Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
89 results about "Frozen tissue" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Frozen tissues are advantageous in the ways where the process is much quicker compared to the FFPE process. The procedure is rapid and used to fix and mount samples using a device called cryostat. It is used in many surgeries that involve the removal of tumors to determine if the tumor has been completely removed by studying the margins.
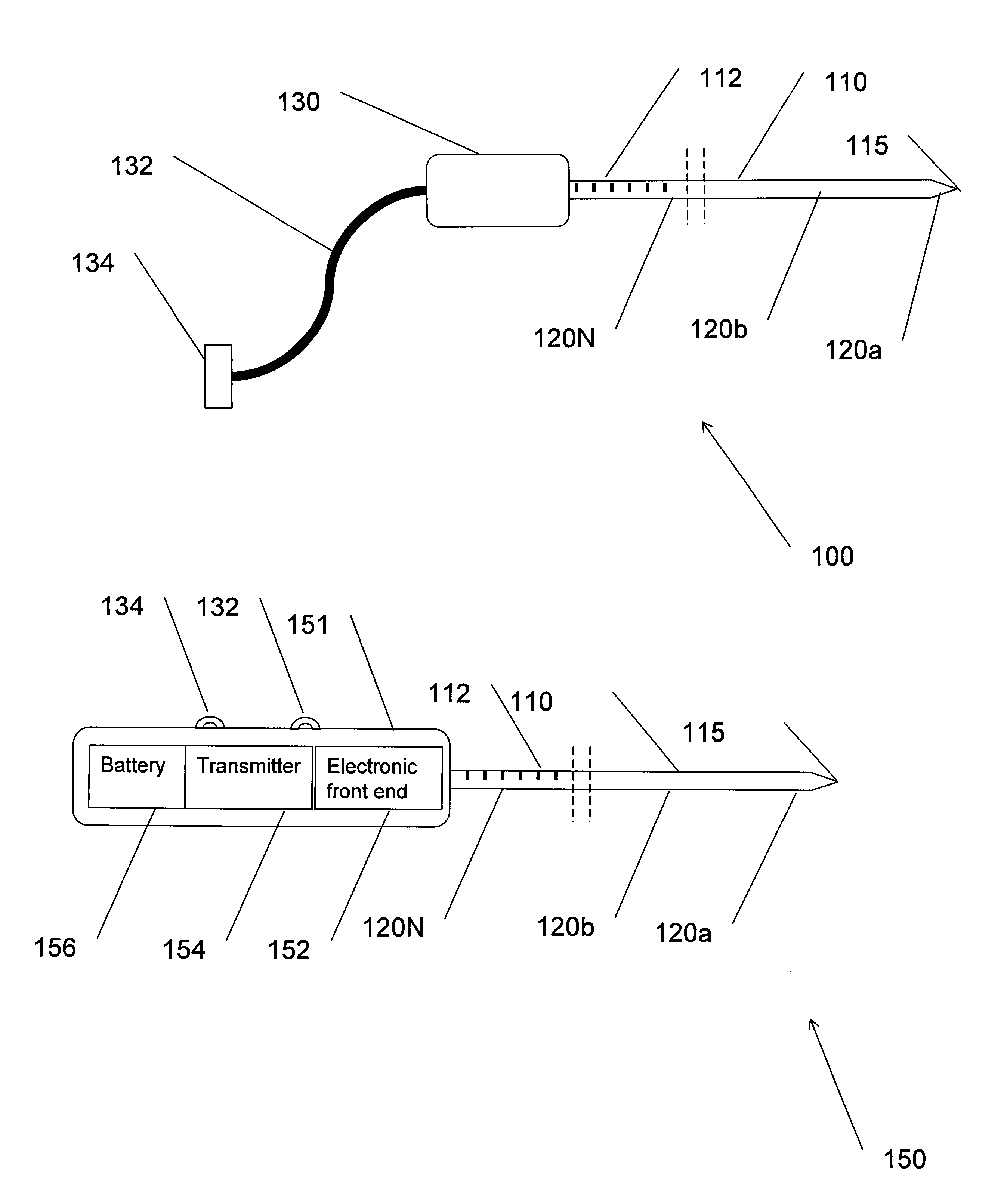
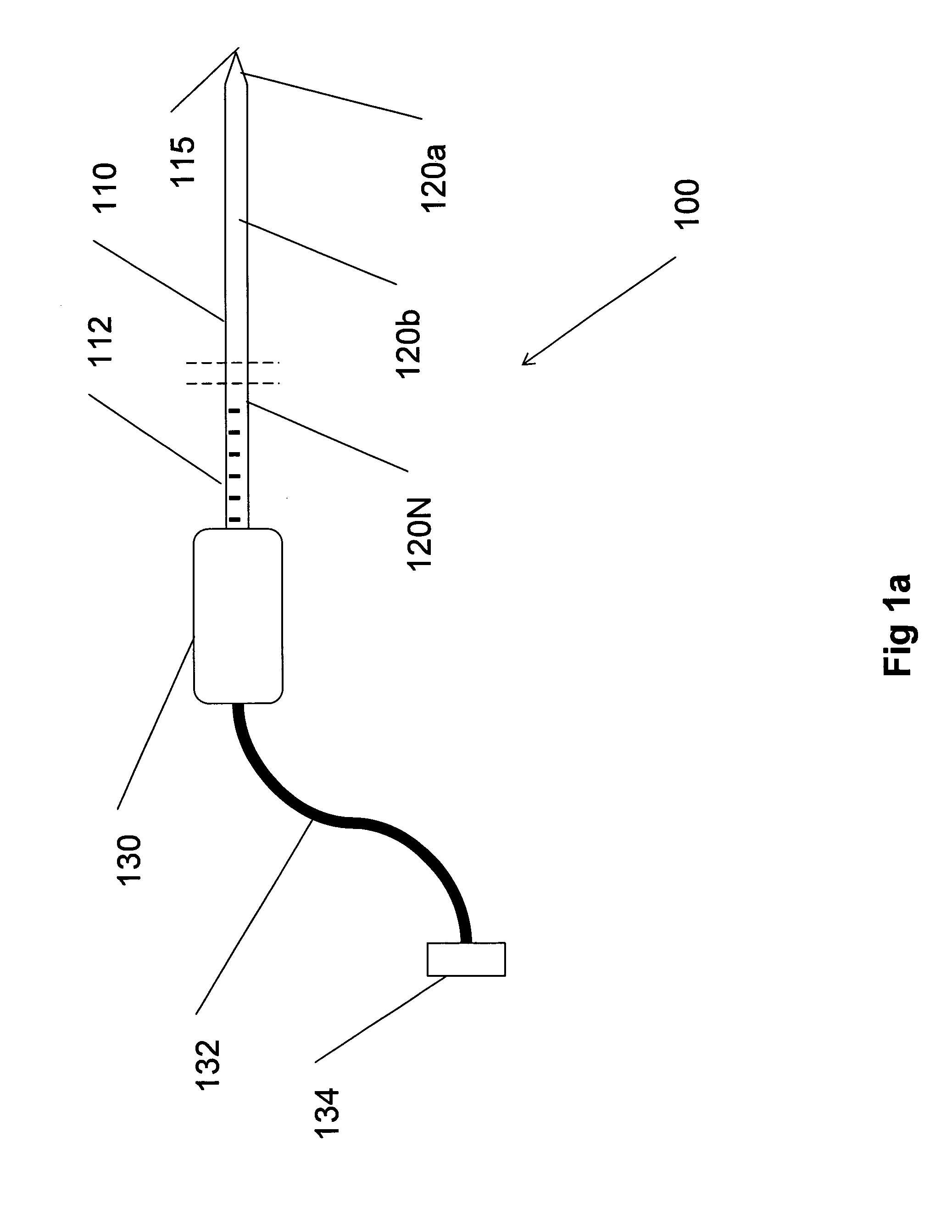
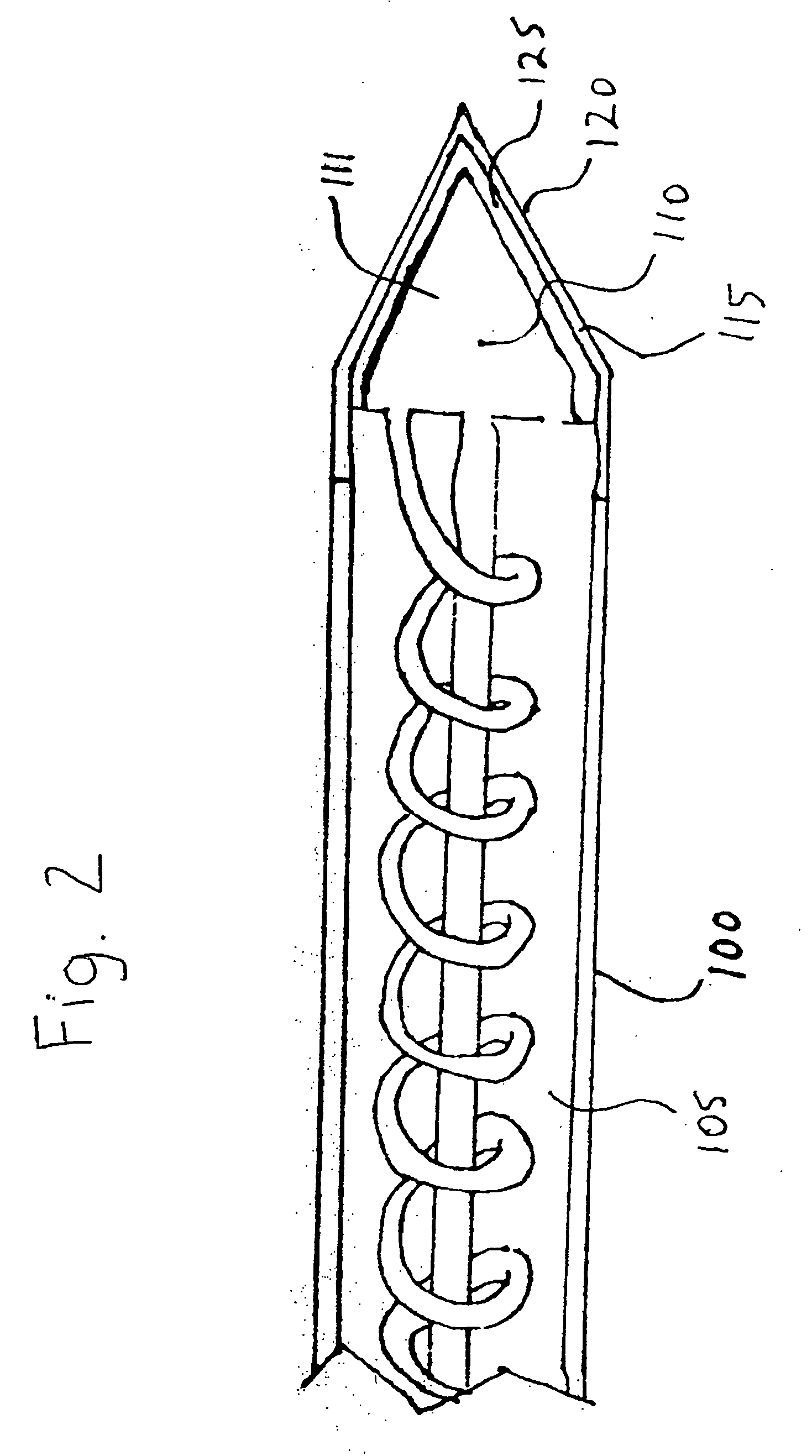
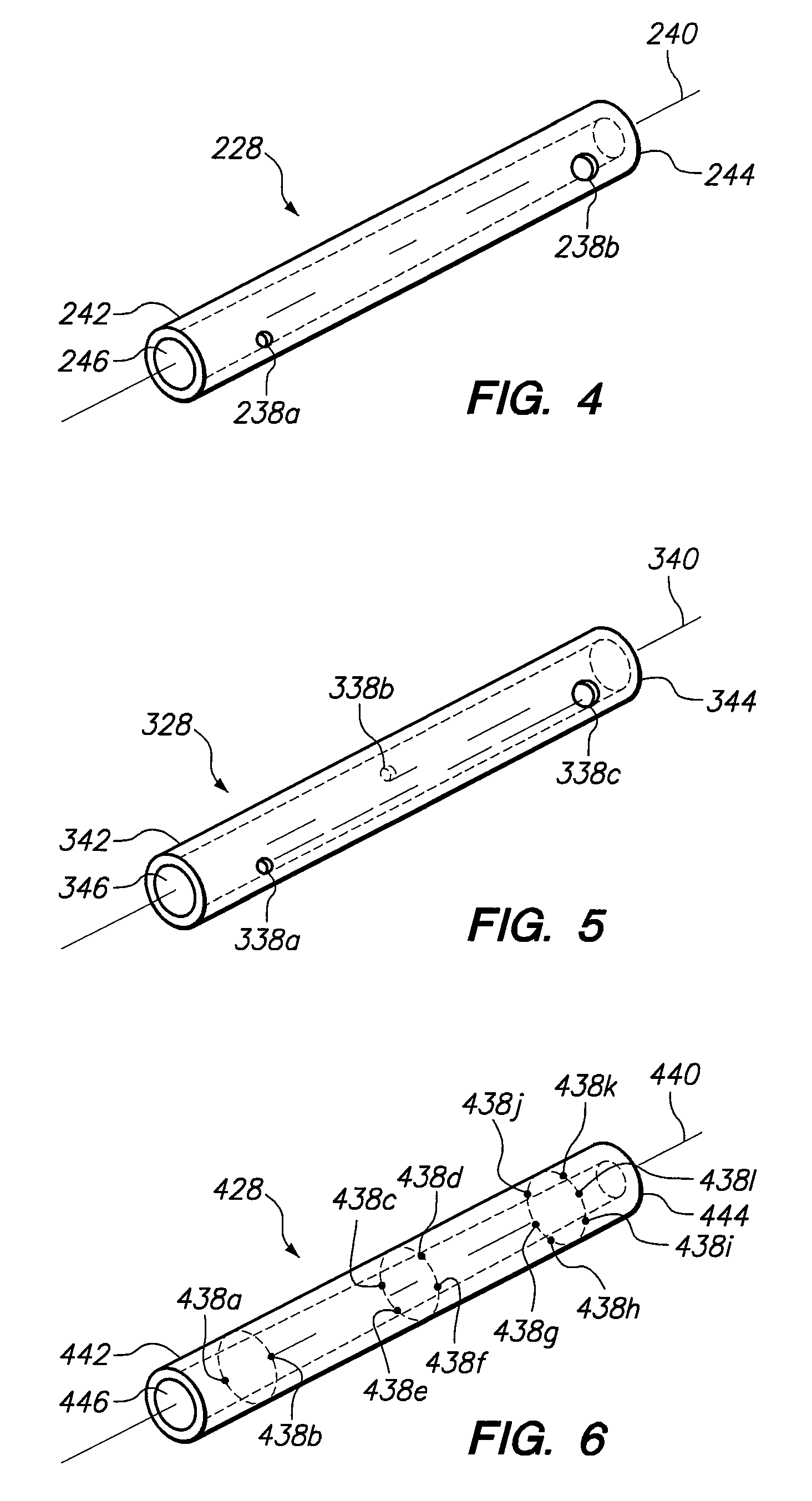
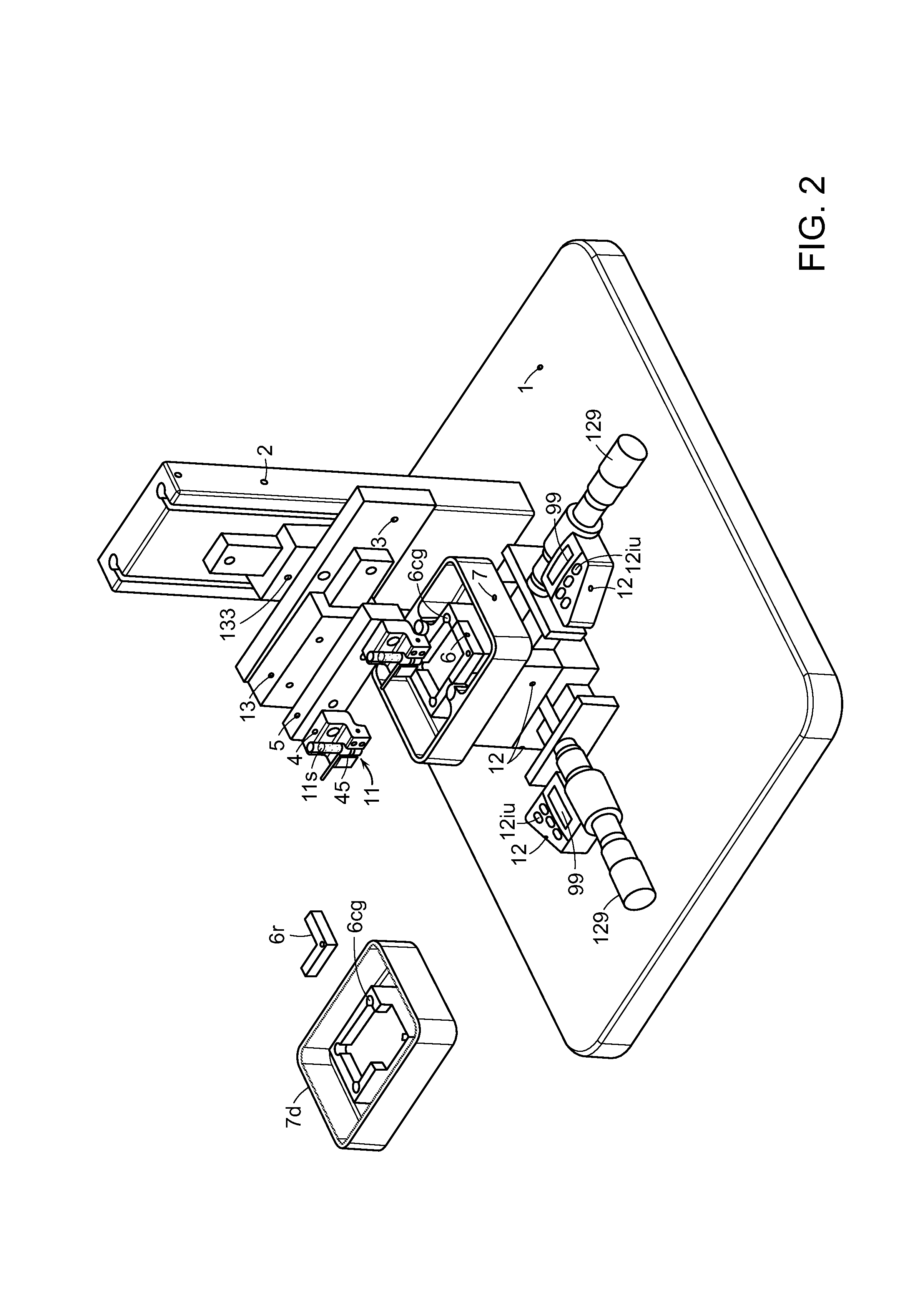
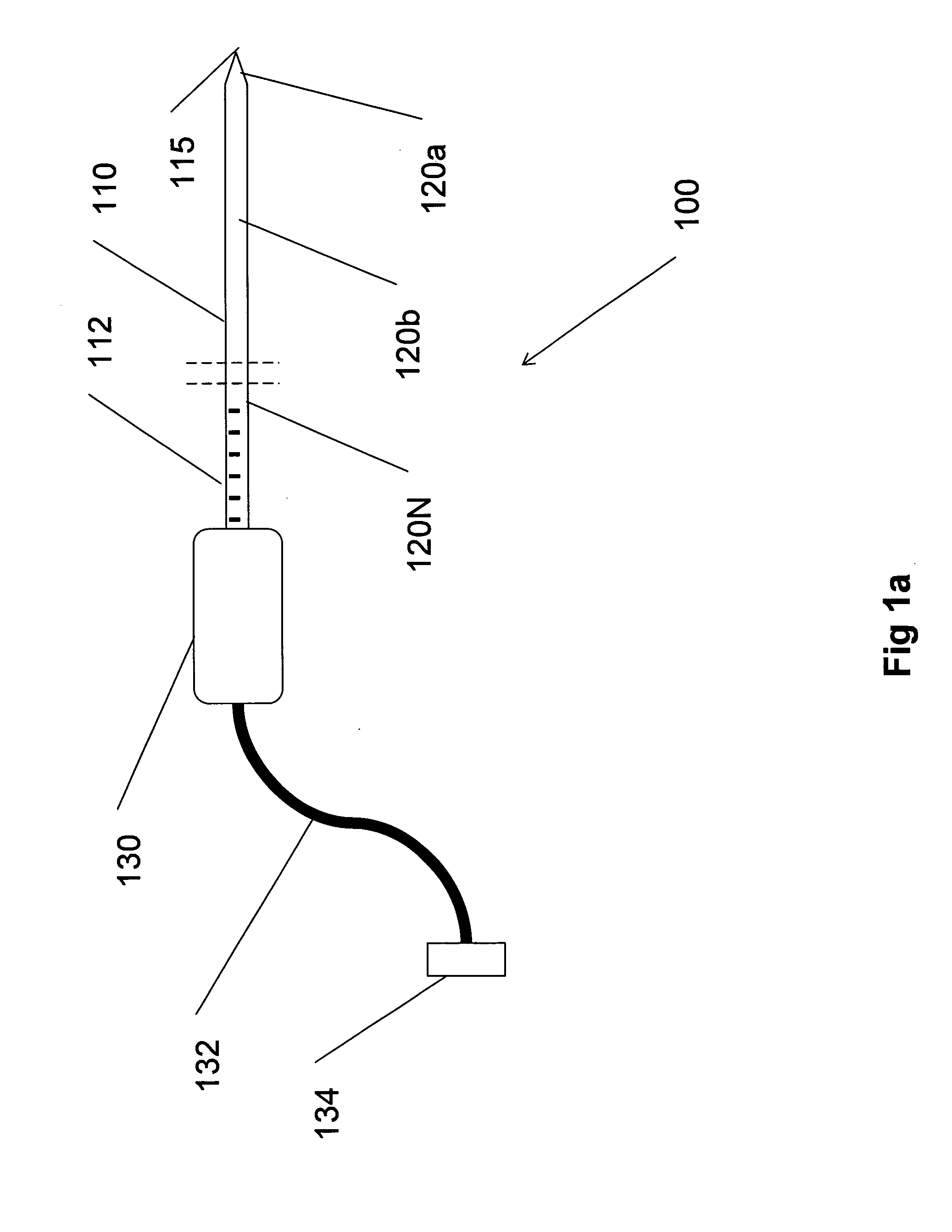
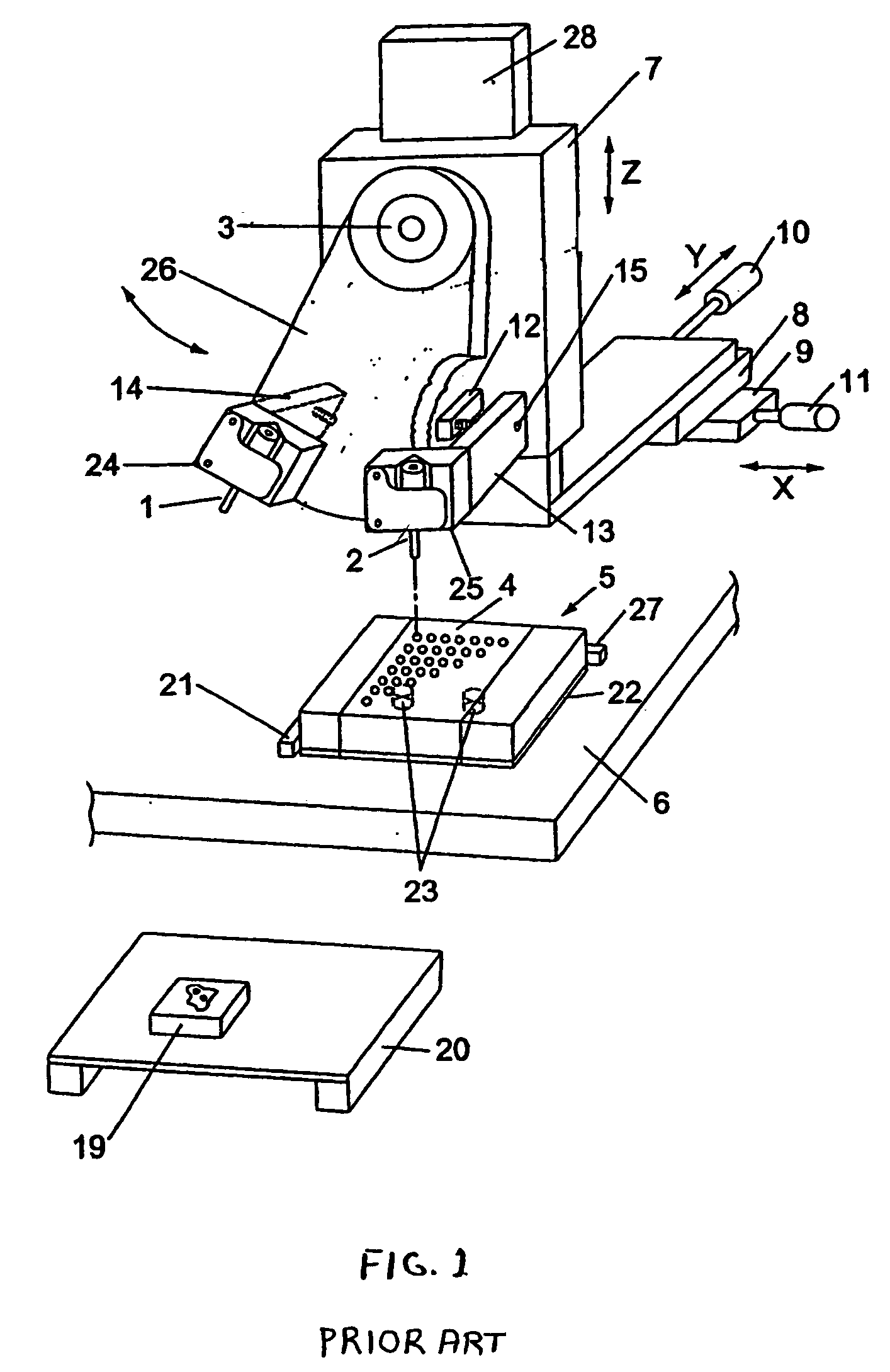
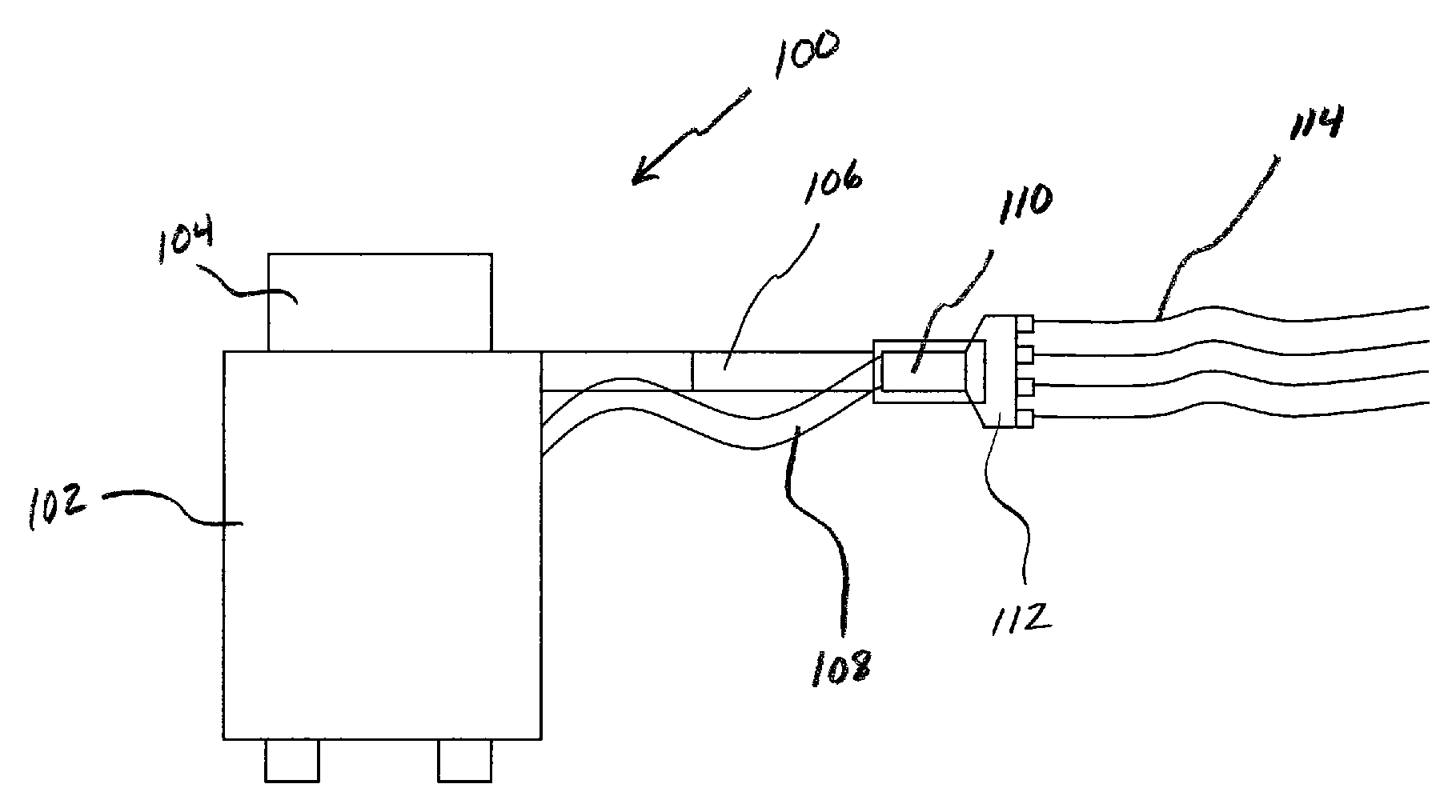
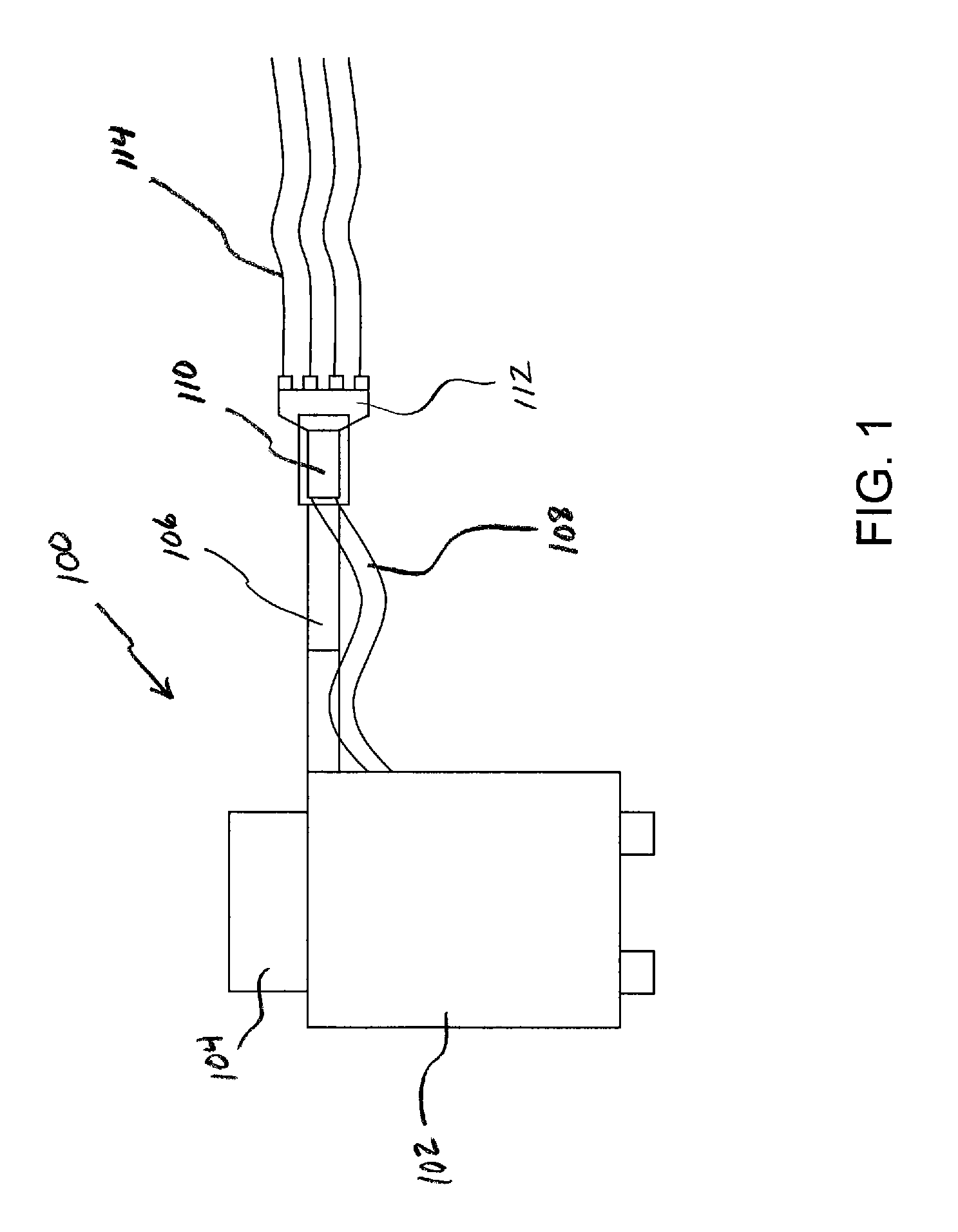
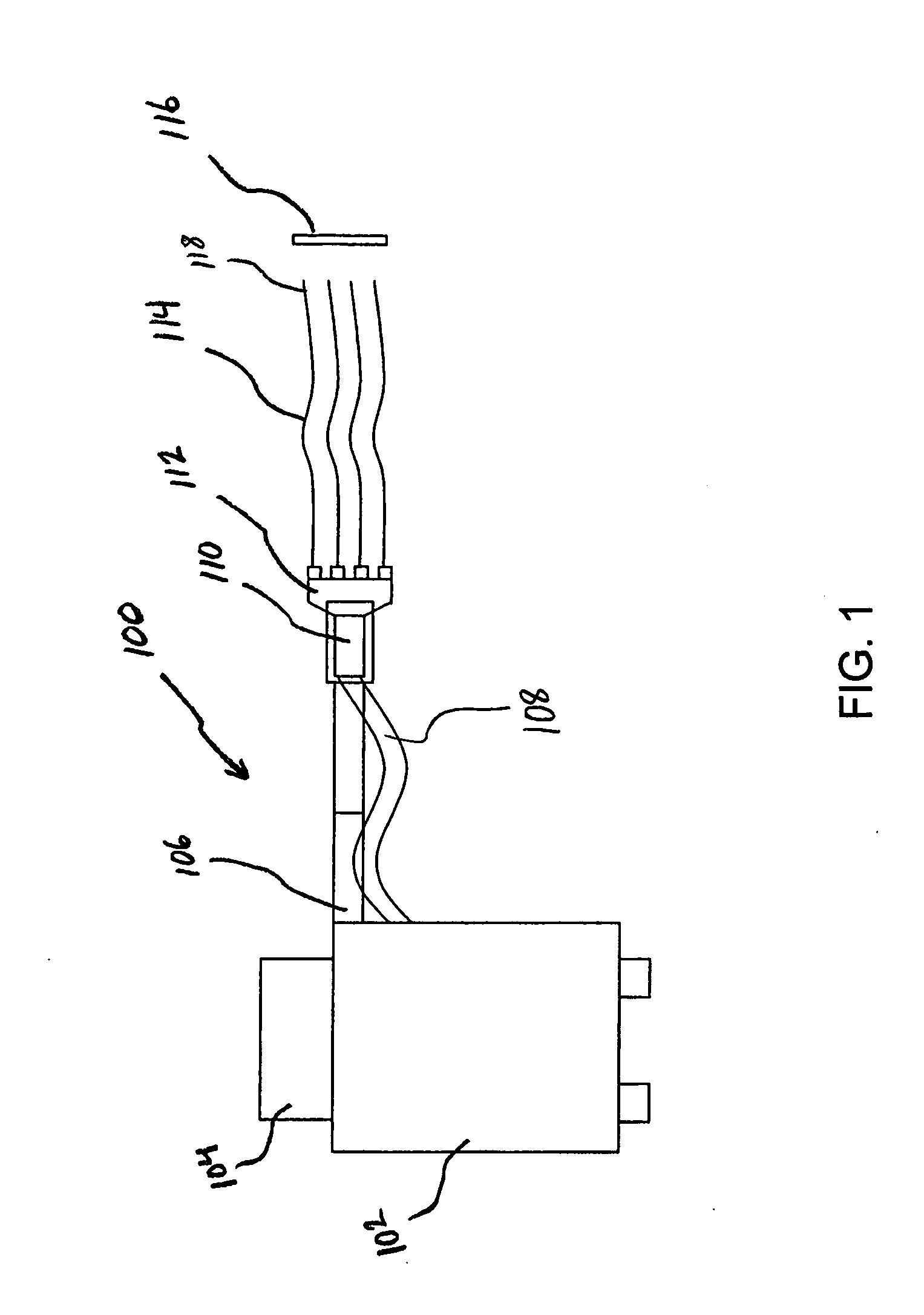
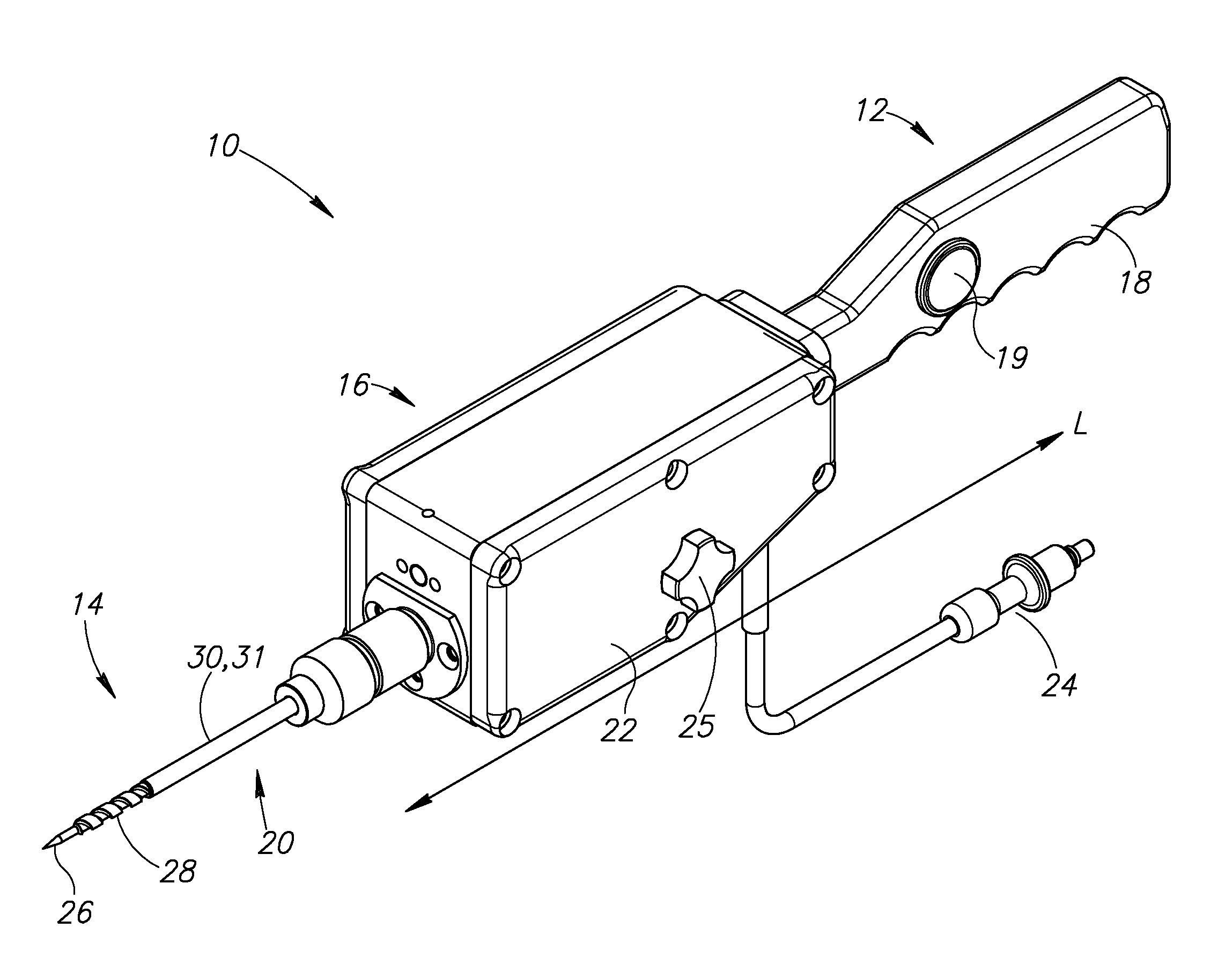
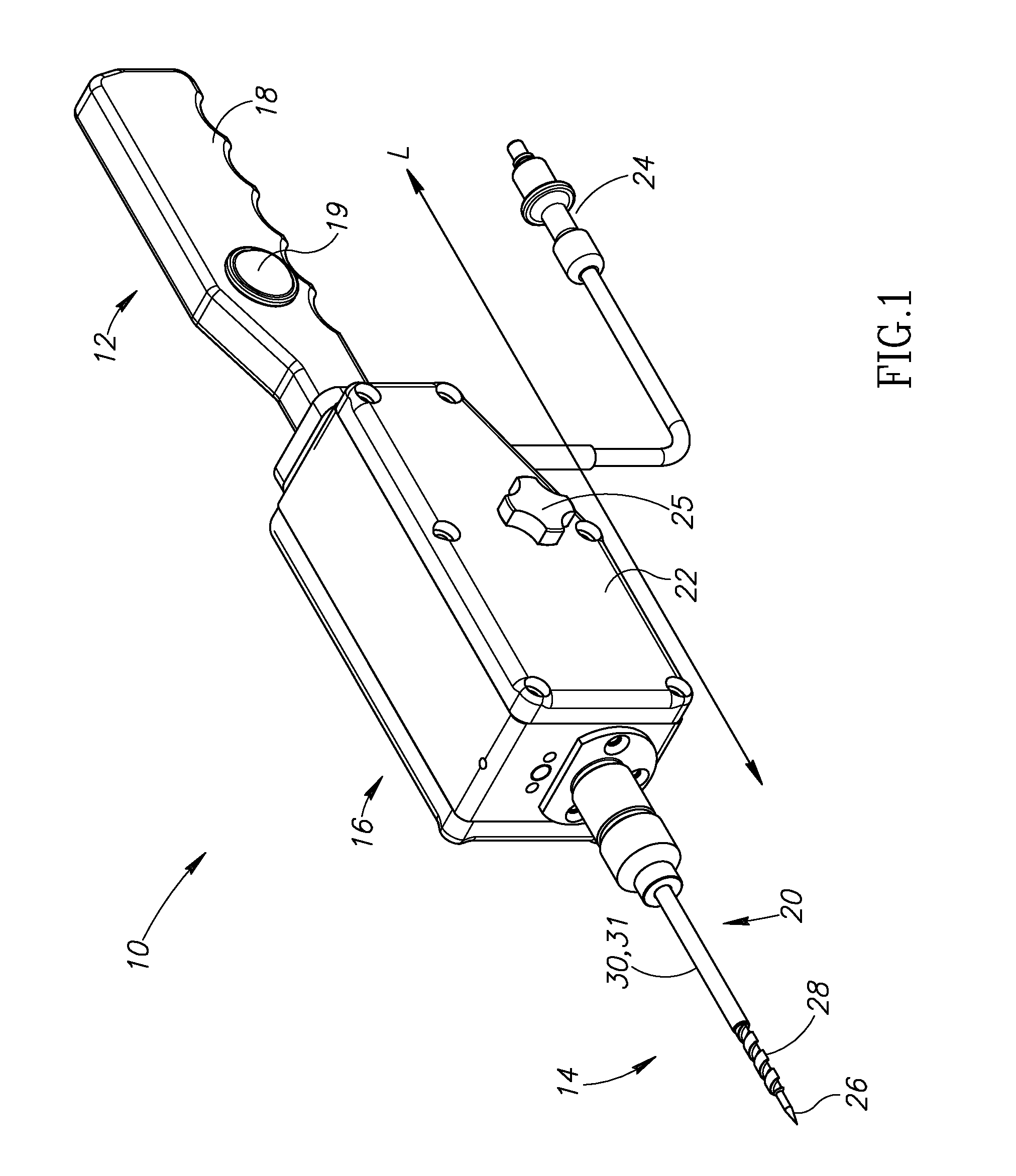
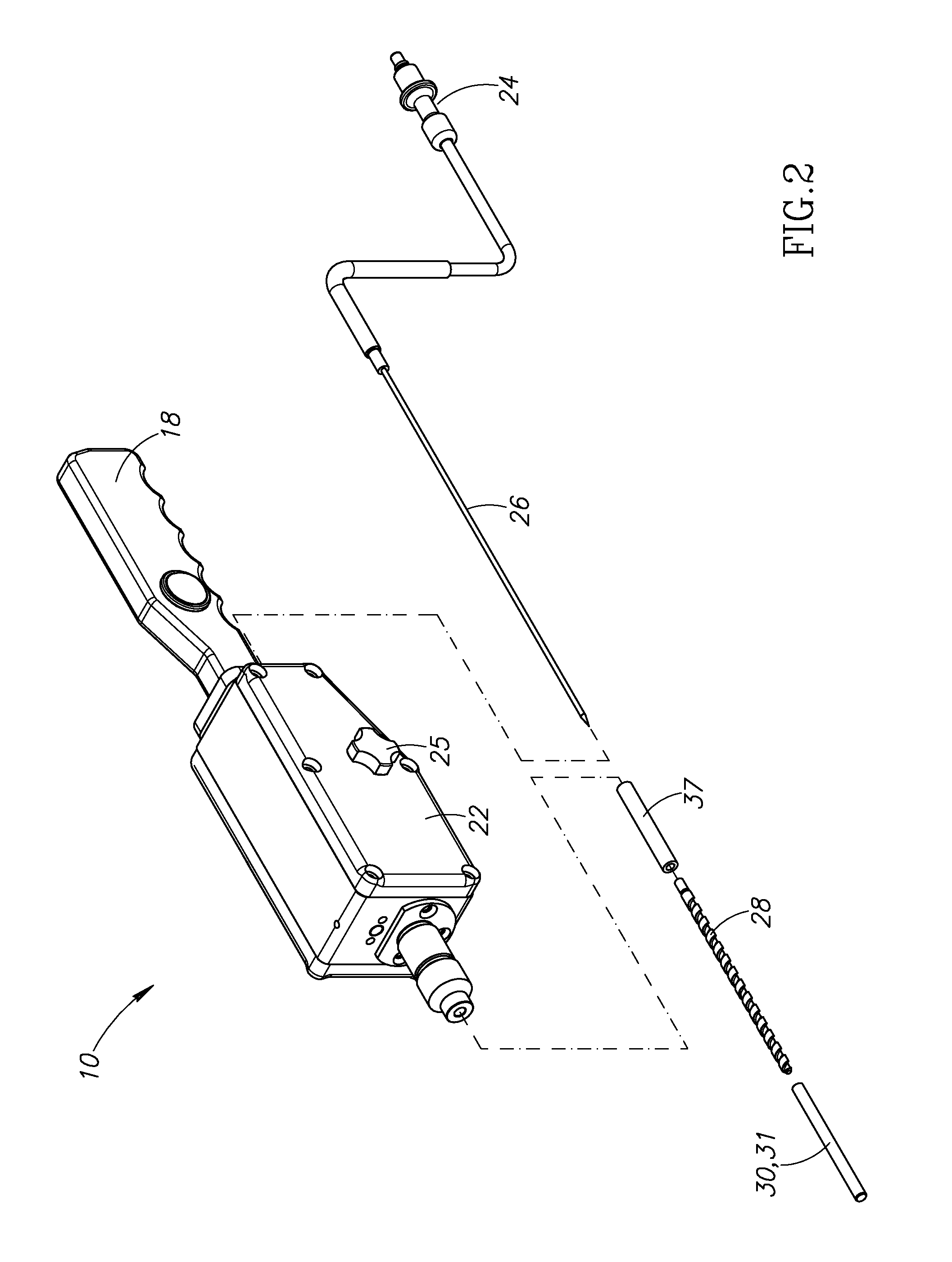
Multiple sensor device for measuring tissue temperature during thermal treatment
ActiveUS8348855B2Easy constructionThermometer detailsLine/current collector detailsThermal probeMultiple sensor
