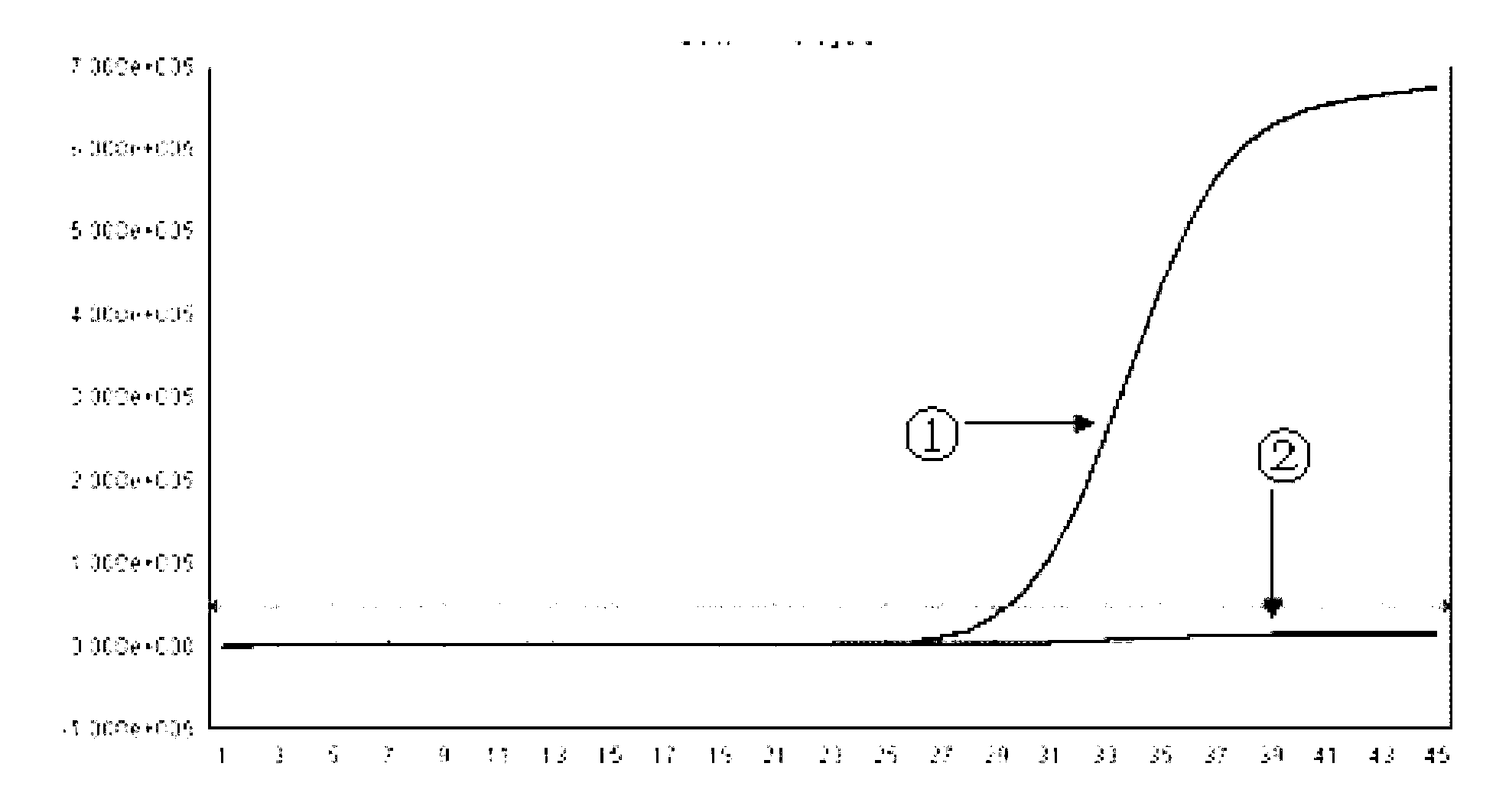
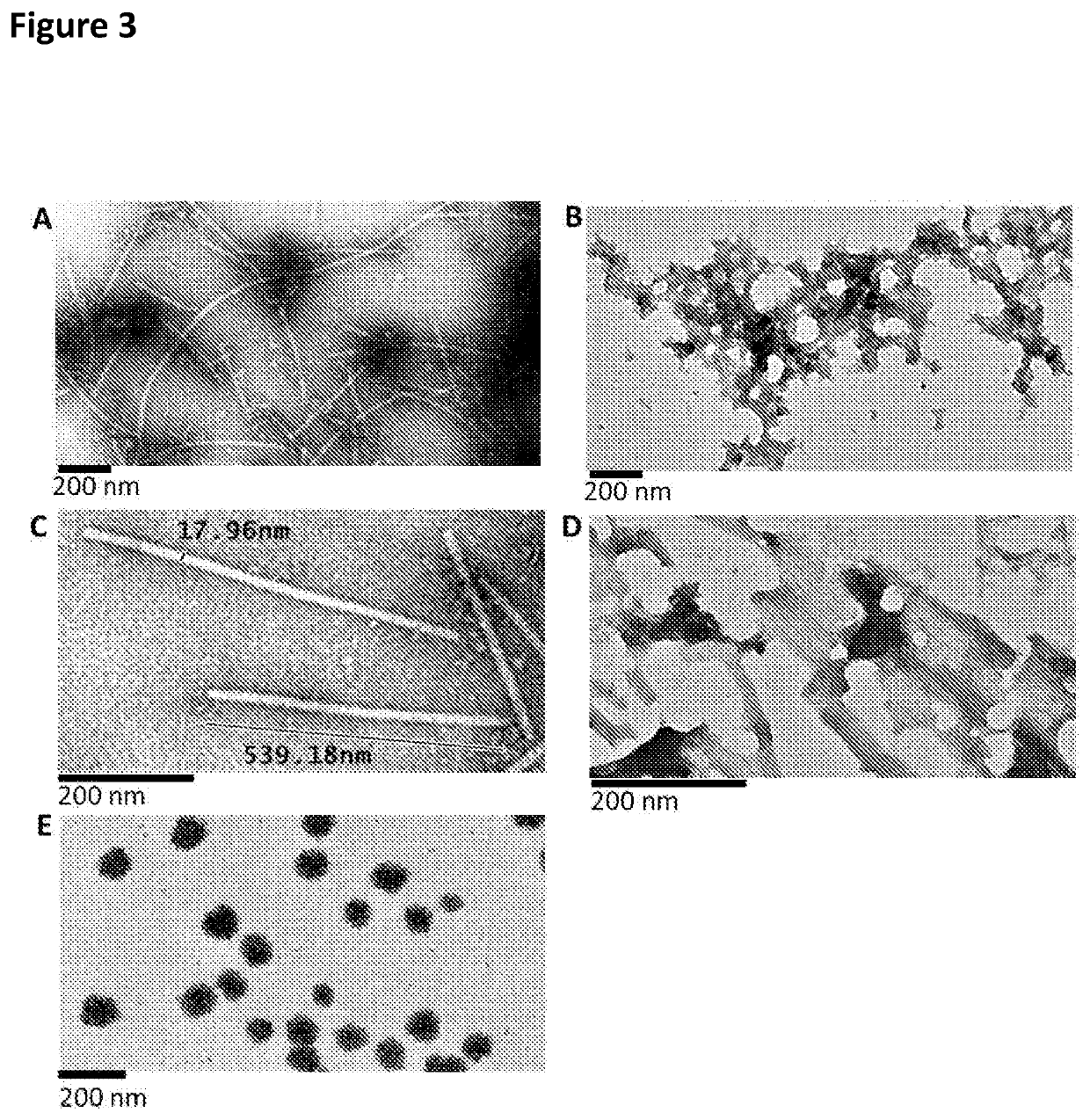
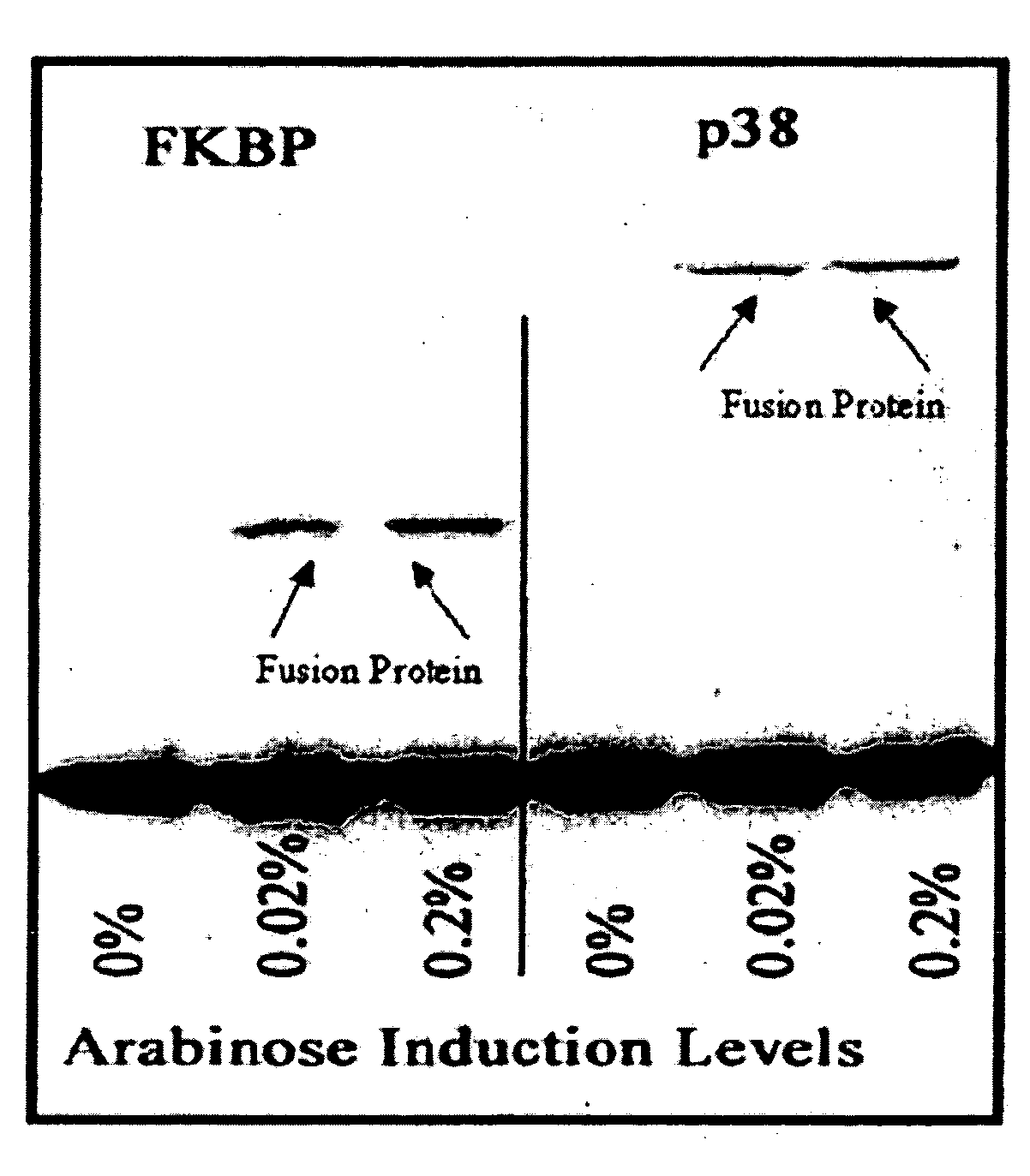
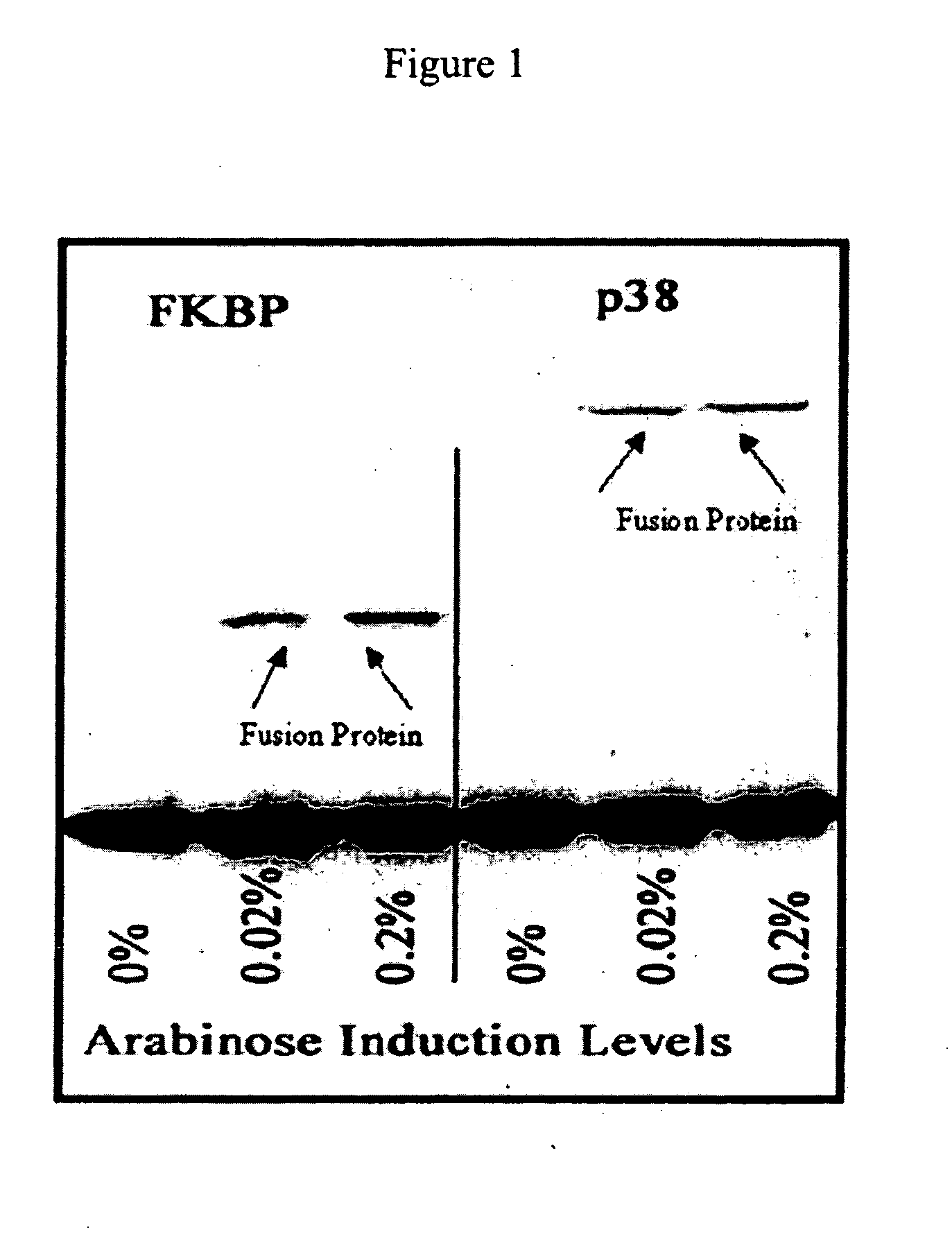
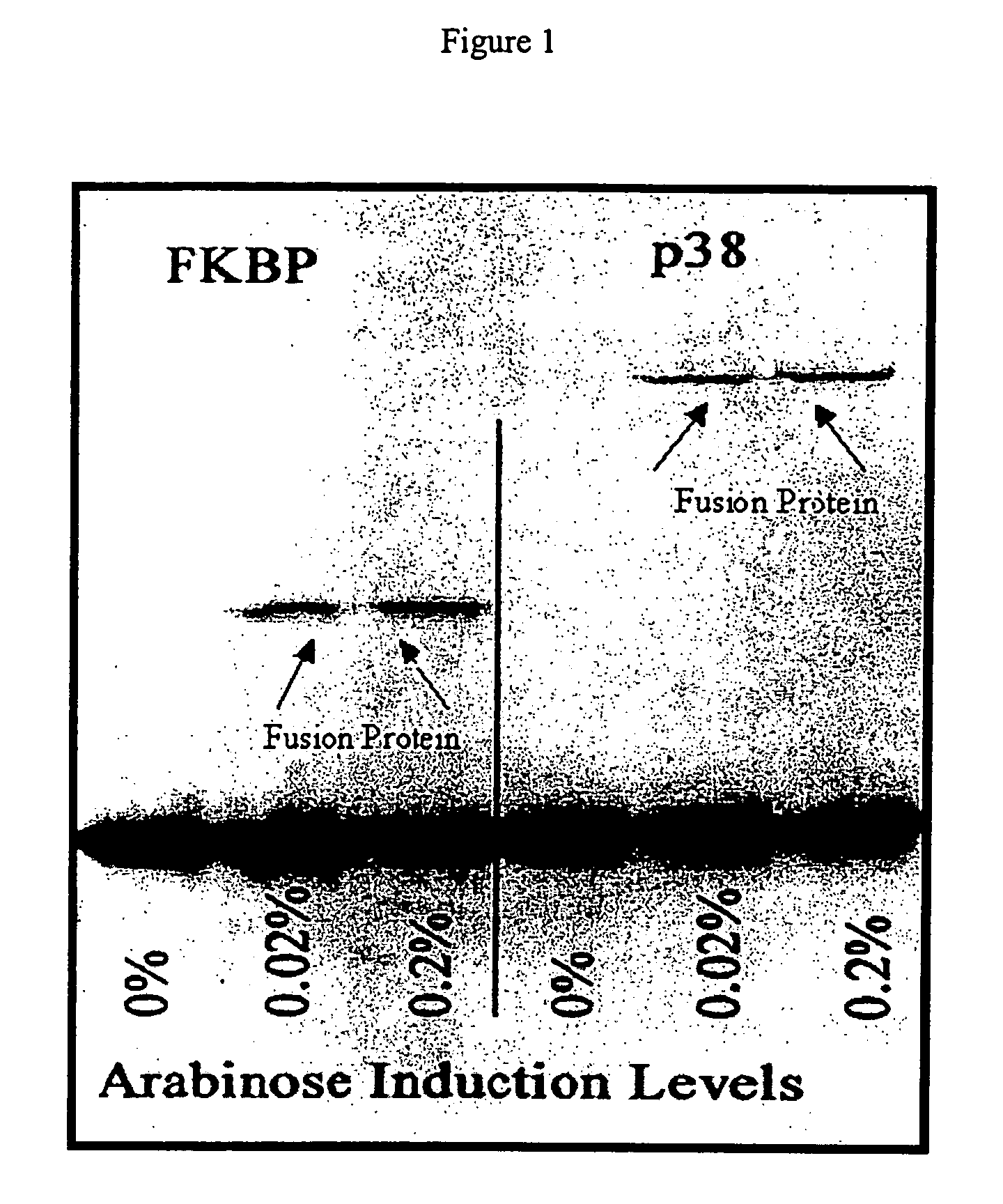
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89 results about "Coat Proteins" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Coat protein may refer to: Viral coat protein , a component of the capsid Variable surface glycoproteins or procyclins , surface coat proteins of either the bloodstream form or the procyclic form of the parasite Trypanosoma brucei
Modified plant virus particles and uses therefor
InactiveUS20120015899A1Broadening arrayEasy to assembleFusion with RNA-binding domainBiocideVirus-like particleCoat Proteins
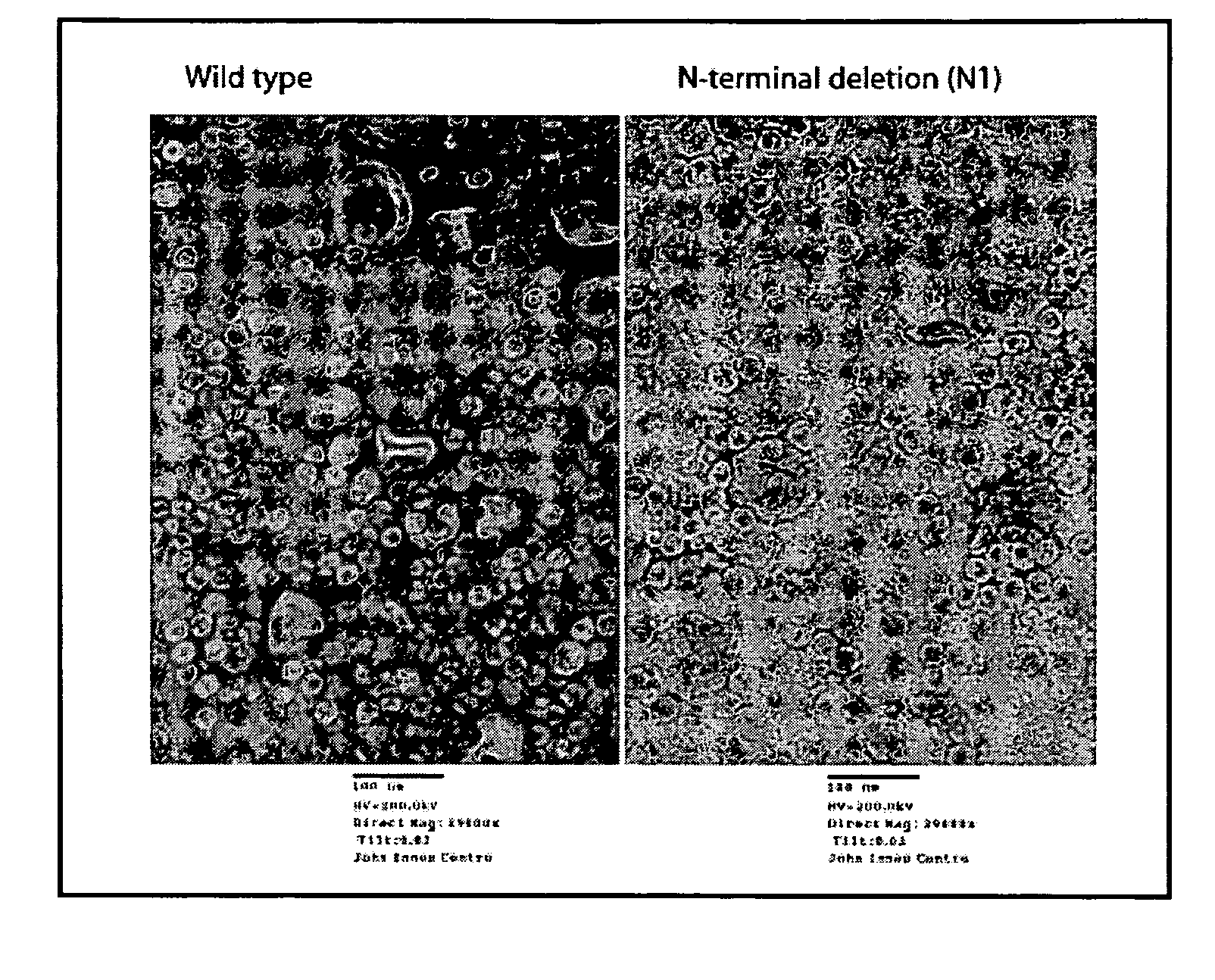
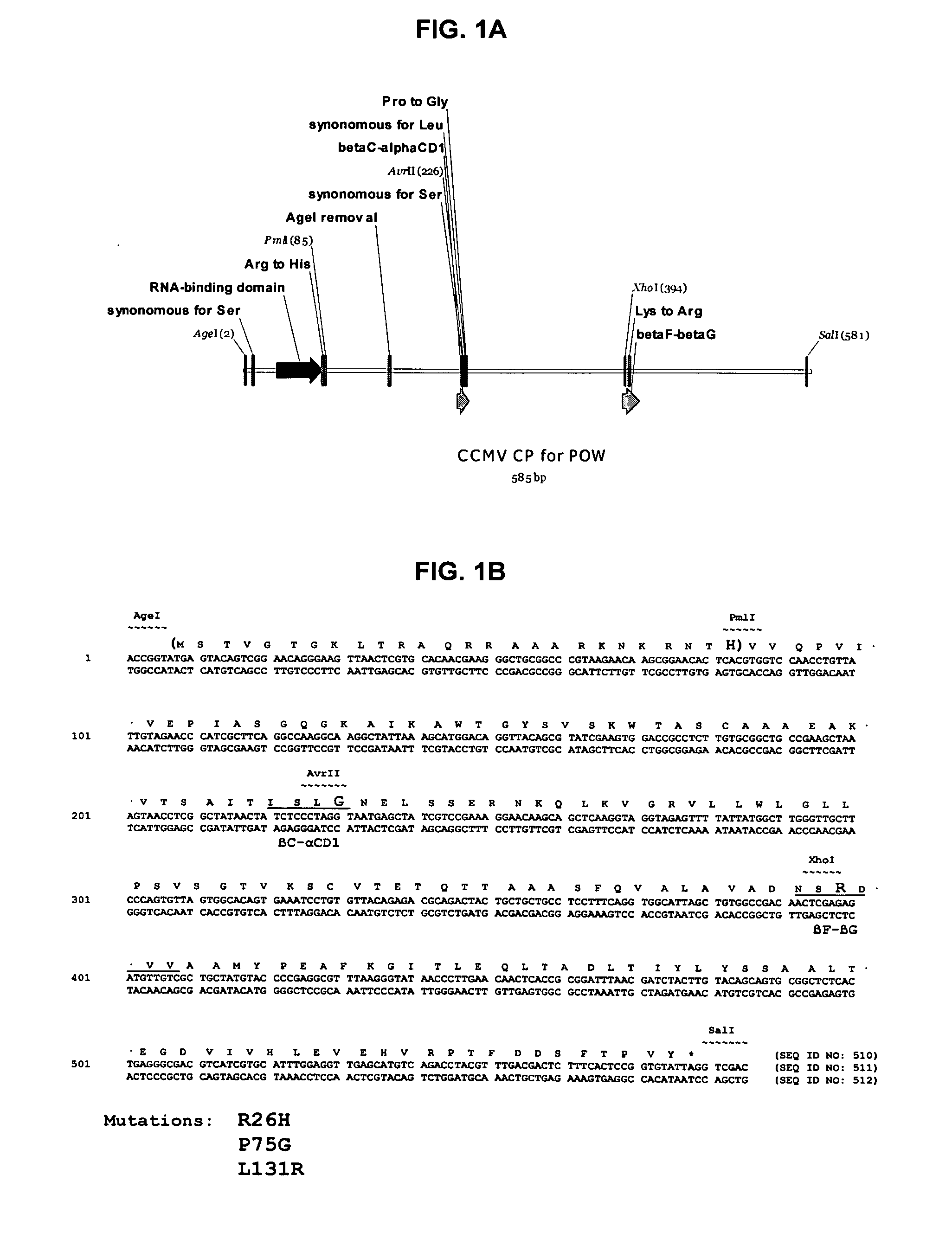
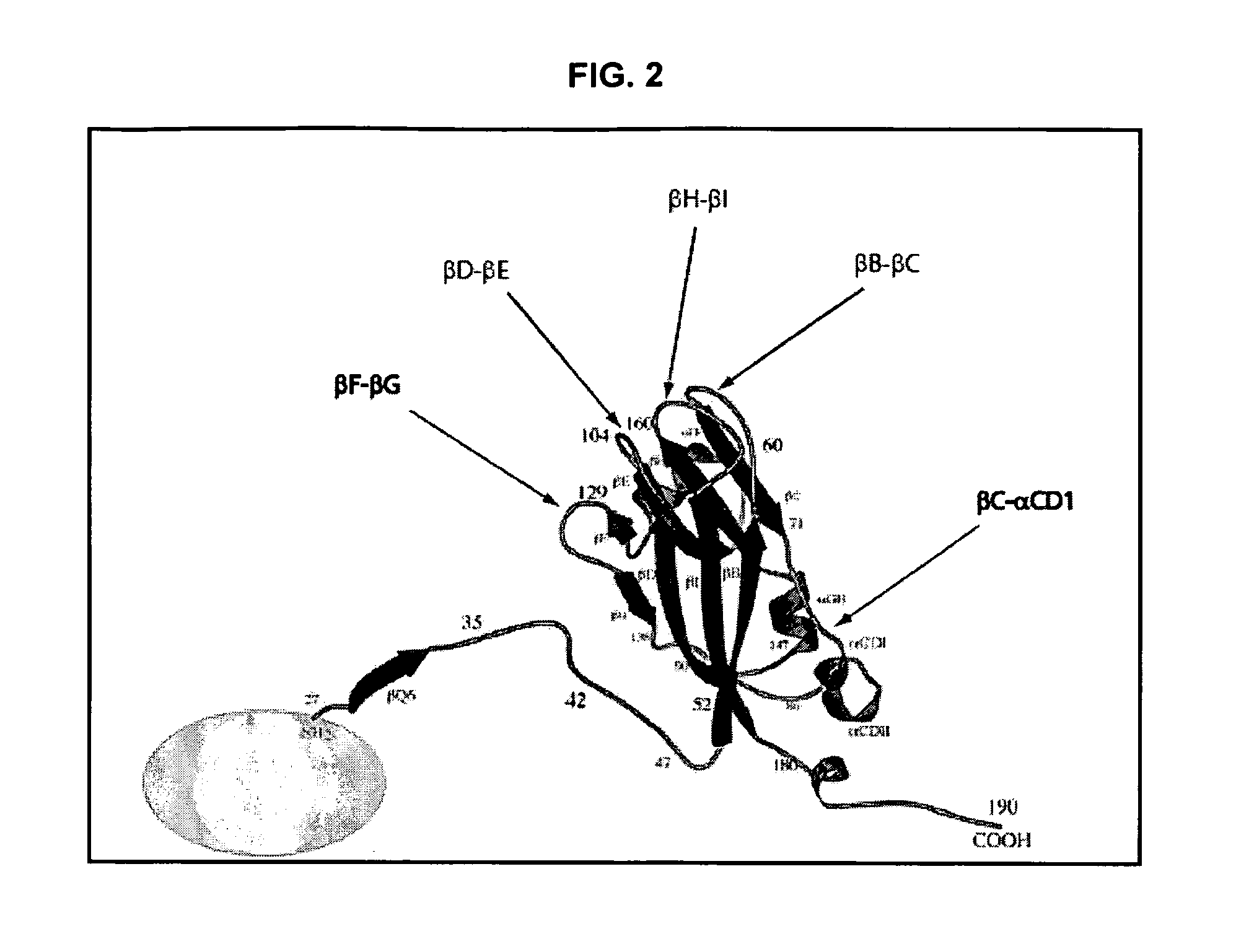
Aspects of the invention provide modified virus-like particles that are designed for therapeutic applications. In particular, aspects of the invention provide CCMV coat proteins that are modified to generate virus-like particles, including mosaic virus-like particles, that can package and / or deliver one or more diagnostic and / or therapeutic agents. The invention also provides methods for treating subjects with one or more modified virus-like particles.