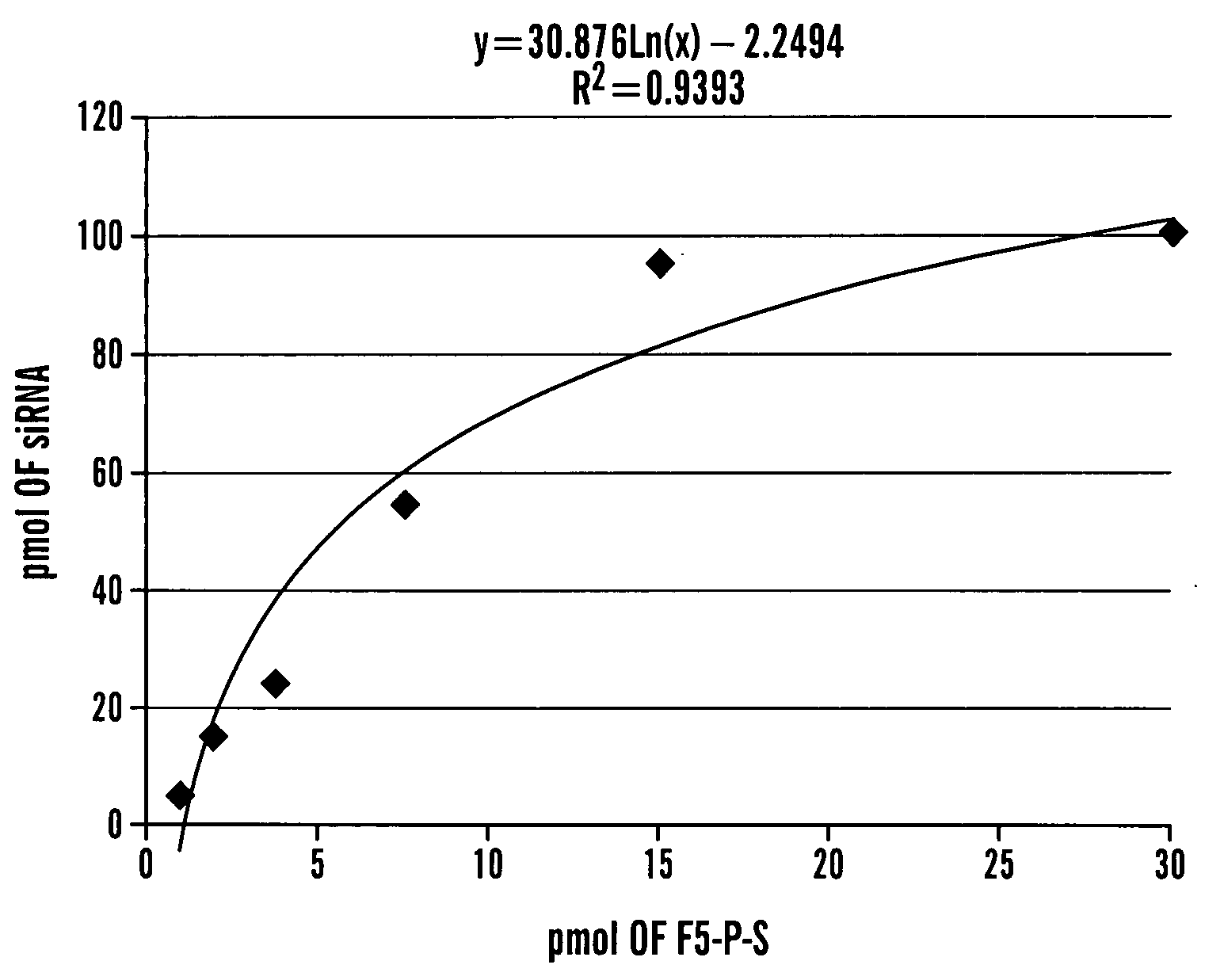
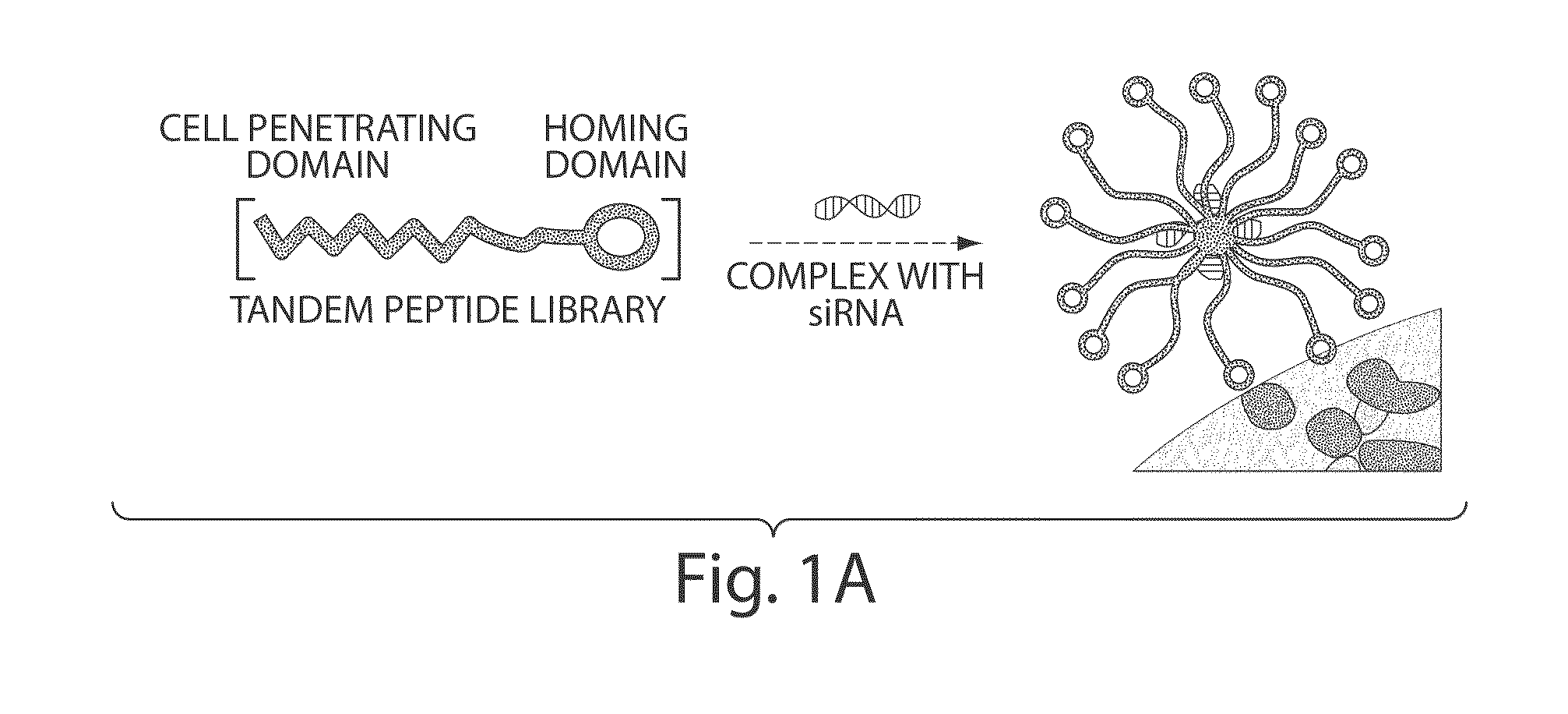
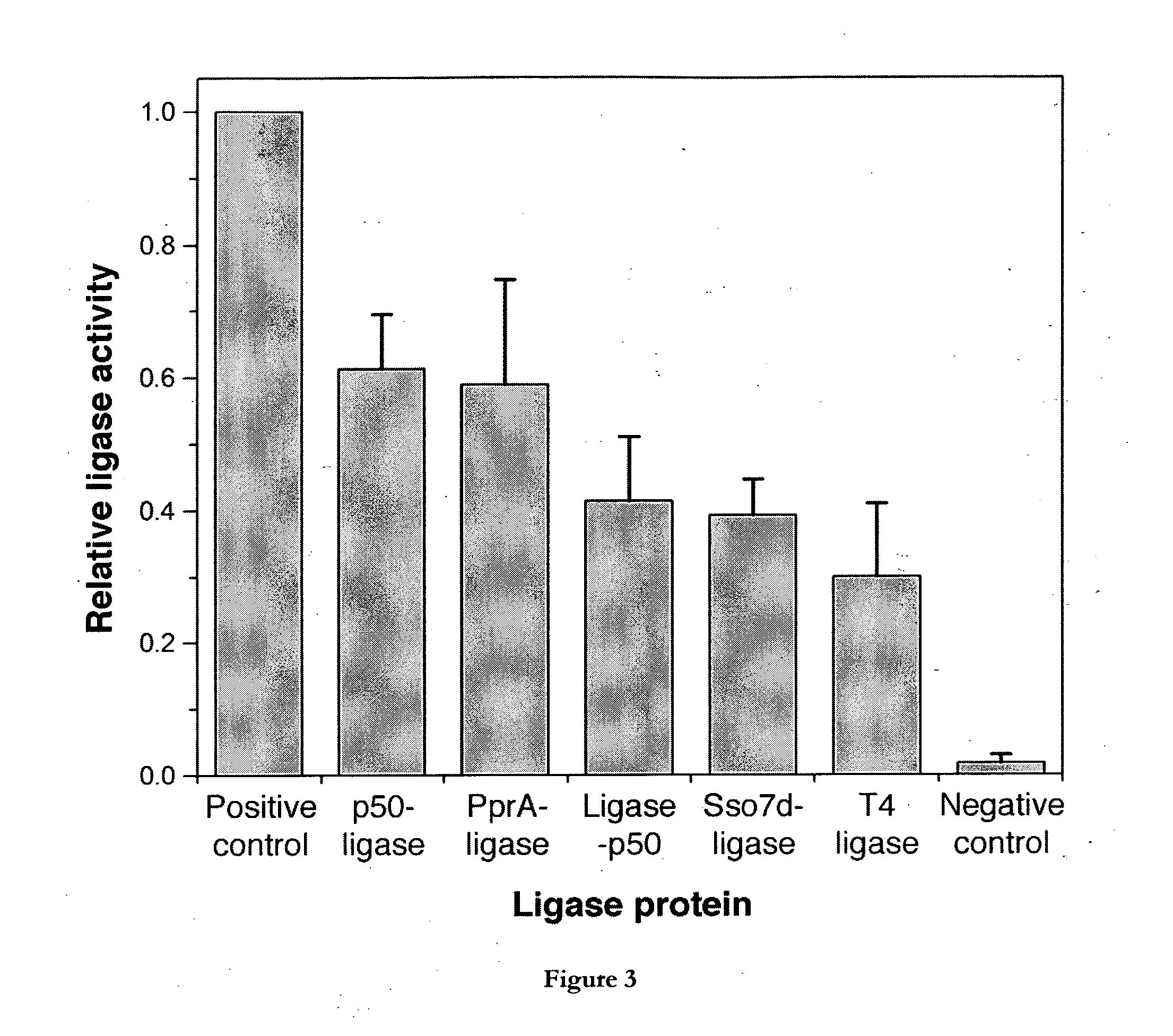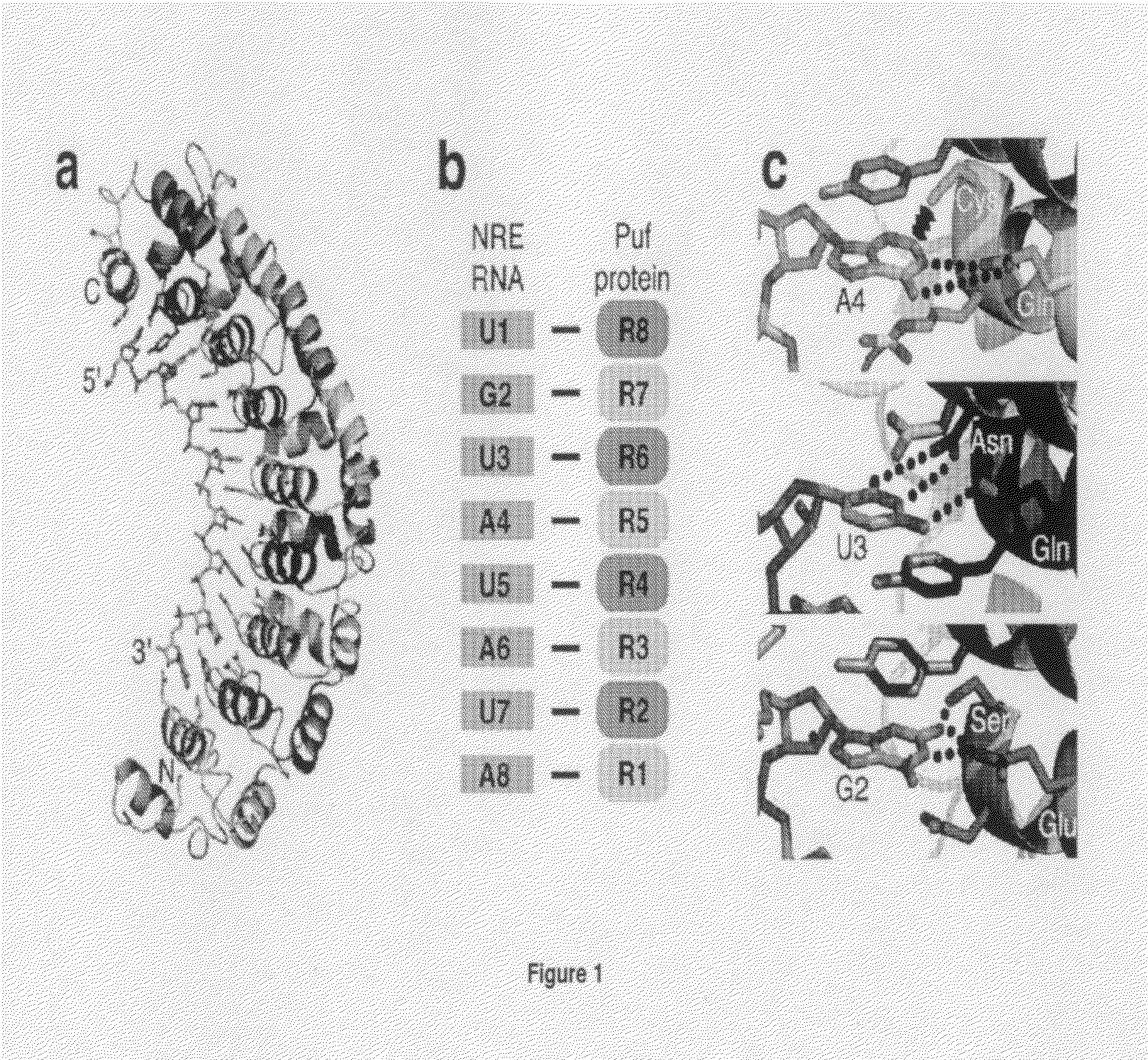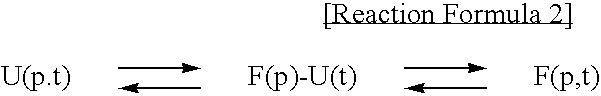Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
98results about "Fusion with RNA-binding domain" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Use of cationic lipids to deliver cas9
ActiveUS20150071903A1Prevent and delay onsetSlow onsetFusion with RNA-binding domainFusion with DNA-binding domainDiseaseLipid formation
Compositions, methods, strategies, kits, and systems for the supercharged protein-mediated delivery of functional effector proteins into cells in vivo, ex vivo, or in vitro are provided. Compositions, methods, strategies, kits, and systems for delivery of functional effector proteins using cationic lipids and cationic polymers are also provided. Functional effector proteins include, without limitation, transcriptional modulators (e.g., repressors or activators), recombinases, nucleases (e.g., RNA-programmable nucleases, such as Cas9 proteins; TALE nuclease, and zinc finger nucleases), deaminases, and other gene modifying / editing enzymes. Functional effector proteins include TALE effector proteins, e.g., TALE transcriptional activators and repressors, as well as TALE nucleases. Compositions, methods, strategies, and systems for the delivery of functional effector proteins into cells is useful for therapeutic and research purposes, including, but not limited to, the targeted manipulation of a gene associated with disease, the modulation of the expression level of a gene associated with disease, and the programming of cell fate.
Owner:PRESIDENT & FELLOWS OF HARVARD COLLEGE
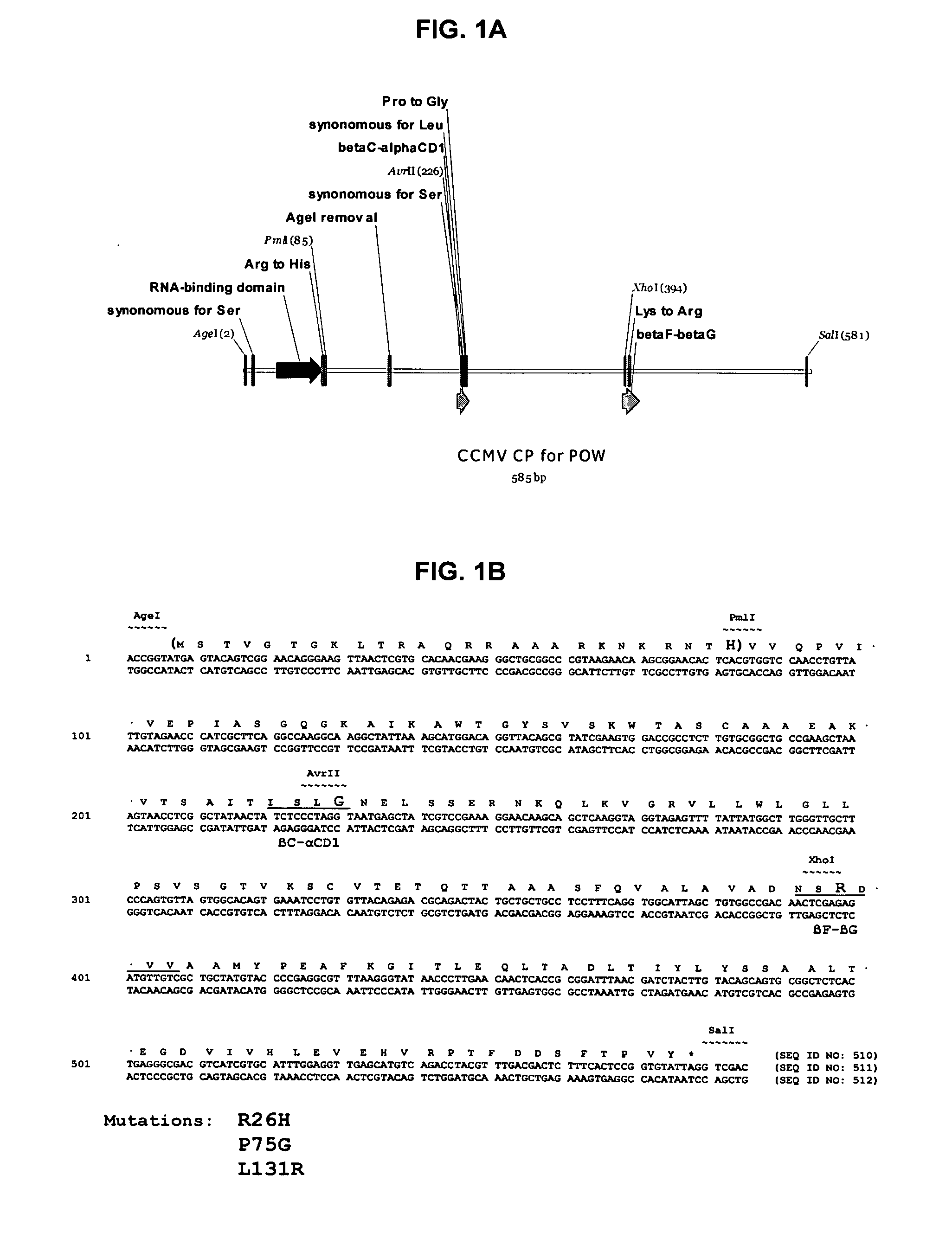
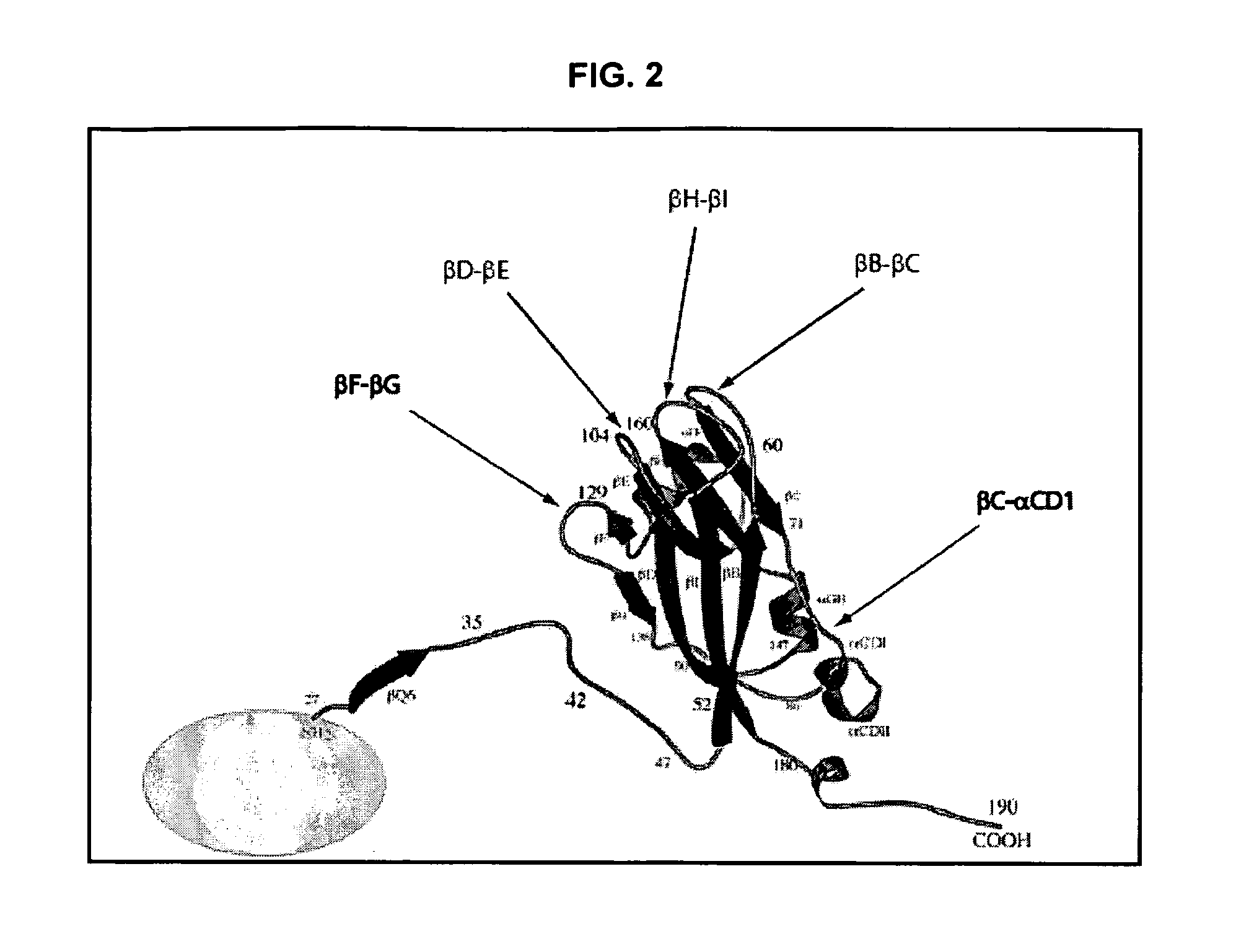
Modified plant virus particles and uses therefor
InactiveUS20120015899A1Broadening arrayEasy to assembleFusion with RNA-binding domainBiocideVirus-like particleCoat Proteins
Aspects of the invention provide modified virus-like particles that are designed for therapeutic applications. In particular, aspects of the invention provide CCMV coat proteins that are modified to generate virus-like particles, including mosaic virus-like particles, that can package and / or deliver one or more diagnostic and / or therapeutic agents. The invention also provides methods for treating subjects with one or more modified virus-like particles.
