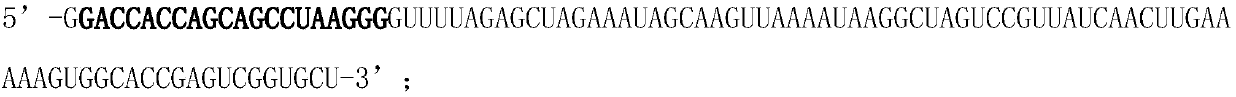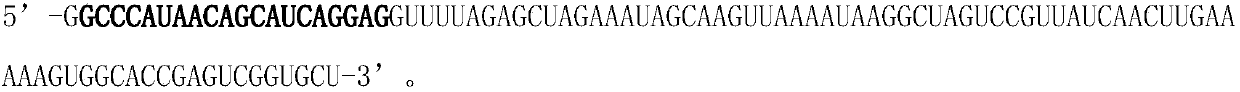Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
177 results about "Insertion sequence" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
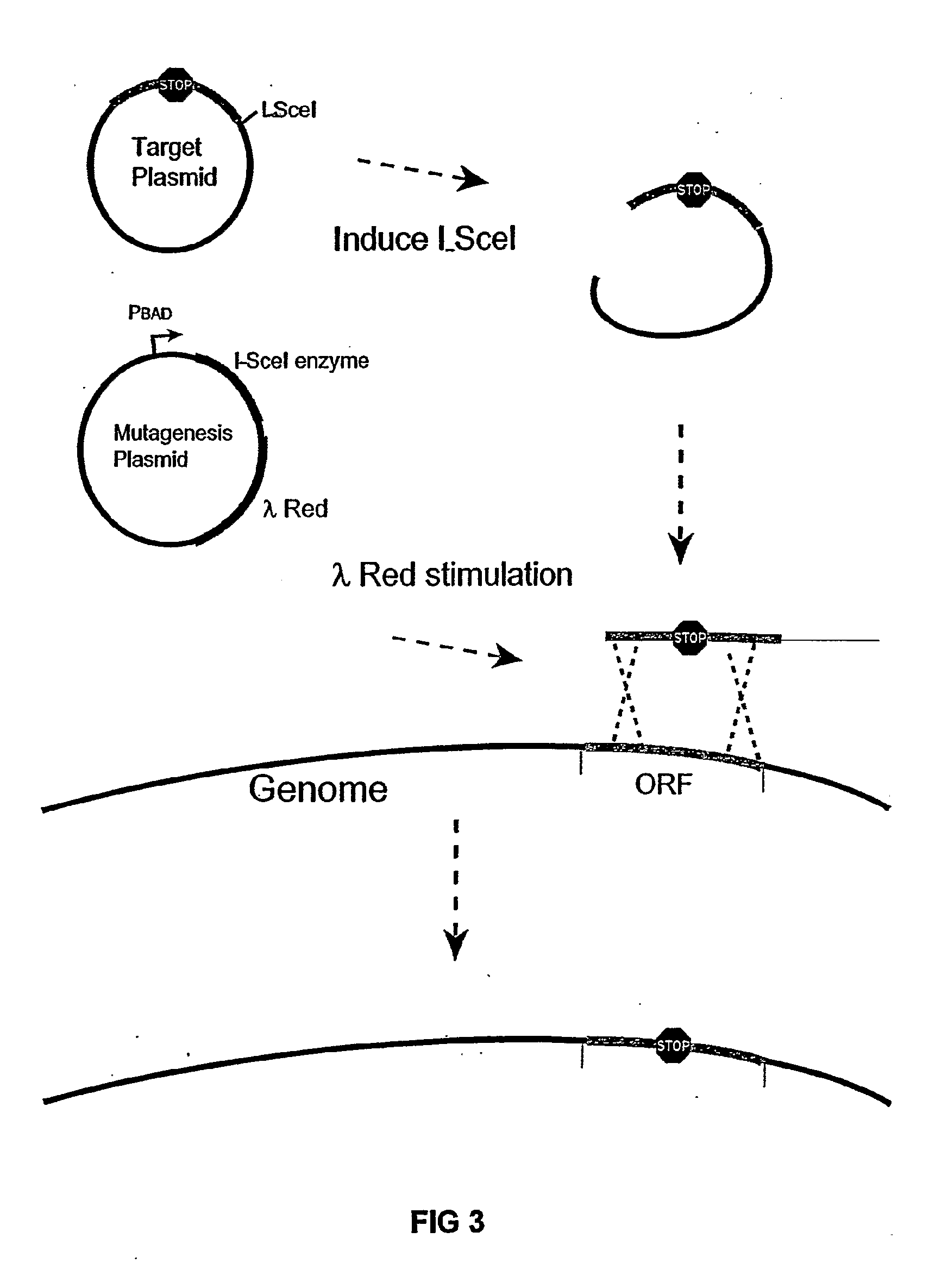
Insertion element (also known as an IS, an insertion sequence element, or an IS element) is a short DNA sequence that acts as a simple transposable element. Insertion sequences have two major characteristics: they are small relative to other transposable elements (generally around 700 to 2500 bp in length) and only code for proteins implicated in the transposition activity (they are thus different from other transposons, which also carry accessory genes such as antibiotic resistance genes). These proteins are usually the transposase which catalyses the enzymatic reaction allowing the IS to move, and also one regulatory protein which either stimulates or inhibits the transposition activity. The coding region in an insertion sequence is usually flanked by inverted repeats. For example, the well-known IS911 (1250 bp) is flanked by two 36bp inverted repeat extremities and the coding region has two genes partially overlapping orfA and orfAB, coding the transposase (OrfAB) and a regulatory protein (OrfA). A particular insertion sequence may be named according to the form ISn, where n is a number (e.g. IS1, IS2, IS3, IS10, IS50, IS911, IS26 etc.); this is not the only naming scheme used, however. Although insertion sequences are usually discussed in the context of prokaryotic genomes, certain eukaryotic DNA sequences belonging to the family of Tc1/mariner transposable elements may be considered to be, insertion sequences.
Methods for accurate sequence data and modified base position determination
ActiveUS20100121582A1Microbiological testing/measurementBiological testingInsertion sequenceLocation determination
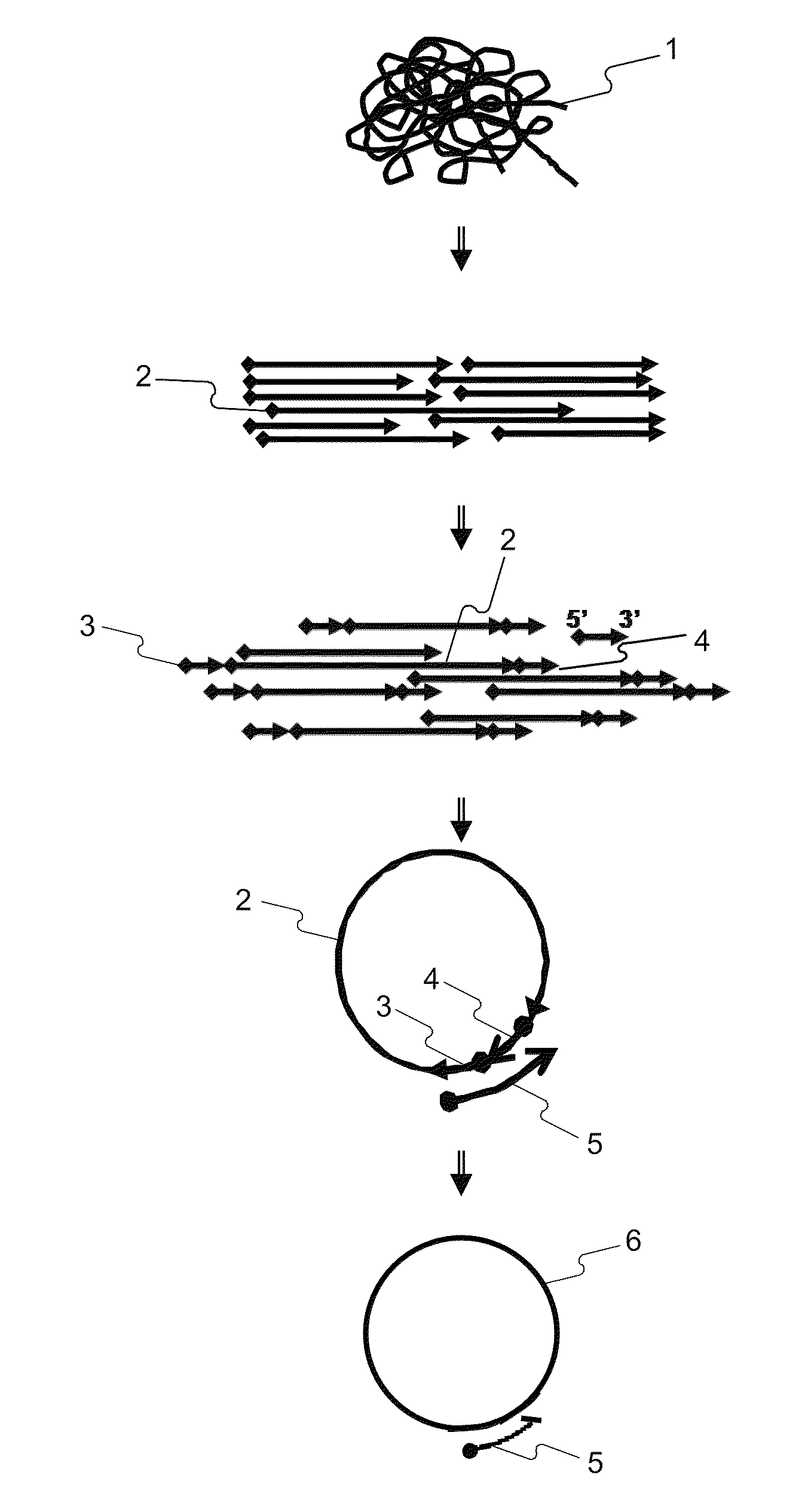
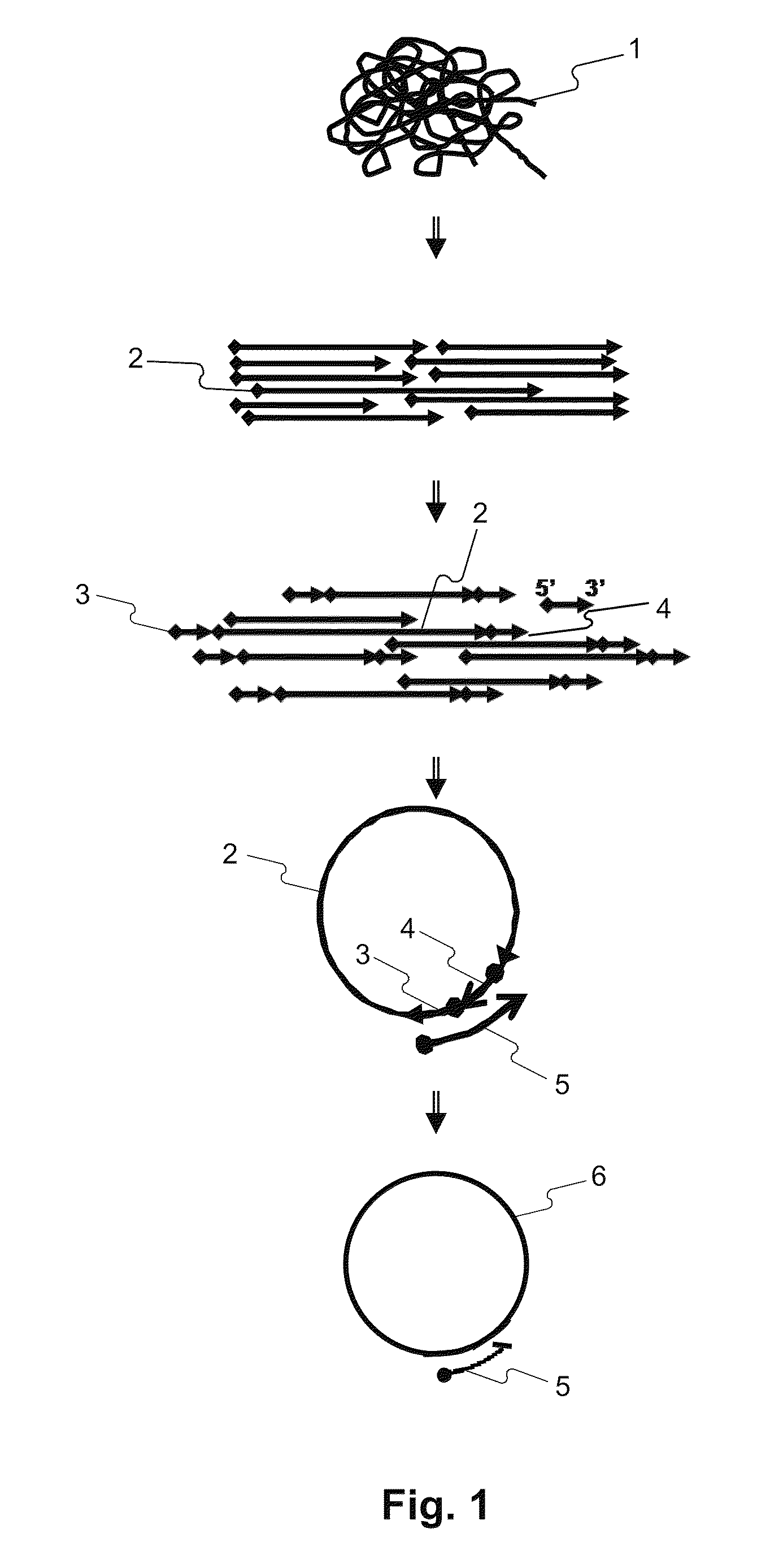
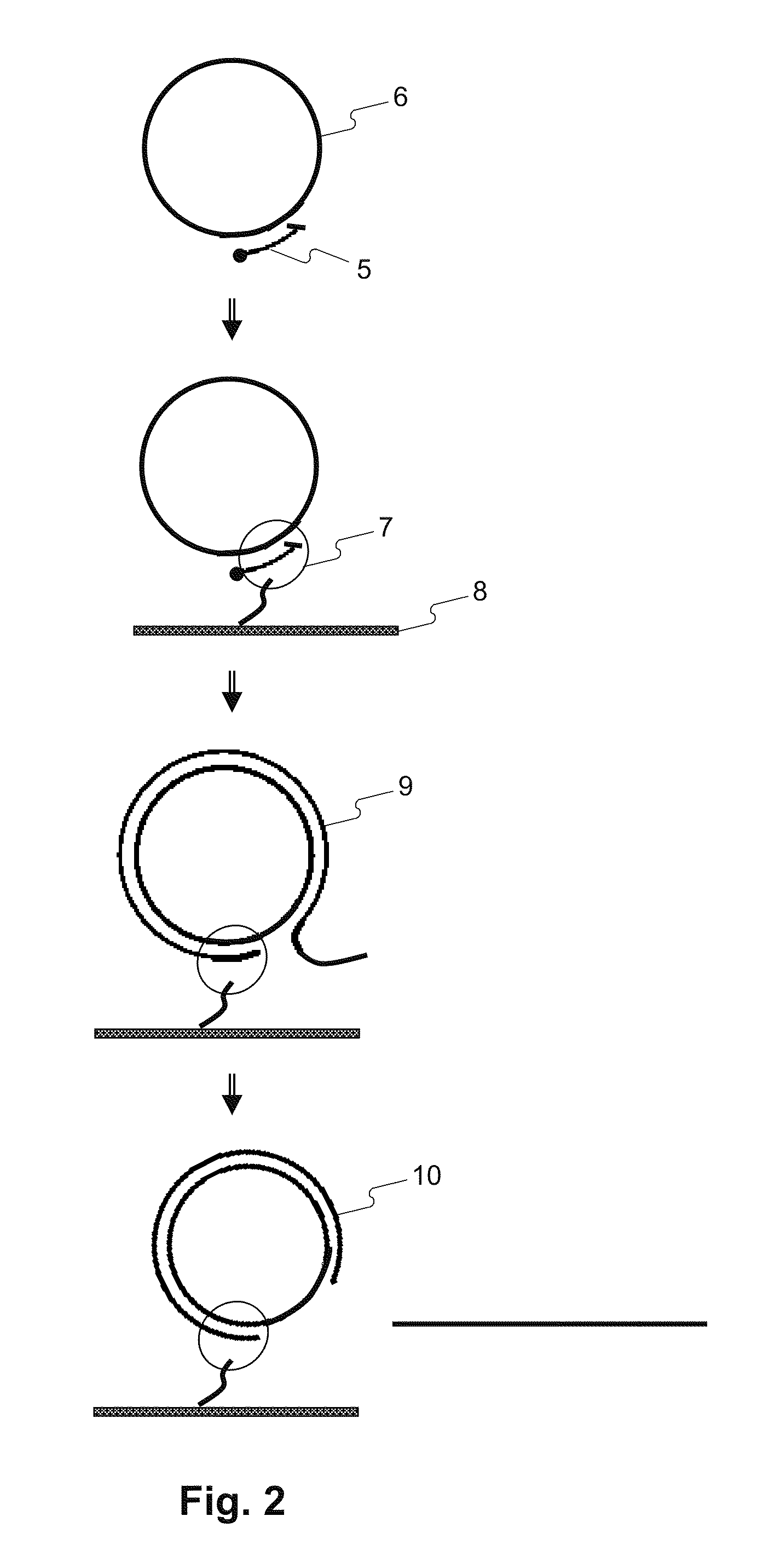
Disclosed herein are methods of determining the sequence and / or positions of modified bases in a nucleic acid sample present in a circular molecule with a nucleic acid insert of known sequence comprising obtaining sequence data of at least two insert-sample units. In some embodiments, the methods comprise obtaining sequence data using circular pair-locked molecules. In some embodiments, the methods comprise calculating scores of sequences of the nucleic acid inserts by comparing the sequences to the known sequence of the nucleic acid insert, and accepting or rejecting repeats of the sequence of the nucleic acid sample according to the scores of one or both of the sequences of the inserts immediately upstream or downstream of the repeats of the sequence of the nucleic acid sample.
