Method for multicopy integration of target gene to saccharomyces cerevisiae genome
A Saccharomyces cerevisiae, multi-copy technology, applied in the field of microorganisms, can solve the problems of difficult to achieve gene integration, affect the target sequence, and cumbersome steps, and achieve the effects of reducing the number of PCR times, short time consumption, and simple operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment
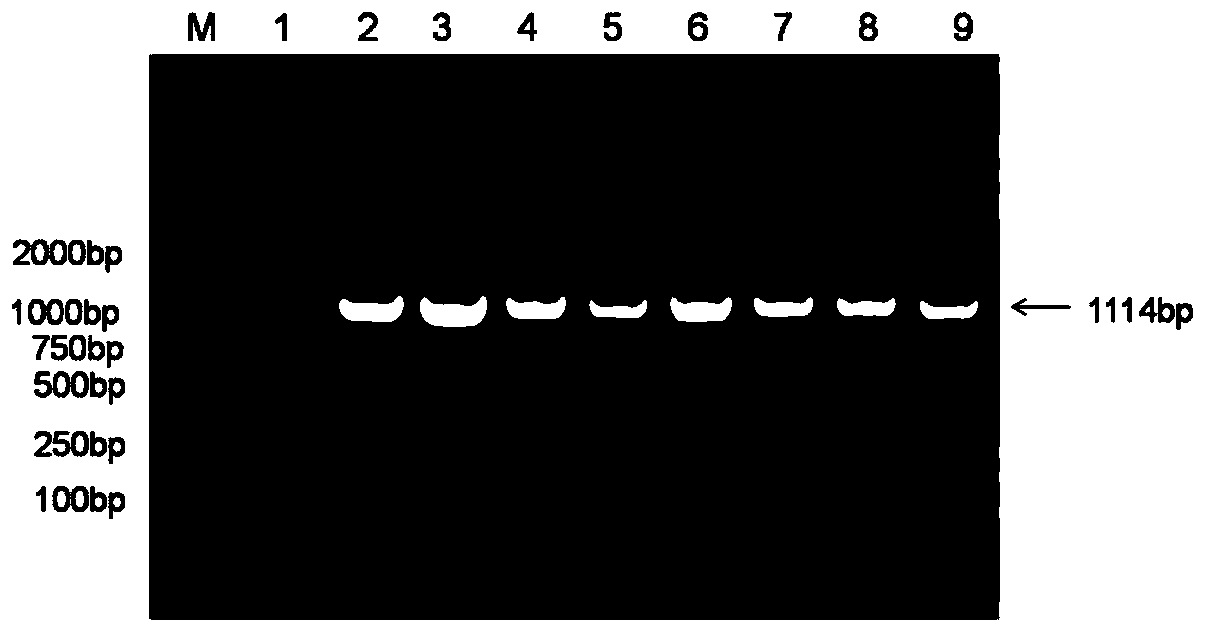
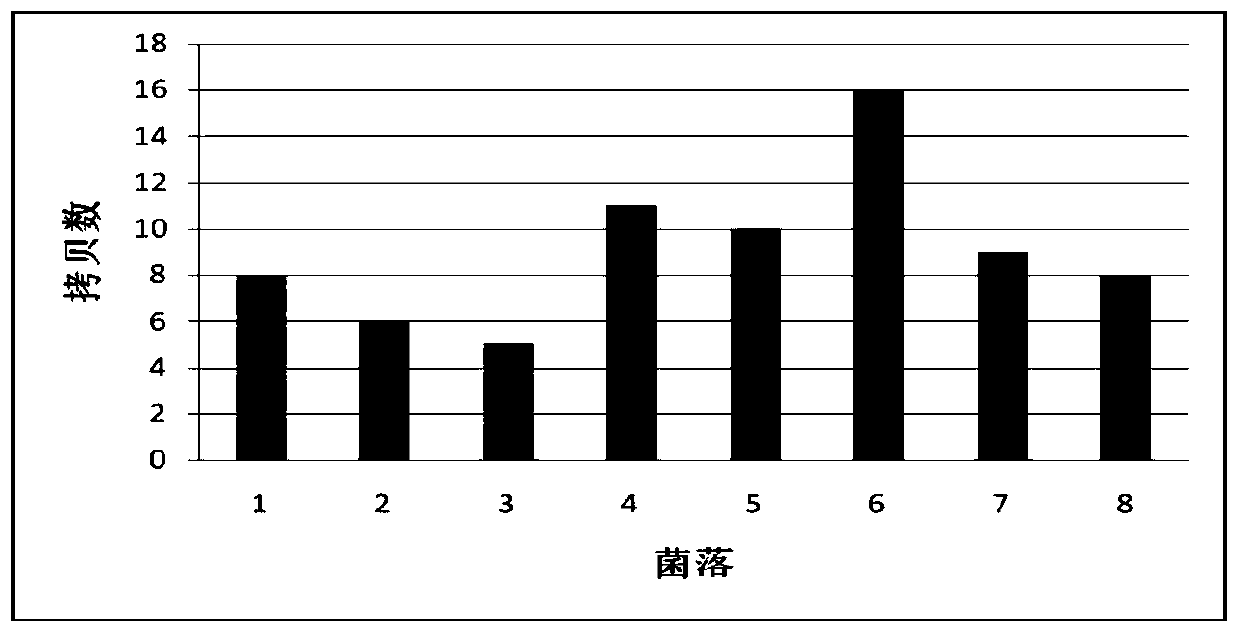
[0034] Example Green Fluorescent Protein Gene (gfp) Multi-copy Integration at Saccharomyces cerevisiae S288c Strain rDNA Site
[0035] 1. Expression of Cas9 nuclease in Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain
[0036]Transform the Cas9 nuclease expression vector pHCas9 into the Saccharomyces cerevisiae strain by the lithium acetate method (other methods such as electroporation are also available), screen the transformants on a YPD solid plate containing noursstatin (100 μg / mL), and extract the transformants The genome was verified by PCR, and the PCR products were purified and sent for sequencing, and the strains with correct sequencing results were cultured in YPD medium containing noerscencin (100 μg / mL) for later use.
[0037] 2. Select the target sequence in the non-transcribed region of rDNA repeat unit NTS2 and extract the vector plasmid for corresponding transcribed gRNA
[0038] The selected target sequence of the present invention is located in the NTS2 non-transcribed regio...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com