Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
134 results about "Multimodal imaging" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
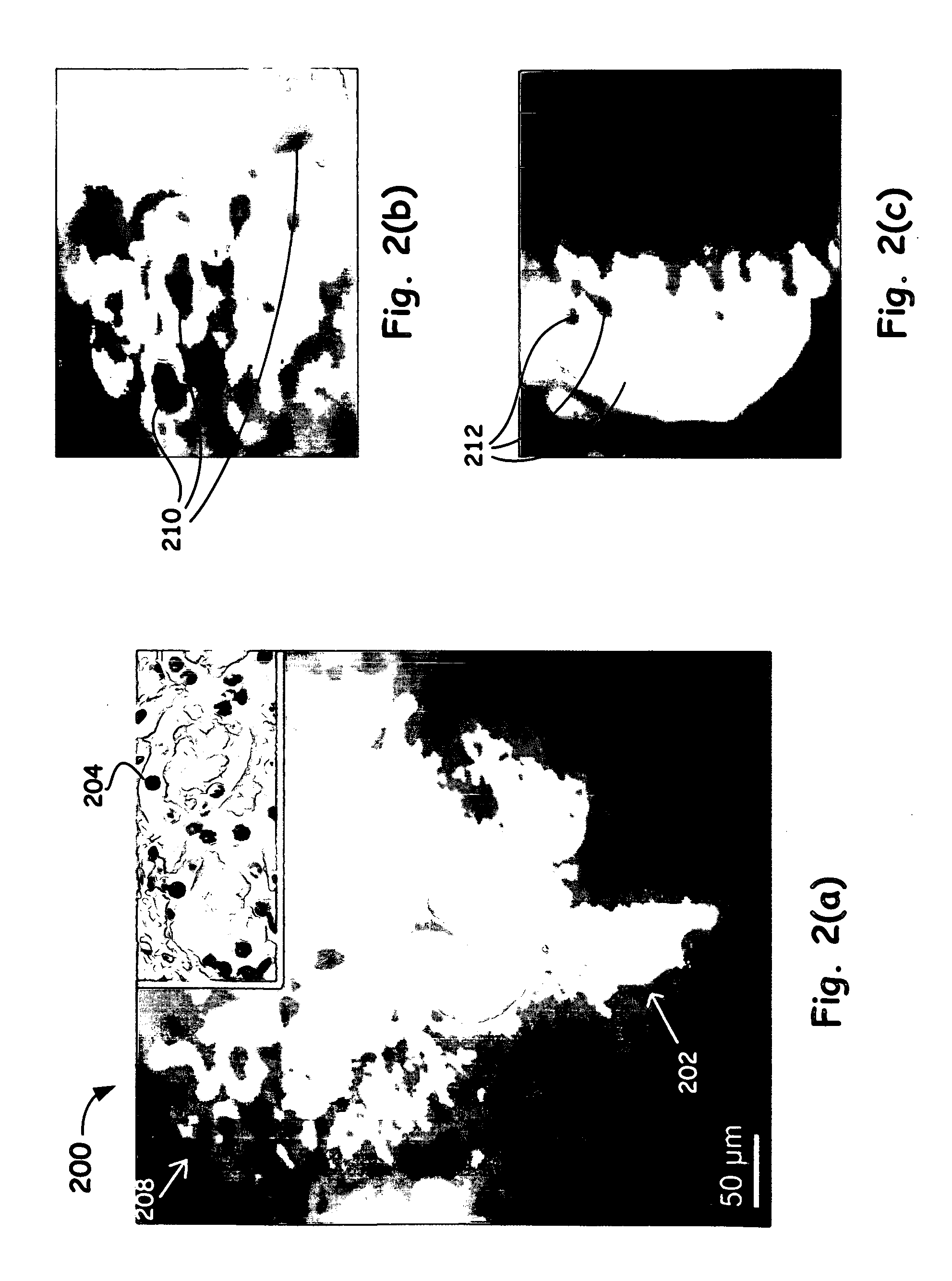
Multimodal Imaging A wide range of optical imaging modalities based on different contrast mechanisms have emerged in recent years. We have developed an integrated microscope that can perform structural and functional imaging of cells in 3-D and for extended periods of time.
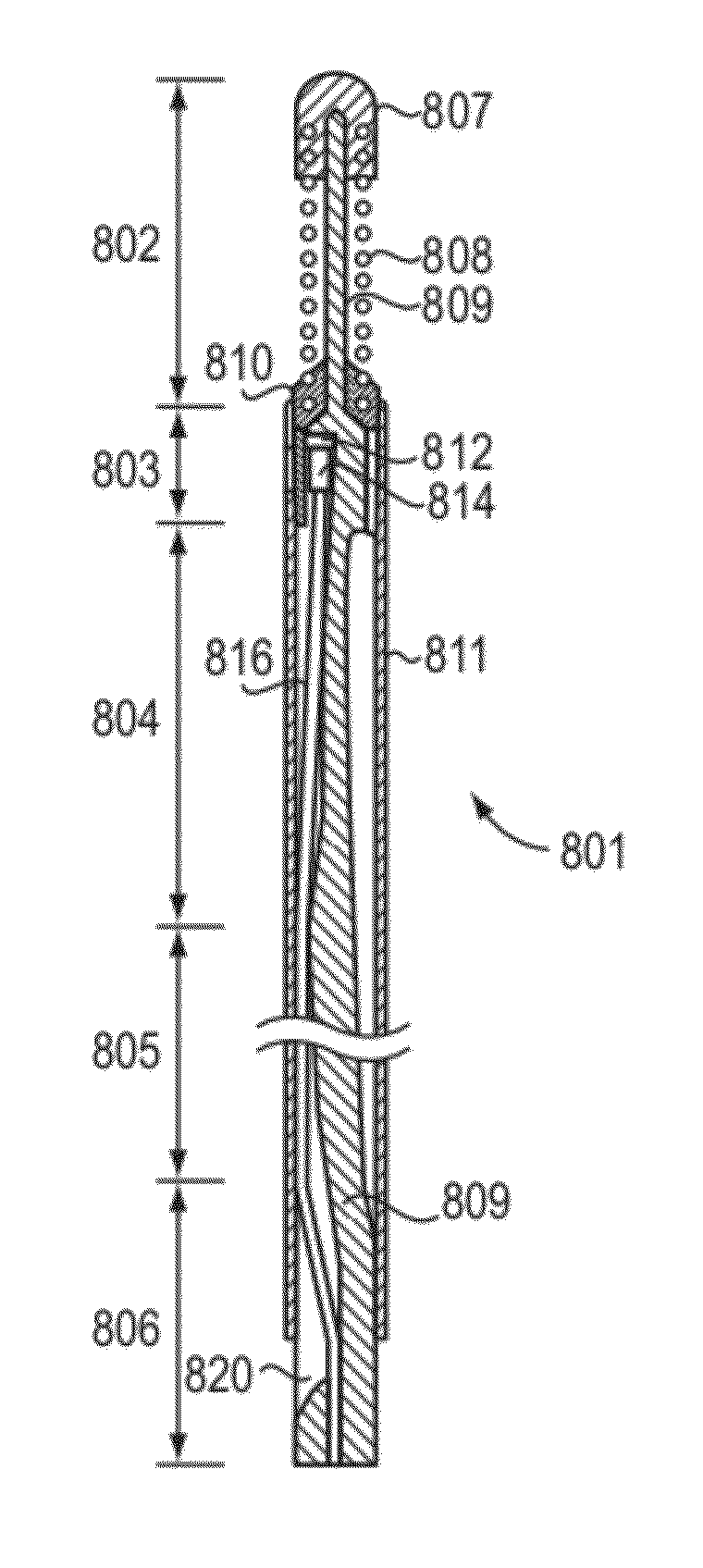
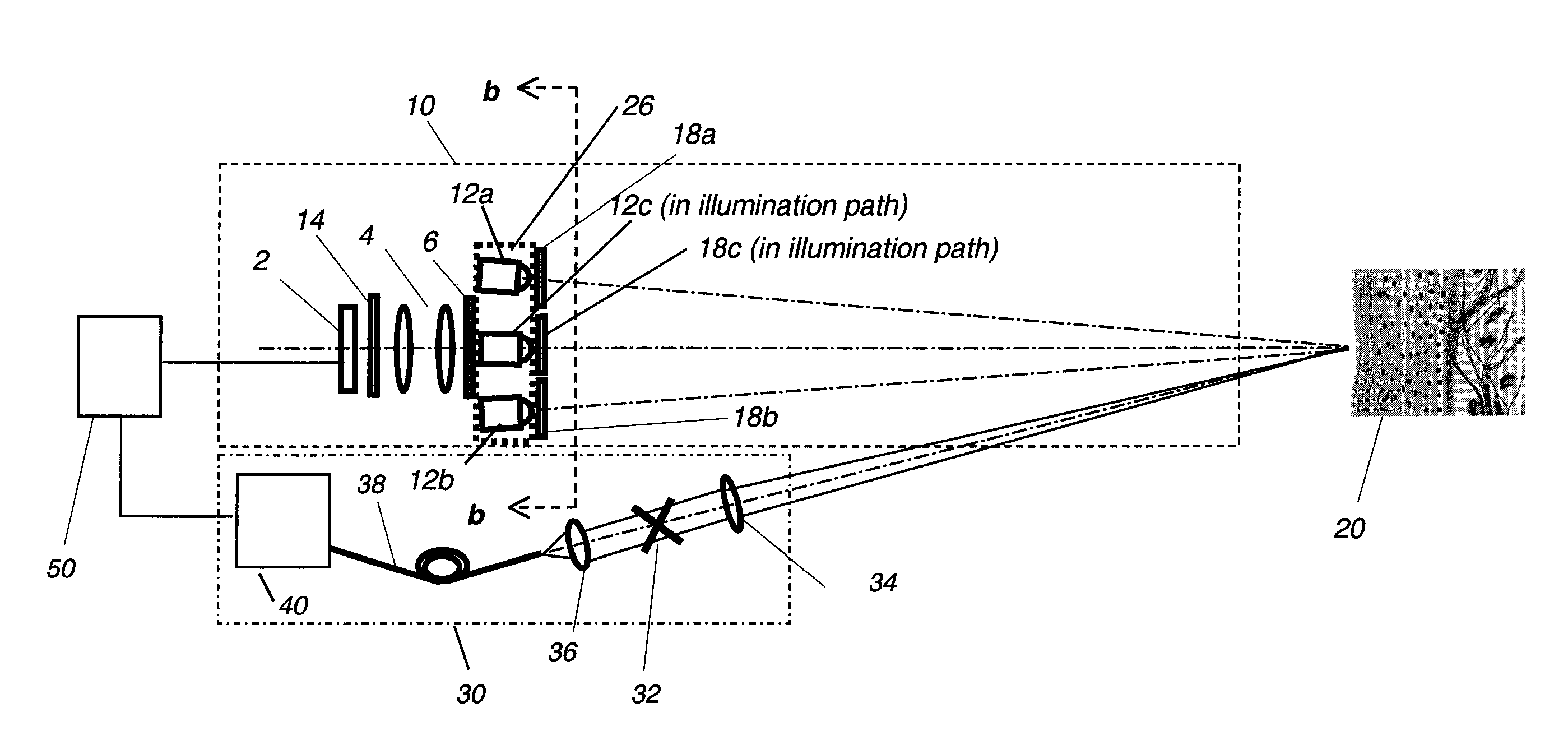
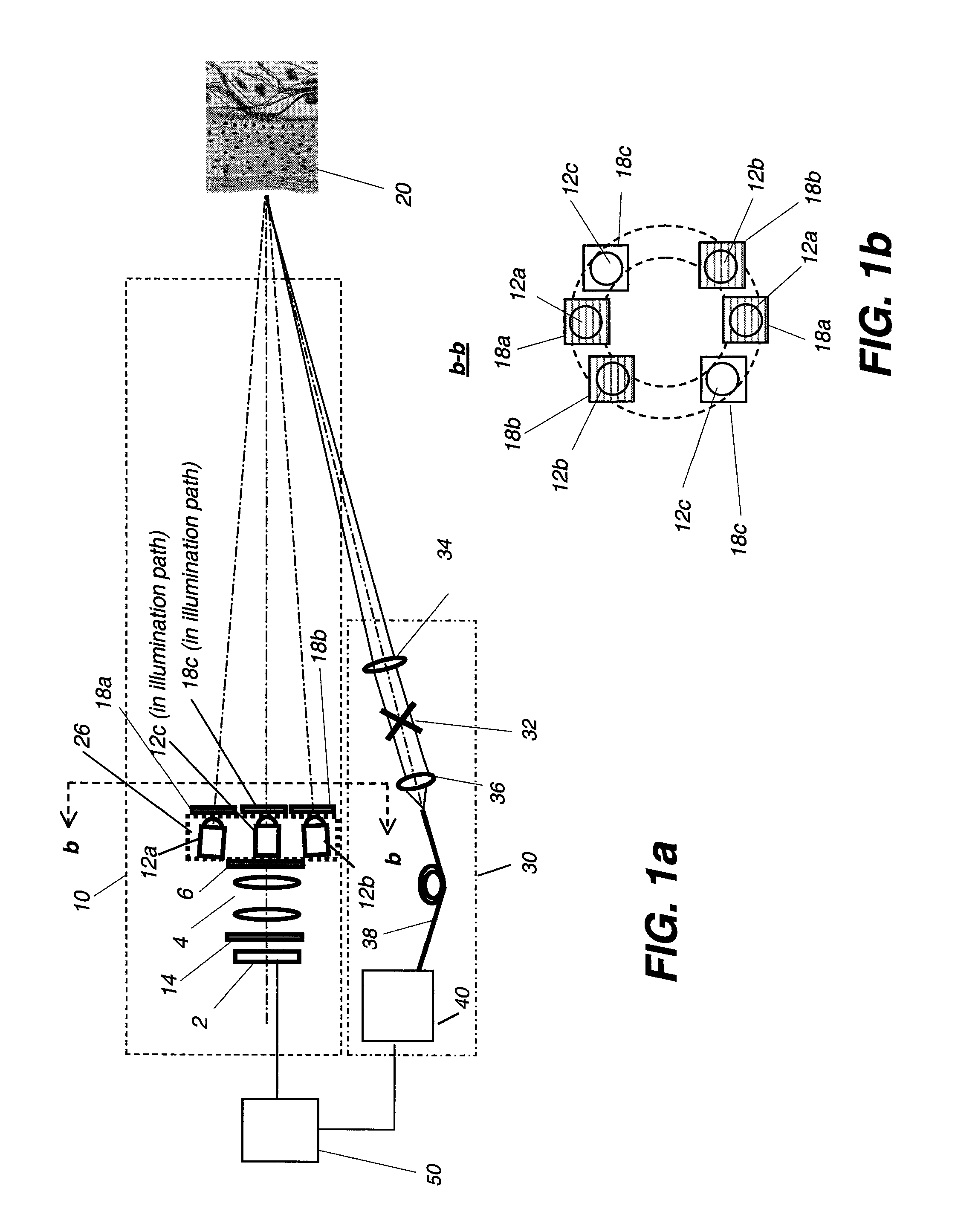
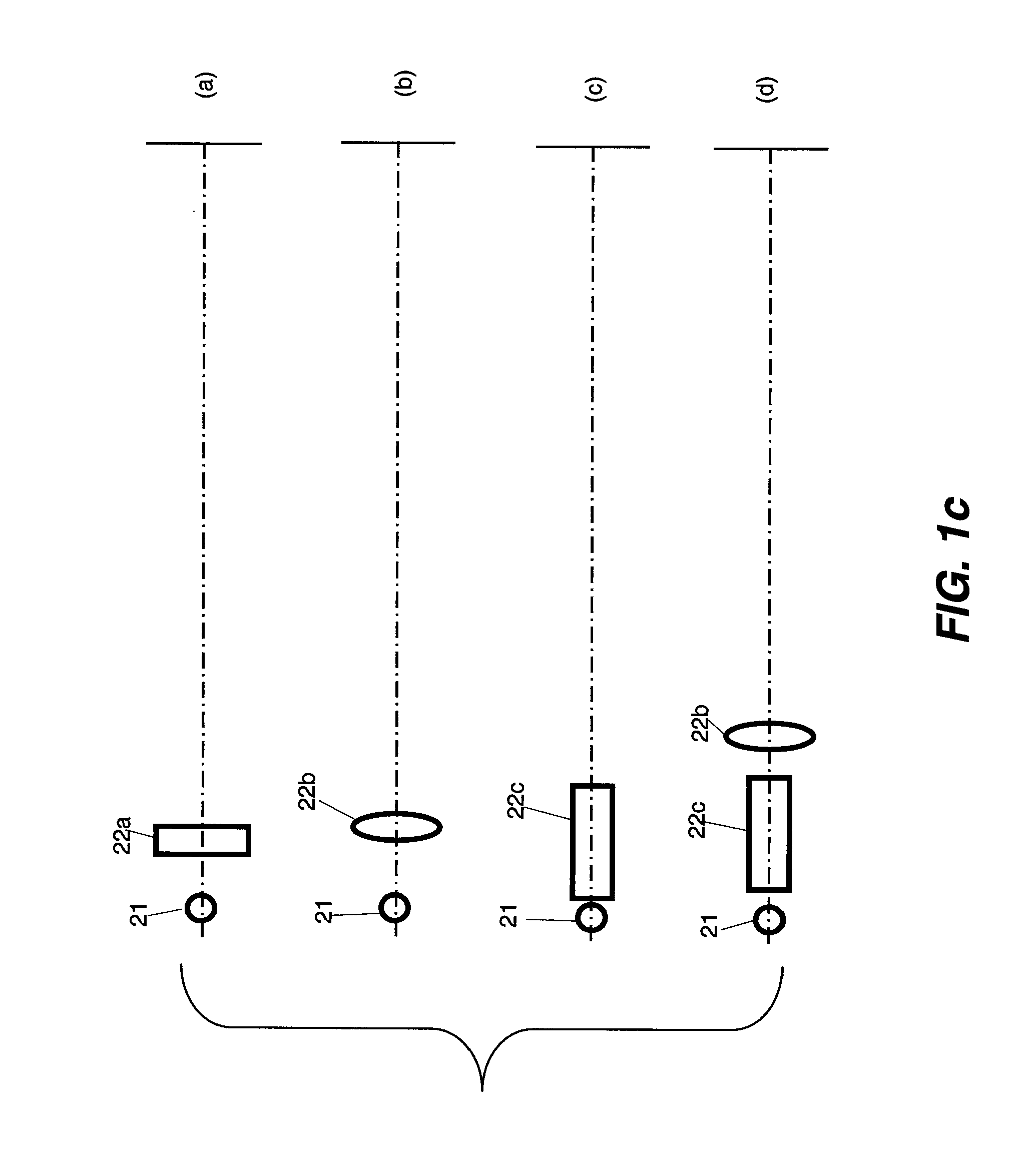
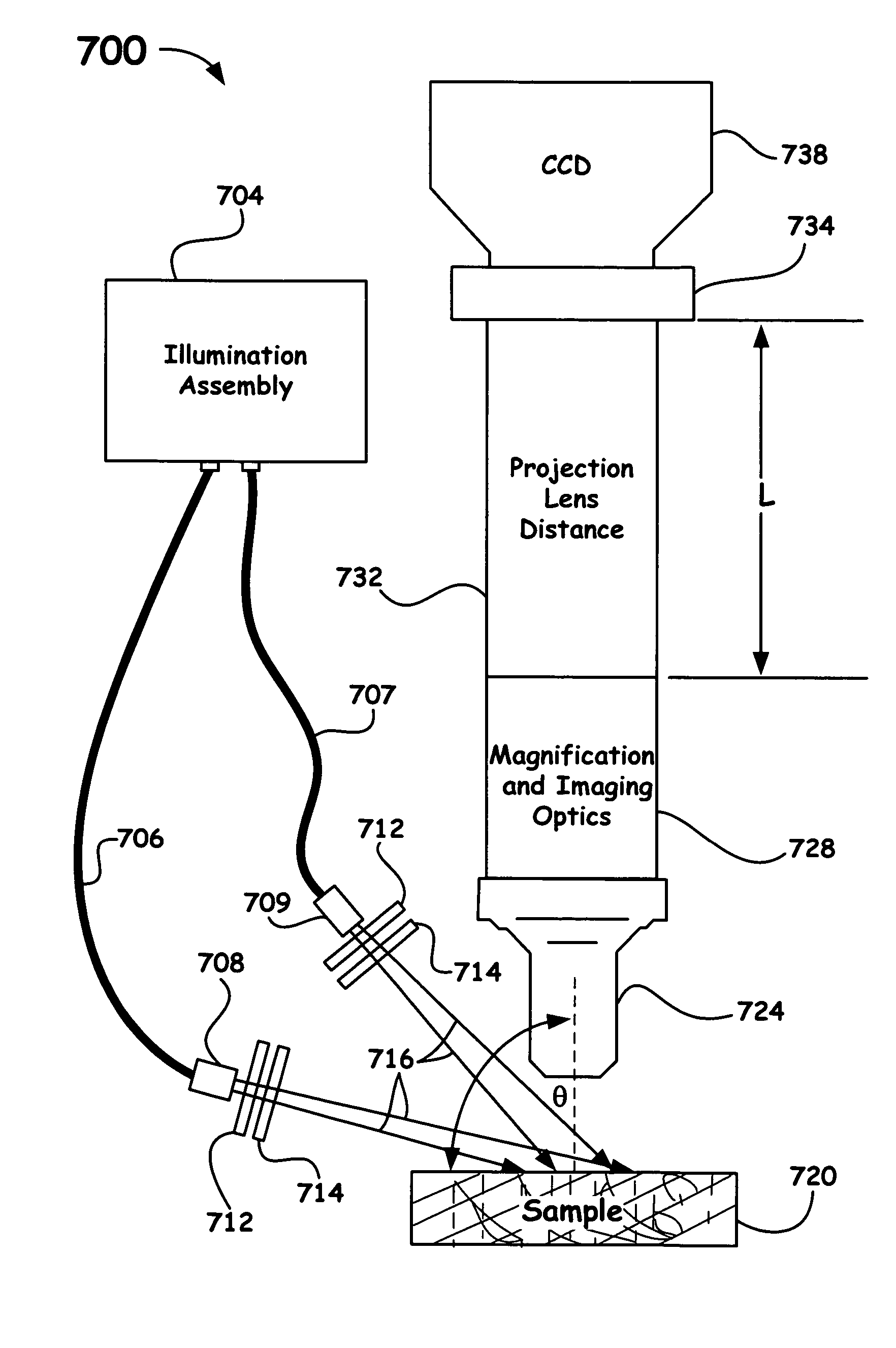
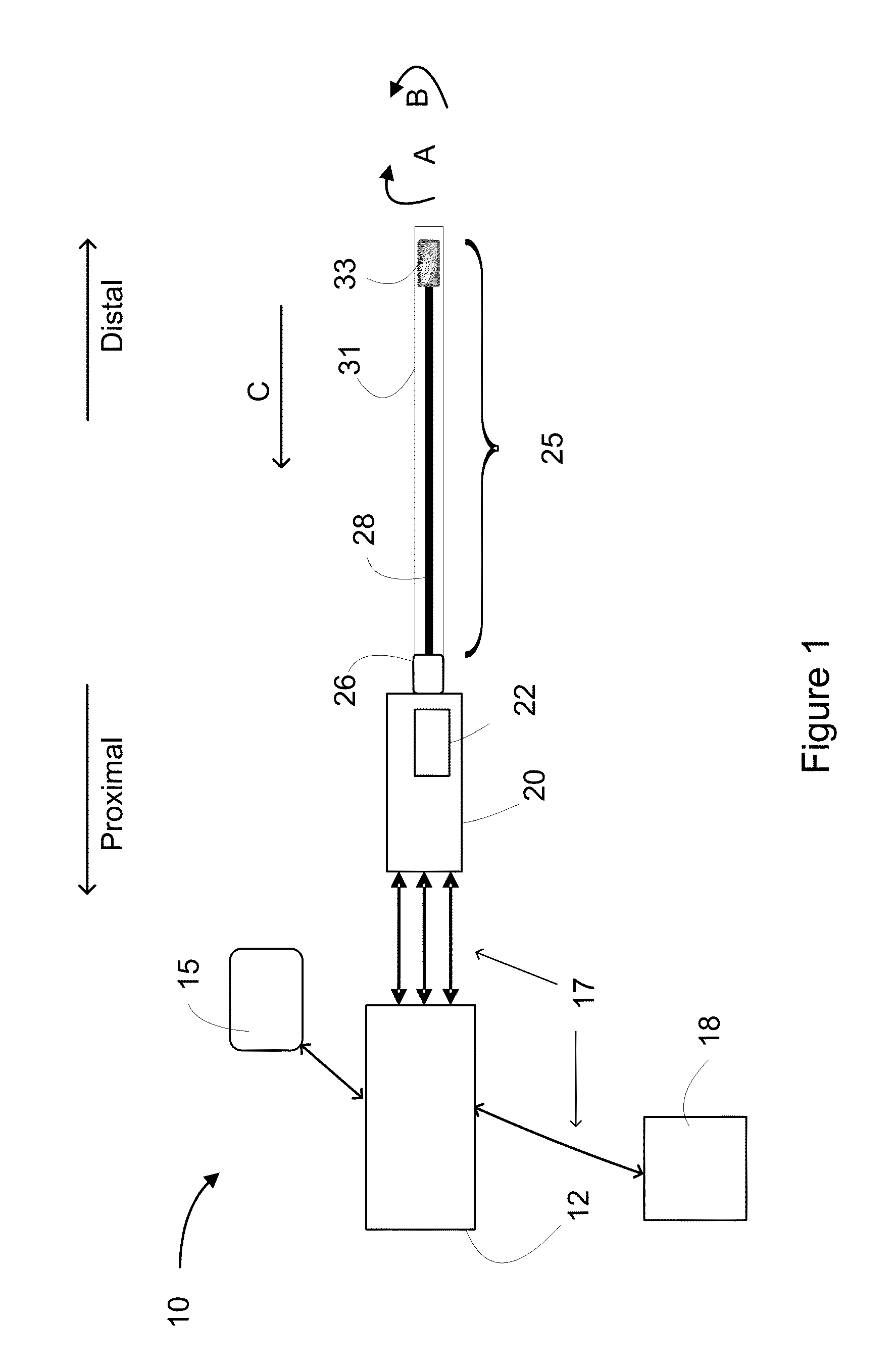
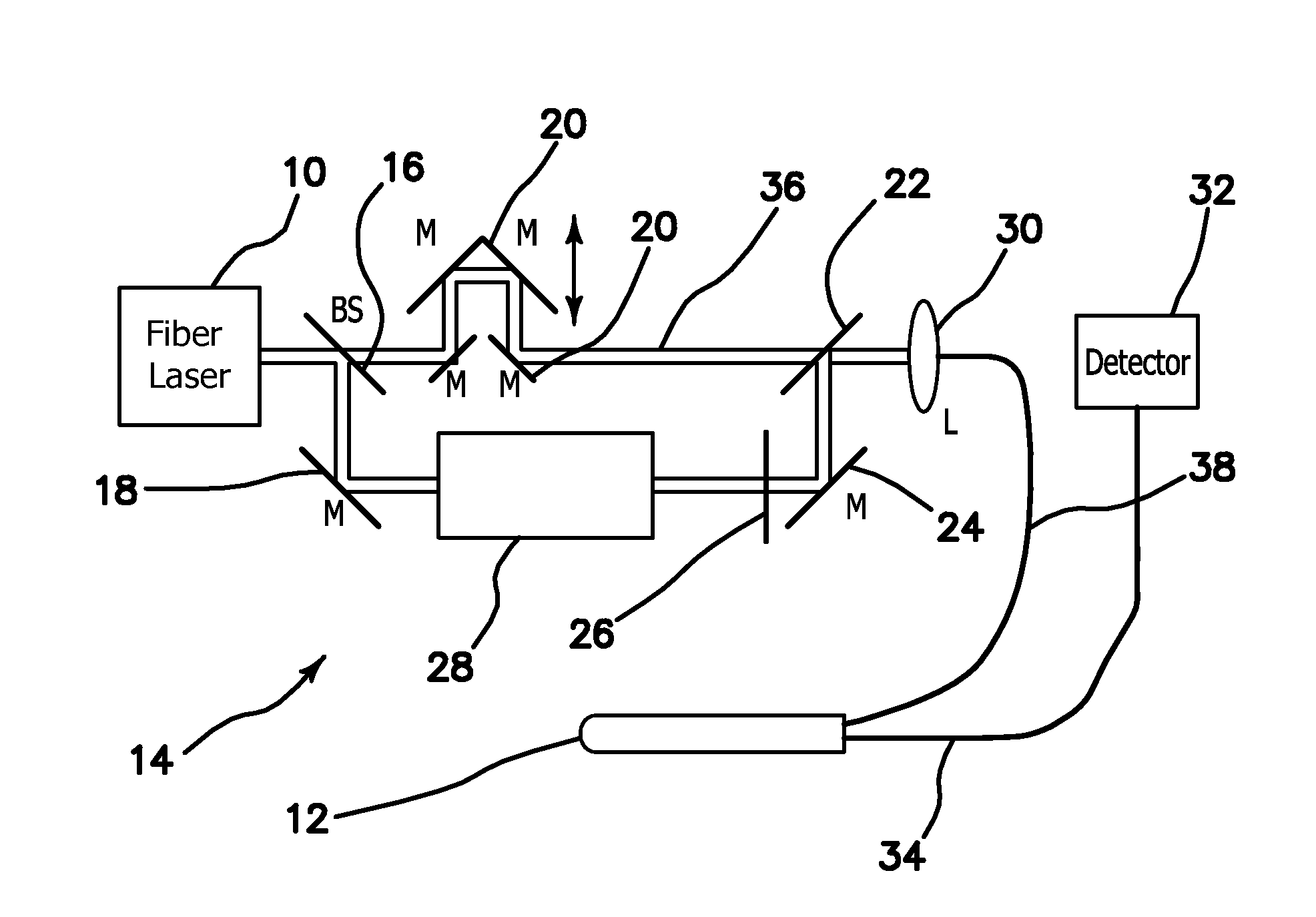
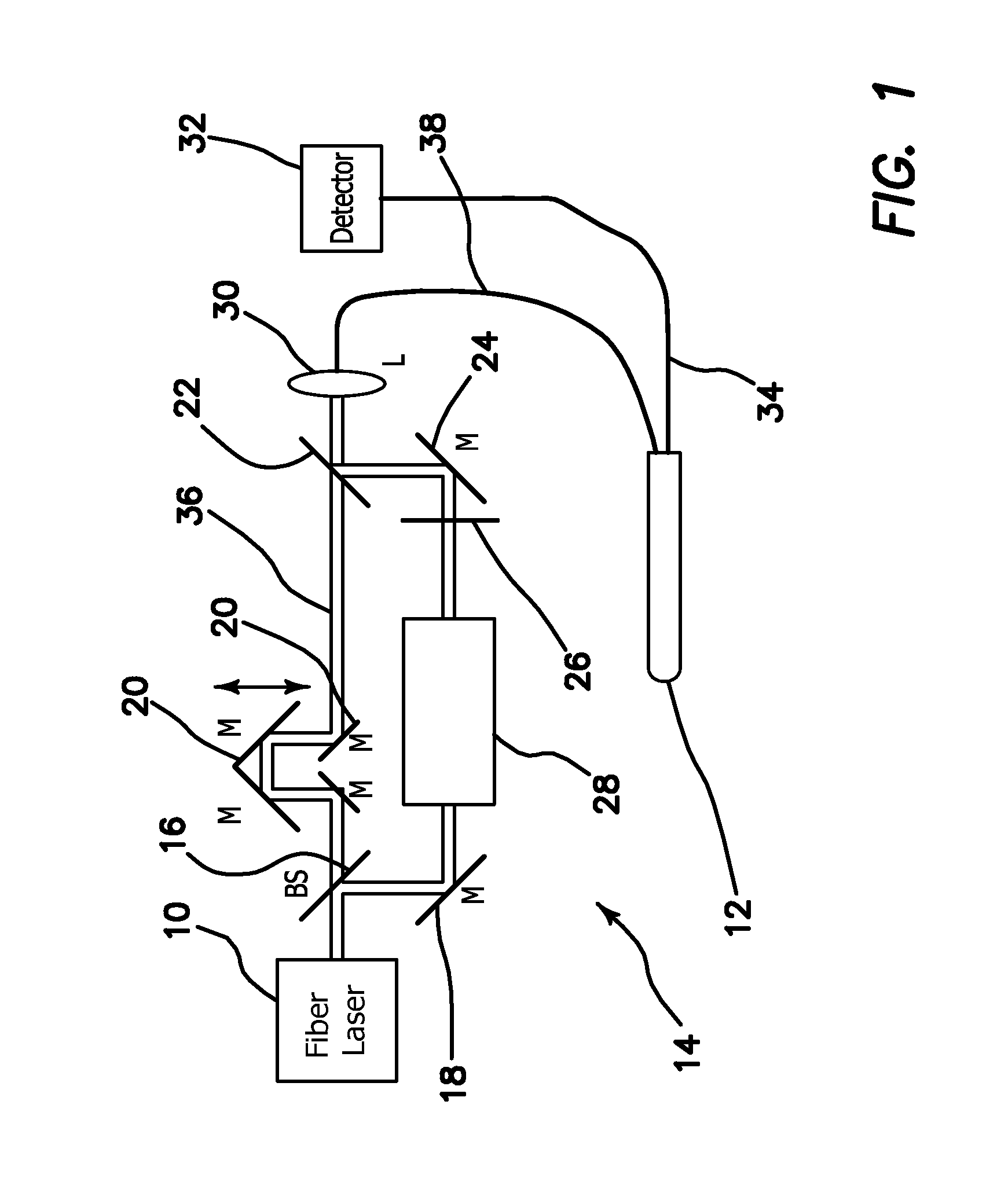
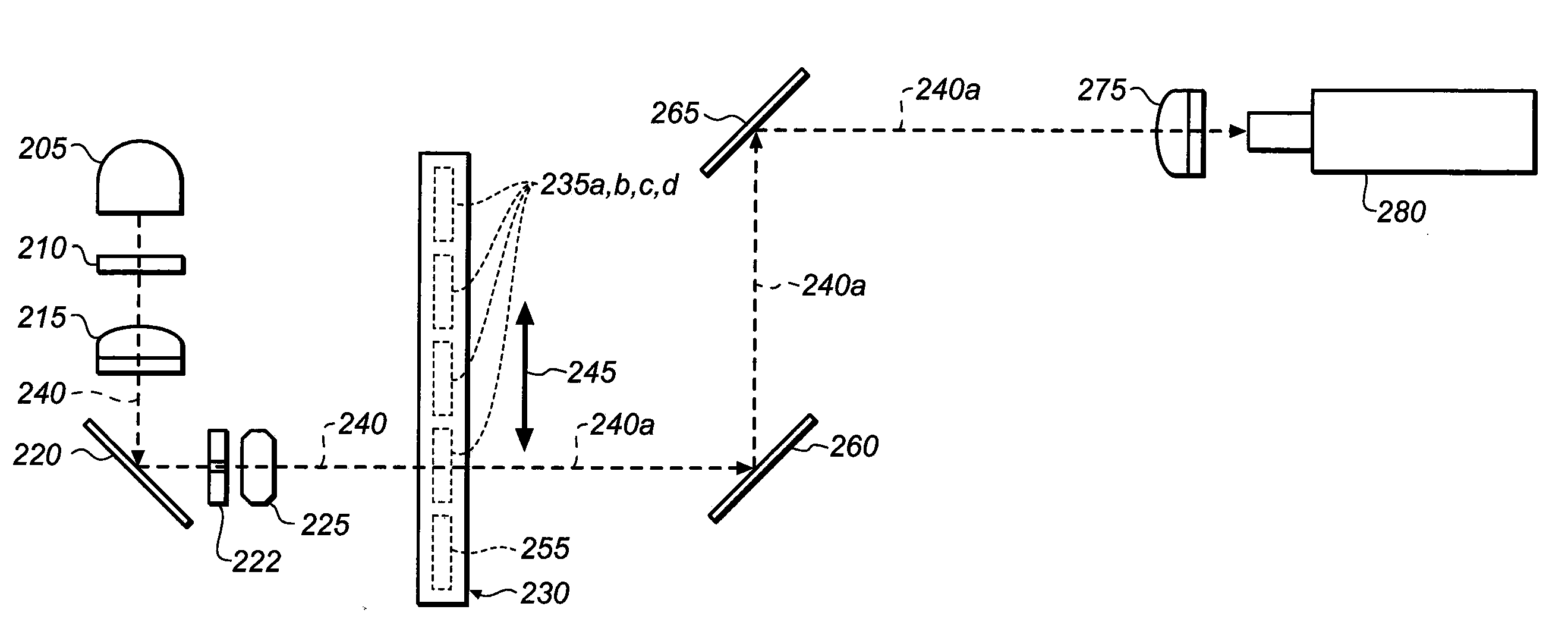
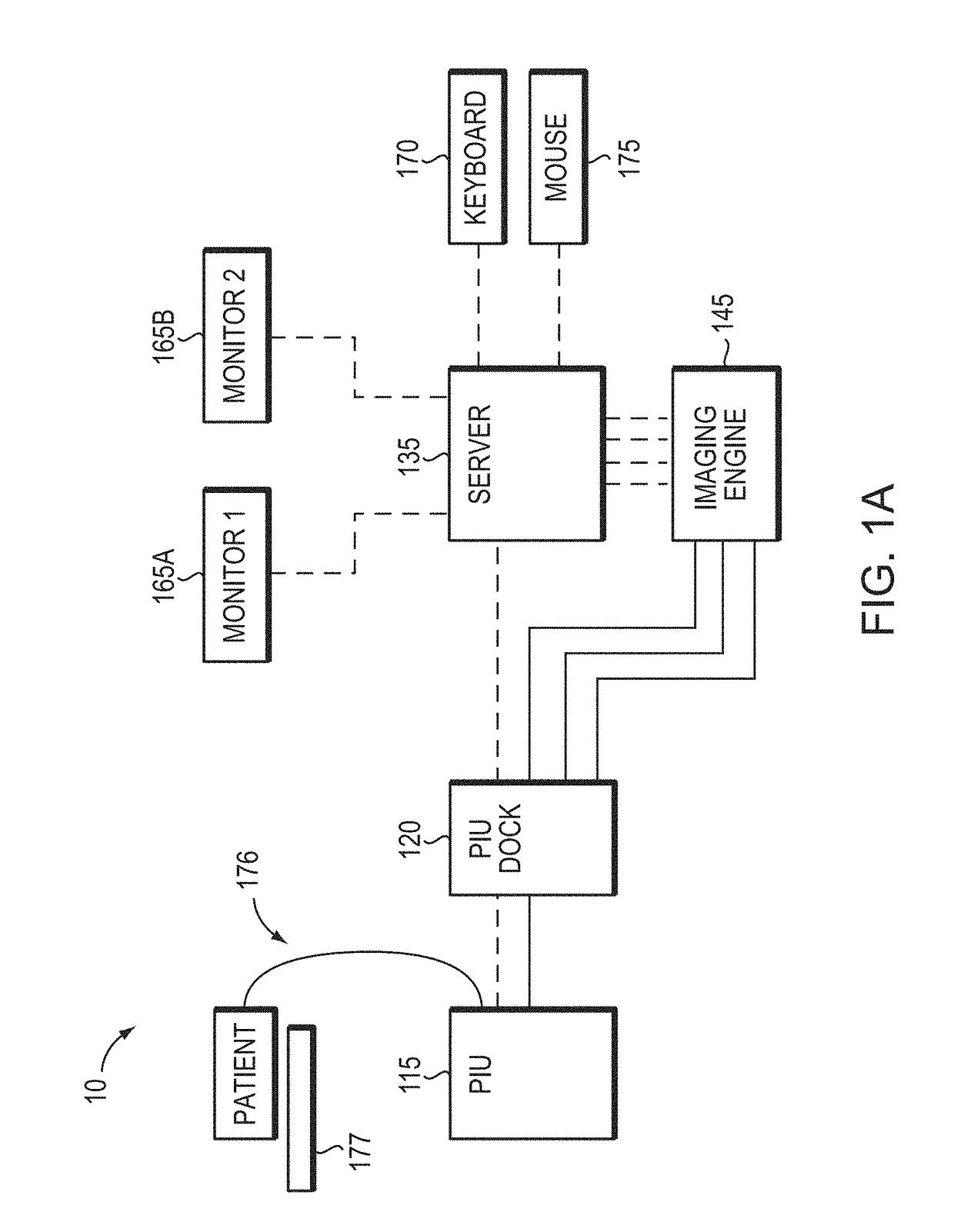
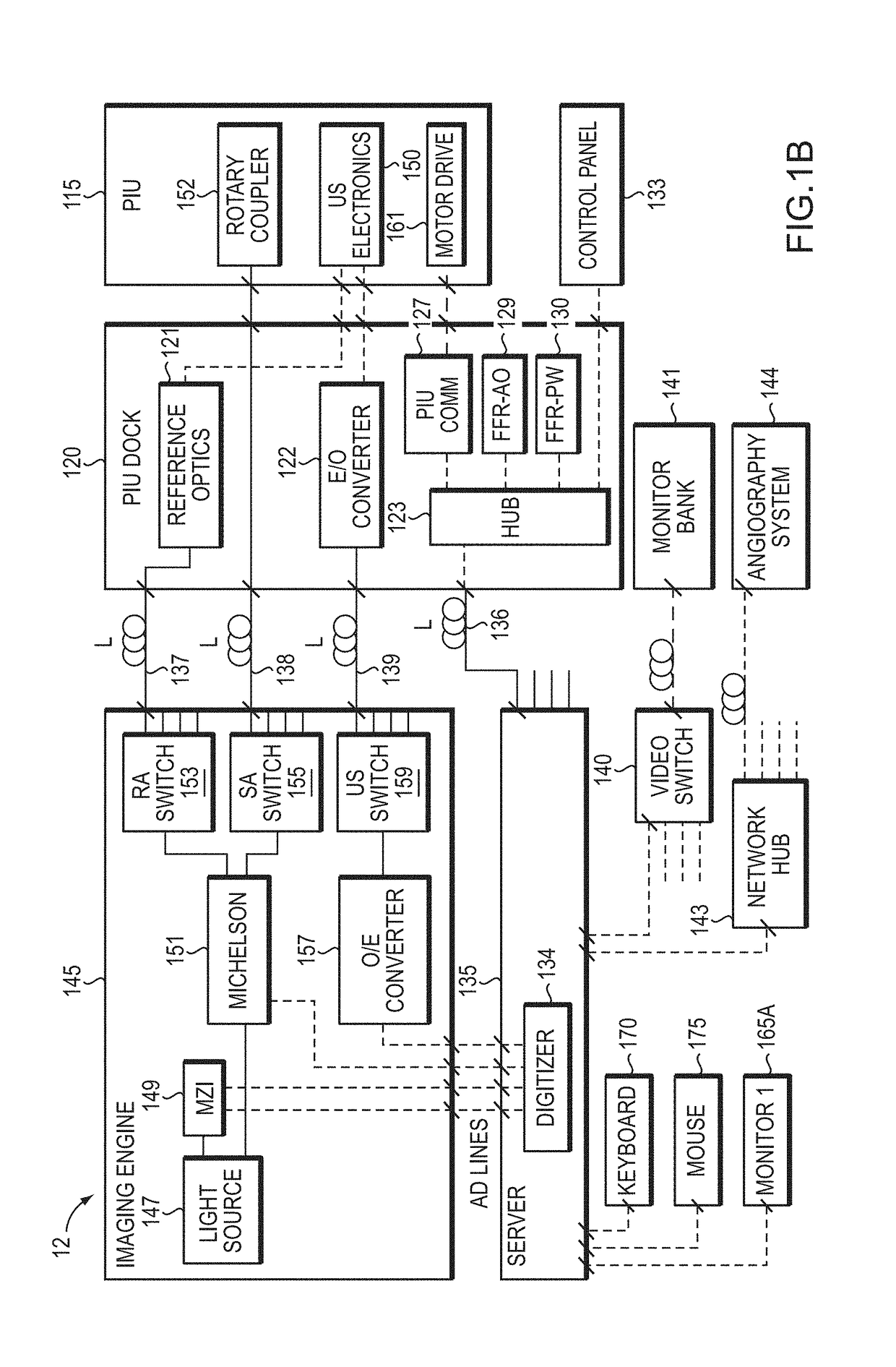
Multimodal Imaging System, Apparatus, and Methods
In part, the invention relates to an image data collection system. The system can include an interferometer having a reference arm that includes a first optical fiber of length of L1 and a sample arm that includes a second optical fiber of length of L2 and a first rotary coupler configured to interface with an optical tomography imaging probe, wherein the rotary coupler is in optical communication with the sample arm. In one embodiment, L2 is greater than about 5 meters. The first optical fiber and the second optical fiber can both be disposed in a common protective sheath. In one embodiment, the system further includes an optical element configured to adjust the optical path length of the reference arm, wherein the optical element is in optical communication with the reference arm and wherein the optical element is transmissive or reflective.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
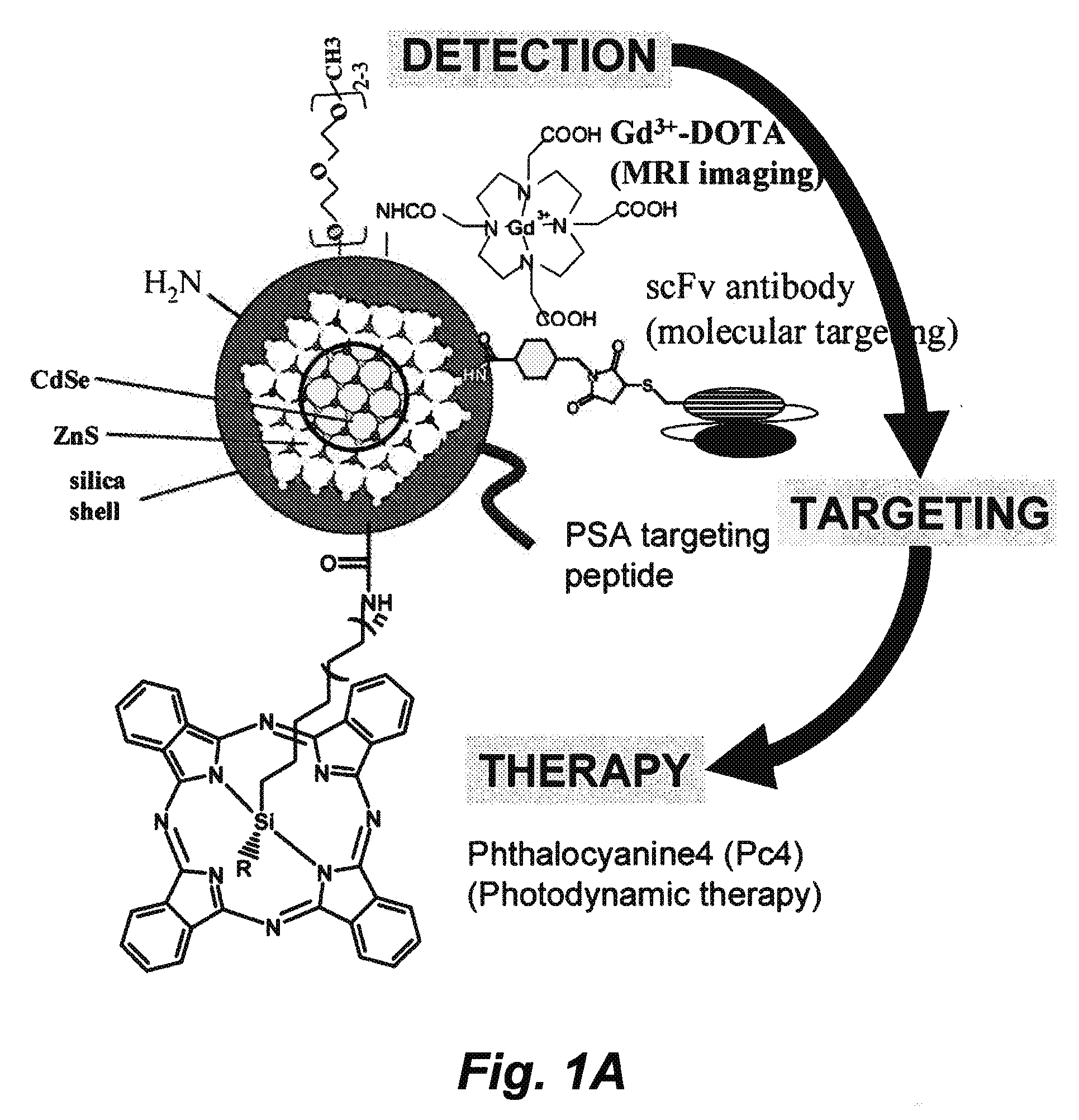
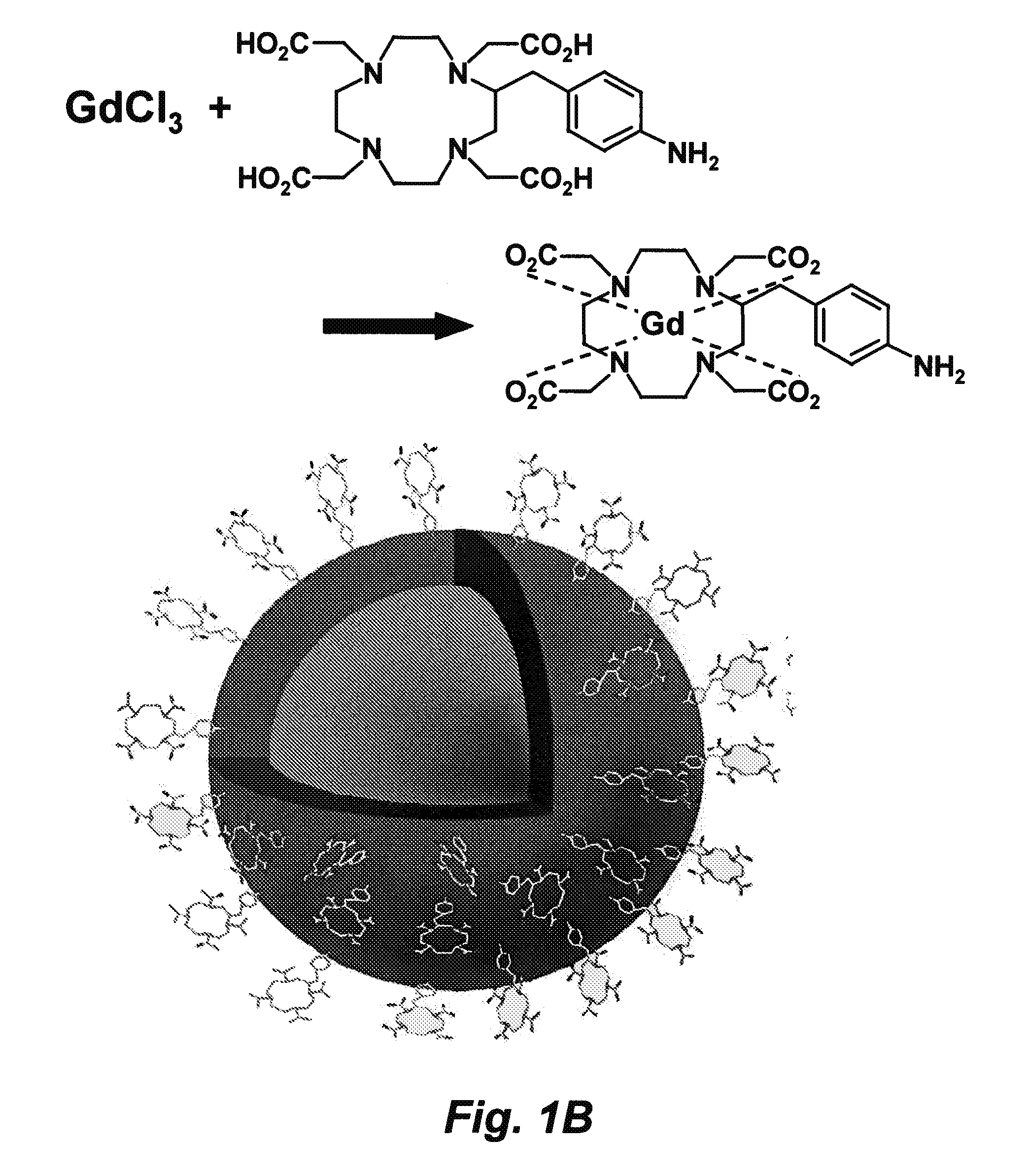
Multimodal imaging probes for in vivo targeted and non-targeted imaging and therapeutics
In certain embodiments this invention provides a nanoparticle-based technology platform for multimodal in vivo imaging and therapy. The nanoparticle-based probes detects diseased cells by MRI, PET or deep tissue Near Infrared (NIR) imaging, and are capable of detecting diseased cells with greater sensitivity than is possible with existing technologies. The probes also target molecules that localize to normal or diseased cells, and initiates apoptosis of diseased cells.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
