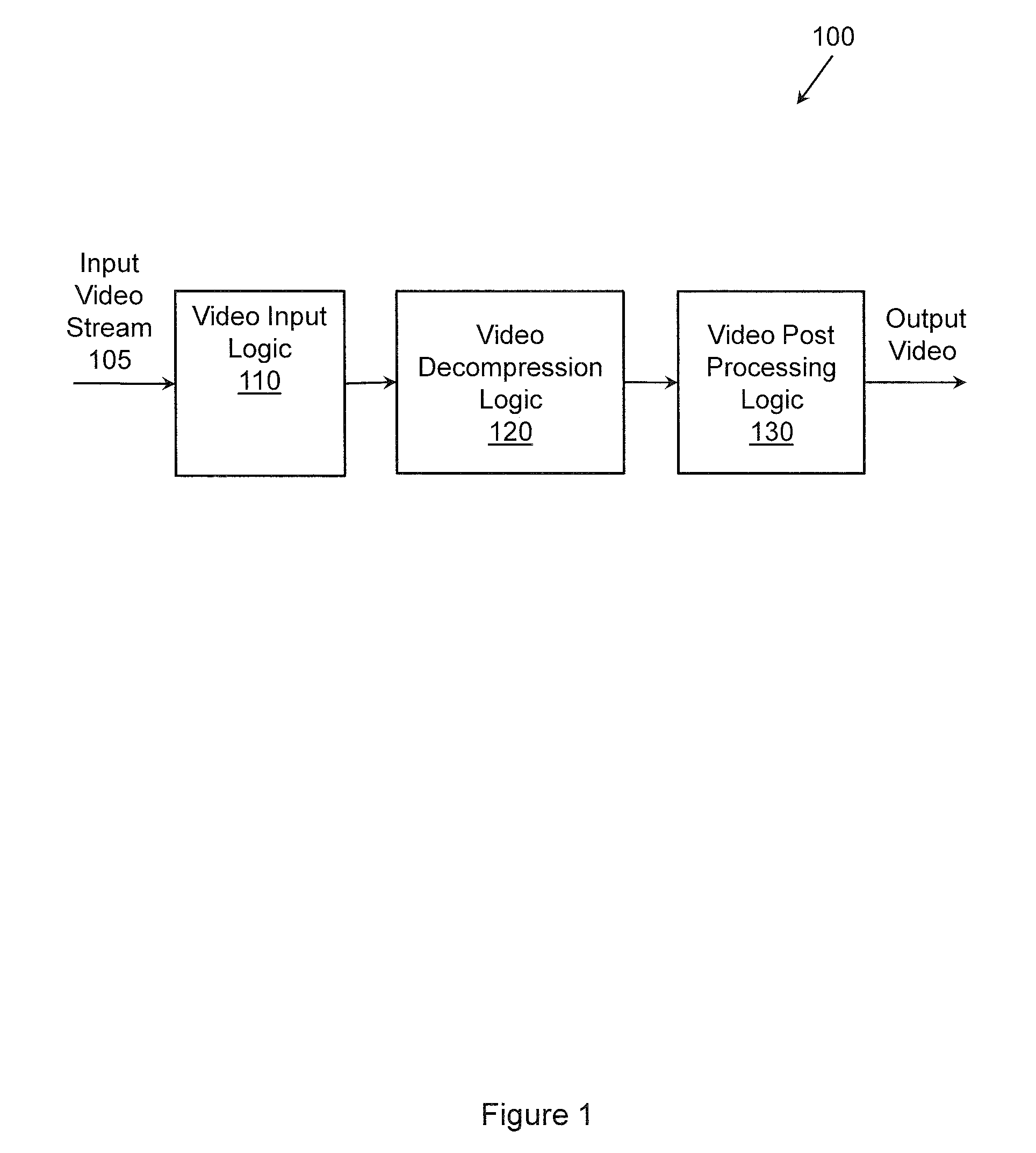
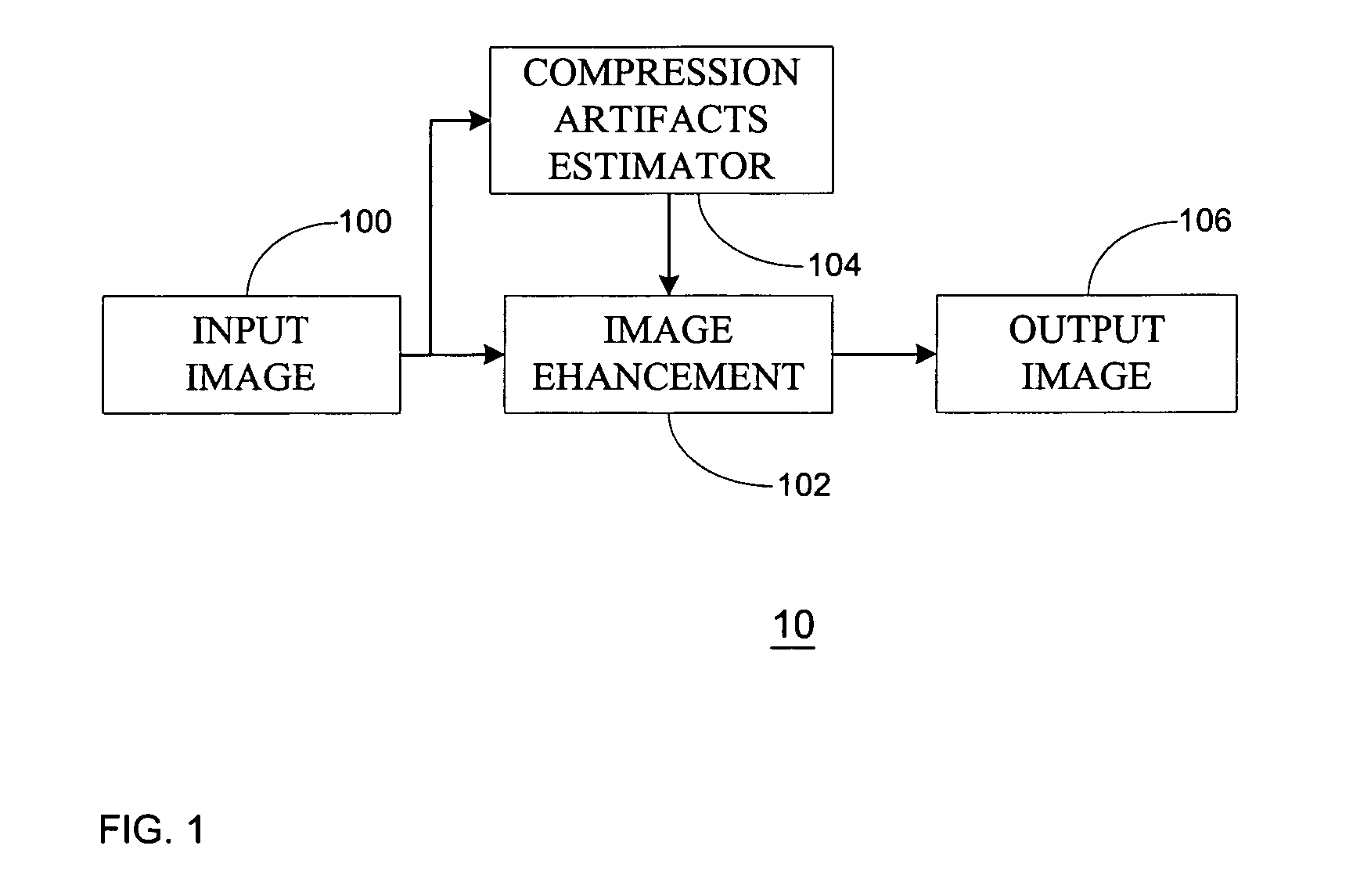
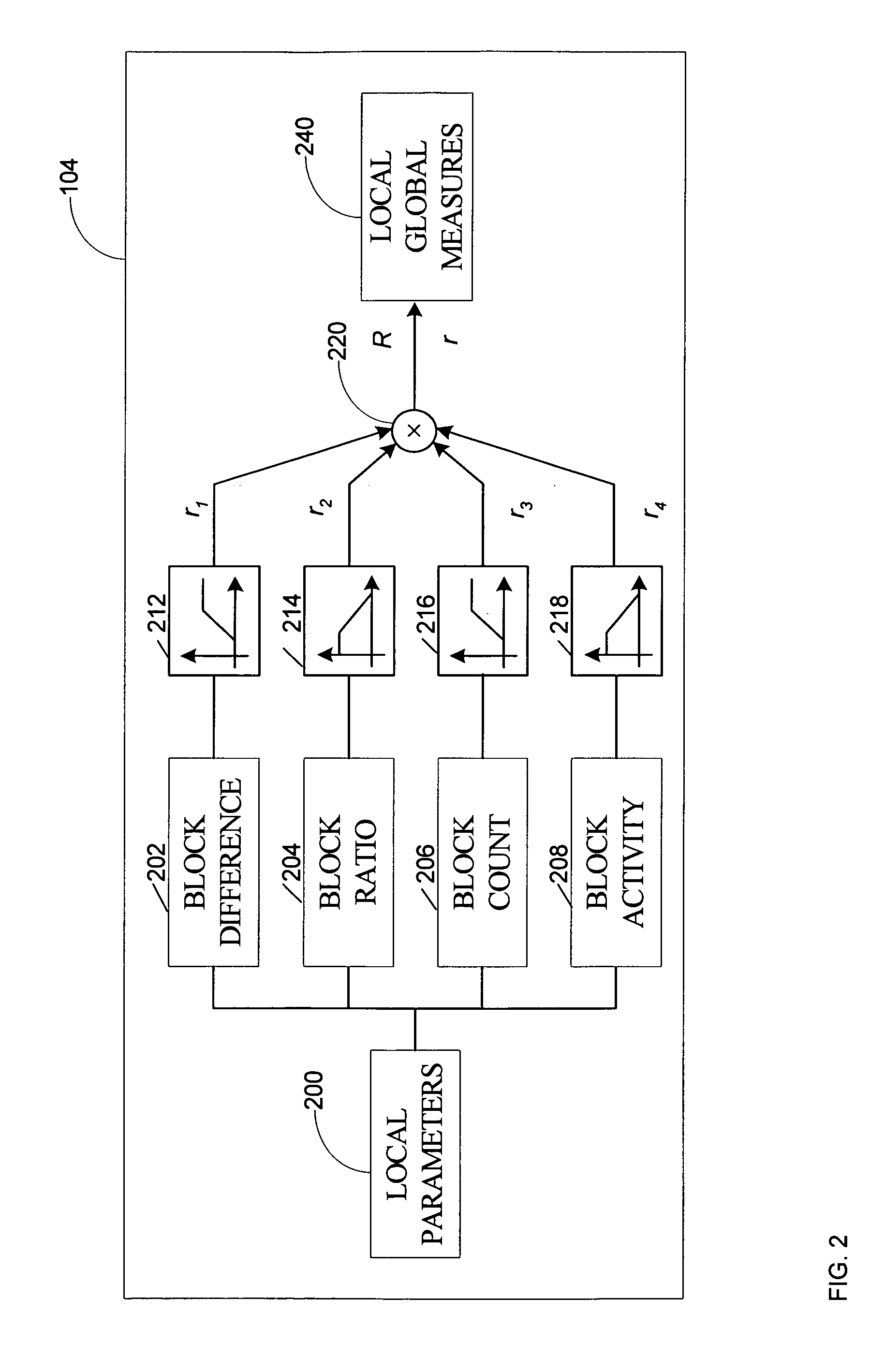
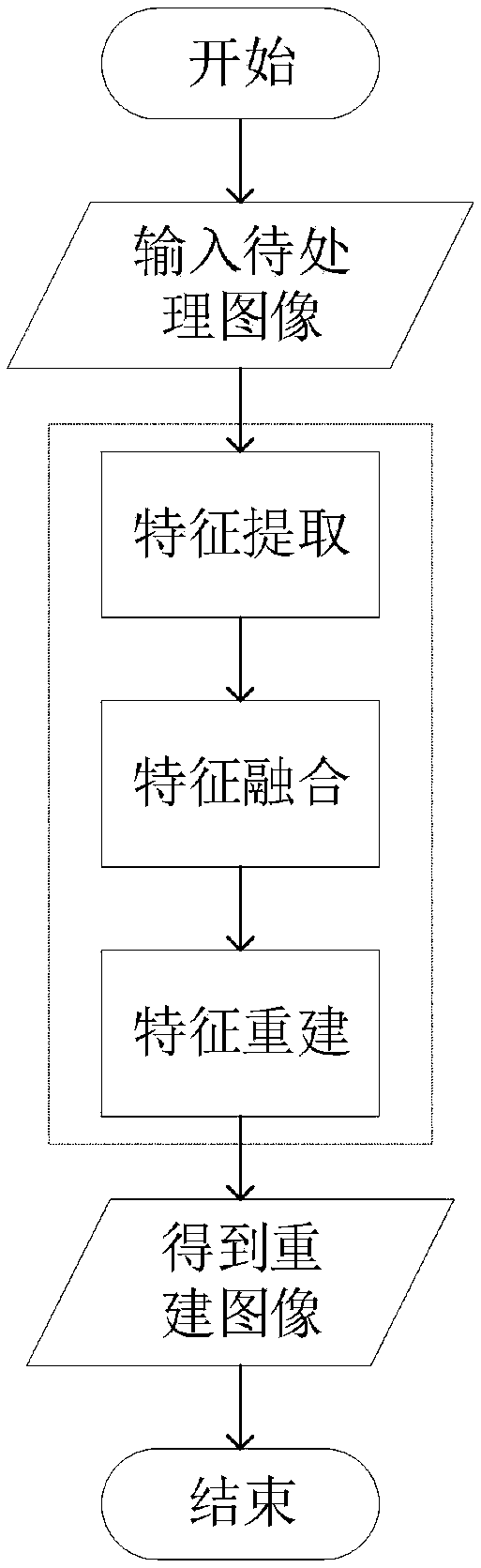
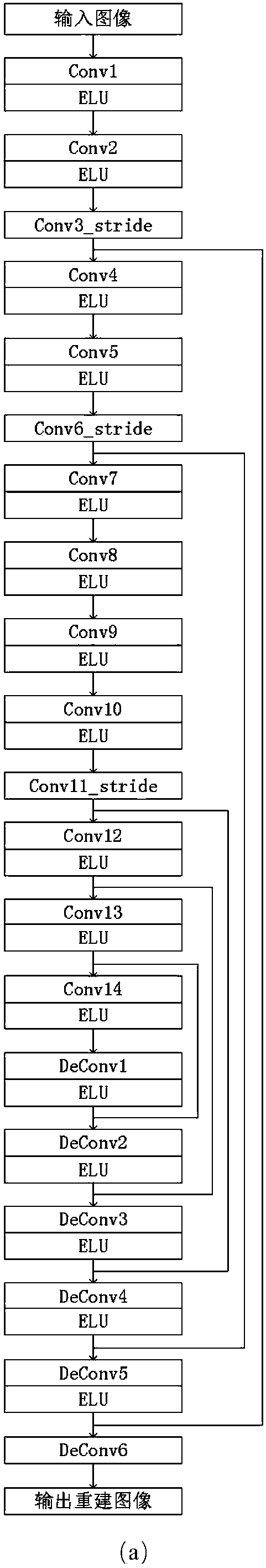