The present invention relates to devices and methods for measuring tissue temperature during thermal treatment of a body. More particularly, the present invention relates to a thermal probe comprising a plurality of thermal sensors operable to measure tissue temperatures during thermal treatments such as cryosurgery. Embodiments of the invention enable simultaneous measurements, using a single probe, of temperatures at a plurality of positions within body tissues. A preferred embodiment enables movement of sensors with respect to tissues while the probe is immobilized by being embedded in frozen tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Cryoprobe with reduced adhesion to frozen tissue, and cryosurgical methods utilizing same
The present invention relates to devices and methods for cryosurgery. More particularly, the present invention relates to a cryoprobe which does not form strong adhesive or mechanical bonds with body tissues when such tissues are frozen by cooling action of the probe. Embodiments of the present invention include a cryoprobe having a distal cooling module with an outer surface layer of non-polar molecules, a probe having a distal cooling module with a microscopically smooth outer surface, and a cryoprobe comprising a mechanism for coating a distal cooling module thereof with non-polar lubricant during movement of the cryoprobe within body tissues of a patient. Also presented are methods utilizing disclosed cryoprobes to facilitate cryosurgery and to enhance accuracy of cryoablation of user-selected cryoablation targets.
Owner:GALIL MEDICAL
Frozen tissue microarray technology for analysis RNA, DNA, and proteins
InactiveUS6893837B2Withdrawing sample devicesPreparing sample for investigationAnalysis dnaTissue Arrays
The invention disclosed herein improves upon existing tissue microarray technology by using frozen tissues embedded in tissue embedding compound as donor samples and arraying the specimens into a recipient block comprising tissue embedding compound. Tissue is not fixed prior to embedding, and sections from the array are evaluated without fixation or post-fixed according to the appropriate methodology used to analyze a specific gene at the DNA, RNA, and / or protein levels. Unlike paraffin tissue arrays which can be problematic for immunohistochemistry and for RNA in situ hybridization analyses, the disclosed methods allow optimal evaluation by each technique and uniform fixation across the array panel. The disclosed arrays work well for DNA, RNA, and protein analyses, and have significant qualitative and quantitative advantages over existing methods.
