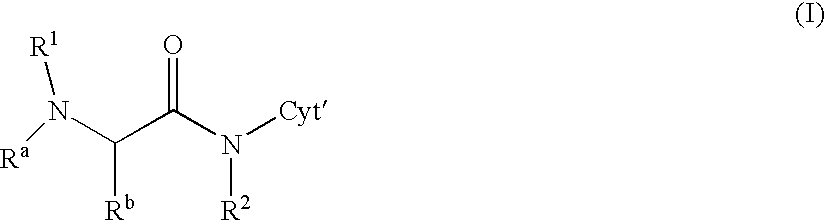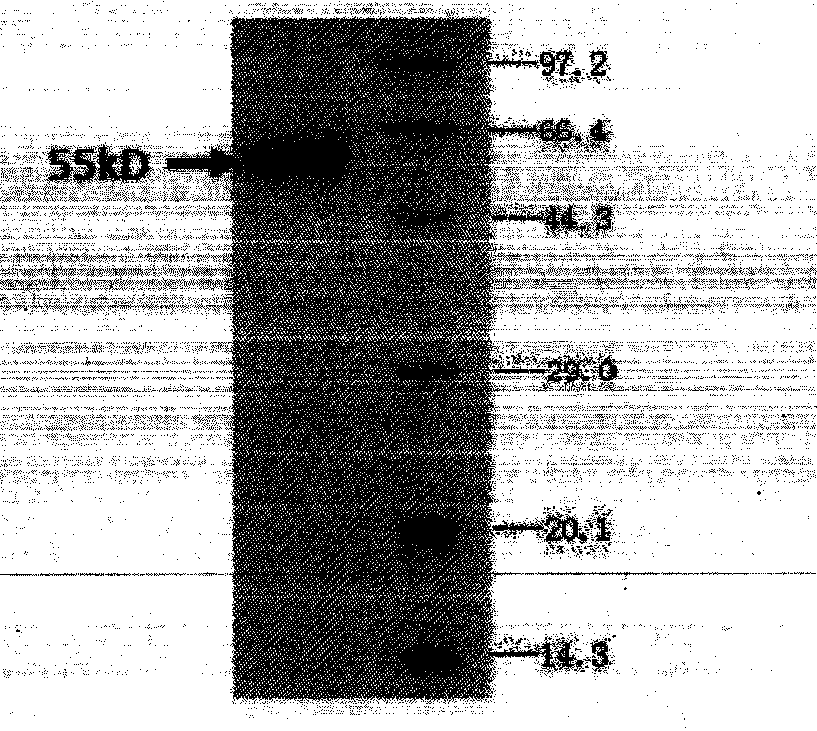Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
4092 results about "Protide" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
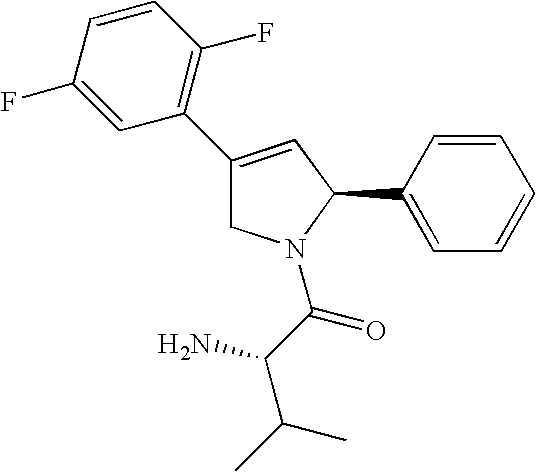
The ProTide technology is a prodrug approach used in molecular biology and drug design. It is designed to deliver nucleotide analogues (as monophosphate) into the cell (ProTide: PROdrug + nucleoTIDE). It was discovered by Chris McGuigan (School of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences, Cardiff University) in the early 1990s.
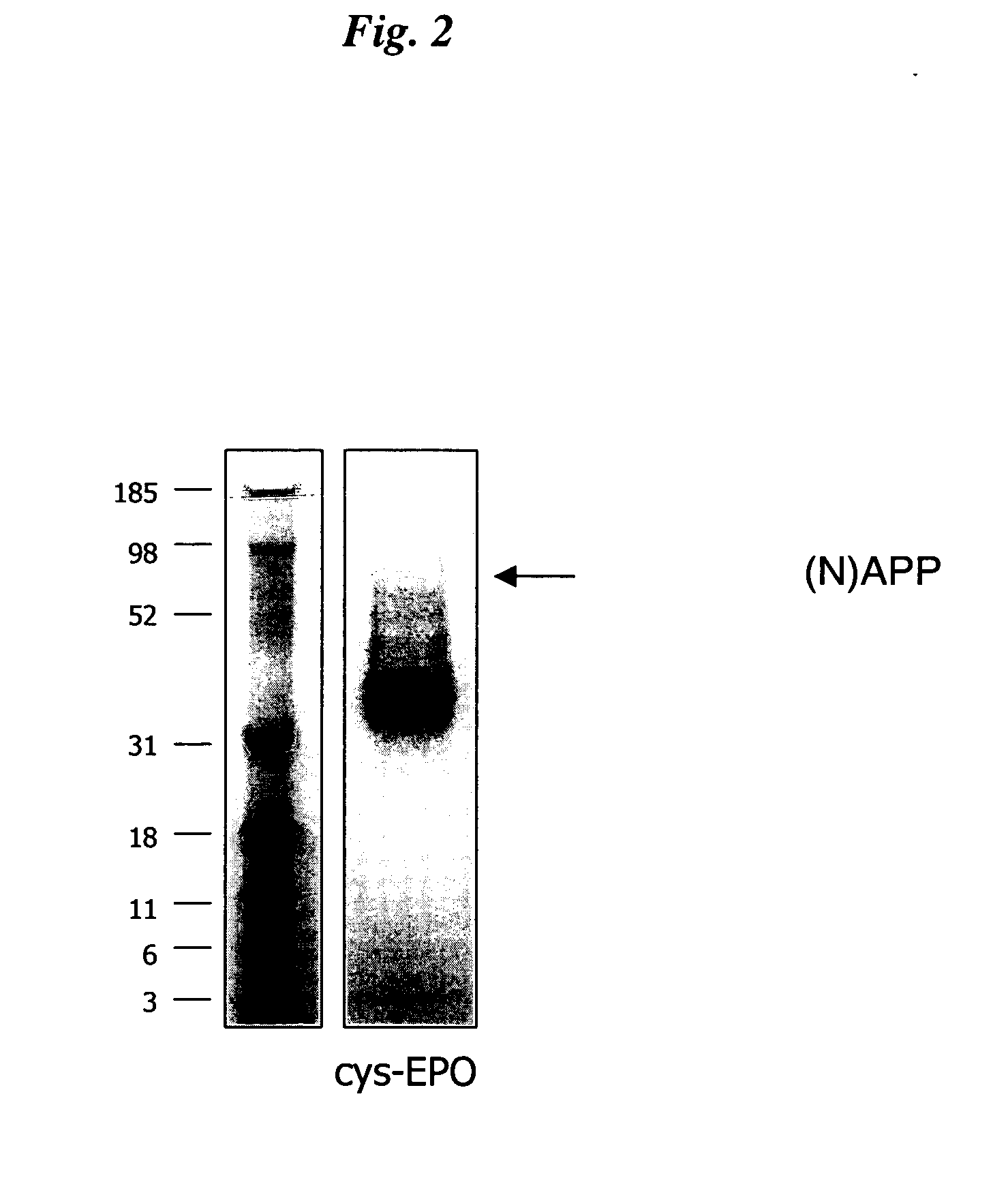
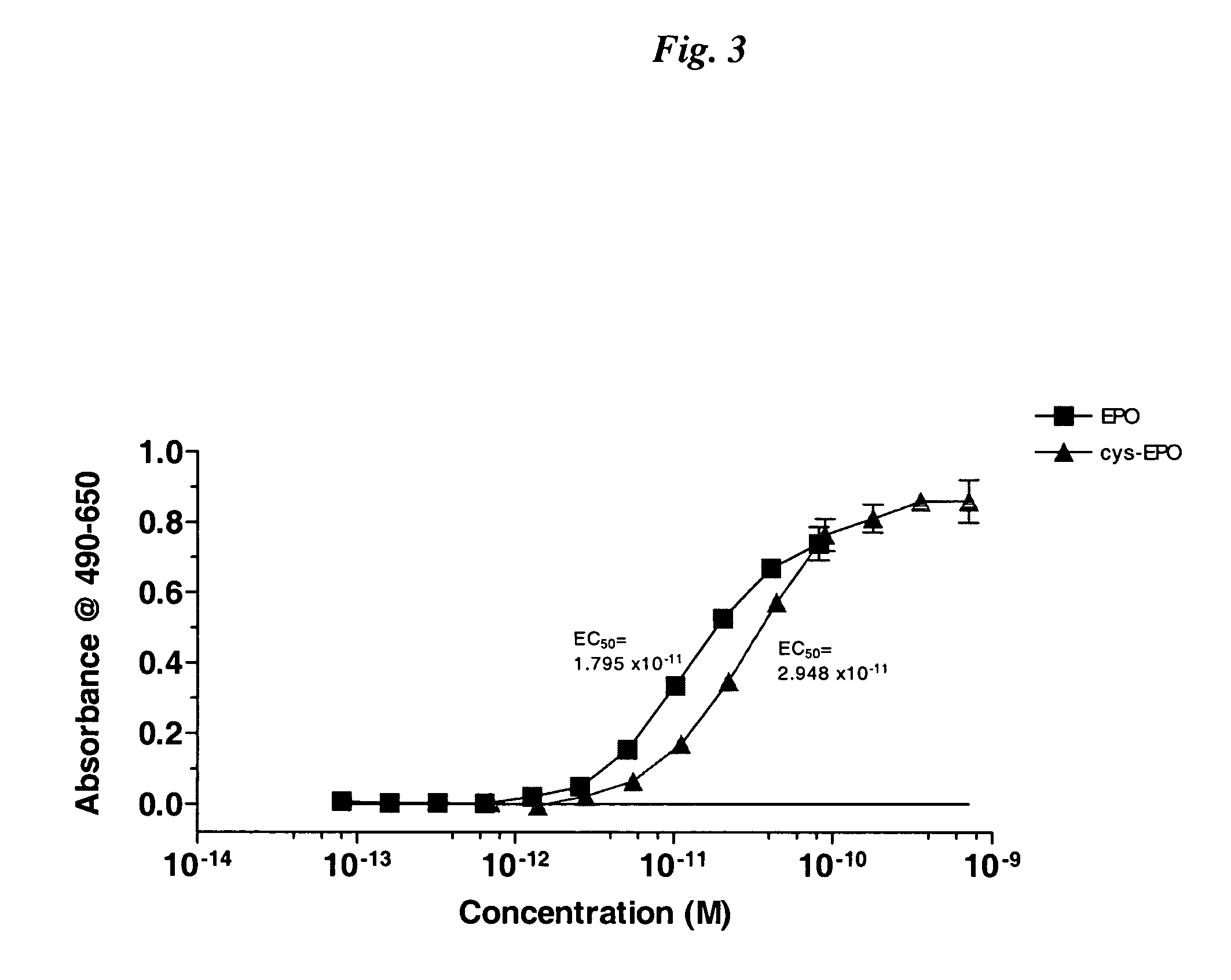
Novel recombinant proteins with N-terminal free thiol
InactiveUS20050170457A1Extended half-lifeIncreases circulating serum half-lifePeptide/protein ingredientsTissue cultureCysteine thiolateHalf-life
The present invention relates to novel modified proteins having N-terminal free thiols that can be produced by recombinant methods and are ready for further chemical derivatization. In particular, the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds having altered biochemical, physiochemical and pharmacokinetic properties. More particularly, one embodiment of the invention relates to erythropoietin conjugate compounds of the formula: (M)n-X-A-cys-EPO (I) where EPO is an erythropoeitin moiety selected from erythropoietin or an erythropoietin variant having at least one amino acid different from the wild-type human EPO, or any pharmaceutical acceptable derivatives thereof having biological properties of causing bone marrow cells to increase production of red blood cells; cys represents the amino acid cysteine and occurs at position −1 relative to the amino acid sequence of the erythropoietin moiety; A indicates the structure of the residual moiety used to chemically attach X to the thiol group of −1Cys; X is a water soluble polymer such as a polyalkylene glycol or other polymer; M is an organic molecule (including peptides and proteins) that increases the circulating half-life of the construct; and N is an integer from 0 to 15.
Owner:CENTOCOR
Methods for drug target screening
InactiveUS6165709AMicrobiological testing/measurementRecombinant DNA-technologyProtein targetProtein activity
The present invention provides methods for identifying targets of a drug in a cell by comparing (i) the effects of the drug on a wild-type cell, (ii) the effects on a wild-type cell of modifications to a putative target of the drug, and (iii) the effects of the drug on a wild-type cell which has had the putative target modified of the drug. In various embodiments, the effects on the cell can be determined by measuring gene expression, protein abundances, protein activities, or a combination of such measurements. In various embodiments, modifications to a putative target in the cell can be made by modifications to the genes encoding the target, modification to abundances of RNAs encoding the target, modifications to abundances of target proteins, or modifications to activities of the target proteins. The present invention also provides methods for drug development based on the methods for identifying drug targets.
Owner:FRED HUTCHINSON CANCER RES CENT
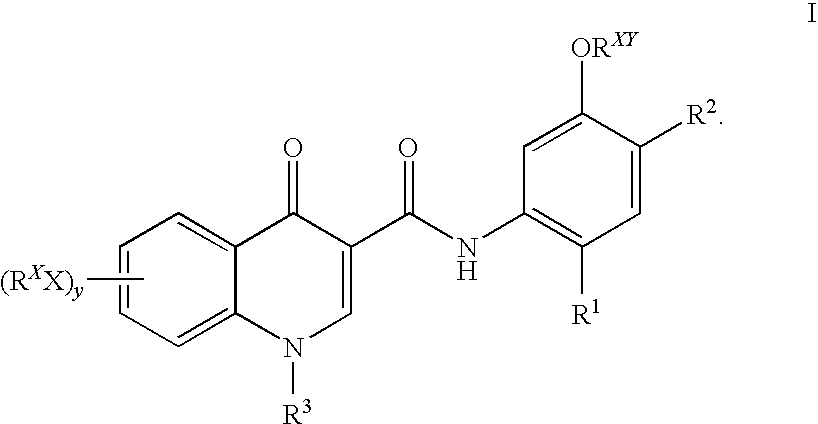
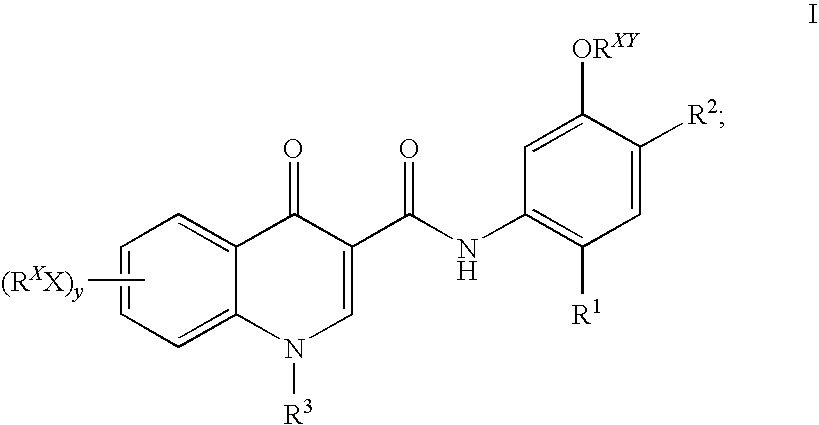
Prodrugs of modulators of ABC transporters
InactiveUS20090105272A1Good water solubilityImprove bioavailabilityAntibacterial agentsCompound screeningDiseaseStereochemistry
The present invention relates to prodrugs of modulators of ABC transporters, particularly, CFTR modulators, compositions thereof, and methods therewith. The present invention also relates to methods of treating ABC transporter mediated diseases using such modulators.
