Construction method of gene engineered bacteria for arteannuic acid production
A technology of genetically engineered bacteria and artemisinic acid, applied in the field of microbial fermentation, can solve the problems of relying on the selection of enzyme cutting sites, high cost, and great difficulty, and achieve good industrial application prospects, high efficiency of homologous recombination, and shorten construction time Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0037] The experimental scheme design of this embodiment is as follows:
[0038] In Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742 (purchased from EUROSCARF, No. Y10000, strain information: MATα; his3△1; leu2△0; lys2△0; ura3△0) expressing three genes ads from the artemisinin synthesis pathway of Artemisia annua (GenBank: DQ241826), amo (GenBank: DQ872632) and cpr (GenBank: DQ984181), optimized by yeast preference codons, and simultaneously expressing the ble gene (Zeocin resistance gene) as a selection marker, and selecting the yeast chromosome δ site for integration site, the integration and assembly sequence of each gene module on the chromosome is as follows: figure 1 shown. The promoters and genes are numbered respectively, as shown in Table 1.
[0039] Table 1. Promoters and gene numbers
[0040] promoter number promoter name gene number gene name A TEF1p 1 ads
[0041] B TPI1p 2 amo C PGK1p 3 cpr
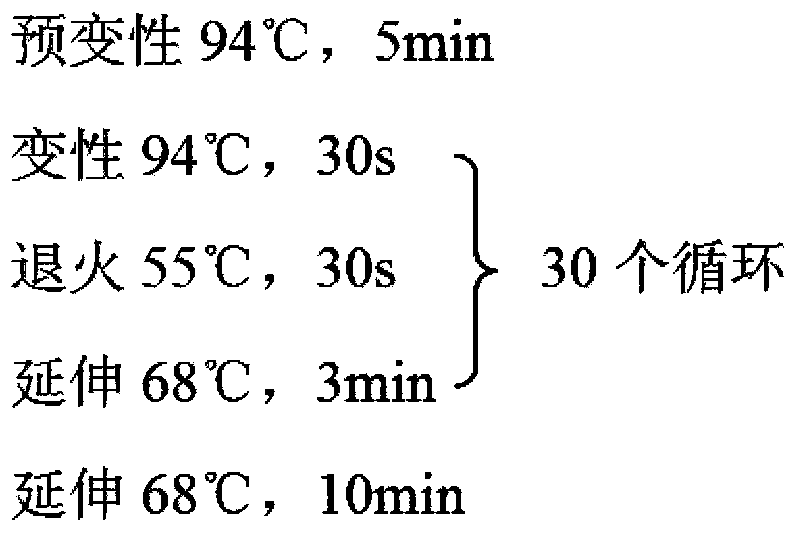
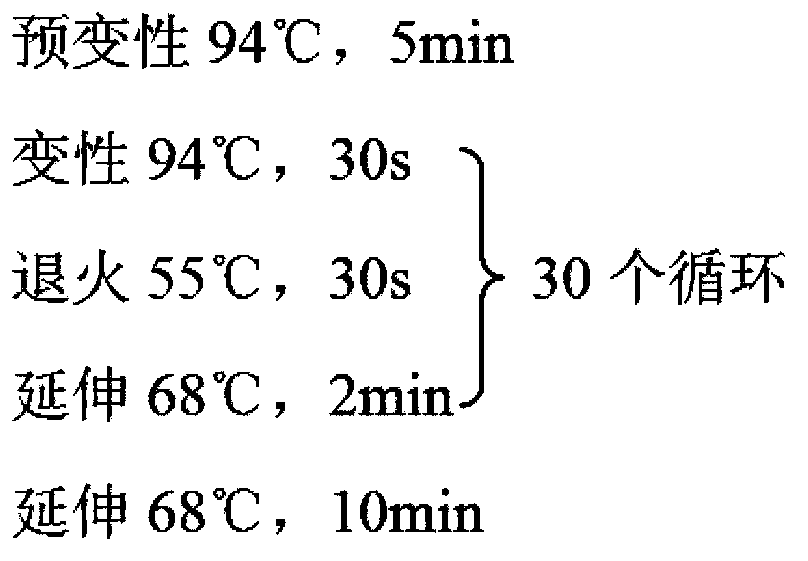
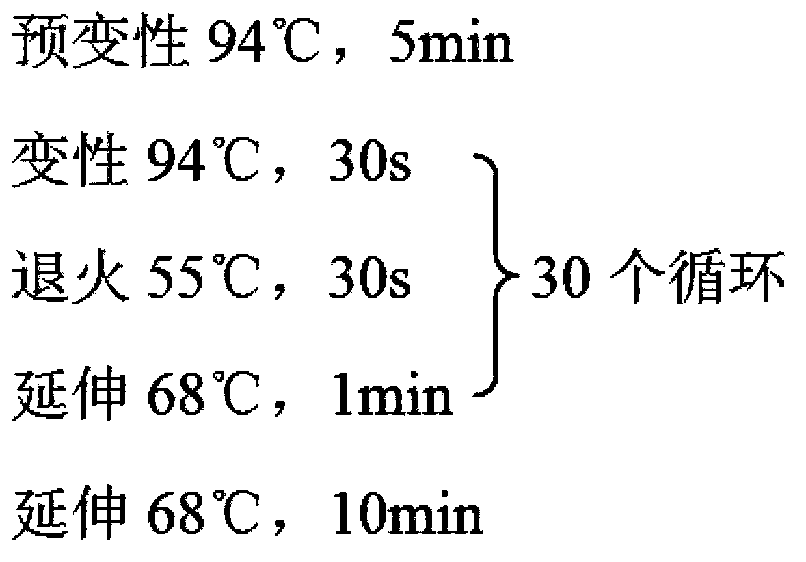
[0042]The following gene ex...
Embodiment 2
[0051] 2.1. Construction of plasmids pLYADS, pLYAMO and pLYCPR