Owner:RGT UNIV OF CALIFORNIA
Tissue punch and tissue sample labeling methods and devices for microarray preparation, archiving and documentation
InactiveUS20060199169A1Avoid mistakesWaste of tissueBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVertical tubeTissue Arrays
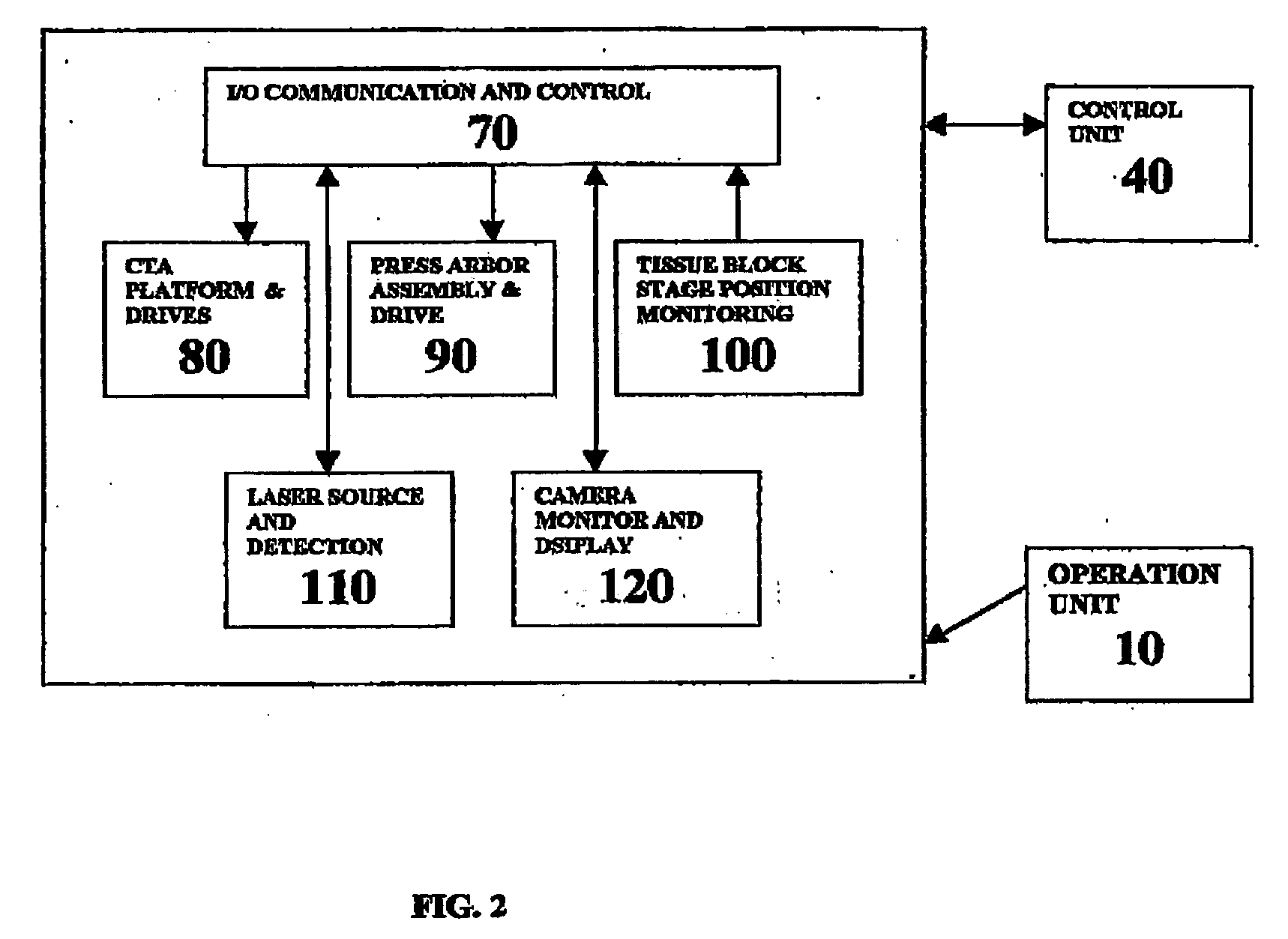
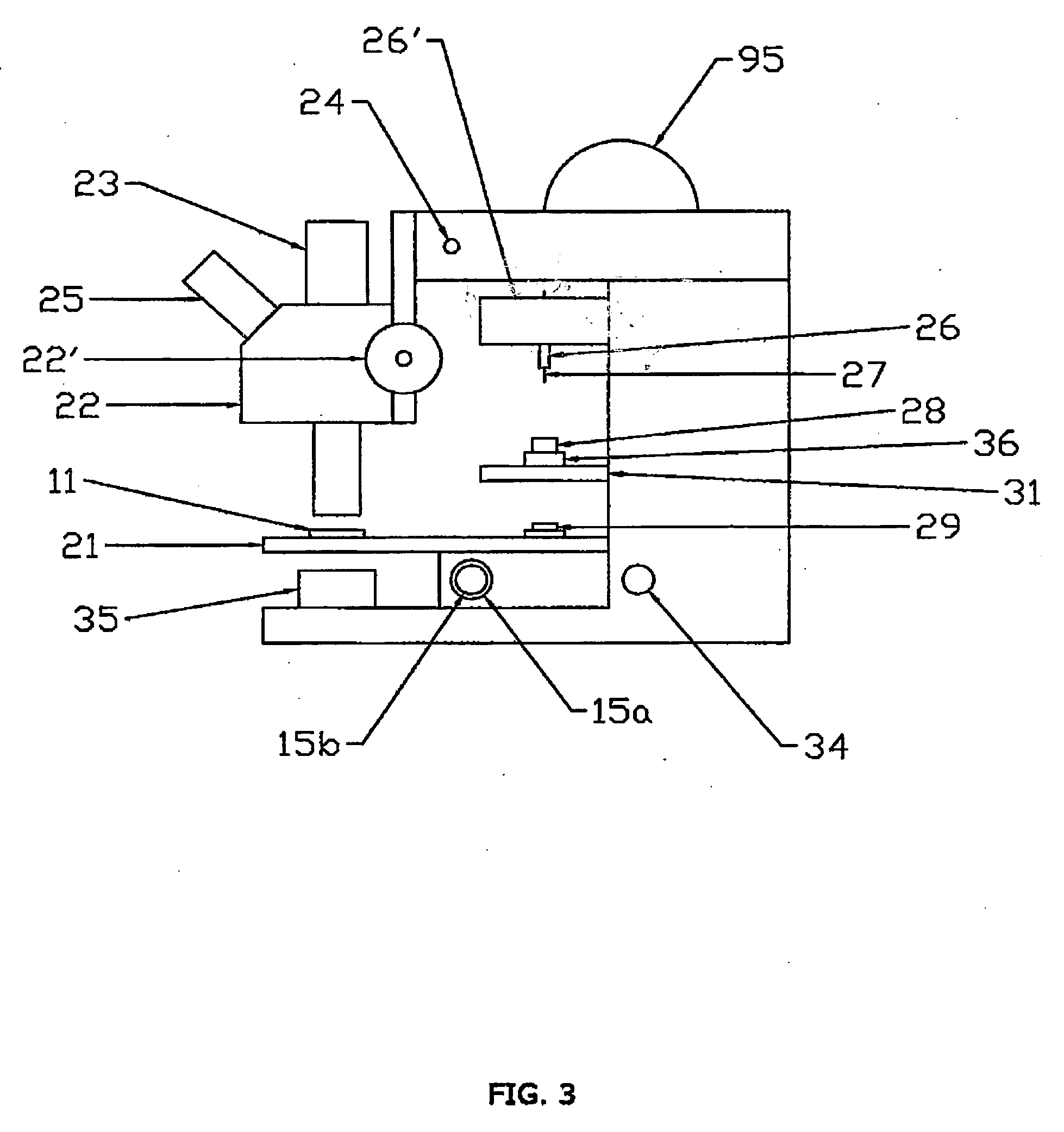
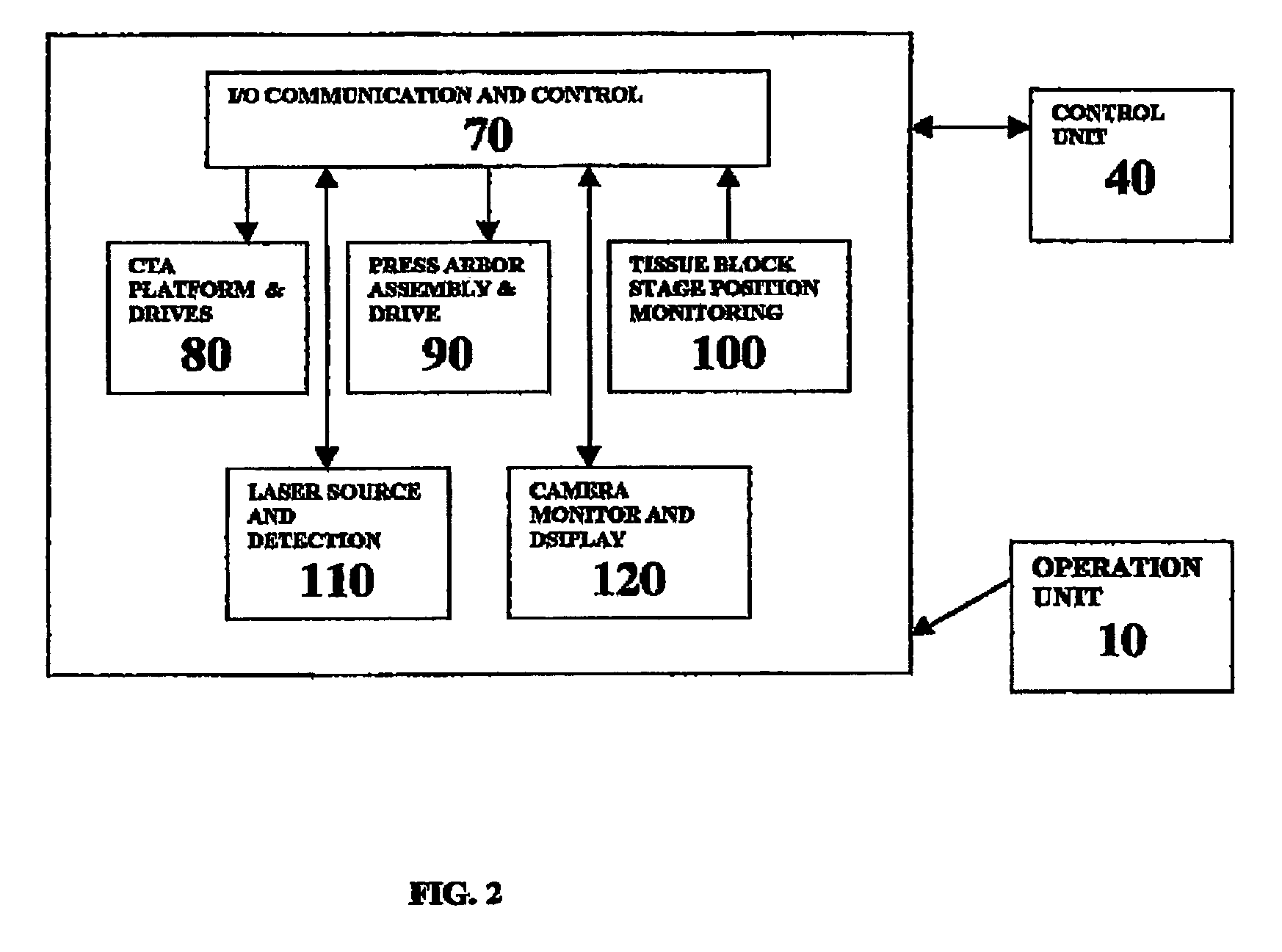
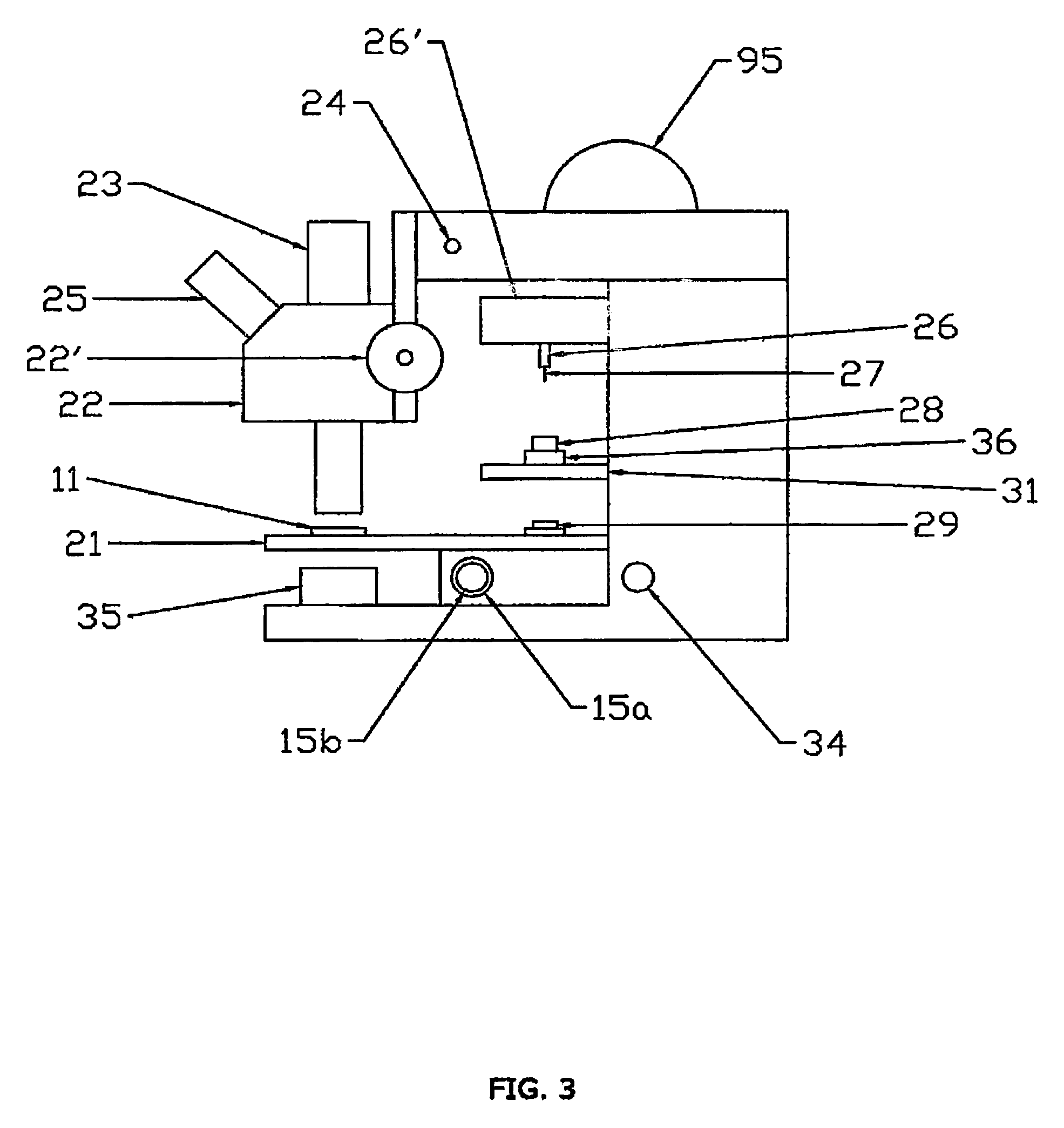
A workstation that provides an efficient method to collect biological tissues in a column tissue array format from blocks of embedded, frozen tissues, or fresh tissues. The workstation has a control unit for directing operations of the workstation and the operation unit for performing the production of the tissue column array. The operation unit comprises an array of vertical tubes in a platform, an arbor which engages and presses down the designated tube in the array, the embedded tissue block which is mounted directly below the designated tube, assemblies of motors responsive to the control unit for driving the platform and the tissue block, a light source block for generating an alignment signal, and a light detector block which measures the signal from the light source to determine the degree of alignment between the arbor, punch tubes, and the specimen block.
Owner:EXB TECH
Compositions for the detection of enzyme activity in biological samples and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS6936687B1Fluorescence enhancementFluorescent signal enhancementPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteinase activityFluorophore
The present invention provides for novel reagents whose fluorescence increases in the presence of particular proteases. The reagents comprise a characteristically folded peptide backbone each end of which is conjugated to a fluorophore. When the folded peptide is cleaved, as by digestion with a protease, the fluorophores provide a high intensity fluorescent signal at a visible wavelength. Because of their high fluorescence signal in the visible wavelengths, these protease indicators are particularly well suited for detection of protease activity in biological samples, in particular in frozen tissue sections. Thus this invention also provides for methods of detecting protease activity in situ in frozen sections.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Cryoablation segment for creating linear lesions
ActiveUS20080300584A1Reduce the cross-sectional areaLess pressure dropCatheterSurgical instruments for coolingFrozen tissueRefrigerant
An applicator for cryoablating tissue to form linear (i.e. straight line and curvilinear) lesions in targeted tissue includes a fluid refrigerant delivery system having a source of a fluid refrigerant and a tubular cryoablation segment. Structurally, the segment has an open proximal end and a distal end, and is formed with a lumen. Also, the segment is formed with at least one distal port and at least one proximal port, with each port connected in fluid communication with the segment's lumen. The proximal end of the tubular segment is operably connected in fluid communication with the source of fluid refrigerant. For the system, the ports can be selectively sized to outflow liquid refrigerant through the distal and proximal ports at a substantially same mass flow rate.
