Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
54 results about "Cotransformation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Cotransformation is the simultaneous transformation of two or more genes. Only genes in the same chromosomal vicinity can be transformed; the closer together the genes lie, the more frequently they will be cotransformed. By contrast, genes sufficiently far apart that they cannot appear together on a fragment of foreign DNA will almost never be cotransformed, because transformation is so inefficient that recipient cells usually take up only a single DNA.
Double T-DNA carrier and its application in cultivating of non selecting sign transgene rice
InactiveCN1597969ASmall molecular weightHigh co-transformation efficiencyFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionGenetically modified ricePlant nodule
The invention provides a simple and convenient Agrobacterium Tumefacies dual carrier containing double T-DNA structural regions, and a method of using the carrier system to cultivate transgenic rice without resistance selection label. With the help of the principle of co-conversion mediated by root nodule Agrobacterium Tumefacies, the system contains two separate T-DNA structural sections, where the first T-DNA region contains antibiotic resistance selection label gene and the second one contains a universal polyclonal site able to be arbitrarily inserted with destination gene. The double-T-DNA carrier has small molecular weight, easy to clone and after the destination gene and necessary regulation and control series are cloned in the T-DNA region containing the polyclonal site, it realizes rice co-conversion; by selfing, it selects transgenic individual with destination gene but without selectin label gene from the self-bred progeny, thus eliminating the negative effect on transgenic plant commercialized production, etc, possibly caused by selection label gene.
Owner:YANGZHOU UNIV
Methods and apparatus for transformation of naturally competent cells
The present invention includes compositions and methods of co-transformation of naturally competent cells. In one aspect of the invention, a method is included for introducing nucleic acid sequences into one or more naturally competent cells in parallel. In other aspects, a heterogenic pool of co-transformed naturally competent cells and an apparatus for introducing two or more populations of nucleic acid sequences into a population of naturally competent cells in parallel are also included.
Owner:TUFTS UNIV
Recombinant adenovirus of porcine reproductive and respirator syndrome virus and porcine Circovirus, and vaccine
InactiveCN1800375AHas the copy featureStable potencyViruses/bacteriophagesAntibody medical ingredientsEscherichia coliCircovirus
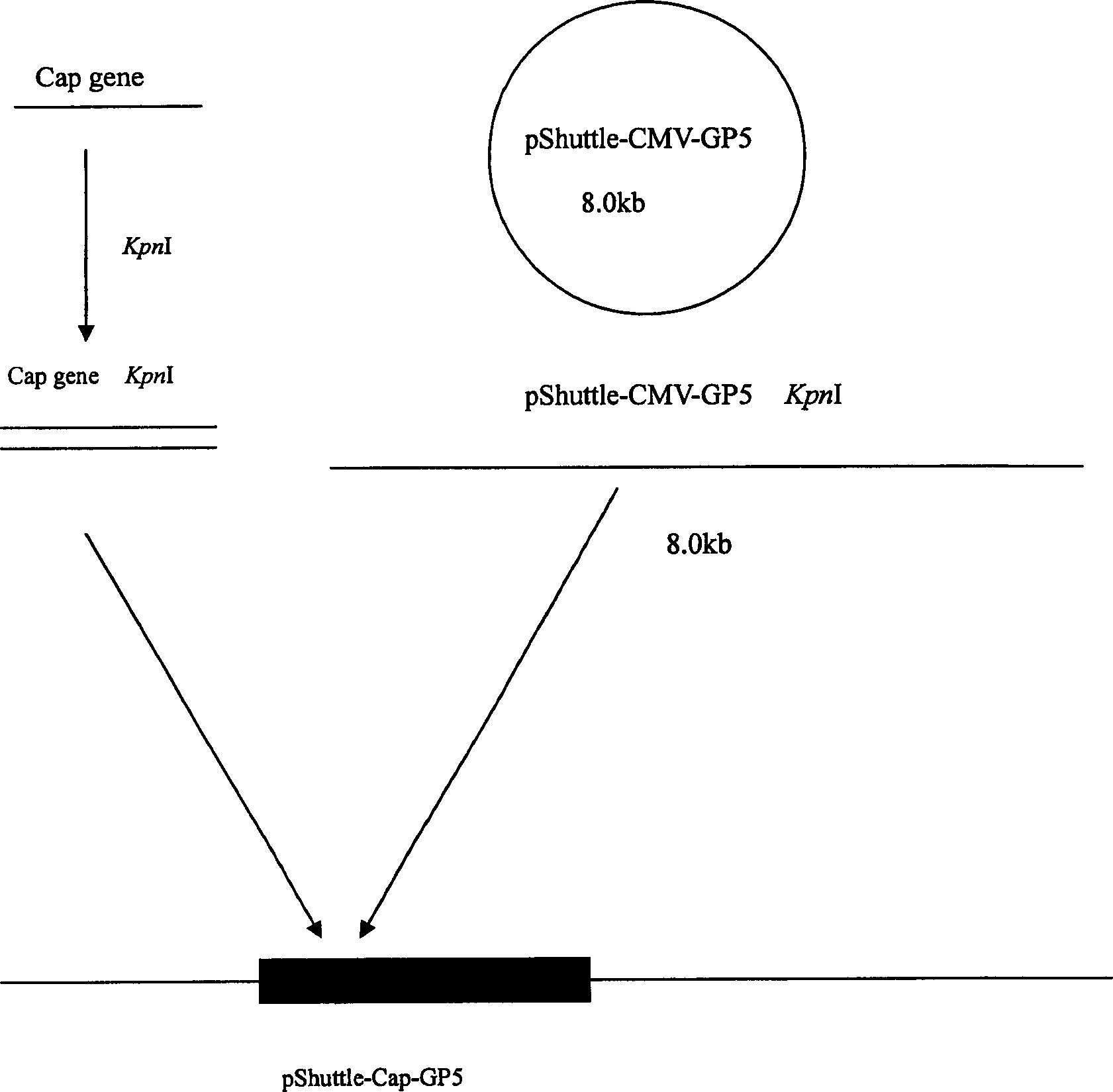
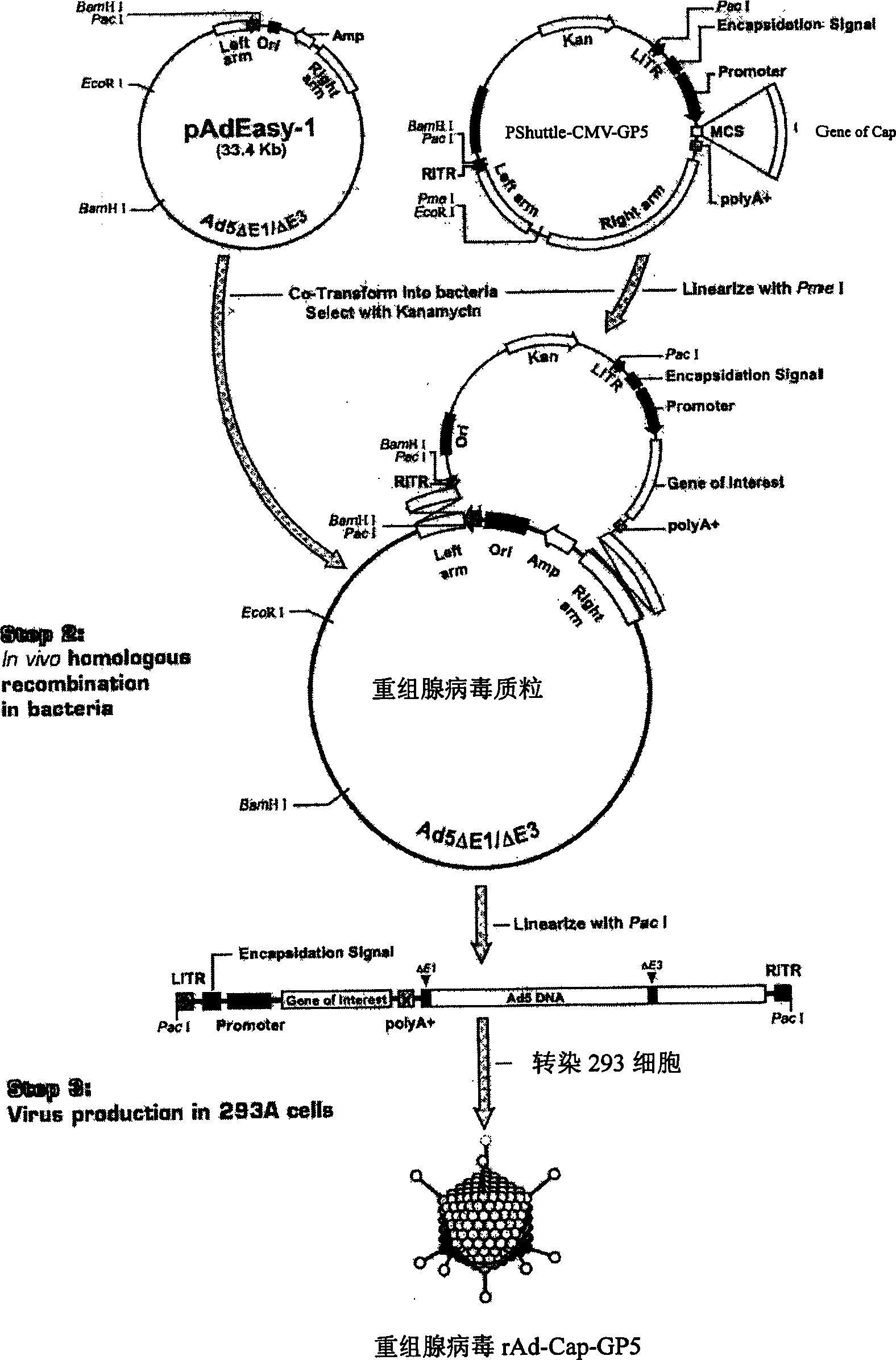
The invention relates to a pig breeding and breathing complex virus (PPRSV) and pig 2-type loop virus (PCV 2) series gene recombination adenovirus and vaccine in the field of high and new biotechnology. It uses PCR technology to clone the Cap protein gene into the plasmid carrier pShuttle-CMV-GP5 by open type reading rule and transforms tobacillus coli BJ5183strain with cage carrier pAdEasy-1 to capture the recombination plasmid; it uses recombination plasmid HEK293-A cell to capture recombination adenovirus and purifies it to express the recombination adenovirus rAd-Cap-GP5 of PRRSV GP5protein and PCV-2 Cap protein.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Pig breeding and respiratory syndrome recombined adenovirus and vaccine