Owner:VERTEX PHARMA INC
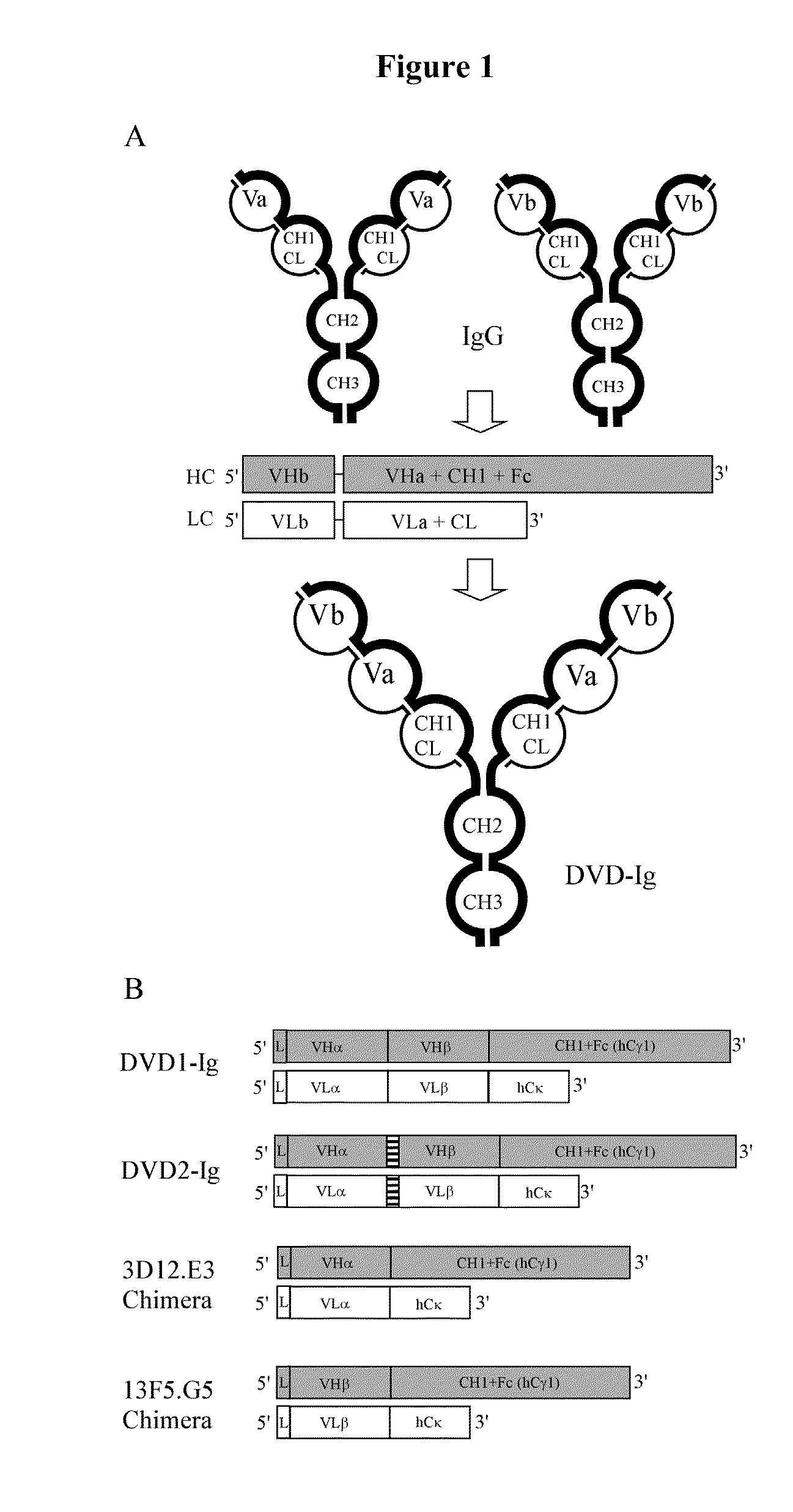
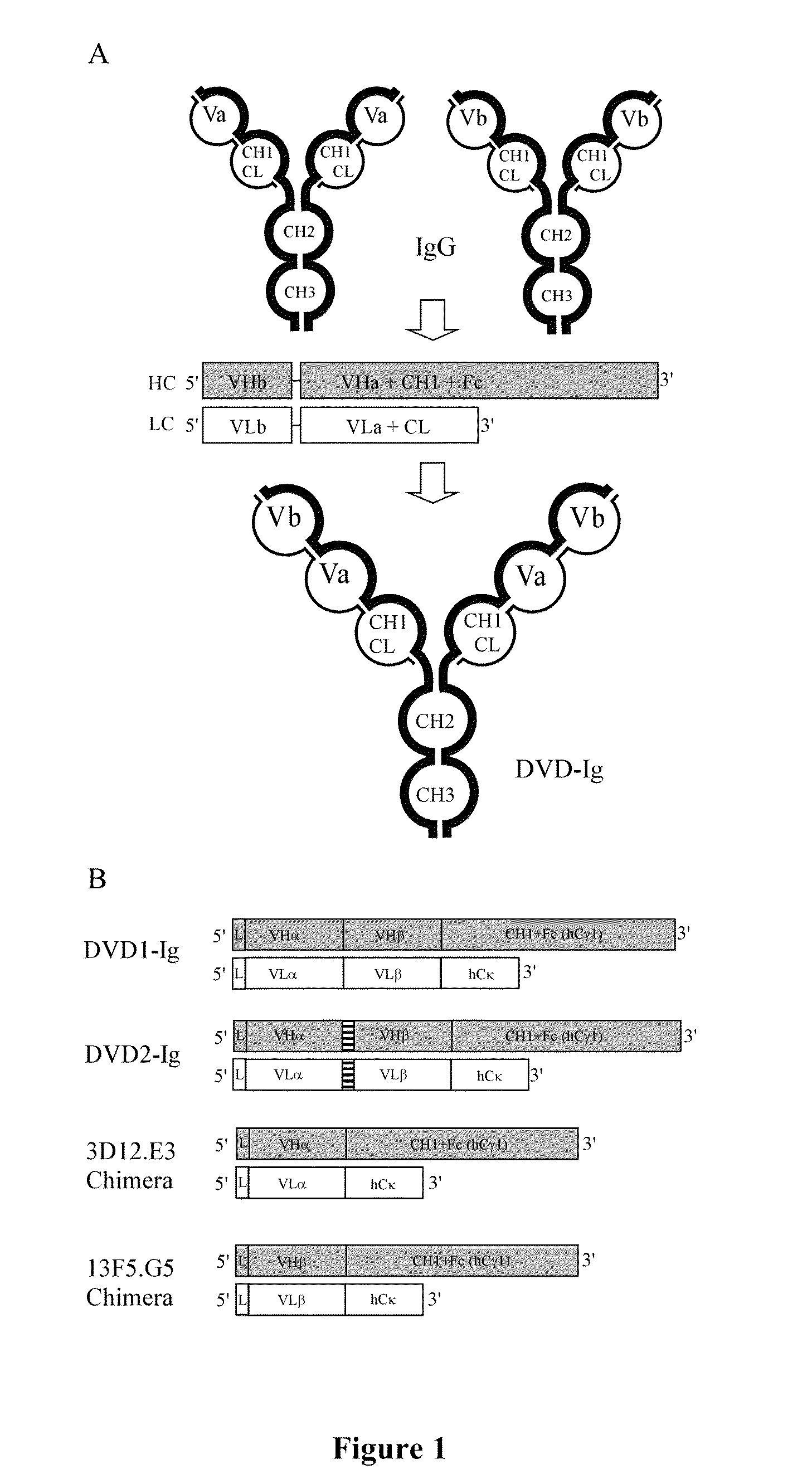
Dual Variable Domain Immunoglobulins and Uses Thereof
The present invention relates to engineered multivalent and multispecific binding proteins, methods of making, and specifically to their uses in the prevention, diagnosis, and / or treatment of disease.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
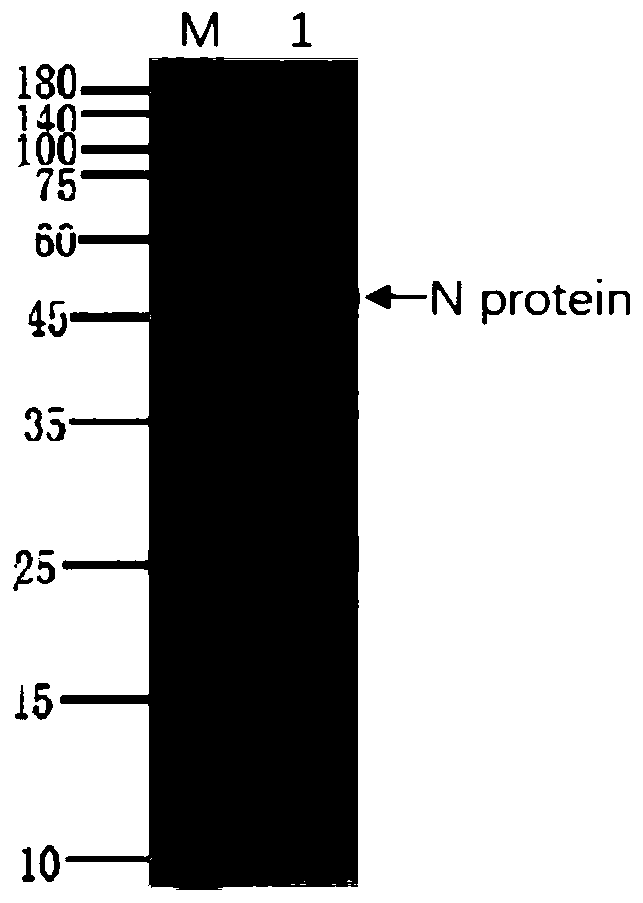
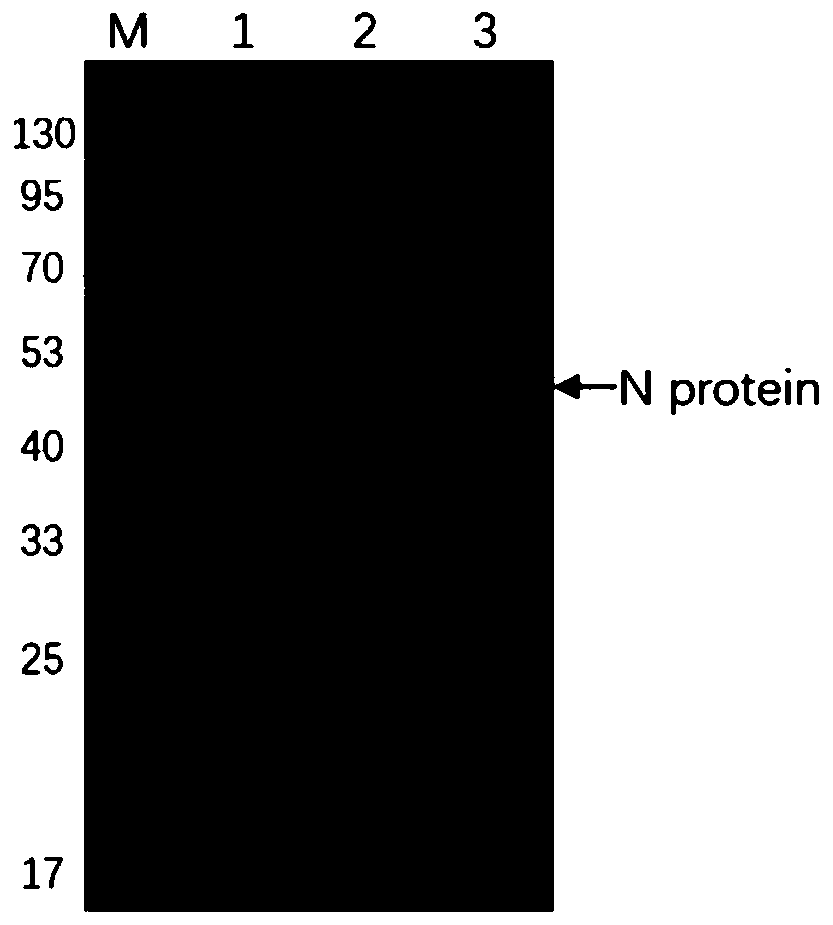
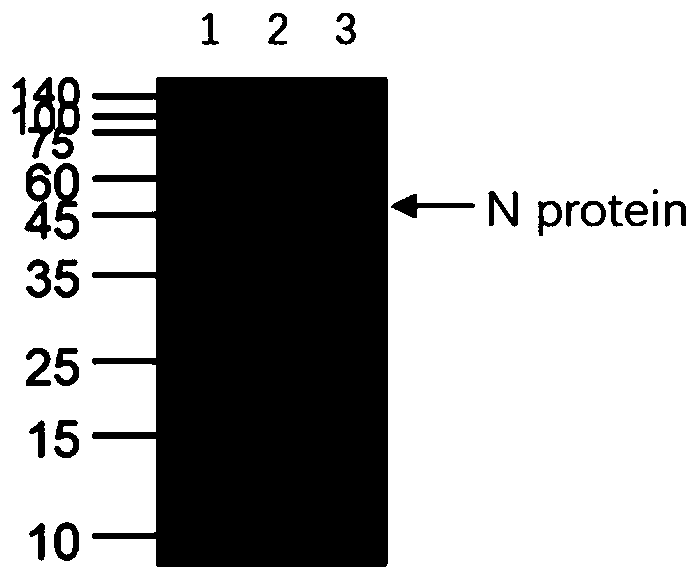
Human SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody and preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN111153991AHigh affinityStrong specificitySsRNA viruses positive-senseVirus peptidesBALB/cMonoclonal antibody agent
The invention discloses a human SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody. The preparation method of the human SARS-CoV-2 monoclonal antibody comprises the steps: adopting SARS-CoV Nucleocapsid recombinant protein as immunogen, immunizing BALB / c mice, performing fusion and subcloning on spleen cells and myeloma cells of mice, then performing a large amount of repeated screening and domestication of cell lines through commercialized products SARS-CoV-2 Nucleocapsid and MERS Nucleocapsid so as to obtain a hybridoma cell line capable of secreting the SARS-CoV-2-resistant N monoclonal antibody with high affinity and high specificity finally and successfully, and finally performing ascites preparation and purification so as to obtain the monoclonal antibody, wherein the amino acid sequence of the SARS-CoVNucleocapsid recombinant protein is shown in SEQ ID No. 1. The invention also discloses application of the monoclonal antibody in preparation of SARS-CoV-2 virus detection products and preparation ofdrugs for inhibiting the SARS-CoV-2 viruses. The monoclonal antibody can be used for detecting the SARS-CoV-2 in human throat swabs / pulmonary secretions and other samples by using a double-antibody sandwich method, and can be applied to diagnosis and prevention and control of SARS-CoV-2 virus infection and scientific researches of viruses and other study.