Owner:PLANT BIOSCI LTD +1
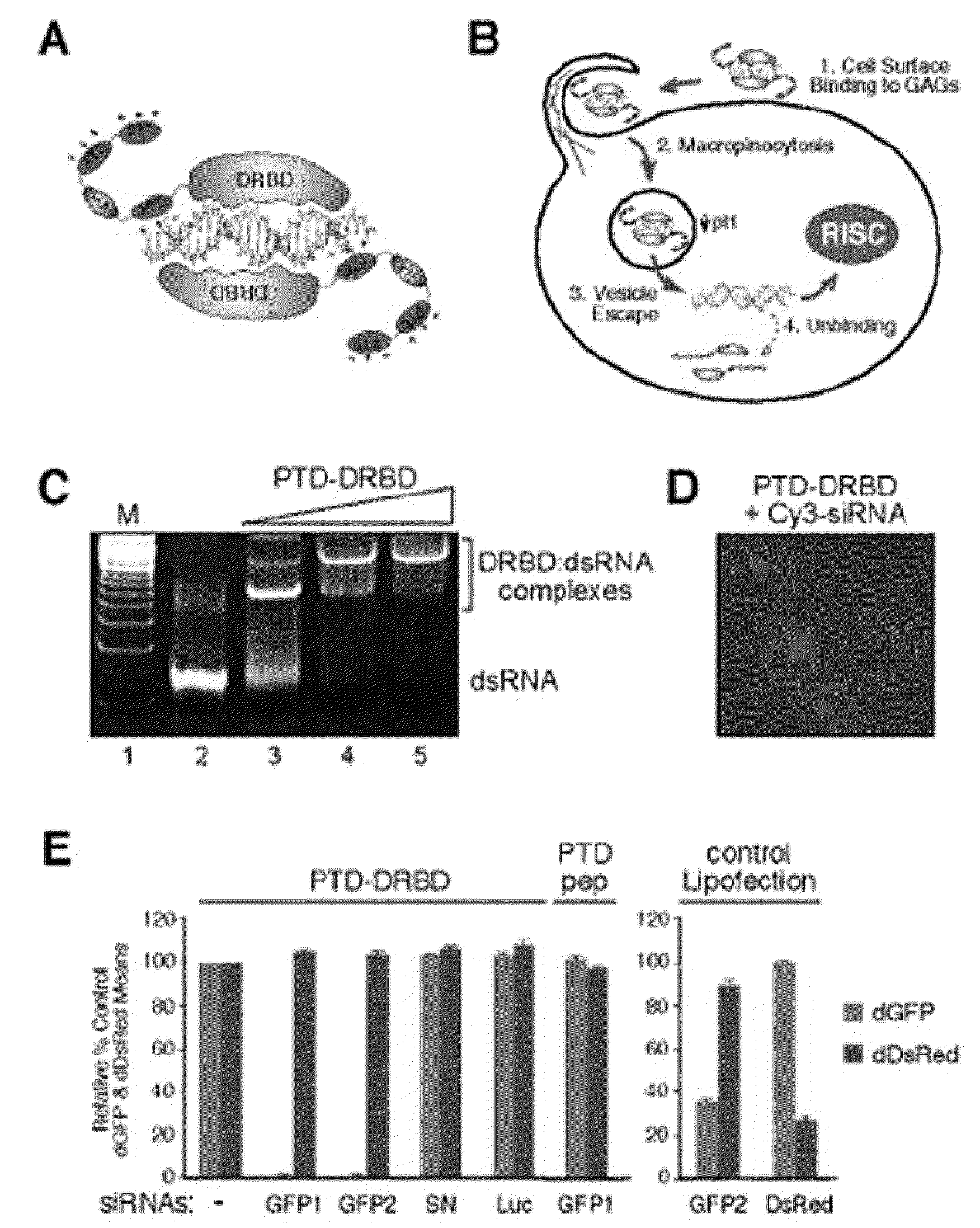
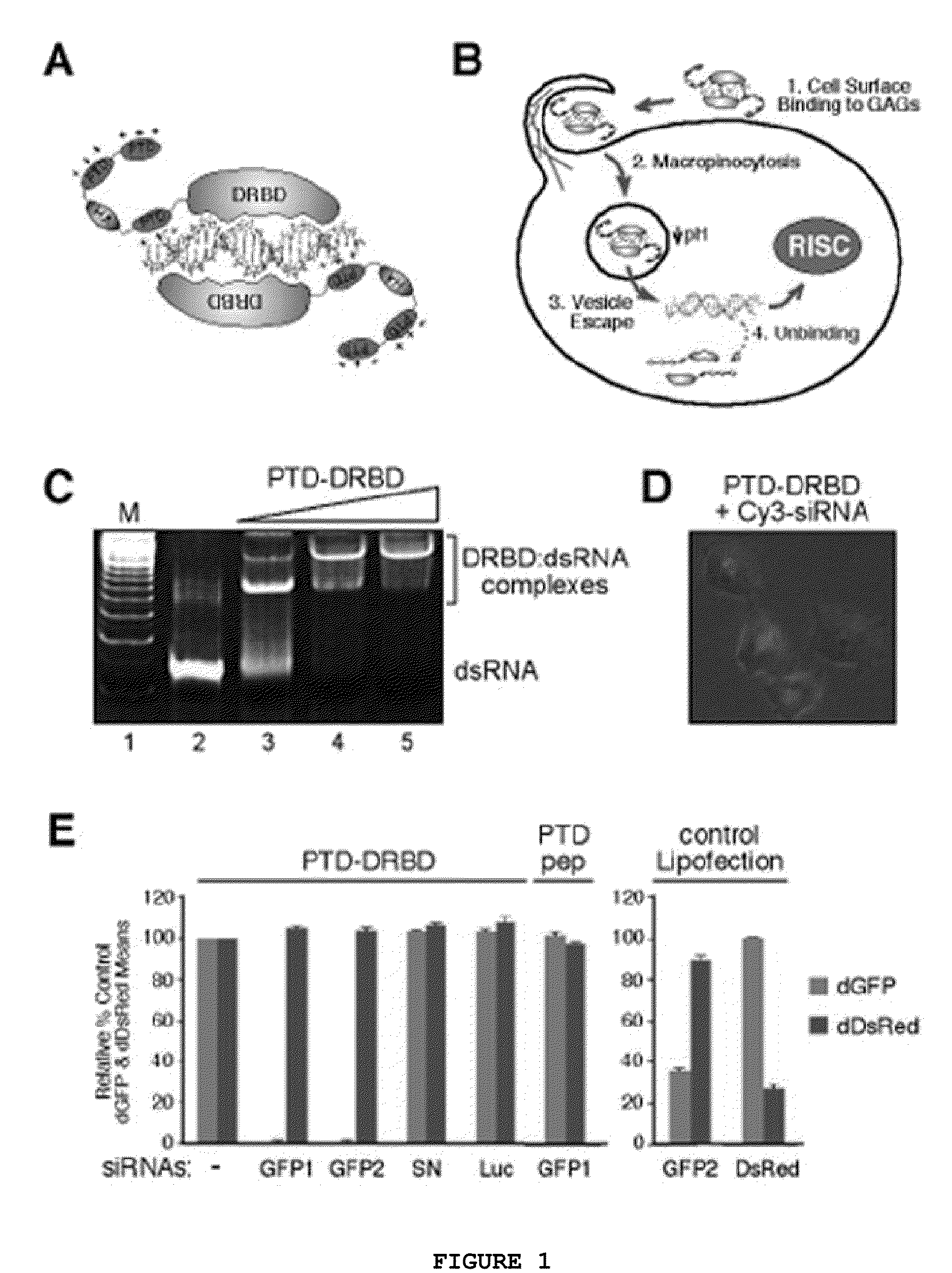
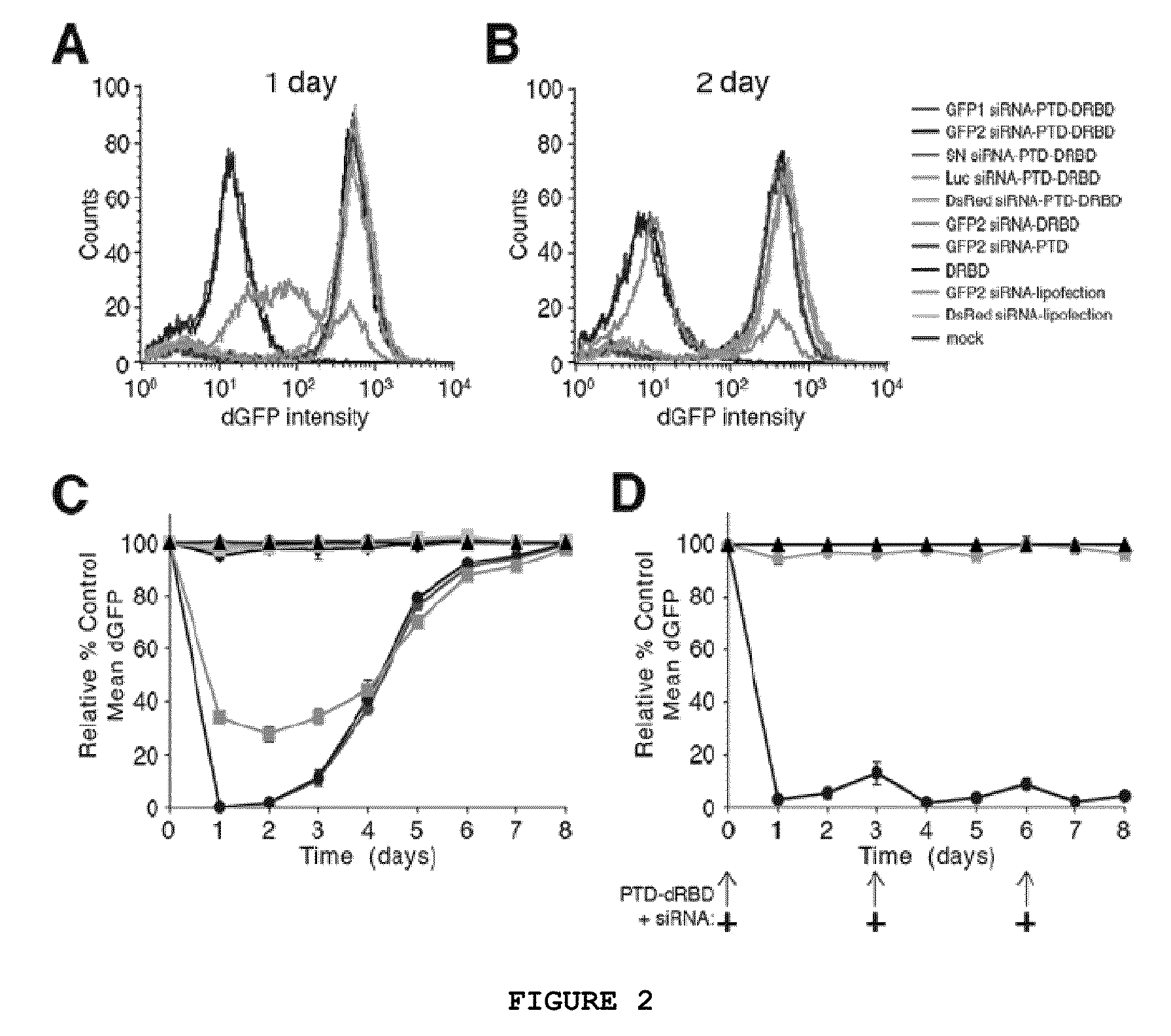
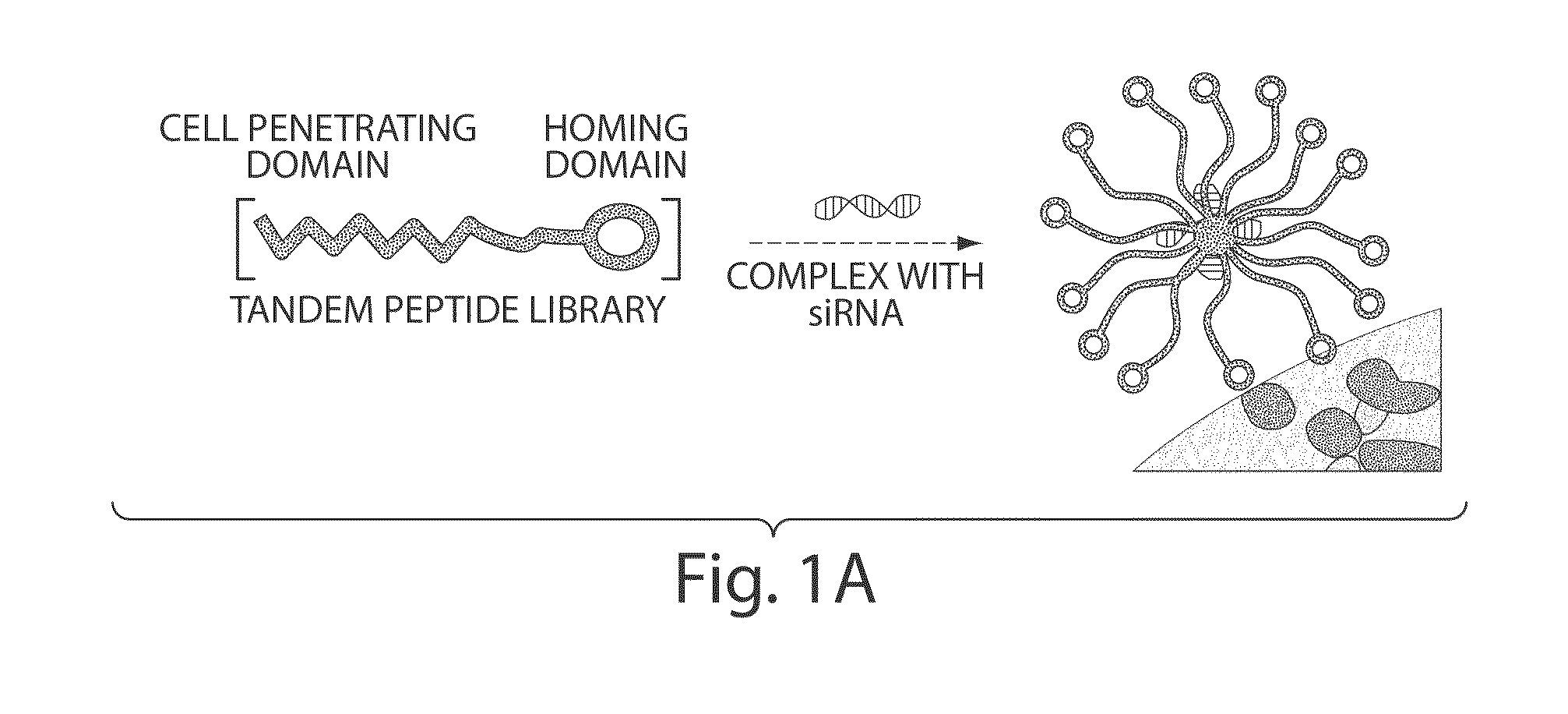
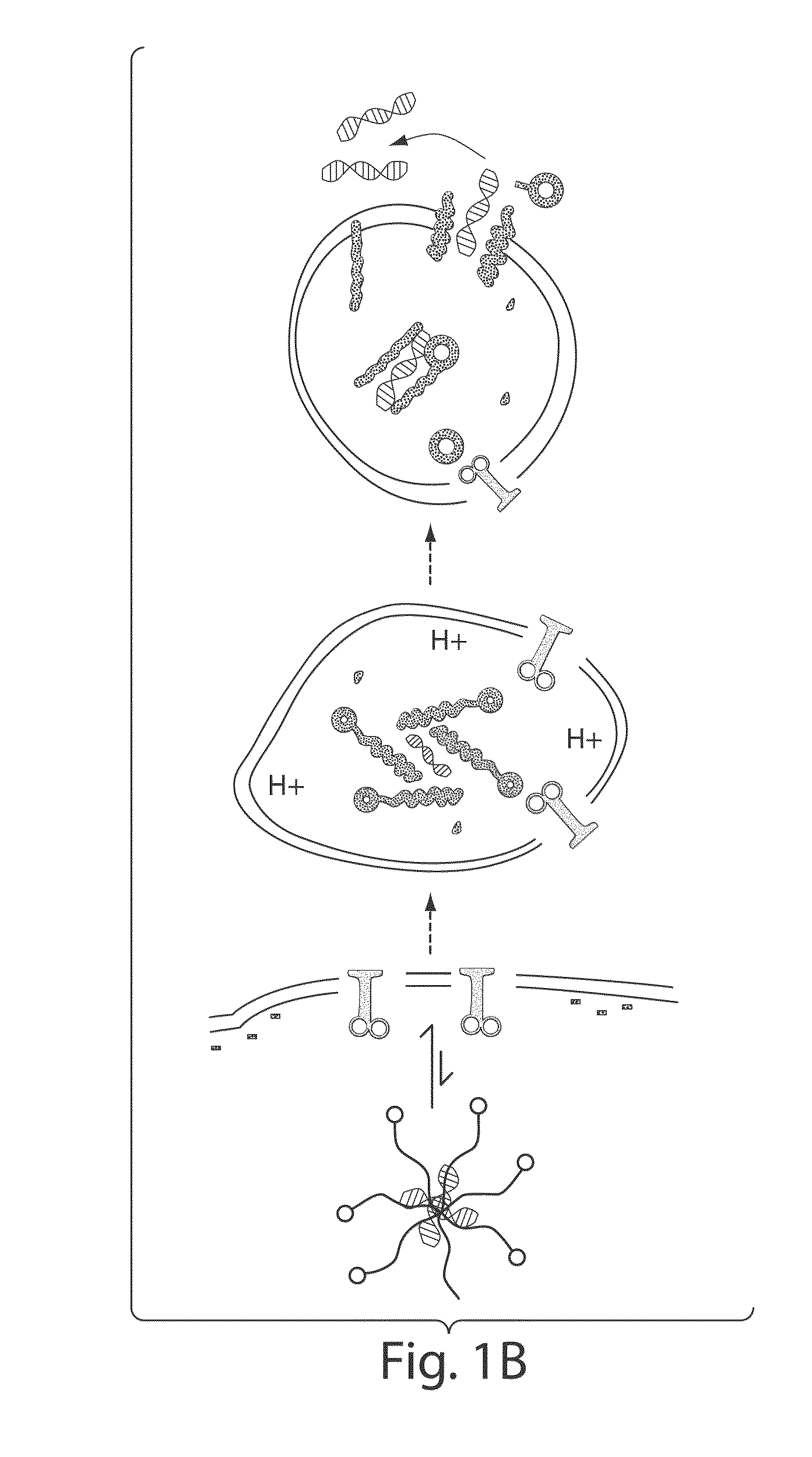
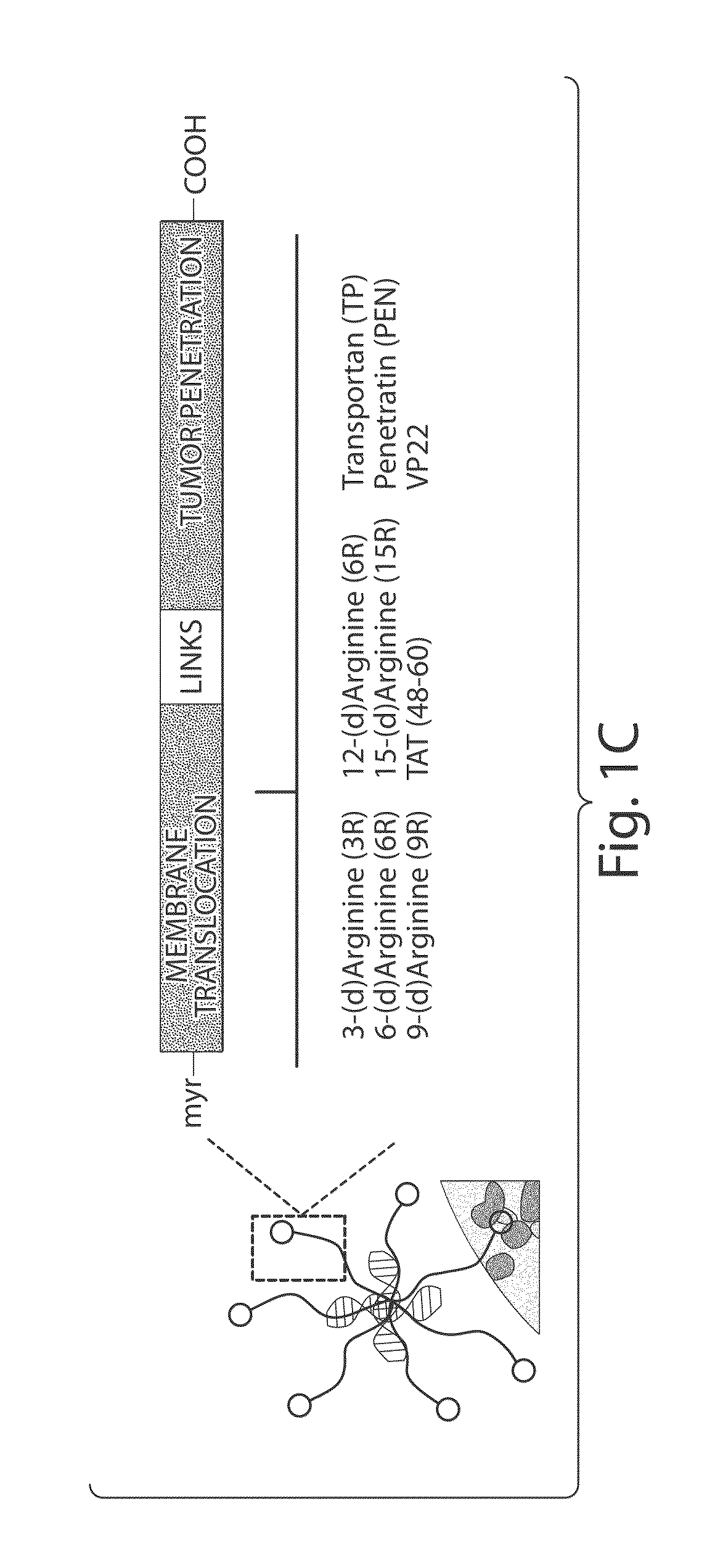
TRANSDUCIBLE DELIVERY OF siRNA BY dsRNA BINDING DOMAIN FUSIONS TO PTD/CPPS
ActiveUS20090093026A1Inhibit aggregationInduces macropinocytosisFusion with RNA-binding domainSpecial deliveryDiseaseProtein transduction domain
The disclosure provides fusion polypeptides and constructs useful in delivering anionically charged nucleic acid molecules including diagnostics and therapeutics to a cell or subject. The fusion constructs include a protein transduction domain and a nucleic acid binding domain, or a protein transduction domain and a nucleic acid that is coated with one or more nucleic acid binding domains sufficient to neutralize an anionic charge on the nucleic acid. Also provided are methods of treating disease and disorders such as cell proliferative disorders.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
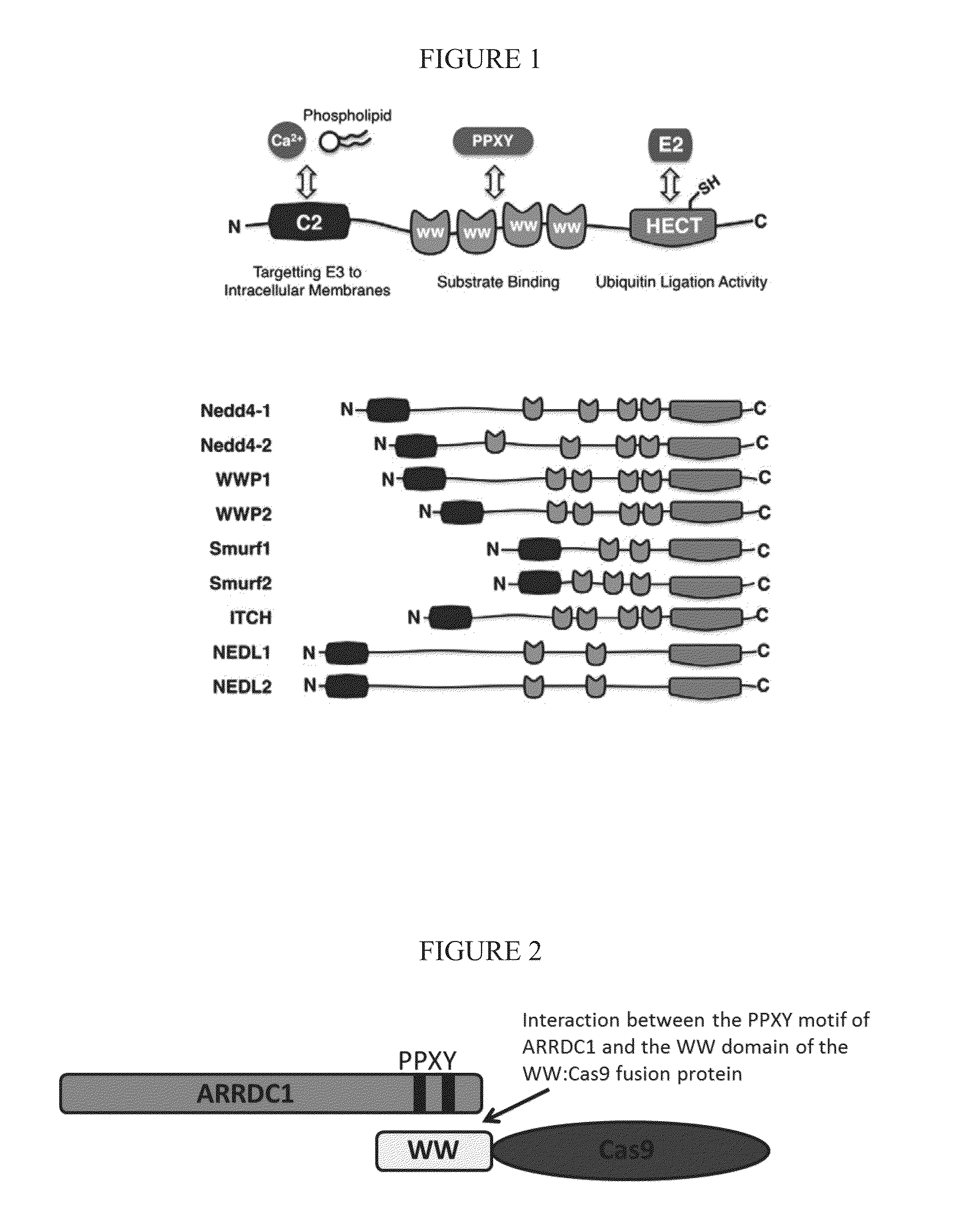
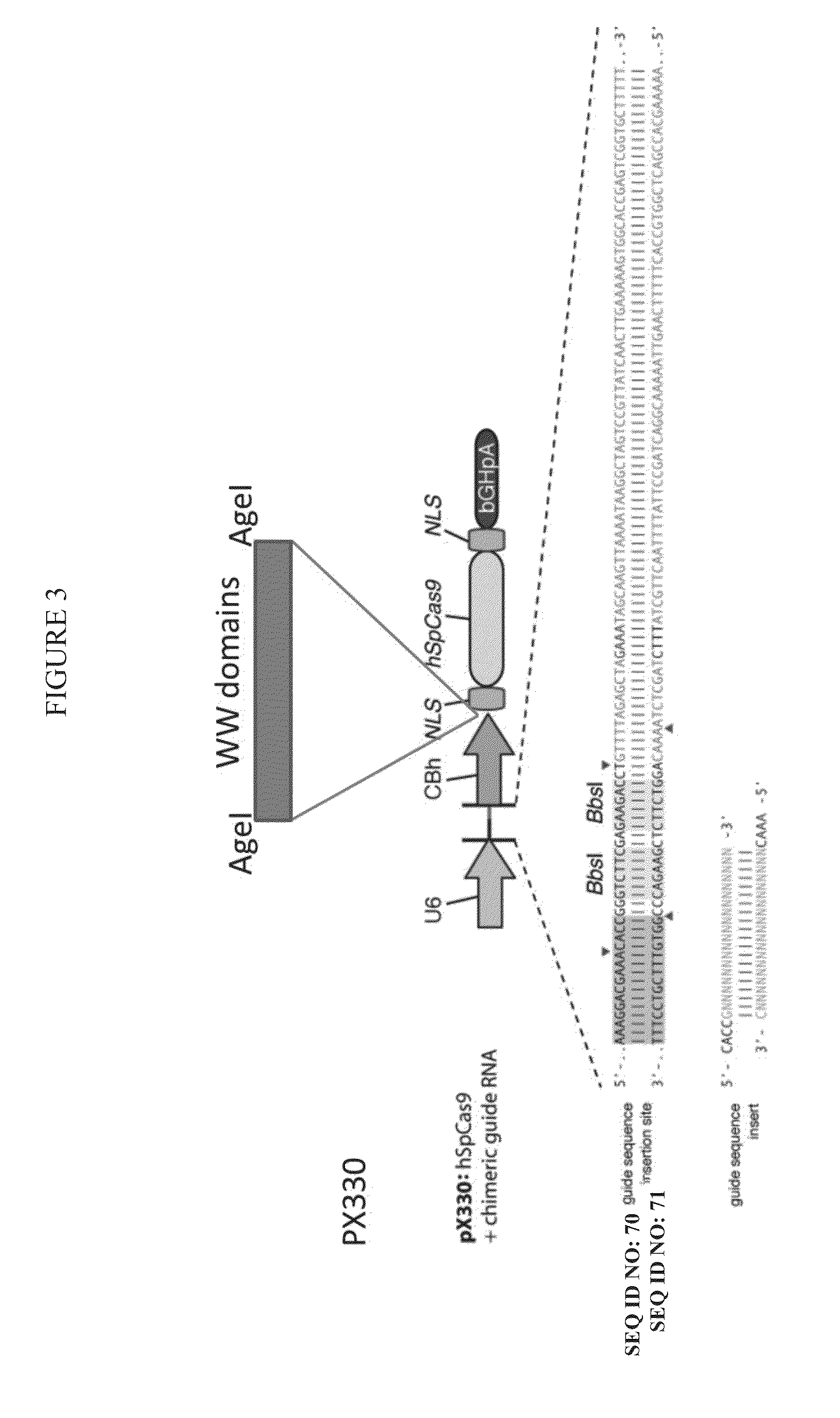
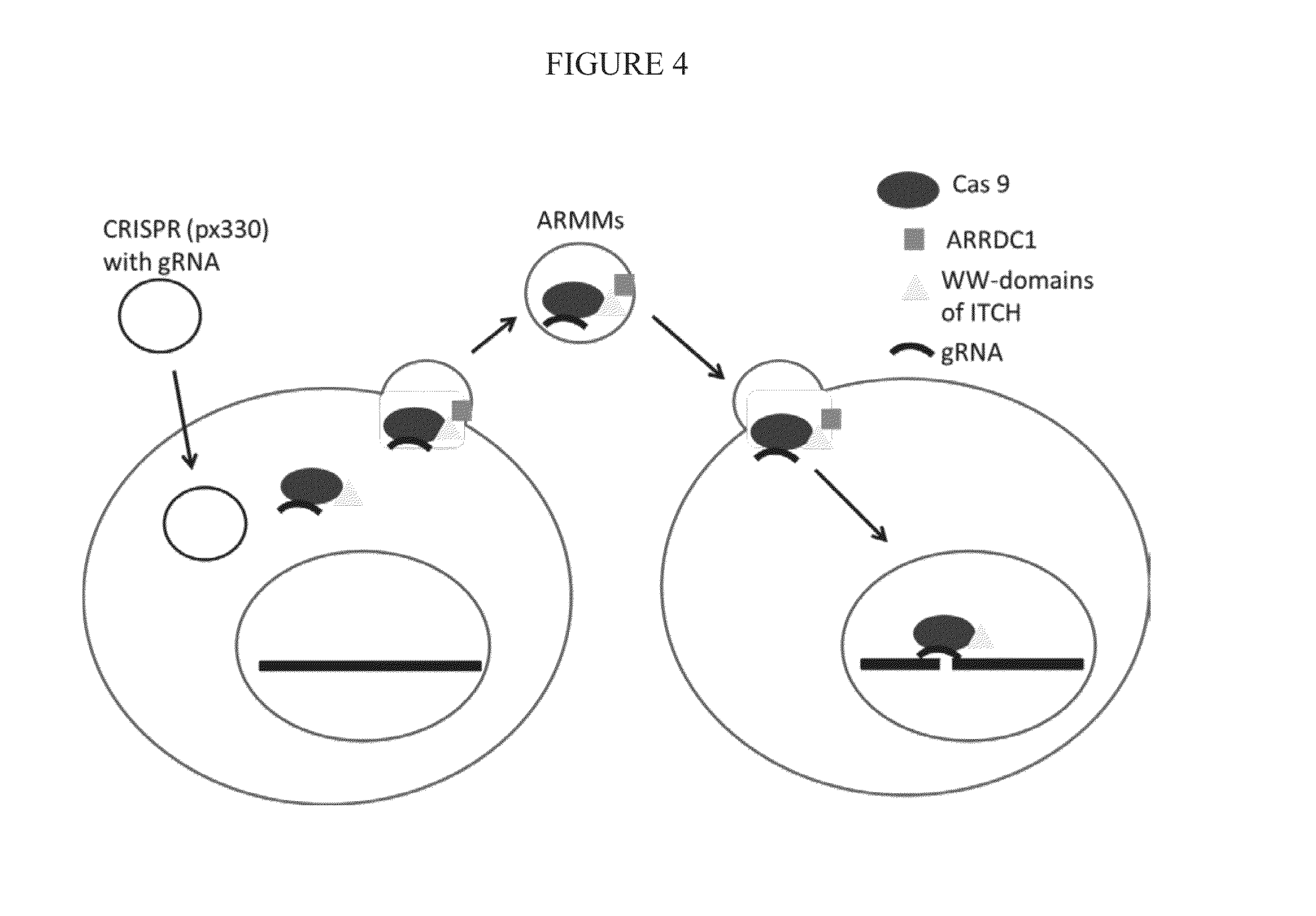
Delivery of cas9 via arrdc1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMS)
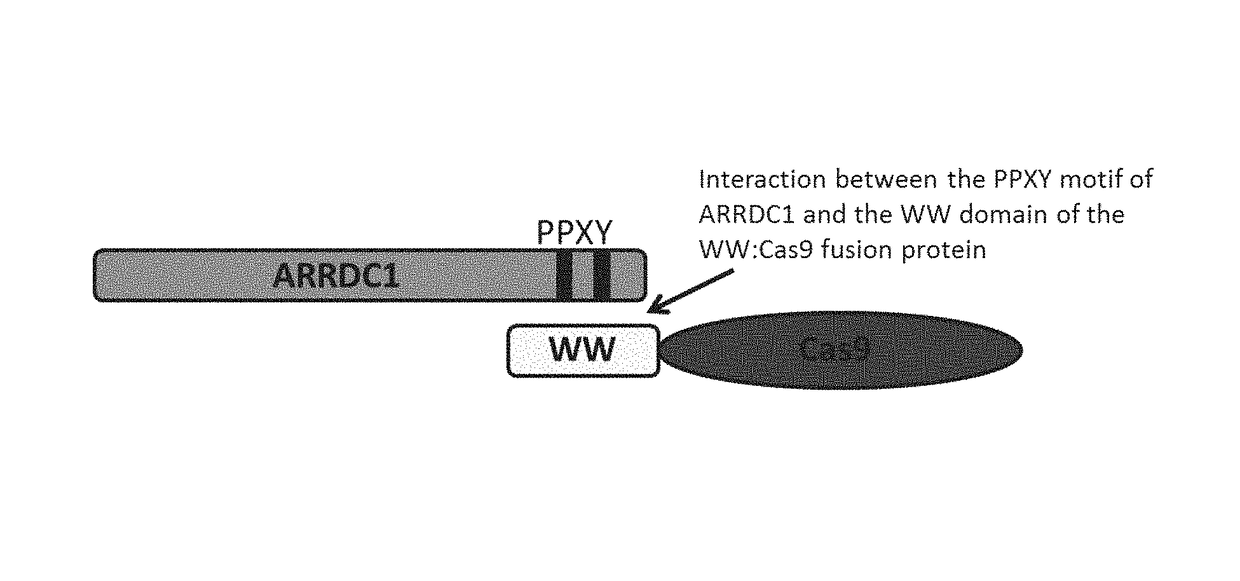
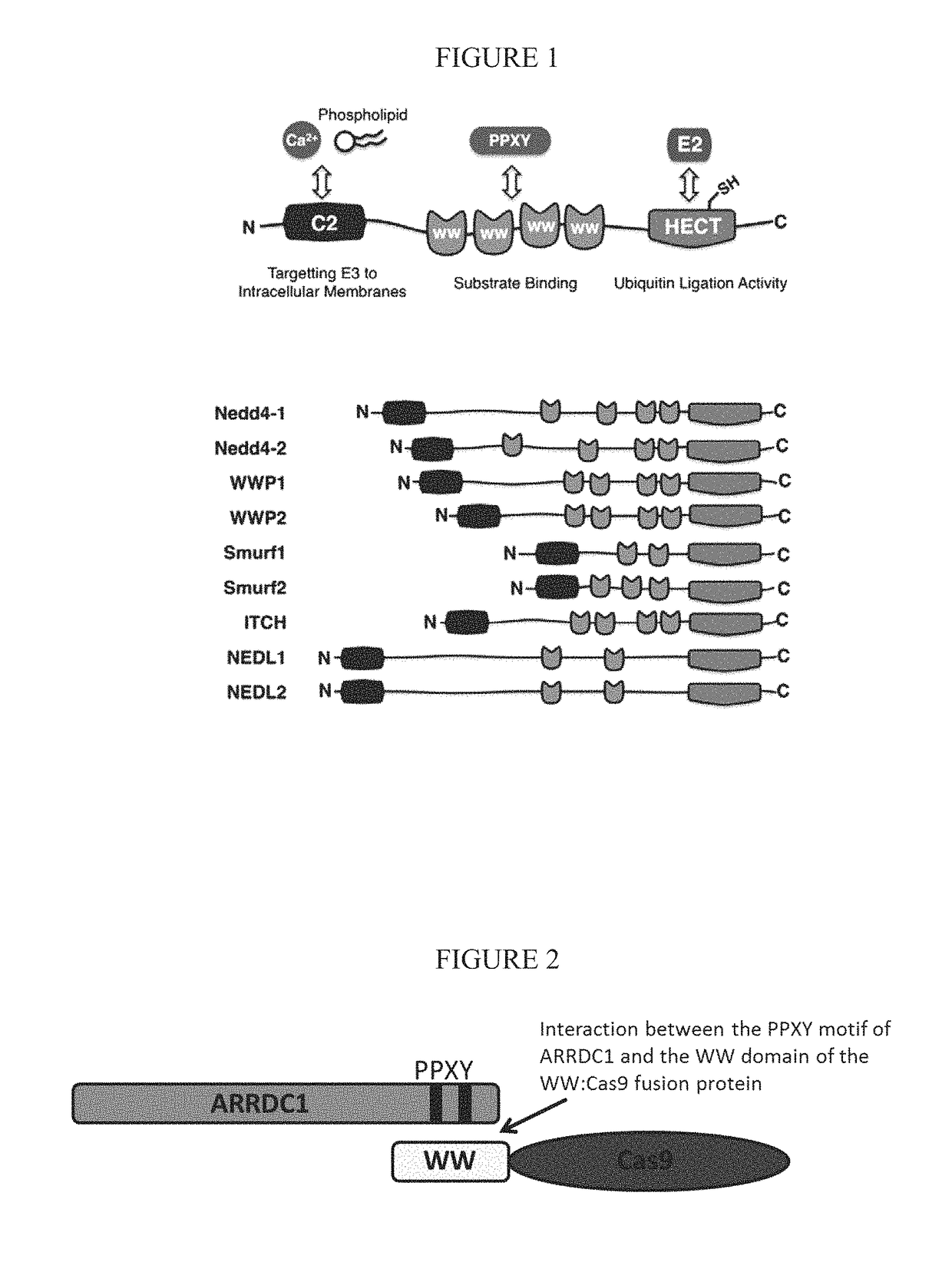
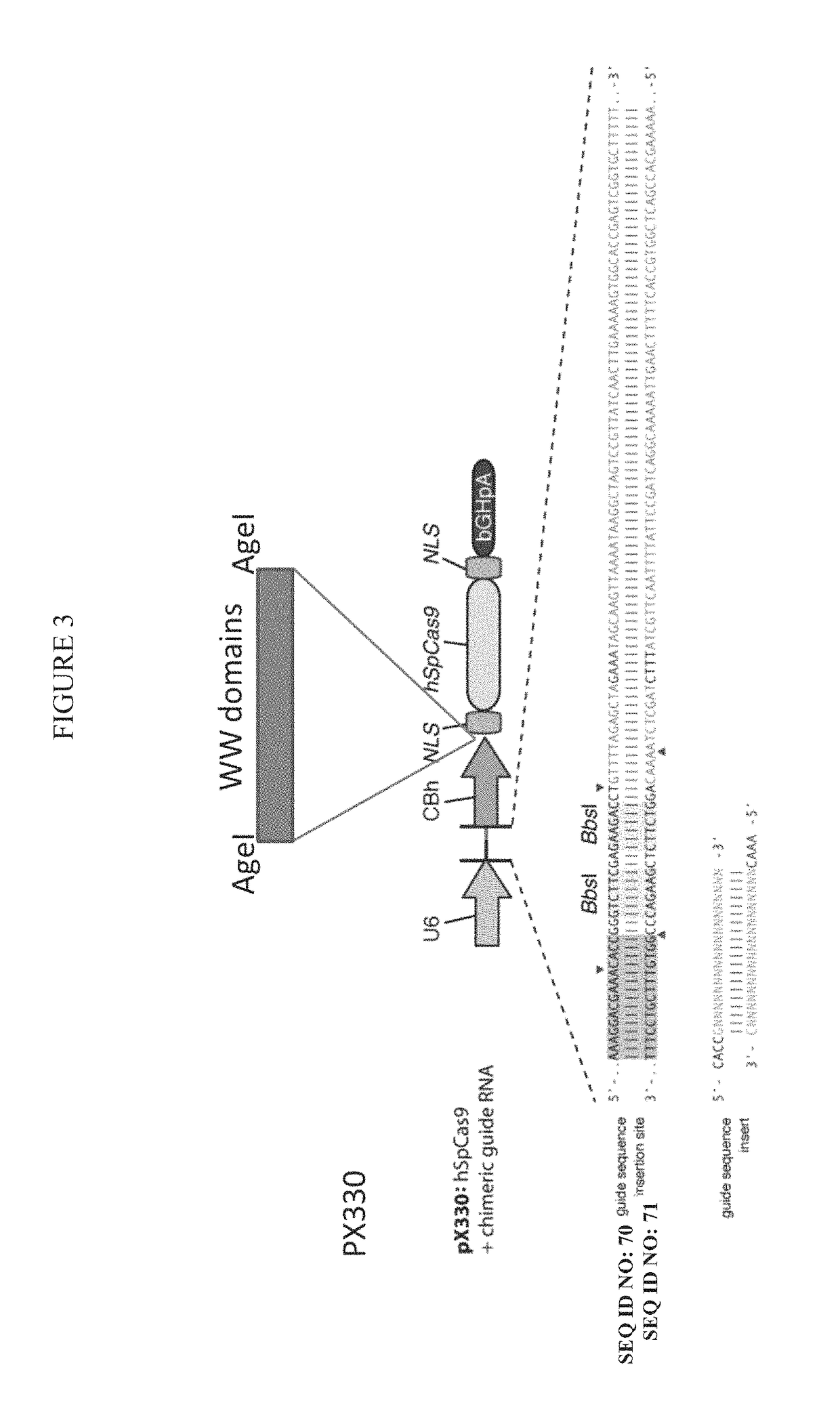
ActiveUS20160206566A1Easy loadingConvenience to mergePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainWW domainTSG101
Methods, systems, compositions and strategies for the delivery of WW domain-containing fusion proteins into cells in vivo, ex vivo, or in vitro via ARMMs are provided. Methods, systems, compositions and strategies for the delivery of Cas9 proteins and / or Cas9 variants into cells in vivo, ex vivo, or in vitro via fusion to ARMM associated proteins (e.g., ARRDC1 or TSG101) are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