Owner:CRYOCOR
Probe and sequence combination for simultaneous detection of various mutation types
InactiveCN106480205ARealize multiple comprehensive detectionAccurate detectionMicrobiological testing/measurementDNA/RNA fragmentationHydrothoraxTherapeutic effect
The invention discloses a probe and a sequence combination for simultaneous detection of various mutation types and particularly provides a kit, a method, a gene chip, a probe and a sequence combination which are high in sensitivity and specificity and used for simultaneous detection of point mutation, short segment insertion and deletion, copy number variation and fusion genes of 57 tumor driver genes listed in a detection list. The invention further discloses a sequence combination and probe associated gene chip and kit and a method for simultaneous detection of various mutation types. By detection of body fluid including blood, hydrothorax, abdominal dropsy and the like and tumor frozen tissues or paraffin sections, comprehensive tumor driver gene mutation information can be acquired, sensitivity and accuracy in tumor gene detection are improved, and accordingly clinicians can be assisted in making of individualized medication schemes to achieve best accurate treatment effects.
Owner:BEIJING GENEPLUS TECH +1
Methods of making frozen tissue microarrays
InactiveUS8278034B2Bioreactor/fermenter combinationsSequential/parallel process reactionsDiseaseTissue microarray
The invention provides microarrays comprising a plurality of frozen tissues and / or cell samples and methods of preparing and using the same. By using frozen samples, the microarrays provide optimal samples from which to detect the expression of both nucleic acids (e.g., mRNAs) and proteins in high throughput parallel analyses. The microarrays enable gene identification, molecular profiling, selection of promising drug targets, sorting and prioritizing of expressed sequence array data, and the identification of abnormal physiological processes associated with disease.
Owner:NUCLEA BIOMARKERS
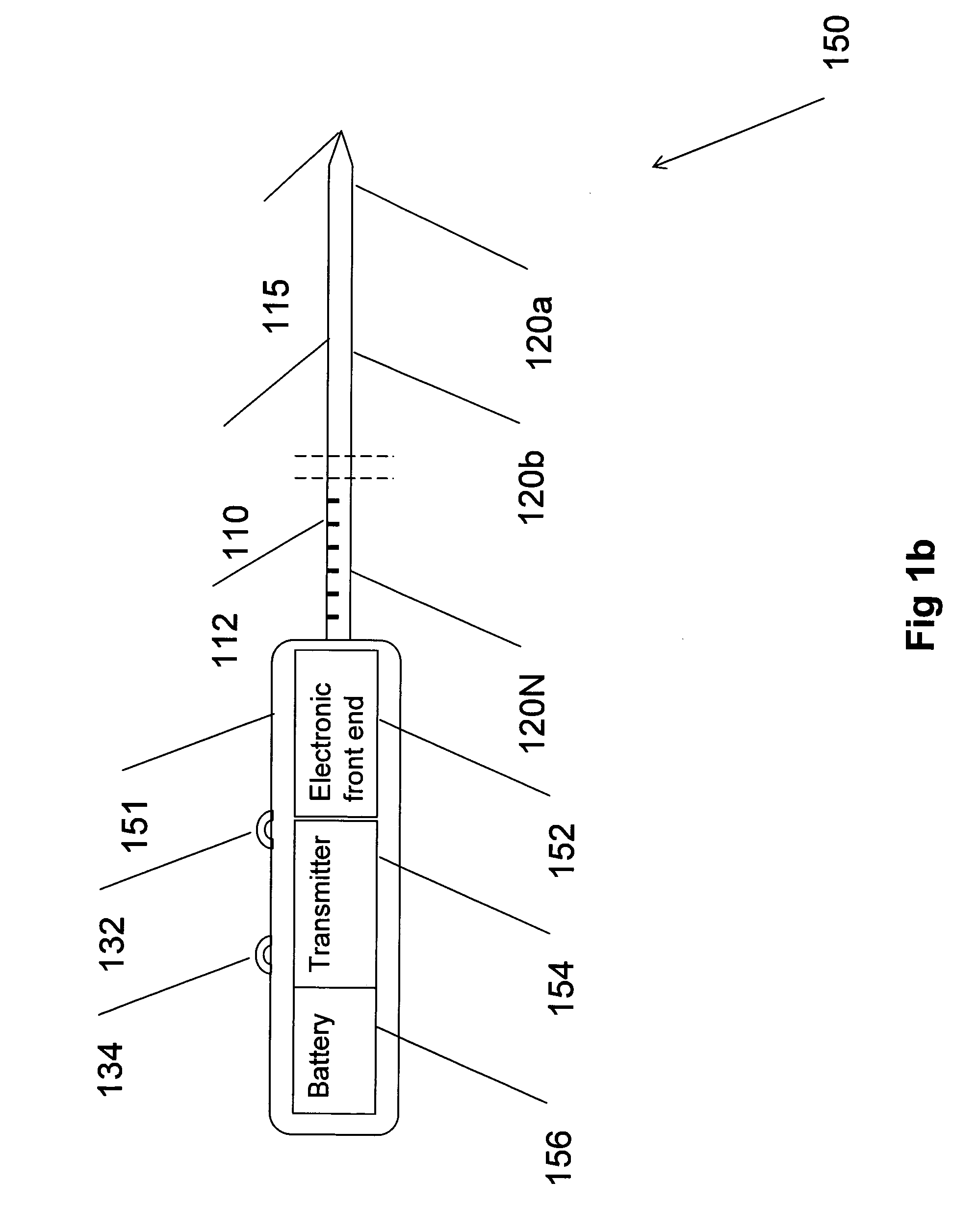
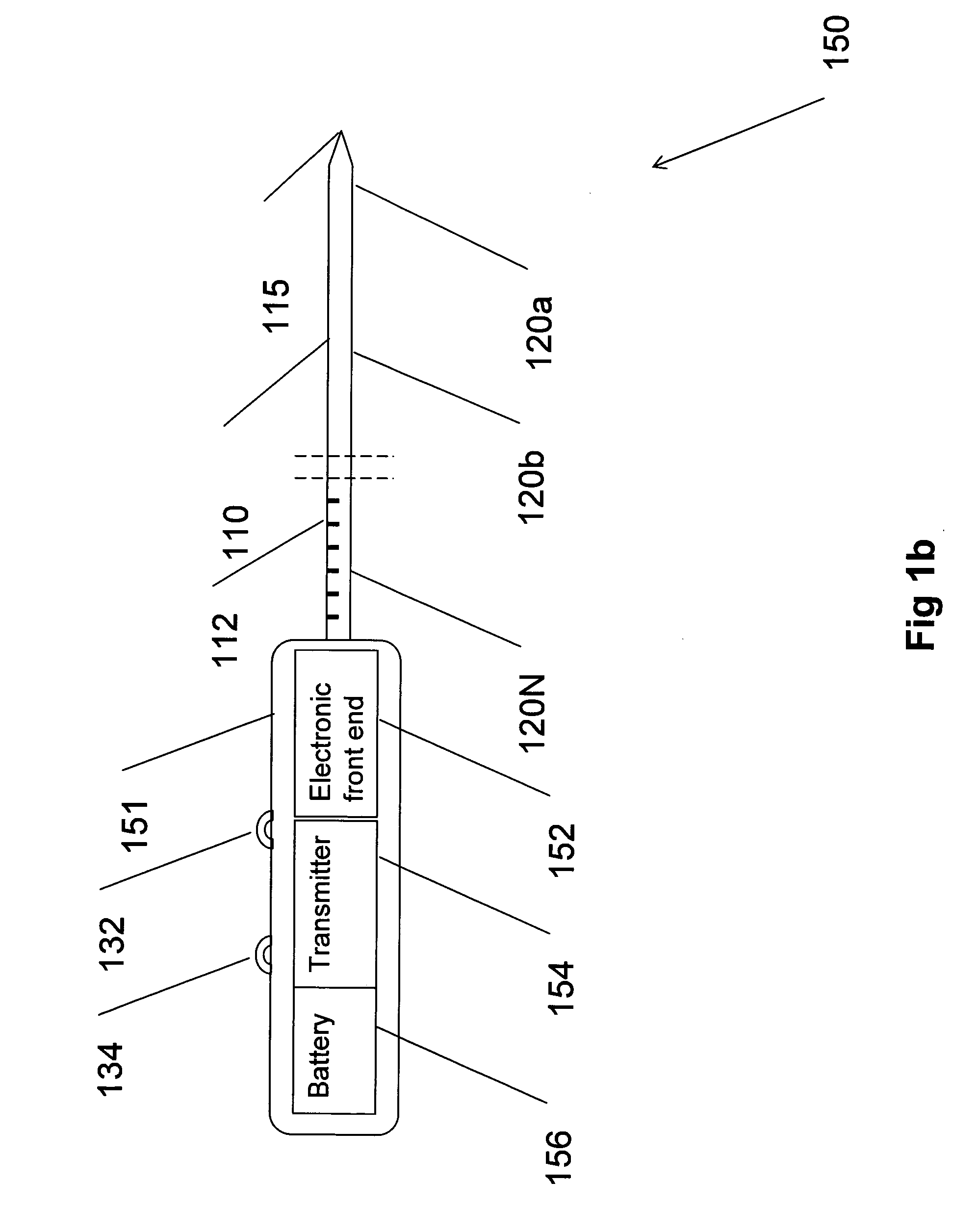
Multiple sensor device for measuring tissue temperature during thermal treatment
ActiveUS20090306638A1Easy constructionThermometer detailsLine/current collector detailsThermal probeMultiple sensor
The present invention relates to devices and methods for measuring tissue temperature during thermal treatment of a body. More particularly, the present invention relates to a thermal probe comprising a plurality of thermal sensors operable to measure tissue temperatures during thermal treatments such as cryosurgery. Embodiments of the invention enable simultaneous measurements, using a single probe, of temperatures at a plurality of positions within body tissues. A preferred embodiment enables movement of sensors with respect to tissues while the probe is immobilized by being embedded in frozen tissue.
Owner:BOSTON SCI SCIMED INC
Tissue punch and tissue sample labeling methods and devices for microarray preparation, archiving and documentation
InactiveUS7405056B2Waste of tissueWaste of timeBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsVertical tubeTissue Arrays
A workstation that provides an efficient method to collect biological tissues in a column tissue array format from blocks of embedded, frozen tissues, or fresh tissues. The workstation has a control unit for directing operations of the workstation and the operation unit for performing the production of the tissue column array. The operation unit comprises an array of vertical tubes in a platform, an arbor which engages and presses down the designated tube in the array, the embedded tissue block which is mounted directly below the designated tube, assemblies of motors responsive to the control unit for driving the platform and the tissue block, a light source block for generating an alignment signal, and a light detector block which measures the signal from the light source to determine the degree of alignment between the arbor, punch tubes, and the specimen block.
Owner:EXB TECH
Extraction method of apostichopus japonicus body-wall total RNA
InactiveCN101864414AMeet Gene Expression AnalysisFulfil requirementsDNA preparationWater bathsTotal rna
The invention discloses a high-extraction-purity, good-integrity and high-yield extraction method of apostichopus japonicus body-wall total RNA (Ribonucleic Acid). The method comprises the following steps of: quickly freezing apostichopus japonicus body-wall tissue in liquid nitrogen; grinding and putting the frozen tissue in lysate to homogenate, centrifugate and take supernatant fluid; adding chloroform to the supernatant fluid and centrifugating to take the supernatant fluid to another centrifuge tube; then, adding a high-salt solution and isopropyl alcohol and filtering precipitation with ethanol; dissolving the precipitation with DEPC (diethypyrocarbonate) treated water to have constant volume; sequentially adding a DNA enzyme buffer solution without RNA enzymes, DNA enzymes without RNA enzymes and an RNA enzyme inhibitor to the dissolved solution to mix; carrying out a water bath at 37 DEG C to obtain DNA lysate; adding phenol and chloroform in a ratio of 5:1 to the DNA lysate to mix, centrifugate and take supernatant fluid; adding a glycogen solution, a potassium acetate solution and pre-cooling ethanol to the supernatant fluid; mixing and staying over night; centrifugating to discard the supernatant fluid; washing and dying the precipitation with ethanol; dissolving the solution with the DEPC treated water to have constant volume of 20 mu l; and storing at 80 DEG C below zero.
Owner:DALIAN OCEAN UNIV
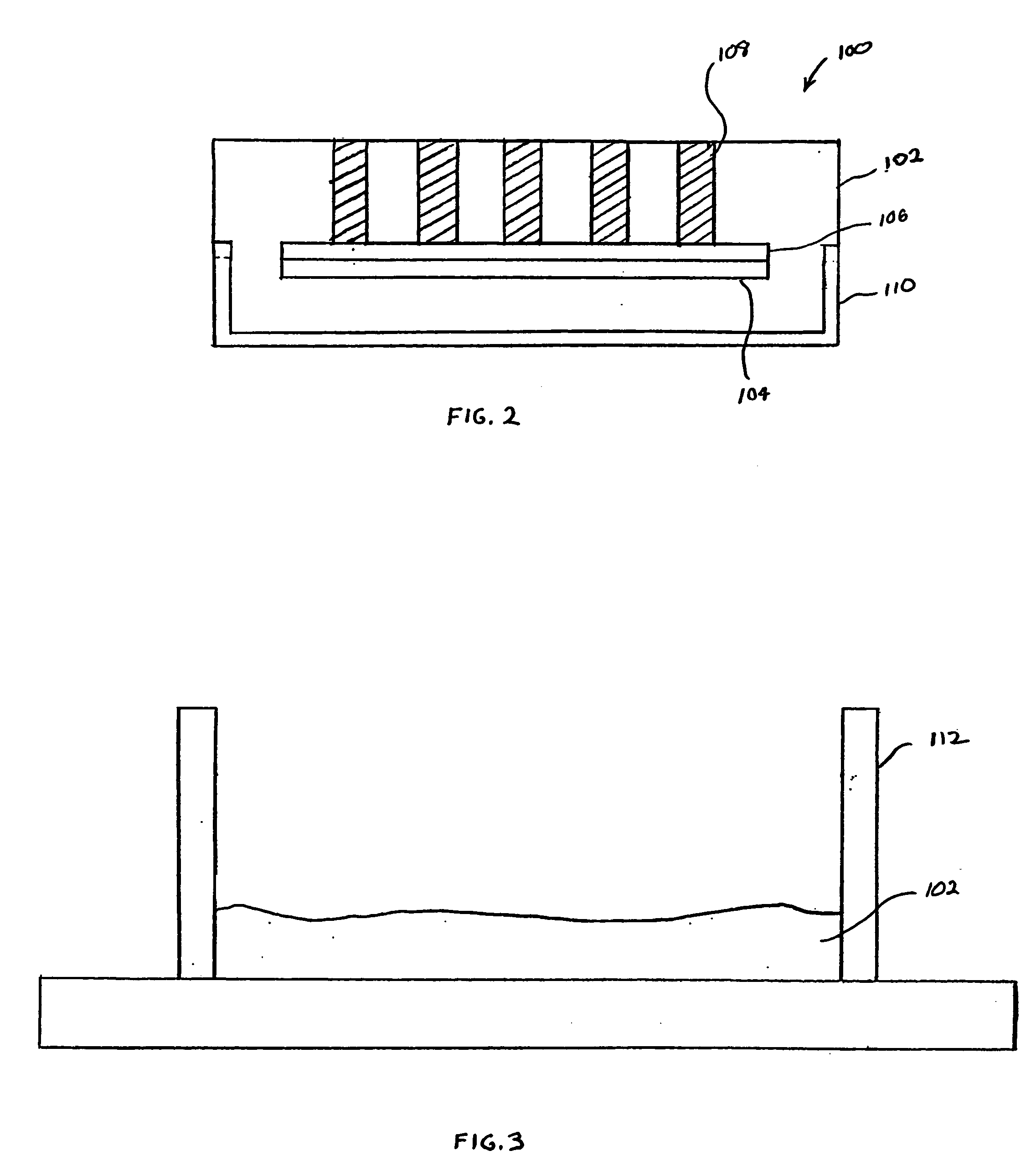
Frozen tissue microarray
InactiveUS20050282246A1Easy to disassembleBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFrozen tissueBiomedical engineering
A tissue microarray includes frozen tissue cores that extend from the top of the tissue microarray to a release. The release is a material from which embedding material of the tissue microarray can easily be removed. A stiffener is used with the release to maintain a flat shape of the release. The tissue cores may be formed from whole (i.e., paraffin-free) frozen tissue. A method and tool for manufacturing the tissue microarray are also disclosed.
