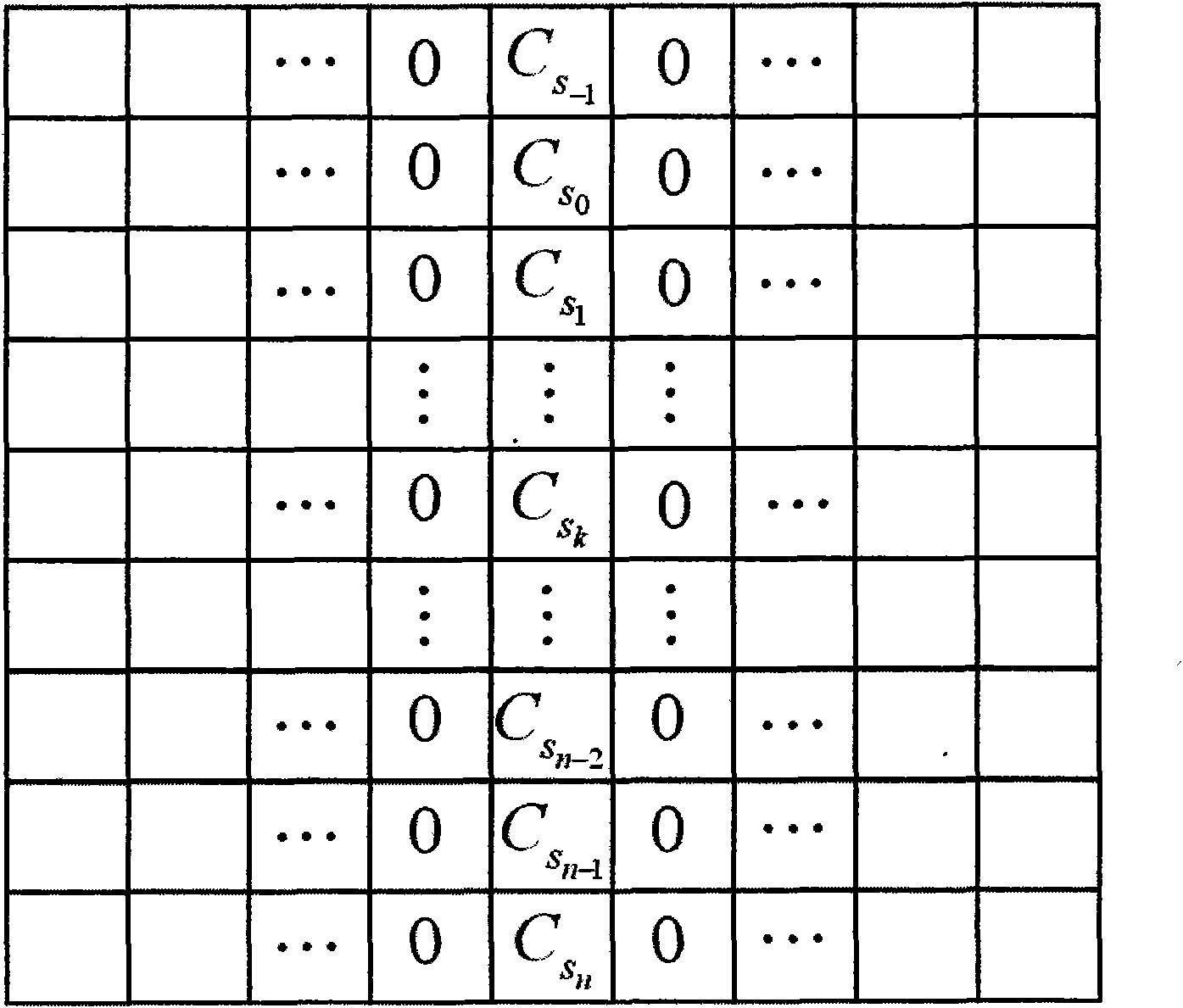
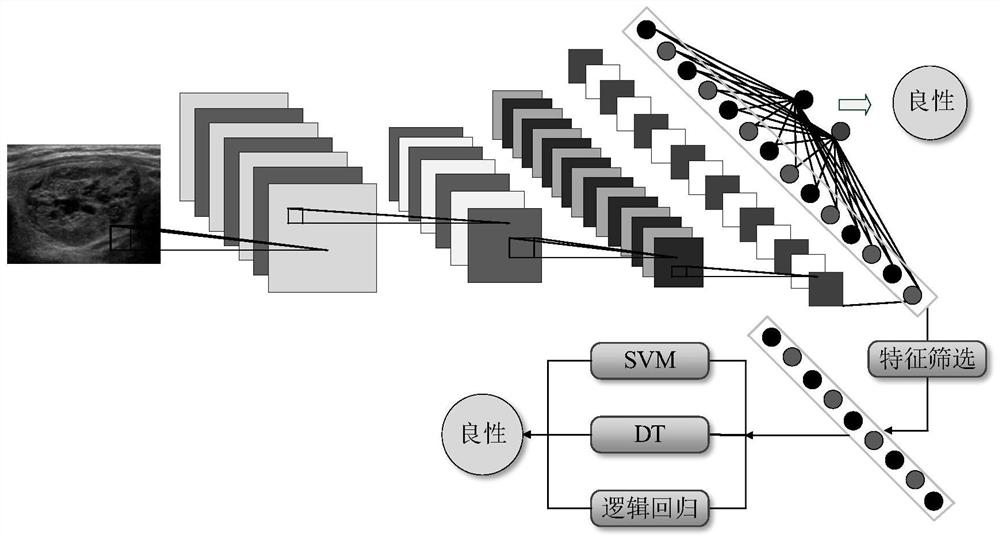
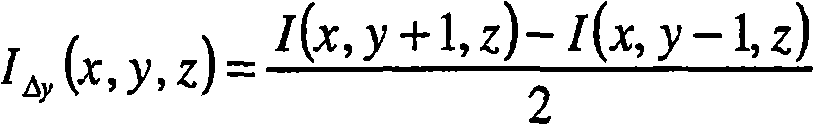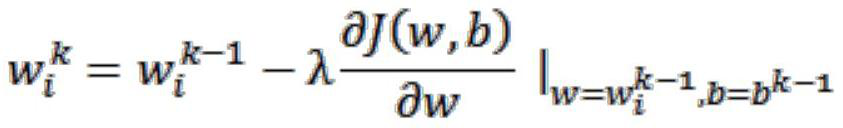Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
92 results about "Biomedical image" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
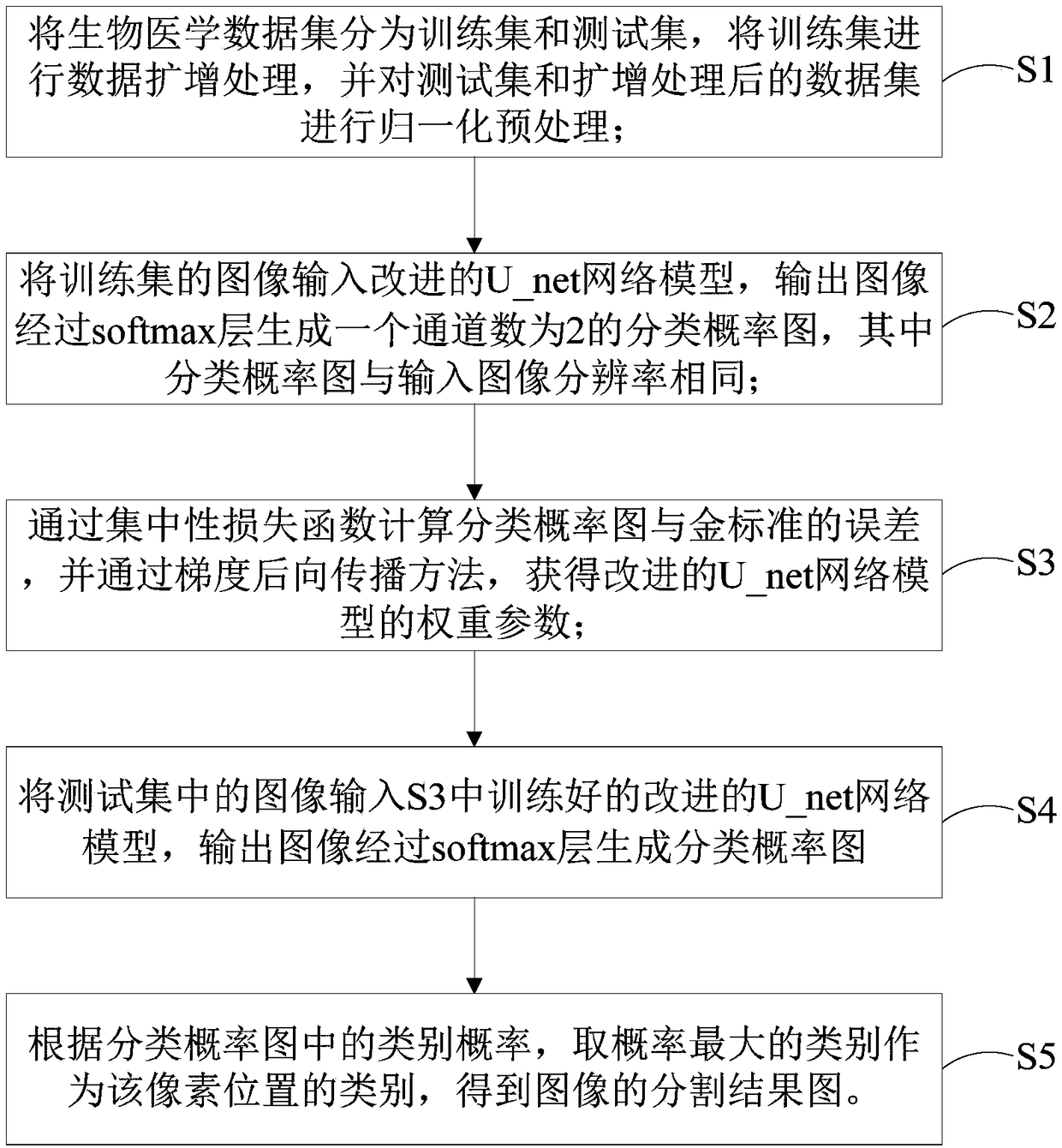
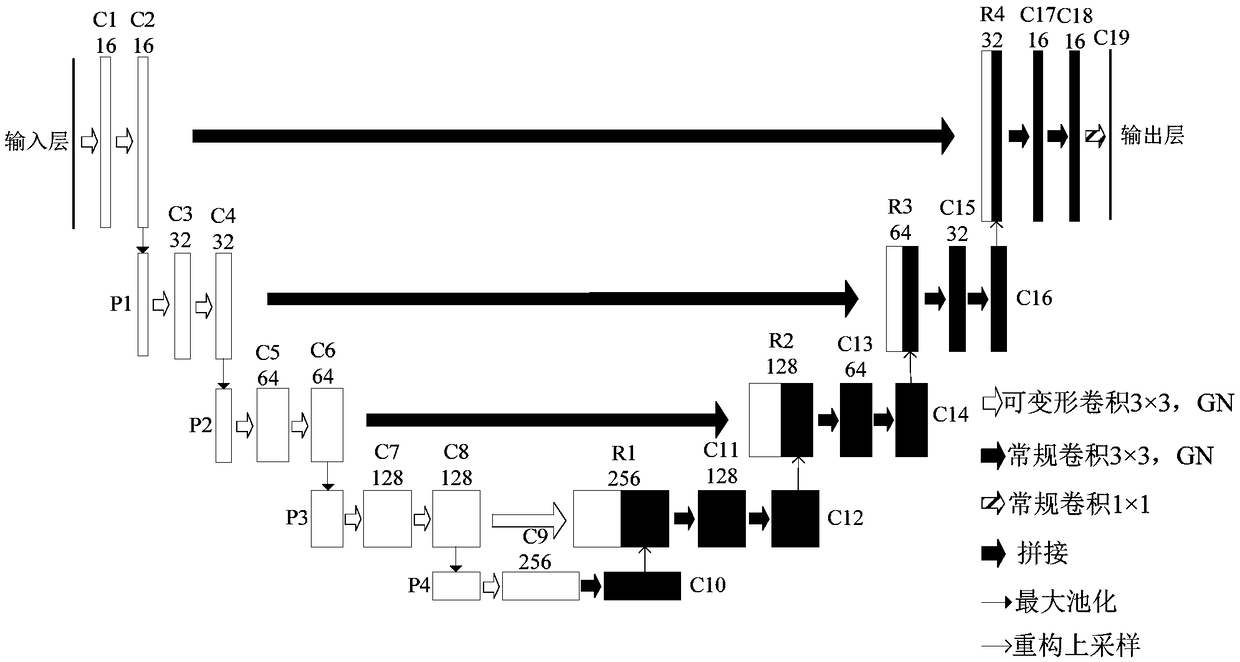
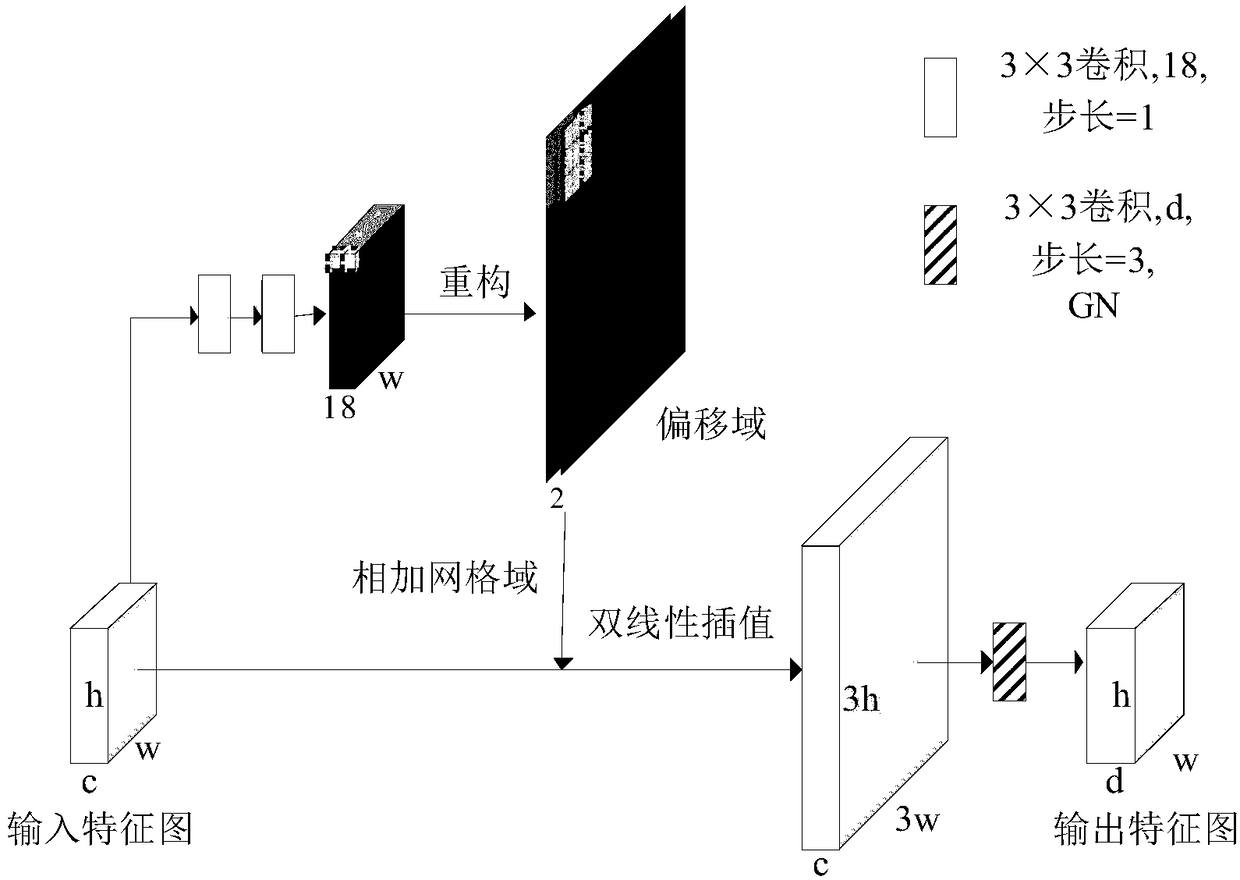
A novel biomedical image automatic segmentation method based on a U-net network structure
ActiveCN109191476AIncrease the number ofImprove segmentationImage enhancementImage analysisData setVisual technology
The invention belongs to the technical field of image processing and computer vision, and relates to a novel biomedical image automatic segmentation method based on a U-net network structure, including dividing a biomedical data set into a training set and a test set, and normalizing the test set and augmented test set; inputting the images of the training set into the improved U-net network model, and generating a classification probability map by output image passing through a softmax layer; calculating the error between classification probability diagram and gold standard by a centralized loss function, and obtaining the weight parameters of network model by a gradient backpropagation method; entering the images in the test set into the improved U-net network model, and outputting the image to generate a classification probability map through the softmax layer; according to the class probability in the classification probability graph, obtaining the segmentation result graph of theimage. The invention solves the problems that simple samples in the image segmentation process contribute too much to the loss function to learn difficult samples well.
