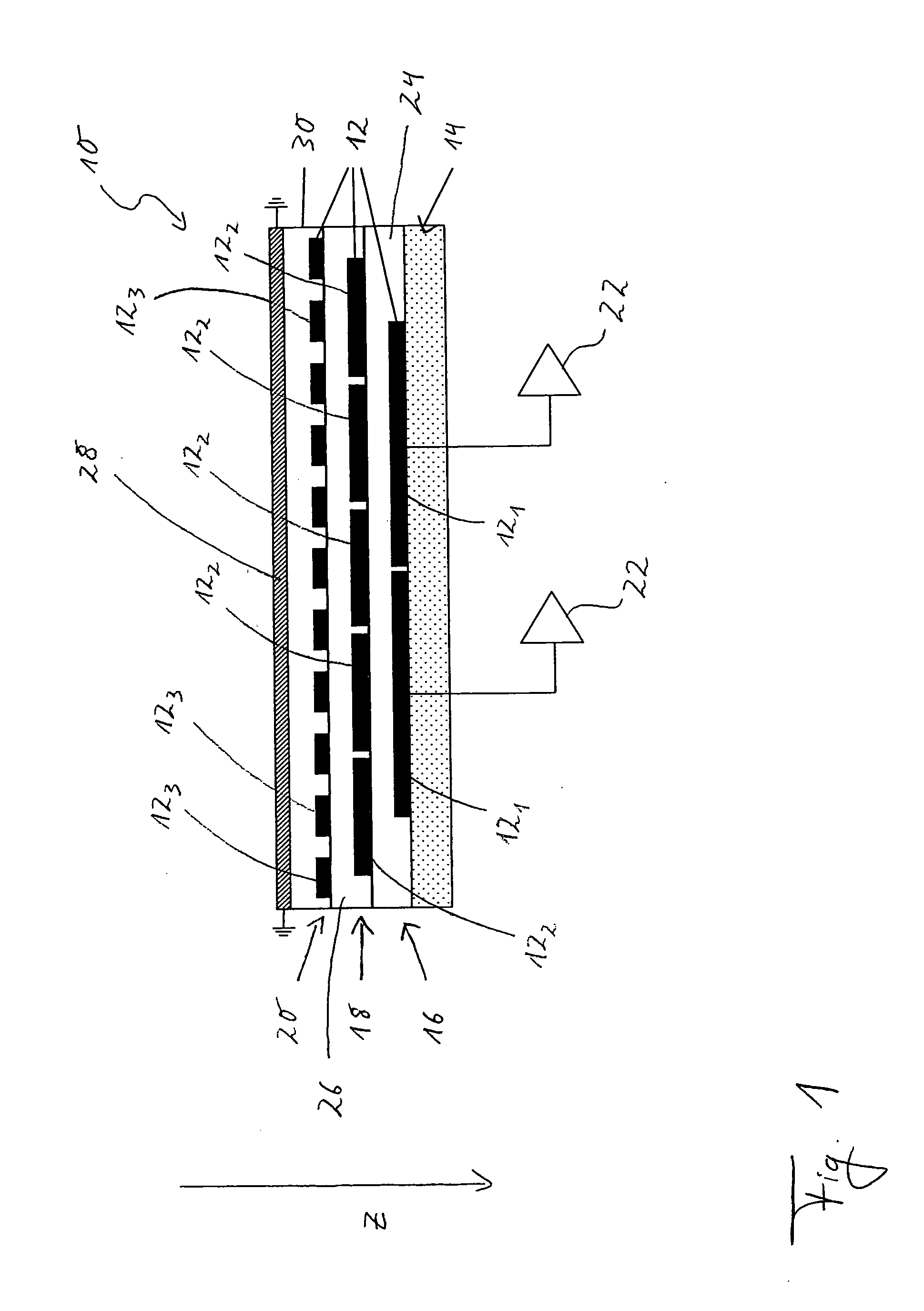
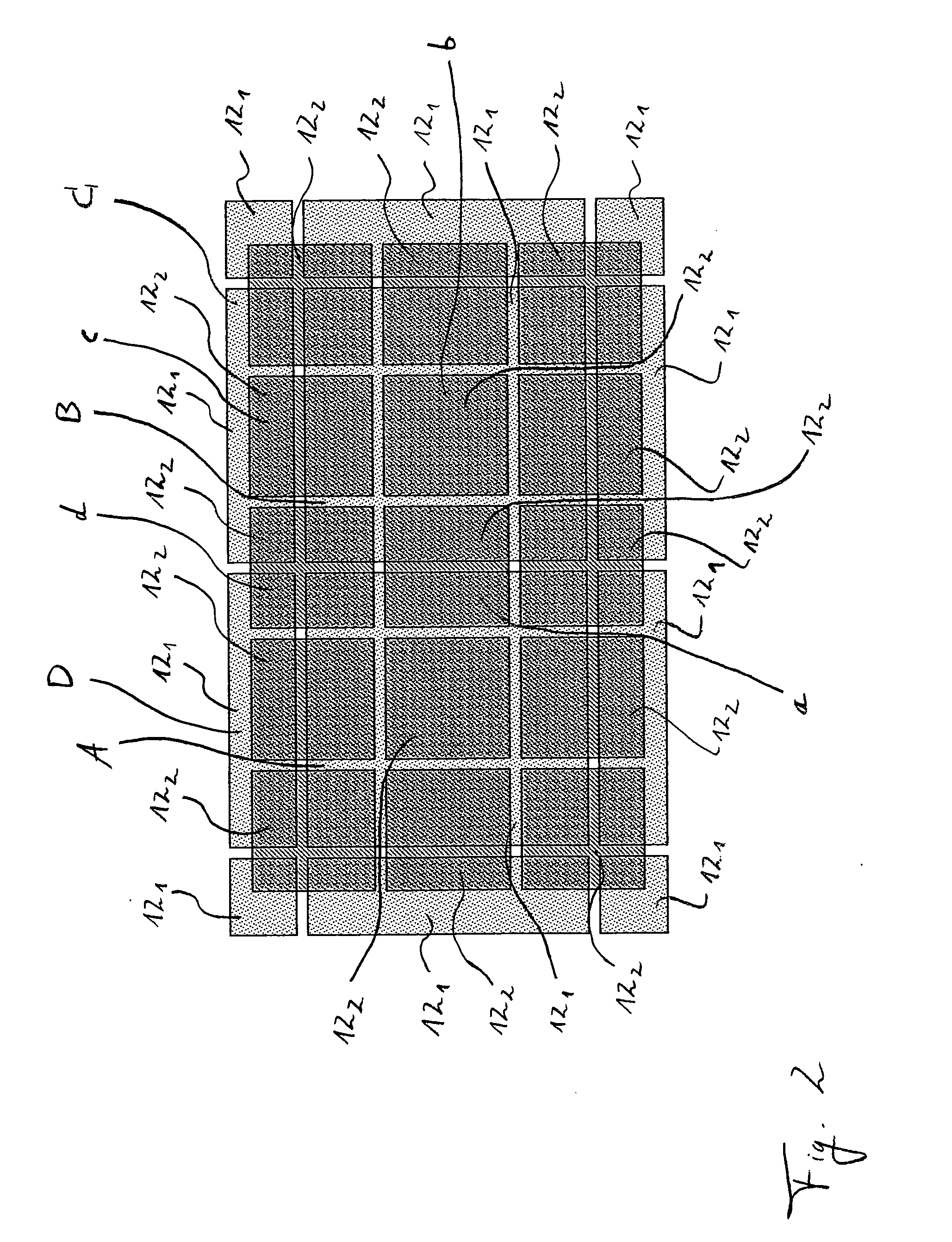
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
115 results about "Readout electronics" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Multi-functional control and entertainment systems
InactiveUS20050276448A1Big knobReduce in quantityDashboard fitting arrangementsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsInformation processingDriver/operator
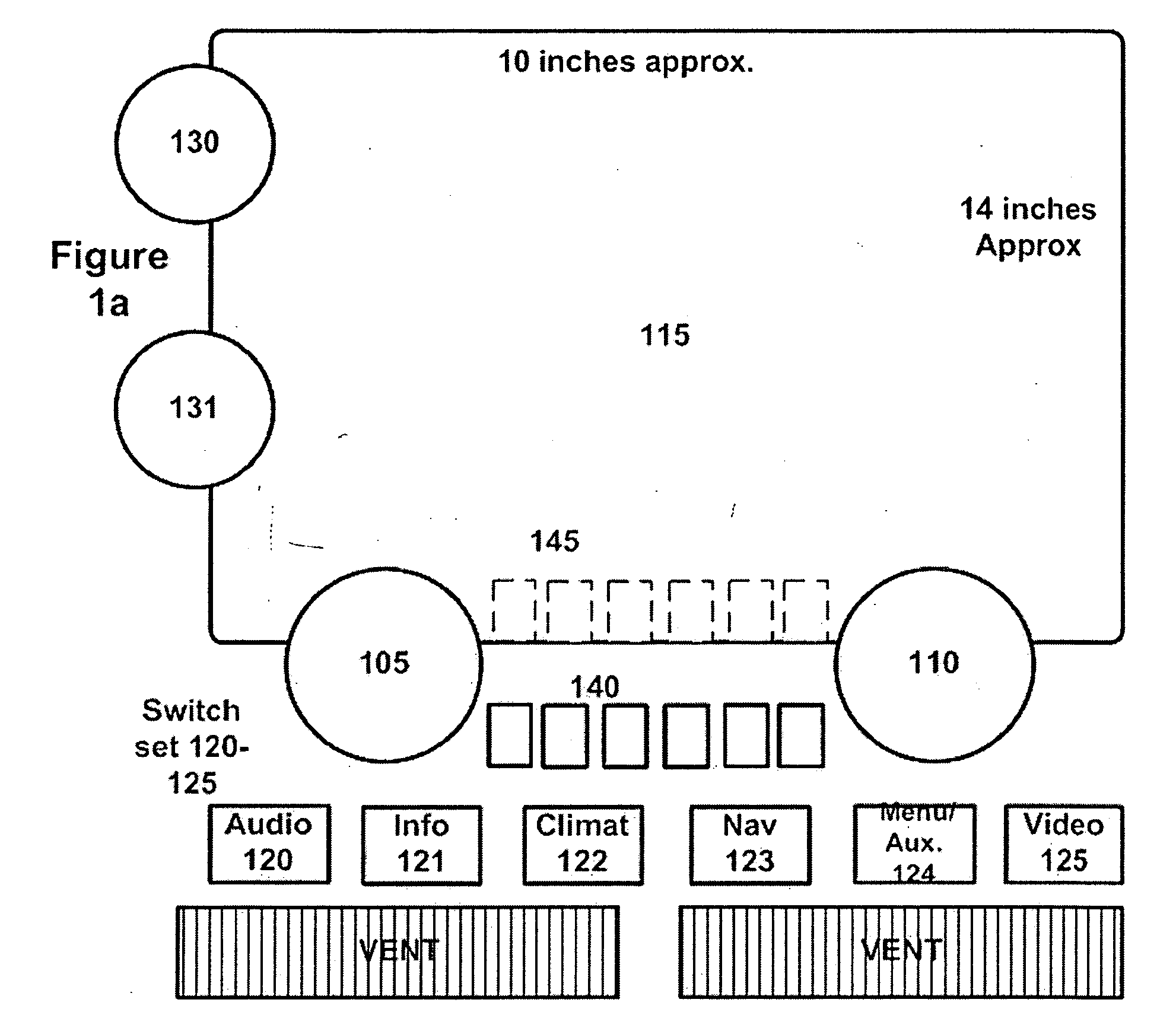
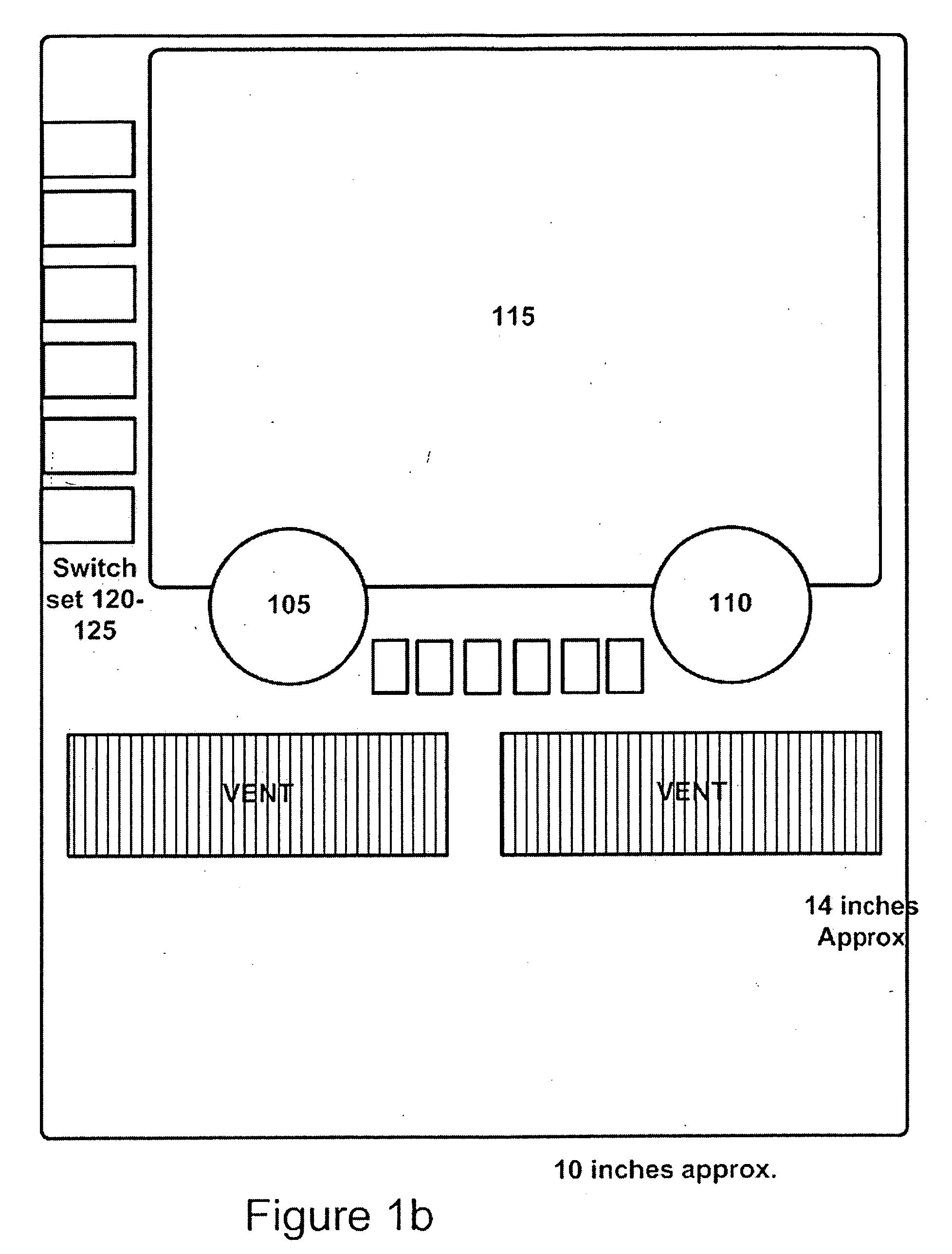
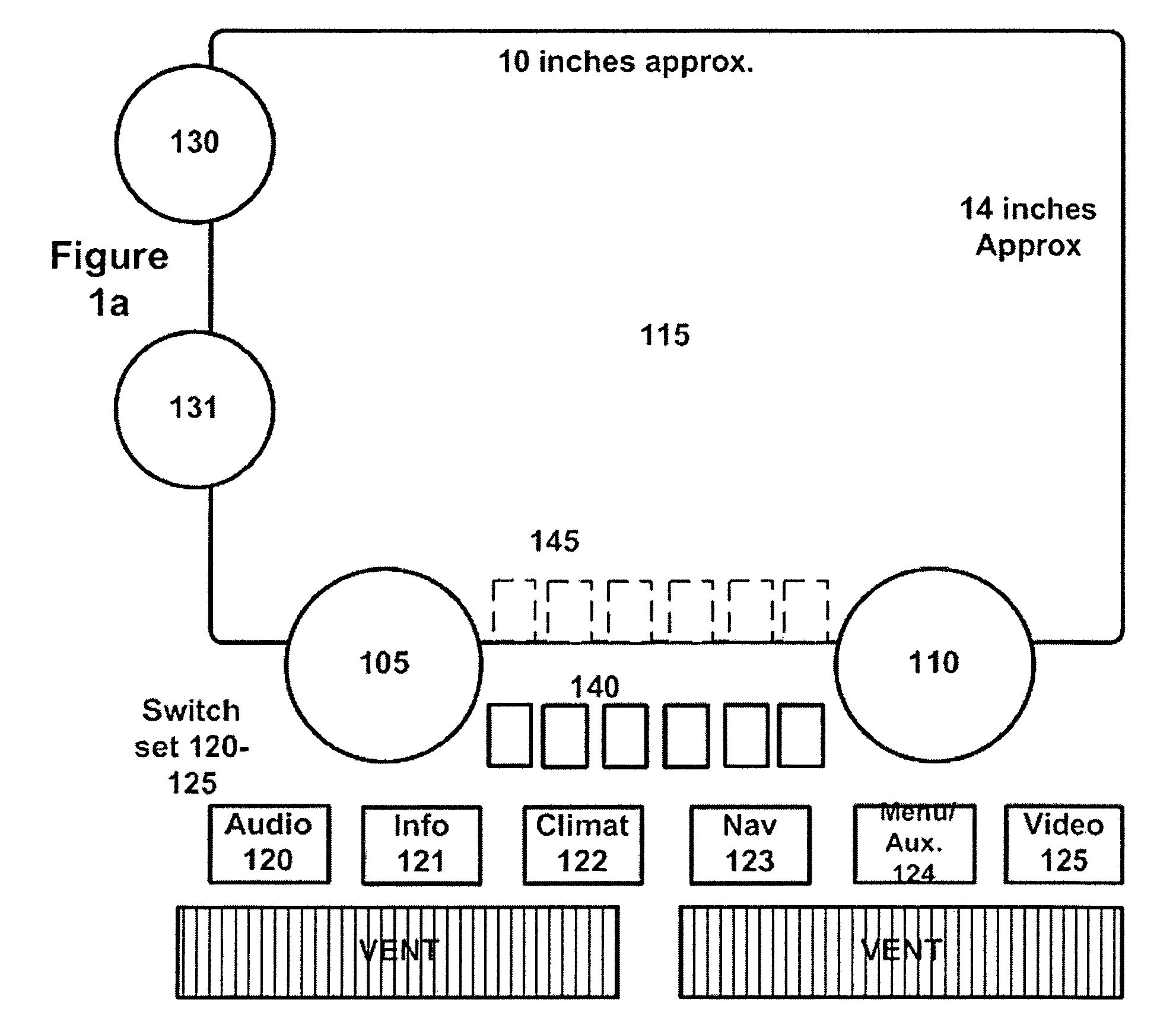
For use in vehicles, it is desirable to have multi-functional (also known as reconfigurable) controls in the center stack portion of the instrument panel in order to best provide electronic and telematic functions to the driver. Disclosed are methods and apparatus to allow reconfiguration of classical controls such as knobs, sliders, and switches most familiar to the vast majority of the motoring public which may, if desired, utilize conventional flat panel displays (e.g., LCD based) and conventional readout electronics and switching. Also disclosed are projection based controls and new forms of rear seat entertainment controls and related apparatus for minivans and other vehicles.