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD +1
Virus coat protein/receptor chimeras and methods of use
InactiveUS7311920B1Sufficient amountMethod can be usedCompound screeningApoptosis detectionCXCR4Immunodeficiency virus
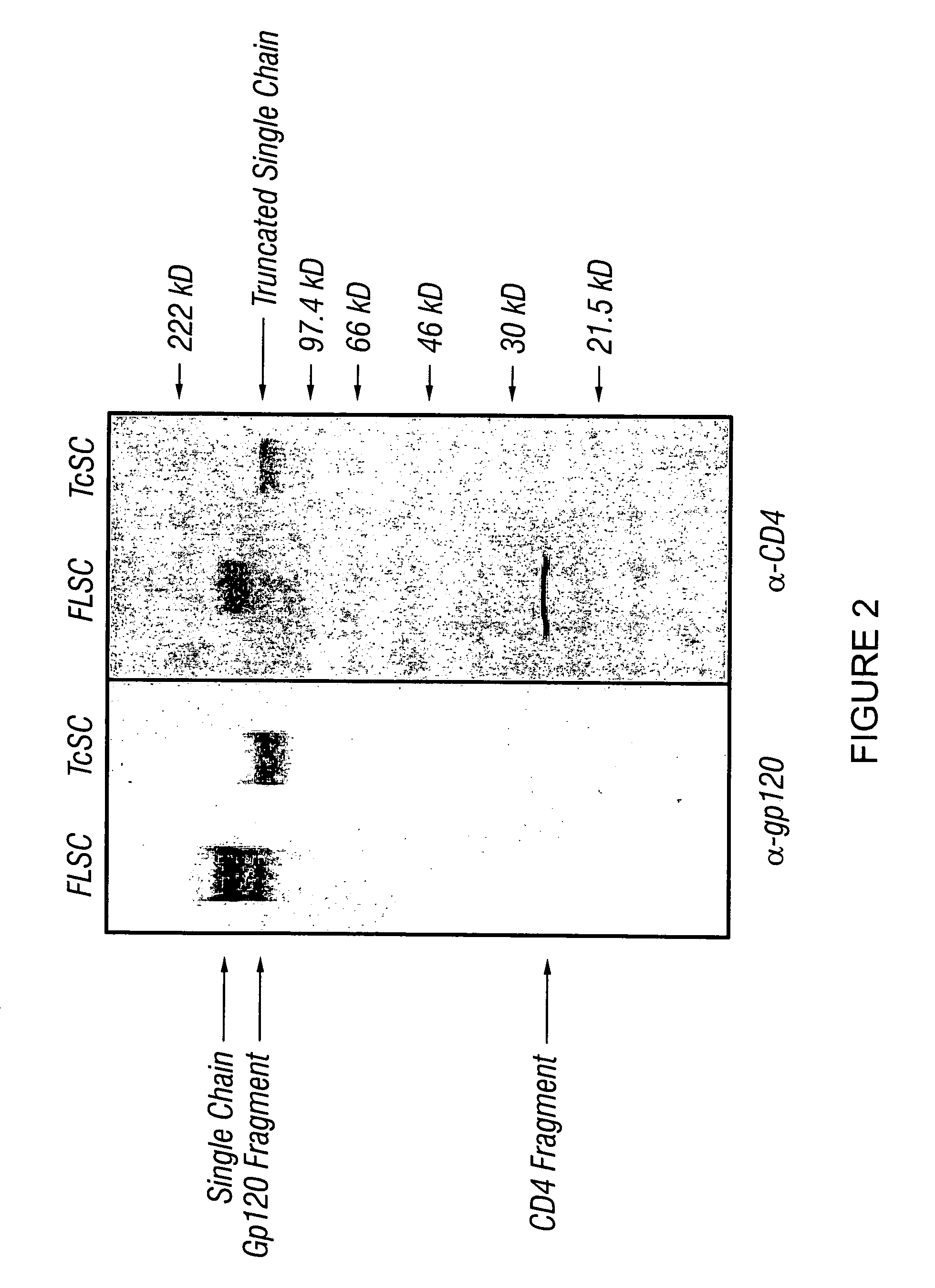
The invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising a virus coat sequence and a receptor sequence that can interact with each other to form a complex that is capable of binding a co-receptor. Such chimeric molecules therefore exhibit functional properties characteristic of a receptor-coat protein complex and are useful as agents that inhibit virus infection of cells due to occupancy of co-receptor present on the cell, for example. In particular aspects, the chimeric polypeptide includes an immunodeficiency virus envelope polypeptide, such as that of HIV, SIV, FIV, FeLV, FPV and herpes virus. Receptor sequences suitable for use in a chimeric polypeptide include, for example, CCR5 and CXCR4 sequences.