Owner:CHONGQING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
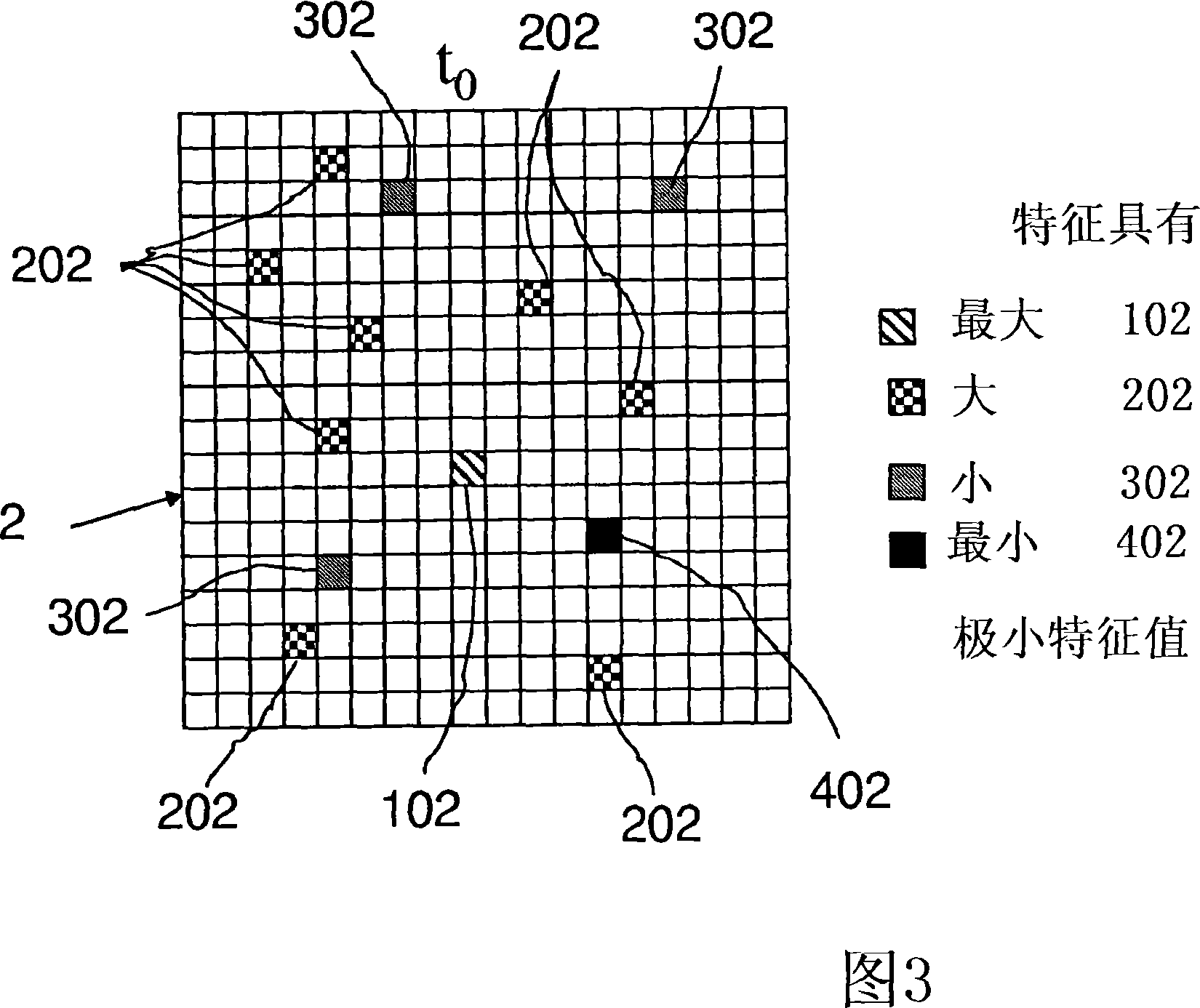
Method of registering images, algorithm for carrying out the method of registering images, a program for registering images using the said algorithm and a method of treating biomedical images to reduc
In a method for registering biomedical images such as at least a first and a second digital or digitalized image or set of cross-sectional images of the same object, within the first image or set of images a certain number of landmarks, so called features are individuated by selecting a certain number of pixels or voxels. The position of each pixel or voxel selected as a feature is tracked from the first to the second image or set of images by determining the optical flow vector from the first to the second image or set of images for each pixel or voxel selected as a feature. Registration of the first and second images or set of images is carried out by applying the inverse optical flow to the pixels or voxels of the second image or set of images. The invention provides for an automatic trackable landmark selection step consisting in defining a pixel or voxel neighbourhood around each pixel or voxel of the first image or first set of cross-sectional images; for each target pixel or voxel determining one or more characteristic parameters which are calculated as a function of the parameters describing the appearance of the said target pixel or voxel and of each or a part of the pixels or voxels of the window and as a function of one or more characteristic parameters of either the numerical matrix or of a transformation of the said numerical matrix representing the pixels or voxels of the said window. The pixels or voxels coinciding with validly trackable landmarks are determined as a function of the said characteristic parameters of the target pixels or voxels.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
PET-CT lung tumor segmentation method combining three dimensional graph cut algorithm with random walk algorithm
ActiveCN105701832AThe segmentation result is accurateImage enhancementImage analysisPET-CTGraph cut algorithm
The invention belongs to the field of biomedical image processing and specifically relates to a PET-CT lung tumor segmentation method combining a three dimensional graph cut algorithm with a random walk algorithm. The method comprises the following steps of: performing linear up-sampling on an original PET image and performing affine registration on PET and CT images; calibrating tumor seed points and non-tumor seed point; performing random walk algorithm segmentation on the PET image in combination with the tumor seed points; acquiring a foreground target area Ro completely including a target lung tumor area, using the areas, except the Ro, as a background area Rb of a non-lung tumor area; establishing gauss mixture models for the foreground area Ro and the background area Rb separately; computing energy items according to the gauss mixture models of the foreground area Ro and the background area Rb and obtaining a final segmentation result by using an graph cut algorithm. The method fully utilizes the function information and the PET image and the structure information of the CT image, enables complements between the random walk algorithm and the graph cut algorithm, and achieves an accurate lung tumor segmentation result.
Owner:SUZHOU BIGVISION MEDICAL TECH CO LTD
Method and computer program product for registering biomedical images with reduced imaging arefacts caused by object movement
A method of registering biomedical images to reduce imaging artefacts caused by object movement is disclosed, wherein a certain number of features or landmarks is automatically defined and tracked in a first and second image to be registered to determine the optical flow vector between the first and second image. Registration then takes place by applying the inverse optical flow to the second image. The automatic feature selection step is carried out by determining the mean signal intensity in a defined neighborhood for every pixel, which mean signal intensity is then compared to a predetermined threshold. If the mean signal intensity value of said neighborhood is higher than the predetermined threshold the pixel is defined as a feature and is added to a list of features to be tracked.
Owner:BRACCO IMAGINIG SPA
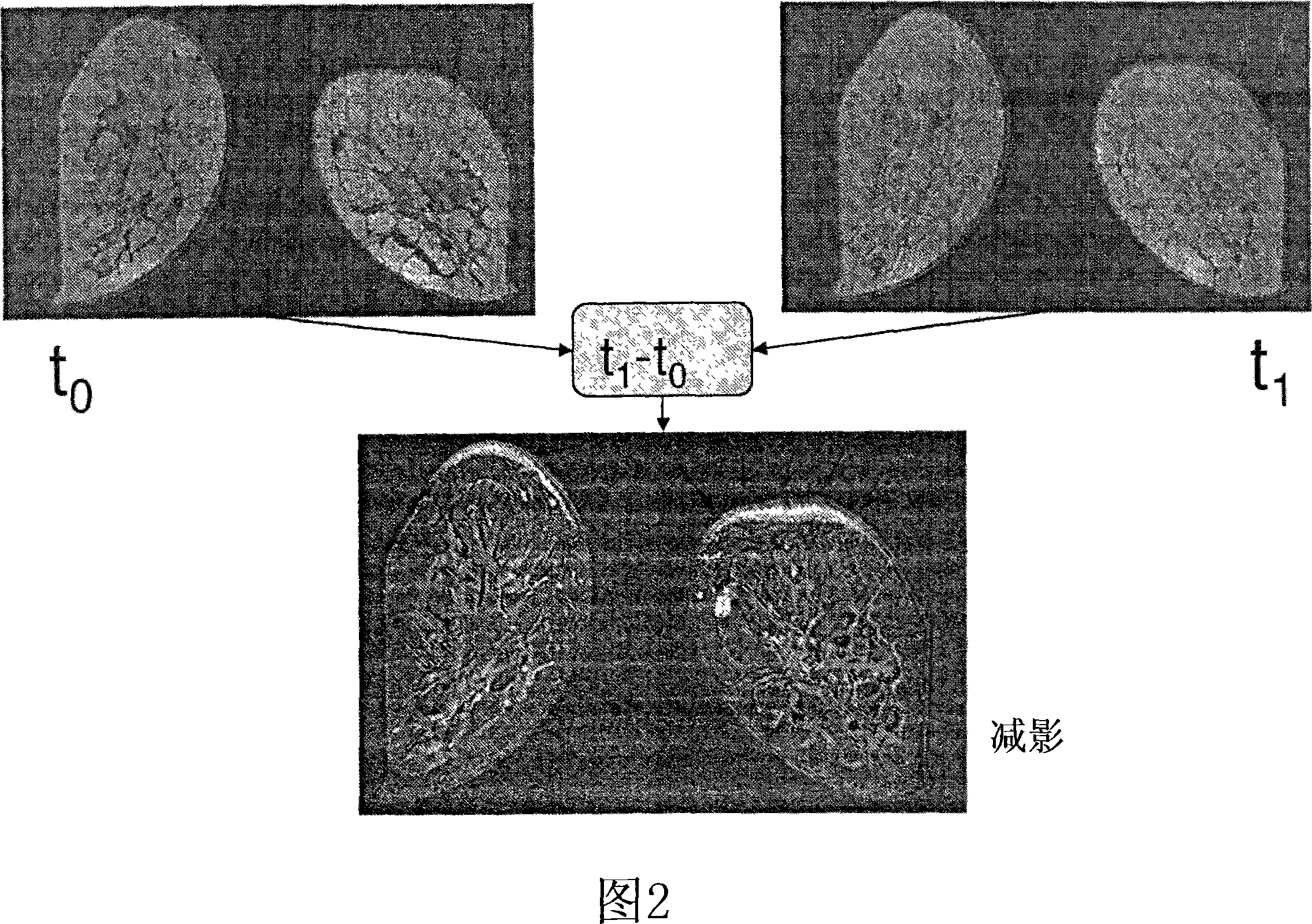
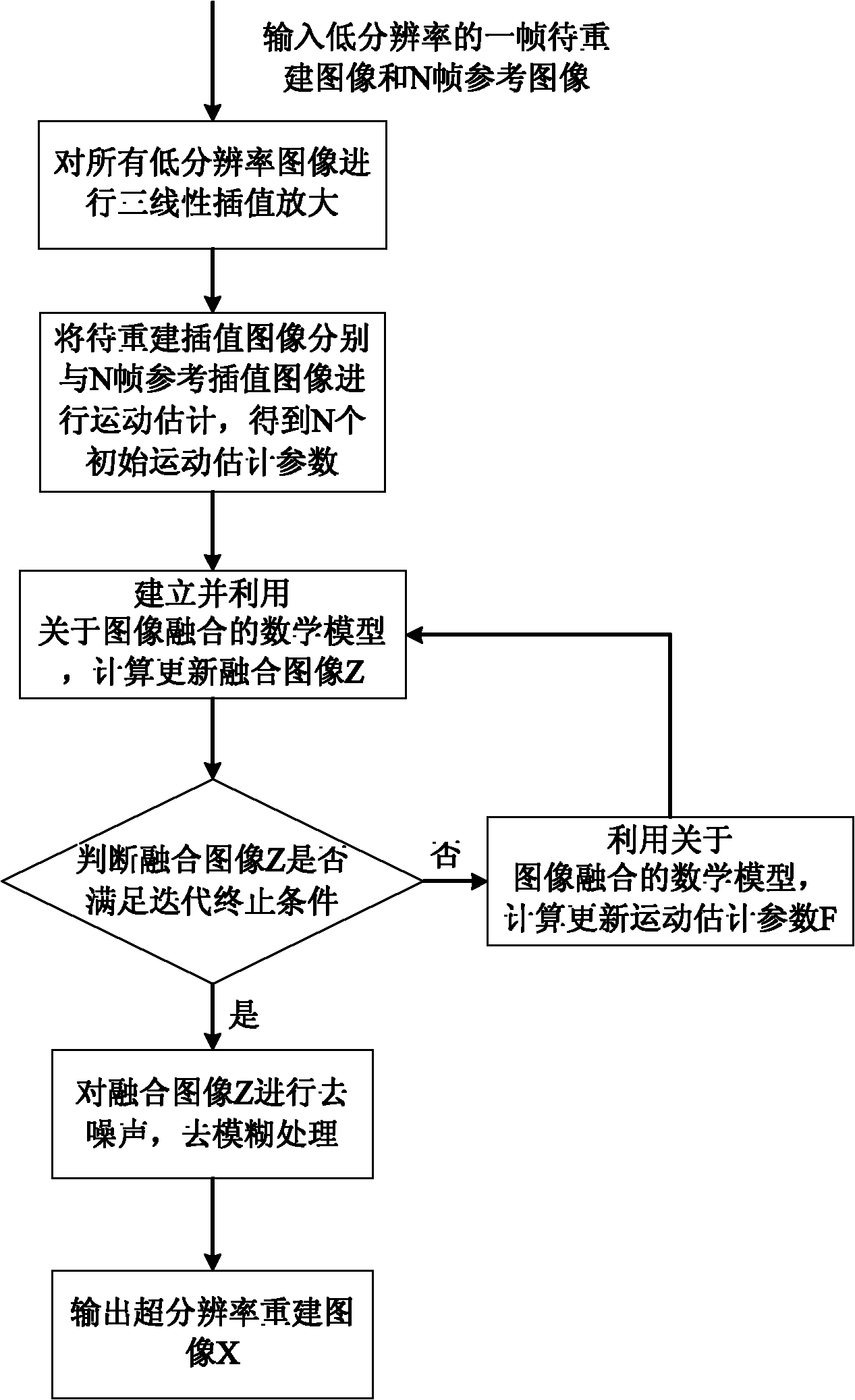
Image reconstruction method based on combination of motion estimation and super-resolution reconstruction
InactiveCN102194222AImprove reconstruction effectHigh precisionImage enhancementImage resolutionReconstruction method
The invention discloses an image reconstruction method based on combination of motion estimation and super-resolution reconstruction, and the method comprises the following steps: (1) performing interpolation amplification on all low-resolution images; (2) performing motion estimation on the image to be reconstructed and the reference images respectively; (3) fusing the images, thus getting a fused image; and (4) performing denoising treatment on the fused image, thus getting the super-resolution reconstructed image. The motion estimation process and the super-resolution reconstruction process are combined together, and the relation between a plurality of the reference images with different low resolutions and a motion estimation parameter of the image to be reconstructed is utilized, so that the precision of the motion estimation parameter is simultaneously optimized during the super-resolution reconstruction process, and the super-resolution reconstruction effect is effectively enhanced. Therefore, the method can be widely applied in the field of satellite remote sensing of biomedical images, image repairing and the like.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
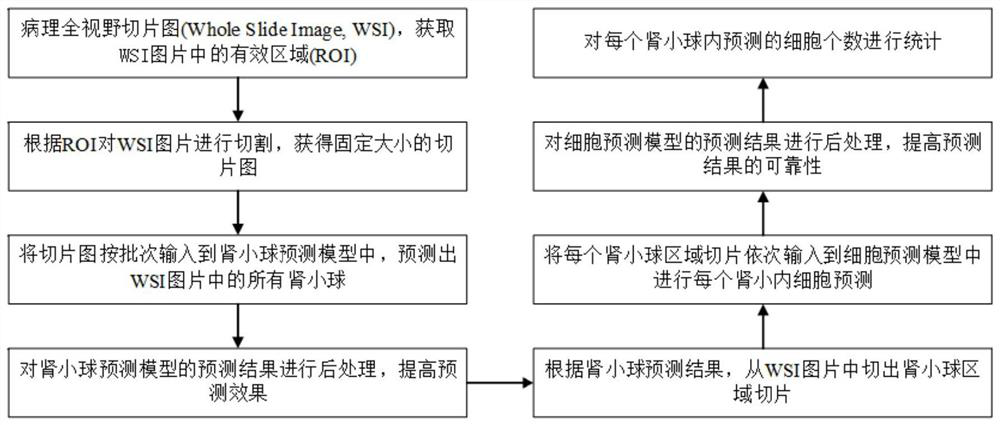
Glomerular cell image recognition method based on deep neural network
ActiveCN111951221AAccurate segmentationGood effectImage enhancementImage analysisImage manipulationRadiology
The invention discloses a glomerular cell image recognition method based on a deep neural network, and the method comprises the steps: obtaining a to-be-detected pathological image based on an artificial intelligence and deep learning technology; preprocessing the pathological image to obtain a plurality of slice images; inputting each slice image into a preset neural network model for identification and segmentation to obtain a glomerular region map; carrying out cell counting on the glomerular region map; Sub-images of the glomerulus in the kidney in the pathological image can be quickly andaccurately segmented, and cells in the glomerulus are counted by using a traditional method and a deep learning fusion model, so that the problems of large workload, low efficiency and high misdiagnosis rate of artificial identification of the glomerulus in the pathological image are solved; the invention optimizes the algorithm of glomerular sub-image segmentation and glomerular cell counting inpathological images, uses more data training algorithms, improves the accuracy of segmentation and counting, and relates to the field of biomedical image processing.
