Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
64 results about "Biomedical data" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
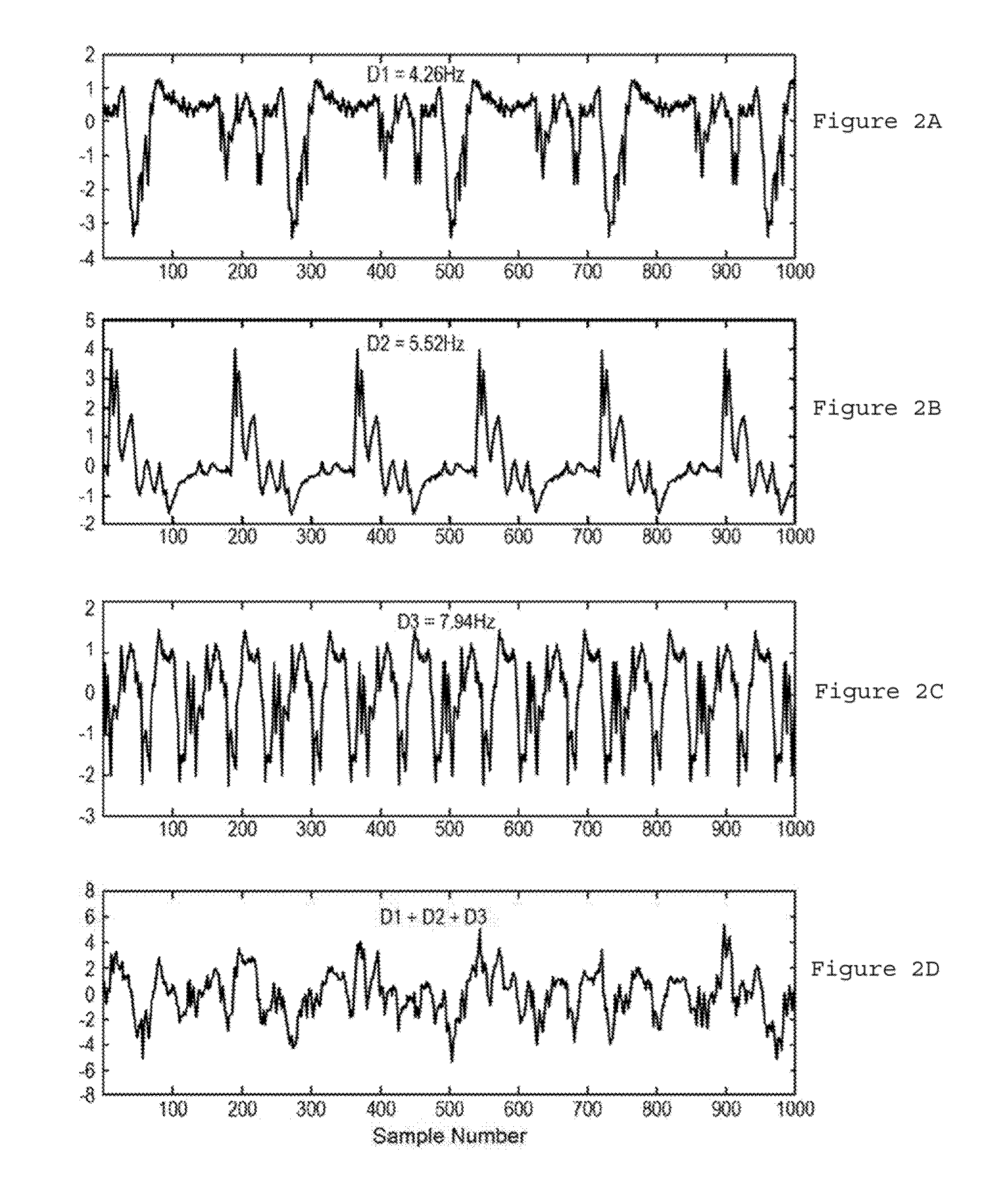
Apparatus, method and computer-accessible medium for transform analysis of biomedical data
InactiveUS20150051452A1Prevent reinductionImprove understandingSurgeryEndoscopesStructure of Management InformationComputer science
Owner:THE TRUSTEES OF COLUMBIA UNIV IN THE CITY OF NEW YORK
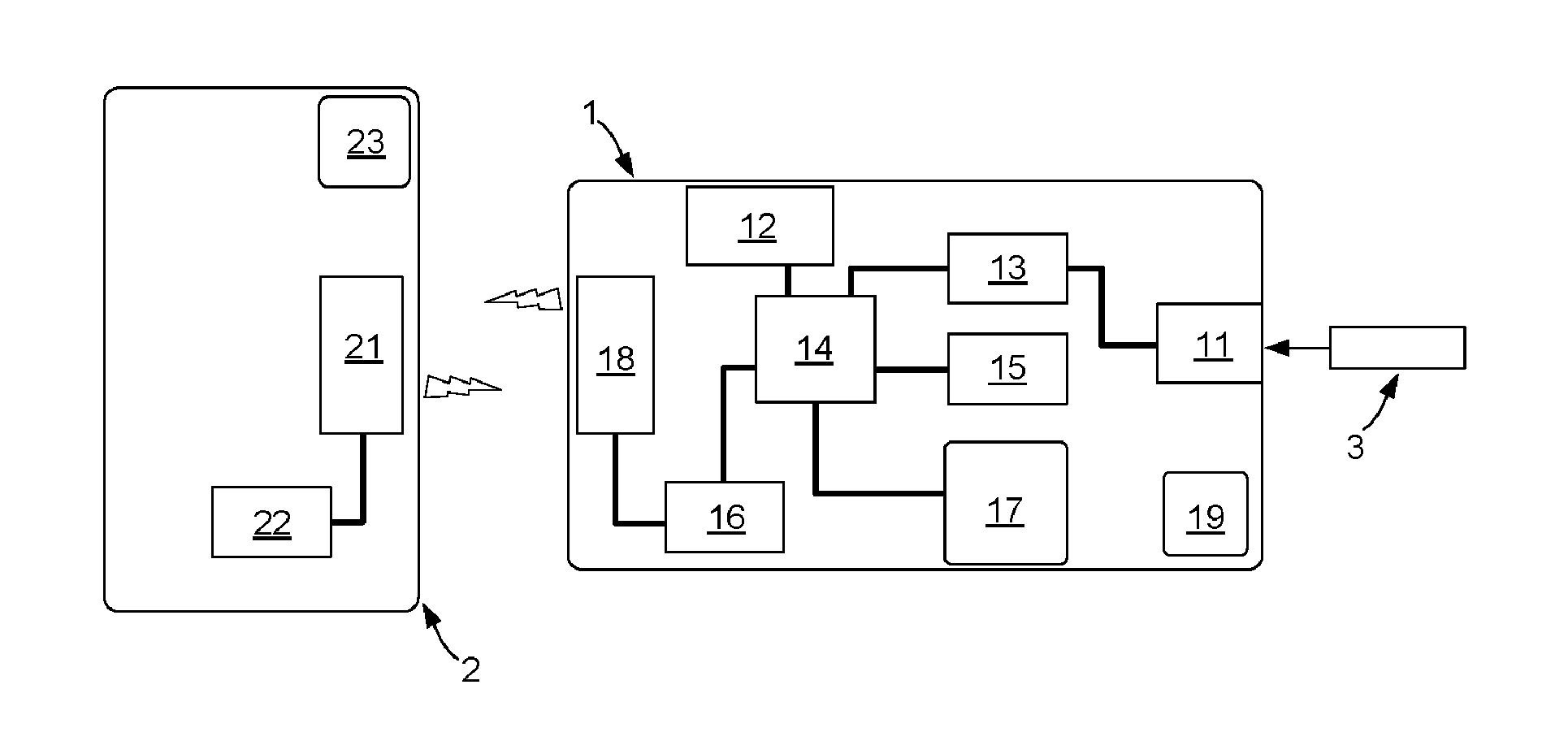
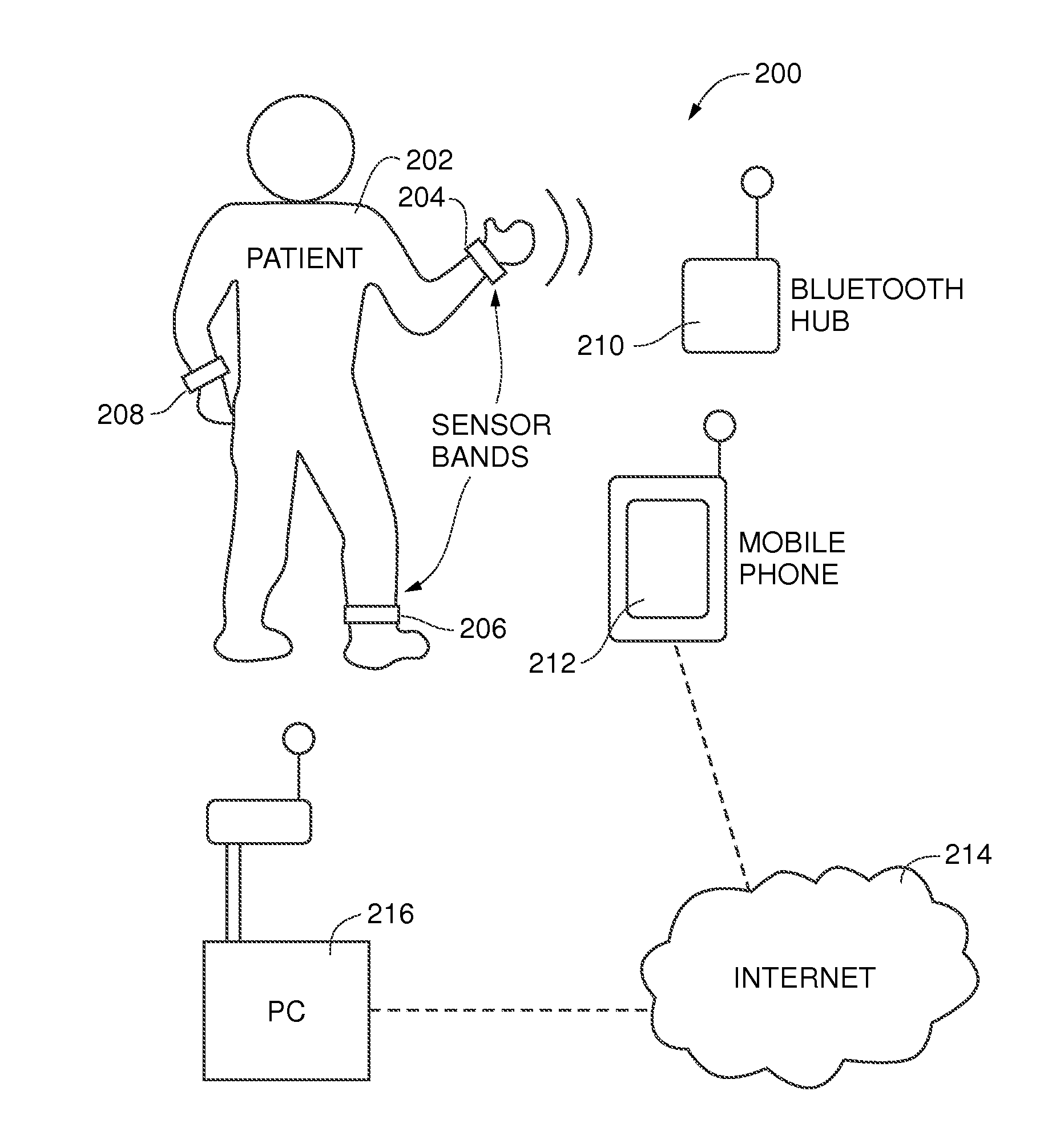
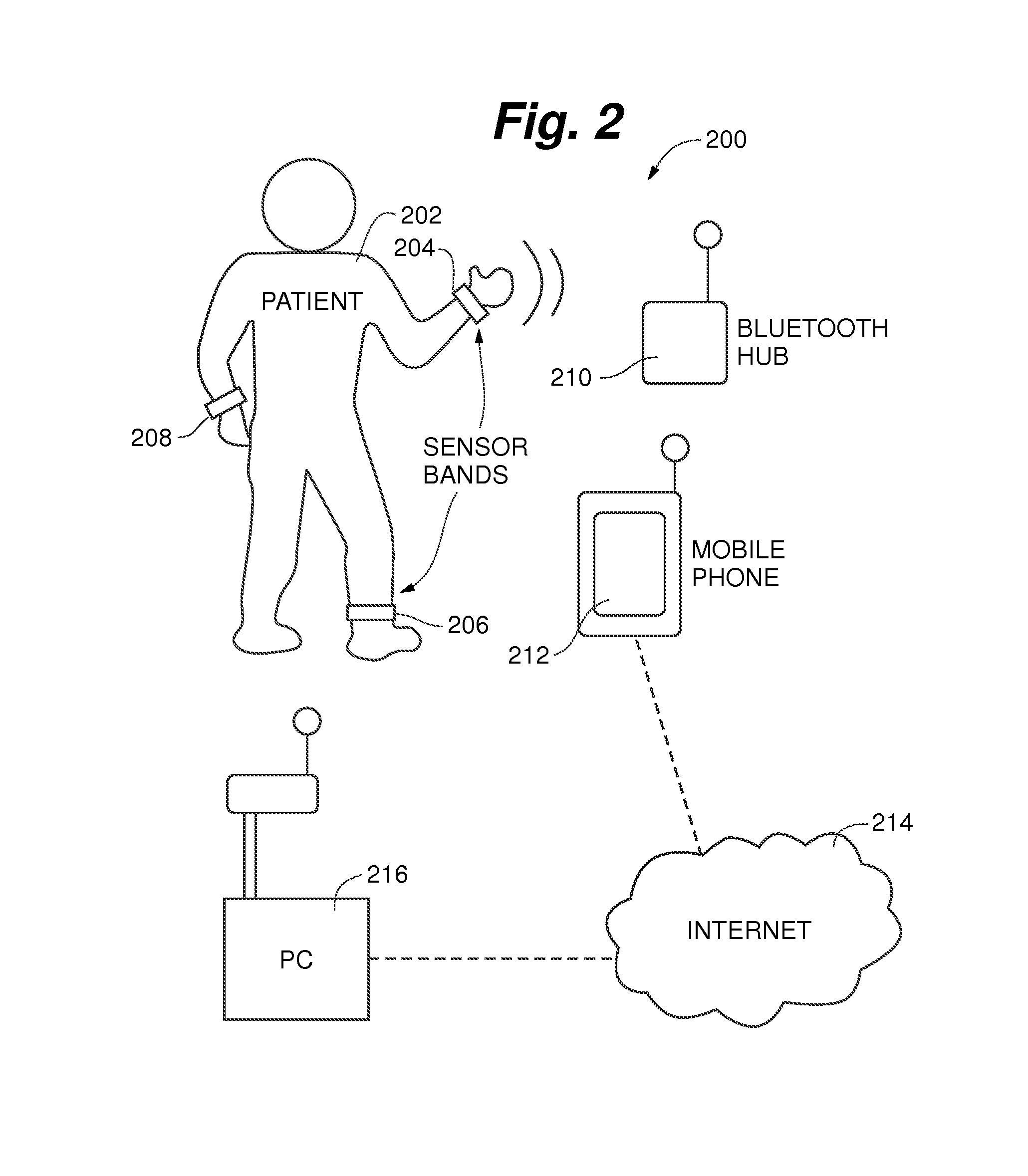
Body worn latchable wireless medical computing platform
InactiveUS20050090754A1Quick attachFast replacementElectroencephalographyElectrocardiographyNon invasiveMedical treatment
A non-invasive body worn computing platform is capable of long term unattended operation to capture, analyze, store, biosensor data and communicate health and system events, ECG waves and other biomedical data from the patient recorded, produced, or analyzed. The non-invasive body worn computing platform operates as a node within a wireless distributed collaborative network. The body worn computing platform has a latch-able mechanical and electrical interface for rapid swapping of the device and power source to and from biosensors, body harness, and power sources.
