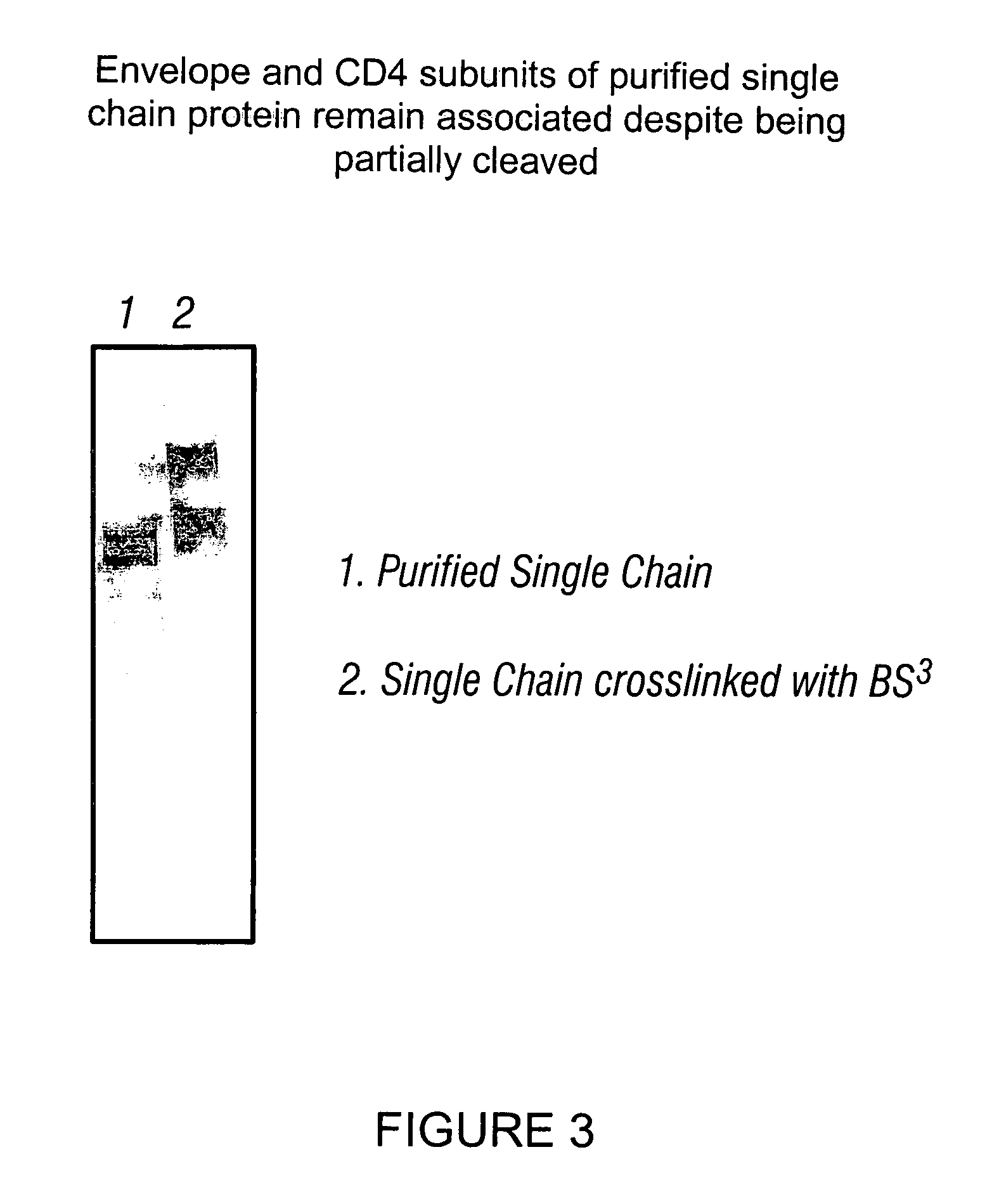
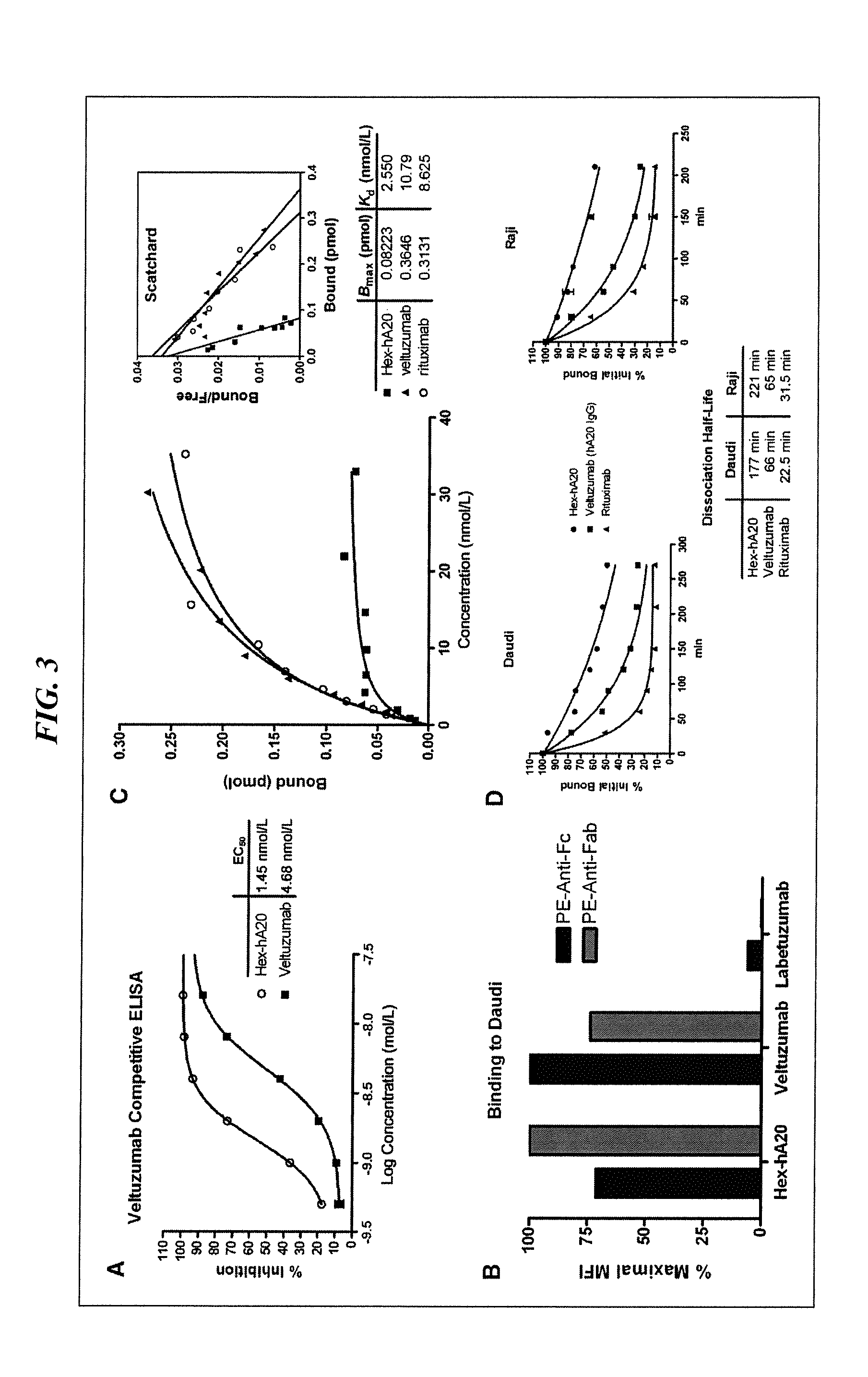
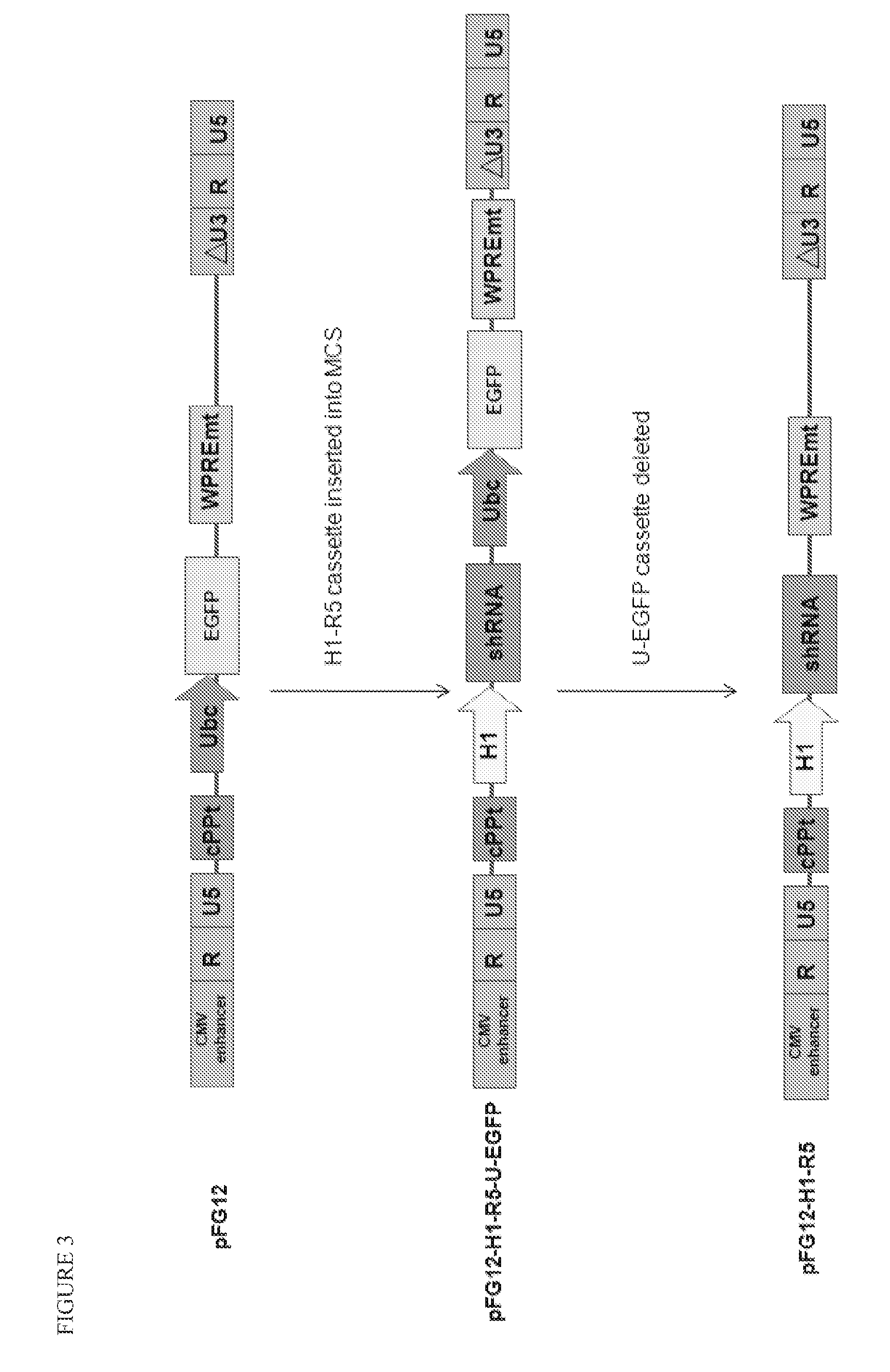
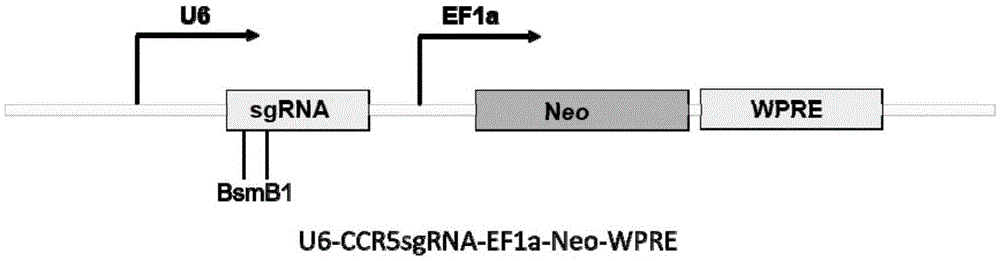
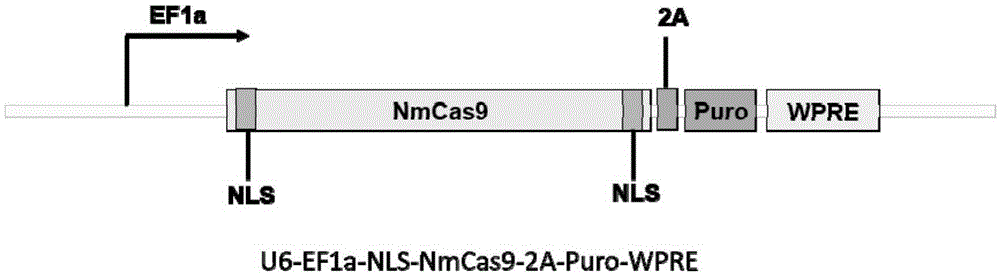
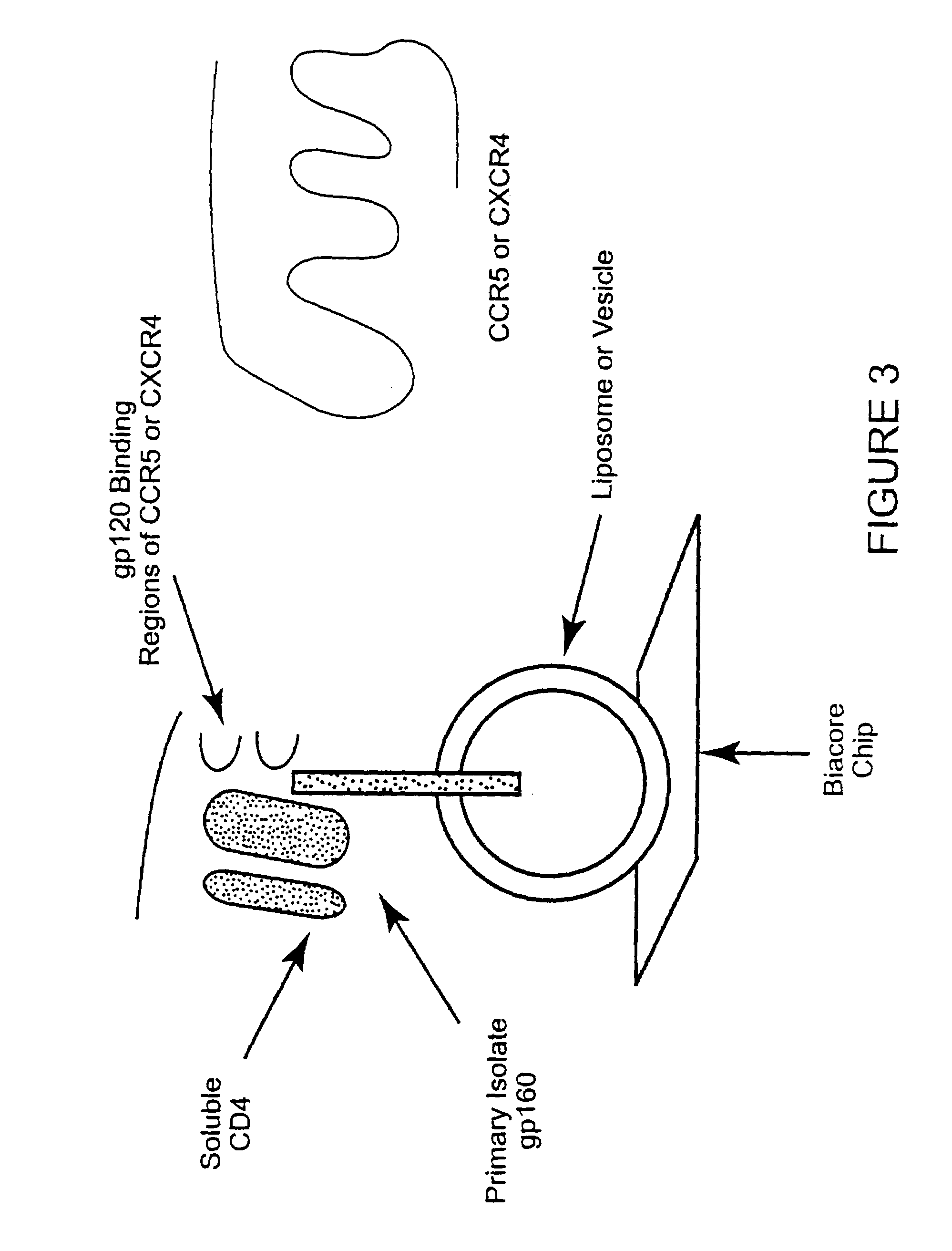
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
171 results about "HIV receptor" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
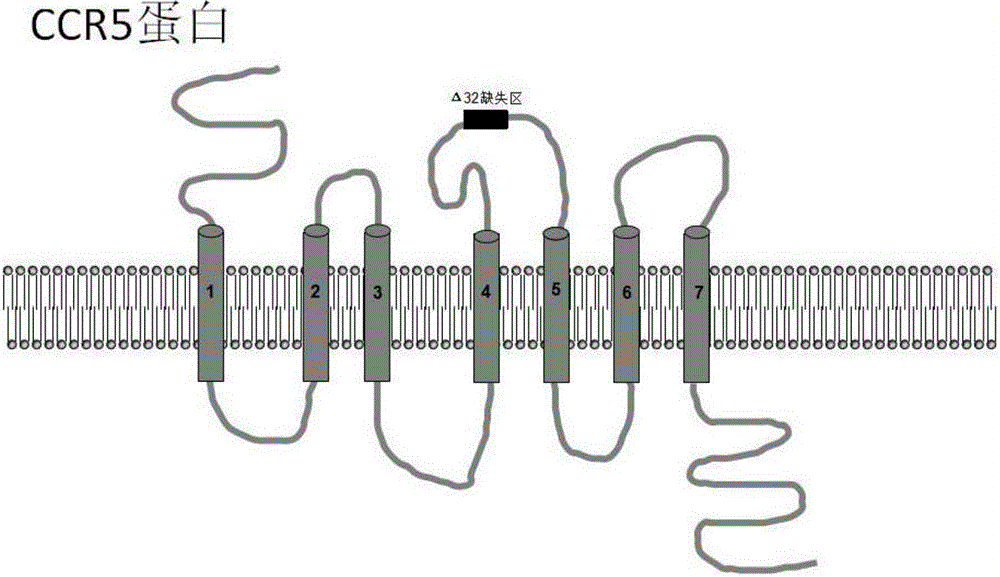
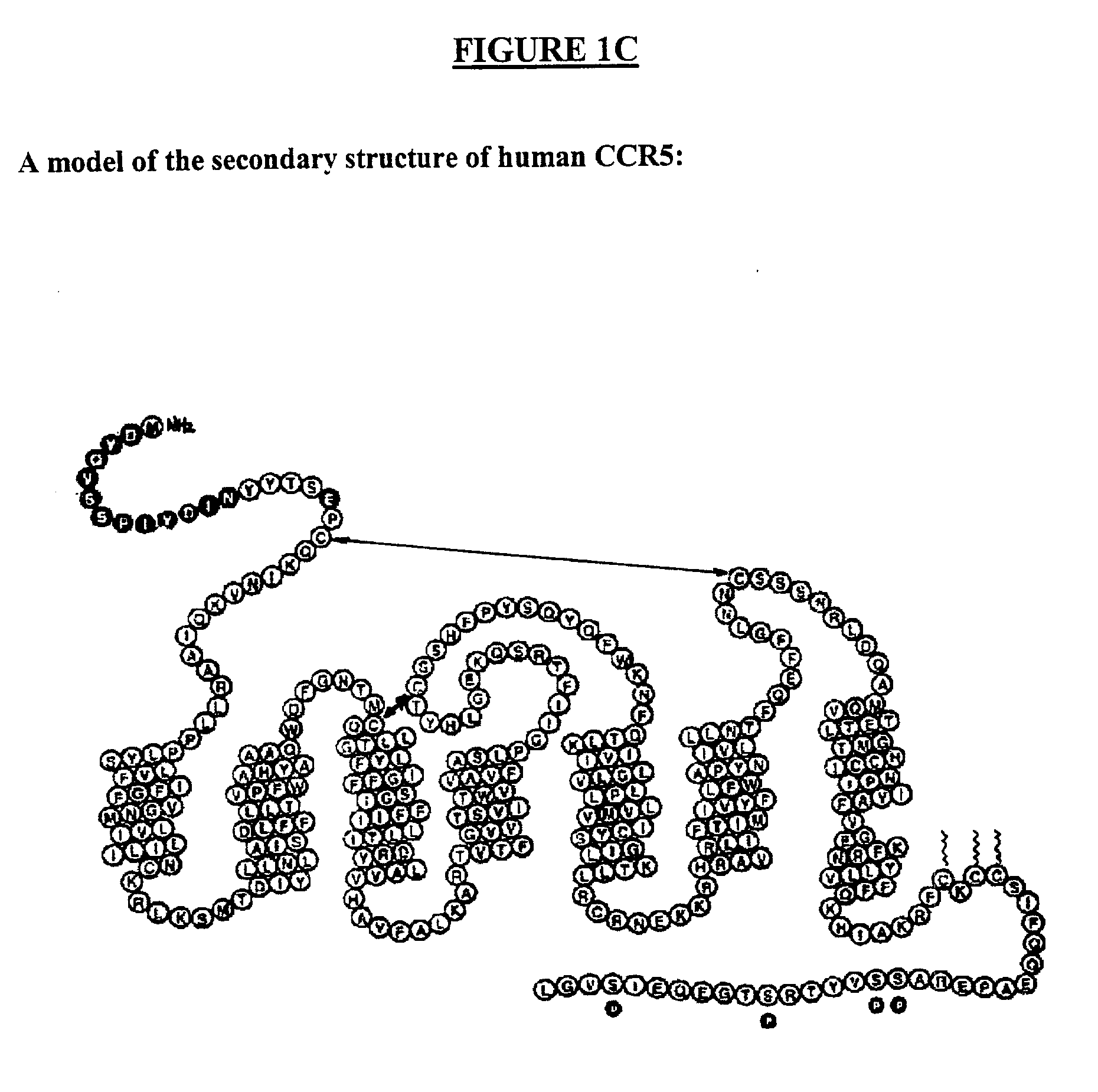
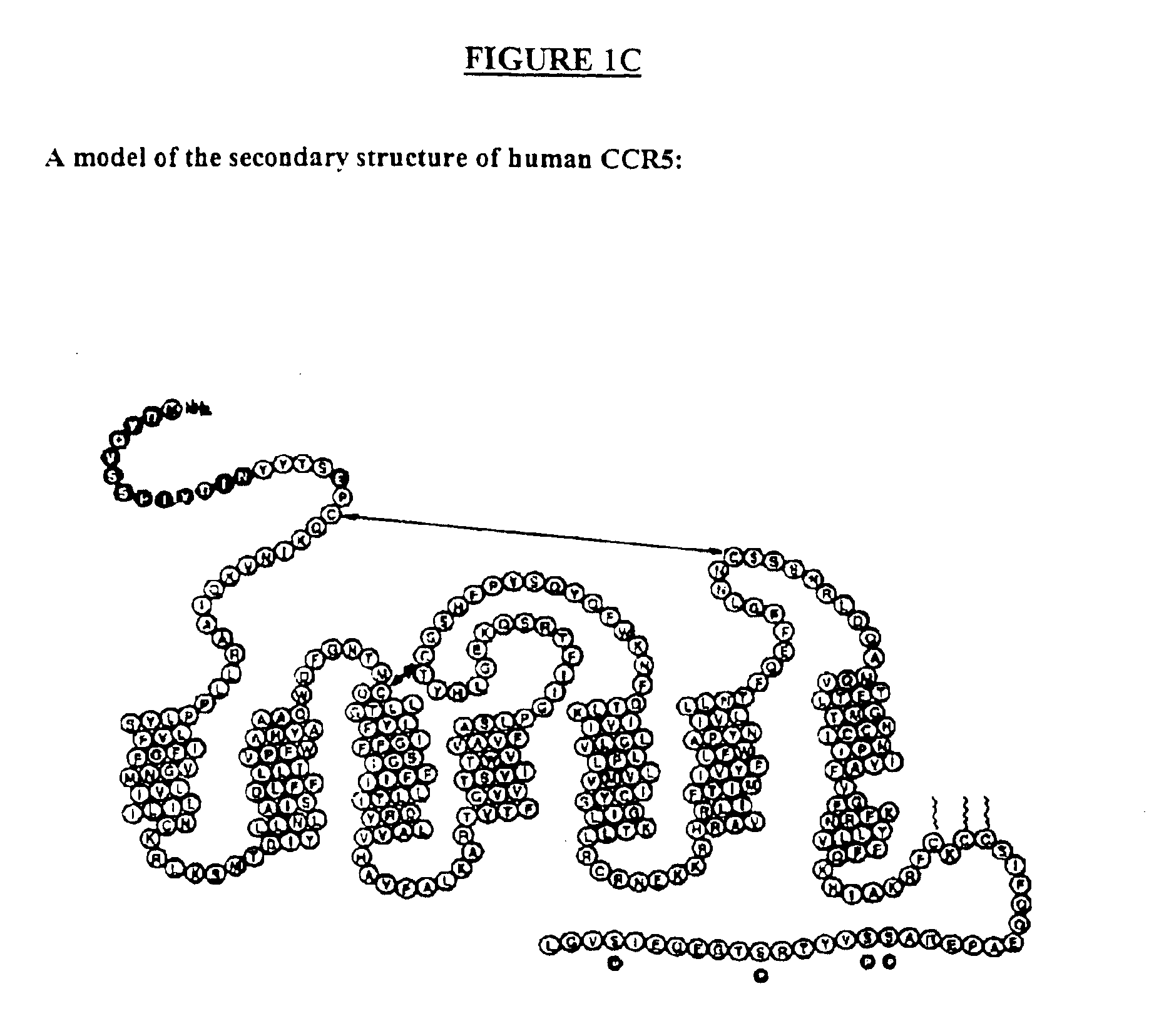
HIV-1 most commonly uses the chemokine receptors CCR5 and/or CXCR4 as co-receptors to enter target immunological cells. These receptors are located on the surface of host immune cells whereby they provide a method of entry for the HIV-1 virus to infect the cell.
Virus coat protein/receptor chimeras and methods of use