Owner:IND TECH RES INST
Methods and combinations for gene targeting by homologous recombination
InactiveUS20050118648A1Microbiological testing/measurementStable introduction of DNAA-DNAInsertion sequence
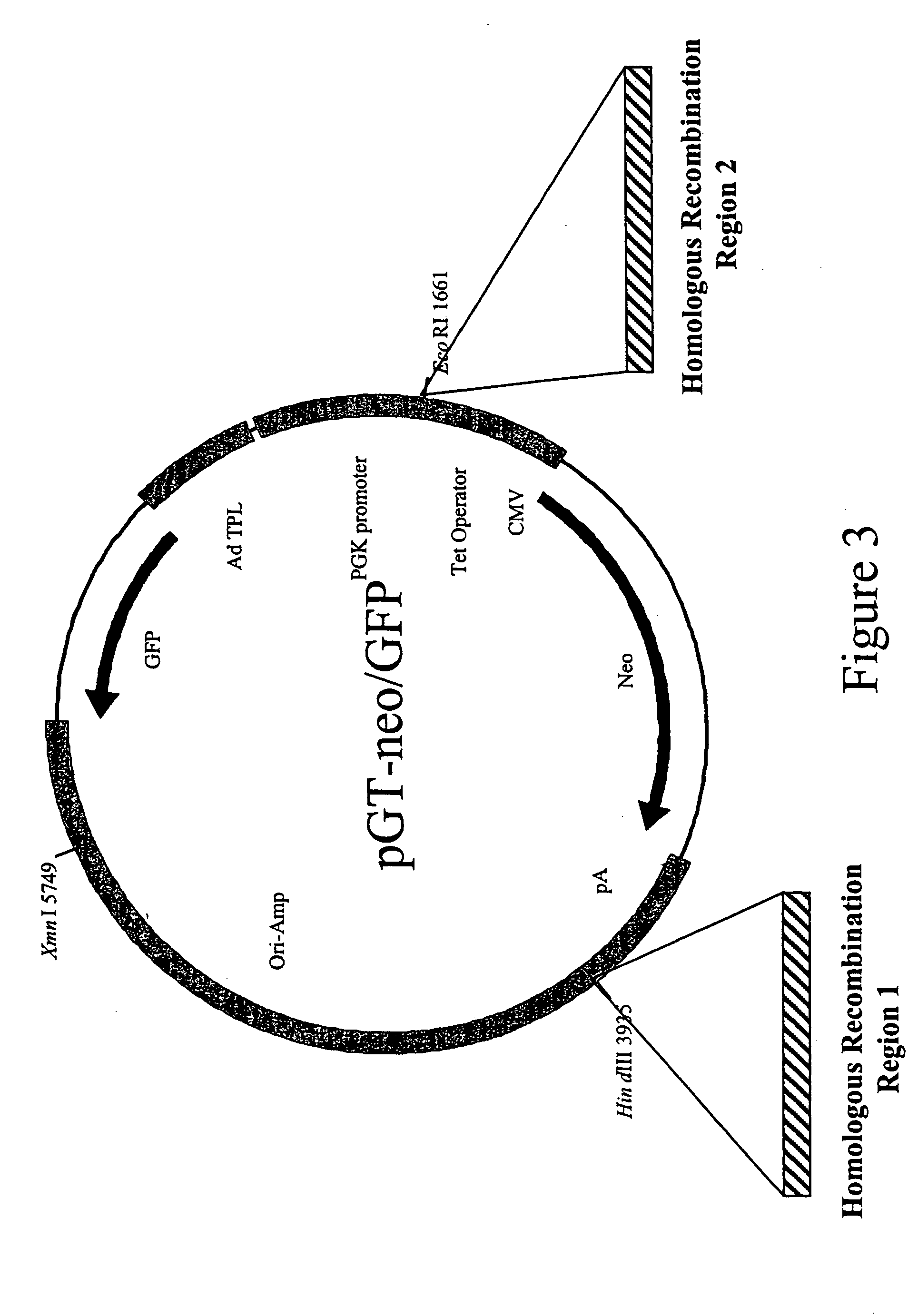
The invention provides methods and compositions for inserting a DNA sequence in the genome of a cell by homologous recombination. In particular, the method utilizes a selection scheme in which a selection marker gene that encodes a fluorescence protein, such as a green fluorescence protein, is used for selection against random, non homologous insertions.
Owner:FUNCTIONAL GENETICS
Process for amplifying nucleic acid
InactiveUS20060160084A1Meet growth requirementsEfficient amplificationSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementNucleic acid sequencingInsertion sequence
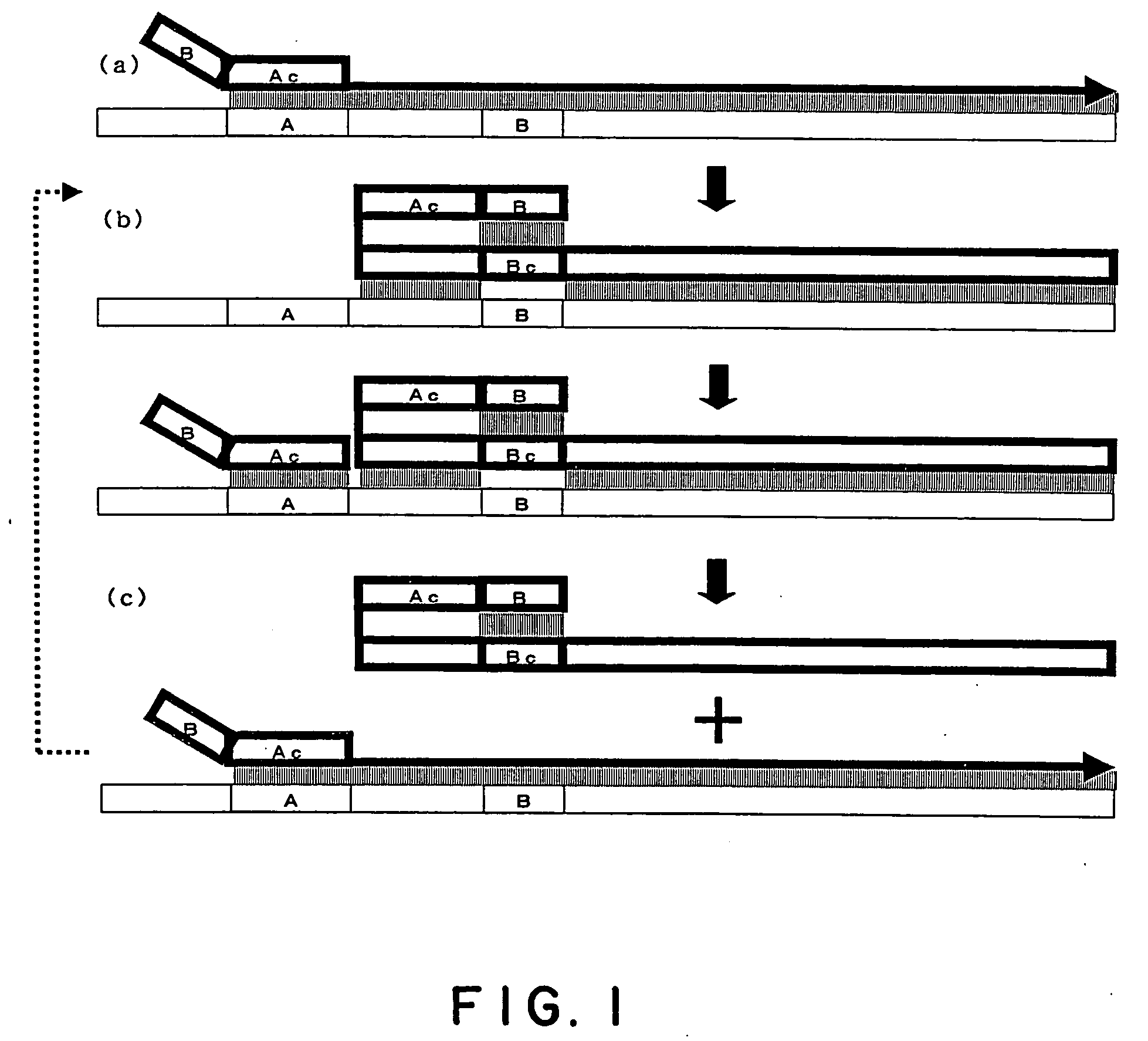
The present invention relates to a process for synthesizing or amplifying efficiently a nucleic acid comprising a target nucleic acid sequence. In the process according to the present invention, a primer comprising in its 3′-end portion a sequence (Ac′) which hybridizes a sequence (A) in the 3′-end portion of the target nucleic acid sequence, and in the 5′-side of said sequence (Ac′) a sequence (B′) which hybridizes the complementary sequence (Bc) of a sequence (B) positioned in the 5′-side of said sequence (A) on the target nucleic acid sequence, wherein {X−(Y−Y′)} / X is in the range of −1.00 to 1.00, in which X denotes the number of bases in said sequence (Ac′), Y denotes the number of bases in the region flanked by said sequences (A) and (B) in the target nucleic acid sequence, and Y′ denotes the number of bases in an intervening sequence between said sequences (Ac′) and (B′) (Y′ may be zero).
Owner:RIKEN +1
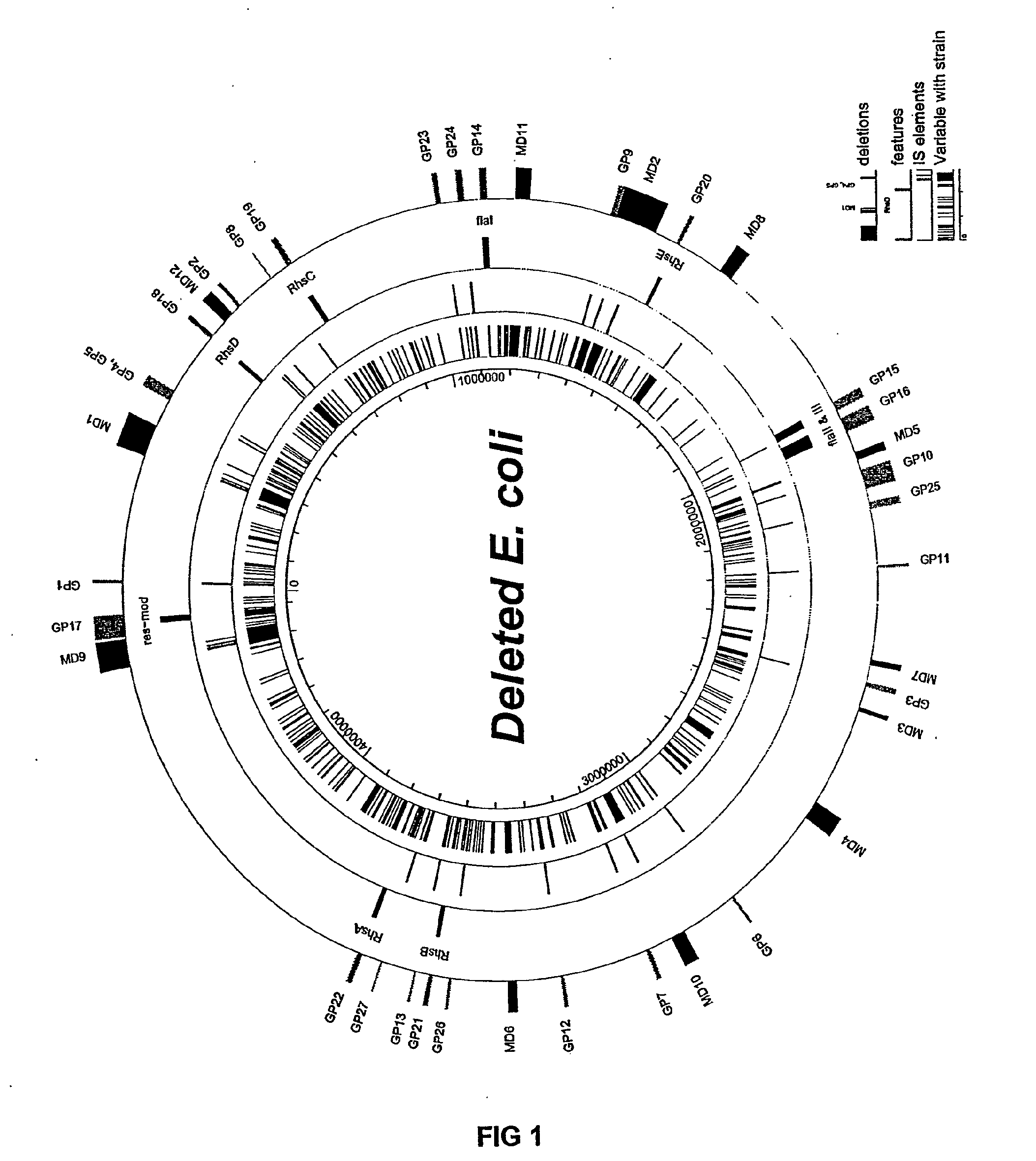
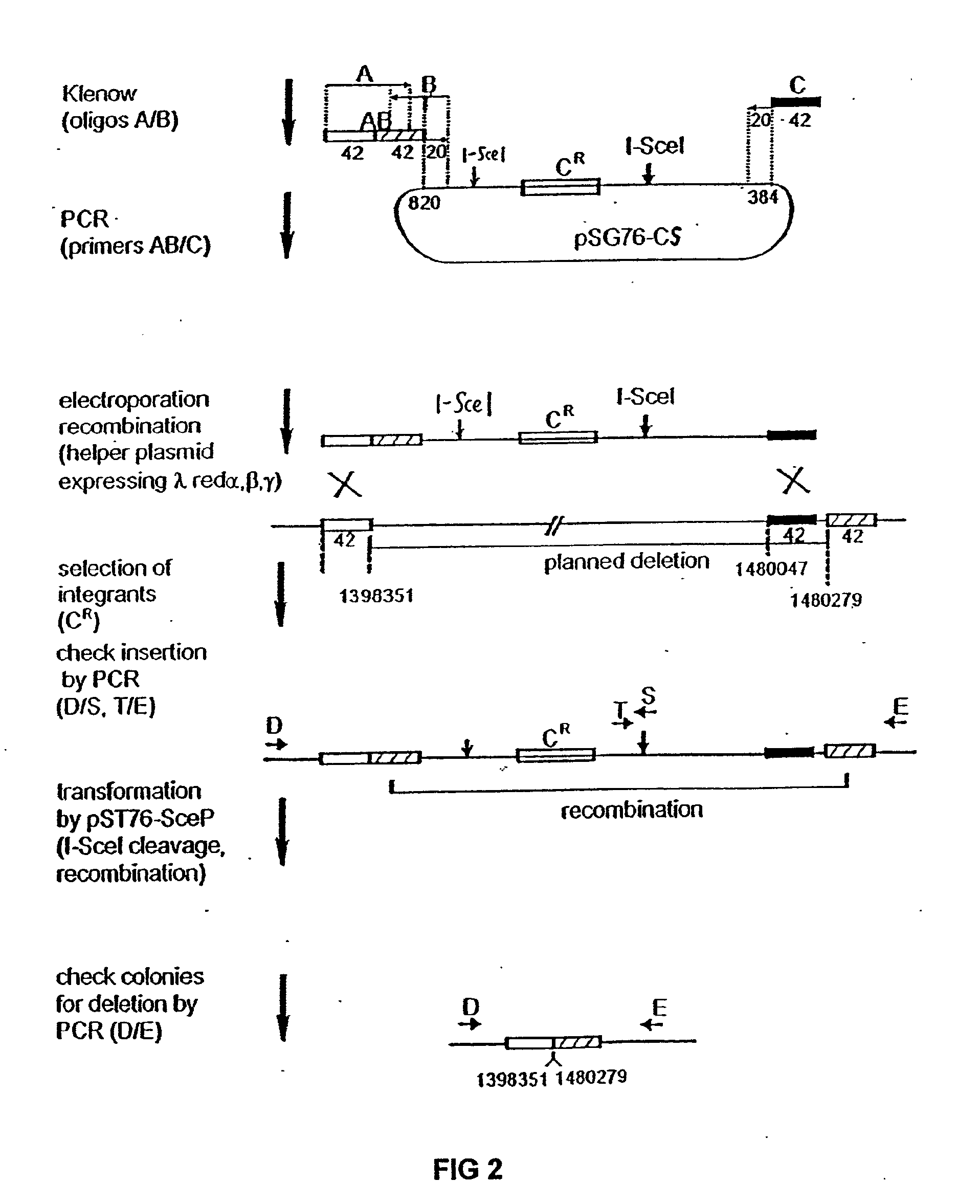
Insertion sequence-free bacteria
InactiveUS8039243B2Reducing genomeEfficient processingBacteriaSugar derivativesBacteroidesBacterial genome size
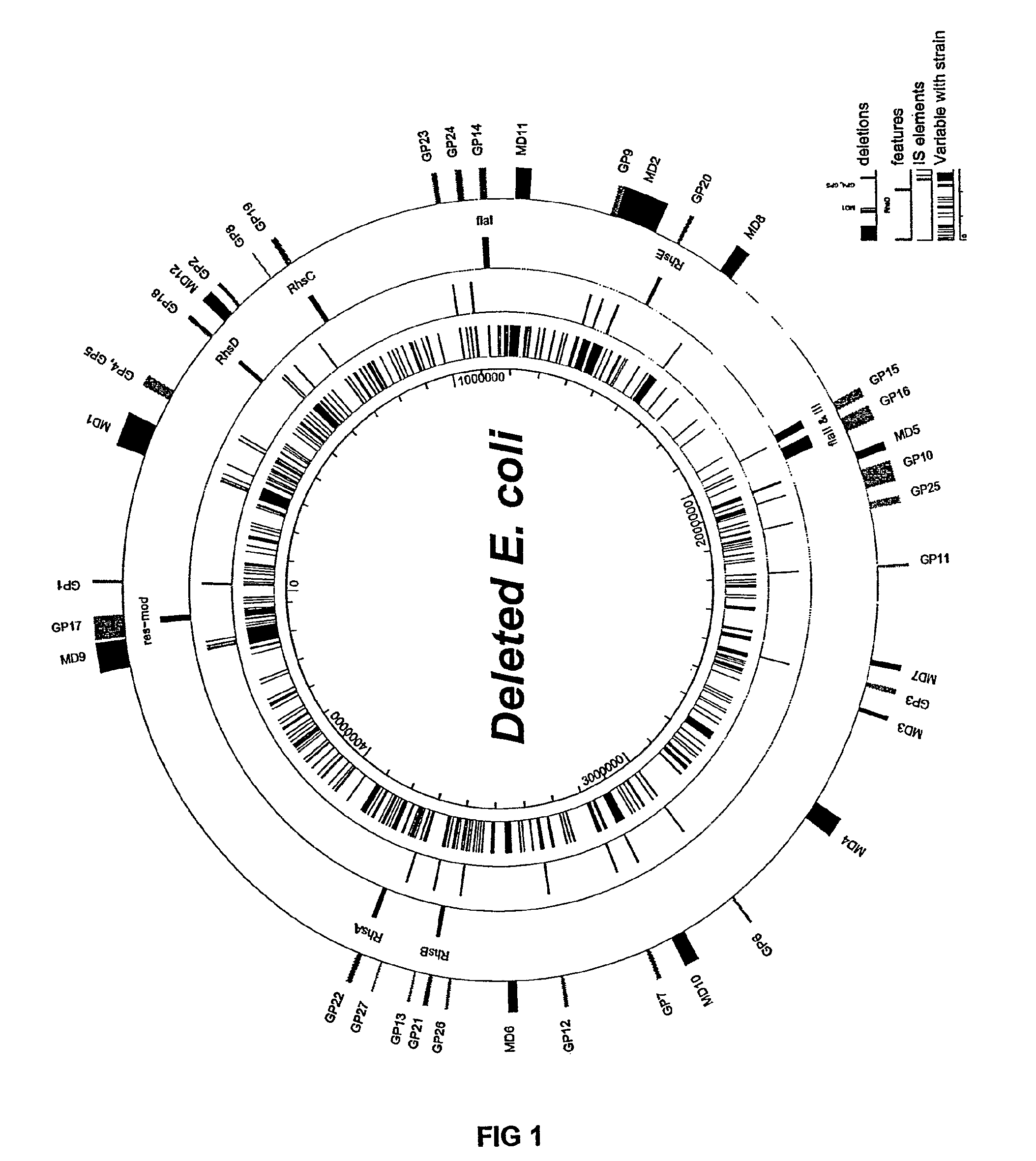
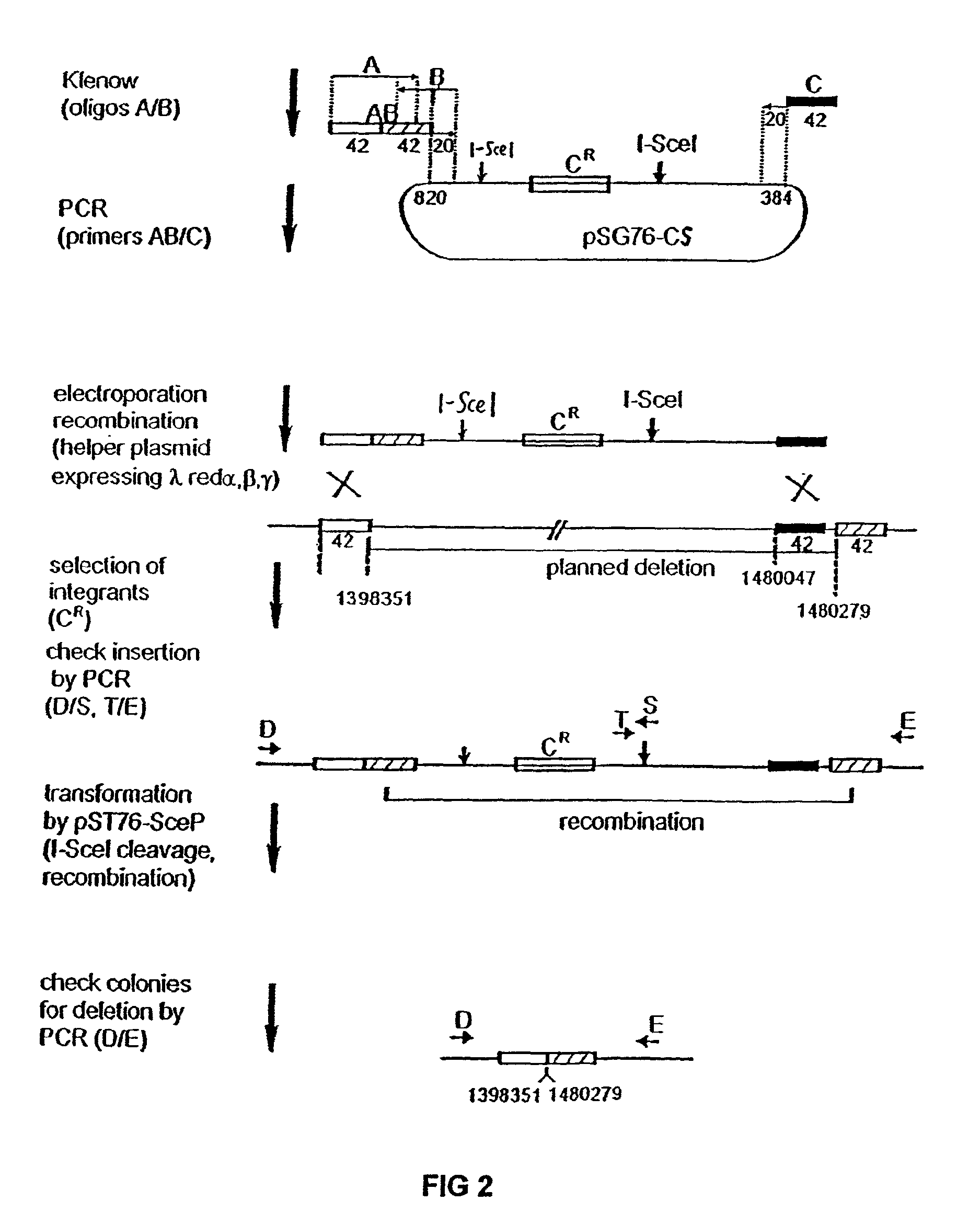
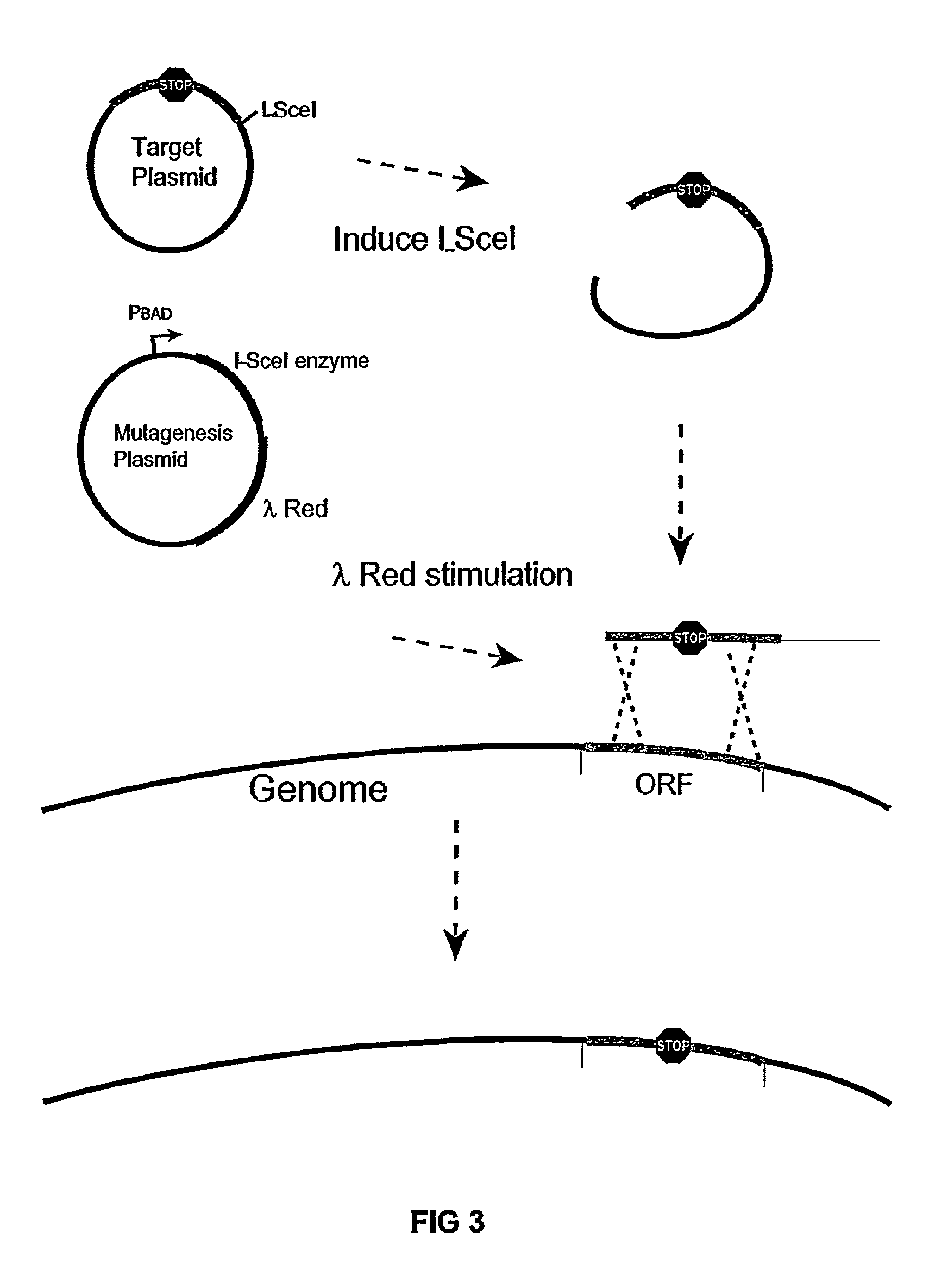