Owner:清影医疗科技(深圳)有限公司 +1
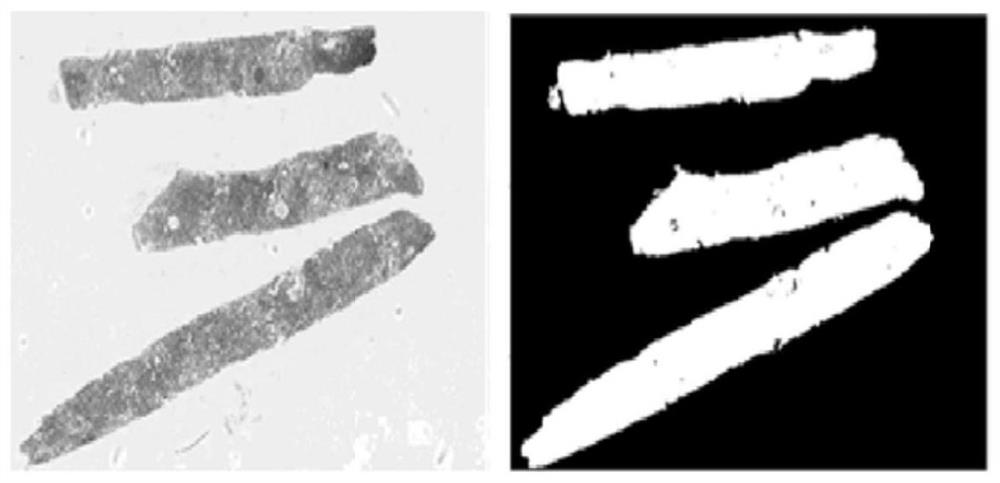
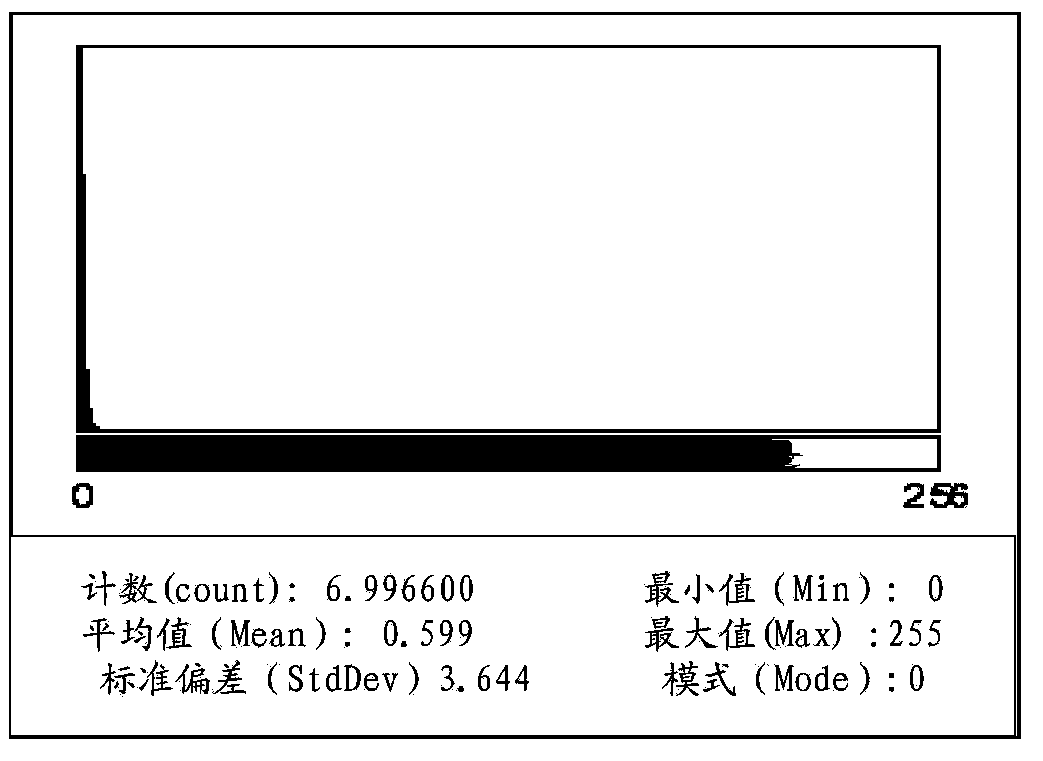
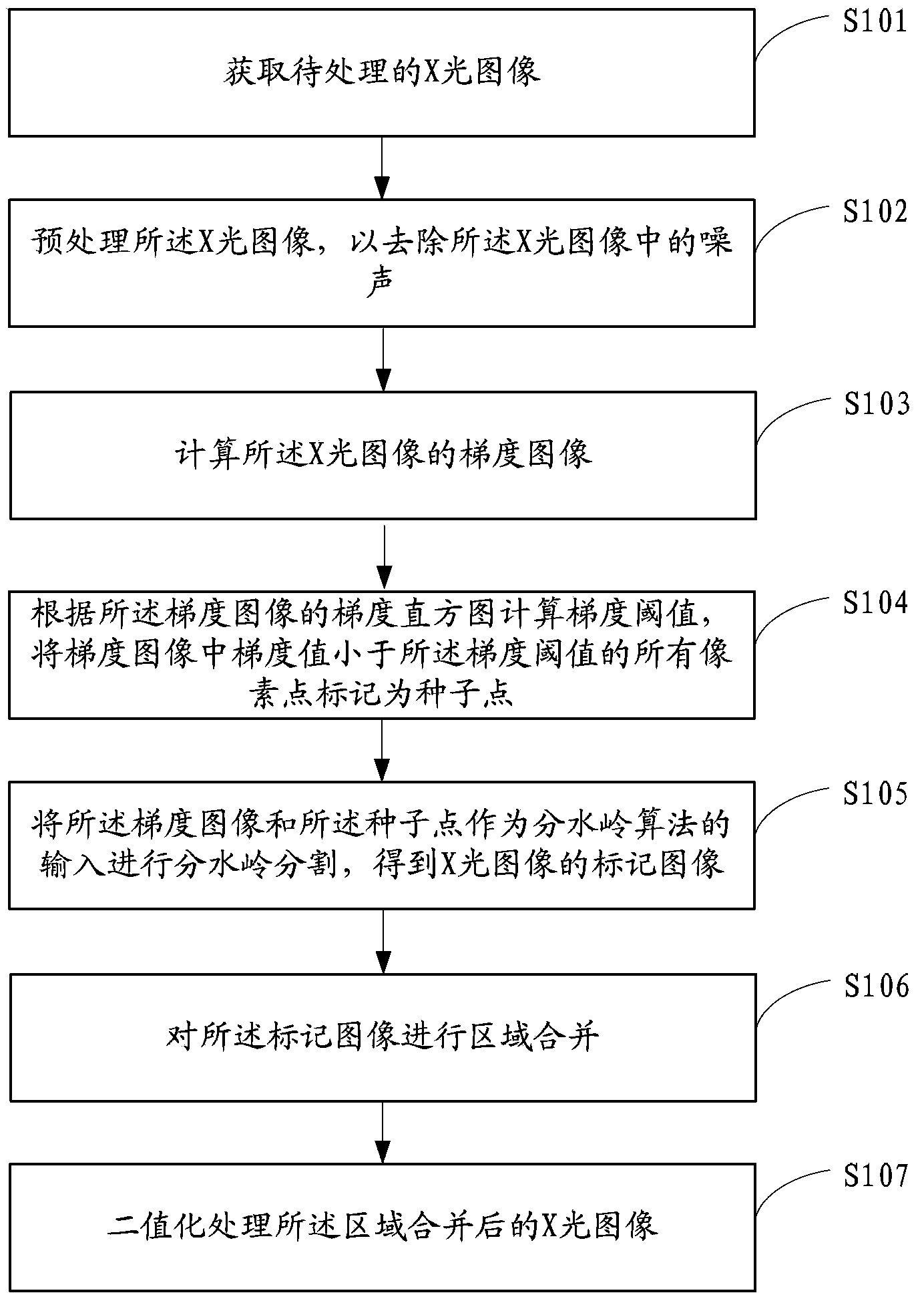
X-ray image processing method and system and X-ray image processing equipment
ActiveCN103903254ASmall amount of calculationImprove robustnessImage enhancementImage analysisX-rayX ray image
The invention is suitable for the technical field of biomedical image processing, and provides an X-ray image processing method and system and X-ray image processing equipment. The method includes the steps that an X-ray image to be processed is obtained; the X-ray image is preprocessed so as to remove noise in the X-ray image; the gradient image of the X-ray image is calculated; a gradient threshold is calculated according to the gradient histogram of the gradient image; all pixels with gradient values being less than the gradient threshold in the gradient image are marked as seed points; watershed segmentation is conducted on the gradient image and the seed points for serving as input so as to obtain a marked image of the X-ray image; region merging is conducted on the marked image, and binarization processing is conducted on the X-ray image undergoing region merging. The calculated amount in the X-ray processing process is greatly reduced, the processing time is short, the accuracy is high, the roughness is enhanced, and the capacity for processing X-ray images with complicated backgrounds is improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Feature selection method for FMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) data
InactiveCN104504373AFully reflect the structuralStable Feature Importance MeasureCharacter and pattern recognitionFault toleranceResonance
The invention discloses a feature selection method for FMRI (Functional Magnetic Resonance Imaging) data, belongs to the technical field of biomedical image mode identification, and particularly relates to the feature selection method of a functional magnetic resonance image. The method comprises the following steps of randomly selecting a submatrix of data, calculating the weight vectors of selected features by using an elastic net method, and converting the obtained weight vectors into stable score vectors; repeating the process p (p is greater than 1,000) times to obtain the selected time vector of each feature, acquiring feature importance metrics according to the calculated accumulated stable score vectors and time vectors, and performing feature sequencing and selection. The method disclosed by the invention has the characteristics of high fault tolerance, high stability and the like. A novel effective technology is provided for feature selection and sequencing in the fields of magnetic resonance data mode identification and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
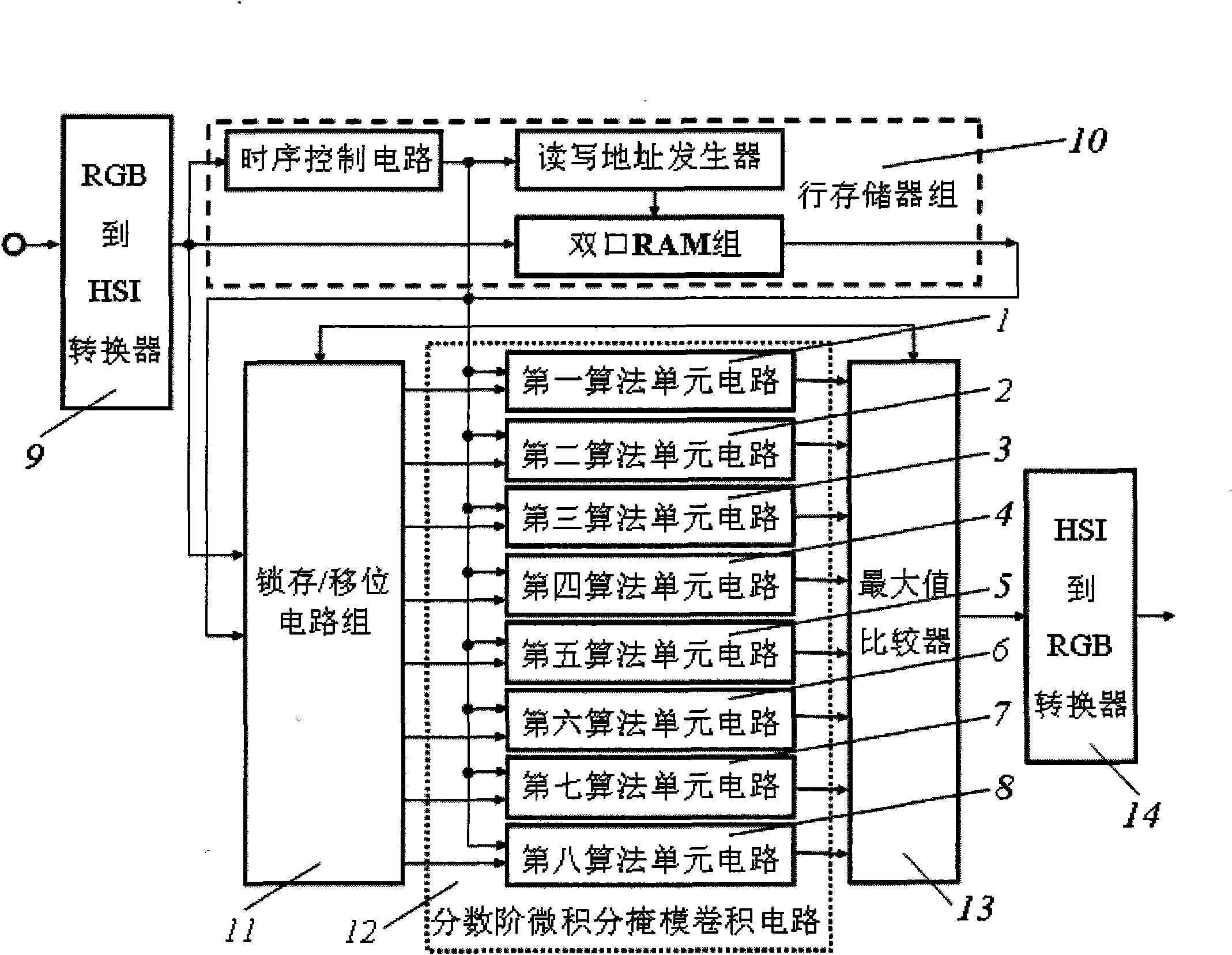
Fractional calculus filter of digital images of high-precision computation
InactiveCN101848319ATelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsDigital imageComputer science
The invention provides a fractional calculus filter of digital images of high-precision computation, which is a circuit device for fractionally enhancing or smoothing complex texture detail characteristics of digital images at high precision. The filter is formed by connecting a RGB-to-HSI converter, a line memory group, a phase locking / shift circuit group, a fractional calculus mask convolution circuit, a maximum comparator and an HSI-to-RGB converter in cascade. Special fractional calculus mask convolution algorithms are used by a first algorithm unit circuit to an eighth algorithm unit circuit in the fractional calculus mask convolution circuit to realize high-precision computation of fractional calculus. The fractional calculus filter of digital images of high-precision computation, which is provided by the invention, is especially suitable for application occasions for fractionally enhancing or smoothing complex texture detail characteristics of high-definition digital televisions, biomedical images, bank bills, satellite remote sensing images, biological characteristic patterns and the like at high precision.
Owner:深圳璞芯智能科技有限公司
Method for processing biomedical images
InactiveUS20090274349A1Reduce specific mortalityReduce mortalityImage enhancementImage analysisBiomedical imageComputer science
The present invention relates to a method for highlight and to diagnose regions of interest in biomedical radiographic images, useful in the context of a CAD tool processing operating as second reader during the normal clinical and screening routine, so reducing the costs of management of the “double reading” procedure.