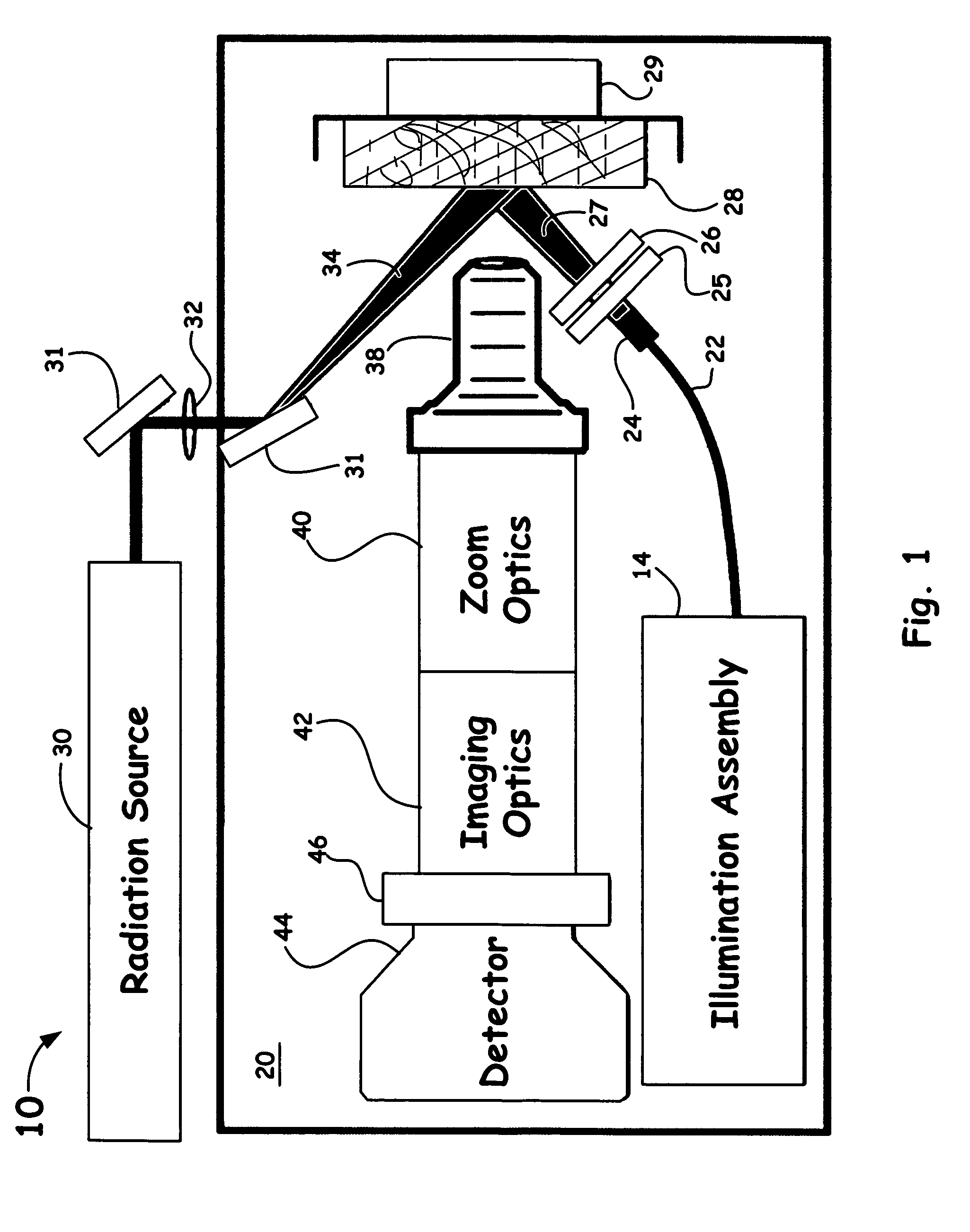
Hyperspectral microscope for in vivo imaging of microstructures and cells in tissues
InactiveUS20070160279A1Improve image contrastImprove visibilityDiagnostics using spectroscopyMaterial analysis by optical meansOff-axis illuminationIn vivo
An optical hyperspectral / multimodal imaging method and apparatus is utilized to provide high signal sensitivity for implementation of various optical imaging approaches. Such a system utilizes long working distance microscope objectives so as to enable off-axis illumination of predetermined tissue thereby allowing for excitation at any optical wavelength, simplifies design, reduces required optical elements , significantly reduces spectral noise from the optical elements and allows for fast image acquisition enabling high quality imaging in-vivo. Such a technology provides a means of detecting disease at the single cell level such as cancer, precancer, ischemic, traumatic or other type of injury, infection, or other diseases or conditions causing alterations in cells and tissue micro structures.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
Multimodal imaging system for tissue imaging
InactiveUS20090131800A1Eliminate specular reflectionsEnhance the imageDiagnostics using lightSensorsFluorescenceUltraviolet lights
An apparatus for obtaining area images and optical coherence tomography (OCT) image of a tissue comprises an image sensor, a first illumination means providing broadband polarized polychromatic light, a second illumination means providing narrow-band ultraviolet light, a third illumination means providing Near-Infrared light, an optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging apparatus, one or more polarization elements, and an optical filter. An image processor identifies a region of interest according to area image, which can be a polarized reflectance image, a fluorescence light image, or both for the OCT imaging apparatus to obtain an OCT image over the region of interest.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Hyperspectral microscope for in vivo imaging of microstructures and cells in tissues
InactiveUS7945077B2Increase contrastImprove visibilityDiagnostics using spectroscopyMaterial analysis by optical meansDiseaseOff-axis illumination