The present invention provides a bacterium having a genome that is genetically engineered to be smaller than the genome of its native parent strain. A bacterium with a smaller genome can produce a commercial product more efficiently. The present invention also provides methods for deleting genes and other DNA sequences from a bacterial genome. The methods provide precise deletions and seldom introduces mutations to the genomic DNA sequences around the deletion sites. Thus, the methods can be used to generate a series of deletions in a bacterium without increasing the possibility of undesired homologous recombination within the genome. In addition, some of the methods provided by the present invention can also be used for replacing a region of a bacterial genome with a desired DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
Intergenic regions as novel sites for insertion of HIV DNA sequences in the genome of modified vaccinia virus ankara
ActiveUS20060188961A1Stably express multiple HIV proteinsRaise the possibilitySsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesInsertion siteIntergenic region
Owner:BAVARIAN NORDIC AS
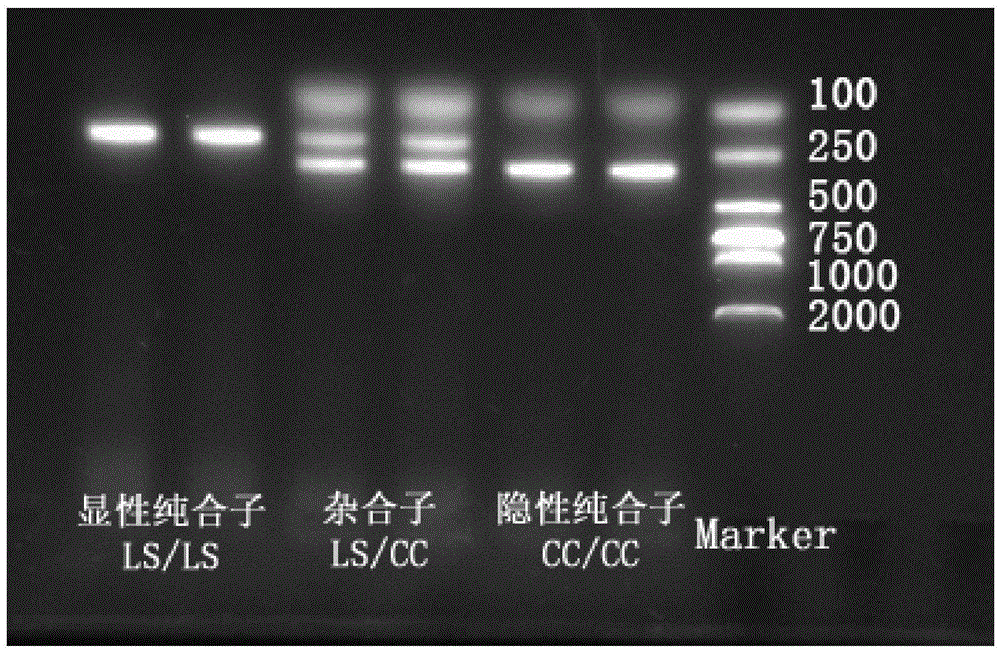
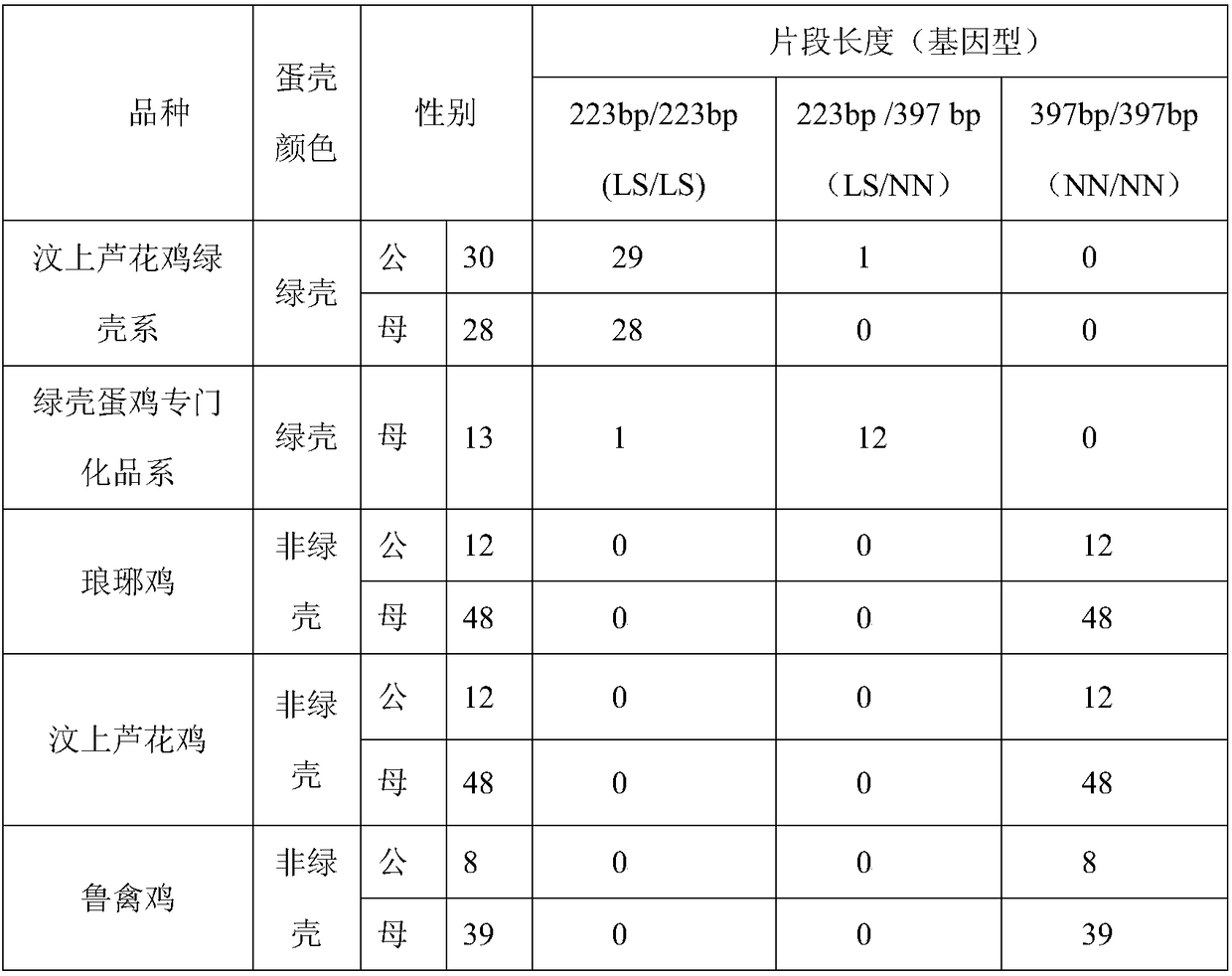
Primer composition for discriminating green-shelled-egg chicken genotype and use thereof
InactiveCN104830843AMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGallus gallus gallusGenotype
The invention discloses a primer composition for discriminating a green-shelled-egg chicken genotype and a use thereof. The primer composition comprises two primer pairs, one primer pair comprises SLCO1B3 gene inserted EAV-HP sequence primers respectively shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO. 1 and 2, and the other primer pair comprises SLCO1B3 gene non-inserted sequence primers respectively shown in the formulas of SEQ ID NO. 1 and 3. A DNA genome of a chicken to be detected is used as a template and is subjected to PCR amplification under the action of the primer pairs so that a PCR amplification product is obtained. Through detection of the amplified 209bp and 312bp bands, it is determined if the chicken to be detected can produce green-shelled eggs. The primer composition can discriminate the green-shelled-egg chicken genotype.