Owner:MEDICAD
Deep learning classification method based on feature screening
PendingCN112434732AHigh precisionAvoid the influence of irrelevant featuresCharacter and pattern recognitionMachine learningData setDimensionality reduction
The invention discloses a deep learning classification method based on feature screening. An accurate image classification model can be obtained by training and testing a data set by using the deep learning classification method based on feature screening provided by the invention. According to the method, accurate classification of the images can be efficiently completed, the number (dimensionality reduction) of the features can be reduced through a feature screening method under the conditions that serious over-fitting, redundancy, much noise and the like exist between the features and the target, and therefore the generalization ability of the model is improved to obtain higher classification accuracy. In an image classification task, data and features determine the upper limit of machine learning, and a model and an algorithm only approach the upper limit. Therefore, the feature engineering plays a very important role in machine learning. The classification of the input data can bepredicted, so that the method is widely applied to the fields of traffic scene object recognition, vehicle counting, license plate recognition and internet and biomedical image analysis in the security field and the traffic field.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
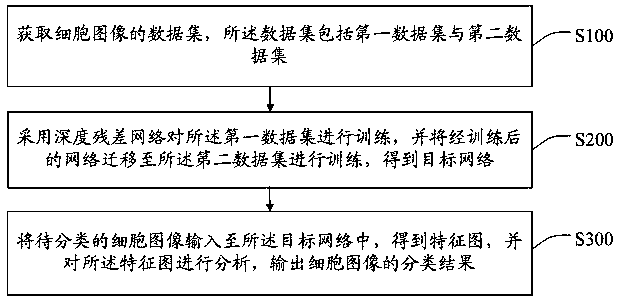
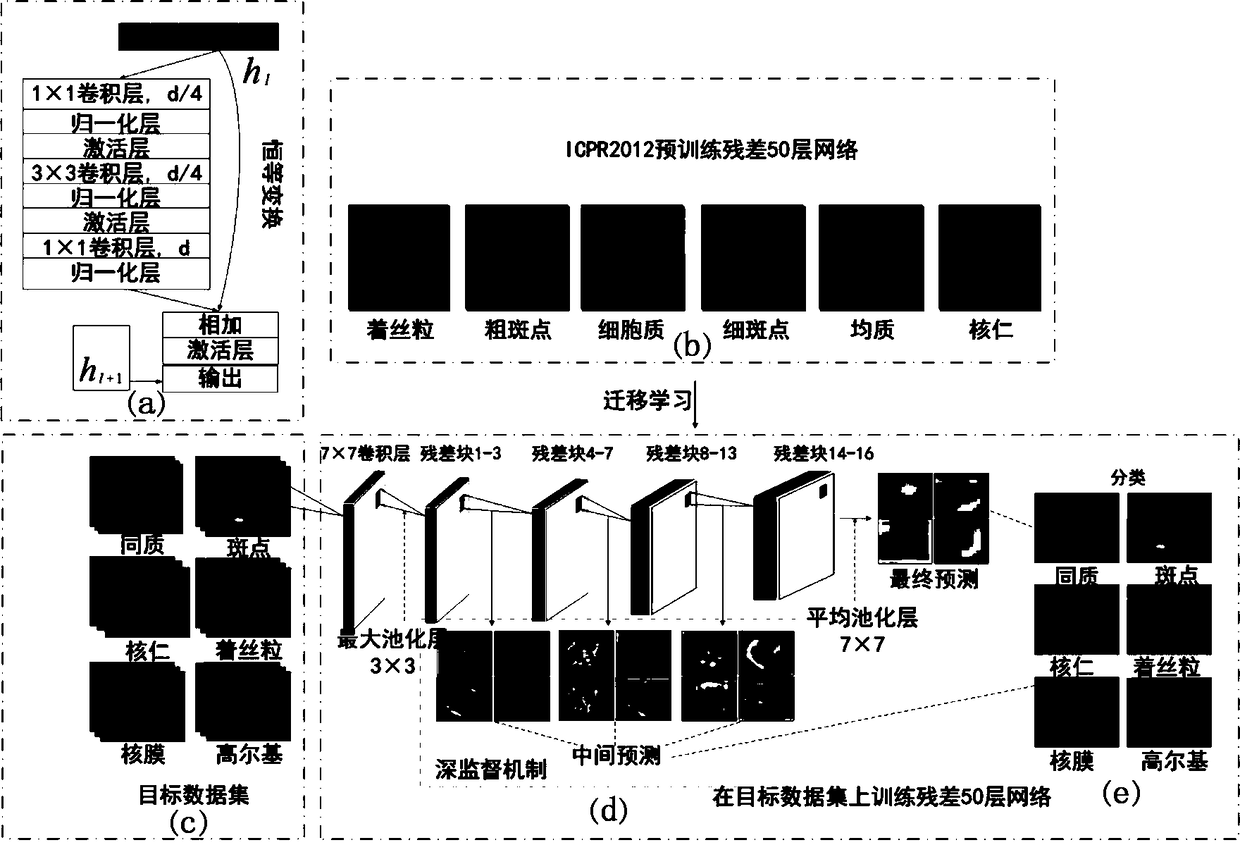
Cell classification method and system based on deep residual network
ActiveCN108510004AFix small problemsImprove accuracyCharacter and pattern recognitionData setNetwork structure
The invention discloses a cell classification method and system based on a deep residual network. The method includes: acquiring a data set of cell images, wherein the data set includes a first data set and a second data set; using the deep residual network for training on the first data set, and transferring the trained network to the second data set to carry out training to obtain a target network; and inputting a to-be-classified cell image into the target network to obtain a feature map, analyzing the feature map, and outputting a classification result of the cell image. According to the method, the residual network is utilized for training on the data set, a method of transfer learning is combined, a network structure which can carry out automatic classification is created, the problem that biomedical image data sets are smaller is effectively solved, occurrence of over-fitting cases is avoided, workloads are reduced, work efficiency is improved, and a correctness rate of automatic cell classification is also effectively improved.
Owner:SHENZHEN UNIV
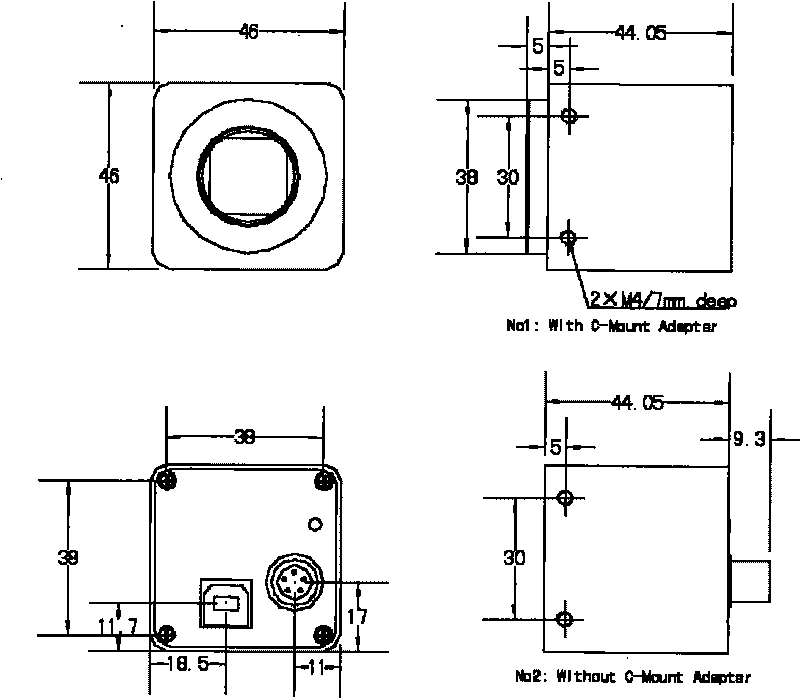
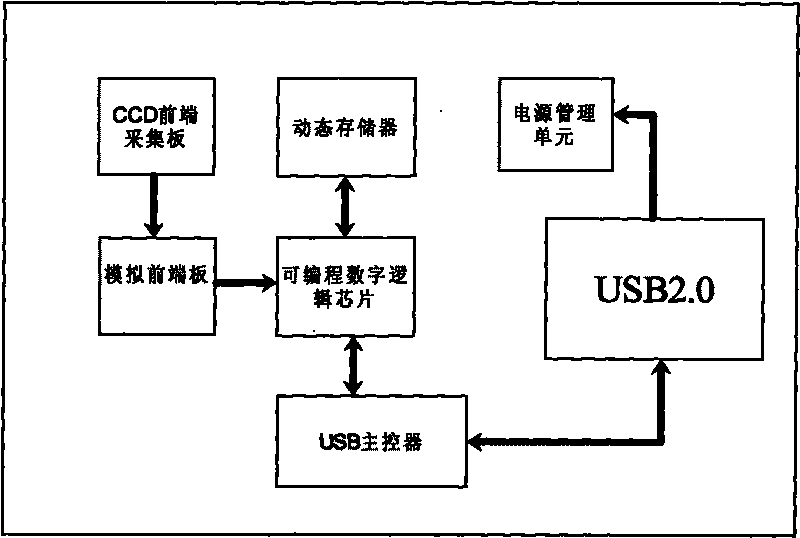
USB digital industrial camera
ActiveCN101738827AGood value for moneyTelevision system detailsColor television detailsMode controlBus interface
The invention relates to a USB digital industrial camera which comprises a camera device and a set of presentation software, wherein the camera device comprises a USB master controller, a programmable digital logic chip, a dynamic memory, an analog front-end plate, a CCD front-end collection plate, a USB 2.0 universal bus interface and a power management unit and has the advantages of fast collection speed, high resolution ratio, simple and intuitive use, and the like; and the presentation software of the camera is operated on a PC and comprises a camera base attribute control module, a camera working mode control module, a camera image processing module and a camera image automatic regulating function control module. The presentation software realizes the high-speed communication with the camera device by utilizing a USB digital interface, thereby controlling the working of the camera device. The invention has small and exquisite appearance, compact structure, functional integration, convenient installation and use and simple software setting, is widely applied in the fields of the detection of semiconductors and parts as well as defects of printed circuit boards, traffic monitoring, biomedical image acquisition, the manufacturing of certificates and cards, the detection of various industrial flaws, the identification of optical characters and bar codes, and the like, and provides solutions with high cost performance for users.
Owner:苏州优纳科技有限公司
Fluorescent-CT bimodal imaging probe and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN104721841AReduce the risk of adverse reactionsLow equipment requirementsX-ray constrast preparationsFreeze-dryingIodixanol
The invention relates to a fluorescent-CT bimodal imaging probe and a preparation method thereof, specifically relates to a fluorescent-CT bimodal iodine doped carbon quantum dot prepared by a one-step hydrothermal carbonization method and application of the fluorescent-CT bimodal iodine doped carbon quantum dot in biomedical images, and belongs to the field of biomedical materials. The specific scheme is as follows: dissolving iodixanol and glycine in an aqueous solution according to a certain mass ratio to serve as precursors, putting the solution in a hydrothermal reaction kettle with polytetrafluoroethylene lining, heating up to 120-200 DEG C to react for 4 hours, dialyzing and freeze drying nigger-brown reaction liquid to remove residues and water to obtain black powdery nanoparticles, namely iodine doped carbon quantum dots. The iodine doped carbon quantum dot prepared by the method has such excellent properties as stable fluorescence, efficient X-ray attenuation capacity and good biocompatibility, and is successfully applied to live cell fluorescent imaging in vitro and CT imaging in vivo. The method has the advantages of simple operation, environmental protection and easy mass production.
Owner:JIANGSU UNIV
Data method for detecting dynamic brain spontaneous activity based on fMRI
InactiveCN106037741AImprove robustnessImprove stabilityDiagnostic signal processingSensorsResonanceSlide window
The invention discloses a data method for detecting the dynamic brain spontaneous activity based on fMRI, belongs to the technical field of biomedical image pattern recognition, and particularly relates to a method for detecting the dynamic brain spontaneous activity based on a functional magnetic resonance imaging time series. According to the invention, according to the dynamic change characteristics of the brain spontaneous activity, and by utilizing the attribute that brain signals are stable (pseudo stable) within the short time interval, a method combining a sliding-window and signal amplitude (ALFF) is provided, and by combining with a variance value, a quantitative computing method for the dynamic brain spontaneous activity is provided. The method provided by the invention has the characteristics of high robustness, strong stability and the like, and a novel effective technology is provided for the dynamic detection on the brain spontaneous activity in the fields of magnetic resonance data pattern recognition and the like.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
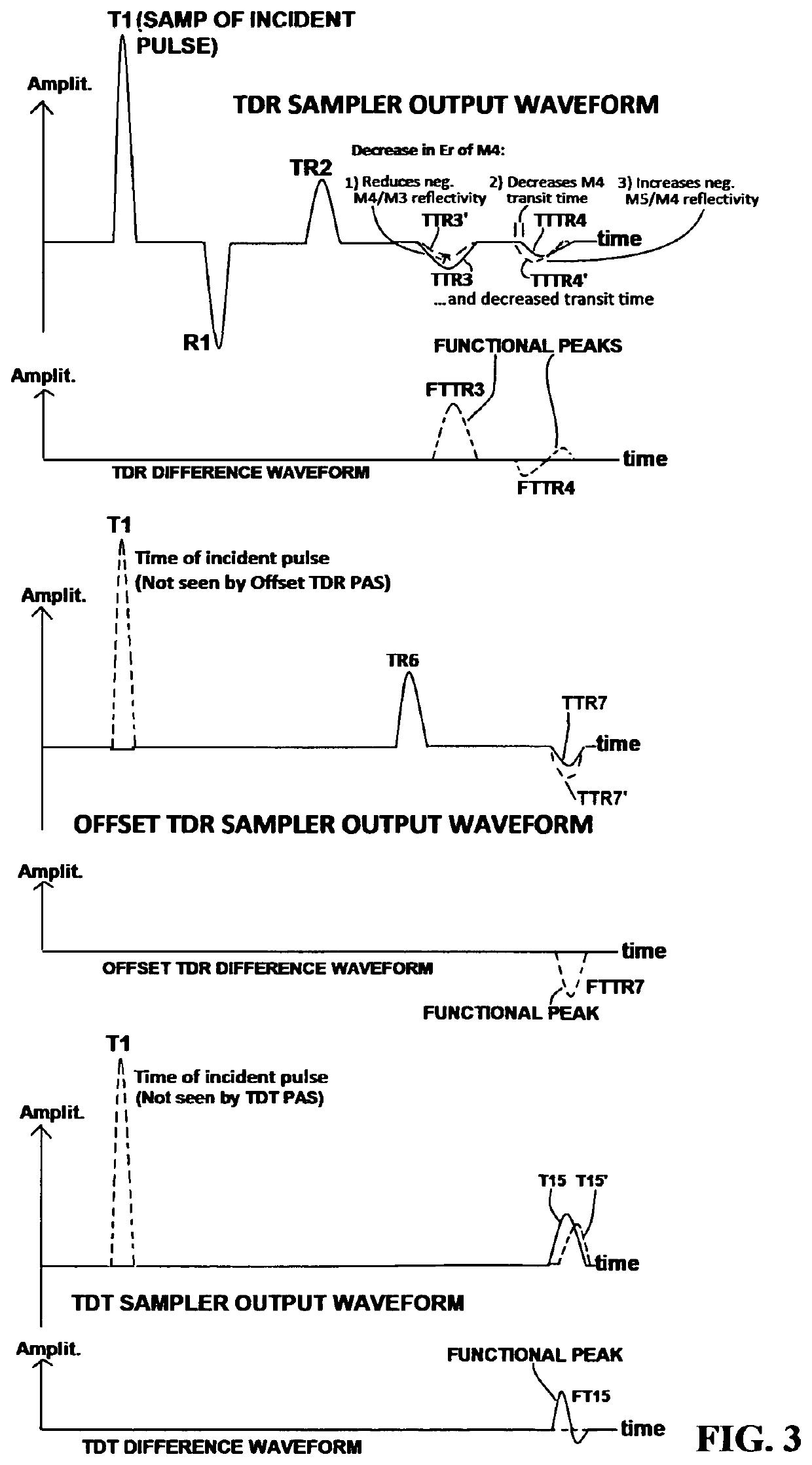
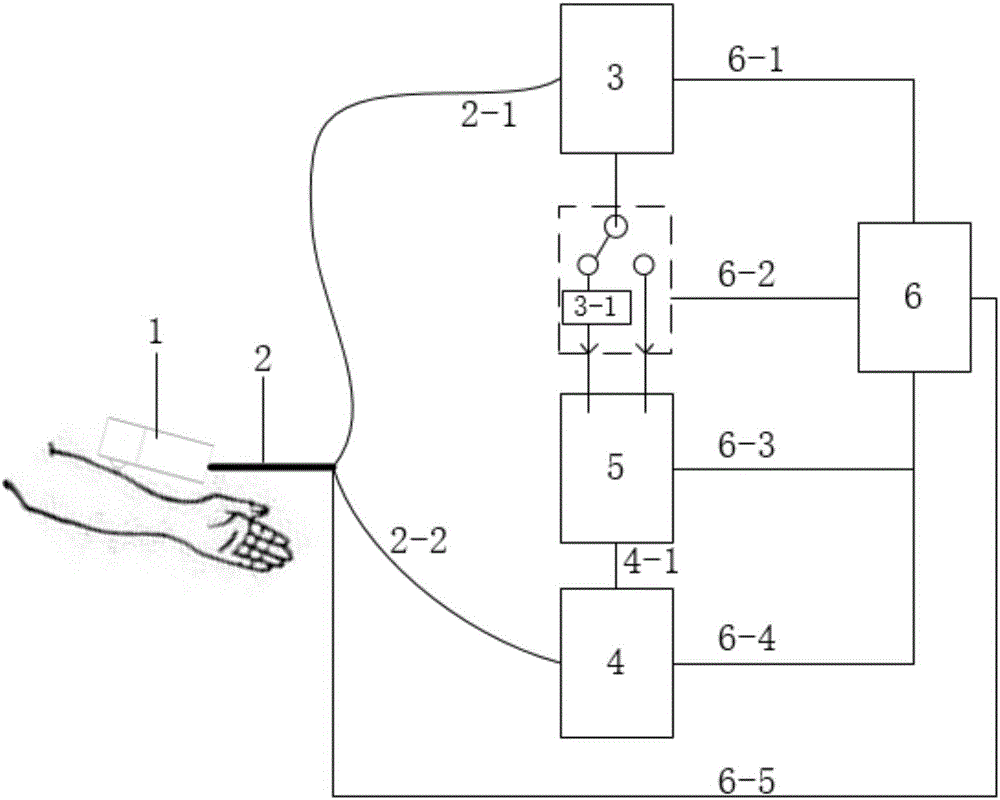
Method and apparatus for non-invasive real-time biomedical imaging of neural and vascular activity
ActiveUS10660531B1Non invasiveQuick changeElectroencephalographyMedical imagingUltra-widebandHuman body
Biomedical images of both anatomical structure and real-time changes in neuronal, metabolic, positional, and vascular function in humans and animals is described. Ultra-wideband (UWB) pulse or square wave generators and electrical samplers, implemented using integrated circuits are used to make arrays of miniaturized microwave modules that are placed around the portion of interest in the body or head, allowing images to be made through either time-domain transmission of these pulsed waves through the body, or time domain reflectivity of the waves from internal structures, or their combination. Signal processing separate and extract the time-varying functional information from the static structural image data. The time-varying functional information from certain brain regions can be interpreted in order to control prosthetics, Brain-Machine-Interfaces and the like.