An optical hyperspectral / multimodal imaging method and apparatus is utilized to provide high signal sensitivity for implementation of various optical imaging approaches. Such a system utilizes long working distance microscope objectives so as to enable off-axis illumination of predetermined tissue thereby allowing for excitation at any optical wavelength, simplifies design, reduces required optical elements, significantly reduces spectral noise from the optical elements and allows for fast image acquisition enabling high quality imaging in-vivo. Such a technology provides a means of detecting disease at the single cell level such as cancer, precancer, ischemic, traumatic or other type of injury, infection, or other diseases or conditions causing alterations in cells and tissue micro structures.
Owner:LAWRENCE LIVERMORE NAT SECURITY LLC
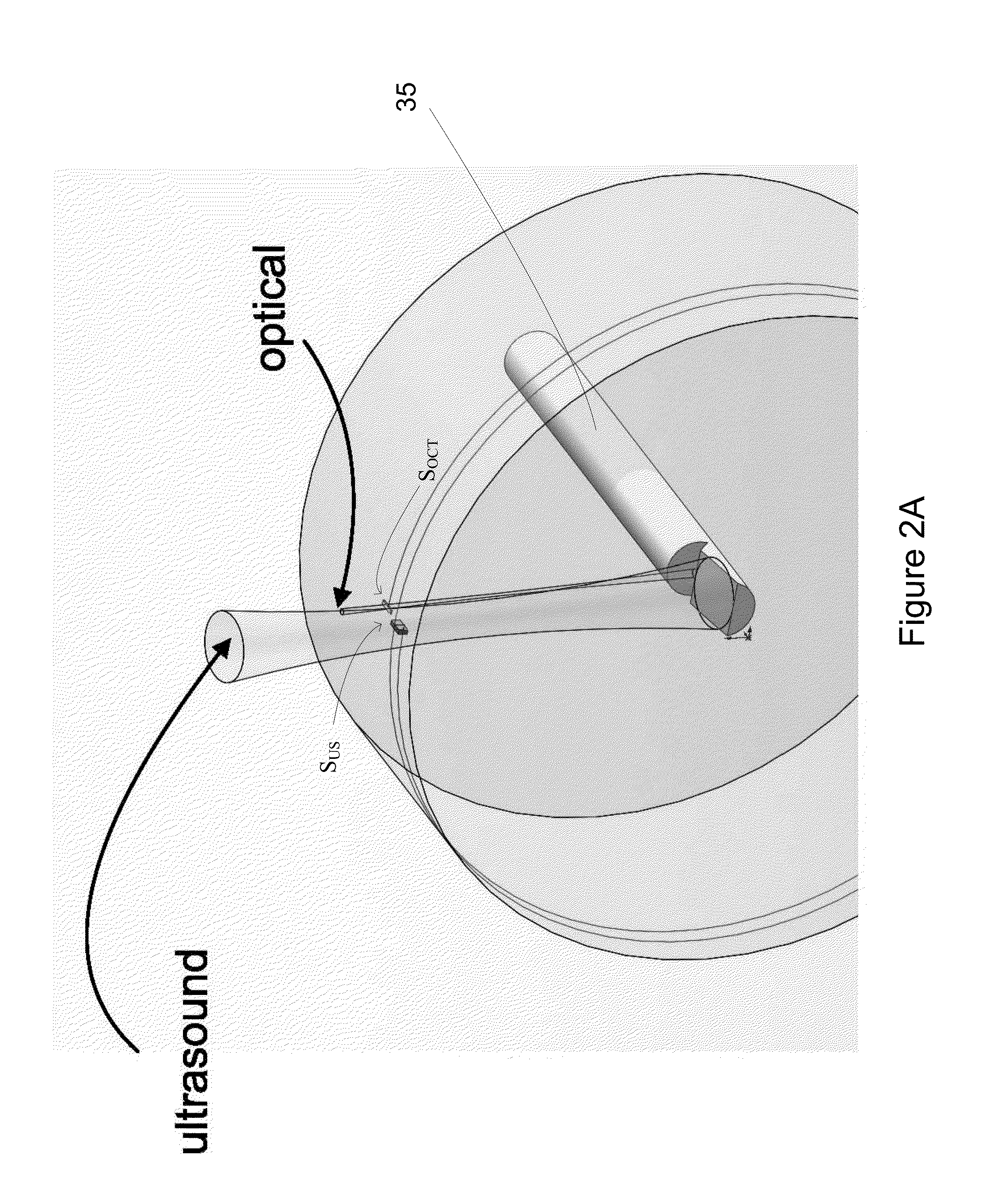
Multimodal Imaging Systems, Probes and Methods
ActiveUS20140142432A1Reduce exerciseEnhanced signalUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsAcoustic sensorsTransceiverCollection system
In part, the invention relates to a probe suitable for use with image data collection system. The probe, in one embodiment, includes an optical transceiver, such as a beam director, and an acoustic transceiver such as an ultrasound transducer. The optical transceiver is in optical communication with an optical fiber in optical communication with a beam director configured to transmit light and receive scattered light from a sample such as a wall of a blood vessel. The acoustic transceiver includes an ultrasound device or subsystem such as a piezoelectric element configured to generate acoustic waves and receive reflected acoustic waves from the sample.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Multimodal imaging sources
A multimodal source for imaging with at least one of a gamma camera, a positron emission tomography (PET) scanner and a single-photon-emission computed tomography (SPECT) scanner, and at least one of a computed tomography (CT) scanner, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner and optical scanner. The multimodal source has radioactive material permanently incorporated into a matrix of material, at least one of a material that is a target for CT, MRI and optical scanning, and a container which holds the radioactive material and the CT, MRI and / or optical target material. The source can be formed into a variety of different shapes such as points, cylinders, rings, squares, sheets and anthropomorphic shapes. The material that is a target for gamma cameras, PET scanners and SPECT scanners and / or CT, MRI and / or optical scanners can be formed into shapes that mimic biological structures.