Owner:SICHUAN AGRI UNIV
Routing system and route update method
InactiveUS20070165543A1Data switching by path configurationSecuring communicationRouting tableRoute search
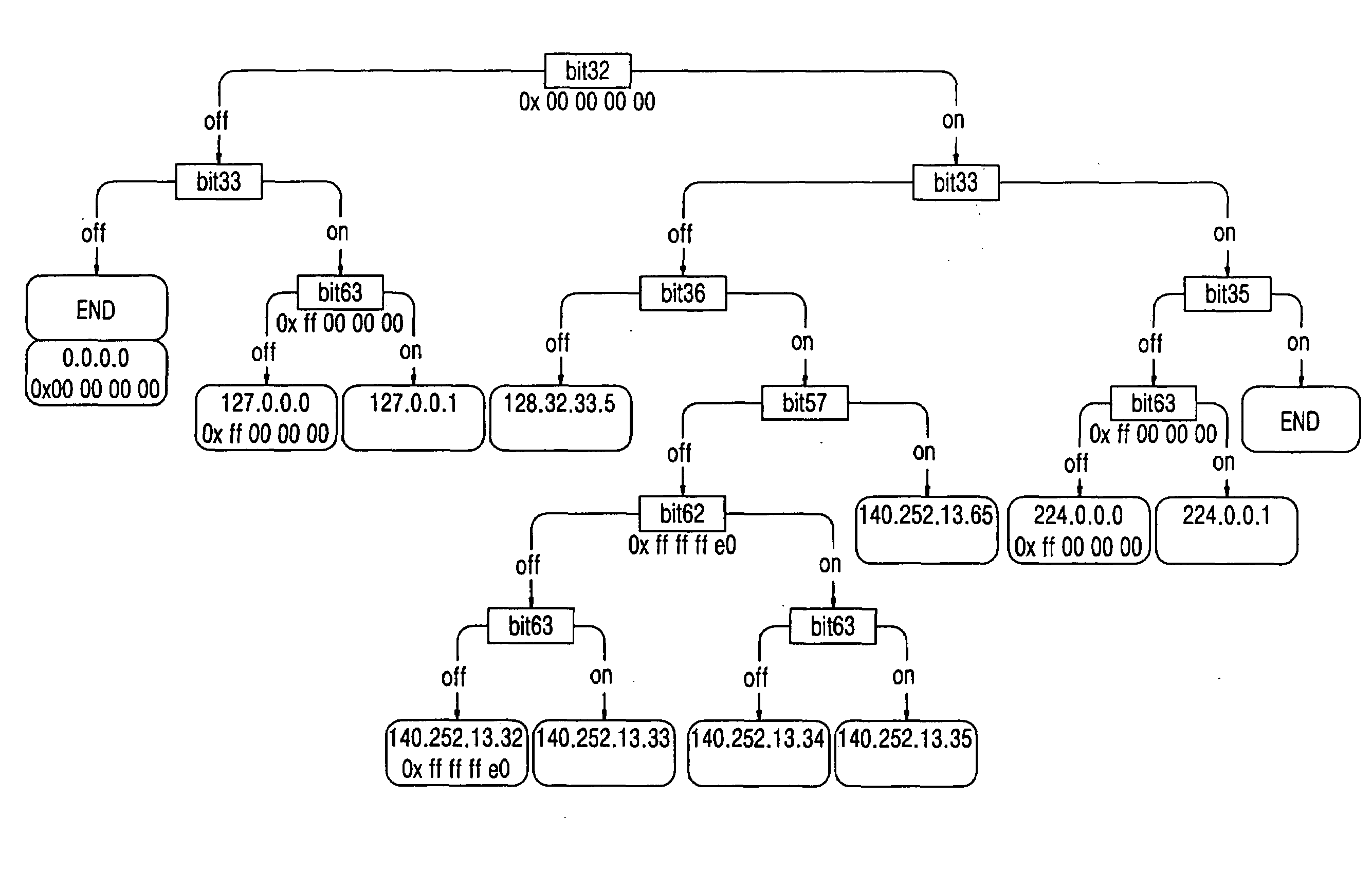
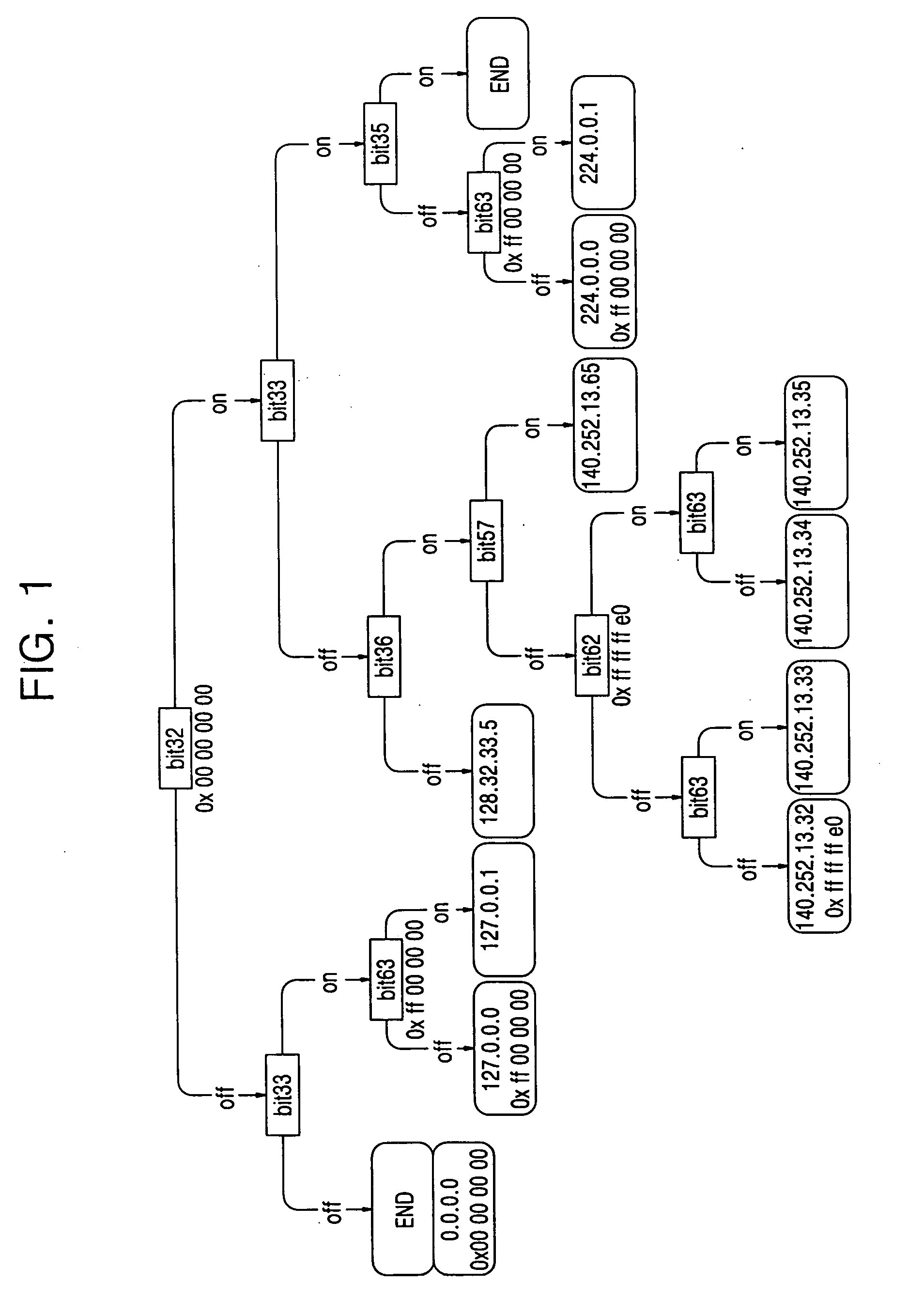
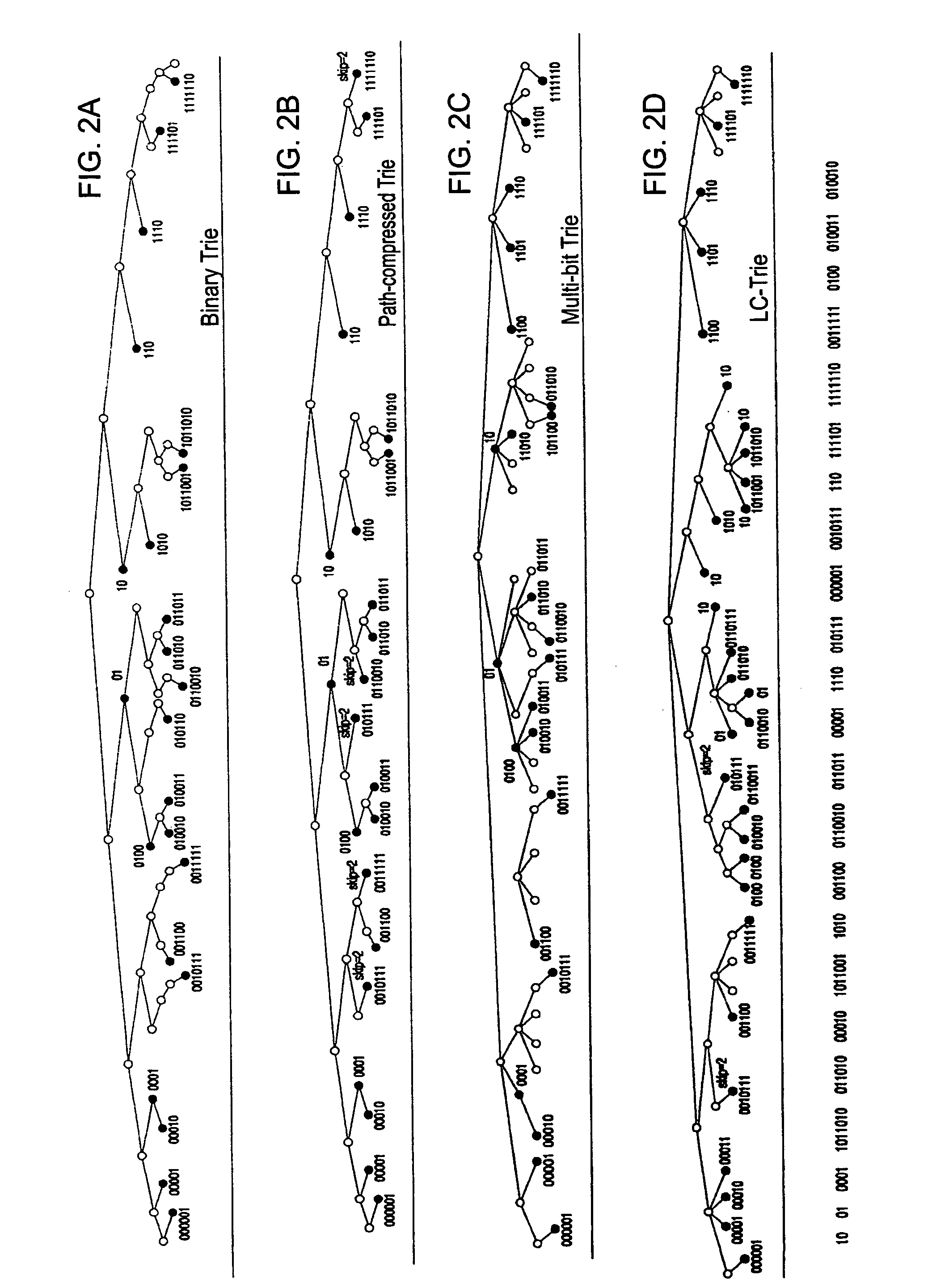
A route update method includes: storing information on route insertion sequence by each routing protocol in respective entries in a routing table; performing a prefix search according to the stored route insertion sequence upon a restart of a routing module, and updating a corresponding routing entry upon a prefix matching occurring as a result of the prefix search, and performing a search according to a general Trie structure upon a prefix matching failure to succeed occurring as a result of the prefix search. Accordingly, the route search time is reduced upon a route update.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Insertion sequence element derived from ralstonia solanacearum
InactiveUS20030009026A1Useful industriallyReduce pathogenicitySugar derivativesHydrolasesRalstonia solanacearumInsertion sequence
Owner:NAT INST OF AGROBIOLOGICAL SCI
Recombinant adenoviral vector system
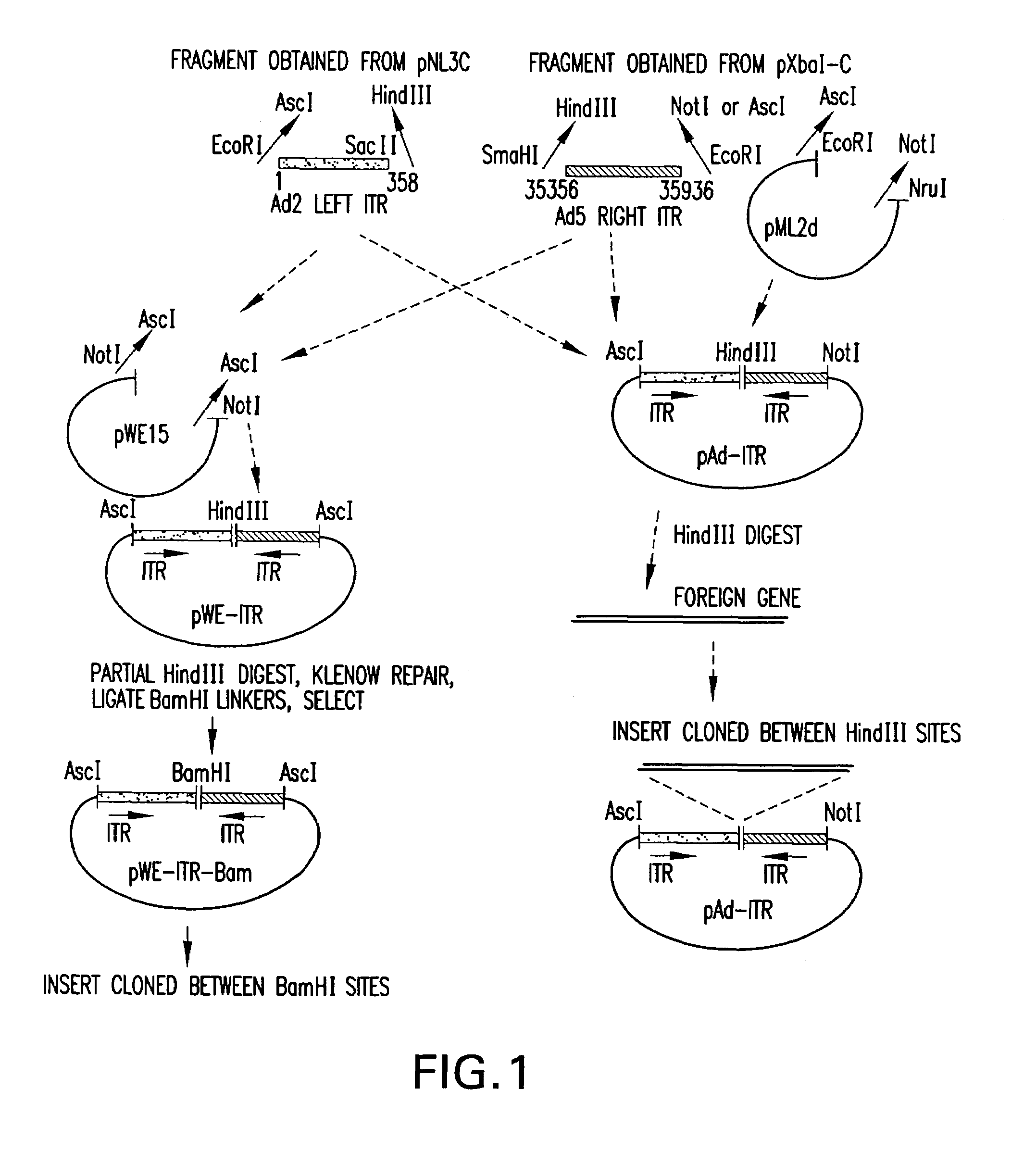
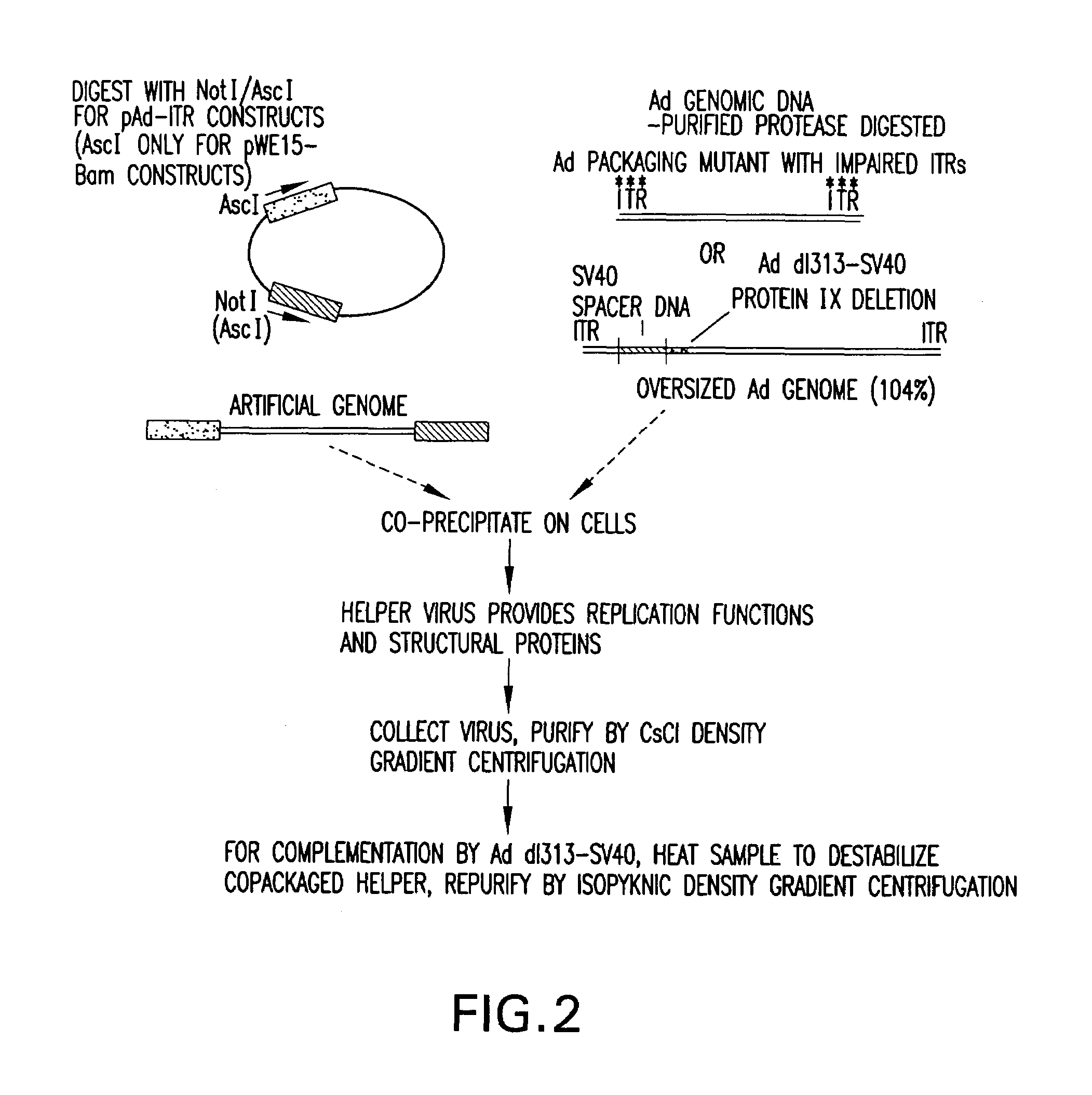
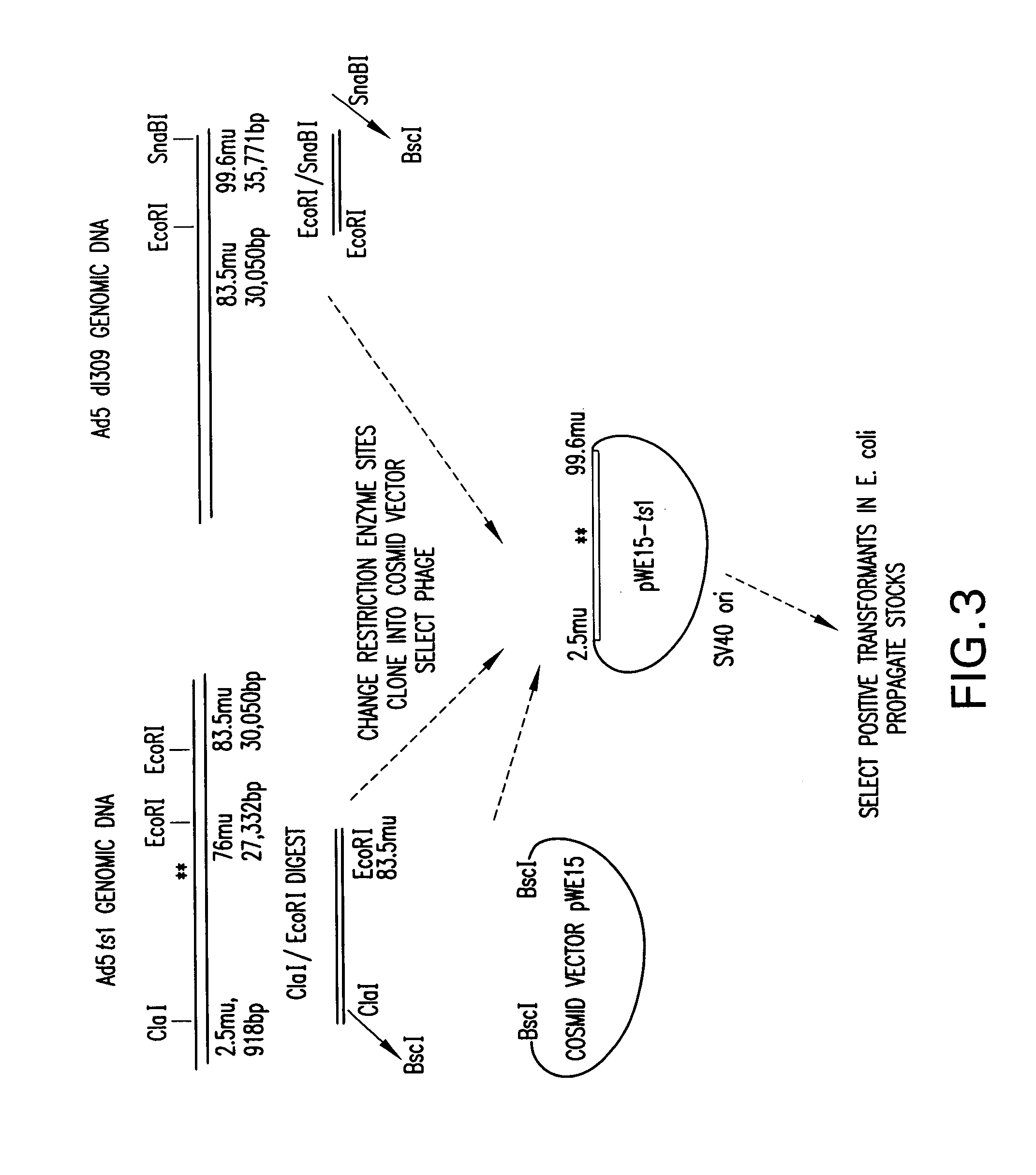
InactiveUS7348178B1Minimize and eliminate contaminationMinimize of cell viabilityGenetic material ingredientsOther foreign material introduction processesVector systemViral vector
The present invention relates to a novel Ad based packaging system that can be used for incorporation of heterologous DNA into infectious but replication defective viral particles. The components of the invention include an “artificial genome”, i.e., a recombinant vector which contains elements that function as adenovirus replication and packaging signals flanking an intervening DNA sequence. The elements may comprise the minimum genomic Ad sequences required to direct replication of heterologous DNA and packaging into viral particles. The system also includes a means for expressing complementing helper functions to provide in trans viral proteins required for replication and packaging of recombinant viral vectors, but without contaminating the stock of recombinant, trans-packaged viral particles.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV MEDICAL CENT
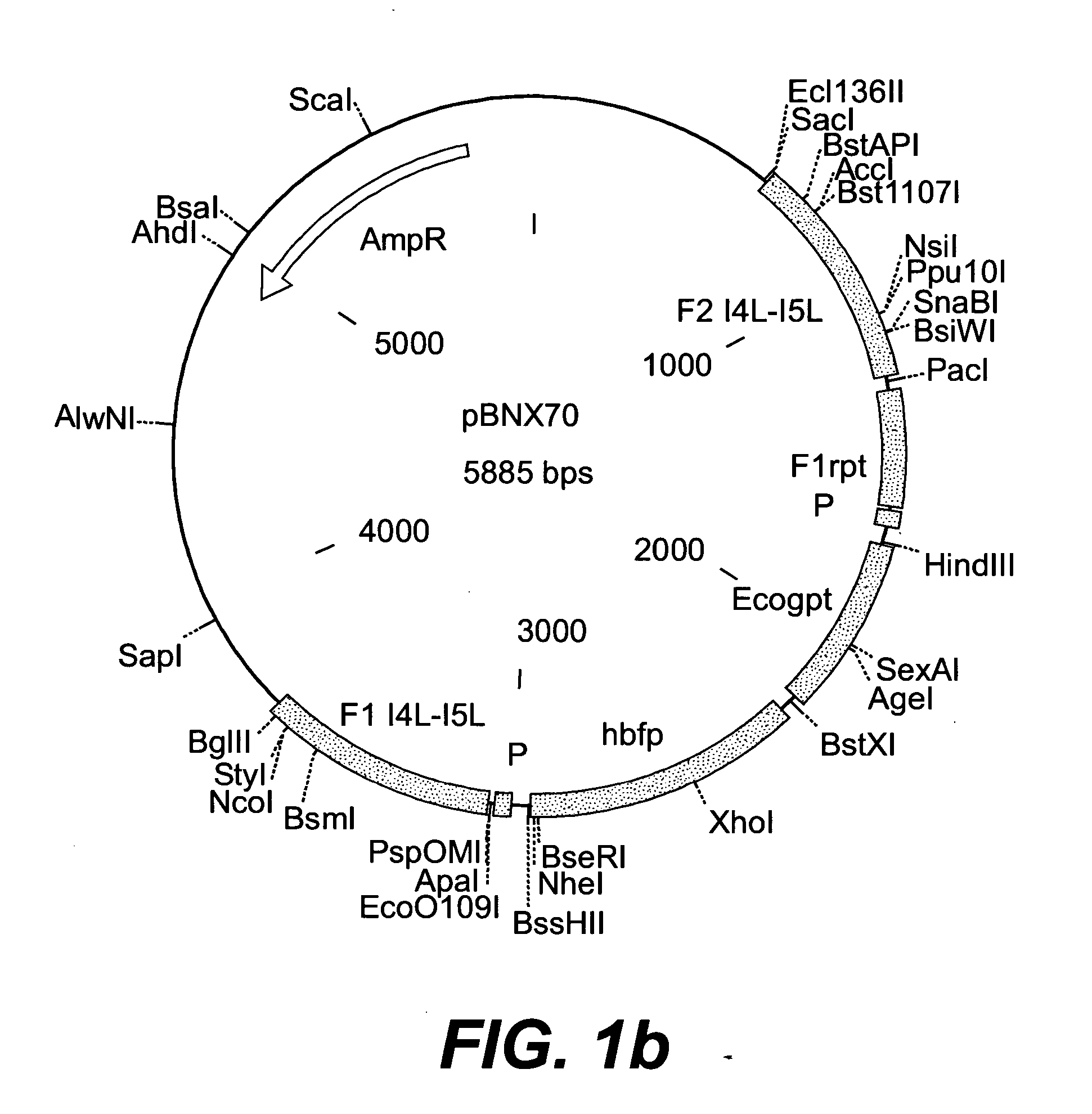
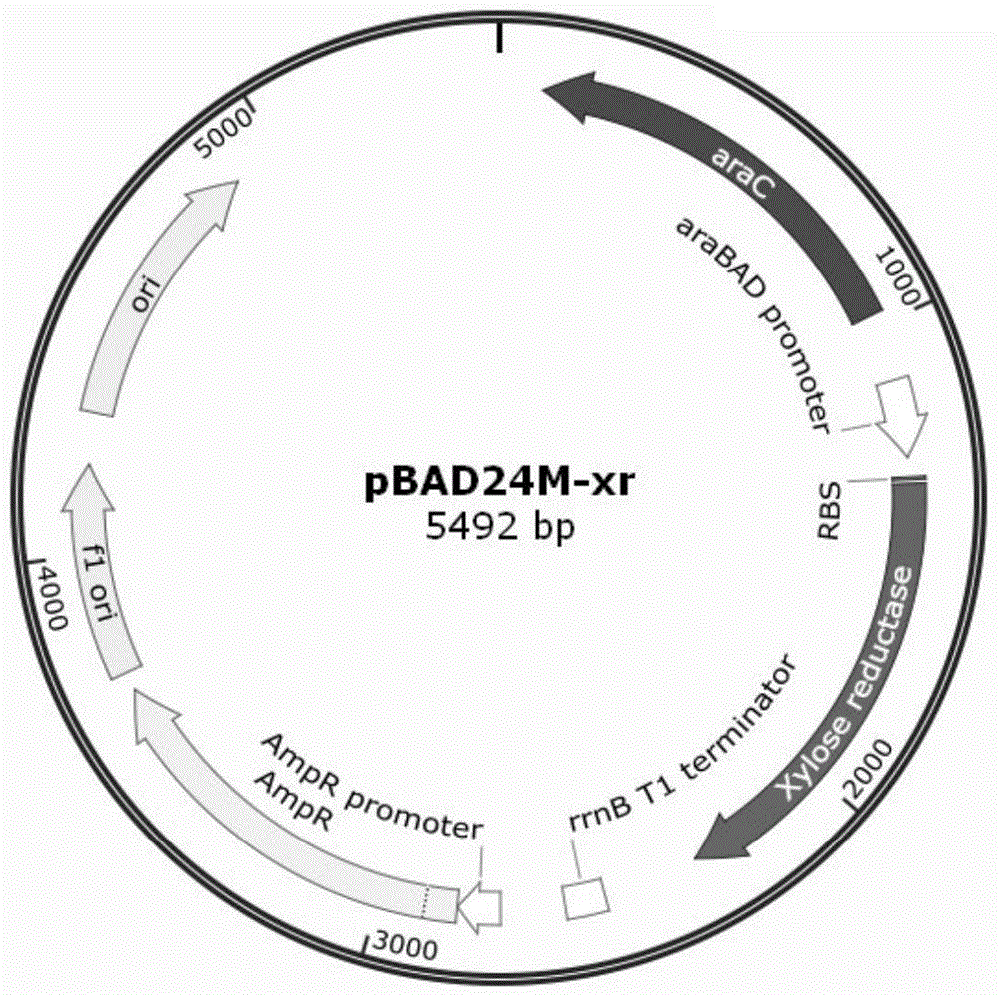
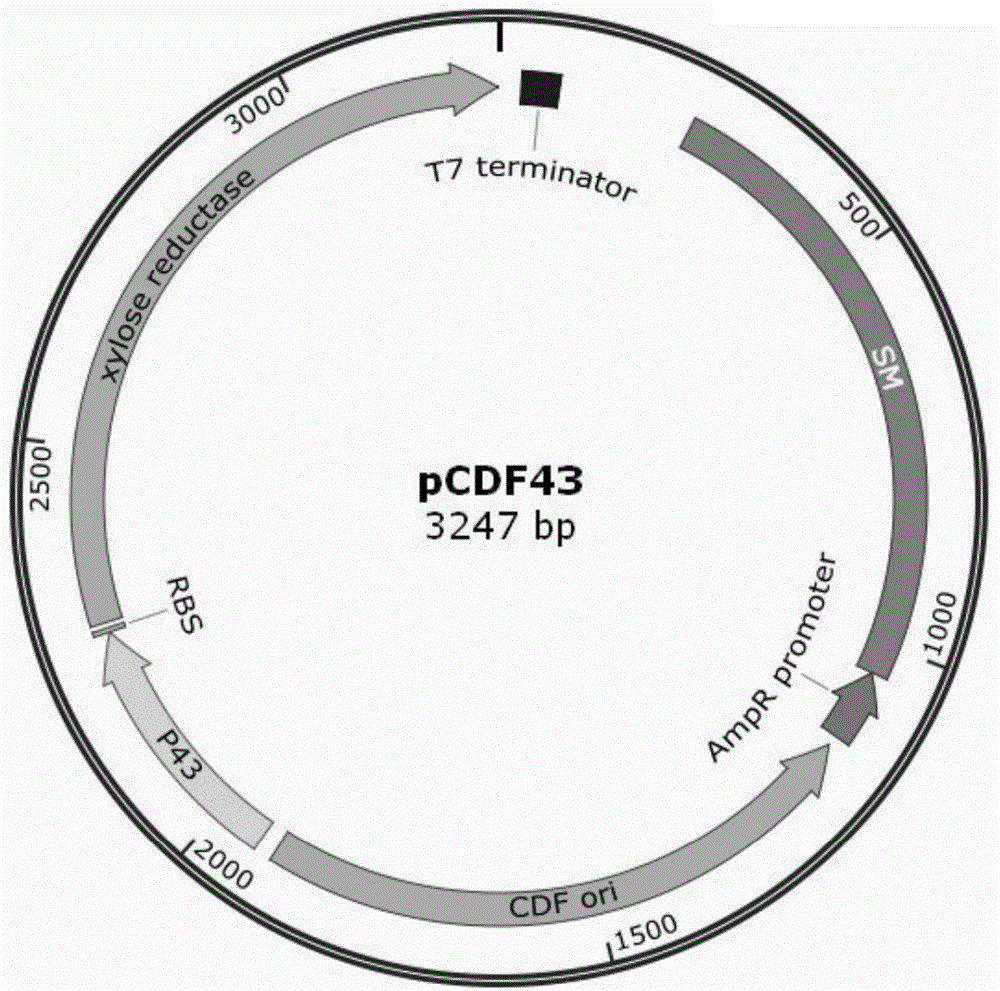
Escherichia coli genome integration vector, genetically engineered bacterium and application of genetically engineered bacterium to xylitol production
InactiveCN104789586AGenetic stabilityEasy to integrateBacteriaFermentationEscherichia coliInsertion sequence
The invention discloses an escherichia coli genome integration vector, a genetically engineered bacterium and an application of the genetically engineered bacterium to xylitol production. The escherichia coli genome integration vector comprises a replicon, an expression original, a target gene, a resistant gene and an integration site, wherein the integration site is an IS (insertion sequence). The genetically engineered bacterium comprises escherichia coli and the integration vector integrated in an escherichia coli genome. The IS with relatively high copy number in the escherichia coli genome is taken as the integration site for performing integration of the vector and the genome, so that an integration method is simple, the target gene integrated on the genome is genetically stable, problems of high metabolic burden, unstable separation and uncontrollable protein expression of engineered bacterium when a plasmid serves as an expression vector are solved, an existing integration technology is simplified, and problems of complexity, high time consumption and the like of multi-copy integration in the existing integration technology are solved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Corynebacterium glutamicum establishment method for increasing yield of L-lysine and improving stability of L-lysine
ActiveCN110106206AIncrease productionImprove stabilityStable introduction of DNAMicroorganism based processesCorynebacterium efficiensNucleotide
The invention relates to a corynebacterium glutamicum establishment method for increasing the yield of L-lysine and improving the stability of the L-lysine. According to the method, after a Tnp7a geneof corynebacterium glutamicum is inactivated, the corynebacterium glutamicum is established, and an amino acid sequence of the Tnp7a gene is shown in SEQ ID NO:1. According to the corynebacterium glutamicum establishment method for increasing the yield of the L-lysine and improving the stability of the L-lysine, the endogenous gene Tnp7a of the established corynebacterium glutamicum is inactivated, the transposition effect, caused when an insertion sequence is activated due to an environment change, of the corynebacterium glutamicum in the preservation and fermentation process is lowered, thestrain degeneration progress, caused by mutation or frame shift generated by transposition or adjustment on expression of adjacent genes through promoters carried by a genome, of the genome is blocked, and the yield of the L-lysine is increased.