Owner:BEIJING BIOSYNTHESIS BIOTECH
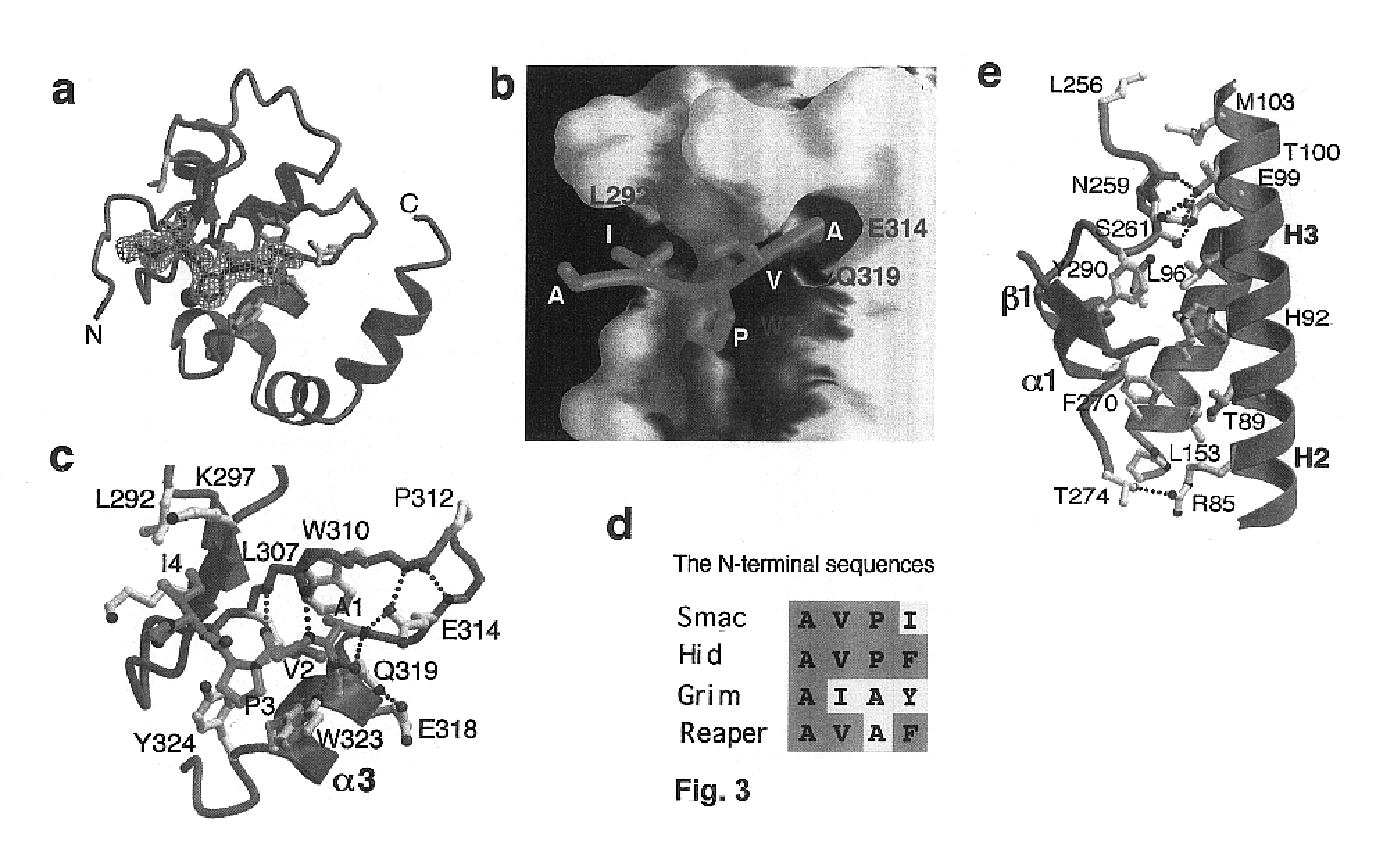
Compositions and method for regulating apoptosis
ActiveUS6992063B2Suppress programmed cell deathRelieve suppressionTripeptide ingredientsPeptide preparation methodsInhibitor of apoptosisApoptosis
Peptides and peptidomimetics capable of modulating apoptosis through their interaction with cellular IAPs (inhibitor of apoptosis proteins) are disclosed. The peptides and mimetics are based on the N-terminal tetrapeptide of IAP-binding proteins, such as Smac / DIABLO, Hid, Grim and Reaper, which interact with a specific surface groove of IAP. Also disclosed are methods of using these peptides and peptidomimetics for therapeutic purposes and for rational drug design.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV
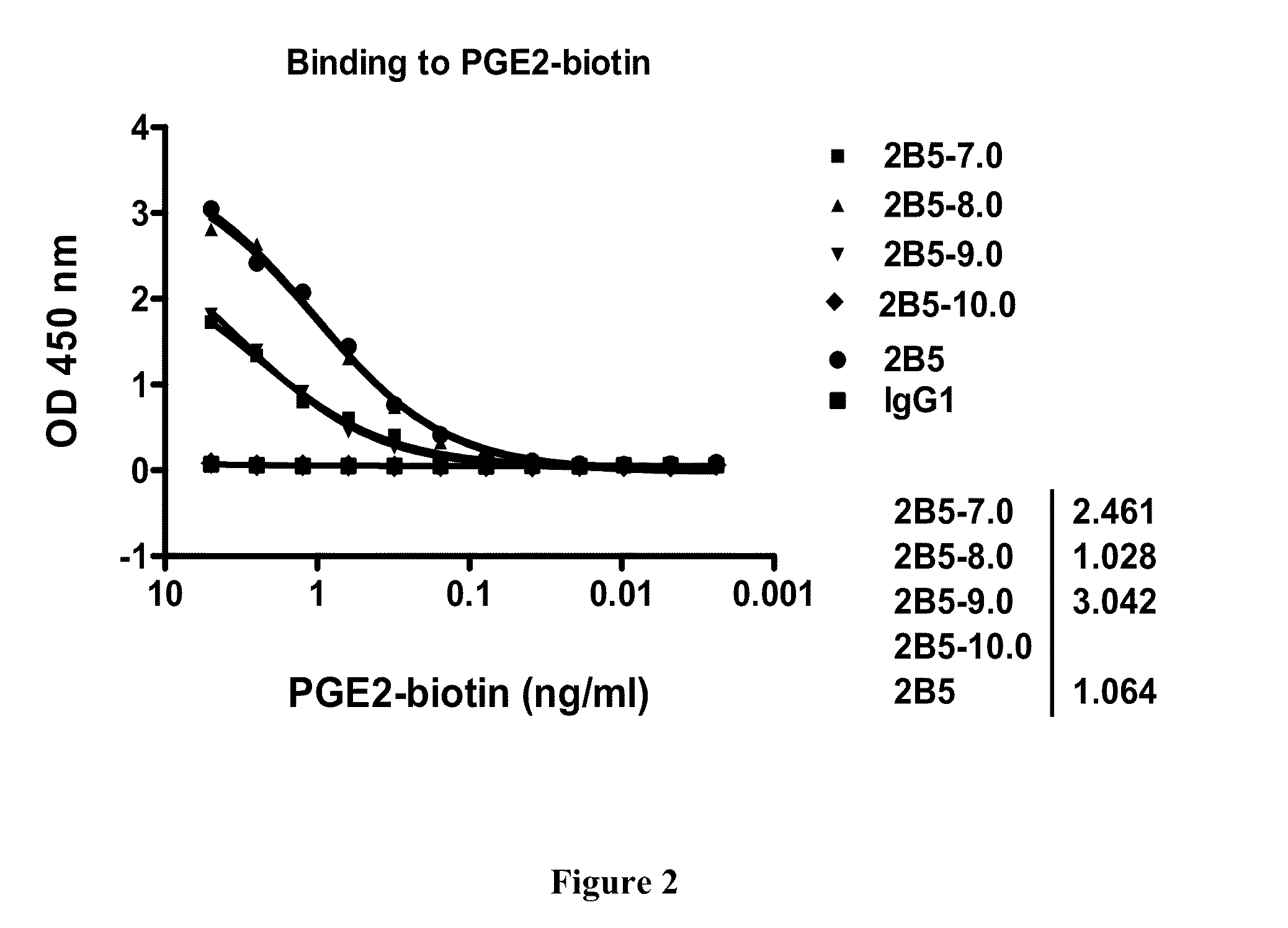
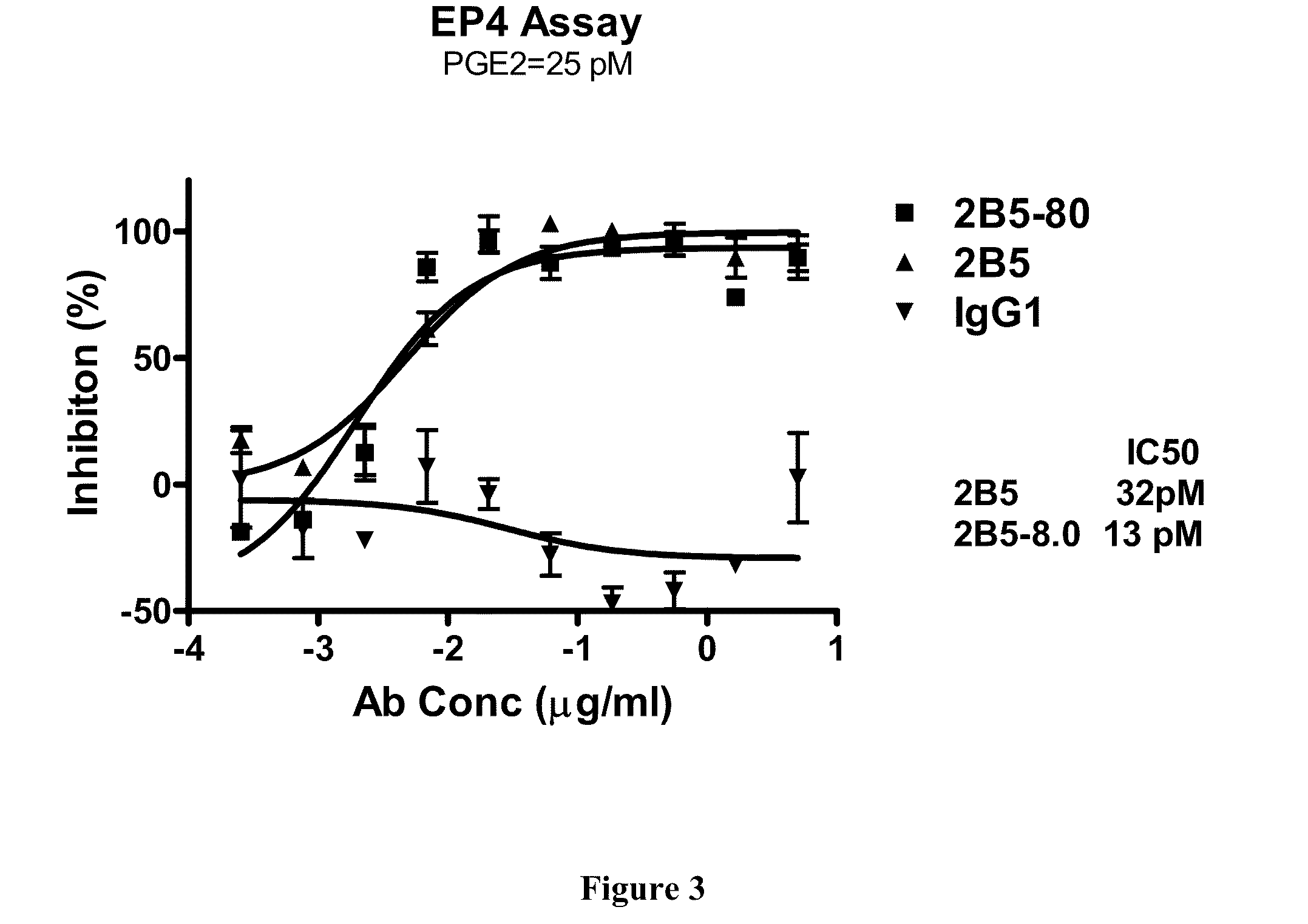
Prostaglandin E2 dual variable domain immunoglobulins and uses thereof
The present invention relates to engineered multivalent and multispecific binding proteins, methods of making, and specifically to their uses in the prevention, diagnosis, and / or treatment of disease.
Owner:ABBVIE INC
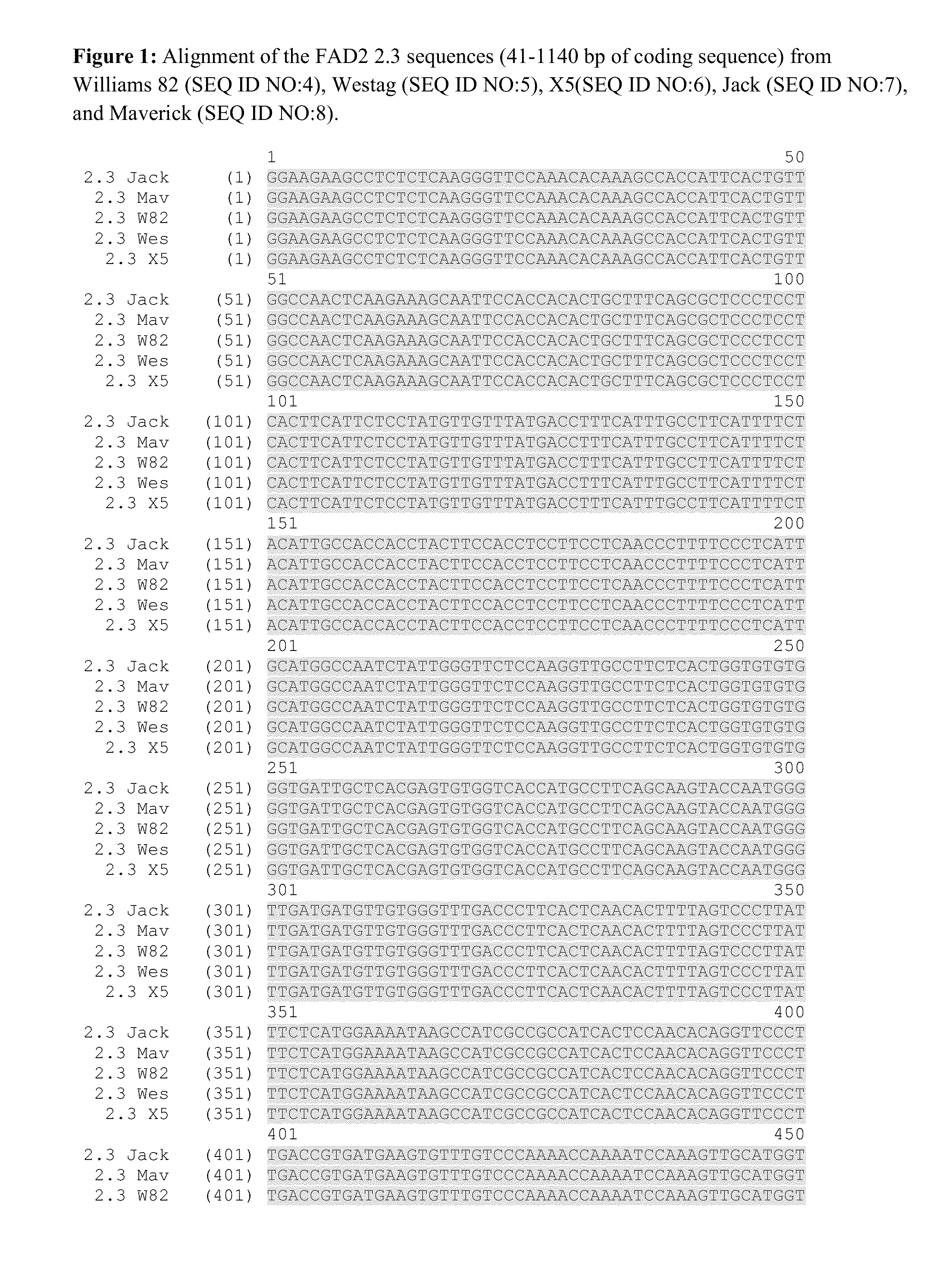
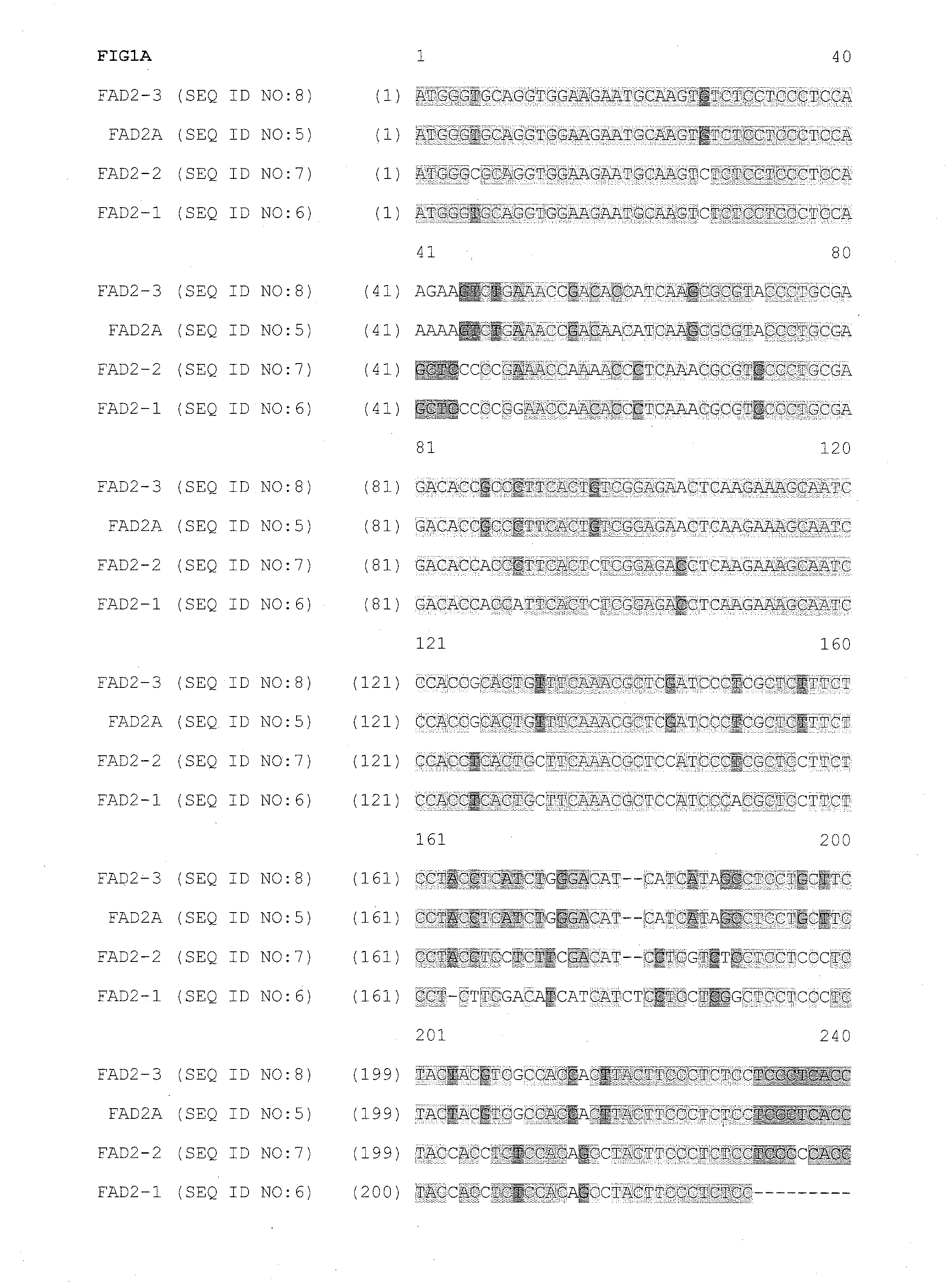
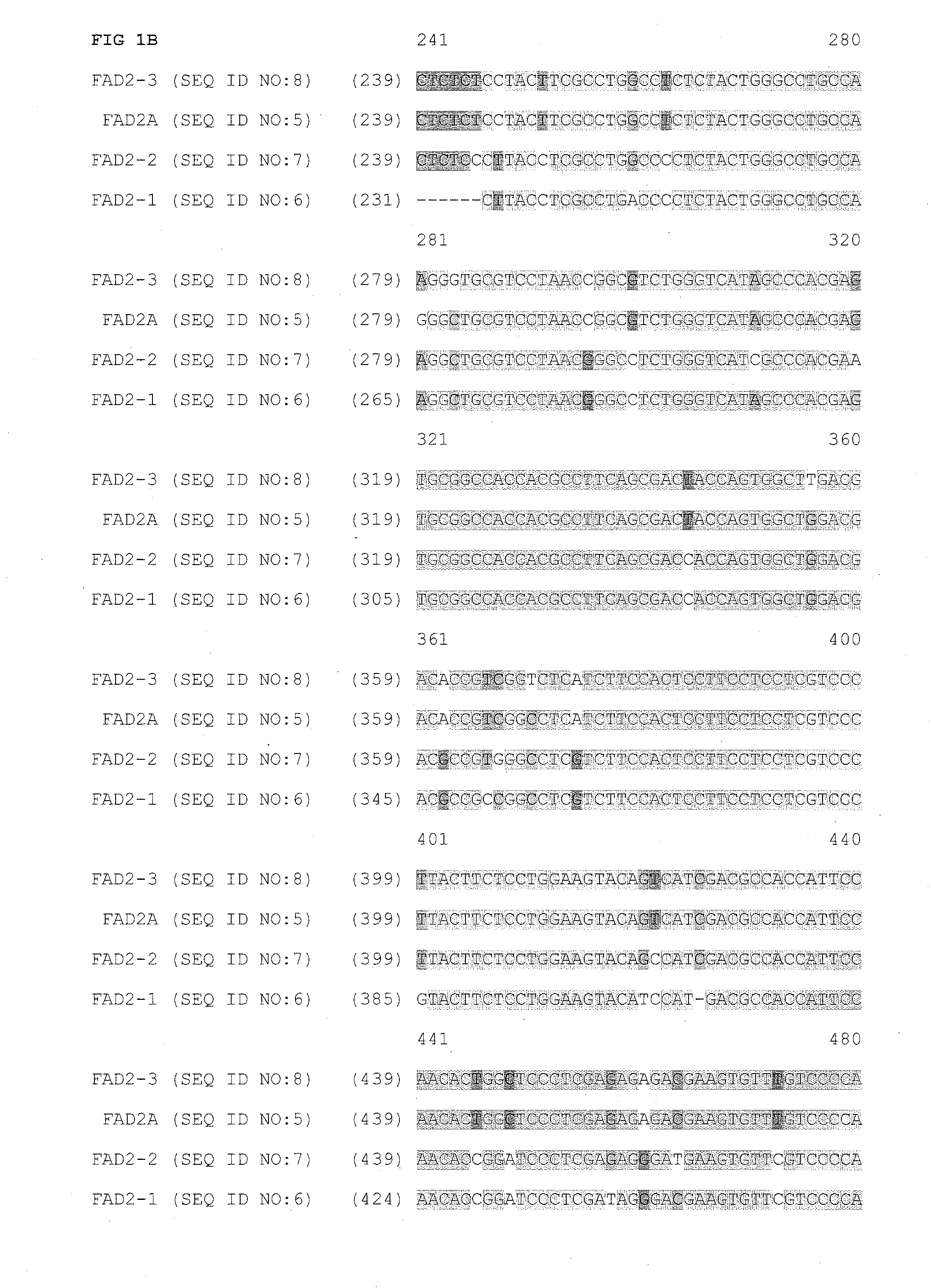
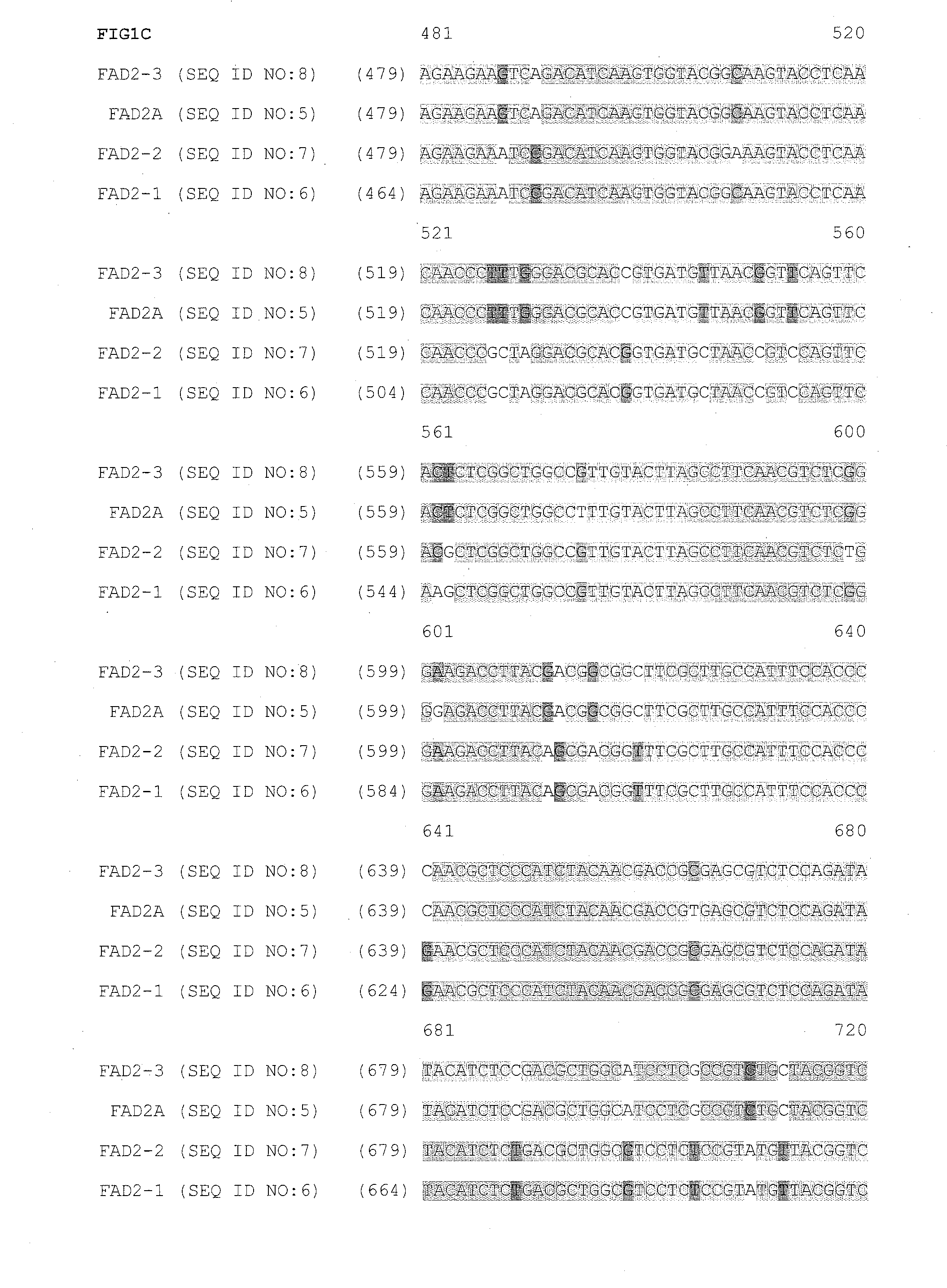
Fad2 performance loci and corresponding target site specific binding proteins capable of inducing targeted breaks
ActiveUS20140090116A1Minimal adverse impactFusion with DNA-binding domainHydrolasesA-siteBioinformatics
Methods and compositions for gene disruption, gene editing or gene stacking within a FAD2 loci by cleaving, in a site directed manner, a location in a FAD2 gene in a soybean cell, to generate a break in the FAD2 gene and then optionally integrating into the break a nucleic acid molecule of interest is disclosed.
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC +1