Owner:MATRYX GRP
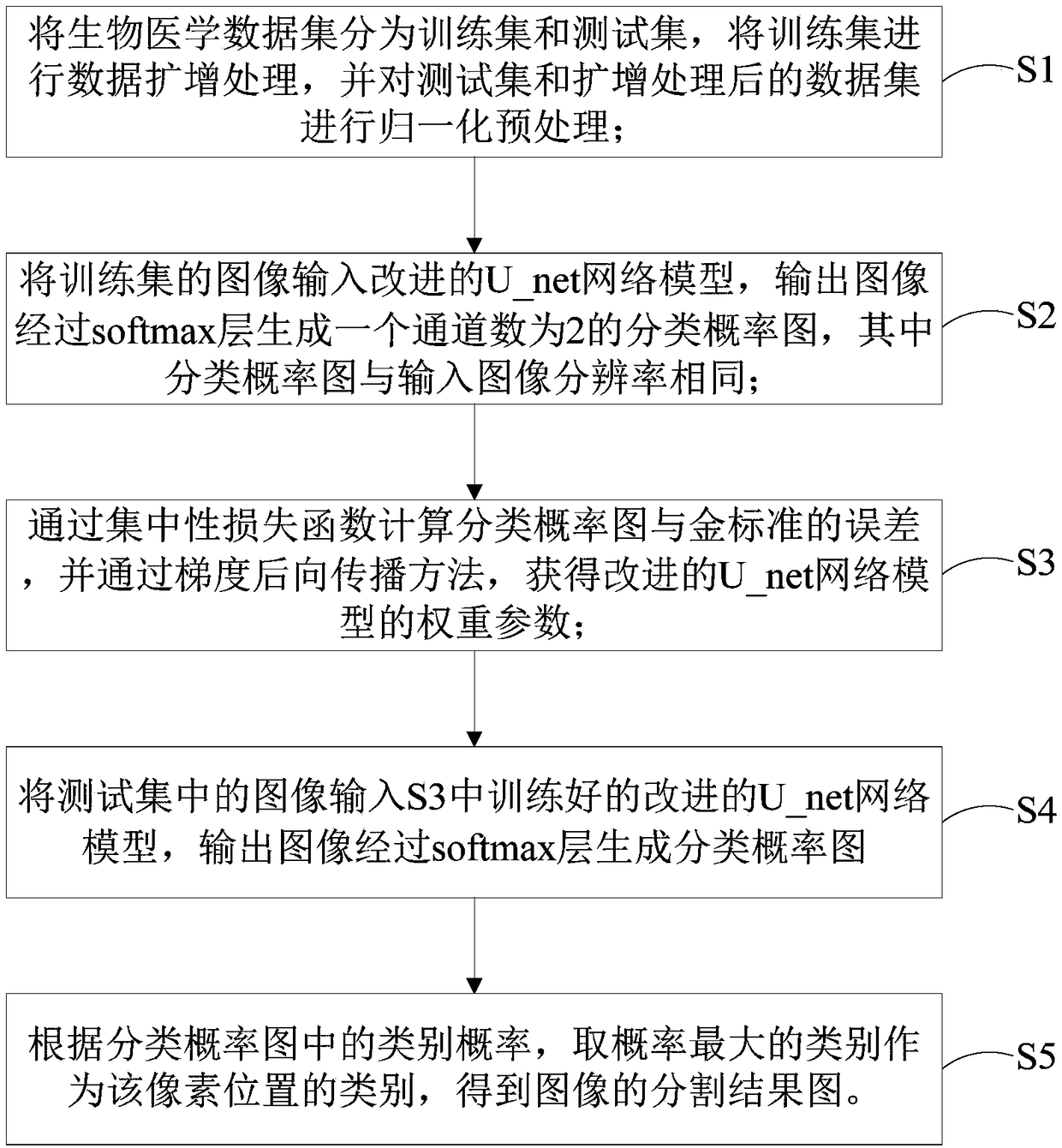
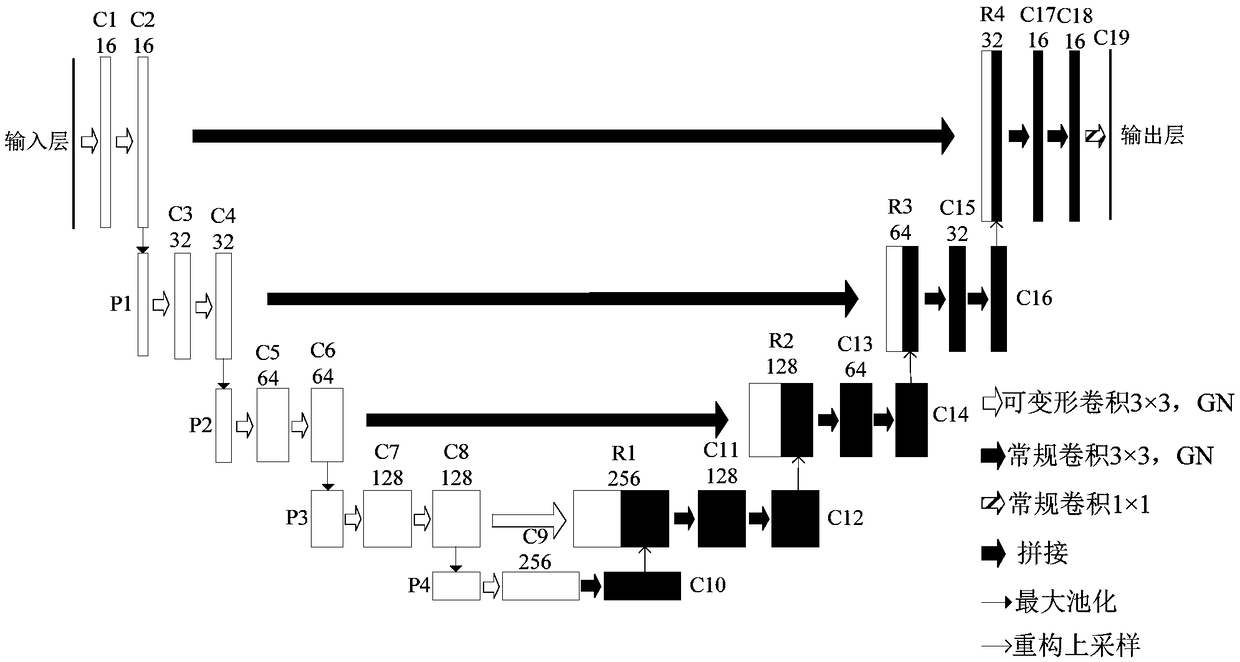
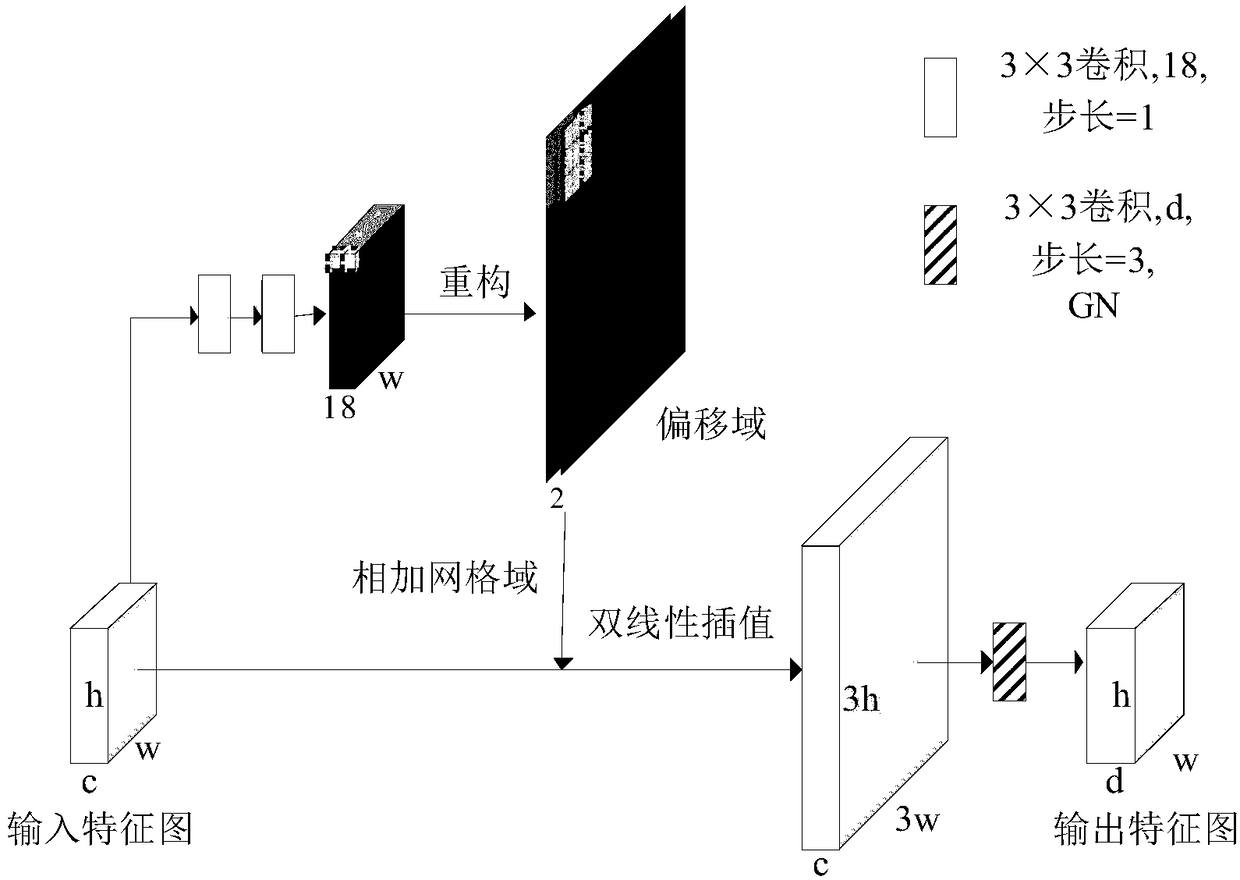
A novel biomedical image automatic segmentation method based on a U-net network structure
ActiveCN109191476AIncrease the number ofImprove segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisData setVisual technology
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing and computer vision, and relates to a novel biomedical image automatic segmentation method based on a U-net network structure, including dividing a biomedical data set into a training set and a test set, and normalizing the test set and augmented test set; inputting the images of the training set into the improved U-net network model, and generating a classification probability map by output image passing through a softmax layer; calculating the error between classification probability diagram and gold standard by a centralized loss function, and obtaining the weight parameters of network model by a gradient backpropagation method; entering the images in the test set into the improved U-net network model, and outputting the image to generate a classification probability map through the softmax layer; according to the class probability in the classification probability graph, obtaining the segmentation result graph of theimage. The invention solves the problems that simple samples in the image segmentation process contribute too much to the loss function to learn difficult samples well.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
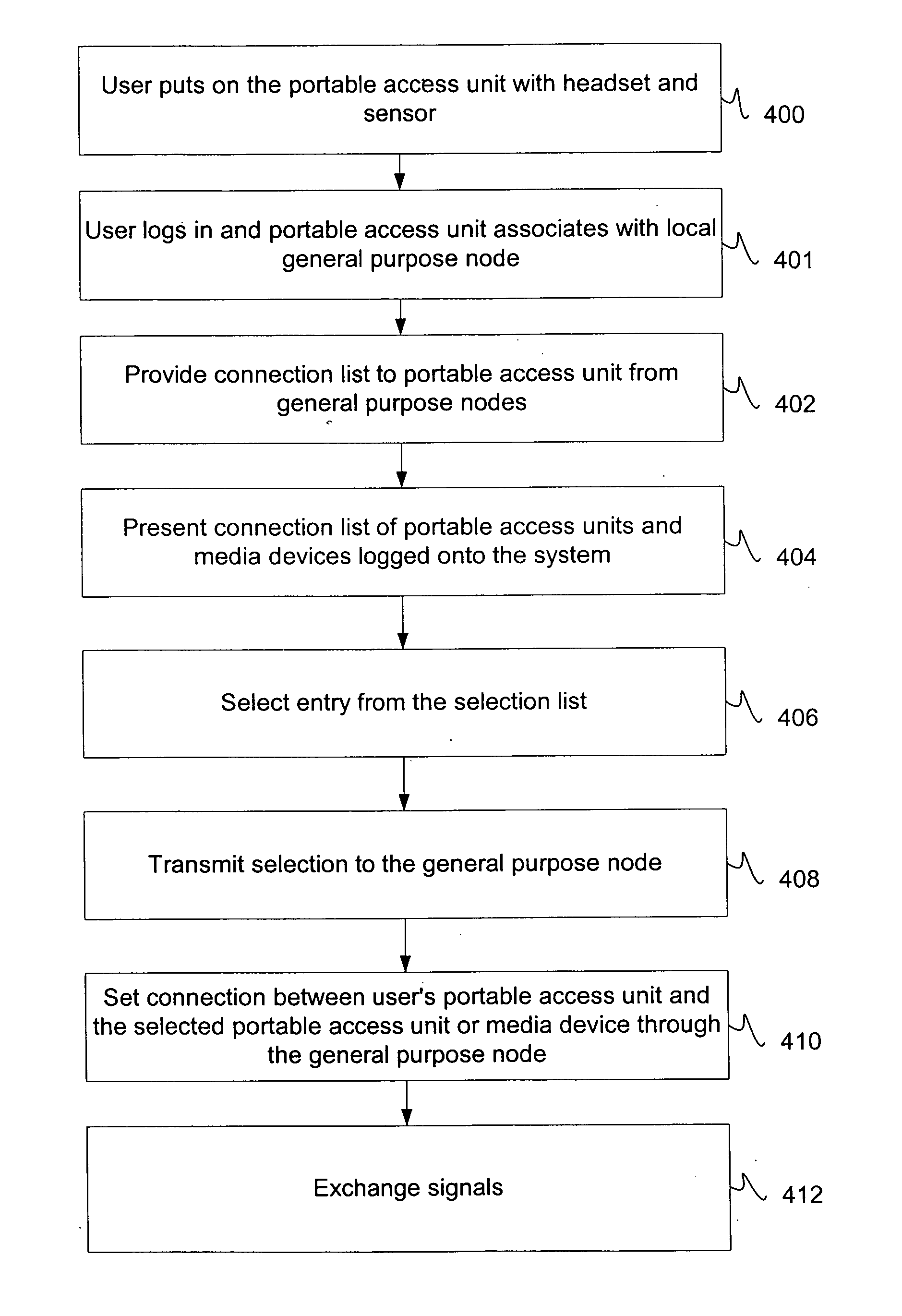
Wireless augmented reality communication system
InactiveUS7035897B1Improve efficiencyImprove mobilityTransmission systemsConnection managementPagerNetwork architecture
The system of the present invention is a highly integrated radio communication system with a multimedia co-processor which allows true two-way multimedia (video, audio, data) access as well as real-time biomedical monitoring in a pager-sized portable access unit. The system is integrated in a network structure including one or more general purpose nodes for providing a wireless-to-wired interface. The network architecture allows video, audio and data (including biomedical data) streams to be connected directly to external users and devices. The portable access units may also be mated to various non-personal devices such as cameras or environmental sensors for providing a method for setting up wireless sensor nets from which reported data may be accessed through the portable access unit. The reported data may alternatively be automatically logged at a remote computer for access and viewing through a portable access unit, including the user's own.