Owner:ZHUCHENG DONGXIAO BIOTECH
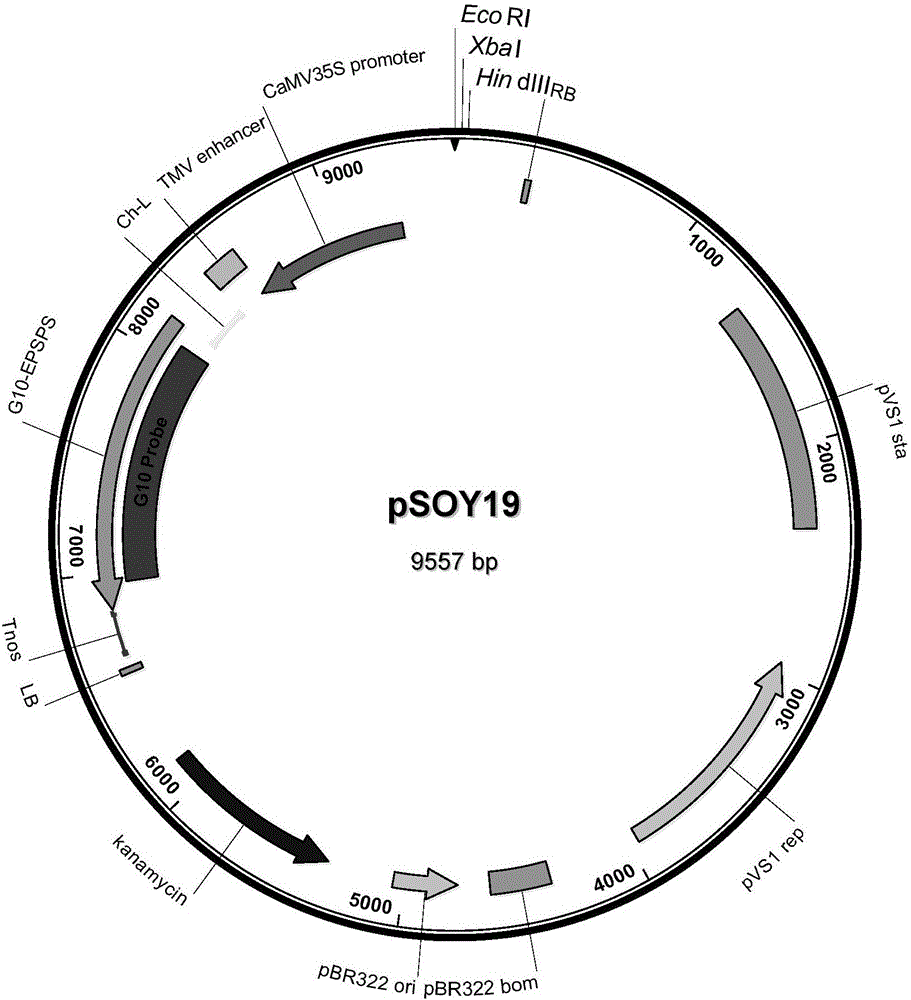
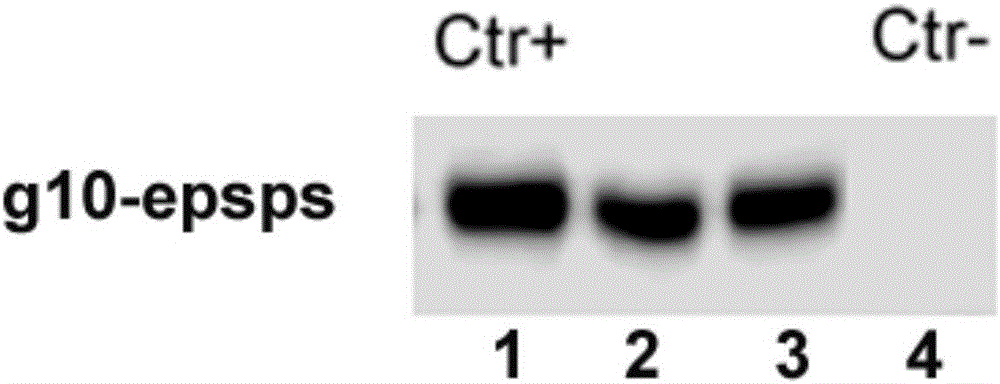
Transgenic soybean ZUTS-33 preparation method, detection and application
InactiveCN106498030AMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisInsertion sequenceGenome
The invention discloses a soybean transformation event ZUTS-33 which comprises an exogenous insertion sequence. A connection sequence formed by a 5'-terminal of the exogenous insertion sequence and endogenous genome DNA is shown as SEQ ID NO:1, and a connection sequence formed by a 3'-terminal of the exogenous insertion sequence and endogenous genome DNA is shown as SEQ ID NO:2. The invention further discloses a detection method for identification of transgenic soybean ZUTS-33, a method for detecting event ZUTS-33 or filial generations thereof in biological samples, a method for detecting exogenous insertion DNA molecules in the event ZUTS-33, a method for detecting event ZUTS-33 derived plant materials and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
High-activity glutathion peroxidase GPX 1 mutant and its preparation method
ActiveCN103320406AIncrease vitalityImprove protectionOxidoreductasesVector-based foreign material introductionGenes mutationNatural source
A high-activity glutathion peroxidase GPX 1 mutant and its preparation method belong to the field of biotechnology. A mutant gene is obtained by a gene mutation or synthesis method, and then a catalytic group SeCys of GPX is introduced into a substrate binding part of the mutant through an auxotroph prokaryotic expression system or an auxotroph and SPP low-temperature combined expression system so as to endow the mutant with high GPX activity; or a target gene, along with a SeCys insertion sequence, is firstly assembled onto a secreting type mammalia cellular expression vector, and then a binding protein 2 of the SeCys insertion sequence is assembled onto an intracellular mammalia cellular expression vector, contransfection of the same lactation cell strain is carried out by the two vectors, and GPX is synthesized by the lactation cell in the presence of sodium selenite. The method provided by the invention is simple. The mutant provided by the invention has advantages of high activity, high yield and good stability. Yield decreasing and inactivation caused by renaturation of an inclusion body are avoided. Thus, natural GPX source limitation and unstable properties are solved.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
Oligonucleotide inhibition of cell adhesion
Compositions and methods are provided for the treatment and diagnosis of diseases amenable to treatment through modulation of the synthesis or metabolism of intercellular adhesion molecules. In accordance with preferred embodiments, oligonucleotides are provided which are specifically hybridizable with nucleic acids encoding intercellular adhesion molecule-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule-1, and endothelial leukocyte adhesion molecule-1. The oligonucleotide comprises nucleotide units sufficient in identity and number to effect said specific hybridization. In other preferred embodiments, the oligonucleotides are specifically hybridizable with a transcription initiation site, a translation initiation site, 5'-untranslated sequences, 3'-untranslated sequences, and intervening sequences. Methods of treating animals suffering from disease amenable to therapeutic intervention by modulating cell adhesion proteins with an oligonucleotide specifically hybridizable with RNA or DNA corresponding to one of the foregoing proteins are disclosed. Methods for treatment of diseases responding to inhibition of cell adhesion molecules are disclosed.
Owner:IONIS PHARMA INC
Insertion Sequence-Free Bacteria
InactiveUS20060199257A1Reducing genomeEfficient processingSugar derivativesBacteriaGenomic DNAInsertion sequence
The present invention provides a bacterium having a genome that is genetically engineered to be smaller than the genome of its native parent strain. A bacterium with a smaller genome can produce a commercial product more efficiently. The present invention also provides methods for deleting genes and other DNA sequences from a bacterial genome. The methods provide precise deletions and seldom introduces mutations to the genomic DNA sequences around the deletion sites. Thus, the methods can be used to generate a series of deletions in a bacterium without increasing the possibility of undesired homologous recombination within the genome. In addition, some of the methods provided by the present invention can also be used for replacing a region of a bacterial genome with a desired DNA sequence.