InactiveUS7311920B1Sufficient amountMethod can be usedCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCXCR4Immunodeficiency virus
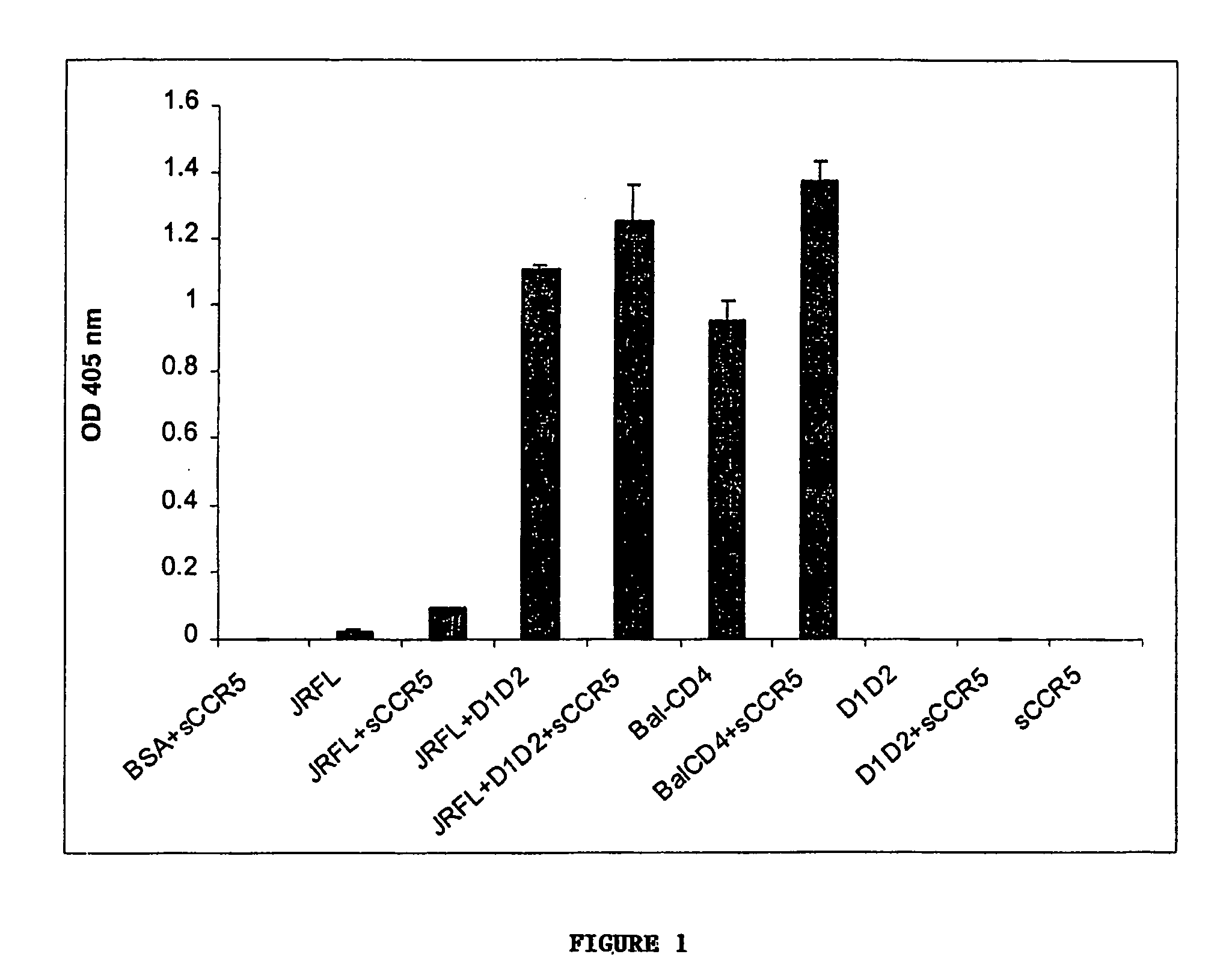
The invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising a virus coat sequence and a receptor sequence that can interact with each other to form a complex that is capable of binding a co-receptor. Such chimeric molecules therefore exhibit functional properties characteristic of a receptor-coat protein complex and are useful as agents that inhibit virus infection of cells due to occupancy of co-receptor present on the cell, for example. In particular aspects, the chimeric polypeptide includes an immunodeficiency virus envelope polypeptide, such as that of HIV, SIV, FIV, FeLV, FPV and herpes virus. Receptor sequences suitable for use in a chimeric polypeptide include, for example, CCR5 and CXCR4 sequences.