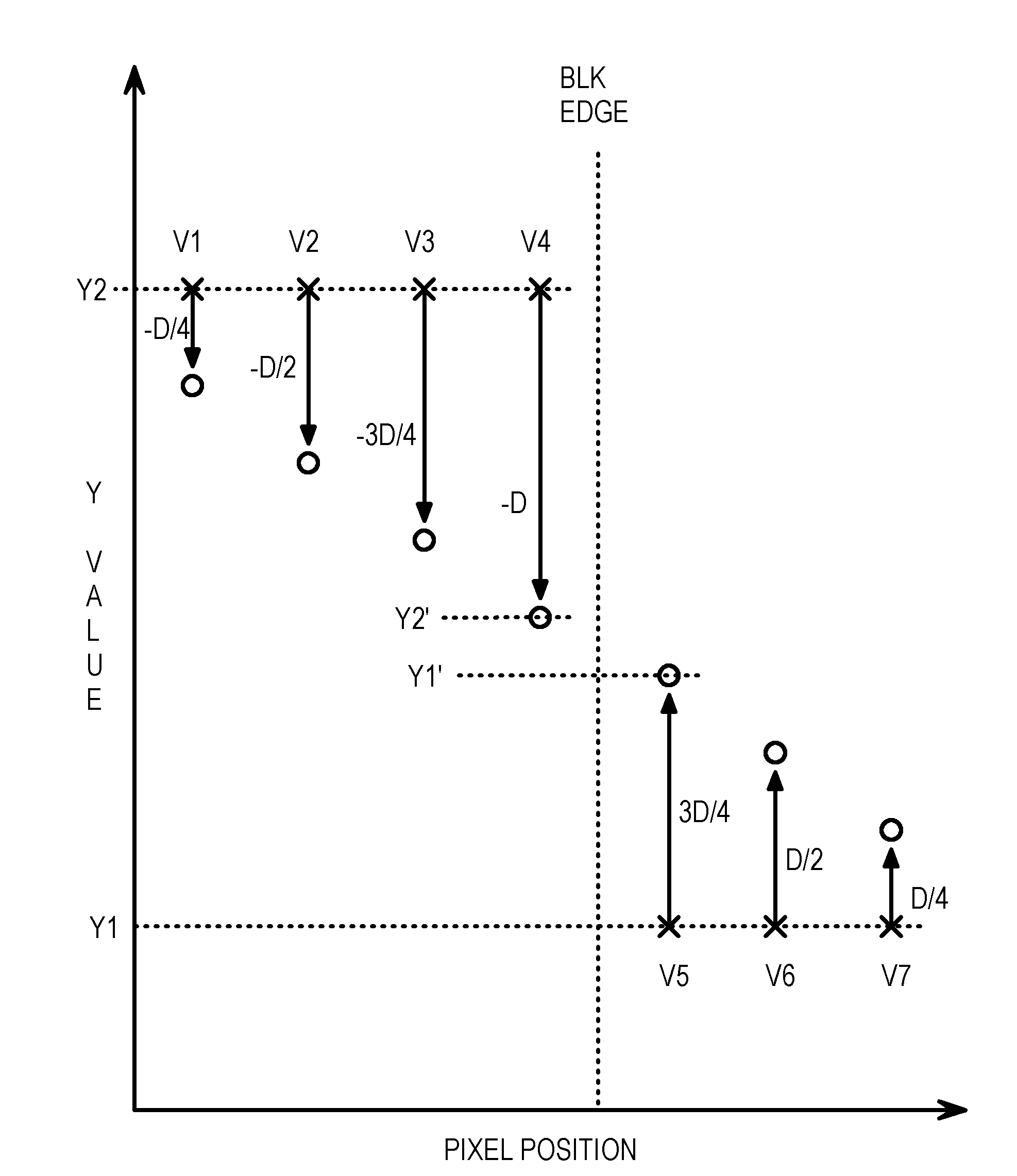
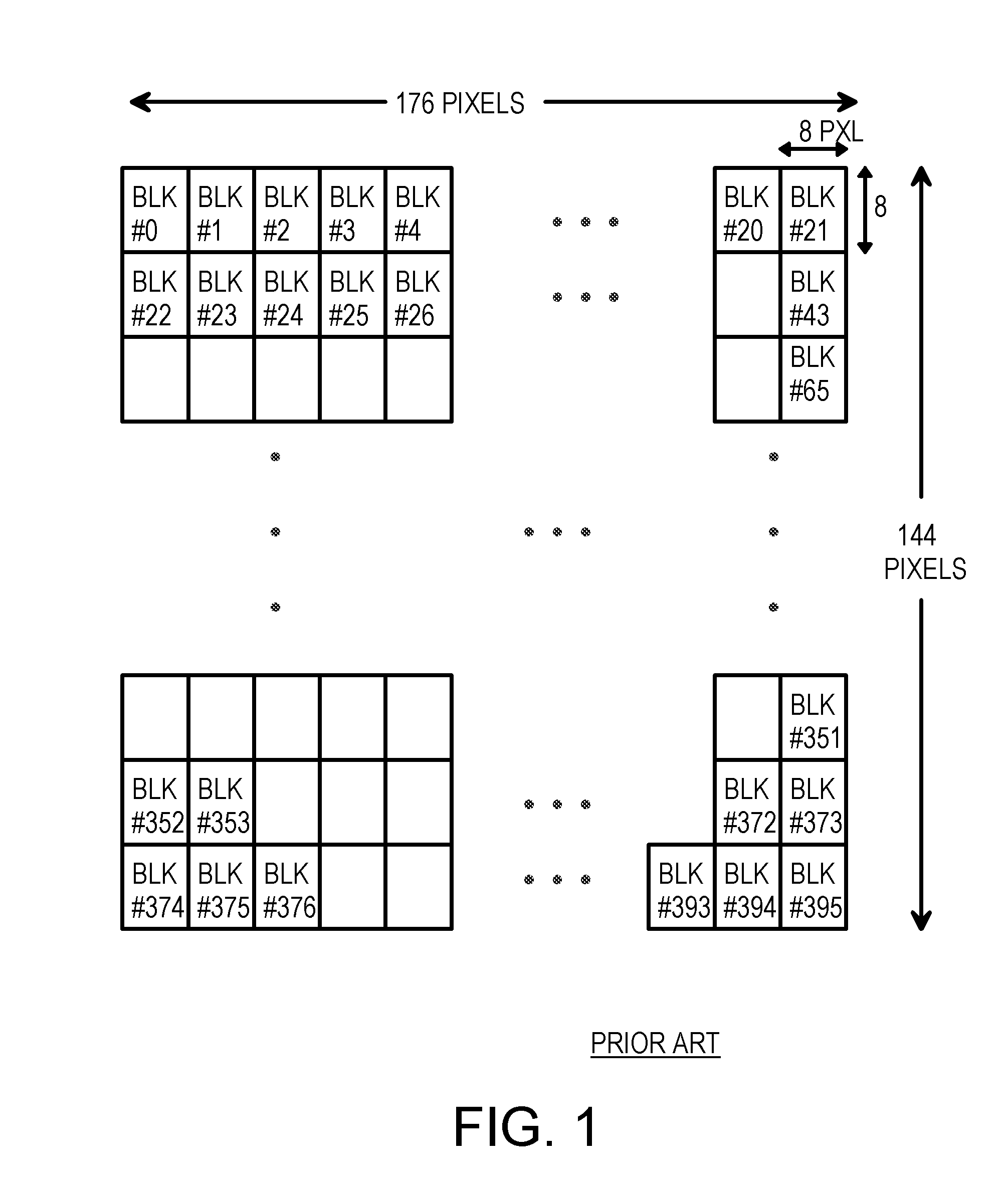
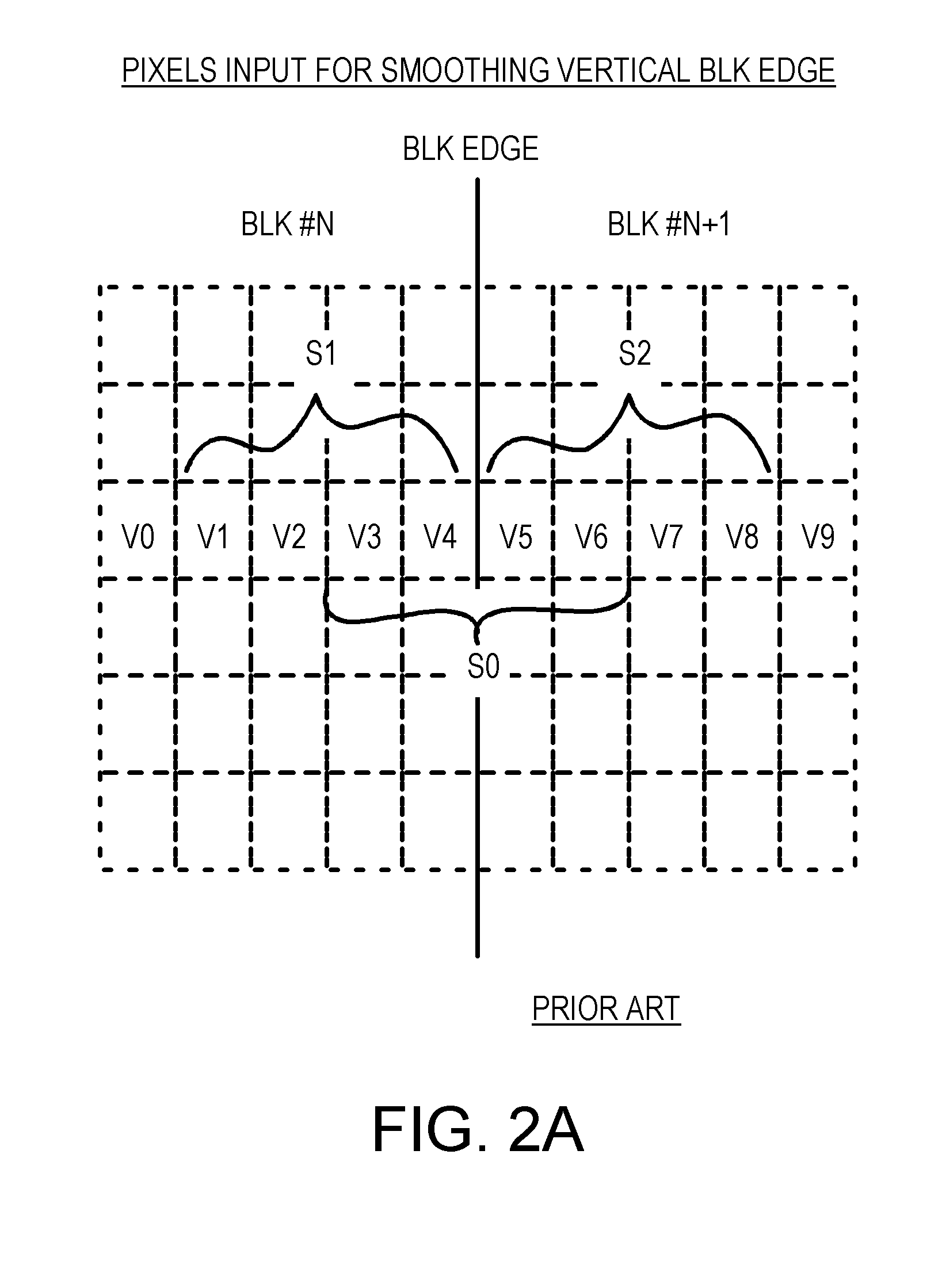
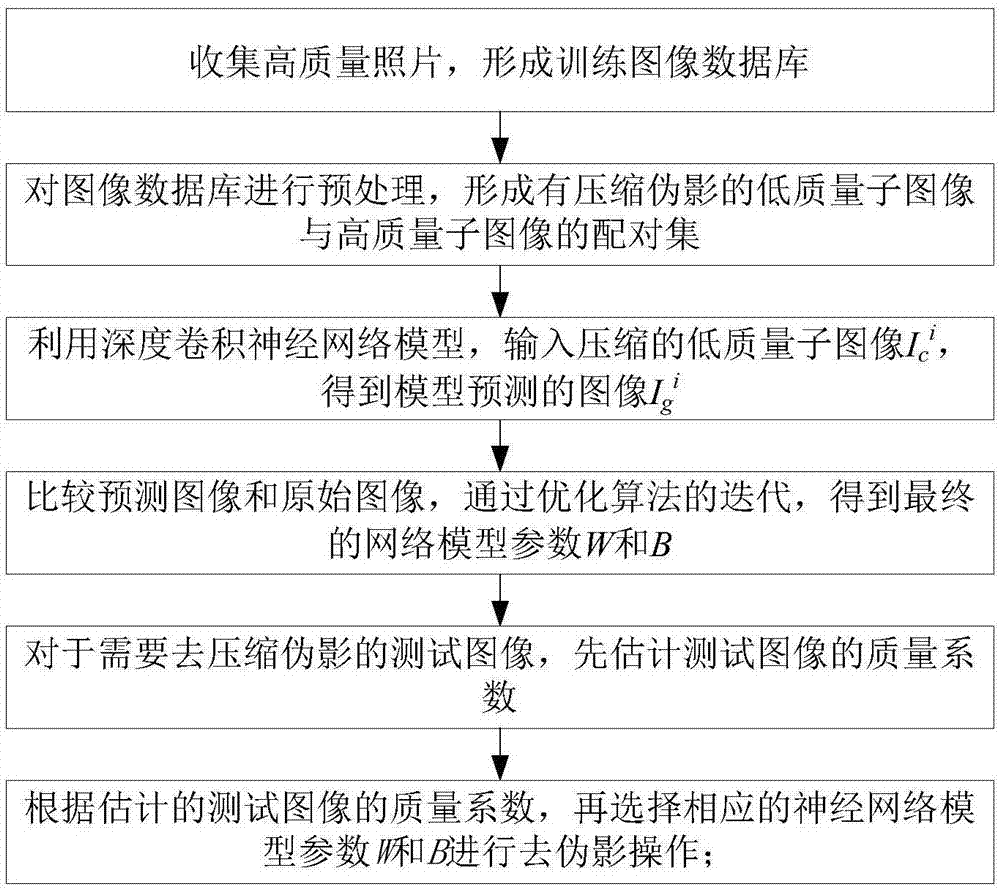