Owner:WISCONSIN ALUMNI RES FOUND
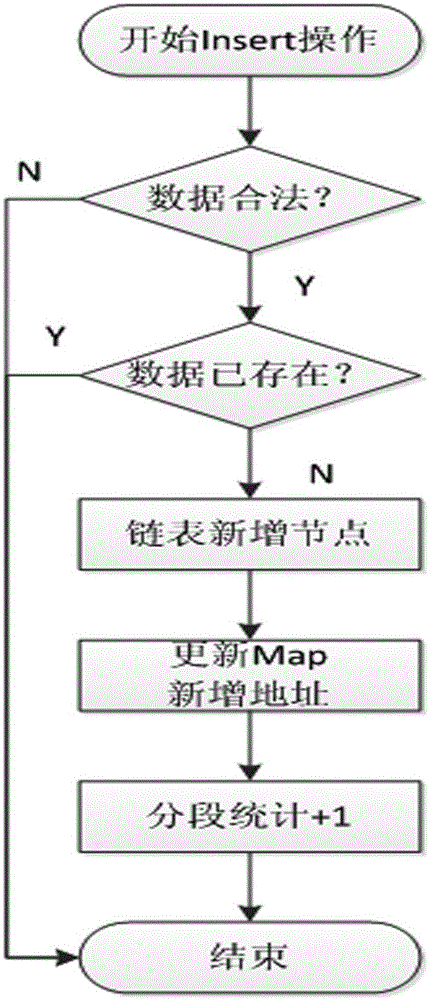
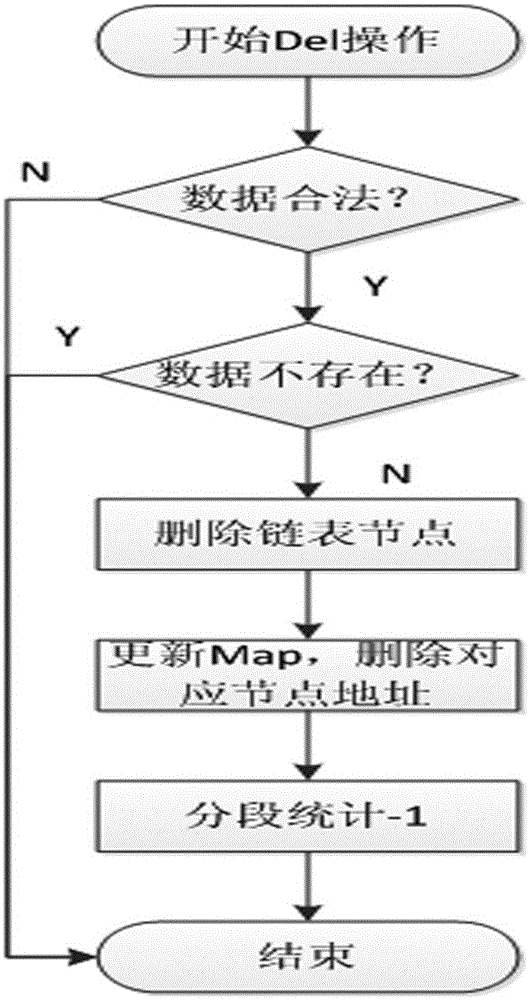
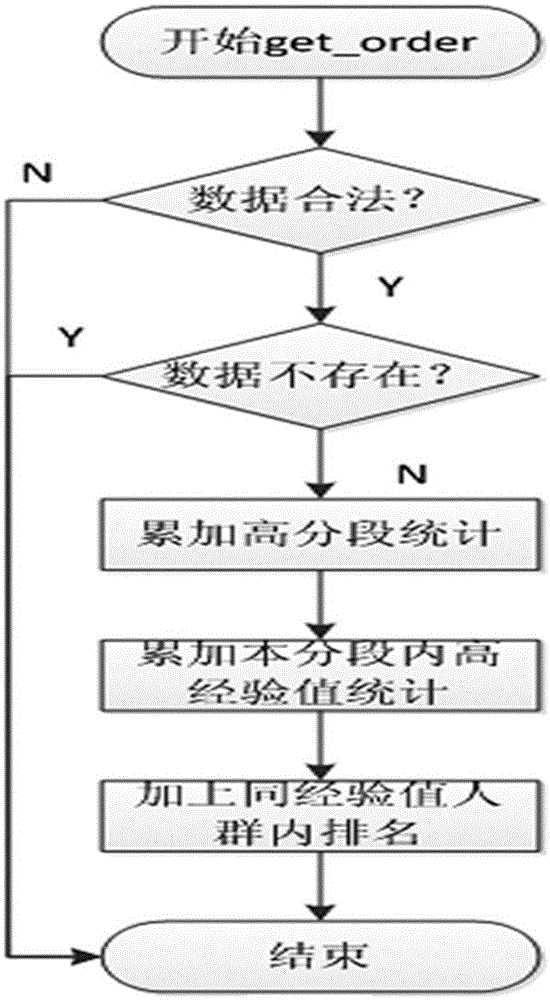
Mass data real-time sorting and inquiring method and system
InactiveCN105159950AAdd deleteWeb data indexingSpecial data processing applicationsRankingInsertion sequence
The present invention discloses a mass data real-time sorting and inquiring method and system. The method comprises: a sorting step of partitioning users into n+1 levels from 0-n according to experience values, storing all id numbers at each level by using a linked list, respectively storing user data into each node of the linked lists, and establishing experience value inked lists, wherein an insertion sequence of the users at a current experience value level is also stored in the corresponding experience value linked list, and each experience value linked list uses a head pointer and a tail pointer which respectively point at a first node and a last node; and an inquiring step of firstly, accumulating a total people number at each experience value level from the beginning of the maximum experience value, i.e. the n+1 level, then carrying out traversal inquiring in the experience value linked lists to which the users correspondingly belong so as to find rankings of the users in the users with the same experience values, and carrying out accumulation to obtain a total ranking in the system. According to the mass data real-time sorting and inquiring method and system which are disclosed by the present invention, functions of microsecond-level inquiry, addition, deletion, real-time sorting and the like can be provided for mass data at the level of hundred millions of users.
Owner:深圳市光息谷科技发展有限公司
CAR-T cytotoxicity indicating vector
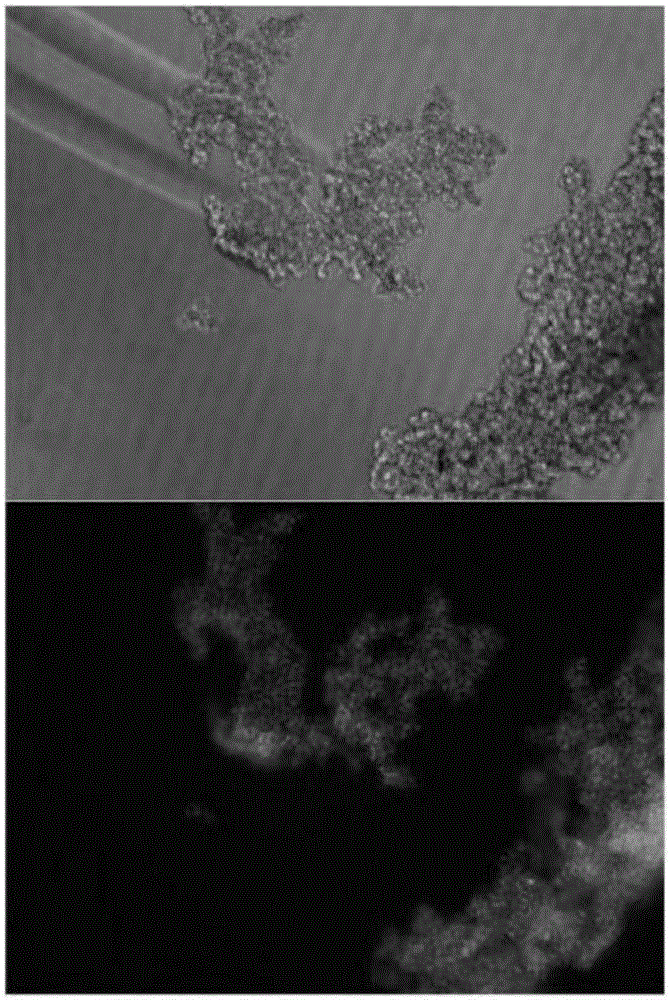
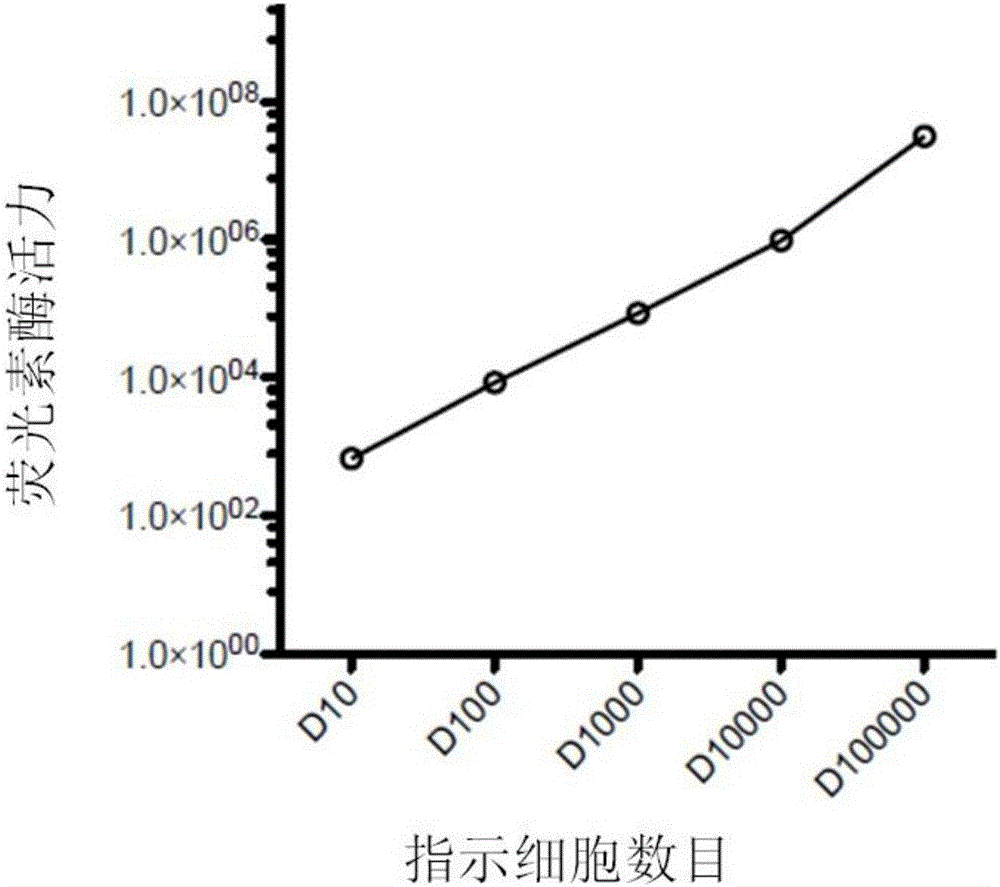
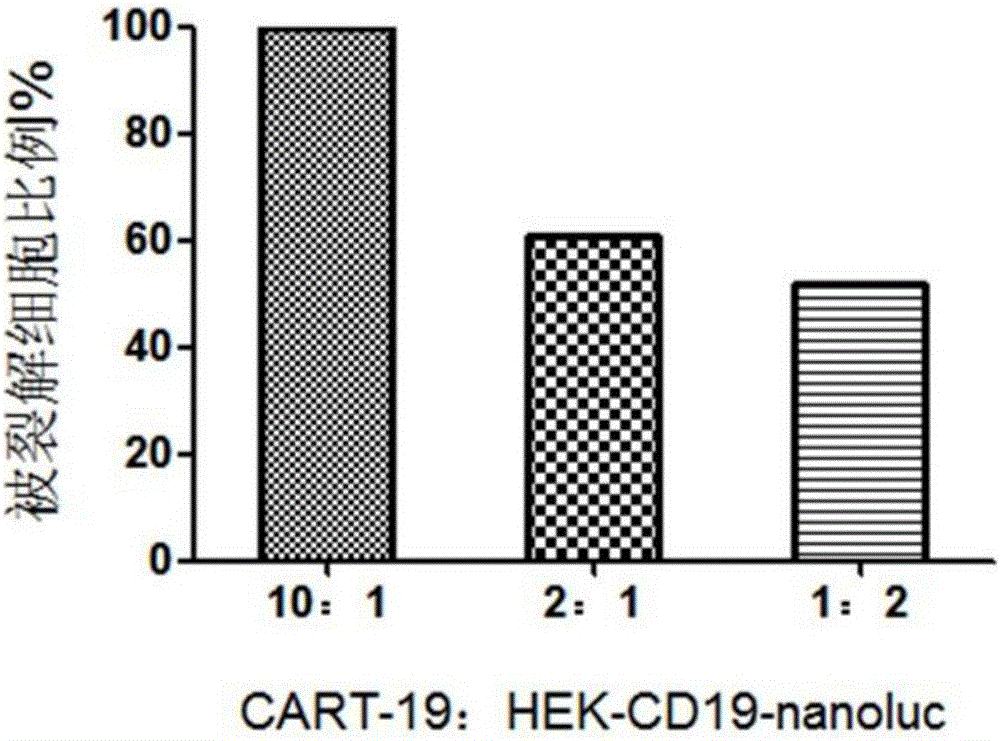
ActiveCN106086078ARealize analysisDirect detection methodImmunoglobulin superfamilyMicrobiological testing/measurementInsertion sequenceLuciferases
The invention belongs to the field of cellular immunotherapy and particularly relates to a CAR-T cytotoxicity indicating vector. The cytotoxicity indicating vector is a recombined lentiviral vector and is composed of an original lentiviral vector and an insertion sequence. The insertion sequence is composed of a tumor-correlation target antigen coding gene, a connection peptide coding gene and a luciferase coding gene from the 5' terminal to the 3'terminal in sequence. After CAR-T cells and CAR-T cytotoxicity indicating cells are mixed, a tumor-correlation target antigen expressed by the indicating cells can perform target guiding on CAR-T for combination, the indicating cells are split, and luciferase is released. Due to the fact that split cells are located in supernatant and the un-split cells are located in precipitate, the number of spit cells and the number of un-split cells can be worked out according to the relation between the indicating cell number and the luciferase activity value by detecting the activity value of luciferase in the supernatant and the activity value of luciferase in the precipitate, the proportion of the split cells is calculated, and the CAR-T cytotoxicity is indicated.
Owner:济南宜明医疗科技有限公司
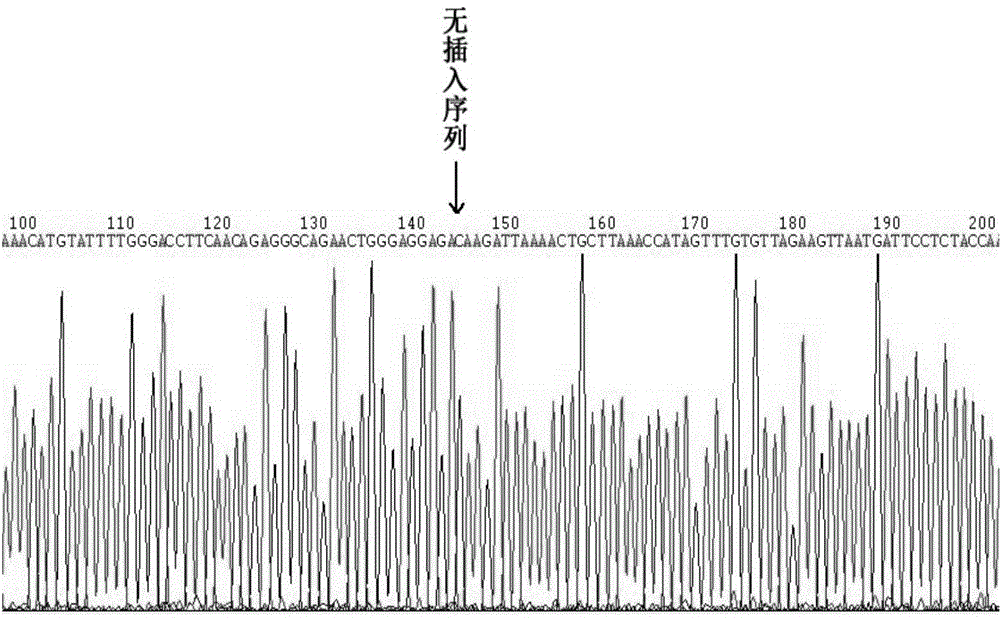
Hematopoietic stem cell gene modification method for targeting hemoglobin HBB mutant gene
The invention discloses a hematopoietic stem cell gene modification method for targeting a hemoglobin HBB mutant gene. The method 1 comprises the following steps: electro-transforming gRNA1, gRNA2 andthe mRNA of spCas9-2.0 into CD34+ cells containing the hemoglobin HBB mutant gene; and culturing the cells for one day, and transferring rAAV-HBB into the CD34+ cells, and harvesting the cells. The method 2 comprises the following steps: mixing and recombining a Cas9 protein with the gRNA1 and the gRNA2, and electro-transforming the recombinant Cas9 protein into the CD34+ cells; and culturing thecells for one day, and transferring the rAAV-HBB into the CD34+ cells, and harvesting the cells. The CD41 / 42 (-CTTT) in the most common HBB mutation in Guangxi province and Guangdong province in China is targeted, no other mutation or insertion sequences are left in chromosomes after gene editing is completed, and the gene editing efficiency can reach 15-20%.
Owner:YINFENG BIOLOGICAL GRP +1
Gene engineering method for preparing a recombinant glutathion peroxidase
ActiveCN103224915AHigh activity of recombinant GPXAvoid yieldEnzymesFermentationInclusion bodiesPeroxidase
The invention provides a gene engineering method for preparing a recombinant glutathion peroxidase, which belongs to the field of biological technology. The method comprises the following steps: assembling a target gene to a secretion type prokaryotic expression vector, introducing a catalytic group SeCys of GPX into a substrate combination position of GPX by a gene mutant method in an auxotroph prokaryotic expression system or an auxotroph and SPP combined expression system, thereby the activity of the GPS is very high; or assembling the target gene with the SeCys insertion sequence into a secretion type mammalia cell expression vector, assembling a SeCys insertion sequence binding protein 2 into an intracellular type mammalia cell expression vector, and cotransfecting the two vectors into the same lactation cell strain, and synthesizing the GPX under the existence of sodium selenite. The invention the advantages of simple method, recombined GPX vitality, high output and good stability, thereby avoiding decreased yield and inactivation caused by renaturation of an inclusion body, and solving the problem that the natural GPX source is limited and the property is not stable.