Owner:COVANCE
Device and Method for Ambient Storage of Fresh/Frozen Tissue Sections Via Desiccation
ActiveUS20100221830A1Effectively and economically store and preserveEliminate needBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsFrozen tissueDesiccation
The present invention discloses a method for storing and preserving previously sectioned, snap-frozen, and desiccated biological tissue samples at ambient conditions. Also disclosed are devices and systems for ambient storage of biological tissue sections, and methods for forming said devices.
Owner:UNIV OF SOUTHERN CALIFORNIA
Compositions for the detection of enzyme activity in biological samples and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS20080199898A1Fluorescent signal enhancementFluorescence enhancementMicrobiological testing/measurementBiological material analysisProteinase activityFluorophore
The present invention provides for novel reagents whose fluorescence increases in the presence of particular proteases. The reagents comprise a characteristically folded peptide backbone conjugated to two fluorophores such that the fluorophores are located opposite sides of a cleavage site. When the folded peptide is cleaved, as by digestion with a protease, the fluorophores provide a high intensity fluorescent signal at a visible wavelength. Because of their high specificity and their high fluorescence signal in the visible wavelengths, these protease indicators are particularly well suited for detection of protease activity in biological samples, in particular in frozen tissue sections. Thus this invention also provides for methods of detecting protease activity in situ in frozen sections.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
Apparatus and methods for freezing tissue samples for sectioning
InactiveUS20100223935A1Freeze fastEasy to disassembleWork holdersMachines using refrigerant evaporationTetrafluoroethyleneTissue sample
Apparatus and methods for freezing a tissue sample in preparation of sectioning. Generally, the apparatus comprises a chuck and a tissue heat sink that are adapted to rapidly freeze a tissue sample before being sectioned in a cryostat. While the chuck and heat sink may be made of any suitable material, in some cases, the chuck and heat sink include copper, a copper alloy, bronze, or a bronze alloy. To keep the chuck and heat sink from tarnishing, they can be covered with a non-tarnishing coating material, such as tetrafluoroethylene. Additionally, in order to secure the tissue sample that is embedded in a cutting medium to the chuck, the chuck preferably includes one or more dovetail-shaped apertures, such as a dovetail-shaped groove.
Owner:DONNDELINGER THOMAS M
Method, Processor and Carrier for Processing Frozen Slices of Tissue of Biospecimens
InactiveUS20120276583A1Quality improvementBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsStainingAnatomy
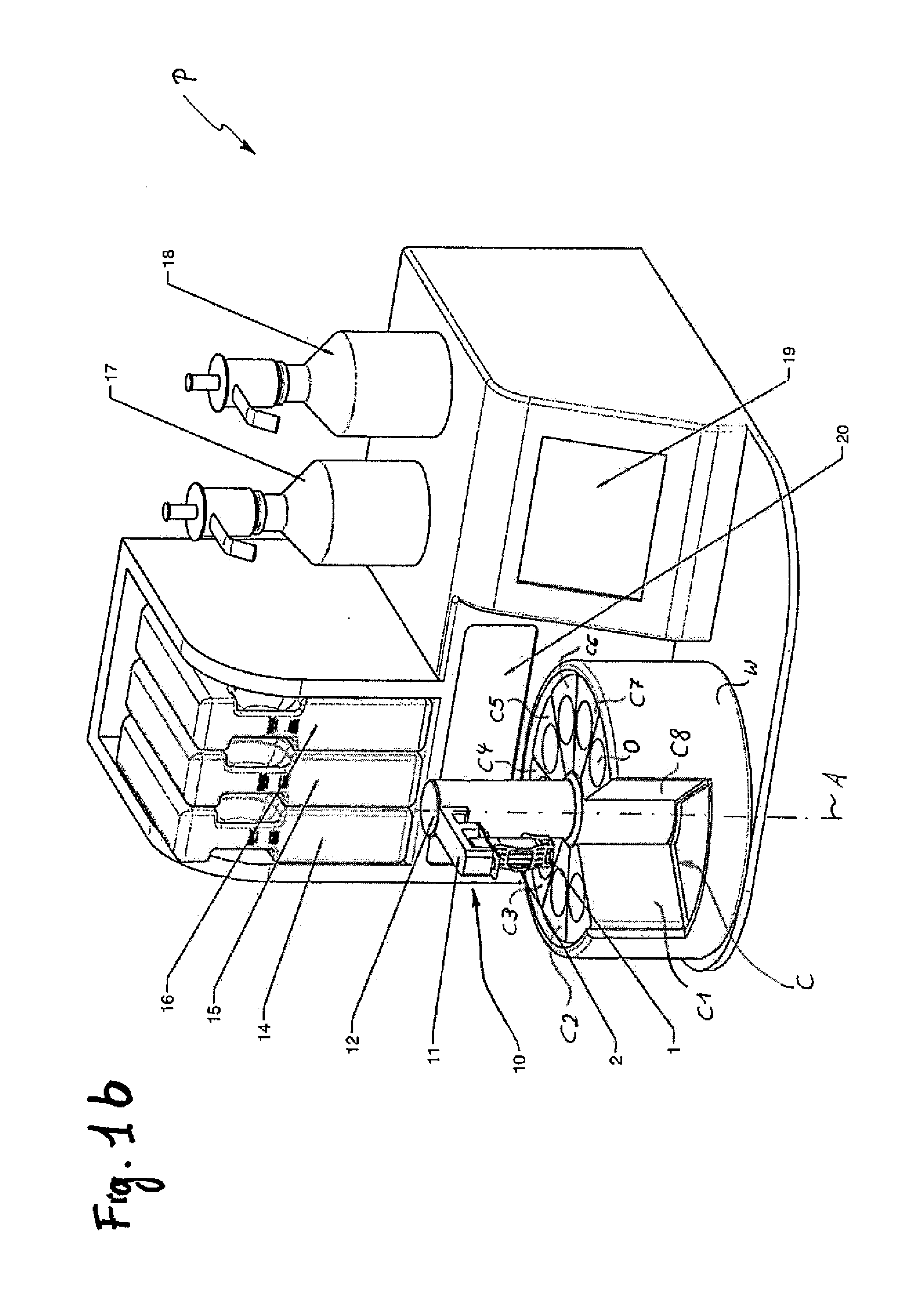
A method for processing frozen slices of tissue of biospecimens mounted on or adhered to glass slides, i.e. forming a frozen section (2), and arranged on a carrier (1), has the following steps: a.) immersing the frozen tissue slices in a fixative, b.) staining the tissue slice, c.) dehydrating the tissue slice, and d.) optionally clearing the tissue slice. Steps a.) to d.) are performed by automatically transferring the frozen sections (2) on the carrier (1) between and into and out of at least a container (C1) holding a fixative, at least one or optionally more, preferably two containers (C3, C5) holding a staining solution, a container (C6, C7) holding a dehydrating solution, and optionally a container (C8) holding a clearing solution. The transfer and the time duration during which the tissue slices are in said containers (C) are controlled by a control unit controlling an actuator (10).
Owner:MILESTONE SRL
Method for extracting high-quality cell nucleus DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol
The invention discloses a method for extracting a high-quality cell nucleus DNA (Deoxyribonucleic Acid) of a plant rich in polysaccharide and polyphenol, relating to the field of plant functional genomics. The method comprises the following steps of: firstly, grinding a plant material by using liquid nitrogen; secondly, resuspending by using an HB (Haemoglobin) extraction buffer solution, mixing uniformly through volution and filtering; thirdly, centrifuging, washing precipitation with an extraction buffer solution 1 three times and resuspending; fourthly, carrying out water bath by using an extraction buffer solution 2 and RnaseH at the temperature of 65DEG C for 30 minutes; fifthly, extracting once by using chloroform-isoamylol and precipitating by using isopropanol; and sixthly, washing precipitation by using 75 percent pre-cooled ethanol 1-2 times and dissolving by using a TE (Tris-Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) buffer solution. According to the pretreatment step in the methoddisclosed by the invention, DNAs of cell organelles such as mitochondria and chloroplast can be effectively removed; the inference on the nucleic acid extraction step caused by a large mount of secondary metabolites such as polysaccharide and polyphenol existing in the plant material is avoided; and the method is suitable for healthy tissues of wide plant species or frozen tissues with more complete cell structures and is especially suitable for high throughout sequencing in the subsequent researches.
Owner:WUHAN BOTANICAL GARDEN CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
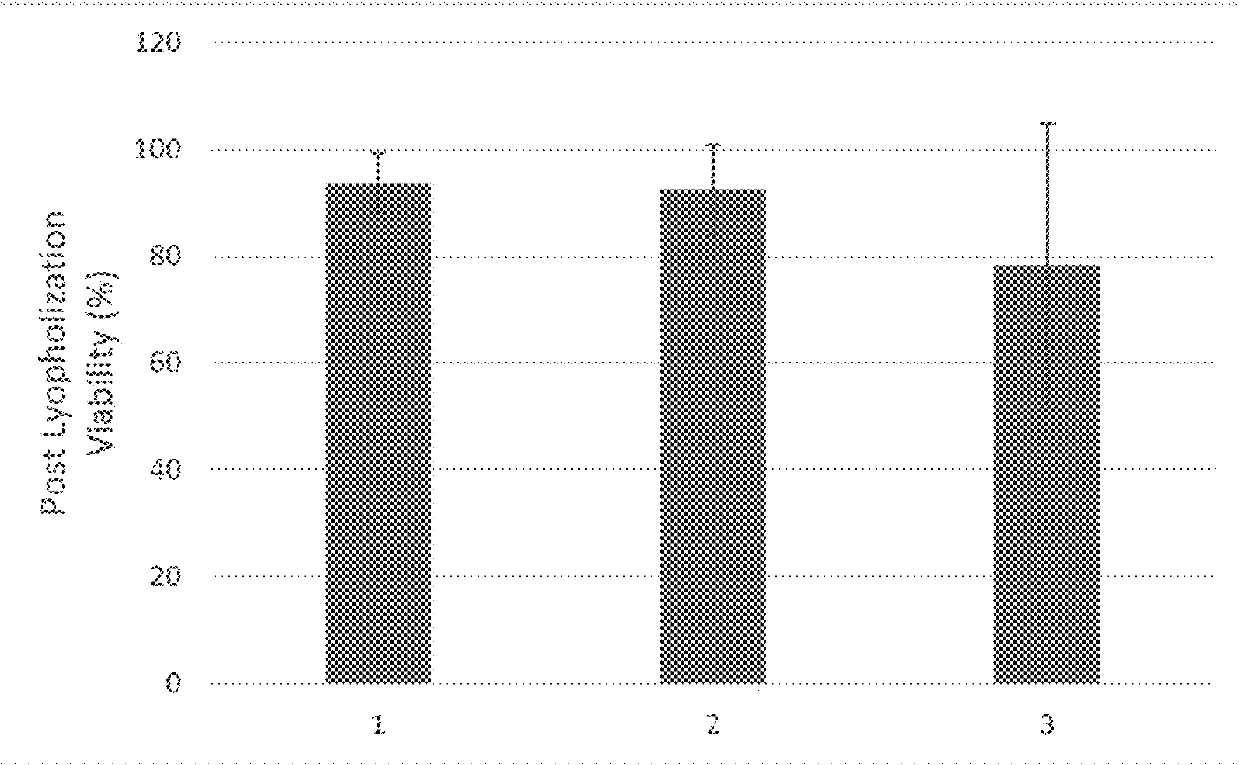
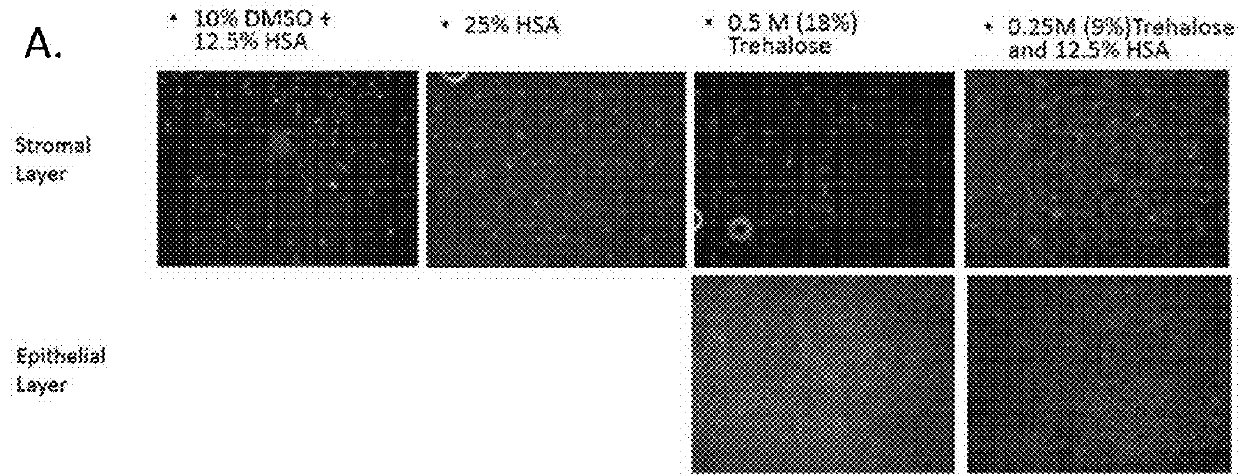
Viable lyophilized compositions derived from human tissues and methods of making the same
InactiveUS20180104282A1Improved tissue preservationPowder deliveryMammal material medical ingredientsTissue defectTissue sample
Disclosed are methods of lyophilizing a tissue sample comprising obtaining a tissue sample, contacting the tissue sample with a lyoprotectant solution, freezing the tissue sample, performing a first drying step of the tissue sample after freezing, and performing a second drying step of the tissue sample after the first drying step. Disclosed are lyophilized tissues prepared using the disclosed methods of lyophilizing a tissue sample comprising obtaining a tissue sample, contacting the tissue sample with a lyoprotectant solution, freezing the tissue sample, performing a first drying step of the tissue sample after freezing, and performing a second drying step of the tissue sample after the first drying step. Disclosed are methods of treating a wound or tissue defect comprising administering a reconstituted lyophilized tissue to the wound or tissue defect.
Owner:OSIRIS THERAPEUTICS
Treatment method for improving iron casting frozen tissue
The cast iron solidifying structure improving method features that to grey cast iron with carbon equivalent of 2.5-5.0 %, pulse current is led in before and during cast iron solidification while the cast iron temperature is 1000 deg.c to 1500 deg.c. The pulse current parameters includes pulse frequency of 0.1-10000 Hz, pulse voltage of 50-5000 V, and pulse current peak value of 400-100,000 A. The current may be led into the crucible or ladle or in the cast mold.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
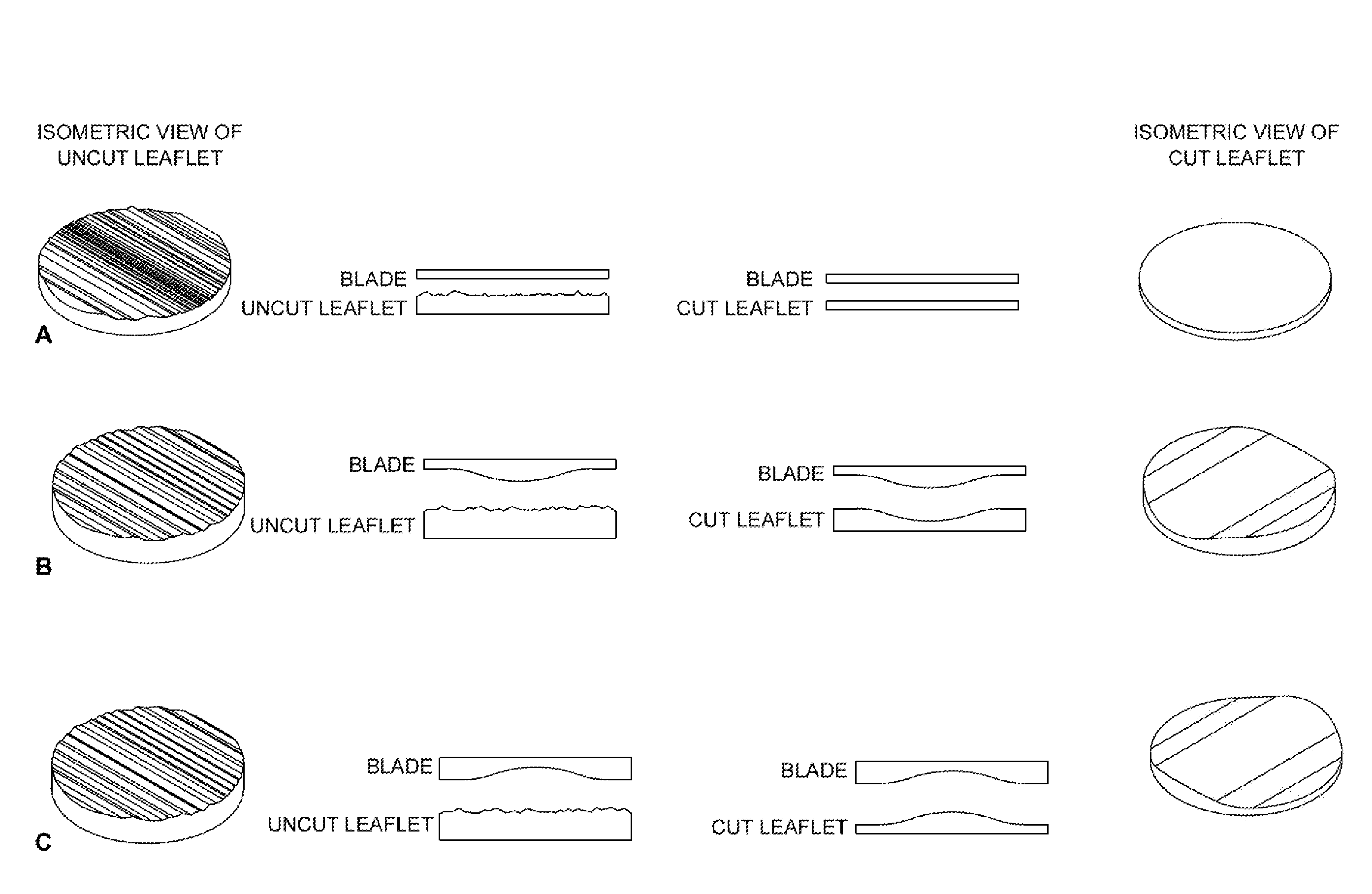
Method of preparing a tissue swatch for a bioprosthetic device
ActiveUS20140257472A1Increasing the thicknessHeart valvesMovable spraying apparatusMedicineFrozen tissue
A method of preparing a tissue swatch comprising one or more desired thicknesses for use in the manufacture of a bioprosthetic device, said method comprising sectioning a sheet of frozen tissue to produce a tissue swatch of said one or more desired thicknesses.
