Method for converting disease-resistance genes of rice and obtaining transgenic descendants without selective markers
A technology without selectable markers and disease-resistant genes, applied in biochemical equipment and methods, horticultural methods, botanical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of heavy analysis work and difficult screening of transgenic individuals without selectable markers, and achieve improved screening Efficiency and workload reduction effects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
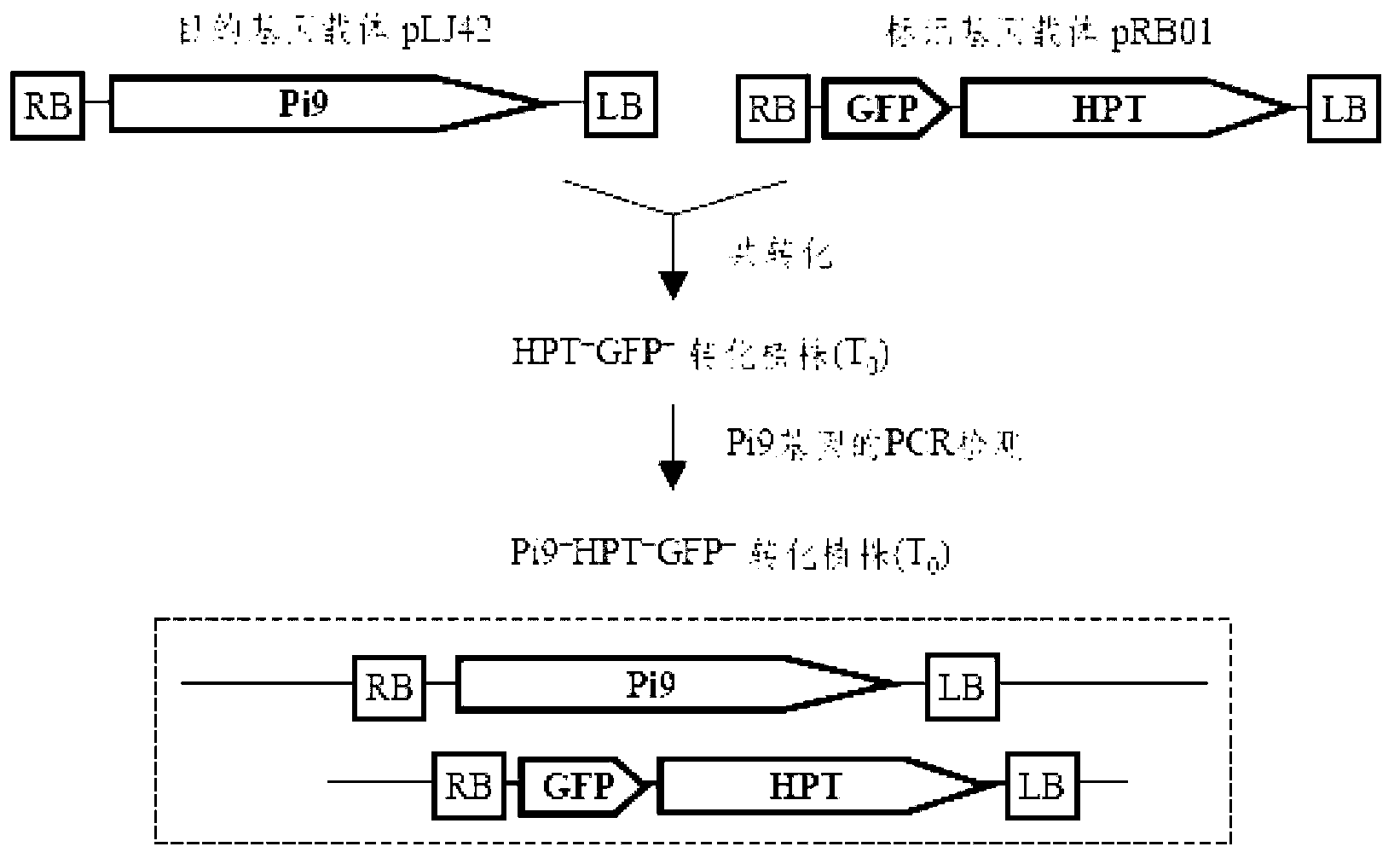
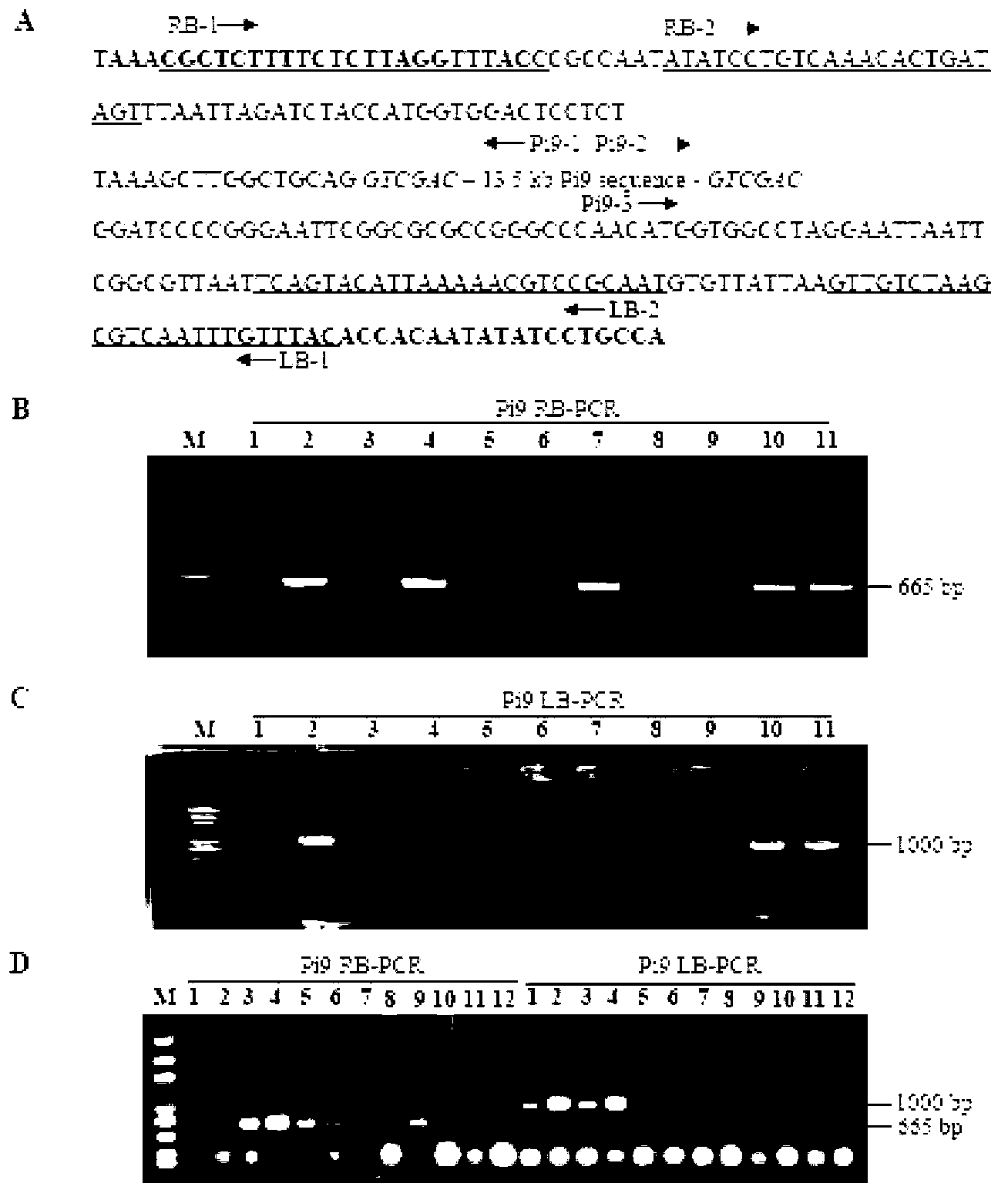
[0021] Example: Taking the transformation of rice broad-spectrum rice blast resistance gene Pi9 as an example, through an improved double-strain (double-vector) co-transformation system, a rice germplasm material without a selection marker for the disease-resistant gene was created.
[0022] Vector construction: co-transformation vector system includes marker gene vector (pRB01) and target gene vector (pLJ42), such as figure 1 . The green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene controlled by the maize ubiquitin promoter Ubi was cloned into the HindIII and EcoRI restriction sites of the Agrobacterium transformation vector pCAMBIA1300 (Genbank AF234296) to generate the marker gene vector pRB01, which also carries the cauliflower mosaic virus Hygromycin phosphotransferase gene (HPT) controlled by the CaMV35S promoter. HPT is used as a hygromycin resistance selection marker to screen transformed rice cells, and GFP gene is used as a visible genetic marker to track transformed rice cells, ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com