Owner:TURE TECH PARTNERS
Dual mode adaptive threshold architecture for 3-D ladar FPA
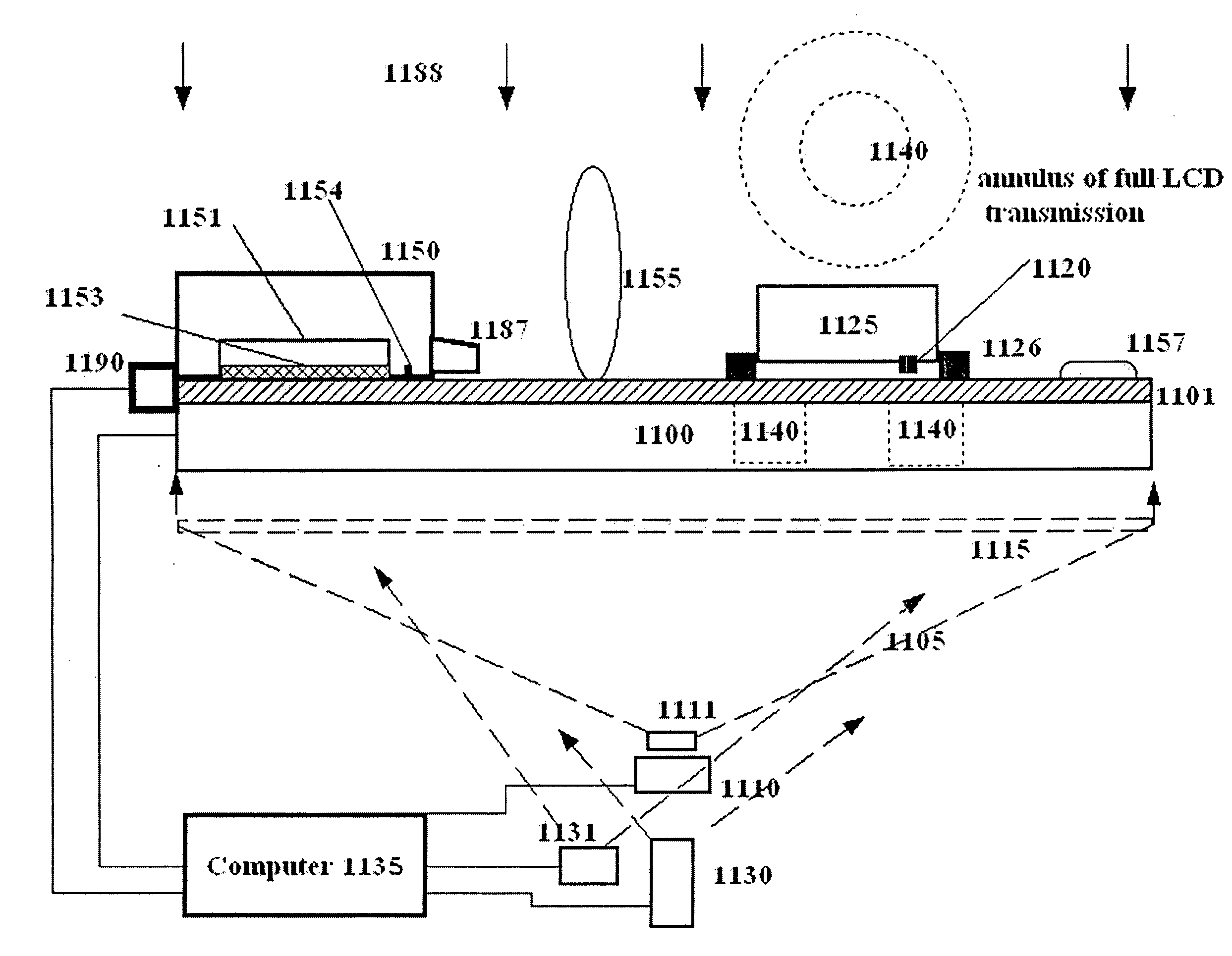
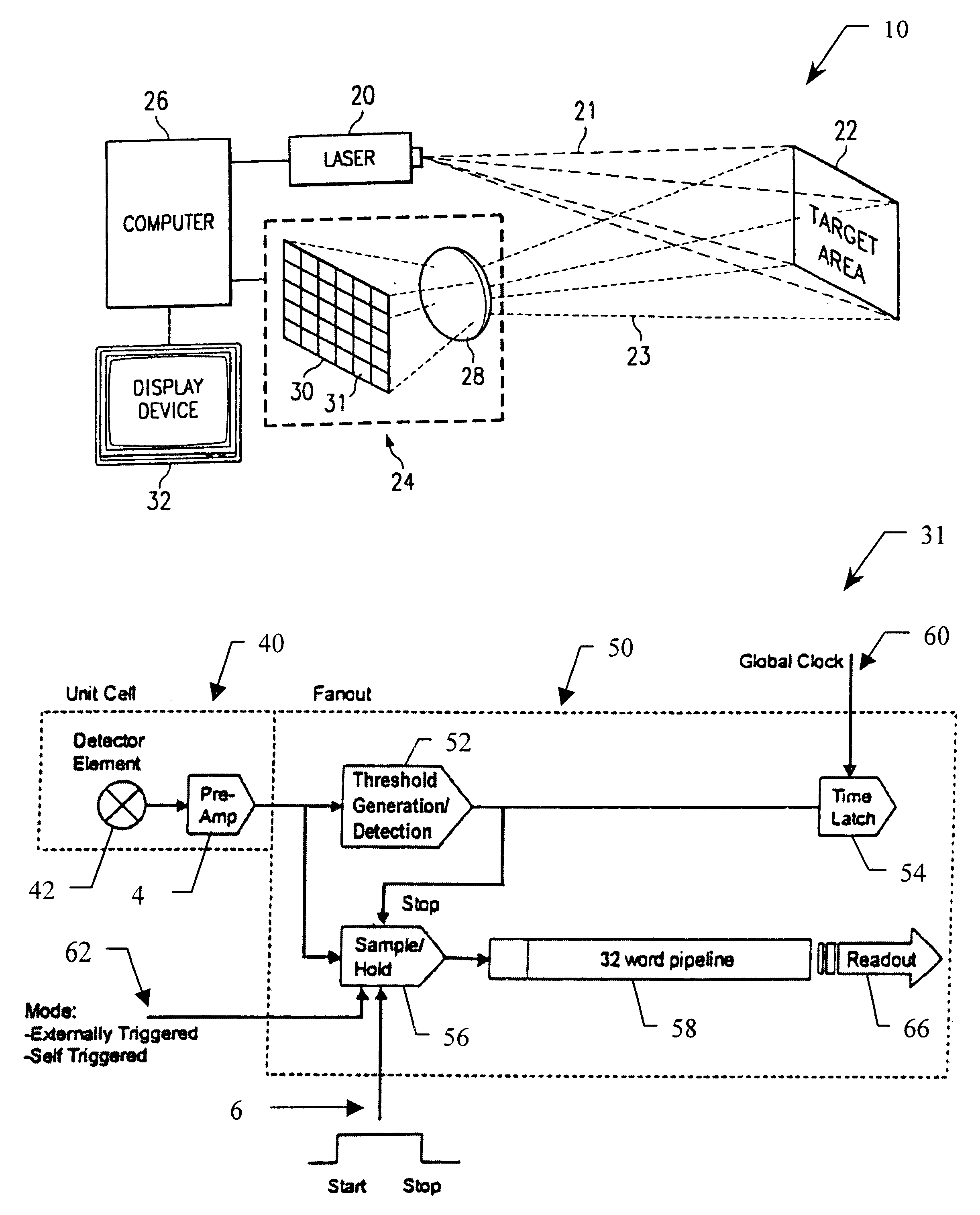
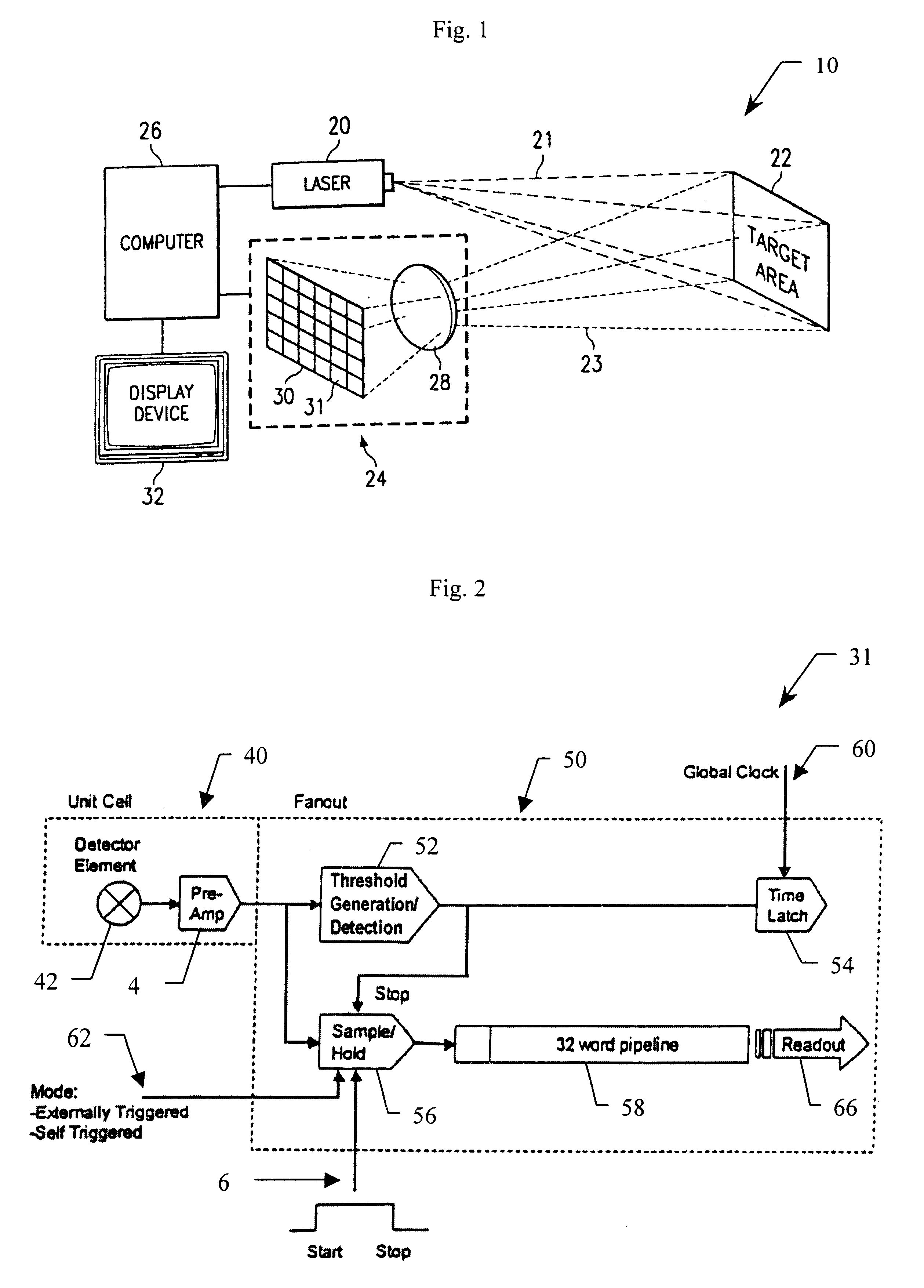
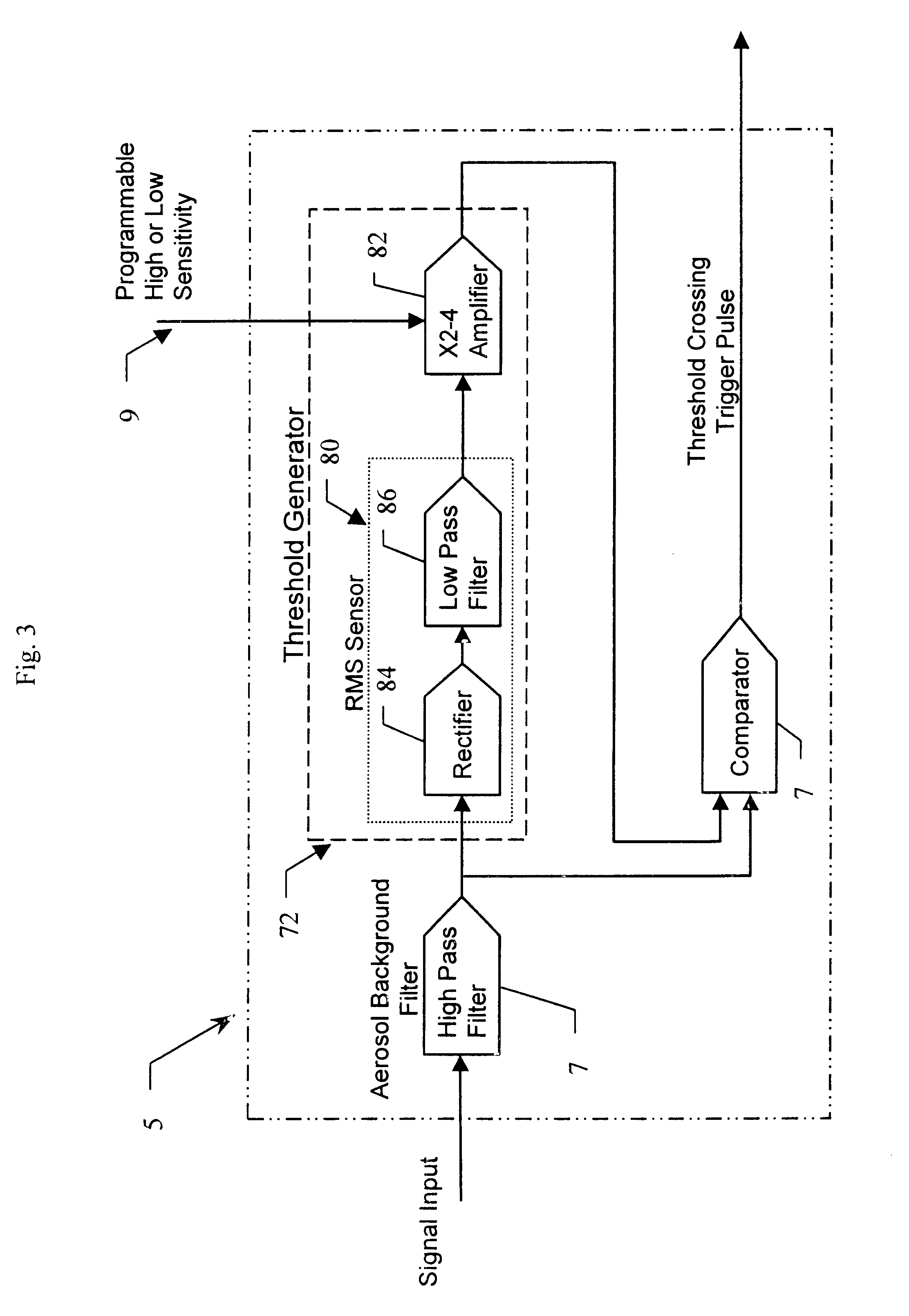
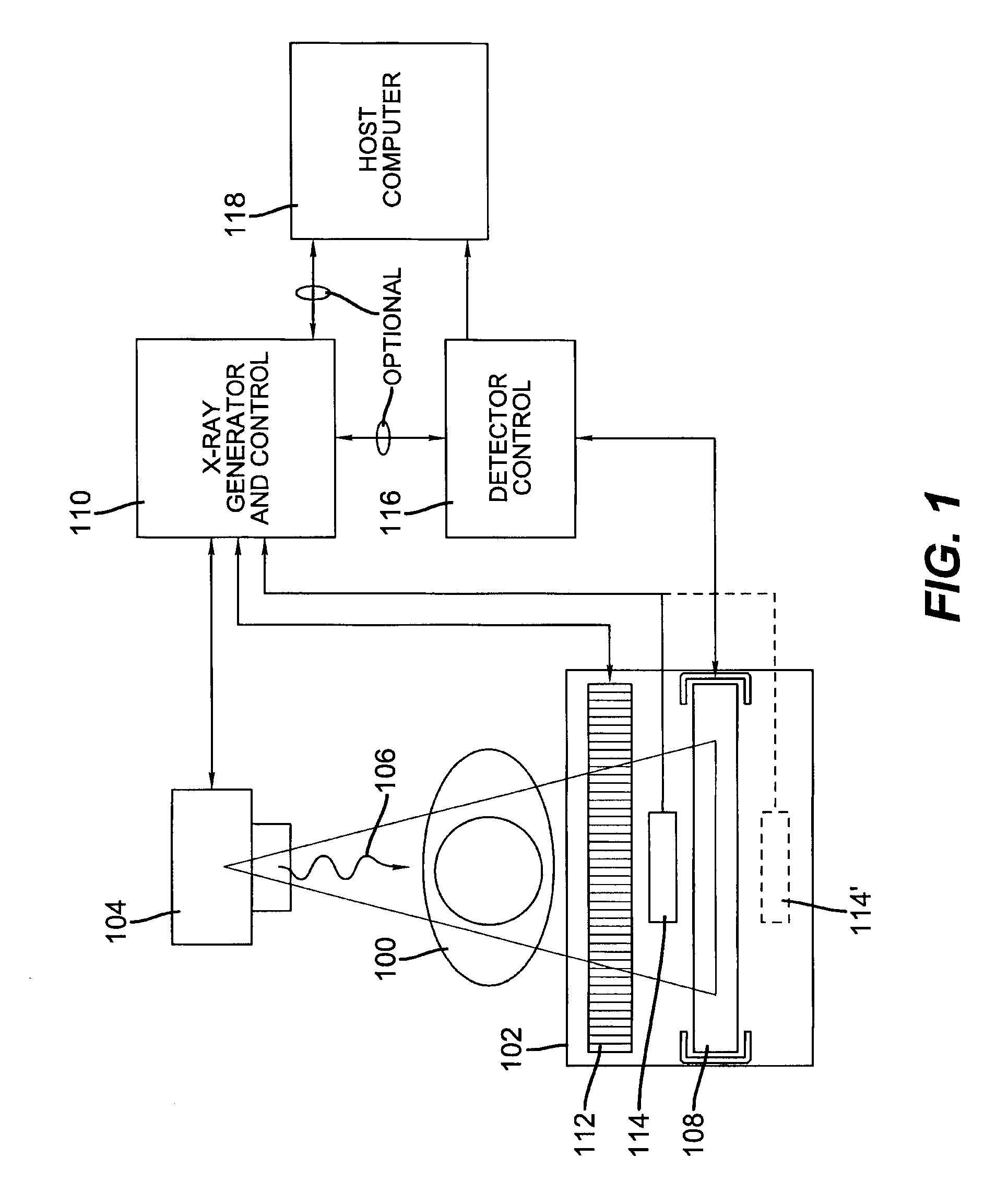
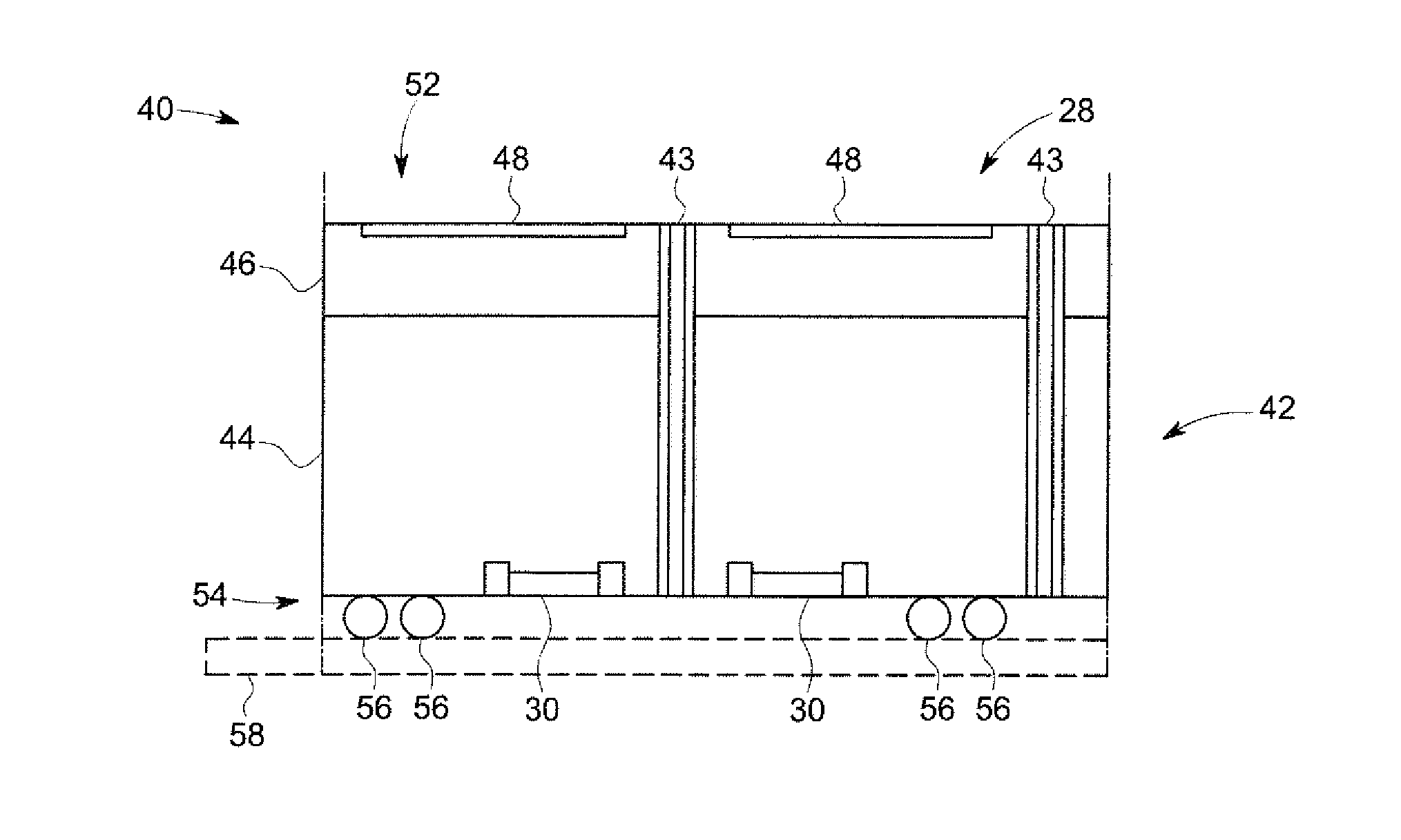
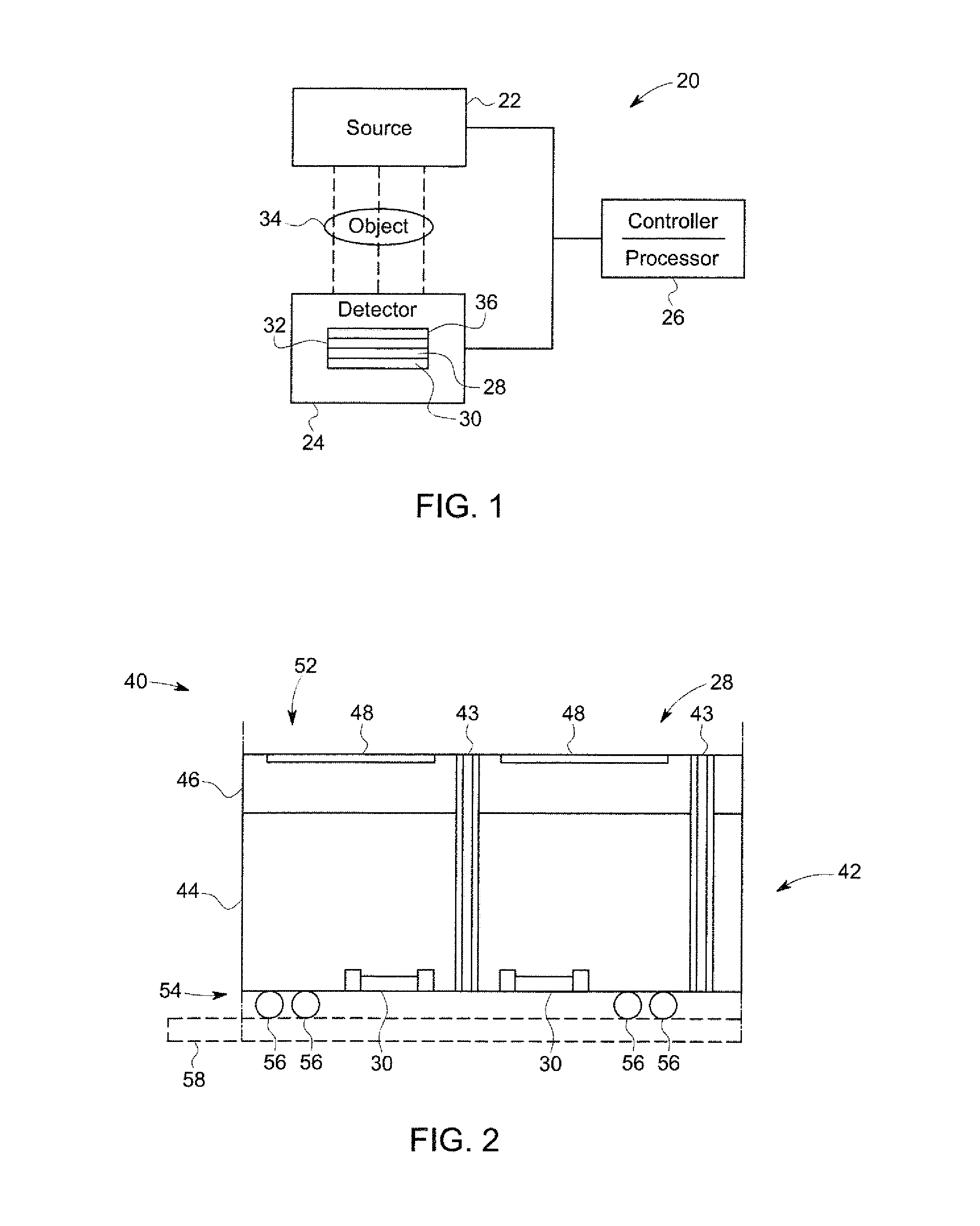
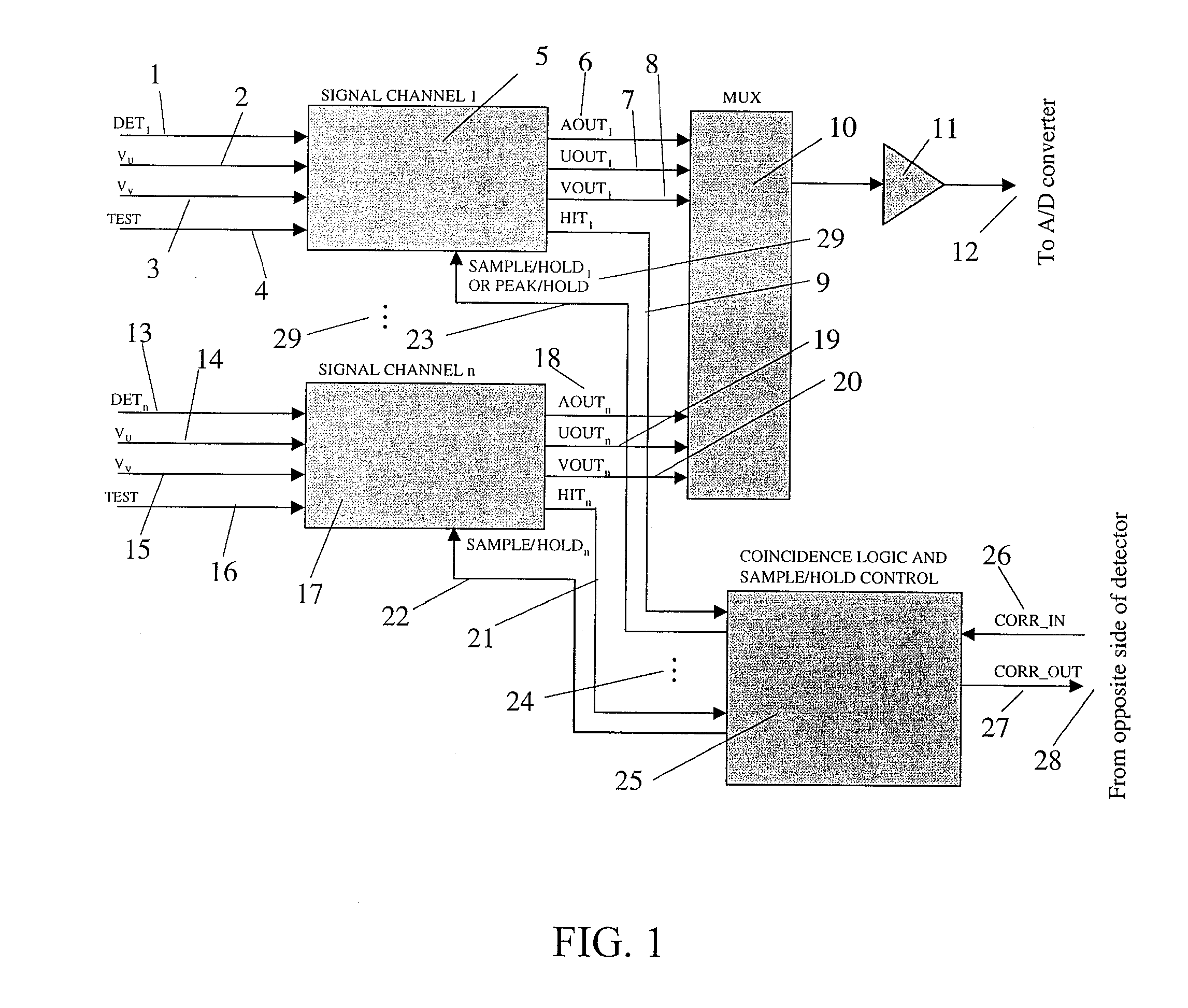
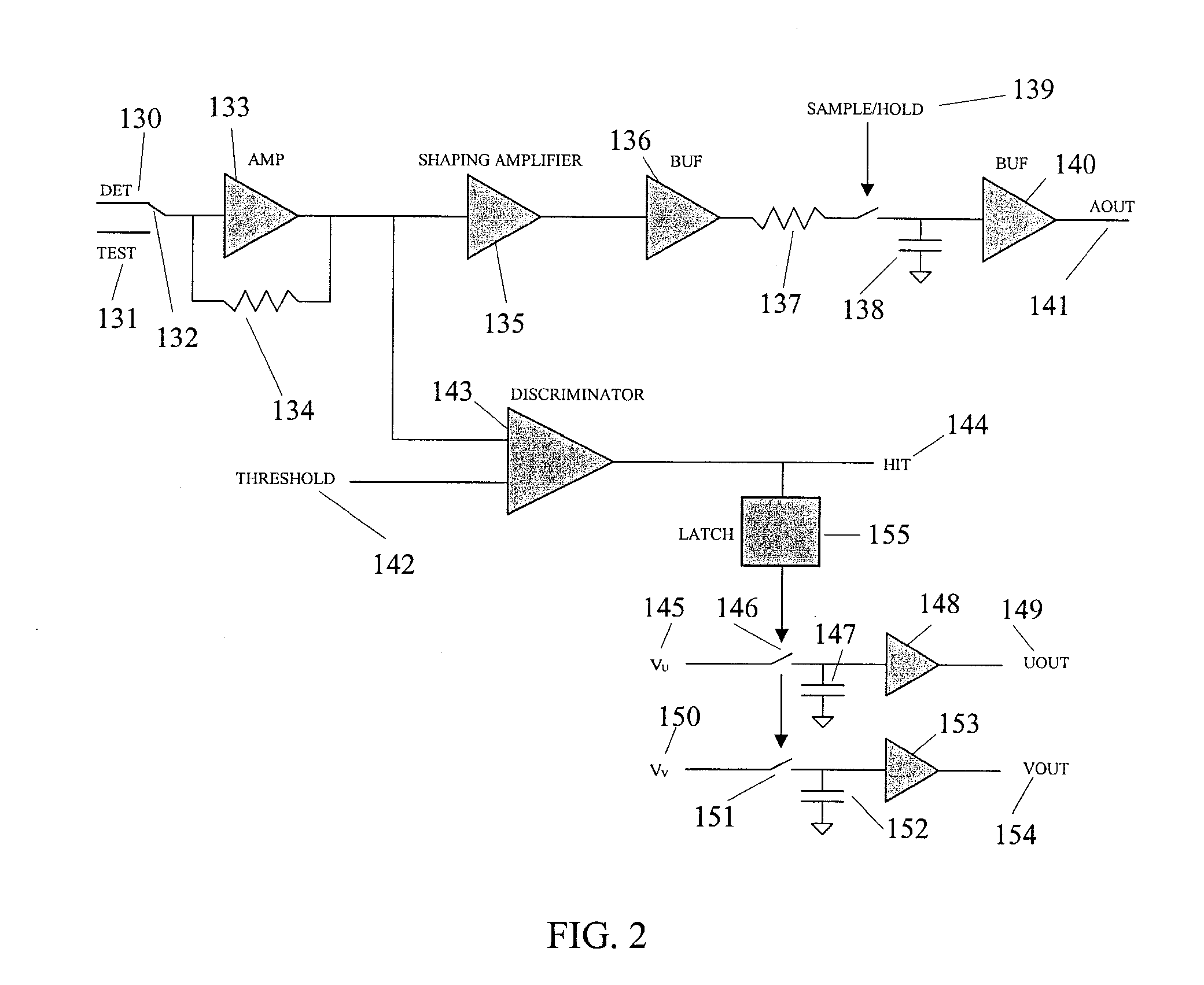
An integrated detector and signal processor (31) for ladar focal plane arrays (30) which internally compensates for variations in detector gain, noise, and aerosol backscatter. The invention (31) is comprised of a detector element (42) for receiving an input signal, a circuit (72) for generating a threshold based on the RMS noise level of the input signal, and a circuit (74) determining when the input signal is above that threshold. The detector element (42) is physically located in the interior of the detector array (30), while the signal processing circuitry (50) is located on the periphery of the array (30). In the preferred embodiment, the signal processor (31) also includes a circuit (56) for sampling the input signal and a circuit (58) storing multiple samples, allowing for multiple returns to be detected. In the preferred embodiment, the signal processor (31) can be operated in two modes: self triggered and externally triggered (range-gate mode). In the self triggered mode, the detector continually monitors and samples the incoming signal until a return is detected (by the thresholding circuit). In the range-gate mode, the detector stops sampling when it receives a signal from an external source. Once the data has been acquired, readout electronics (66) output the stored samples along with the stored "stopped" time code to an external computer (26).