InactiveCN1554766ALittle changeChange propertiesGenetic material ingredientsInactivation/attenuationEscherichia coliBiotechnology
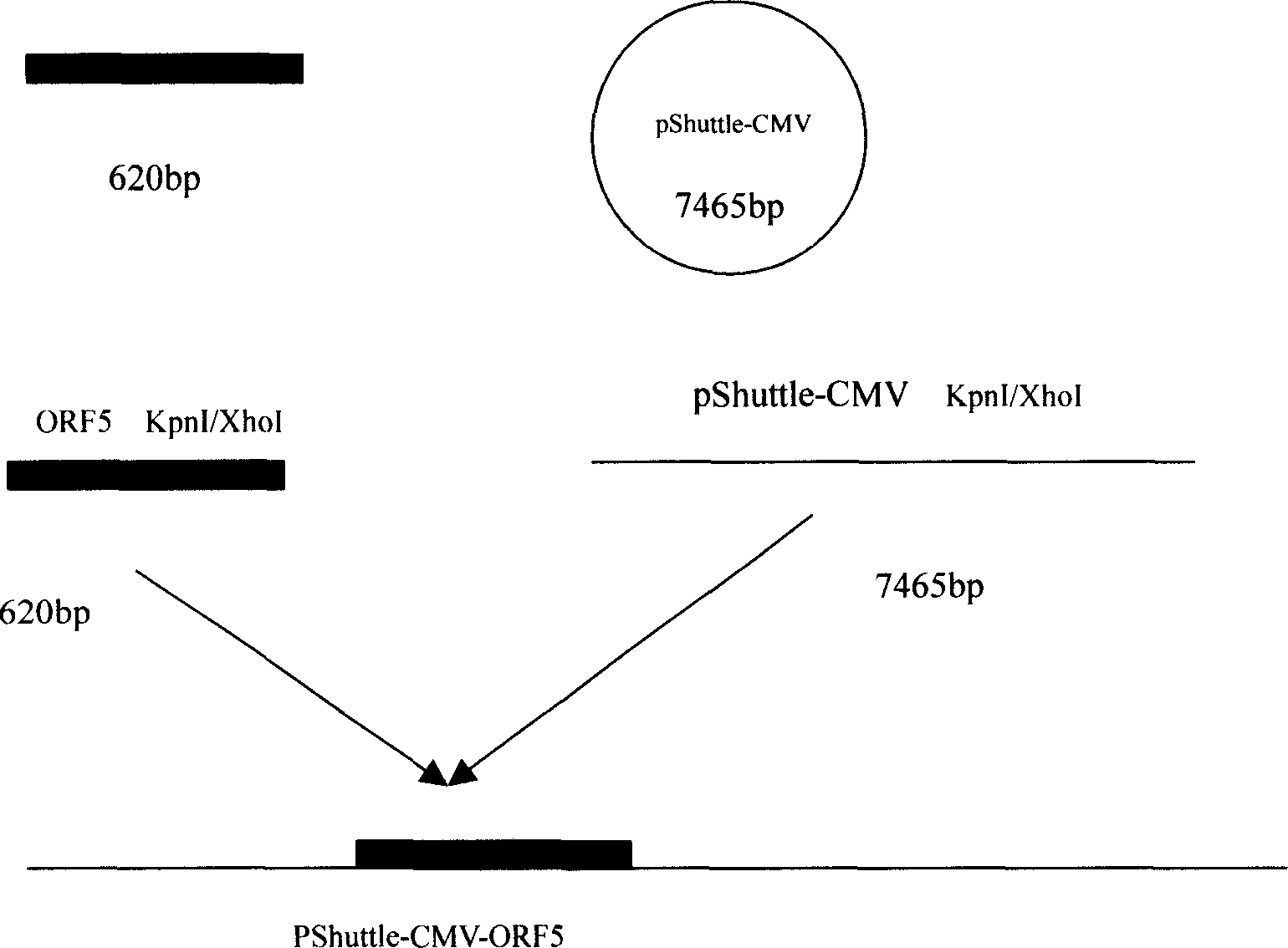
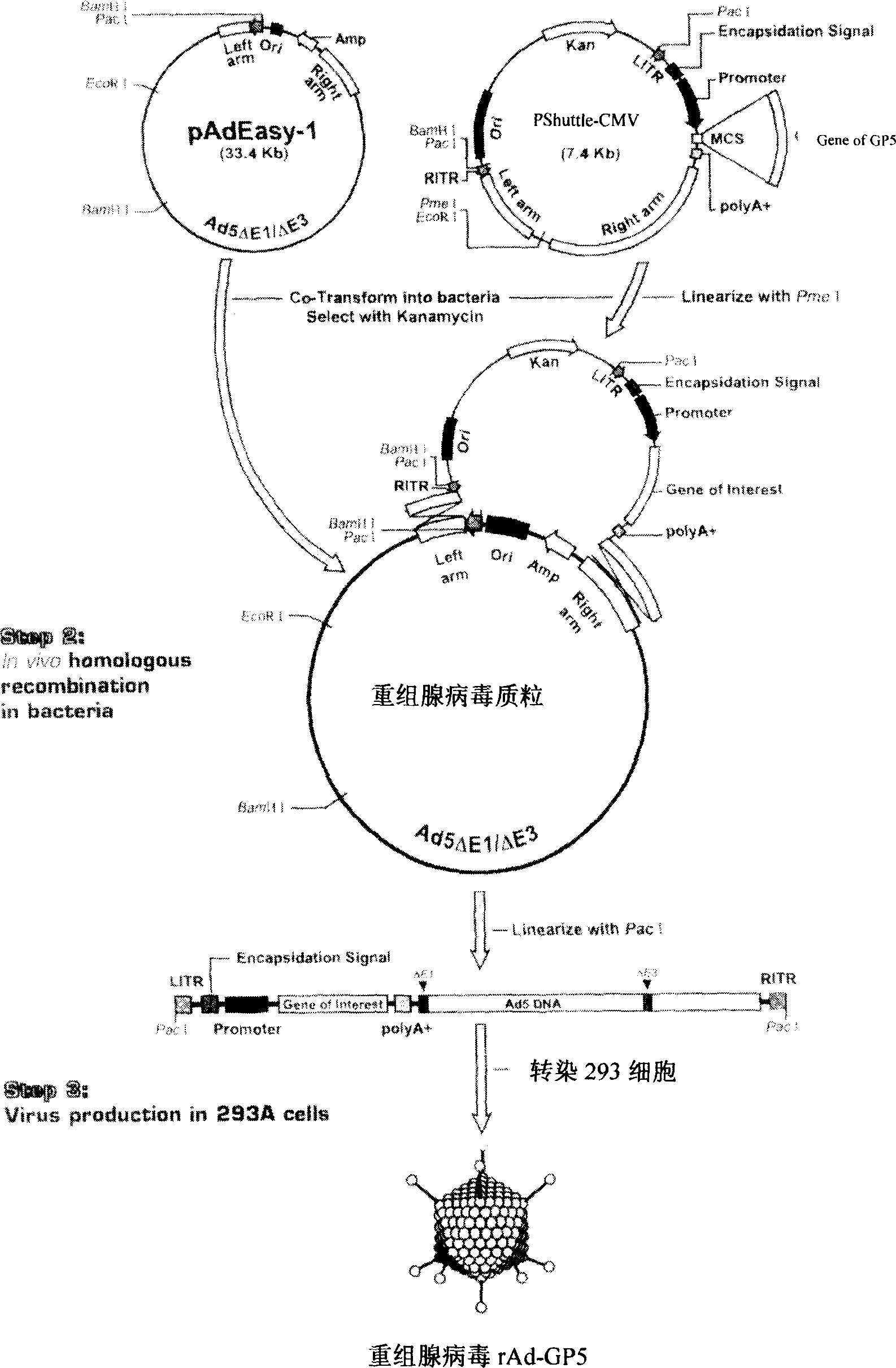
The present invention relates to pig reproduction and respiratory syndrome virus recombined adenovirus and vaccine, and belongs to the field of biological high-tech. Through RT-PCR process to proliferate whole PRRSV GP5 sequence, cloning the gene sequence to the shuttle vector pShuttle-CMV of adenovirus carrier system, cotransforming colibacillus BJ5183 strain together with the skeleton vector of adenovirus carrier system to obtain recombinant plasmid, transfecting HEK293-A cell to obtain recombinant adenovirus and plaque purification, and RT-PCR and indirect immunofluorescence technique inspection, the recombinant adenovirus rAd-GP5 expressing PRRSV GP5 protein is constituted. The recombinant adenovirus can set ahead the expression of PRRSV GP5 protein and raise the expression amount to simulate the immune protecting reaction of body effectively.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
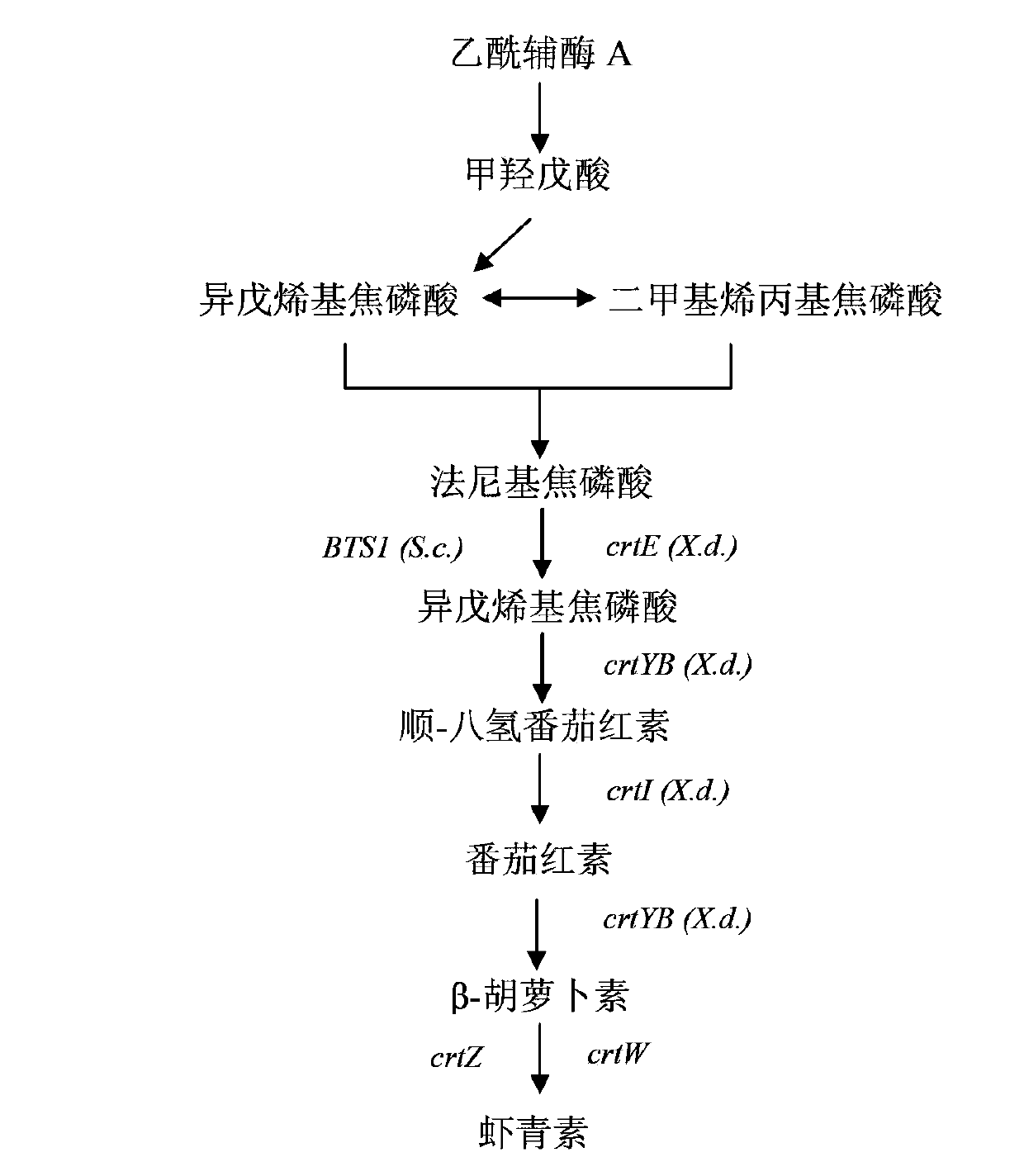
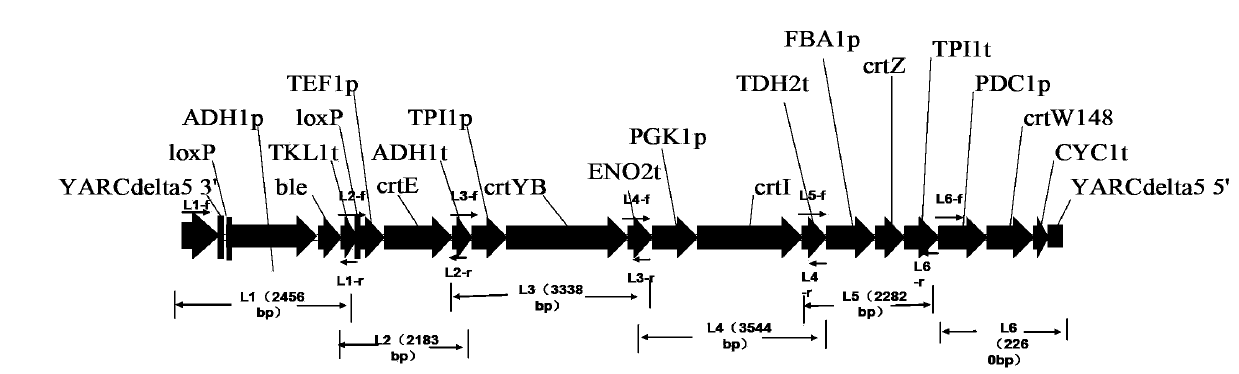
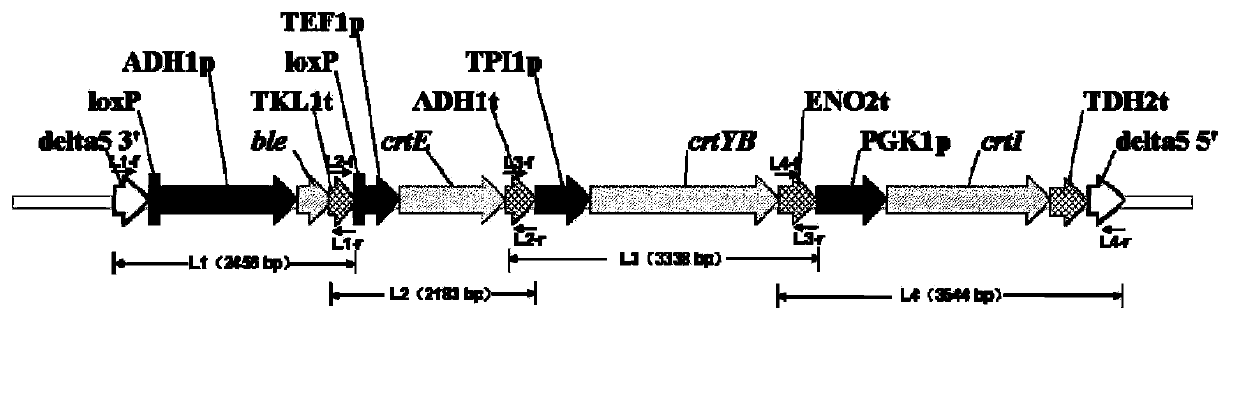
Construction method of genetically engineered bacterium for producing astaxanthin
InactiveCN103865818AReduce build timeHigh homologous recombination efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyRestriction Enzyme Cut Site
The invention discloses a construction method of genetically engineered bacterium for producing astaxanthin, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: A)constructing a gene expression module, wherein the gene expression module comprises relative gene for producing astaxanthin, a promoter at the upstream of relative gene for producing astaxanthin and a terminator at the downstream of the relative gene for producing astaxanthin; and B)performing cotransformation of the gene expression module to saccharomyces cerevisiae. The method has the advantages of simple, rapid and high efficiency performance, multi-grade clone is avoided, restriction enzyme cutting site is not required for depending on, multiple fragments enable cotransformation, the homologous recombination efficiency is high, and the engineering bacteria construction time can be obviously shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI LAIYI BIOMEDICAL RES & DEV CENT +1
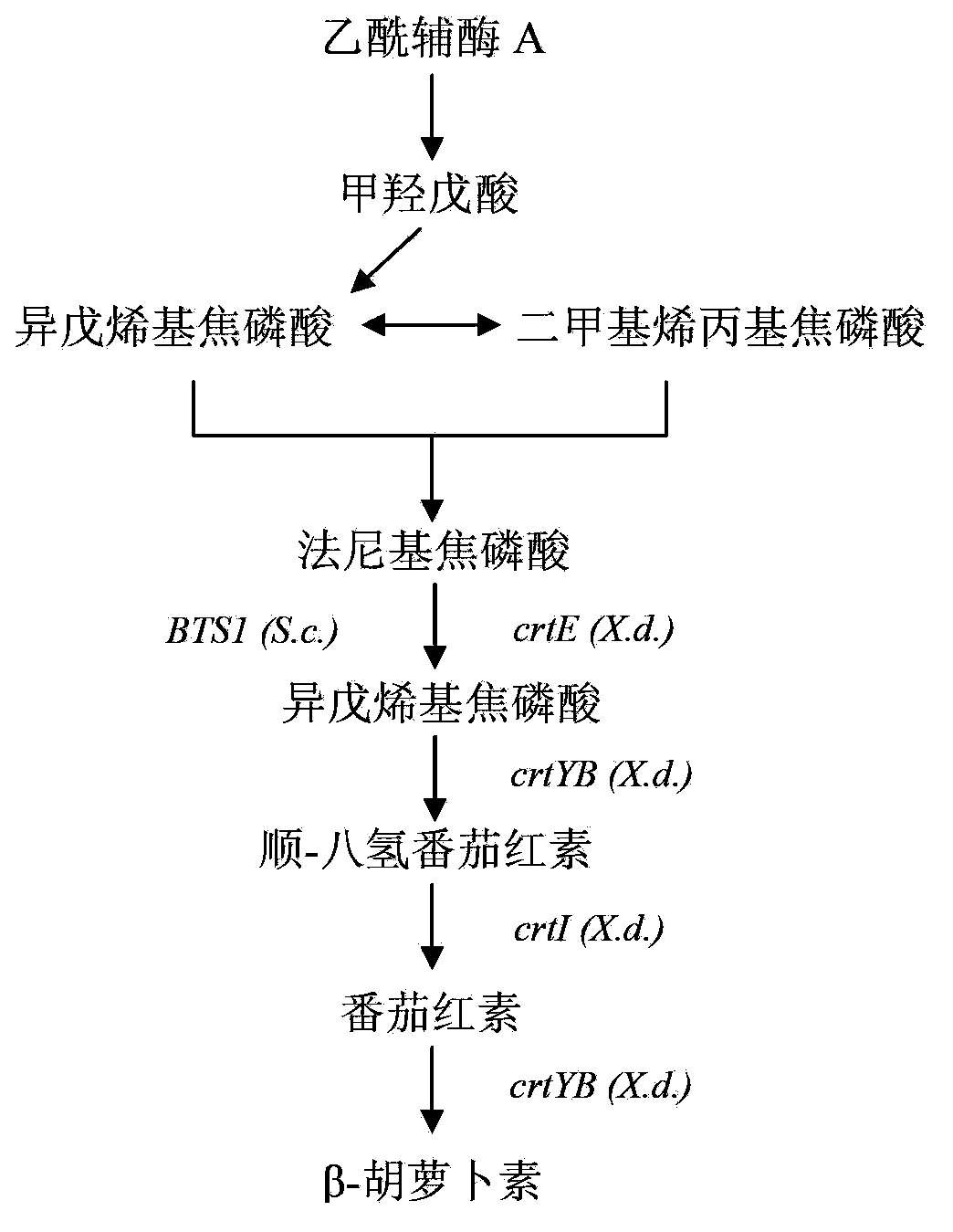
Construction method of genetically engineered bacterium for producing beta-carotene
InactiveCN103865817AReduce build timeHigh homologous recombination efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyRestriction Enzyme Cut Site
The invention discloses a construction method of genetically engineered bacterium for producing beta-carotene, which is characterized by comprising the following steps: A)constructing a gene expression module, wherein the gene expression module comprises relative gene for producing beta-carotene, a promoter at the upstream of relative gene for producing beta-carotene and a terminator at the downstream of the relative gene for producing beta-carotene; and B)performing cotransformation of the gene expression module to saccharomyces cerevisiae. The method has the advantages of simple, rapid and high efficiency performance, multi-grade clone is avoided, restriction enzyme cutting site is not required for depending on, multiple fragments enable cotransformation, the homologous recombination efficiency is high, and the engineering bacteria construction time can be obviously shortened.