Owner:JILIN UNIV
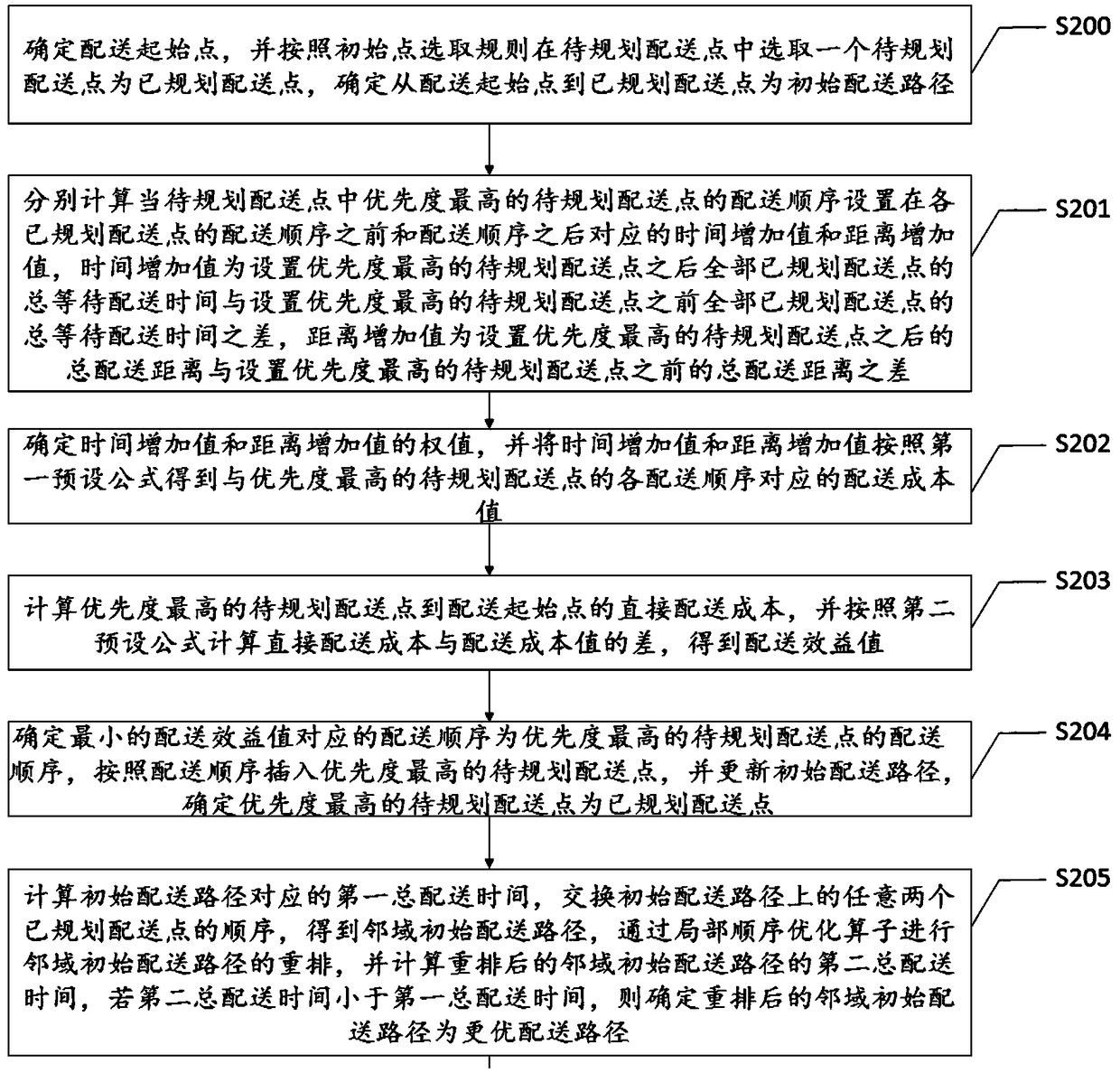
Distribution path planning method and apparatus
InactiveCN108846610AAccurately determineImprove accuracyForecastingLogisticsInsertion sequenceLocal sequence
The invention discloses a distribution path planning method and apparatus. Distribution planning is performed according to the priority level, an optimal insertion sequence of a current planning pointto be distributed is calculated in turn, a distance cost and a time cost are considered in the determination of the optimal insertion sequence, and a mechanism of local sequence transformation is added on the basis of an initial distribution path, therefore the accuracy of the path planning is improved, and the following technical problem is solved: the existing distribution path planning methodis to generally arrange the sequences of all distribution points to be planned based on the overall consideration, calculate the distribution cost and the select the distribution path with the lowestcost, this method can accurately determine the planning path for a small number of distribution objects, but for a large number of distribution objects, huge computing power of a server is required, and more computing resources are consumed.
Owner:品信科技有限公司
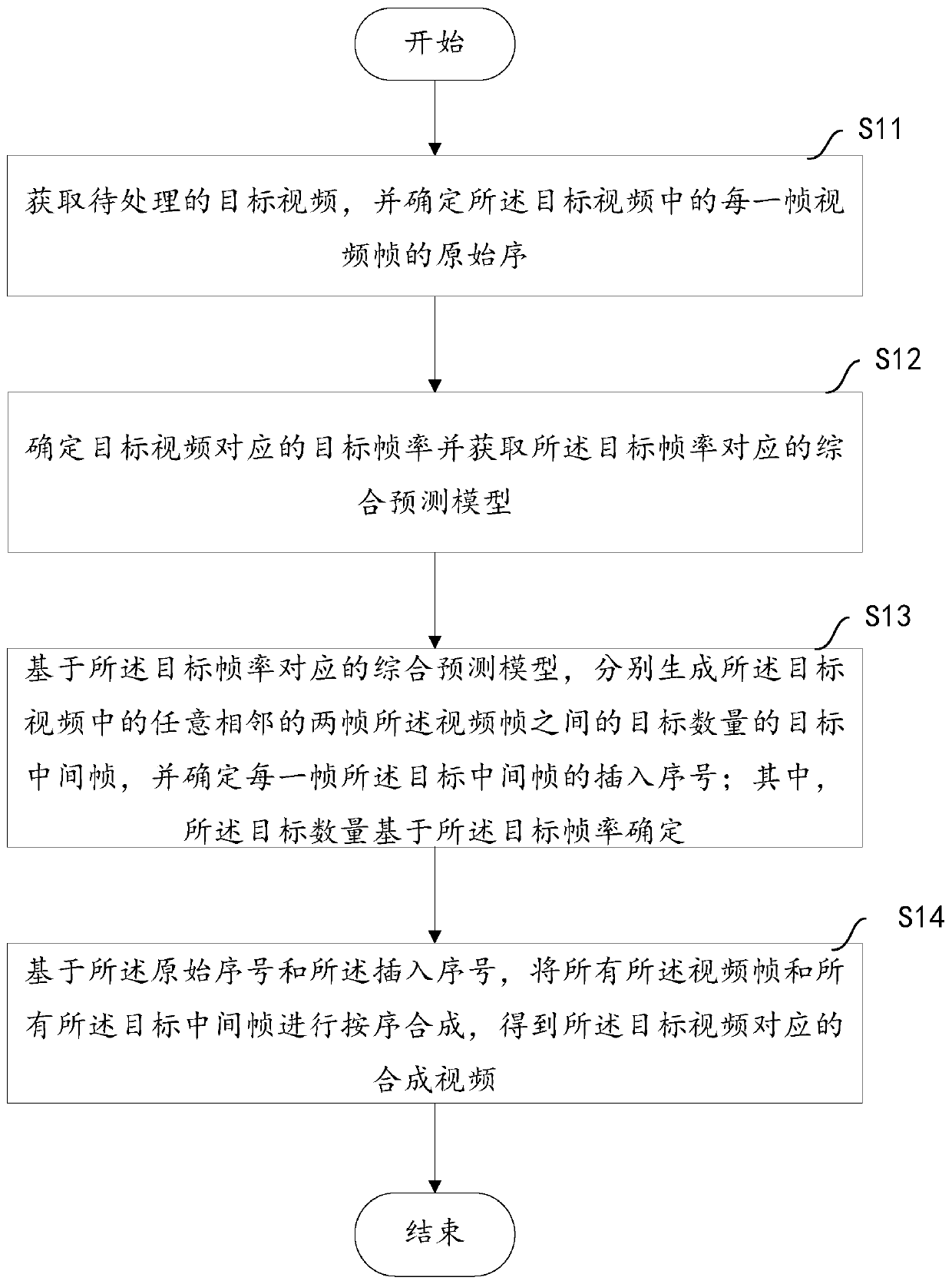
Video processing method and terminal
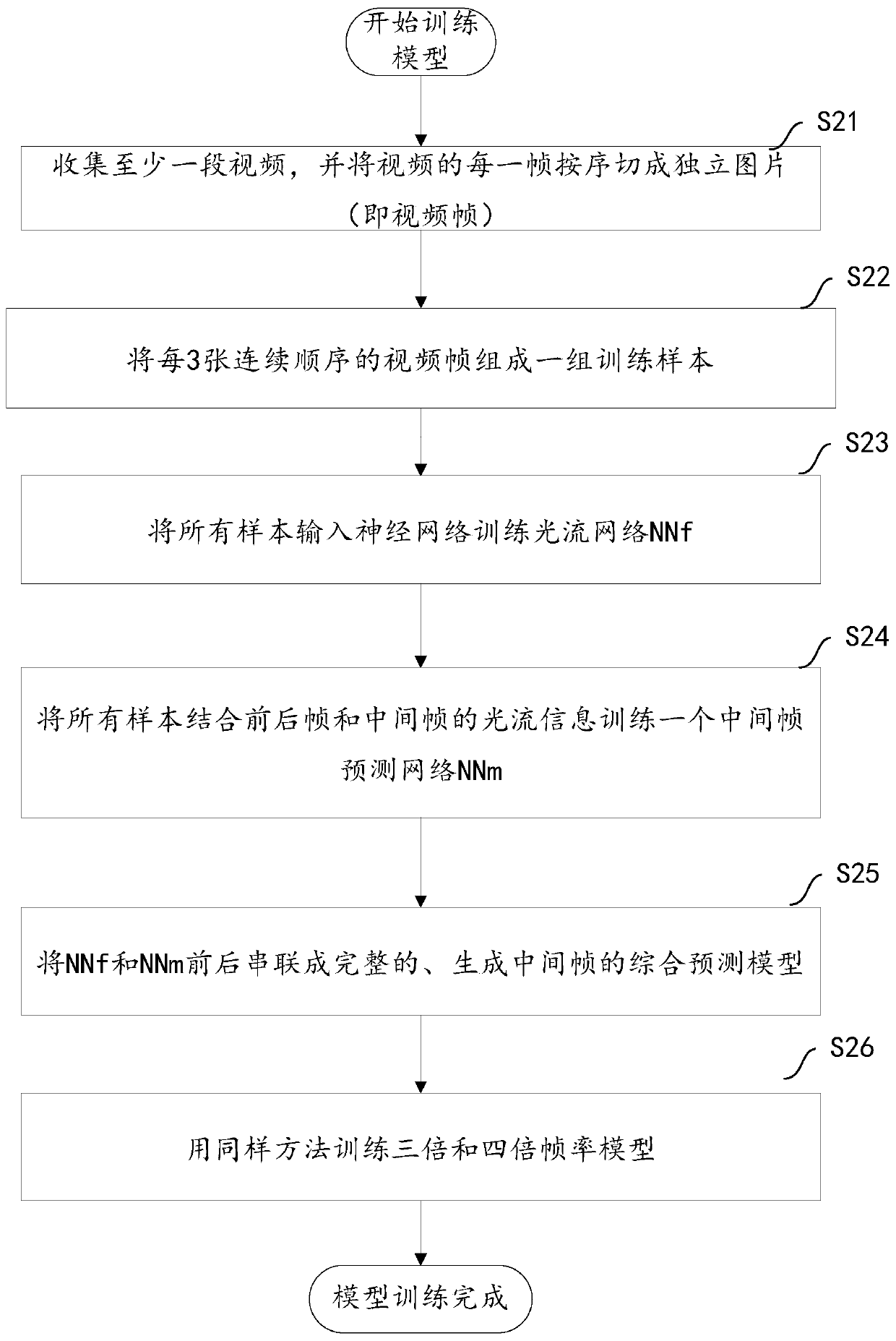
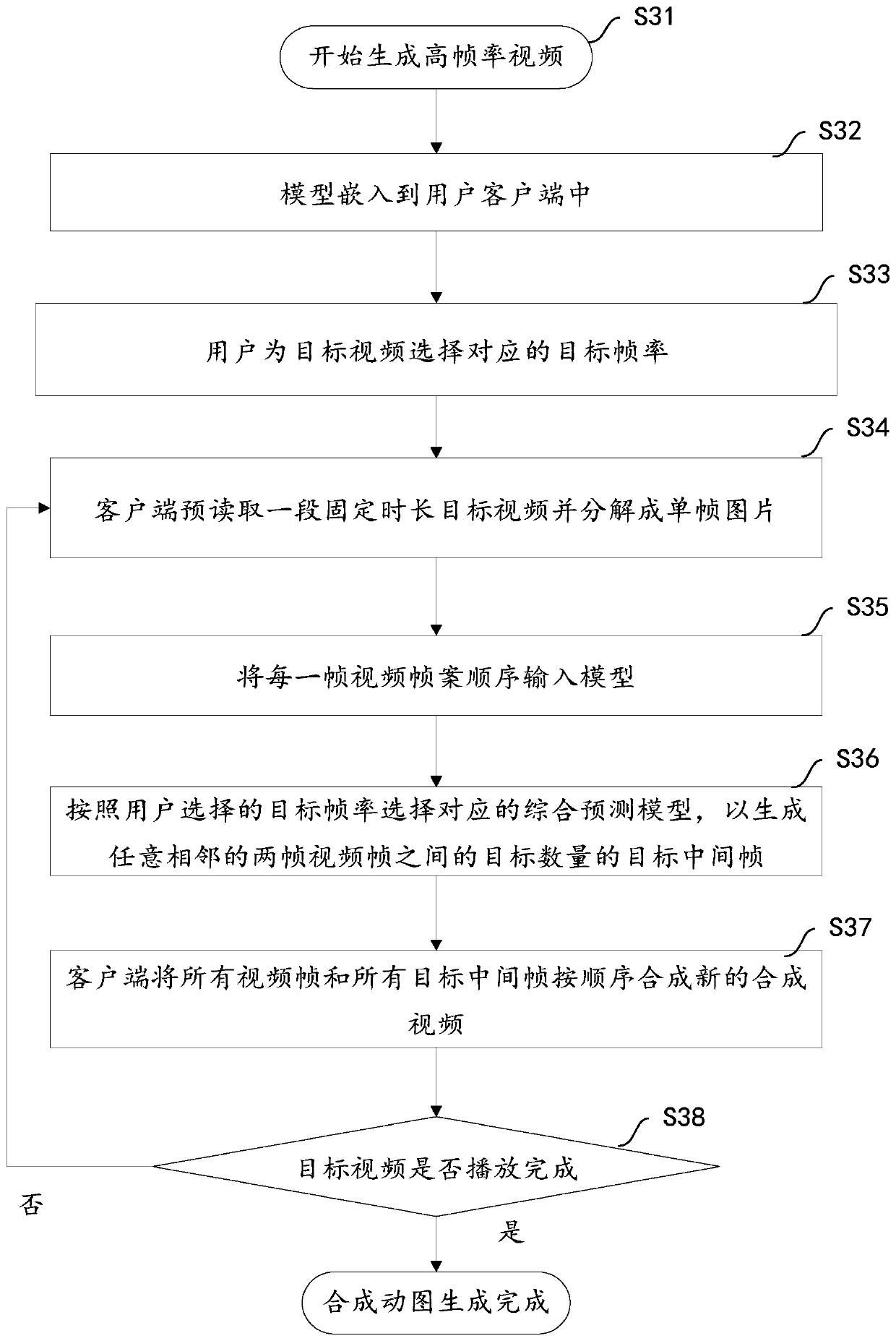
ActiveCN110267098AImprove fluencyImprove experienceTelevision system detailsColor television detailsHigh frame rateVideo processing
The invention aims to provide a video processing method and a terminal. The method comprises the steps of obtaining a to-be-processed target video through the terminal and determining an original serial number of each video frame in the target video; determining a target frame rate corresponding to the target video, and obtaining a comprehensive prediction model corresponding to the target frame rate; respectively generating a target number of target intermediate frames between any two adjacent video frames in the target video based on a comprehensive prediction model corresponding to the target frame rate, and determining an insertion sequence number of each target intermediate frame, the target number being determined based on the target frame rate; synthesizing all the video frames and all the target intermediate frames in sequence based on the original sequence number and the insertion sequence number to obtain a synthesized video corresponding to the target video. According to the method and the device, a mode of adding the intermediate frame to the target video is realized, the consistency of the target video is improved, the frame rate of the target video is improved, and the user experience of watching the high-frame-rate composite video is improved.
Owner:LIANSHANG XINCHANG NETWORK TECH CO LTD
Inserting out-of-band data into in-band data streams
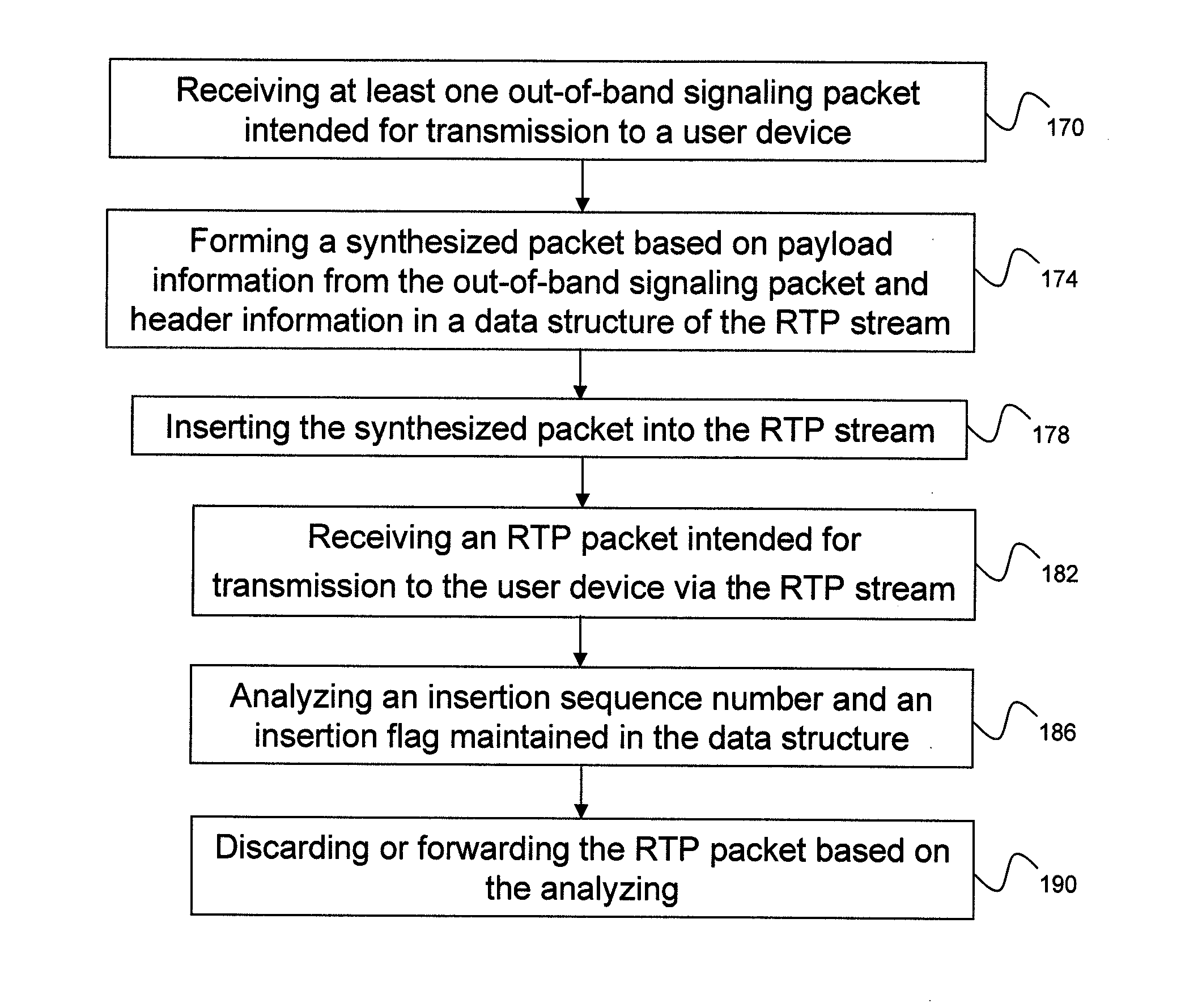
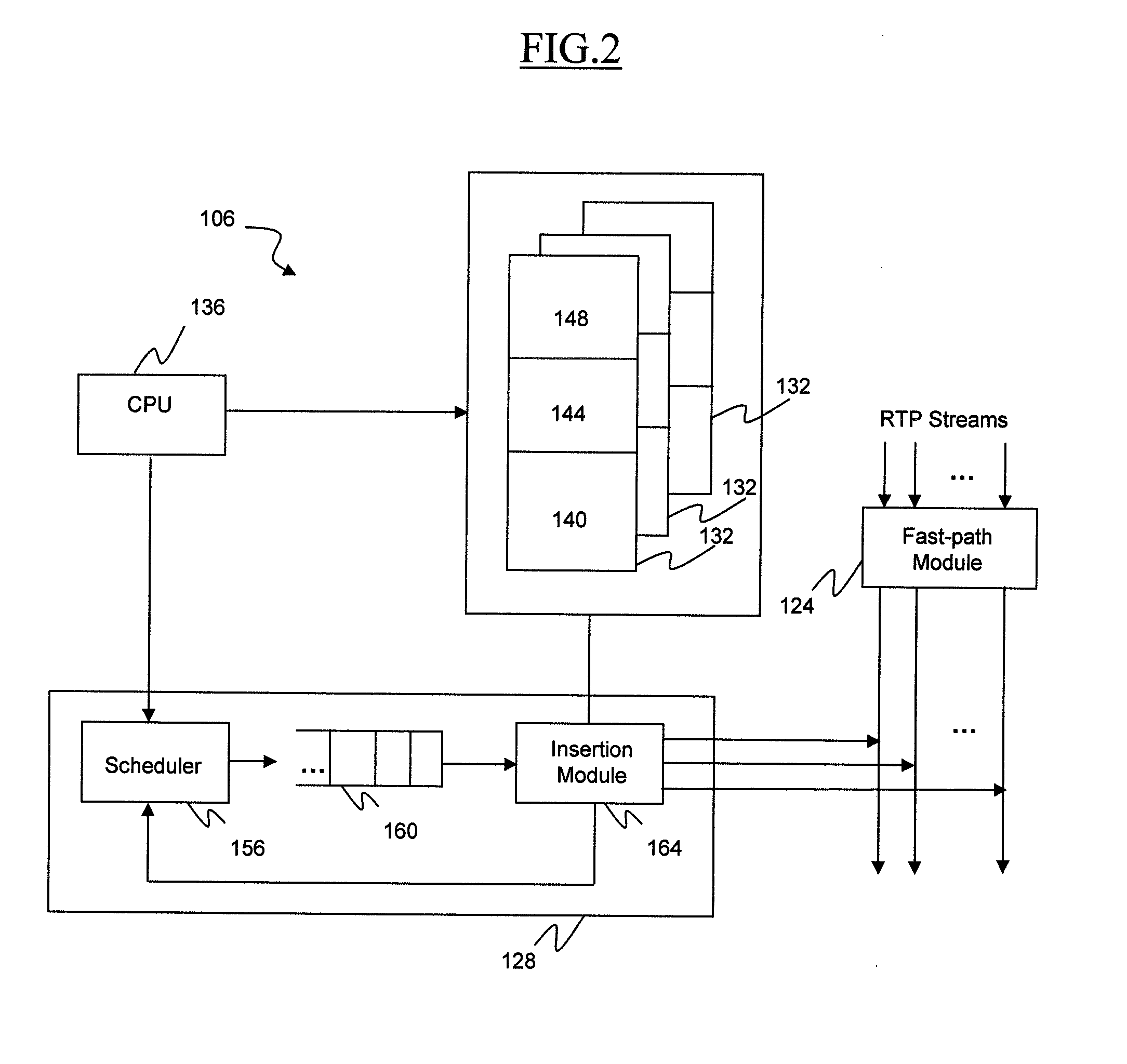
ActiveUS20120281690A1Efficient insertionHigh complexityNetwork connectionsComputer hardwareData stream
A computer-implemented method for inserting an out-of-band signaling packet into a real-time protocol (RTP) stream is provided. The method includes receiving the out-of-band signaling packet intended for transmission to a user device and forming a synthesized packet based on payload information from the out-of-band signaling packet and header information stored in a data structure describing the RTP stream. The method also includes inserting the synthesized packet into the RTP stream. The method further includes receiving an RTP packet intended for transmission to the user device via the RTP stream, analyzing an insertion sequence number and an insertion flag maintained in the data structure, and discarding or forwarding the RTP packet via the RTP stream based on the analyzing.