Owner:ISO SCI LAB
Real-time contemporaneous multimodal imaging and spectroscopy uses thereof
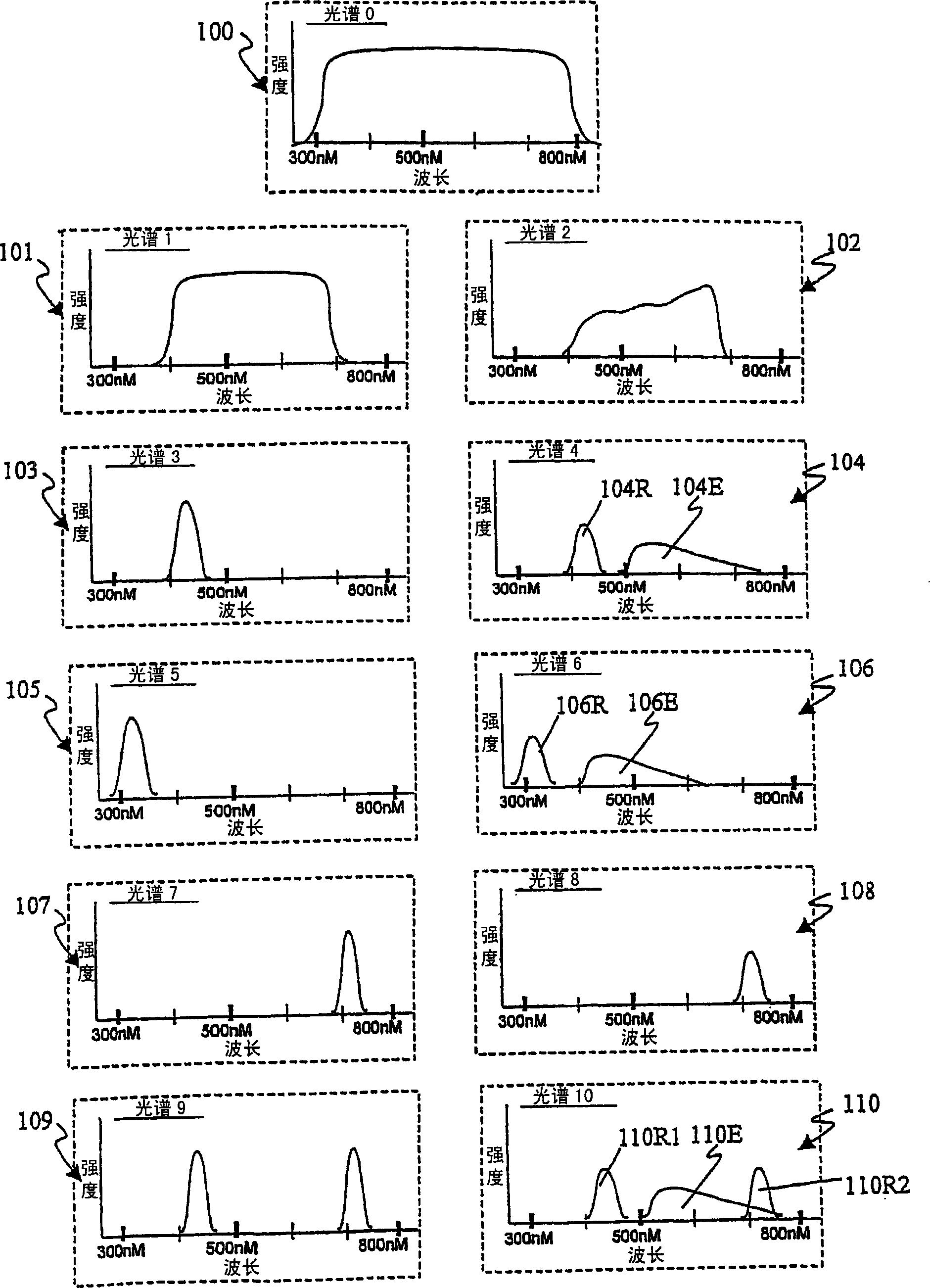
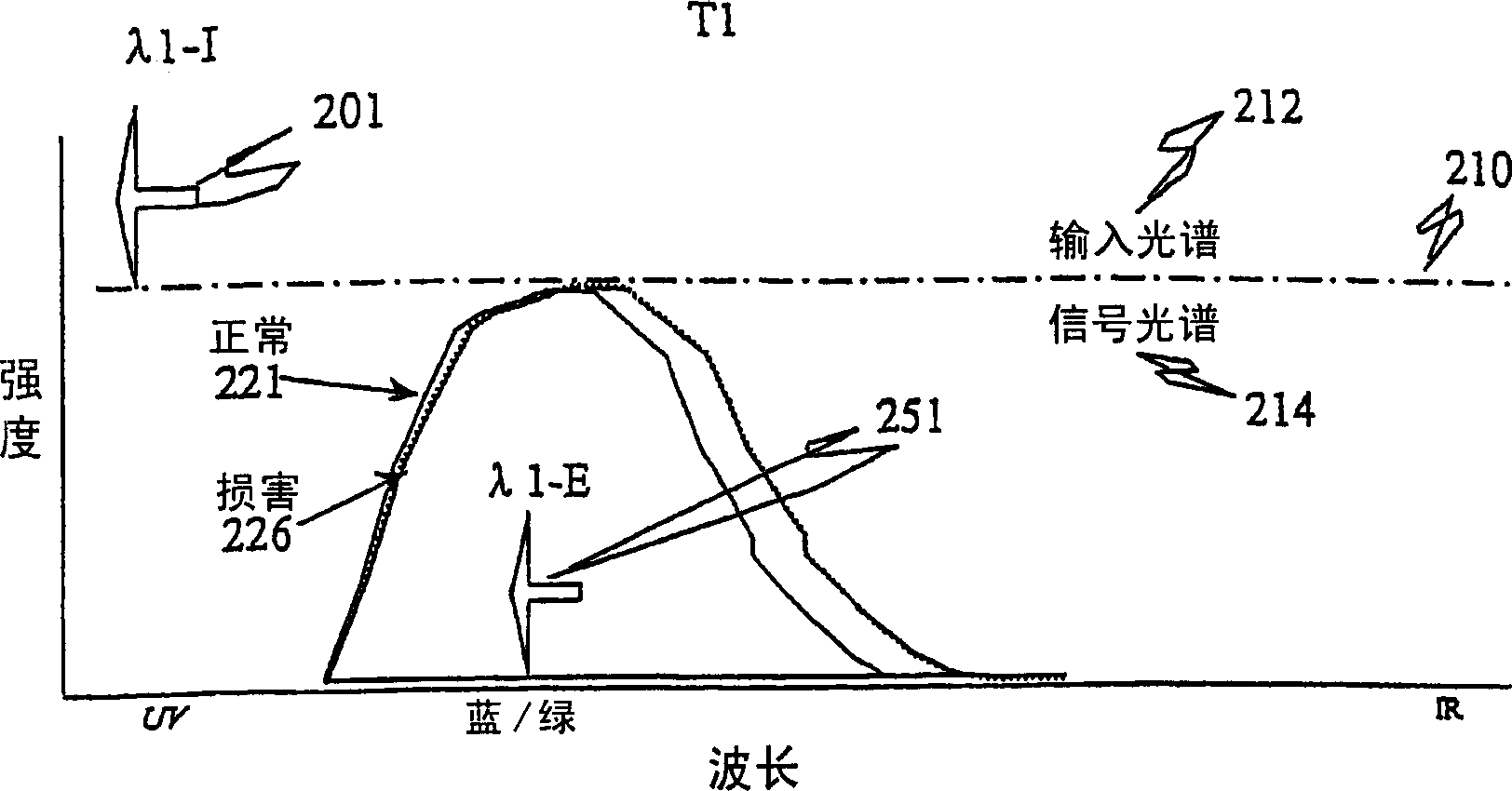
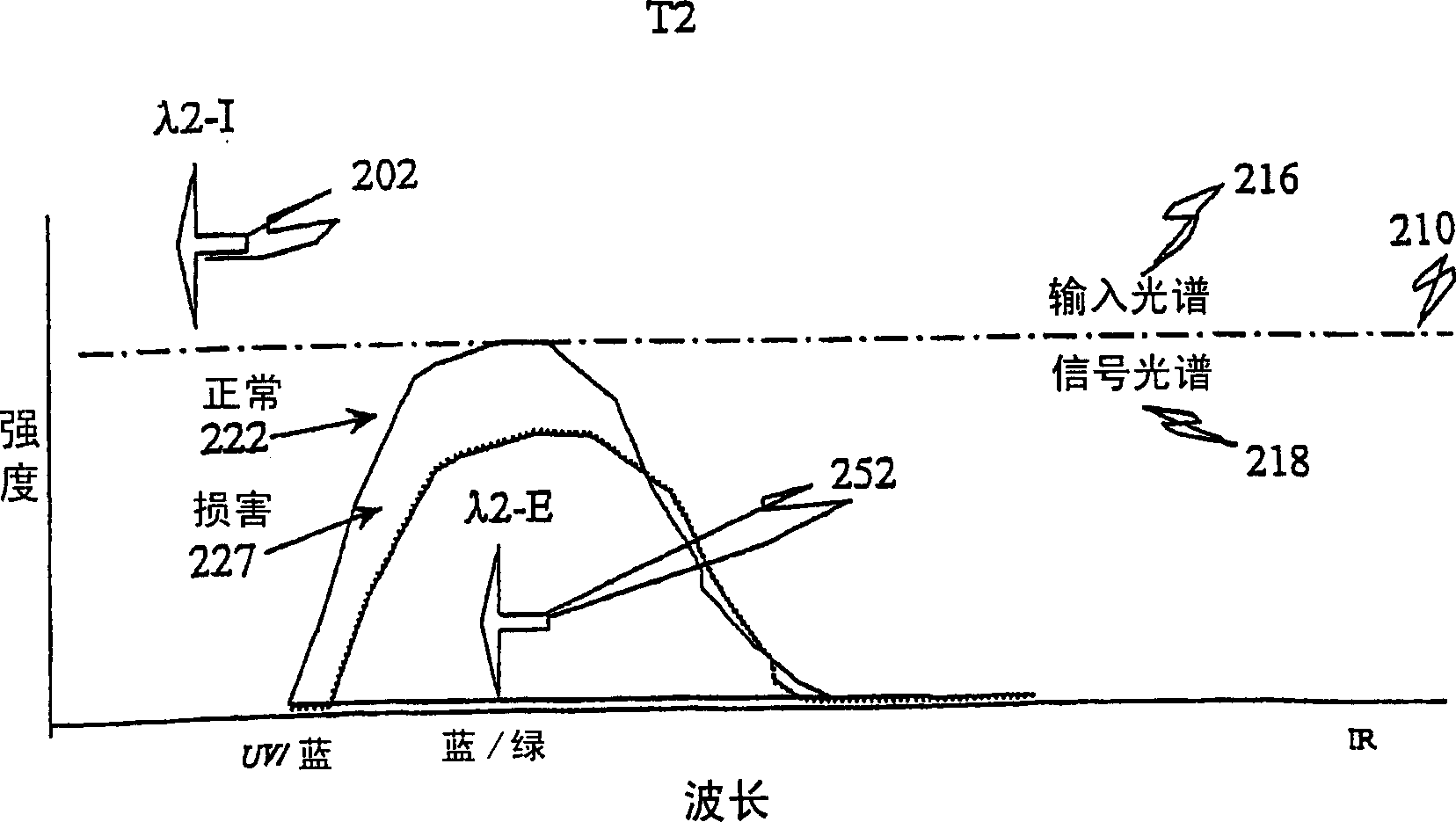
The present invention comprises an optical apparatus, methods and uses for real-time (video-rate) multimodal imaging, for example, contemporaneous measurement of white light reflectance, native tissue autofluorescence and near infrared images with an endoscope. These principles may be applied to various optical apparati such as microscopes, endoscopes, telescopes, cameras etc. to view or analyze the interaction of light with objects such as planets, plants, rocks, animals, cells, tissue, proteins, DNA, semiconductors, etc. Multi-band spectral images may provide morphological data such as surface structure of lung tissue whereas chemical make-up, sub-structure and other object characteristics may be deduced from spectral signals related to reflectance or light radiated (emitted) from the object such as luminescence or fluorescence, indicating endogenous chemicals or exogenous substances such as dyes employed to enhance visualization, drugs, therapeutics or other agents. Accordingly, one embodiment of the present invention discusses simultaneous white light reflectance and fluorescence imaging. Another embodiment describes the addition of another reflectance imaging modality (in the near-IR spectrum). Input (illumination) spectrum, optical modulation, optical processing, object interaction, output spectrum, detector configurations, synchronization, image processing and display are discussed for various applications.
Owner:PERCEPTRONIX MEDICAL +1
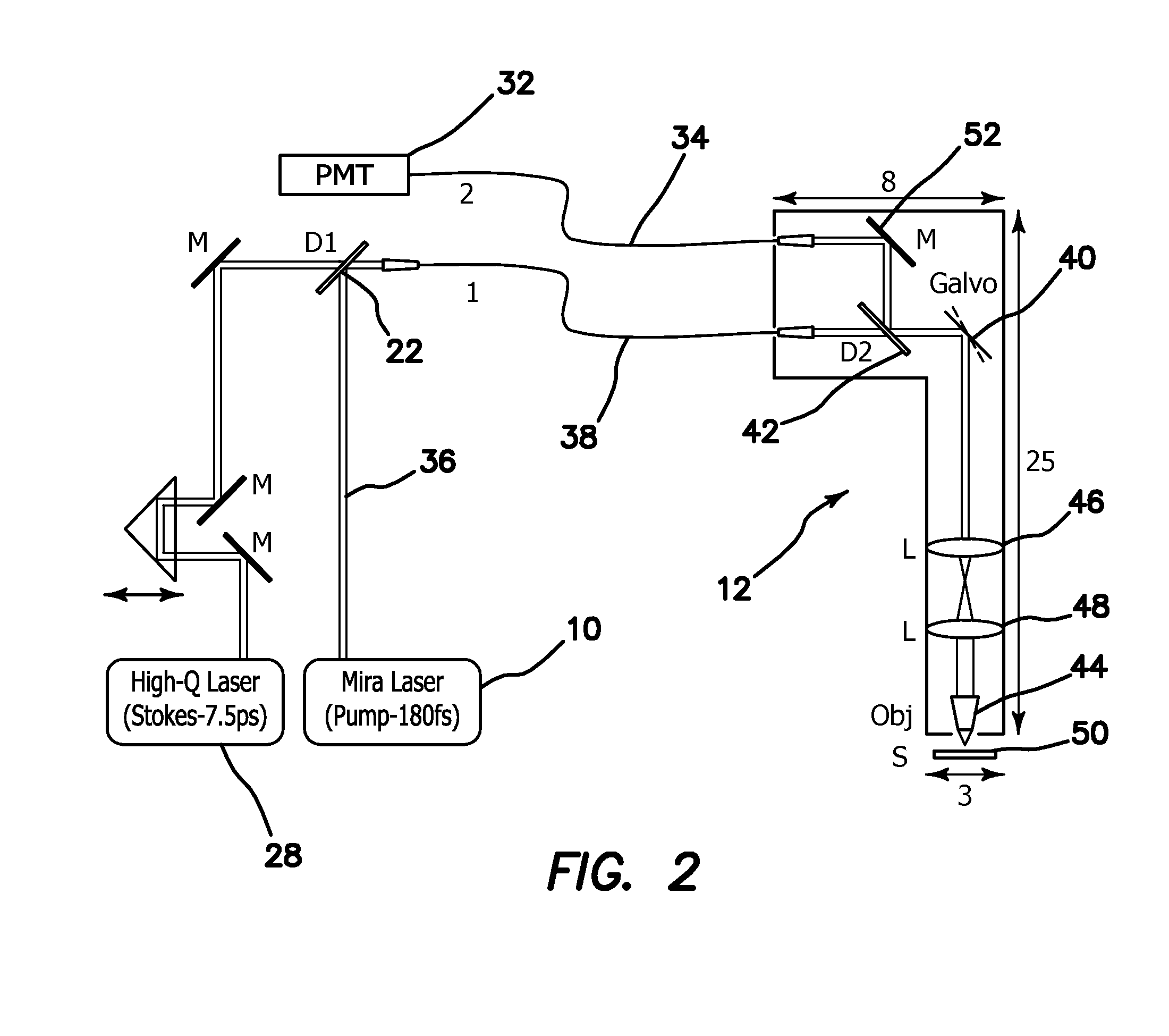
System and Method for Efficient Coherence Anti-Stokes Raman Scattering Endoscopic and Intravascular Imaging and Multimodal Imaging
ActiveUS20110282166A1Complicate interpretationEliminate the problemRadiation pyrometryEndoscopesFiberStokes component
A fiber-delivered probe suitable for CARS imaging of thick tissues is practical. The disclosed design is based on two advances. First, a major problem in CARS probe design is the presence of a very strong anti-Stokes component in silica delivery fibers generated through a FWM process. Without proper spectral filtering, this component affects the CARS image from the tissue sample. The illustrated embodiments of the invention efficiently suppress this spurious anti-Stokes component through the use of a separate fiber for excitation delivery and for signal detection, which allows the incorporation of dichroic optics for anti-Stokes rejection. Second, the detection of backscattered CARS radiation from the sample is optimized by using a large core multi mode fiber in the detection channel. This scheme produces high quality CARS images free of detector aperture effects. Miniaturization of this fiber-delivered probe results in a practical handheld probe for clinical CARS imaging.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
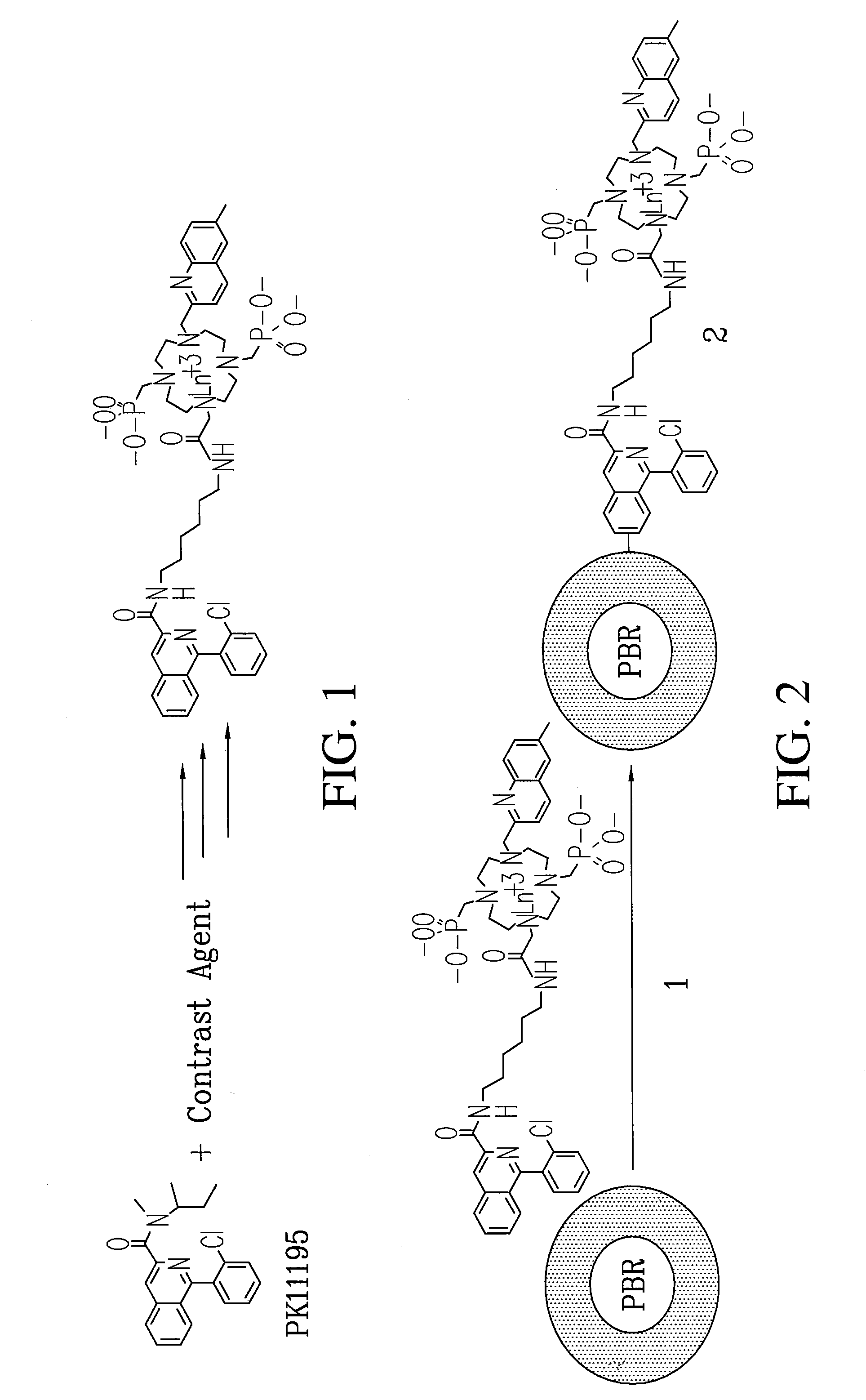
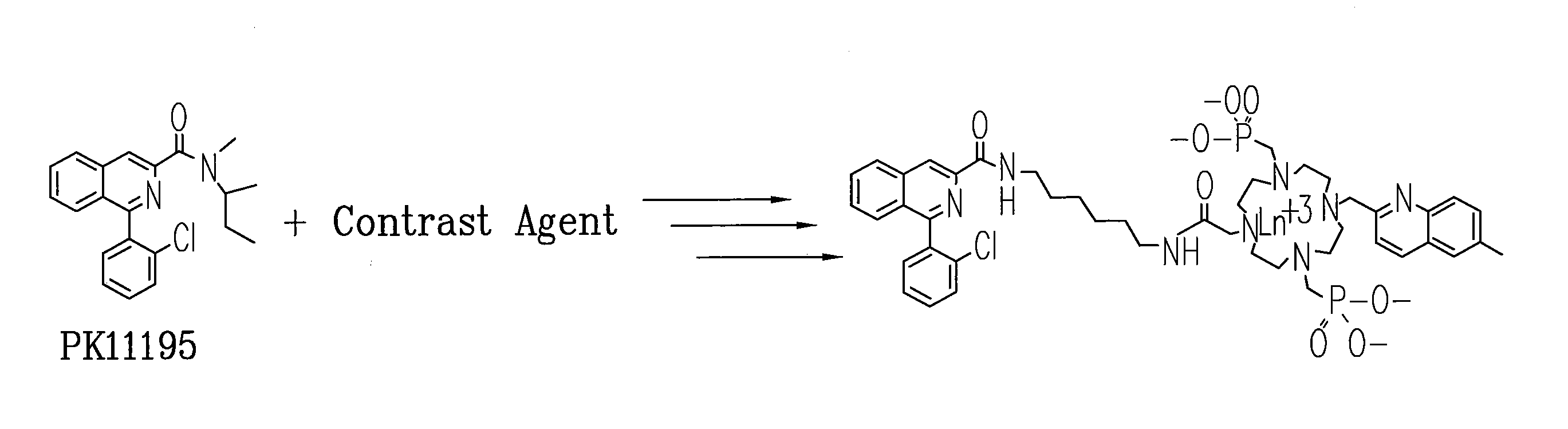
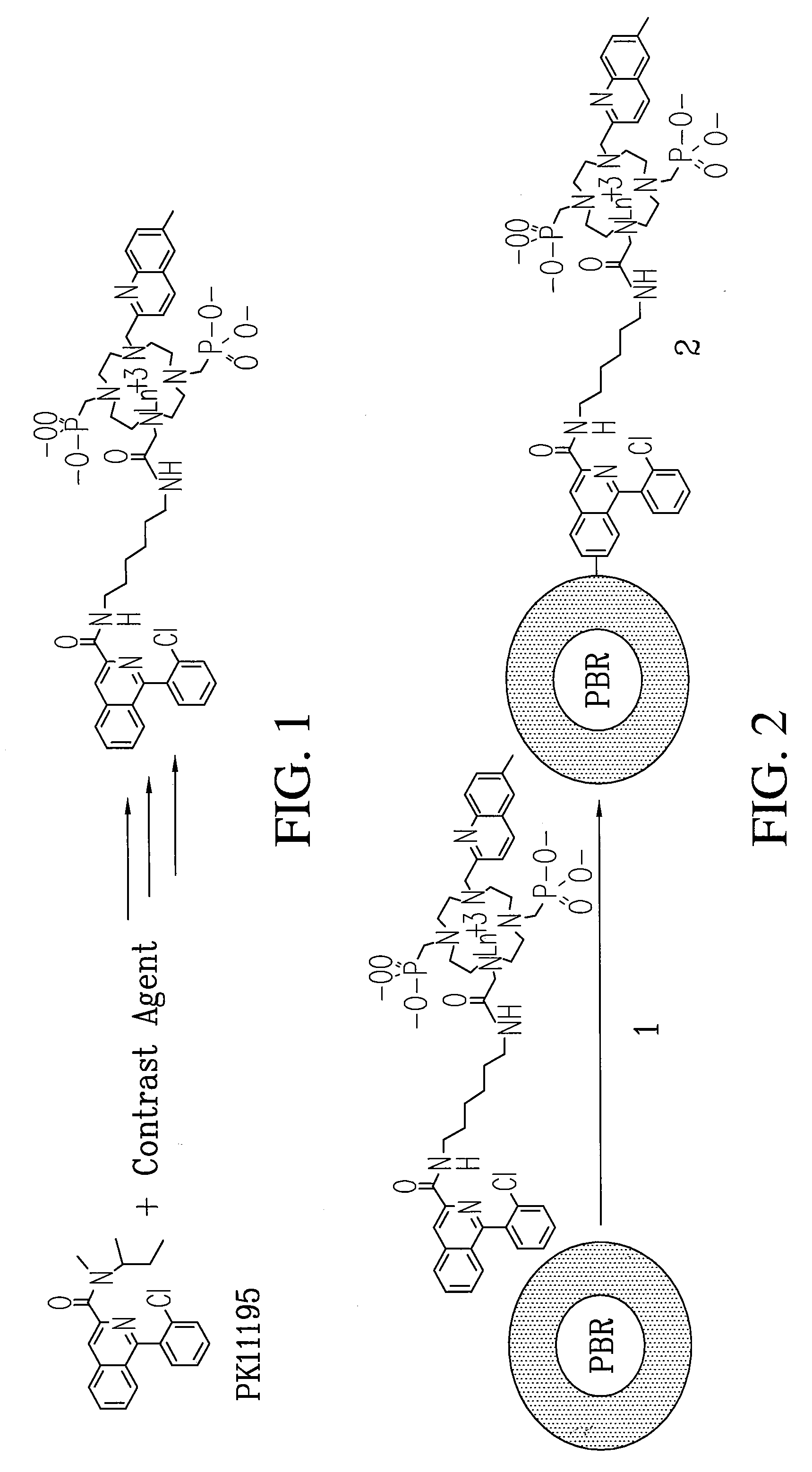
Multi-use multimodal imaging chelates
InactiveUS7338651B2Improve discriminationEasy to detectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellFluorescence
Cyclen-based chelates can be used as contrast agents for multi-modal imaging of tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates are preferably polyazamacrocyclic molecules formed from 1,4,7,10 tetraazacyclododecane (“cyclen”) having varying chelating ions, phosphoester chains, and light harvesting moieties. By changing the chelating ion, phosphoester chain length and / or the light harvesting moiety different imaging techniques, such as MRI, CT, fluorescence and absorption, x-ray and NIR, may be employed to image the tissue cells. Additionally, the cyclen-based chelates may be conjugated to provide for site-specific delivery of the cyclen-based chelate to the desired tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates may also be delivered to the tissue cells by attaching the cyclen-based chelates to a polymeric delivery vehicle. Although these cyclen-based chelates have a wide variety of application, the preferred use is for imaging of cancer cells, such as brain cancer, for improving resection of a cancerous tissue.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST +1