Owner:THROOP LLC
Information processing method and system for synchronization of biomedical data
InactiveUS20040172225A1Convenient treatmentSimpler to stratifyMedical simulationMedical data miningInformation processingPatient data
An information processing method and system, for synchronization of disease progression data of individual patients, includes receiving disease progression data in an aperiodic form and representing the disease progression data as a set of functions having finite asymptotic values. The parameters of the set of functions are clustered and the step of representing the disease progression data as a set of functions includes transforming the functions into time invariant form and thereby synchronizing individual patient data that is clustered.
Owner:PROSANOS CORP
Storage, retrieval, analysis, pricing, and marketing of personal health care data using social networks, expert networks, and markets
InactiveUS20150154646A1Facilitate communicationMedical communicationMedical data miningFinancial transactionBiological data
Systems and processes are provided for securely storing, retrieving, sharing, and selling private data, such as genome wide sequences, sequence related metadata, electronic healthcare data, biological data, demographic data, medical data, and other biomedical data, which, in turn, may allow the usage of genomic variations at multiple scales and across multiple population strata. In some examples, users may be matched with healthcare experts based on a medical need or interest. In other examples, an information-based market for utilizing the available data in a privacy-preserving manner may be provided. In these examples, individual or group data may be tracked, compared, rated, analyzed, and priced to allow individuals to establish connections and / or carry out financial transactions using their data with other participants, healthcare practitioners, and businesses.
Owner:SEQSTER PDM INC +1
Method for monitoring and communicating biomedical electromagnetic fields
The present invention provides a system and a method of monitoring and communicating biomedical data to a remote receiver. Specifically, the present invention provides a system and method that can monitor a biomedical-based electromagnetic field, e.g., heart rate variability (HRV) field, emitted from a human user (“sender”), and / or communicate the biomedical-based electromagnetic field to a remote receiver by measuring the biomedical-based electromagnetic field emitted from the sender, creating an electronic signal corresponding to the field and transmitting or broadcast and / or apply the signal to a remote receiver.
Owner:IBM CORP
Enhanced multi-protocol analysis via intelligent supervised embedding (empravise) for multimodal data fusion
ActiveUS20140037172A1Image analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionAlgorithmDimensionality reduction
The present invention provides a system and method for analysis of multimodal imaging and non-imaging biomedical data, using a multi-parametric data representation and integration framework. The present invention makes use of (1) dimensionality reduction to account for differing dimensionalities and scale in multimodal biomedical data, and (2) a supervised ensemble of embeddings to accurately capture maximum available class information from the data.
Owner:RUTGERS THE STATE UNIV
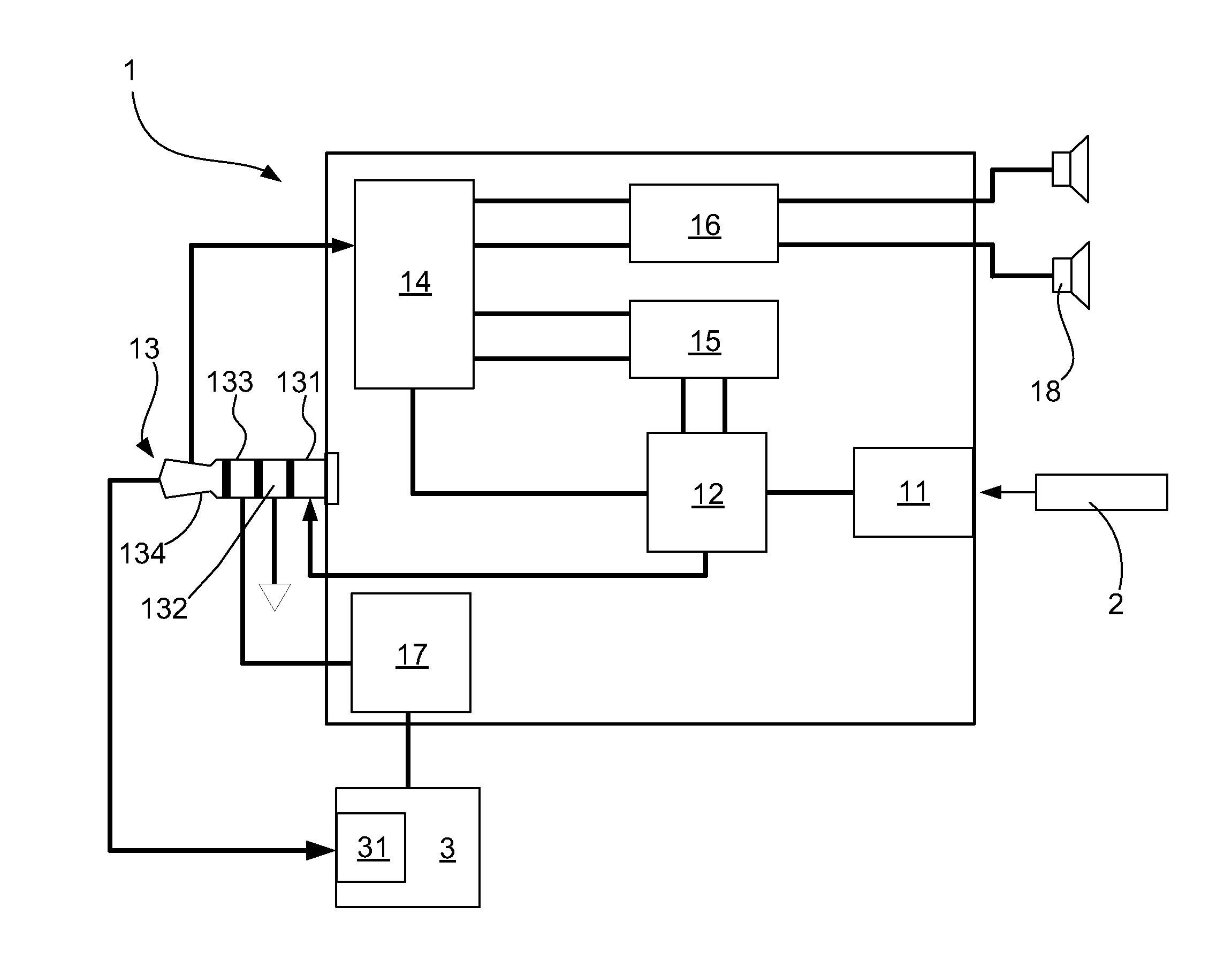
Biomedical device with near field communication (NFC) function and method thereof for user identification, biomedical data measurement, biomedical data upload/download, biomedical data management, and remote medical care
The present invention relates to a biomedical device with near field communication (NFC) function and a method thereof for user identification, biomedical data measurement, biomedical data upload / download, biomedical data management, and remote medical care, the biomedical device comprises: a measuring unit, a environment sensing unit, a data transforming unit, a micro control unit, a memory unit, a smart card unit, a display unit, and a near field communication unit, wherein by way of near field communication unit, the biomedical device is able to communicate with a portable device and a user individual information and the relative biomedical data thereof can be transmitted to the portable device, such that multi men are allowed for using the identical biomedical device and the situation about misrecording and misjudging of data would not be occurred; moreover, through the portable device, the biomedical data can be uploaded to a cloud server and a user history data and an optimized setting data for personalization biomedical device can be downloaded from the cloud server.
Owner:PENSIERO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CORP
Coiled circuit bio-sensor
A coiled bio-medical device has a base layer coiled to form a plurality of concentric cylinders. The base layer comprises an inner surface. The coiled bio-medical includes a bio-sensor arranged on the inner surface of the base layer. The bio-sensor is adapted to collect bio-medical data from an organism. A transmitter is arranged on the inner surface of the base layer and is adapted to transmit the collected bio-medical data.