Owner:FURAXA
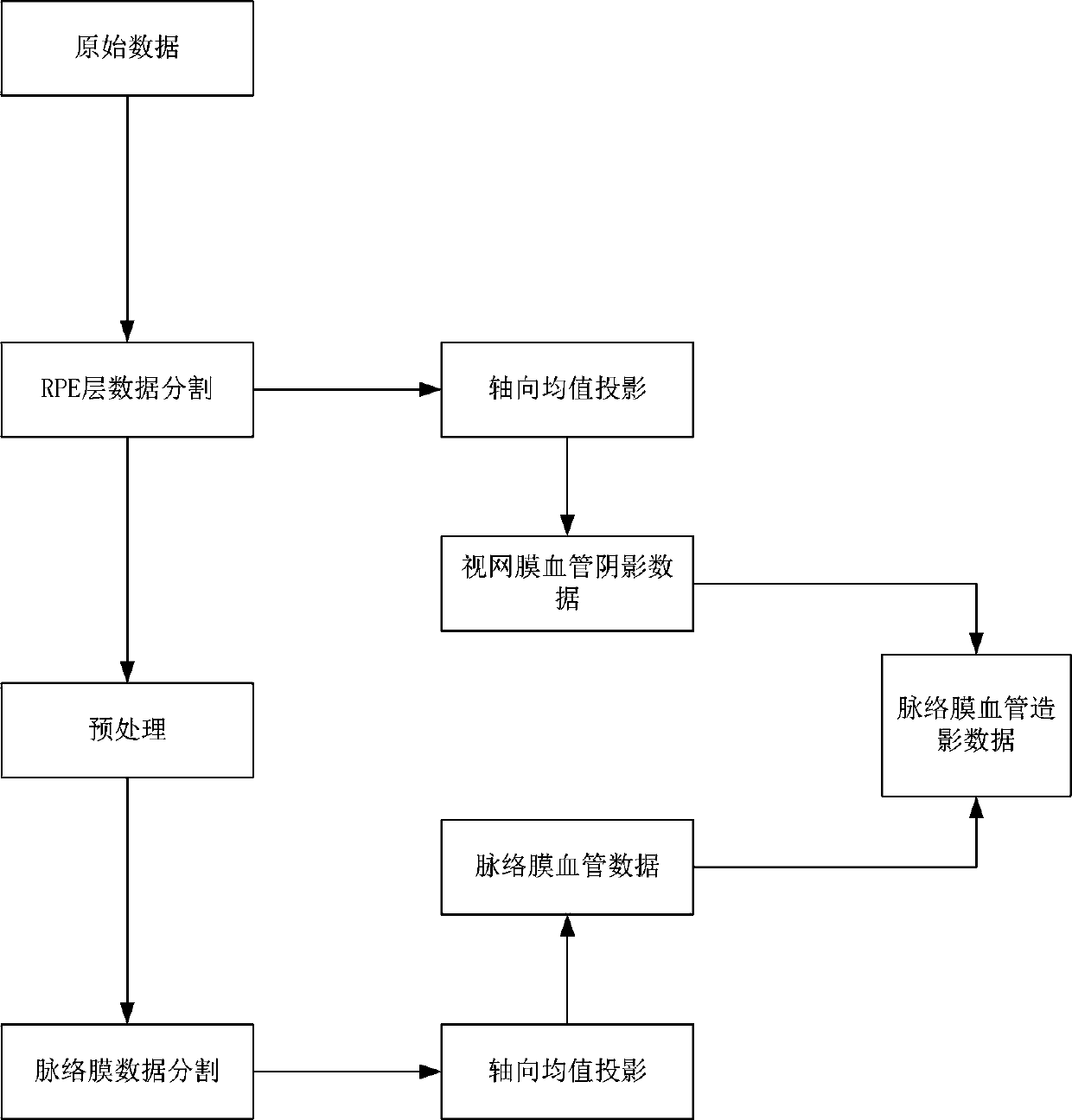
Choroidal angiography method and device based on optical coherence tomography imaging body scanning
InactiveCN109730633ARemove shadowsEasy extractionDiagnostic recording/measuringSensorsOriginal dataProjection image
The invention relates to the field of biomedical image processing, in particular to a choroidal angiography method based on optical coherence tomography imaging body scanning. The method can be widelyused for screening and diagnosis of medical ophthalmic diseases. The method includes the steps of S1, acquiring original data of OCT body scanning fundus; S2, extracting retinal blood vessel shadow data and choroidal blood vessel data from the original data; S3, using the retinal blood vessel shadow data for masking the choroidal blood vessel data to obtain choroidal angiography data. According to the technical scheme above, by extracting the retinal blood vessel shadow data to mask the choroidal blood vessel data, retinal blood vessel shadows in the choroidal blood vessel data are removed, so that the influence of the retinal blood vessel shadows on the contrast and continuity of choroidal blood vessel projection images is reduced, and choroidal vessels can be completely and clearly displayed.
Owner:CIXI INST OF BIOMEDICAL ENG NINGBO INST OF MATERIALS TECH & ENG CHINESE ACAD OF SCI +1
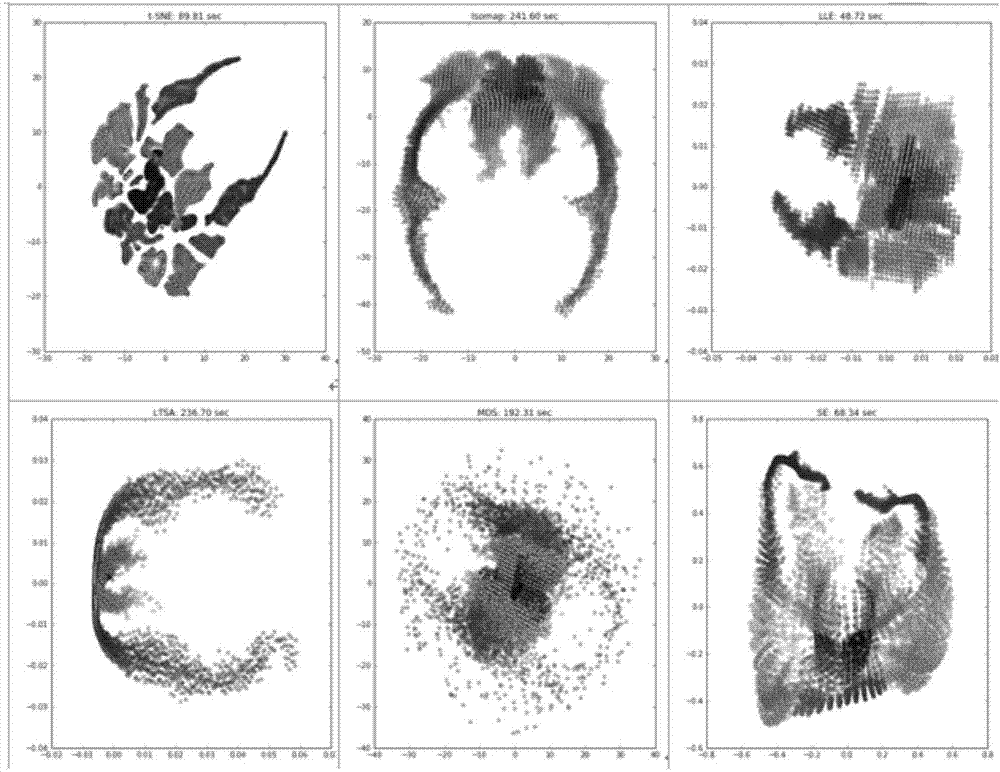
Two dimensional visualization method of fMRI data based on popular learning algorithm
ActiveCN107330948ARealize 2D visualizationEfficiencyImage enhancementReconstruction from projectionNonlinear dimensionality reductionVoxel
The invention discloses a two-dimensional visualization method of fMRI data based on a popular learning algorithm, the method belonging to the technical field of biomedical image pattern recognition, and in particular relates to a dimensionality reduction visualization method of functional magnetic resonance image data. According to the invention, by using a popular learning algorithm, dimensionality reduction is carried out for fMRI data and two-dimensional visualization of brain voxels is realized, with high efficiency and high stability. Moreover, a dimensionality reduction mechanism of the t-SNE algorithm also determines that the result of two-dimensional visualization can maintain an original spatial topological relationship of the data. The invention puts forward the new and effective method for the two-dimensional visualization of the functional magnetic resonance data, which applies the popular learning algorithm to the two-dimensional visualization of the brain fMRI data for the first time and can be used as a supplementary means of the traditional cortex developed view and expansion graph.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
Composite nanometer photoacoustic contrast agent based on polybutyl acrylate, and preparation process thereof
InactiveCN104984364AGood biocompatibilityHigh biosecurityIn-vivo testing preparationsMeth-Engineering
The present invention discloses a composite nanometer photoacoustic contrast agent based on polybutyl acrylate, and a preparation process thereof, wherein the main component is a biomedical material polybutyl acrylate, the entrapped component is methylene blue or indocyanine green, the particle diameters respectively are 525.1 nm and 272.0 nm, and the potentials respectively are -4.52 mV and -5.98 mV. According to the present invention, the preparation process has characteristics of mild process, environmental protection, low energy consumption, no generation of three-waste, radiation, noise and other pollutions, simple separation and purification process operation, high yield, high entrapping rate and easy industrial production achieving, and is the universal process for preparing the composite nanometer photoacoustic contrast agent; and the composite nanometer photoacoustic contrast agent has characteristics of good biocompatibility, good safety and high photoacoustic imaging sensitivity, such that the composite nanometer photoacoustic contrast agent is expected to be widely used in the fields of biomedical imaging, targeted diagnosis and treatment, drug screening and optimization, in vivo labeling and tracing and the like, and has potential values in the fields of personalized medicine and the like.
Owner:WENZHOU INST OF BIOMATERIALS & ENG
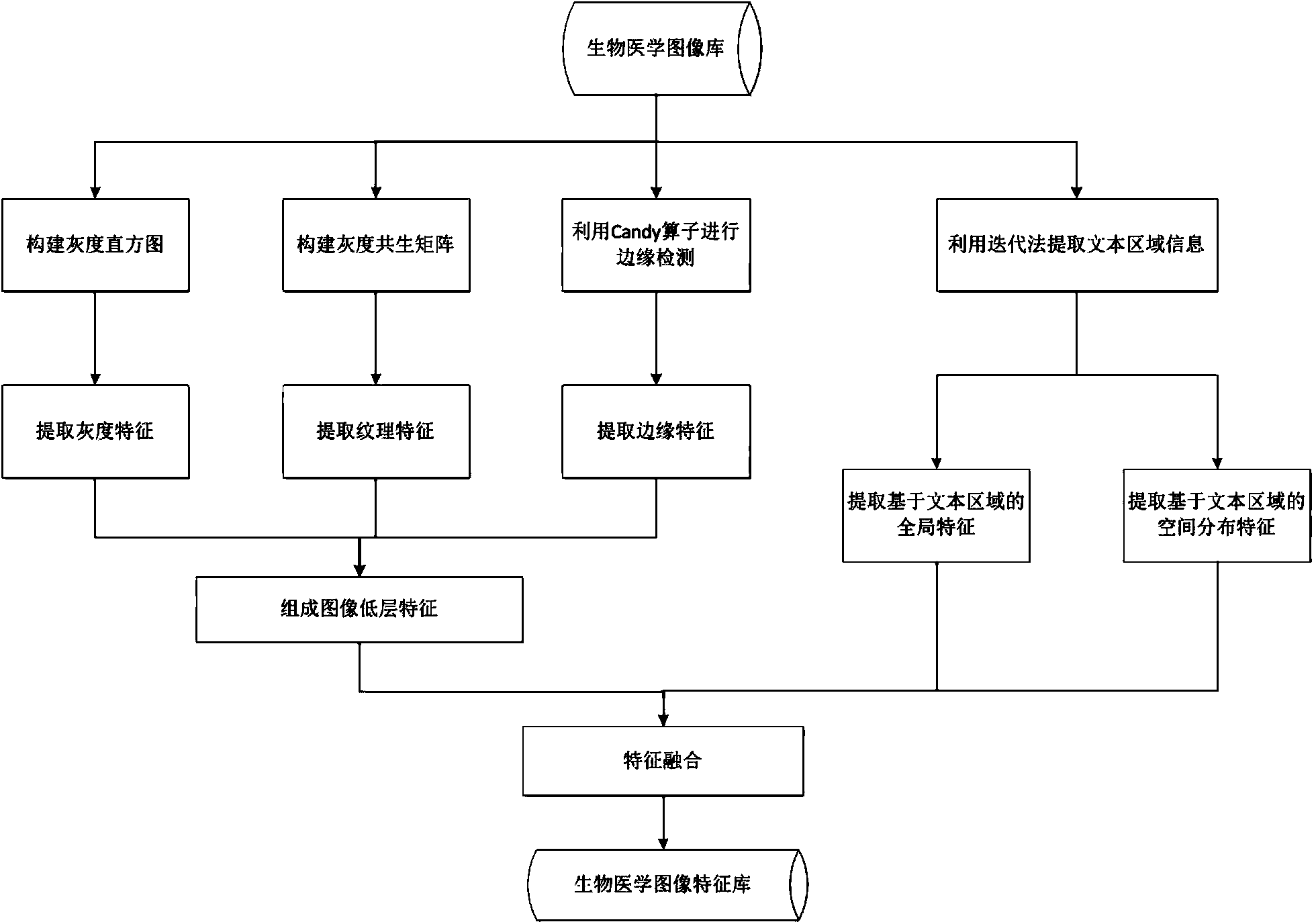
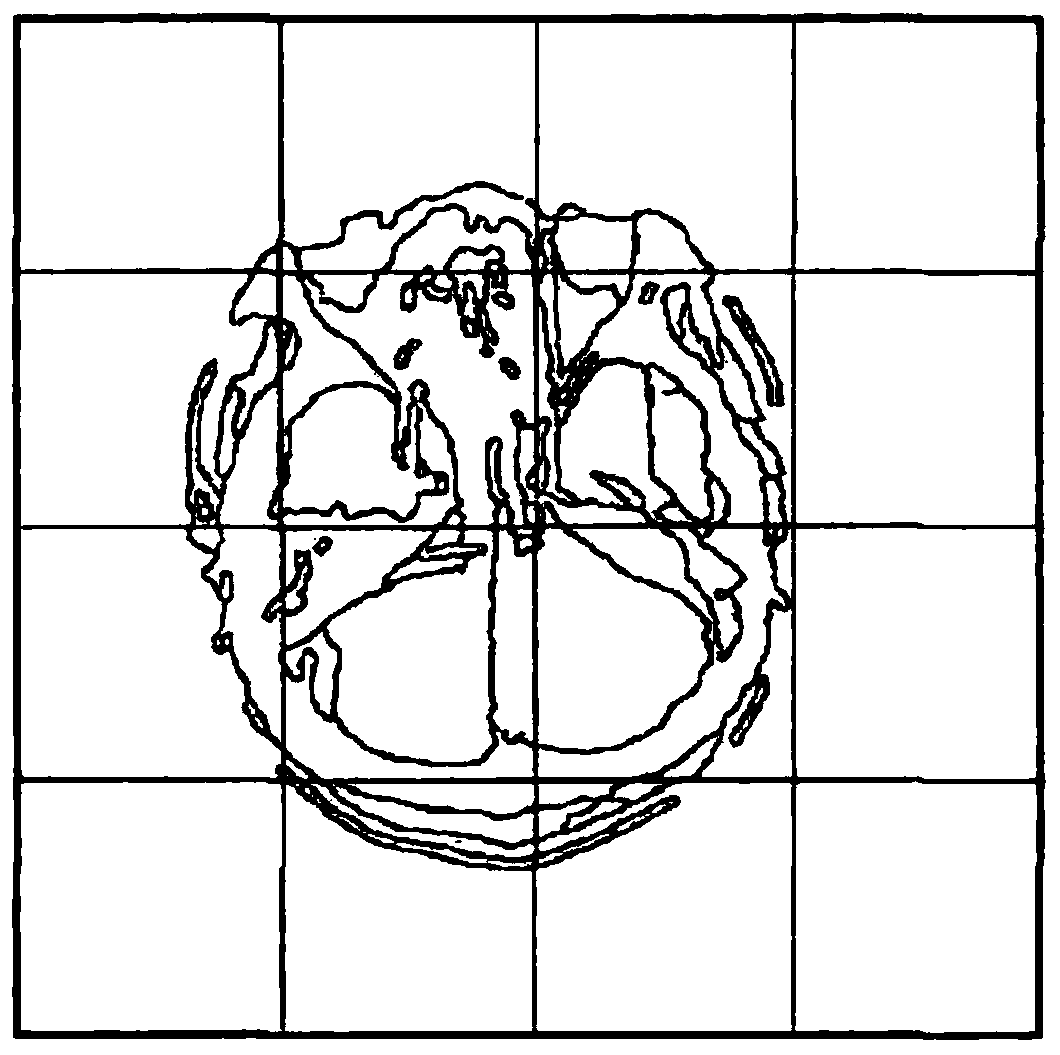
Biomedical image feature extraction method
The invention discloses a biomedical image feature extraction method. The method comprises the first step of extracting lower-layer visual features (grey features, textural features and edge features) of a biomedical image, the second step of extracting a text region from the biomedical image to obtain pixel information and position information of the text region, the third step of extracting global features from the text region of the biomedical image, the fourth step of dividing the image into sub-regions through a sub-region division method, analyzing text region distribution of all the sub-regions and extracting spatial distribution features of the image, and the fifth step of conducting feature fusion on the three kinds of image features to obtain final image visual features. By means of the method, the essential properties of the biomedical image can be described comprehensively by analyzing lower-layer visual information and text region information of the image, so the classification accuracy of the biomedical image is effectively improved, and the effect is better when the method is used for identifying flow charts and graphs.