Method of Delivering Rna Interference and Uses Thereof
InactiveUS20080153737A1Limiting potential side effectQuantity minimizationAntibacterial agentsFusion with RNA-binding domainGeneticsDouble strand
Owner:CHILDRENS MEDICAL CENT CORP
Targeted delivery of nucleic acids
ActiveUS9006415B2Reduce deliveryEasy to integrateCompounds screening/testingFusion with RNA-binding domainBioinformaticsNucleic acid
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
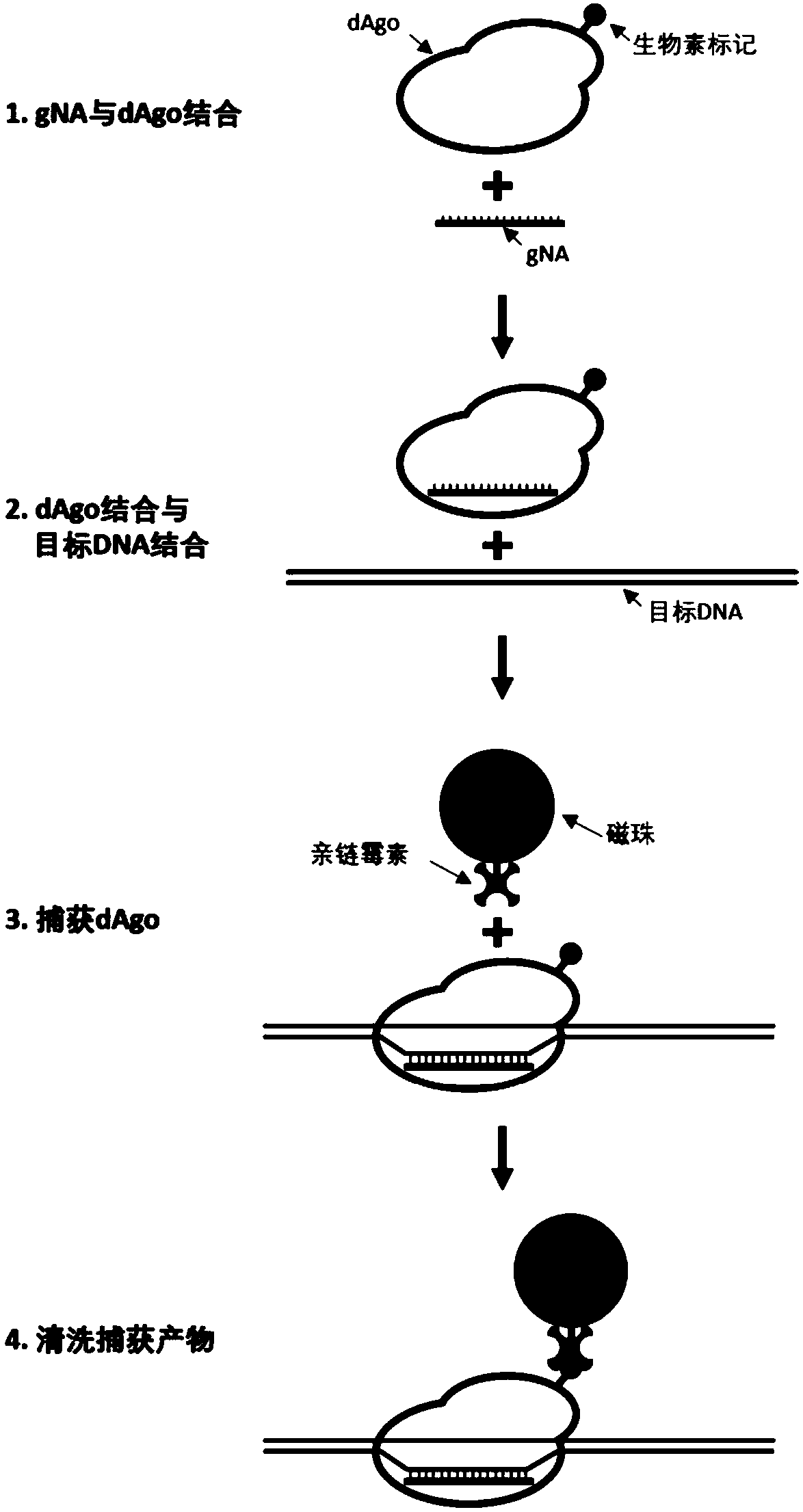
Argonaute protein mutant and application thereof
ActiveCN110229799APromote enrichmentReduce lossesFusion with RNA-binding domainNucleotide librariesTernary complexMutant
The present invention relates to an Argonaute protein mutant which lacks DNA cleavage activity, but has DNA binding activity. The mutation of the mutant is located in a PIWI domain. The invention alsorelates to application of the protein mutant particularly in the enrichment of target DNA and in the construction of a sequencing library. Therefore, the present invention also relates to a method for enriching the target DNA. The method comprises the steps of: (a) designing a leader sequence for a specific sequence in the target DNA; (b) combining the mutant, the leader sequence and the target DNA according to the present invention to obtain a mutant-leader sequence-target DNA ternary complex; (c) capturing the mutant-leader sequence-target DNA ternary complex through a capture medium; and (d) isolating the target DNA from the captured mutant-leader sequence-target DNA ternary complex to obtain enriched target DNA.