Owner:RAYTHEON CO
Multi-functional control and entertainment systems
InactiveUS7466843B2Increase display areaReduce in quantityDashboard fitting arrangementsInstrument arrangements/adaptationsDriver/operatorIn vehicle
For use in vehicles, it is desirable to have multi-functional (also known as reconfigurable) controls in the center stack portion of the instrument panel in order to best provide electronic and telematic functions to the driver. Disclosed are methods and apparatus to allow reconfiguration of classical controls such as knobs, sliders, and switches most familiar to the vast majority of the motoring public which may, if desired, utilize conventional flat panel displays (e.g., LCD based) and conventional readout electronics and switching. Also disclosed are projection based controls and new forms of rear seat entertainment controls and related apparatus for minivans and other vehicles.
Owner:TURE TECH PARTNERS
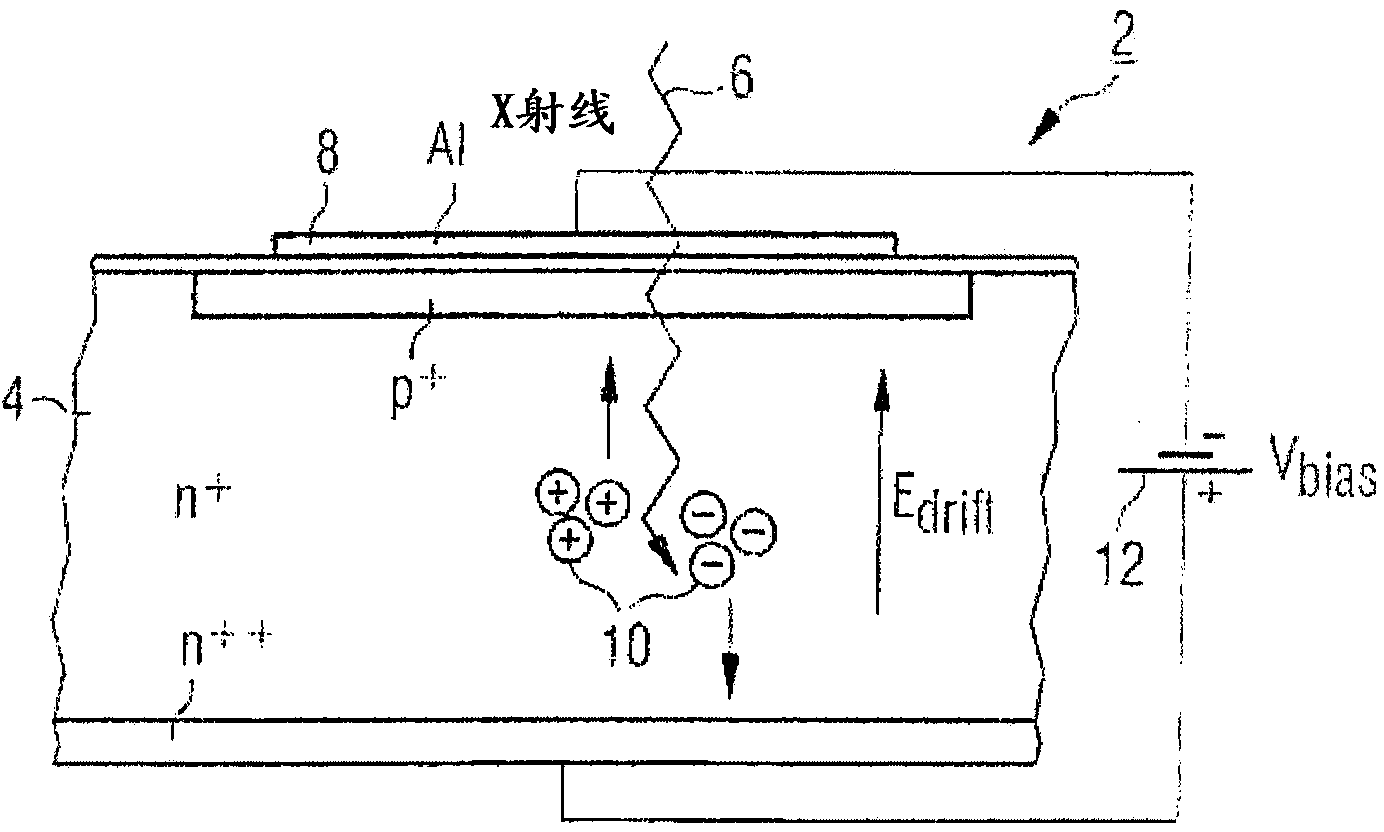
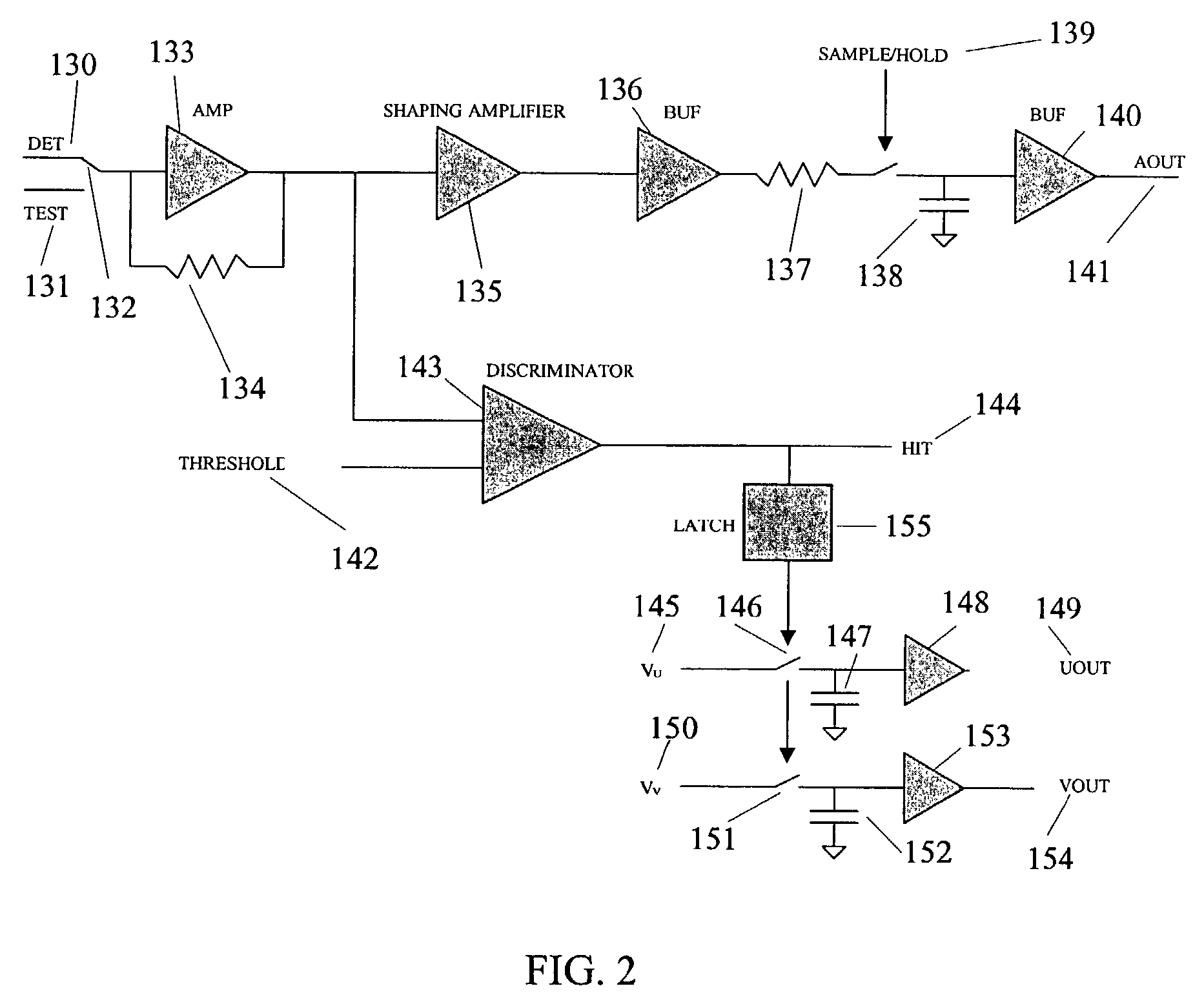
Readout electronics for photon counting and energy discriminating detectors
ActiveUS20100329425A1Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDiscriminatorData acquisition
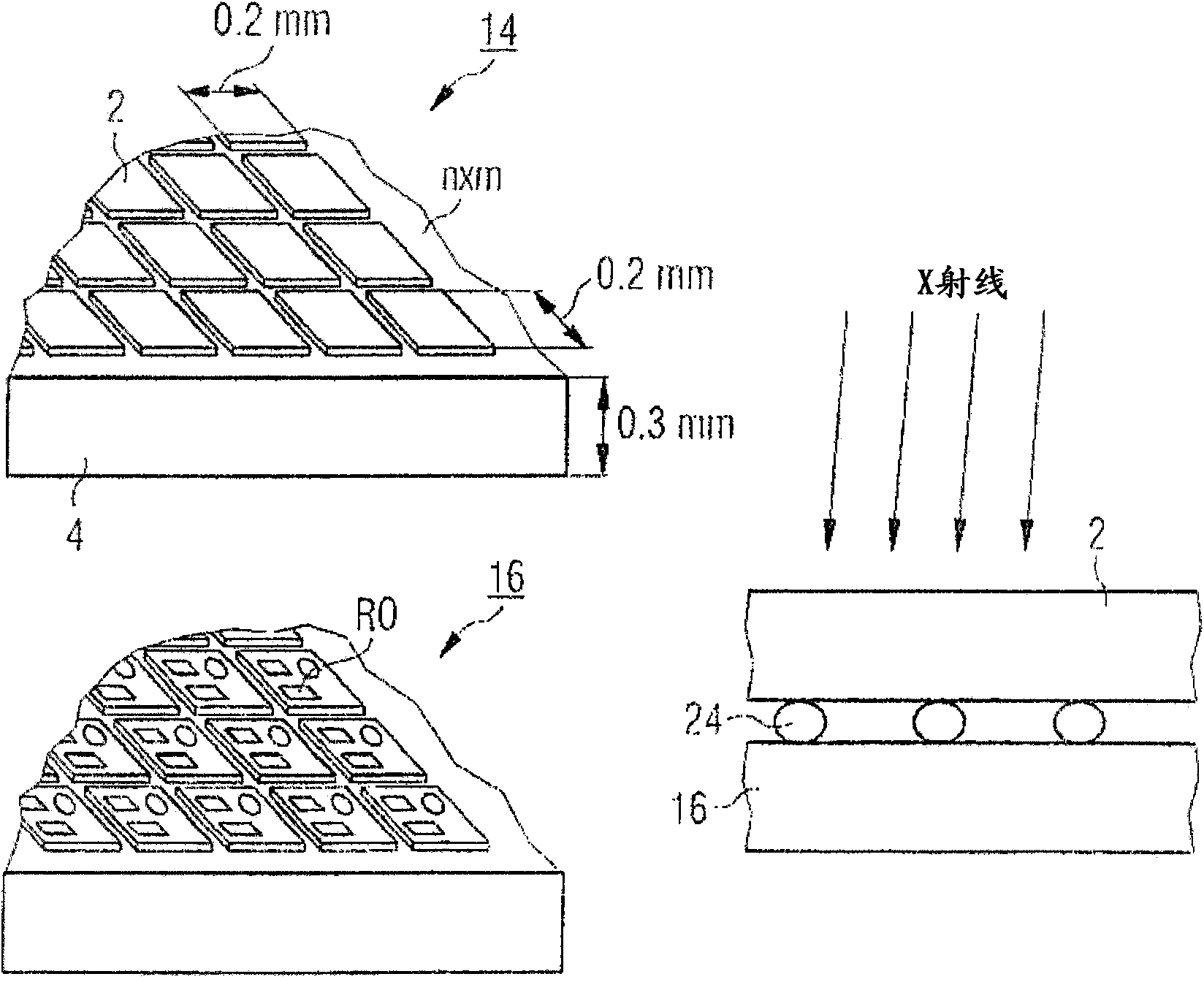
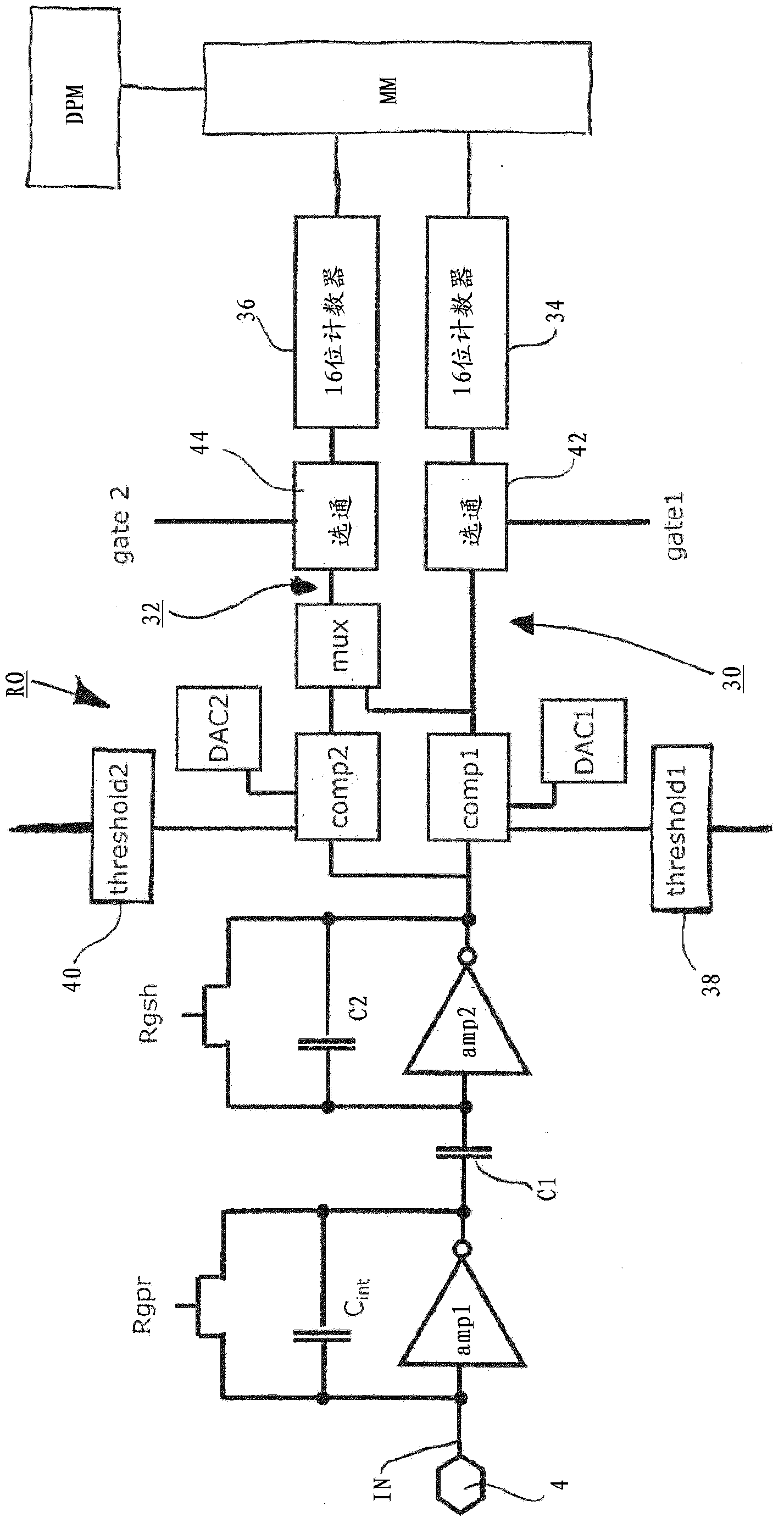
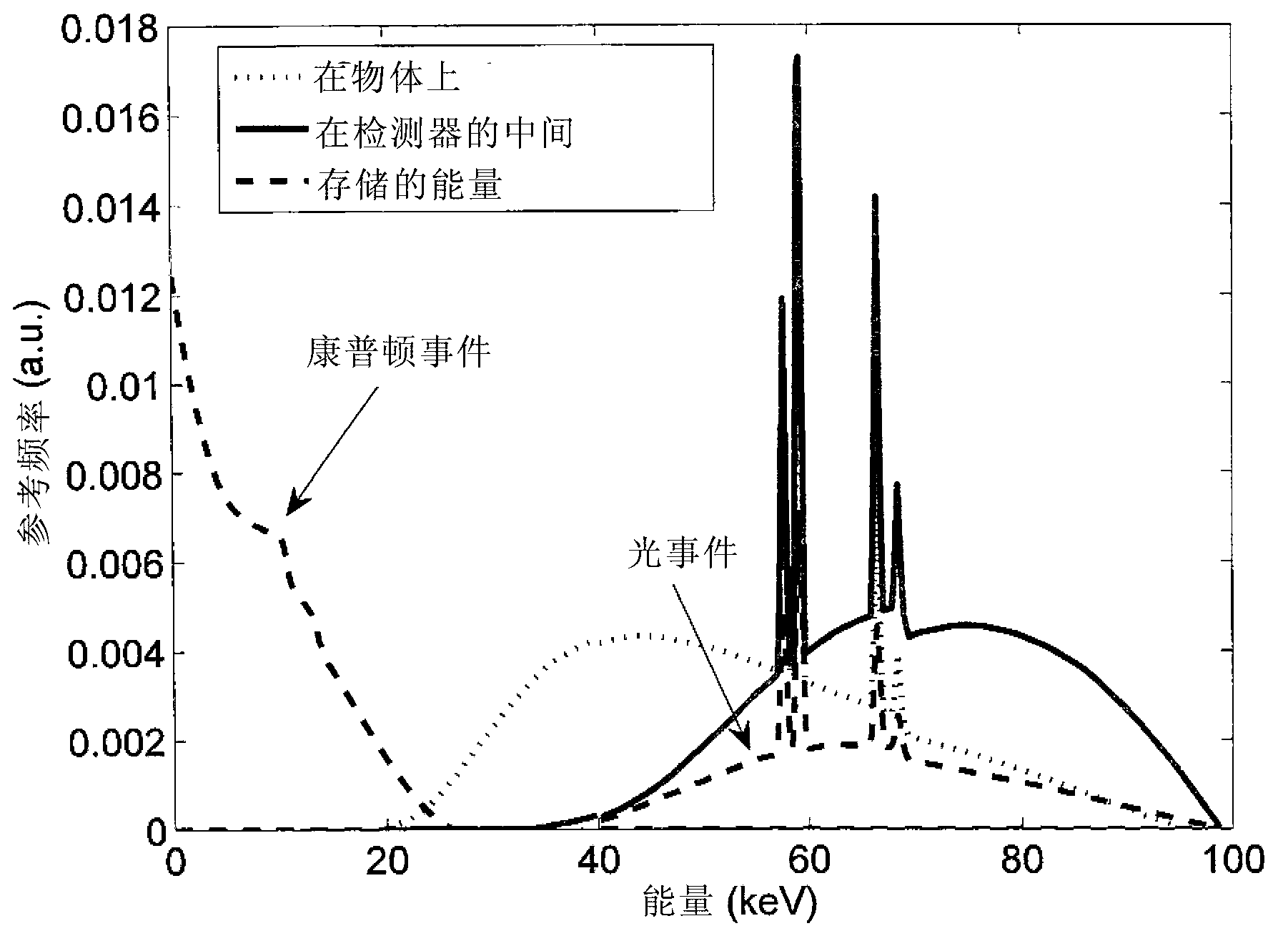
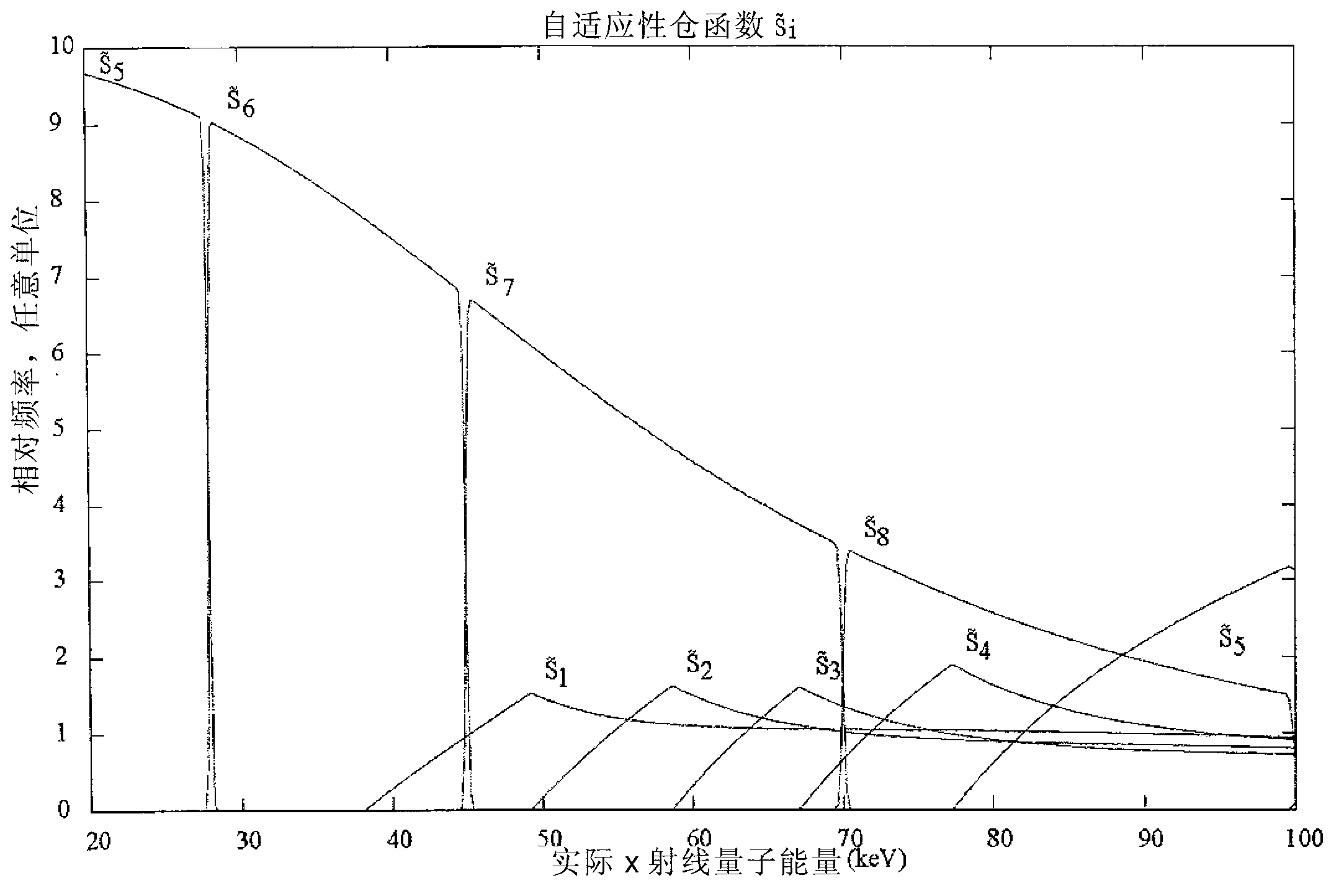
A data acquisition system includes a charge-sensitive amplifier (CSA) configured to receive a charge from an x-ray detector, the CSA includes a high-gain electronic voltage amplifier, an electrical energy storage device coupled with the amplifier, and an electrical resistor coupled with the amplifier. The data acquisition system includes a baseline sampling circuit configured to receive an output from the CSA and to sample a baseline signal from the CSA, at least one discriminator coupled to an output of the CSA and to an output of the baseline sampling circuit, the at least one discriminator configured to output a voltage if the output of the CSA exceeds a threshold, and a counter coupled to an output of the discriminator and configured to output a digital signal indicative of a photon count received at the x-ray detector and based on the output from the CSA and on the signal from the CSA.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Two-dimensional CMOS-based flat panel imaging sensor
InactiveUS20060192087A1Speed up preparationPerforms betterTelevision system detailsSolid-state devicesCMOSElectricity
The present invention provides a large-area flat plate detector. The detector includes a conversion layer which converts incident electromagnetic radiation into electric charges. The detector has a first electrode in communication with the conversion layer and a second electrode formed as a plurality of pixels arranged in a matrix. The detector includes an array of CMOS tiles, each of the tiles comprised of a plurality of pixels and having four side abuttability. The tile array is configured so that each of the tiles is separated by a spacing equal to about one pixel length from every adjacent tile and internally configured to allow for a high readout rate. Each of the tile pixels is arranged in electrical communication with and mapped in one-to-one fashion with the pixels of the second electrode. The readout electronics is capable of reading out CMOS provided data at a rate of at least 30 fps.