Owner:MARYLAND BIOTECH INST UNIV OF
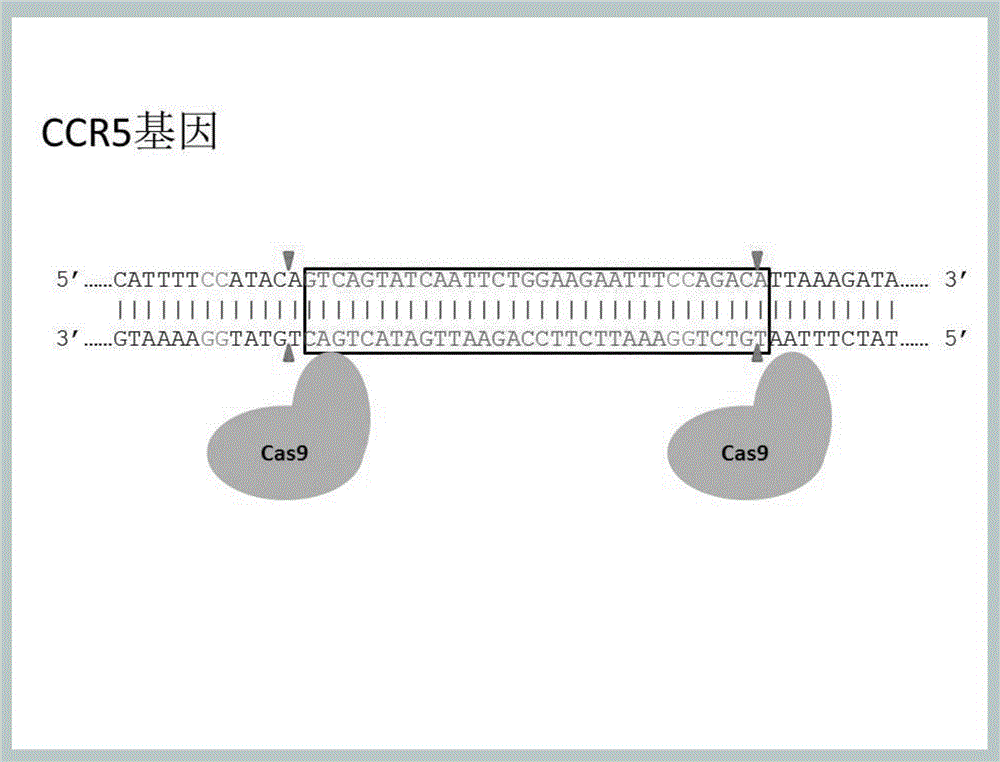
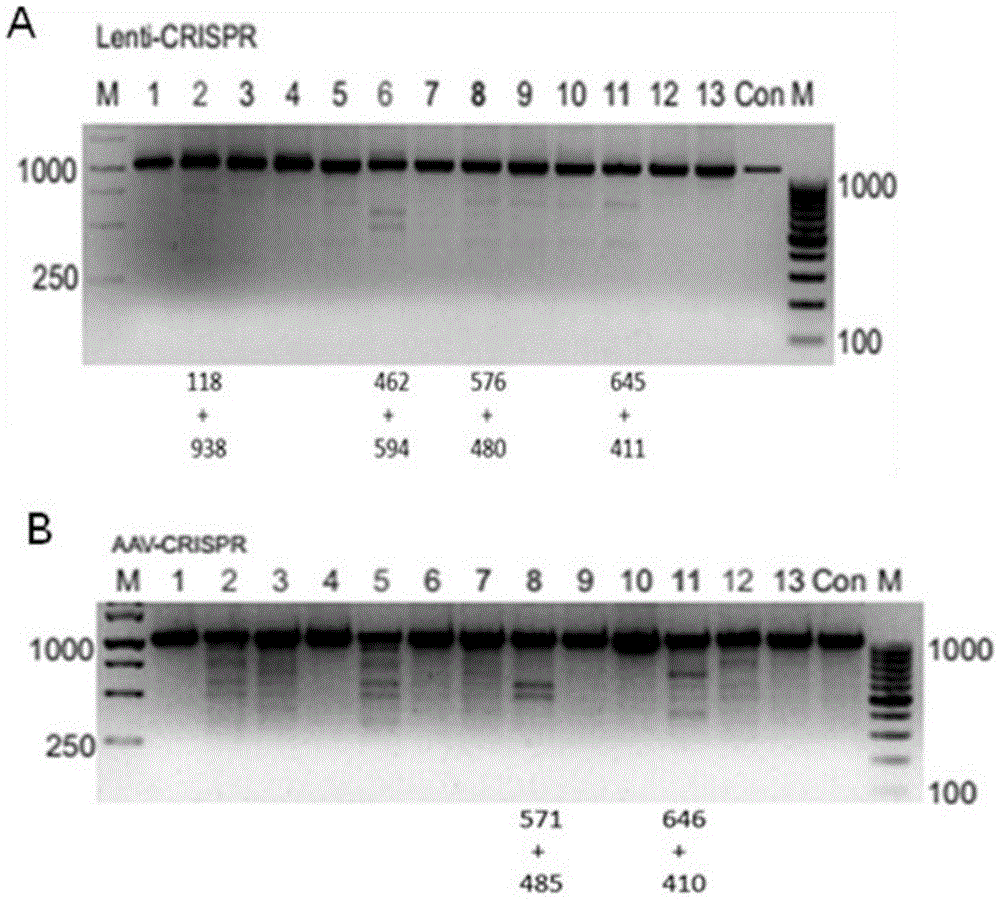
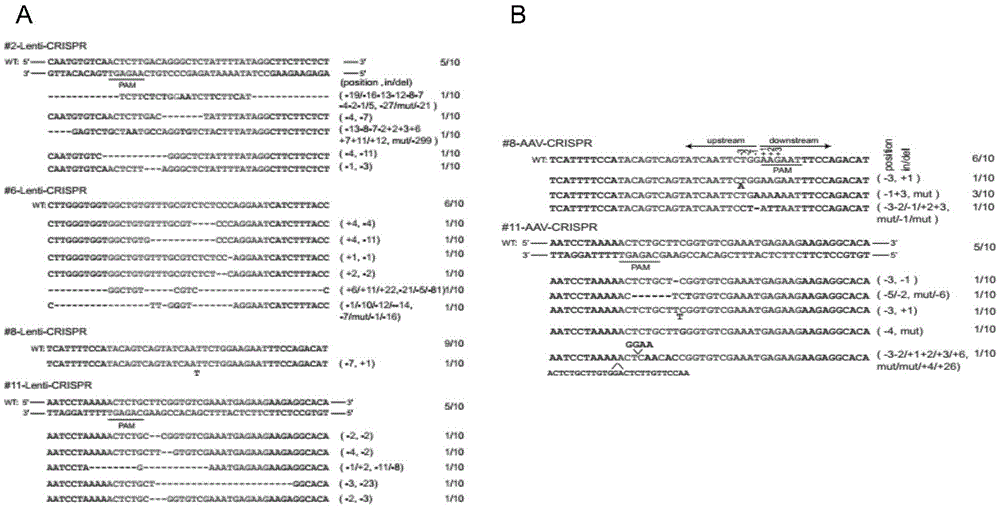
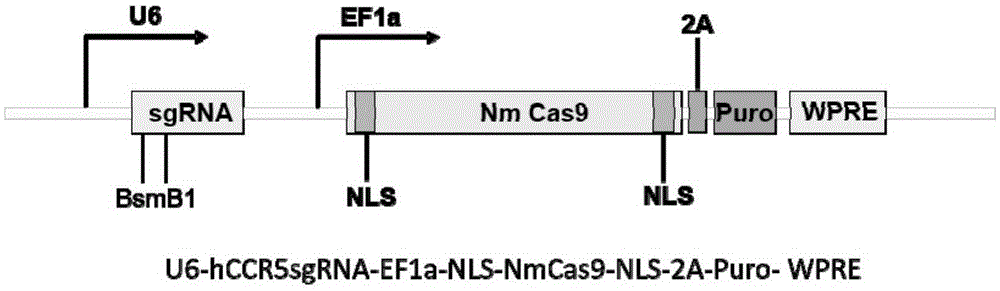
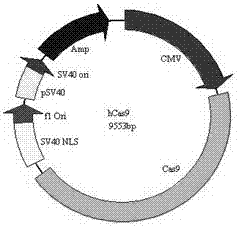
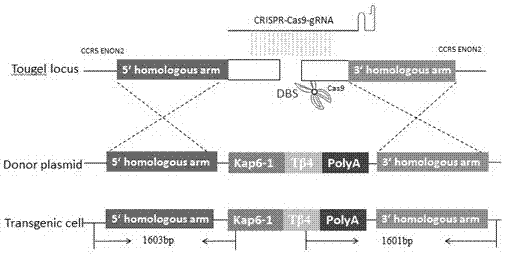
Method for inducing CCR5-delta32 deletion with genome editing technology CRISPR-Cas9
The invention relates to a method for successfully inducing cell chemokine receptor CCR5 genes to be mutated into CCR5-delta32 deletion-type genes with a new genome editing technology CRISPR-Cas9. CCR5 is an important receptor for human immunodeficiency viruses (HIV) to invade personal host cells. CCR5-delta32 deletion means deletion of 32 basic groups occurs in a CCR5 coding region, so that the sequence after the 185th amino acid is changed, and early termination occurs. CCR5-delta32 biallelic-gene homozygous deletion has natural resistance to HIV infection, and can not be infected by HIV. By means of the method, a slow virus packaging system and the CRISPR technology are used at the same time; as the slow virus infecting host range is wide, the method can be applied to cells such as bone marrow stem cells and CD4T cells, and the CCR5-delta32 deletion-type genes hopefully become medicine for treating acquired immune deficiency syndrome or other diseases.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
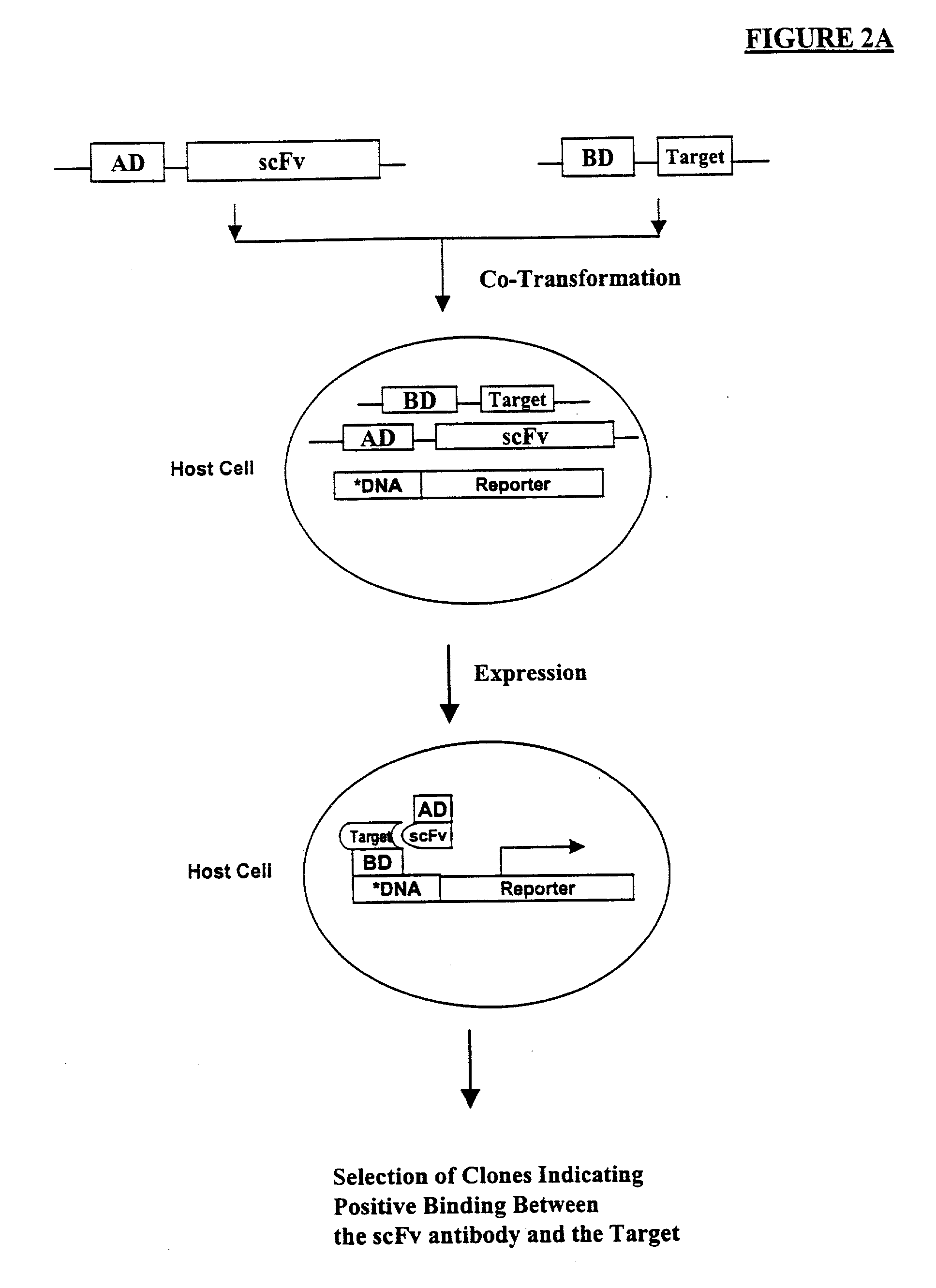
High throughput generation of human monoclonal antibody against peptide fragments derived from membrane proteins
InactiveUS20030165988A1FungiAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsHigh-Throughput Screening MethodsSingle-Chain Antibodies
Methods are provided for efficient, high throughput screening of antibody libraries against proteins targets, especially membrane proteins. In particular, methods are provided for screening a fully human antibody library against membrane proteins such as HIV coreceptors in yeast. More particularly, a library of human single chain antibodies is screened against peptide fragments derived from extracellular domains of human CCR5 and high affinity monoclonal antibodies against CCR5 are selected.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
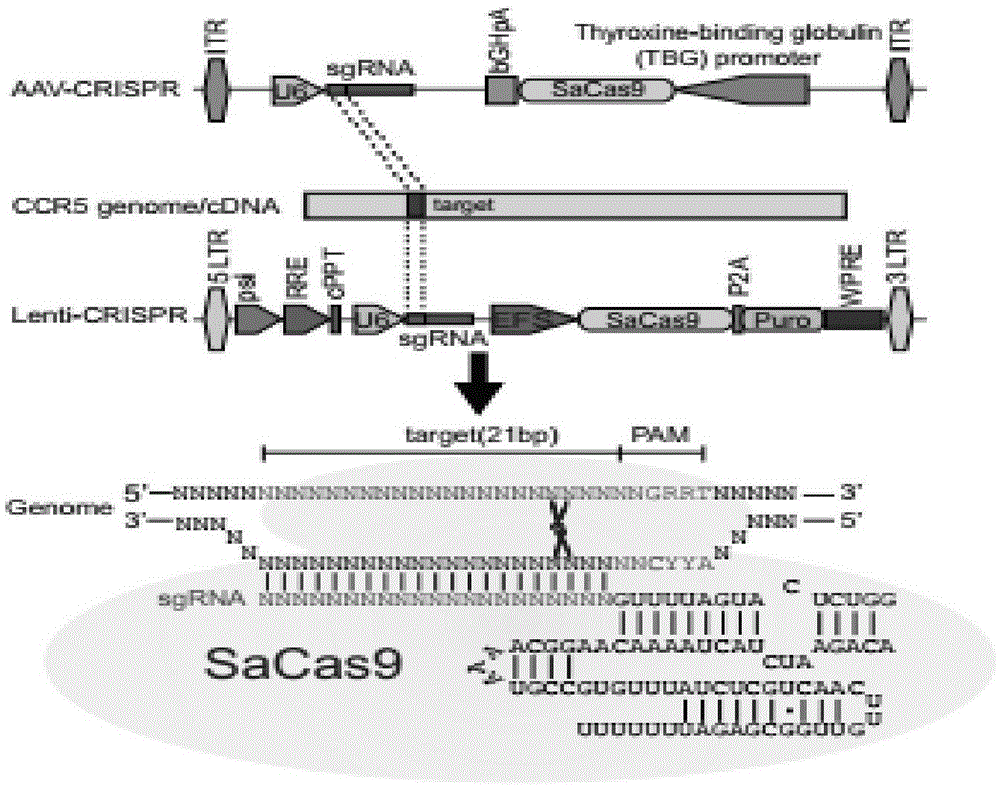
CRISPR/SaCas9 system for gene therapy of AIDS
InactiveCN105567688AImprove efficiencyPrevent intrusionGenetic material ingredientsAntiviralsVector systemLentivirus
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering, and particularly relates to a method for specifically knocking out CCR5 genes of human bodies through CRISPR / SaCas9 and sgRNA used for specifically targeting CCR5 genes. The invention provides the method for specifically knocking out the CCR5 genes of the human bodies through CRISPR / SaCas9 and sgRNA used for specifically targeting the CCR5 genes and relates to a CRISPR / SaCas9 recombinant lentivirus and adeno-associated virus vector system and application. CRISPR / SaCas9 recombinant lentivirus and adeno-associated virus vectors can express SaCas9-RNA aiming at the CCR5 target spot of one same gene of the human bodies and rhesus monkeys, therefore, the application range is wider, and the efficiency is higher. The preparation method is easy to construct, the targeting efficiency is high, and a novel technology is provided for the gene therapy of HIV.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
