Transgenic soybean ZUTS-33 preparation method, detection and application
A technology of ZUTS-33, transgenic soybean, applied in the field of plant genetic engineering technology and breeding
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0085] Embodiment 1, vector construction
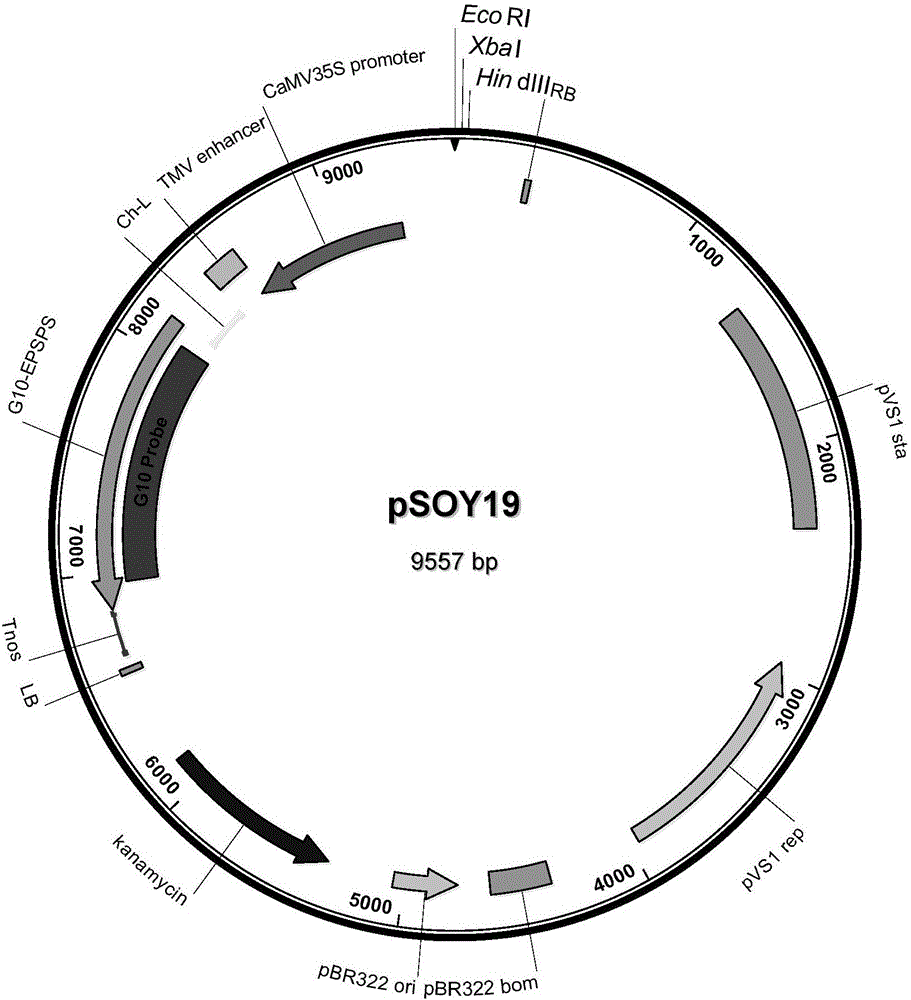
[0086] Map of target gene and vector construction:
[0087] The transgenic soybeans in this experiment were carried by Agrobacterium such as figure 1 The indicated binary plasmid pSOY19 was transformed. The vector is from the T-DNA region from the right border (T-Border-RB) (sequence as described in SEQ ID NO:1) to the left border (T-Border-LB) (sequence as described in SEQ ID NO:2) region The full length is 6284bp, and this region is mainly composed of 4 parts except the multiple cloning site:
[0088] 1), the promoter (CaMV35Spromoter) of the cauliflower mosaic virus 35 protein that can produce constitutive expression in plants;
[0089] 2), the signal peptide Ch-L from Arabidopsis thaliana, which can guide the protein encoded by the same expression frame to be transported into the chloroplast, the nucleotide sequence of the chloroplast leader peptide encoded by Ch-L is as SEQ ID NO: 13 The deduced amino acid sequence of the chl...
Embodiment 2
[0095] Embodiment 2, soybean conversion
[0096] Genetically modified method:
[0097] Agrobacterium-mediated transformation (Song et al., 2013) is used for soybean transgenesis, in which Agrobacterium integrates the segment between the left and right borders of the binary plasmid T-DNA into plant cells. The recipient cells in transformation are undifferentiated axillary buds between cotyledonary nodes of germinated seeds. The binary vector pSOY19 with g10-epsps constructed in Example 1 is transformed into Agrobacterium, and the plant tissue and Agrobacterium after Agrobacterium infection After 4 days of co-infection, the infected tissues were placed on cluster bud induction medium containing glyphosate and antibiotics for selection and culture for a total of four weeks. Glyphosate and antibiotics in the medium were used to prevent the growth of non-transformed cells and Agrobacterium, respectively.
[0098] After four weeks of cluster bud induction, the soybean cotyledon no...
Embodiment 3
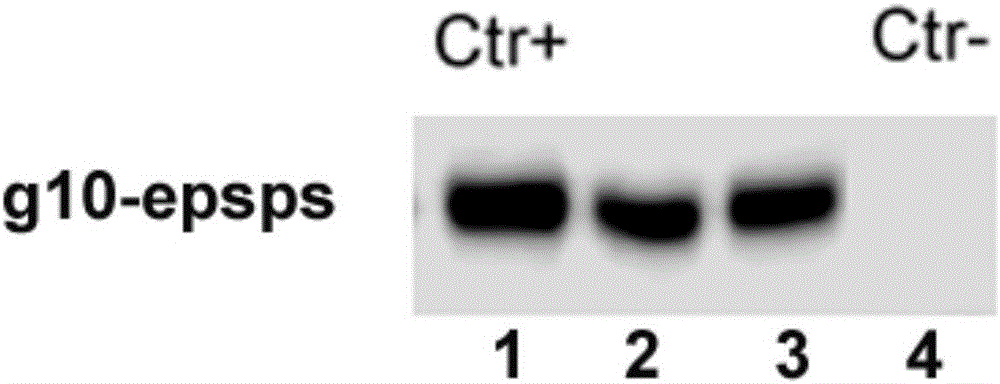
[0099] Embodiment 3, identification and screening of transgenics
[0100] 1. DNA extraction and PCR identification of soybean leaves
[0101] 1.1 SDS method to extract DNA
[0102] 1) Take 0.05g ground leaves or seeds, add 700μl SDS extract and 3μl 10mg / ml proteinase K (no need to add proteinase K to leaf materials), mix well, and bathe in 60°C water bath for 40min-1h (leaf materials should turn brown Take it out later), and mix it upside down every 10 minutes.
[0103] 2) Add an equal volume of phenol / chloroform (1:1) and gently invert and mix for 10 minutes, let stand for more than 30 minutes, centrifuge at 10000g for 10 minutes, and take the supernatant.
[0104] 3) Add an equal volume of phenol / chloroform (1:1) to mix, and let stand for 10 minutes. Centrifuge at 10,000 g for 10 min, take the supernatant, add 2 times the volume of absolute ethanol, precipitate, and let stand for more than 10 min. Centrifuge at 10,000 g for 1 min, discard the supernatant, and wash the pe...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com