Owner:NORTHROP GRUMMAN SYST CORP
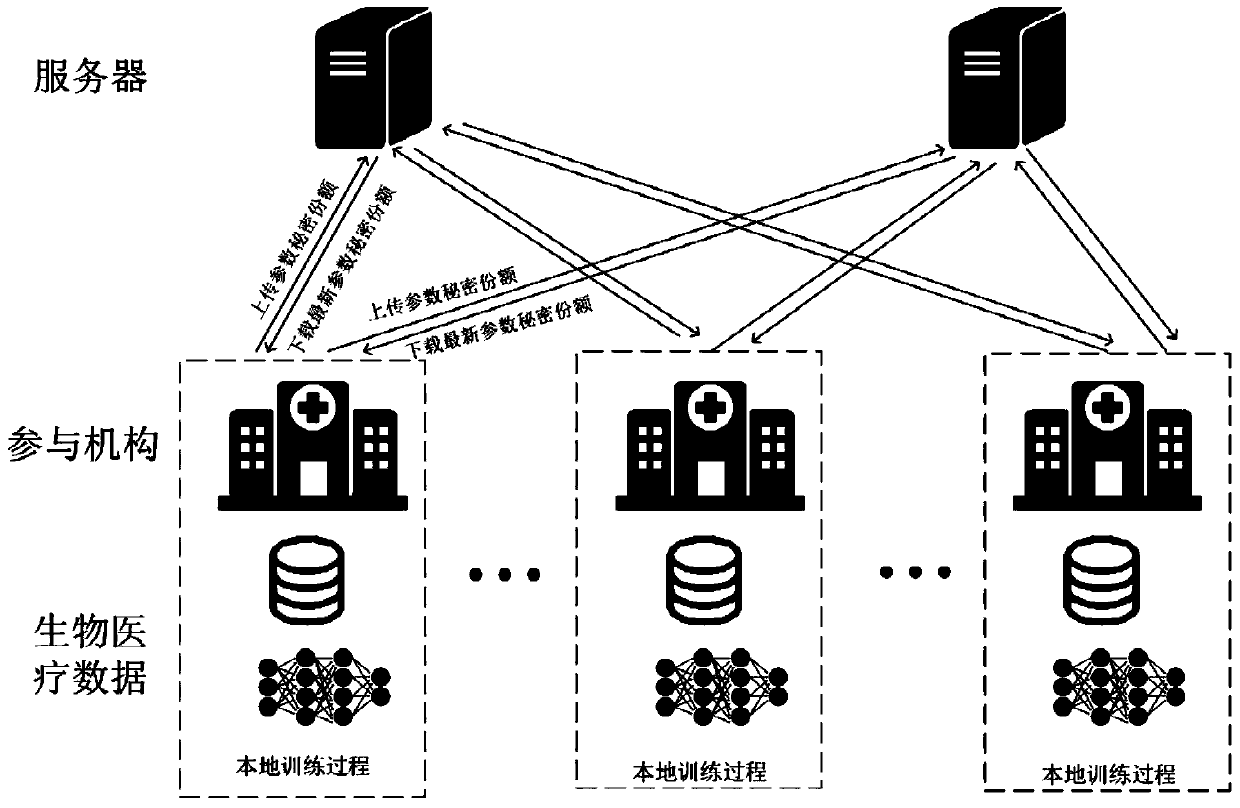
Data sharing method based on collaborative deep learning
InactiveCN109977694AGuaranteed data privacyDefense against aggressive behaviorDigital data protectionSecret shareModel parameters
The invention discloses a data sharing method based on collaborative deep learning. The system comprises two servers and a plurality of participation mechanisms. Each participation mechanism has biomedical data in the same format. The server is responsible for updating and maintaining the model parameters uploaded by the participation mechanism; each participation mechanism only needs to downloadthe latest parameter secret share from the two servers. Secrete reconstruction and recovery are carried out locally to obtain a latest parameter; and then deep learning model training is carried out locally by utilizing the parameters and private biomedical data of the two servers, the updated model parameters are split into two secret shares through a secret sharing scheme after training is completed, and the two servers carry out parameter updating operation on the secret shares respectively for downloading of the participating institutions. The cooperative deep learning method and the secret sharing scheme are used, data privacy in the biomedical data sharing process is protected, and great significance is achieved for promoting sharing of biomedical data.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
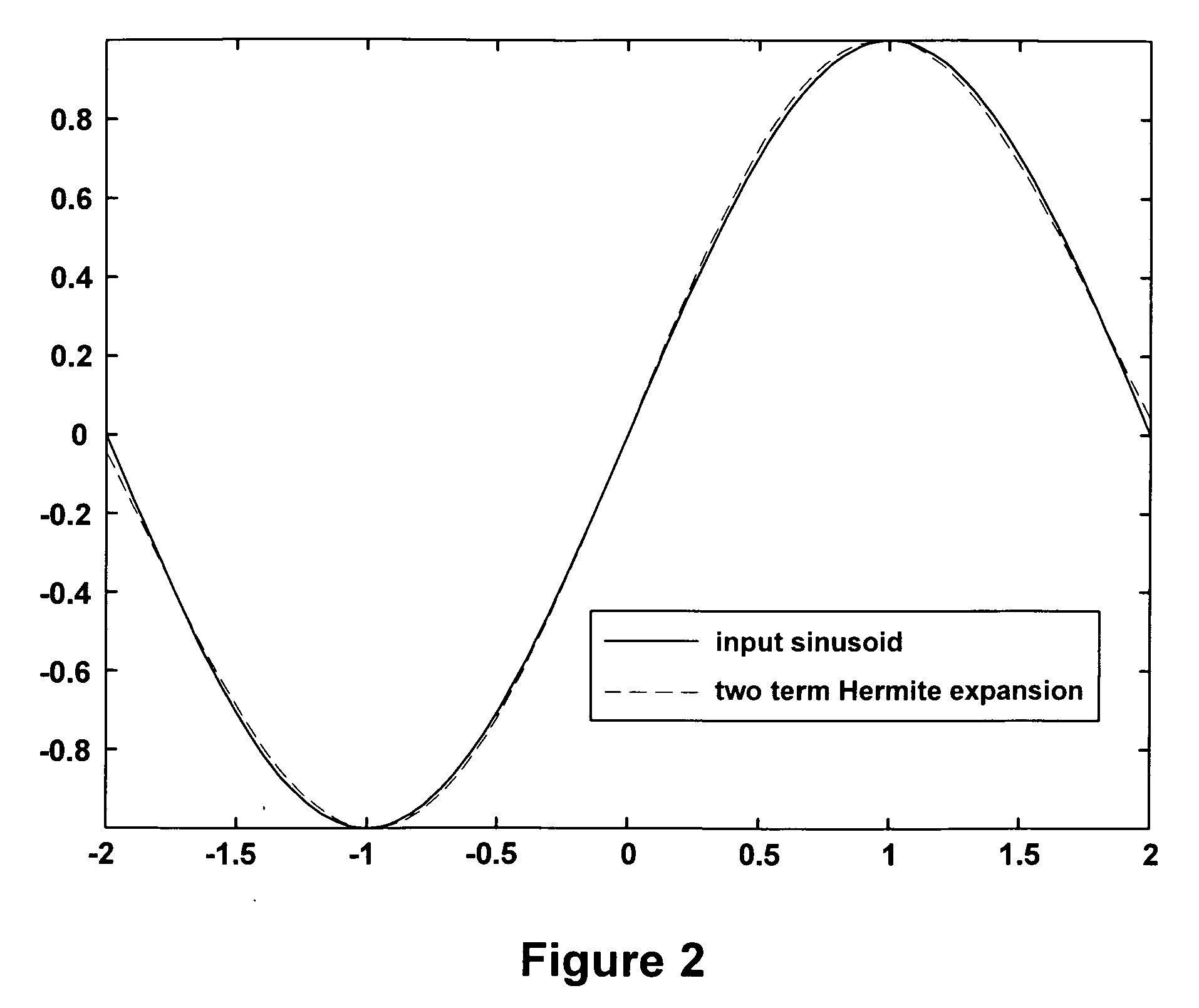
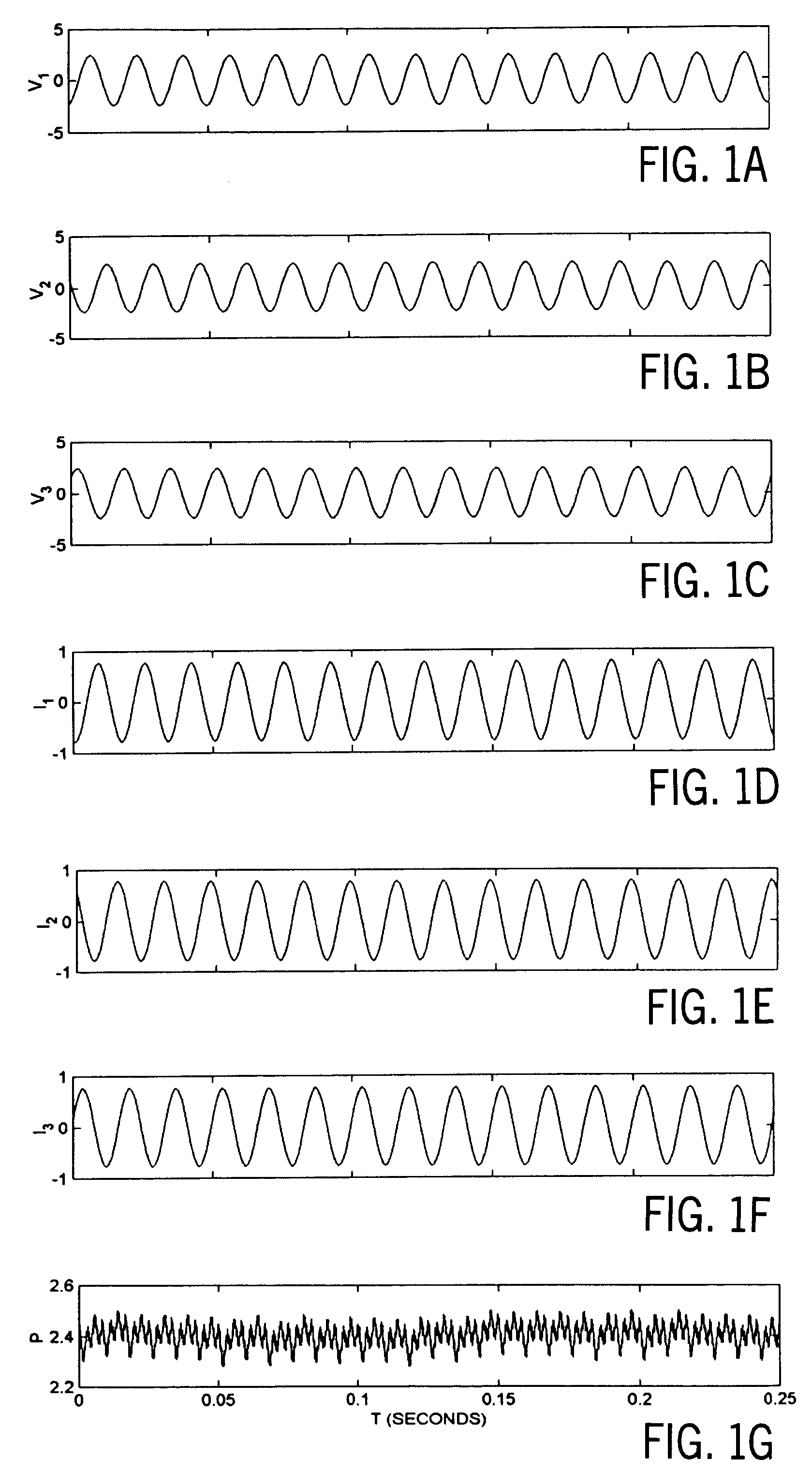
General diagnostic and real-time applications of discrete hermite functions to digital data
InactiveUS20080262367A1Accurate modelingData augmentationElectrocardiographySensorsDigital dataComputer science
The present invention relates to general diagnostic and real-time applications of discrete Hermite functions to digital data. More specifically, the invention relates to methods and systems for the application of dilated discrete digital Hermite functions (DDHF) to biomedical data, for example, to extract features from digital signals, including but not limited to, ECGs, EMGs, EOGs, EEGs, and others, by expanding the measured signals using a computationally efficient technique. These digital Hermite functions form the basis for the new discrete Hermite transform, generated on a beat by beat basis, which provides information about the shape of the signals, such as that in the BCG artifact in an EEG or in an ECG interval, or any noise in any other electrical signal. An automated system and method for real-time interpretation of any abnormalities present in a digital biomedical signal is provided.