Owner:BERRYGENOMICS CO LTD
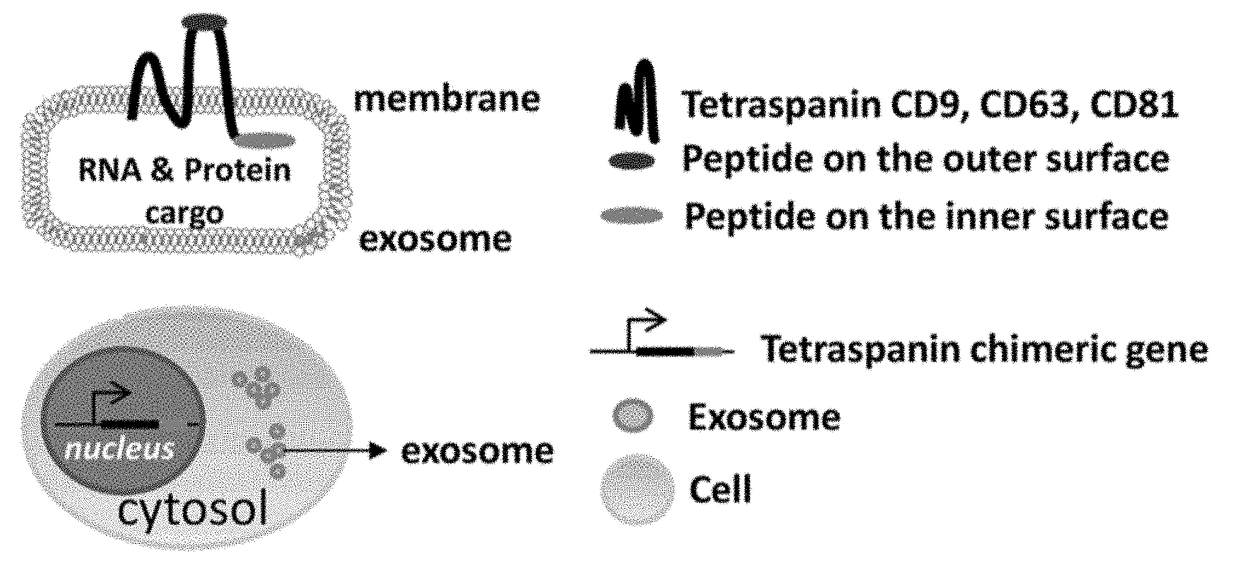
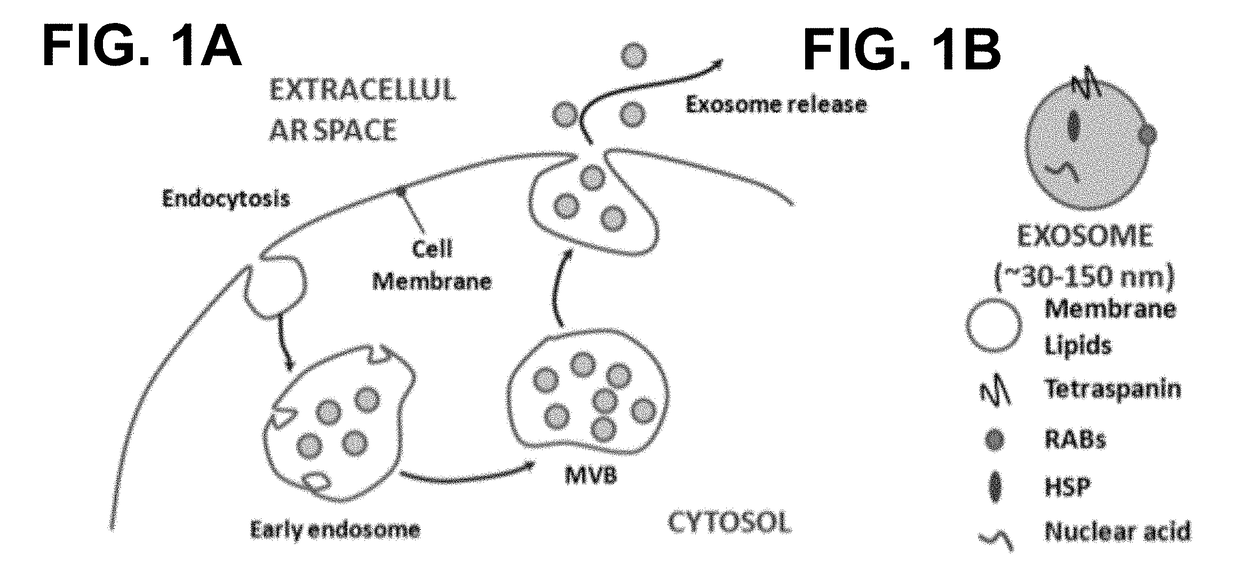
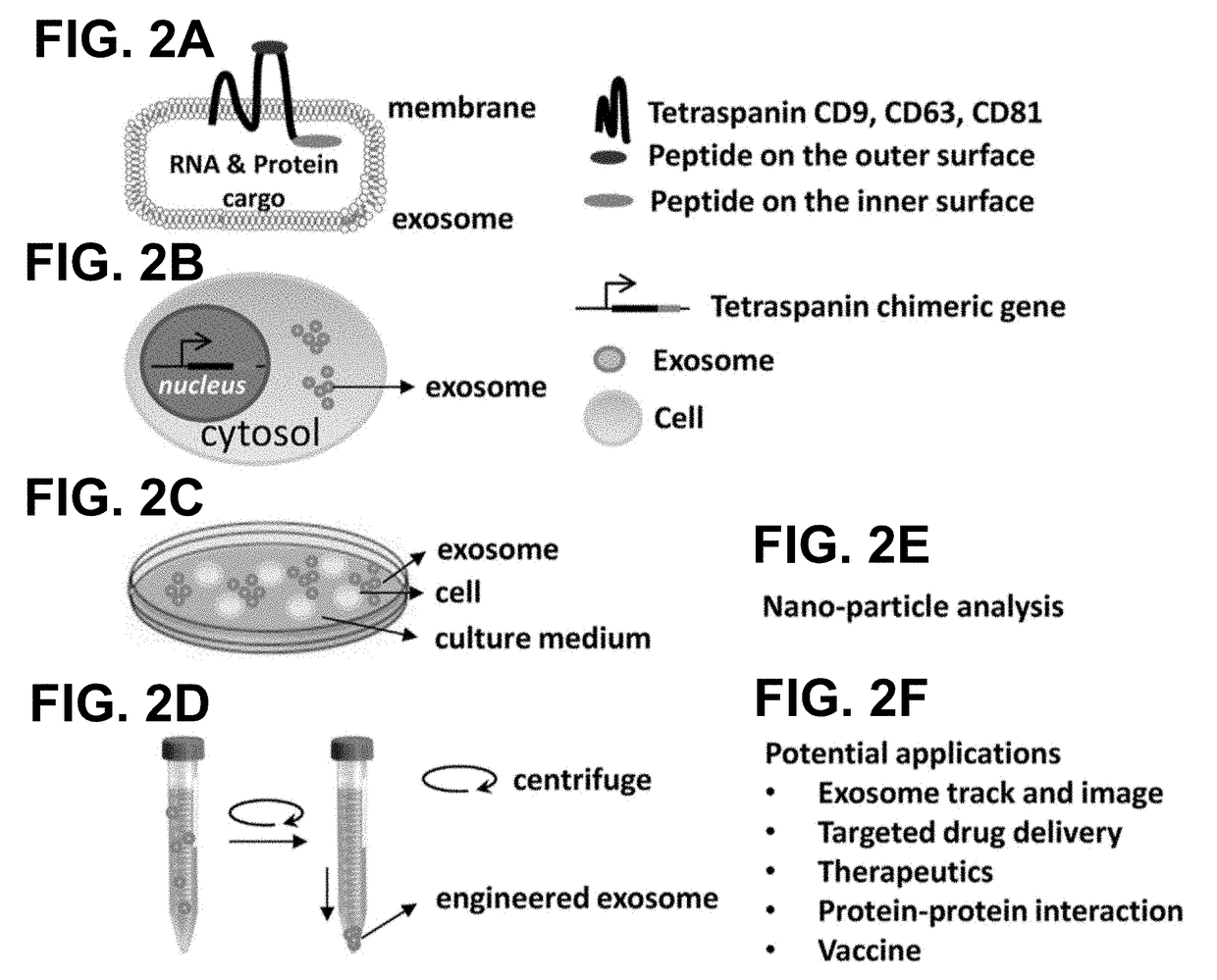
Engineered Exosomes for the Delivery of Bioactive Cargo Using Transmembrane Tetraspanins
ActiveUS20180015182A1Efficient secretionPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainTetraspaninAttachment site
Engineered exosomes for the delivery of bioactive cargo are provided. The exosomes incorporate a tetraspanin transmembrane anchoring scaffold onto the membrane of the exosome. The tetraspanin transmembrane anchoring scaffold has a C-terminal attachment site in the inner-vesicle space of the exosome, a N-terminal attachment site in the inner-vesicle space or the outer-vesicle space, and / or a loop attachment site in the outer-vesicle space. Peptides can be attached to the different attachments sites in any form or combination. Tetrapanins naturally anchor on the exosome membrane, are biocompatible, and allow for robust loading and delivery of bioactive cargos in mammalian system.
Owner:SANTA CLARA UNIVERSITY
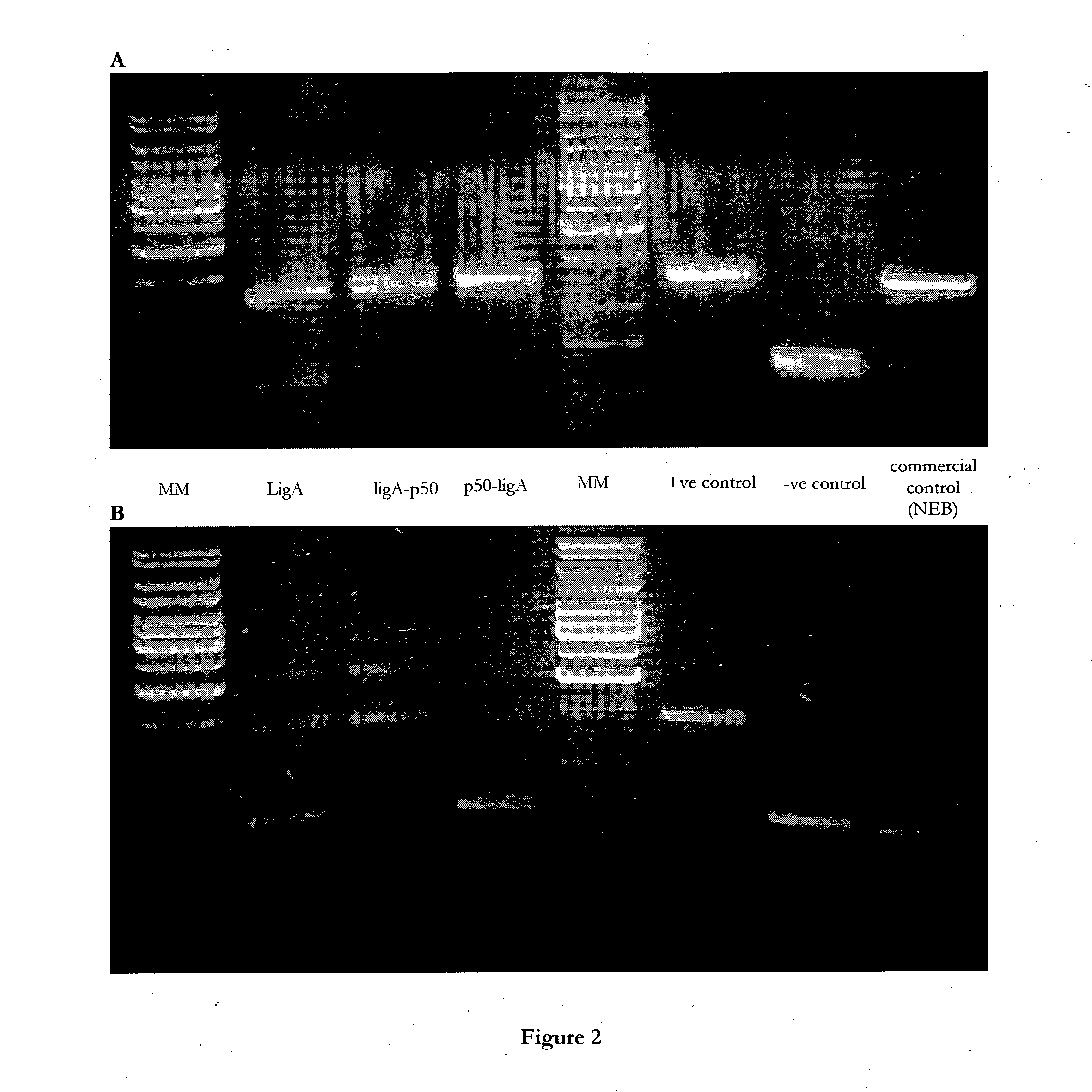
Fusion polypeptides and uses thereof
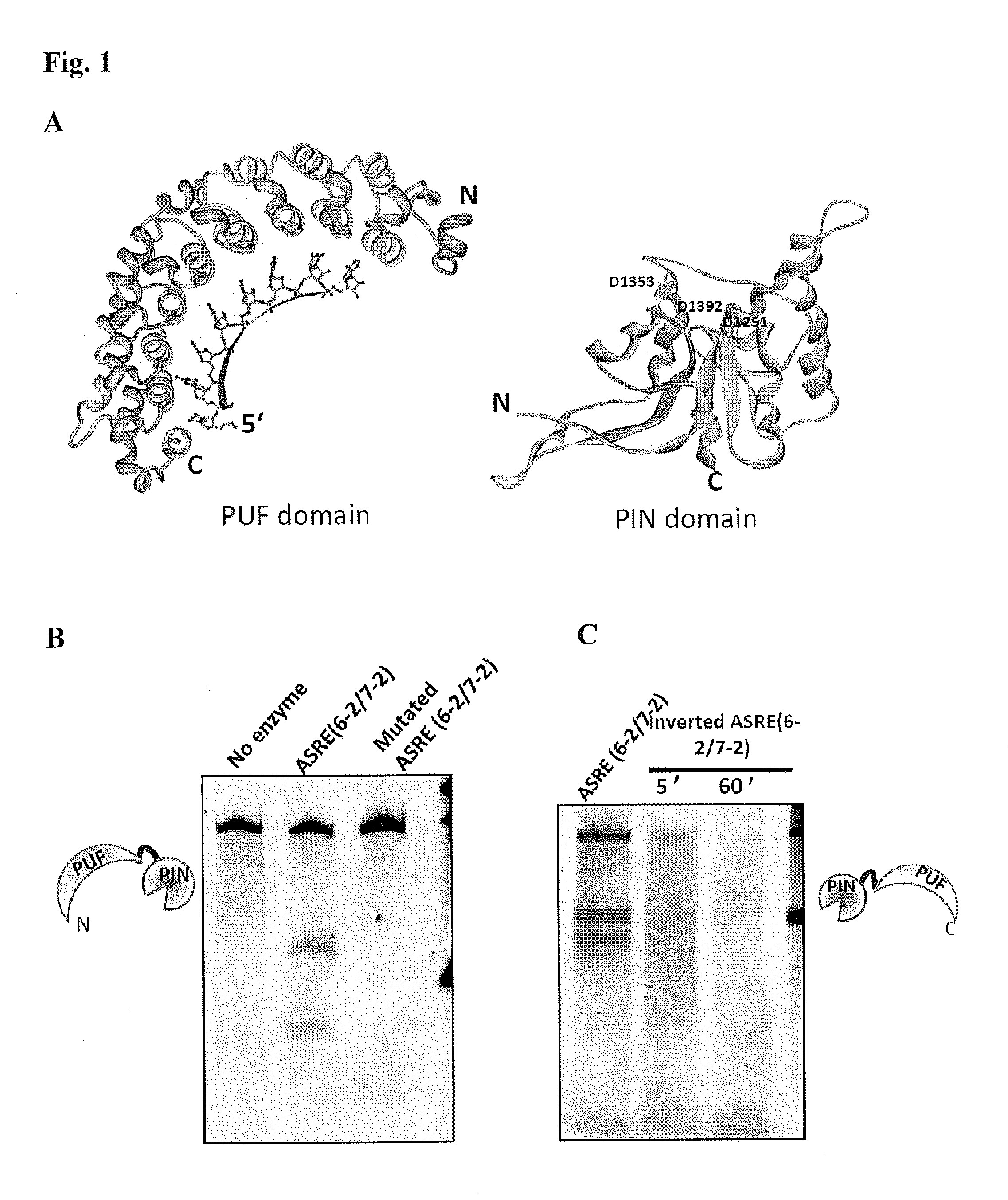
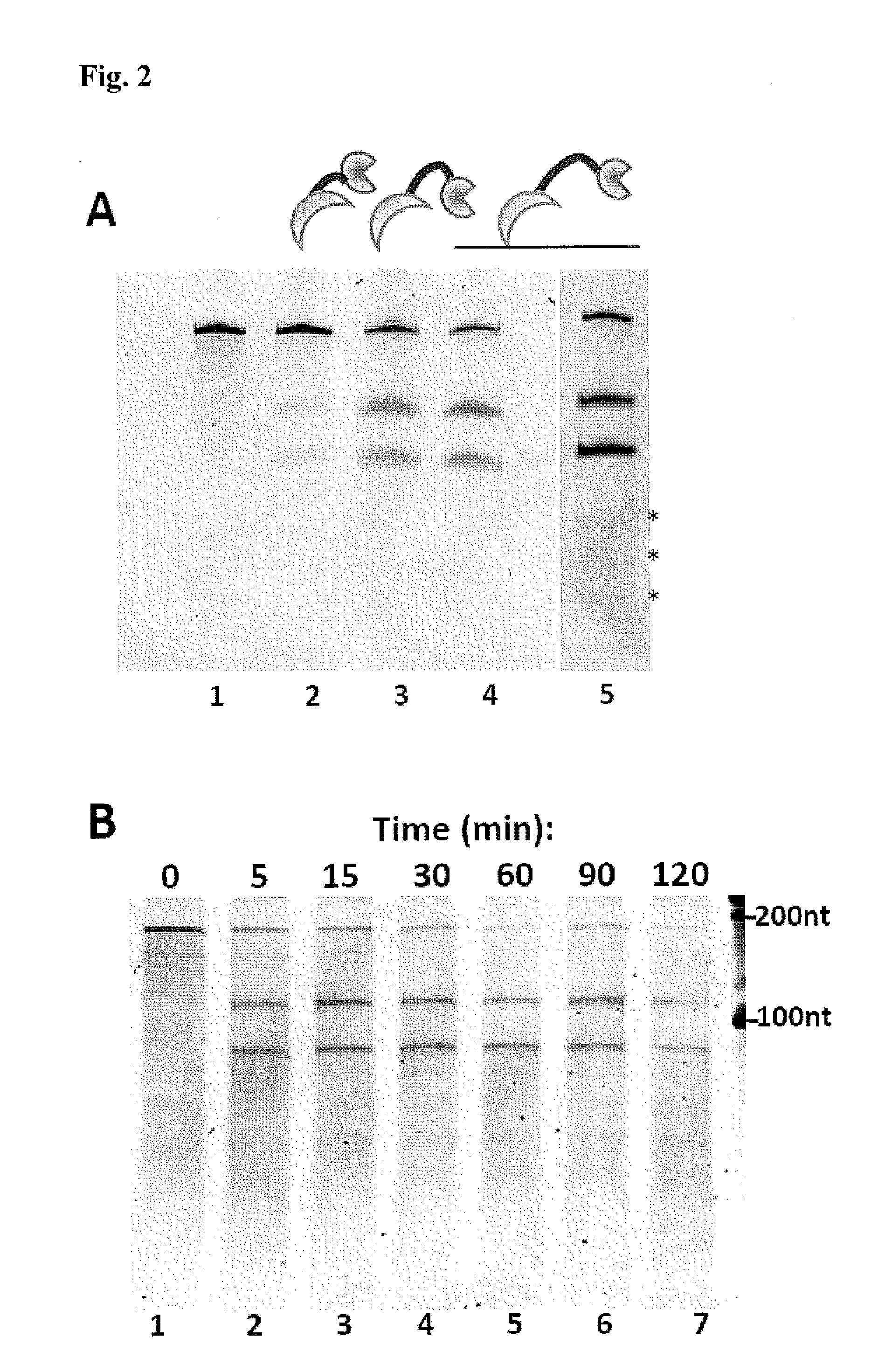
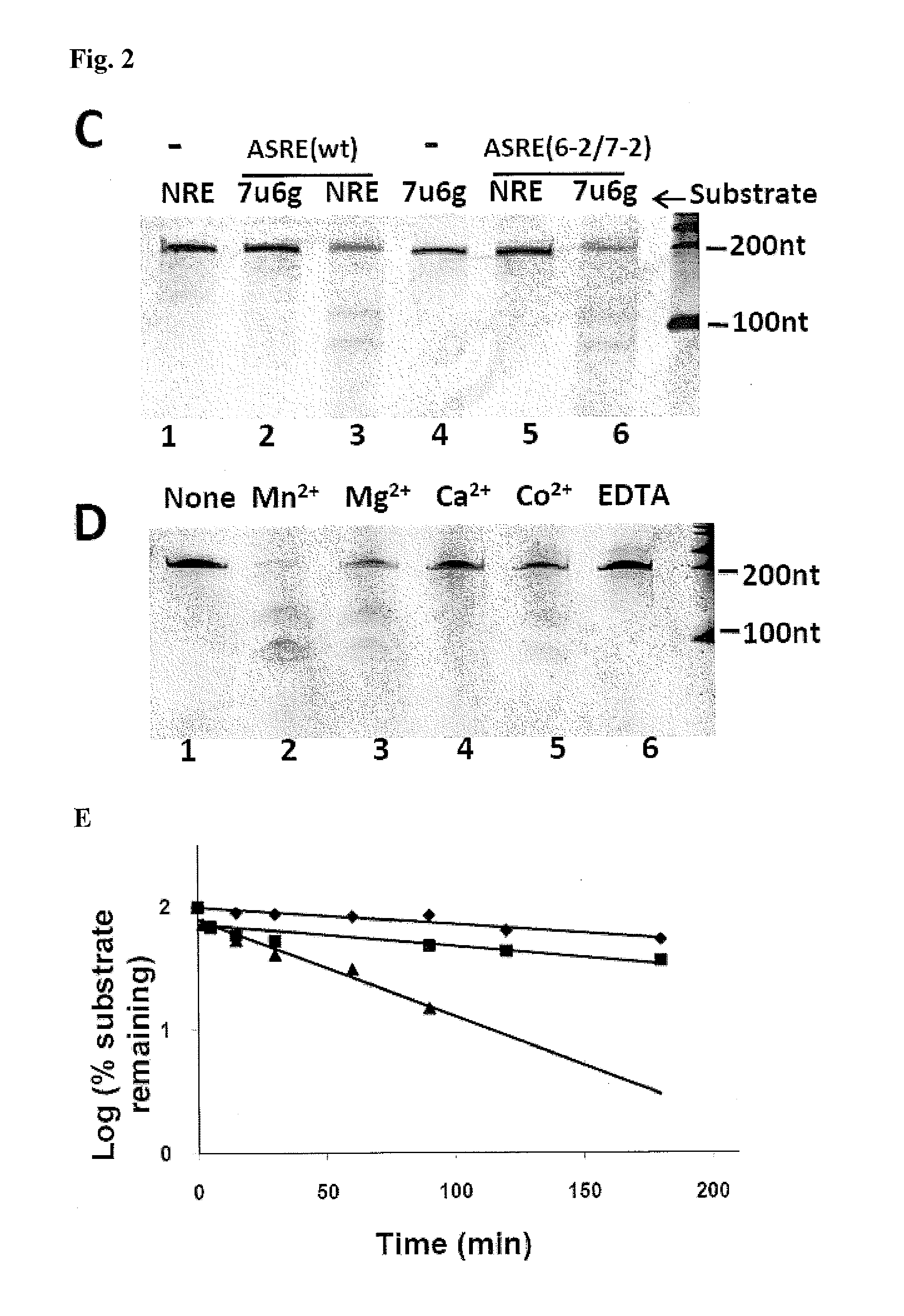
The invention relates to fusion polypeptides comprising a polynucleotide-binding domain, such as a DNA-binding domain, and a ligase domain, such as a DNA ligase domain, methods for the production of such fusion polypeptides, and uses of the fusion polypeptides, for example in a range of molecular biological techniques as well as applications in the diagnostics, protein production, pharmaceutical, nutraceutical and medical fields.