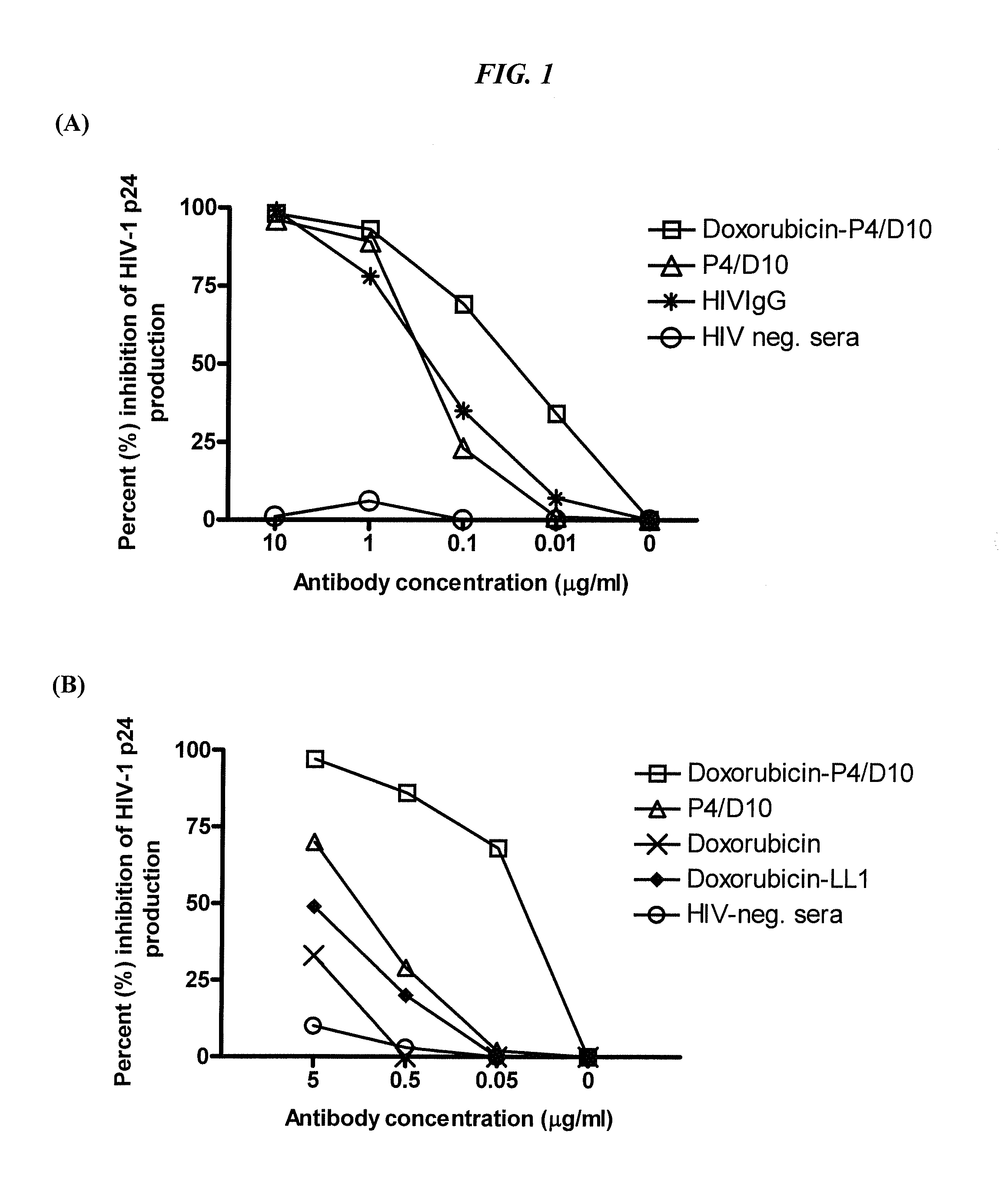
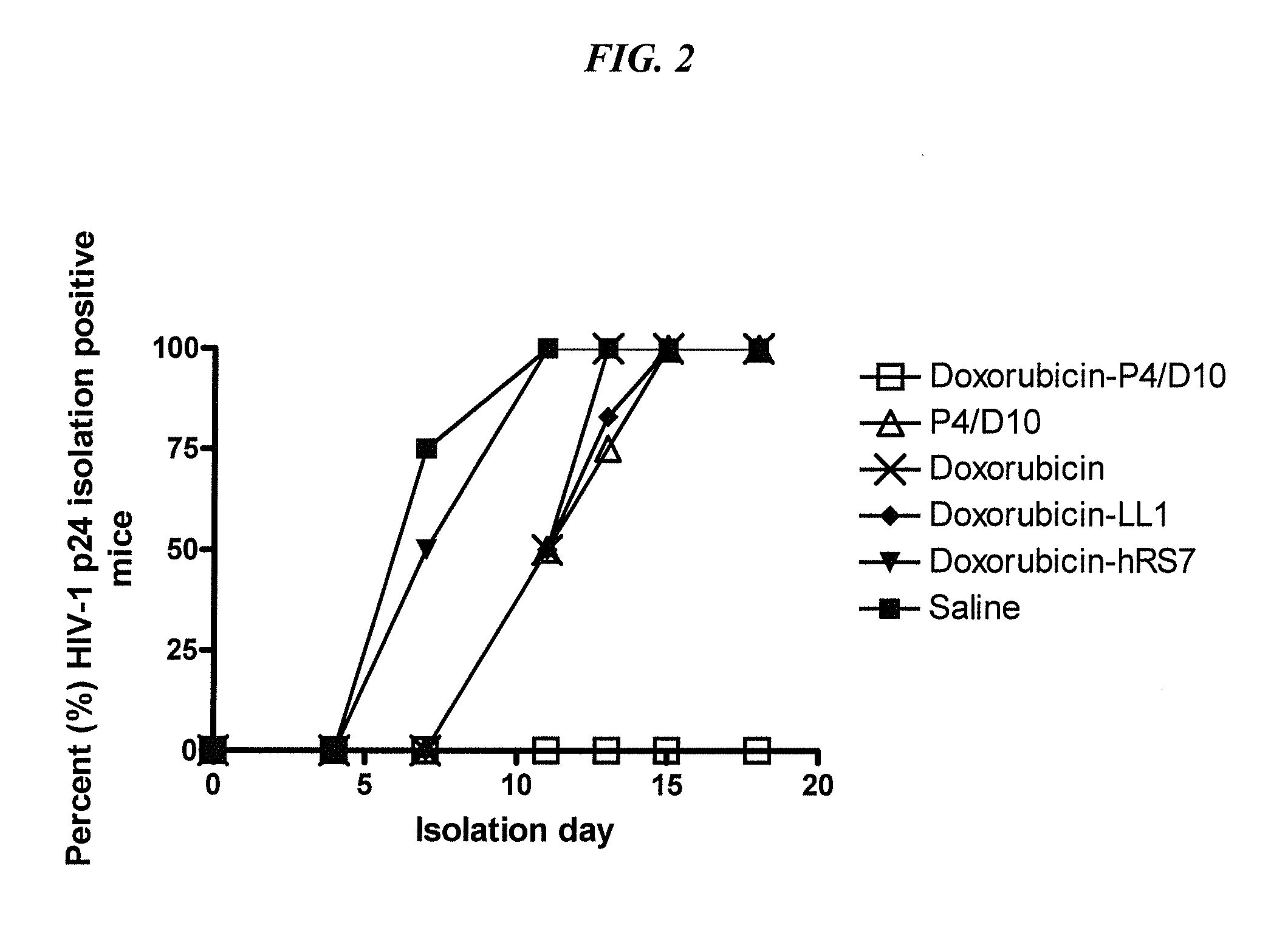
Dock-and-lock (DNL) constructs for human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) therapy
ActiveUS8481041B2Reduce eliminateReduce and eliminate focusOrganic active ingredientsImmunoglobulins against virusesAntigenAntibody fragments
The present invention concerns methods and compositions for treatment of HIV infection in a subject, utilizing a DNL complex comprising at least one anti-HIV therapeutic agent, attached to an antibody, antibody fragment or PEG. In a preferred embodiment, the antibody or fragment binds to an antigen selected from gp120, gp41, CD4 and CCR5. In a more preferred embodiment the antibody is P4 / D10 or 2G12, although other anti-HIV antibodies are known and may be utilized. In a most preferred embodiment, the anti-HIV therapeutic agent is a fusion inhibitor, such as T20, T61, T651, T1249, T2635, CP32M or T-1444, although other anti-HIV therapeutic agents are known and may be utilized. The DNL complex may be administered alone or may be co-administered with one or more additional anti-HIV therapeutic agents.
Owner:IBC PHARMACEUTICALS INC
Dual vector for inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus
The present invention provides an expression vector for preventing or inhibiting HIV entry, fusion or replication in mammalian cells. In particular, the invention provides a recombinant retroviral vector that encodes an inhibitor of a HIV co-receptor, such as CCR5 or CXCR4, and a protein that inhibits HIV fusion to target cells and / or HIV replication. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising such constructs and methods of use thereof to prevent or treat HIV infection in a patient are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
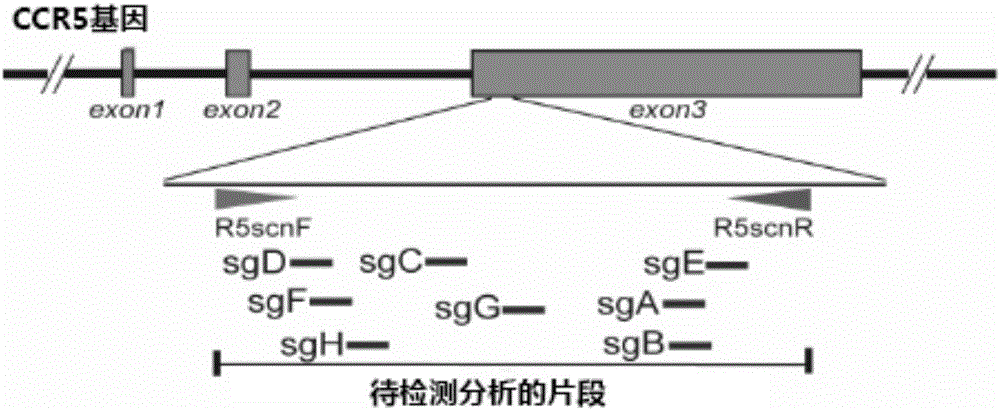
Human CCR5 gene target sequence identified by neisseria meningitidis CRISPR-Cas9 system, sgRNA and application of target sequence and sgRNA
InactiveCN105331609AAchieve preventionAchieve therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesGene targetsHIV receptor
The invention belongs to the field of gene engineering and discloses a target sequence identified by a CRISPR-Cas9 system from neisseria meningitidis. The target sequence is as shown in the nth-24th sites of optional one of SEQ ID No. 1-20, and n=1-9. The invention further discloses sgRNA and coding DNA molecules thereof, the sequence of the sgRNA is 5'-identificiation sequence-sequence recruiting Cas9 protein-3', and the DNA sequence corresponding to the identification sequence is identical with the target sequence. The invention also discloses the CRISPR-Cas9 system which comprises the Cas9 protein, the sgRNA and / or a coding sequence carrying the Cas9 protein and a vector of the coding sequence of the sgRNA. The invention also discloses application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system to editing of CCR5 genes and preparation of medicine for HIV infection. By the CRISPR-Cas9 system, the CCR5 genes can be edited, and cells cannot be infected by HIV.