Owner:MARYLAND BIOTECH INST UNIV OF
Human papillomavirus shell protein L1 short peptide and application thereof
InactiveCN101186636ASerum immunoglobulinsImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAlphapapillomavirusCoat protein
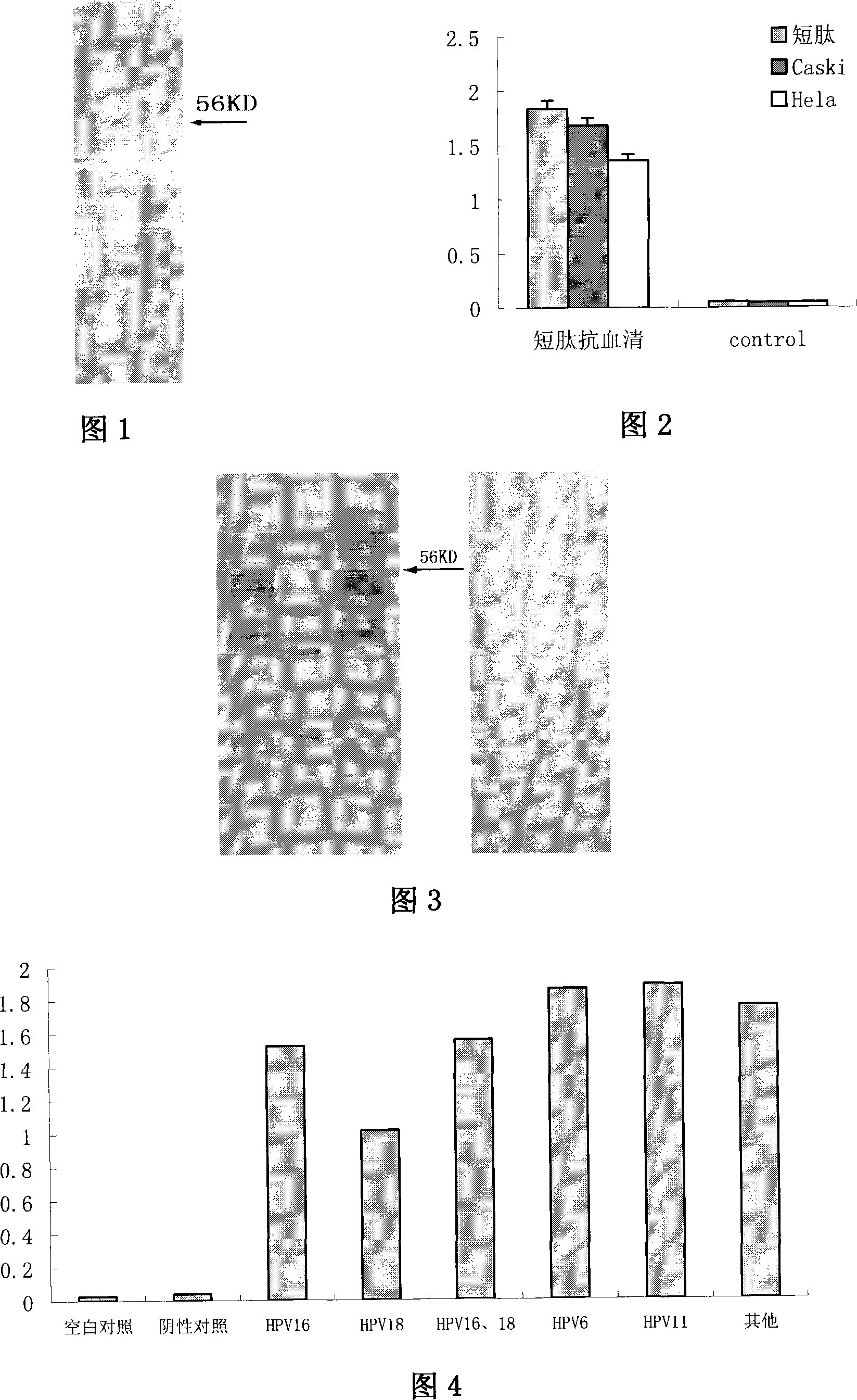
The invention relates to a polypeptide, in particular to a human papilloma virus coat protein L1 short peptide and relative application. The invention is characterized in that the sequence of the human papilloma virus coat protein L1 short peptide is N-EVNLKEKFSADLDQFPLGRKFLLQAGLKAK-C. The invention can simultaneously induce human papilloma virus coat protein L1 short peptide with immunity reaction on high risk type and low risk type, which can induce and form the antibody for various human papilloma virus (HPV) and coat protein (HPV L1), to check various HPV or HPV L1, while the antibody can be used in biological pharmaceutical engineering, to purify and prepare various HPV or HPV L1.
Owner:CHINA THREE GORGES UNIV
Virus coat protein/receptor chimeras and methods of use
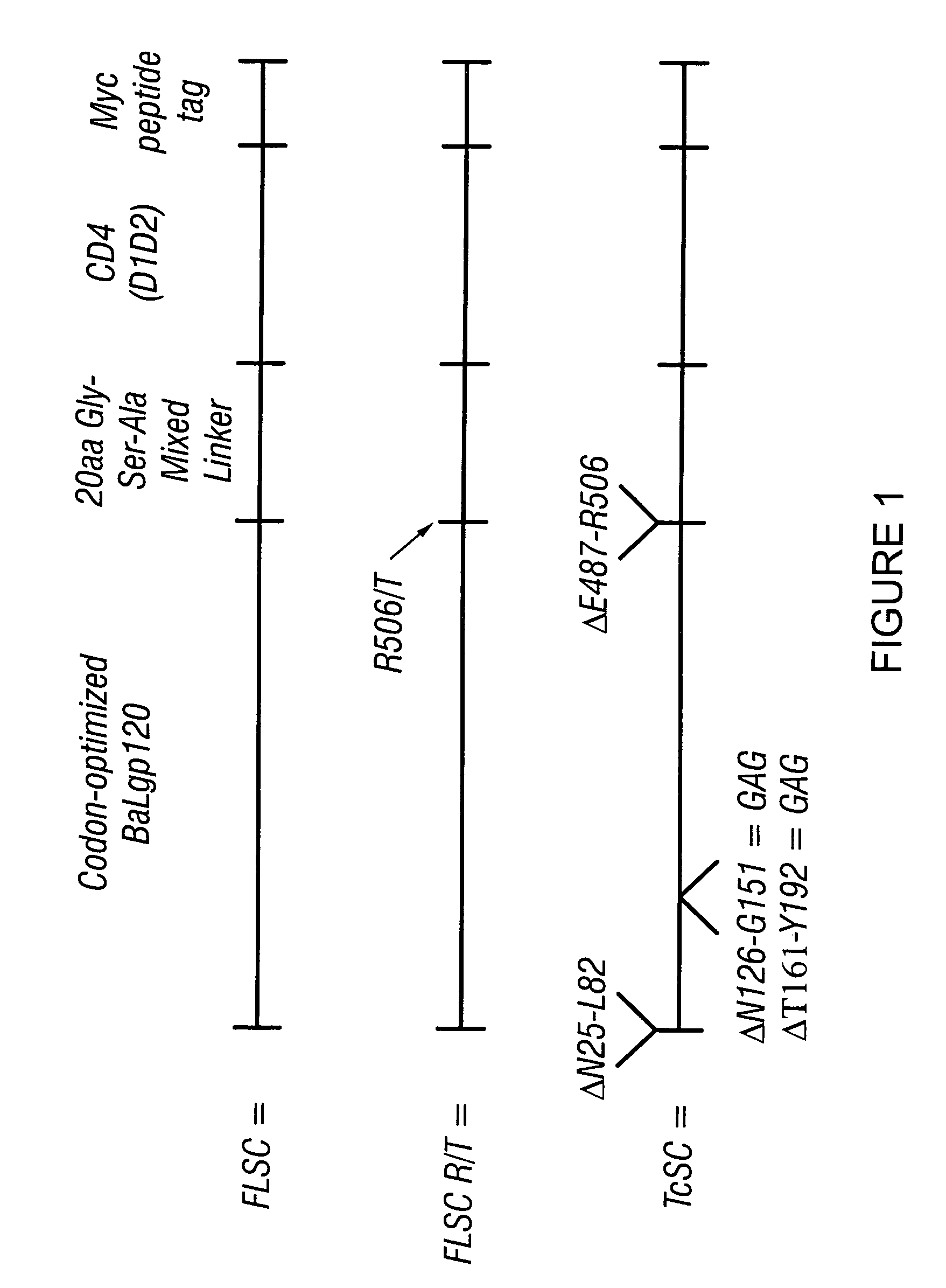
The invention relates to chimeric molecules comprising a virus coat sequence and a receptor sequence that can inter-act with each other to form a complex that is capable of binding a co-receptor. Such chimeric molecules therefore exhibit functional properties characteristic of a receptor-coat protein complex and are useful as agents that inhibit virus infection of cells due to occupancy of a co-receptor present on the cell. In particular aspects, the chimeric polypeptide includes an immunodeficiency virus envelope polypeptide, such as that of HIV, SIV, FIV, FeLV, FPV and herpes virus. Receptor sequences suitable for use in a chimeric polypeptide include, for example, CD4 D1D2 and CD4M9 sequences.
Owner:MARYLAND UNIV OF BIOTECH INST
Organism degradable star-type structure poly (glycolide-lactide) medicine carrier microsphere and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1927906AImprove poor wrapping abilityImprove drug loading and embedding efficiencyPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsLong actingDrug
The present invention relates to one kind of biodegradable medicine-carrying polyglycolide-lactide microsphere in star structure and its preparation process. The biodegradable medicine-carrying polyglycolide-lactide microsphere has coating material of star polyglycolide-lactide, coated protein polypeptide medicine of bovine serum albumin or leuteinizing hormone-releasing homone (LH-RH) analog, medicine carrying amount of 17.56-67.51 mcg / mg microsphere and embedding rate of 28.68-78.39 wt%. It is prepared through a W / O / W composite emulsifying process to coat protein polypeptide medicine into star polyglycolide-lactide to form microsphere. Compared with linear medicine-carrying polyglycolide-lactide microsphere, the present invention has obviously increased medicine carrying amount and embedding rate and obvious long-acting and slowly releasing effect.
Owner:NANKAI UNIV
System For Expression of Genes In Plants
ActiveUS20080241931A1Facilitates systemic spreadReducing and eliminating riskSsRNA viruses positive-senseOther foreign material introduction processesBiotechnologyPlant virus
The present invention provides trans-complementation systems for expressing gene products in plants. In general, the invention provides systems including a carrier vector and a producer vector, both based on plant viruses. The producer vector is defective for at least one function needed for successful systemic infection of a plant, e.g., replication, cell-to-cell movement, or long distance movement. The carrier vector supplies the missing function in trans. Certain producer vectors lack a functional coat protein coding sequence, in which case the corresponding producer vector supplies coat protein in trans. The invention also provides novel plant viral vectors and methods of use, e.g., to produce polypeptides or active RNAs in plants.