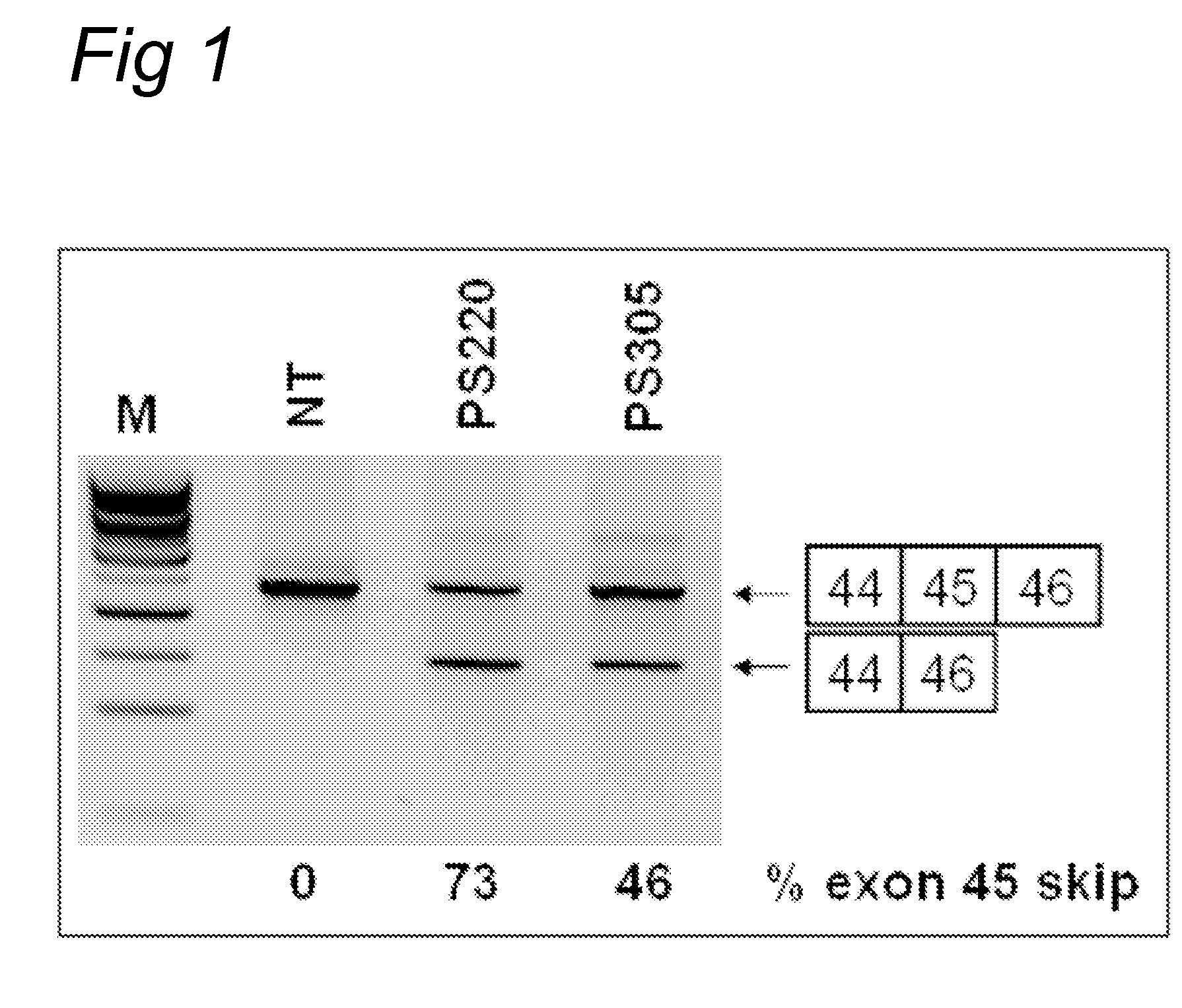
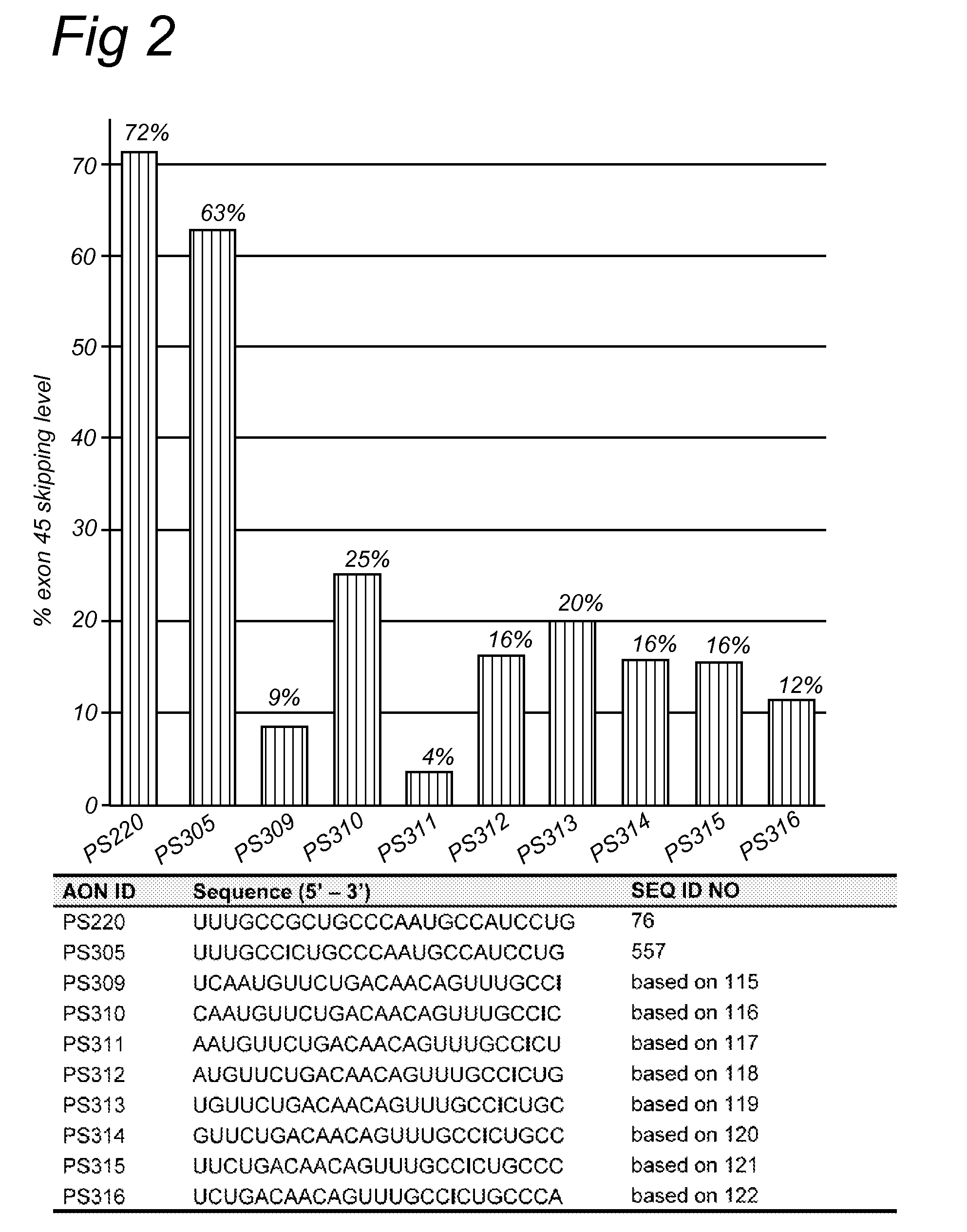
Antisense oligonucleotides for inducing exon skipping and methods of use thereof
An antisense molecule capable of binding to a selected target site to induce exon skipping in the dystrophin gene, as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 to 202.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Antisense oligonucleotides for inducing exon skipping and methods of use thereof
An antisense molecule capable of binding to a selected target site to induce exon skipping in the dystrophin gene, as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 to 202.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Synthetic lethal screen using RNA interference
InactiveUS20050181385A1Modulate activityFew or no effectsSugar derivativesMicrobiological testing/measurementDiseaseDNA damage
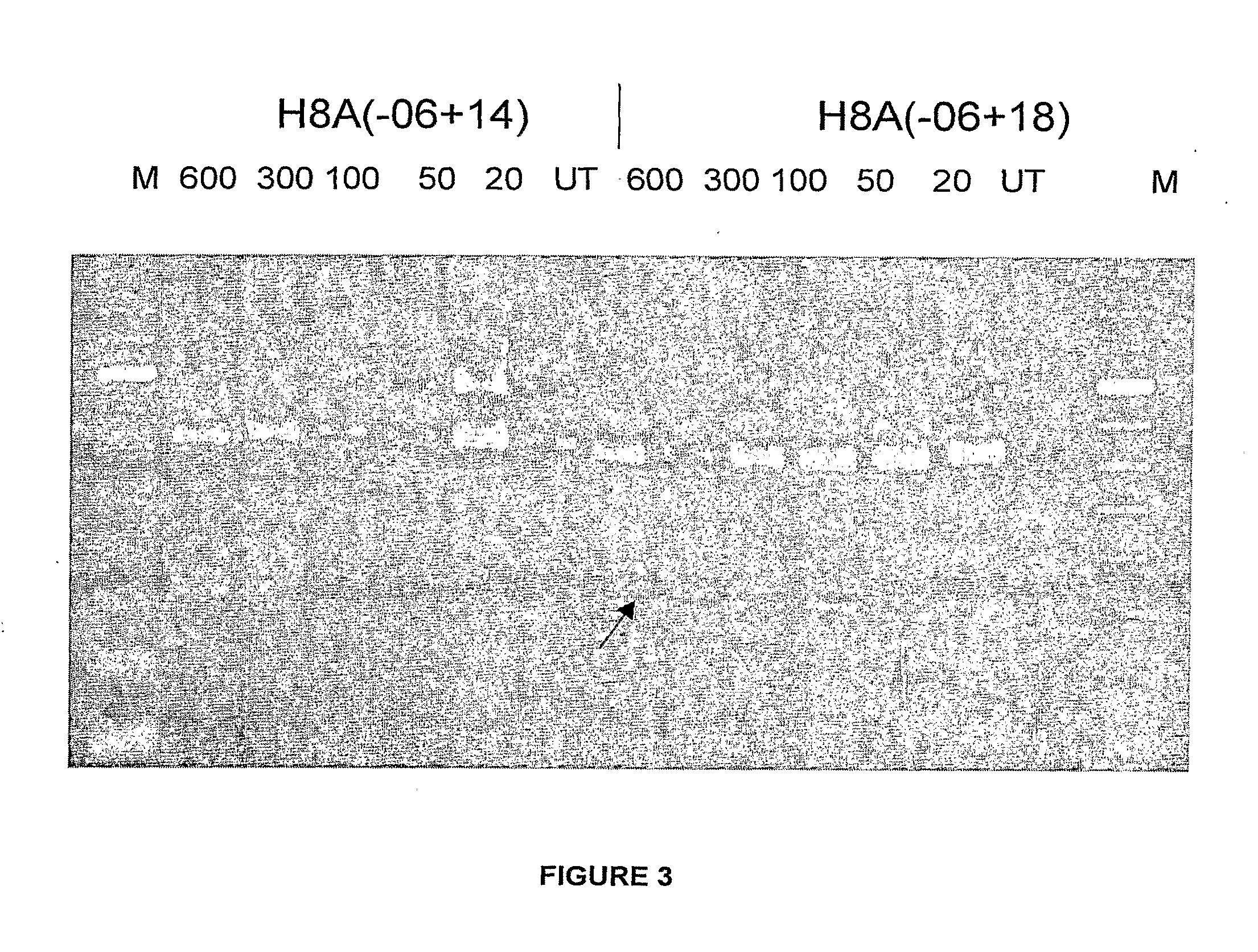
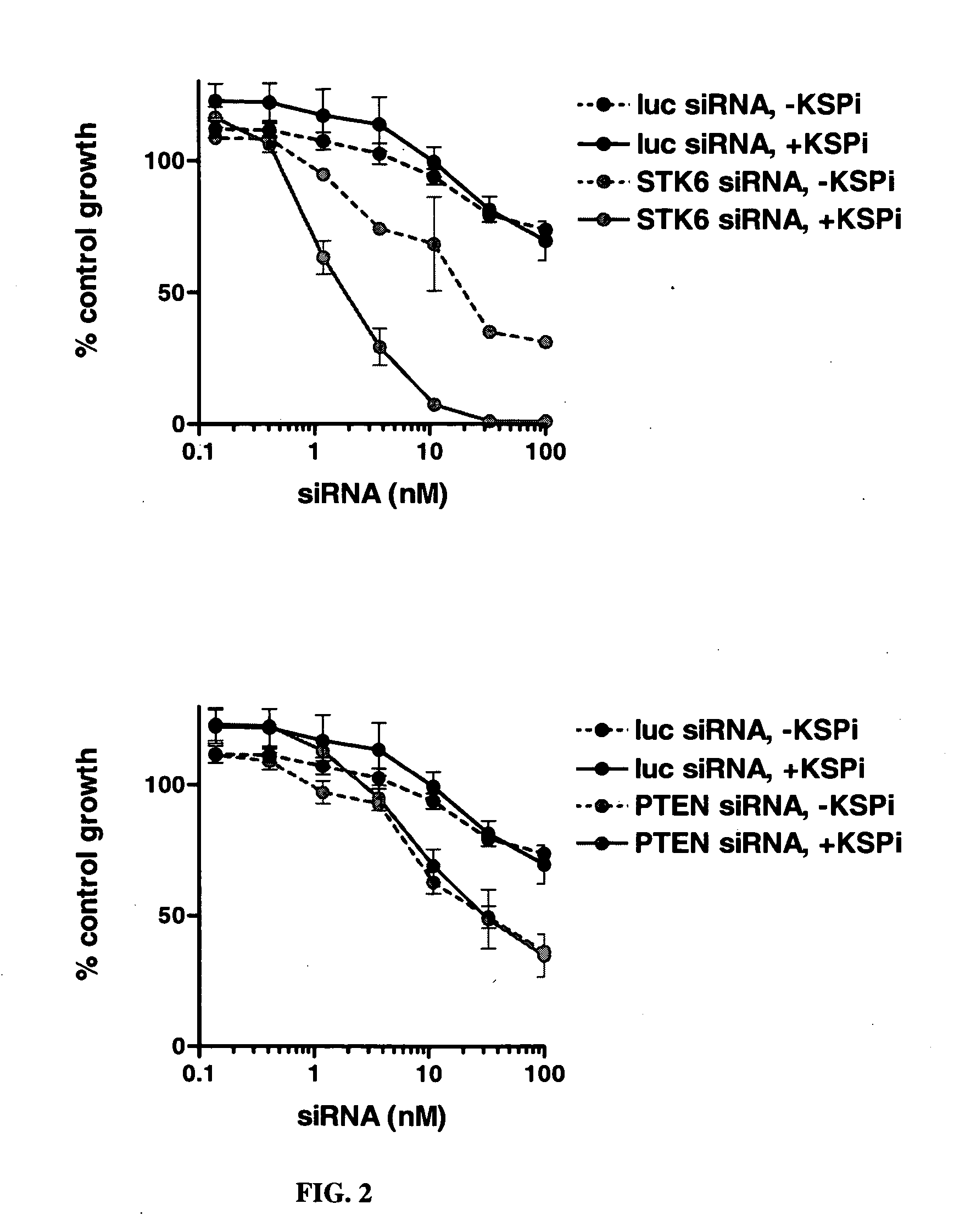
The invention provides a method for identifying one or more genes in a cell of a cell type which interact with, e.g., modulate the effect of, an agent, e.g., a drug. For example, an identified gene may confer resistance or sensitivity to a drug, i.e., reduces or enhances the effect of the drug. The invention also provides STK6 and TPX2 as a gene that exhibits synthetic lethal interactions with KSP encoding a kinesin-like motor protein, and methods and compositions for treatment of diseases, e.g., cancers, by modulating the expression of STK6 or TPX2 gene and / or the activity of STK6 or TPX2 gene product. The invention also provides genes involved in cellular response to DNA damage, and their therapeutic uses.
Owner:MERCK SHARP & DOHME CORP
Antisense oligonucleotides for inducing exon skipping and methods of use thereof
An antisense molecule capable of binding to a selected target site to induce exon skipping in the dystrophin gene, as set forth in SEQ ID NO: 1 to 202.