Owner:THE UNIVERSITY OF AKRON
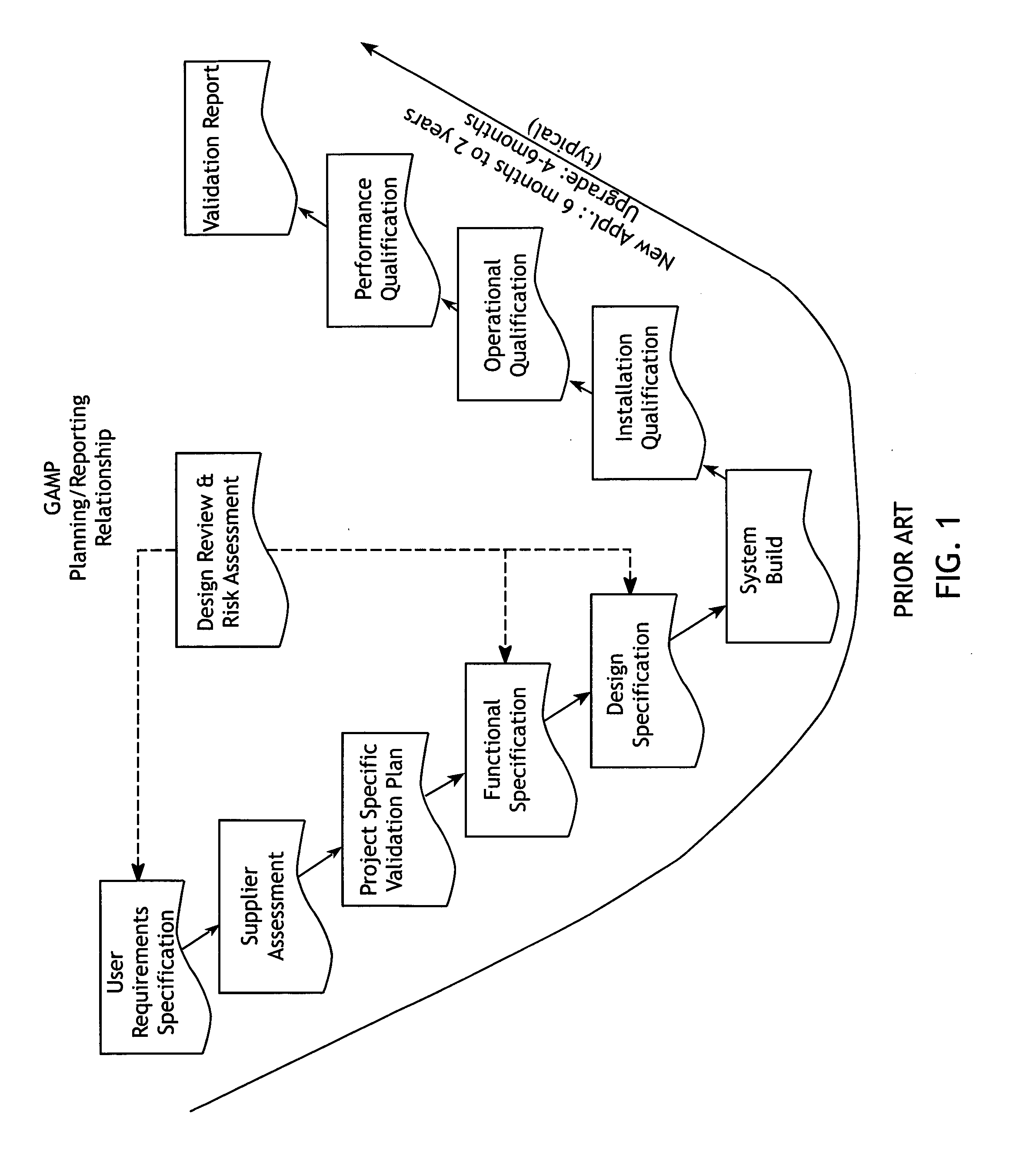
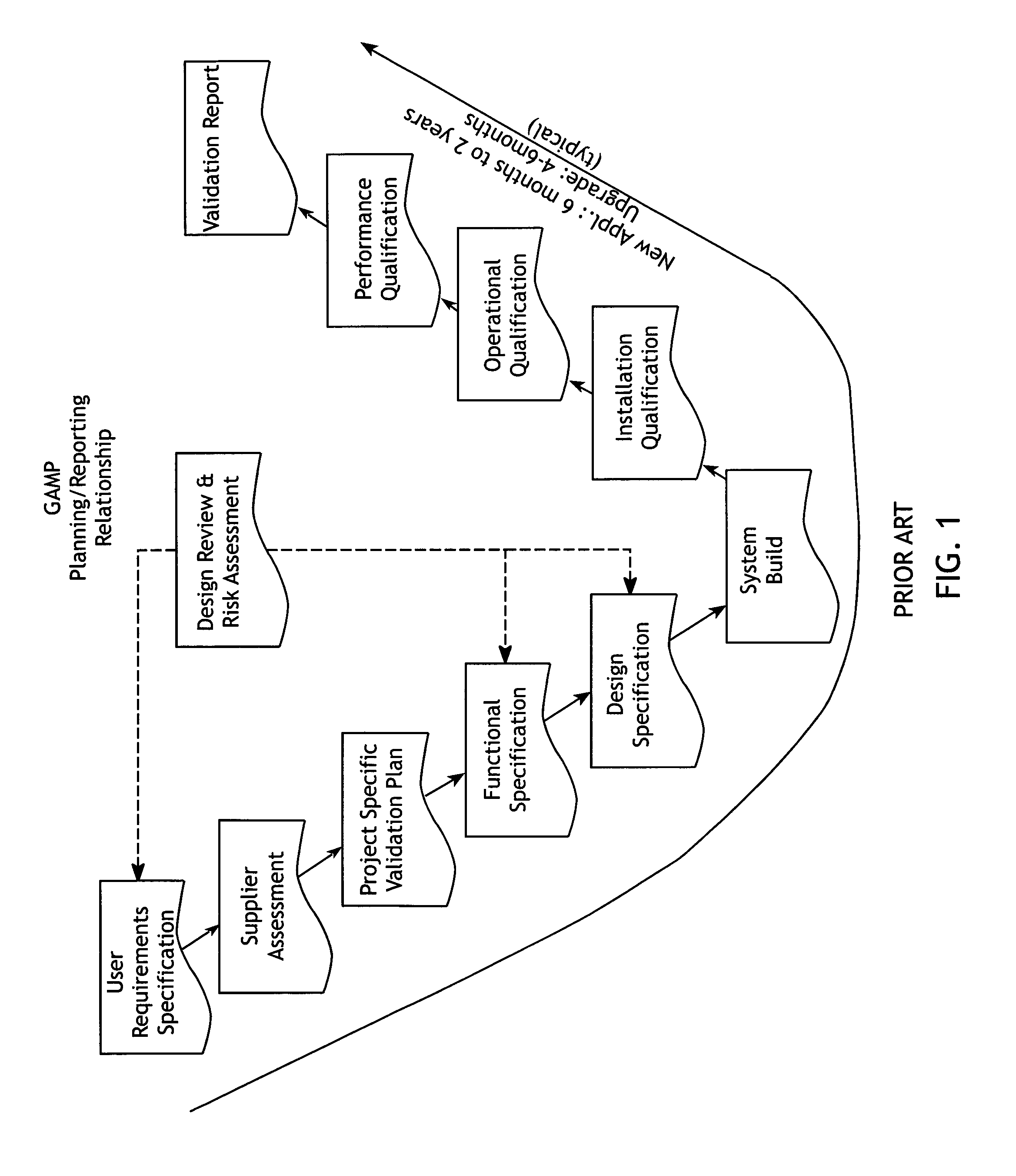
Virtual validation of software systems
InactiveUS20080178144A1Shorten the timeReduces time and effortError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsRegulated IndustrySoftware system
A method for building and verifying and validating a software system that is used for regulated industry software related activities, such as FDA trials, field trials, biomedical data gathering, and similar efforts includes building the application into a virtual appliance using, for example, Vmware. The application and the supporting software are encapsulated in a single virtual file to create a virtual appliance that is independent of hardware and dependent only on virtual appliance support.
Owner:VIRTUAL PURPLE +1
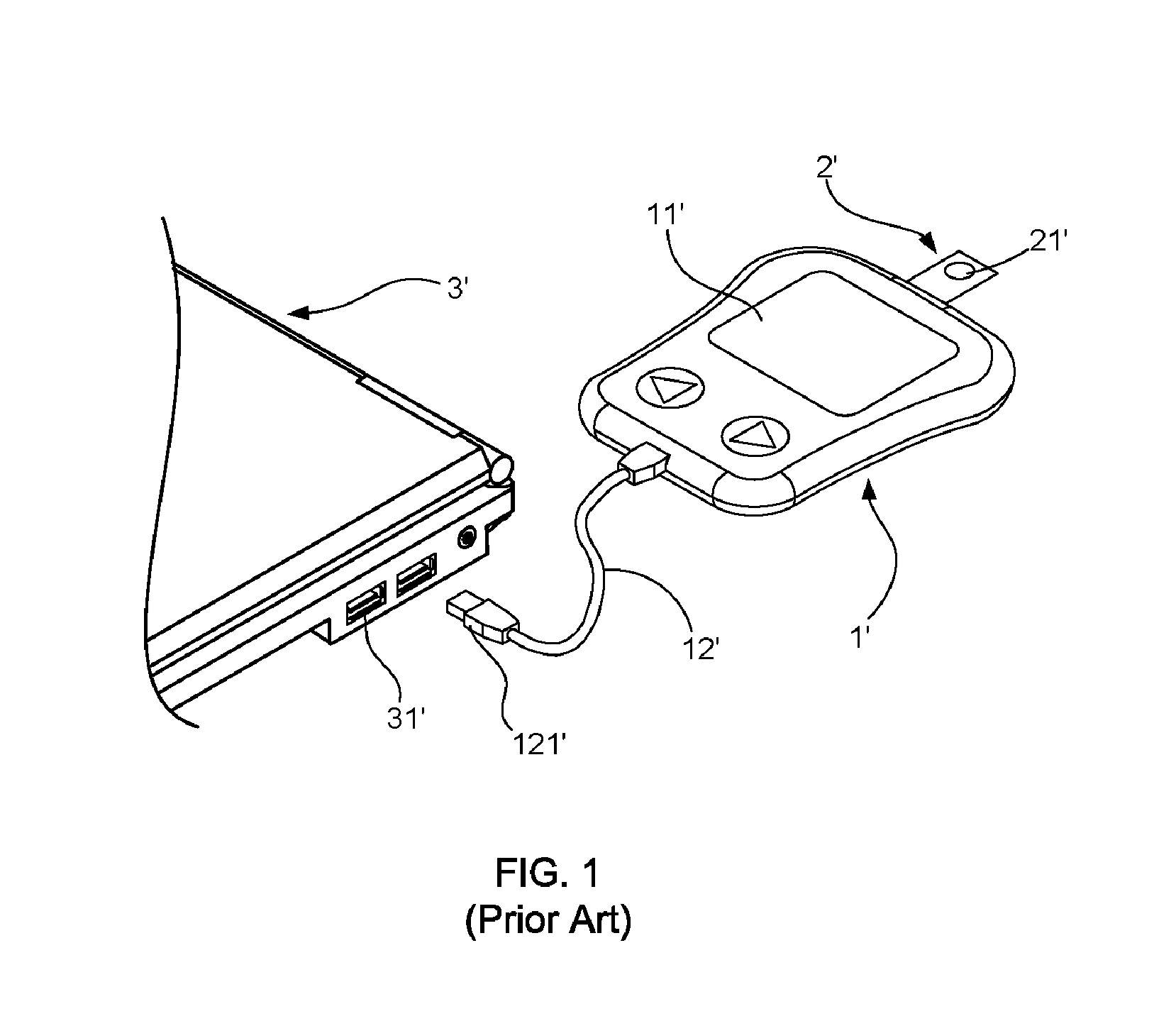
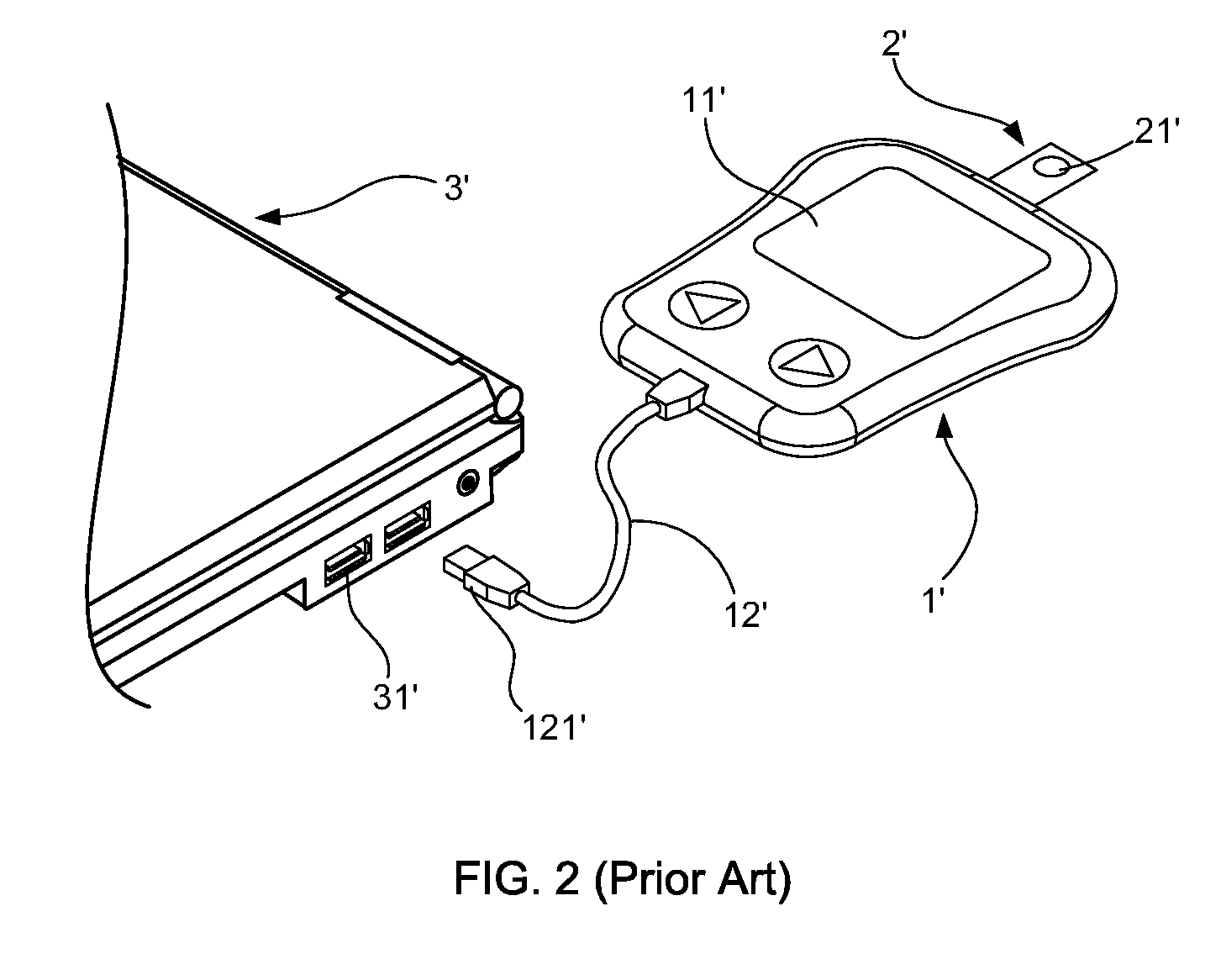
Biomedical devcie capable of using an earphone and microphone plug to transmit data and method for transmitting data
The present invention relates to a biomedical device capable of using an earphone and microphone plug to transmit data and a method for transmitting data, wherein the biomedical device comprises: a measuring unit, a micro-control unit, an earphone and microphone plug, a switch unit, a level shift unit, an amplifying unit, and a power management unit. By way of inserting the earphone and microphone plug into an earphone and microphone jack of a portable electronic device, the biomedical device is able to transmit data to the portable electronic device without passing the certification of the transmission format defined by a potable electronic device vender in advance. Moreover, through the method, a user can input biomedical data into the portable electronic device, so as to record and trace the daily biomedical data thereof; in addition, the biomedical data can be uploaded to a Cloud Database via the portable electronic device for a telemedicine management.