Owner:SHANGHAI LAIYI BIOMEDICAL RES & DEV CENT +1
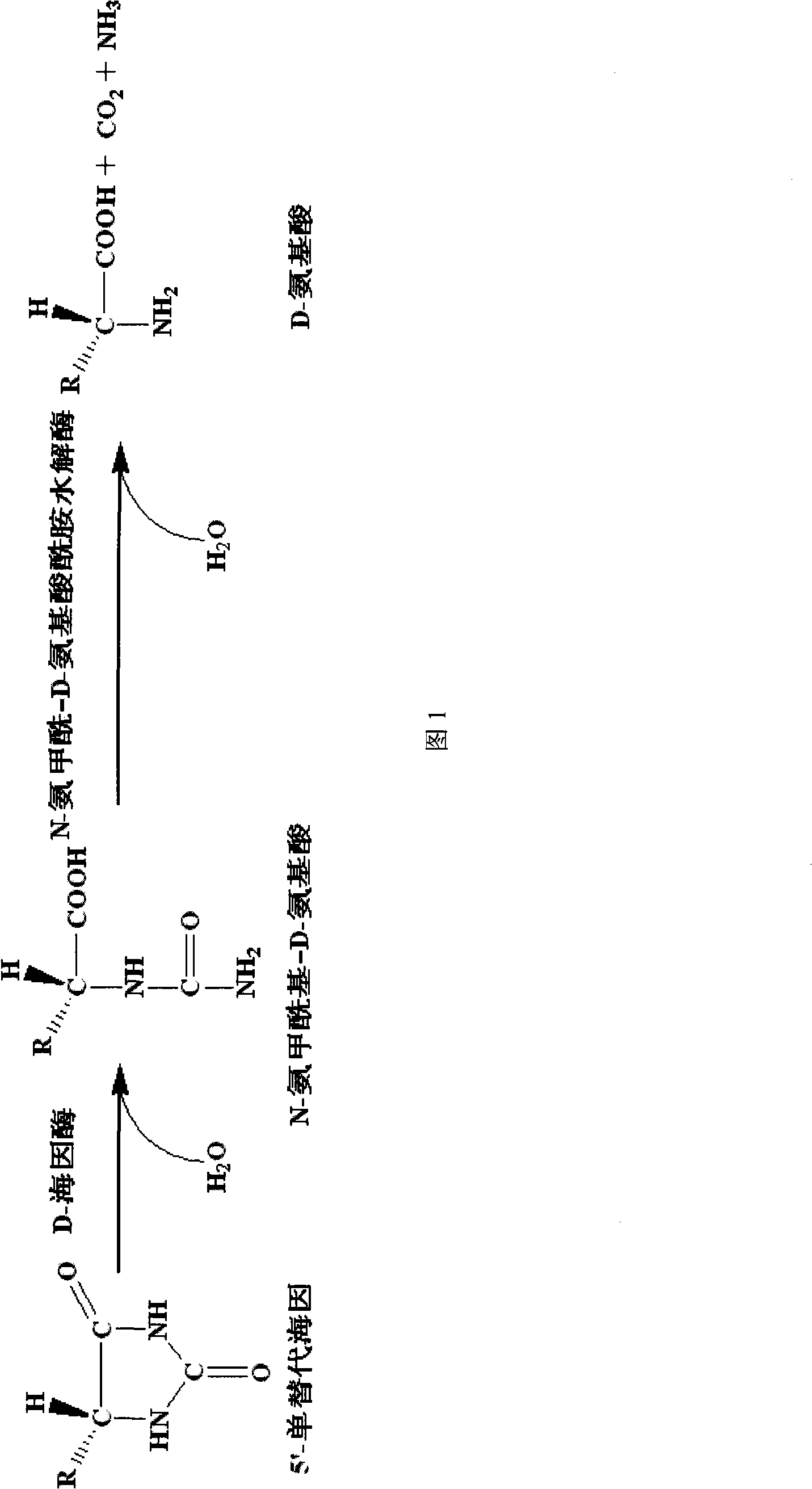
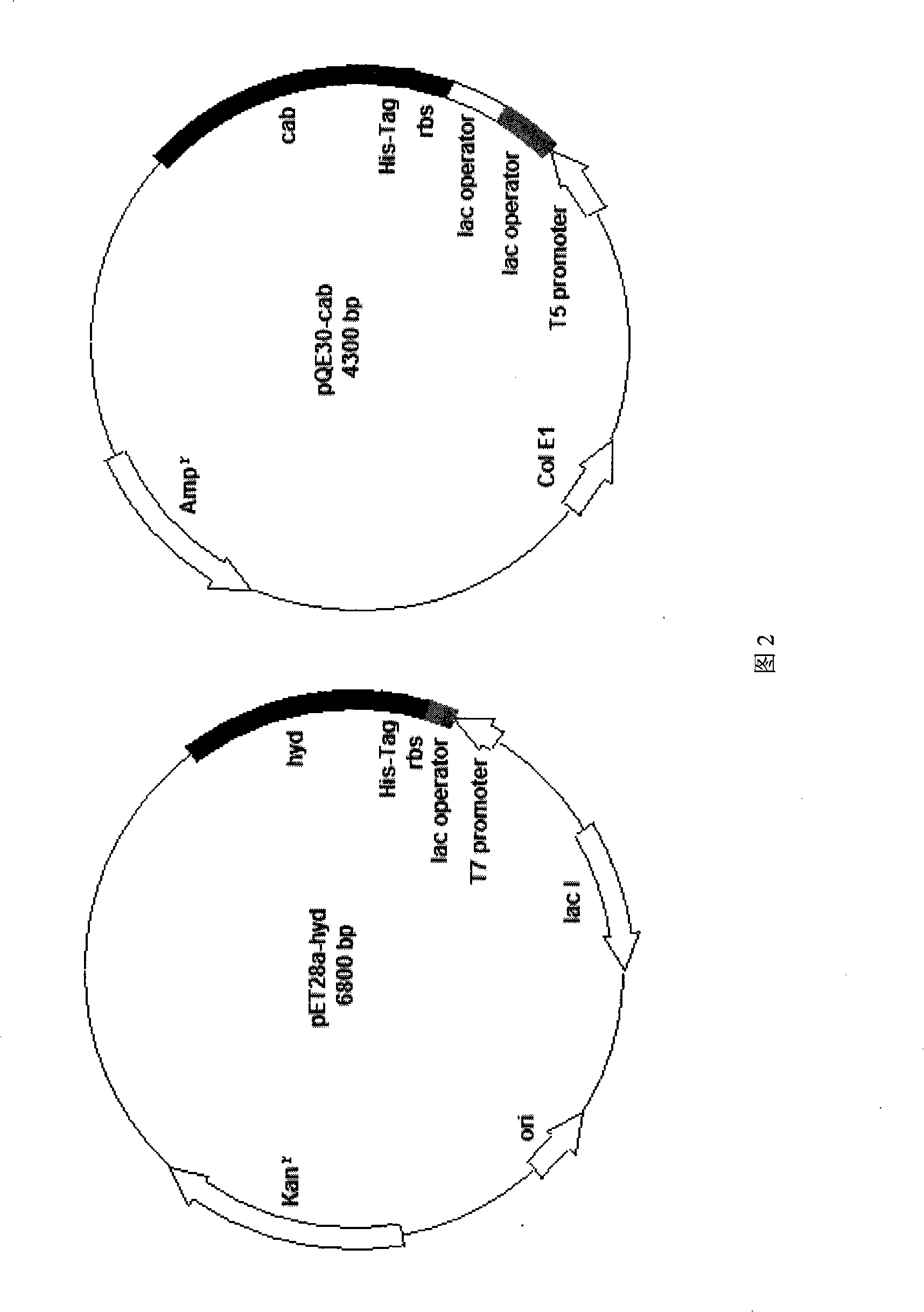
Engineering bacterium, construction thereof and method for preparing D-valine by using the same
InactiveCN101260381APrevent oxidationImprove conversion efficiencyBacteriaMicroorganism based processesEnzyme GeneValine
The invention provides an engineering strain, which can simultaneously express D-hydantoin enzyme and N-carbamoyl-D-amino amidohydrolase. The construction method of the invention is as follows: a D-hydantoin enzyme gene is cloned to a plasmid ET-28a and an N-carbamoyl-D-amino amidohydrolase gene is cloned to a plasmid pQE-30, and then two recombinant plasmids pET28a-hyd and pQE30-cab are shifted into the same Escherichia coli cell by utilization of a co-conversion technology. The invention also provides a method for producing D-valines by utilization of the engineering strain to convert 5'-opropyl hydantoin. The method is characterized by high optical purity of products, simple manufacturing technique, and environmental protection and so on; moreover, compared with the prior market products, the method is low in production cost.
Owner:SHANXI UNIV
Method for converting disease-resistance genes of rice and obtaining transgenic descendants without selective markers
InactiveCN102703499AQuick screeningReduce workloadMicrobiological testing/measurementPlant tissue cultureDiseaseFluorescence
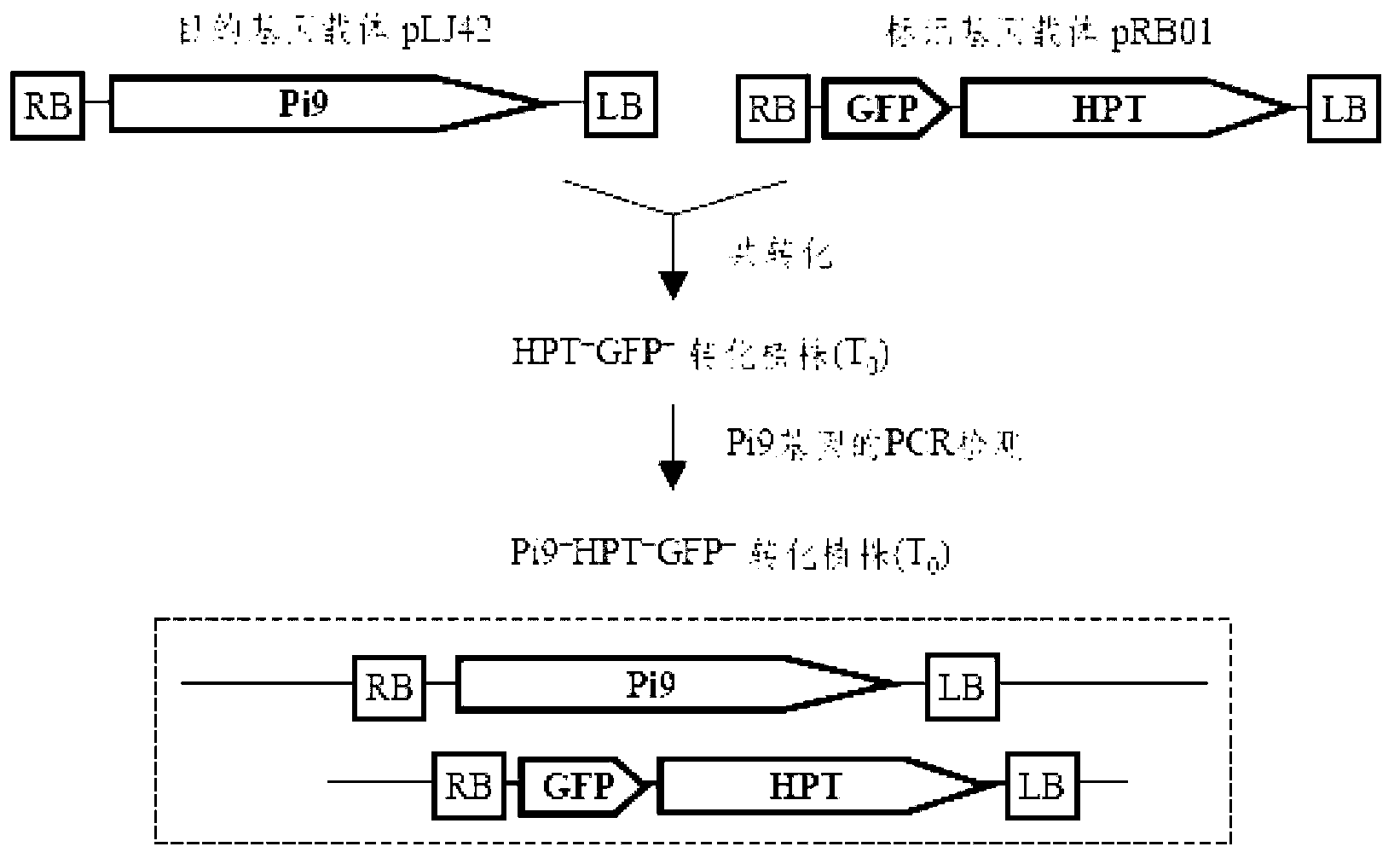
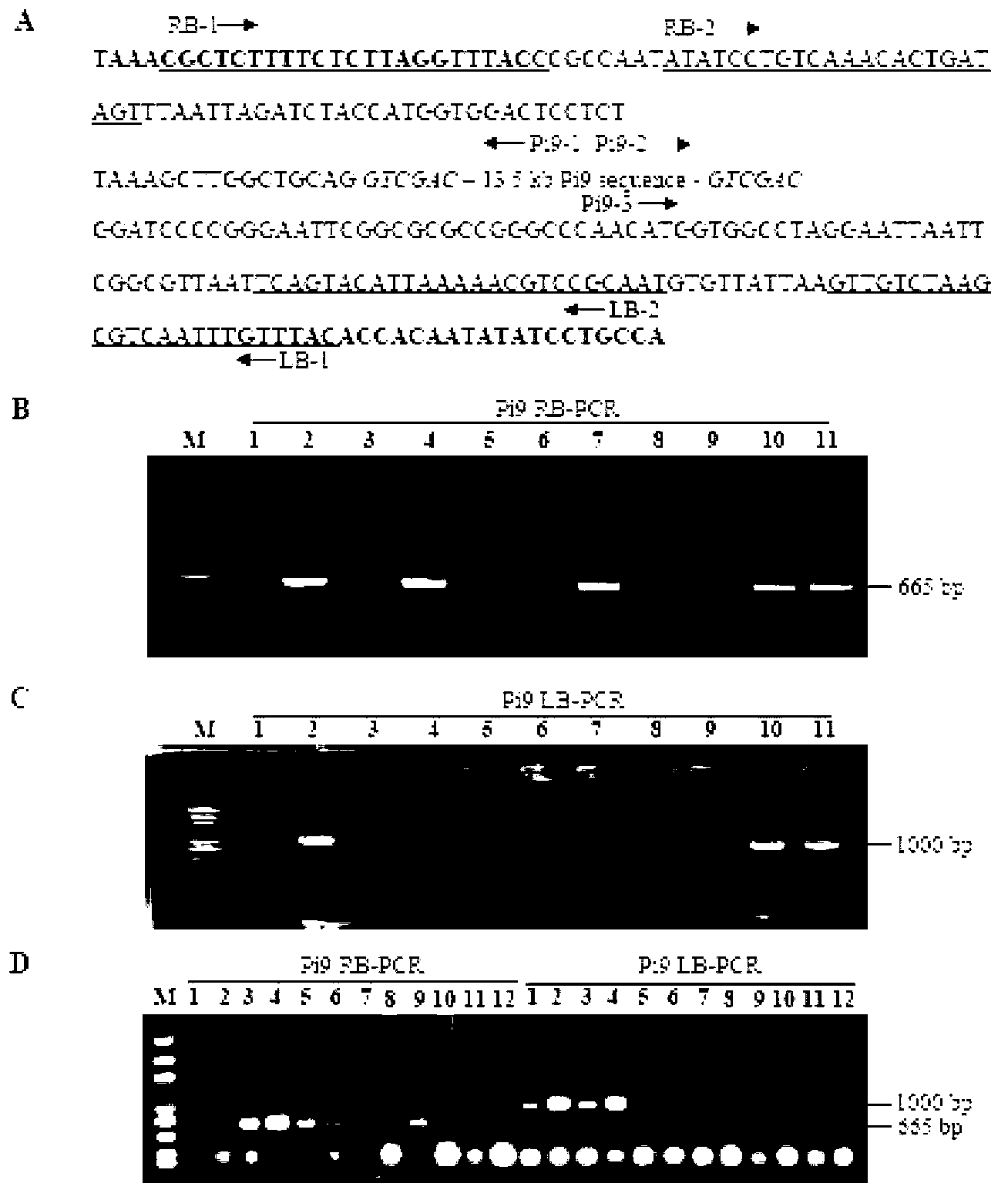
The invention relates to a method for converting disease-resistance genes of rice and obtaining transgenic descendants without selective markers. The method comprises the following steps: first, cloning green fluorescent protein (GFP) and hygromycin phosphotransferase (HPT) on a marker gene carrier, placing a target gene in other T-DNA carrier, mixing strains of agrobacterium tumefaciens carrying the marker gene carrier and strains of agrobacterium tumefaciens carrying the target gene carrier and converting callus of the rice, performing PCR (polymerase chain reaction) detection on the disease-resistance genes of the target gene carrier by a specific primer, and screening to obtain co-transformation plants (T0); then, screening the marker gene plants with positive GFP rapidly and massively by means of a desk lamp fluorescence detector in segregative generations (T1 or T2) of the co-transformation plant for removing, and performing PCR detection for disease-resistance genes to the plants with negative GFP so as to obtain the individuals without selective markers of the transgenic disease-resistance genes. The method can be applied to transgenic breeding without selective markers of rice blast-resistant genes or other functional genes of the rice, and enhances the disease resistance of the rice or improves other agronomic traits.