Owner:张竞方
sgRNA (singleguide Ribonucleic Acid), lentiviral vector constructed by the same and application thereof
InactiveCN106801056AEffective knockoutExcellent anti-virus infection abilityCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsAntiviralsTreatment fieldHIV receptor
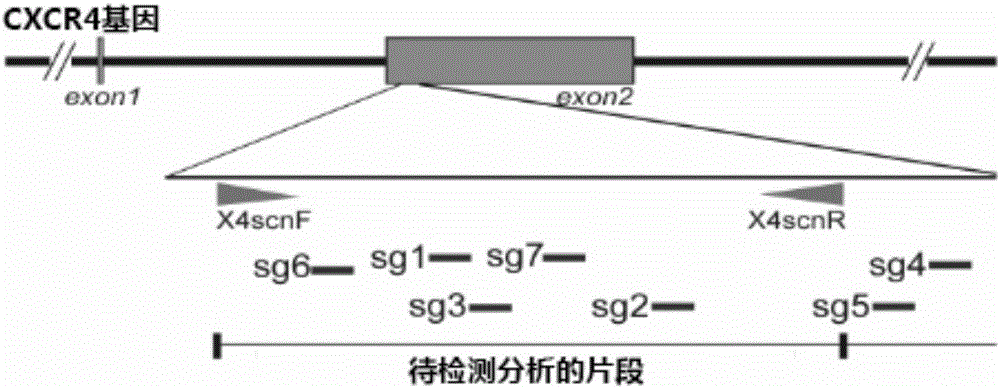
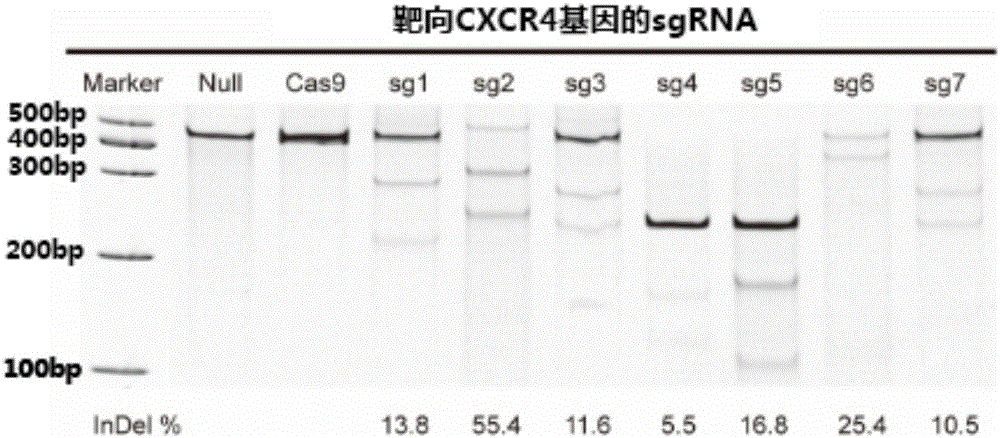
The invention relates to the field of gene therapy, in particular relates to sgRNA (singleguide Ribonucleic Acid), as well as a lentiviral vector constructed by the same and application thereof and specifically relates to sgRNA with SIVmac1A11 lentivirus as a framework to express SpCas9 protein and gene specificity. The sgRNA is applied to treating human and simian AIDS (Acquired Immune Deficiency Syndrome). A nucleotide sequence of the sgRNA is shown as SEQ ID NO.1 to 2. According to the sgRNA disclosed by the invention, a current most efficient CRISPR / Cas9 gene editing tool is utilized, a designed CXCR4 / CCR5 gene sgRNA locus has gene knockout activity superior to other loci reported by existing research, and the sgRNA is applied to gene therapy of SIV infected rhesus monkeys for the first time. Compared with ZFN and TALEN, the sgRNA has the advantages of being convenient to operate, low in cost and the like.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF BIOMEDICINE & HEALTH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Method for constructing mouse model for conditional knockout of CCR5 gene of endothelial cell
ActiveCN107858373ALow densityIntegrity breachStable introduction of DNAAnimals/human peptidesKnockout animalHIV receptor
The invention discloses a method for constructing a mouse model for conditional knockout of CCR5 gene of endothelial cell. The method comprises the following steps of firstly, obtaining a CCR5loxp / loxp mouse, and mating with a Tie-2-cre / ERT2 mouse, so as to obtain heterozygous mice with specific knockout of CCR5 gene of the endothelial cell; mutually mating the heterozygous mice, so as to obtain homozygous mice with specific knockout of CCR5 gene out of the endothelial cell. The constructing method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that the mouse with conditional knockout of endothelial cell gene is constructed via the CRISPR / Cas9 system, the mutation is led into the mouse by a cell specificity method, the missing of the CCR5 target gene occurs at the certain tissue organ of the test animal, the controllability of mechanism study is furthest realized, and the disadvantages that different tissues or cells are not distinguished, and target genes in all tissues or cells of themouse body are all removed in the conventional gene knockout technique is overcome.
Owner:SHANDONG KEYUAN PHARMA
Methods for reducing viral load in HIV-1-infected patients
InactiveUS20070026441A1Reduce the possibilityStrong inhibitory activityPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementReduced doseHIV receptor
This method provides a method for reducing HIV-1 viral load in an HIV-1-infected human subject which comprises administering to the subject at a predefined interval effective HIV-1 viral load-reducing doses of (a) a humanized antibody designated PRO 140, or of (b) an anti-CCR5 receptor monoclonal antibody. This invention also provides a method for inhibiting in a human subject the onset or progression of an HIV-1-associated disorder, the inhibition of which is effected by inhibiting fusion of HIV-1 to CCR5+CD4+ target cells in the subject. This invention also provides a method for treating a subject infected with HIV-1 comprising administering to the subject (a) a monoclonal antibody which (i) binds to a CCR5 receptor on the surface of the subject's CD4+ cells and (ii) inhibits fusion of HIV-1 to the subject's CCR5+CD4+ cells, and (b) a non-antibody CCR5 receptor antagonist, in amounts effective to treat the subject.
Owner:PROGENICS PHARMA INC
CRISPR/Cas9 technology mediated down producing goat VEGF gene fixed-point knock-in method
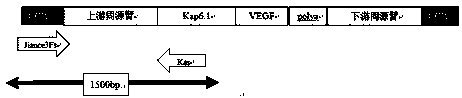
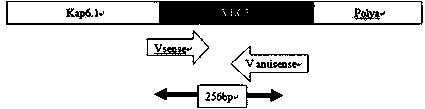
ActiveCN108570479AGrowth and development effectsAvoid combiningHydrolasesStable introduction of DNANuclear transferHIV receptor
The invention provides a method for finishing down producing goat VEGF gene fixed-point knock-in mediated by a CRISPR / Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: establishing a gRNA expression vector and a VEGF homologous recombination vector on the basis of the CRISPR / Cas9 system according to a CCR5 gene sequence of down producing goats; then jointly transferring three optimized vectors into fibroblasts of down producing goat fetuses to obtain VEGF gene fixed-point knocked-in positive cells; and preparing VEGF gene fixed-point integrated down producing goats by using a somatic nuclear transfer technology. The established targeting vector based on the CRISPR / Cas9 system provides a simple, rapid and safe path for fixed-point knock-in of goat VEGF genes. The method does not involve any screening marker genes in a cell line screening process, therefore, the safety of transgenic animals is greatly improved, and the method has high value on research of genetic breeding and gene functions of down producing goats.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
Method for mediating site-directed knock-in of goat Tbeta4 gene based on CRISPR/Cas 9 technology