Owner:REAL TIME RADIOGRAPHY
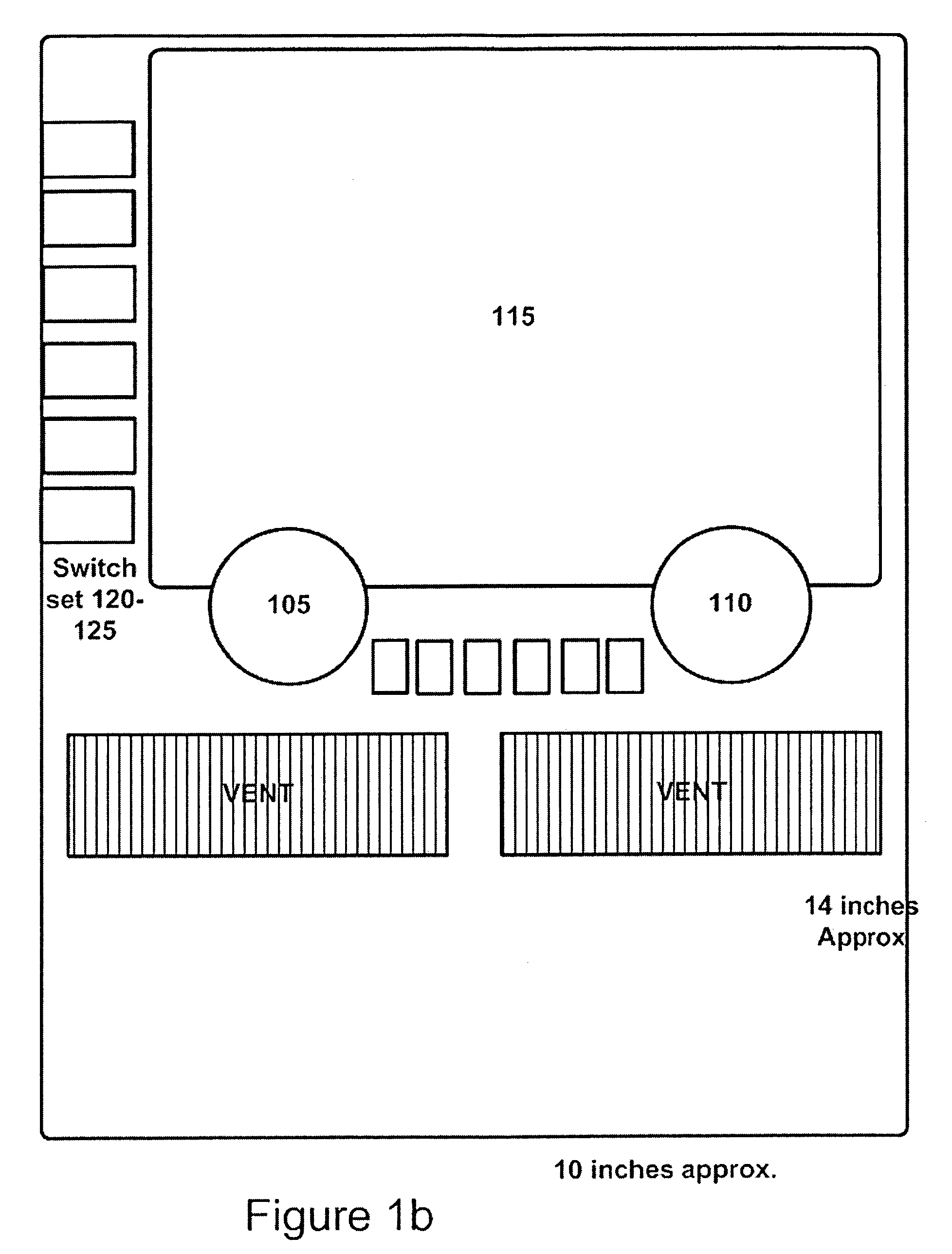
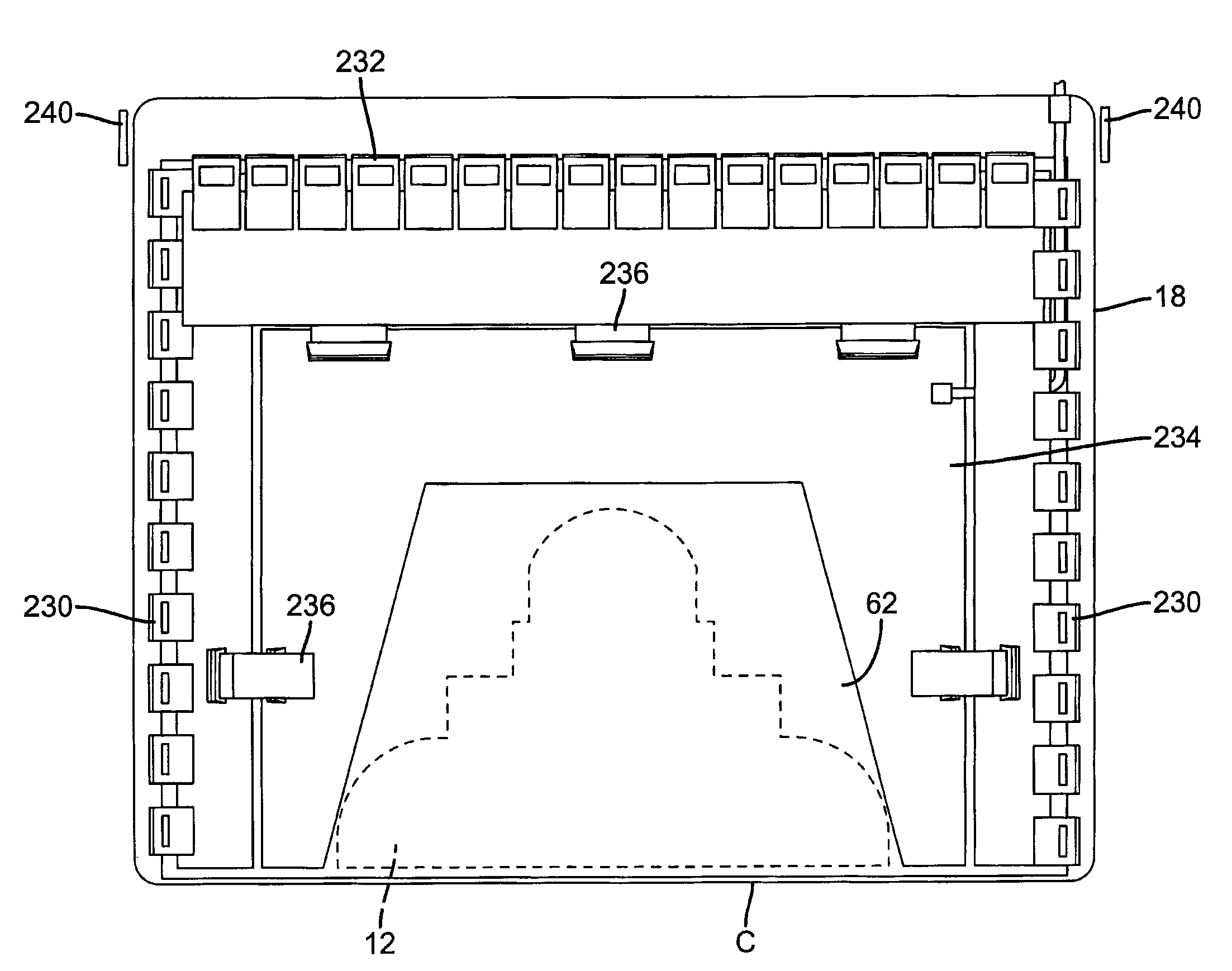
Retrofit digital mammography detector
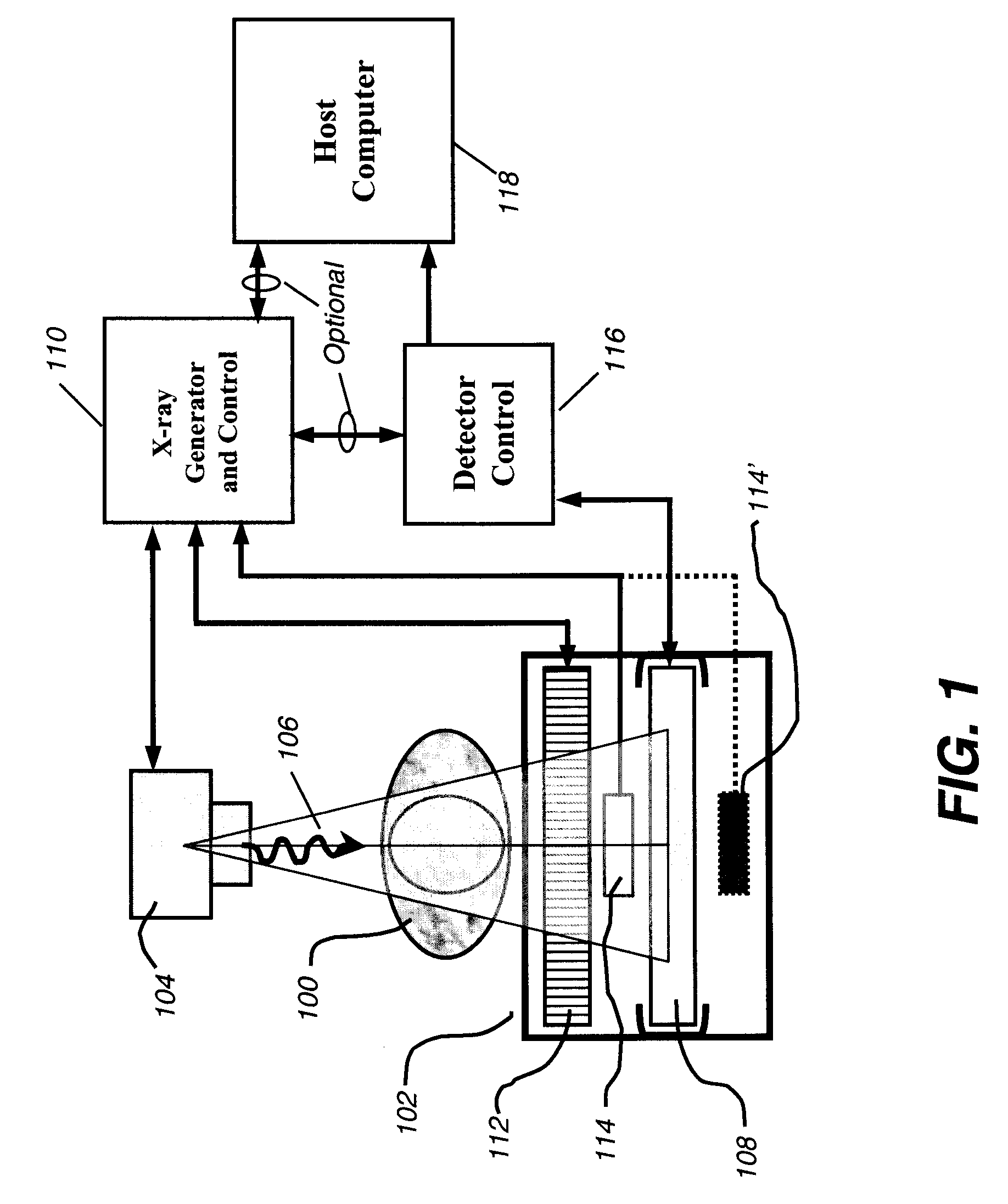
ActiveUS7429737B2Solid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansX-ray shieldDigital mammography
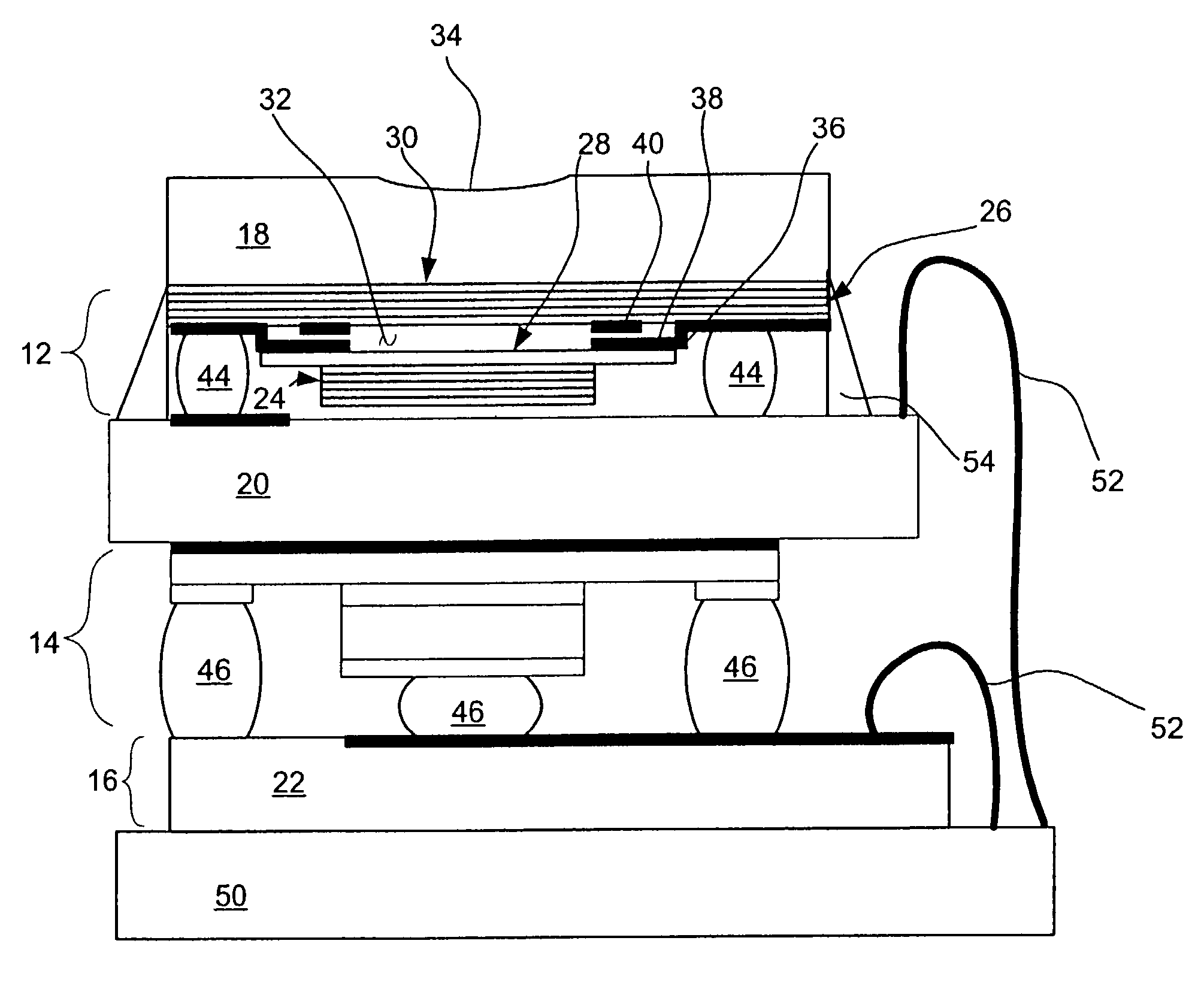
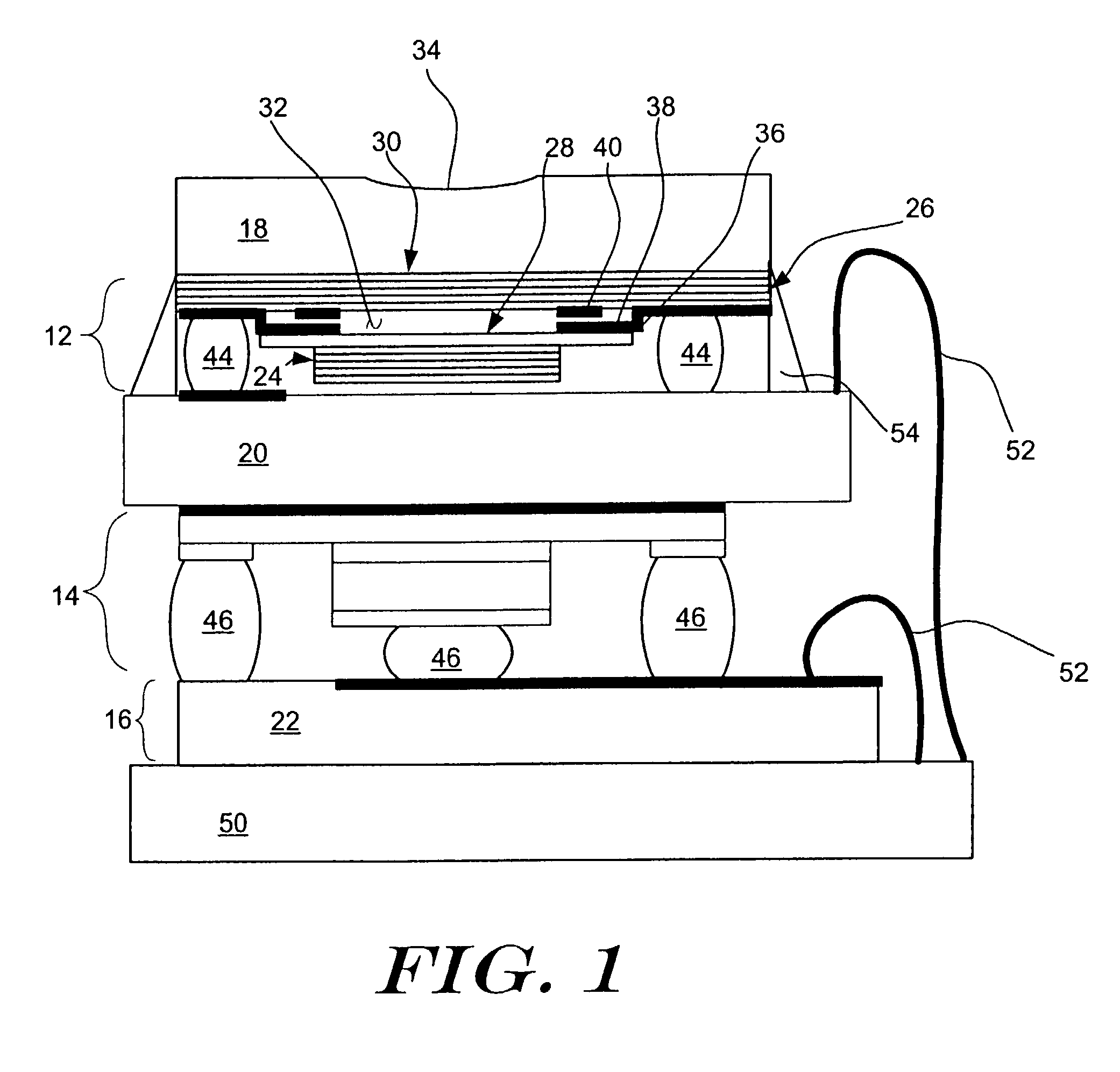
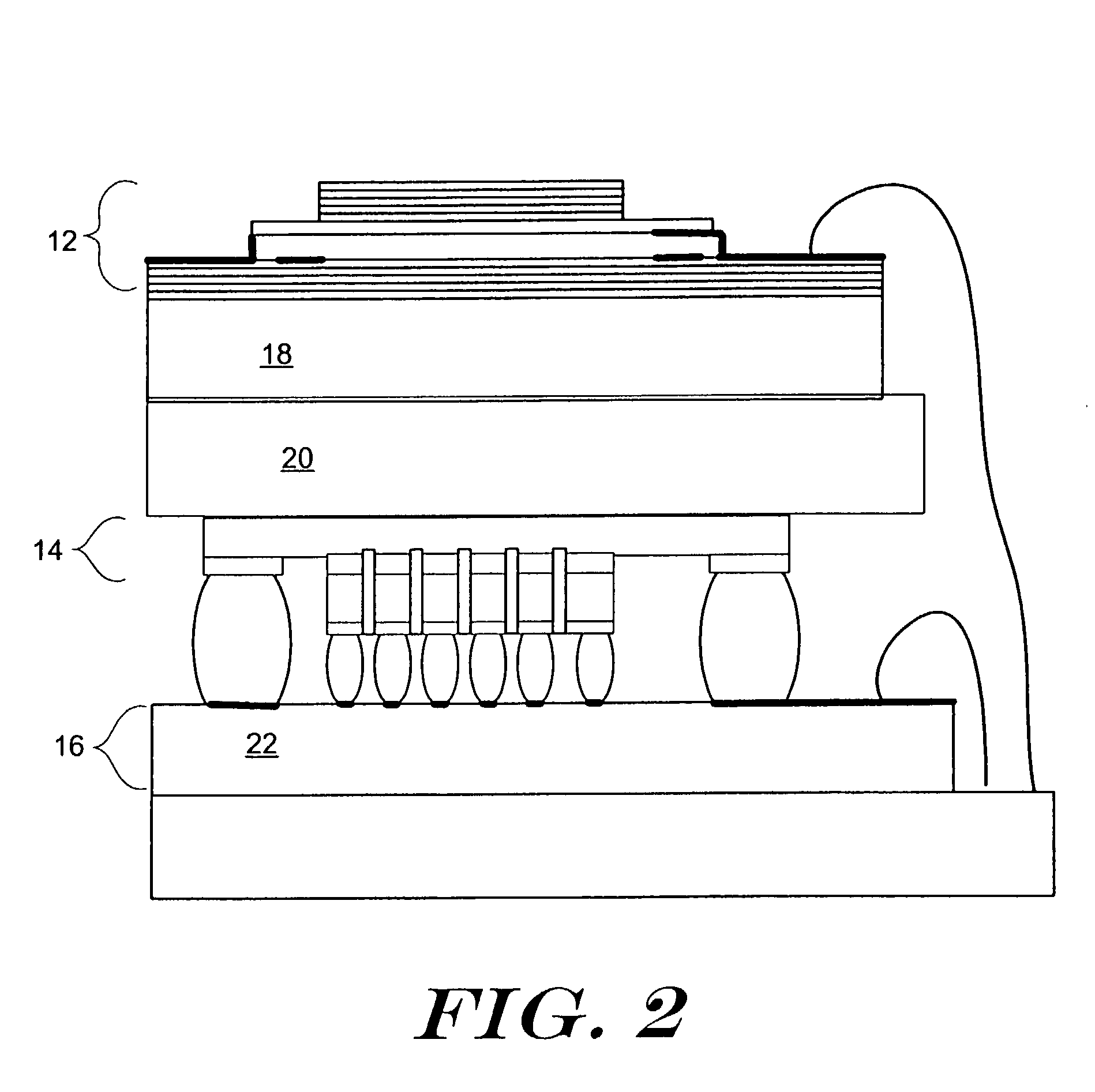
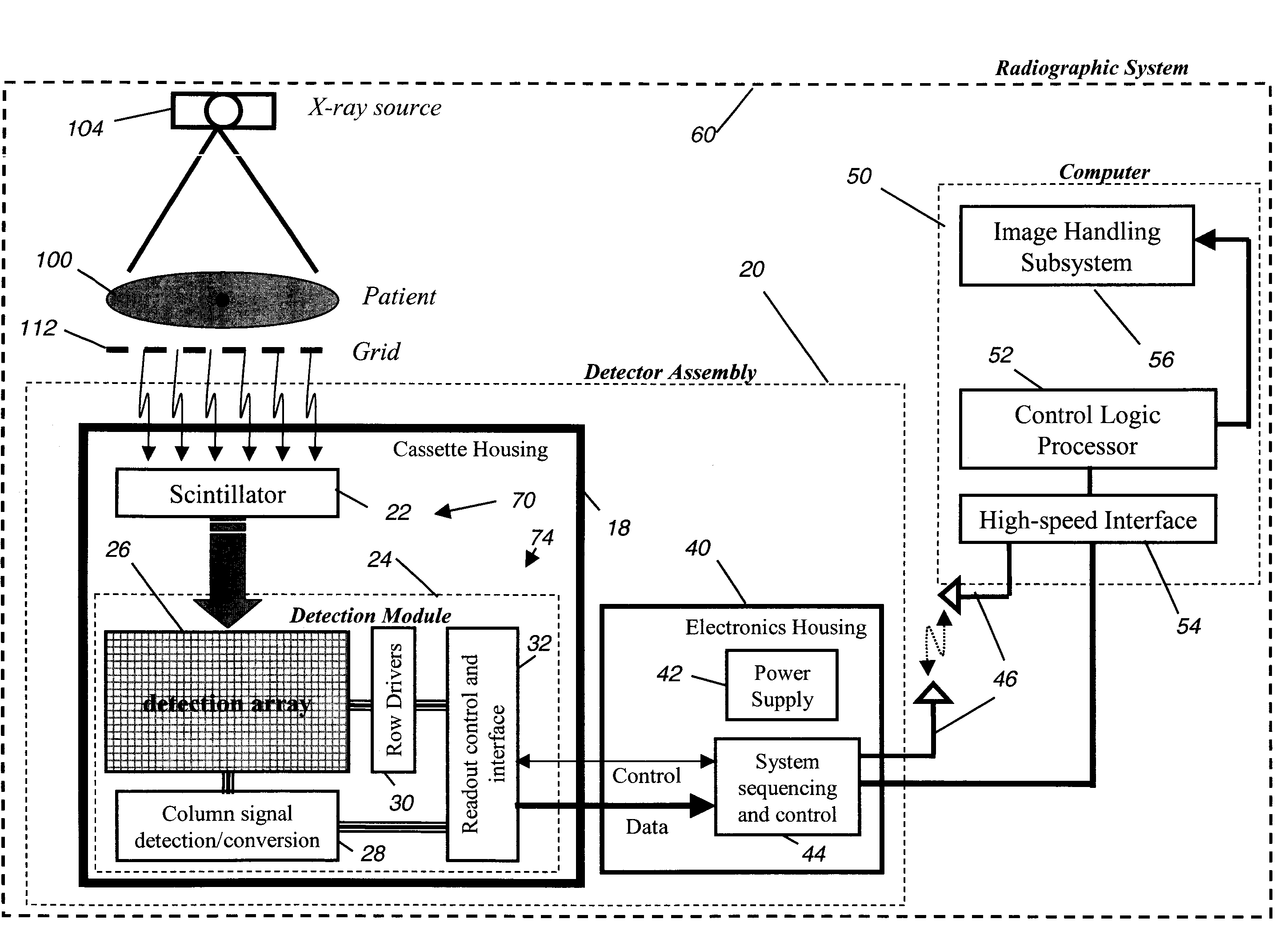
A digital radiography (20) detector has a first housing (18) having substantially the form factor of a film cassette and having a chest wall edge (C). The first housing (18) has an X-ray converter (70) with a detection array (26), each detector generating a signal according to an amount of radiation received. Readout electronics (74) are coupled with switching elements in the detection array for obtaining the signals therefrom. The readout electronics (74) include elements formed from crystalline silicon and are distributed toward outer edges of the first housing (18) and away from the chest wall edge (C). X-ray shielding selectively protects the readout electronics (74) and is located beneath a portion of the detection array. A second housing (40), electrically connected to the first housing (18) has a power source for the detector, readout and control electronics for obtaining signals provided from the detection array (26).
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
Spectrally tunable detector
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
Retrofit digital mammography detector
A digital radiography (20) detector has a first housing (18) having substantially the form factor of a film cassette and having a chest wall edge (C). The first housing (18) has an X-ray converter (70) with a detection array (26), each detector generating a signal according to an amount of radiation received. Readout electronics (74) are coupled with switching elements in the detection array for obtaining the signals therefrom. The readout electronics (74) include elements formed from crystalline silicon and are distributed toward outer edges of the first housing (18) and away from the chest wall edge (C). X-ray shielding selectively protects the readout electronics (74) and is located beneath a portion of the detection array. A second housing (40), electrically connected to the first housing (18) has a power source for the detector, readout and control electronics for obtaining signals provided from the detection array (26).