Owner:ZHEJIANG ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURE SCIENCES
Method for producing trans-4-hydroxyproline from glucose in fermentation manner
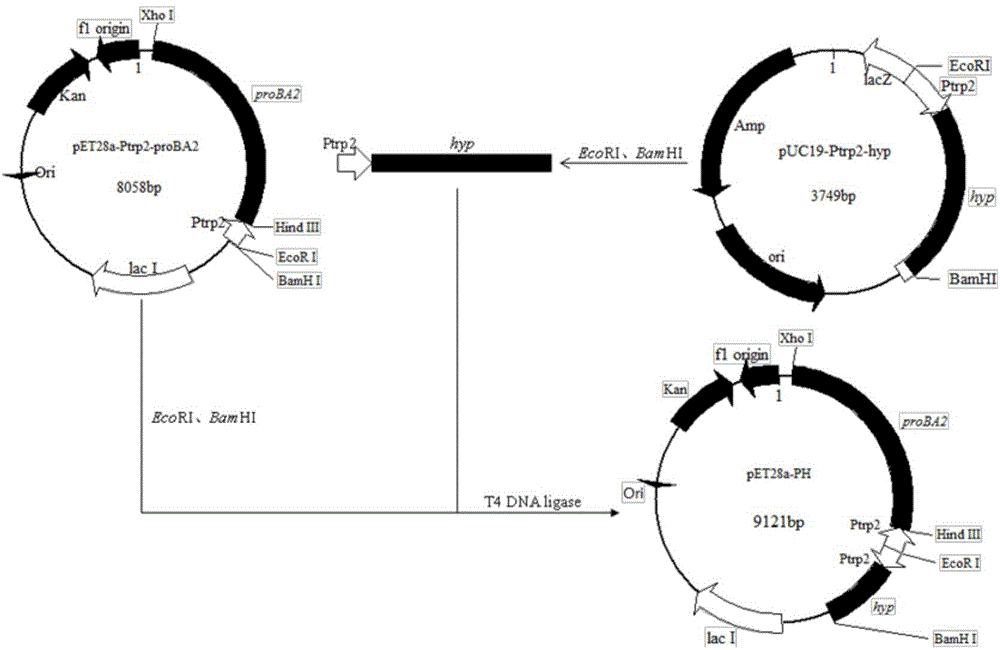
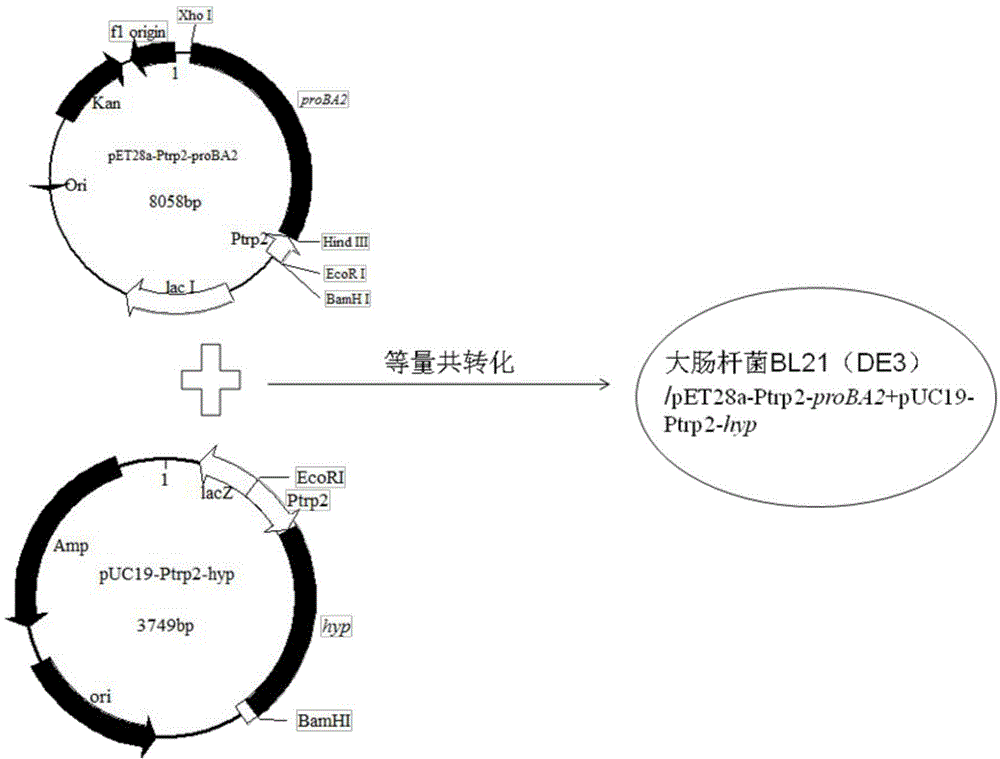
The invention discloses a method for producing trans-4-hydroxyproline from glucose in a fermentation manner by virtue of recombinant Escherichia coli without adding exogenous L-proline. A recombinant plasmid carried by the recombinant Escherichia coli has a mutant gene proBA2 and hyp (4-hydroxyproline), wherein proBA2 is mutated on a glutamyl kinase encoding gene proB, and the inhibition effect of L-proline on glutamyl kinase encoded by the mutated gene is remarkably reduced. proBA2 and hyp are co-expressed, and trans-4-hydroxyproline can be produced directly from glucose in the fermentation manner without adding exogenous L-proline. The recombinant plasmid is obtained by recombining proBA2 and hyp onto the same expression plasmid or by co-transforming recombinant plasmids which contain the two genes respectively and have different resistances. The invention further discloses the application of the Escherichia coli to the production of hydroxyproline.
Owner:JIANGNAN UNIV
Multi-gene binary expression vector constructed by using homologous recombination and preparation method and application of multi-gene binary expression vector
InactiveCN102329812AHigh co-transformation efficiencyVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsTransformation efficiencyGenetic engineering
The invention relates to the field of gene engineering, in particular to a multi-gene binary expression vector constructed by using homologous recombination. The multi-gene binary expression vector is formed by connecting single genes or multiple genes into a multi-gene polymer through polyclonal enzyme cutting sites so as to form a homologous recombination intermediate vector and adding the single-gene or multi-gene polymer into a basic binary vector by homologous recombination, wherein the homologous recombination can be performed for multiple times, so that the T-DNA length of the basic binary vector is gradually increased. The invention also discloses a construction method of the multi-gene binary expression vector and application in plant transgenes. The multi-gene binary expression vector applied in plant genetic modification can transfer multiple target genes at the same time, and has the advantage of high co-transformation efficiency.
Owner:SOUTHWEST UNIVERSITY
Method for enhancing arteannuin content in southernwood using gene cyp71av1 and cpr co-transformation
InactiveCN101182543AIncrease contentMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationBiotechnologyForeign object
The invention is a method for adopting the cotransformation of genes cyp71av1 and cpr to increase the arteannuin content in southernwood in the gene engineering technology field. The invention clones the gene cyp71av1 of the CYP71AV1 and the gene cpr of the CPR from the southernwood to construct the plant expression vector which contains DNA molecules and agrobacterium tumefaciems is used for mediation; the genes of cyp71av1 and cpr are admitted into the southernwood for regenerating plant; a PCR is used for detecting the integration situation of the foreign object genes of the cyp71av1 and the cpr and a high-efficiency liquid phase chromatography-evaporative light scattering detector is used for detecting the arteannuin content in southern wood and the transgenic southernwood plant with increased arteannuin content is selected. The invention obtains the transgenic southernwood with obviously increased arteannuin content and the highest content is 1.82 times the content of the non-transgenic plant.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV SUBEI RES INST
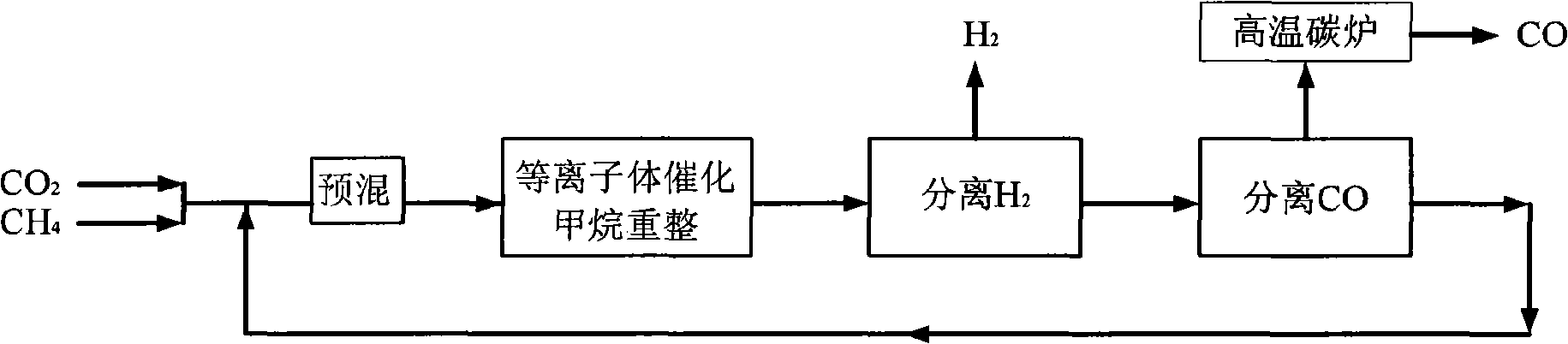
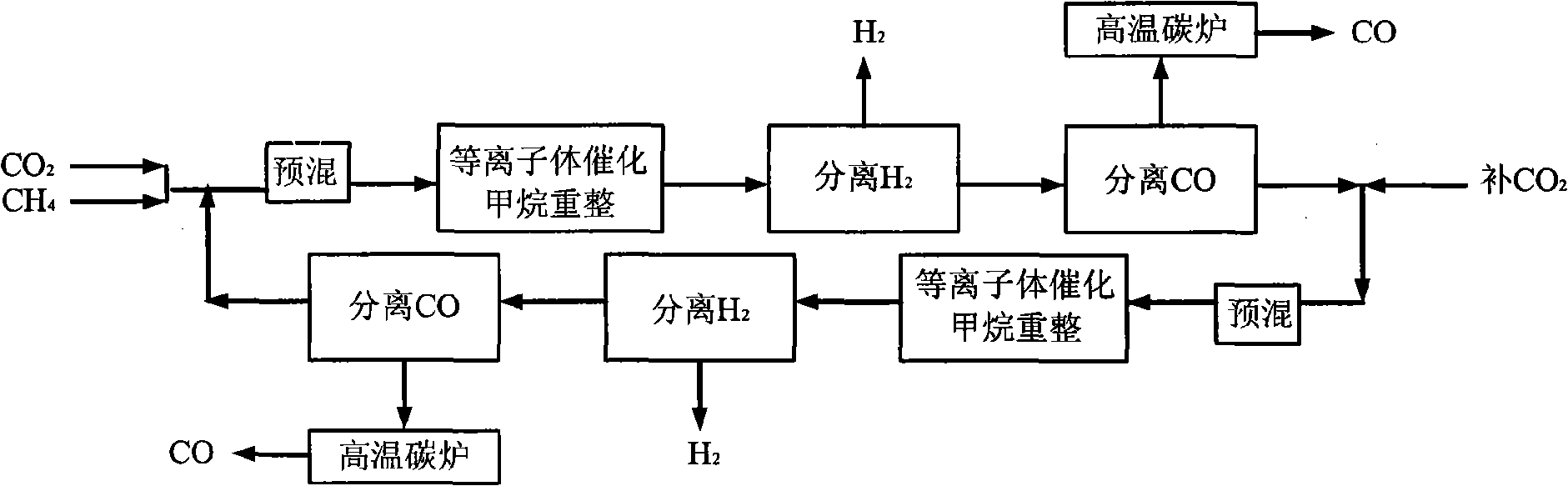
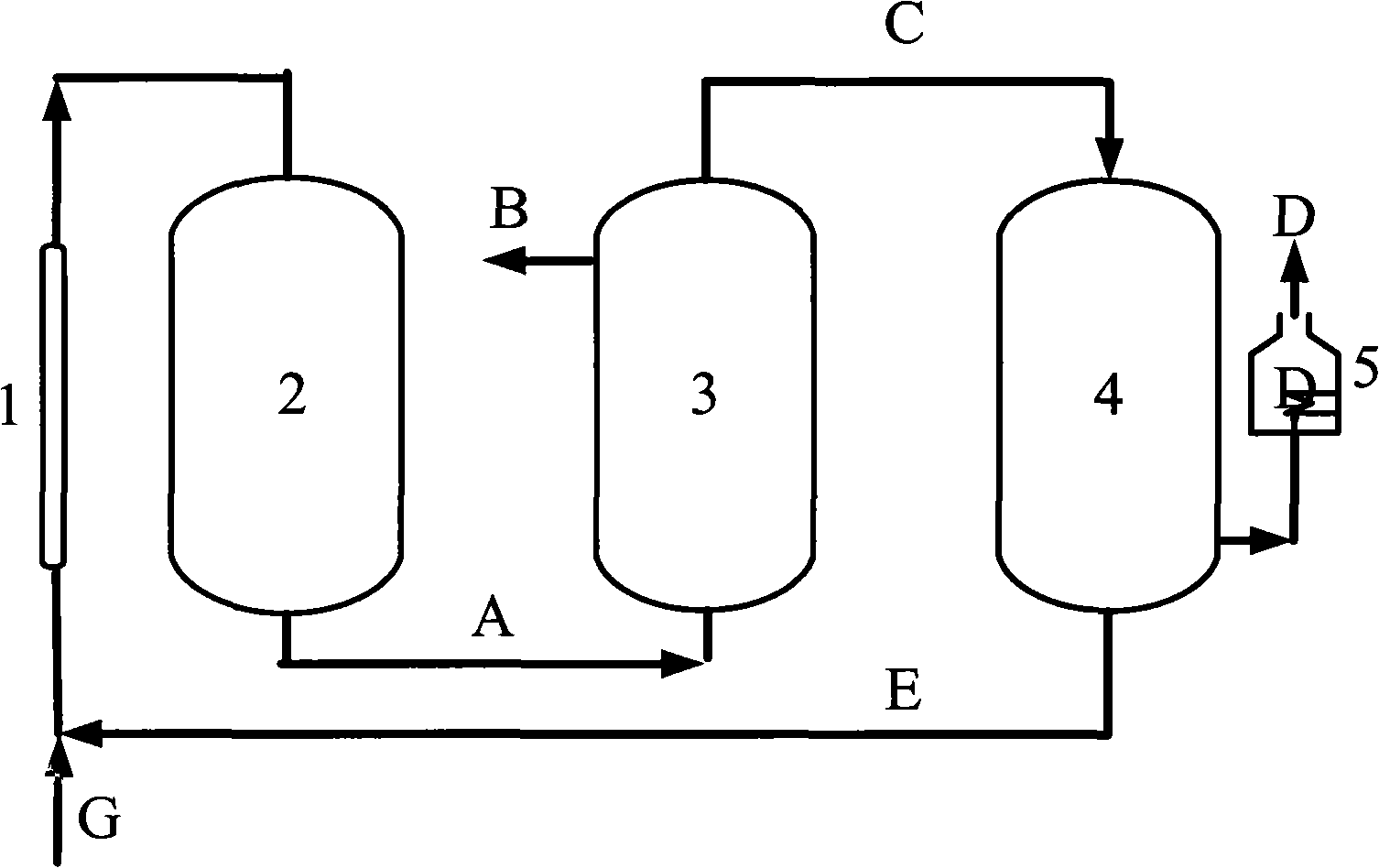
Process and device for preparing H2 and CO by co-transformation of CH4 and CO2