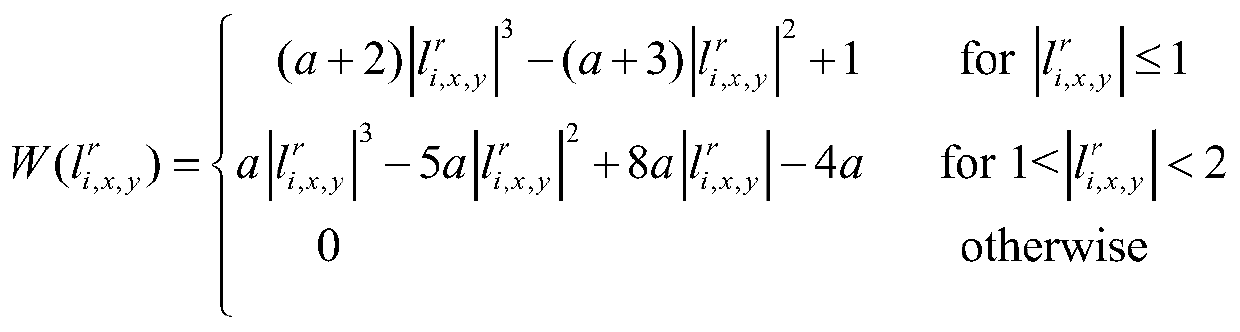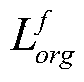Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
135 results about "Compression artifact" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A