Owner:MASSEY UNIVERISTY
Delivery of CAS9 via ARRDC1-mediated microvesicles (ARMMs)
ActiveUS9816080B2Easy loadingConvenience to mergePolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainWW domainProtein C
Methods, systems, compositions and strategies for the delivery of WW domain-containing fusion proteins into cells in vivo, ex vivo, or in vitro via ARMMs are provided. Methods, systems, compositions and strategies for the delivery of Cas9 proteins and / or Cas9 variants into cells in vivo, ex vivo, or in vitro via fusion to ARMM associated proteins (e.g., ARRDC1 or TSG101) are also provided.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV +1
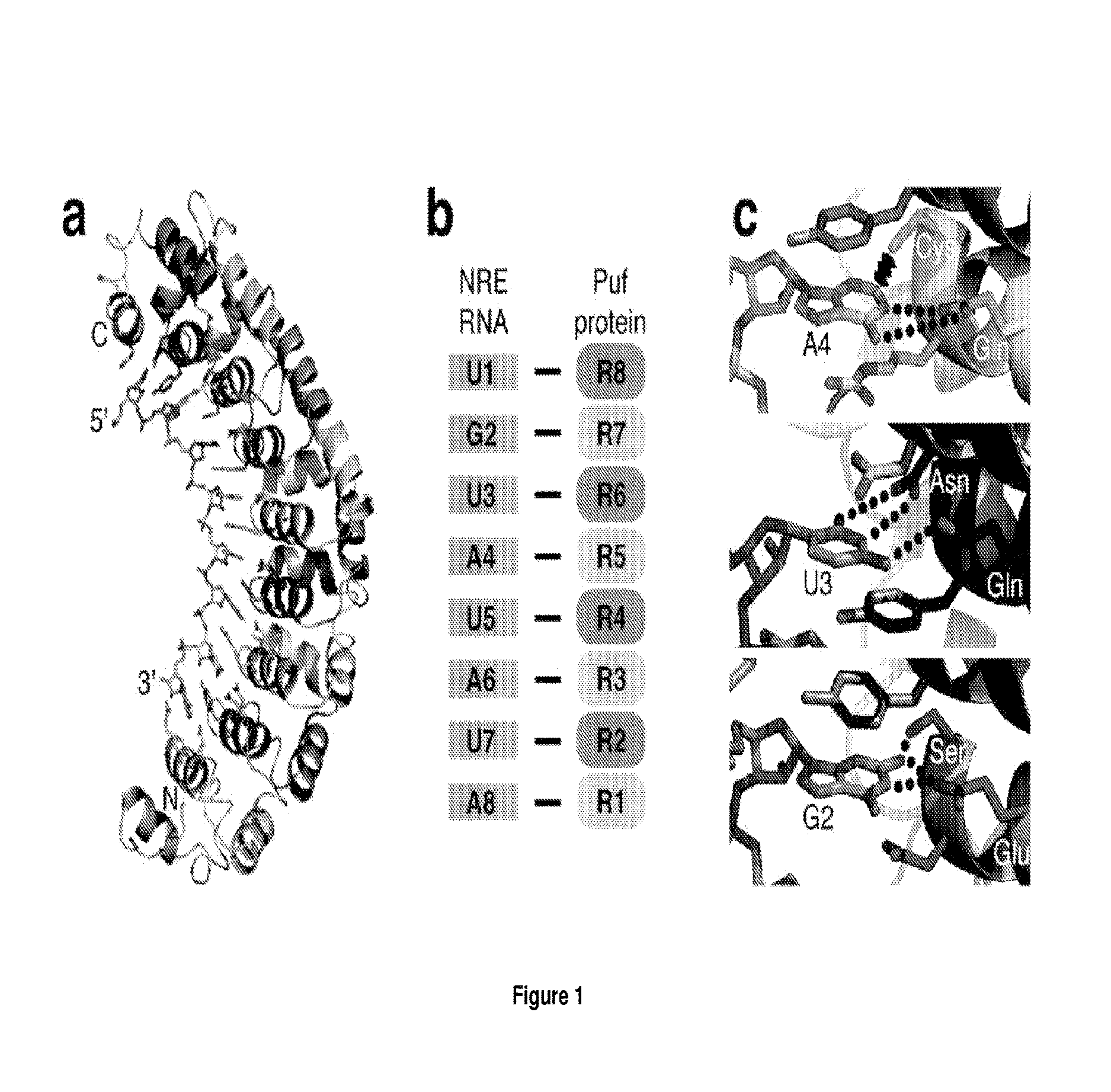
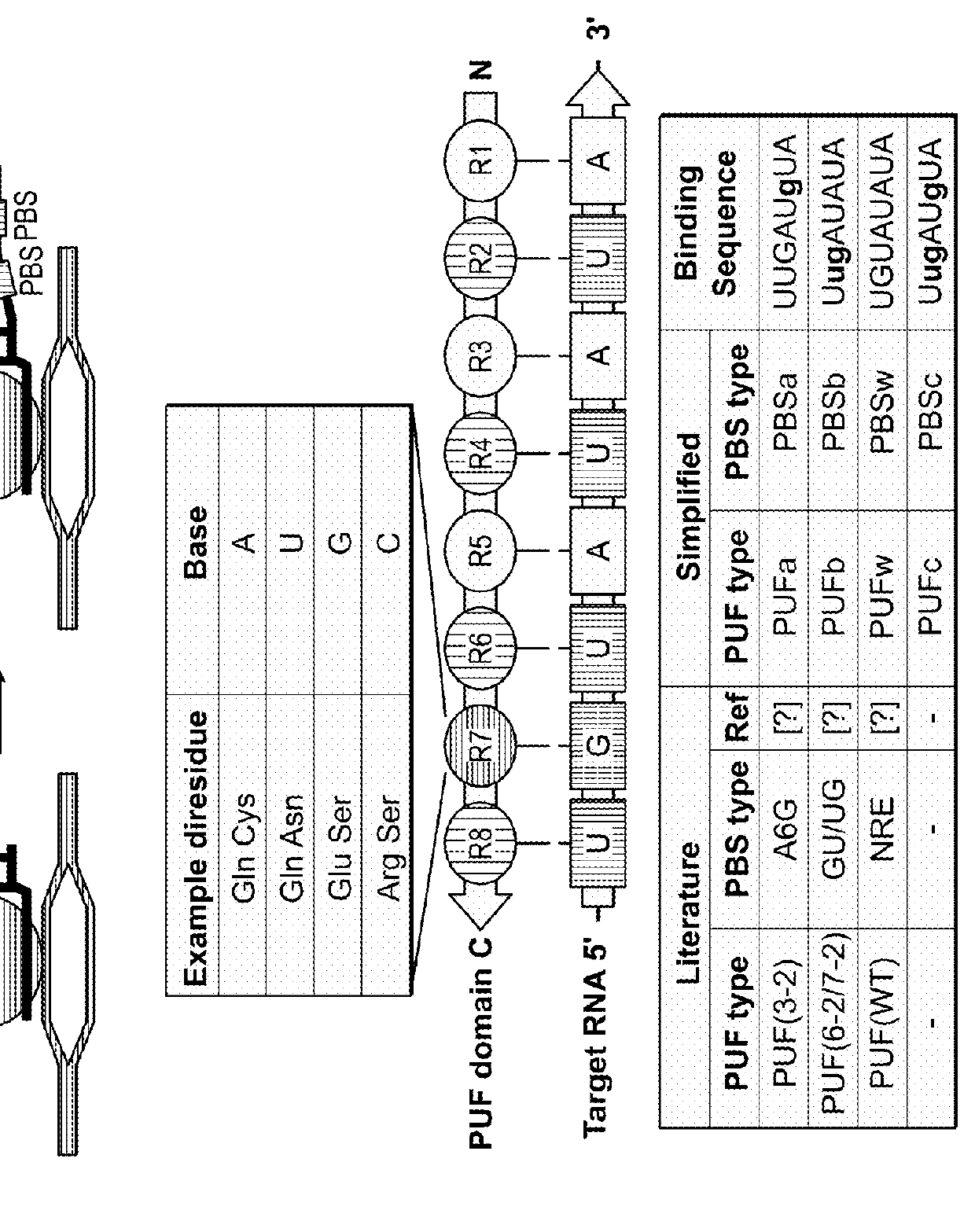
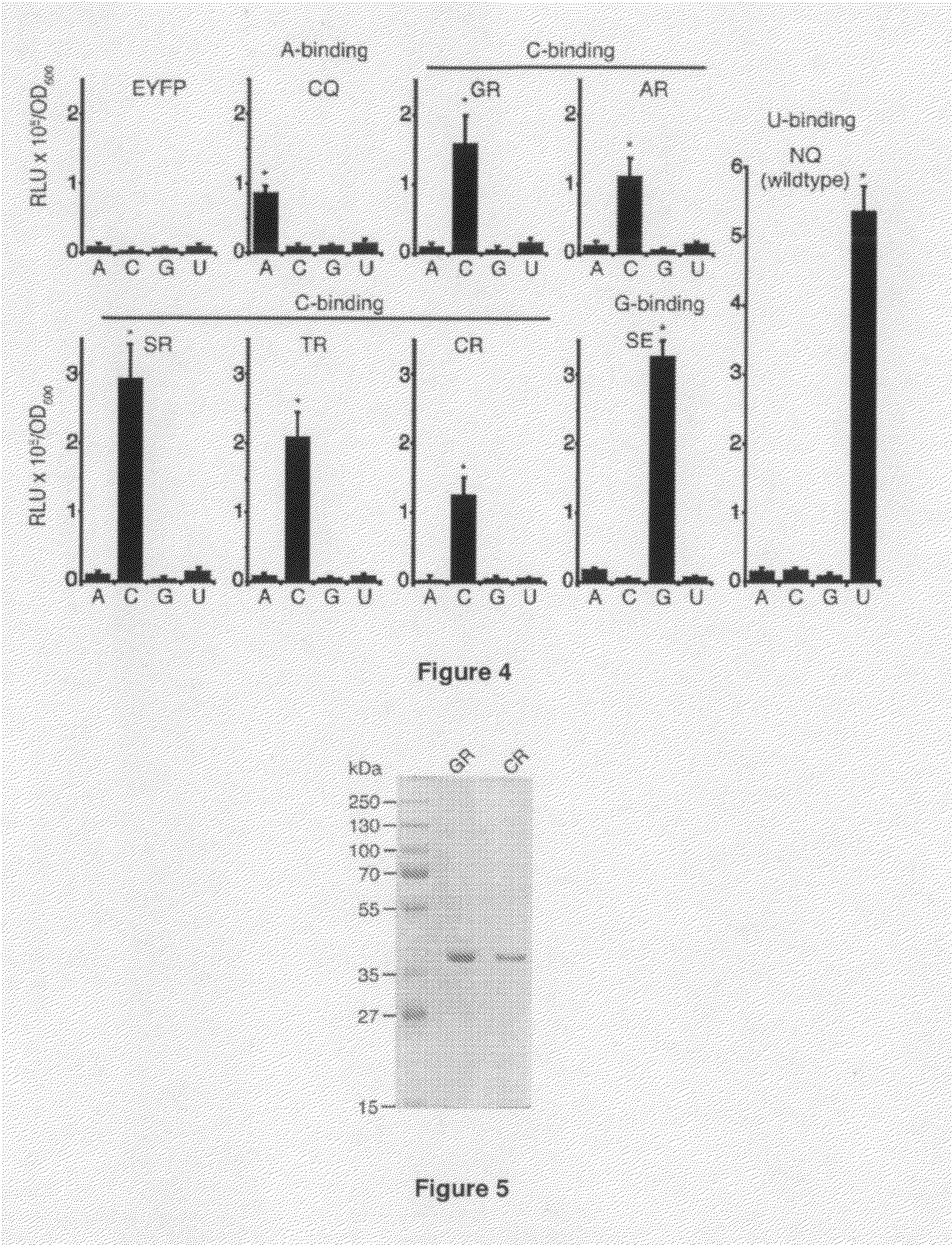
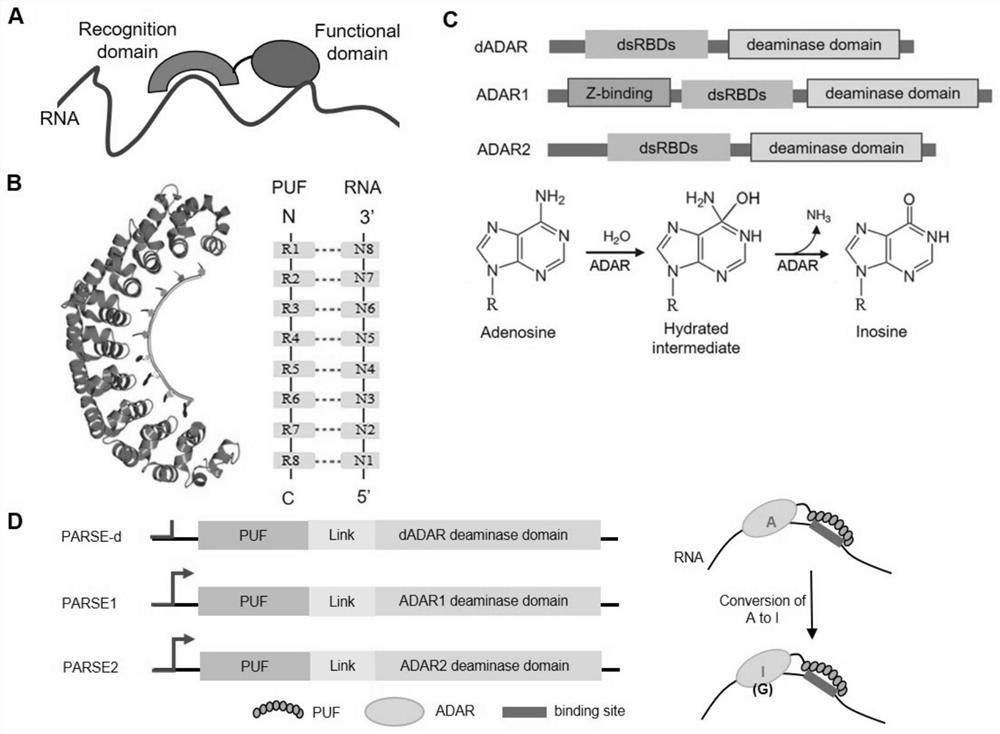
Peptides for the specific binding of RNA targets
A recombinant polypeptide is described including at least one PUF RNA-binding domain capable of specifically binding to a cytosine RNA base. The PUF RNA-binding domain of the polypeptide includes at least one RNA base-binding motif of the general formula X1X2X3X4X5X6X7X8X9X10X11 wherein X1 is selected from a defined group and wherein the RNA base-binding motif is operably capable of specifically binding to a cytosine RNA base.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Exosomes comprising RNA therapeutics
ActiveCN111629760AAdverse immune responseFusion with RNA-binding domainOrganic active ingredientsExtracellular vesicleEngineering protein
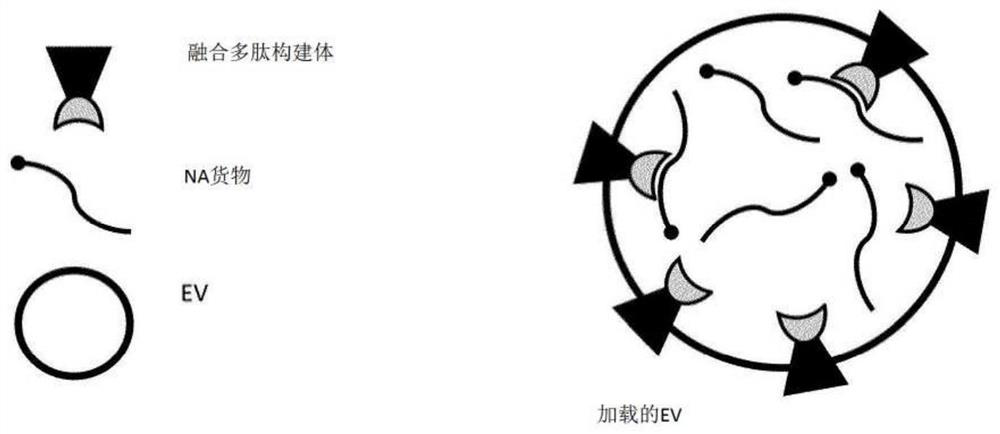
The present invention pertains to extracellular vesicle (EV) therapeutics, wherein the EVs comprise nucleic acid (NA)-based therapeutics such as m RNAs, circular RNAs, mi RNAs, sh RNAs, circular RNA and / or DNA molecules. The NA therapeutics are loaded into EVs using inventive engineering protein and NA engineering strategies to enhance loading into EVs and to facilitate release of the NA cargo molecules inside target cells.
Owner:EVOX THERAPEUTICS LTD
Fusion polypeptides and uses thereof
InactiveCN102597006ADoes not affect functionReserved functionFusion with RNA-binding domainFusion with DNA-binding domainBinding domainA-DNA
The invention relates to fusion polypeptides comprising a polynucleotide-binding domain, such as a DNA-binding domain, and a ligase domain, such as a DNA ligase domain, methods for the production of such fusion polypeptides, and uses of the fusion polypeptides, for example in a range of molecular biological techniques as well as applications in the diagnostics, protein production, pharmaceutical, nutraceutical and medical fields.
Owner:MASSEY UNIVERISTY
Methods and Compositions for Sequence Specific RNA Endonucleases
The present invention provides sequence specific restriction enzymes for site-specific cleavage of RNA, as well as methods of their use.
Owner:THE UNIV OF NORTH CAROLINA AT CHAPEL HILL
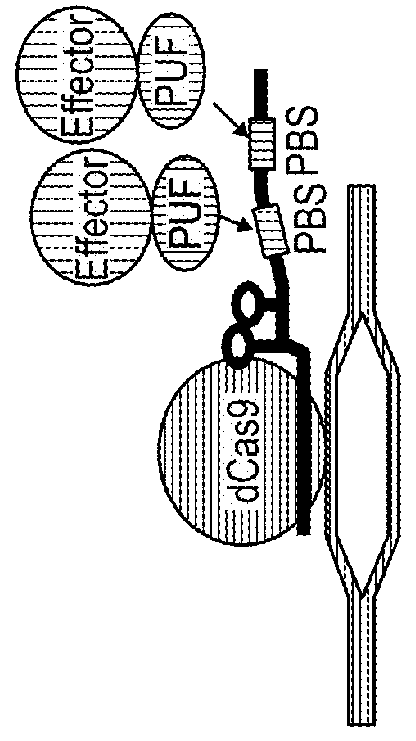
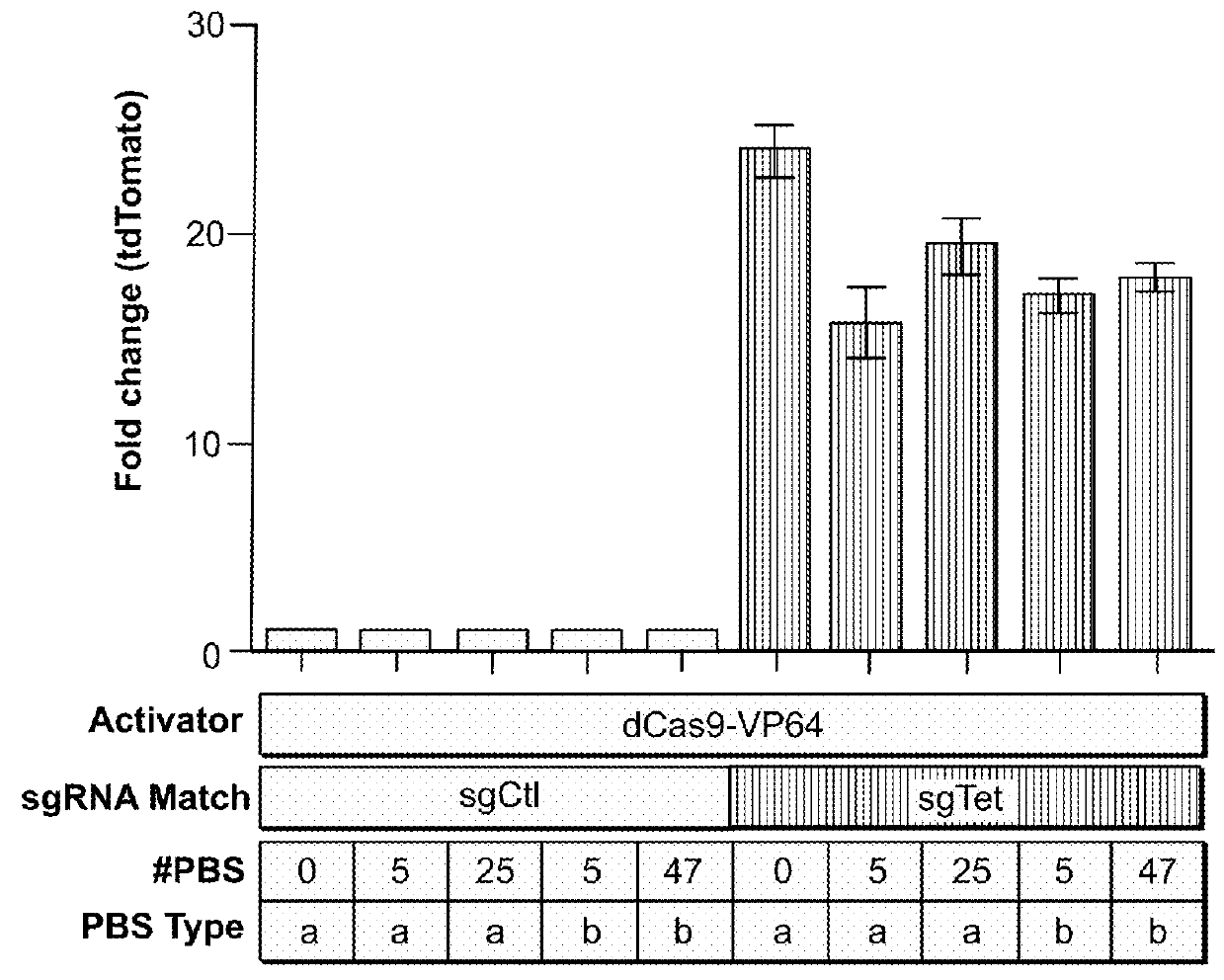
Three-component crispr/cas complex system and uses thereof
ActiveUS20180094257A1Lack nuclease activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainGenomeDNA
The invention described herein provides compositions and reagents for assembling a tripartite complex at a specific location of a target DNA. The invention also provides methods for using the complex to, for example, label a specific genomic locus, to regulate the expression of a target gene, or to create a gene regulatory network.
Owner:JACKSON LAB THE
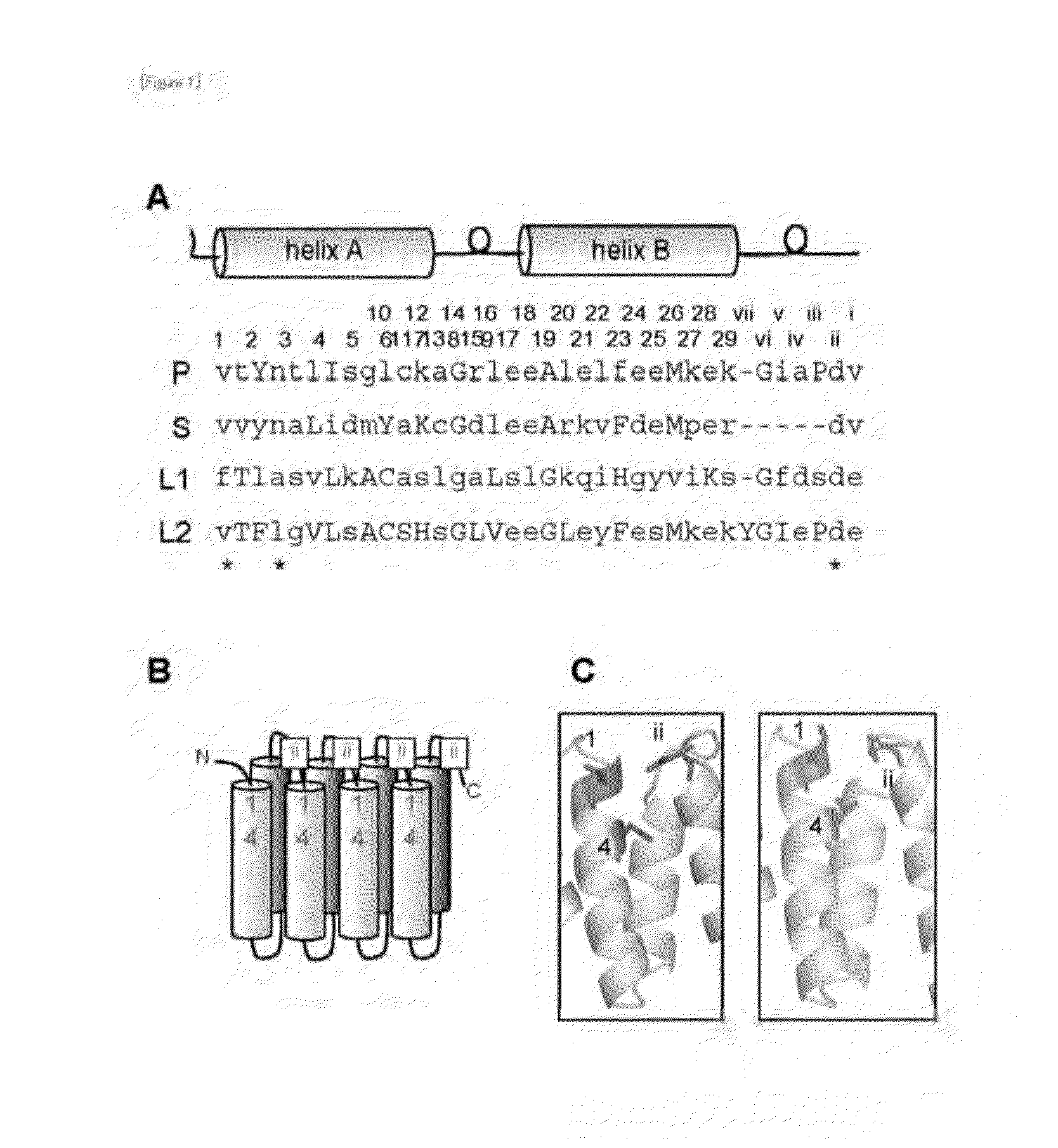
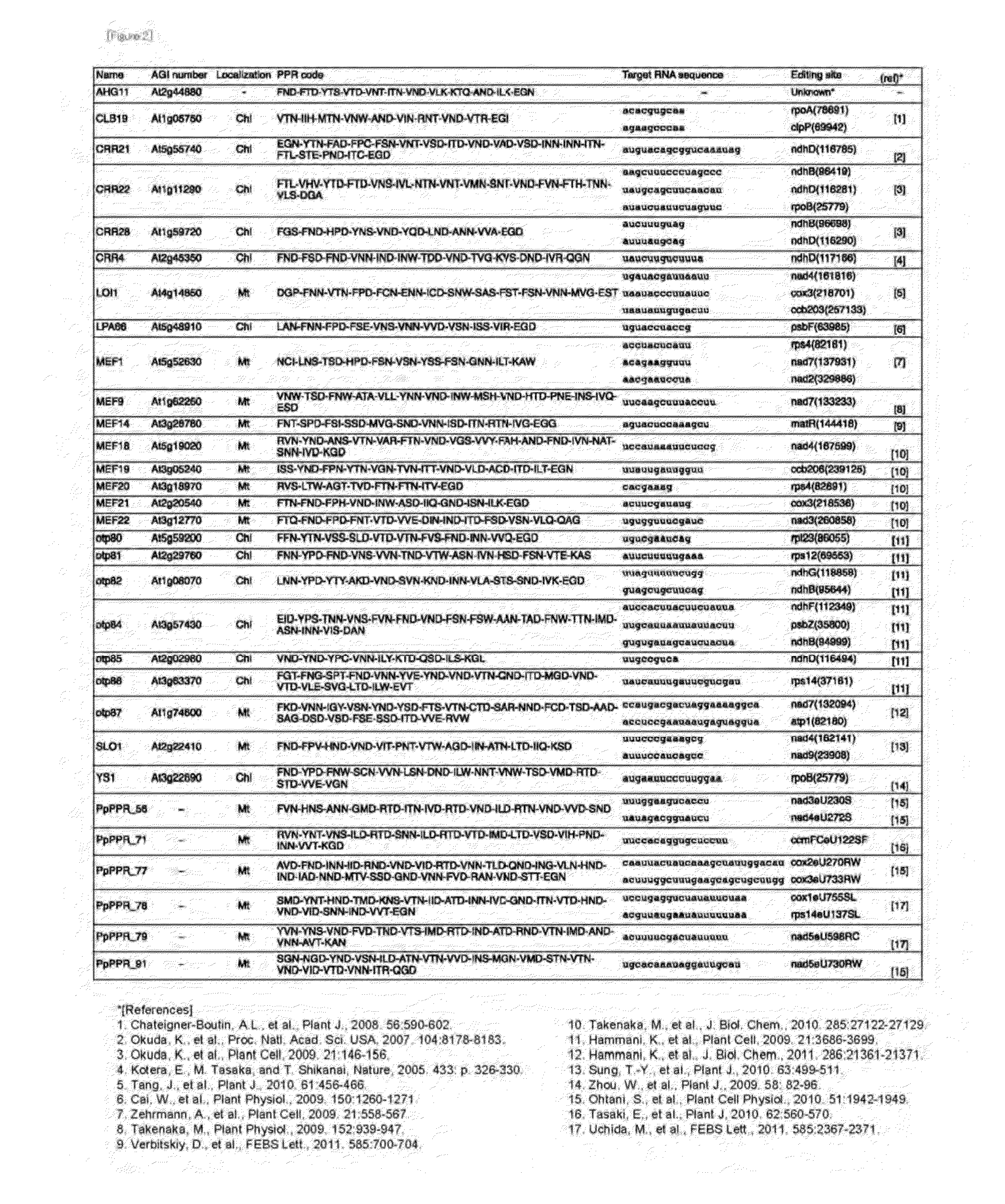
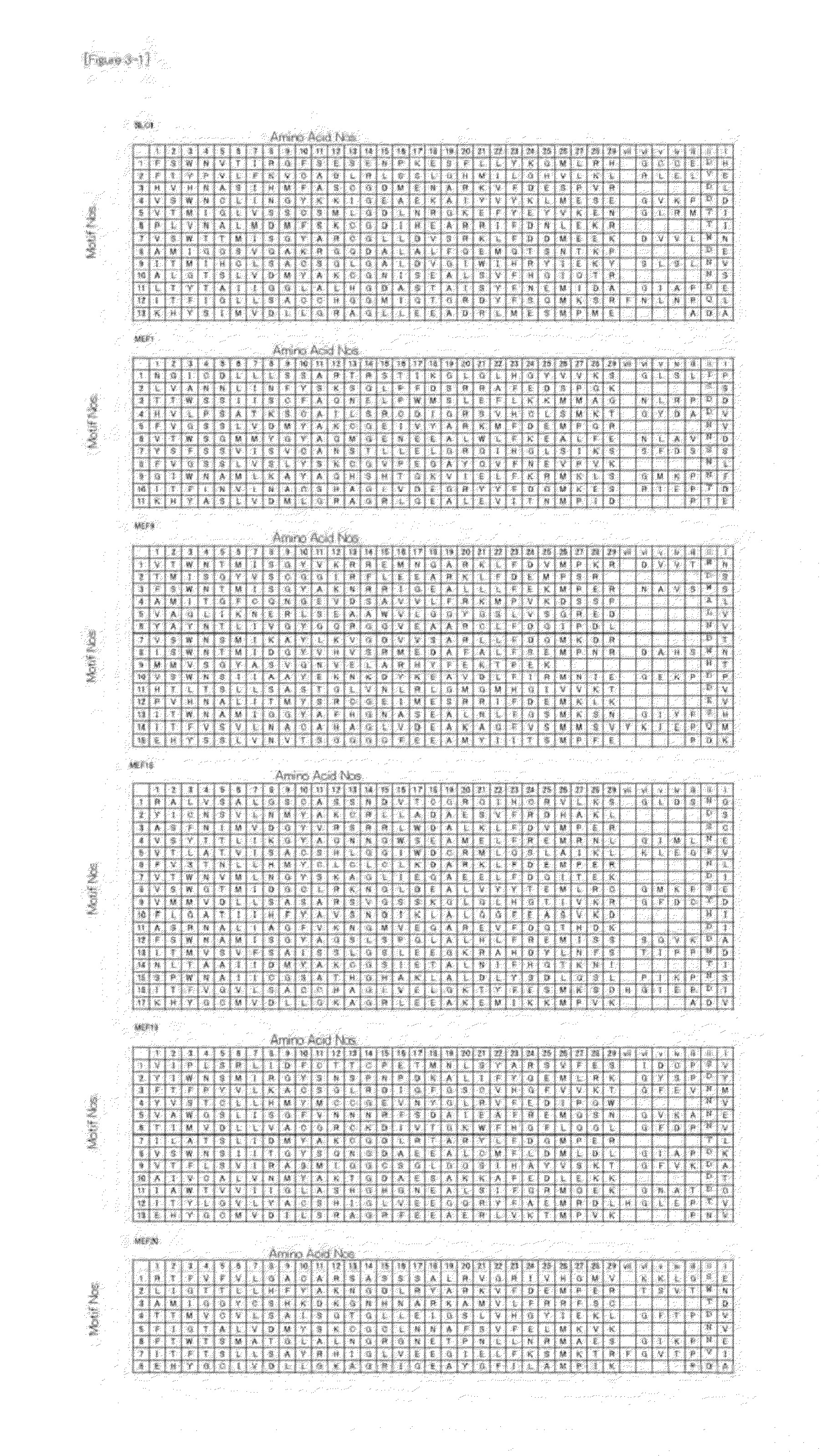
Method for Designing RNA Binding Protein Utilizing PPR Motif, and Use Thereof
ActiveUS20140335521A1Raise the possibilityFusion with RNA-binding domainMutant preparationProtein insertionC-terminus
A method for designing a protein capable of binding in an RNA base selective manner or RNA base sequence specific manner is provided. The protein of the present invention is a protein containing one or more of PPR motifs (preferably 2 to 14 PPR motifs) each consisting of a polypeptide of 30- to 38-amino acid length represented by the formula 1 (wherein Helix A is a moiety of 12-amino acid length capable of forming an α-helix structure, and is represented by the formula 2, wherein, in the formula 2, A1 to A12 independently represent an amino acid; X does not exist, or is a moiety of 1- to 9-amino acid length; Helix B is a moiety of 11- to 13-amino acid length capable of forming an α-helix structure; and L is a moiety of 2- to 7-amino acid length represented by the formula 3, wherein, in the formula 3, the amino acids are numbered “i” (-1), “ii” (-2), and so on from the C-terminus side, provided that Liii to Lvii may not exist), and combination of three amino acids A1, A4 and Lii, or combination of two amino acids A4, and Lii is a combination corresponding to a target RNA base or base sequence.