InactiveCN101289166AEfficient conversionReduce energy consumptionHydrogenCarbon monoxidePetrochemicalCoal chemical industry
The invention relates to a method for preparing H2 and CO through the cotransformation of CH4 and CO2 and a device thereof, which pertain to the technical filed of petrochemical industry and coal-chemical industry. The reactant gases CH4 and CO2 are premixed by mole ration of 1:1 to 4:1, sent into a plasma reactor for reaction, separated by a polysulphone membrane H2 separator and then separated by a CO separator, with the left gas sent back to be premixed with feed gas, thereby obtaining H2 and CO by circulative preparation. A gas premixer (1), a plasma reactor (2), an H2 separator (3) and a CO separator (4) are connected in sequence, and the outlet that does not separates gas of the CO separator is connected with the inlet of the premixer. The invention also provides a method and a device that include the steps of reaction-separation-separation-reaction-separation-separation for twice or a plurality of times. The method and the device of the invention avoid terminated reaction caused by inactivated catalyst and realize the preparation of H2 and CO at low temperature, effectively reduce the energy consumption and have high transformation rate of CH4 and CO2 and good product selectivity.
Owner:TSINGHUA UNIV
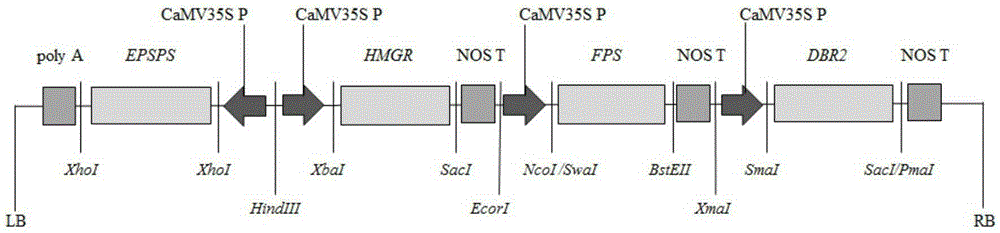
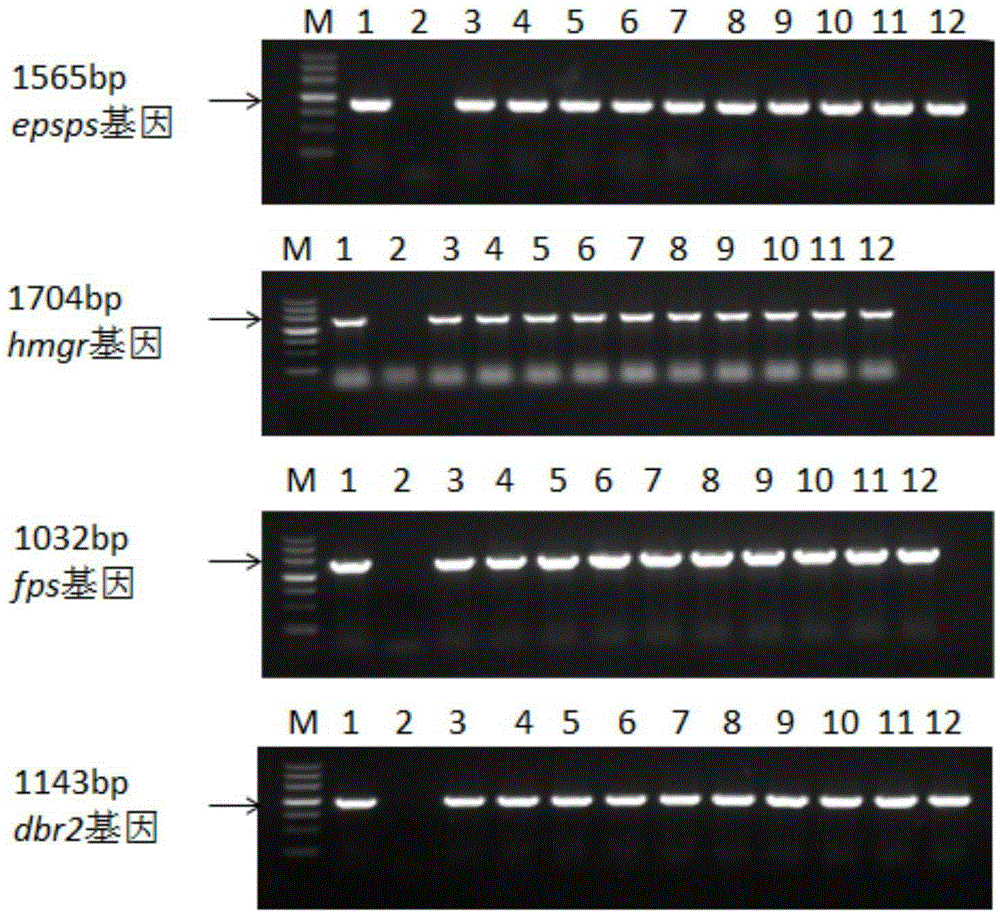
Transgenic sweet wormwood plant and cultivation method thereof
InactiveCN105296536AMaintain metabolismIncrease resistanceBacteriaComponent separationGlyphosateProtein Artemis
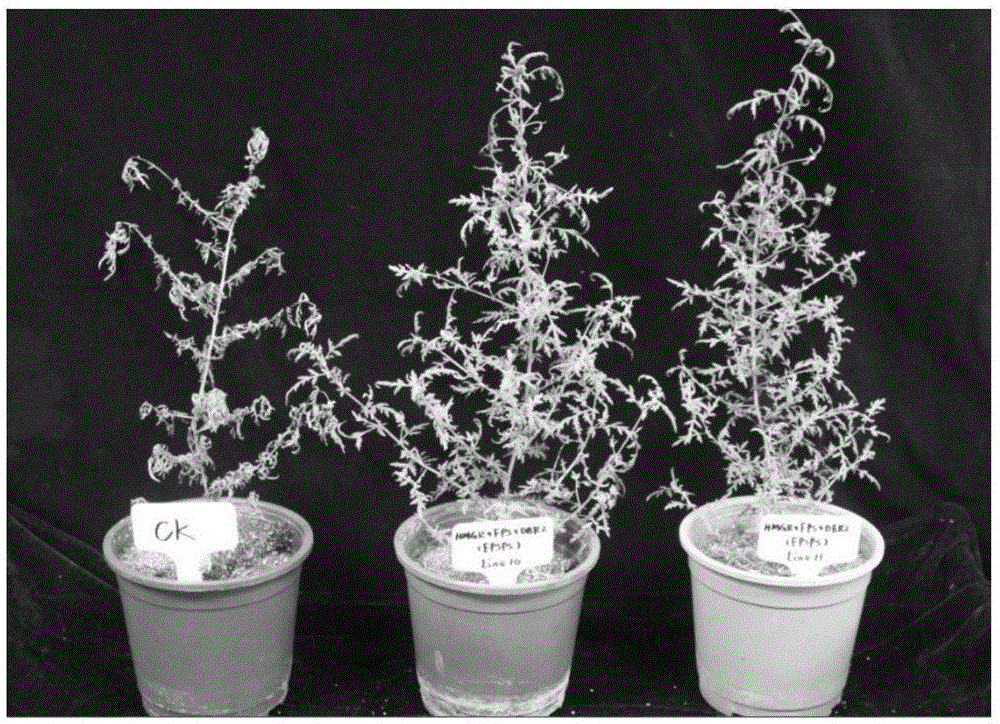
The invention discloses a transgenic sweet wormwood plant in which exogenous target genes consisting of hmgr, fps, dbr2 and epsps are introduced, and a cultivation method thereof. The cultivation method comprises the following steps: (1) constructing a plant expression vector containing the hmgr, fps, dbr2 and epsps genes; 2) transforming the obtained plant expression vector into Agrobacterium tumefaciems; 3) transforming the obtained Agrobacterium tumefaciems containing the hmgr, fps, dbr2 and epsps genes into sweet wormwood and detecting obtained transgenic sweet wormwood plants; 4) measuring the content of artemisinin in the transgenic sweet wormwood plants; and 5) screening transgenic sweet wormwood plants with glyphosate resistance by using glyphosate. The method capable of stably improving the artemisinin content and glyphosate resistance of sweet wormwood is established by using a metabolic engineering strategy of cotransformation of the hmgr, fps, dbr2 and epsps genes; the transgenic sweet wormwood plant capable with high yield of artemisinin is obtained; and an ideal method and material are provided for large-scale production of artemisinin.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Yeast recombinant human III-type triple helix collagen and preparation method thereof
The invention provides a yeast recombinant human III type triple helix collagen and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: S1, constructing a pPICZ alpha B plasmid containing a human III type collagen alpha 1 chain; s2, constructing a double-promoter expression vector of the alpha subunit and the beta subunit of the human P4H; s3, co-transforming the double-promoter expression vector and the pPICZ alpha B plasmid into saccharomycetes, so as to obtain a co-expression strain; s4, screening a yeast recombination strain containing a P4H alpha subunit and a beta subunit from the co-expression strain; and S5, carrying out induced expression on the yeast recombinant strain to obtain the yeast recombinant human III-type triple helix collagen. According to the preparation method disclosed by the invention, the problem of pyrogen does not exist, the generation of immunogenicity is effectively avoided, and the interaction force, the thermal stability and the anti-enzymolysis level among collagen molecules are effectively improved.