Owner:ST JUDE MEDICAL CARDILOGY DIV INC
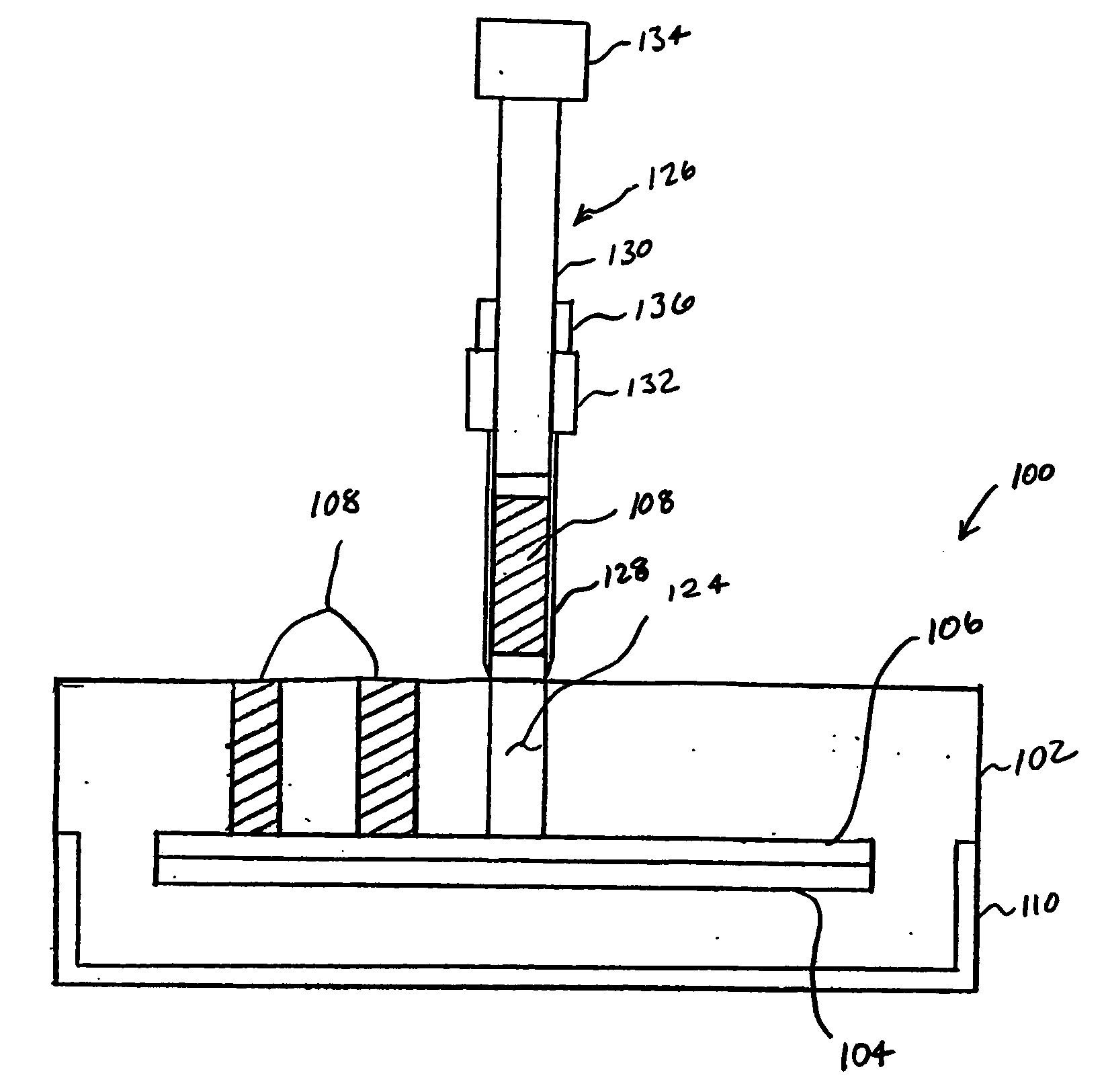
Apparatus and method for affixing frozen tissue sections to glass or membrane microscope slides
InactiveUS20120058509A1Great RNA stabilityDecreasing necessary reagentBioreactor/fermenter combinationsBiological substance pretreatmentsMicroscope slideLaser micro dissection
This invention is an apparatus and method for affixing frozen tissue sections to microscope slides. It has three elements; teasing implements, an affixing block and a heating element. The elements are used inside a cryostat prior to processing for molecular biology procedures such as immunohistochemistry or laser micro dissection. The tissue sections are collected onto an affixing block which has indentations that decrease the contact surface area while providing structural support. The tissue sections are then transferred onto a slide via transient application of a heating element to the back of slide. The invention decreases folding of tissue sections, increases morphological consistency, enables the placement of many sections on one slide and enables the adherence of tissue sections with greater thickness.
Owner:LEININGER ERIC JEFFORDS +1
Compositions for the detection of enzyme activity in biological samples and methods of use thereof
InactiveUS7312302B2Fluorescent signal enhancementFluorescence enhancementPeptide/protein ingredientsMicrobiological testing/measurementProteinase activityFluorophore
The present invention provides for novel reagents whose fluorescence increases in the presence of particular proteases. The reagents comprise a characteristically folded peptide backbone conjugated to two fluorophores such that the fluorophores are located opposite sides of a cleavage site. When the folded peptide is cleaved, as by digestion with a protease, the fluorophores provide a high intensity fluorescent signal at a visible wavelength. Because of their high specificity and their high fluorescence signal in the visible wavelengths, these protease indicators are particularly well suited for detection of protease activity in biological samples, in particular in frozen tissue sections. Thus this invention also provides for methods of detecting protease activity in situ in frozen sections.
Owner:ONCOIMMUNIN
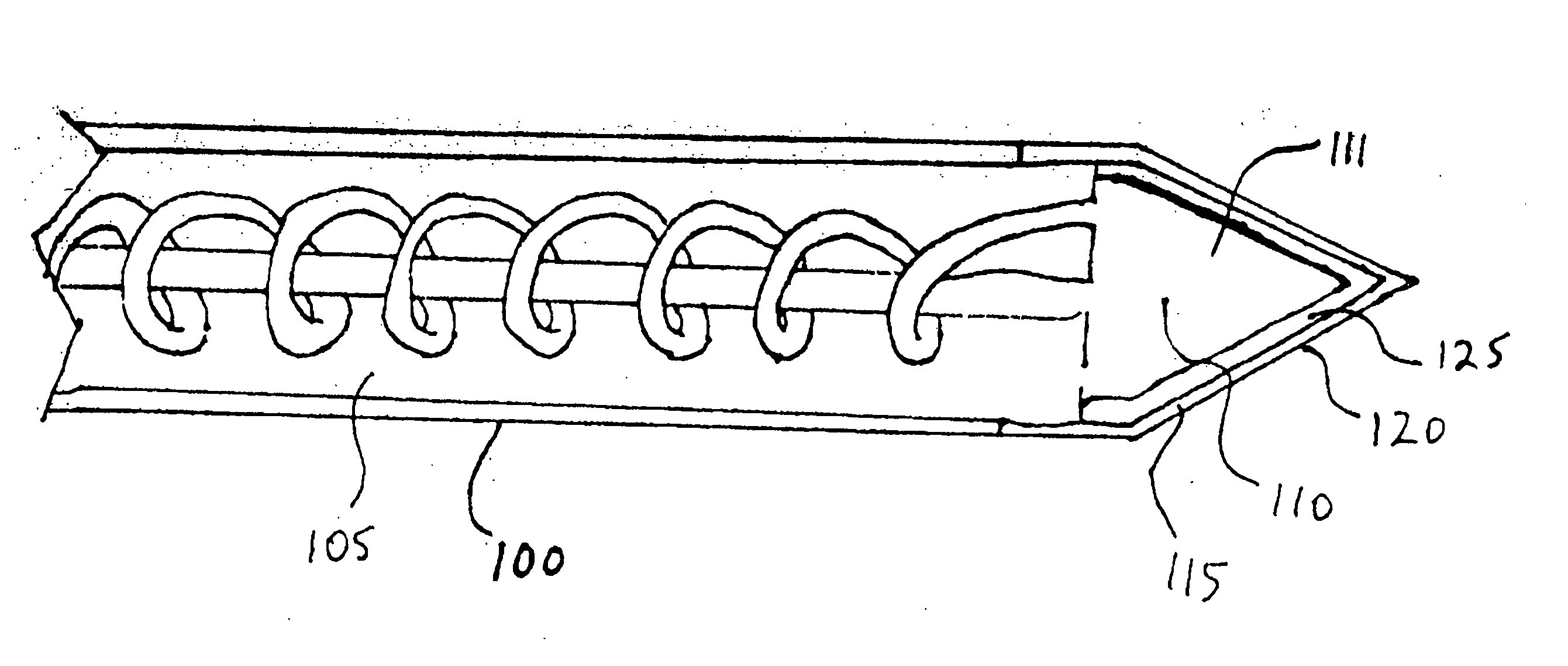
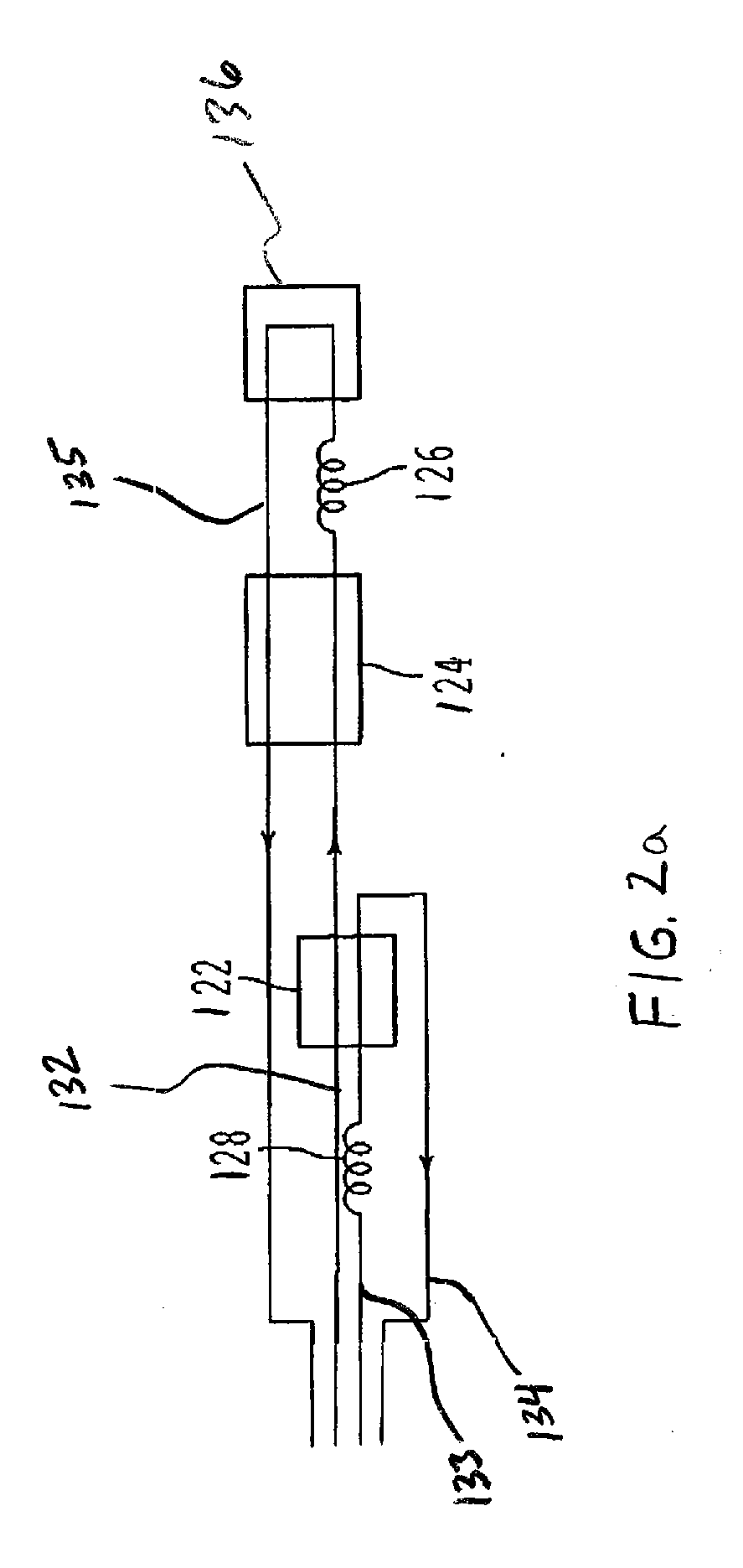
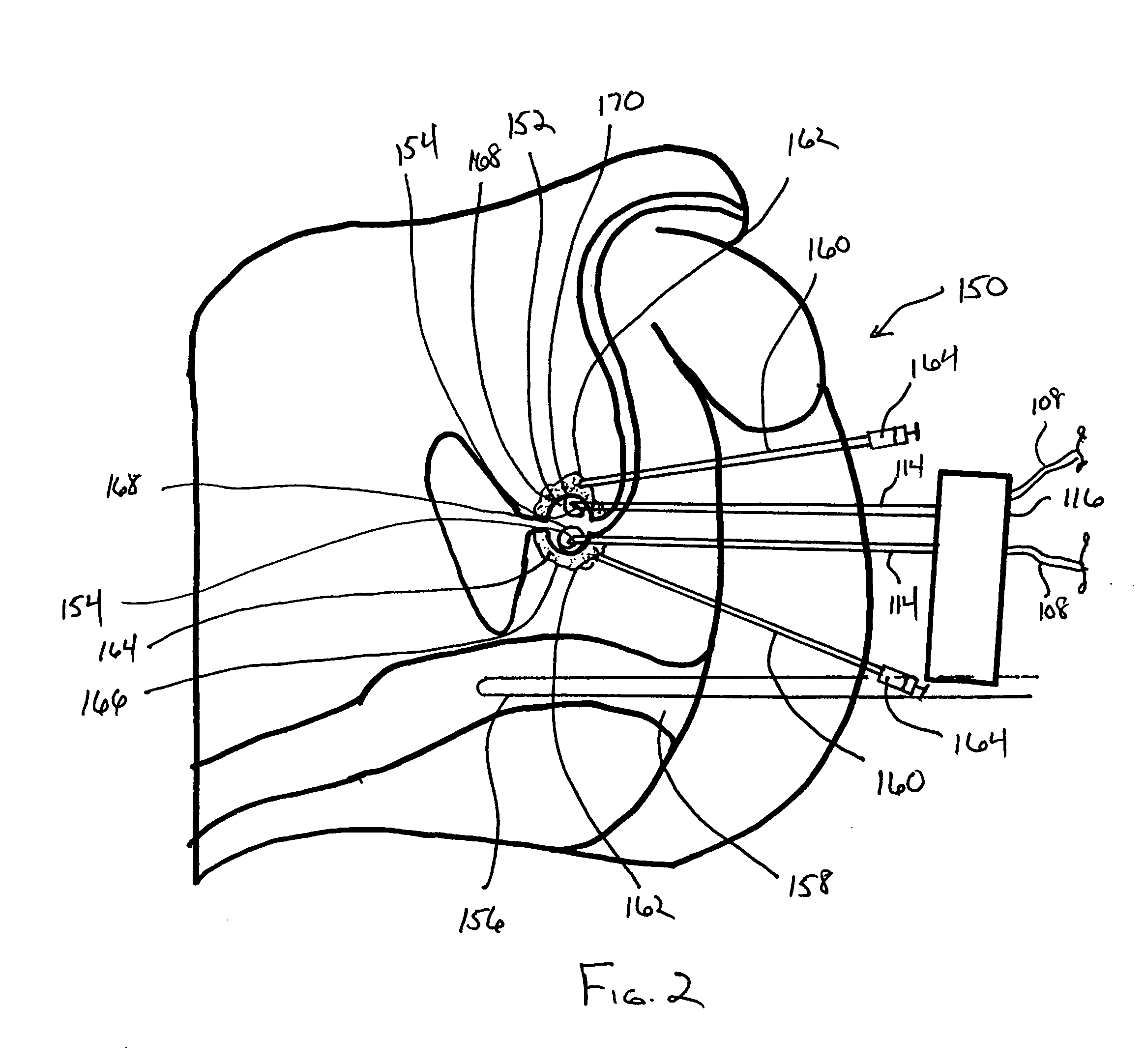
Closed Loop Cryosurgical System
InactiveUS20080114347A1Avoid overall overheatingAvoid meltingSurgical instruments for coolingSurgical treatmentFreezing thawing
An improved closed loop cryosurgical system and related methods of use. The closed loop cryosurgical system can utilize a reduced size cryoprobe by moving a pre-cool heat exchanger into a control console for the system. The cyroprobe can further include a sheath having at least one thermal wire spaced around the sheath that can be heated using the control console so as to thaw frozen tissue. By incorporating thermal wiring into the sheath, the time necessary for a cryosurgical procedure can be significantly reduced, especially where multiple freeze-thaw cycles are conducted. In another aspect, an improved, environmentally friendly mixed gas refrigerant can be provided for use in cooling the cyroprobes. The mixed gas refrigerant avoids the use of the refrigerant R22 while also providing faster and more efficient ice ball formation at the cryoprobe tip, therefore allowing the cryosurgical treatment to be accomplished in less time.