compression artifact (or artefact) is a noticeable distortion of media (including images, audio, and video) caused by the application of lossy compression. Lossy data compression involves discarding some of the media's data so that it becomes small enough to be stored within the desired disk space or transmitted (streamed) within the available bandwidth (known as the data rate or bit rate). If the compressor can not store enough data in the compressed version, the result is a loss of quality, or introduction of artifacts. The compression algorithm may not be intelligent enough to discriminate between distortions of little subjective importance and those objectionable to the user.
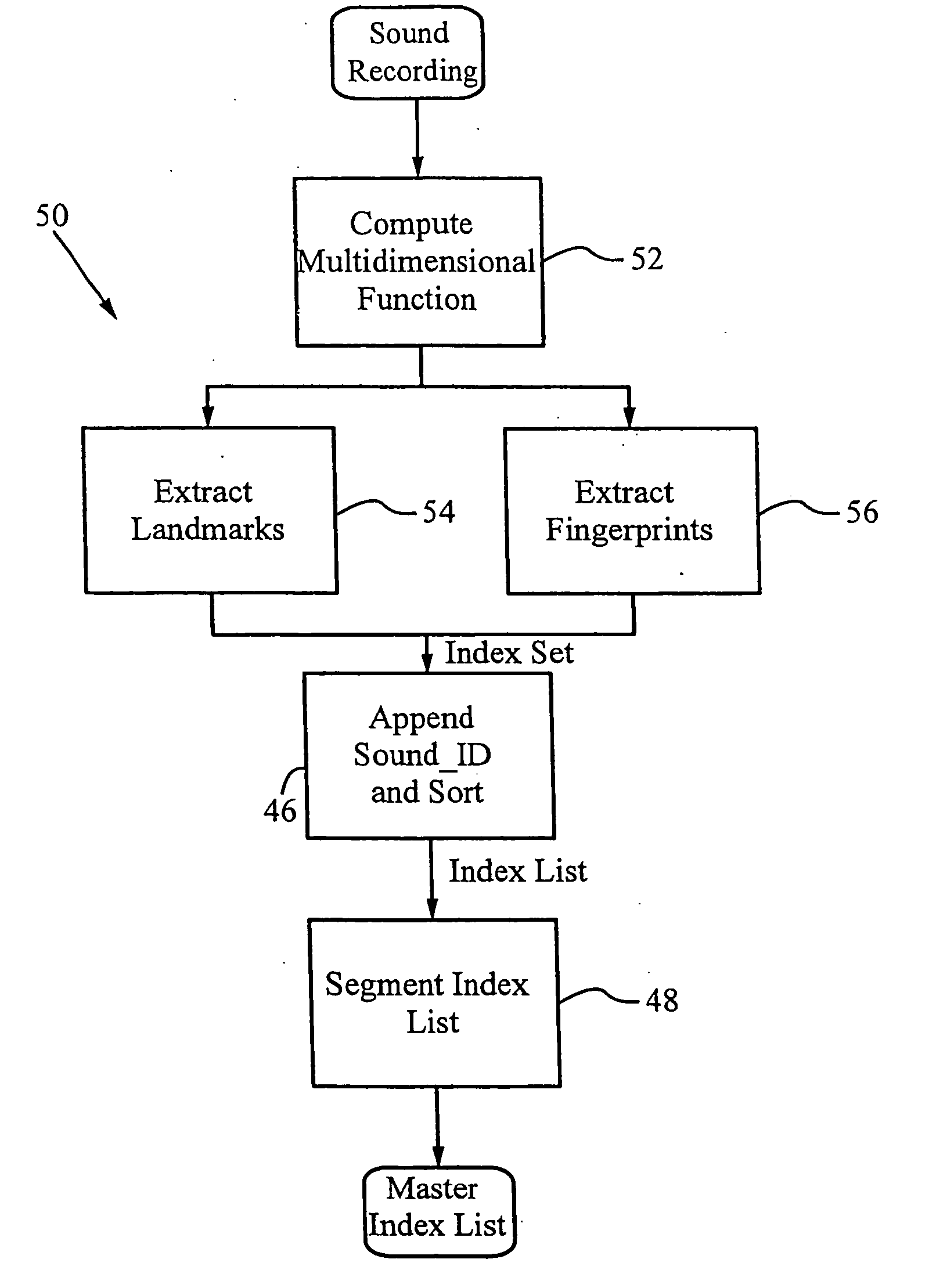
System and methods for recognizing sound