ActiveCN107541525AImprove securityImprove gene editing efficiencyOther foreign material introduction processesVector-based foreign material introductionSkeletal Muscle Satellite CellsHIV receptor
The invention employs a CRISPR-Cas9 system to complete mediation of a goat Tbeta4 gene for site-directed knock-in. A gRNA expression vector and a Tbeta 4 homologous recombinant vector based on the CRISPR-Cas9 system are constructed according to a CCR5 gene sequence of the goat. An optimized CRISPR-Cas9 vector and a constructed gRNA expression vector and the Tbeta 4 homologous recombinant vector are transferred to skeletal muscle satellite cells together, in order to obtain cells with the site-directed Tbeta4 gene. A targeting vector constructed based on the CRISPR-Cas9 system provides a simple, fast and safe pathway for site-directed knock-in of the goat Tbeta4 gene. Any screening marker genes are not related in a cell line screening process, safety of transgenic animals is greatly improved, and the method has important value for genetic breeding of goats and research of gene function.
Owner:INNER MONGOLIA UNIVERSITY
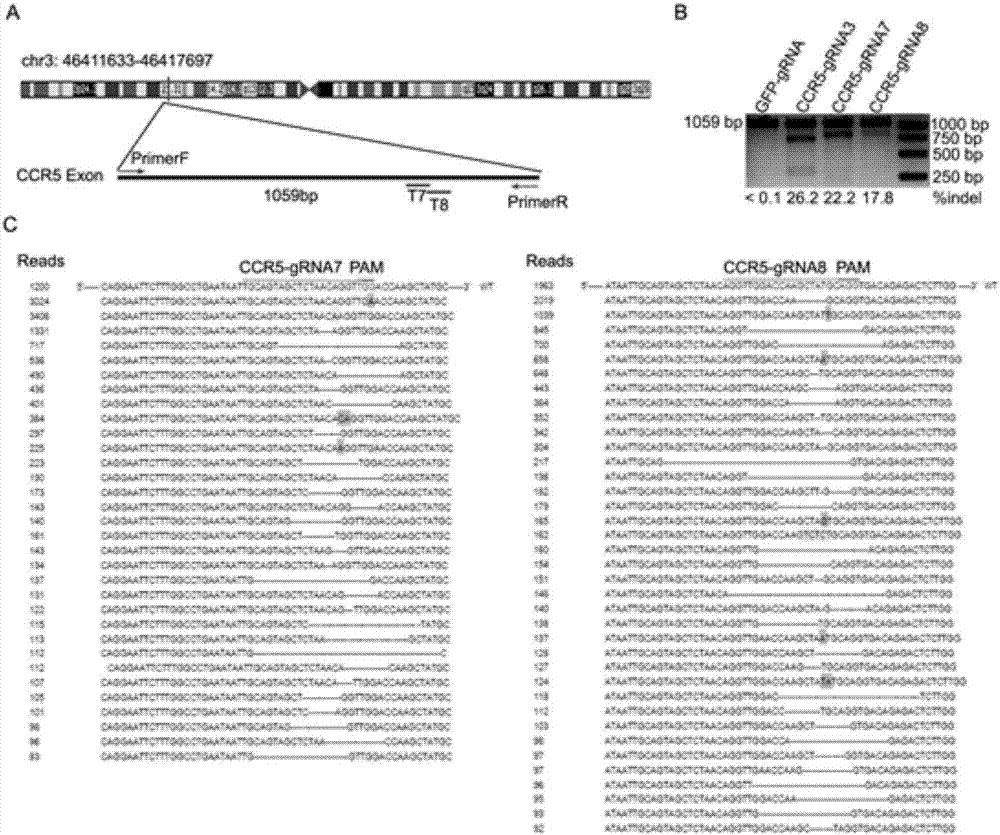
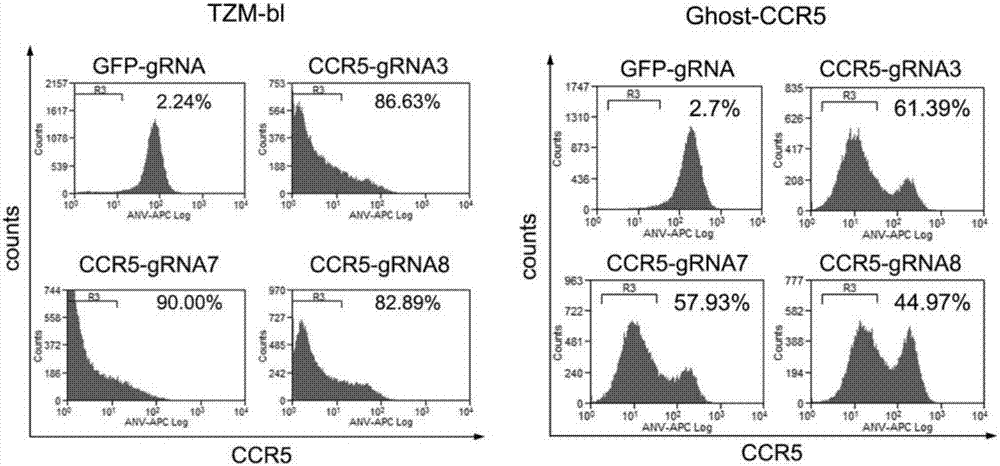
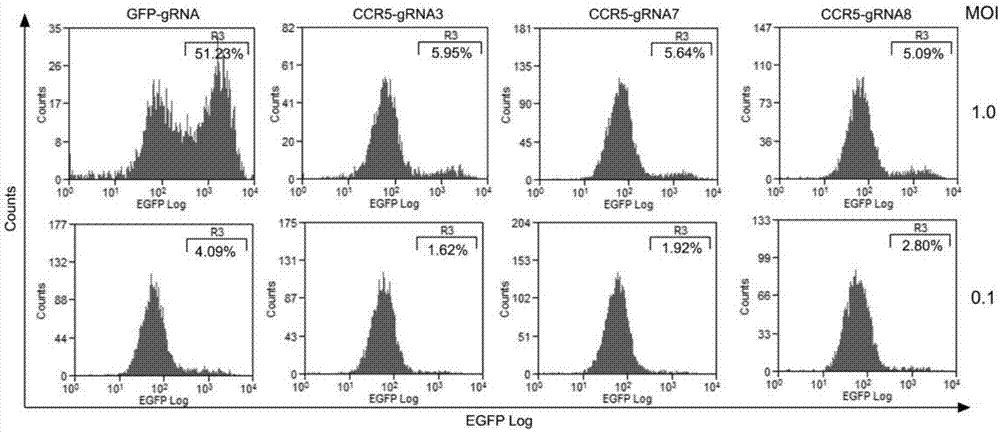
CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat)/Cas9 Recombinant lentiviral vector containing gRNA sequence specifically targeting CCR5 and application thereof
ActiveCN107312798AAvoid infectionInfection efficiency dropsOrganic active ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsRandom mutationLentivirus
The invention discloses a CRISPR (clustered regularly interspaced short palindromic repeat) / Cas9 recombinant lentiviral vector containing gRNA sequence specifically targeting CCR5 and application thereof. A lentivirus of the CRISPR / Cas9 recombinant lentiviral vector containing gRNA sequence specifically targeting CCR5 gene Delta 32 region is constructed that the lentivirus can introduce cells into a CRISPR / Cas9 system specific to CCR5, double-chain breakage occurs to a specific site of CCR5 gene, a random mutation is introduced to a breakage site after repairing by means of nonhomogeneous recombinant terminal binding, and the mutation rate reaches 90% and above. As gRNA is a nonhomogeneous region of CCR5 and CCR2, detection shows that the missing efficiency of the two gRNAs is lower than 0.2%. Cells modified via the recombinant lentivirus have significantly decreased efficiency of HIV (human immunodeficiency virus) infection. The system is quick to construct, simple and low in price, and is applicable to gene therapy of acquired immune deficiency syndrome.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Combination therapy comprising the use of protein kinase C modulators and Histone Deacetylase inhibitors for treating HIV-1 latency
InactiveUS20100166806A1Adverse propertyPrevent HIV-1-induced cytotoxicityBiocideOrganic chemistryReverse transcriptaseHydroxamic acid
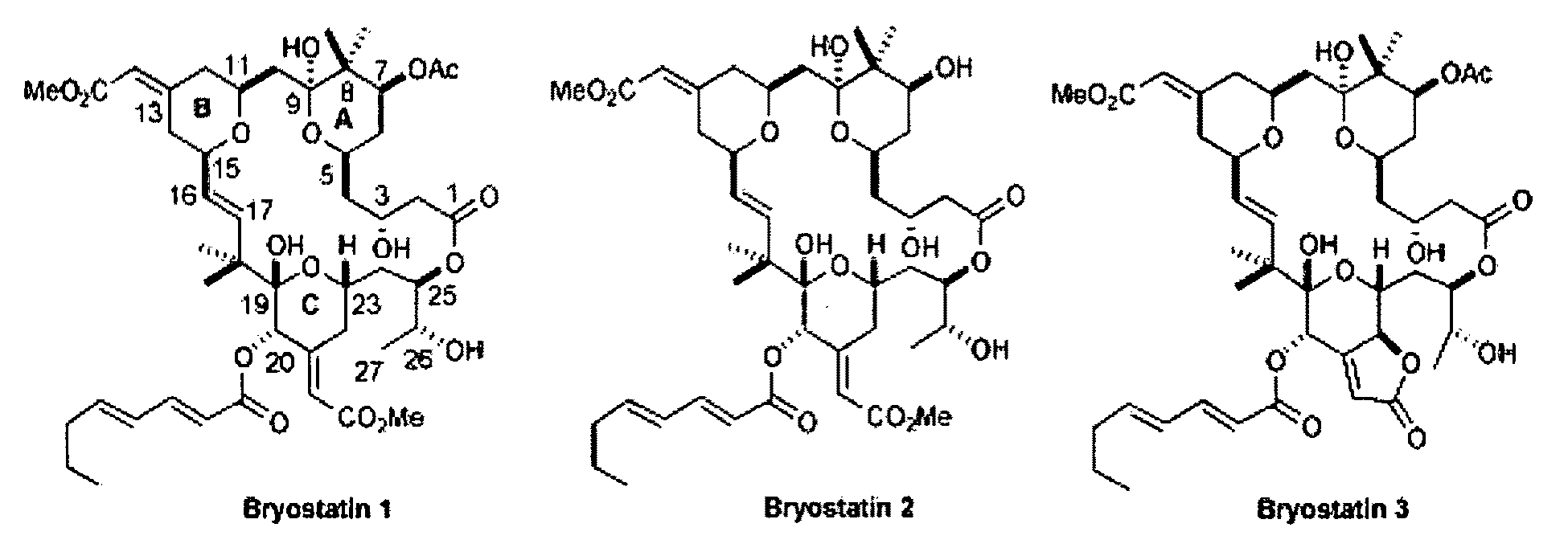
The invention relates to a combination of treatments, more particularly a combination treatment for HIV-1 infection. The present invention is directed to the use of bryostatin-1 and their natural and synthetic derivatives for AIDS therapy, in particular to the use of bryostatins in combination with other active drugs such as Histone Deacetylases (HDACs) inhibitors and anti-retrovirals, for the treatment of HIV-1 latency. According to the present invention, we provide a combination therapy for the treatment of HIV-1 latency which employs bryostatin-1 (and analogues) and one of the following HDAC inhibitors; valproic acid, butyrate derivatives, hydroxamic acids and benzamides. While HDACi can be used in continuous dosing protocol, bryostatins can be used following a cyclical dosing protocol. Bryostatins can be formulated in pharmaceutical acceptable carriers including nanoparticles, phospholipids nanosomes and / or biodegradable polymer nanospheres. This combination therapy needs to be used in patients treated with antiretroviral therapy (HIV-1 protease inhibitors, HIV-1 reverse transcriptase inhibitors, HIV-1 integrase inhibitors, CCR5 co-receptor inhibitors and fusion inhibitors).
Owner:APHIOS
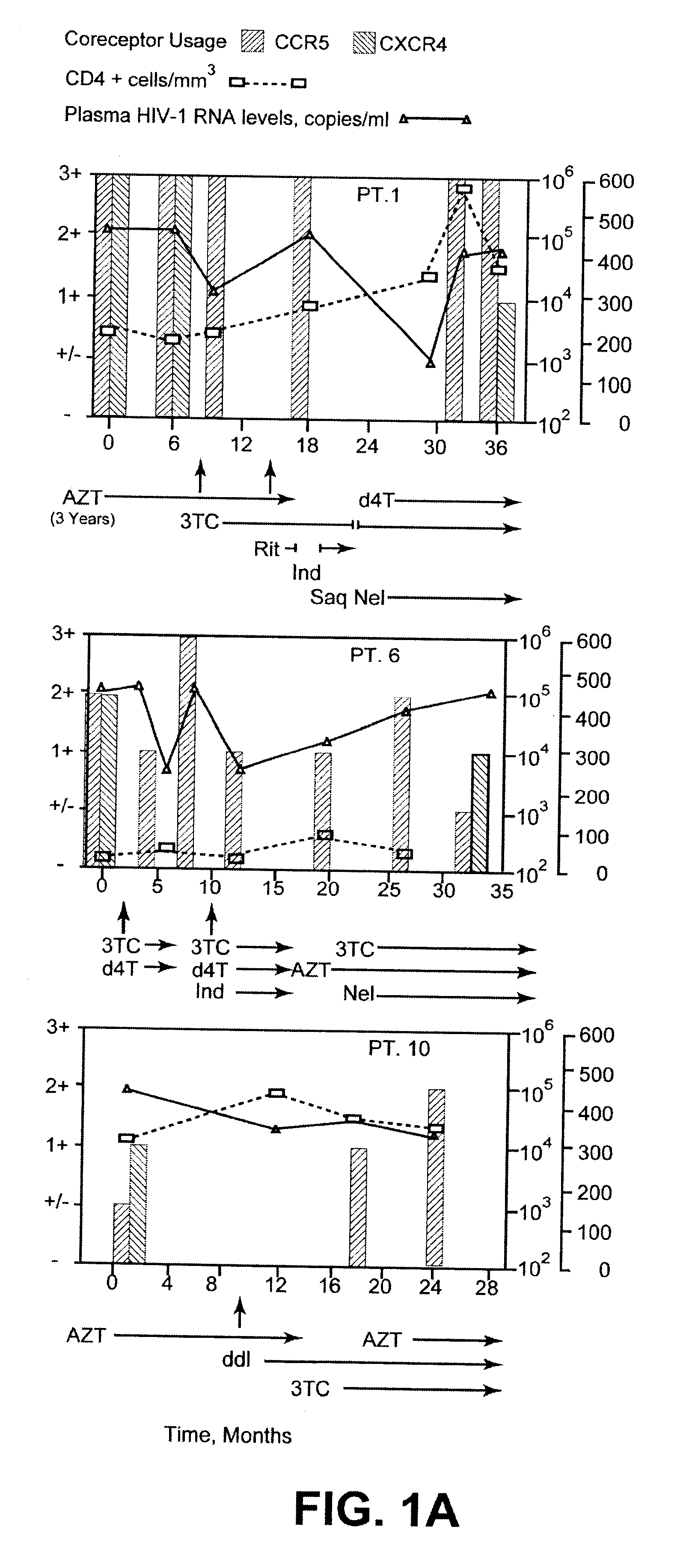
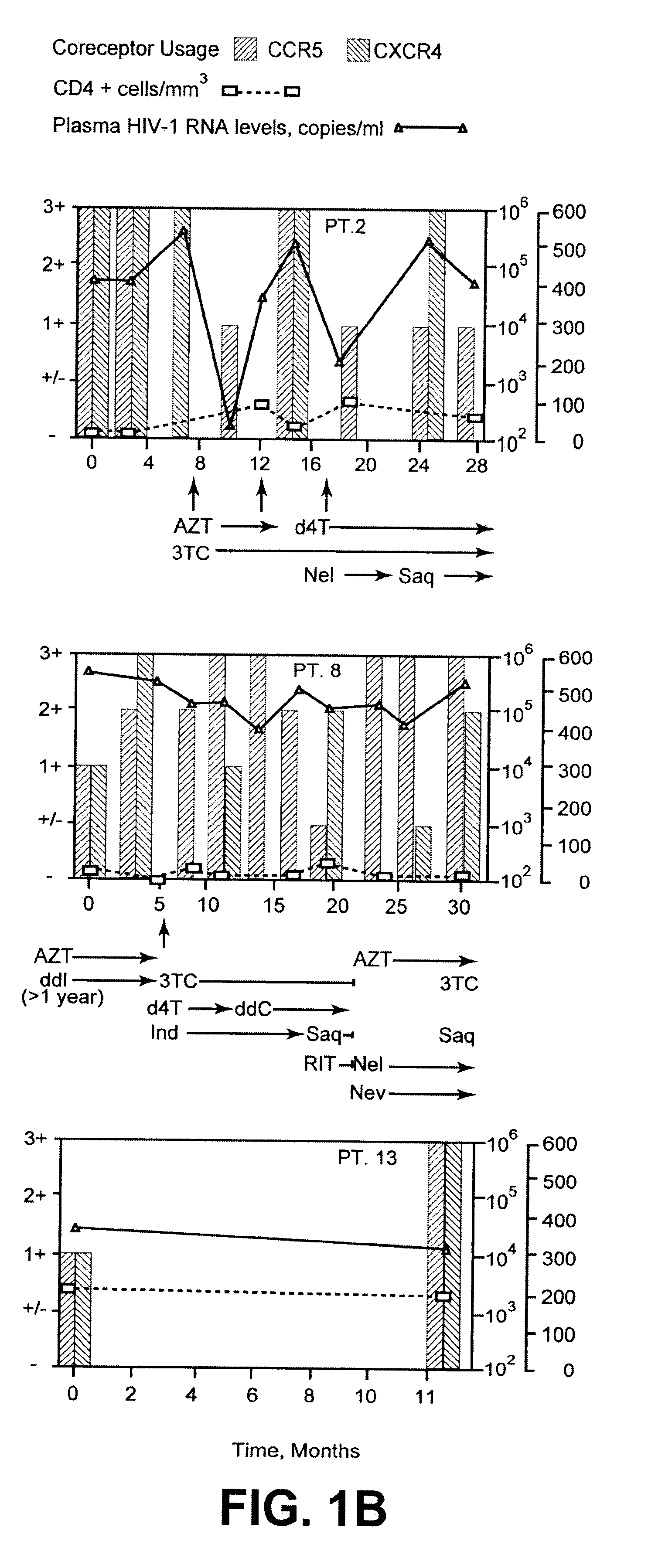
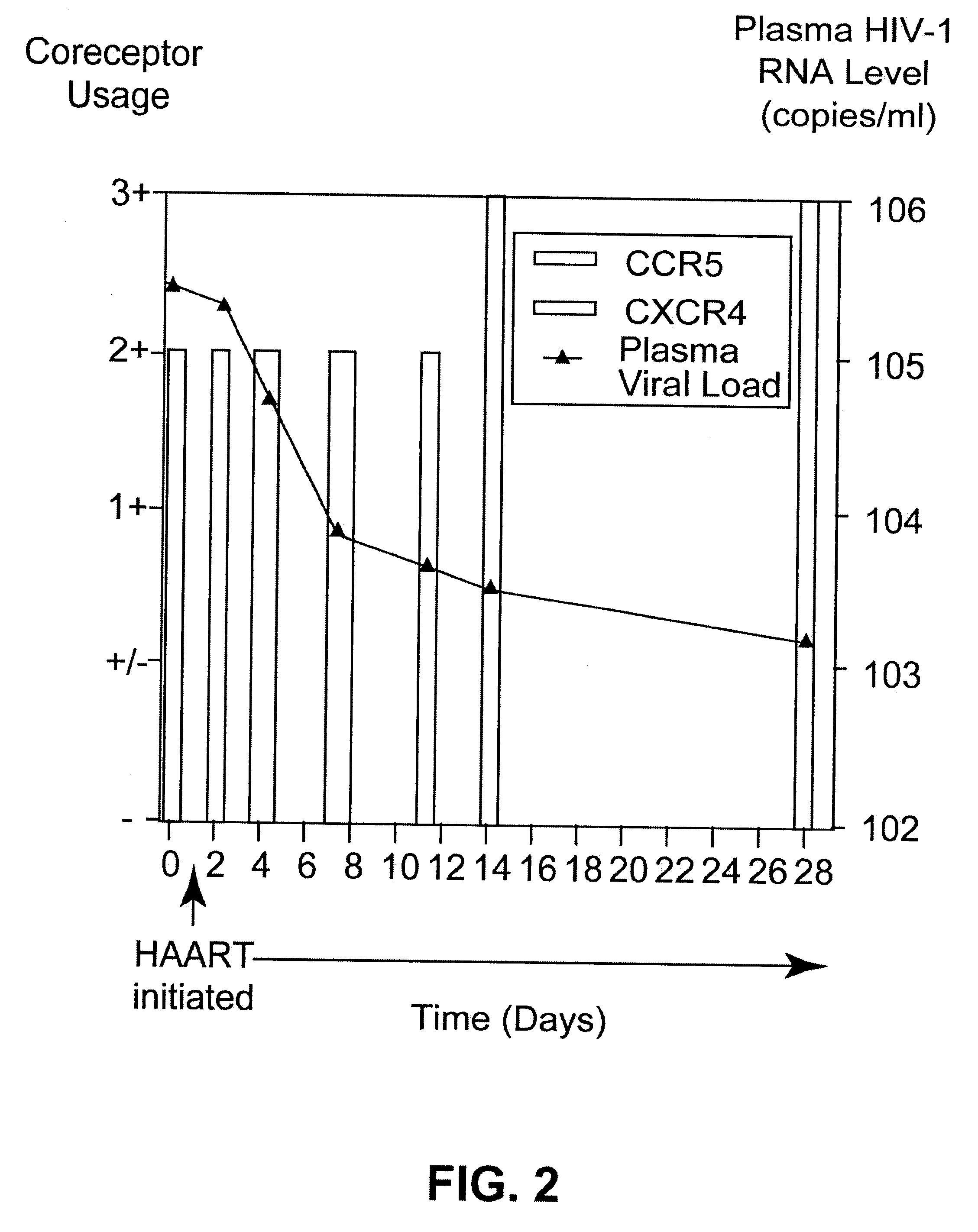
Analysis of HIV-1 coreceptor use in the clinical care of HIV-1-infected patients
InactiveUS6727060B2Accurate predictionMore effectivenessMicrobiological testing/measurementArtificial cell constructsImmunodeficiency virusHIV positives
A change in viral tropism occurs in many HIV positive individuals over time and can be indicated by a shift in coreceptor use from CCR5 to CXCR4. The shift in coreceptor use to CXCR4 has been shown to correlate with increased disease progression. In patients undergoing HAART, the predominant populations of virus can be shifted back to CCR5-mediated entry after the CXCR4-specific strains have emerged. The present invention relates to a diagnostic method to monitor coreceptor use in the treatment of human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection. The present invention further relates to a diagnostic method applied to HIV-positive individuals undergoing HAART to monitor the suppression of CXCR4 specific strains. The diagnostic methods can be used to assist in selecting antiretroviral therapy and to improve predictions of disease prognosis over time.