Owner:UNIV OF WESTERN AUSTRALIA
Fad2 performance loci and corresponding target site specific binding proteins capable of inducing targeted breaks
Owner:SANGAMO BIOSCIENCES INC +1
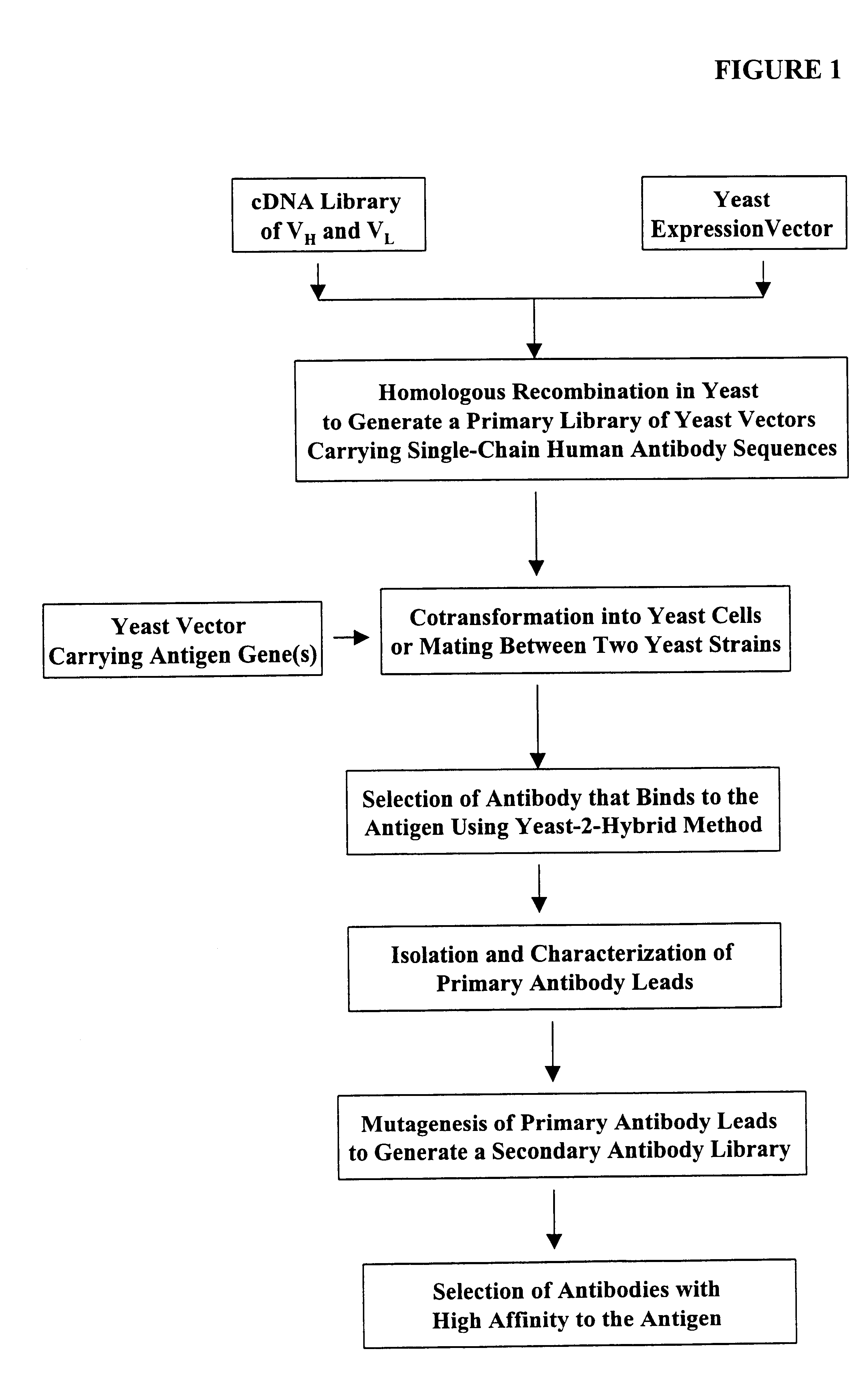
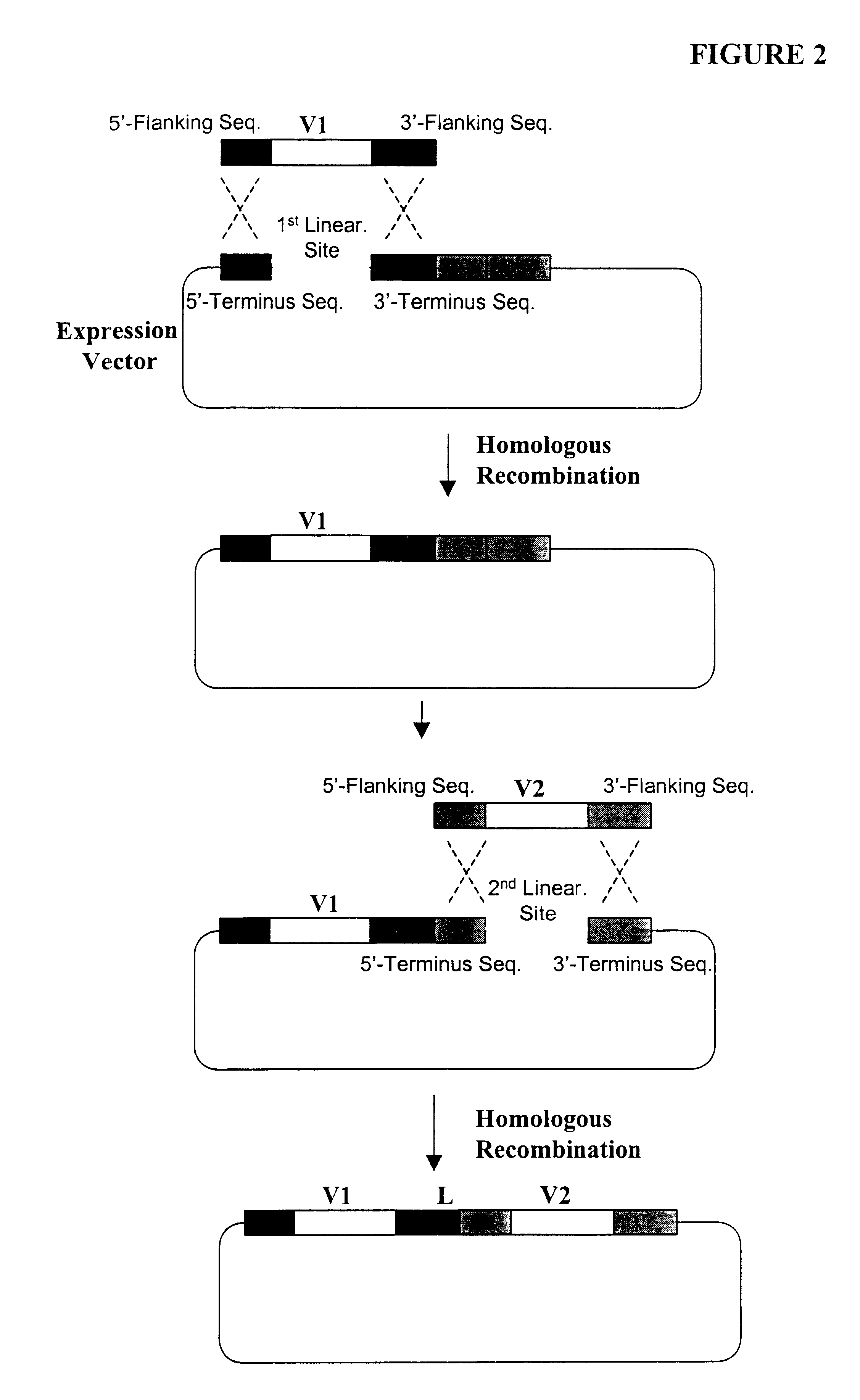
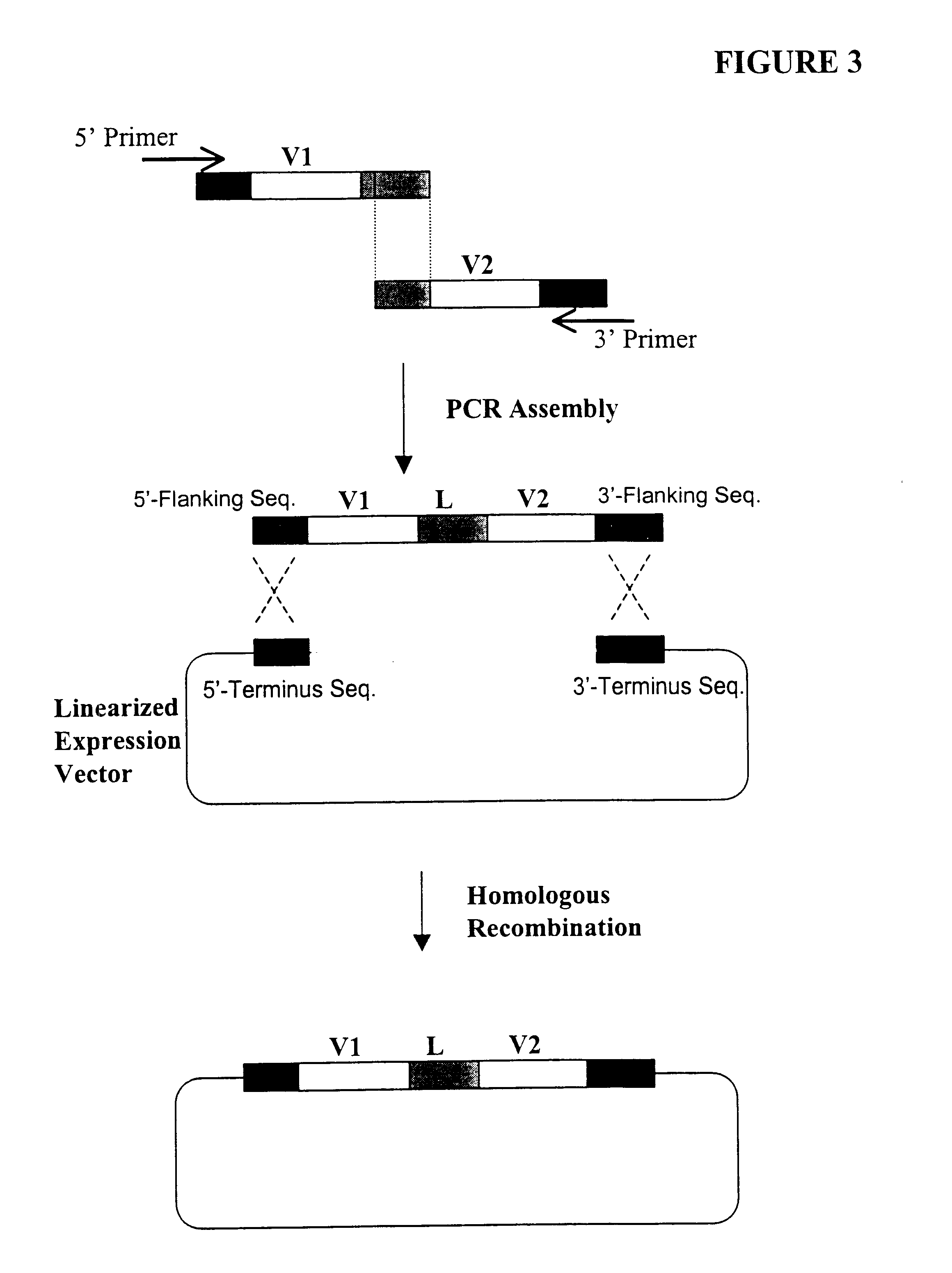
Generation of highly diverse library of expression vectors via homologous recombination in yeast
InactiveUS6410271B1High affinityEasy to assembleFusion with DNA-binding domainImmunoglobulinsDouble strandedYeast
Methods are provided for generating highly diverse libraries of expression vectors encoding fusion proteins such as single-chain antibodies via homologous recombination in yeast. The method comprises: transforming into yeast cells a linearized yeast expression vector having a 5'- and 3'-terminus sequence at the site of linearization and a library of insert nucleotide sequences that are linear and double-stranded; and having homologous recombination occur between the vector and the insert sequence such that the insert sequence is included in the vector in the transformed yeast cells. The insert sequence comprises a first nucleotide sequence encoding a first polypeptide subunit, a second nucleotide sequence encoding a second polypeptide subunit, a linker sequence encoding a linker peptide that links the first and second polypeptide subunits, and a 5'- and 3'-flanking sequence at the ends of the insert sequence which are sufficiently homologous to the 5'- and 3'-terminus sequences of the linearized yeast expression vector, respectively, to enable homologous recombination to occur. The first polypeptide subunit, the second polypeptide subunit, and the linker polypeptide are expressed as a single fusion protein; and the first and second nucleotide sequences each independently varies within the library of expression vectors.