Owner:CARESTREAM HEALTH INC
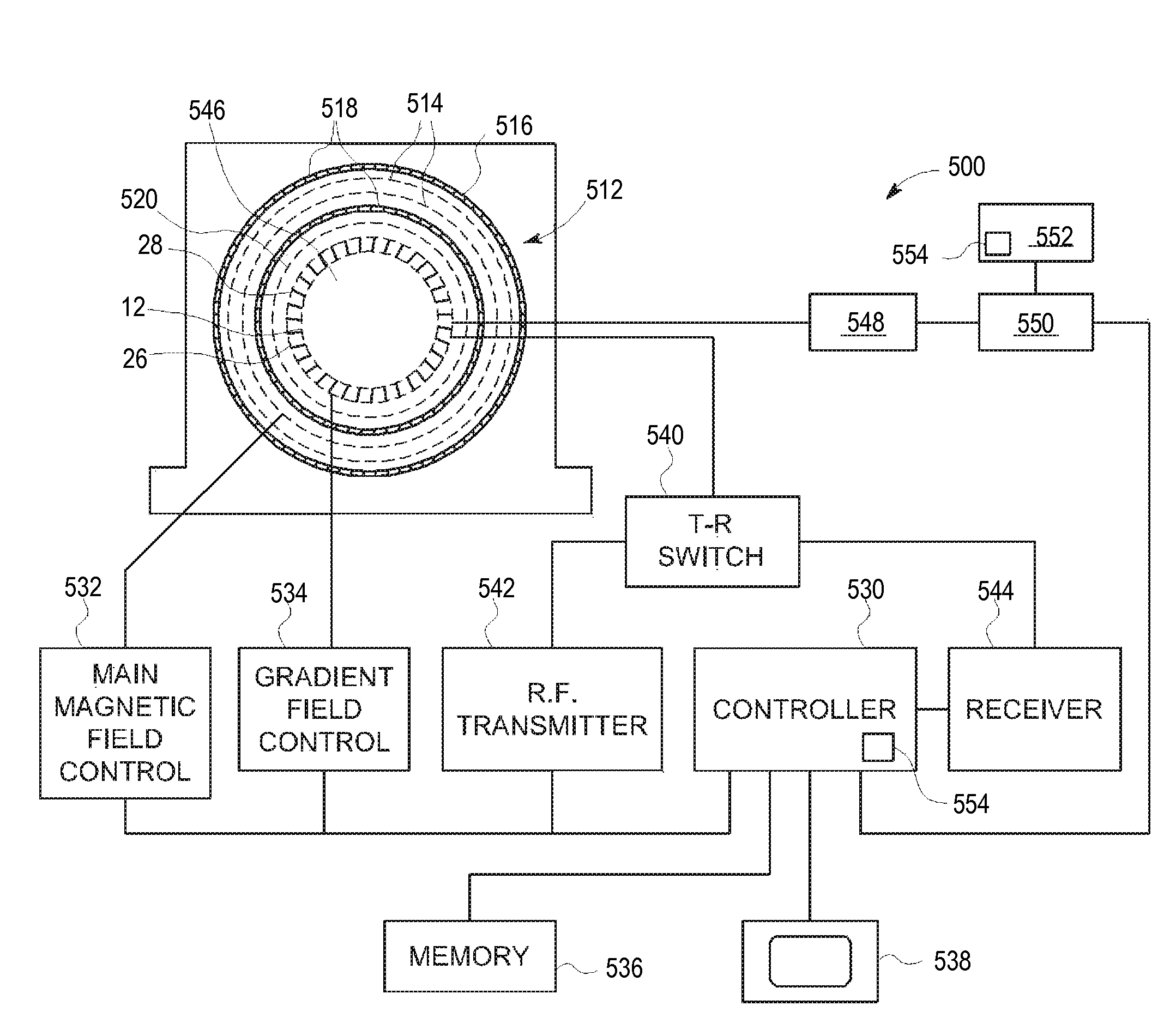
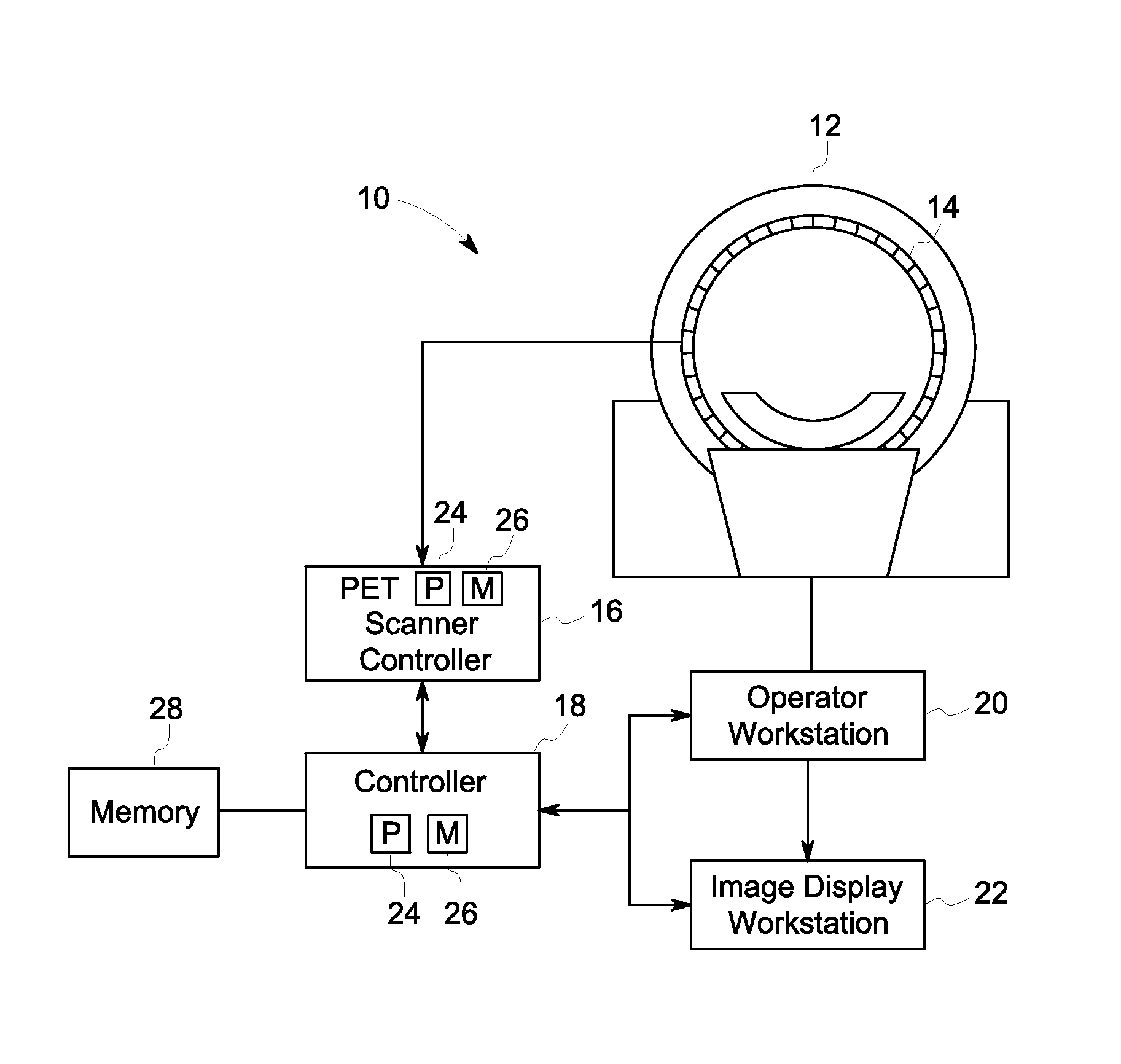
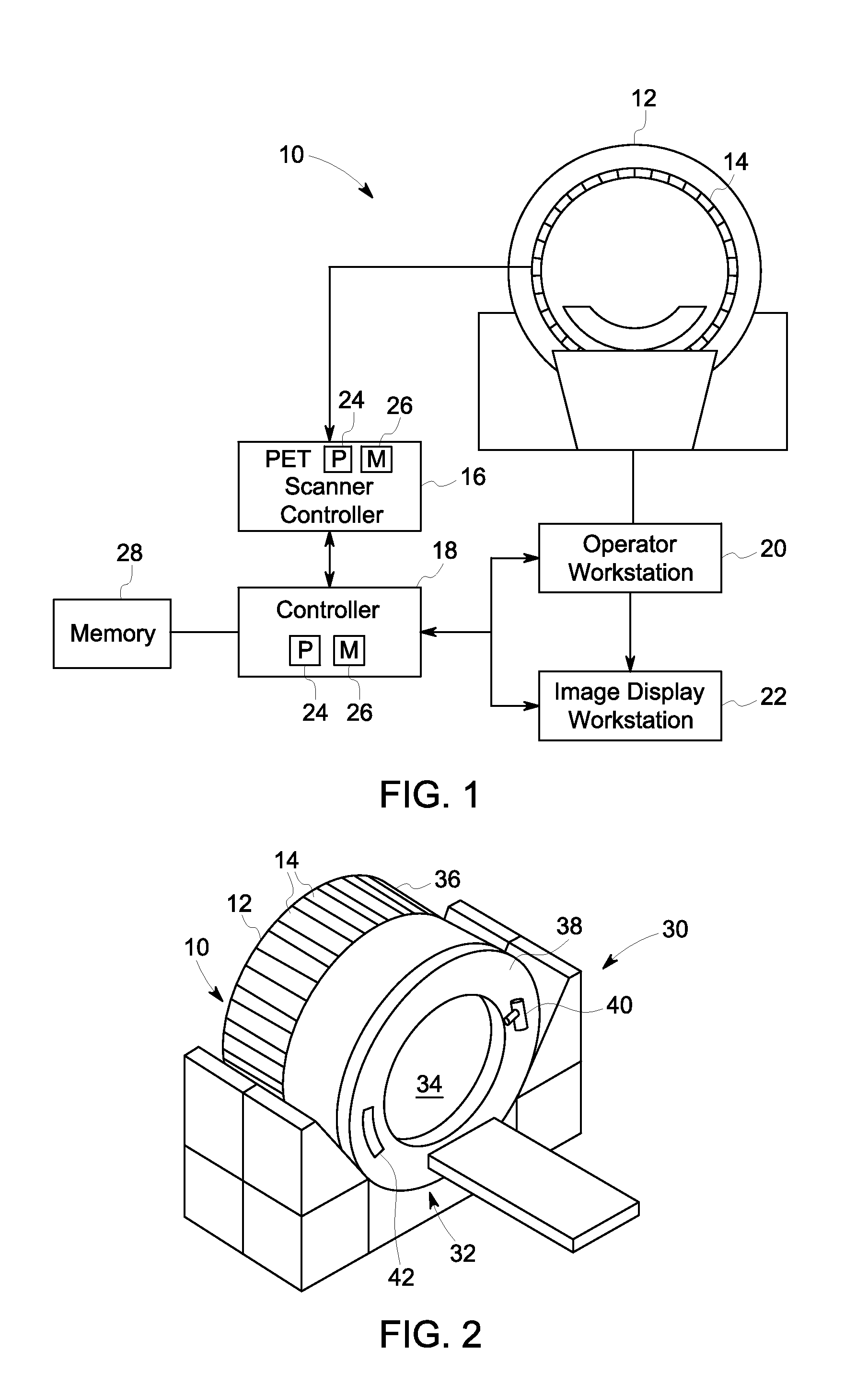
Positron emission tomogrpahy detector for dual-modality imaging
InactiveUS20130284936A1Magnetic measurementsMaterial analysis by optical meansEngineeringConductive materials
A Positron Emission Tomography (PET) detector assembly includes a cold plate having a first side and an opposite second side, the cold plate being fabricated from a thermally conductive and electrically non-conductive material, a plurality of PET detector units coupled to the first side of the cold plate, and a readout electronics section coupled to the second side of the cold plate. A radio frequency (RF) body coil assembly and a dual-modality imaging system are also described herein.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Single photon counting detector system having improved counter architecture
ActiveCN103430533ABuildup problems are reduced or completely eliminatedIncrease the number of countsTelevision system detailsMaterial analysis using wave/particle radiationMultiplexingPhoton counting detector
Owner:PAUL SCHERRER INSTITUT
Compact Endocavity Diagnostic Probes for Nuclear Radiation Detection
ActiveUS20110286576A1Improve image qualityEasy to carrySolid-state devicesEndoscopesNuclear radiationRadiation imaging
This invention relates to the field of radiation imaging. In particular, the invention relates to an apparatus and a method for imaging tissue or an inanimate object using a novel probe that has an integrated solid-state semiconductor detector and complete readout electronics circuitry.
Owner:HYBRIDYNE IMAGING TECH
Method and apparatus for micro-machined sensors using enhanced modulated integrative differential optical sensing
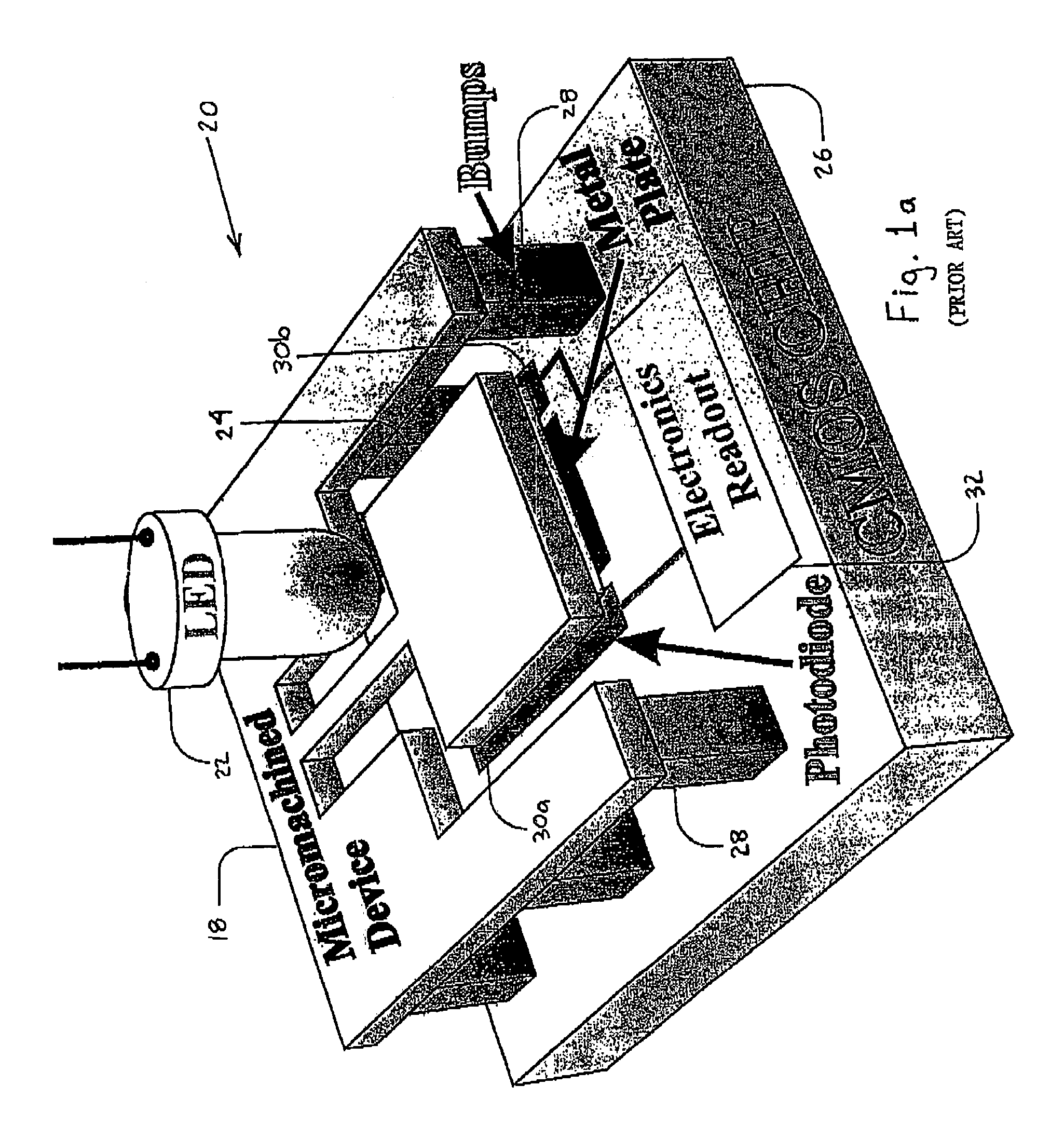
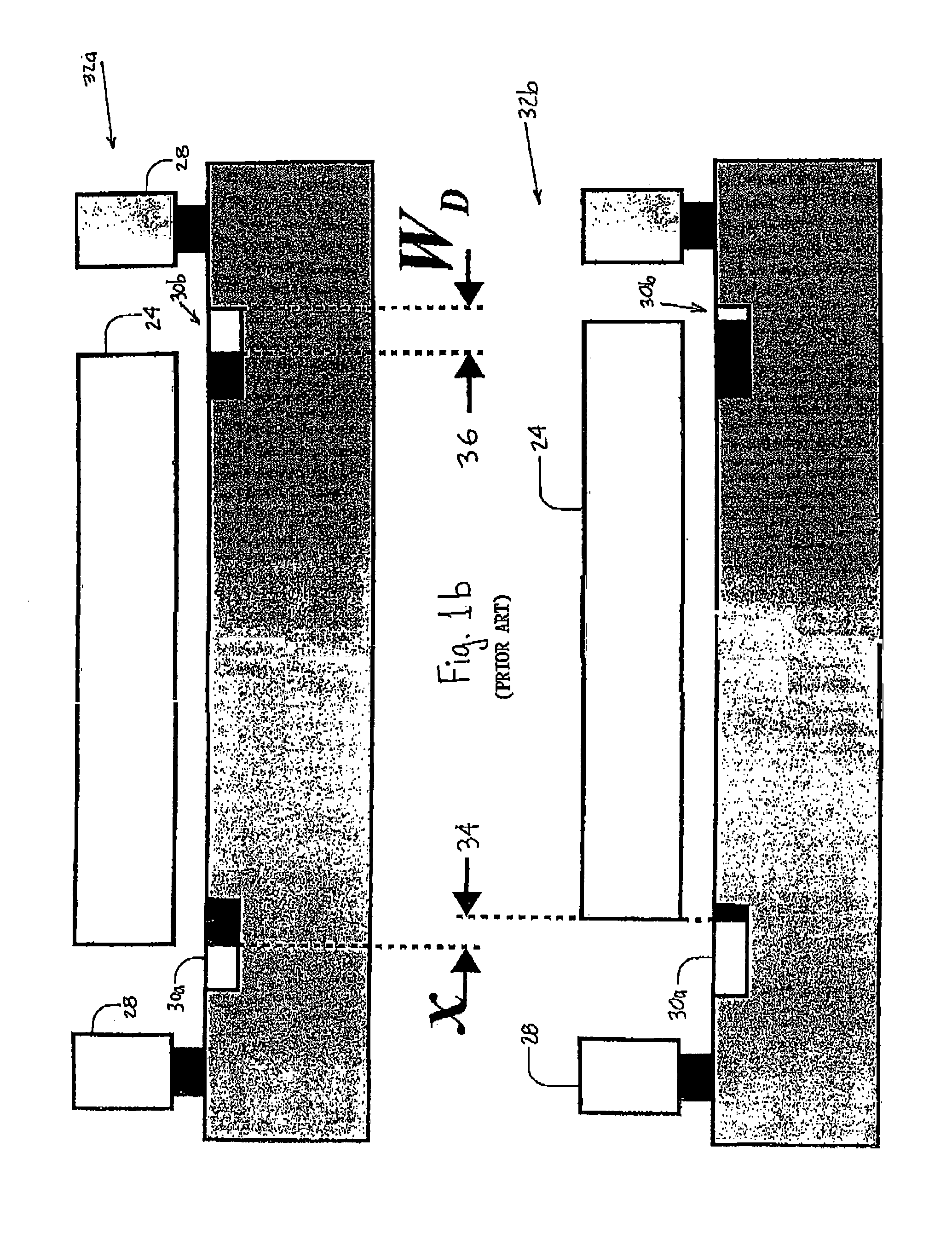
InactiveUS7091715B2Improved versionOvercome limitationsAcceleration measurement using interia forcesSemiconductor/solid-state device manufacturingOptical sensingPhotodiode
Method and apparatus for sensing the displacements of micromachined devices and sensors. The method is referred to as the enhanced modulated integrative differential optical sensing (EMIDOS). The target micromachined proof-mass, for which displacements are measured, includes a grid of slits. The micromachined device is bonded to a CMOS chip containing a matching photodiodes array and their readout electronics. The grid is aligned with the photociiodes. An illumination source, such as an LED, is then mounted above the micromachined device. A model for the noise equivalent displacement (NED), including mechanical, electrical and optical domains, as well as all noise sources is derived. The model predicts that displacements below 10−3 [√{square root over ( )}Hz] can be measured. The design comprises innovative inertial sensors, an accelerometer and a rategyroscope employing the EMIDOS. Performance models for the noise equivalent acceleration (NEA) and noise equivalent rate (NER) are also derived. The models show that an accelerometer with a very low NEA can be realized.
Owner:TECHNION RES & DEV FOUND LTD +1
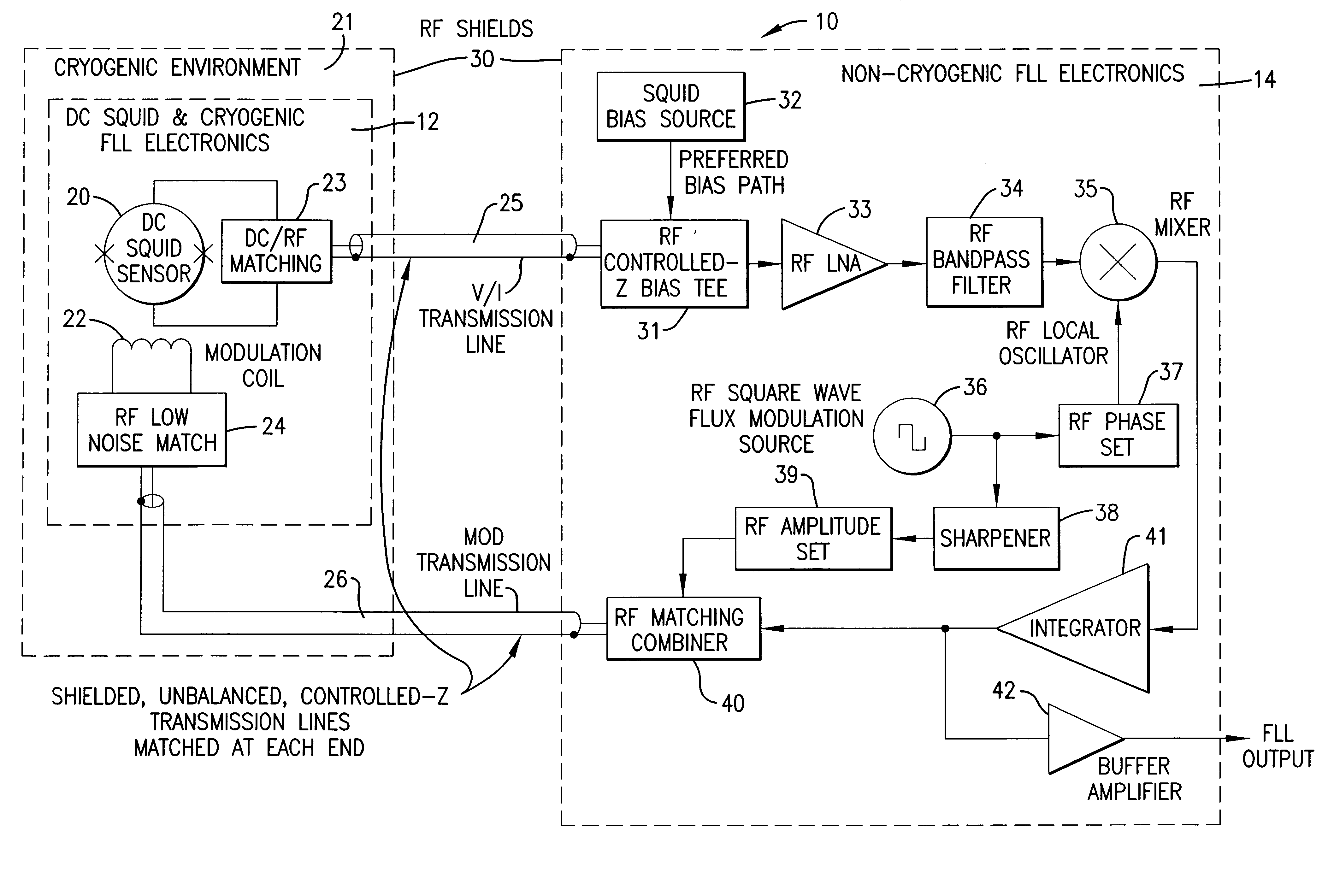
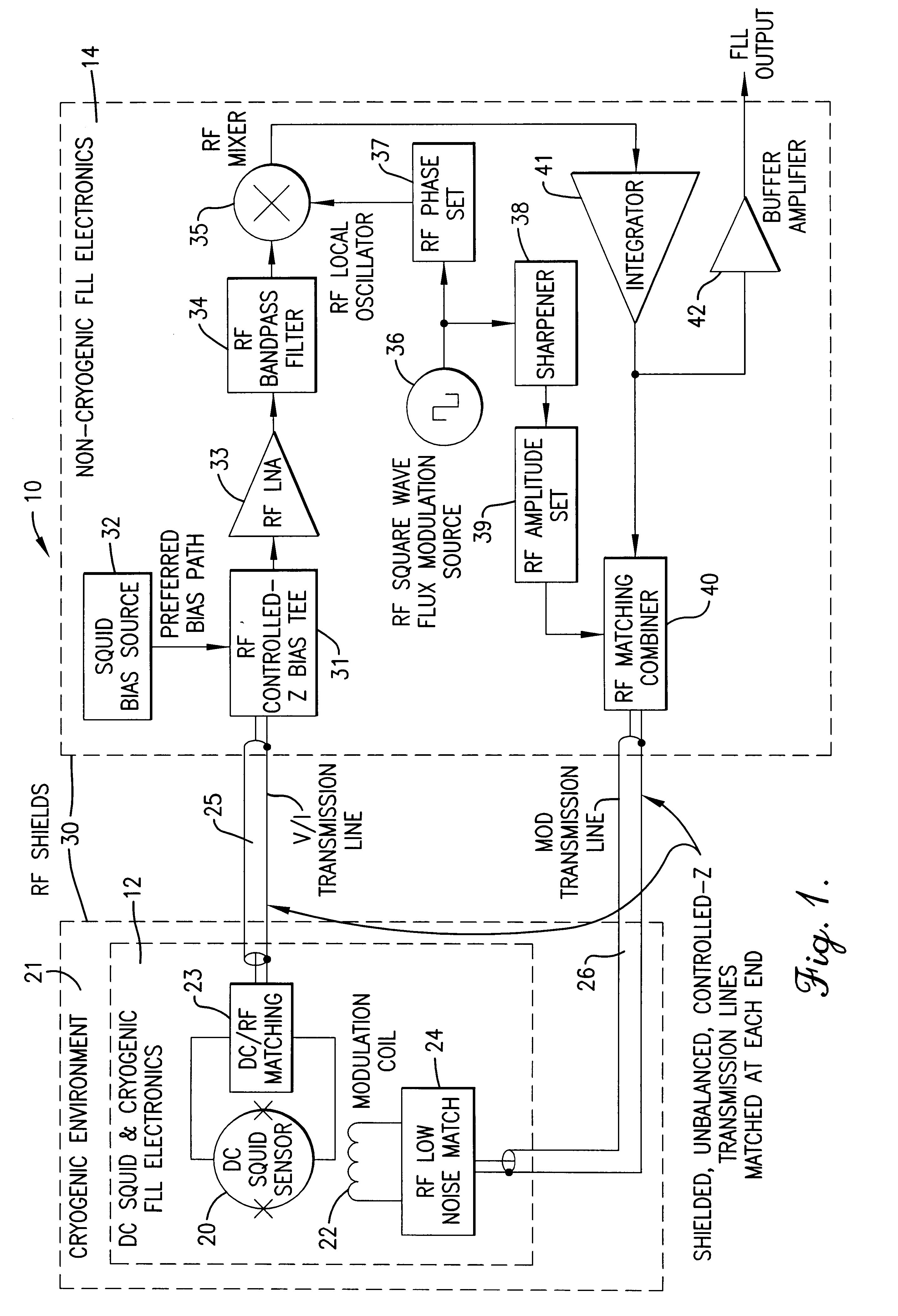
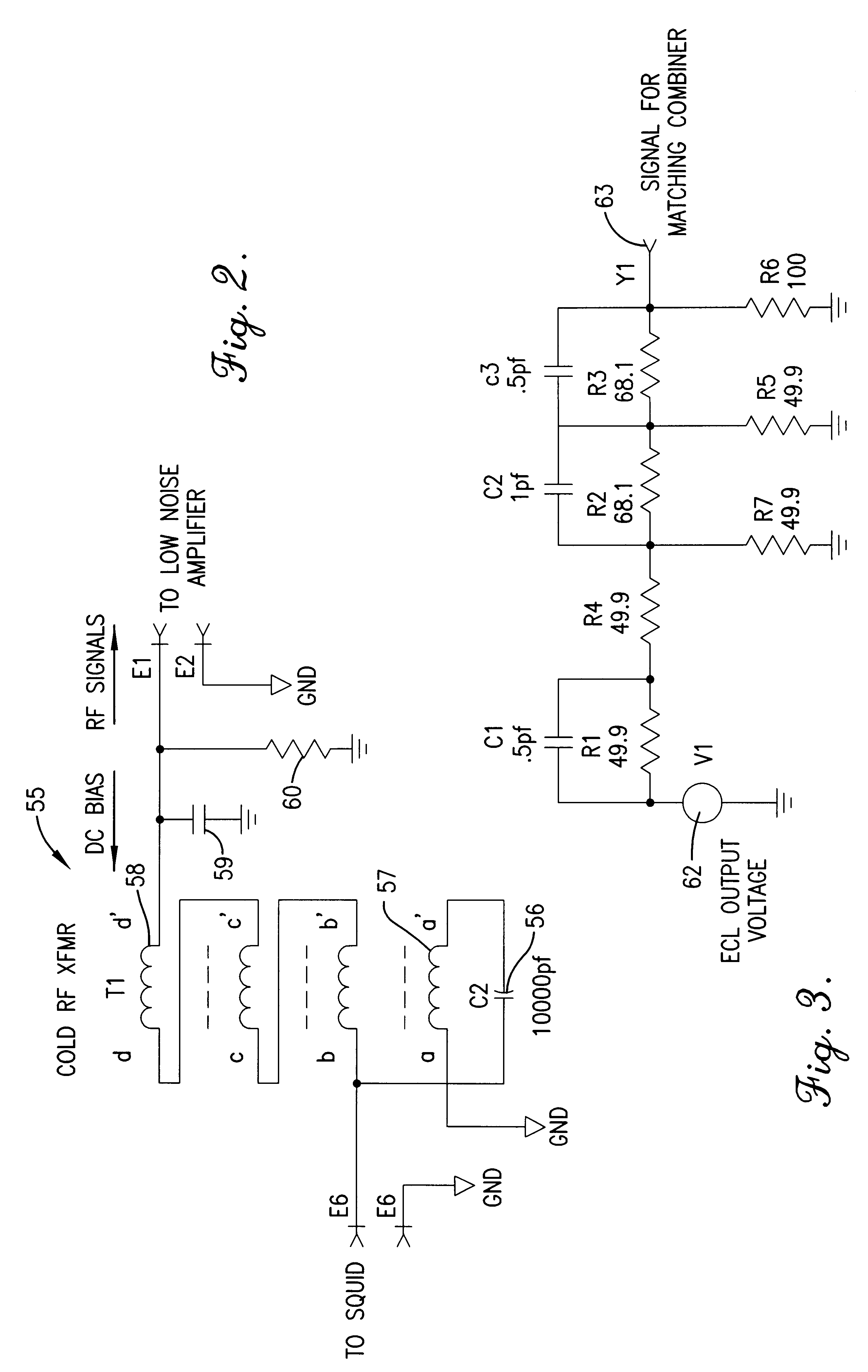
Fast flux locked loop
InactiveUS6448767B1Benefit control loop DC stabilityReduce effective amplifier input noiseMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesPulse generation by super conductive devicesElectricityMagnetic measurements
A flux locked loop for providing an electrical feedback signal, the flux locked loop employing radio-frequency components and technology to extend the flux modulation frequency and tracking loop bandwidth. The flux locked loop of the present invention has particularly useful application in read-out electronics for DC SQUID magnetic measurement systems, in which case the electrical signal output by the flux locked loop represents an unknown magnetic flux applied to the DC SQUID.