Owner:HEALTH RES INC
Human monoclonal antibody against coreceptors for human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS7005503B2Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsCXCR4Immunodeficiency virus
Compositions are provided that comprise antibody against coreceptors for human immunodeficiency virus such as CCR5 and CXCR4. In particular, monoclonal human antibodies against human CCR5 are provided that bind to CCR5 with high affinity and are capable of inhibiting HIV infection at low concentrations. The antibodies can be used as prophylactics or therapeutics to prevent and treat HIV infection, for screening drugs, and for diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with interactions with HIV coreceptors.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
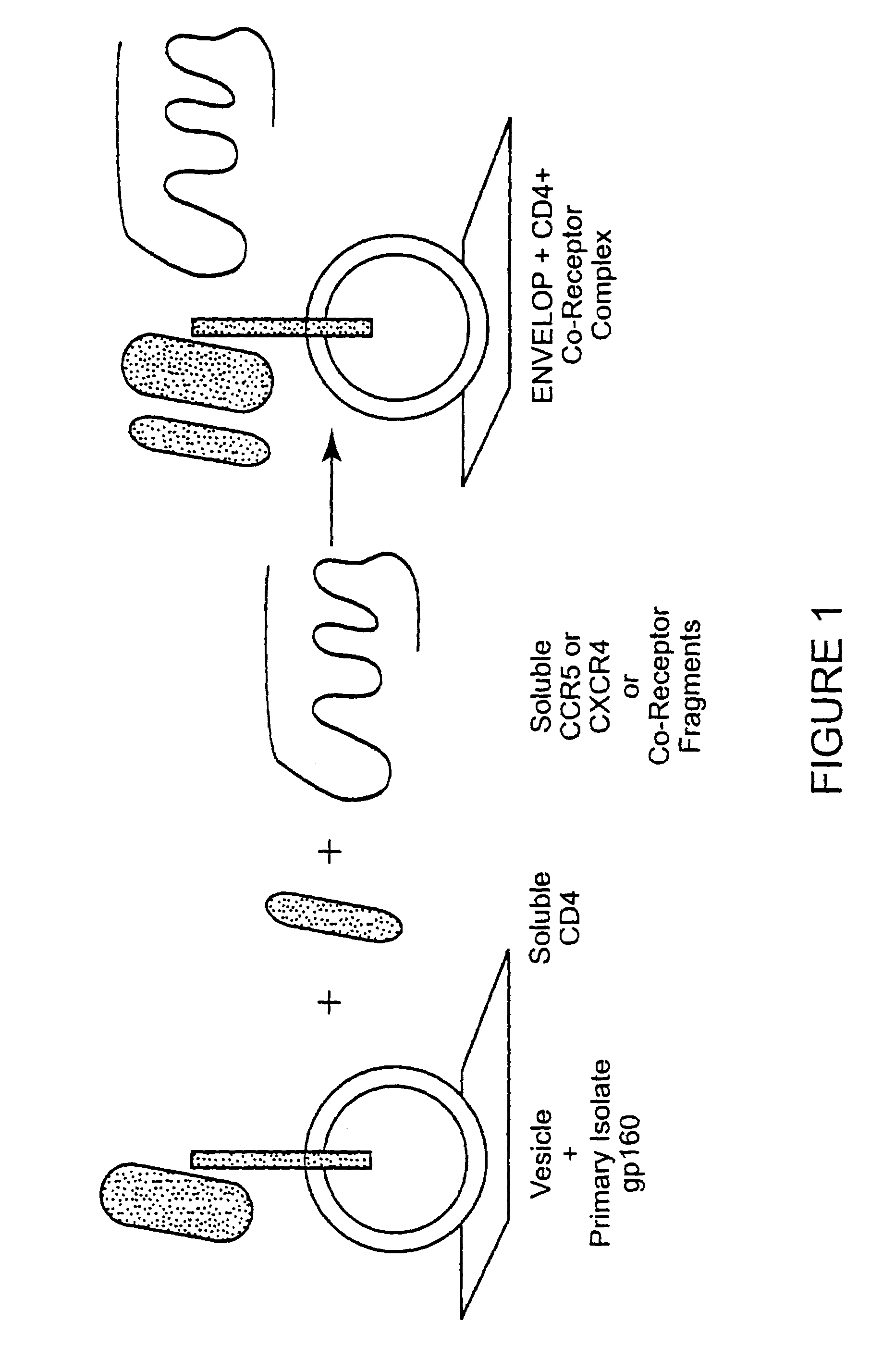
Broadly cross-reactive neutralizing antibodies against human immunodeficiency virus selected by Env-CD4-co-receptor complexes
InactiveUS7223844B2Increase exposurePeptide/protein ingredientsAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsAntibody fragmentsMammal
The present invention features antibodies and antibody fragments that specifically bind a CD4-inducible HIV gp120 epitope that is enhanced by binding a co-receptor for HIV, such as CCR5 or CXCR4, and pharmaceutical compositions comprising the antibodies or antibody fragments. The invention also features nucleic acids encoding the antibodies or antibody fragments, pharmaceutical compositions comprising the nucleic acids encoding the antibodies or antibody fragments, vectors comprising the nucleic acids, and cells comprising the vectors. The invention further features methods of identifying antibodies or antibody fragments with broadly neutralizing activity against HIV. The invention also features methods of inhibiting HIV entry into cells and methods of inhibiting replication of HIV in mammals, using the antibodies and nucleic acids of the invention.
Owner:THE SCRIPPS RES INST +1
Compositions for down-regulation of CCR5 expression and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20060154857A1Reduces receptor sitesSuppressing transcriptionBiocideAntiviralsG1/S checkpointHIV receptor
The present invention relates to the downregulation of surface receptor CCR5 expression through manipulation of the cell cycle in activated lymphocytes by administering a composition that arrests the G1 phase of the cell cycle, thereby reducing receptor sites for entry of HIV into T cells, and thus, the effects of HIV. Further, compositions are disclosed that include at least one G1 phase arresting agent and at least one antiviral agent, wherein the combination of agents synergistically enhances the activity of the antiviral agent.
Owner:UNIV OF MARYLAND
Dual vector for inhibition of human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS20160243169A1Organic active ingredientsPeptide/protein ingredientsCXCR4Immunodeficiency virus
The present invention provides an expression vector for preventing or inhibiting HIV entry, fusion or replication in mammalian cells. In particular, the invention provides a recombinant retroviral vector that encodes an inhibitor of a HIV co-receptor, such as CCR5 or CXCR4, and a protein that inhibits HIV fusion to target cells and / or HIV replication. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising such constructs and methods of use thereof to prevent or treat HIV infection in a patient are also disclosed.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA +1
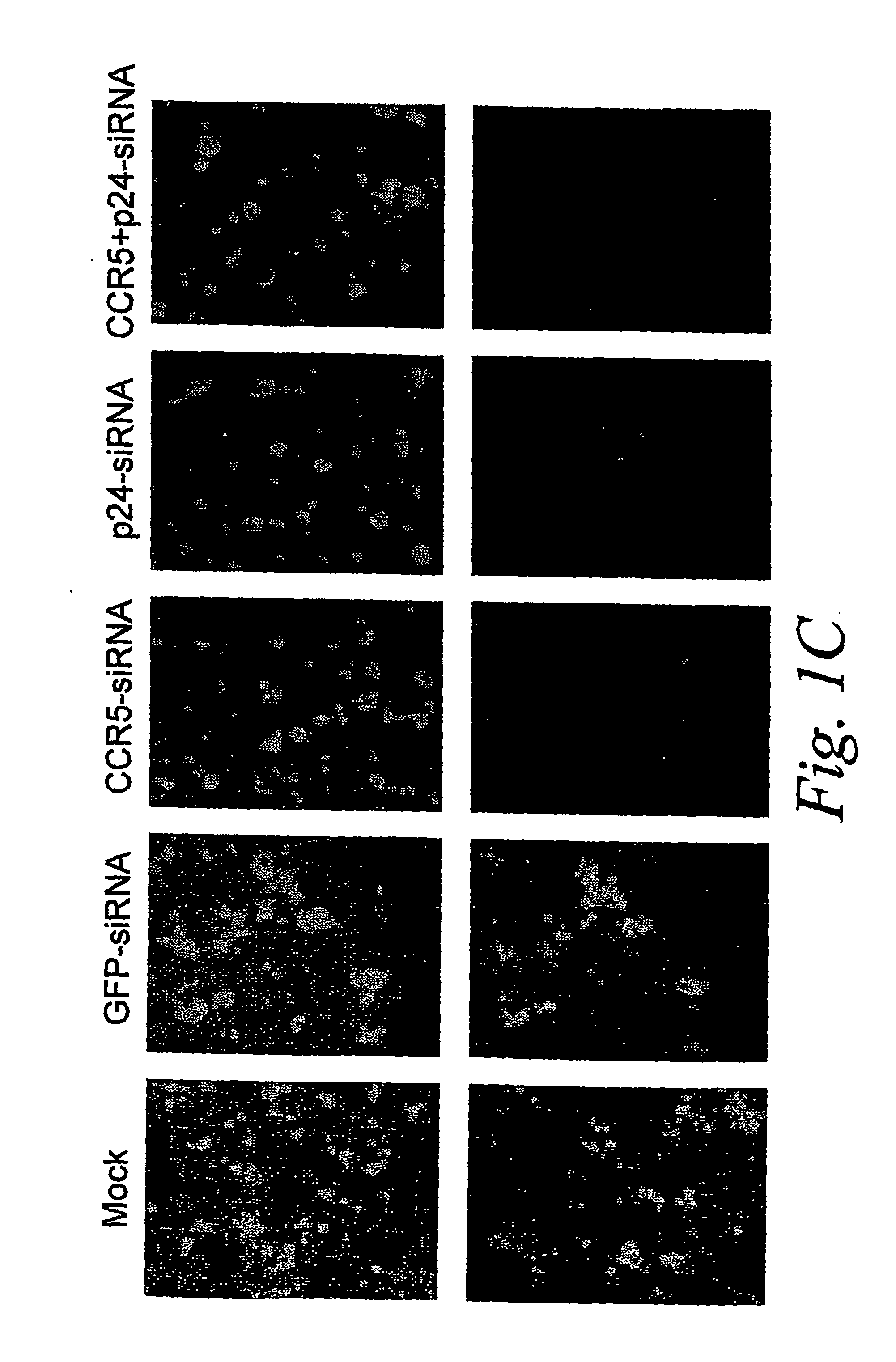
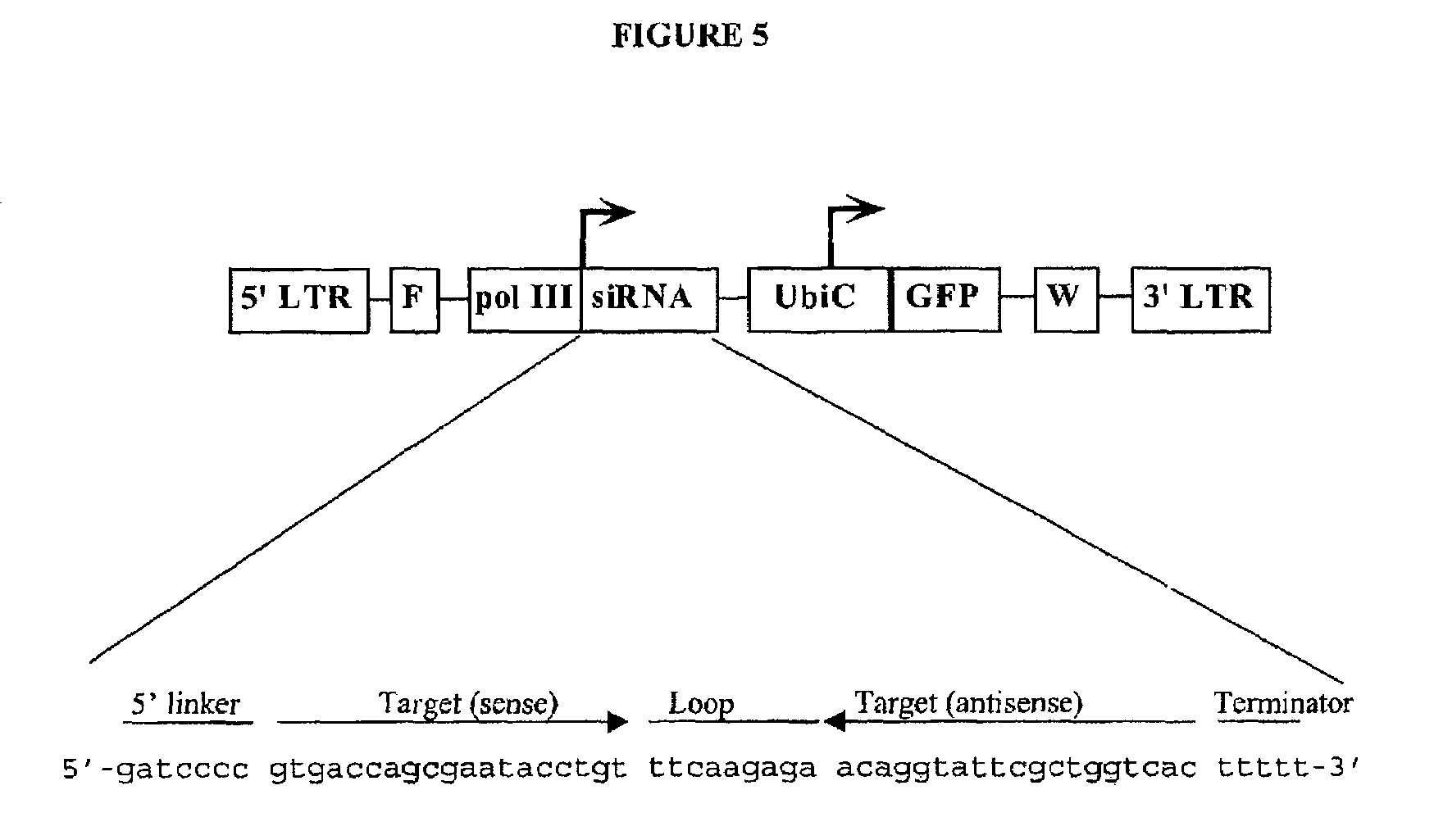
Inhibition of gene expression using rna interfering agents
ActiveUS20060293262A1Peptide/protein ingredientsGenetic material ingredientsPrevention infectionInfectious Disorder
The present invention is based, at least in part, on the discovery of compositions and methods for the treatment and prevention of infectious diseases or disorders, e.g., HIV infection, AIDS, and AIDS-related diseases. In particular, the present invention pertains to methods of modulating cellular gene expression or protein activity, e.g., CCR5, gene expression or protein activity and / or gene expression or protein activity of a gene or sequence of an infectious agent, in order to treat or prevent infectious diseases or disorders, HIV infection, AIDS, or an AIDS-related disease or disorder. In one embodiment the combination of an RNA interfering agent targeting a cellular gene in combination with an RNA interfering agent targeting a gene or sequence of an infectious agent results in prolonged prevention of infection by an infectious agent The present invention is based on the identification of novel RNA interference agents, e.g., siRNA molecules, which target cellular genes, e.g., chemokine receptors, e.g., the CCR5 gene, and result in inhibition of target gene expression on target gene expressing cells, thereby inhibiting entry of infectious agents, e,g., HIV infection into target cells, prevention infection, and / or suppressing replication in established infection.