Owner:IBIO
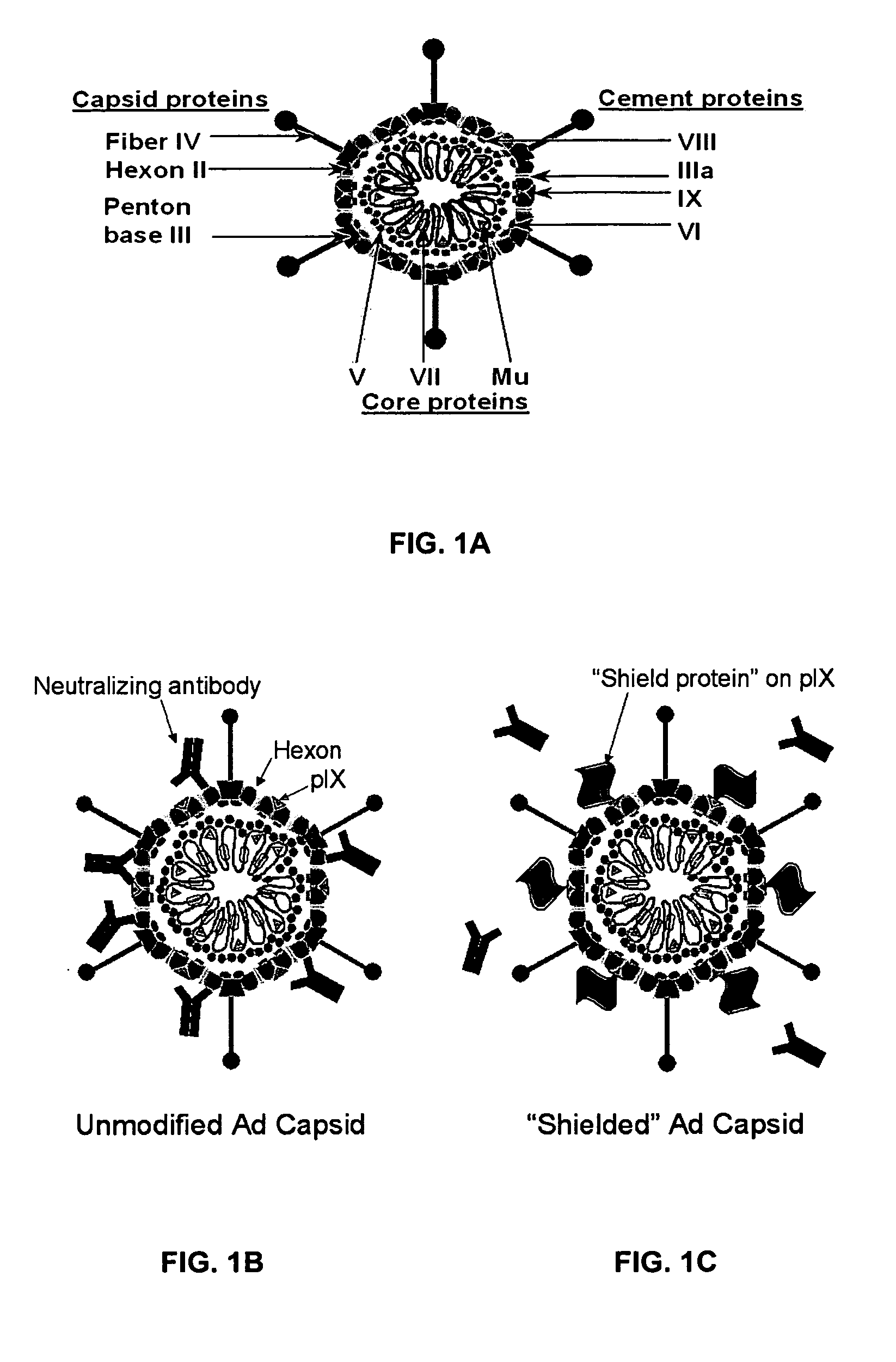
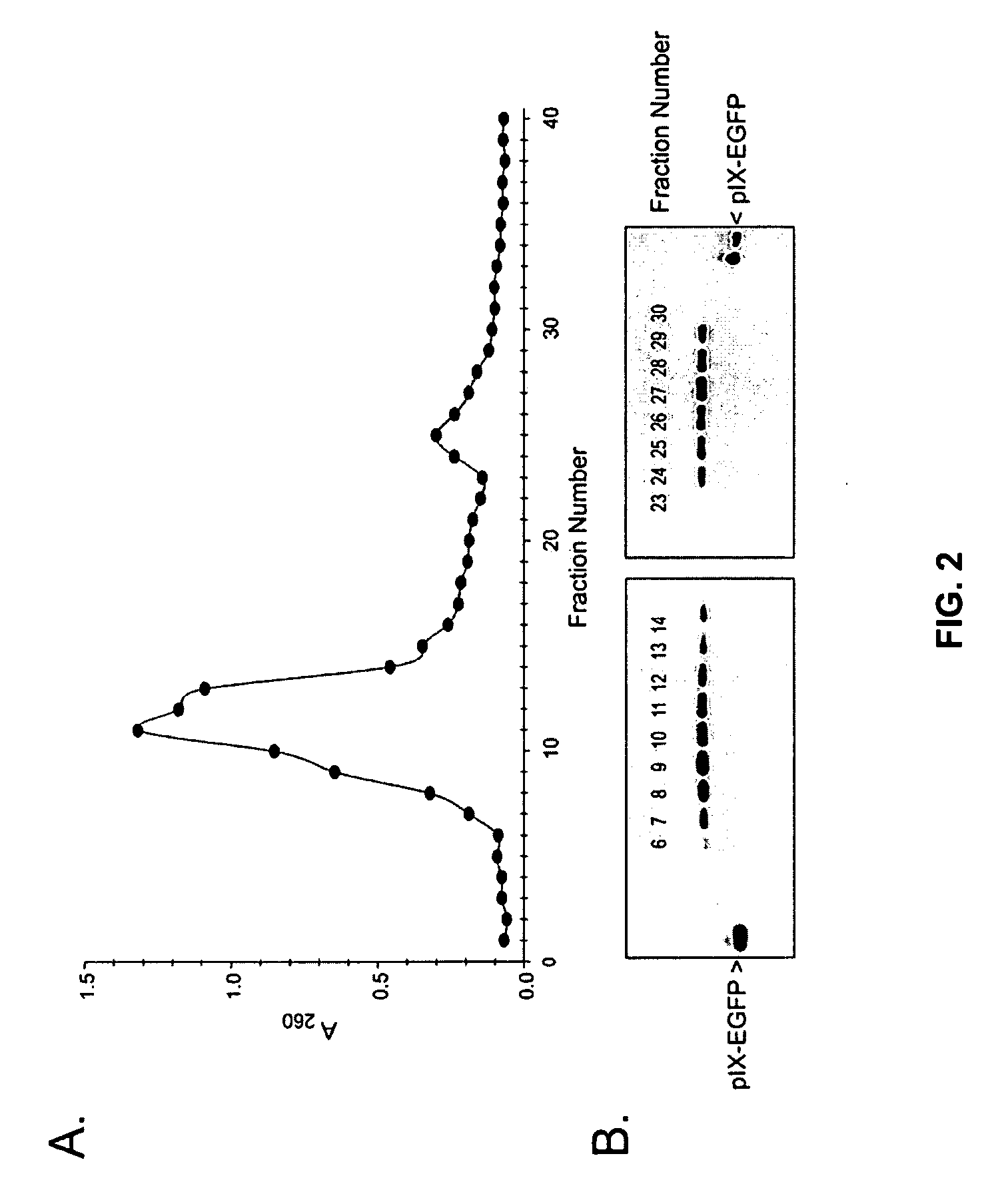
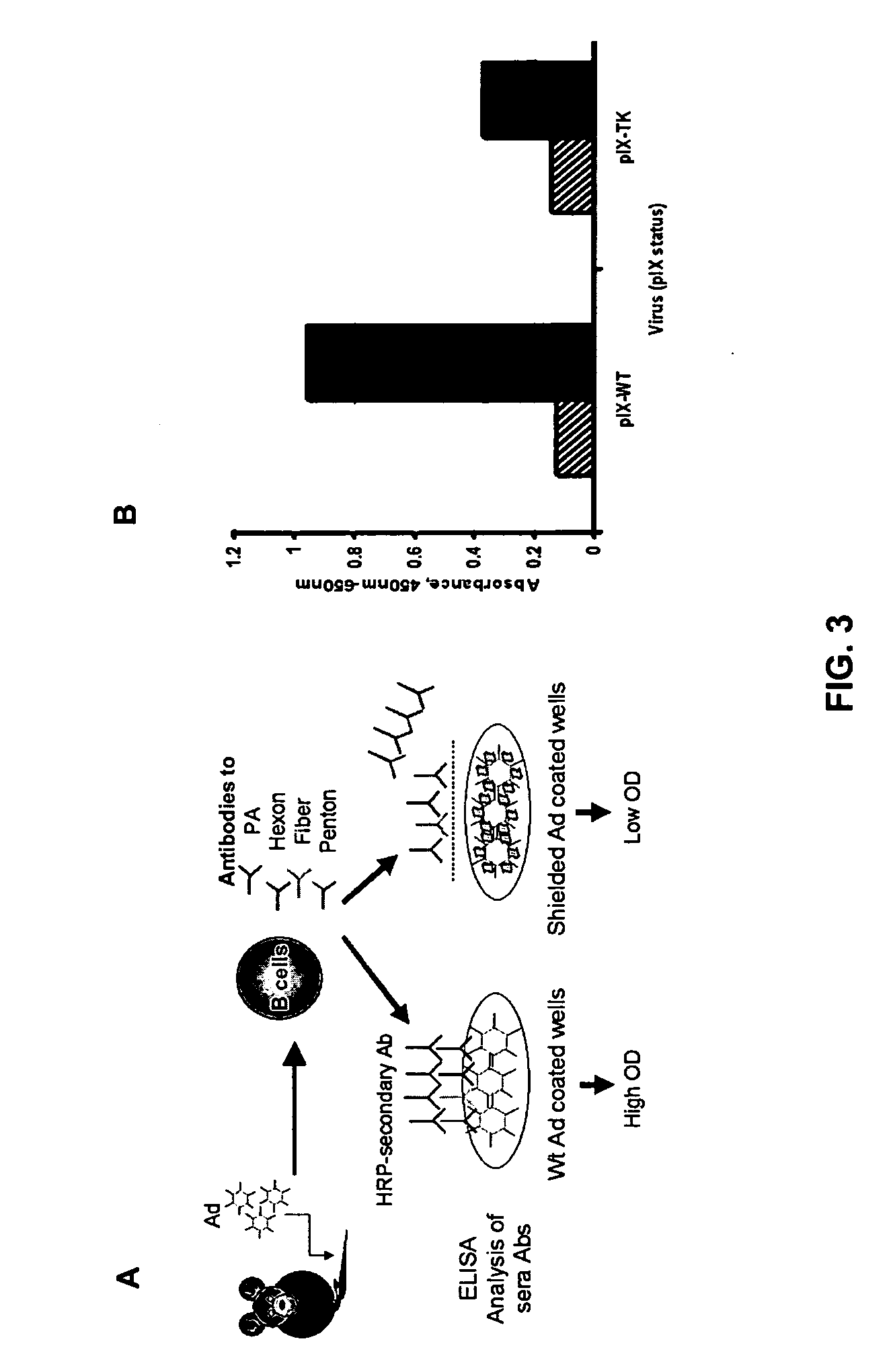
Shielded adenoviral vectors and methods of use
InactiveUS20080112929A1Keep for a long timeEnough timeBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsNucleic acid sequencingCoat protein
The present invention encompasses replication deficient or a replication competent adenoviral vectors which may comprise moieties covering and shielding the vector from the effects of humoral immune responses, as well as a method of constructing and using such vectors. The preferred viral constructs may incorporate the shielding moieties into the pIX coat protein of the adenovirus vectors. The invention also provides recombinant viral vectors with both shielding and specific targeting abilities. Preferably, the viral vector may comprise a nucleic acid sequence, which codes for therapeutically important genes. Methods for treating of a host with an effective amount of adenovirus vector of the present invention are also provided.
Owner:VECTORLOGICS
Herpes virus EBV (Epstein-Barr Virus) detection kit
ActiveCN103060473AEasy to operateSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceEBV InfectionsPotassium
The invention provides a herpes virus EBV (Epstein-Barr Virus) detection kit. The kit comprises a nucleic acid releasing agent and PCR (polymerase chain reaction) reaction solution, wherein the nucleic acid releasing agent comprises 0.01-0.5 mM / L of surfactin, 20-300 mM / L of potassium chloride, 0.01-2% of sodium dodecyl sulphate and 0.05-1% of ethanol; and the PCR reaction solution comprises an upstream primer and a downstream primer used for target polynucleotide amplification, and a probe used for target polynucleotide detection. The detection result of the method for releasing nucleic acid by the nucleic acid releasing agent in the kit disclosed by the invention has no obvious difference with the detection result of a boiling method, a strong protein denaturing agent is used during nucleic acid extraction in the kit disclosed by the invention for rapidly breaking the coat protein structure of a pathogen and releasing the nucleic acid of the pathogen, and release and extraction for DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) can be rapidly finished without heating; the sensitivity of the EBV detection of the kit disclosed by the invention can achieve 400 copies / ml, and the quantitative linear range is 400-4.00E+09 copies / ml; by applying the kit, rapid and accurate detection can be performed on EBV-DNA in the unknown samples of blood plasma, throat swab, peripheral blood and the like, and reliable experimental basis is provided for diagnosing EBV infection.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
Low carbohydrate coating system for breaded foods
This invention is directed to a protein containing composition for coating a food product, containing a liquid batter protein material having a liquid and a soy protein material wherein the weight ratio of liquid to soy protein material is from about 3-20 to 1; and a soy fiber material; wherein the food product coating has a non-fiber carbohydrate content of not more than 5 grams non-fiber carbohydrate per serving. Said invention may also include a pre-dust protein material; a breading protein material containing at least 50% soy protein by weight on a moisture free basis; and a liquid clear coat protein material.