Owner:PENSIERO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CORP
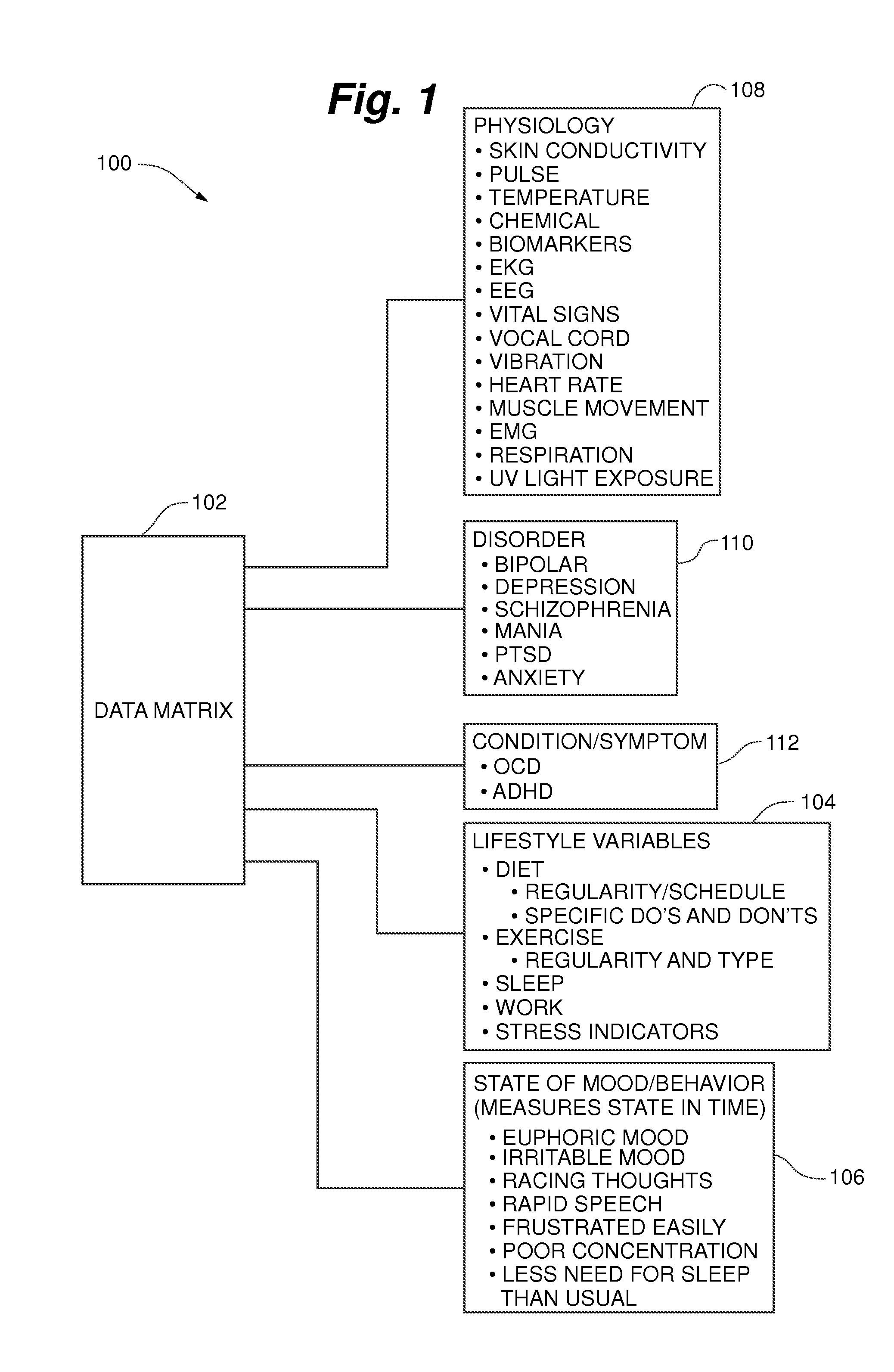
Methods and systems for creating a preventative care plan in mental illness treatment
InactiveUS20150148621A1Averting irreversible brain damageStatistical accuracy in predictionPerson identificationCatheterDiseaseBipolar mood disorder
Disclosed are methods, systems, and devices for generating sleep predicators to avoid preventable mental episodes from breaking through, thereby averting an irreversible brain damage to a patient, that may be caused by such future mental episodes. In one embodiment, the present invention is a method comprising: acquiring biomedical data from a patient by using a means of signal acquisition; forming a database of the biomedical records in which the database further comprises a sleep prediction algorithm, psychiatric records, and a statistical engine to compute the data and the psychiatric records using the algorithm; mapping the acquired data in reference to the sleep prediction algorithm; validating the sleep predictors; and providing an output of the sleep predicators to a patient or caretaker. The present invention can be used to treat mania, depression, bipolar disorder, schizophrenia, PTSD, anxiety, and other chronic mental health conditions.
Owner:SIER GRANT JOSEPH
Methods for improved forewarning of critical events across multiple data channels
InactiveUS7209861B2Good choiceStructural/machines measurementDiagnostic recording/measuringStatistical analysisEngineering
This disclosed invention concerns improvements in forewarning of critical events via phase-space dissimilarity analysis of data from mechanical devices, electrical devices, biomedical data, and other physical processes. First, a single channel of process-indicative data is selected that can be used in place of multiple data channels without sacrificing consistent forewarning of critical events. Second, the method discards data of inadequate quality via statistical analysis of the raw data, because the analysis of poor quality data always yields inferior results. Third, two separate filtering operations are used in sequence to remove both high-frequency and low-frequency artifacts using a zero-phase quadratic filter. Fourth, the method constructs phase-space dissimilarity measures (PSDM) by combining of multi-channel time-serial data into a multi-channel time-delay phase-space reconstruction. Fifth, the method uses a composite measure of dissimilarity (Ci) to provide a forewarning of failure and an indicator of failure onset.
Owner:UT BATTELLE LLC
Gesture-Based Visualization System for Biomedical Imaging and Scientific Datasets
InactiveUS20140324400A1Analogue computers for chemical processesComputation using non-denominational number representationData setComputer vision
Three-dimensional visualization of biomedical datasets in an immersive visual environment includes creating a finite element mesh patient specific three-dimensional mode. Points from the finite element mesh are removed to produce a refined patient specific three-dimensional model. The three-dimensional model and simulation are interpolated onto a uniform rectilinear grid. The refined patient specific three-dimensional model and the simulation data are transformed to a scale of the IVE. The refined patient specific three-dimensional model and the simulation data are presented within the IVE with a three-dimensional visualization system.
Owner:MARQUETTE UNIVERSITY +1
Telemedicine system for remote consultation, diagnosis and medical treatment services
InactiveUS20150261930A1Medical communicationData processing applicationsSystem usageComputer science
The invention relates to a telemedicine system including improved methods, systems and techniques for providing remote consultation, diagnosis and / or medical treatment. Said system uses a Basic Telemedicine Unit BTU and Specialist Telemedicine Unit STU comprising the simultaneous and independent display, on the local interface and on the remote interface, of all of the patient-related audio, video, biomedical data signals and clinical data, the concurrent annotation of images and videos, and processing for the protection of the personal data of the patients.
Owner:ESPINOSA ESCALONA FERNANDO PABLO JOSE +2
Semi-supervised biomedical text semantic disambiguation method
InactiveCN108491382AImprove accuracySemantic analysisCharacter and pattern recognitionLabel propagationStudy methods
The invention provides a semantic disambiguation method for biomedical text polysemes. The method mainly comprises the steps of performing word vectorized representation on a biomedical text by utilizing Word2Vec; based on a bidirectional LSTM model, constructing vectorized representations of context sentences for a word vector language model; propagating existing labels for labeling medical datato most similar unlabeled data according to probabilities in combination with a label propagation method by utilizing a sentence vector space similarity relationship; and finally performing semantic disambiguation on the biomedical text in combination with all the labeled data. The biomedical data has the characteristics of strong speciality, numerous terms and the like, so that the operation of manually processing the medical data is time and labor-consuming and high in error rate; by using the method, the manual labeling cost can be greatly reduced; and compared with a conventional machine learning method, the semantic disambiguation accuracy can be effectively improved.
Owner:SICHUAN UNIV
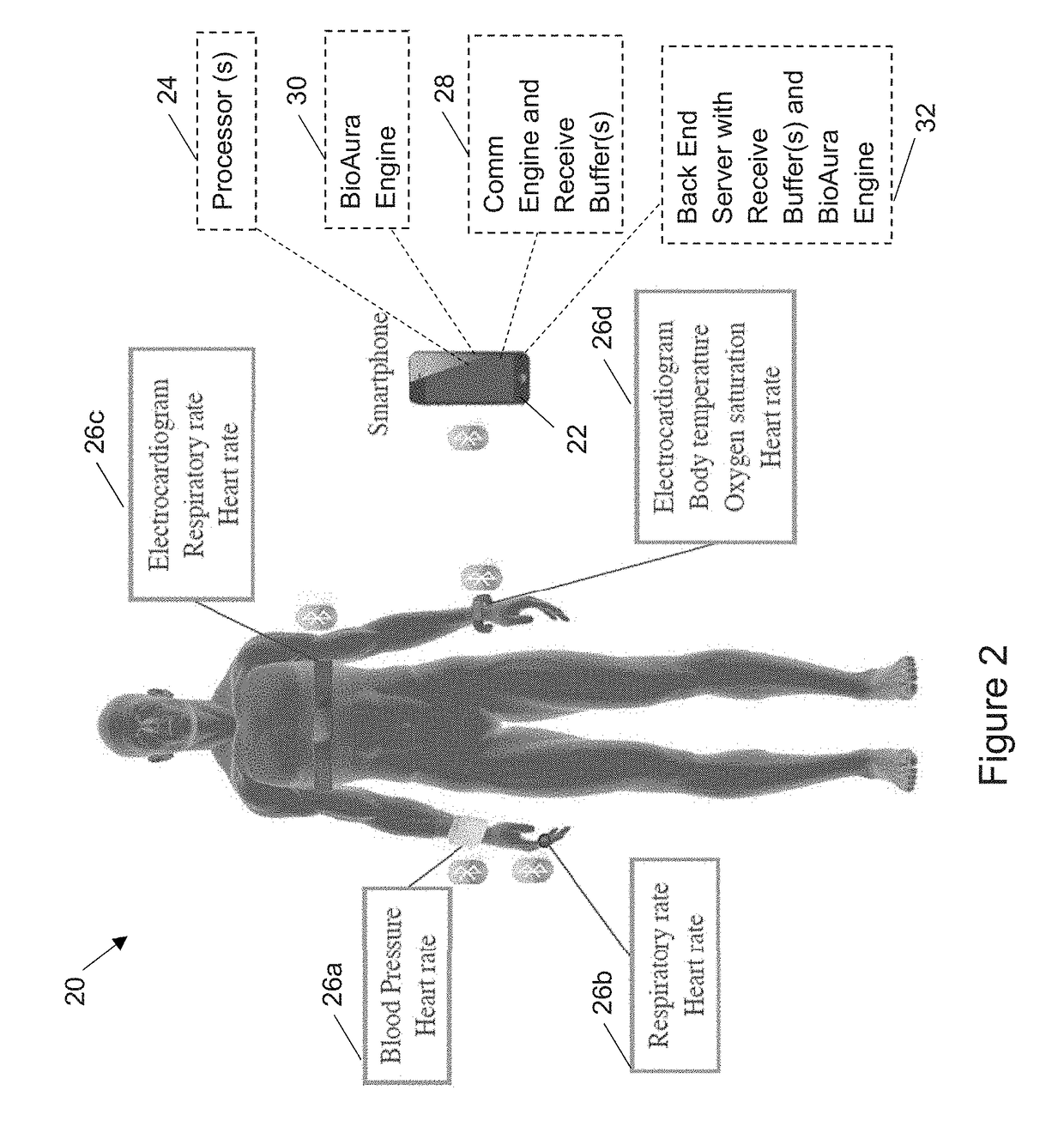
Continuous authentication system and method based on bioaura
ActiveUS20170230360A1Attenuation bandwidthContinuous operationPerson identificationEvaluation of blood vesselsComputer hardwareUser authentication
A user authentication system for an electronic device for use with a plurality of wireless wearable medical sensors (WMSs) and a wireless base station that receives a biomedical data stream (biostream) from each WMS. The system includes a BioAura engine located on a server, the server has a wireless transmitter / receiver with receive buffers that store the plurality of biostreams, the biostream from a single WMS lacks the discriminatory power to identify the user, the BioAura engine has a look up stage and a classifier, the classifier generates an authentication output based on the plurality of biostreams, the authentication output authenticates the user's access to the electronic device. The wireless base station has a transmitter / receiver having receive buffers that store the biomedical data from each WMS, the wireless base station has a communication engine that retrieves the biostream from each WMS and transmits the plurality of biostreams to the server.