Owner:JIANGSU TRAUTEC MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method for enhancing content of vitamin E in plants by gene cotransformation of gamma-tmt and hpt
InactiveCN101736020AIncrease vitamin E contentHigh nutritional valueComponent separationMicrobiological testing/measurementNutritive valuesEnzyme Gene
The invention belongs to the technical field of biology, in particular relates to a method for enhancing the content of vitamin E in plants by the cotransformation of double key enzyme genes of gamma-tmt and hpt. The method comprises the following steps of: cloning the genes of the gamma-tmt and the hpt from the plants, constructing a plant expression vector containing the DNA molecule, mediating by agrobacterium tumefaciens, introducing the genes of the gamma-tmt and the hpt into the plants simultaneously, regenerating plants, detecting the integration condition of the extraneous target genes of the gamma-tmt and the hpt by PCR, measuring the content of the vitamin E in the plants by a high-efficiency liquid chromatography-ultraviolet light detector and sieving to obtain a transgenic plant with the enhanced content of the vitamin E. The content of the vitamin E in the leaves of the obtained transgenic plant is obviously enhanced, and the highest content reaches 4 times of that of non-conversion check plants. The invention has an important meaning for enhancing the nutritive value of the plants.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
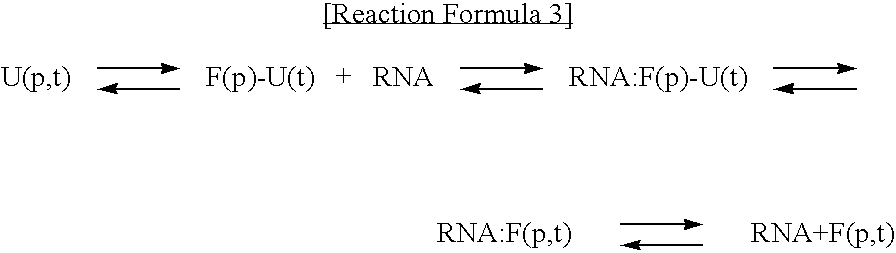
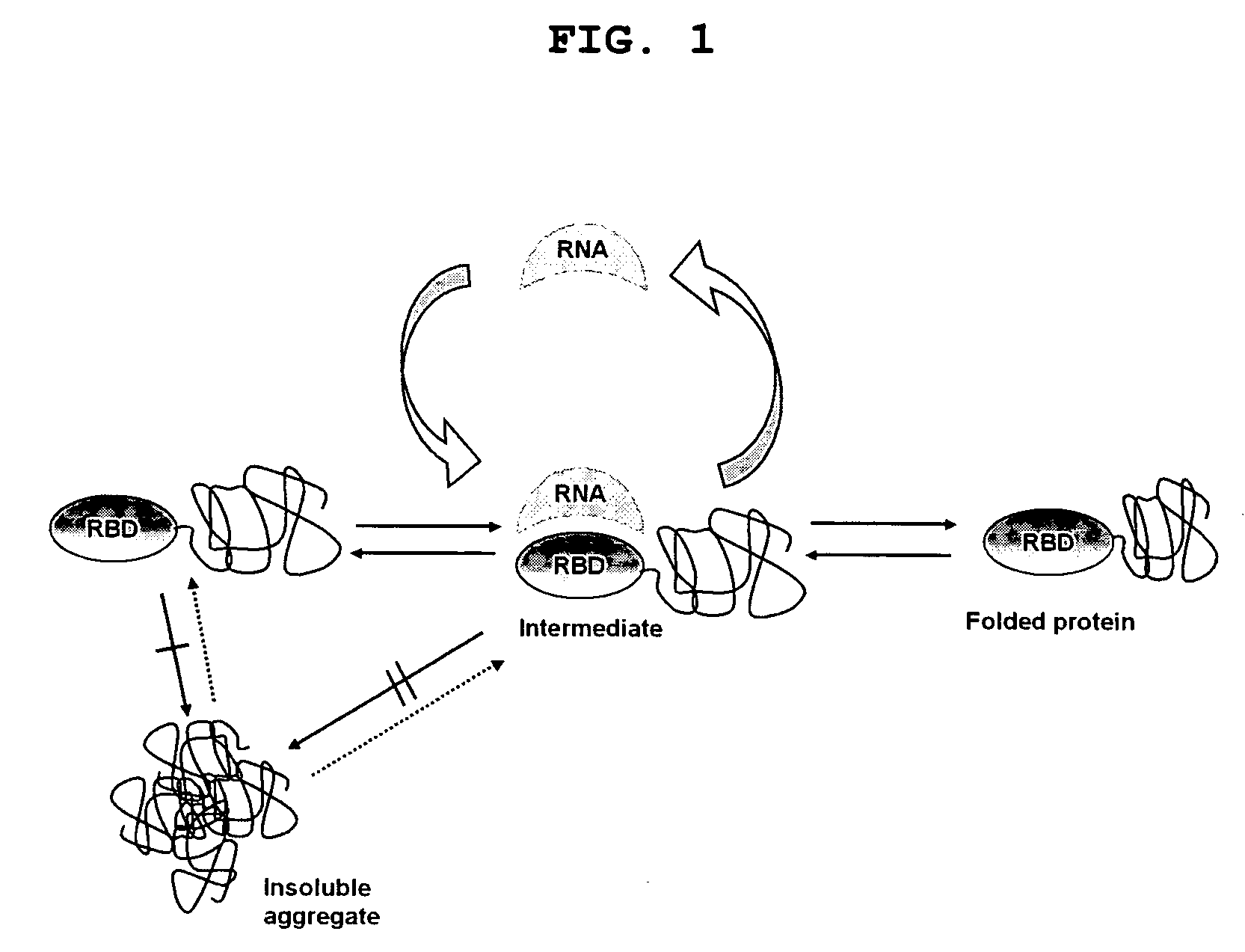
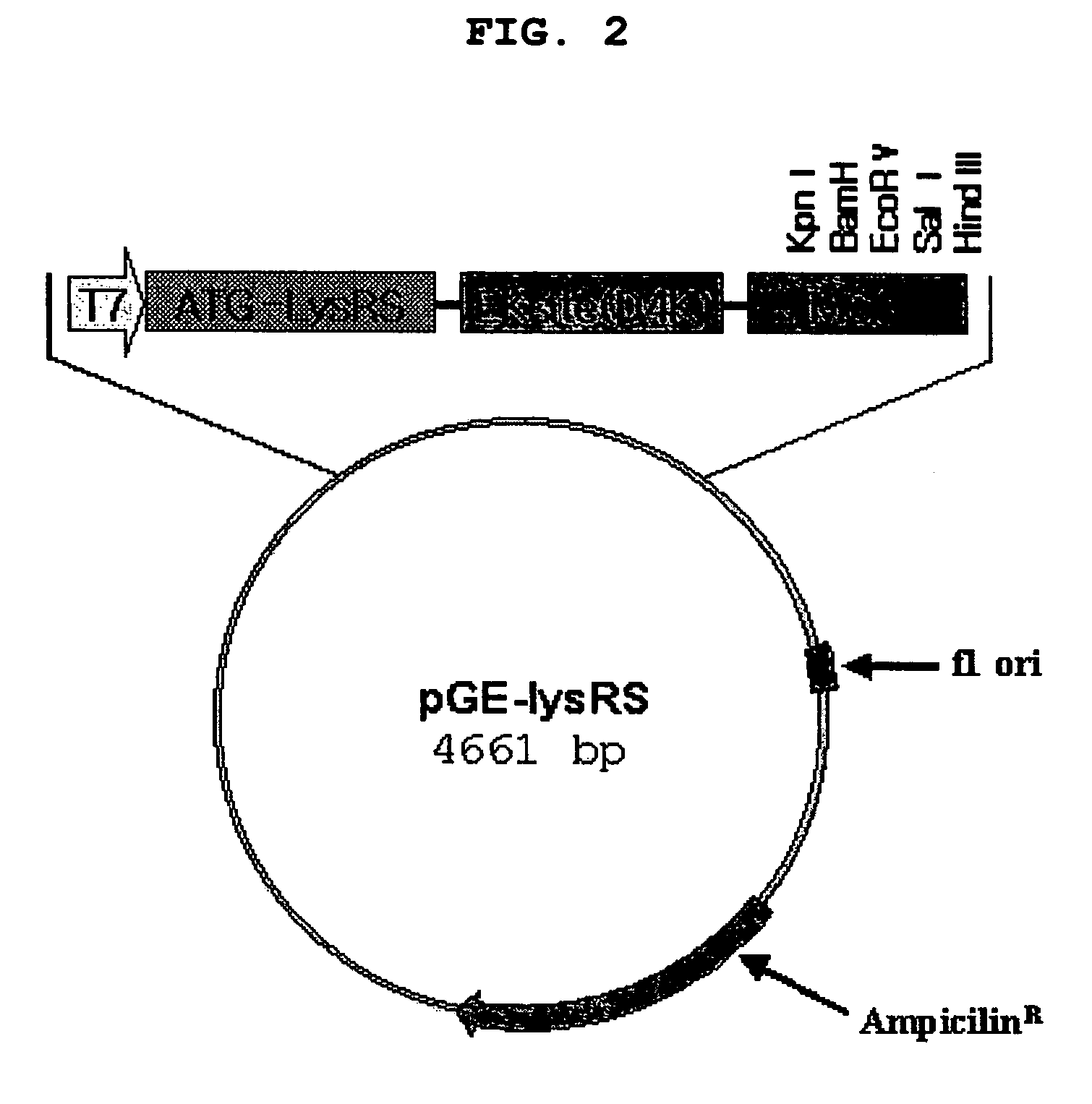
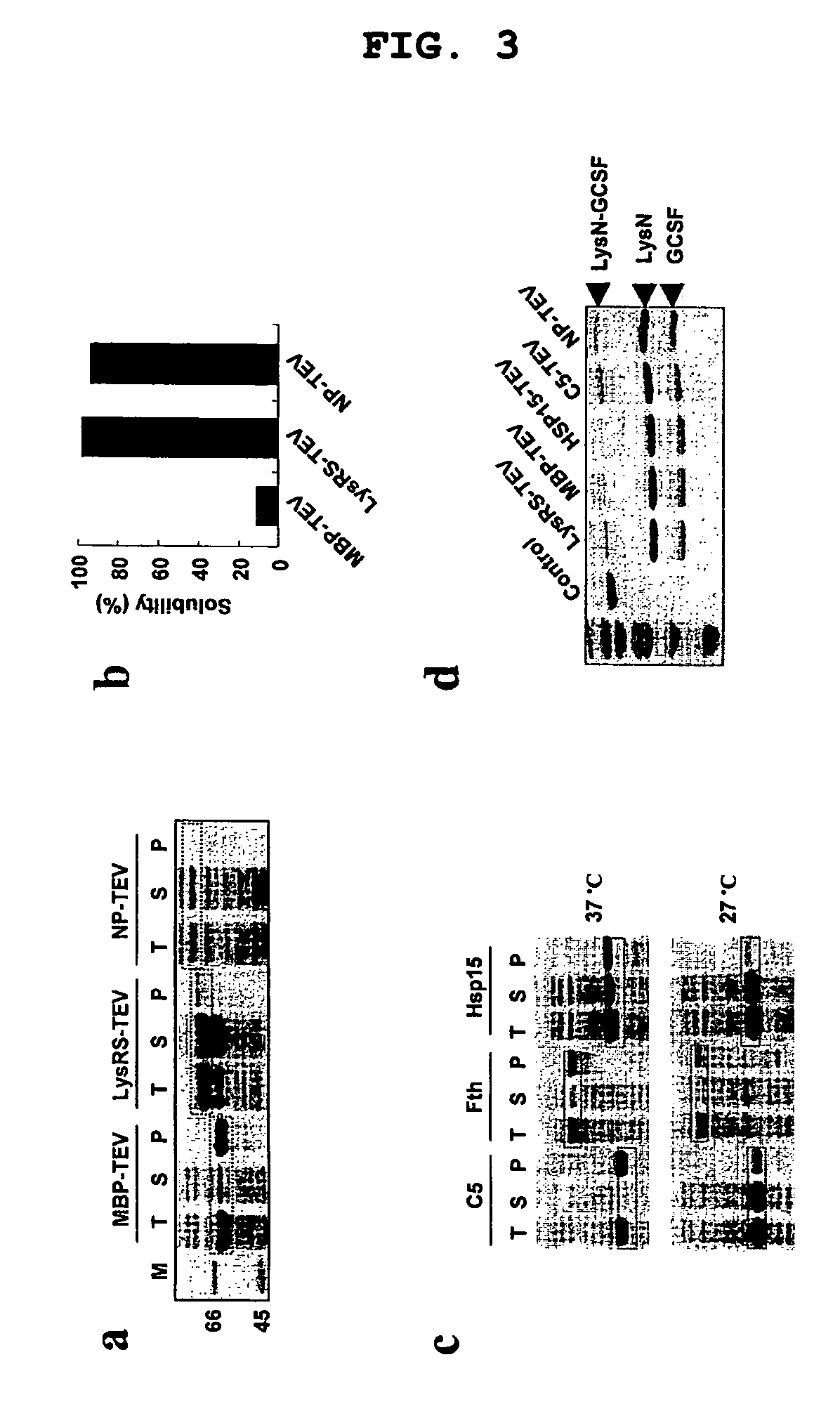
Method for improving solubility and folding efficiency of target proteins using RNA as molecular chaperone
InactiveUS20060292667A1Improve efficiencyImprove solubilityFusion with RNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityProtein target
Disclosed is a method for improving folding efficiency and solubility of a target protein linked to a RNA-binding protein by using RNA molecule as a molecular chaperone, wherein the RNA molecule interacts with the RNA-binding protein. More particularly, the present invention discloses method for improving folding efficiency and solubility of a target protein by transformation of a host cell with a expression vector comprising a polynucleotide encoding the target protein linked to an RNA-binding protein; culturing the transformed host cell in an appropriate culture medium under the condition that an RNA molecule either resident inside the host cell or provided by cotransformation of the host cell with polynucleotide encoding the RNA molecule interacts with the RNA-binding protein; and purifying the soluble protein from host cell lysate. The method of the present invention is very useful for production of soluble proteins for therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic applications.
Owner:XCELL THERAPEUTICS INC
Construction method of gene engineered bacteria for arteannuic acid production
InactiveCN103981110AReduce build timeHigh homologous recombination efficiencyFungiMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyEnzyme digestion
The invention discloses a construction method of gene engineered bacteria for arteannuic acid production, and the construction method comprises the following steps: A) construction of a gene expression module including an artemisinic acid production related gene, an upstream promoter of the artemisinic acid production related gene, and a downstream terminator of the artemisinic acid production related gene; and B) co-transformation of the gene expression module into saccharomyces cerevisiae. The method has the advantages of being simple and fast and efficient, avoids multiple cloning, and does not rely on enzyme digestion sites, many fragments can be together transformed, the homologous recombination efficiency is high, and the method can significantly shorten the construction time of the gene engineered bacteria.
Owner:SHANGHAI LAIYI BIOMEDICAL RES & DEV CENT +1
Method for multicopy integration of target gene to saccharomyces cerevisiae genome
InactiveCN110699383AAchieving multi-copy integrationShort timeHydrolasesStable introduction of DNANucleaseGene expression
A method for multicopy integration of a target gene to a saccharomyces cerevisiae genome includes: selecting target sequences, designing homologous arm primers in length of 15-90bp on two sides of each cleavage site in the corresponding target sequences to primer front ends of amplification target gene cassettes to synthesize homologous arm loaded primers, and amplifying the target gene cassettesto obtain donor DNA fragments; subjecting transcribed gRNA vectors in corresponding target sequences and the donor DNA fragments to co-transformation into Cas9 nuclease expressing saccharomyces cerevisiae to realize gene integration; removing Cas9 nuclease expression vectors and the transcribed gRNA vectors by a non-resistant flat plate. The method has advantages that the homologous arm primers ontwo sides of each cleavage site is in sequence length of 15-90bp, and by respective adding of the homologous arm primers to upstream and downstream primers of the target gene cassettes, an integratorgene template can be obtained directly through once PCR, so that multi-copy integration of target genes is realized. Compared with an existing method, the method has advantages of low time consumption and simplicity in operation.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Gene editing application of prokaryotic Argonaute protein
The invention discloses a gene editing application of a prokaryotic Argonaute protein, which comprises the following steps: constructing a prokaryotic expression vector of the Argonaute protein derived from bacteria, detecting the degradation of the expression vector and a co-transformation vector of the Argonaute protein after transforming a host cell, and detecting genome sites. It is found that the gene has the ability of being activated by a specific transcript and targeting a specific DNA target sequence, and gene editing with the inDel frequency of 3% is carried out on a genome target sequence under the participation of guide RNA transcribed in eukaryotic cells. Experimental results show that the prokaryotic Argonaute protein can be used for developing intracellular gene editing tools.