Owner:GENETASTIX CORP
Method for knocking off animal myostatin gene by using CRISPR-Cas9 system
InactiveCN104531705AThe identification rules are simpleEasy to operateMicroinjection basedVector-based foreign material introductionBiotechnologyTranscription initiation site
The invention provides a method for knocking off an animal myostatin gene by using a CRISPR-Cas9 system. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, acquiring a DNA sequence aiming at an sgRNA recognition area of a second myostatin exon, wherein the base sequence of the DNA sequence is as shown in SEQ ID NO.1; secondly, establishing an sgRNA expression structure of the second myostatin exon, inserting a T7 starter before an sgRNA transcriptional start site, establishing an in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 protein, and regulating and controlling by using the T7 starter. Cas9 mRNA and sgRNA are obtained through the in-vitro transcription carrier of Cas9 and sgRNA, and the method can be used for knocking off the animal myostatin gene.
Owner:CHINA AGRI UNIV
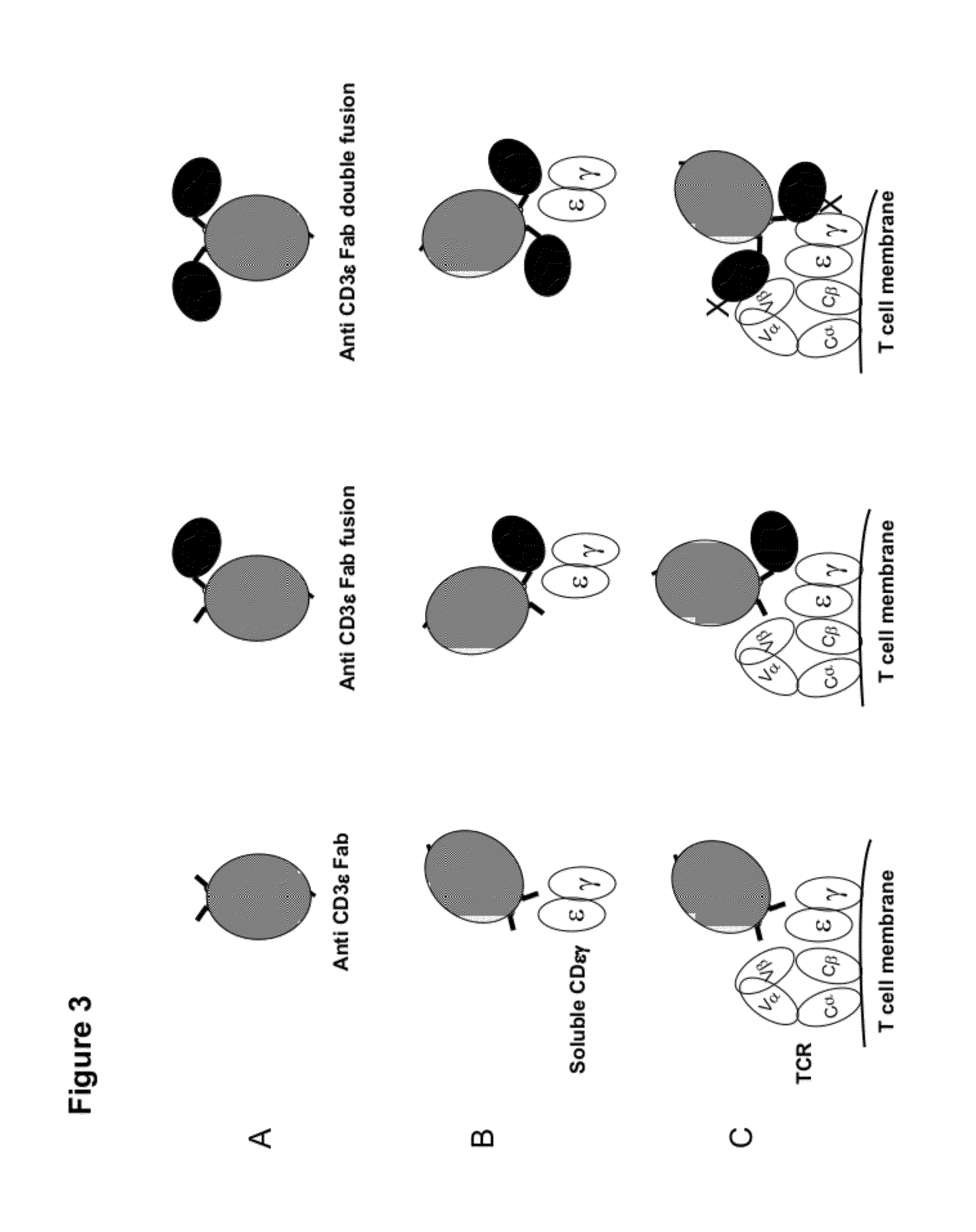
Multi-specific FAB fusion proteins and methods of use
ActiveUS8846042B2Hybrid immunoglobulinsCell receptors/surface-antigens/surface-determinantsSide effectControl manner
Owner:ITABMED (HK) LTD
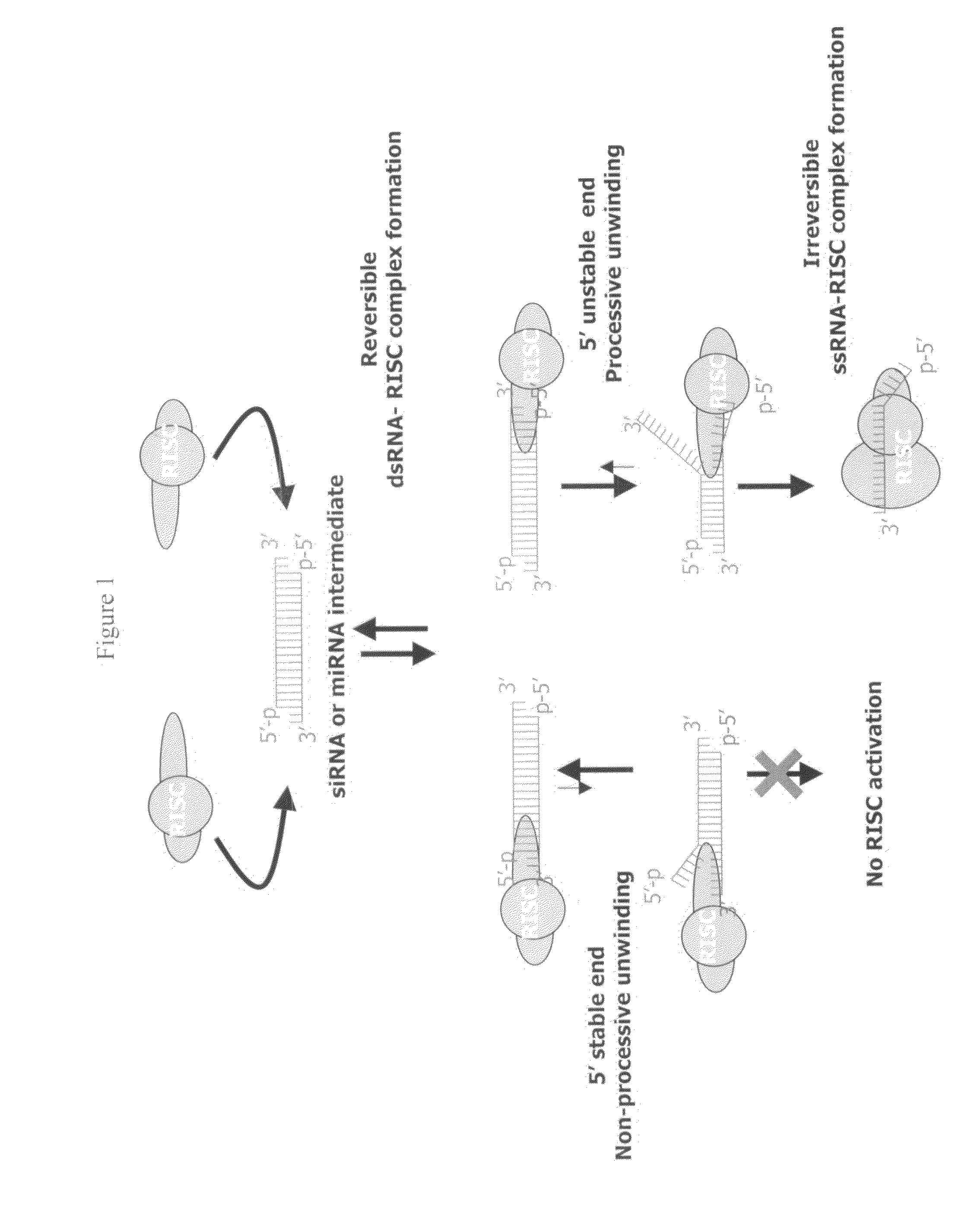
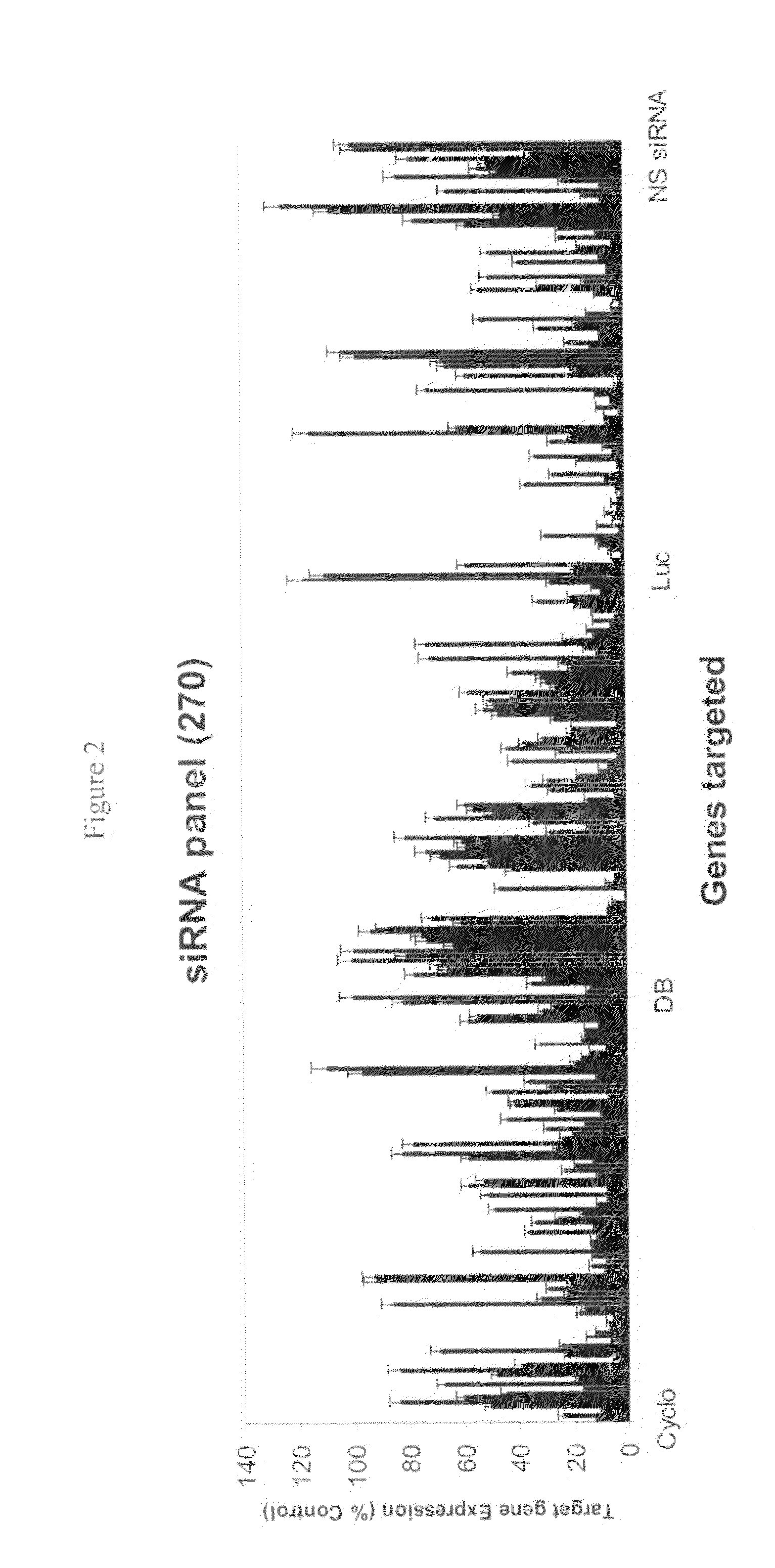
siRNA targeting cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor 1B (p27, Kip1) (CDKN1B)
InactiveUS7612196B2Improve efficiencyGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsSugar derivativesSilent geneGene silencing
Efficient sequence specific gene silencing is possible through the use of siRNA technology. By selecting particular siRNAs by rational design, one can maximize the generation of an effective gene silencing reagent, as well as methods for silencing genes. Methods, compositions, and kits generated through rational design of siRNAs are disclosed including those directed to nucleotide sequences for CDKN1B.