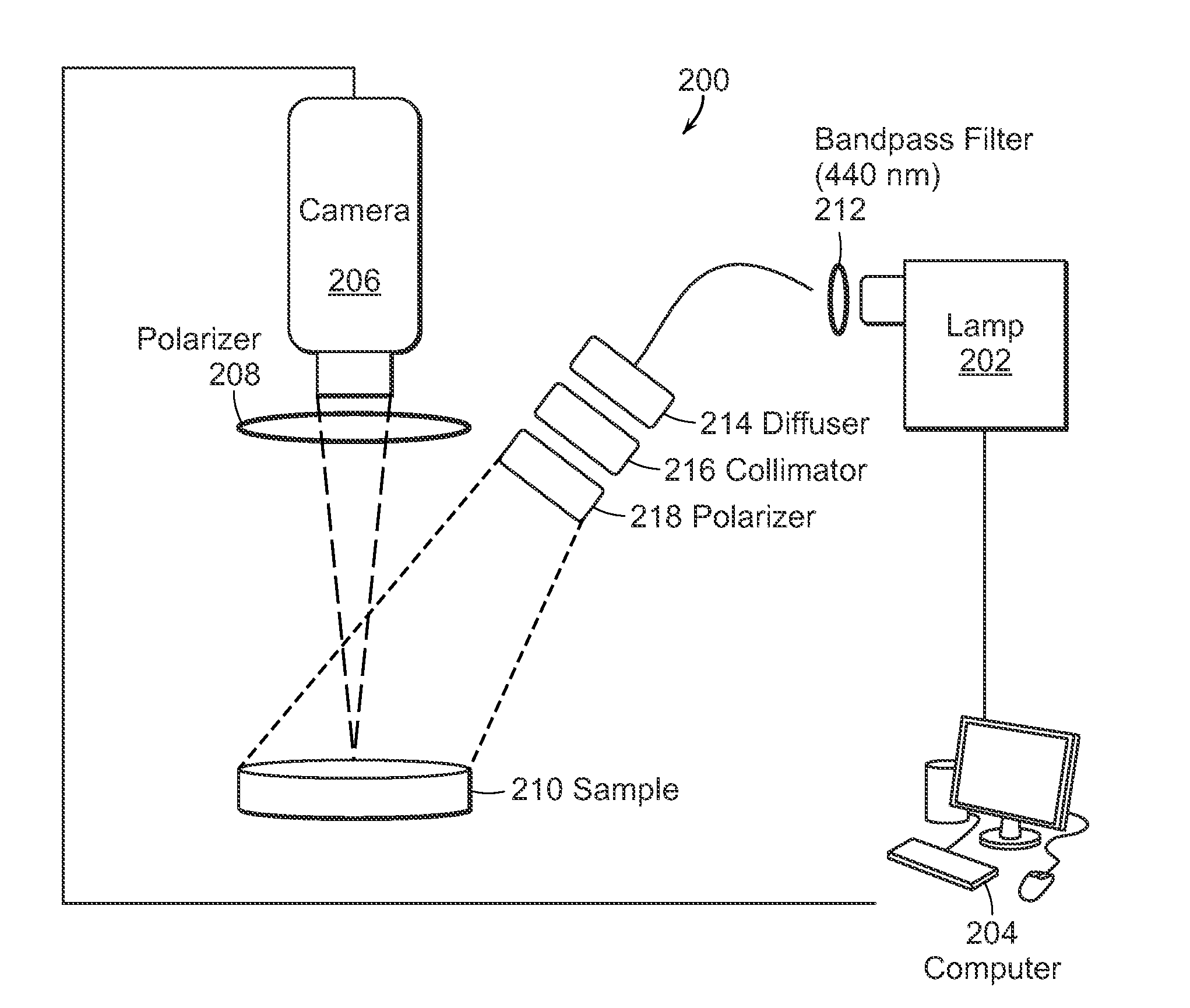
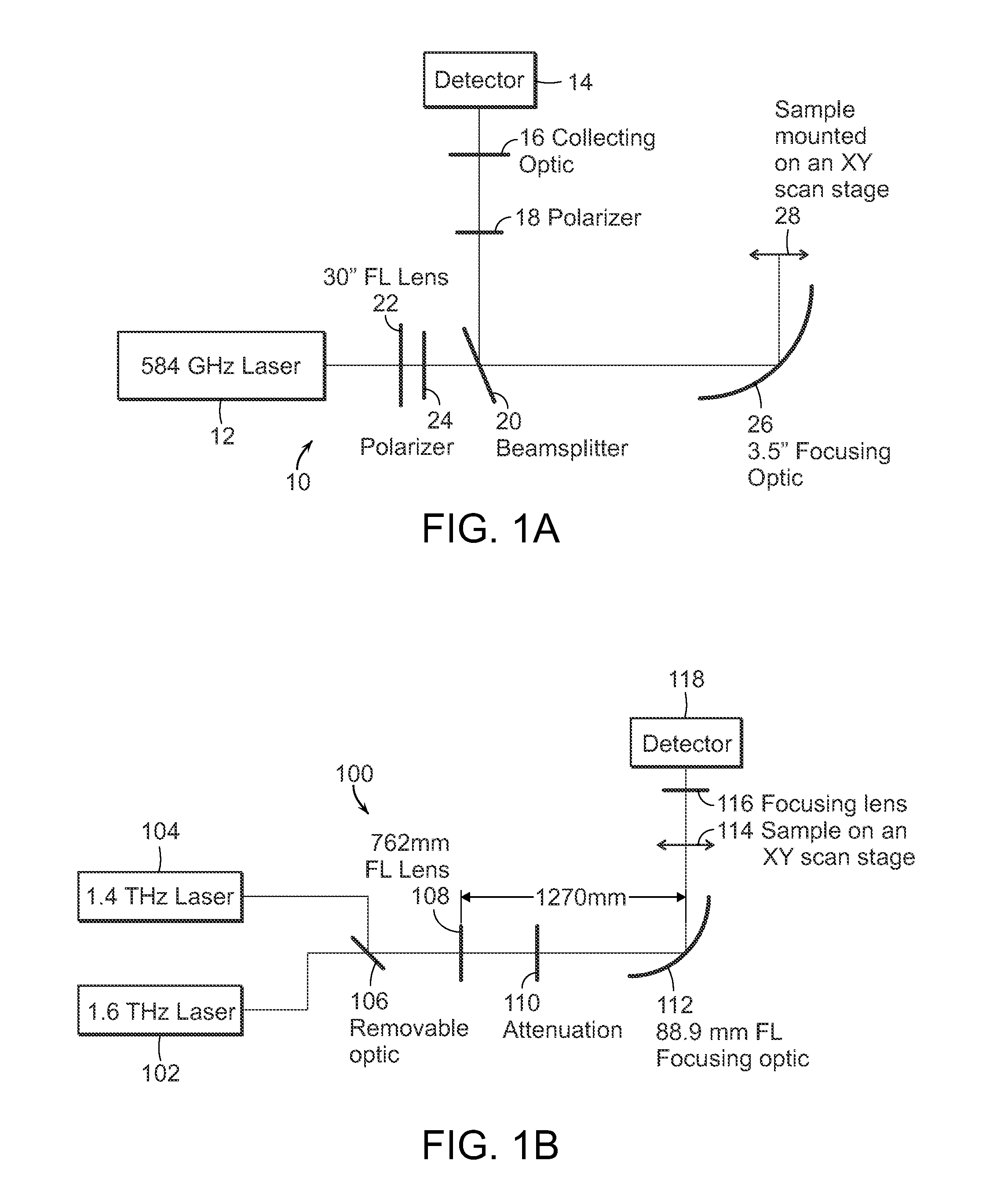
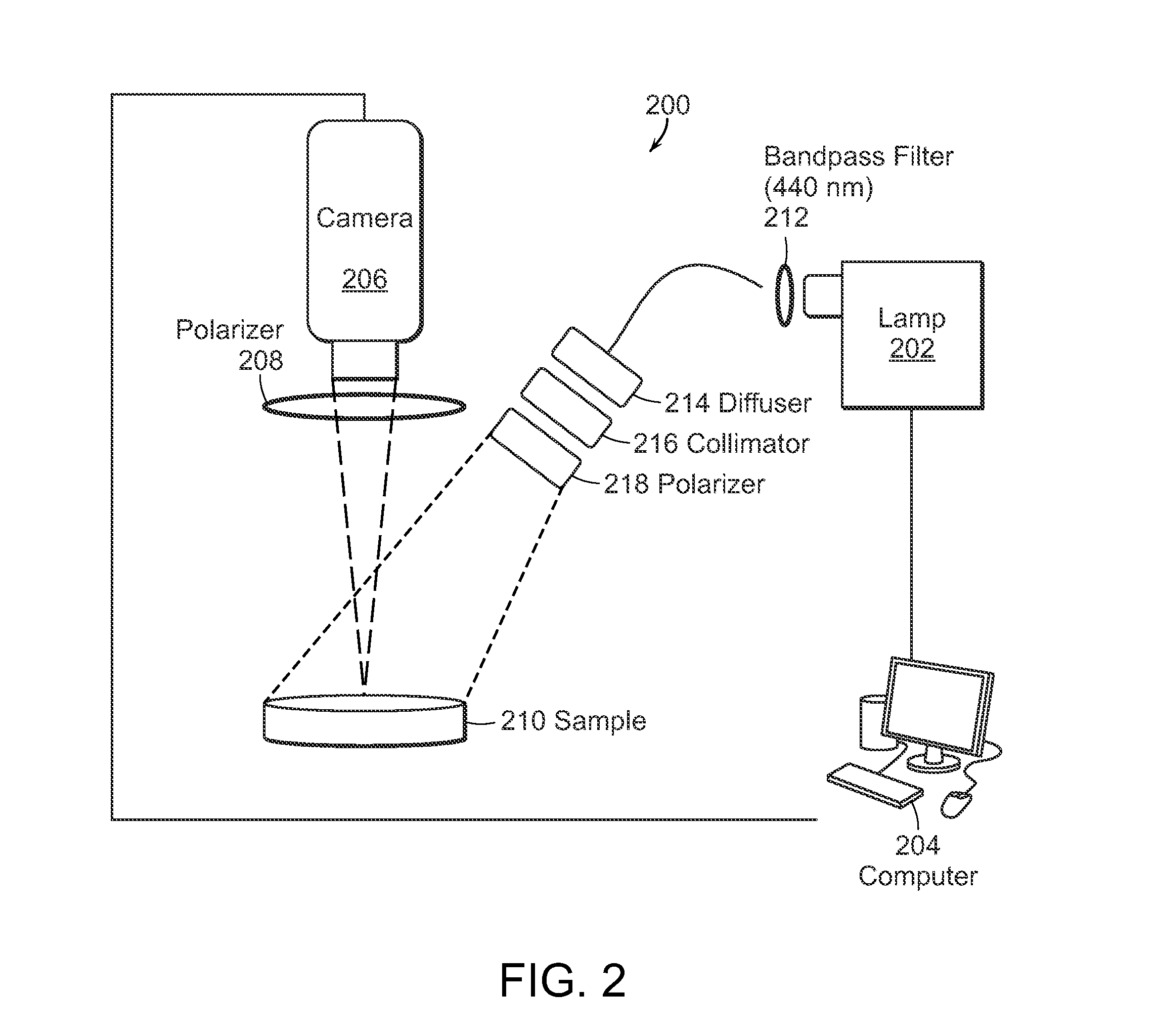
Multimodal imaging for the detection of tissue structure and composition
InactiveUS20150164327A1Accurately presentedSolution value is not highMedical imagingPolarisation-affecting propertiesTumor marginLight delivery
The present invention relates to the use of optical and terahertz imaging of tissue for measuring characteristics to assist in diagnosis. A light delivery and collection system is used that can aid in the detection of tumor margins, for example. A data processor processes the image data to determine characteristics of a region of tissue.
Owner:UNIV OF MASSACHUSETTS
Enhanced multi-protocol analysis via intelligent supervised embedding (empravise) for multimodal data fusion
ActiveUS20140037172A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmDimensionality reduction
The present invention provides a system and method for analysis of multimodal imaging and non-imaging biomedical data, using a multi-parametric data representation and integration framework. The present invention makes use of (1) dimensionality reduction to account for differing dimensionalities and scale in multimodal biomedical data, and (2) a supervised ensemble of embeddings to accurately capture maximum available class information from the data.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
Cloud computation based early oncotherapy efficacy evaluation system and method
The invention discloses a cloud computation based early oncotherapy efficacy evaluation system and method. The system comprises a multimodal imaging acquisition device in the oncotherapy process, a voxel-based multimodal image registration and fusion cloud computation device, a voxel-based early evaluation cloud computation device for efficacies in the oncotherapy process, and a posttreatment cloud computation evaluation device. The system and method provides more accurate, reliable and real-time information abundant in information amount to doctors, and accurate bases are provided for establishing patient-orientated personalized treatment programs. By establishment of a molecular image guided early oncotherapy efficacy evaluation cloud system with high-speed processing capacity, a posttreatment historical data reference platform is provided for medical staff, and a platform used for providing bases to timely adjustment, fast tracking or implementation of treatment schemes on the basis of real-time data in the current treatment course can be provided.
Owner:苏州动影信息科技有限公司
Multimodal imaging system for tissue imaging
An apparatus for obtaining area images and optical coherence tomography (OCT) image of a tissue comprises an image sensor, a first illumination means providing broadband polarized polychromatic light, a second illumination means providing narrow-band ultraviolet light, a third illumination means providing Near-Infrared light, an optical coherence tomography (OCT) imaging apparatus, one or more polarization elements, and an optical filter. An image processor identifies a region of interest according to area image, which can be a polarized reflectance image, a fluorescence light image, or both for the OCT imaging apparatus to obtain an OCT image over the region of interest.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
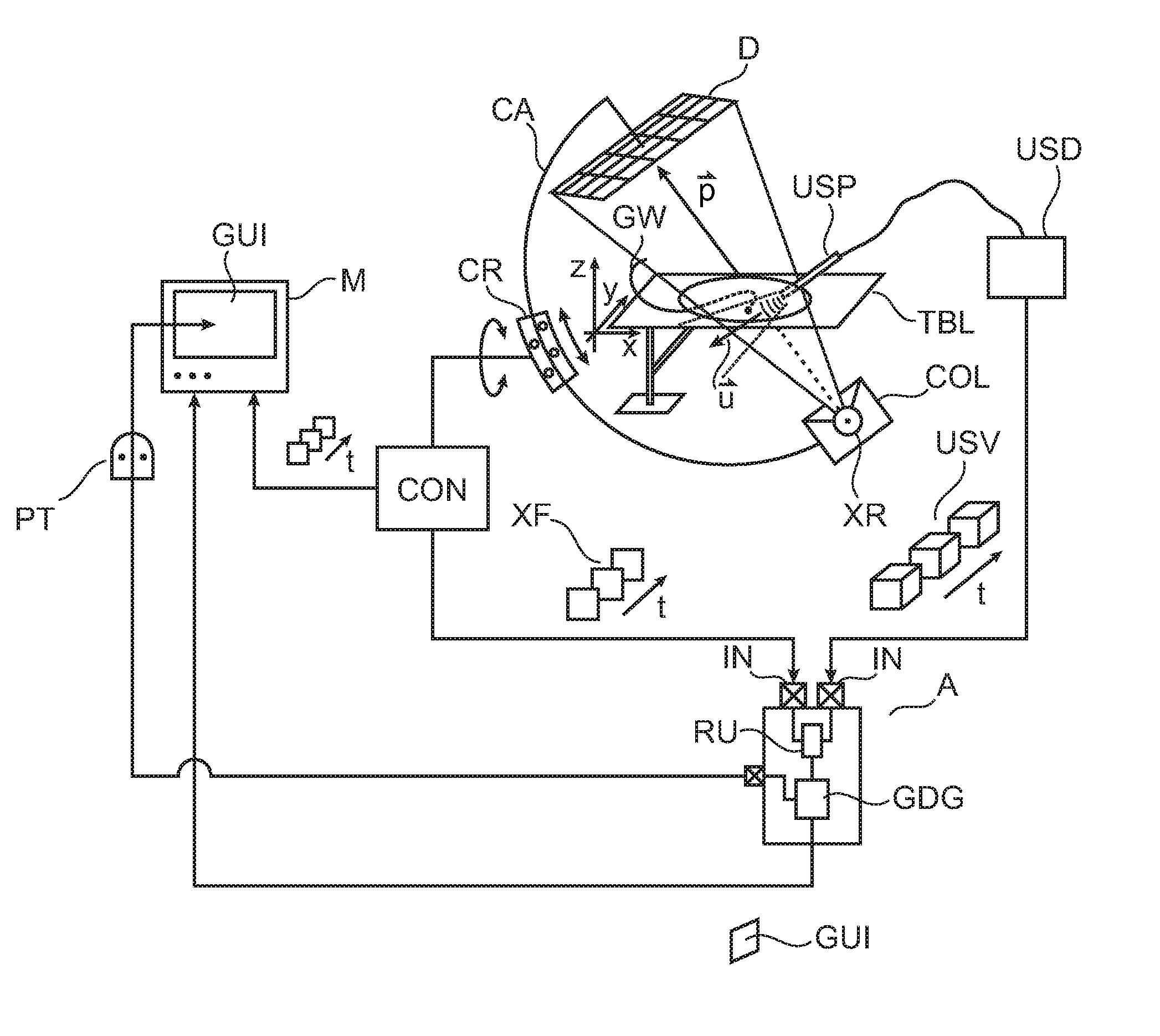
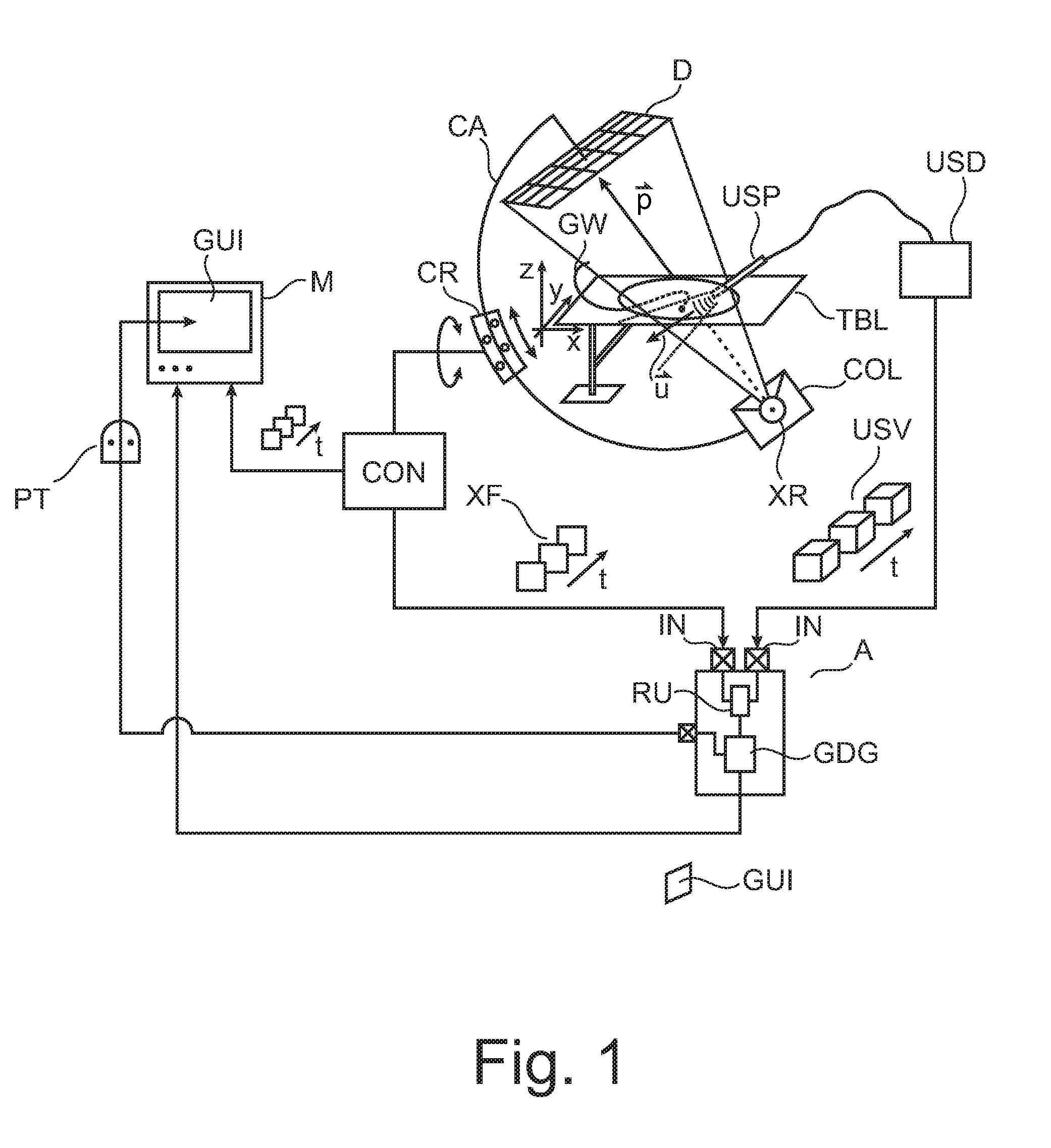
Real-time scene-modeling combining 3D ultrasound and 2d x-ray imagery
ActiveUS20150302634A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementInteractive graphicsSonification
An apparatus for visualizing image material in a multimodal imaging environment. Images (XF, USV) from an X-ray imager (100) and an ultrasound probe (USP) are fused into an interactive graphics display (GUI) to form a 3D scene, where, alongside to a 3D rendering (USS) of an ultrasound volume (USV) an X-Ray projection plan (XF) is displayed in perspective within the same scene. The rendering is according to a user selected view (UV) which is changeable upon user interaction with the interactive graphics display (GUI).