Owner:COOPERSURGICAL INC
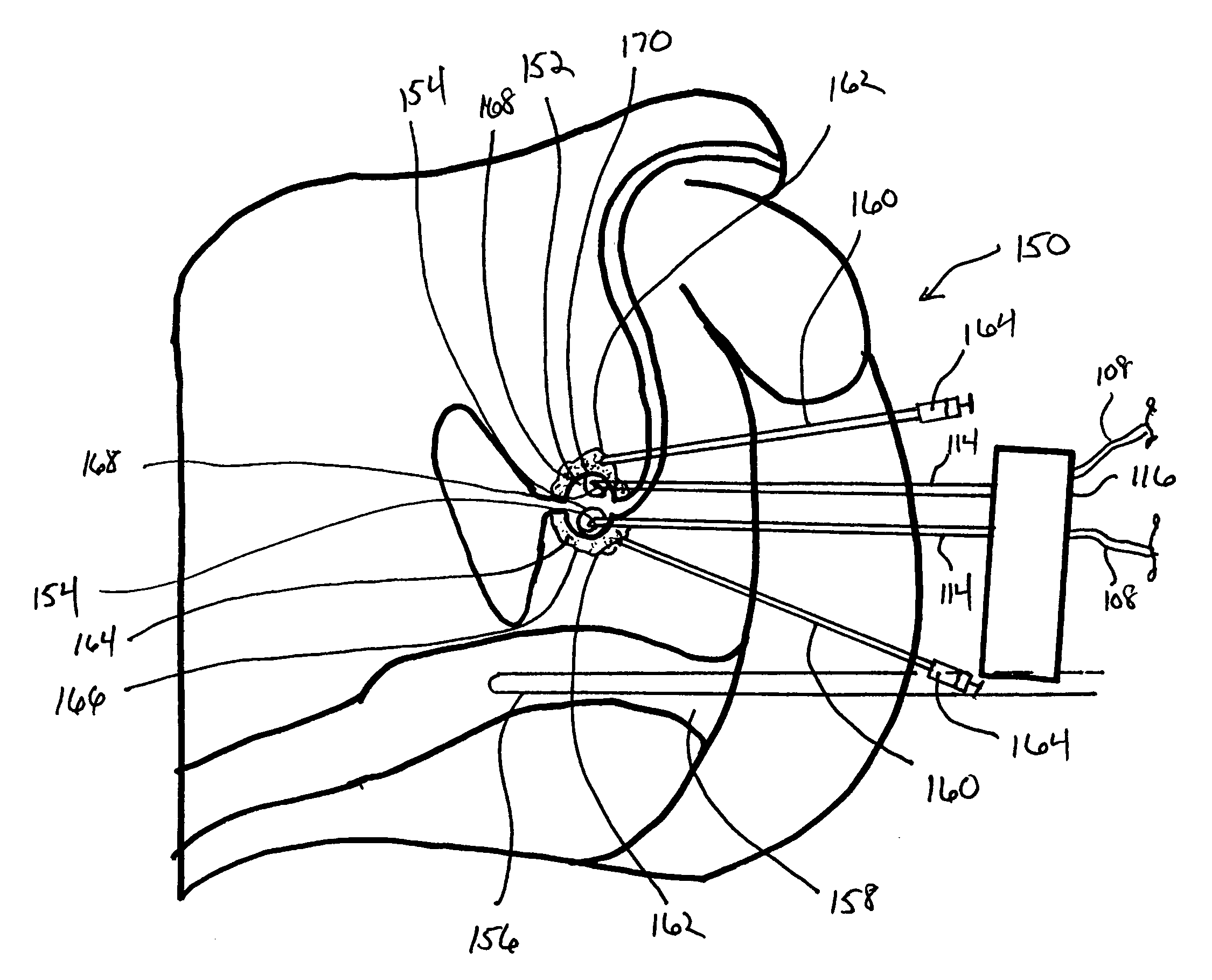
Cryoprotective Agent Delivery
InactiveUS20080114348A1Promote resultsInhibited DiffusionSurgical instruments for coolingDamages tissueFrozen tissue
The present disclosure is directed to the use of a cryoprotective agent to protect healthy tissue while damaged tissue is cryosurgically treated. A cryoprotective agent can be delivered utilizing a delivery probe that is inserted into healthy tissue either prior to or during a freeze portion of a first freeze / thaw cycle. The cryoprotective agent diffuses through the healthy tissue, but diffusion is controlled at the freeze edge by the diffusion limiting characteristics of the tissue that is frozen. When the frozen tissue is thawed, the disrupted tissue will continue to restrict the diffusion of the cryoprotective agent. Additional freeze / thaw cycles can then be conducted and the cryoprotective agent will continue to protect the healthy tissue. The delivery probes can also function as thermal sensor probes that can also be used to monitor the temperature at selected tissue locations.
Owner:COOPERSURGICAL INC
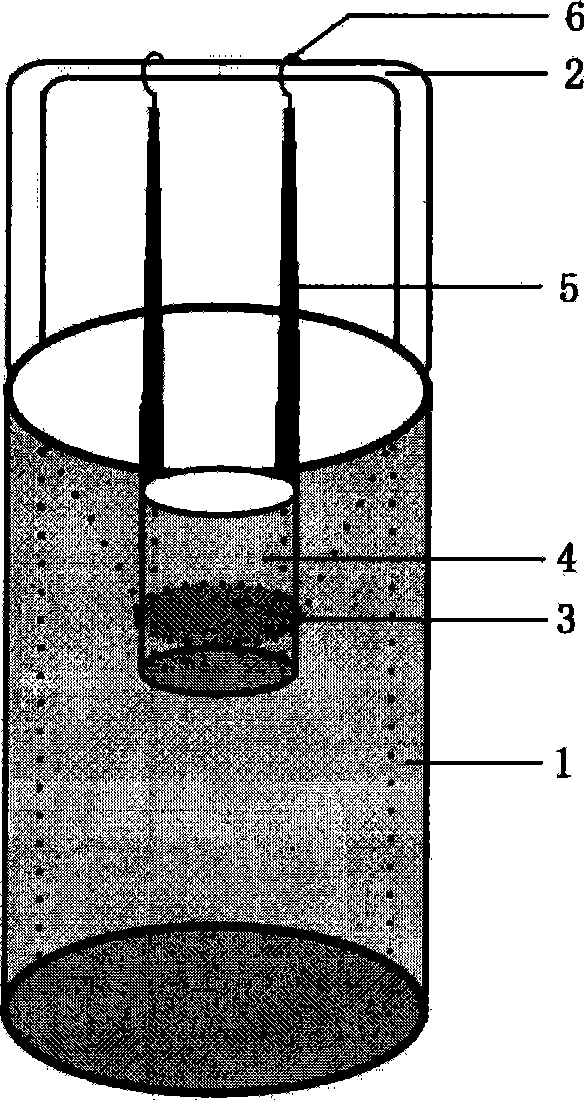
Multifunction organization embedding and refrigerating plant
InactiveCN101451928AReduce volatilityEasy to carryLighting and heating apparatusWithdrawing sample devicesFrozen tissueEmbryo
This invention is a tissue embed-freeze apparatus for frozen tissue section used for life science experiment and medical pathological tissue examination, comprised of a multifunctional liquid nitrogen storage thermostatic bottle and an adjustable suspending water tank. The multifunctional liquid nitrogen storage thermostatic bottle is internally designed with a conical baffle for the adjustable suspending water tank to enter, used for freezing the embedded tissue and reducing volatilization of liquid nitrogen therein. The adjustable suspending water tank is disposed with two freely operable pull rods on two sides thereof, in order to adjust immerging depth and position of the water tank into the liquid nitrogen in the thermostatic bottle within 0 to 30cm according to actual need. With utilization, this invention can rapidly and conveniently carry out high quality freezing process can be carried out on embedded tissue and embryo as a special tissue embed-freeze apparatus, especially suitable for life science, pathology and anatomy, etc., which simultaneously bring new improvement for existing tissue embed-freeze module.
Owner:INST OF ANIMAL SCI OF CHINESE ACAD OF AGRI SCI
Improved frozen slicing method and applications thereof
InactiveCN104634626AEasy to operateShorten the timePreparing sample for investigationBiological macromoleculeSample preparation
The invention relates to the field of tissue sample preparation and pathogenic research, and particularly relates to an improved frozen slicing method and applications thereof. The improved frozen slicing method comprises the following steps: tissue pretreatment step, tissue embedding step, tissue freezing and sliding steps, wherein frozen tissue slices can be obtained after the slicing step, and a freezing protecting agent is adopted for soaking a tissue sample in the tissue pretreatment step. According to a tissue sample preparation method, not only can a fine tissue structure similar to a wax slice effect be obtained, but also the high quality of biological macromolecules, such as DNA, RNA and protein, can be guaranteed so as to meet the whole genome detection and analysis of the biological macromolecules. The improved frozen slicing method has the advantages of being simple, strong in universality, short in sample preparation time, wide in application prospect, and the like.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Prognosis evaluation system for patients with early-stage lung adenocarcinoma (LUAD) and application thereof
ActiveCN111394456AFacilitate understanding of the interaction mechanismMicrobiological testing/measurementProteomicsDiseasePulmonary adenocarcinoma
The invention discloses a prognosis evaluation system for patients with early-stage LUAD and application thereof. According to the invention, disease-free survival data of 632 patients with early-stage LUAD in three independent queues are integrated, and an individual IBRS model for patients with early-stage LUAD is established and verified. The three independent queues include TCGA, GSE31210 and68 cases of frozen tissues. The IBRS model is composed of the following nine genes: DYNC1I2, THOC1, ADAM10, SERPINB6, CCL20, WNT2B, SLC11A1, MAPT and PSEN1. The establishment of the IBRS model for patients with early-stage LUAD is not only beneficial for understanding of the complex interaction mechanism between immune molecules, but also brings great help to the recurrence prediction of the patients with early-stage LUAD and the optimization of a treatment scheme.
Owner:CANCER INST & HOSPITAL CHINESE ACADEMY OF MEDICAL SCI
Biological frozen tissue cutting device
InactiveCN104960007AAchieve reductionAdjustable numberMetal working apparatusMotor driveFrozen tissue
The invention discloses a biological frozen tissue cutting device which is used for achieving the fast cutting on frozen biological tissues. The biological frozen tissue cutting device comprises a base, a support, a stand column, a pressing plate, cutting tools and a splash guard cover, wherein the upper portion of the base is provided with the support, one side of the support is provided with the stand column moving vertically relative to the support, and a driving assembly used for driving the stand column to ascend and descend is arranged between the stand column and the support; the pressing plate is fixed onto the bottom of the stand column, the bottom of the pressing plate is provided with a plurality of installing frames, the installing frames are located on the same circumference and evenly distributed on the circumference, at least two of the installing frames are provided with the cutting tools, and the cutting tools are provided with blades used for cutting biological tissues; the splash guard cover is arranged on the position, under the pressing plate, of the base, and biological frozen tissues to be cut are placed in the splash guard cover. According to the biological frozen tissue cutting device, a motor drives the pressing plate to descend to drive the blades to descend, the blades extrude the frozen tissues to achieve the cutting of the frozen tissues, and the problem that direct manual pressing of the blades wastes time and strength is solved.
Owner:UNIV OF JINAN
Systems and Methods For Natural Cryoprotectants For Preservation Of Cells
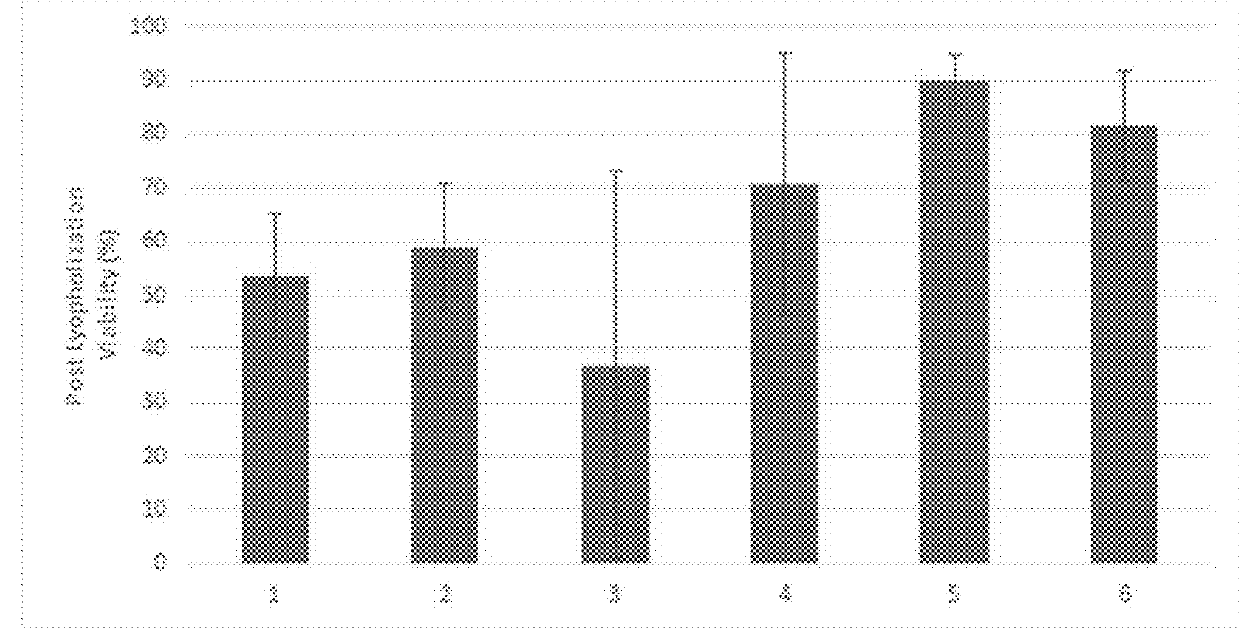
ActiveUS20190269123A1Reducing post-thaw survivalReduce exerciseDead animal preservationEmbryonic cellsPlant SourcesFrozen tissue
Embodiments of the present invention provide plant-derived extracts as a replacement for traditional cryoprotectants used to freeze tissue and cell s providing a method to decrease post-thaw damage as created by the cryoprotectant. For example, extracts from the genus Hippophae or other plant sources or compositions may be used as a cryoprotectant or may even be used to replace at least some of a traditional cryoprotectant.
Owner:MEMBRANE PROTECTIVE TECH
Cryogenic biopsy system and method
ActiveUS20120322070A1Avoid curlMicrobiological testing/measurementSurgical needlesBiopsy devicePathology diagnosis
A cryogenic biopsy device is configured to provide thin, frozen tissue samples, which may be viewed under a microscope and selected for biomarker analysis. The device is configured to provide slices which are less than 50 micrometers in thickness, while snap-freezing the tissue and maintaining the sample in a deep-frozen state until it reaches the pathology lab for further processing. Alternatively, thicker slices can be harvested by the device and additional sectioning can be done in the pathology lab by using cryomicrotome. The device of the present invention may be used in rigid instruments and in flexible devices, such as endoscopes, for example, and may be suitable for single use or multiple use.
Owner:NEVO EREZ
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com