Owner:NORTHWEST A & F UNIV
Preparation method and application of Coxsackie virus B3 virus-like particles
The invention discloses a preparation method of Coxsackie virus B3 virus-like particles. The method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: 1) cloning a VP1 gene and a VP4 gene of the Coxsackie virus B3 to a target plasmid 1 to obtain a recombinant expression vector 1; and cloning a VP2 gene and a VP3 gene to a target plasmid 2 to obtain a recombinant expression vector 2; 2) cotransforming the recombinant expression vector 1 and the recombinant expression vector 2 obtained in the step 1 ) to a yeast cell to obtain a recombinant yeast cell expressing the VP1 gene, the VP2 gene, the VP3 gene and the VP4 gene; and 3) cracking the recombinant yeast cell obtained in the step 2 ), and separating to obtain the Coxsackie virus B3 virus-like particles. Experiments show that Coxsackie virus B3 virus-like particles are successfully prepared by the method provided by the invention in the yeast expression system, and can be further used in candidate preventive vaccines and pharmaceutical compositions for virus myocarditis and diabetes type I.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
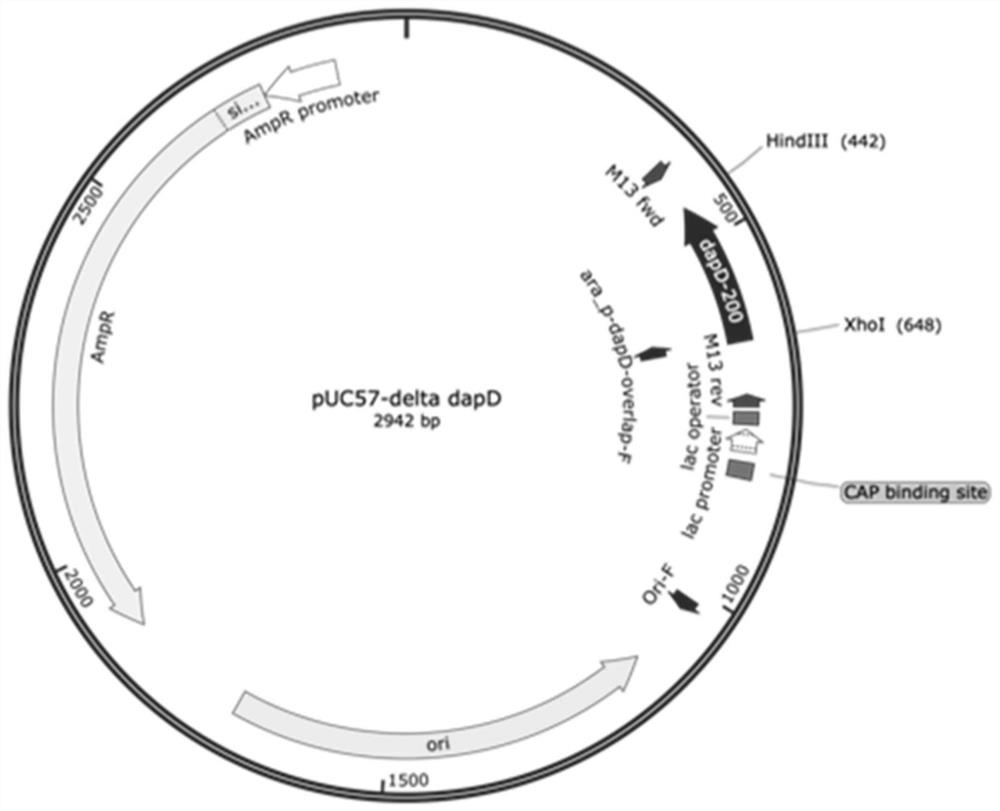
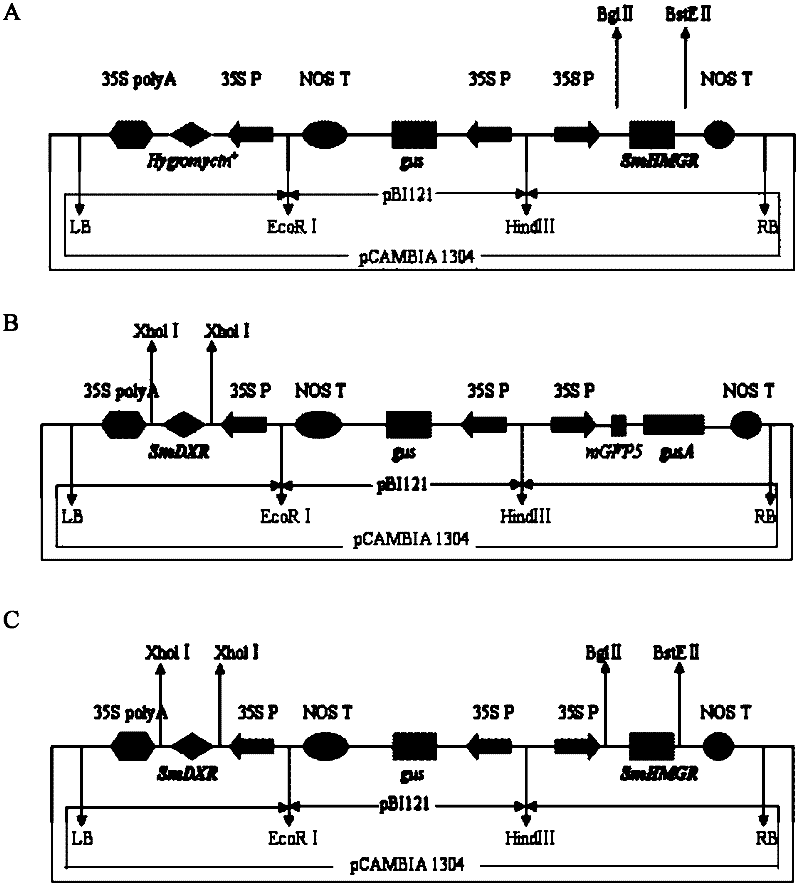
Method of increasing content of tanshinone in hairy roots of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge through cotransformation of SmHMGR and SmDXR double genes
InactiveCN102337279ALow pricePrice reliefMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationSalvia miltiorrhizaPromotion effect
The invention relates to the field of biological technology and discloses a method of increasing the content of tanshinone. According to the method, the 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl coenzyme A reductase gene SmHMGR and the 1-deoxy-D-xylosone-5-phosphate reductase gene SmDXR of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge are used to construct a recombinant vector, and genetic transformation is carried out on leaves of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge so as to obtain hairy roots of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge with transgenic SmHMGR and SmDXR genes. The content of tanshinone in the obtained transgenic hairy roots of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge in the invention substantially increases, and total tanshinone content in a line (HD34) of cotransformed SmHMGR and SmDXR double genes is 5.30 times of that of a comparison hairy root of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge. The invention provides the method for increasing content of tanshinone in the hairy roots of salvia miltiorrhiza bunge, providing a novel high-quality drug source for producing tanshinone in critical clinical demand and having a positive promotion effect in alleviating shortage of drug sources for tanshinone.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Novel method for co-transformation of pichia pastoris through multiple genes
The invention discloses a novel method for co-transformation of pichia pastoris through multiple genes. By adopting the novel method, the fact that multiple exogenous genes required to be expressed are connected to the same pichia pastoris expression vector is realized, and in the expression vector, each gene is positioned in an independent expression frame; the fact that multiple genes are efficiently, simultaneously and stably integrated into a pichia pastoris genome is achieved by adopting a built coexpression vector to transform the pichia pastoris. The invention provides the efficient novel method provided for achieving that multiple genes are simultaneously and independently expressed in the same pichia pastoris cell.
Owner:HUAIHUA UNIV
A method for the rapid assembly of multi-fragmented DNA in yeast
ActiveCN104419701BHigh speedIncrease success rateFermentationVector-based foreign material introductionCompetent cellYeast
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
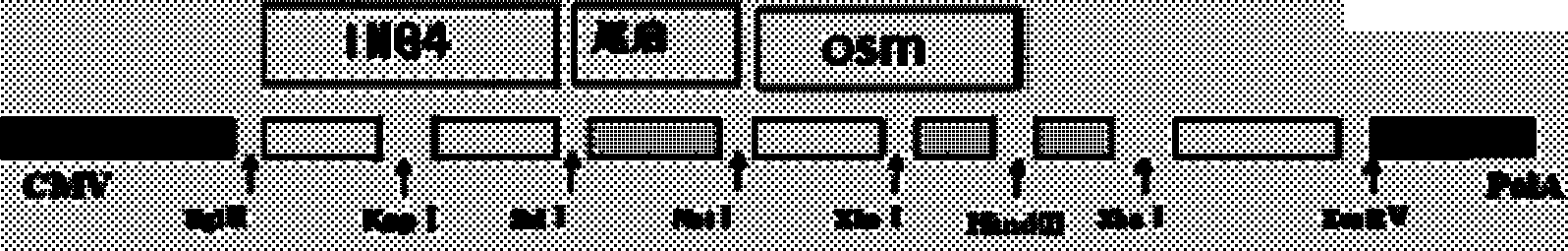
ING4 and OSM double-gene co-expression vector and application thereof
ActiveCN102352368AGrowth inhibitionInhibit apoptosisGenetic material ingredientsFermentationRestriction siteApoptosis
The invention belongs to the field of adenovirus vectors and in particular discloses a recombinant adenovirus vector Ad-ING4-OSM and a preparation method thereof. The preparation method comprises the following steps: on the basis of a transfer plasmid pAdTrack-CWV-polyA-promoter, inserting an ING4 segment between BglII and SalI polyclonal sites of the transfer plasmid and inserting an OSM segment between NOtI and HindIII restriction sites of the transfer plasmid so as to prepare a recombinant transfer plasmid pAdTrack-CWV-ING4-poly-A-promoter-OSM; carrying out co-transformation on the recombinant transfer plasmid and a pAsEasy-1 adenovirus skeleton plasmid to BJ5183 competence bacteria with a calcium chloride method; screening, carrying out PacI restriction, and transfecting QBI-293A cells with a liposome; and carrying out multi-time infection and amplification so as to obtain the recombinant adenovirus vector Ad-ING4-OSM. Compared with the Ad-ING4 and Ad-OSM single genomes, the recombinant adenovirus vector Ad-ING4-OSM shows obvious tumor-inhibiting synergy and radiotherapy sensitizing synergistic effect on human laryngocarcinoma Hep-2 cells and nude mouse transplanted tumor thereof and shows superimposed anticancer synergy for inhibiting growth of SPC-A1 pulmonary adenocarcinoma cells and inducing apoptosis.
Owner:SUZHOU UNIV
A standardized, high-precision, and general-purpose method for building functional modules
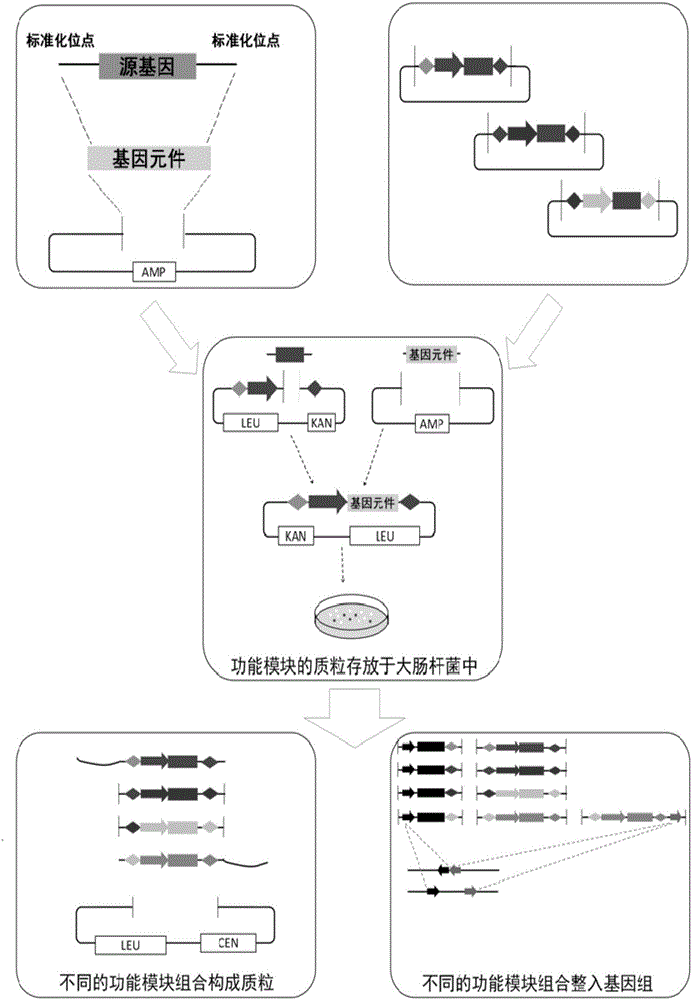
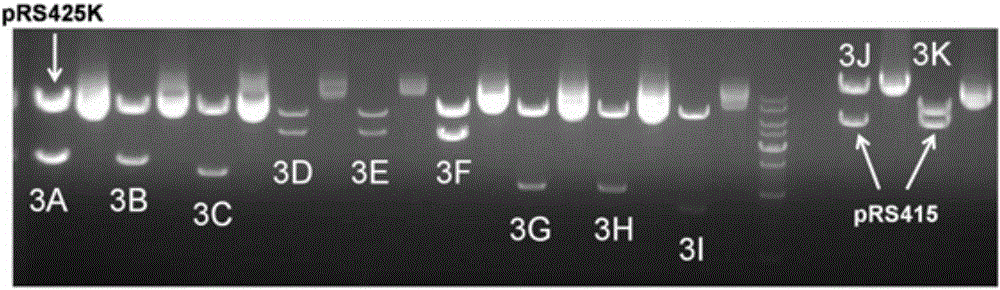
ActiveCN104419716BDifferent combinationsAchieve combinationFungiVector-based foreign material introductionYeast plasmidEngineering
The invention discloses a standardized, high-precision, and general-purpose functional module construction method, which includes the following steps: (1) Adding standardized sites to the source gene to form a genetic element, and connecting the genetic element to the plasmid pLD-Blunt to form a genetic (2) Get the gene element from the plasmid with the gene element and connect it to the following gap in the module tool plasmid: terminator 1-promoter-AATG-gap-TAAA-terminator 2 ; Construct plasmids with different functional modules; (3) Transfer different functional modules from plasmids with different functional modules, and co-transform S. The functional modules are stored in the plasmid; the present invention has versatility, standardization, high precision and free selectivity.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
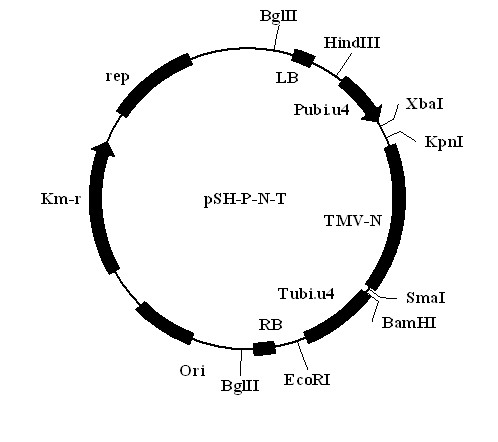
Intraspecific gene improvement method for common tobacco mosaic virus resistance
InactiveCN102690839AMicrobiological testing/measurementFermentationNicotiana tabacumTobacco mosaic virus
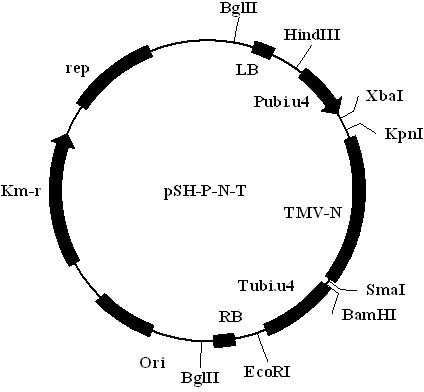
The invention discloses an intraspecific gene improvement method for common tobacco mosaic virus resistance, belonging to the technical field of biology. The method comprises the following steps of: (1) building a Pubi.u4 promoter from the common tobacco to drive the TMV-N (tobacco mosaic virus) gene expression and the tobacco intraspecific gene expression vector pSH-P-N-T of which expression is stopped by Tubi.u4; (2) carrying out co-transformation on the tobacco explant by the intraspecific gene expression vector pSH-P-N-T and the expression vector pSh737 which only contains the marker gene through sonication-assisted agrobacterium-mediated transformation, and screening to obtain T0 generation transformed tobacco plant; and (3) carrying out T1 generation genetic segregation and screening test to obtain the intraspecific gene improvement plant of the marker gene-free common tobacco mosaic virus resistance (TMW). According to the method, the maker-free transformation of the common tobacco can be realized, and the influence of the non-tobacco source gene sequence can be eliminated, so that the transgenosis safety can be furthest realized.