Owner:KYUSHU UNIV
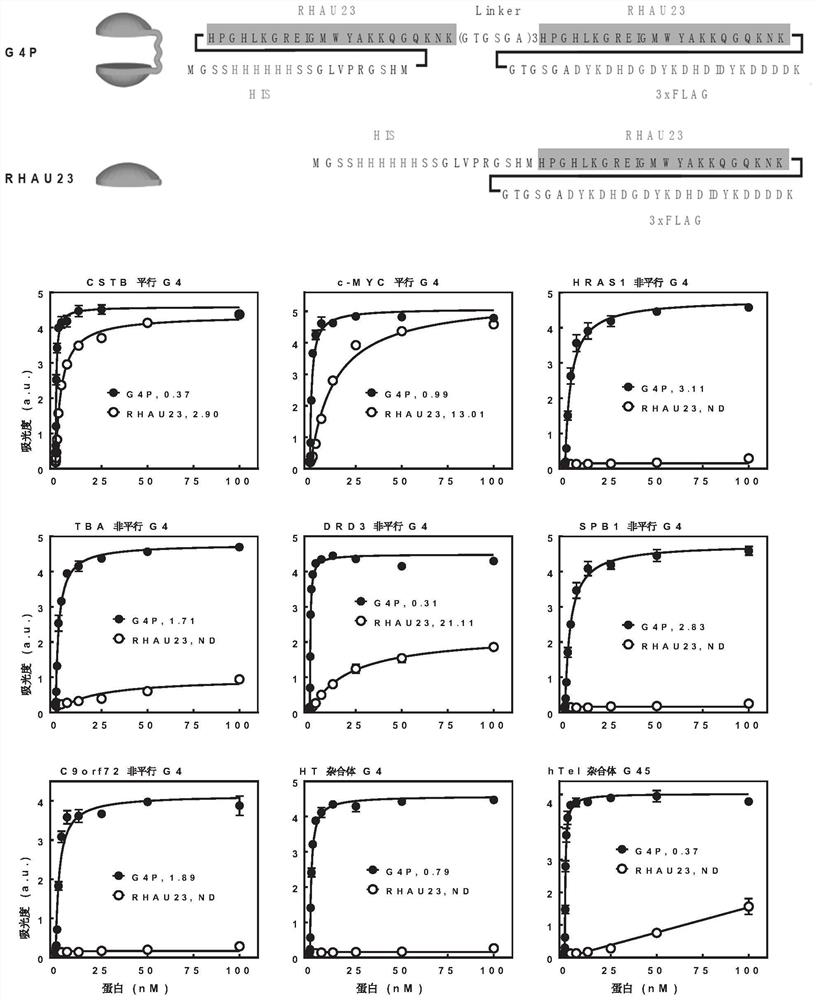
Polypeptide probe for recognizing G-quadruplex and application of polypeptide probe in detection of G-quadruplex in cells
PendingCN111647052AStrong opposite sexSimple structureFusion with RNA-binding domainFusion with DNA-binding domainIntracellularAmino acid
The invention discloses a polypeptide probe for recognizing G-quadruplex and application of the polypeptide probe in detection of the G-quadruplex in the cells. The polypeptide probe for recognizing the G-quadruplex contains 2-4 G-quadruplex combined structural domains and linking peptides for connecting the adjacent G-quadruplex combined structural domains, wherein each G-quadruplex combined structural domain contains one specific structural region, and an amino acid sequence of the specific structural region is PGHLKGREIGMWY (SEQ ID NO.1). The polypeptide probe provided by the invention is strong in specificity, is compatible with reducing environments in the cells and can be applied to the detection of the G-quadruplex in the cells.
Owner:长治医学院
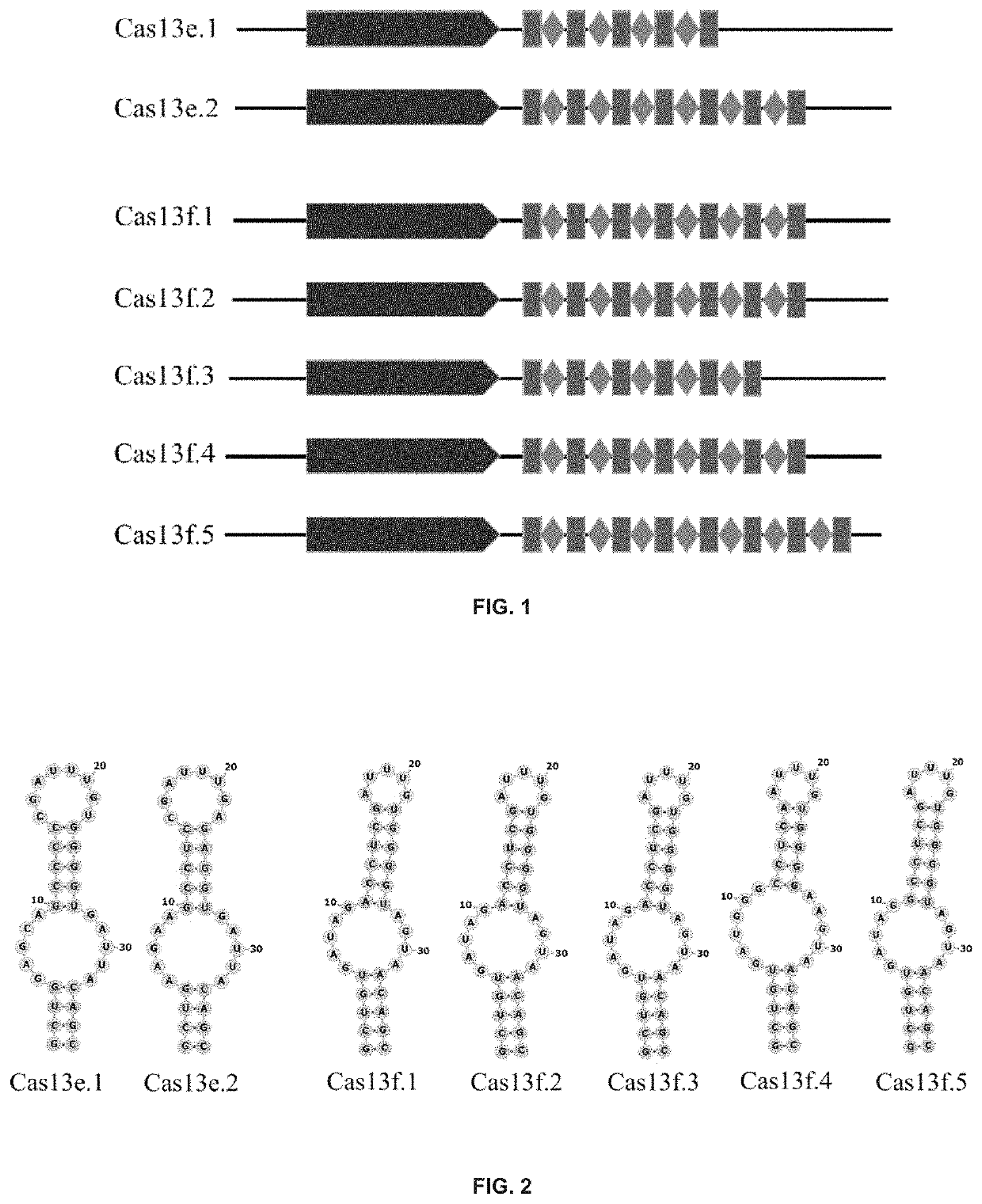
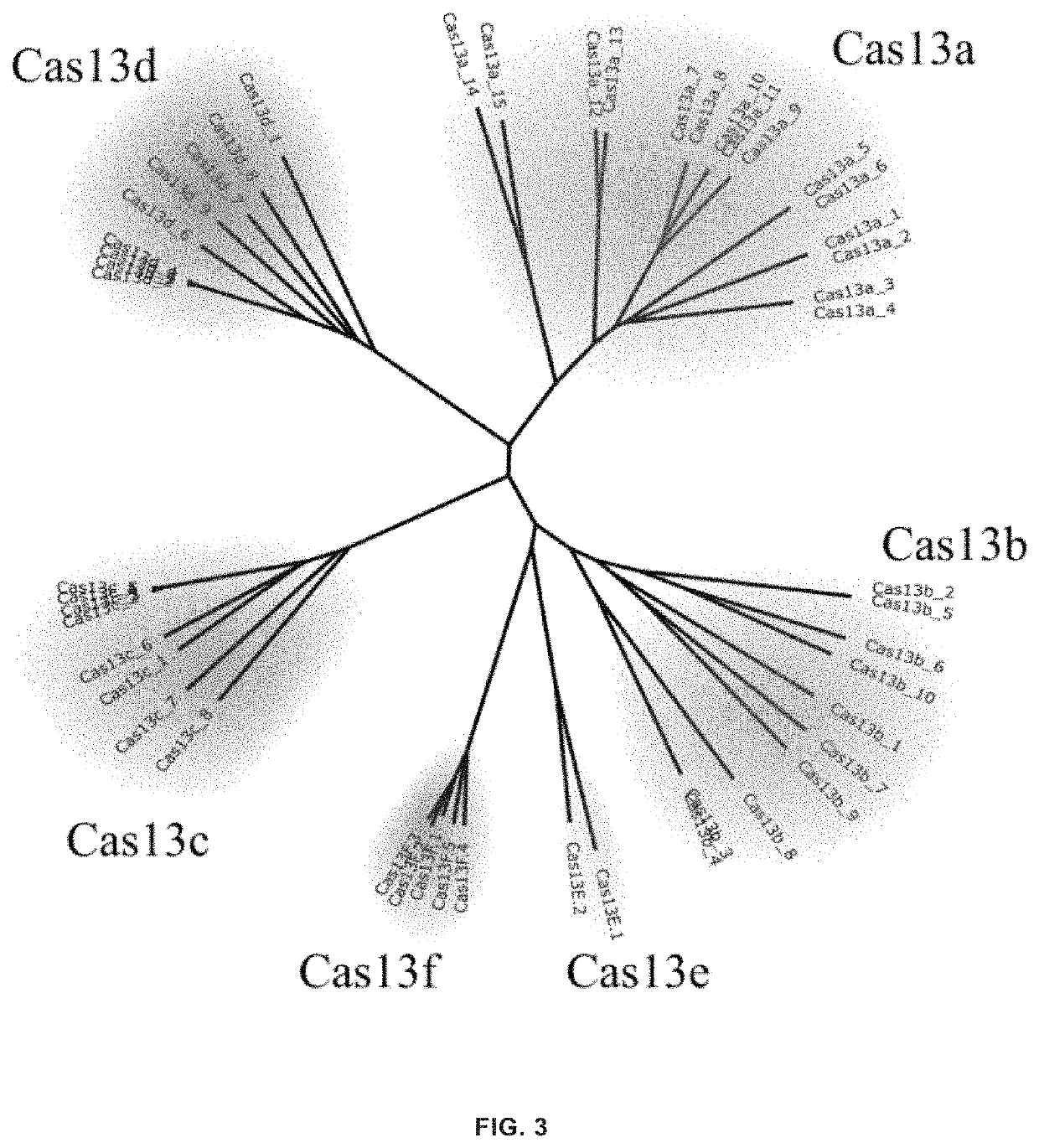
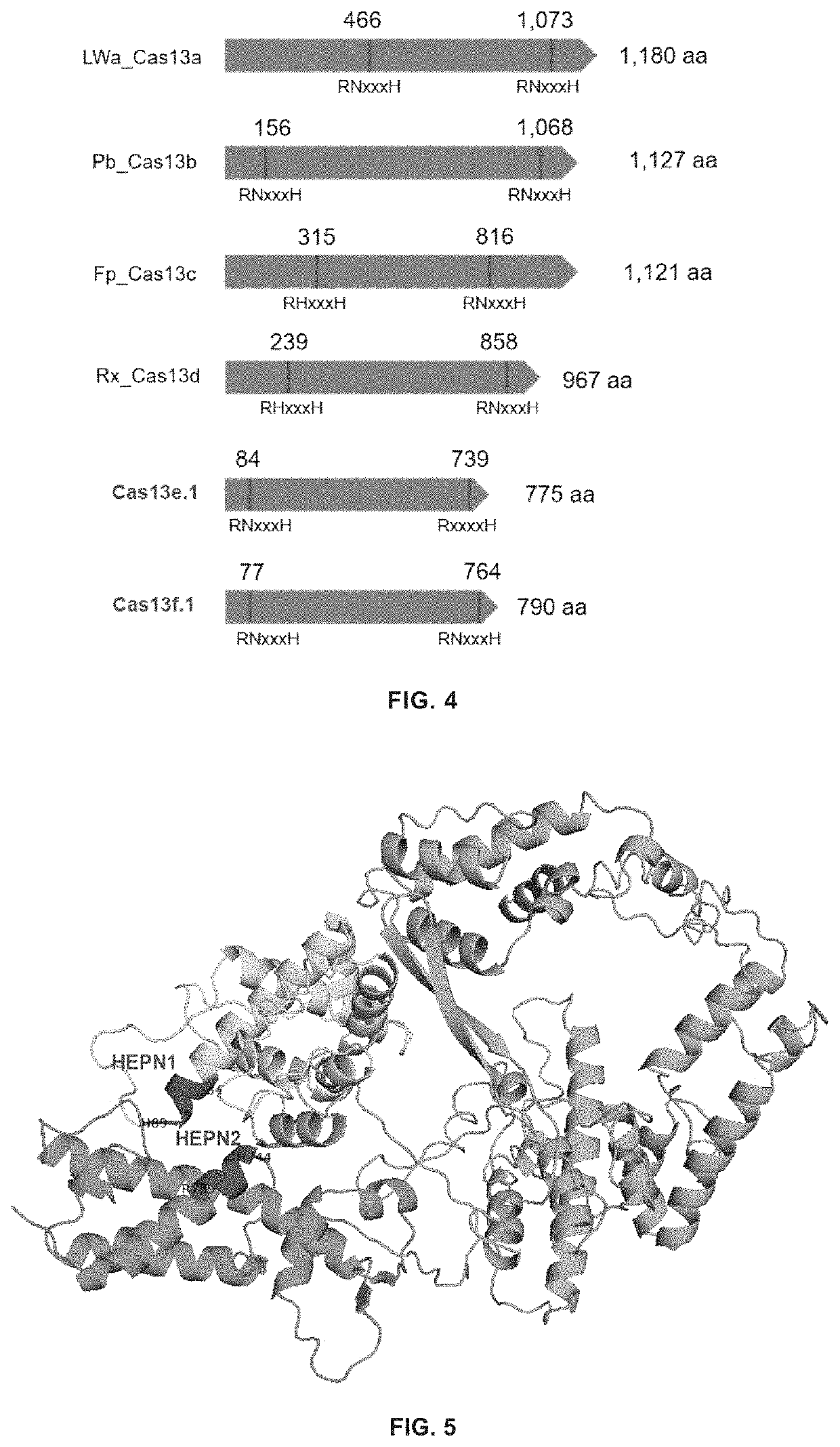
Type VI-E and type VI-F CRISPR-Cas system and uses thereof
The invention provides novel CRISPR / Cas compositions and uses thereof for targeting nucleic acids. In particular, the invention provides non-naturally occurring or engineered RNA-targeting systems comprising a novel RNA-targeting Cas13e or Cas13f effector protein, and at least one targeting nucleic acid component such as a guide RNA (gRNA) or crRNA. The novel Cas effector proteins are among the smallest of the known Cas effector proteins, at about 800 amino acids in size, and are thus uniquely suitable for delivery using vectors of small capacity, such as an AAV vector.
Owner:HUIGENE THERAPEUTICS CO LTD
Peptides for the specific binding of RNA targets
ActiveUS20130323813A1Fusion with RNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsCytosineBinding domain
A recombinant polypeptide is described including at least one PUF RNA-binding domain capable of specifically binding to a cytosine RNA base. The PUF RNA-binding domain of the polypeptide includes at least one RNA base-binding motif of the general formula X1X2X3X4X5X6X7X8X9X10X11 wherein X1 is selected from a defined group and wherein the RNA base-binding motif is operably capable of specifically binding to a cytosine RNA base.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
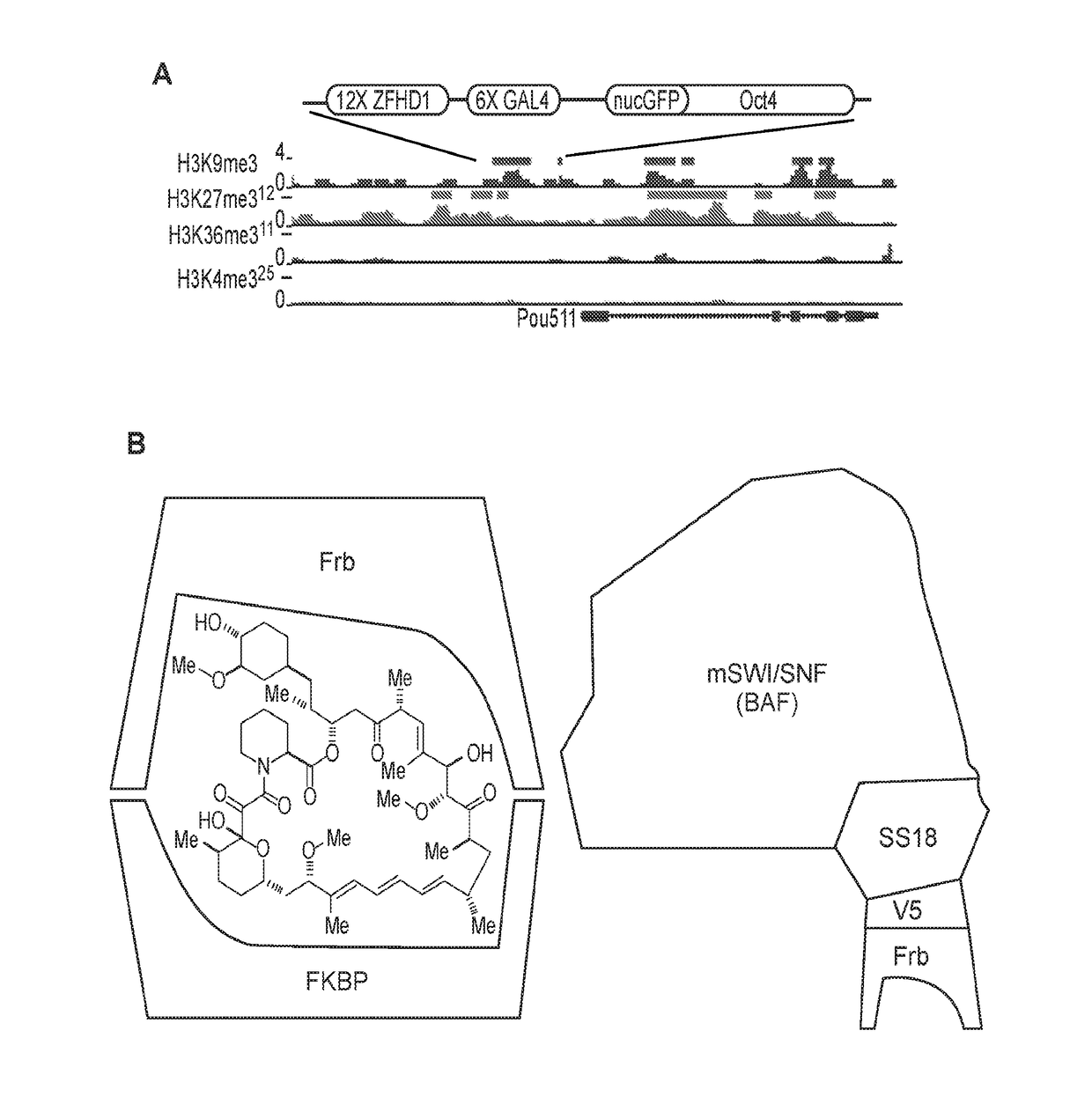
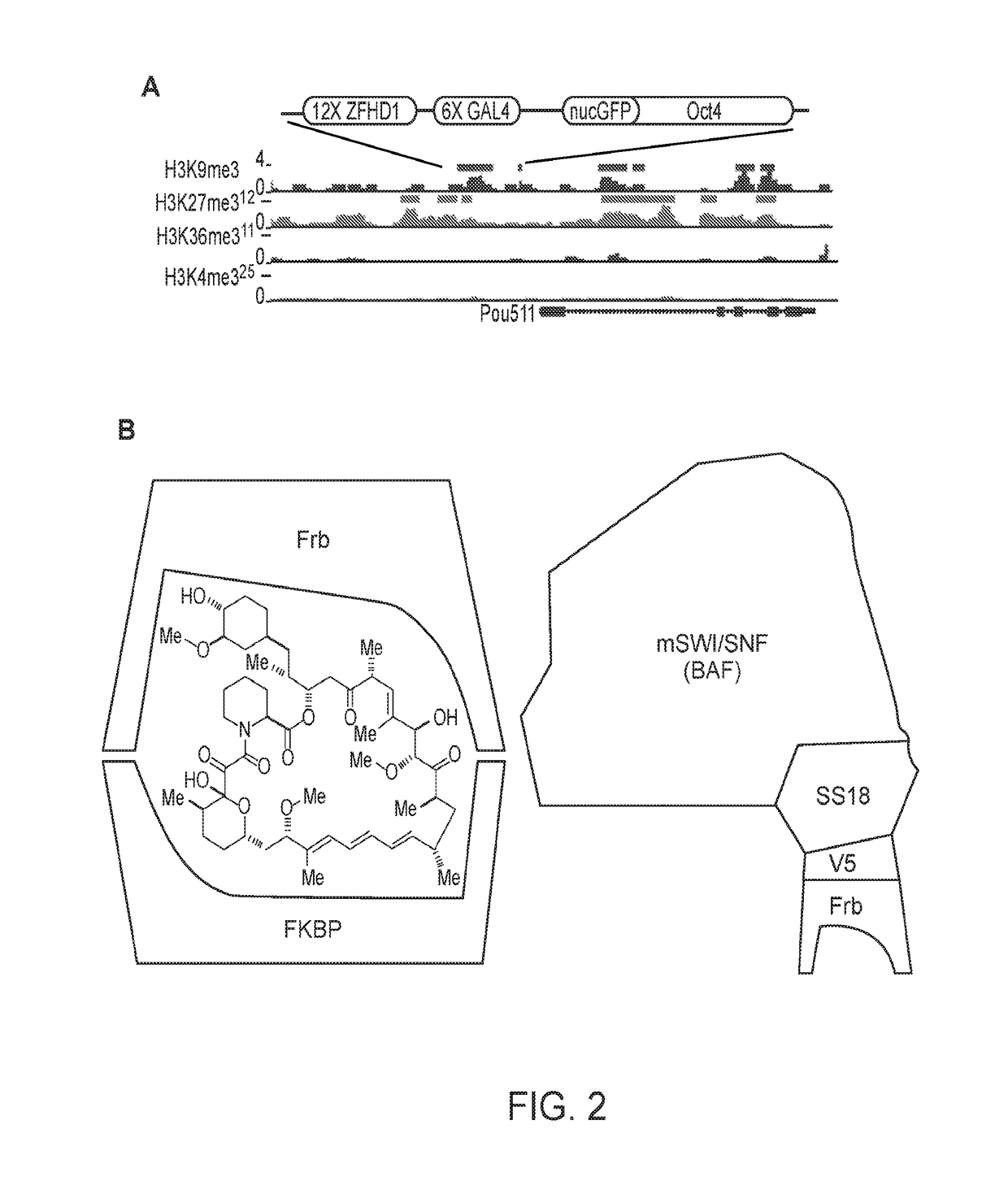
Methods of Inducibly Targeting Chromatin Effectors and Compositions for Use in the Same
InactiveUS20180305424A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainTranscription controlInducer
Methods of inducibly targeting a chromatin effector to a genomic locus are provided. Aspects of the methods include employing a chemical inducer of proximity (CIP) system. Aspects of the invention further include methods of screening candidate agents that modulate chromatin-mediated transcription control and methods of inducibly modulating expression of a coding sequence from genomic locus. Also provided are compositions, e.g., cells, reagents and kits, etc., that find use in methods of the invention.