Owner:SOLAE LLC
Bran coat antitumor active protein, as well as preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN102617718AHigh activityObvious side effectsPeptide/protein ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsActive proteinIon exchange
The invention provides a bran coat antitumor active protein, a preparation method of the protein, and applications of the protein in preparing antitumor drugs and health foods. The preparation method of the protein comprises the steps of pulverizing all natural bran coat, adding protein extracting solution, extracting at low temperature after one night, then adding precooled acetone to precipitate protein at low temperature so as to obtain bran coat protein, adding ammonium sulfate powders with different saturation levels into coarse protein extracting solution for fractional precipitation of the protein, enabling the protein precipitated by the ammonium sulfate to permeate through a Q anion exchange chromatographic column, collecting penetrating fluid, enabling the penetrating fluid to permeate through the Q anion exchange chromatographic column again, performing elution with Tris-NaCl eluant with the concentration of 0.1mol / L, and collecting eluting peaks to obtain the bran coat antitumor active protein (FMB). The protein can obviously restrain the proliferation and the metastasis of colorectal cancer cells and can be applied to preparation of the antitumor drugs and the health foods.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
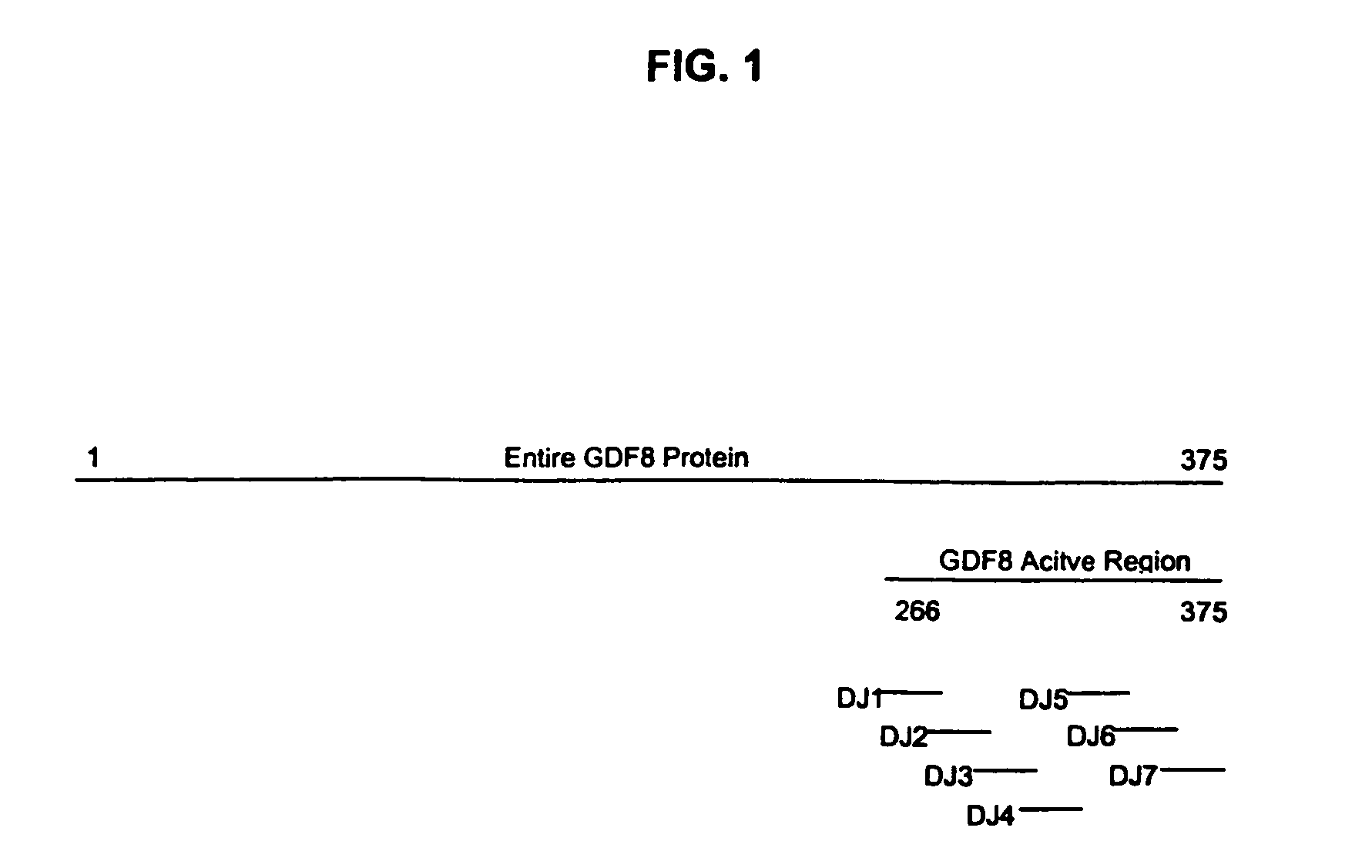
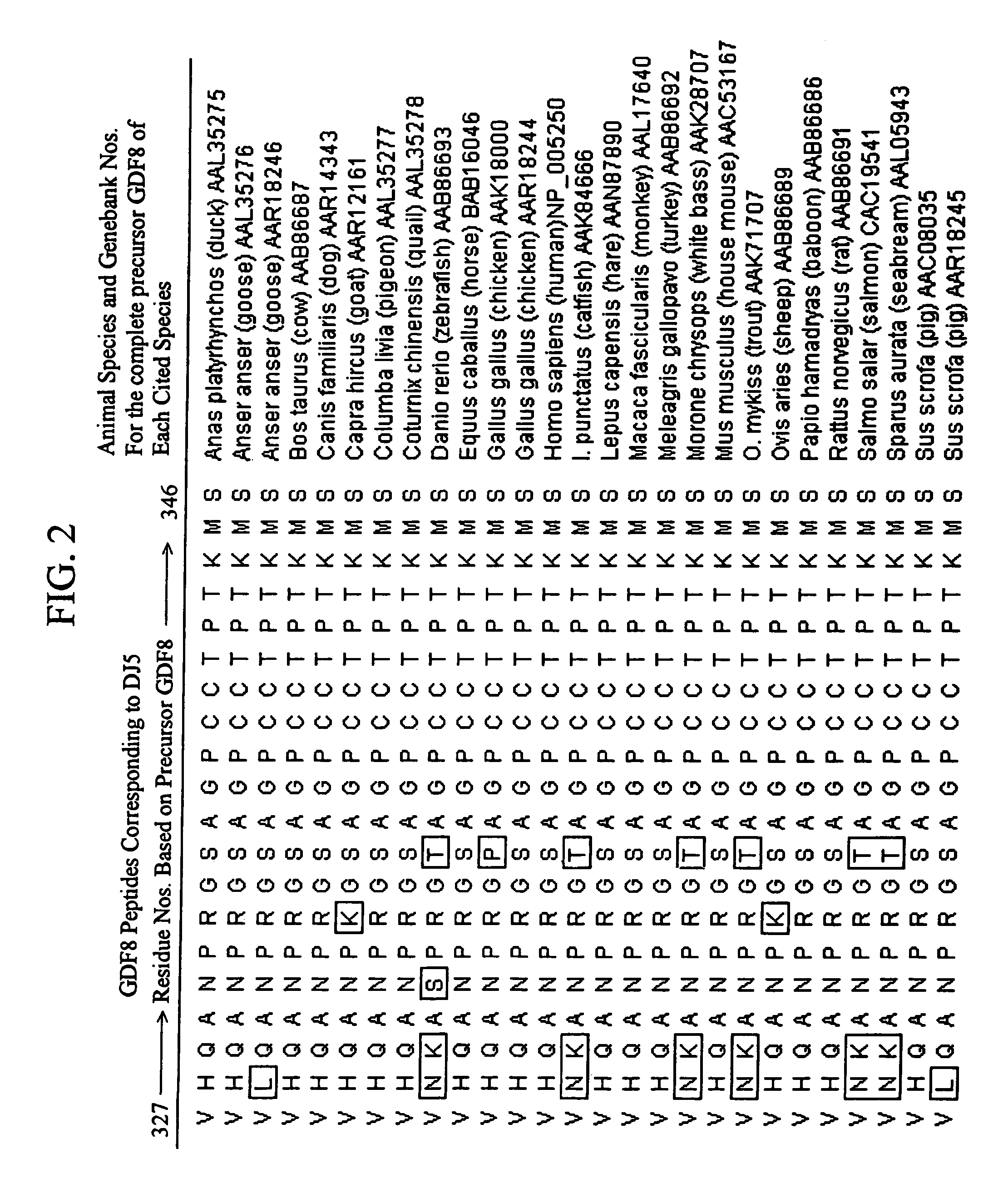
Plant virus coat fusion proteins with GDF8 epitopes and vaccines thereof
Owner:SCHERING PLOUGH ANIMAL HEALTH +1
Metamaterial Optical Elements Self-Assembled on Protein Scaffolds
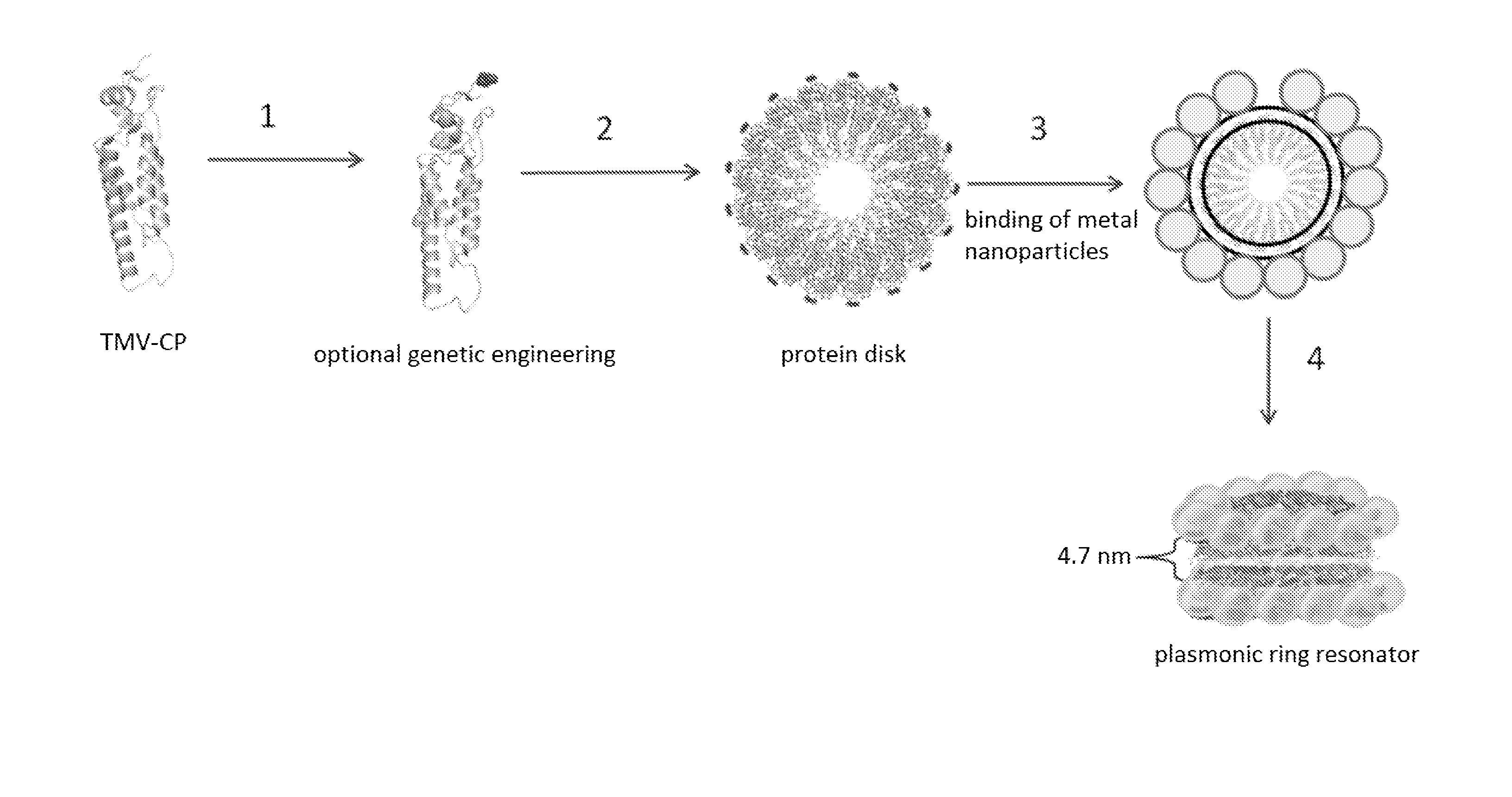
InactiveUS20130181171A1Polarising elementsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringCoat Proteins
Protein scaffolds from tobacco mosaic virus coat protein modified to incorporate polyhistidine can bind to a metal or a dye while having improved self-assembly characteristics. The scaffold can take the form of tubes or disks, and can further be formed into dual plasmonic ring resonators. Such self-assembled structures provide useful optical properties.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA
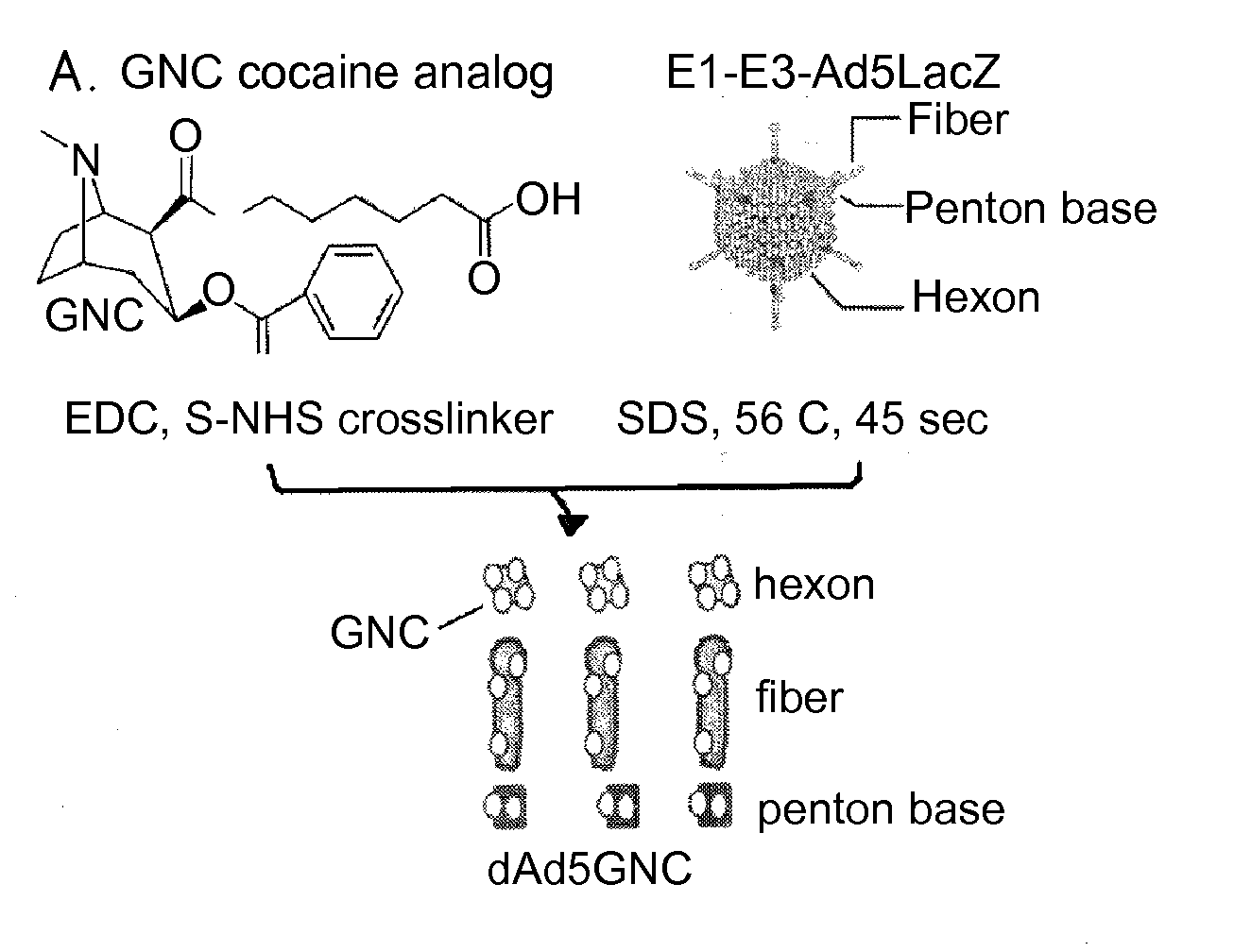
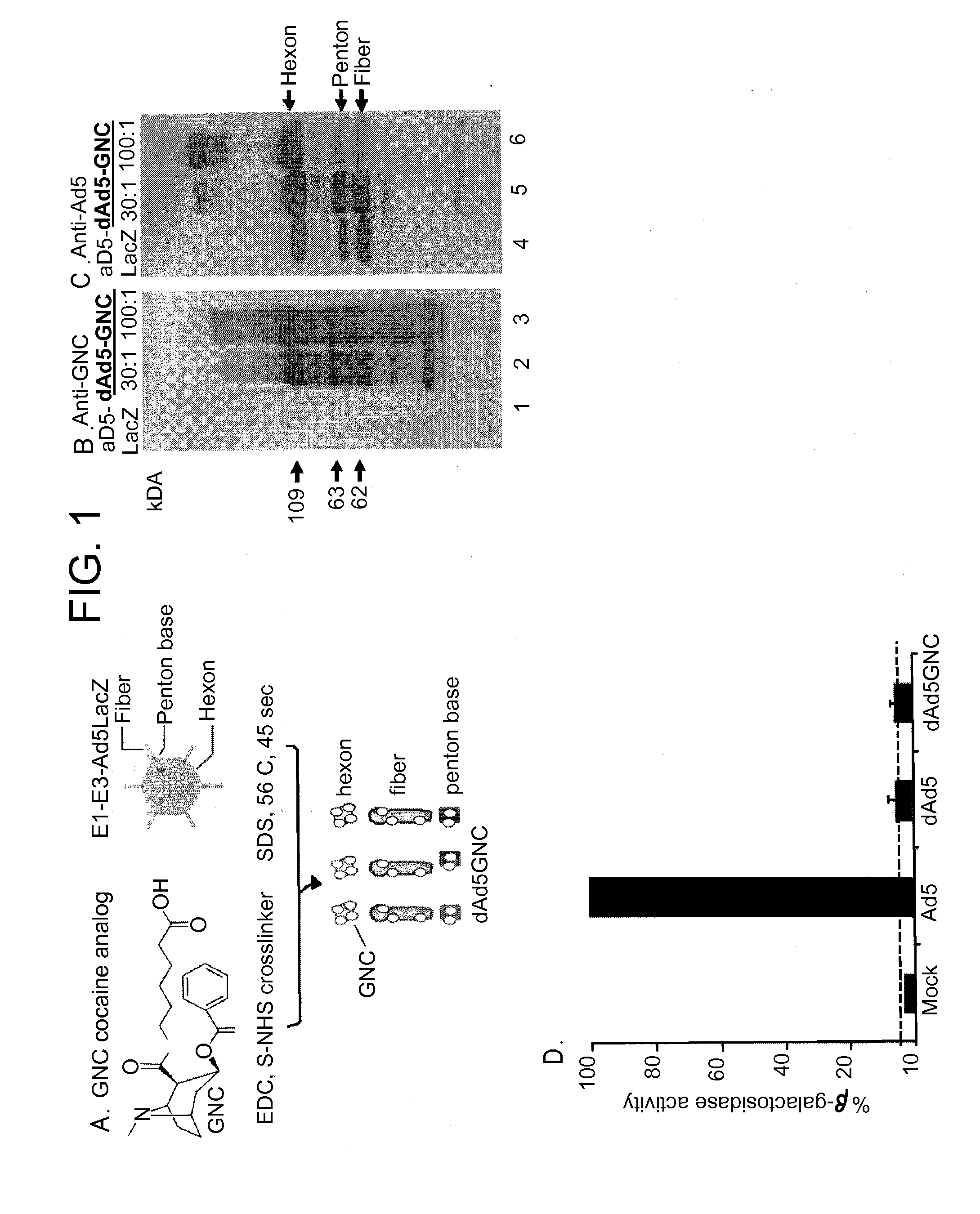
Disrupted adenovirus-based vaccine against drugs of abuse
The invention is directed to an adenovirus-antigen conjugate comprising (a) a disrupted adenovirus with a coat protein and (b) an antigen conjugated to the coat protein of the disrupted adenovirus, as well as a conjugate comprising (a) a disrupted adenovirus with a coat protein and (b) an antigen conjugated to the coat protein of the disrupted adenovirus. The invention also provides a method of inducing an immune response against an antigen in a human using the aforementioned conjugates. The invention further provides an adeno-associated viral vector comprising a nucleic acid sequence which encodes an antibody directed against cocaine.