Owner:HONEYWELL INT INC
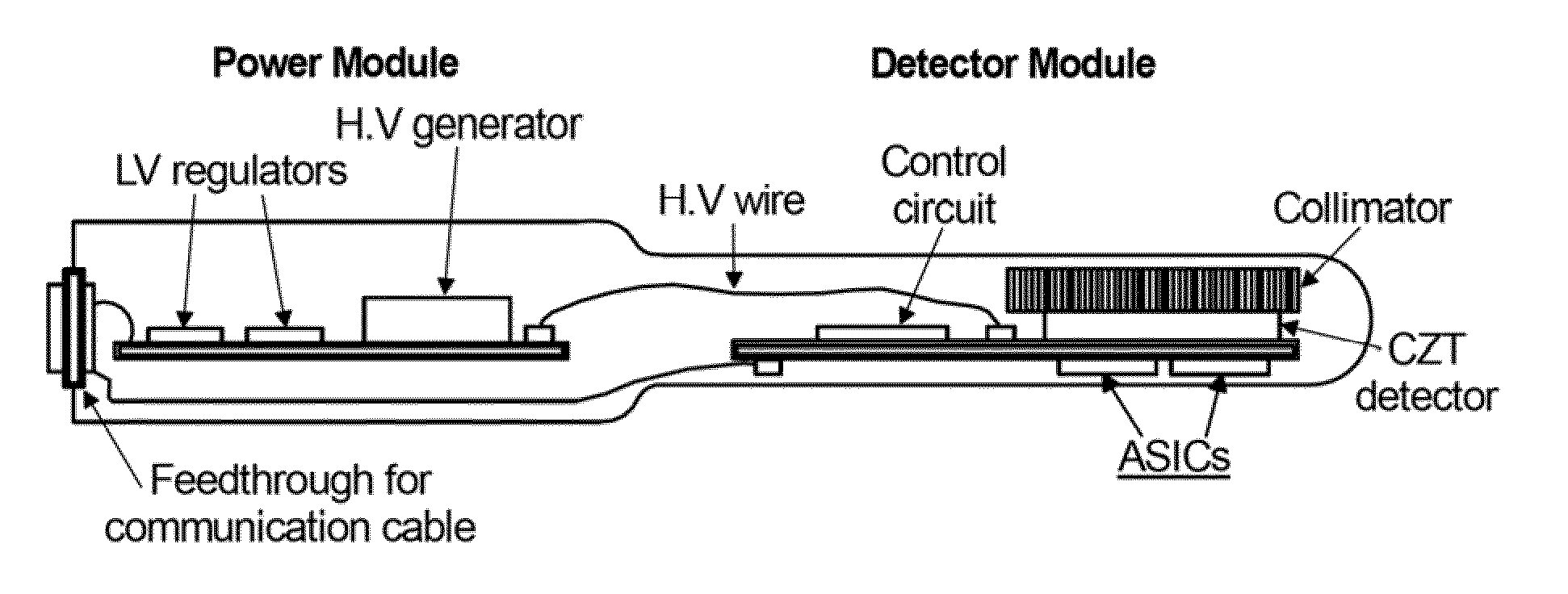
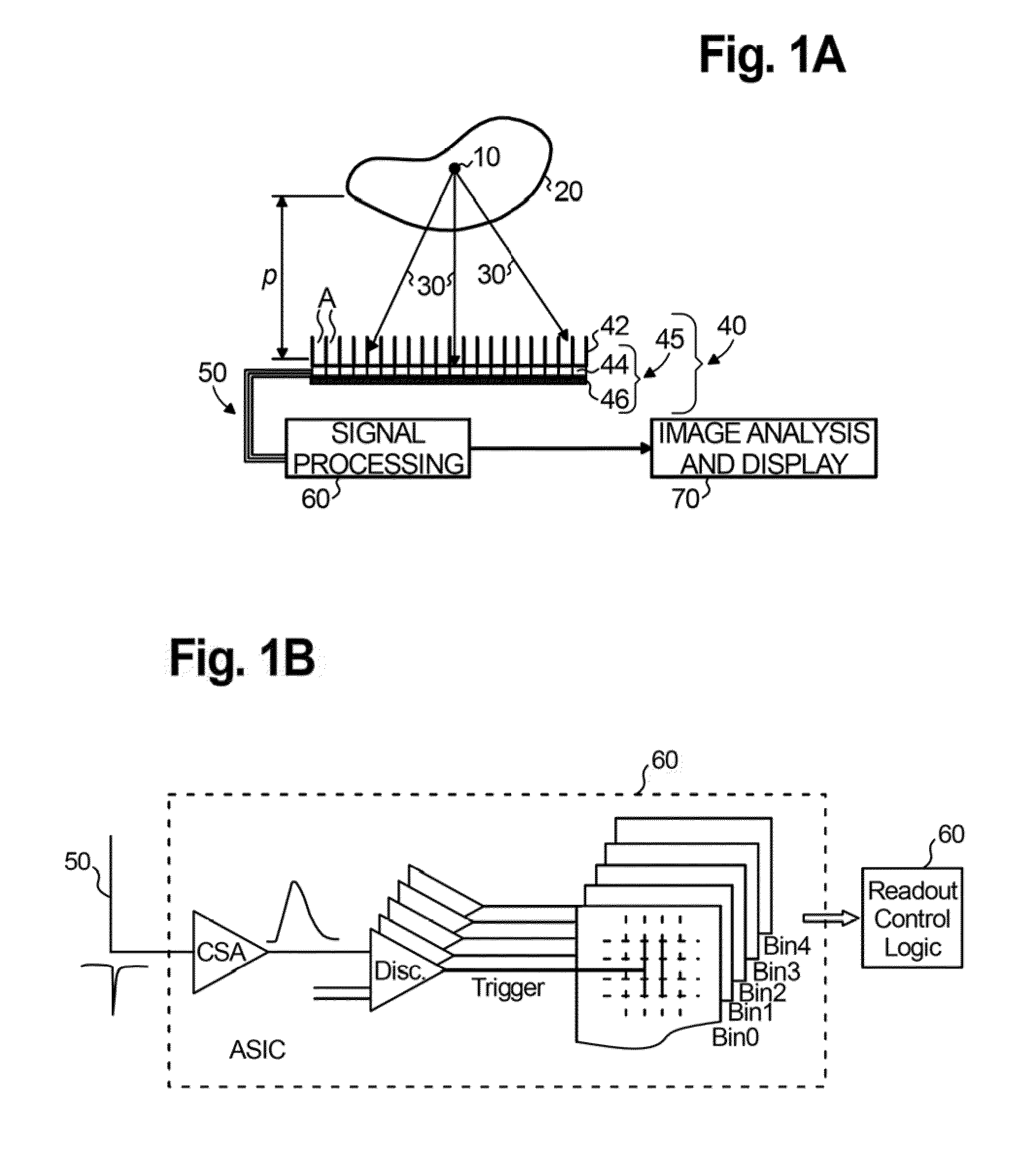
X-ray and gamma ray detector readout system
ActiveUS7818047B2Uniform spatial resolutionImprove efficiencySolid-state devicesMaterial analysis by optical meansDiscriminatorX-ray
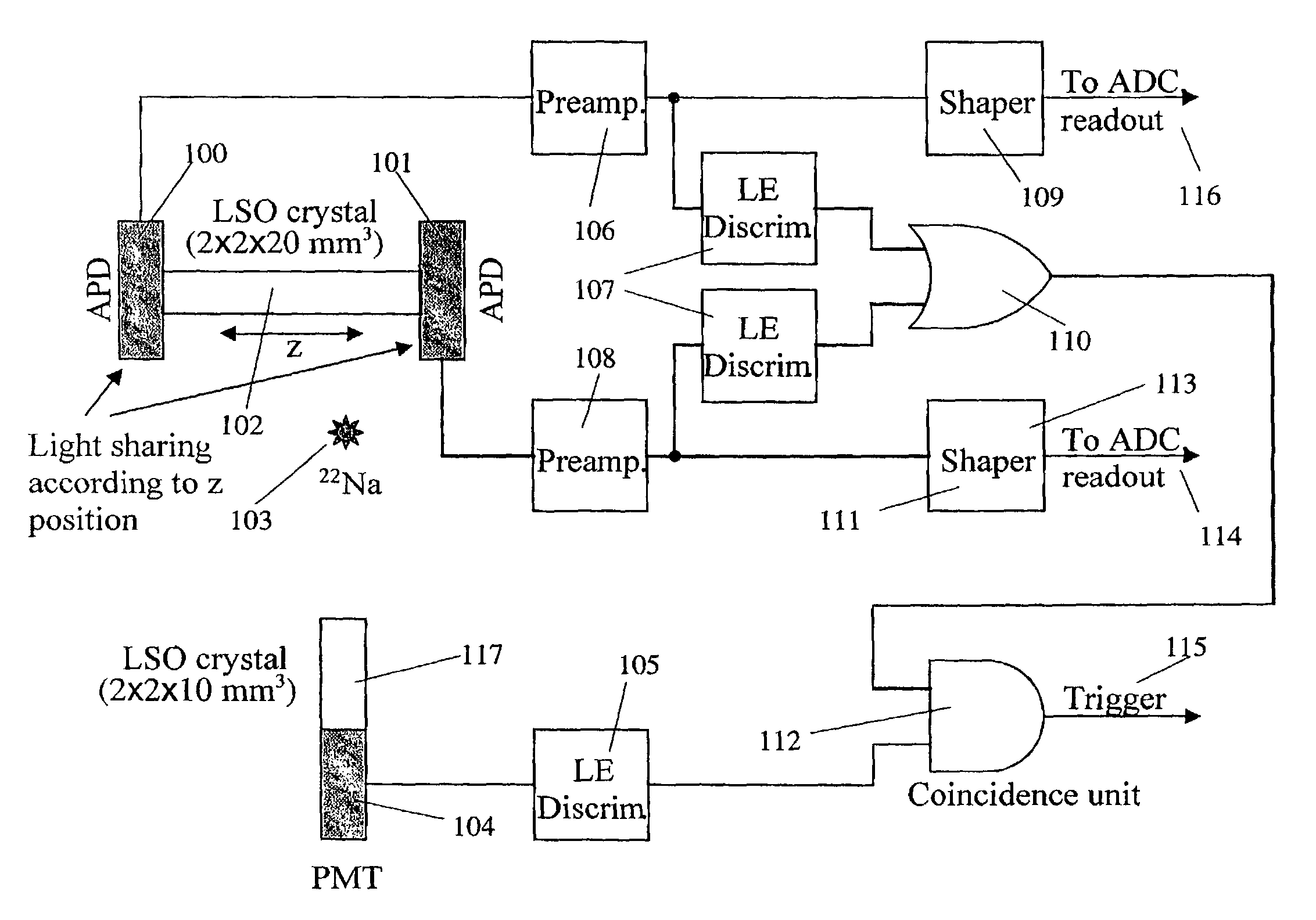
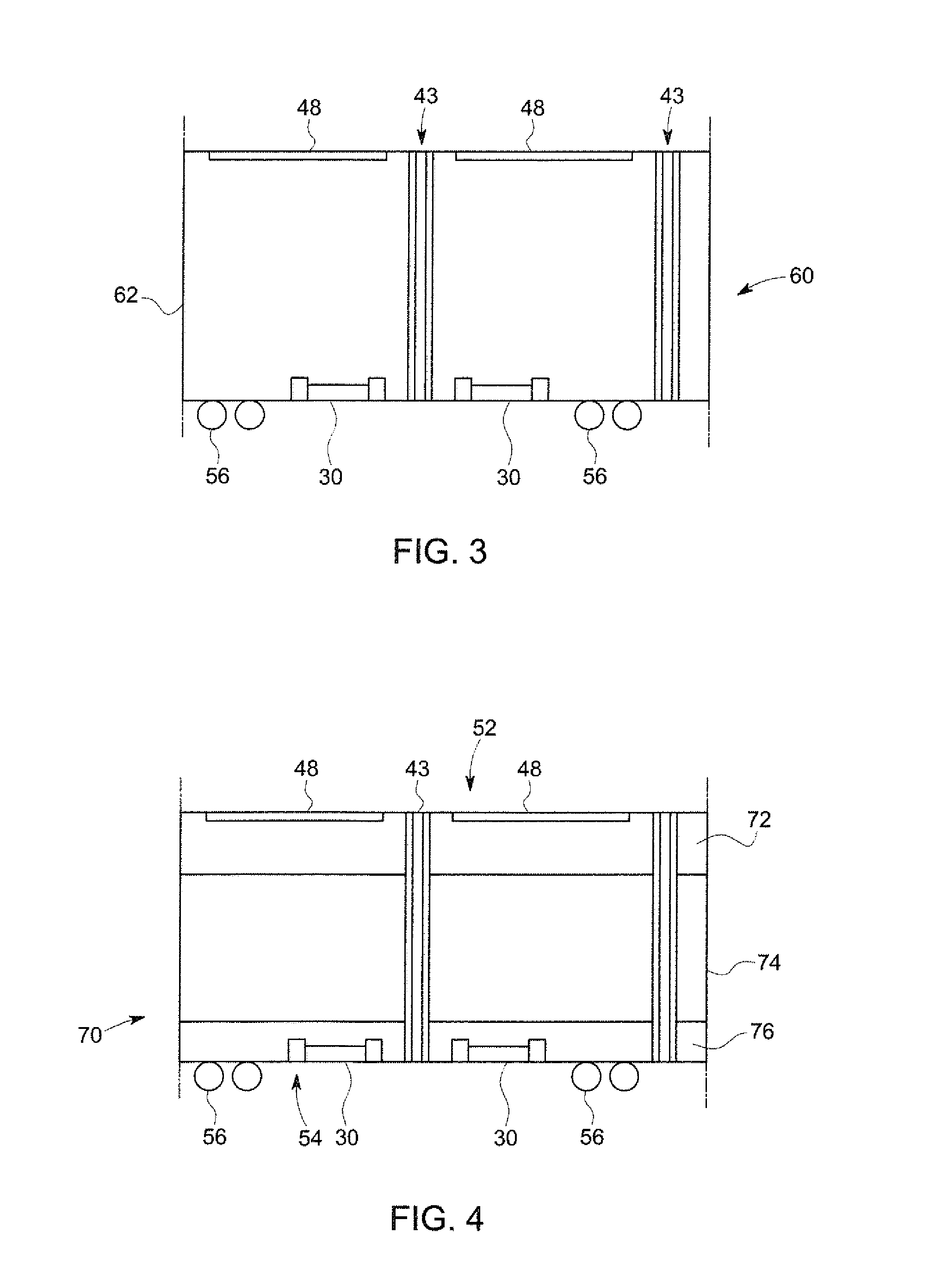
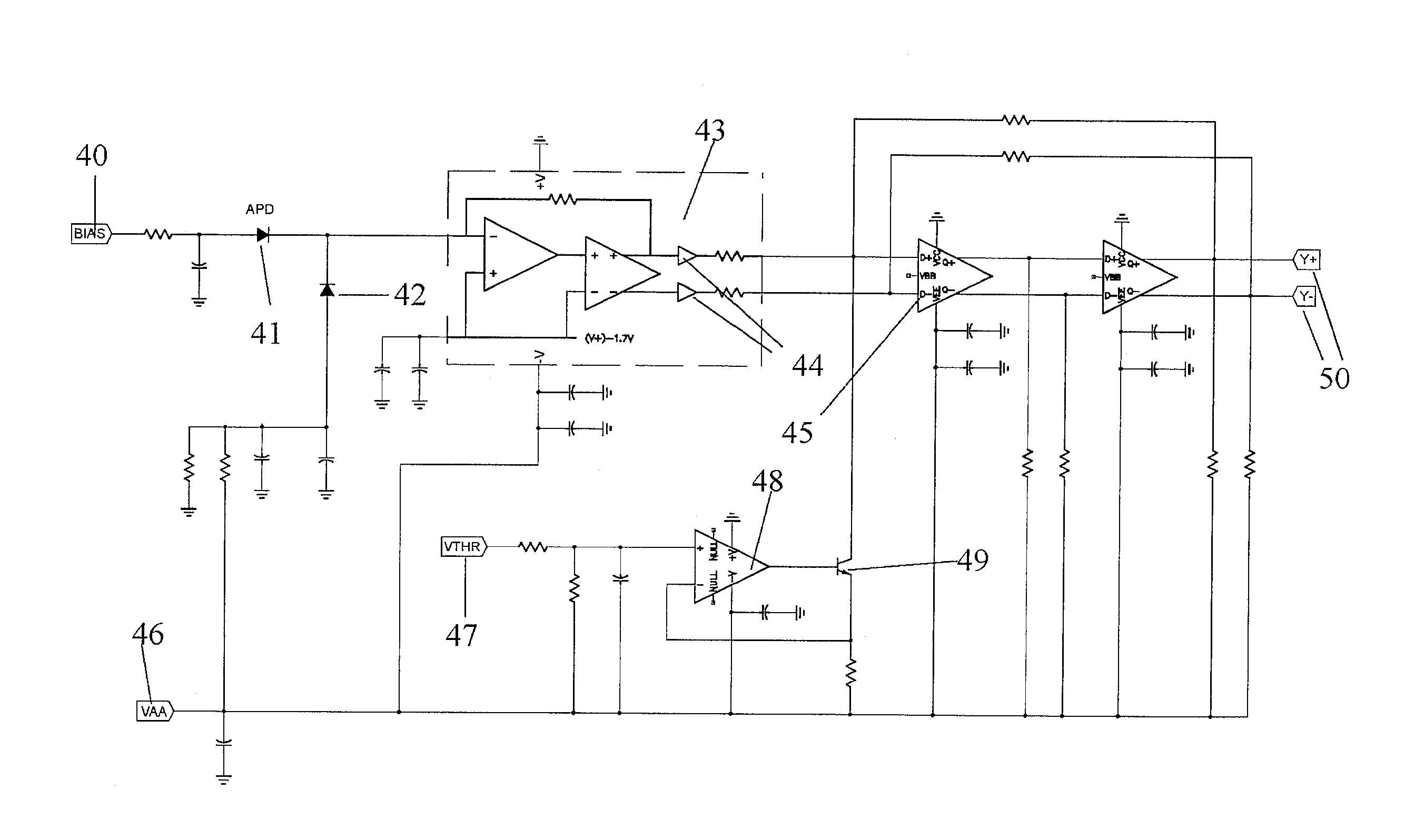
A readout electronics scheme is under development for high resolution, compact PET (positron emission tomography) imagers based on LSO (lutetium ortho-oxysilicate, Lu2SiO5) scintillator and avalanche photodiode (APD) arrays. The key is to obtain sufficient timing and energy resolution at a low power level, less than about 30 mW per channel, including all required functions. To this end, a simple leading edge level crossing discriminator is used, in combination with a transimpedance preamplifier. The APD used has a gain of order 1,000, and an output noise current of several pA / √Hz, allowing bipolar technology to be used instead of CMOS, for increased speed and power efficiency. A prototype of the preamplifier and discriminator has been constructed, achieving timing resolution of 1.5 ns FWHM, 2.7 ns full width at one tenth maximum, relative to an LSO / PMT detector, and an energy resolution of 13.6% FWHM at 511 keV, while operating at a power level of 22 mW per channel. Work is in progress towards integration of this preamplifier and discriminator with appropriate coincidence logic and amplitude measurement circuits in an ASIC suitable for a high resolution compact PET instrument. The detector system and / or ASIC can also be used for many other applications for medical to industrial imaging.