Owner:IMMUNE DISEASE INST INC
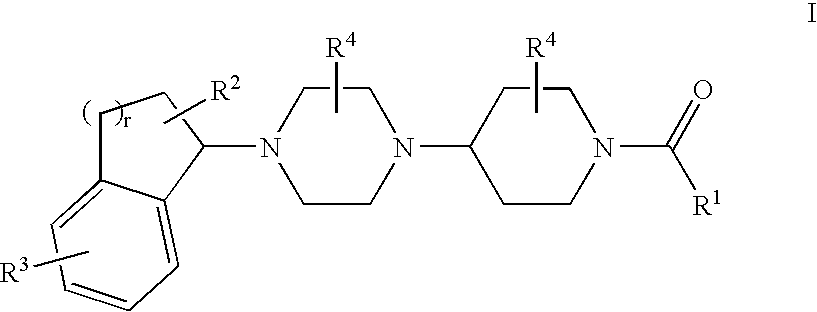
Heterocyclic antiviral compounds
InactiveUS20060014767A1Useful in treatmentBiocideOrganic active ingredientsChemokine Receptor AntagonistImmunodeficiency virus
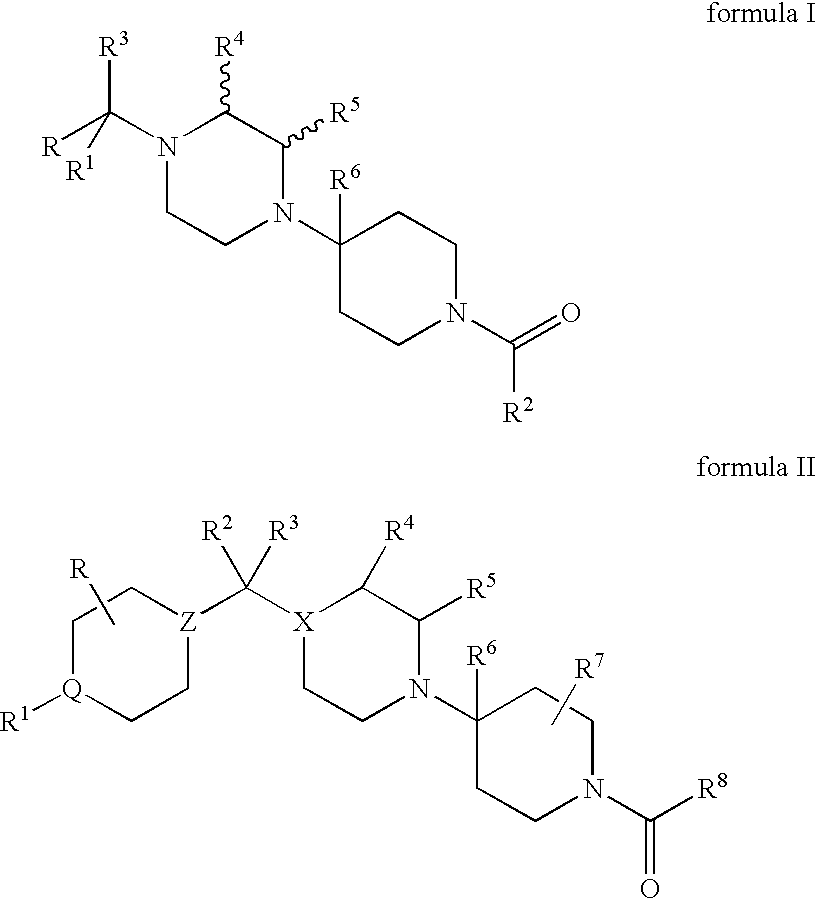
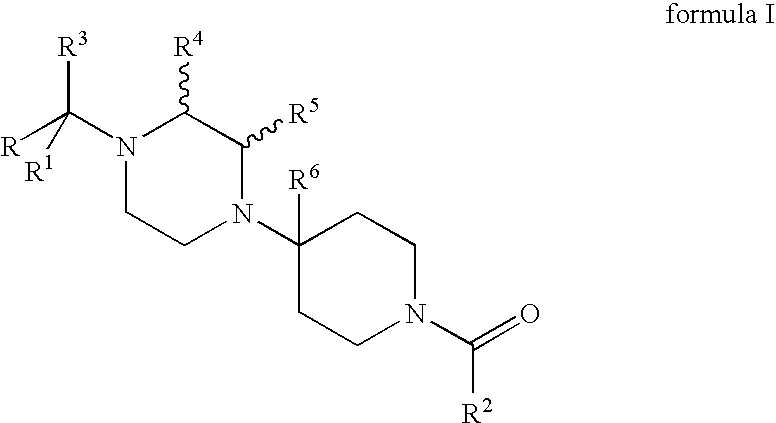
Chemokine receptor antagonists, in particular, 3,7-diazabicyclo[3.3.0]octane compounds according to formula (I) are antagonists of chemokine CCR5 receptors which are useful for treating or preventing an human immunodeficiency virus (HIV) infection, or treating AIDS or ARC. The invention further provides methods for treating diseases that are allieviated with CCR5 antagonists. The invention includes pharmaceutical compositions and methods of using the compounds for the treatment of these diseases. The invention further includes processes for the preparation of compounds according to formula I.
Owner:ROCHE PALO ALTO LLC
Human monoclonal antibody against coreceptors for human immunodeficiency virus
InactiveUS20030152913A1Microbiological testing/measurementImmunoglobulins against virusesCXCR4Immunodeficiency virus
Compositions are provided that comprise antibody against coreceptors for human immunodeficiency virus such as CCR5 and CXCR4. In particular, monoclonal human antibodies against human CCR5 are provided that bind to CCR5 with high affinity and are capable of inhibiting HIV infection at low concentrations. The antibodies can be used as prophylactics or therapeutics to prevent and treat HIV infection, for screening drugs, and for diagnosing diseases or conditions associated with interactions with HIV coreceptors.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Piperazinylpiperidine derivatives as chemokine receptor antagonists
ActiveUS20050261310A1Improve actionReduce releaseSilicon organic compoundsOrganic active ingredientsChemokine Receptor AntagonistHIV receptor
The present invention relates to compounds of Formula I: wherein variable substituents are defined herein, that modulate the activity of or bind to chemokine receptors such as CCR5. In some embodiments, the compounds of the invention are selective for CCR5. The compounds can be used, for example, to treat diseases associated with chemokine receptor expression or activity such as inflammatory diseases, immune diseases and viral infections.
Owner:INCYTE HLDG CORP
Immunogen comprising an HIV envelope protein, a ligand and H2 peptide
The invention relates to an immunogen comprising an HIV envelope protein bound to a ligand, which ligand upregulates at least one of the CD4 binding site and the CCR5 binding site on the protein, and bound to an HR-2 peptide. The invention also relates to a method of inducing anti-HIV antibodies using such an immunogen.
Owner:DUKE UNIV
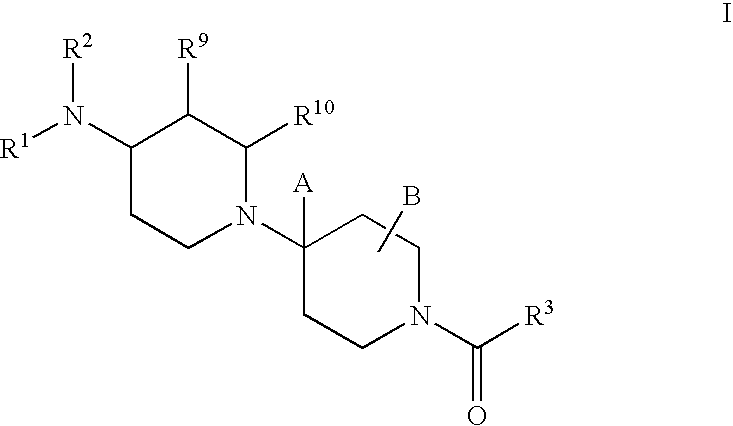
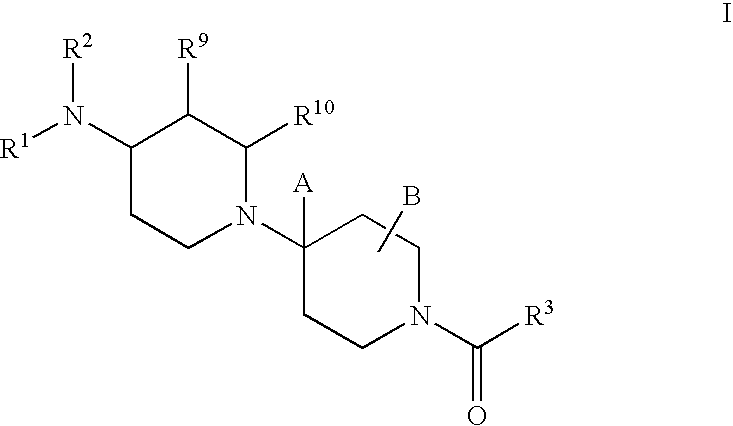
Piperidine derivatives useful as CCR5 antagonists
The present invention provides a compound of the formula or a pharmaceutically acceptable salt or solvate thereof, wherein R<1>, R<2>, R<3>, R<9>, R<10>, A and B are as defined in the specification. The present invention also provides pharmaceutical compositions containing the compound of this invention, and methods of treatment using the compound of this invention. The invention also relates to the use of a combination of a compound of this invention and one or more antiviral or other agents useful in the treatment of Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV). The invention further relates to the use of a compound of this invention, alone or in combination with another agent, in the treatment of solid organ transplant rejection, graft v. host disease, arthritis, rheumatoid arthritis, inflammatory bowel disease, atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, asthma, allergies or multiple sclerosis.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Combination therapy for treating viral infections
A method of treating viral infections, particularly Hepatitis B (HBV) and Human Immunodeficiency Virus (HIV) infections, by administering Elvucitabine and a second active agent to a patient suffering viral infection is provided herein. The second active agent is, for example, an immunomodulatory compound, an anti-viral agent, or a combination comprising one or more of the foregoing active agents. For example the anti-viral agent may be a tyrosine kinase inhibitor, a CCR5 inhibitor, a non-nucleoside reverse transcriptase inhibitor, a protease inhibitor, an integrase inhibitor. Further provided herein are combination dosage forms comprising Elvucitabine and a second active agent. The combination dosage may be administered once per day. The Elvucitabine may be administered less frequently than the second active agent. Packaged pharmaceutical compositions comprising Elvucitabine, a second active agent, and instructions for using the composition for treating a viral infection by administering Elvucitabine and the second active agent are also provided.
Owner:ACHILLION PHARMA INC
Method for expression of small antiviral RNA molecules with reduced cytotoxicity within a cell
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Molecules and Methods of Using Same for Treating CCR5/CCR5 Ligands Associated Diseases
Soluble molecules are provided. Thus, for example, provided is a soluble molecule which comprises a heterologous amino acid sequence conjugated to a CCR5 amino acid sequence being capable of binding a CCR5 ligand, and wherein the molecule is devoid of an N-terminus domain of CCR5. Also provided are pharmaceutical compositions which comprise the above molecules and methods and uses of same.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD
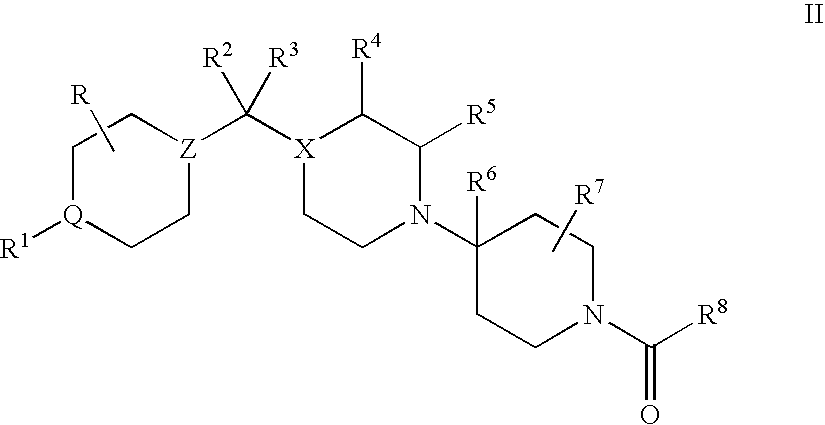
Compositions comprising a combination of CCR5 and CXCR4 antagonists
A composition including a CXCR4 antagonist and a CCR5 antagonist represented by formula I or II: or an acceptable salt, solvate or ester thereof. The CXCR4 antagonist includes at least one of AMD-070, CS-3955, KRH-1120, KRH-2731, and KRH-1636.
Owner:SCHERING CORP
Modified erythrocytes and uses thereof
InactiveUS20070082392A1Genetically modified cellsArtificial cell constructsRed cell acanthocytosisHIV receptor
The present invention provides modified erythrocytes which comprise viral receptor proteins capable of mediating entry of respective viruses into the modified erythrocytes. The present invention also provides methods of using the modified erythrocytes for the treatment or prevention of viral infections. In one embodiment, the modified erythrocytes of the present invention comprise CD4 and at least one HIV coreceptor, such as CXCR4 or CCR5. The modified erythrocytes, when administered to an HIV patient, bind to the plasma virus and induce the injection of the HIV ribonucleoprotein complex into the cells. The entrapped viral content is either degraded or deactivated within the erythrocytes, or destroyed by erythrophagocytosis.
Owner:GLASER LAWRENCE F
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com