Owner:THE TRUSTEES FOR PRINCETON UNIV +2
Method for monitoring and communicating biomedical electromagnetic fields
The present invention provides a system and a method of monitoring and communicating biomedical data to a remote receiver. Specifically, the present invention provides a system and method that can monitor a biomedical-based electromagnetic field, e.g., heart rate variability (HRV) field, emitted from a human user (“sender”), and / or communicate the biomedical-based electromagnetic field to a remote receiver by measuring the biomedical-based electromagnetic field emitted from the sender, creating an electronic signal corresponding to the field and transmitting or broadcast and / or apply the signal to a remote receiver.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
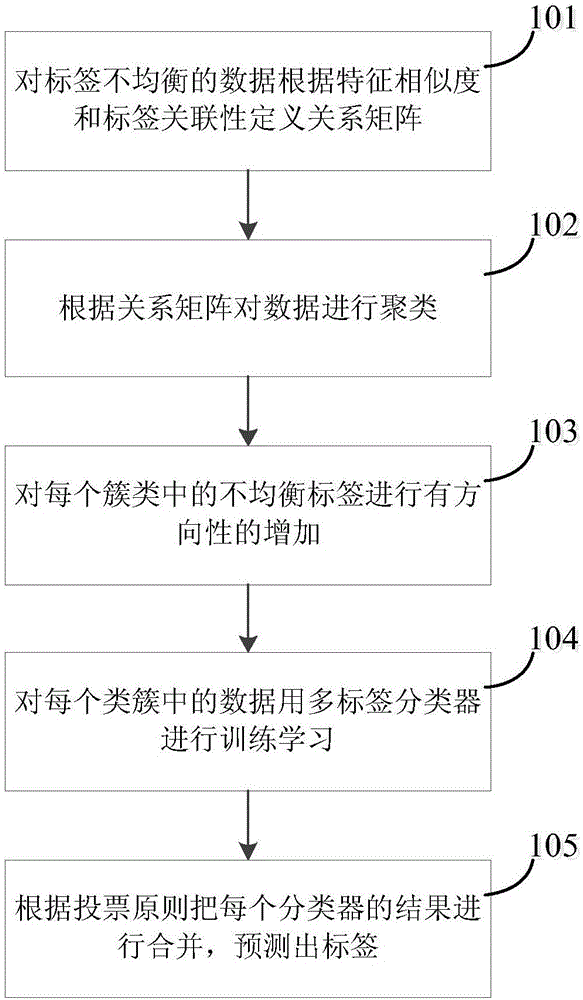
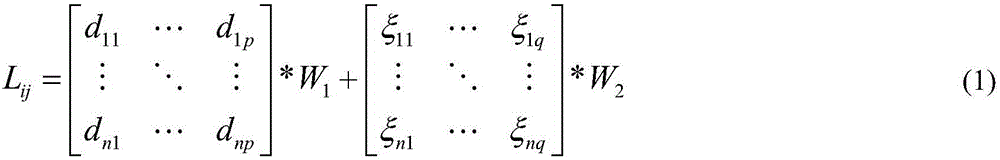
Cluster-based multi-label imbalance biomedical data classification method
ActiveCN106599913AReduce imbalanceImprove reliabilityCharacter and pattern recognitionMedical automated diagnosisMulti-label classificationClassification methods
The invention relates to a cluster-based multi-label imbalance biomedical data classification method. The method includes the following steps of S101 defining a relation matrix for the label imbalance data according to the feature similarity and label relevance; S102 clustering the data according to the relation matrix; S103 directionally increasing the imbalance labels in each cluster; S104 training and learning the data in each cluster by means of a multi-label classifier; and S105 combining the result of each classifier according to the polling rule and predicting the label. The data is clustered by means of a hierarchical clustering method, the label relevance is considered during the clustering to reduce the imbalance of the labels in the clusters, so that the reliability for new data generation by means of a re-sampling method is improved, and the probability for noise data is reduced.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Virtual validation of software systems
InactiveUS8266578B2Reduces time and effortReduce buildError detection/correctionDigital computer detailsRegulated IndustrySoftware system
Owner:VIRTUAL PURPLE +1
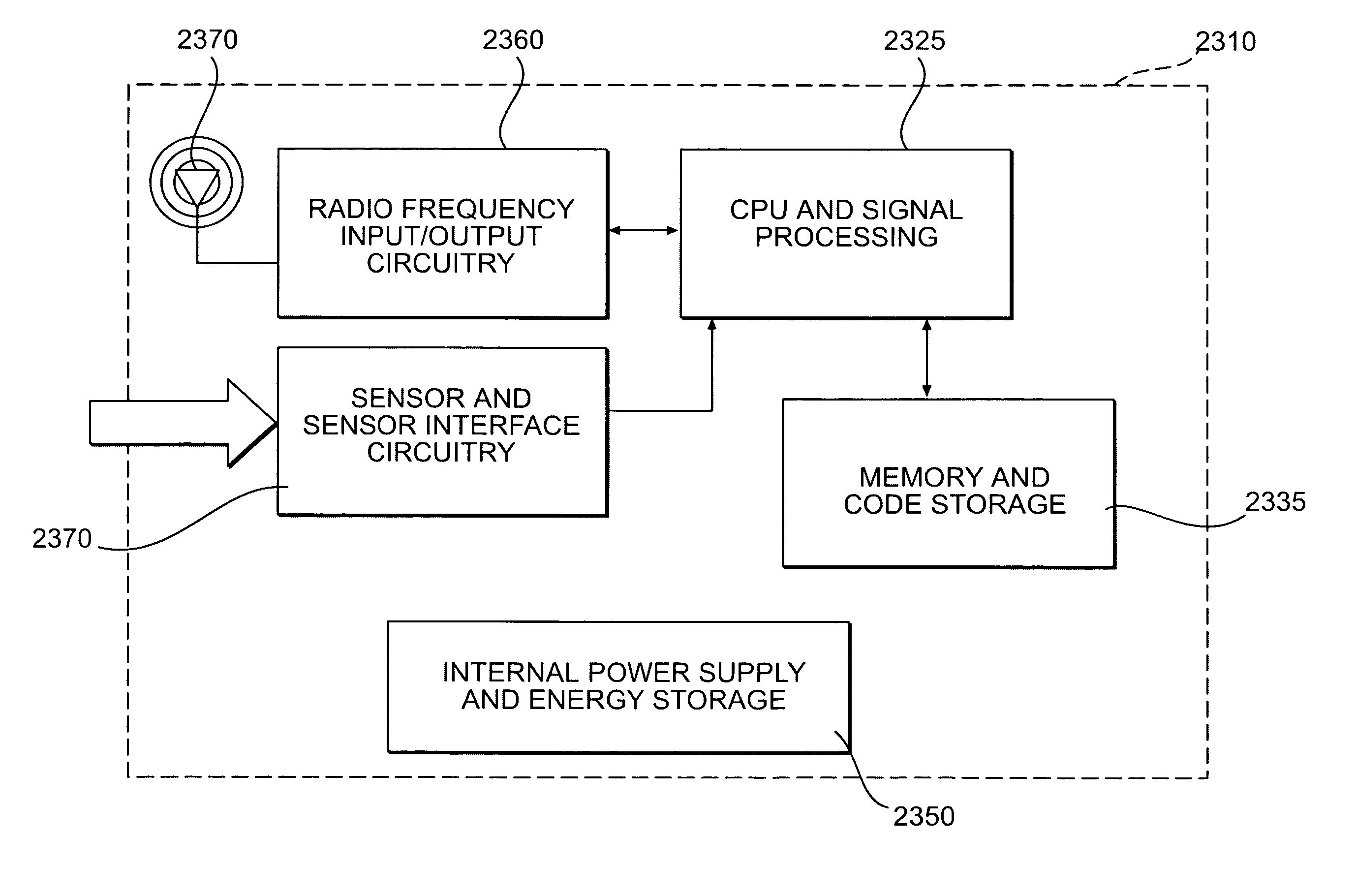
Methods and Systems for Stream-Processing of Biomedical Data
ActiveUS20170318119A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationDigital data information retrievalData streamFile system
A method for stream-processing biomedical data includes receiving, by a file system on a computing device, a first request for access to at least a first portion of a file stored on a remotely located storage device. The method includes receiving, by the file system, a second request for access to at least a second portion of the file. The method includes determining, by a pre-fetching component executing on the computing device, whether the first request and the second request are associated with a sequential read operation. The method includes automatically retrieving, by the pre-fetching component, a third portion of the requested file, before receiving a third request for access to least the third portion of the file, based on a determination that the first request and the second request are associated with the sequential read operation.
Owner:SEVEN BRIDGENOMICS
Biomedical device with function of short-range wireless transmission and application method thereof
InactiveCN102670174AImmediate medical attentionSimple structureTransmission systemsDiagnostic recording/measuringMicrocontrollerSmart card
The invention relates to a biomedical device with a function of short-range wireless transmission and an application method thereof. The biomedical device comprises a measuring unit, an environment sensing unit, a data conversion unit, a microcontroller unit, a storage unit, a smart card unit, a display unit and a near-field communication unit. The biomedical device is communicated with a handheld device through the near-field communication unit and is capable of transmitting a user's personal information and biomedical data corresponding to the same to the handheld device. Therefore, the biomedical device is available for multiple users, and false recording and determination of data can be avoided. In addition, the biomedical data can be uploaded to a cloud server through the handheld device, and historical data and personal biomedical-device optimal setting data can be downloaded from the cloud server through the handheld device.
Owner:PENSIERO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CORP
Biomedical device capable of transmitting data by using earphone microphone plug and method thereof
InactiveCN102457788AEvaluation of blood vesselsEarpiece/earphone attachmentsManagement unitPower Management Unit
The invention relates to a biomedical device capable of transmitting data by using an earphone microphone plug and a method thereof. The biomedical device comprises a measurement unit, a microcontrol unit, the earphone microphone plug, a switch unit, a positioning migration unit, an amplification unit and a power source management unit. The earphone microphone plug is plugged in an earphone microphone jack, so that the biomedical device can carry out data transmission with a portable electronic device without passing through a transmission format certification program prescribed by a manufacturer in advance. Furthermore, through the method that biomedical data are transmitted to the portable electronic device by using the earphone microphone plug, a user can input the biomedical data into the portable electronic device so as to record and track daily biomedical data by using the portable electronic device; and meanwhile, the biomedical data measured every day can be uploaded to a cloud database through the portable electronic device for long-distance medical management.
Owner:PENSIERO MEDICAL ELECTRONICS CORP
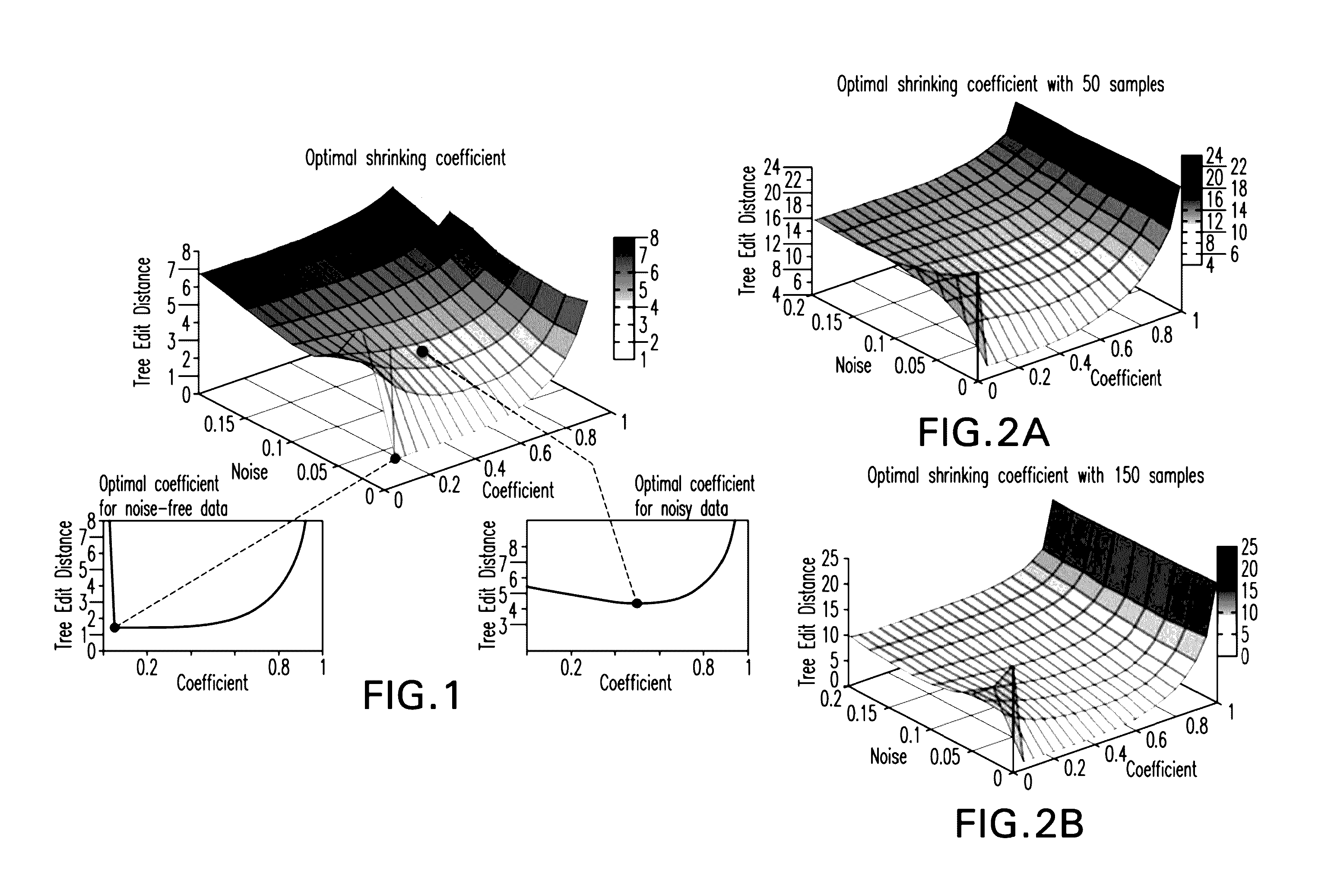
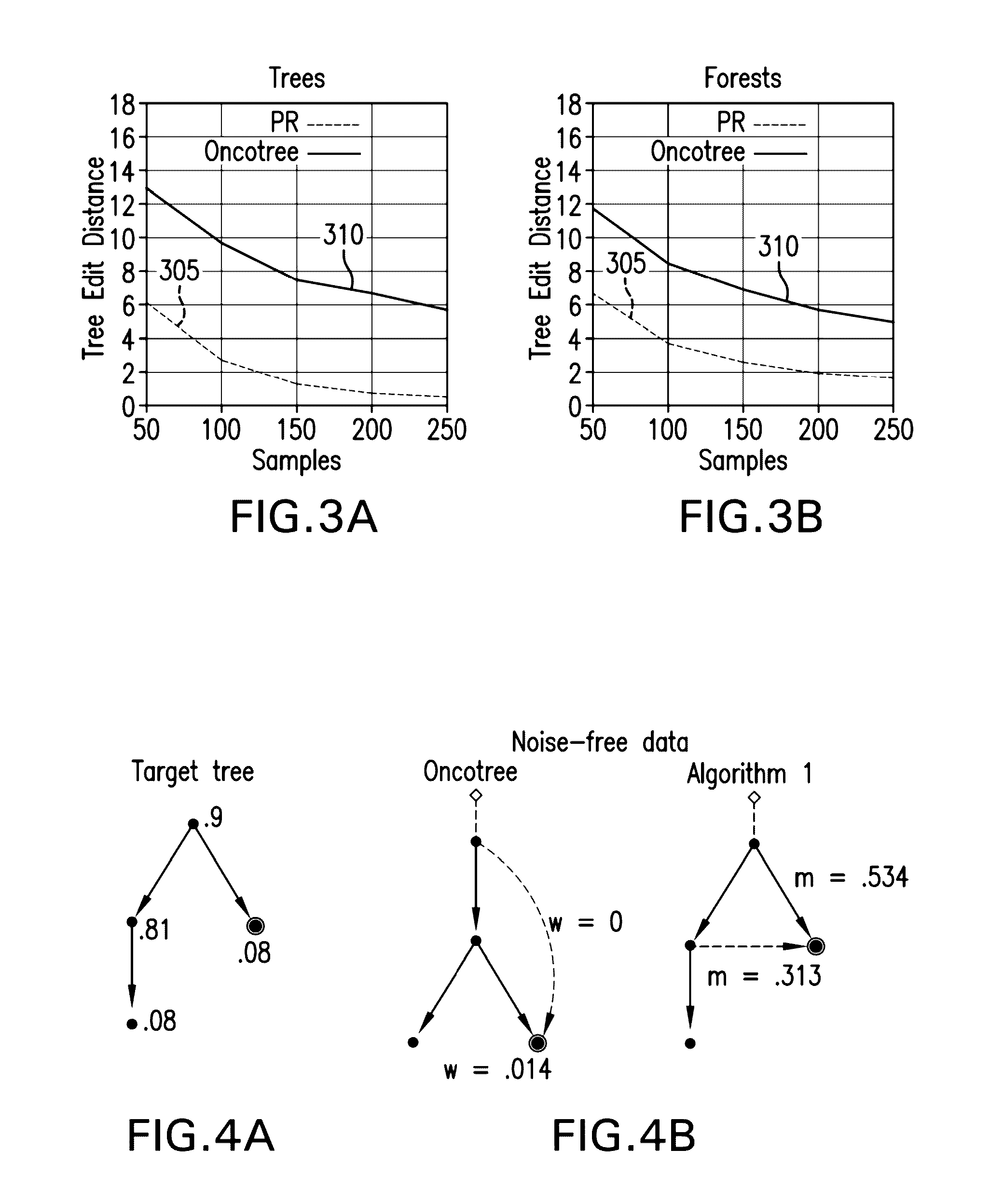
Methods, computer-accessible medium and systems to model disease progression using biomedical data from multiple patients
An exemplary embodiment of system, method and computer-accessible medium can be provided to reconstruct models based on the probabilistic notion of causation, which can differ fundamentally from that can be based on correlation. A general reconstruction setting can be complicated by the presence of noise in the data, owing to the intrinsic variability of biological processes as well as experimental or measurement errors. To gain immunity to noise in the reconstruction performance, it is possible to use a shrinkage estimator. On synthetic data, the exemplary procedure can outperform currently known procedures and, for some real cancer datasets, there are biologically significant differences revealed by the exemplary reconstructed progressions. The exemplary system, method and computer accessible medium can be efficient even with a relatively low number of samples and its performance quickly converges to its asymptote as the number of samples increases.