Owner:THERMO FISHER SCIENTIFIC INC
FAP-activated anti-tumor compounds
The invention relates to a prodrug that is capable of being converted into a drug by the catalytic action of human fibroblast activation protein (FAPalpha), said prodrug having a cleavage site which is recognised by FAPalpha, and said drug being cytotoxic or cytostatic under physiological conditions.
Owner:BOEHRINGER INGELHEIM PHARM KG
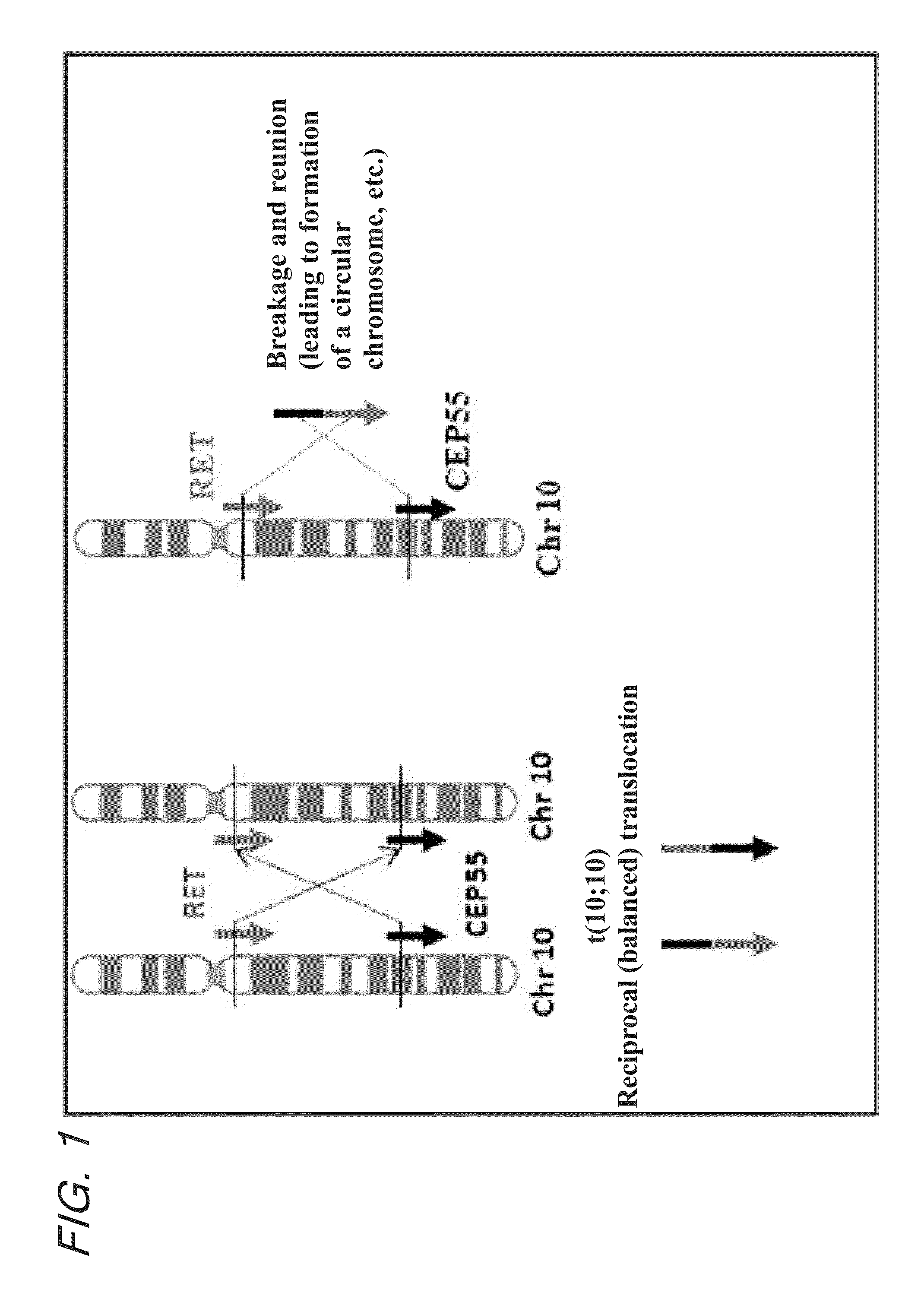
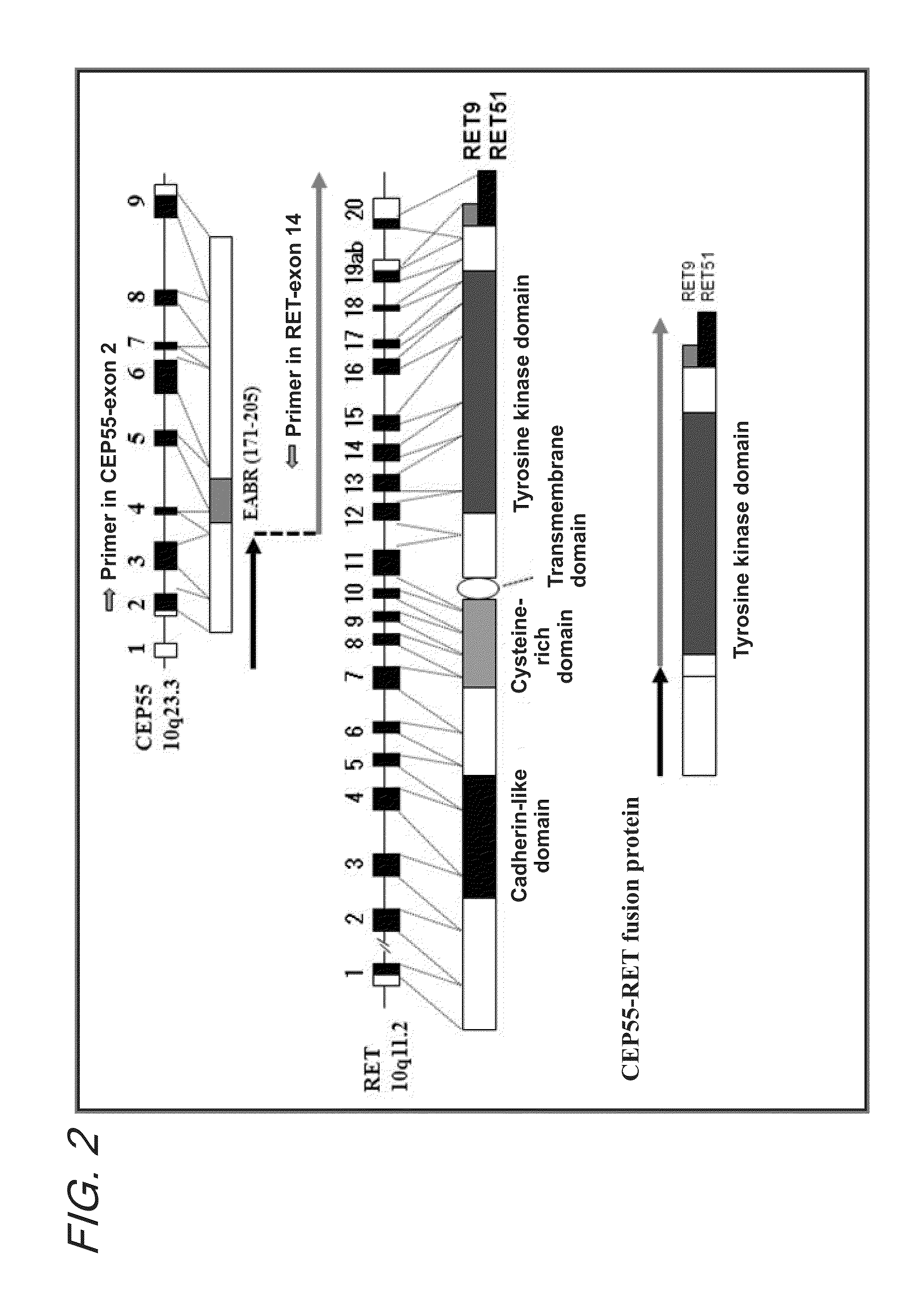
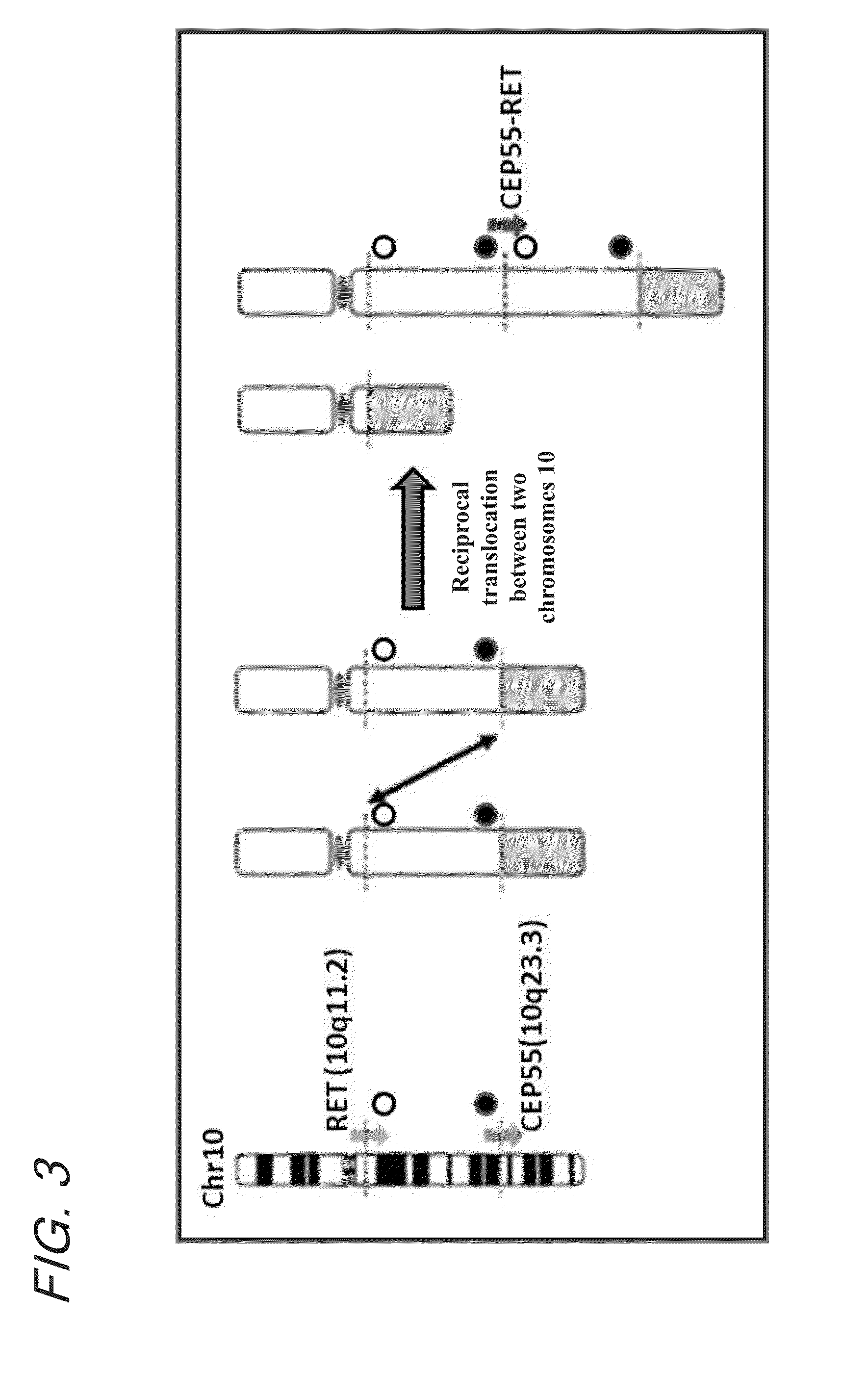
Fusion gene of cep55 gene and ret gene
InactiveUS20150177246A1Efficient detectionEffective treatment of cancerBiocideAntibody mimetics/scaffoldsRet geneTyrosine-kinase inhibitor
In order to identify genes that can serve as indicators for predicting the effectiveness of drug treatments in cancers and provide novel methods for predicting the effectiveness of treatments with drugs targeting said genes, transcriptome sequencing was performed of diffuse-type gastric cancer. As a result, in-frame fusion transcripts between the CEP55 gene and the RET gene were identified. It was also found that said gene fusions induce activation of RET protein, thereby causing canceration of cells. Further, it was demonstrated that the RET protein activation and canceration caused by said gene fusion can be suppressed by using a RET tyrosine kinase inhibitor, and that treatments with a RET tyrosine kinase inhibitor are effective in patients with detection of said gene fusion.
Owner:NAT CANCER CENT +1
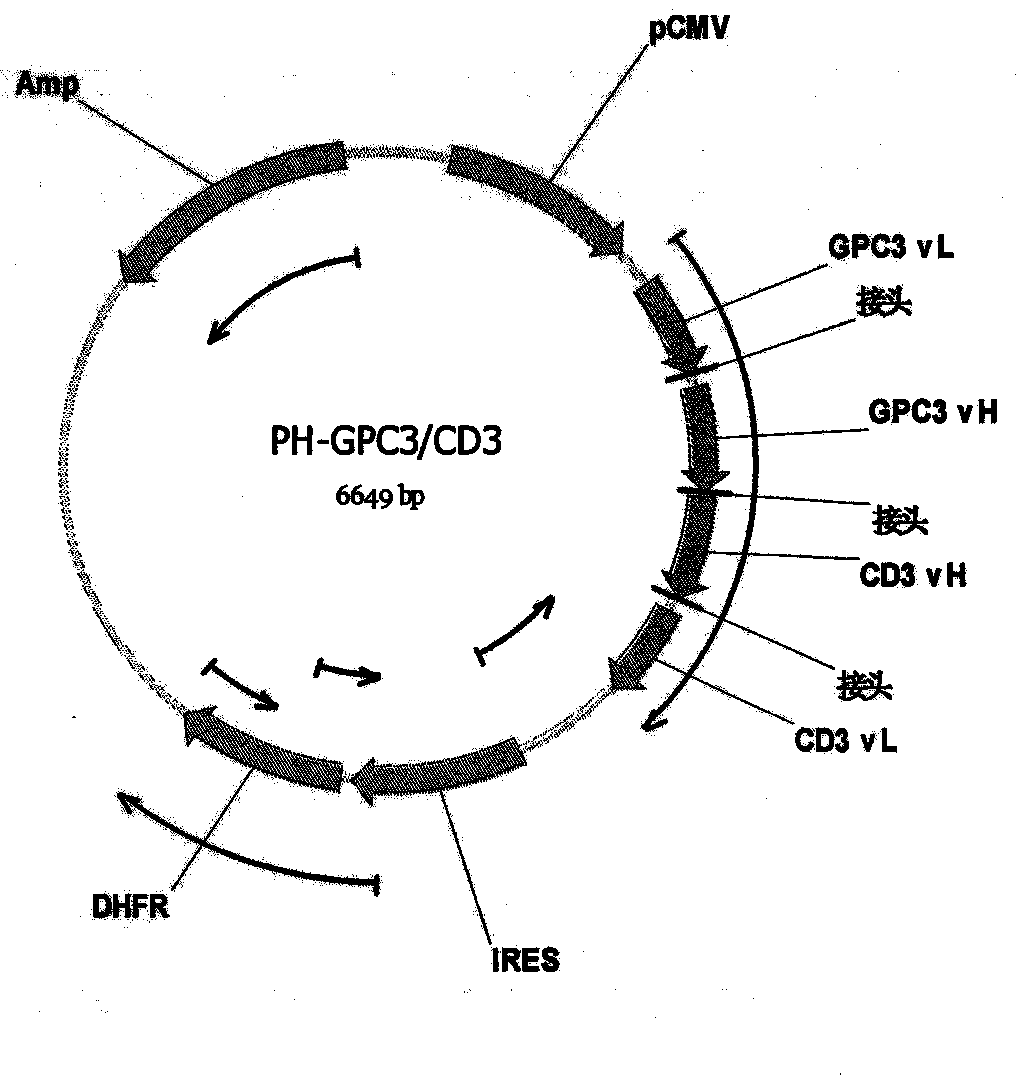
Bispecific antibody aiming at phosphatidylinositols protein polysaccharide-3 and T cell antigen
InactiveCN103833852ABacteriaImmunoglobulins against cell receptors/antigens/surface-determinantsAntigenNucleotide
The first aspect of the invention relates to a bispecific antibody, which comprises a first functional domain for specific identification of phosphatidylinositol protein polysaccharide-3, a second domain for specific identification of human T cell antigen CD3, and a connection for connecting the functional domains. The second aspect of the invention relates to a nucleotide sequence encoding the above antibody. The third aspect of the invention relates to a carrier containing the above nucleotide sequence, and includes an expressive vector. The fourth aspect of the invention relates to a eukaryotic or prokaryotic expression system containing the above carrier. The fifth aspect of the invention relates to application of the above antibody to preparation of medicament for treating or preventing tumor.
