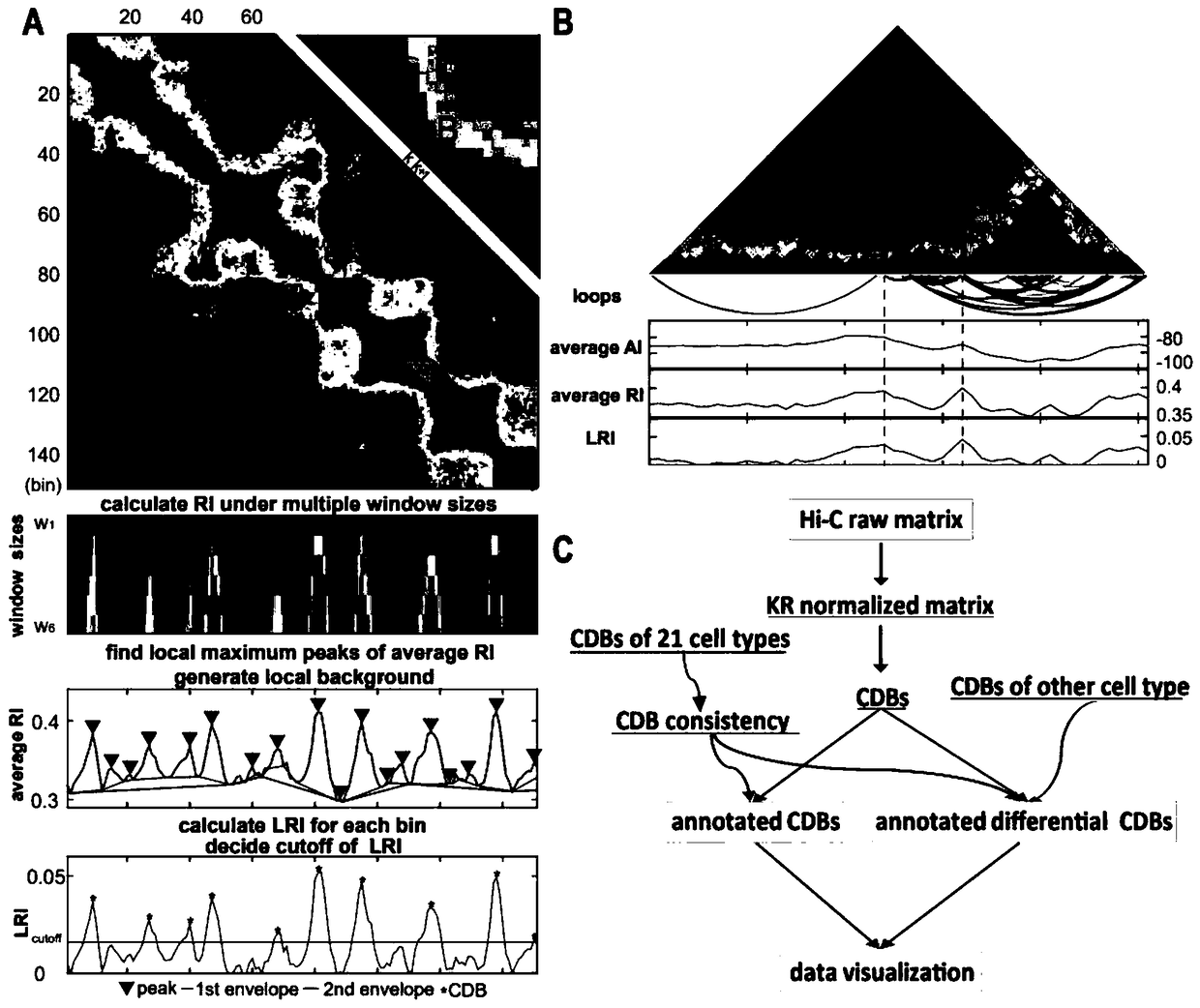
Analysis method for chromatin topological domain boundaries
A topology and chromatin technology, applied in the field of chromatin structure analysis, can solve the problems of low accuracy, high computational