Owner:RIBBON COMM OPERATING CO INC
PCR detection kit for zaocys dhumnades
The invention relates to a kit for detecting zaocys dhumnades by using a PCR technology. The kit is composed of three systems of DNA extraction, PCR amplification and agarose gel detection, wherein positive control of PCR in the kit is pGEM-WS plasmids with an insertion sequence of SEQ ID.5; and the negative of PCR in the kit is pGEM-HS plasmids with an insertion sequence of SEQ ID.5. With the kit, determination for sample authenticity can be completed by simple DNA extraction, PCR amplification and electrophoresis detection without preparing any reagents. The kit has the advantages of simple operation, strong specificity, good repeatability and the like, and can be used for quick determination of zaocys dhumnade medical materials, preparations containing zaocys dhumnades and zaocys dhumnade living materials.
Owner:INST OF CHINESE MATERIA MEDICA CHINA ACAD OF CHINESE MEDICAL SCI
Solving method for delayed and leaked messages in group chat and instant messaging tool
InactiveCN105306348AImprove experienceEasy to handleSpecial service provision for substationDemarcation pointTime segment
The invention provides a solving method for delayed and leaked messages in a group chat, comprising the steps of: adding an ID field into each group chat message, wherein the ID fields are progressively increased according to the insertion sequence of the group chat messages; adopting the ID field of the latest group chat message read each time as a demarcation point for distinguishing the historical messages and the new messages; and then taking out the group chat messages with the ID fields larger than the demarcation point, sequentially displaying on a group chat page, and at last adopting the ID field of the last group chat message as the new demarcation point. The solving method for the delayed and leaked messages in the group chat is high in timeliness, and more beneficial to user experience. The problem that, as a time period is taken backward in the prior art, time periods for taking the messages are overlapped and then tedious treatment of filtering repeated messages by many times of comparison is needed before display of the messages, and thereby real-time display of the messages is influenced due to many times of comparison in the case of many people and frequent sending of messages, is solved.
Owner:PHICOMM (SHANGHAI) CO LTD
Enhancement of Microbial Ethanol Production
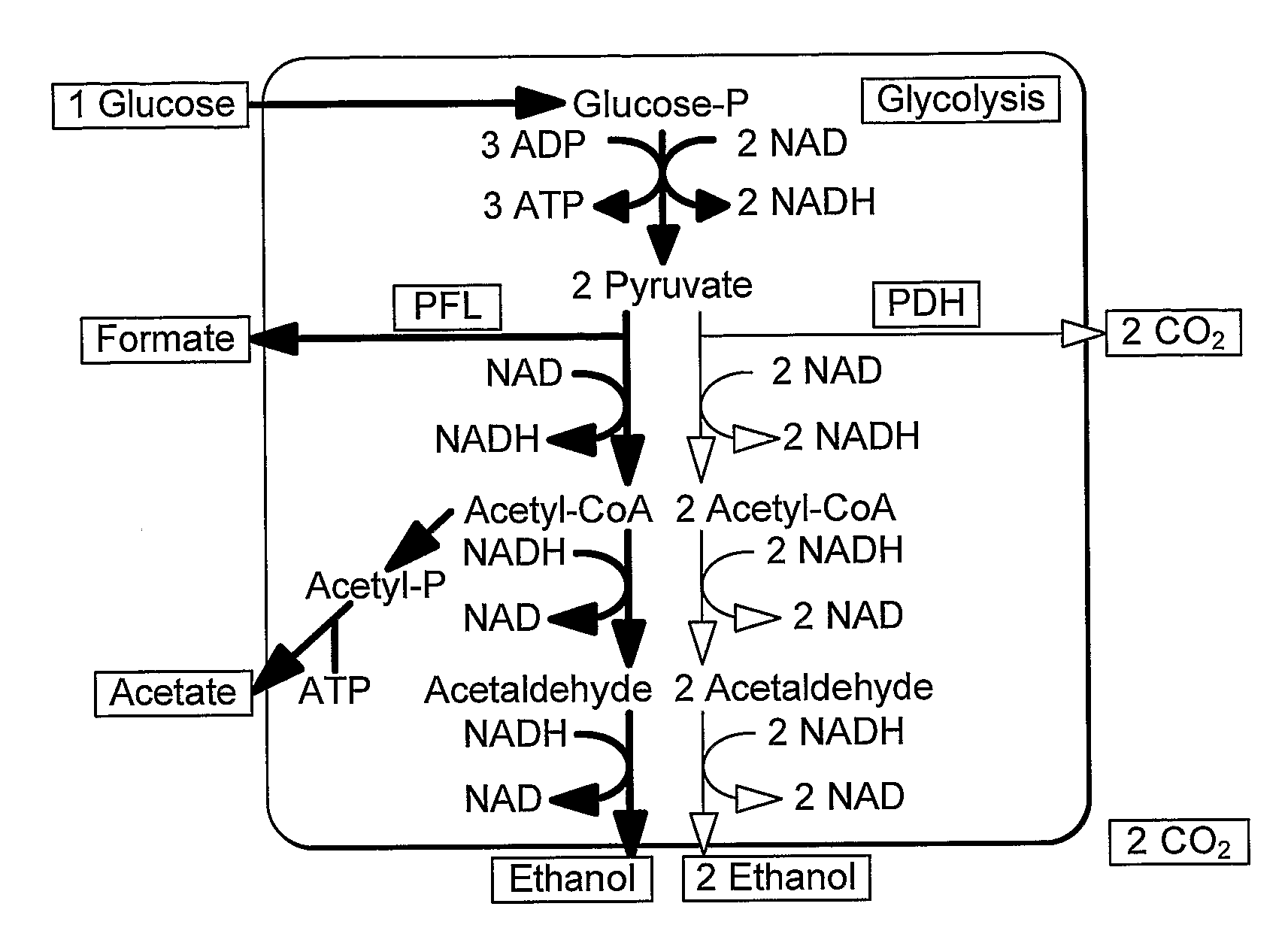
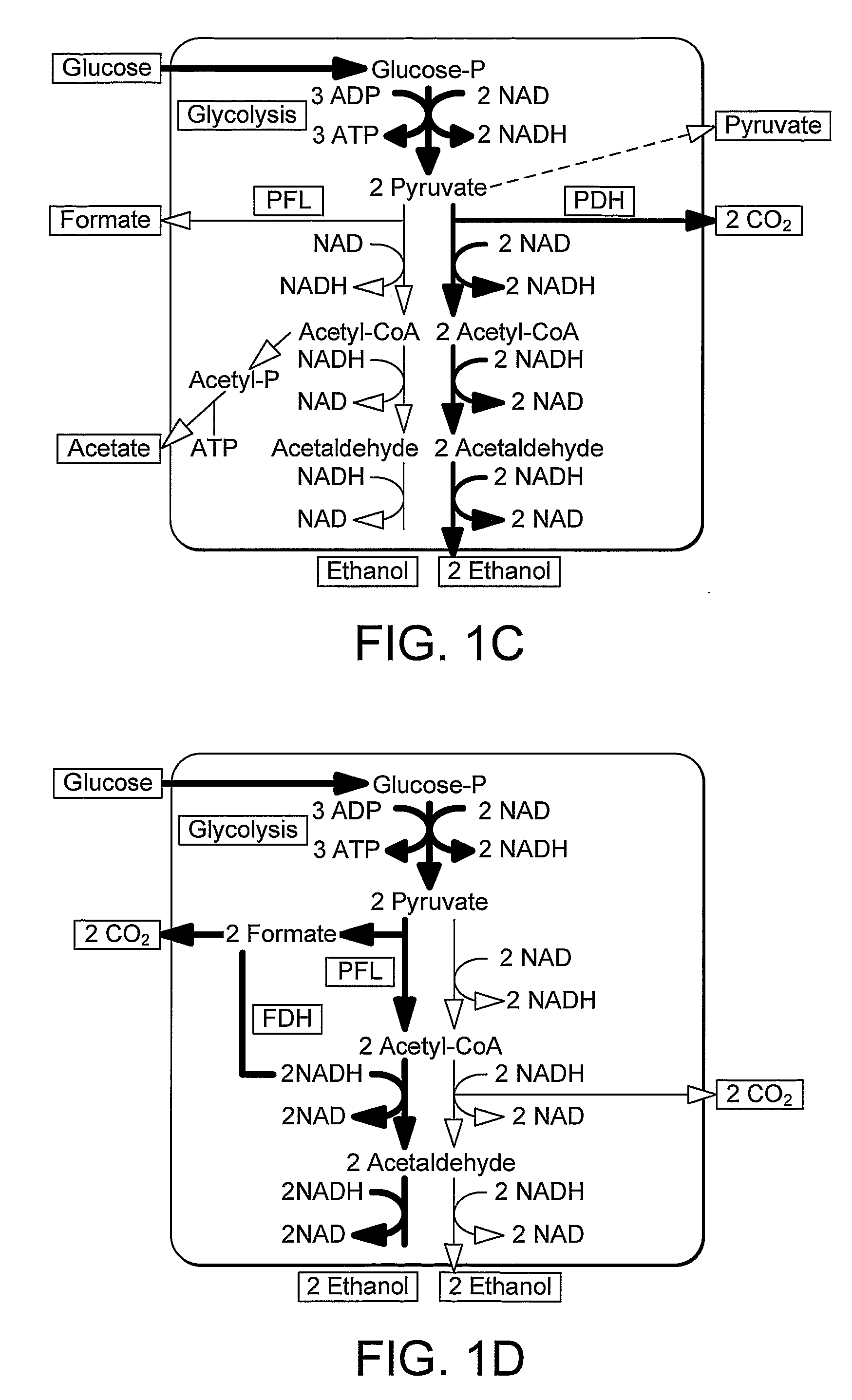
InactiveUS20090226992A1Easy to transformEfficient fermentationSugar derivativesBacteriaLactate dehydrogenaseDNA construct
A thermophilic microorganism lacks lactate dehydrogenase activity and preferably contains an active pyruvate formate lyase pathway. The thermophilic microorganism contains a gene encoding an NAD-linked formate dehydrogenase. The gene encoding an NAD-linked formate dehydrogenase is preferably a codon optimised version of the gene encoding a thermostable NAD-linked formate dehydrogenase. DNA constructs allow stable expression of the gene encoding an NAD-linked formate dehydrogenase in the thermophilic microorganism. The DNA constructs are based upon use of an insertion sequence to achieve stable expression or recombination to insert the gene encoding an NAD-linked formate dehydrogenase into the lactate dehydrogenase gene, thus achieving gene knockout and new functionality in a single step. The microorganisms are useful in fermentation of sugars to produce ethanol.
Owner:BIOCONVERSION TECH LTD
Kit for detecting proviral DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of bovine leukemia virus (BLV) and application of kit
InactiveCN103045762AEasy to makeThe method is simple and fastMicrobiological testing/measurementFluorescence/phosphorescenceForward primerFluorescence
The invention provides a kit for detecting proviral DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid) of bovine leukemia virus (BLV). The kit comprises (a) fluorescent PCR (polymerase chain reaction) liquid reactant, (b) a fluorescent probe, (c) hot start Tag enzyme, (d) a standard positive template and (e) negative control, wherein the fluorescent PCR liquid reactant contains forward primers and reverse primers; the sequence of the forward primers is shown in SEQ ID NO:2; the sequence of the reverse primers is shown in SEQ ID NO:3; the sequence of the fluorescent probe is shown in SEQ ID NO:4; fluorescent substance is designed at the 5' end of the sequence of the fluorescent probe; cancellation substance is designed at the 3' end of the sequence of the fluorescent probe; and the nucleotide insertion sequence of the standard masculine template is shown in SEQ ID NO:5. The invention further provides application of the kit to detecting proviral DNA of BLV in whole blood. The PCR detection kit provided by the invention can be used for quickly and accurately detecting BLV and is applicable to quick diagnosis of BLV, epidemiological investigation and risk assessment.
Owner:SHANGHAI ANIMAL EPIDEMIC PREVENTION & CONTROL CENT
Method for sequencing unknown flanking sequence at both sides of known sequence
ActiveCN103667481ALower quality requirementsAvoid mutationMicrobiological testing/measurementA-DNAInsertion sequence
A method for sequencing an unknown flanking sequence at both sides of a known sequence comprises library construction, flanking sequence capturing and sequencing. The method comprises: employing a site directed mutagenesis PCR process, designing an appropriate primer on the known sequence (without mutation sites), taking the constructed library as the template, screening numerous plasmids in the library to obtain a DNA fragment containing the known sequence sites, screening out target sites in the plasmid library by employing the PCR process, and further obtaining an insertion sequence 2 Kb-5 Kb and a plasmid library containing the known sequence, and taking the plasmid library as the target point to obtain the flanking sequence at the both sides of the known sequence. The provided sequencing method helps to realize full view acquisition of genome, helps to solve the technological restriction that researchers cannot describe the full view of a gene and consequently cannot precisely research the functions of the gene when carrying out comprehensive research on the gene, and is beneficial to improve the efficiency of related researches.
Owner:重庆巴斯德生物医药科技有限公司
Multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers and method for identifying genotypes of green-shell laying hens
InactiveCN108315444AStrong designGuaranteed reliabilityMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationGenotypeInsertion sequence
The invention discloses multiplex polymerase chain reaction (PCR) primers and a method for identifying the genotypes of green-shell laying hens. Three primers F, R1 and R2 are firstly designed, wherein F and R2 are fragments in a SLCO1B3 gene of a chicken normal genome. If an individual does not carry an insert fragment, the F and the R2 are paired, a single purpose band of 397 bp is only amplified, and no green-shell egg is produced. The R1 is a fragment of an EAV-HP insertion sequence; if the individual carries the insert fragment, the F and the R1 are paired, a single purpose band of 223 bpis only amplified, and green-shell eggs are produced. If one chromosome of the individual carries the insert fragment and the other one chromosome does not carry the insert fragment, two purpose bands of 223 bp and 397 bp are amplified, and green-shell eggs are still produced. Compared with other identification methods, the primer combination enables the two bands in heterozygote to be more clearly separated, and is beneficial to increment of the genotype identification accuracy of the individual to be tested.
Owner:POULTRY INST SHANDONG ACADEMY OF AGRI SCI
Pcr-based genotyping
InactiveUS20110059437A1Improve analysisHigh sample throughputSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementInsertion sequenceBiology
A Mycoplasma bovis PCR-based genotyping method was developed that exploits the proximity of insertion sequences (IS) within the genome by using outward facing primers that selectively amplify sequences between IS elements. The method was applied to 16 field isolates of M. bovis, originating from pneumonic lung or arthritic joints, collected from the United States (Iowa or Kansas) between 2004 and 2005. The genomic fingerprints generated 14 distinct amplification profiles consisting of 4-8 fragments ranging in size from 200-3000 bp. Three isolates presented identical patterns and were isolated from two calves (one calf with pneumonic lung and the other with both pneumonic lung and arthritic joint) from a single farm during an outbreak and probably represent multiple infections with the same genotype. To demonstrate the stability of IS markers for molecular fingerprinting, 3 of the 16 field isolates were subjected to high number passage which resulted in patterns identical to the initial isolates. The results of these studies demonstrate the method can be used for simple and rapid molecular fingerprinting and differentiating M. bovis isolates with extension to epidemiology.
Owner:BOEHRINGER LNGELHEIM VETMEDICA GMBH
Human platelet-derived growth factor receptors
InactiveUS7105305B2Inhibit bindingPeptide/protein ingredientsHydrolasesGrowth factor receptorOn cells
DNA sequences encoding human platelet-derived growth factor receptors (hPDGF-R), and expression constructs comprising sequences which encode a receptor that can be secreted or incorporated into the membrane of a mammalian cell. Peptide fragments with functions equivalent to the wild-type receptor, conferring a PDGF-sensitive mitogenic response on cells lacking the receptor are provided. The constructs can be used for enhancing PDGF response of cells, determining the regions involved in transducing the signal in response to PDGF binding, providing mutated analogs and evaluating drugs for their physiologic activity. Soluble fragments comprising PDGF receptor sequences are also provided, including important intracellular kinase insert sequences which interact with intracellular proteins.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com