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
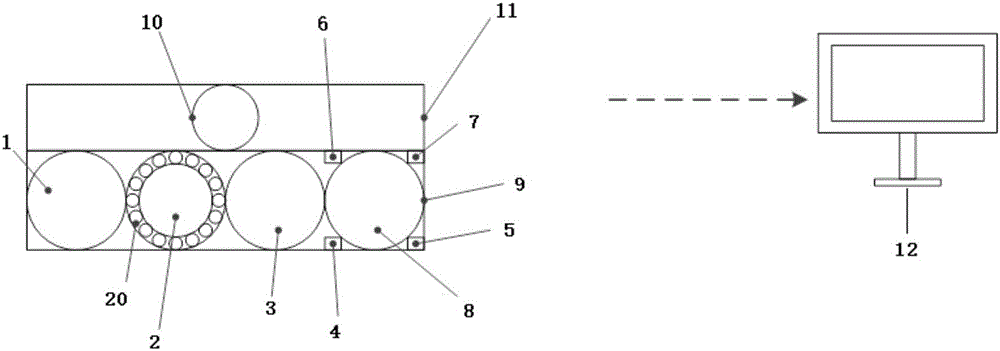
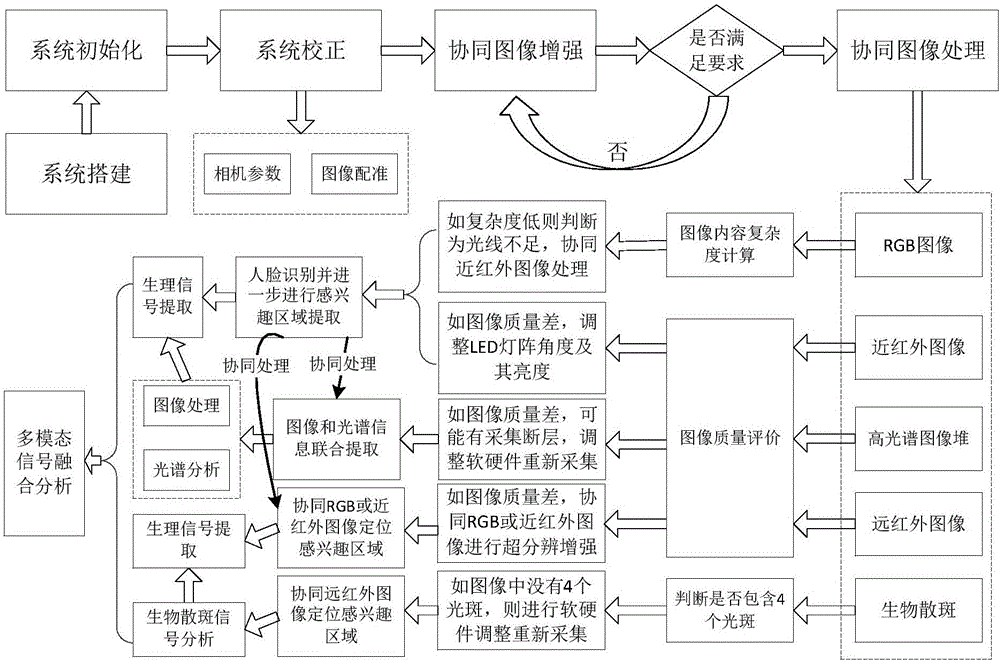
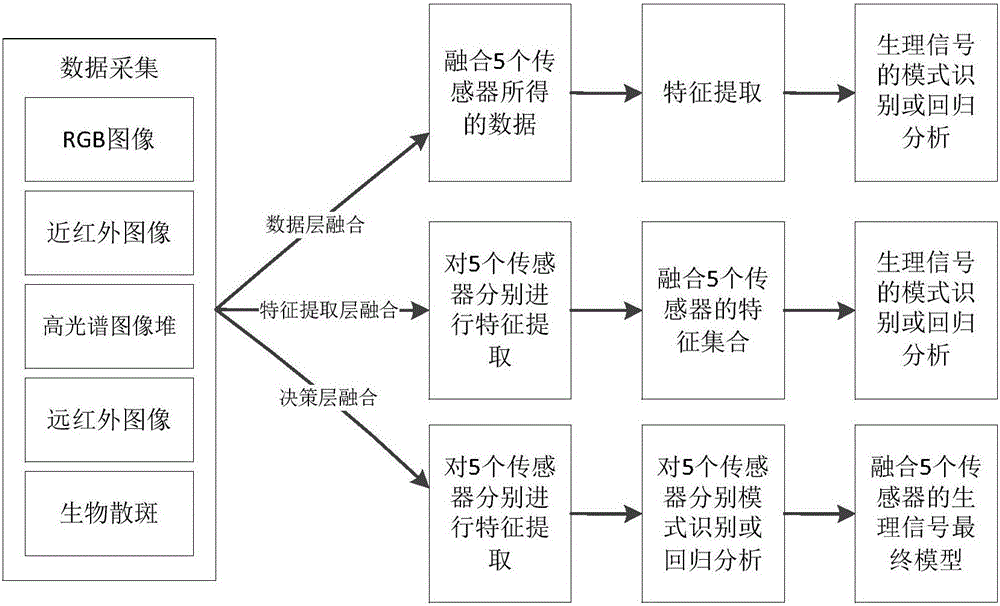
Physiological signal remote monitoring system based on multimodal imaging technique and application thereof
ActiveCN106580294AImprove accuracyImprove robustnessDiagnostics using spectroscopySensorsMonitoring systemData acquisition
The invention provides a physiological signal remote monitoring system based on multimodal imaging technique and application thereof; the physiological signal remote monitoring system comprises an integrated imaging module, a hyperspectral imaging module and a control terminal; the hyperspectral imaging module is disposed above the integrated imaging module, and the integrated imaging module and the hyperspectral imaging module are respectively in communication connection with the control terminal. The physiological signal remote monitoring system integrating the 5 imaging modes of hyperspectral mode, visible light mode, near-infrared mode, far-infrared mode and laser bio-speckle mode can provide high-precision extraction and analysis for physiological signals; meanwhile, the physiological signal remote monitoring system allows coordinated data acquisition among multimodal devices and coordinated processing and analysis among data, such that the different application needs such as sleep monitoring and diseased pig screening are met.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Compositions and Method for Multimodal Imaging
ActiveUS20080206131A1Enhance the imagePrevent leakageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDispersion deliveryDiagnostic Radiology ModalityRetention efficiency
Provided are signal modifying compositions for medical imaging comprising a carrier and two or more signal modifying agents specific for two or more imaging modalities. The compositions are characterized by retention efficiency, with respect to the signal modifying agents, which enables prolonged contrast imaging without significant depletion of the signal modifying agents from the carrier. The carriers of the present invention are lipid based or polymer based, the physico-chemical properties of which can be modified to entrap or chelate different signal modifying agents and mixtures thereof and to target specific organs or tumors or tissues within a mammal.
Owner:UNIV HEALTH NETWORK
Cross-blood-brain-barrier targeting multimodal nano-medicine used in brain tumor diagnosis
InactiveCN103083689AGood target traceabilityHigh sensitivityEmulsion deliveryIn-vivo testing preparationsDiagnostic Radiology ModalityFluorescence
The invention belongs to the field of imaging medicines, and relates to a cross-blood-brain-barrier (cross-BBB) targeting multimodal nano-medicine used in brain tumor diagnosis. The invention especially relates to the synthesis of magnetic / fluorescent nano-diagnostic medicines with cross-BBB receptor active targeting effect and intermediate thereof. The invention also relates to an application of the medicine and the intermediate in living noninvasive brain tumor multimodal imaging. The multimodal nano-diagnostic medicine provided by the invention is respectively marked with tumor new vessel targeting group, cross-BBB transporting group, and magnetic and optical imaging group. The medicine is first targeted to tumor peripheral new vessels, then is delivered into brain with a receptor-mediated cross-BBB transportation effect, and is secondarily targeted to tumor cells. With magnetic resonance imaging / optical multimodal imaging techniques, and with the medicine, noninvasive high SNR tracing of brain tumor and especially BBB-undamaged brain tumor can be realized. The medicine provided by the invention can provide a novel reference approach for brain tumor preoperative localization and brain tumor resection under real-time image guidance.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
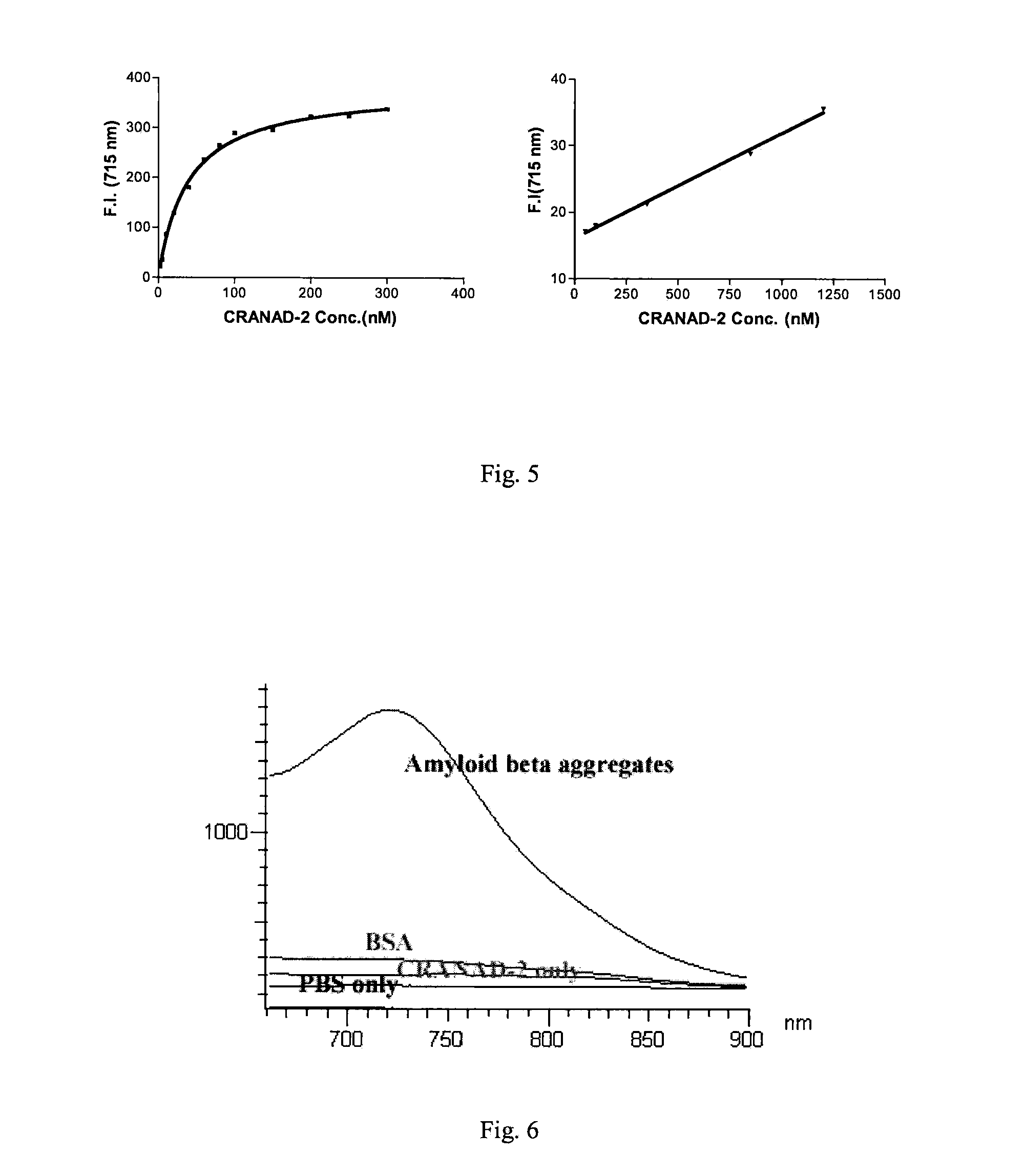
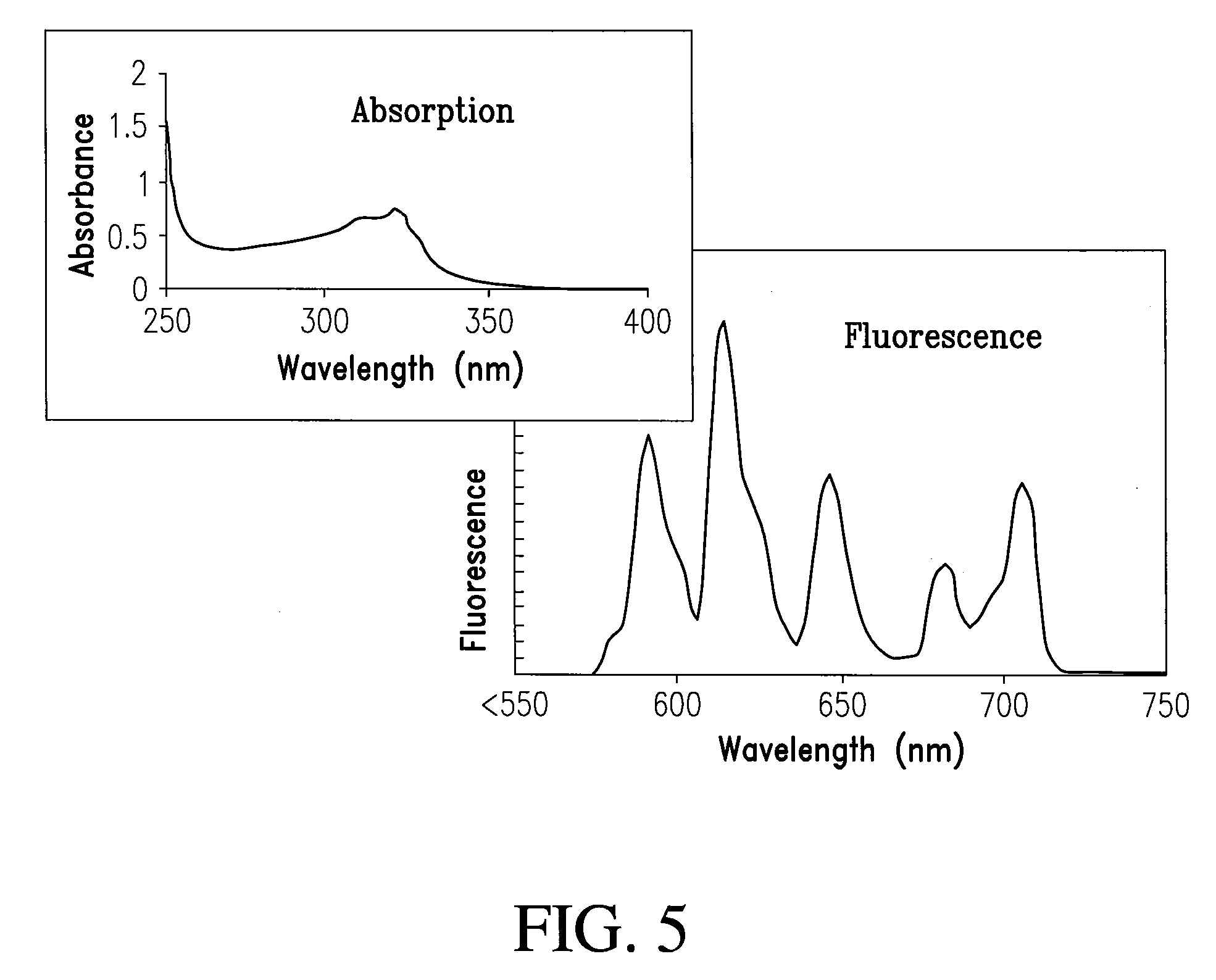
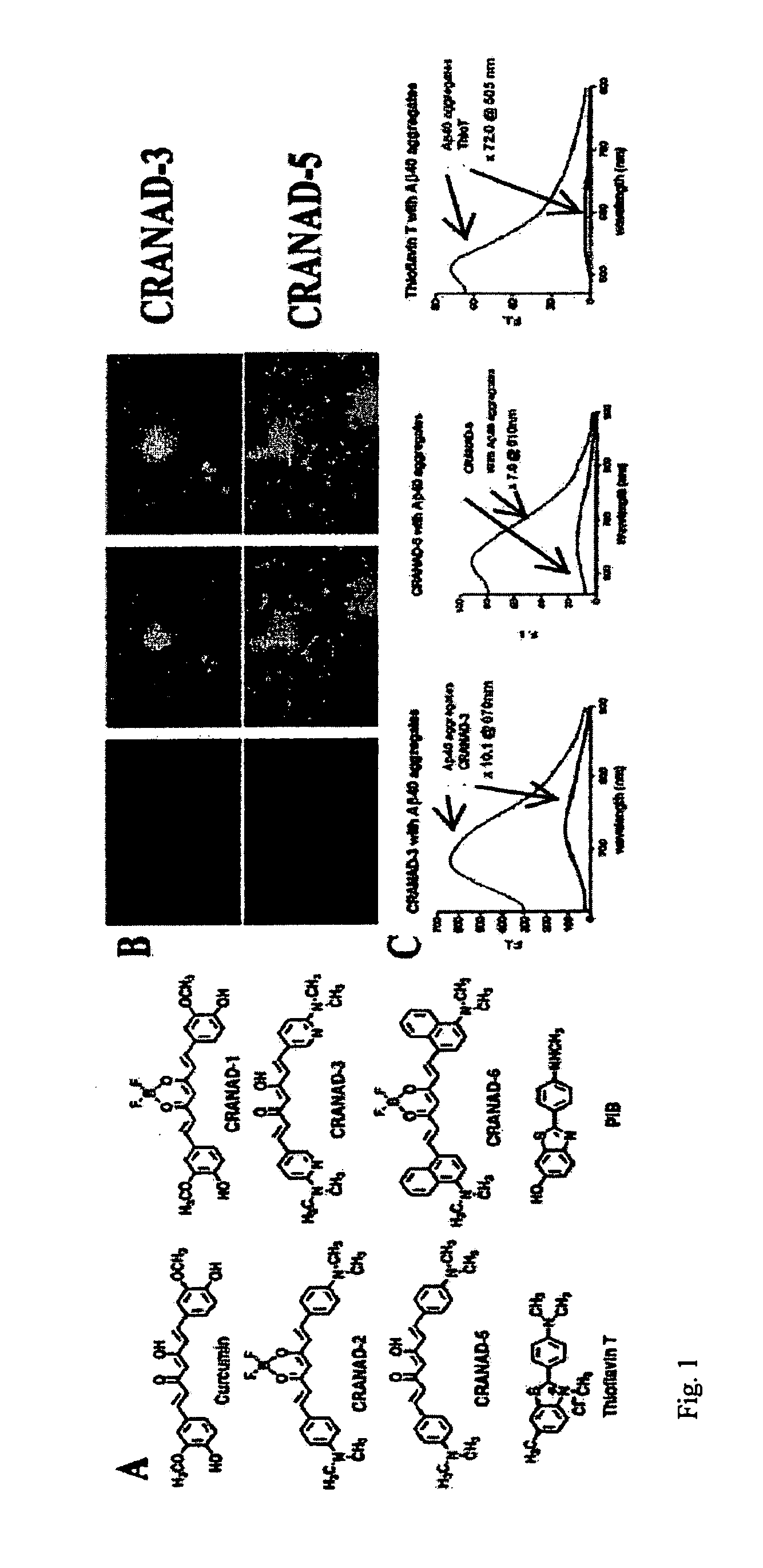
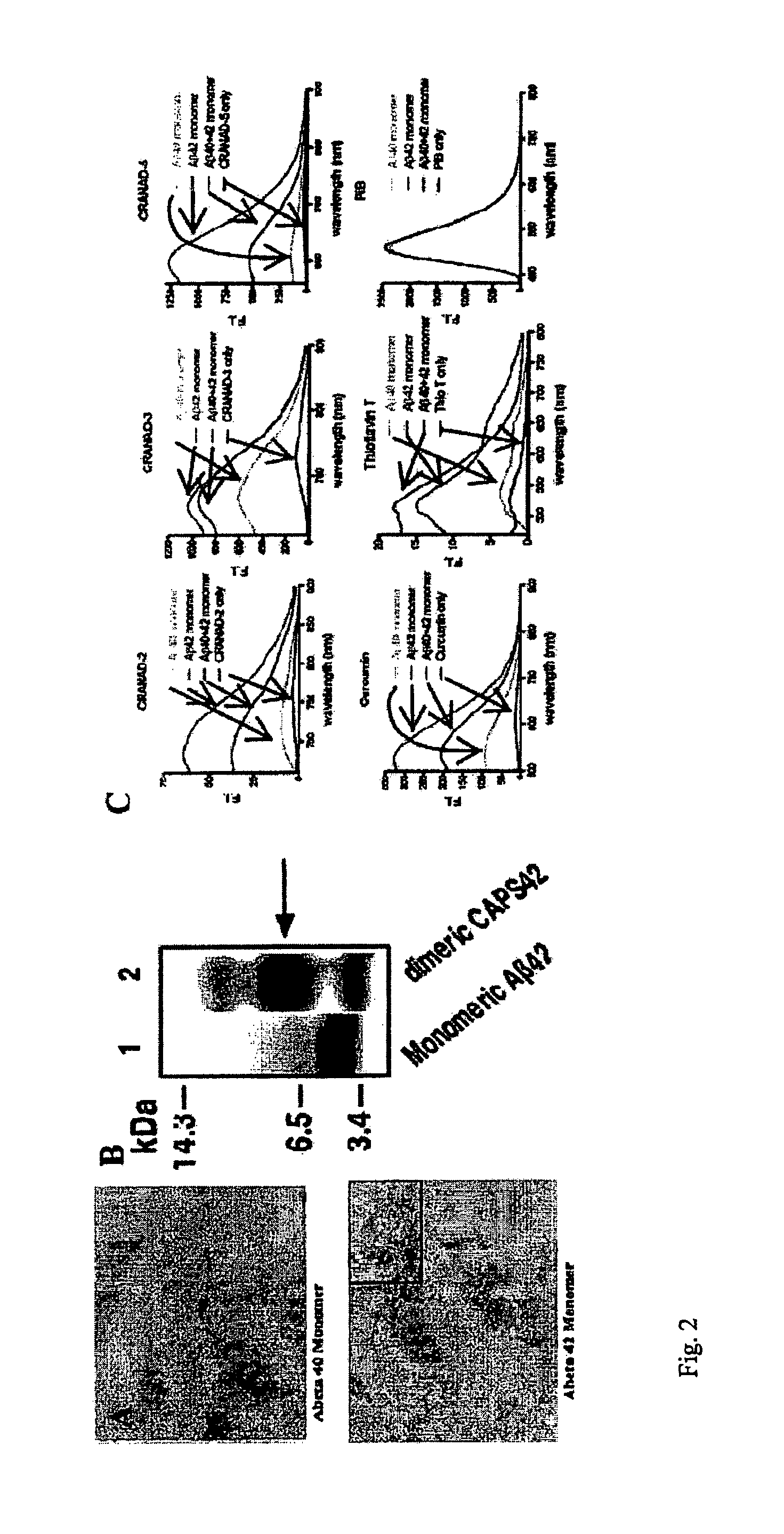
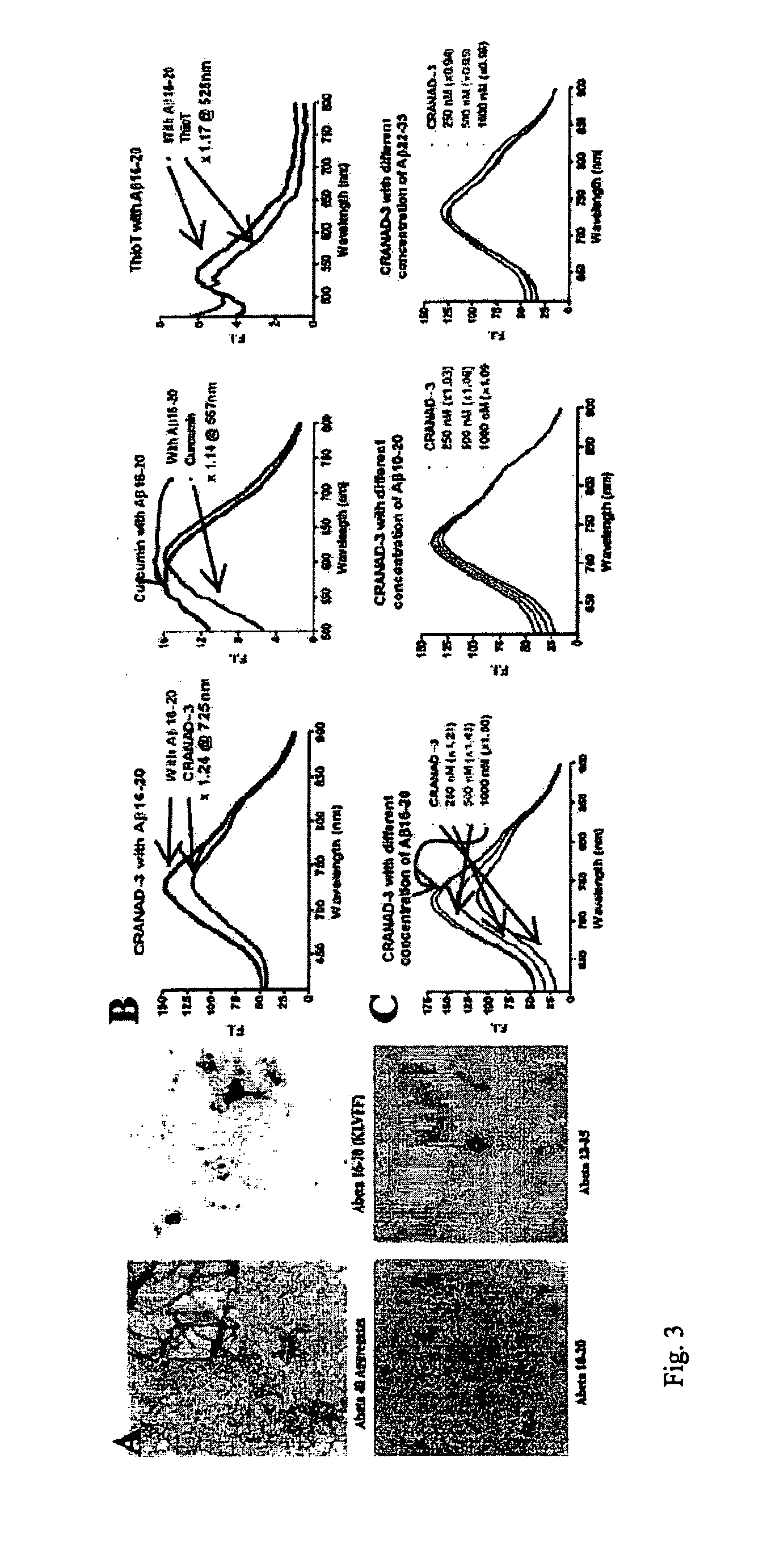
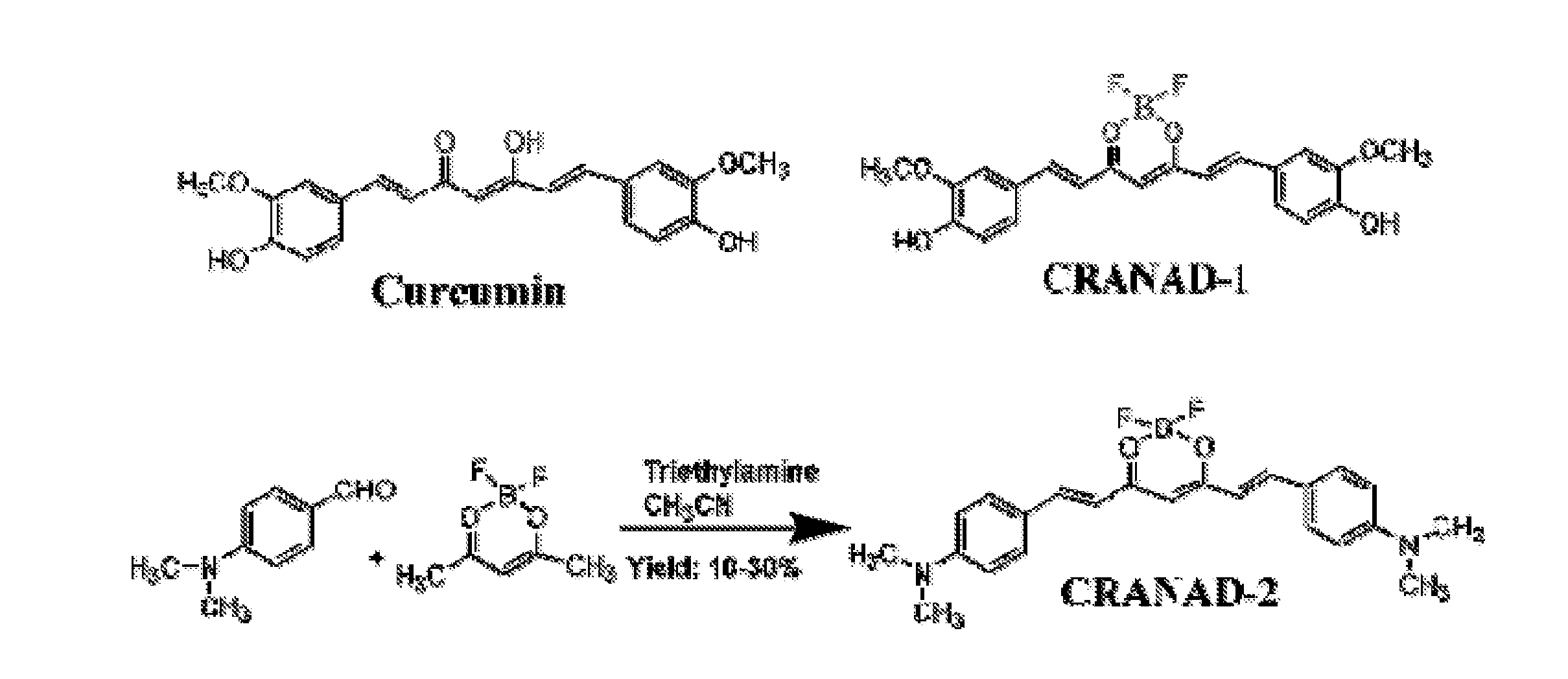
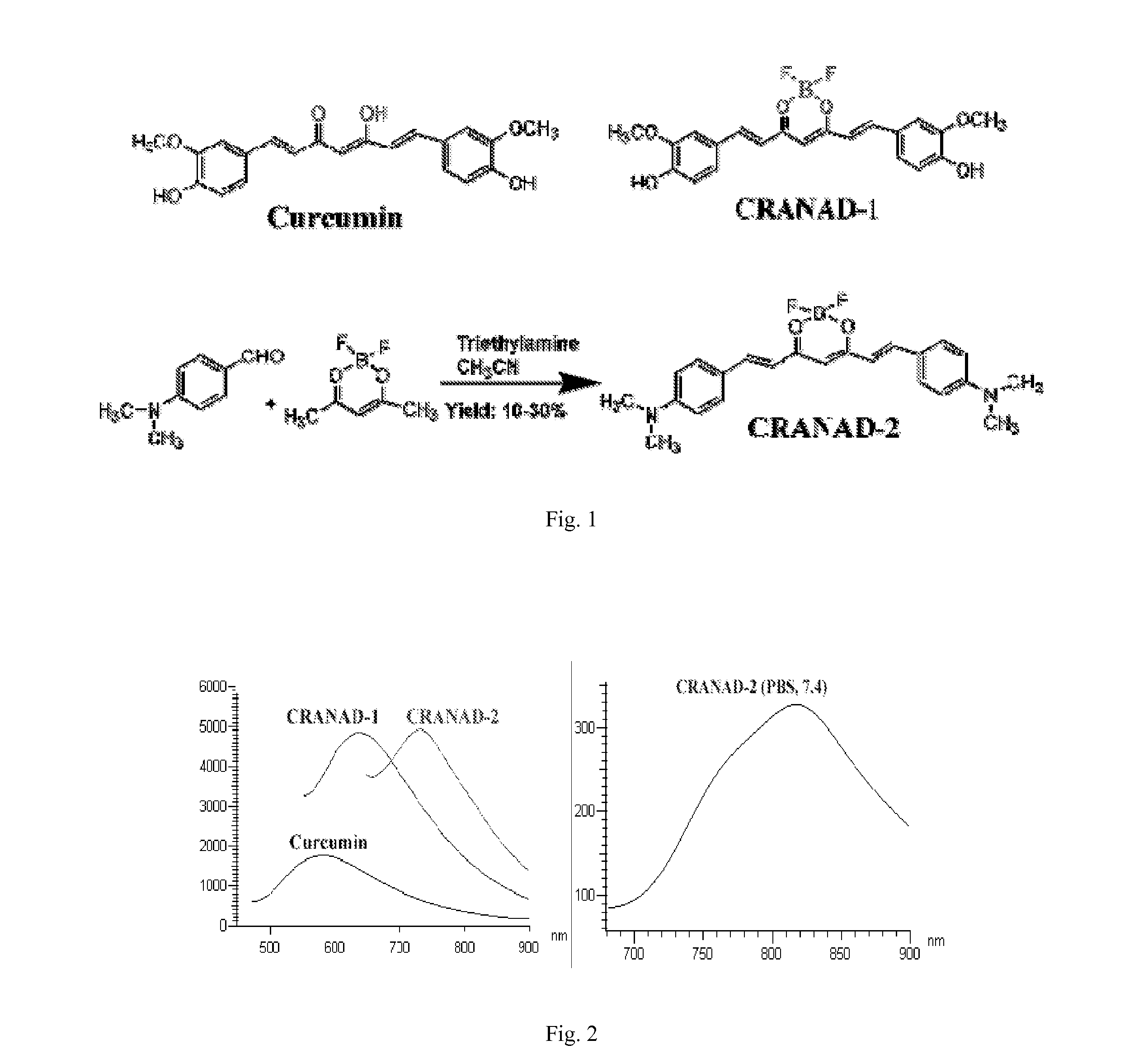
Curcumin Derivatives for Amyloid-Beta Plaque Imaging
InactiveUS20110208064A1Significant fluorescence property changeImprove lipophilicityNervous disorderMagnetic measurementsInfraredAmyloid beta