complexity, and unsuitable Hi-C matrix for detecting topological domains.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
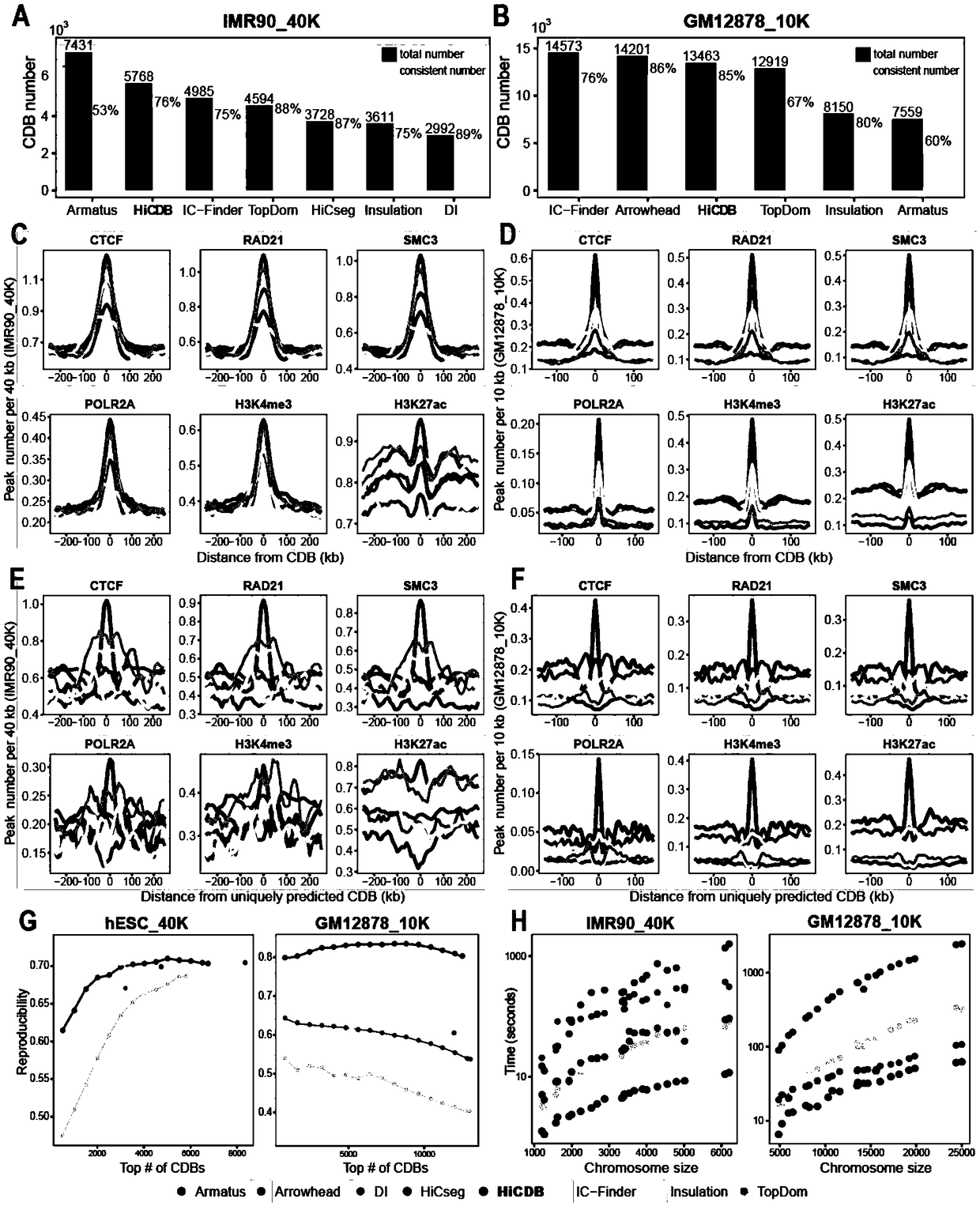
[0146] Example 1 Comparison between HiCDB and existing CDB detection methods.