Owner:CORNELL UNIVERSITY
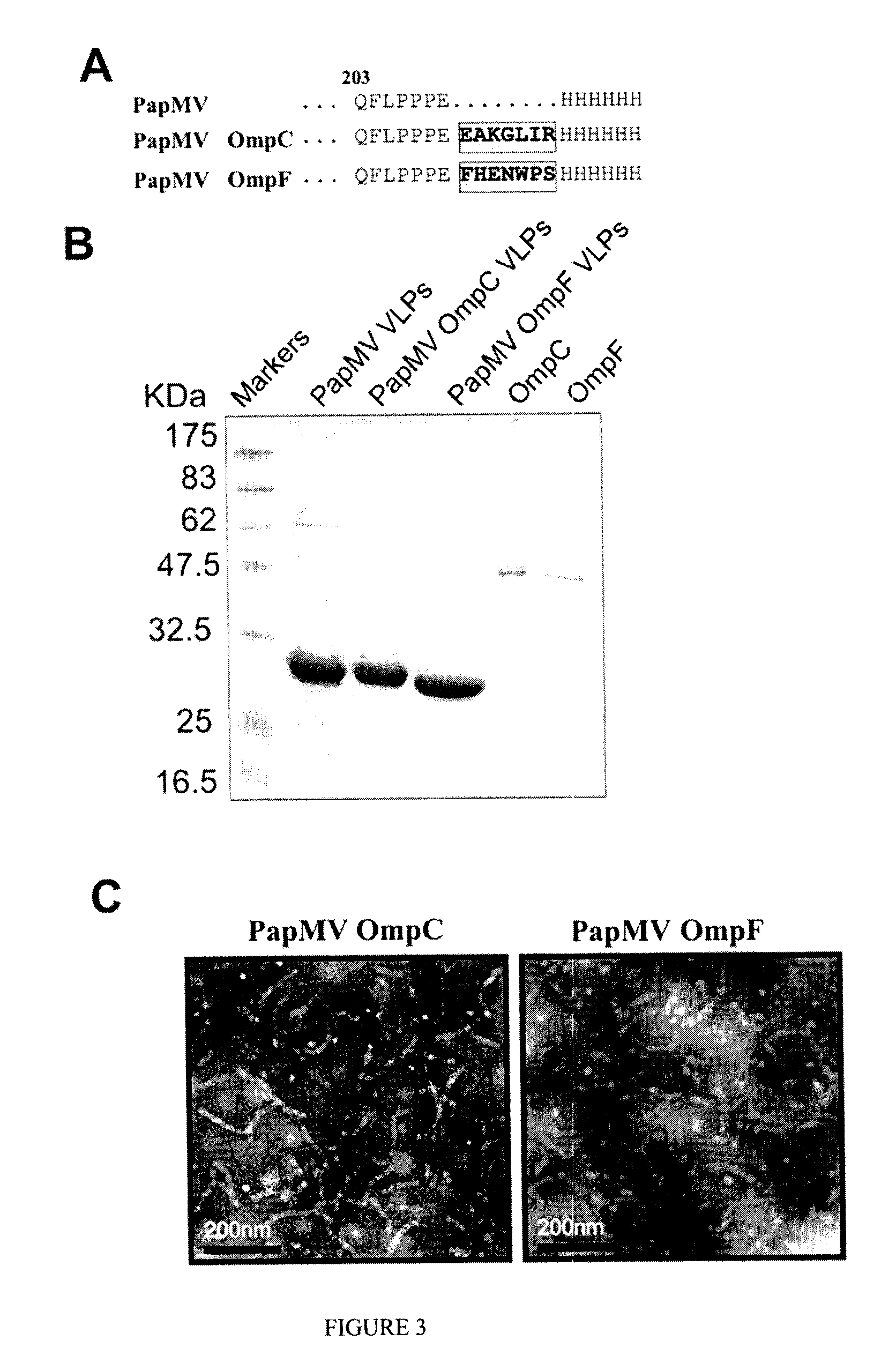
Immunogenic Affinity-Conjugated Antigen Systems Based on Papaya Mosaic Virus and Uses Thereof
An affinity-conjugated antigen system (ACAS) comprising one or more antigens conjugated via a plurality of affinity moieties to a papaya mosaic virus (PapMV) or virus-like particle (VLP) derived from the coat protein of PapMV is provided. The affinity moieties are molecules or compounds that are capable of specifically binding to the antigen(s) of interest and which can be attached, for example by chemical or genetic means, to the coat protein of the PapMV or PapMV VLP. The ACAS can optionally further comprise one or more additional antigens, which may be the same as, or different to, the conjugated antigen(s) comprised by the ACAS. Also provided are immunogenic compositions, including vaccines, comprising an ACAS. The immunogenic compositions are useful in the treatment, including prevention, of various diseases and disorders for which a humoral and / or cellular response in the animal is required.
Owner:FOLIA BIOTECH
Preparation, detection and application of polyclonal antibody of Yam mild mosaic virus
ActiveCN103539856AEfficient detectionHighly sensitive and accurate detectionSerum immunoglobulinsMicrobiological testing/measurementSorbentSpecific immunity
The invention discloses preparation, detection and application of a polyclonal antibody of a Yam mild mosaic virus (YMMV). Based on a YMMV genome, the inventor purifies a nuclear inclusion protein / coat protein (NIb / CP) of the YMMV through prokaryotic expression and uses the nuclear inclusion protein / coat protein to prepare the polyclonal antibody for an immune rabbit. The polyclonal antibody can specifically identify the Nib / CP protein of YMMV through prokaryotic expression and the Nib / CP protein of the YMMV virus which infects common yam rhizome, and generates specific immunity response. On the basis, the inventor further builds a set of efficient, high sensitive and accurate IC-RT-PCR (Immunocapture-Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction, ELISA (Enzyme-Linked Immuno Sorbent Assay) and Western blot methods which can specifically detect the YMMV from a common yam rhizome plant which is infected by YMMV. By applying the invention, a material basis and a technical support can be provided for research on interaction of the YMMV and the host, quick detection of the virus and somatotype and molecular biology study, thereby laying a solid foundation for epidemiologically monitoring and preventing treating the virus.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
Hybridoma cell strain capable of secreting tomato yellow leaf curl virus monoclonal antibody and application of monoclonal antibody
ActiveCN102559603AAccurate detectionSensitive detectionImmunoglobulins against virusesMicroorganism based processesDiseaseBALB/c
The invention discloses a hybridoma cell strain capable of secreting a tomato yellow leaf curl virus (TYLCV) monoclonal antibody and application of the monoclonal antibody. A coat protein gene of a tomato yellow leaf curl virus separator (TYLCV-SH2) is cloned; the coat protein of the virus is expressed by a prokaryotic expression system; BALB / c mice are immunized by using expression and purification protein as antigen; a hybridoma cell strain D10 capable of performing passage stably and secreting the TYLCV monoclonal antibody is obtained through cell fusion, screening and cloning; and the collection number is CGMCC No.5538. The D10 monoclonal antibody ascites indirect ELISA valence reaches more than 10<-6>; and the antibody type and subclass are IgG1 and kappa chains. A dot-ELISA detection method for detecting the TYLCV of the tomatoes is established by the D10 monoclonal antibody; and when the leaf suffering from the disease is diluted according to the ratio of 1:320 (w / v and g / mL), the virus can still be detected. By the dot-ELISA and Tissue-blot ELISA method, the TYLCV of tomato samples in the field can be detected accurately, specifically and sensitively. Due to establishment of a preparation method for the TYLCV monoclonal antibody and a detection method, technological and material support is provided for diagnosis, prediction and scientific prevention and control of the tomato virus disease.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Flexible vaccine assembly and vaccine delivery platform