The present invention provides curcumin-derived near infrared (NIR) imaging probes. Upon interacting with amyloid β aggregates, these probes undergo a range of changes, qualifying them as “smart” probes. The inventors have demonstrated that probes of the invention have the capacity to monitor the progression of Alzheimer's disease in an in vivo animal model. In addition, the present invention encompasses probes useful as PET imaging agents, MRI imaging agents and multimodal imaging agents, as well as related methods of detecting and imaging amyloid β aggregates and plaques.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Multi-use multimodal imaging chelates
InactiveUS20080241873A1Improve discriminationEasy to detectOrganic active ingredientsIn-vivo radioactive preparationsCancer cellFluorescence
Cyclen-based chelates can be used as contrast agents for multi-modal imaging of tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates are preferably polyazamacrocyclic molecules formed from 1,4,7,10 tetraazacyclododecane (“cyclen”) having varying chelating ions, phosphoester chains, and light harvesting moieties. By changing the chelating ion, phosphoester chain length and / or the light harvesting moiety different imaging techniques, such as MRI, CT, fluorescence and absorption, x-ray and NIR, may be employed to image the tissue cells. Additionally, the cyclen-based chelates may be conjugated to provide for site-specific delivery of the cyclen-based chelate to the desired tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates may also be delivered to the tissue cells by attaching the cyclen-based to a polymeric delivery vehicle. Although these cyclen-based chelates have a wide variety of application, the preferred use is for imaging of cancer cells, such as brain cancer, for improving resection of a cancerous tissue.
Owner:BORNHOP DARRYL J +2
Multi-use multimodal imaging chelates
InactiveUS20080241074A1Improve discriminationEasy to detectUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsOrganic active ingredientsCancer cellDelivery vehicle
Cyclen-based chelates can be used as contrast agents for multi-modal imaging of tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates are preferably polyazamacrocyclic molecules formed from 1,4,7,10 tetraazacyclododecane (“cyclen”) having varying chelating ions, phosphoester chains, and light harvesting moieties. By changing the chelating ion, phosphoester chain length and / or the light harvesting moiety different imaging techniques, such as MRI, CT, fluorescence and absorption, x-ray and NIR, may be employed to image the tissue cells. Additionally, the cyclen-based chelates may be conjugated to provide for site-specific delivery of the cyclen-based chelate to the desired tissue cells. The cyclen-based chelates may also be delivered to the tissue cells by attaching the cyclen-based to a polymeric delivery vehicle. Although these cyclen-based chelates have a wide variety of application, the preferred use is for imaging of cancer cells, such as brain cancer, for improving resection of a cancerous tissue.
Owner:TEXAS TECH UNIV SYST +1
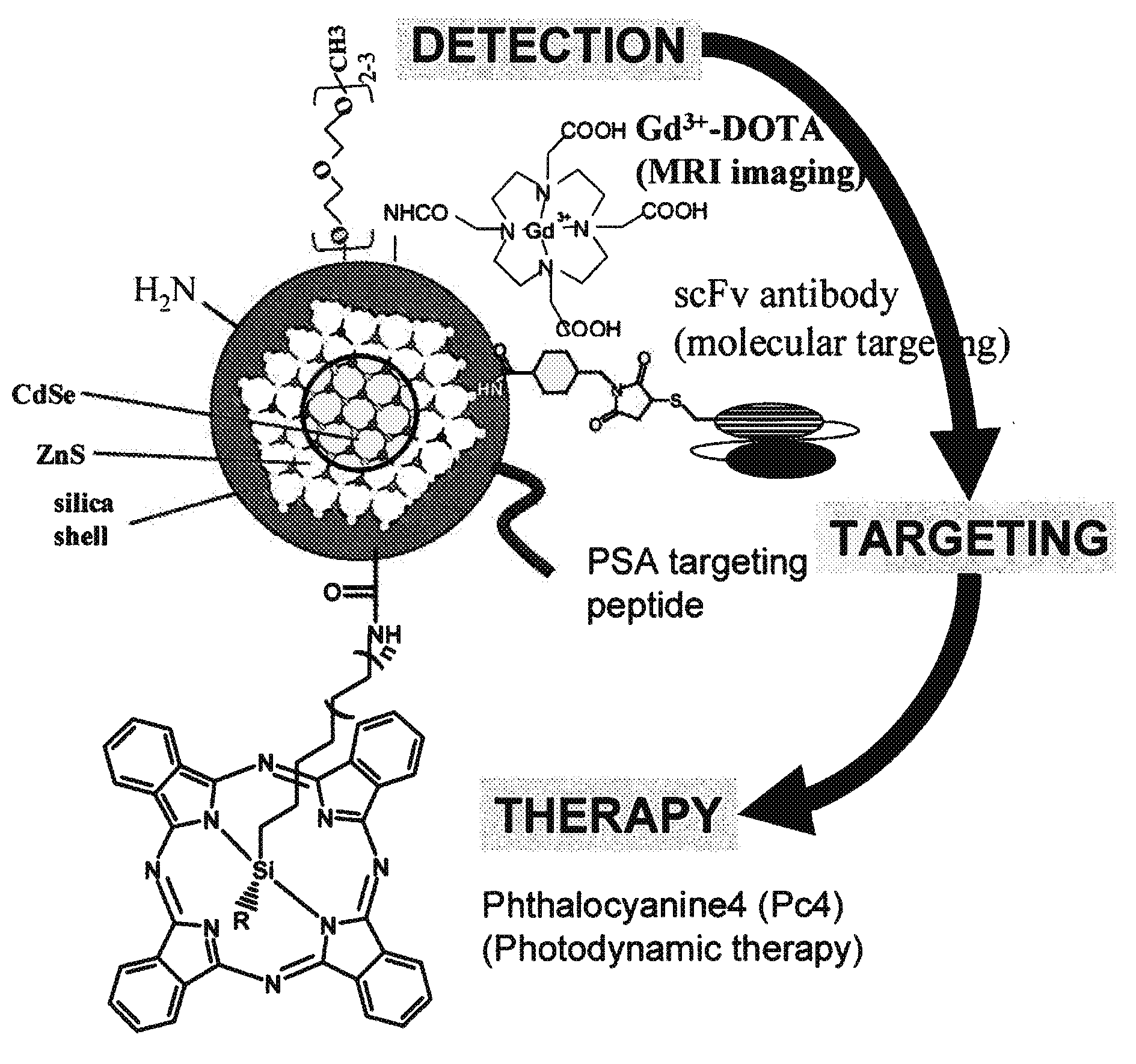
Apparatus and method for multi-modal imaging using nanoparticle multi-modal imaging probes
An apparatus for multimodal imaging of an object includes a support stage for receiving an object to be imaged; an object supported on the stage, the object having been treated with a biocompatible imaging probe comprising nanoparticles carrying one or more targeting moieties and one or more diagnostic components for enabling capture of images of the object; a light source for producing a beam to illuminate the object; a filter positioned to receive and pass the beam toward the object; and a lens and camera system for capturing an image of the object. The apparatus may include a tiltable filter for filtering light from the source. The apparatus may include a mechanism for selectively directing light from the light source through a first filter assembly to produce a first beam of light of a first frequency range for illuminating an object on the stage in a first imaging mode or through a second filter assembly to produce a second beam of light of a second frequency range for illuminating an object on the stage in a second imaging mode, so that the lens and camera system captures light from the object illuminated by either the first or second beam of light to produce a first image in response to the first beam and a second image, different from the first image, in response to the second image. An x-ray source and phosphor plate may be included to provide an additional imaging mode.