[0052] References (Yang RY, Feng LL, Yang XQ, Yin LL, Xu XL, Zeng QP. Quantitative transcript profiling reveals down-regulation of A sterol pathway relevant gene and overexpression of artemisinin biogenetic genes in transgenic Artemisia annua plants. Planta medica, 2008Oct ;74(12):1510-6.Epub2008Sep24.) Ads, amo and cpr genes were obtained, optimized and synthesized by yeast preferred codons (SEQ ID No: 29-31), and inserted into pMD19-T Simple Vector (purchased from Takara company), the plasmids pLYADS, pLYAMO and pLYCPR were obtained and transformed into E.coli strain DH5α for preservation.
[0053] 2.2. Extraction of template DNA
[0054] The extraction method of Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4742 chromosomal DNA is as follows: pick a plump single colony and connect it to a 3ml YPD liquid medium test tube (20ml shake flask), 30°C, 220rpm / min, cultivate overnight for about 18h, collect the bacterial liquid, and us...
Embodiment 3
[0078] 3.1. Fermentation
[0079] The seed cultivation method is as follows:
[0080] Pick a single colony of the positive clone obtained from the screening in Example 2 from the culture plate, insert it into 25ml of YPD medium (250ml shake flask), culture at 30°C, 220rpm / min, for 48h.
[0081] The fermentation culture method is as follows:
[0082] The seed liquid was added to 25ml YPD medium (250ml shake flask) according to the inoculation ratio of 4%, and cultured at 30°C and 220rpm / min for 120h.
[0083] 3.2. Extraction of artemisinic acid
[0084] The extraction method of artemisinic acid is as follows:
[0085] Take an appropriate amount of fermentation broth, adjust the pH to 8.5-9.0, dilute with methanol to the required multiple (such as 50 times), transfer the mixed solution into a centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 4000r / min for 30min, and collect the supernatant.
[0086] 3.3. Detection of artemisinic acid
[0087] Refer to the literature method (Zhang Dong et al.,...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com