Owner:SUN YAT SEN UNIV
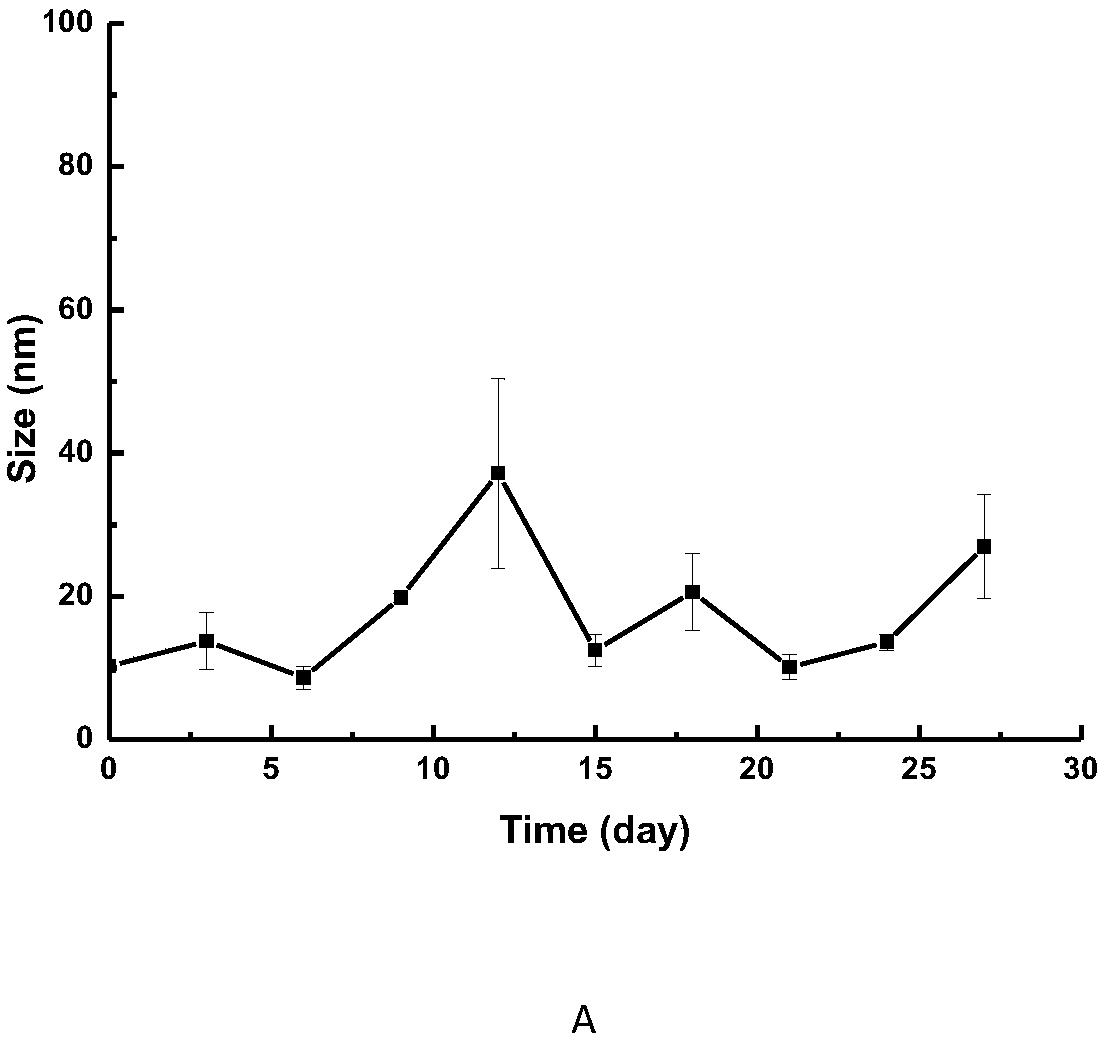
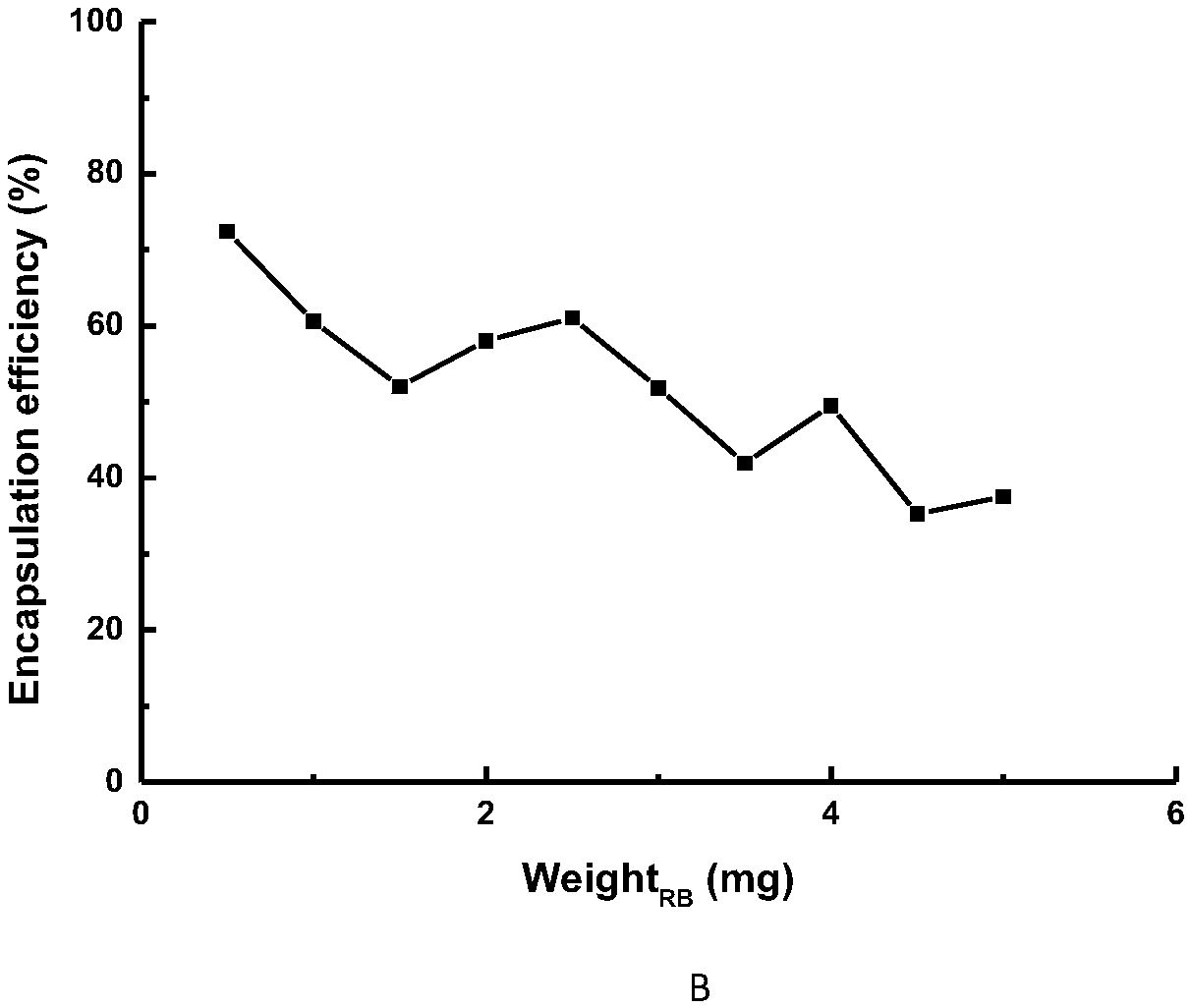
Composite amphipathic peptide nano-micelle and preparation method and applications thereof
InactiveCN109602703AImprove bioavailabilitySimple manufacturing processPhotodynamic therapyEmulsion deliveryFluorescenceBiocompatibility Testing
The invention discloses a composite amphipathic peptide nano-micelle and a preparation method and applications thereof, and particularly relates to a novel composite amphipathic peptide nano-micelle targeting integrin alpha<v>beta<3>, and applications thereof in breast cancer fluorescence imaging, photodynamic therapy and photothermal therapy. Based on the good biocompatibility of the targeted amphipathic peptide nano-micelle, the fluorescence imaging of encapsulating materials and the photodynamic therapy and photothermal therapy functions, the nano-micelle is expected to be widely used in the fields of marker and tracer in vivo, biomedical imaging and early diagnosis and treatment of tumors, and to produce good economic and social benefits in terms of life health and personalized medicine.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Complex visual image reconstruction method based on depth encoding and decoding dual model
The invention discloses a complex visual image reconstruction method based on a depth encoding and decoding dual model and belongs to the visual scene reconstruction technology field in a biomedical image brain decoding. The method is characterized by firstly, collecting and watching functional magnetic resonance signals under a lot of natural images; and then establishing four network models: 1,a coding model, 2, a decoding model, 3, a natural image discrimination model and 4, a visual area response discrimination model, wherein in the coding model, a convolutional neural network is used tocode the natural images into the voxel signals of a visual area; in the decoding model, the convolutional neural network and a deconvolution neural network are used to decode the voxel signals of thevisual area into the natural images; in the natural image discrimination model, true images and false images are discriminated; and in the a visual area response discrimination model, true signals andfalse signals are discriminated. Through training the four designed models, visual scene images can be recovered from a brain signal. In the invention, for the first time, the problem of direct conversion between a natural scene and the brain signal is solved, and the practical application of a brain-computer interface scene can be realized.
Owner:UNIV OF ELECTRONICS SCI & TECH OF CHINA
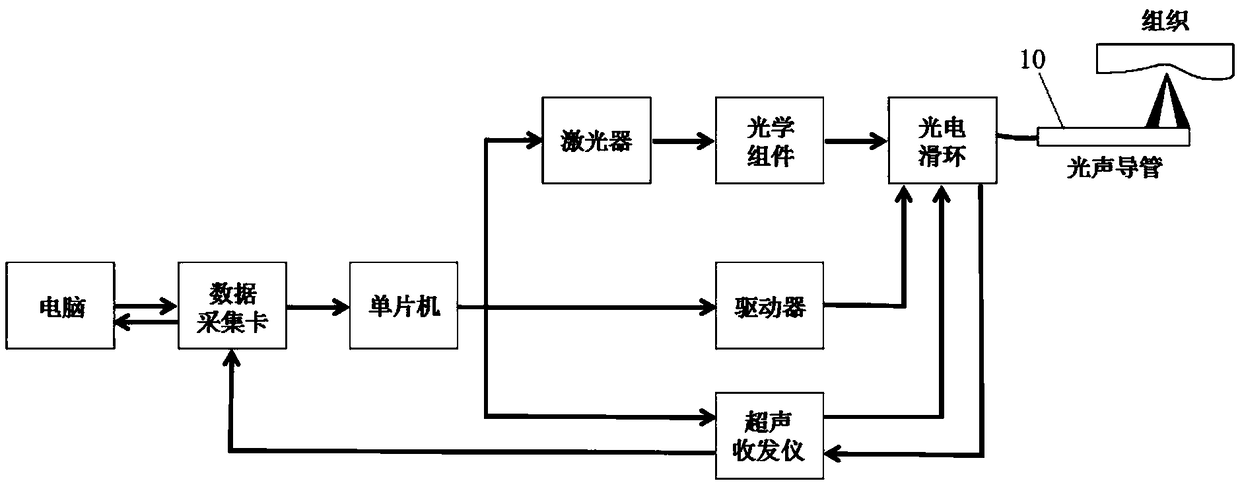
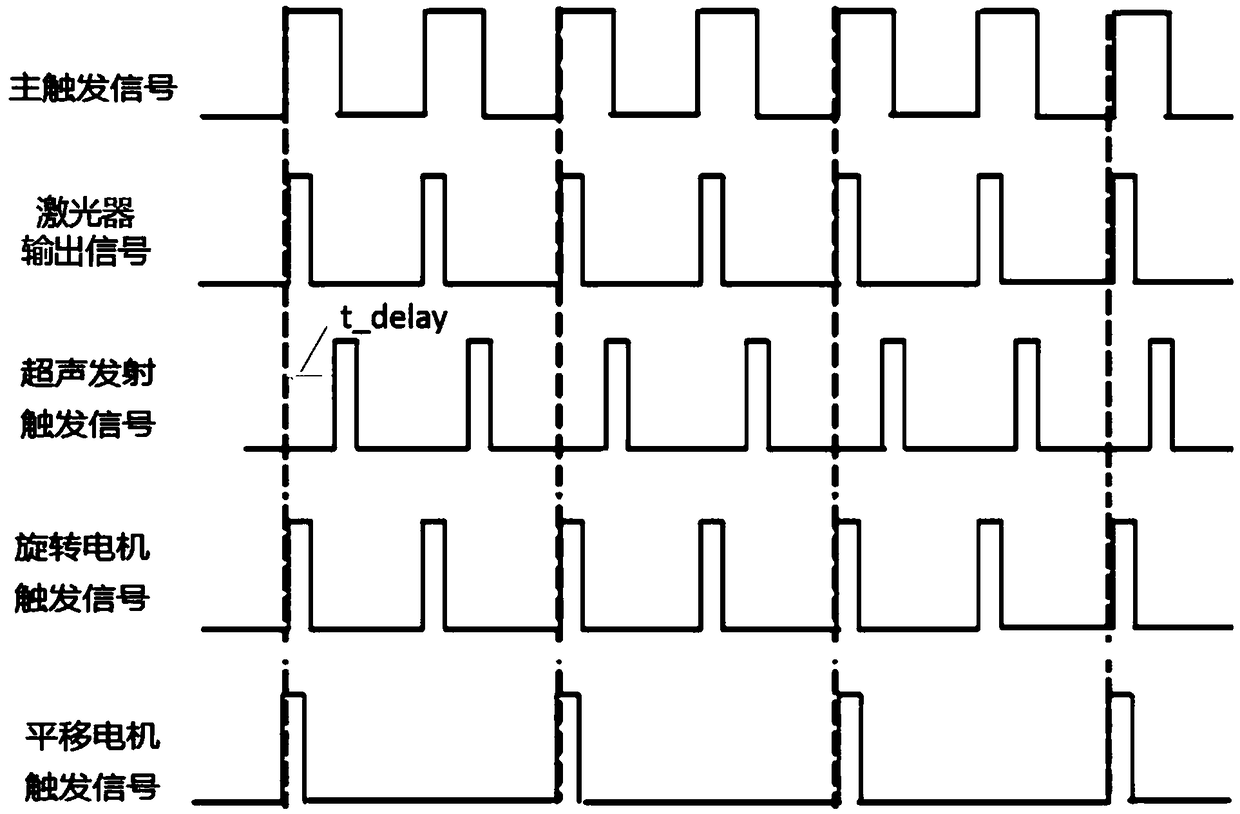
Rapid opto-acoustic/ultrasonic sector-scanning imaging device with large view field and high resolution and method for same
ActiveCN106419839AAchieving photoacoustic imagingRealize the ultrasound imageUltrasonic/sonic/infrasonic diagnosticsDiagnostic recording/measuringNon destructiveImage resolution
The invention discloses a rapid opto-acoustic / ultrasonic sector-scanning imaging device with a large view field and high resolution and a method for the same. The device comprises an integral probe, a laser emission module, a delay module, an ultrasonic emission / reception module, a signal collection module, and a computer control and image rebuilding module. Through electric and mechanical connection of the modules, large-scale tomography of an opto-acoustic mode and an ultrasonic mode can be achieved. According to the invention, a hollow focus-type ultrasonic detector is adopted, so that opto-acoustic and ultrasonic coaxial performance is achieved, and system resolution and detection sensitivity are enhanced; and a micro galvanometer sector scanning mode is adopted, so that large-scope rapid opto-acoustic / ultrasonic sector-scanning imaging is achieved. The device and the method belong to the technical field of biomedical images and non-destructive detection.