Owner:GUIZHOU TOBACCO SCI INST
Method for carrying out cotransformation on double genes of AaPMT and AaTRI to improve content of tropine alkaloid in anisodus acutangulus hairy roots
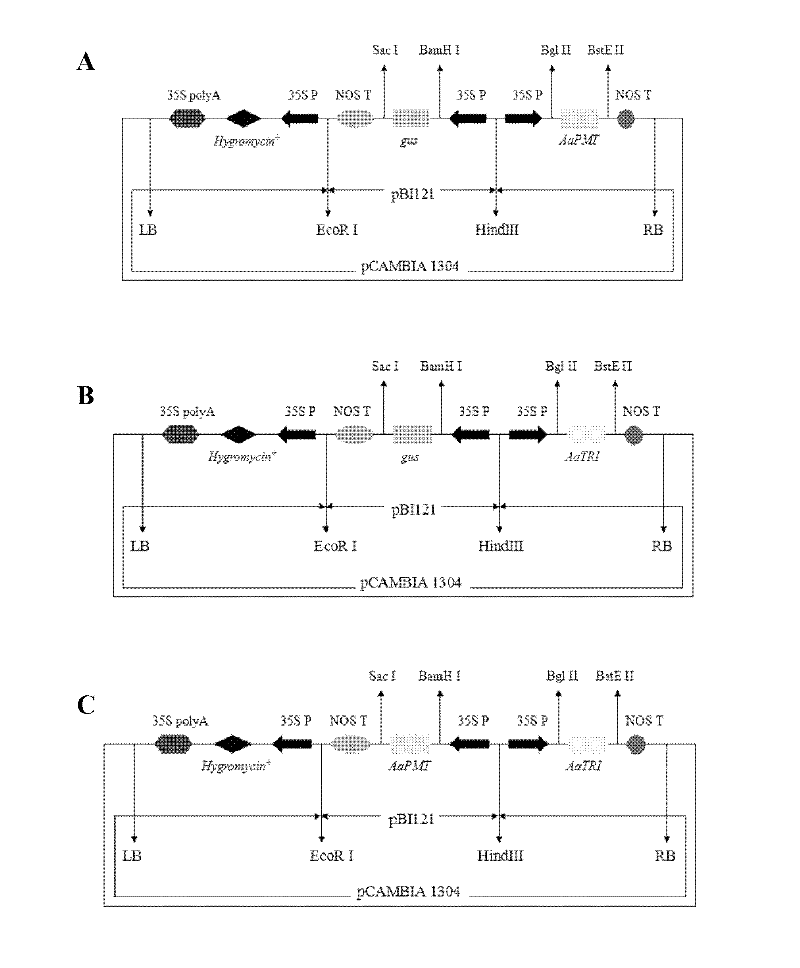
InactiveCN102212548AAlleviate shortagesVector-based foreign material introductionAngiosperms/flowering plantsFrame sequenceGene conversion
The invention relates to a method for carrying out cotransformation on double genes of AaPMT and AaTRI to improve the content of tropine alkaloid in anisodus acutangulus hairy roots, and the method comprises the following steps: constructing a plant diplobivalent efficient expression carrier containing AaPMT and AaTRI genes by utilizing encoding frame sequence of rate-limiting enzyme AaPMT and AaTRI genes cloned from the medicinal plant anisodus acutangulus roots, mediating through agrobacterium rhizogene, and carrying out double-gene transformation on the anisodus acutangulus plant, thus obtaining the anisodus acutangulus hairy roots containing transgene AaPMT and AaTRI, wherein the average content of the tropine alkaloid is obviously improved. The invention provides a method for improving the content of the tropine alkaloid in the trisection hairy roots, thus providing more resources and tremendous commercial demands on tropine alkaloid clinically needed.
Owner:SHANGHAI NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Method for improving solubility and folding efficiency of target proteins using RNA as molecular chaperone
InactiveUS7759303B2Improve efficiencyImprove solubilityFusion with RNA-binding domainPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityProtein target
Disclosed is a method for improving folding efficiency and solubility of a target protein linked to a RNA-binding protein by using RNA molecule as a molecular chaperone, wherein the RNA molecule interacts with the RNA-binding protein. More particularly, the present invention discloses method for improving folding efficiency and solubility of a target protein by transformation of a host cell with a expression vector comprising a polynucleotide encoding the target protein linked to an RNA-binding protein; culturing the transformed host cell in an appropriate culture medium under the condition that an RNA molecule either resident inside the host cell or provided by cotransformation of the host cell with polynucleotide encoding the RNA molecule interacts with the RNA-binding protein; and purifying the soluble protein from host cell lysate. The method of the present invention is very useful for production of soluble proteins for therapeutic, prophylactic and diagnostic applications.
Owner:XCELL THERAPEUTICS INC
Method for constructing target protein interaction network based on high-throughput sequencing
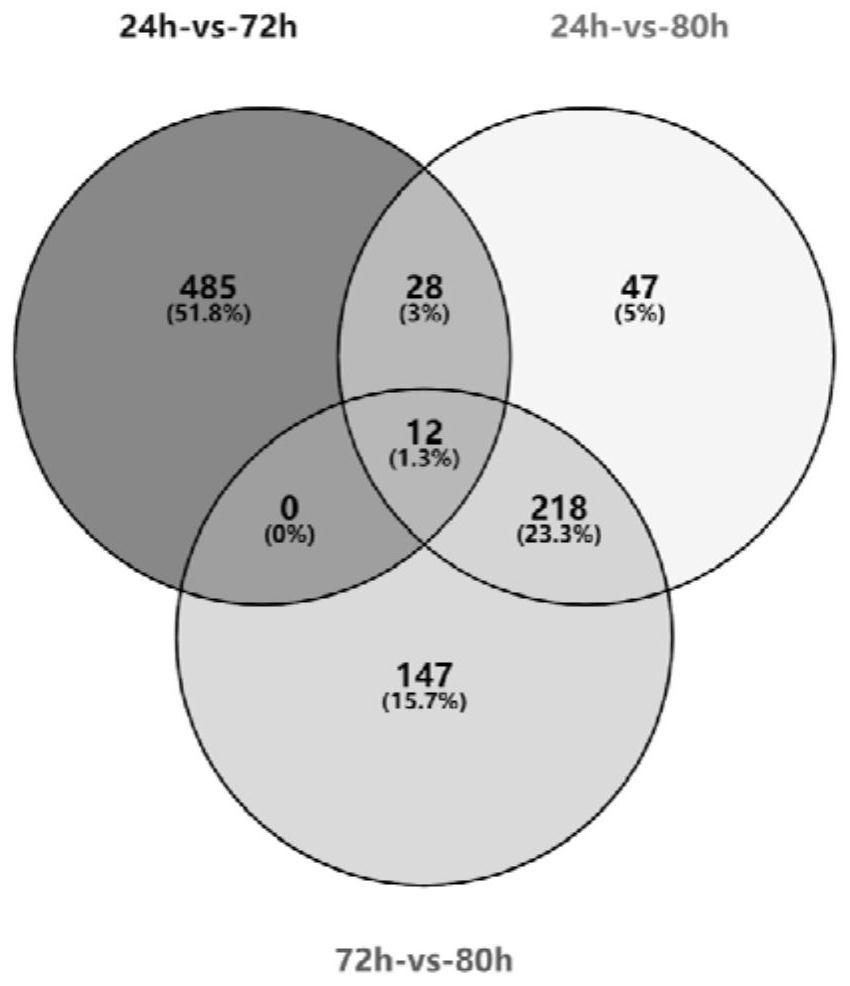
ActiveCN112301117ASimple stepsSolve the problem of missing potential interacting proteinsMicrobiological testing/measurementHybridisationReference genesProtein target
The invention discloses a method for constructing a target protein interaction network based on high-throughput sequencing. According to the method, a BD-bait and a prey library are co-transformed into a Y2H yeast strain, then culturing in a YPDplus culture medium at 30 DEG C for 4 hours, discarding the supernatant, adding 1mL of sterile water medium for suspension, taking 100muL of suspension bacterial liquid and adding into 10ml of SD / -Leu / -Trp / -His / -Ade liquid culture medium for shaking culture, sampling respectively after shaking culture for 24 hours, 72 hours and 80 hours, the sampled bacterial liquids are used as templates for PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction) amplification, carrying out agarose gel electrophoresis to test the screening degree of the bacterial liquids, recycling products, carrying out high-throughput sequencing, carrying out gene abundance and difference analysis after de novo assembly, and taking a difference gene as a protein coding gene interacting with a targetgene in the library, so as to preliminarily construct an interaction network of the target protein. The method is also suitable for constructing a target protein interaction network of species without reference genes. The method simplifies the steps of a yeast two-hybrid screening library, and the method is not limited by the number of clones screened once, and can find all interaction proteins of a target protein in a single library.
Owner:NANJING AGRICULTURAL UNIVERSITY
Phage-assisted cellooligosaccharide transporter continuous directed evolution system and method
PendingCN114807202AImprove transportation capacityRealize visualizationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMutated proteinOligosaccharide
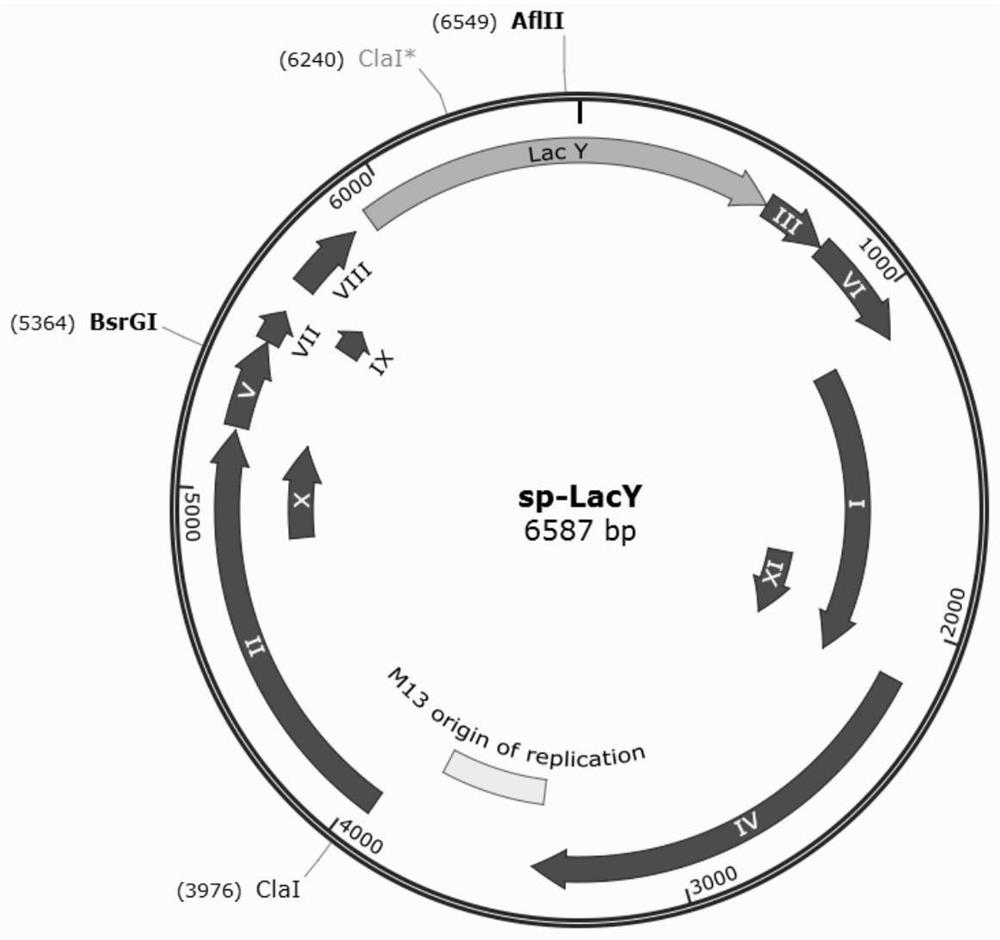
The invention provides a bacteriophage-assisted cellooligosaccharide transporter continuous directed evolution system and a bacteriophage-assisted cellooligosaccharide transporter continuous directed evolution method. The directed evolution system comprises AV1 plasmid, AV2 plasmid and bacteriophage, and nucleotide sequences of the AV1 plasmid and the AV2 plasmid are respectively shown as SEQ ID NO.7 and SEQ ID NO.8. The invention further provides a preparation method of the bacteriophage-assisted cellooligosaccharide transporter continuous directed evolution system. The method for directed evolution of the cello-oligosaccharide transporter comprises the following steps: co-transforming AV1 plasmid and AV2 plasmid into host bacteria to obtain engineering bacteria for evolution; the phage and the engineering bacteria for evolution obtained in the step 1 are subjected to multiple rounds of evolution culture in a culture medium containing the cellooligosaccharide, in the multiple rounds of evolution culture process, the concentration of the cellooligosaccharide in the culture medium is decreased progressively so as to increase the screening pressure, and the mutant protein is obtained. The invention designs a visual bacteriophage-assisted continuous directed evolution system, the system comprises AV1 plasmid and AV2 plasmid, the visual high-throughput evolution process of the cello-oligosaccharide transporter can be realized by adopting the evolution system to evolve the cello-oligosaccharide transporter, excessive human intervention is avoided, the evolution efficiency is higher and more sensitive, and the method is suitable for large-scale popularization and application. Further, the transport capacity of the LacY on the cellooligosaccharides is greatly improved.
Owner:GUANGZHOU INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com