InactiveUS20050282263A1Facilitate efficient immune cell recognitionEasy to processSsRNA viruses positive-senseInactivation/attenuationVaccine deliveryVirus-like particle
Herein described are various methods for making a vaccine that are made of re-assembled virus like particles (VLP). First, the VLPs are disassembled into coat proteins or encapsidation intermediate populations. Each population undergoes, for instance, chemical conjugation of unique peptide or nucleic moieties to form separate populations. Thereafter, a predetermined amount of each of the several (one or more) different coat proteins or encapsidation intermediates from the different populations is mixed and joined, forming intact VLPs, surrounding a nucleic acid core, that are composed of different coat proteins such that the reassembled VLP displays more than one peptide or other molecule. The nucleic acid can function either as a scaffold alone or can be engineered for the expression of an immunomodulatory protein in a eukaryotic cell.
Owner:KENTUCKY BIOPROCESSING
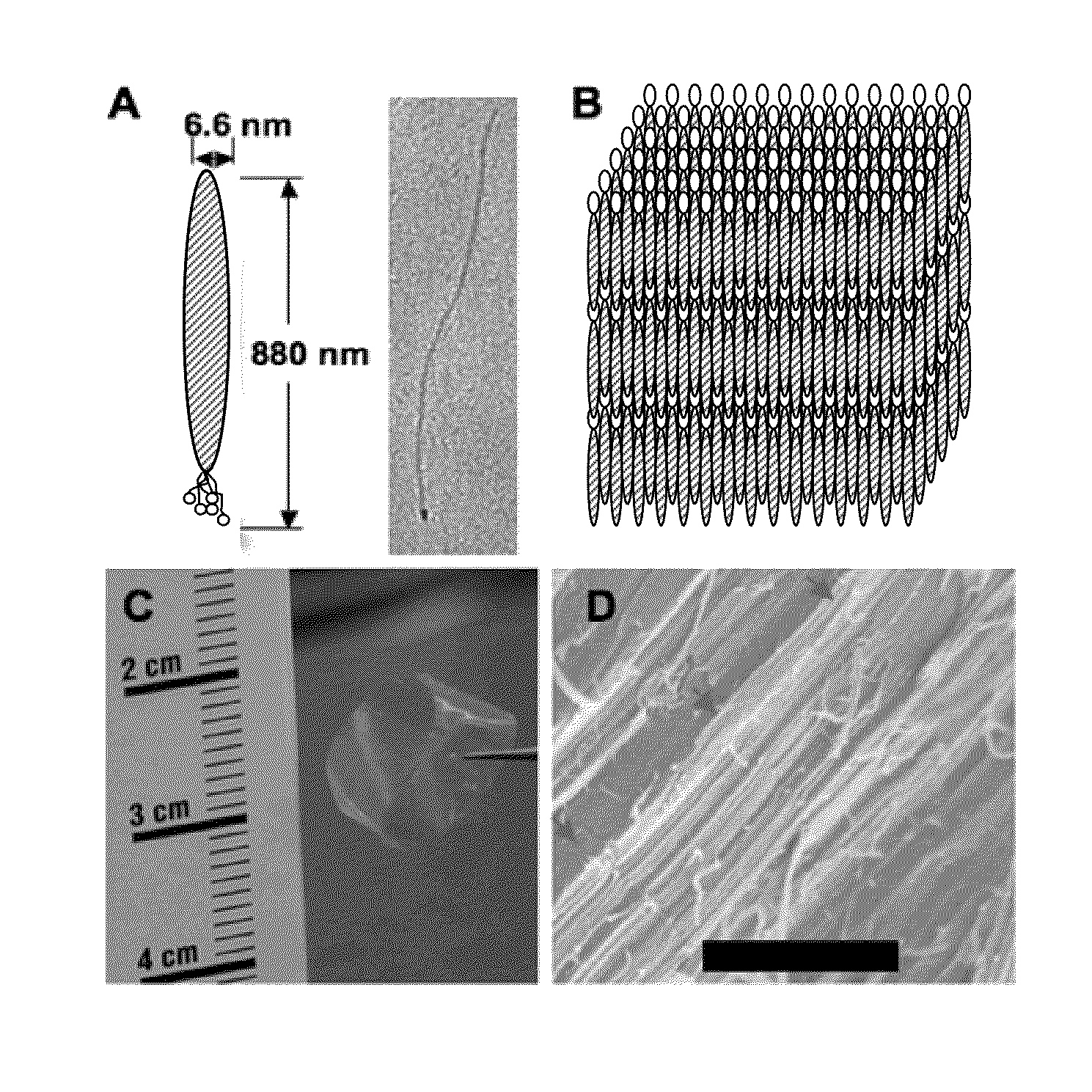
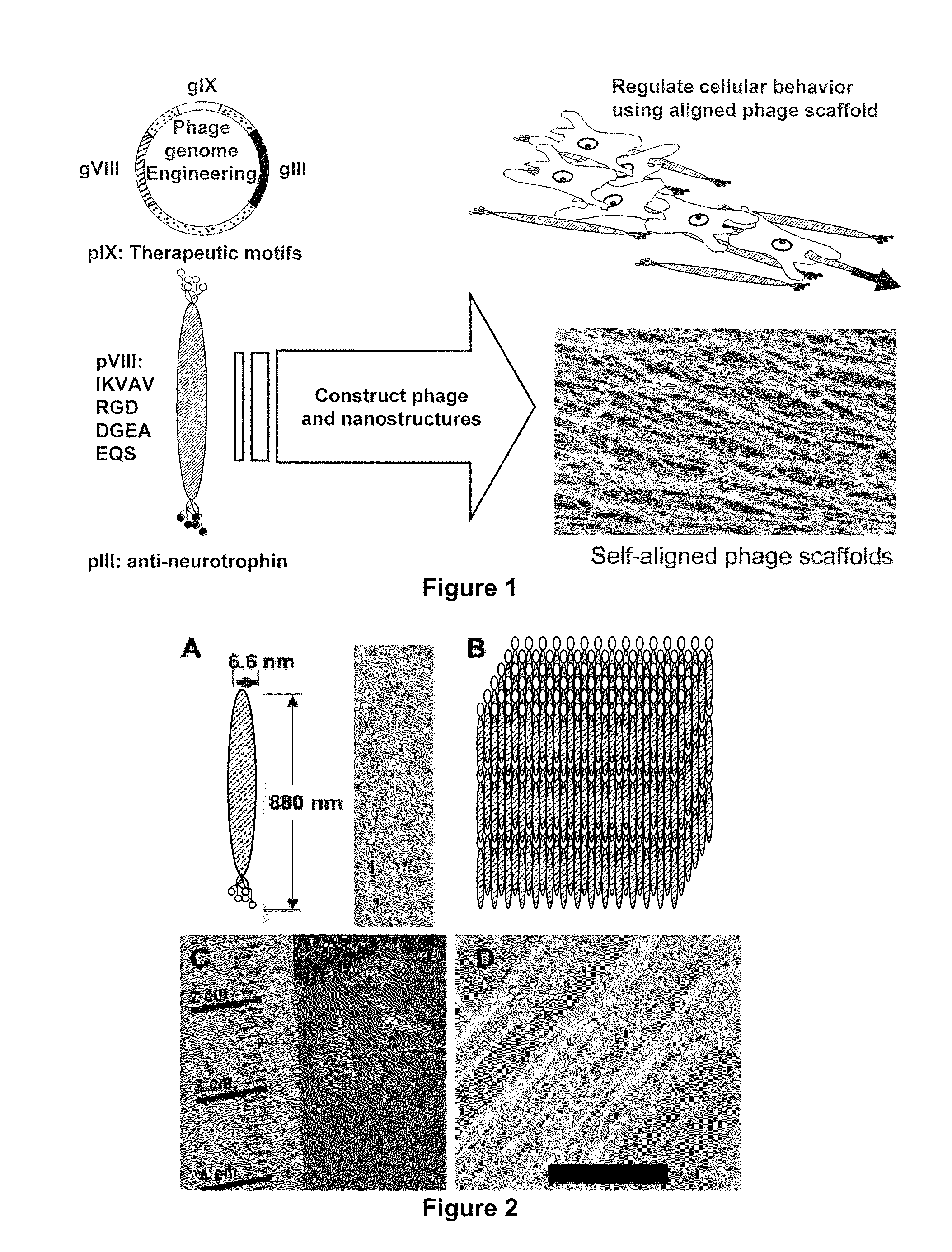
Recombinant Bacteriophages Useful for Tissue Engineering
The invention provides for a composition comprising a genetically engineered bacteriophage capable of guiding cell growth and polarization via signaling peptides and directionally aligned structures. The invention provides for modified bacteriophage and its uses thereof. The present invention also provides for genetically engineered phage capable of guiding cell growth, migration and / or alignment, providing essential biological effects including proliferation and / or differentiation, which can be performed by expressing specific biological motifs, such as the amino acid sequences RGD, IKVAV, DGEA and HPQ, on their coat proteins, on which functional DNA, proteins and cells can be conjugated and / or fixed thereon.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
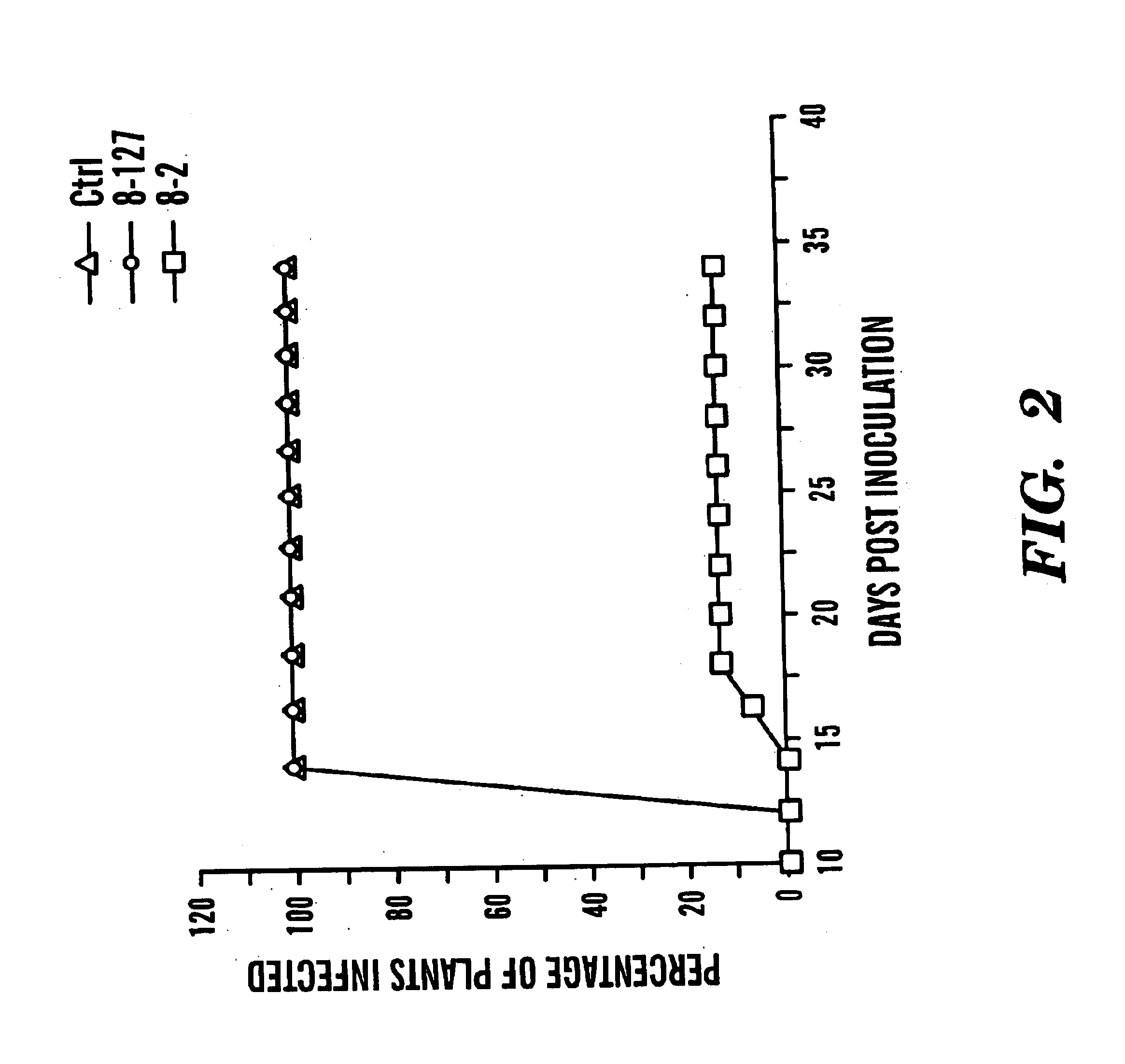
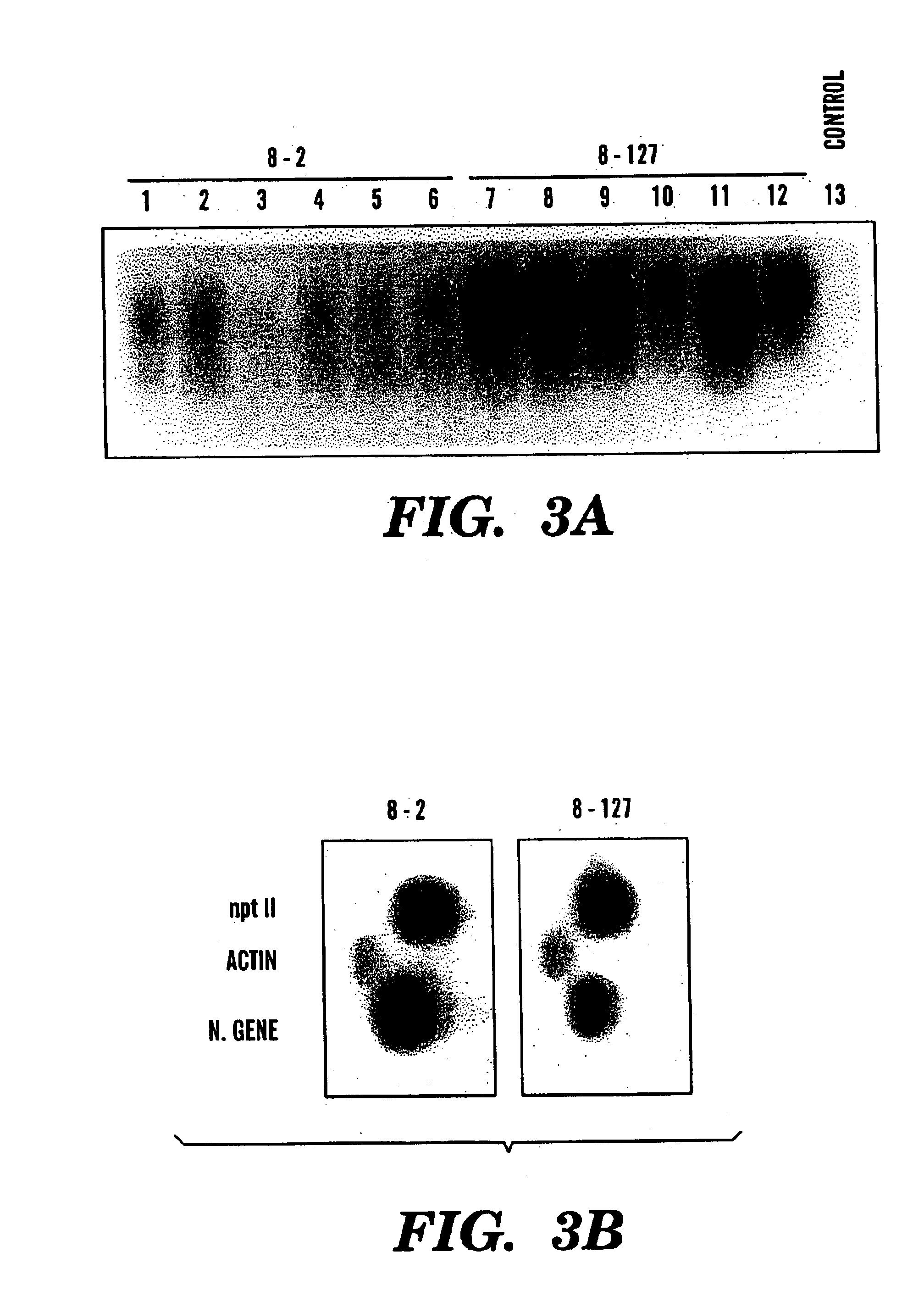
Method of enhancing virus-resistance in plants and producing virus-immune plants
InactiveUS20040068764A1Lower Level RequirementsDelayed and reduced spreadSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementBiotechnologyNucleotide
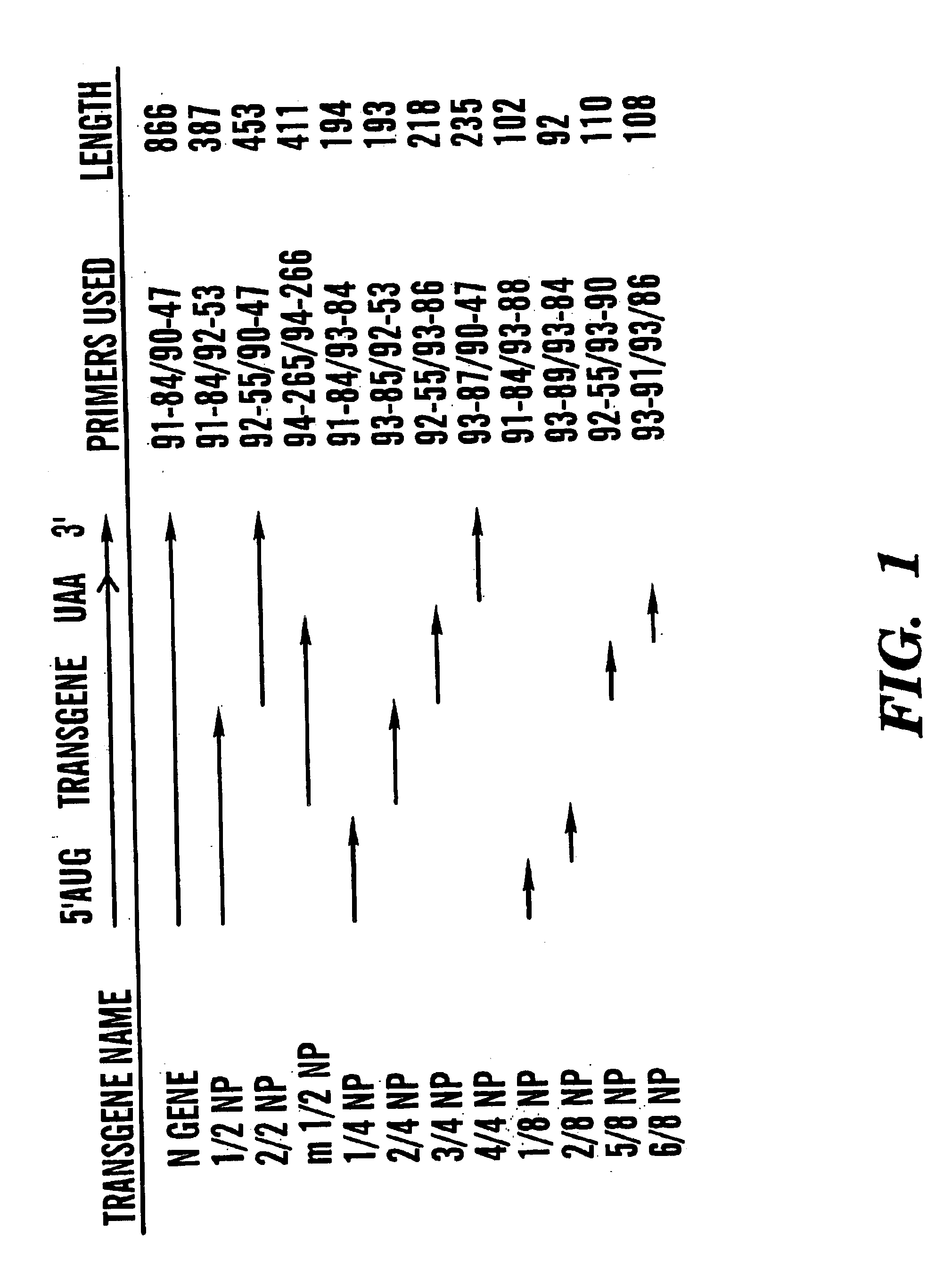
The present invention provides a method of enhancing resistance of plants to one or multiple viruses, comprising introducing to a plant cell, and preferably expressing therein, a nucleotide sequence encoding a virus-encoded polypeptide. The present invention provides a method of enhancing the proportion of virus-resistant or virus-immune lines obtained from a single transformation experiment comprising introducing to a plant cell, a nucleotide sequence encoding a virus-encoded polypeptide operably in connection with a strong promoter sequence. The present invention provides novel gene sequences encoding the coat proteins of a virus and novel dysfunctional replicase sequences as well as gene constructs comprising same, in particular binary vector constructs suitable for introducing into plants and expressing the genes therein. The present invention provides and methods using same to enhance viral resistance in plants. The present invention provides novel methods of testing transgenic plants for the presence of a transgene.