Owner:THE BOARD OF TRUSTEES OF THE LELAND STANFORD JUNIOR UNIV
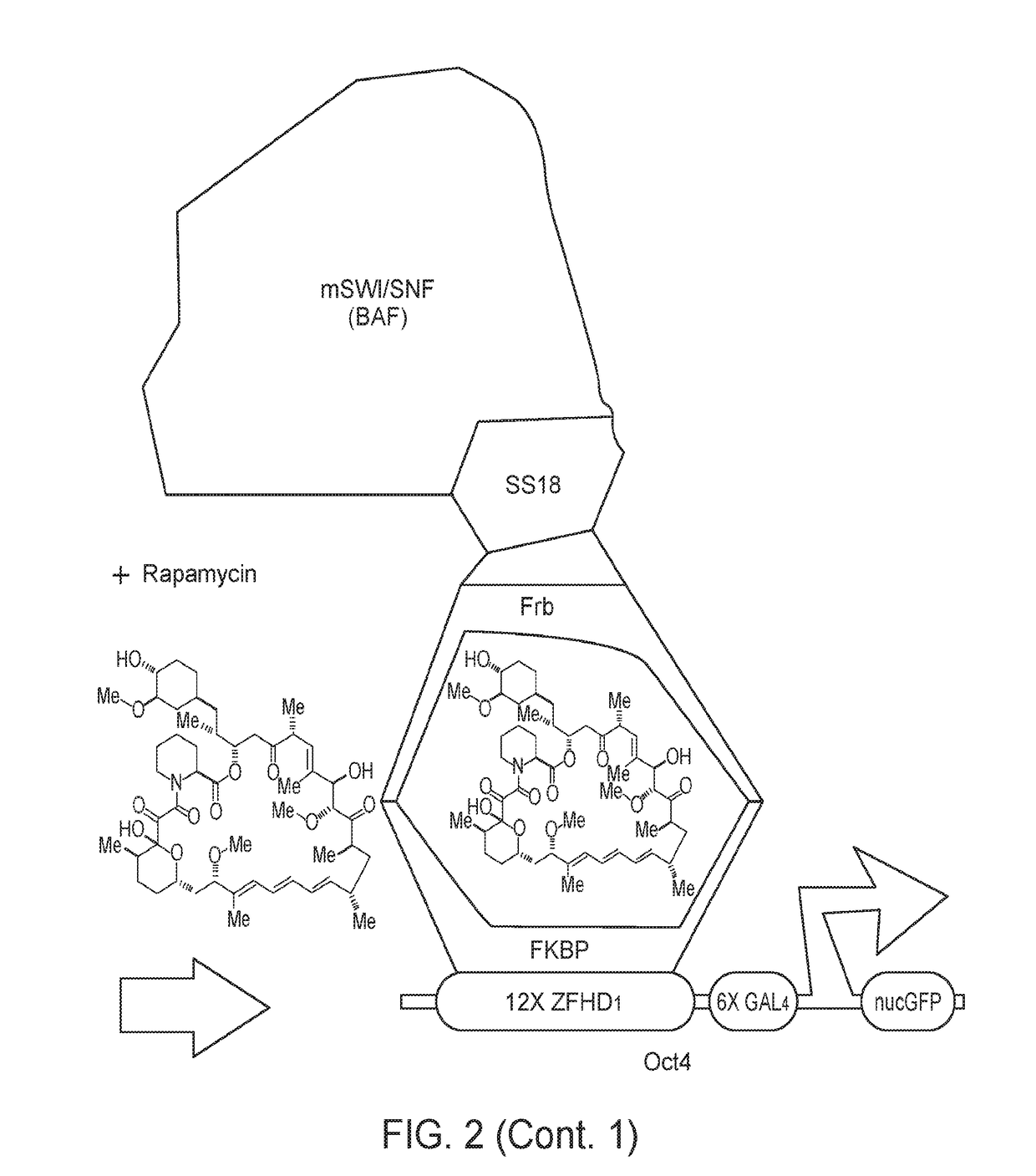
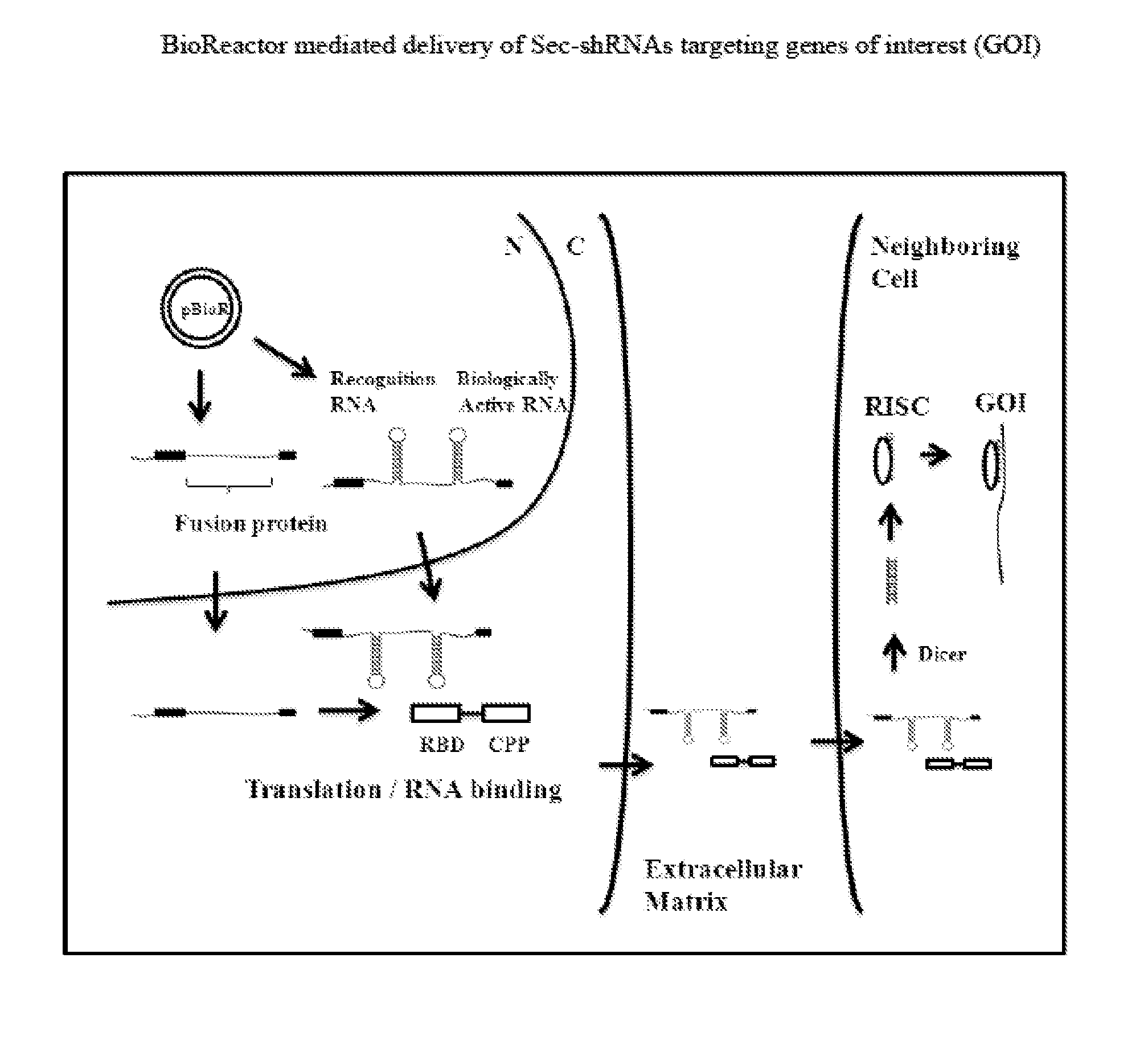
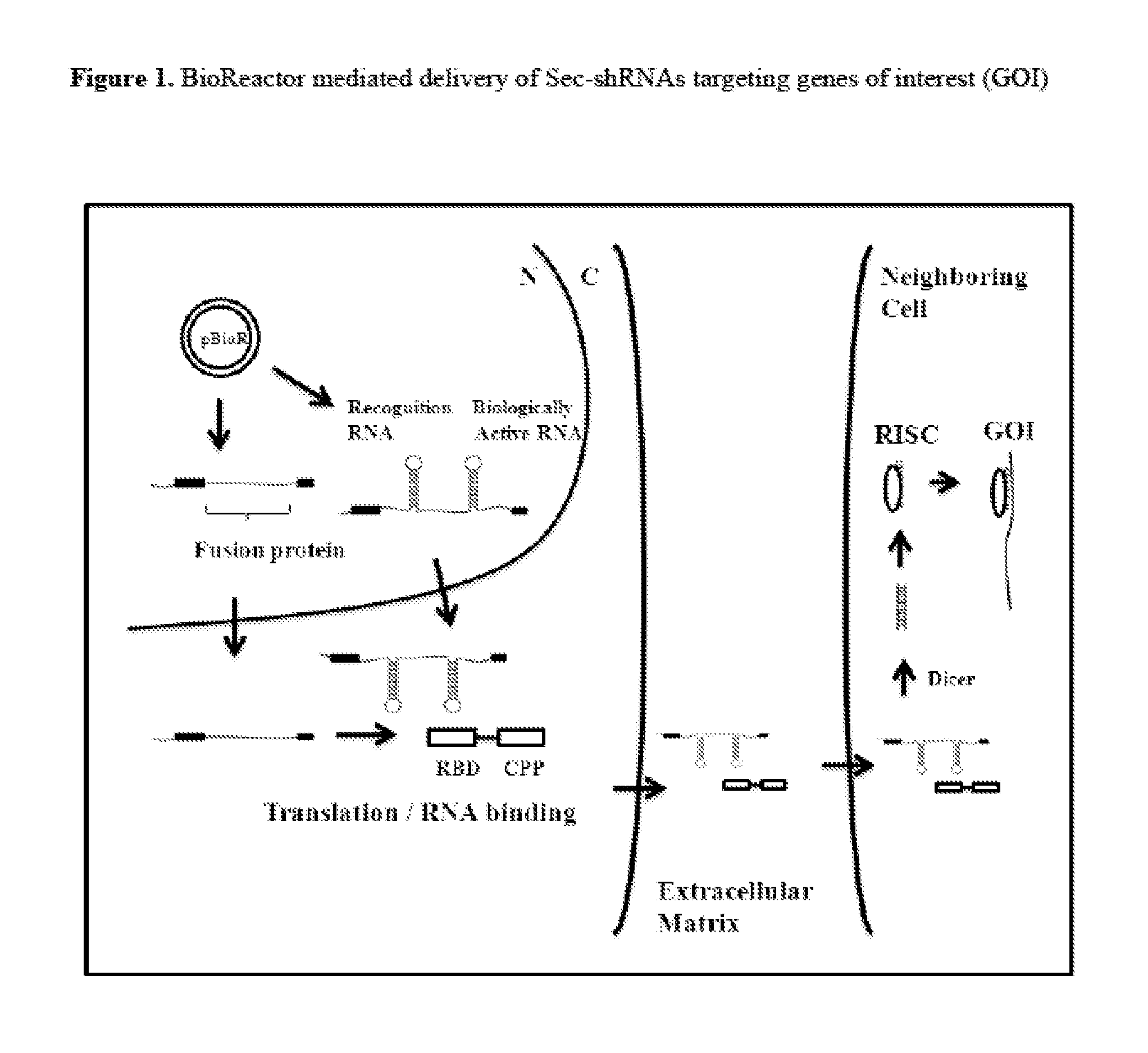
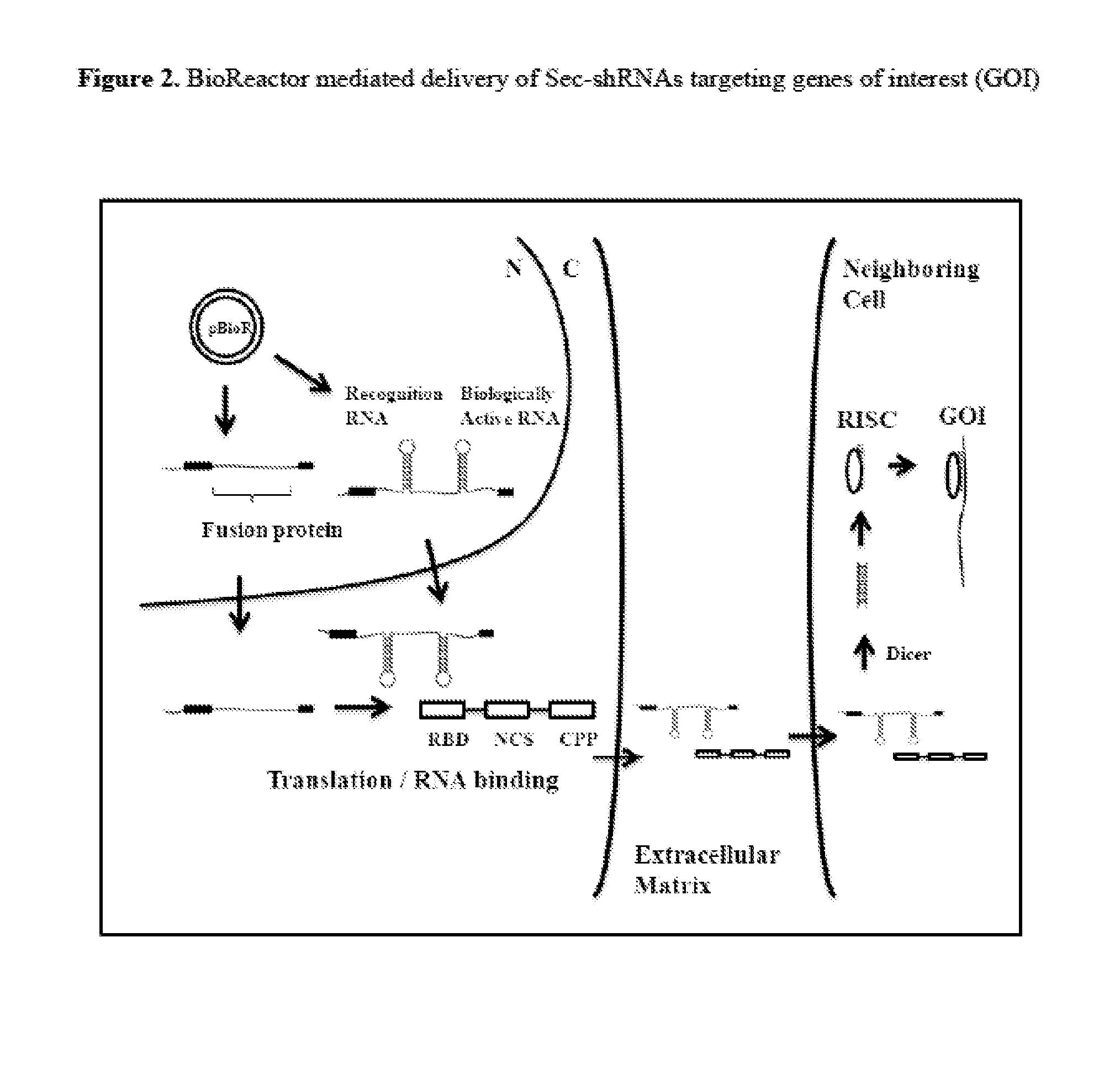
Compositions and Methods for the Delivery of Biologically Active RNAs
InactiveUS20130164845A1Easy to importEnhanced bioreactor activityPolypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainProtein-protein complexPolynucleotide
Novel compounds, compositions, and methods for the delivery of biologically active RNA molecules to cells. Specifically, the invention provides novel nucleic acid molecules, polypeptides, and RNA-protein complexes useful for the delivery of biologically active RNAs to cells and polynucleotides encoding the same. The invention also provides vectors for expressing said polynucleotides. In addition, the invention provides cells and compositions comprising the novel compounds and vectors, which can be used as transfection reagents. The invention further provides methods for producing said compounds, vectors, cells, and compositions. Additionally, vectors and methods for delivering biologically active RNA molecules to cells and / or tissues are provided. The novel compounds, vectors, cells, and compositions are useful, for example, in delivering biologically active RNA molecules to cells to modulate target gene expression in the diagnosis, prevention, amelioration, and / or treatment of diseases, discorders, or conditions in a subject or organism.
Owner:CLSN LAB
Targeted delivery of nucleic acids
ActiveUS20110256088A1Rapid in vivo validationReduce deliveryCompounds screening/testingFusion with RNA-binding domainNucleic acidMolecular biology
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
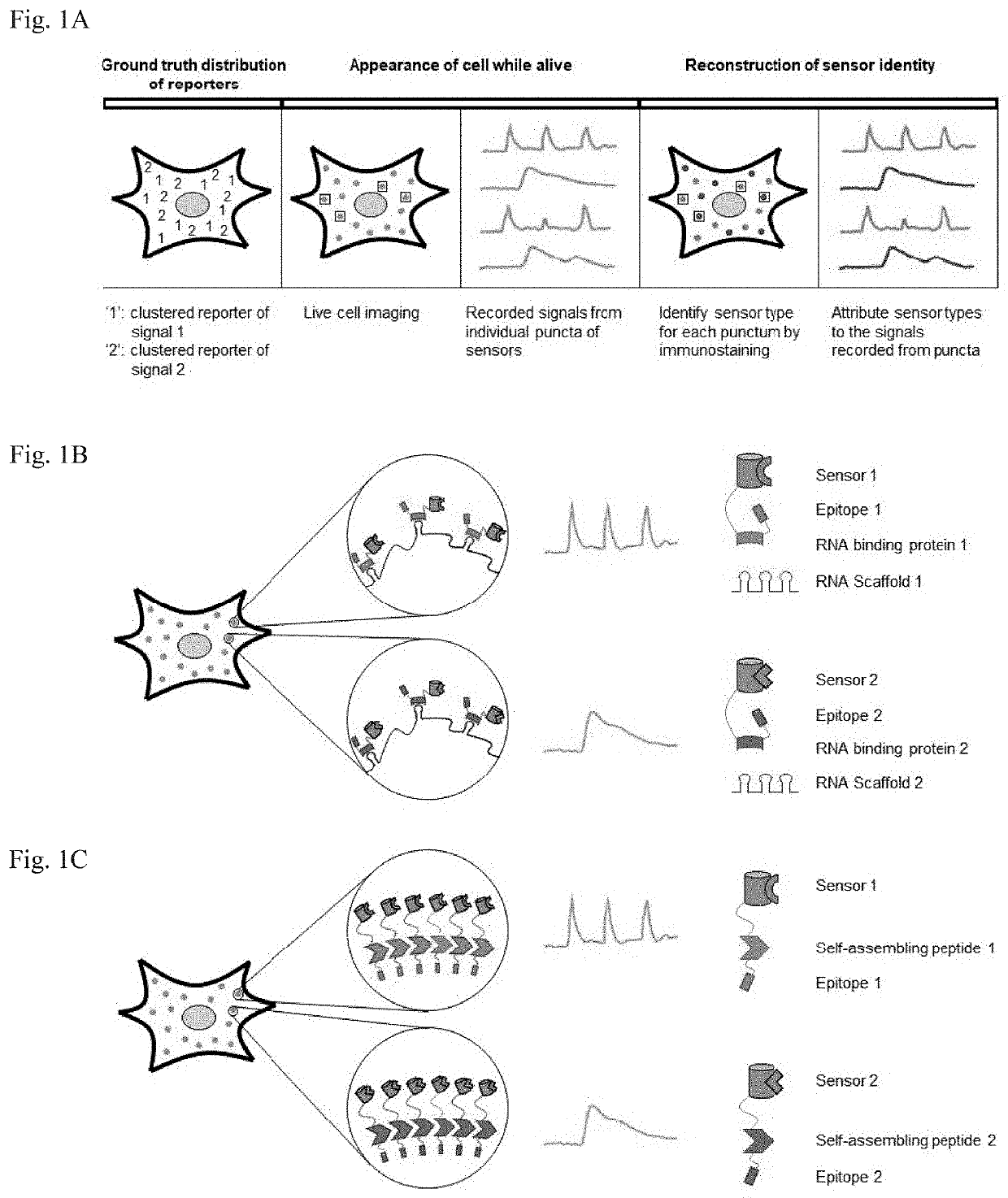
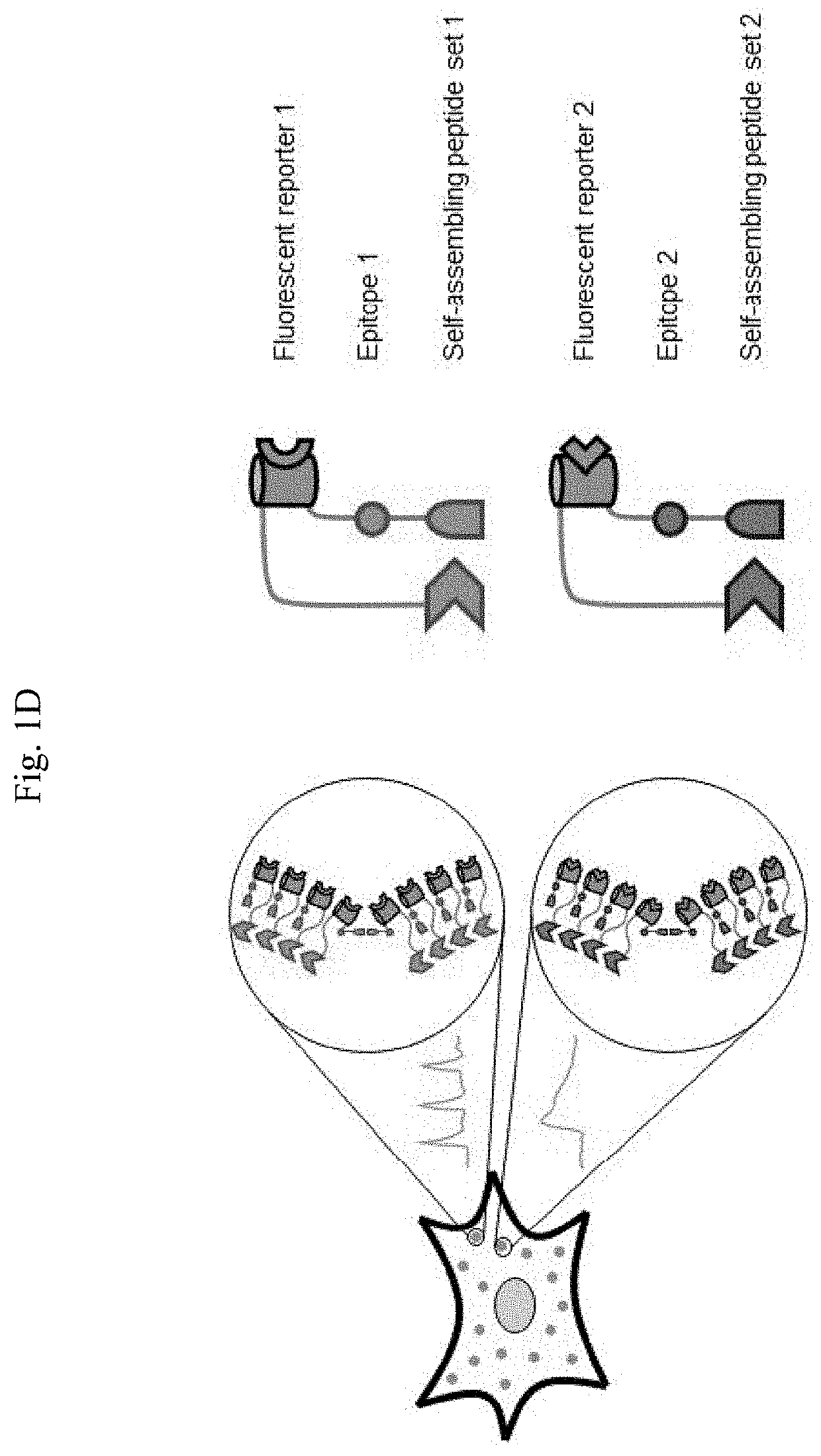
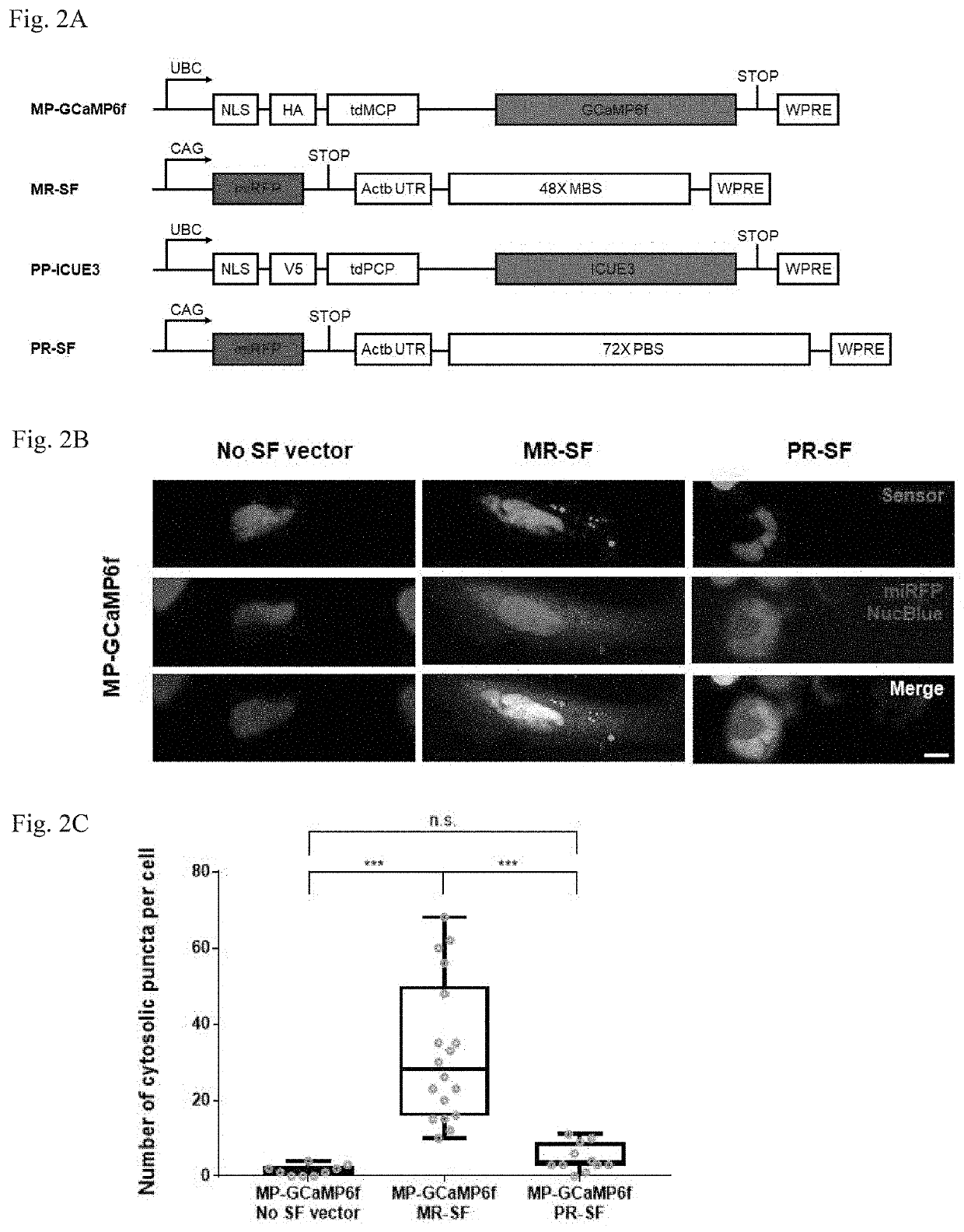
Methods for simultaneous measurement of multiple biological signals from spectrally identical fluorescent reporters
PendingUS20210080472A1Polypeptide with localisation/targeting motifFusion with RNA-binding domainIntracellularBiological signaling
The invention, in some aspects, relates to the preparation and use of signaling reporter islands (SiRIs) in single cells. Compositions of the invention that produce SiRIs can be delivered to a cell resulting in the presence of one or more SiRIs in the cell. Methods of the invention include detecting signals generated by elements in the SiRIs in a cell and use of the detected signals to determine and analyze simultaneous physiological processes within the cell, or cells.