[0147] This example compares the performance of detection methods for different CDBs using medium-resolution (40kb) and higher-resolution (10kb) raw Hi-C data, and measures several quantitative criteria, including CDB number, identity, protein Combines enrichment, robustness, and time complexity. Based on a 40kb dataset, HiCDB was compared with Armatus, DI, HiCseg, IC-Finder, Insulation, and TopDom. In the 10-kb dataset, DI and HiCseg were excluded from the comparison due to their excessive computational time complexity. It was also included in the comparison because Arrowhead was designed for Hi-C experiments at chromatin loop-level resolution and invoked a smaller number of domain boundaries than other methods for 40-kb datasets.
[0148] First, the consistency of each method was analyzed to reflect the accuracy of CDB detection ( figure 2 A and B). HiCDB detected 5768 CDBs, the highest amon...
Embodiment 2
[0153] Example 2 HiCDB can accurately identify smaller-scale CDBs.
[0154] This embodiment compares the CDB distance distribution identified by different methods ( Figure 5 A). Armatus tends to detect many small regions clustered together on both datasets ( Figure 5 C). In the 40kb dataset, the average distance between CDBs detected by HiCDB is 505kb, which is the shortest among all methods except Armatus. Using 10-kb data, the distance between CDBs identified by HiCDB, Arrowhead, TopDom and IC-Finder is about 200 kb. It is worth noting that the CDB distance distributions for Arrowhead and TopDom have two peaks, implying that a small fraction of CDBs detected by these two methods are closely located to each other ( Figure 5 C).
[0155] Due to the high signal-to-noise ratio of deep sequencing data, the CDB detected based on the 10kb chromatin adjacency matrix was more accurate and complete than that based on the 40kb matrix. Next, the CDB detected by more than two me...
Embodiment 3
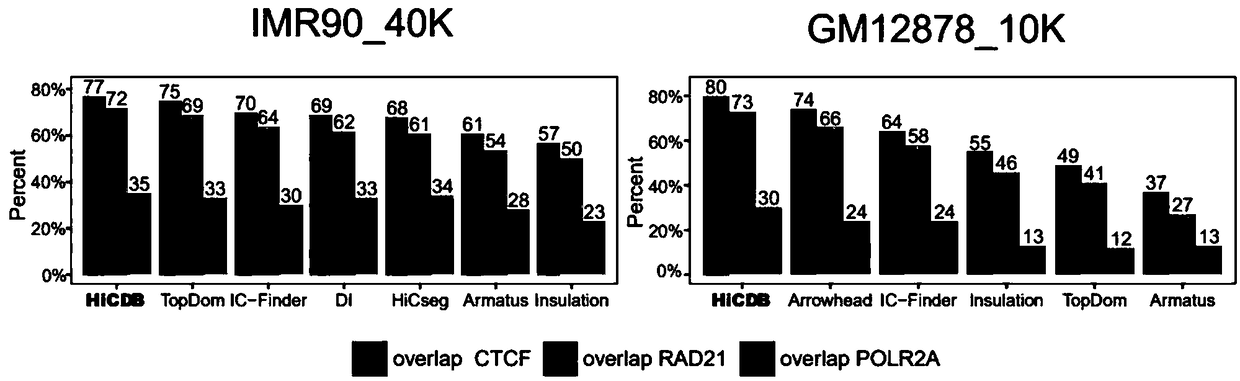
[0158] Example 3 CDB-enriched structural proteins and cell-specific transcription factors detected by HiCDB
[0159] This example verifies the binding sites of CDB predicted by HiCDB to Hi-C ring, ChIA-PET ring and transcription factors. All analyzes were performed on the GM12878 cell line.
[0160] First, CDBs predicted by HiCDB were overlaid with chromHMM annotations to show the relationship of these CDBs to chromatin state. In the 40-kb dataset, CDB was significantly enriched for insulators (2.11-fold) and promoters (1.75-fold). Meanwhile, CDBs detected in the 10-kb dataset were enriched for active promoters (5.86-fold), insulators (3.36-fold) and enhancers (3.23-fold).
[0161] The CDB was subsequently compared with another characteristic Hi-C chromatin loop extracted on HiCCUPHi-C data. It was found that 56% of CDBs were anchored to Hi-C chromatin loops ( Figure 6 ). Of the genomic locations identified only as CDBs but not Hi-C chromatin loop anchors, 25% coincided ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Sensitivity | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com