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
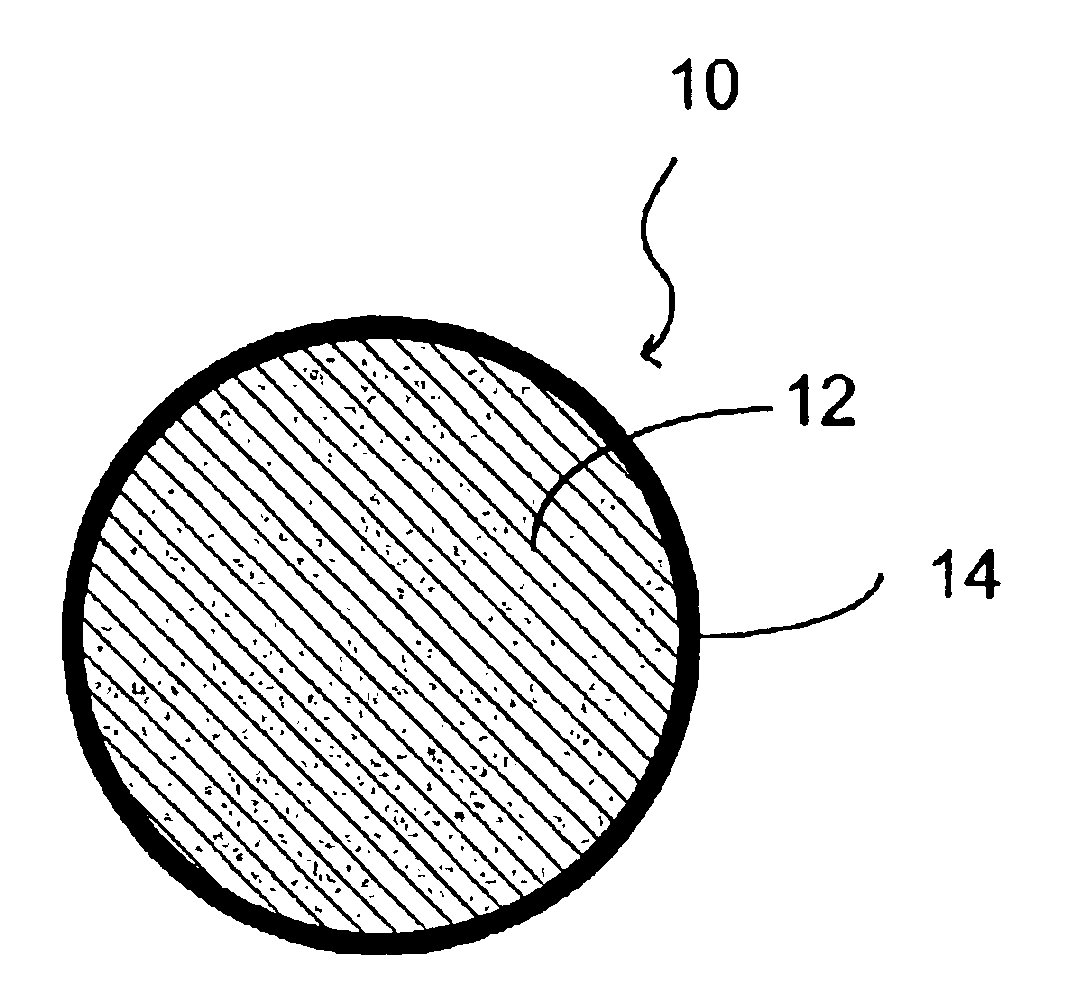
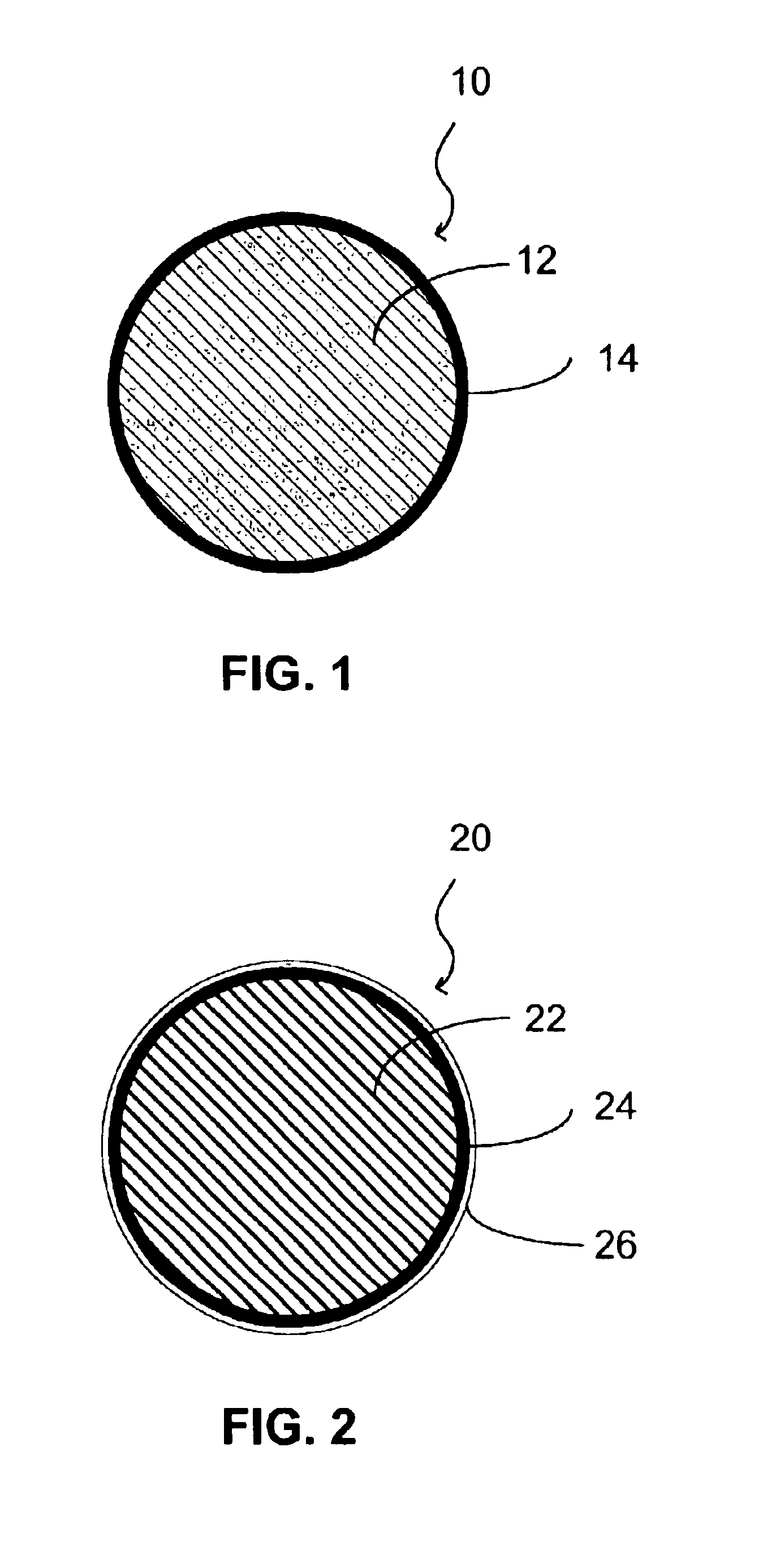
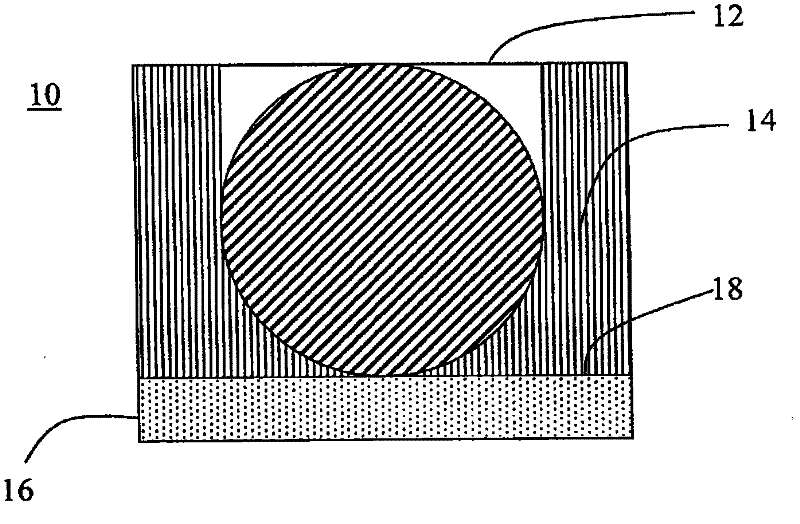
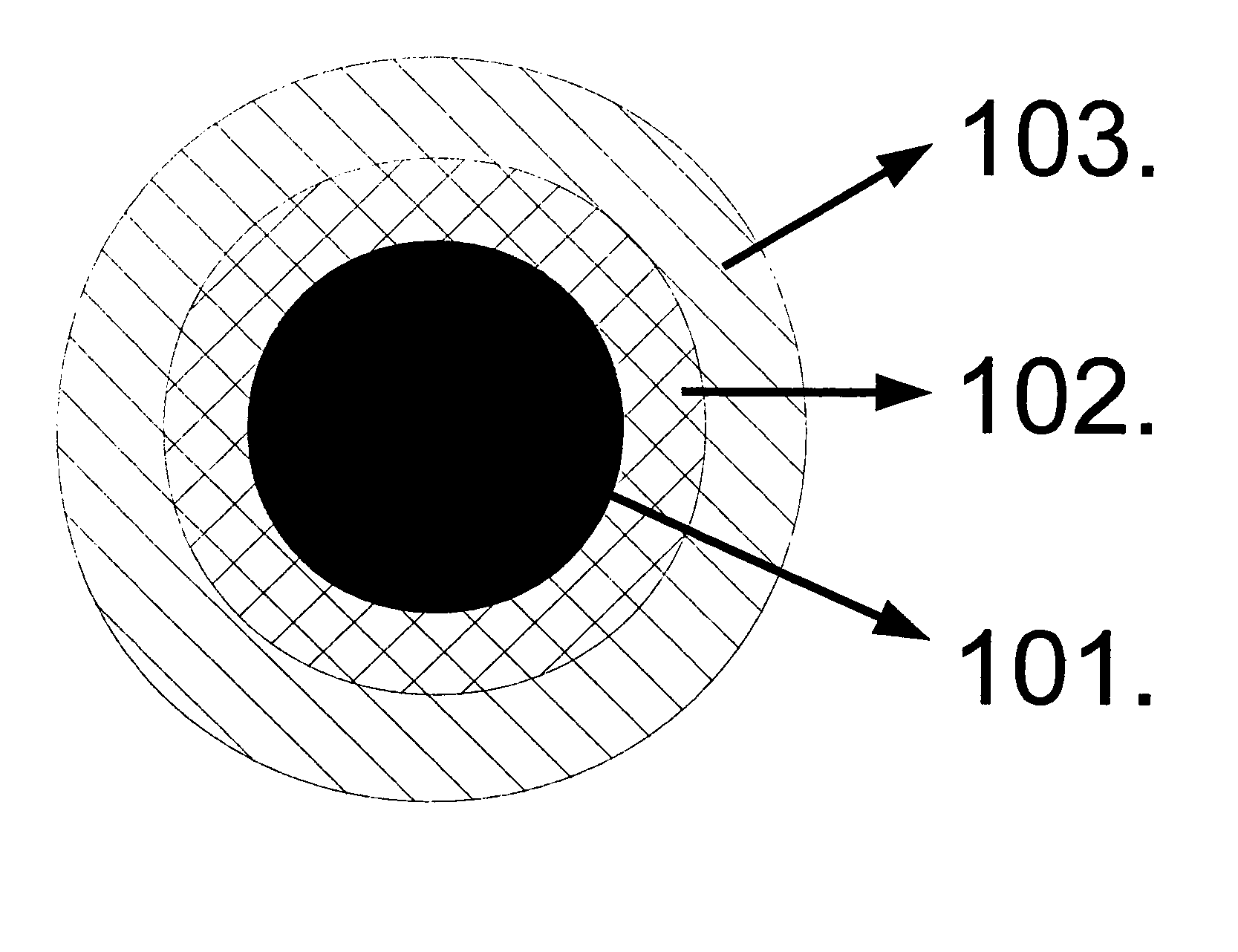
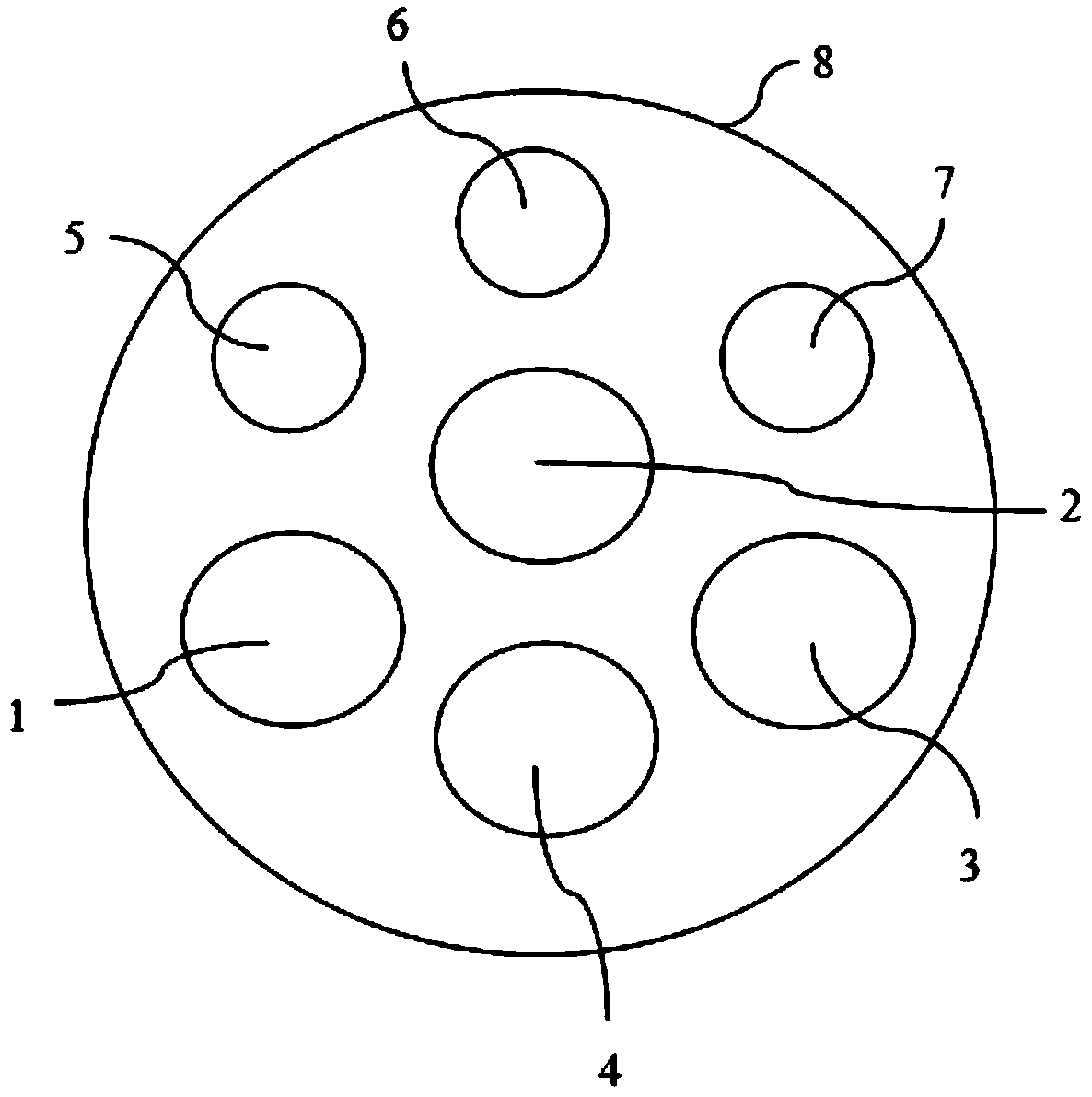
Multimodal imaging fiducial marker
A multimodal fiducial marker (10) for registration of data is disclosed. The multimodal fiducial marker (10) generally comprises a first portion (12) made from at least one radiopaque material and a second portion (14) made from a porous material capable of absorbing at least one radioactive material. The second portion (14) at least partially surrounds the first portion (12).
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
Prussian blue based nanoparticle as multimodal imaging contrast material
The invention relates to a Prussian Blue based nanoparticle comprising a Prussian Blue based metal core doped with one or more metal isotope and an organic biocompatible coating. The invention relates furthermore to a process for the preparation of said nanoparticle, and the use thereof as imaging contrast material or in the therapy.
Owner:SEMMELWEIS EGYETEM
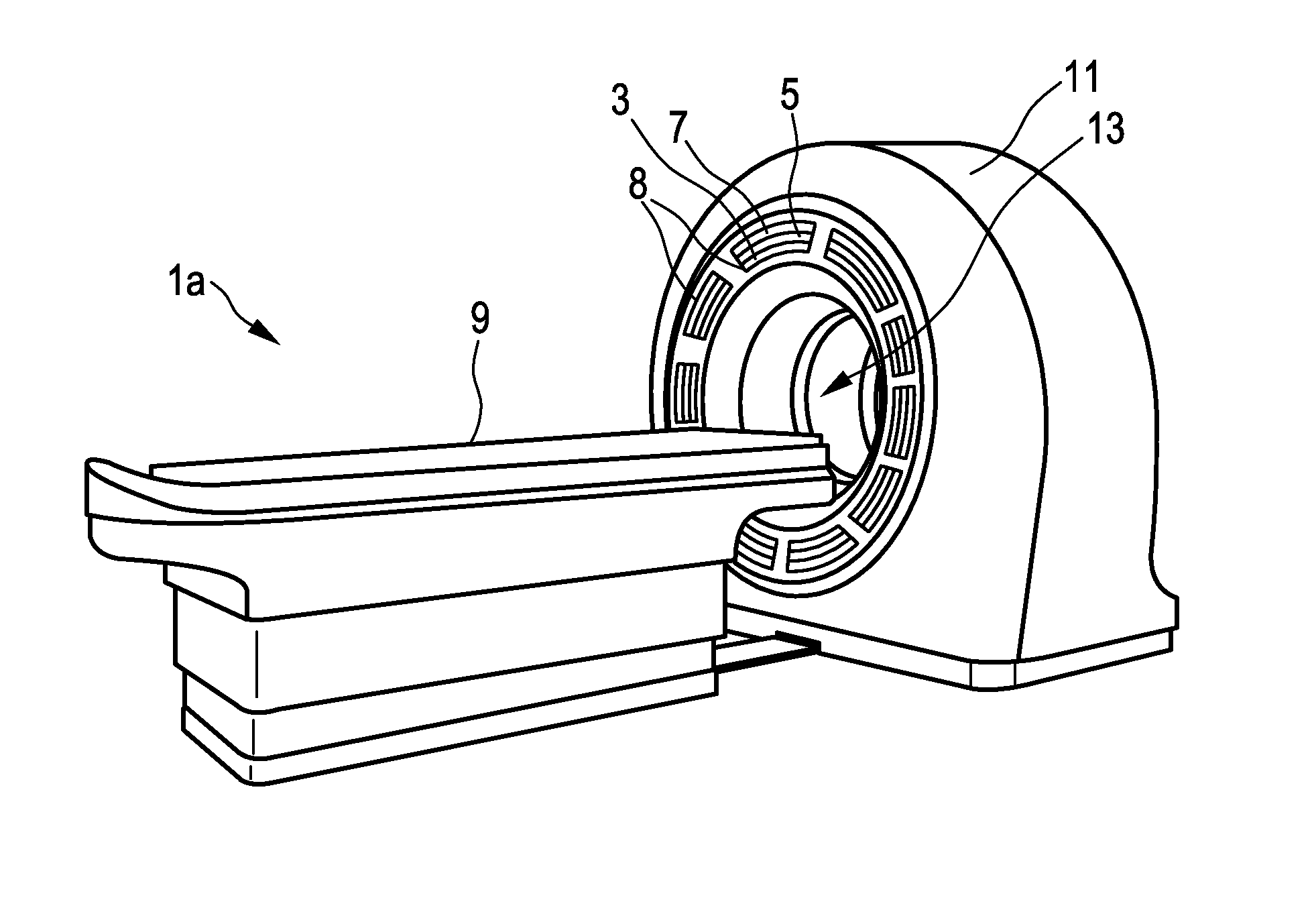
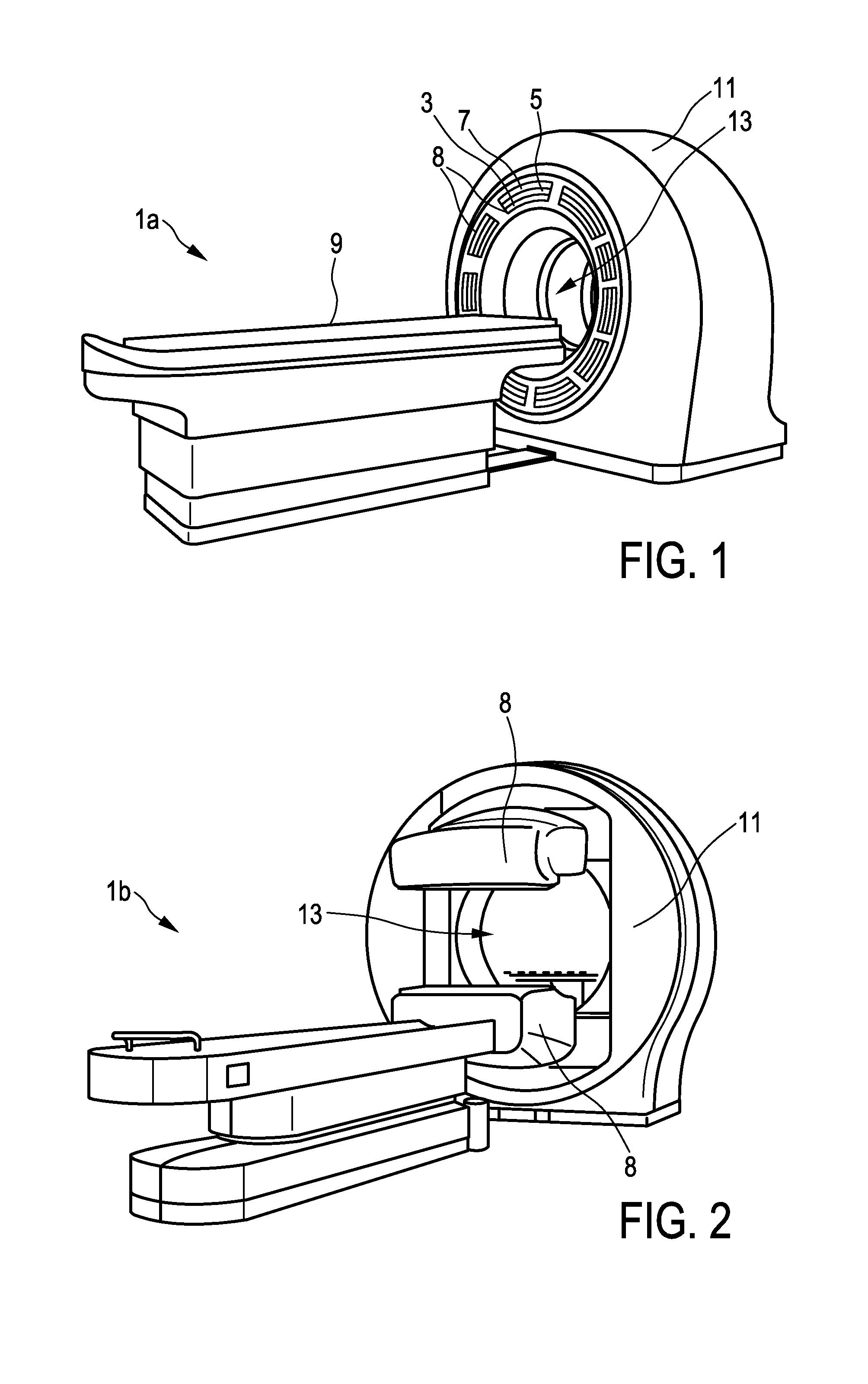
Multimodal imaging apparatus
InactiveUS20160209515A1Conserve costReduce the amount requiredMaterial analysis by optical meansComputerised tomographsRadioactive tracerPhotodetector
The present invention relates to a multimodal imaging apparatus (1a, 1b) for imaging a process (63) in a subject (23), said process (63) causing the emission of gamma quanta (25, 61), said apparatus (1a, 1b) comprising a scintillator (3) including scintillator elements (31) for capturing incident gamma quanta (25, 61) generated by the radiotracer and for emitting scintillation photons (26) in response to said captured gamma quanta (25, 61), a photodetector (5) including photosensitive elements (33) for capturing the emitted scintillation photons (26) and for determining a spatial distribution of the scintillation photons, and a readout electronics (7) for determining the impact position of an incident gamma quantum in the scintillator (3) and / or a parameter indicative of the emission point of the gamma quantum (25, 61) in the subject (23) based on the spatial distribution of the scintillation photons, wherein the imaging apparatus (1a, 1b) is configured to be switched between a first operation mode for detecting low energy gamma quanta and a second operation mode for detecting high energy gamma quanta, wherein the high energy gamma quanta have a higher energy than the low energy gamma quanta, and the scintillator (3) is arranged to capture incident gamma quanta (25, 61) from the same area of interest (65) in the first operation mode and in the second operation mode without requiring a relative movement of the subject (23) versus the scintillator (3), wherein the scintillator (3) comprises an array of scintillator elements (31) including a first region with high energy scintillator elements (27) for capturing high energy gamma quanta and a second region with low energy scintillator elements (29) for capturing low energy gamma quanta; and / or the apparatus (1a, 1b) further comprises a positioning mechanism (35) for changing the orientation and / or position of the scintillator elements (31), in particular for tilting the scintillator elements (31), to switch the imaging apparatus (1a, 1b) between the first operation mode and the second operation mode.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
Multimodal Imaging System, Apparatus, and Methods
ActiveUS20170188831A1Easy to operateImprove usabilityOrgan movement/changes detectionSurgeryOptical tomographyCollection system
In part, the invention relates to an image data collection system. The system can include an interferometer having a reference arm that includes a first optical fiber of length of L1 and a sample arm that includes a second optical fiber of length of L2 and a first rotary coupler configured to interface with an optical tomography imaging probe, wherein the rotary coupler is in optical communication with the sample arm. In one embodiment, L2 is greater than about 5 meters. The first optical fiber and the second optical fiber can both be disposed in a common protective sheath. In one embodiment, the system further includes an optical element configured to adjust the optical path length of the reference arm, wherein the optical element is in optical communication with the reference arm and wherein the optical element is transmissive or reflective.
Owner:LIGHTLAB IMAGING
Multimodal imaging endoscopic system
PendingCN109222865AImprove the detection rateHigh standardEndoscopesDiagnostics using tomographyDiseaseQualitative analysis
The invention discloses a multimodal imaging endoscope system, including an image acquisition unit, a control and processing unit, a synchronization unit, a human-computer interaction unit and a zoomcontrol unit. The multimodal imaging endoscopic system of the invention can be used for multimodal imaging of the same detected target, and the multimodal imaging endoscopic system can be combined with a plurality of imaging results to carry out comprehensive comparison and analysis, thereby facilitating rapid pathological qualitative analysis and improving the detection rate of a plurality of diseases. Doctors can switch to different imaging modes according to different imaging purposes without changing different endoscopic systems. It is also possible to perform simultaneous multimodal imaging comparisons. As a result, a variety of clinical examination means are provided for doctors at one time, the operation is simplified, the waiting time of patients is reduced, and the pain of patients is alleviated.
Owner:JOYMEDICARE (SHANGHAI) MEDICAL ELECTRONIC TECH CO LTD
Methods and System for Detecting Soluble Amyloid-Beta
InactiveUS20120183474A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsComponent separationInfraredAmyloid beta
The present invention provides methods of detecting soluble amyloid β using curcumin-derived near infrared (NIR) imaging probes. Upon interacting with soluble amyloid β, these probes undergo a range of changes, qualifying them as “smart” probes. In addition, the invention provides methods of detecting soluble amyloid β by positron emission tomography (PET), magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and multimodal imaging based on the curcumin-derived NIR imaging probes and derivatives thereof.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Curcumin derivatives for amyloid-beta plaque imaging
InactiveUS20150087937A1Significant fluorescence property changeImprove lipophilicityNervous disorderIn-vivo radioactive preparationsInfraredAmyloid beta
The present invention provides curcumin-derived near infrared (NIR) imaging probes. Upon interacting with amyloid β aggregates, these probes undergo a range of changes, qualifying them as “smart” probes. The inventors have demonstrated that probes of the invention have the capacity to monitor the progression of Alzheimer's disease in an in vivo animal model. In addition, the present invention encompasses probes useful as PET imaging agents, MRI imaging agents and multimodal imaging agents, as well as related methods of detecting and imaging amyloid β aggregates and plaques.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Apparatus and methods for scalable field of view imaging using a multi-source system
ActiveUS20200170590A1Ultrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsImage enhancementNuclear medicineSpiral scanning
Multimodal imaging apparatus and methods include a rotatable gantry system with multiple sources of radiation comprising different energy levels (for example, kV and MV). Fast slip-ring technology and helical scans allow data from multiple sources of radiation to be combined or utilized to generate improved images and workflows, including for IGRT. Features include large field-of-view (LFOV) MV imaging, kV region-of-interest (ROI) imaging, and scalable field-of-view (SFOV) dual energy imaging.
Owner:ACCURAY
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com