Owner:SHANGHAI INST OF ONCOLOGY
Oligonucleotide comprising an inosine for treating dmd
InactiveUS20120046342A1Avoid or decrease a potential multimerisation or aggregation of oligonucleotidesLow efficiencyOrganic active ingredientsSplicing alterationInosineNucleotide
The invention provides an oligonucleotide comprising an inosine, and / or a nucleotide containing a base able to form a wobble base pair or a functional equivalent thereof, wherein the oligonucleotide, or a functional equivalent thereof, comprises a sequence which is complementary to at least part of a dystrophin pre-m RNA exon or at least part of a non-exon region of a dystrophin pre-m RNA said part being a contiguous stretch comprising at least 8 nucleotides. The invention further provides the use of said oligonucleotide for preventing or treating DMD or BMD.
Owner:BIOMARIN TECH BV
Compositions, kits, and methods relating to the human FEZ1 gene, a novel tumor suppressor gene
InactiveUS20070072230A1Increase stringencyInhibiting tumorigenesisSugar derivativesPeptide/protein ingredientsTumour suppressor geneHuman tumor
Owner:THOMAS JEFFERSON UNIV
Targeted/immunomodulatory fusion proteins and methods for making same
ActiveUS20130287802A1Effective compositionEfficient methodBacteriaPeptide/protein ingredientsCancer cellNucleotide
The present invention relates generally to the field of generating fusion proteins to be used in cancer therapy, and more specifically, to nucleotide sequences encoding the fusion proteins, wherein the chimeric fusion proteins comprises at least one targeting moiety and at least one immunomodulatory moiety that counteracts the immune tolerance of cancer cells.
Owner:BIOCON LTD
Novel chimeric proteins and methods for using the same
InactiveUS20030216546A1Compounds screening/testingPeptide/protein ingredientsDiseaseProtein insertion
Novel chimeric proteins are disclosed. The proteins comprise at least two portions. The first portion binds to a first cell and decreases the cell's ability to send a trans signal to a second cell; the second portion sends its own trans signal to the second cell. Methods for making and using these proteins in the treatment of cancer, viral infections, autoimmune and alloimmune diseases are also disclosed, as are pharmaceutical formulations comprising the novel chimeric proteins and genes. Either the proteins themselves or a genetic sequence encoding the protein can be administered. Other methods are also disclosed in which two molecular components result in decrement of a first trans signal from a first cell and the conferring of a second trans signal to a second cell.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF THE UNIV OF PENNSYLVANIA
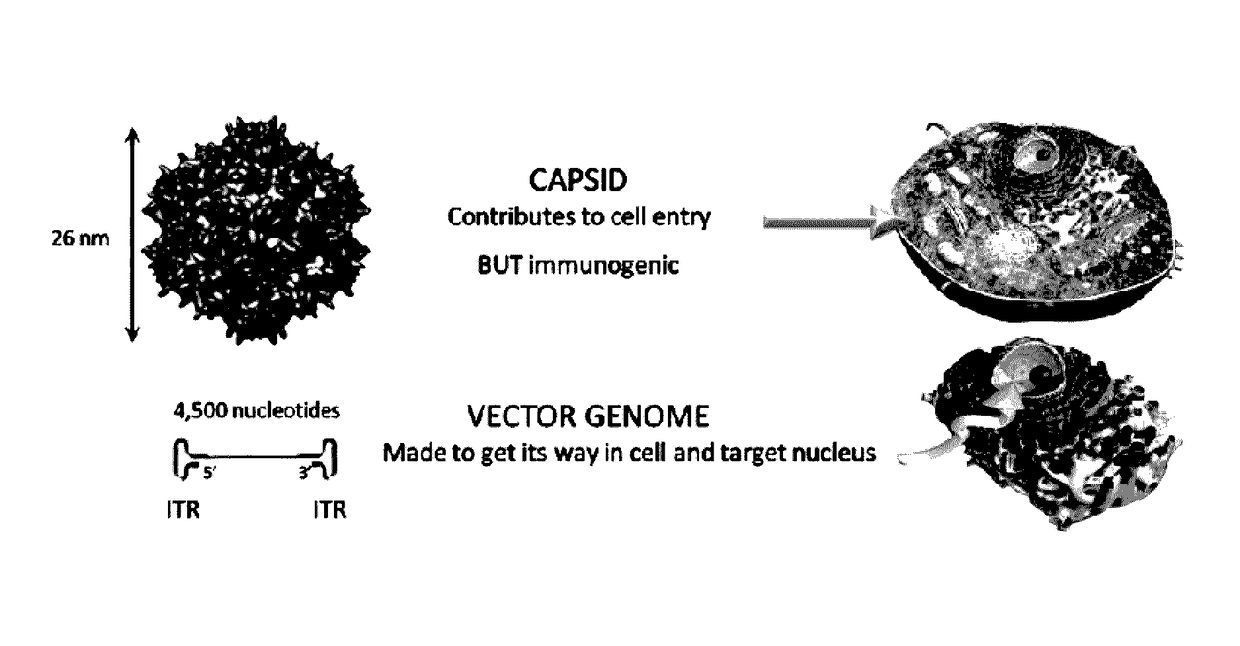
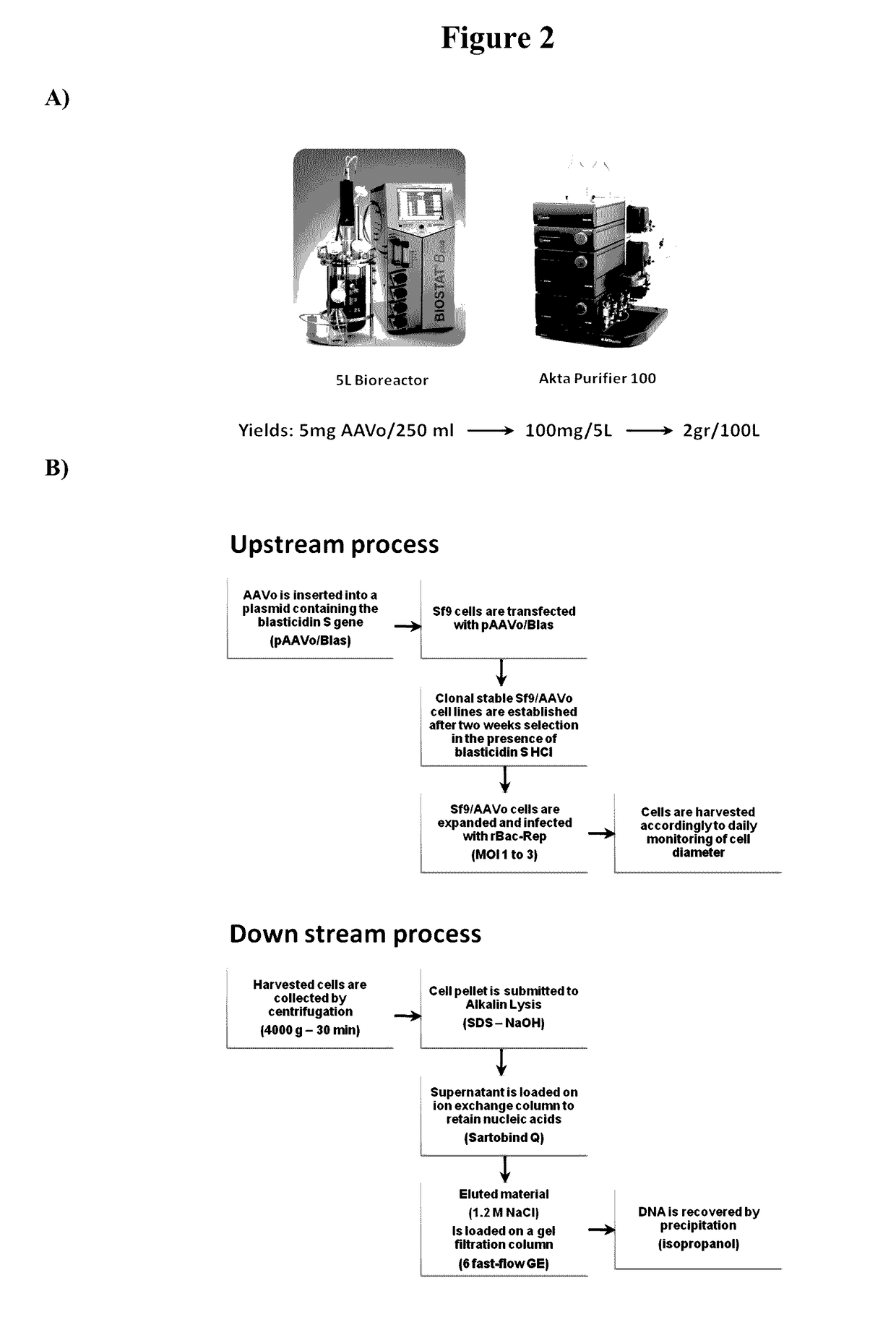
Capsid-free AAV vectors, compositions, and methods for vector production and gene delivery
ActiveUS9598703B2Efficient and convenient methodElectrotherapyNervous disorderGene deliveryTherapeutic intent
An isolated linear nucleic acid molecule comprising in this order: a first adeno-associated virus (AAV) inverted terminal repeat (ITR), a nucleotide sequence of interest and a second AAV ITR, wherein said nucleic acid molecule is devoid of AAV capsid protein coding sequences. The said nucleic acid molecule can be applied to a host at repetition without eliciting an immune response. Methods for producing and purifying this nucleic acid molecule, and use of the same for therapeutic purposes are also provided.
Owner:UNITED STATES OF AMERICA +4
Modified beta-lactamase and method for its preparation
The invention relates to targeted post translational modifi-cation of metallo-beta-lactamase by truncation and inser-tion of a dipeptide at the amino terminal end to reduce amino terminal heterogeneity in a recombinant DNA pro-duction system. A protein K-T-E-ΔBL is expressed, and modified by host proteases to E-ΔBL. Appropriate nucleotide molecules, vectors and hosts are also de-scribed. E-ΔBL is useful in a pharmaceutical composition for treating antibiotic induced adverse effects in the intes-tine of patients treated with beta-lactam antibiotics.
Owner:SYNTHETIC BIOLOGICS INC
Modified polynucleotides for the production of secreted proteins
Owner:MODERNATX INC
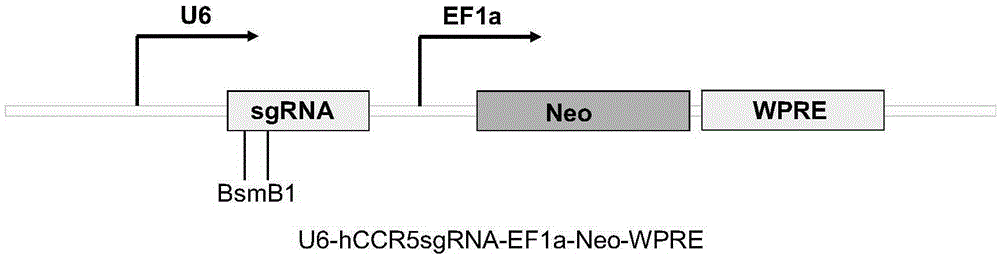
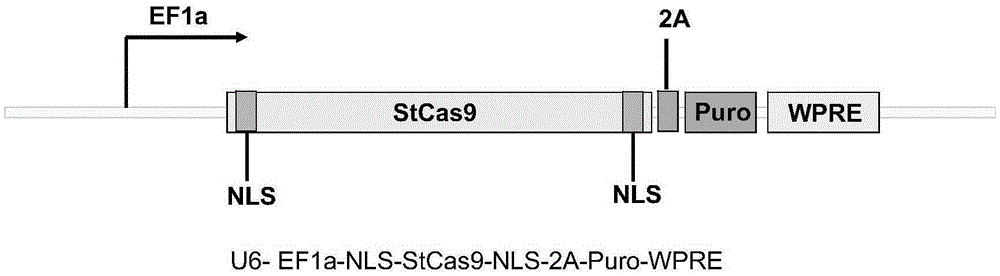
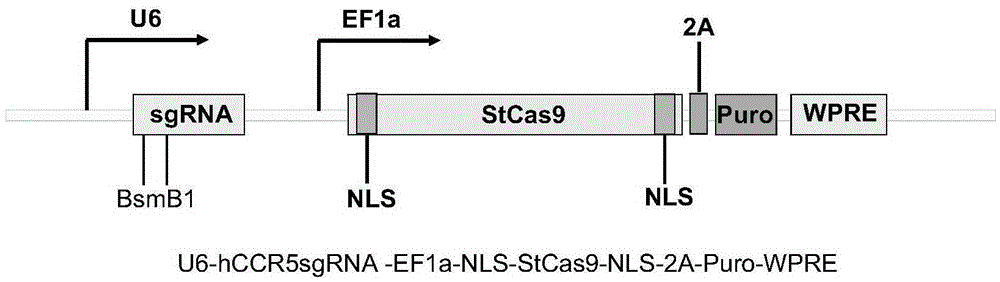
Target sequence, recognized by streptococcus thermophilus CRISPR-Cas9 system, of human CCR5 gene, sgRNA and application of CRISPR-Cas9 system
InactiveCN105400779AHIV prevention and/or treatmentAchieve therapeutic effectOrganic active ingredientsHydrolasesGenetic engineeringStreptococcus thermophilus
The invention belongs to the field of genetic engineering, and discloses a target sequence, recognized by a streptococcus thermophilus CRISPR-Cas9 system, of a human CCR5 gene, sgRNA and an application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system. The target sequence is shown as any one of the nth bit to the 30th bit of the SEQ ID NO:1-30, and n is equal to 1-12. The invention further relates to the sgRNA of the sequence -3' with the sequence of 5'-recognition sequence-recruiting Cas9 protein and a coded DNA molecule thereof. The DNA sequence corresponding to the recognition sequence is identical to the target sequence. The invention further relates to the CRISPR-Cas9 system. The system comprises Cas9 protein, the sgRNA and / or the coded sequence carrying the Cas9 protein and a carrier of the coded sequence of the sgRNA. The invention further relates to the application of the CRISPR-Cas9 system in editing the CCR5 gene and preparing medicine for HIV infection. Editing of the human CCR5 gene can be achieved, and therefore Aids is prevented and treated.
Owner:张竞方
Method for treating cancer based on level of a nucleoside transporter
The present invention provides methods and compositions for treating cancer by administering a) a composition comprising nanoparticles that comprise paclitaxel and an albumin and b) a nucleoside analog (e.g., gemcitabine) based upon levels of a nucleoside transporter (e.g., hENT1).
Owner:ABRAXIS BIOSCI LLC
Solid forms of anti-EGFR antibodies
InactiveUS7960516B2Improve stabilityHigh purityPowder deliveryFrom normal temperature solutionsAdjuvantDissolution
The invention relates to solid forms of antibodies against the EGF receptor, in particular precipitates and crystals of monoclonal antibodies against the EGF receptor, particularly preferably of Mab C225 (cetuximab) and Mab h425 (EMD 72000), which result in biologically active antibody protein through dissolution or suspension in aqueous medium, obtainable by precipitation of the antibody and / or one of its variants and / or fragments dissolved or suspended in aqueous medium by means of a precipitation reagent. The invention furthermore relates to pharmaceutical preparations comprising at least one solid form of above-mentioned antibodies in precipitated non-crystalline, precipitated crystalline or in soluble or suspended form, and optionally excipients and / or adjuvants and / or further pharmaceutical active ingredients, and to a process for the preparation of solid forms of anti-EGFR antibodies according to the invention.
Owner:MERCK PATENT GMBH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com