Owner:NEW YORK UNIV +1
Wireless augmented reality communication system
InactiveUS20070043843A1Efficiently operate and monitorTransmission systemsDigital computer detailsPagerNetwork architecture
The system of the present invention is a highly integrated radio communication system with a multimedia co-processor which allows true two-way multimedia (video, audio, data) access as well as real-time biomedical monitoring in a pager-sized portable access unit. The system is integrated in a network structure including one or more general purpose nodes for providing a wireless-to-wired interface. The network architecture allows video, audio and data (including biomedical data) streams to be connected directly to external users and devices. The portable access units may also be mated to various non-personal devices such as cameras or environmental sensors for providing a method for setting up wireless sensor nets from which reported data may be accessed through the portable access unit. The reported data may alternatively be automatically logged at a remote computer for access and viewing through a portable access unit, including the user's own.
Owner:INNOVATION MANAGEMENT SCI
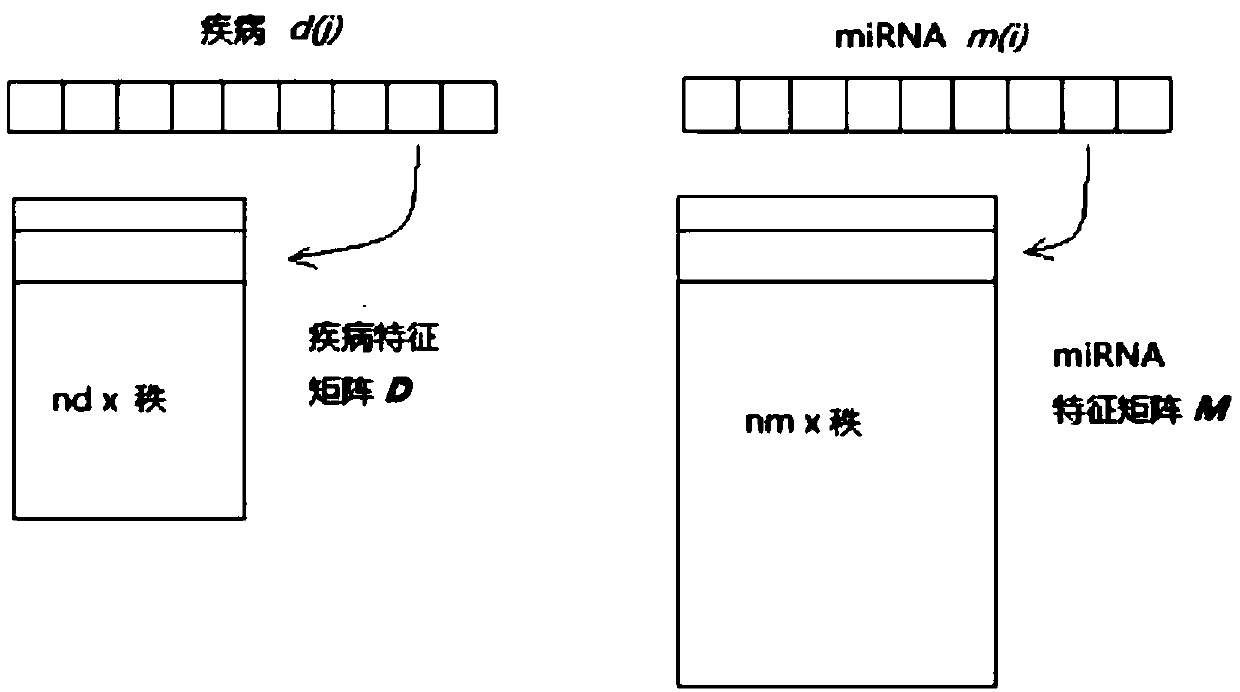
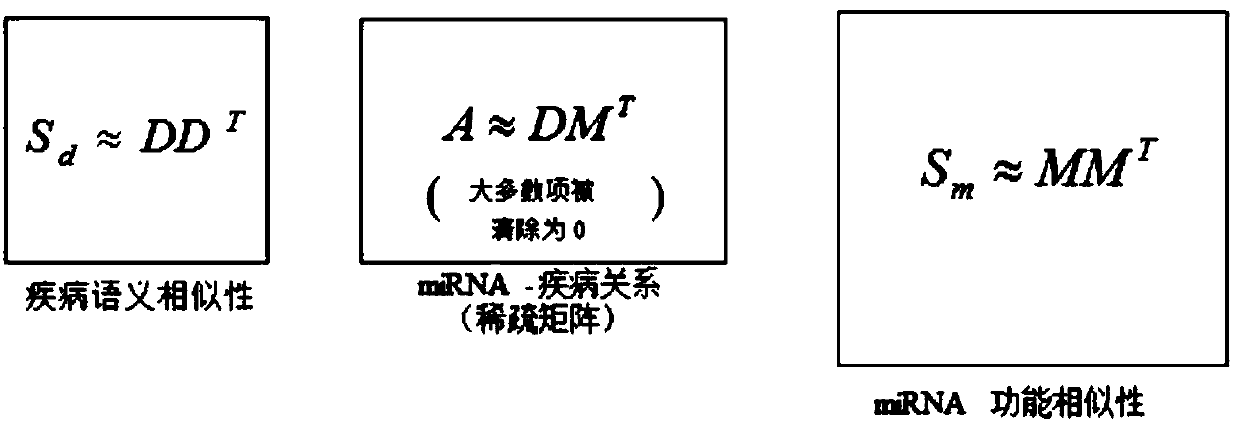
Brand new distributed and privatized miRNA-disease association prediction method
InactiveCN107658029ACooperate wellImprove forecast accuracyMedical data miningSequence analysisData setData mining
The invention discloses a brand new distributed and privatized miRNA-disease association prediction method, which is characterized in that firstly, DPMDA collects, analyzes and estimates matrix factors representing the relationship between miRNAs and diseases, and the prediction accuracy is improved through exchanging information between distributed data sets; secondly, DPFMDA only needs positivesamples, the performance is not easy to be affected by the data sparsity, and the matrix factors from the distributed data set are used for generating a common reference factor; and thirdly, the DPFMDA is a distributed and privatized framework which perfectly realizes and promotes the cooperation between different biomedical databases. The biomedical research will benefit from the prediction results.
Owner:HANGZHOU DIANZI UNIV
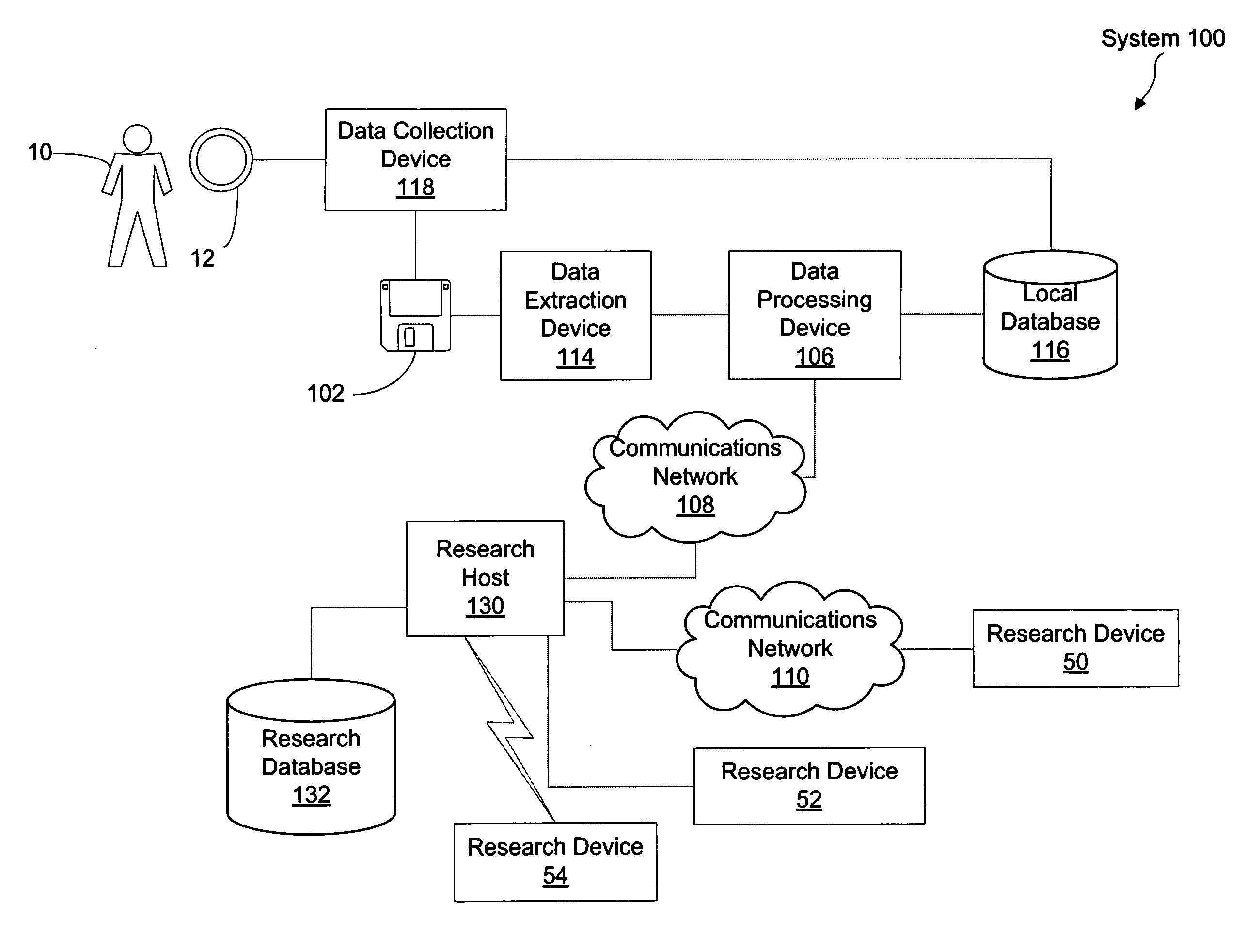
Method and system for archiving biomedical data generated by a data collection device
InactiveUS20100082707A1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsData formatDatabase
A method for archiving biomedical data generated by a data collection device, includes the steps of automatically determining a data format in which the collection device is configured to store the biomedical data onto a computer-readable storage medium, based on the data format, extracting the biomedical data from the storage medium, and transmitting the extracted data to a database in which the extracted data is archived.
Owner:AIR PROD & CHEM INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com