Owner:DAIRY AUSTRALIA +2
Phage display technologies
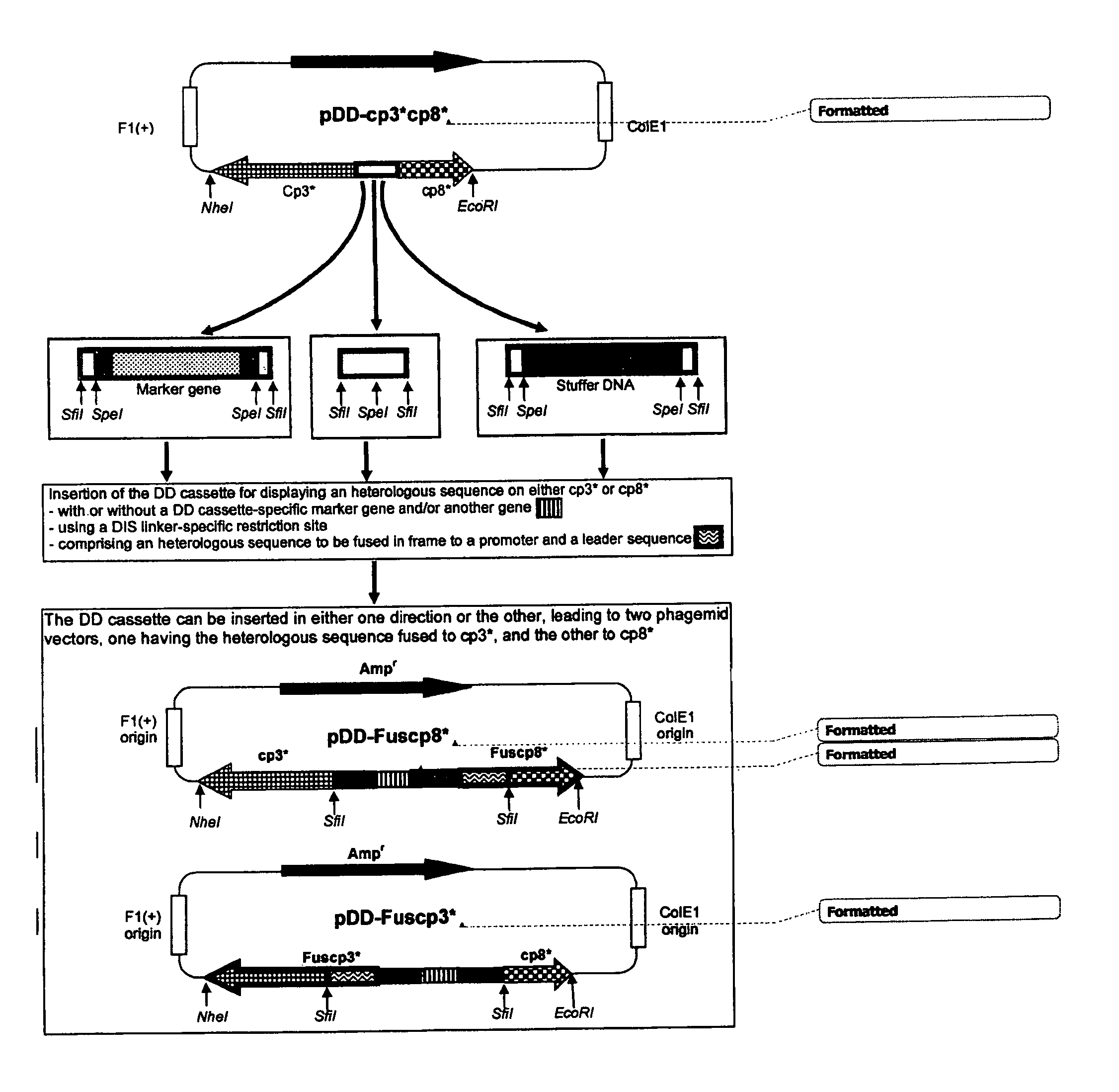
ActiveUS7811973B2Microorganism librariesOther foreign material introduction processesCoat ProteinsPhage Display Techniques
The present invention provides novel technologies for producing and screening fusion proteins on the surface of filamentous phage. In particular, a single vector can be used for generating cell and phage libraries containing a given series of protein sequences fused to either one or other of two phage coat proteins. This approach simplifies and improves the efficiency of the subsequent phage display-based selection of protein-binding molecules having therapeutic or diagnostic utility, such as antibodies, peptides, or epitope-binding regions.
Owner:RIBOVAX BIOTECHNOLOGIES SA
COVID-19 pseudovirus as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN112553172AStrong infection abilityHigh sensitivitySsRNA viruses positive-senseMicrobiological testing/measurementStreptococcal M proteinViral infection
The invention relates to the technical field of biology, in particular to a COVID-19 pseudovirus as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The COVID-19 pseudovirus is formed by virus packaging of coat protein particles and helper plasmids, wherein the coat protein particles comprise plasmids for expressing a COVID-19 S protein, plasmids for expressing a COVID-19 M protein and plasmids for expressing a COVID-19 E protein. The COVID-19 pseudovirus is packaged by adopting a three-plasmid system, and the S / M / E protein is used for replacing expression a VSV-G protein, so that the COVID-19 pseudovirus is stronger in infection capability and higher in sensitivity compared with the pseudovirus only containing the S protein. Moreover, the COVID-19 pseudovirus carries two fluorescentreporter groups, and different fluorescent reporter groups can be applied to different scenes, so that the COVID-19 pseudovirus is simpler and more convenient to apply.
Owner:NOVOPROTEIN SCI INC
Fusion proteins comprising bacteriophage coat protein and asingle-chain T cell receptor
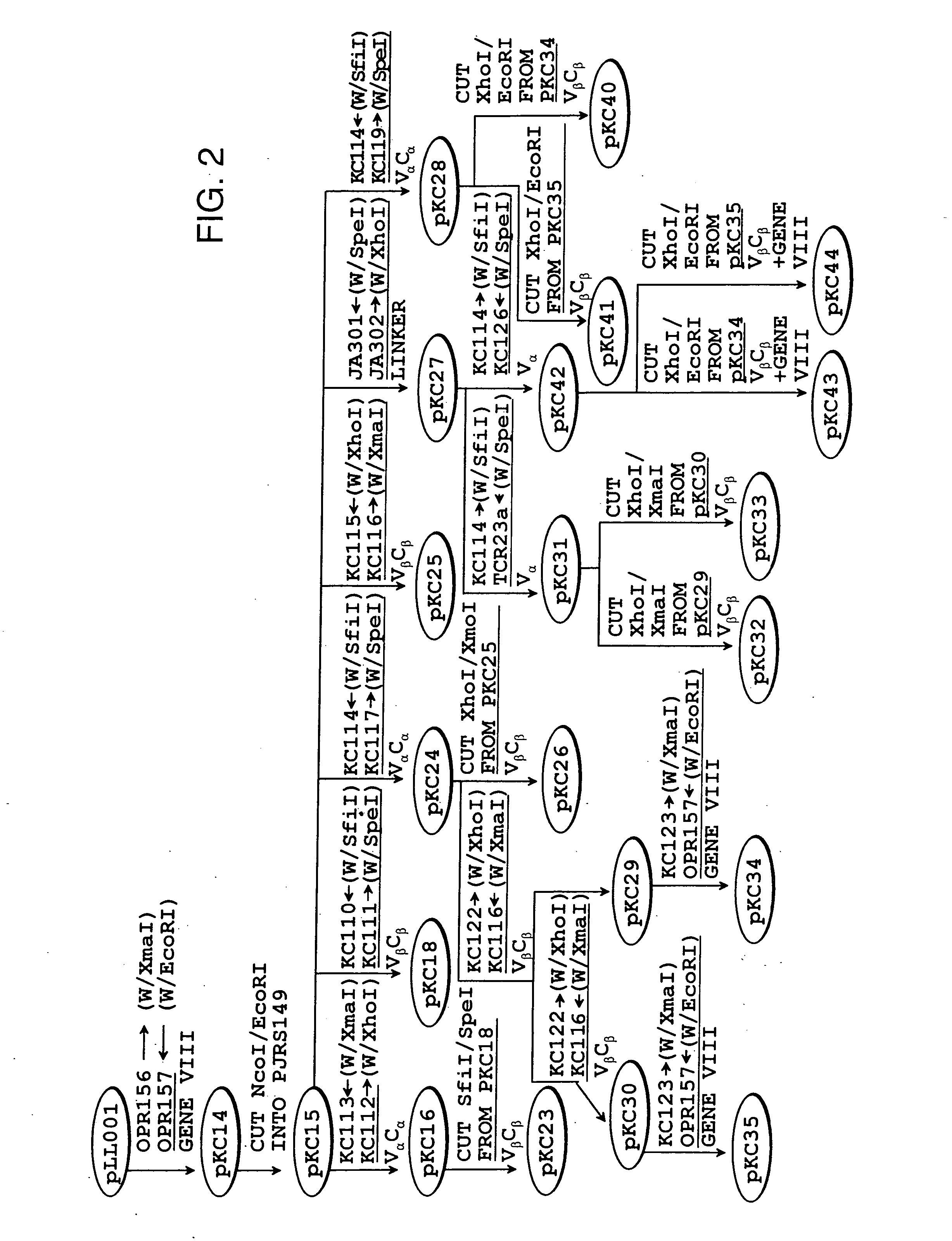
InactiveUS20070116718A1Improve solubilityHigh yieldAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsVirus peptidesGreek letter betaBacteriophage
The present invention relates to novel fusion proteins comprising a bacteriophage coat protein and a single-chain T cell receptor and uses of such complexes. In one aspect, the invention relates to soluble fusion protein comprising a bacteriophage coat protein covalently linked to a single-chain T cell receptor which comprises a V-alpha chain covalently linked to a V-beta chain by a peptide linker sequence. The soluble fusion proteins of the invention are useful for a variety of applications including: 1) making a bacteriophage library for displaying single-chain T cell receptors for use in screens for identification and isolation of ligands that bind single-chain T cell receptors, and 2) methods for isolating soluble and fully functional single-chain T cell receptors from the fusion proteins.
Owner:ALTOR BIOSCIENCE CORP
DNA constructs and methods to impart resistance to at least one virus on plants
InactiveUS6903248B2Impart resistanceProduced easily and cost-effectivelyBiocideSugar derivativesDNA constructViral gene
The present invention is directed to a DNA construct comprising a first DNA molecule having a length insufficient to independently impart resistance to a virus to plants transformed with said first DNA molecule, wherein the first DNA molecule is from a viral coat protein gene and is at least 110 nucleotides in length. The construct also comprises a second DNA of at least 400 nucleotides in length, which is coupled to the first DNA molecule so that the first and second DNA molecules collectively achieve post-transcriptional silencing and impart resistance to the virus. Alternately, the DNA construct can comprise a plurality of DNA molecules each of which is at least 110 nucleotides in length and from a viral gene, wherein the plurality of DNA molecules are at least 510 nucleotides in length.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
Detection method for sugarcane mosaic virus in corn
InactiveCN105506174AReduce potential harmReduce lossesMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesSugarcane mosaic virusCoat protein
The invention relates to a detection method for sugarcane mosaic virus in corn. According to the detection method, a high-quality virus RNA sample is extracted, primers are designed according to the coat protein (CP) genes of the sugarcane mosaic virus, then detection is carried out by utilizing RT-PCR and Real-time RCR technologies, and finally a set of rapid and efficient virus detection method is established. According to the detection method, by effectively detecting the sugarcane mosaic virus with low content in the corn, the potential hazard of the sugarcane mosaic virus is reduced, and the loss of the crop production is reduced.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
Kit for detecting neisseria gonorrheae (NG)
InactiveCN103060453AEasy to operateSimple methodMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceForward primerPotassium
The invention provides a kit for detecting neisseria gonorrheae (NG). The kit comprises a nucleic acid releaser and a PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) solution, wherein the nucleic acid releaser comprises 0.01-0.5mM / L of surfactin, 20-300mM / L of potassium chloride, 0.01-2% of sodium dodecyl sulfate and 0.05-1% of ethanol; and the PCR solution comprises a forward primer and a reverse primer which are used for amplifying targeted polynucleotide, and a probe for detecting the targeted polynucleotide. A method of releasing nucleic acid by using the nucleic acid releaser in the kit provided by the invention is not obviously different from a boiling method in the detection result, and a violent protein denaturant adopted for the nucleic acid extraction in the method provided by the invention quickly breaks a coat protein structure of a pathogen to release pathogen nucleic acid, so the release and extraction of DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) can be realized without heating; besides, the sensitivity of the provided kit for detecting the NG can be 400 copies / ml, the linearity region of the detection is 400-4.00E+10 copies / ml; and moreover, NG-DNA in an unknown sample such as genital secretions can be quickly and precisely detected by using the kit, so a reliable experiment basis is provided for diagnosing NG infection.
Owner:SANSURE BIOTECH INC
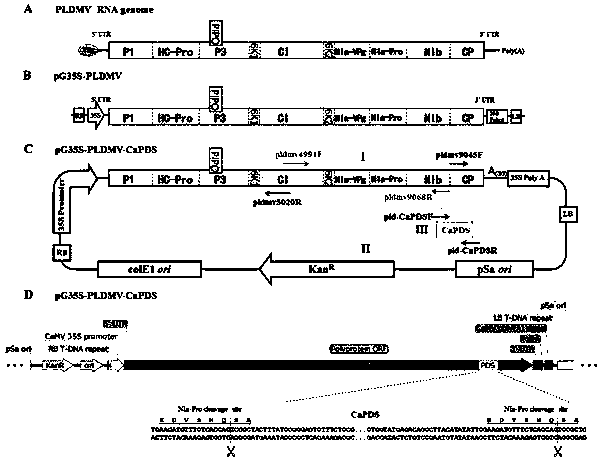
Potyvirus virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) system and application thereof
ActiveCN110951763AGood silence effectGood effectSsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesGenus DependovirusPlant genetic engineering
The invention belongs to the technical field of plant genetic engineering, and discloses a potyvirus virus-induced gene silencing (VIGS) system with a papaya leaf distortion mosaic virus (PLDMV) as avirus vector. According to the system, a target gene is inserted between Nib and coat protein (CP) of the PLDMV, and a NIa-Pro digestion site is introduced between the target gene and the CP. By in-vitro splicing methods such as Gibson splicing or In-Fusion cloning, target gene fragments are seamlessly cloned and inserted between the Nib and the CP to construct a recombinant virus silence vector containing a plant target gene. Plants are inoculated with the recombinant virus silence vector by agrobacterium injection, and phenotypic changes of the plants are observed after the target gene silencing the plants is induced. The potyvirus VIGS system provides a powerful tool to study gene functions of papaya by using the PLDMV silence vector, and has great scientific significance and application prospects.
Owner:INST OF TROPICAL BIOSCI & BIOTECH CHINESE ACADEMY OF TROPICAL AGRI SCI
Nanonets and spherical particles
ActiveUS20200190148A1Improve stabilityHigh yieldPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifSsRNA viruses positive-senseMicron scaleChemical physics
The present invention relates to macromolecular complexes comprising micron-scale networks which include binding motifs thereon which allow the covalent bonding of the micron-scale networks to particles which provide nanoscale display surfaces. In particular the present invention relates to micron-scale networks of TMV coat proteins comprising a peptide tag (e.g. SpyTag) and particles providing a nanoscale display surface comprising GFP and a corresponding binding protein (e.g. SpyCatcher) wherein the peptide tag and binding protein pair are capable of spontaneously forming a covalent bond.
Owner:JAMES HUTTON INSTITUTE
Uncoupling of DNA insert propagation and expression of protein for phage display
ActiveUS20080318298A1High levelHigh expressionSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementHeterologousInsertion sequence
The present invention provides an advance in phage display technology by permitting the uncoupling of the propagation of phages containing inserted sequences encoding heterologous polypeptides from the expression of said polypeptides. The invention provides phage constructs and methods for their use to permit phage coat protein expression, and thus phage propagation, in the absence of display of heterologous polypeptides, which may be expressed as a fusion with said coat protein in a regulated manner.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
Uncoupling of DNA insert propagation and expression of protein for phage display
InactiveUS7833741B2High levelHigh expressionBacteriaMicroorganism separationHeterologousADAMTS Proteins
The present invention provides an advance in phage display technology by permitting the uncoupling of the propagation of phages containing inserted sequences encoding heterologous polypeptides from the expression of said polypeptides. The invention provides phage constructs and methods for their use to permit phage coat protein expression, and thus phage propagation, in the absence of display of heterologous polypeptides, which may be expressed as a fusion with said coat protein in a regulated manner.
Owner:DISCOVERYX CORP
Colloidal gold immunization test strip and detection method for detecting plum pox virus
InactiveCN103048451AHigh sensitivityStrong specificitySerum immunoglobulinsVirus peptidesEscherichia coliCoat protein
The invention discloses a colloidal gold immunization test strip and a detection method for detecting plum pox viruses. The colloidal gold immunization test strip is formed by the steps of: A. extracting RNA (Ribonucleic Acid) of plum pox viruses from materials infected by the plum pox viruses; B. cloning coat protein genes of the plum pox viruses by an RT-PCR (Reverse Transcription-Polymerase Chain Reaction) method, connecting the coat protein genes on a prokaryotic expression vector pET29(a) to obtain pET29a-PPV (porcine parvovirus) recombinant vectors, orderly measuring and finally verifying the recombinant vectors with correct reading frames, carrying out the inducible expression with the coat protein genes of the plum pox viruses, and transforming escherichia coli BL21 (DE3) with the pET29a-PPV recombinant vectors; C. recovering specific expression protein by an affinity column method, and making the rabbits immune to obtain plum pox virus antiserum; and D. adopting the above antiserum to prepare the colloidal gold immunization test strip used for detecting the plum pox viruses by the prepared antiserum. The invention aims to provide the convenient colloidal gold immunization test strip for rapidly detecting the plum pox viruses and the method for detecting plum pox viruses by adopting the test strip.
Owner:陈定虎
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com