Owner:NOVA R & D
Positron emission tomography detector assembly for dual-modality imaging
A positron emission tomography (PET) detector assembly is provided. The PET detector assembly includes a plate having a first side and an opposite second side, the plate being fabricated from a thermally conductive material. The PET detector assembly also includes multiple PET detector units coupled to the first side of the plate. The PET detector assembly further includes a readout electronics section coupled to the second side of the plate, wherein, during operation, the readout electronics section generates heat that is transferred to the plate. The plate comprises a heat pipe disposed within the plate and configured to extract the heat from the plate and to transfer the heat away from the plate.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
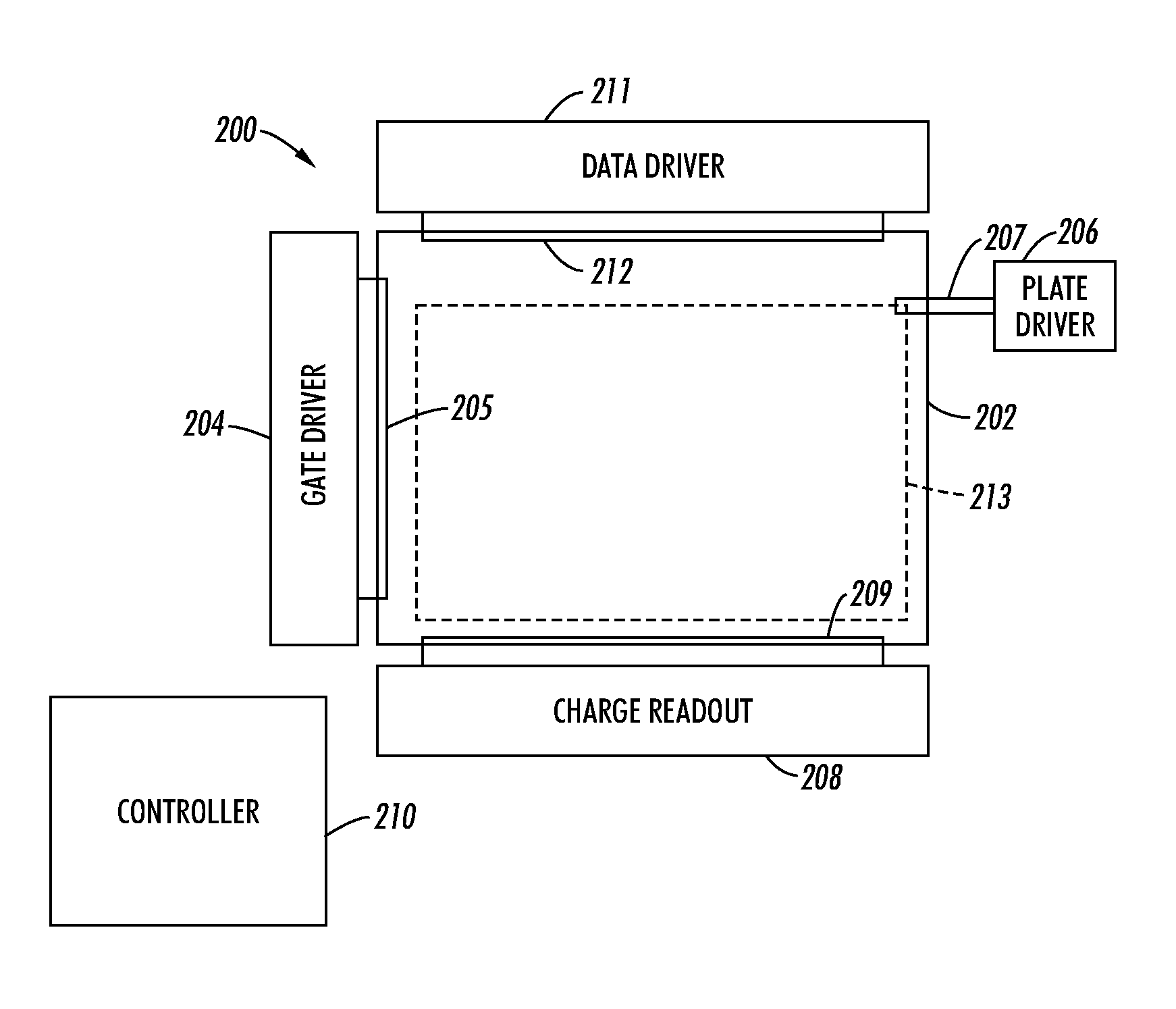
Systems and methods for modular imaging detectors
An imaging system includes plural modular imaging detectors and a readout electronics unit. Each modular imaging detector includes pixels configured to collect imaging data, a substrate on which the pixels are disposed, and a mechanical interconnection feature. The mechanical interconnection feature is configured to cooperate with a corresponding mechanical interconnection feature of at least one other of the modular imaging detectors to directly join the modular imaging detector to the at least one other of the modular imaging detectors. The readout electronics unit is configured to be operably coupled to the modular imaging detectors and to receive signals corresponding to the imaging data from the modular imaging detectors.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Readout electronics for photon counting and energy discriminating detectors
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
Improving image quality in photon counting-mode detector systems
The current invention applies to photon counting silicon x-ray detectors with energy discriminating capabilities and applications in x-ray imaging systems. The overall image quality produced by such a system is improved by the presented novel methods for optimally using the energy information in Compton events and making selective use of counts induced from charges collected in neighboring pixels. The pile-up problem during high-flux imaging regimes is reduced by a novel method for signal reset, which improves the count efficiency by reducing the risk of losing event due to signal pile-up in the read out electronics chain.
Owner:普里马蒂森索斯公司
Method and system for improved testing of transistor arrays
InactiveUS20090219035A1Measurement performanceStatic indicating devicesAir-break switch detailsTransistor arrayCapacitance
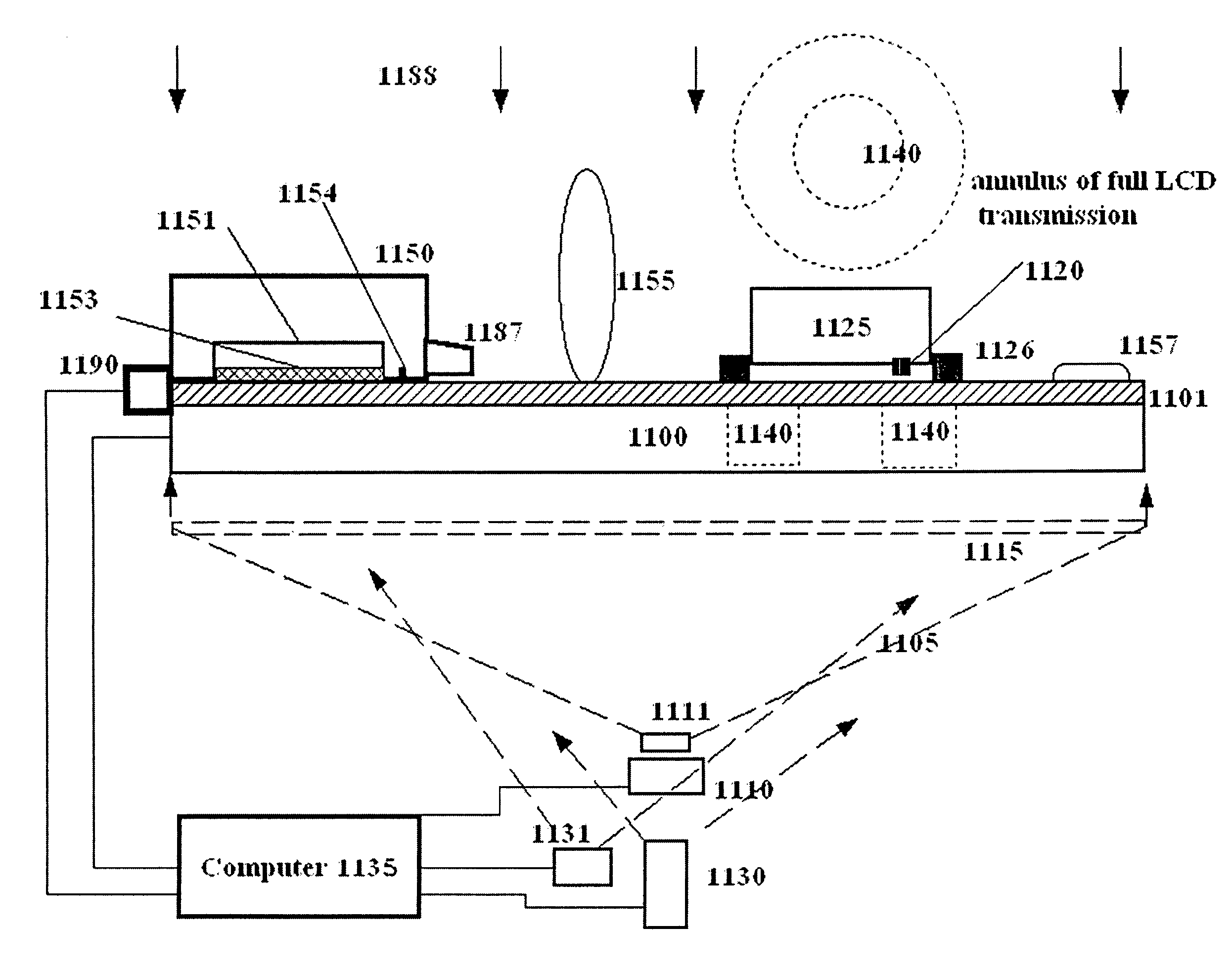
An electronic test system to evaluate the pixel and array properties of active-matrix displays that use charge or current sensitive circuits attached to the array data lines is described. Leakage-current, charging time, and other metrics can be measured for all pixels in the array without electrical or optical connection to the interior of the array. In accordance with the presently described embodiments, charge or current sensitive amplifiers and selected voltage drivers may be used in conjunction with variable timing and voltages to determine individual transistor properties over an entire array in just a few seconds. Signals to be measured may be injected in several ways: first, a capacitive elastomer laminate (or plate) may be applied to the surface of the array, making a capacitance with the pixel pad; second, gate lines may be used to inject charge into pixels that connect to more than one gate line; third, digital or analog drivers connected to the data lines may be used to charge the pixel to varying states; fourth, the dc-bias level of the charge or current sensitive readout electronics may be shifted relative to the gate voltages to charge the pixel. Connection in the system between components is achieved through flex connectors or other appropriate means. Ultimately, an output signal for each pixel is measured. Thus, based on the output signal, the charging time or current, the leakage time or current, and other pixel or transistor parameters may be characterized for the entire array.
Owner:PALO ALTO RES CENT INC
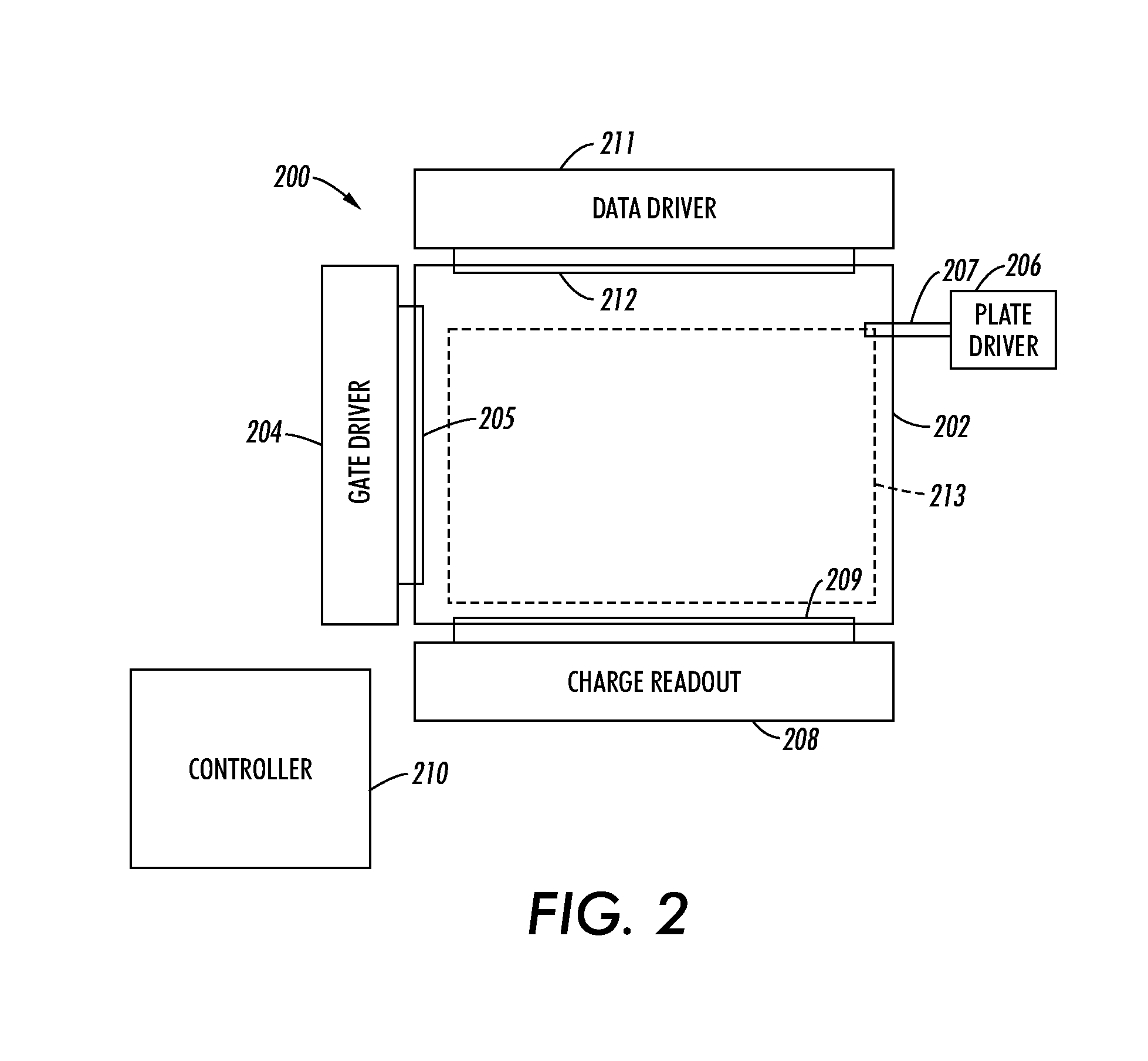
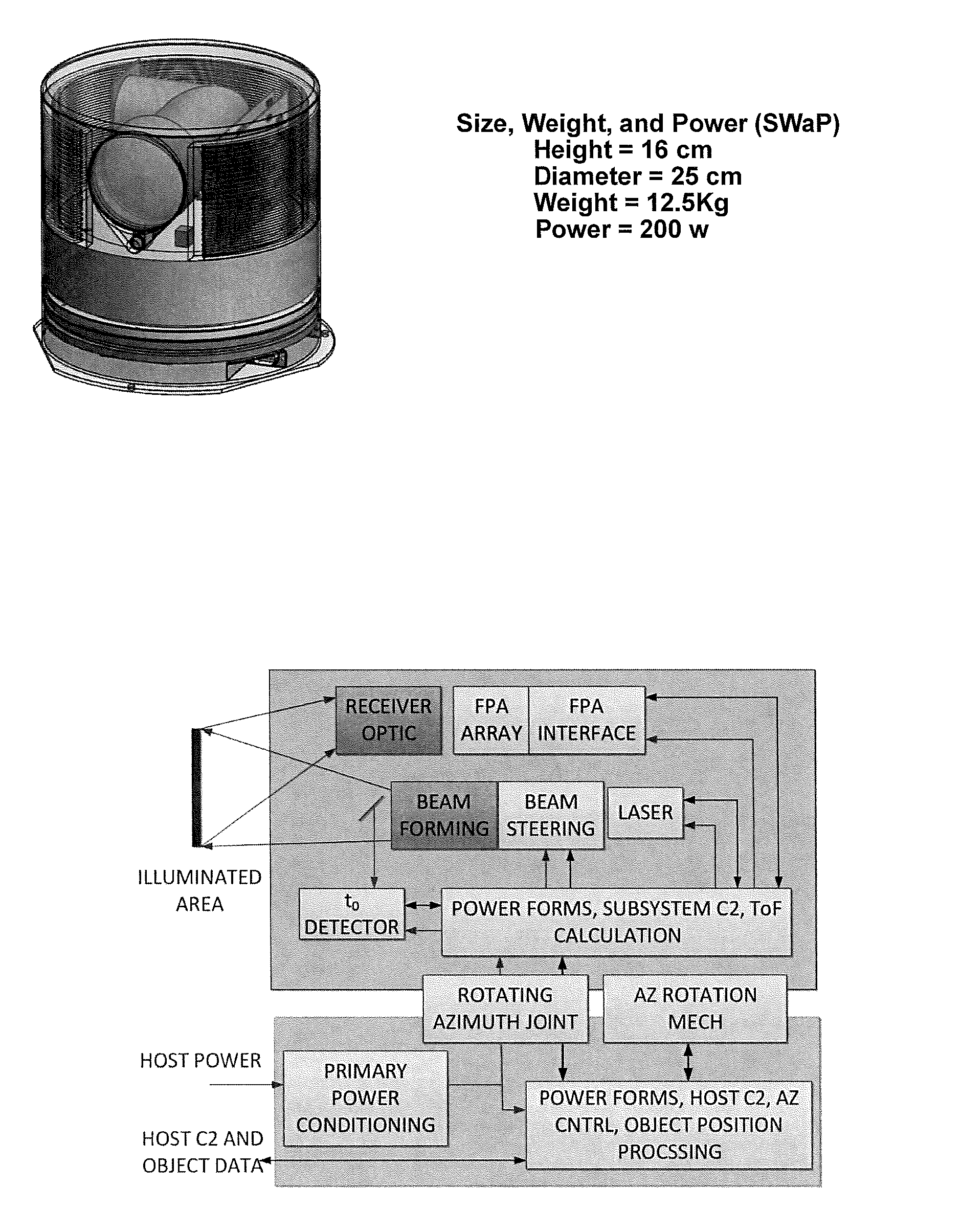
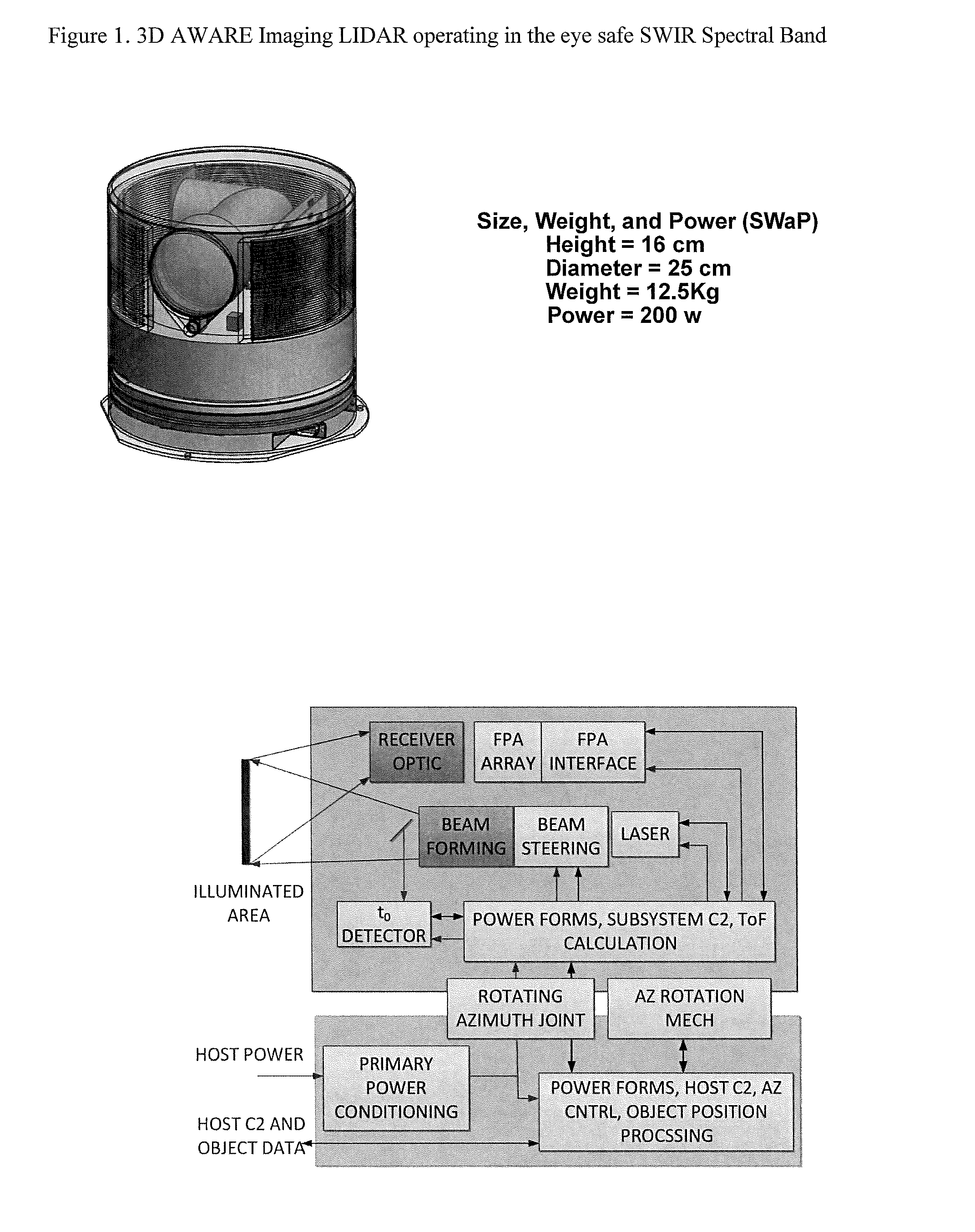
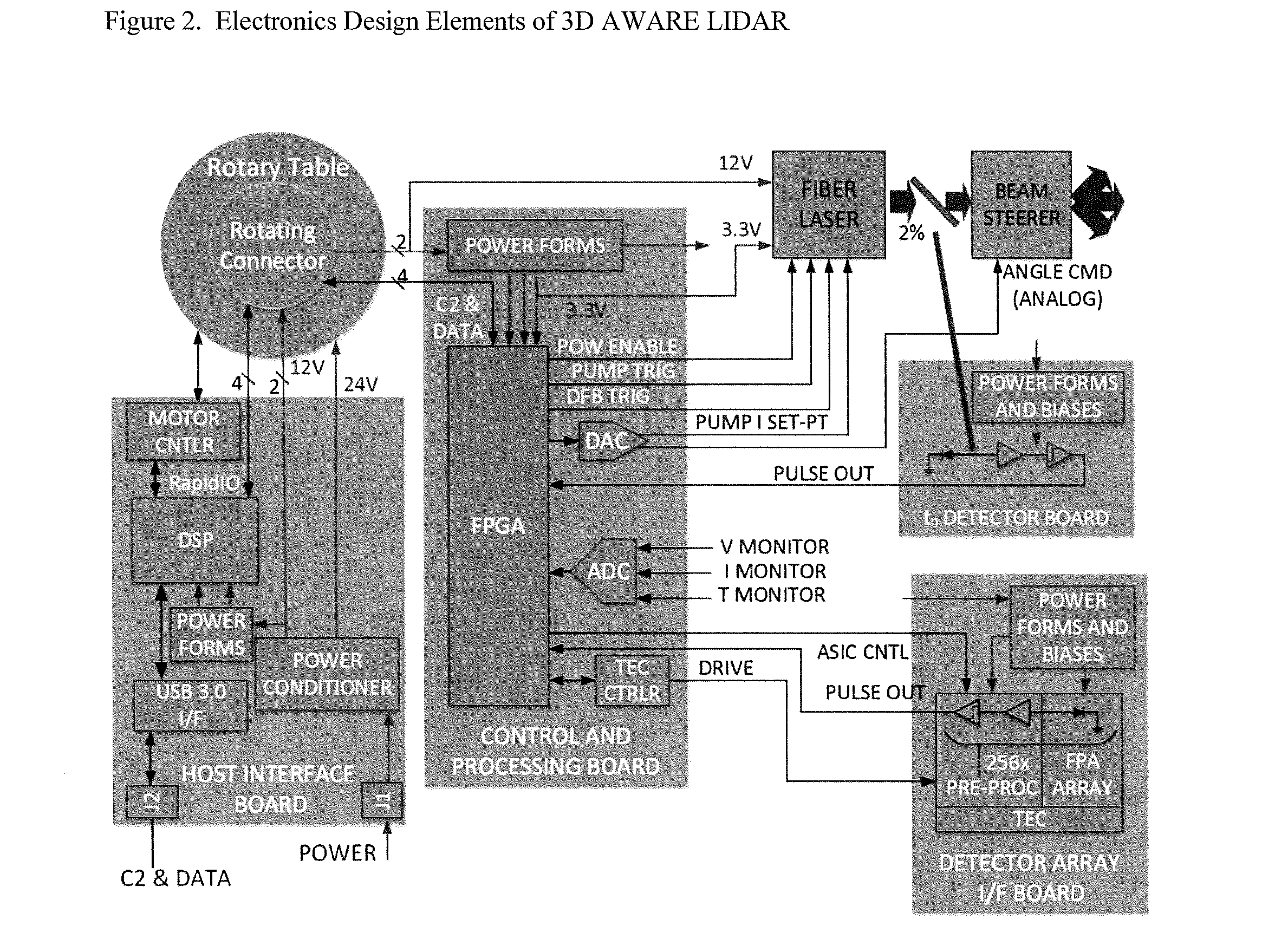
3D Active Warning and Recognition Environment (3D AWARE): A low Size, Weight, and Power (SWaP) LIDAR with Integrated Image Exploitation Processing for Diverse Applications
InactiveUS20160267669A1High resolutionImprove spatial resolutionTelevision system detailsImage analysisWide areaHigh pulse rate
An invention is disclosed for a multi-mode LIDAR sensor system that embodies a high pulse rate fiber laser operating in the SWIR wavelength at 1.5 microns, a long linear array of small SWIR sensitive detectors with very high speed readout electronics, and fully integrated methods and processing elements that perform target detection, classification, and tracking using techniques that emulate how the human visual path processes and interprets imaging data. High resolution three dimensional images are created of wide areas. Image exploitation processing methods detect objects and object activities in real time thus enabling diverse applications such as vehicle navigation, critical infrastructure protection, and public safety monitoring.