Owner:MASSACHUSETTS INST OF TECH
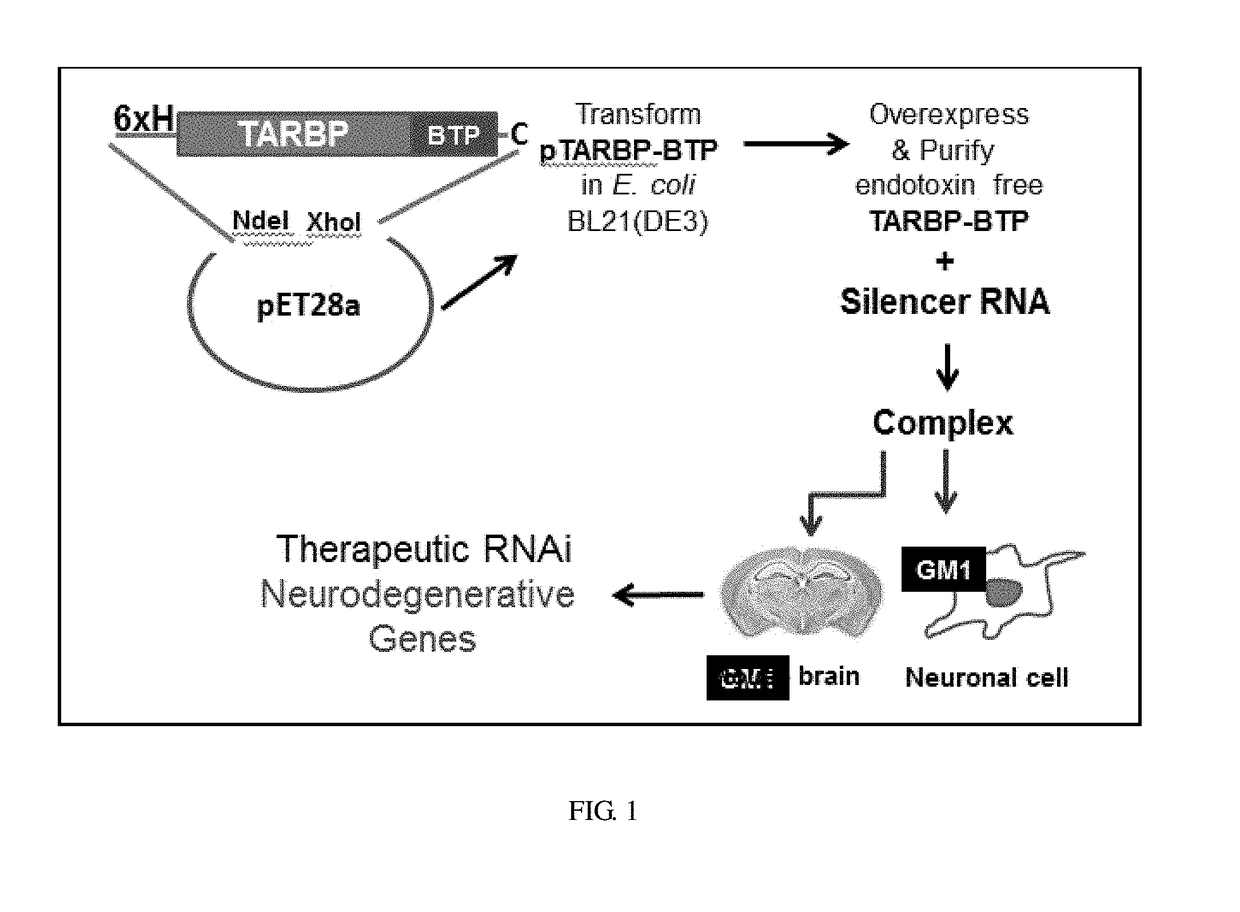
Recombinant protein-based method for the delivery of silencer RNA to target the brain
ActiveUS20180073021A1Well formedOrganic active ingredientsFusion with RNA-binding domainNeural cellCerebral hemisphere
The present invention relates to the design and development of recombinant protein for the delivery of silencer RNA complex to mediate RNA interference since it represents a novel therapeutic approach to modulate several neurodegenerative disease-related genes across the blood-brain barrier (BBB). To overcome challenges due to this barrier for biologics and other biological complex, the present invention describes a method wherein peptide having sequence GGGGHLNILSTLWKYRC represented by SEQ ID NO. 9 known to target specific gangliosides was linked to a double-stranded RNA binding protein to bind and deliver silencer RNA to the brain parenchyma. The designed fusion protein comprising a double-stranded RNA-binding domain (dsRBD) of human Trans Activation response element (TAR) RNA Binding Protein (TARBP2) and a brain targeting peptide sequence that binds GM1. Conformation-specific binding of TARBP2 domain to silencer RNA results in the formation of homogenous serum-stable complex with GM1 targeting potential. Uptake of the complex in neural cells reveals selective requirement of GM1 for entry. Remarkably, the invention pertains to the systemic delivery of the complex comprising TARBP-BTP and silencer RNA in AβPP-PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease (AD) led to distinctive localization primarily in the cerebral hemisphere in the hippocampus and brain cortex and in principle can work across other mammalian CNS targets. Further, the delivery of silencer-RNA mediated by brain targeting peptide fusion led to significant knockdown of BACE1, a therapeutic protease target in both AβPP-PS1 and wild type C57BL / 6 mice. The invention establishes the emergent importance of fusion proteins in delivering therapeutic siRNA as a simple complex to brain tissues to treat neurodegenerative diseases besides Alzheimer's disease (AD). The complex is also useful to study gene function of hitherto unidentified genes / interplay of genes in mammalian systems and central nervous system.
Owner:COUNCIL OF SCI & IND RES
Method for improving solubility and folding efficiency of target proteins using RNA as molecular chaperone
InactiveUS20060292667A1Improve efficiencyImprove solubilityFusion with RNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityProtein target
Disclosed is a method for improving folding efficiency and solubility of a target protein linked to a RNA-binding protein by using RNA molecule as a molecular chaperone, wherein the RNA molecule interacts with the RNA-binding protein. More particularly, the present invention discloses method for improving folding efficiency and solubility of a target protein by transformation of a host cell with a expression vector comprising a polynucleotide encoding the target protein linked to an RNA-binding protein; culturing the transformed host cell in an appropriate culture medium under the condition that an RNA molecule either resident inside the host cell or provided by cotransformation of the host cell with polynucleotide encoding the RNA molecule interacts with the RNA-binding protein; and purifying the soluble protein from host cell lysate. The method of the present invention is very useful for production of soluble proteins for therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic applications.
Owner:XCELL THERAPEUTICS INC
Methods of detecting transcription
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
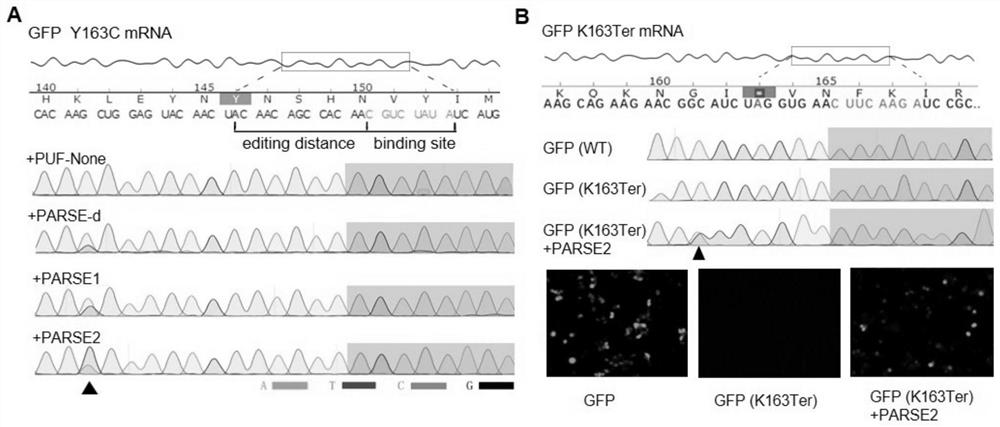
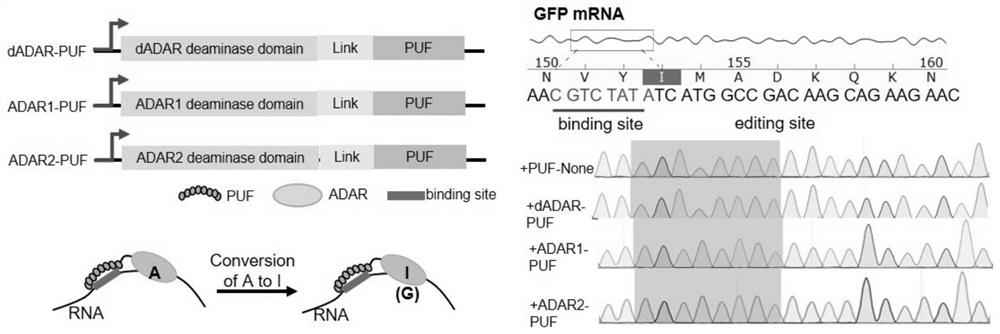
RNA fixed-point editing by artificially constructing RNA editing enzyme and related application
InactiveCN111793627ALow immunogenicityReduce system complexityFusion with RNA-binding domainHydrolasesPathogenicityFunctional protein
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF BIOLOGICAL SCI CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
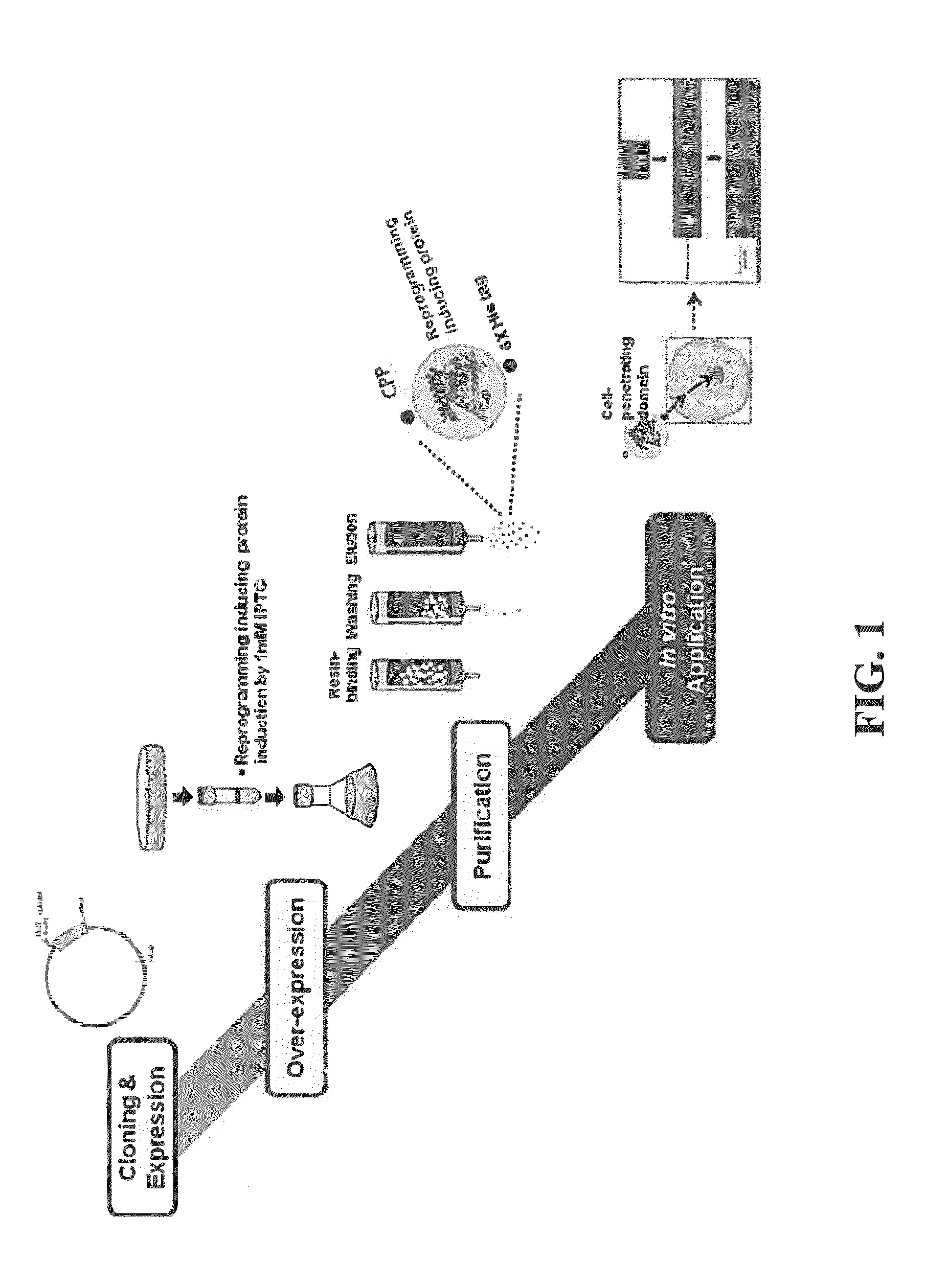
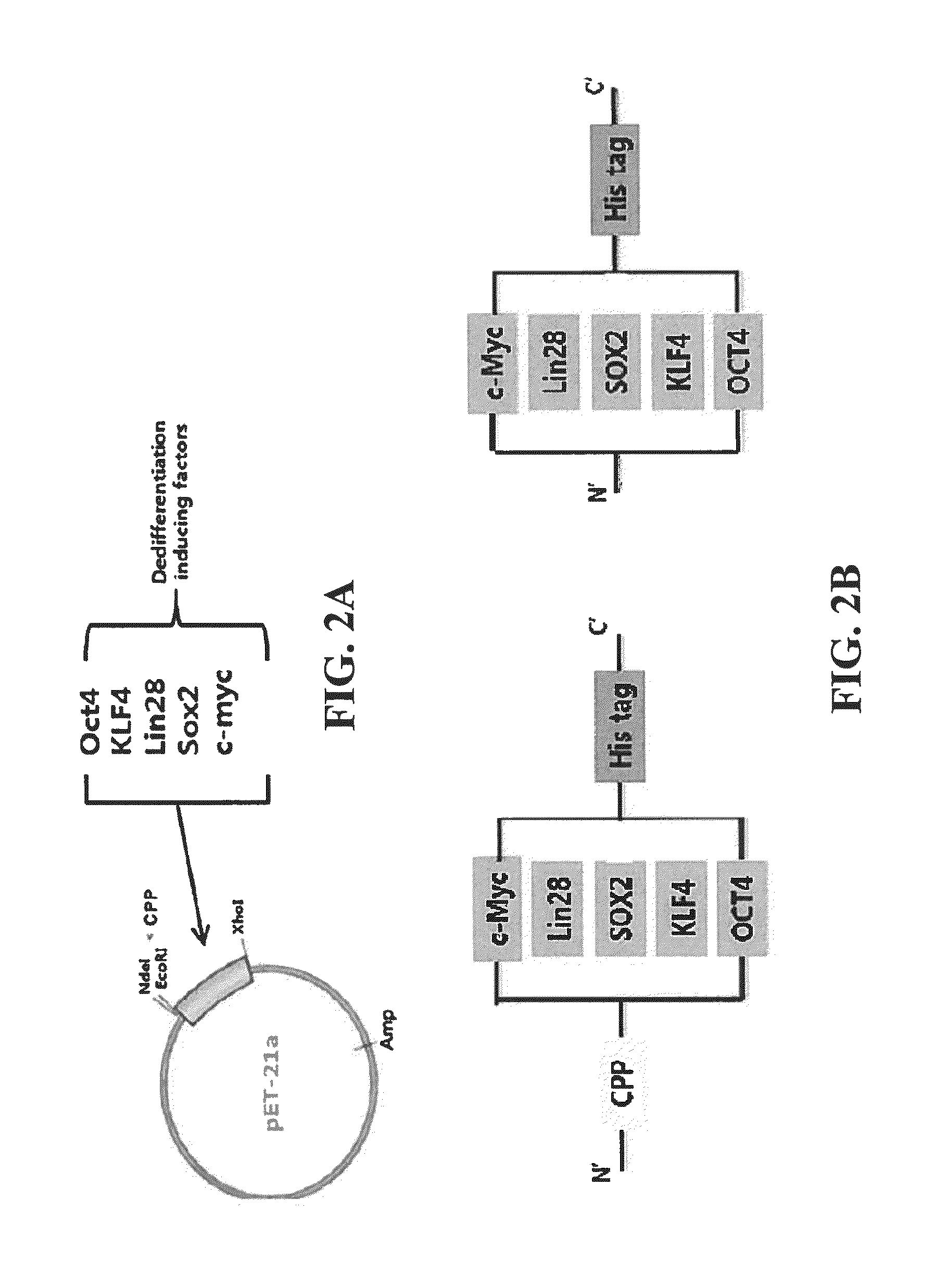
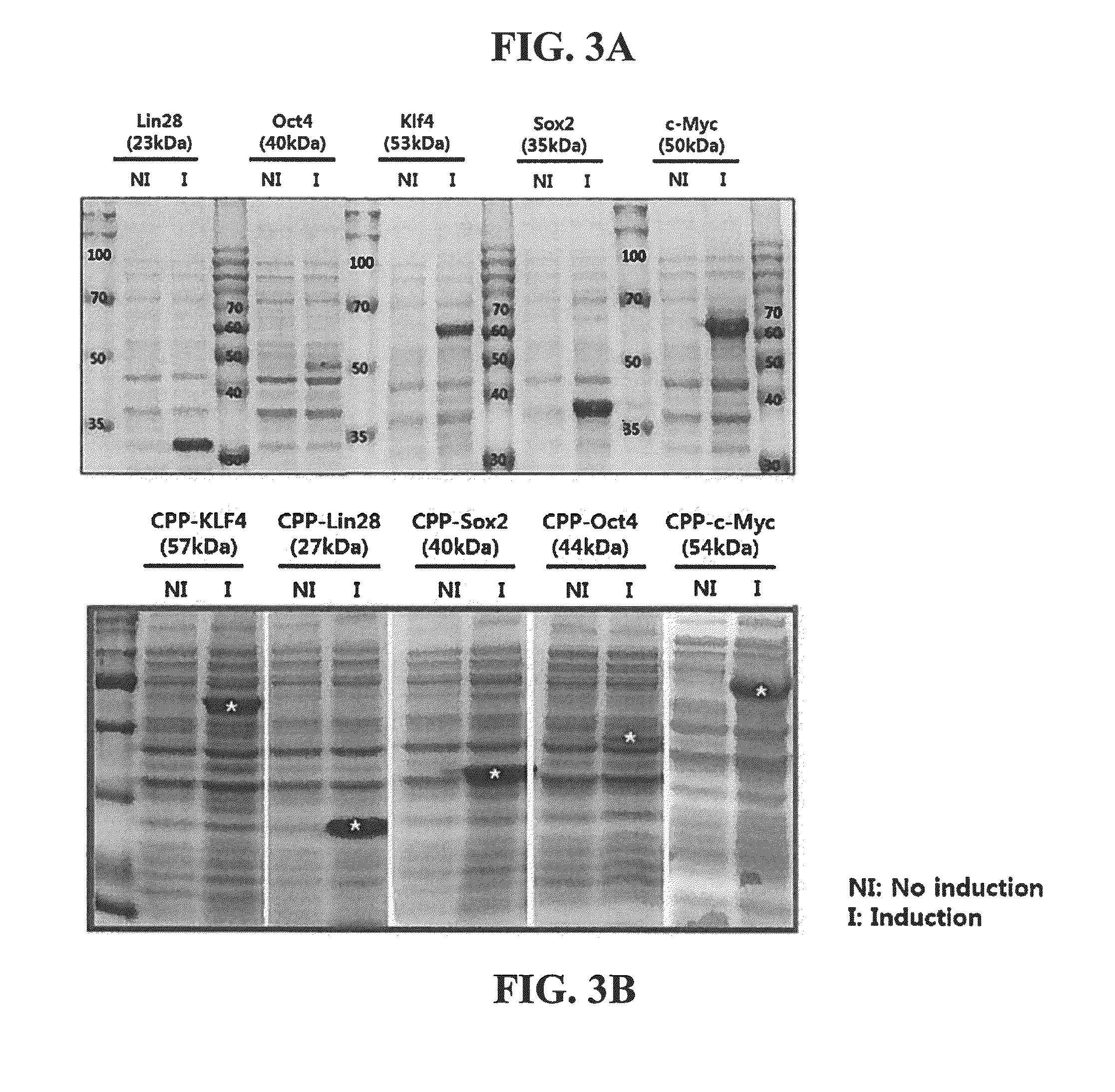
Cell permeable fusion protein for facilitating reprogramming induction and use thereof
ActiveUS20150064783A1Improve efficiencyImprove stabilityFusion with RNA-binding domainFusion with DNA-binding domainReprogrammingSomatic cell
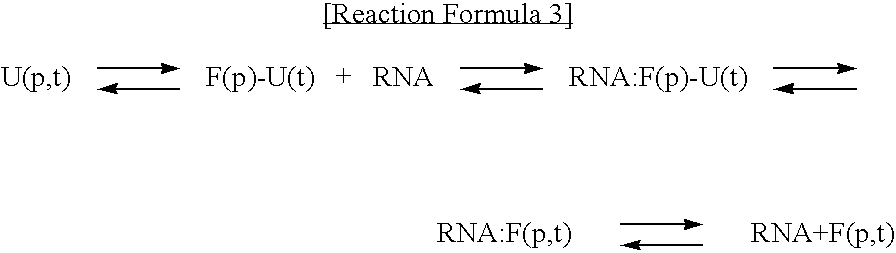
A method of preparing a reprogramming induced pluripotent stem cell from a human-derived somatic cell using a fusion protein in which a reprogramming inducing factor and cell permeable peptide (CPP) are fused, and a fusion protein in which a reprogramming inducing factor and a cell permeable peptide are fused are disclosed.According to the present invention, the induced pluripotent stem cell having high efficiency and high stability can be prepared by maximizing the effect of the reprogramming inducing transcription factor beyond the existing viral peptide transporter, in inducing the reprogramming of the somatic cell.
Owner:SEOUL NAT UNIV R&DB FOUND +1
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com