Owner:广东光声医疗科技有限公司
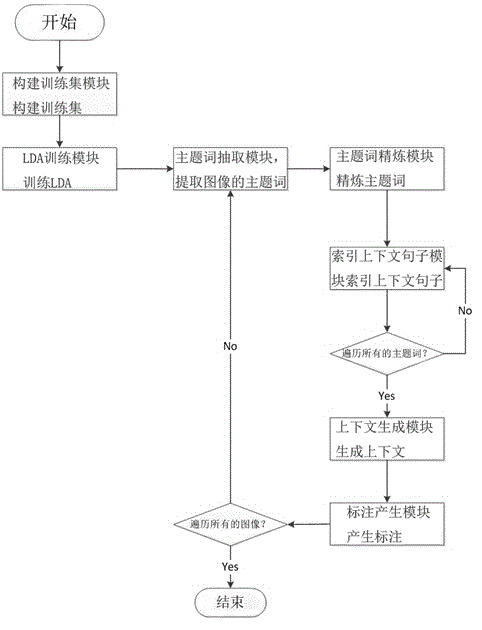
Labeling algorithm for biomedical image based on invisible dirichlet model
InactiveCN104021222AImprove accuracyIn line with text retrieval habitsMetadata still image retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsData setLabelling algorithm
The invention provides a labeling algorithm for a biomedical image based on LDA (Lejeune Dirichlet Allocation), mainly aiming at that the biomedical image is labeled, each image has a corresponding text file in a biomedical image language database and the particularity is combined. The LDA is used for extracting a subject term from captions of the image; then a context is extracted from the corresponding text file of the image according to the captions; and finally, the LDA is used for modeling the context; an obtained subject term is used as a final label of the biomedical image. The labeling algorithm has the beneficial effects that the biomedical image is labeled and the captions and the text file which are related to the image in a data set are sufficiently utilized to dig label words of the image; the accuracy is high and the plurality of label words can be generated at one time. After the biomedical image is accurately labeled, the related image is searched by using keyword index; the labeling algorithm is convenient and rapid and meets a text retrieval habit of people.
Owner:SHENZHEN INSTITUTE OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY +1
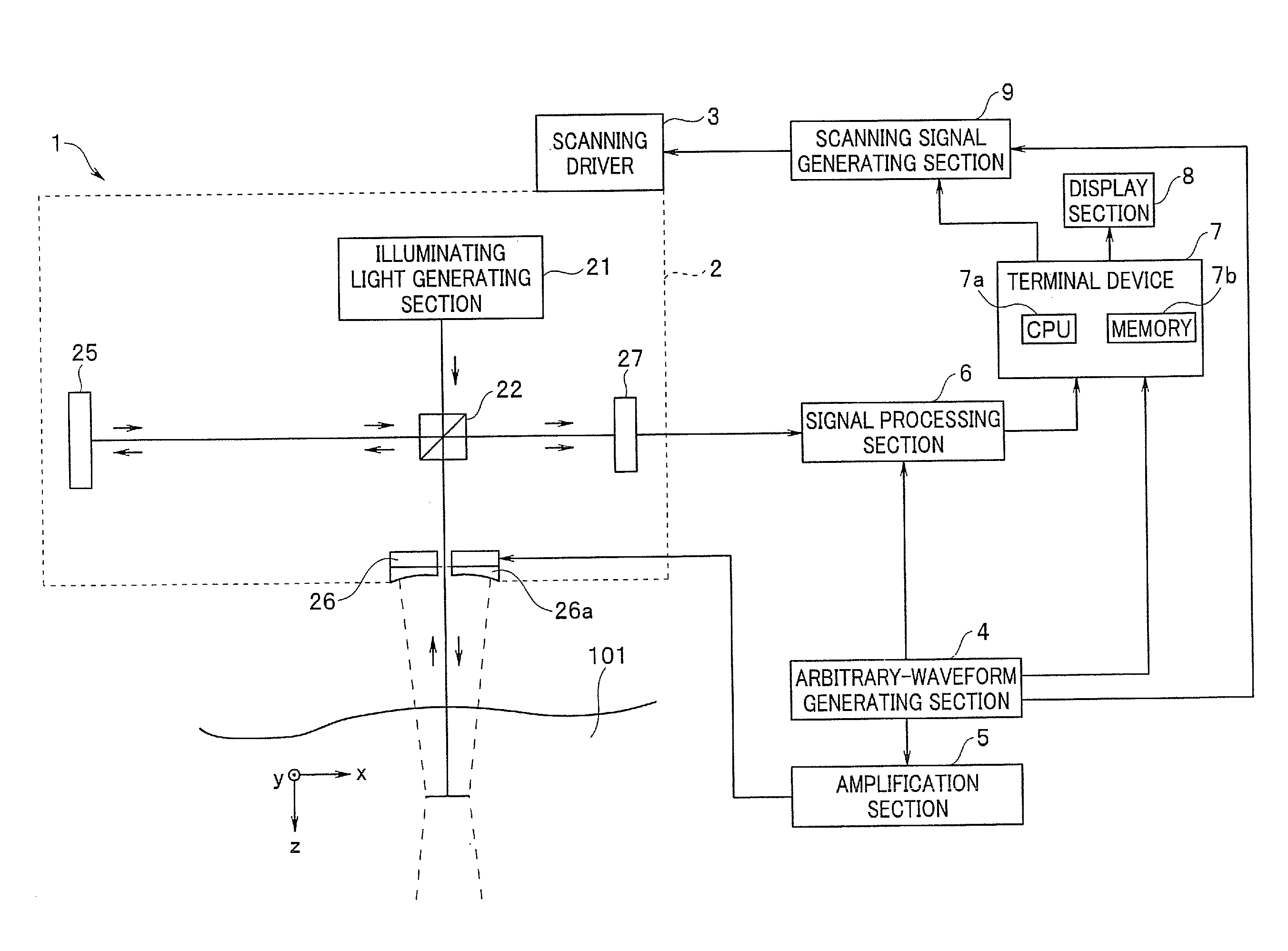
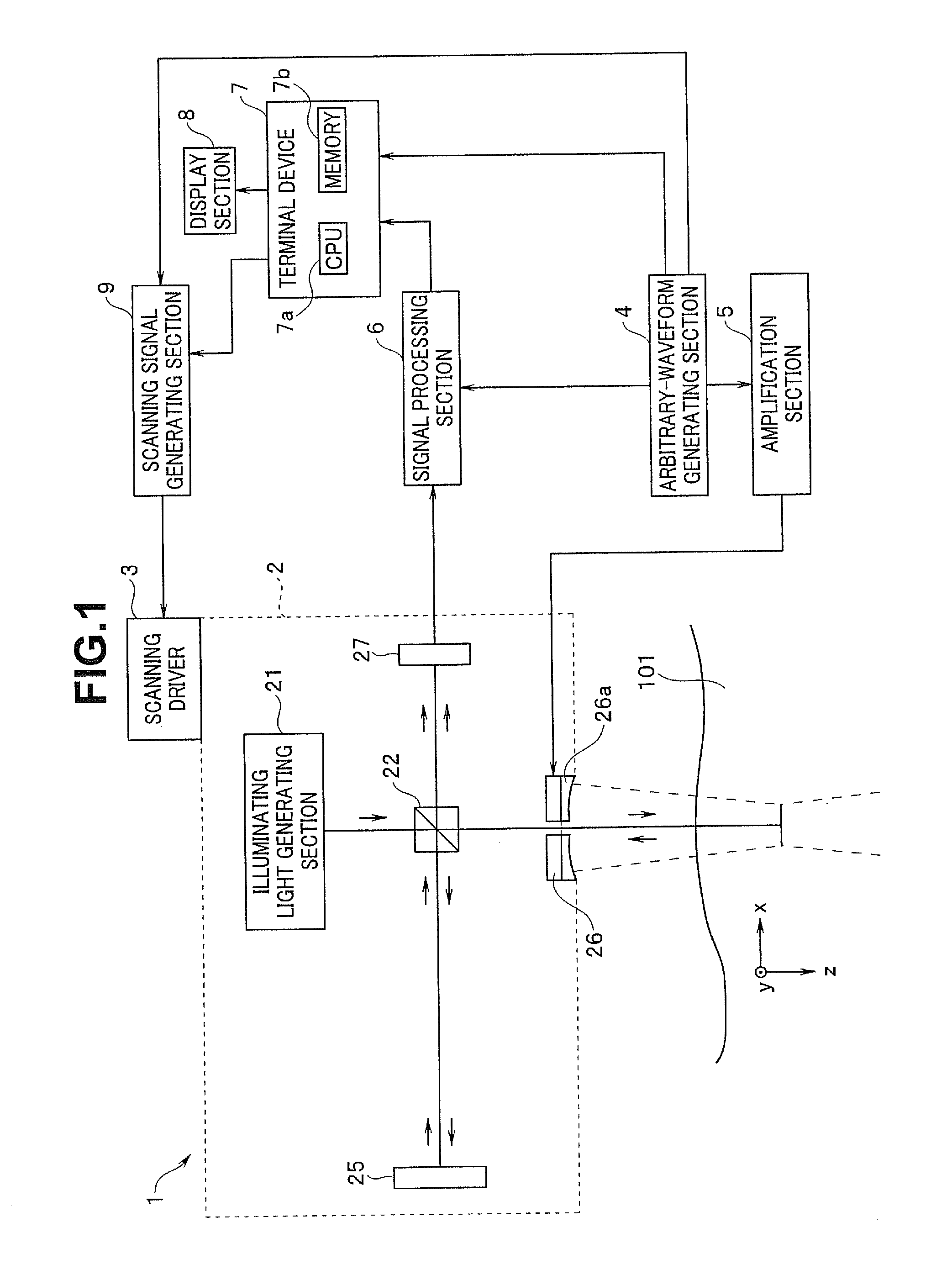
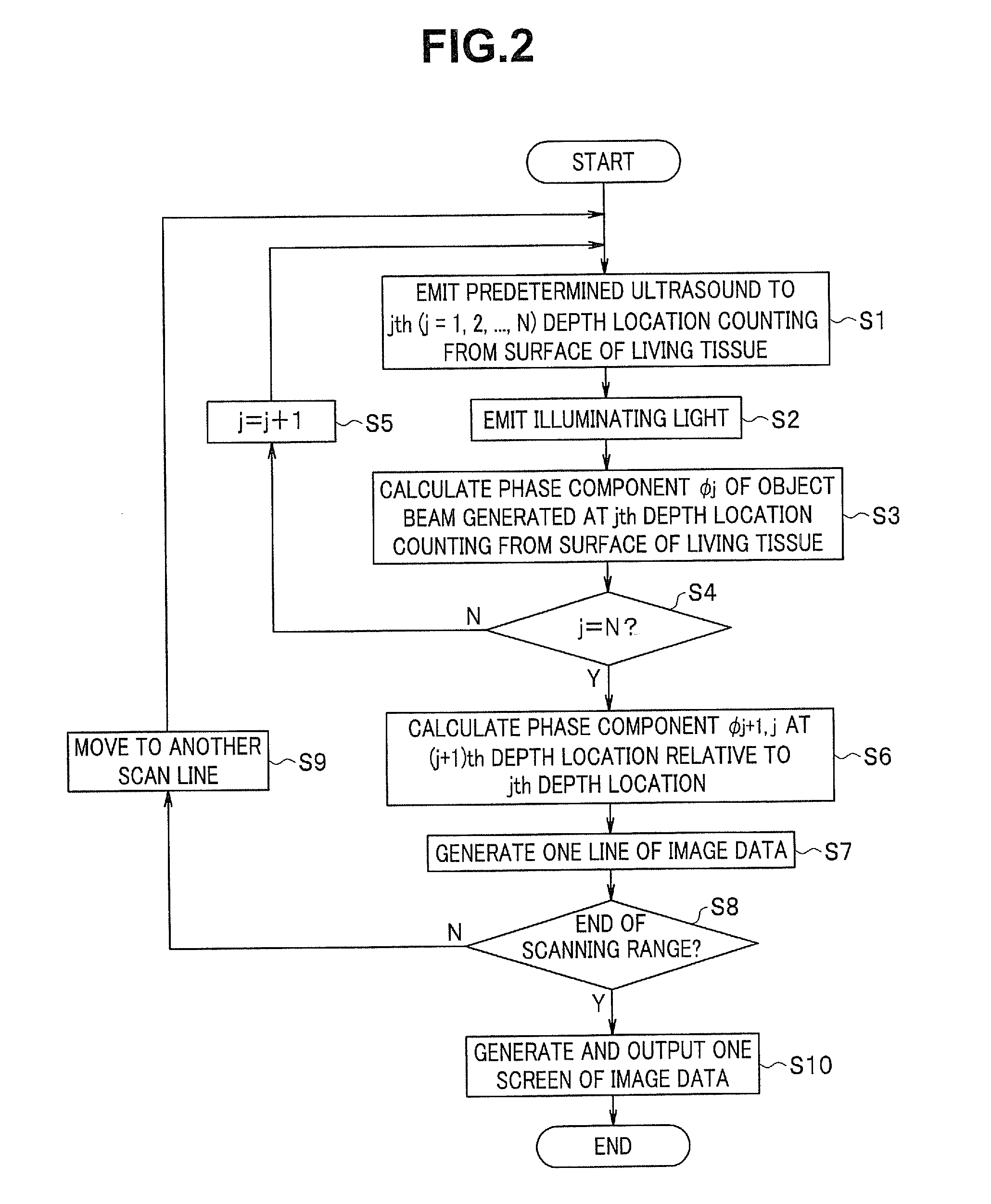
Biomedical imaging apparatus and biomedical tomographic image generation method
InactiveUS20110021907A1Material analysis by optical meansDiagnostics using tomographySonificationTomographic image
A biomedical imaging apparatus according to the present invention includes: an ultrasound generating section configured to output ultrasound to a predetermined region in an object under examination; an illuminating light generating section configured to emit illuminating light to the predetermined region upon which the ultrasound is incident; a phase component detecting section configured to time-resolve return light of the illuminating light emitted to the predetermined region, from the first time point to the Nth time point, and thereby detect the first to the Nth phase components of the return light corresponding to the first time point to the Nth time point; and a computing section configured to perform a process for subtracting a sum of the first to the (N−1)th phase components from the Nth phase component based on the phase components detected by the phase component detecting section.
Owner:OLYMPUS MEDICAL SYST CORP
Biomedical image-based biological tissue segmentation method and communication terminal
PendingCN111325729AFast global contourSolve the problem of segmenting the airwayImage enhancementImage analysisFeature extractionNuclear medicine
The invention discloses a biomedical image-based biological tissue segmentation method and a communication terminal, and aims to solve the problem of segmenting an airway from a medical image. The method comprises the following steps: acquiring a biomedical image of the biological tissue; reducing the size of the biomedical image to a specified size, and performing feature extraction on the biomedical image of which the size is reduced to obtain a global contour of the biological tissue; dividing the biomedical image into a plurality of image blocks, and performing feature extraction on each image block to obtain a local detail structure of the biological tissue included in each image block; and fusing the local detail structure of the biological tissue and the global contour of the biological tissue included in each image block to obtain a complete structure of the biological tissue.