Owner:IRVINE SENSORS
Multimodal imaging apparatus
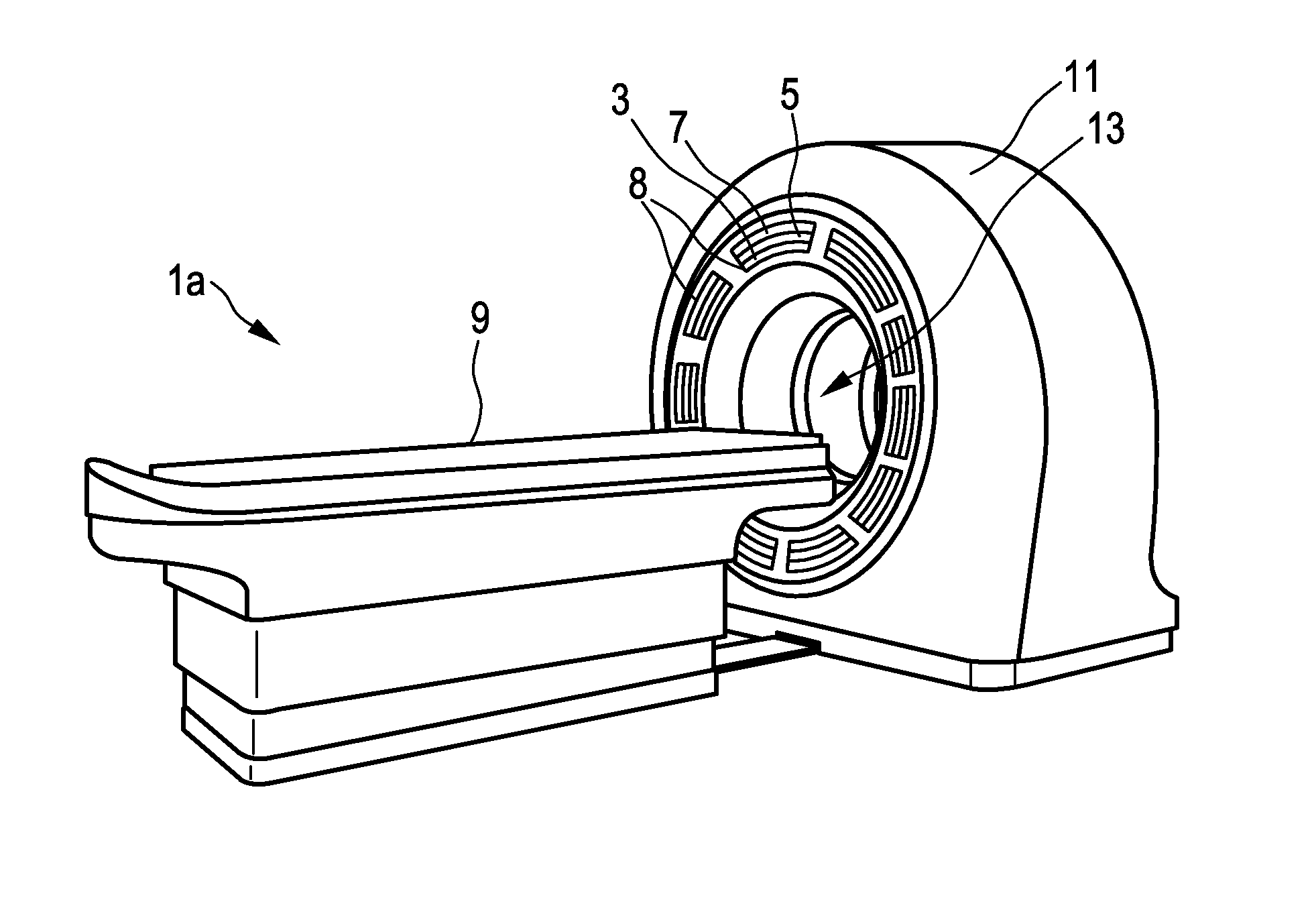
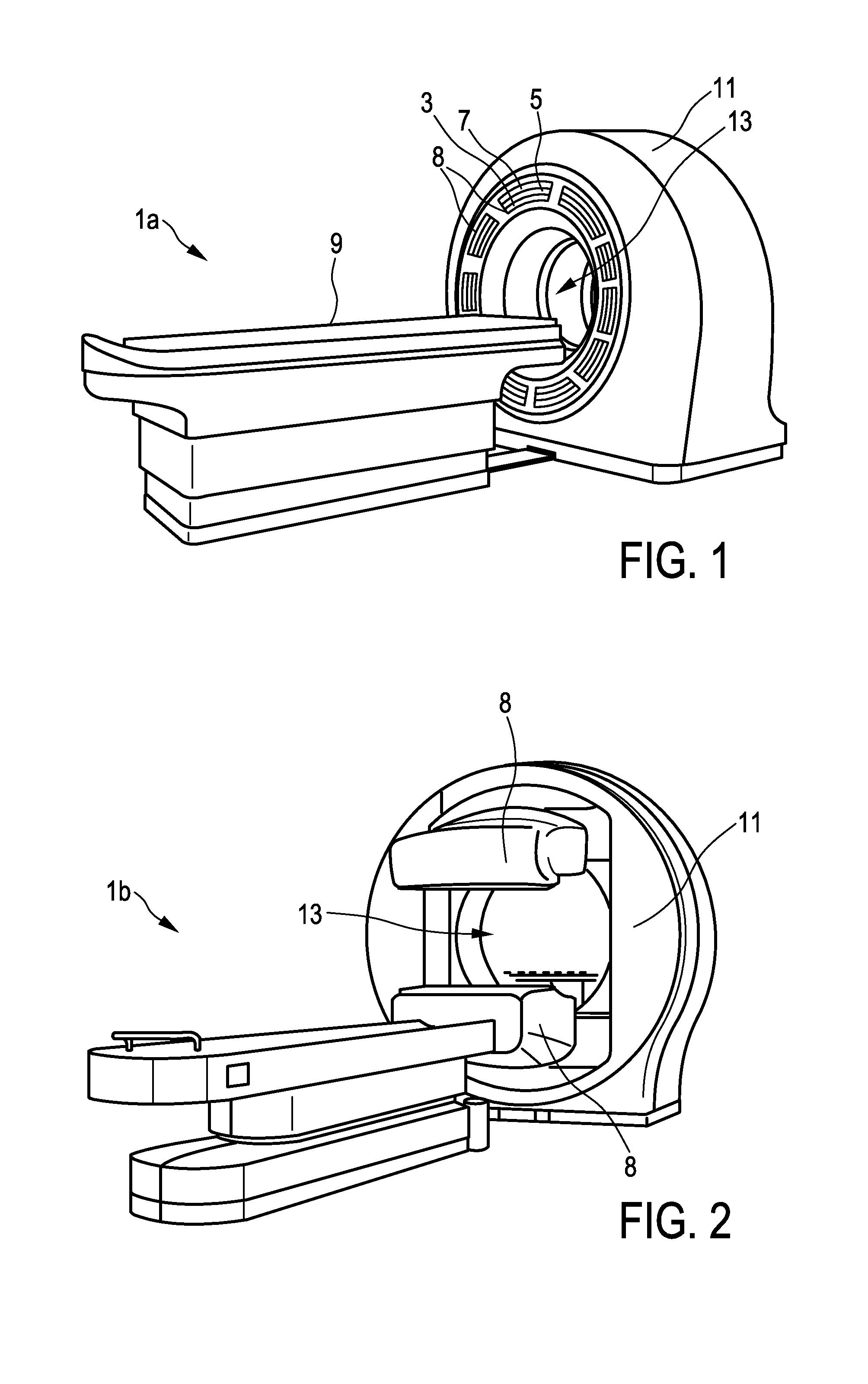
InactiveUS20160209515A1Conserve costReduce the amount requiredMaterial analysis by optical meansComputerised tomographsRadioactive tracerPhotodetector
The present invention relates to a multimodal imaging apparatus (1a, 1b) for imaging a process (63) in a subject (23), said process (63) causing the emission of gamma quanta (25, 61), said apparatus (1a, 1b) comprising a scintillator (3) including scintillator elements (31) for capturing incident gamma quanta (25, 61) generated by the radiotracer and for emitting scintillation photons (26) in response to said captured gamma quanta (25, 61), a photodetector (5) including photosensitive elements (33) for capturing the emitted scintillation photons (26) and for determining a spatial distribution of the scintillation photons, and a readout electronics (7) for determining the impact position of an incident gamma quantum in the scintillator (3) and / or a parameter indicative of the emission point of the gamma quantum (25, 61) in the subject (23) based on the spatial distribution of the scintillation photons, wherein the imaging apparatus (1a, 1b) is configured to be switched between a first operation mode for detecting low energy gamma quanta and a second operation mode for detecting high energy gamma quanta, wherein the high energy gamma quanta have a higher energy than the low energy gamma quanta, and the scintillator (3) is arranged to capture incident gamma quanta (25, 61) from the same area of interest (65) in the first operation mode and in the second operation mode without requiring a relative movement of the subject (23) versus the scintillator (3), wherein the scintillator (3) comprises an array of scintillator elements (31) including a first region with high energy scintillator elements (27) for capturing high energy gamma quanta and a second region with low energy scintillator elements (29) for capturing low energy gamma quanta; and / or the apparatus (1a, 1b) further comprises a positioning mechanism (35) for changing the orientation and / or position of the scintillator elements (31), in particular for tilting the scintillator elements (31), to switch the imaging apparatus (1a, 1b) between the first operation mode and the second operation mode.
Owner:KONINKLJIJKE PHILIPS NV
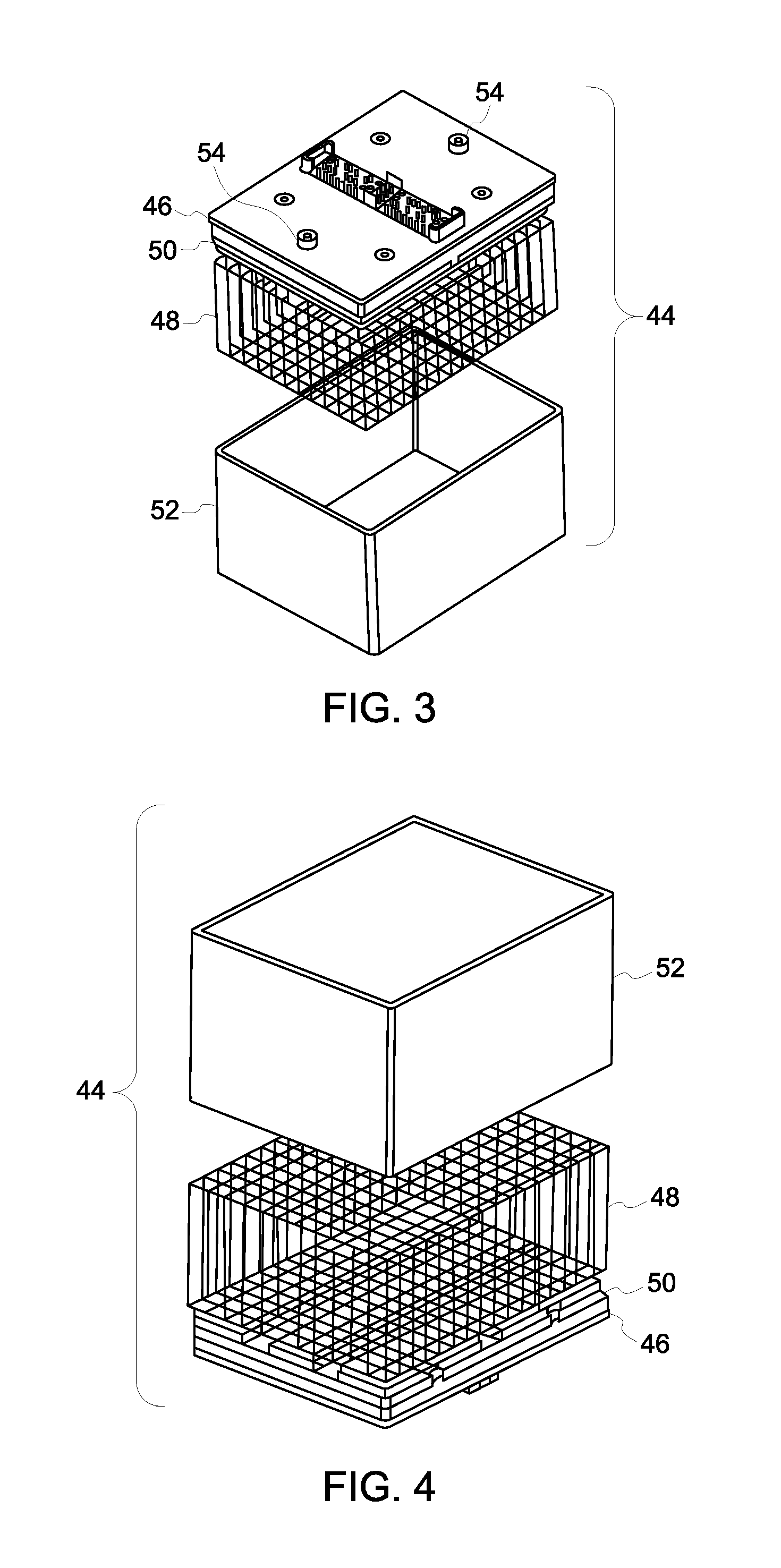
Detector modules and methods of manufacturing
ActiveUS8798229B2Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingComputer moduleReadout electronics
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
X-Ray and Gamma Ray Detector Readout Sytem
InactiveUS20110248765A1Uniform spatial resolutionImprove efficiencyPulse automatic controlTomographyDiscriminatorCompanion animal
A readout electronics scheme is under development for high resolution, compact PET (positron emission tomography) imagers based on LSO (lutetium ortho-oxysilicate, Lu2SiO5) scintillator and avalanche photodiode (APD) arrays. The key is to obtain sufficient timing and energy resolution at a low power level, less than about 30 mW per channel, including all required functions. To this end, a simple leading edge level crossing discriminator is used, in combination with a transimpedance preamplifier. The APD used has a gain of order 1,000, and an output noise current of several pA / √Hz, allowing bipolar technology to be used instead of CMOS, for increased speed and power efficiency. A prototype of the preamplifier and discriminator has been constructed, achieving timing resolution of 1.5 ns FWHM, 2.7 ns full width at one tenth maximum, relative to an LSO / PMT detector, and an energy resolution of 13.6% FWHM at 511 keV, while operating at a power level of 22 mW per channel. Work is in progress towards integration of this preamplifier and discriminator with appropriate coincidence logic and amplitude measurement circuits in an ASIC suitable for a high resolution compact PET instrument. The detector system and / or ASIC can also be used for many other applications for medical to industrial imaging.
Owner:NOVA R&D
Photon counting cone-beam ct apparatus with monolithic CMOS integrated pixel detectors
ActiveUS20170055923A1Reduced radiation dose absorptionEasy to useSolid-state devicesComputerised tomographsHigh energyX-ray
CBCT including monolithic photon counting FPD for medical applications requiring real-time 3D imaging, like mammography, interventional guided procedures or external beam radiotherapy, includes CMOS processed readout electronics monolithically integrated with a single crystalline X-ray absorber by covalent wafer bonding near room temperature and adapted for single photon counting providing high energy, temporal and spatial resolution.
Owner:G RAY SWITZERLAND SA
CMOS APS with stacked avalanche multiplication layer and low voltage readout electronics
InactiveUS7365773B2Reduce decreaseTelevision system detailsTelevision system scanning detailsLow voltageHemt circuits
Owner:APTINA IMAGING CORP
Detector modules and methods of manufacturing
ActiveUS20130083887A1Material analysis using wave/particle radiationRadiation/particle handlingReadout electronicsSilicon
Detector modules and methods of manufacturing are provided. One detector module includes a detector having a silicon wafer structure formed from a first layer having a first resistivity and a second layer having a second resistivity, wherein the first resistivity is greater than the second resistivity. The detector further includes a photosensor device provided with the first layer on a first side of the silicon wafer and one or more readout electronics provided with the second layer on a second side of the silicon wafer, with the first side being a different side than the second side.
Owner:GENERAL ELECTRIC CO
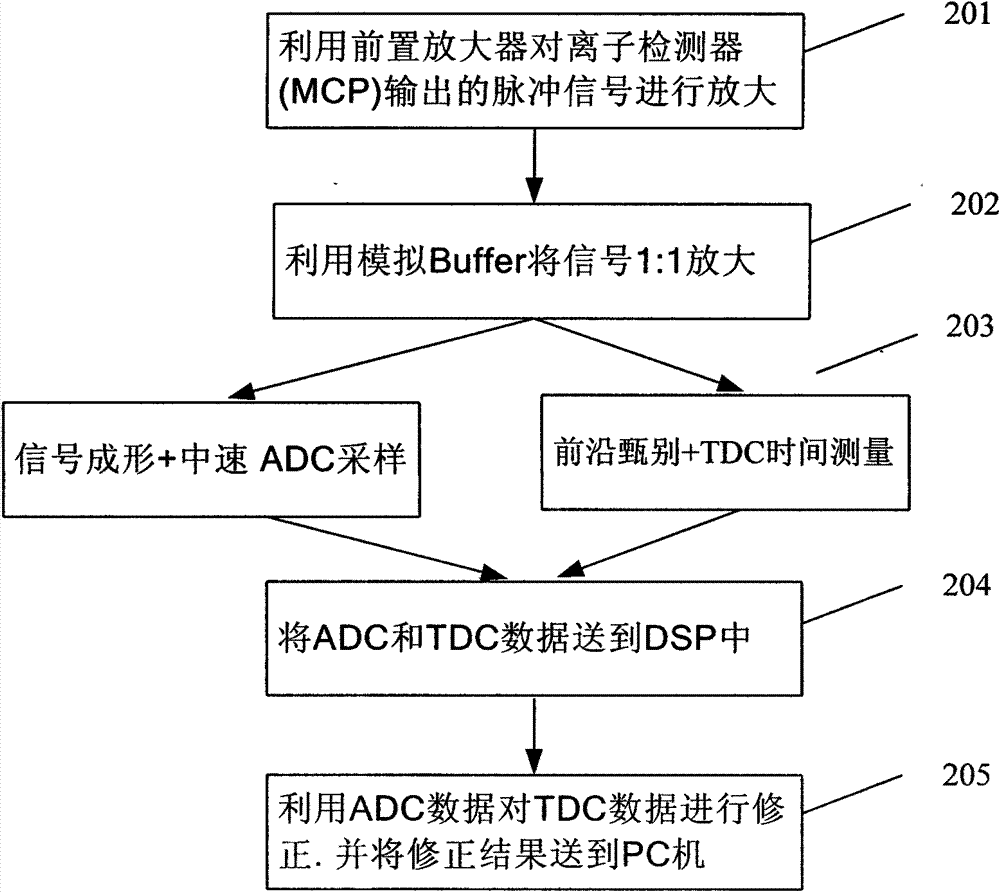
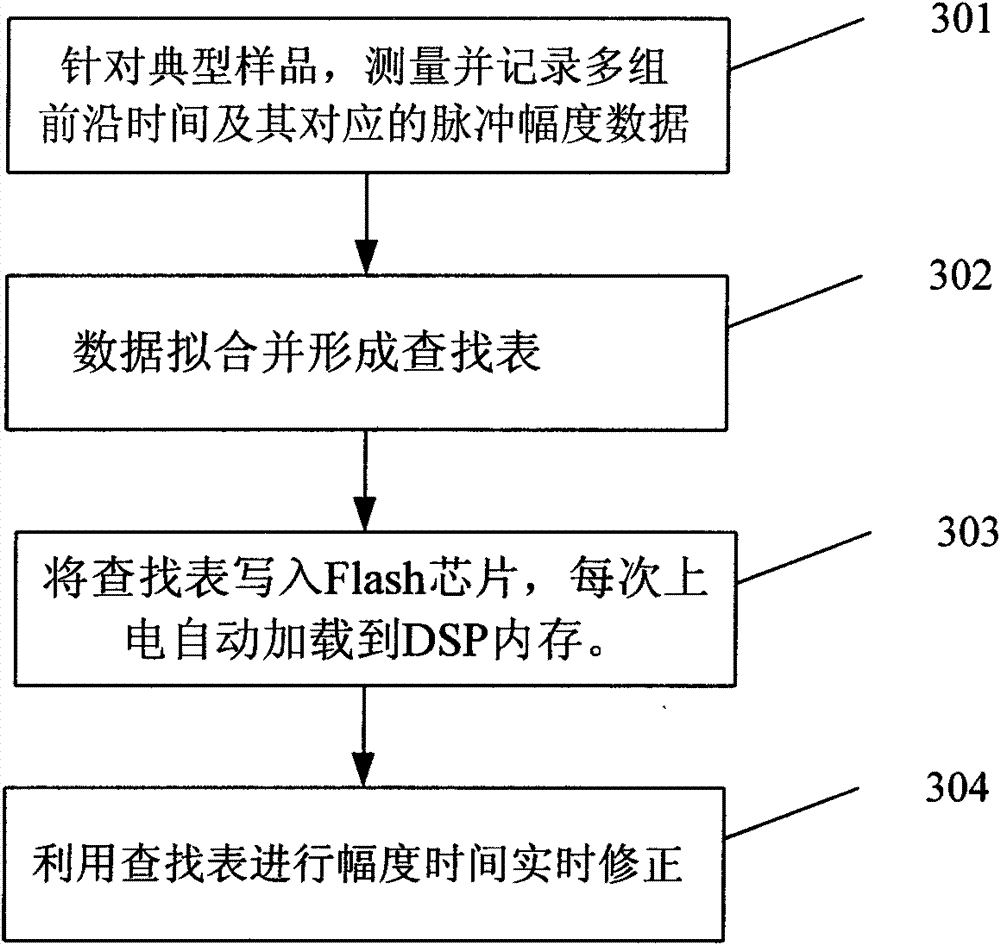
Time-of-flight mass spectrometer electronics reading method based on pulse front edge time measurement and amplitude correction algorithm
InactiveCN102789952AAvoid embargo problemsPromote localizationParticle separator tube detailsLow speedMass analyzer
The invention discloses a time-of-flight mass spectrometer electronics reading method which can improve time resolution and a quantitative performance of a time-of-flight mass spectrometer at the same time and is different from an electronics reading scheme of a traditional time-of-flight mass spectrometer by an ADC (Analog to Digital Converter) waveform sampling or a TDC (Time to Digital Converter) pulse time measuring. The pulse front edge time measurement and a pulse forming sampling scheme are combined; the front edge time measured by the TDC is corrected by amplitude information obtained by a middle and low speed ADC for sampling a formed pulse, so that a time resolution effect is obviously improved, and the quantitative performance of an apparatus is improved. According to the reading method, an expensive high-speed ADC (over 1G SPS (samples per second) ) chip is replaced by a pulse forming circuit and the middle and low-speed ADC (about 100M of SPS); a constant fraction discriminator (CFD) circuit in a traditional time-of-flight mass spectrometer reading electronics is replaced by utilizing direct pulse front edge screening, and apparatus cost is reduced when a performance is improved.
Owner:ANHUI USTC JIANCHENG HAISHENG TECH
Photon counting cone-beam ct apparatus with monolithic CMOS integrated pixel detectors
ActiveUS20180240842A1Reduced radiation dose absorptionEasy to useSemiconductor/solid-state device detailsSolid-state devicesHigh energyX-ray
CBCT including monolithic photon counting FPD for medical applications requiring real-time 3D imaging, like mammography, interventional guided procedures or external beam radiotherapy, includes CMOS processed readout electronics monolithically integrated with a single crystalline X-ray absorber by covalent wafer bonding near room temperature and adapted for single photon counting providing high energy, temporal and spatial resolution.
Owner:G RAY SWITZERLAND SA
Squid-system having increased FLUX voltage transfer function
ActiveUS20110285393A1High measurement sensitivitySimple processMagnetic field measurement using superconductive devicesElectricityAudio power amplifier
The invention relates to a SQUID system having an increased flux voltage transfer function. The object of disclosing a circuit configuration providing an increased flux voltage transfer function of a SQUID, wherein the measurement sensitivity of the system is noticeably increased and the required readout electronics are simplified, is achieved in that at least one SQIF is provided as an amplifier circuit and is connected downstream of the first SQUID, wherein a coupling coil electrically connected to the first SQUID is directly associated with all loops of the SQIF.
Owner:INST FUER PHOTONISCHE TECHNOLOGIEN EV
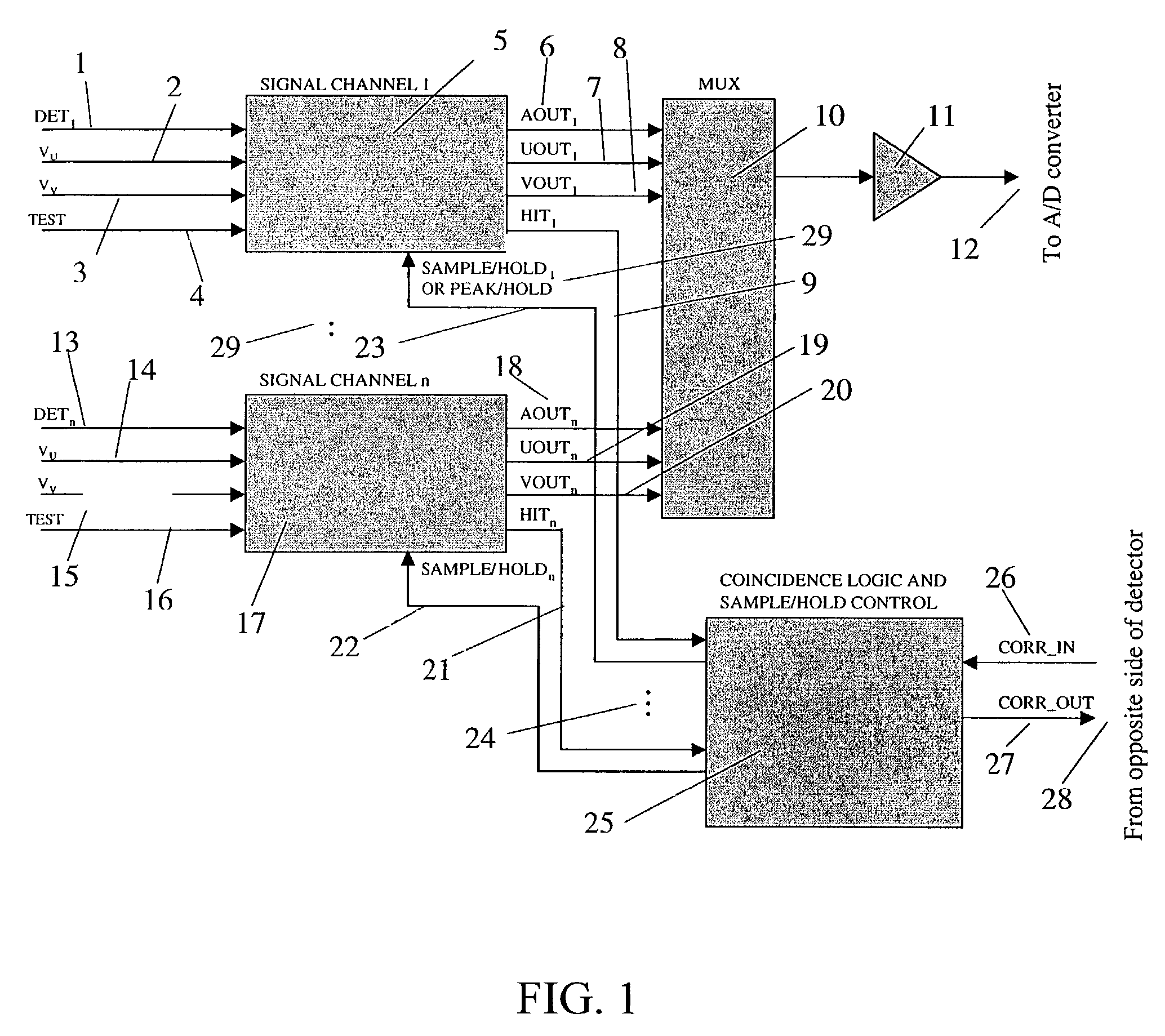
Capacitive Spreading Readout Board
InactiveUS20120261585A1Reduces cost and overall complexity of readoutIncreased physical sizeElectric discharge tubesMaterial analysis by optical meansDielectricCapacitance
A readout board for use in a micropattern gas detector comprises a plurality of detector pads arranged into a plurality of consecutive layers that are separated by dielectric spacer material. An electron cloud hitting the front side of the readout board will induce a charge on one of the detector pads of the uppermost layer. By capacitive coupling, the signal will propagate downwards through the consecutive layers until it reaches the bottom layer, from which the charges are read out and analyzed. The position of the impact can be determined by comparing the charges that have spread to neighboring readout pads. Since only the bottommost layer of the readout pads needs to be connected to readout electronics, incident particles can be localized at high precision despite the relatively large size of the readout pads in the bottom layer. The invention is effective both in a gas electron multiplier (GEM) and in a MicroMegas detector.
Owner:EUROPEAN ORGANIZATION FOR NUCLEAR RESEARCH
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com