Owner:QINGDAO HISENSE MEDICAL EQUIP
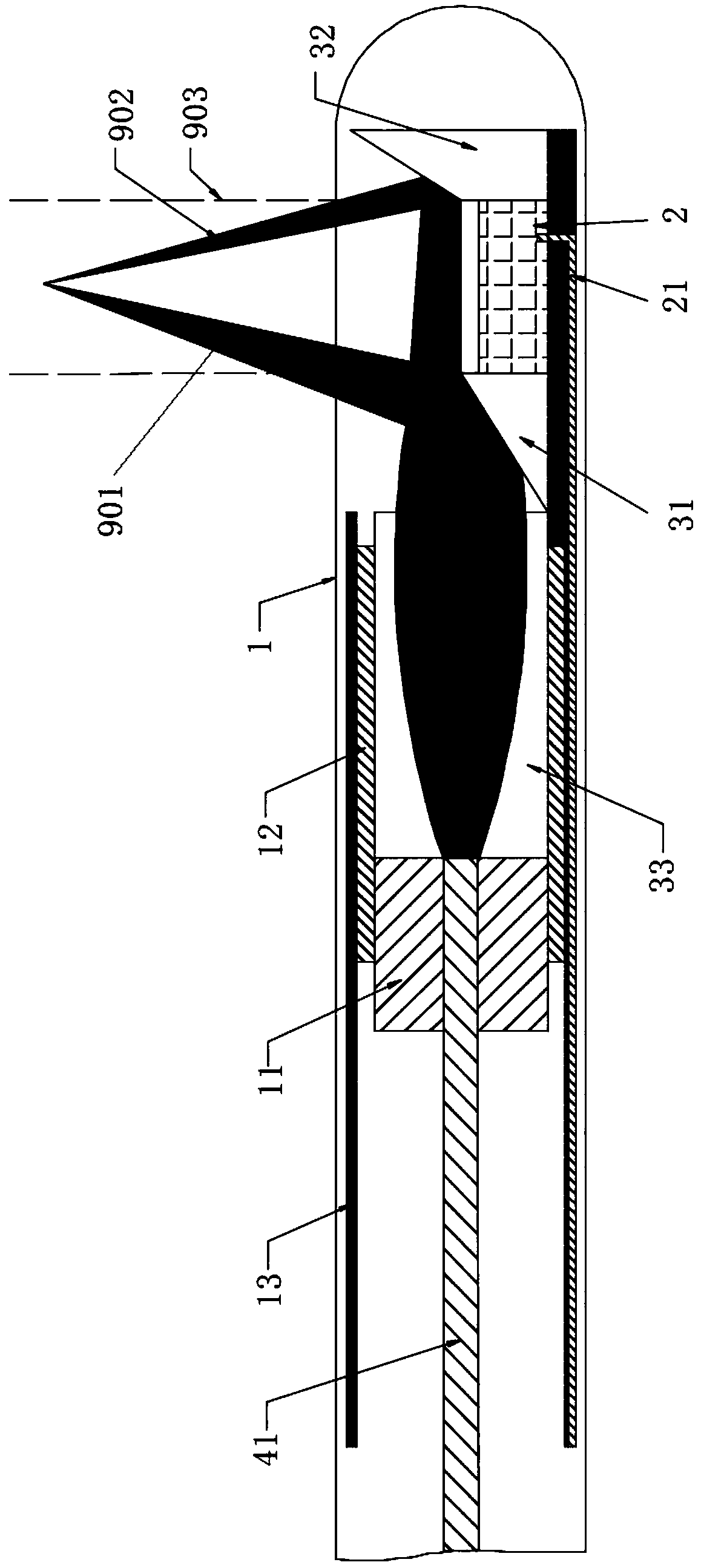
Photoacoustic coaxial endoscopic device, endoscopic system and control method
PendingCN109497950AAvoid the disadvantage of low coupling efficiencyImprove collimation efficiencySurgeryEndoscopesCatheterIrradiation
The invention is suitable for the technical field of biomedicine image equipment and discloses a photoacoustic coaxial endoscopic device, an endoscopic system and a control method. The device comprises a photoacoustic catheter enabling tissue to generate photoacoustic effect, the photoacoustic catheter comprises a catheter body, an irradiation light providing part for generating irradiation lightor guiding the same and an ultrasonic part for emitting ultrasonic wave and capable of receiving the same and photoacoustic signal, the irradiation light providing part is arranged or extends into thecatheter body, and the ultrasonic part is arranged in the catheter body; the photoacoustic catheter further comprises a mirror group for reflecting or refracting the irradiation light and then focusing the same to central axis of the ultrasonic part, and the mirror group is arranged on the outer side. The system comprises the device. The device is photoacoustically coaxial, large in photoacousticoverlapped area and excellent in imaging effect.
Owner:SHENZHEN INST OF ADVANCED TECH
Method for processing biomedical images
InactiveUS8144963B2Reduce specific mortalityHigh sensitivityImage enhancementImage analysisBiomedical imageComputer science
Owner:MEDICAD
Generalized zero sample target classification method based on active learning and variational auto-encoder
ActiveCN113177587AEnable active learningEliminate biasCharacter and pattern recognitionClassification methodsProactive learning
The invention provides a generalized zero sample target classification method based on active learning and a variational auto-encoder. The method is used for solving the problem of bias caused by loss of unknown class supervision information and the problem of low-dimensional feature aggregation caused by projection from high-dimensional features to low-dimensional space in the prior art, and effectively improving the classification accuracy. The method comprises the following implementation steps: acquiring a training sample set Ptrain and a test sample set Ptest; constructing a generalized zero sample classification model H based on the variational auto-encoder; carrying out iterative training on the variational auto-encoder f and a nonlinear classifier fclassifier in the generalized zero sample classification model H based on the variational auto-encoder; and obtaining a target classification result of a generalized zero sample. The method can be applied to the fields of classification of rare species lacking training data, biomedical image recognition and the like.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
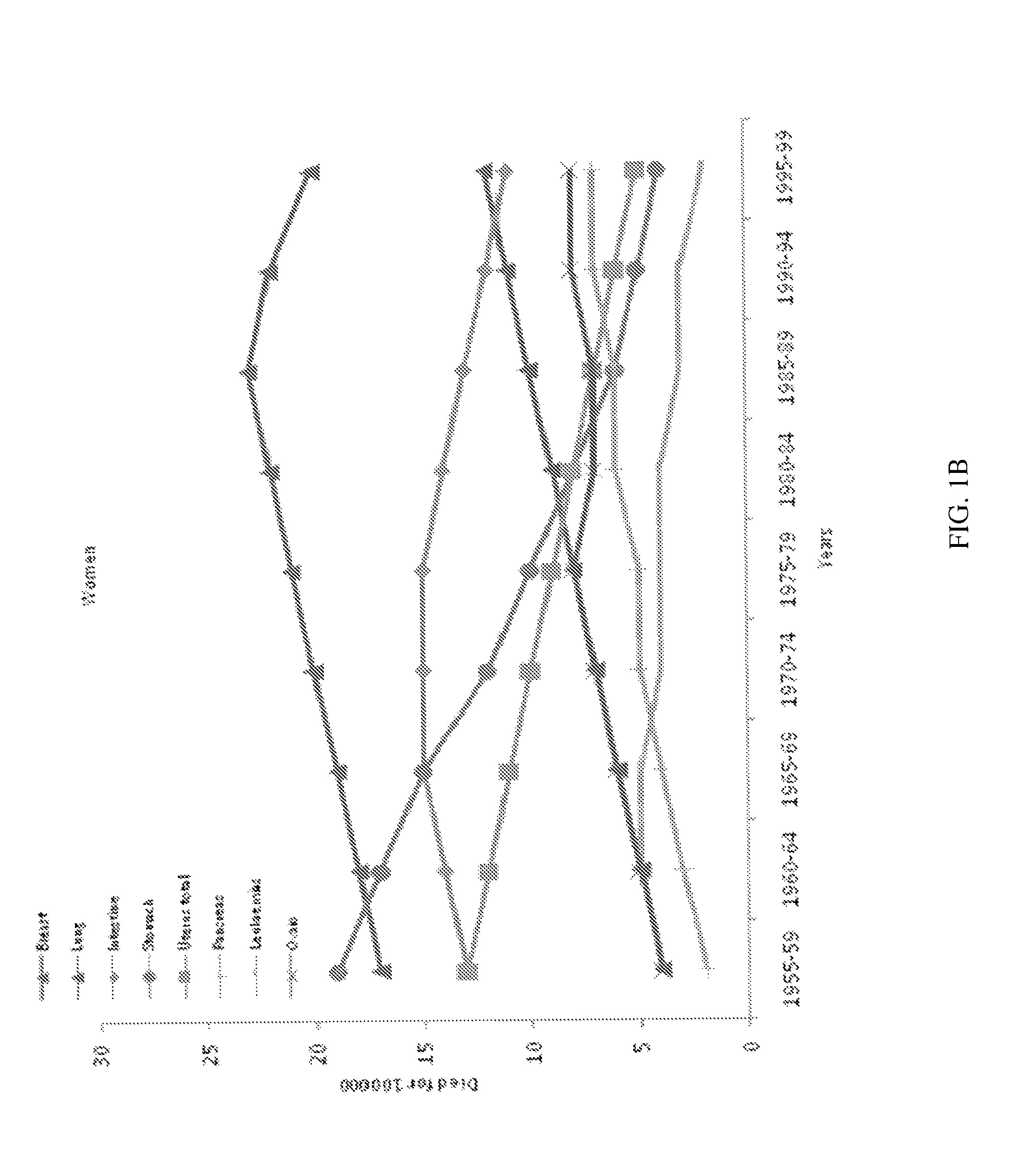
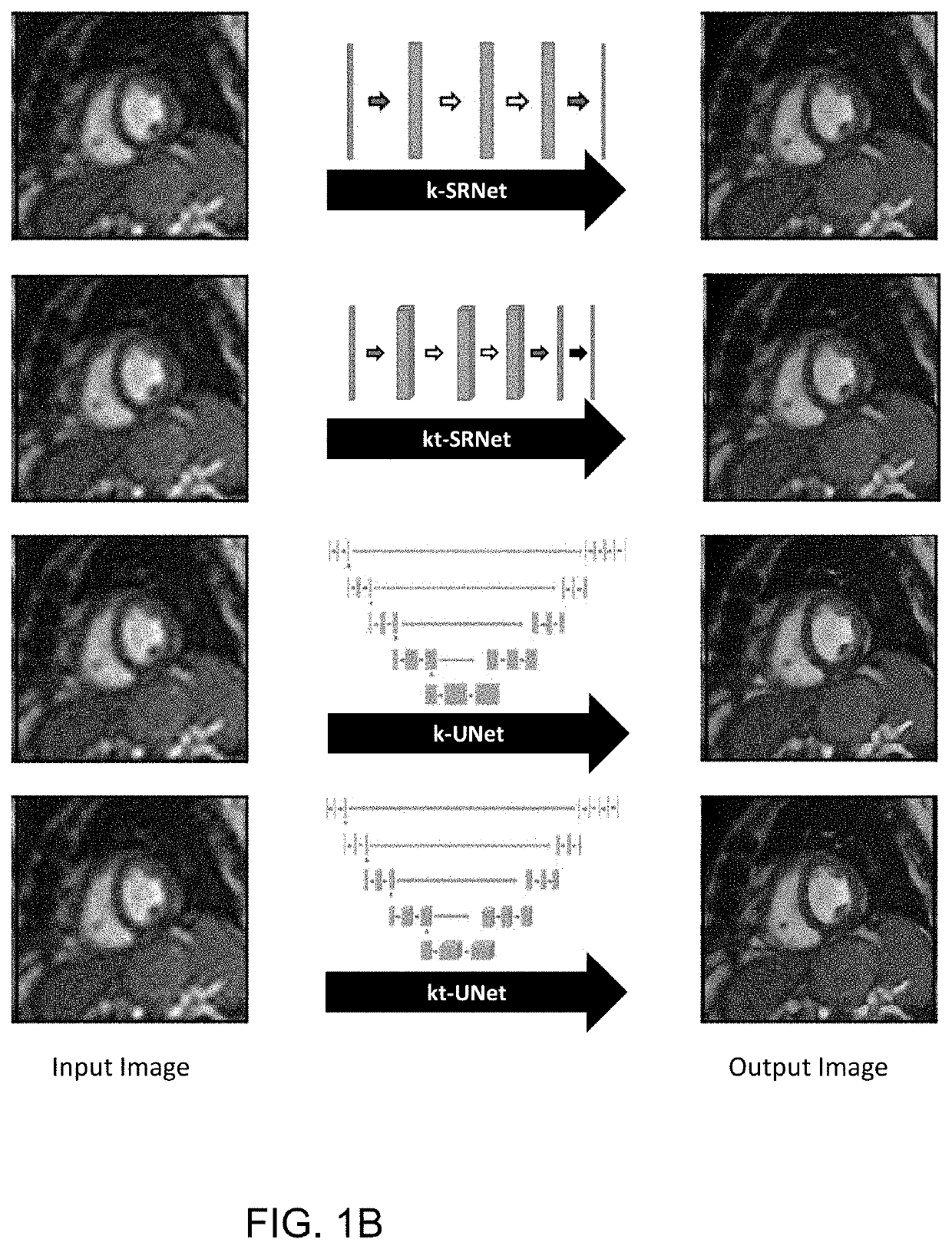
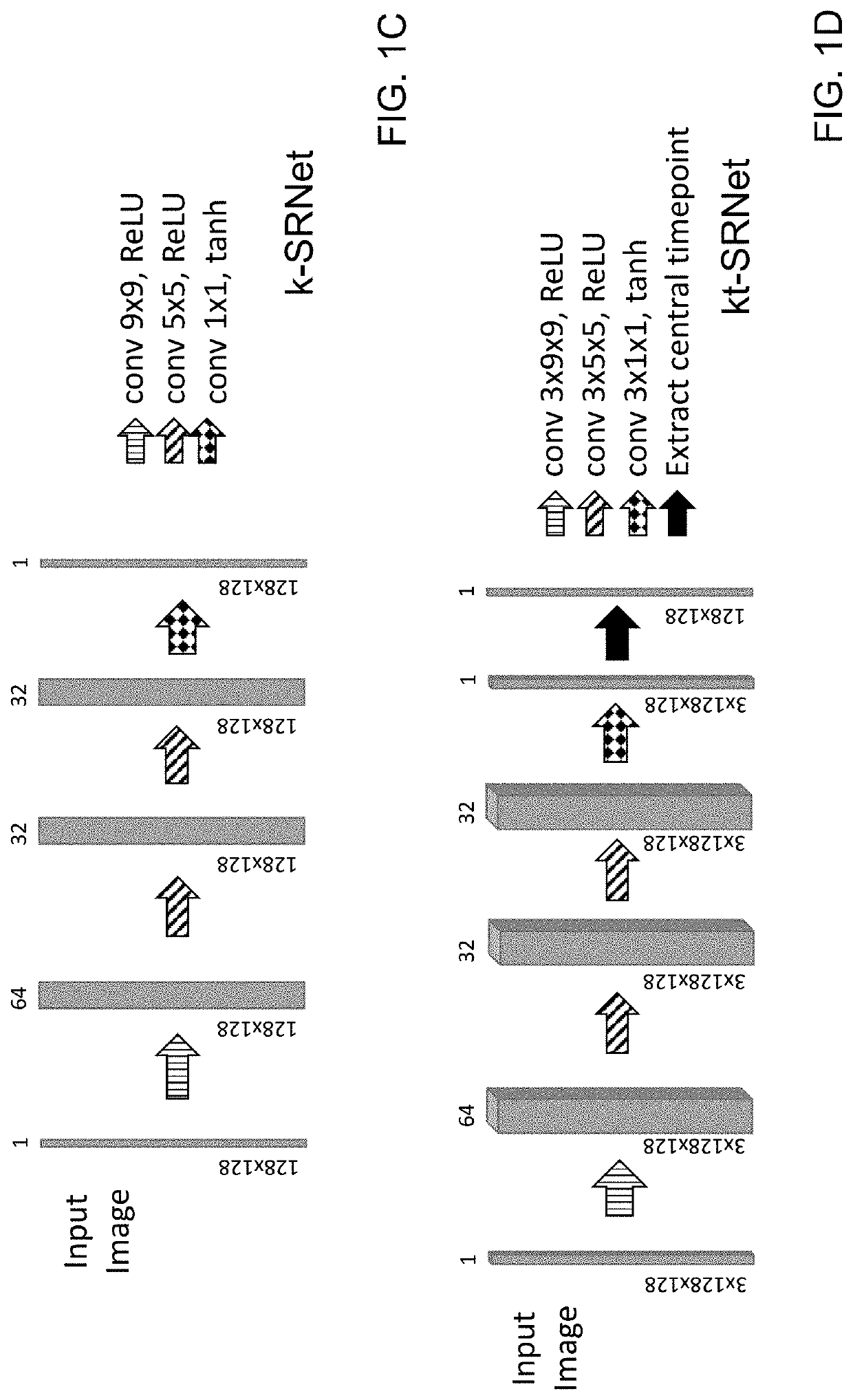
Spatiotemporal resolution enhancement of biomedical images
PendingUS20220114699A1Reduce scan timeImprove diagnostic accuracyDetails involving 3D image dataGeometric image transformationImage resolutionRadiology
A method for improving resolution of a lower resolution image includes inputting at least one digital image into a convolutional neural network (CNN) comprising one of a SRNet and a UNet to output a two-dimensional image having a higher resolution. In some embodiments, multiple image frames may be processed using a 3D CNN to generate a two-dimensional output image.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com