and music signals in high noise and distortion
ActiveUS6990453B2High of distortionHigh levelGearworksMusical toysNonlinear distortionLinear correlation
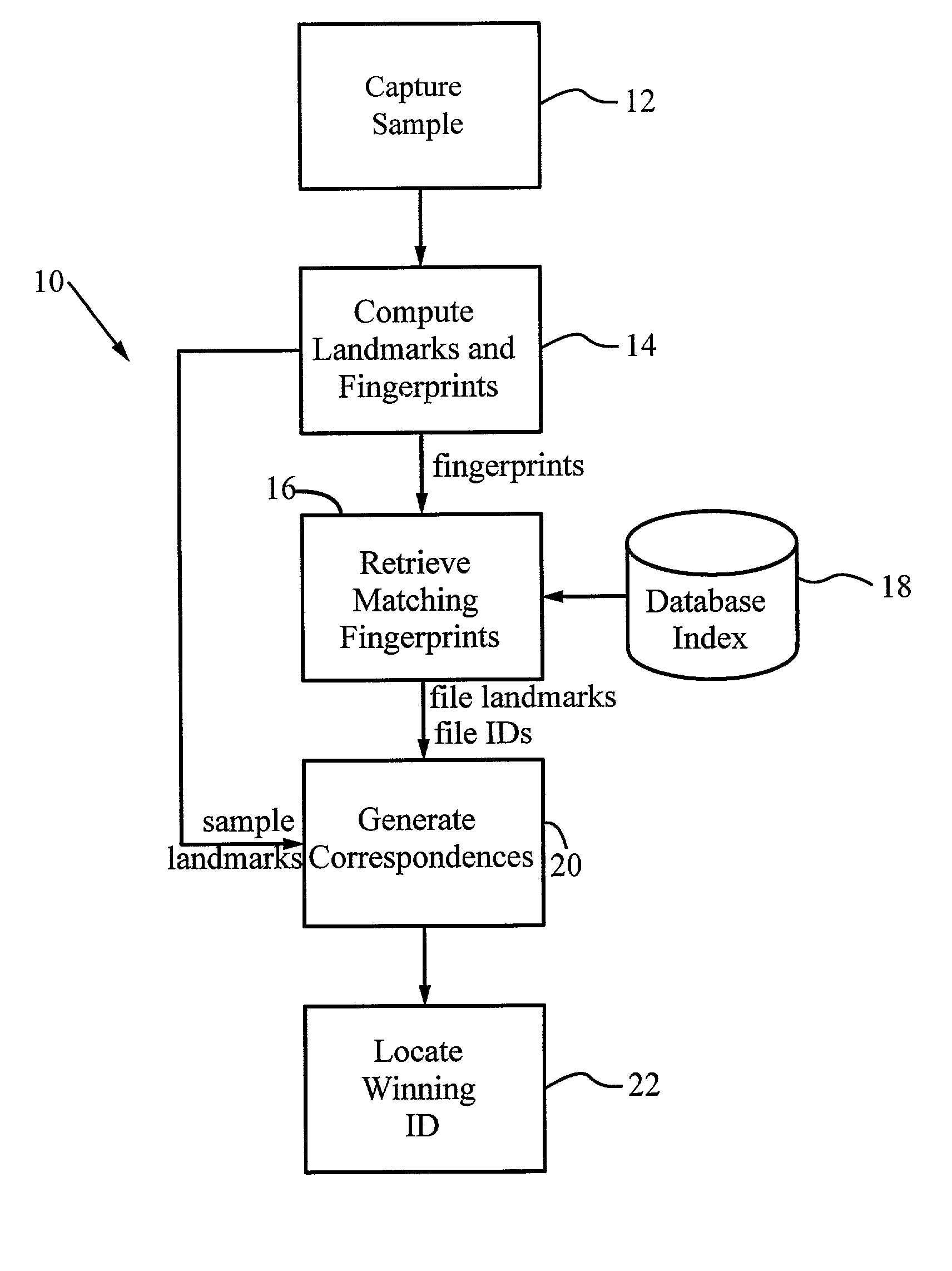
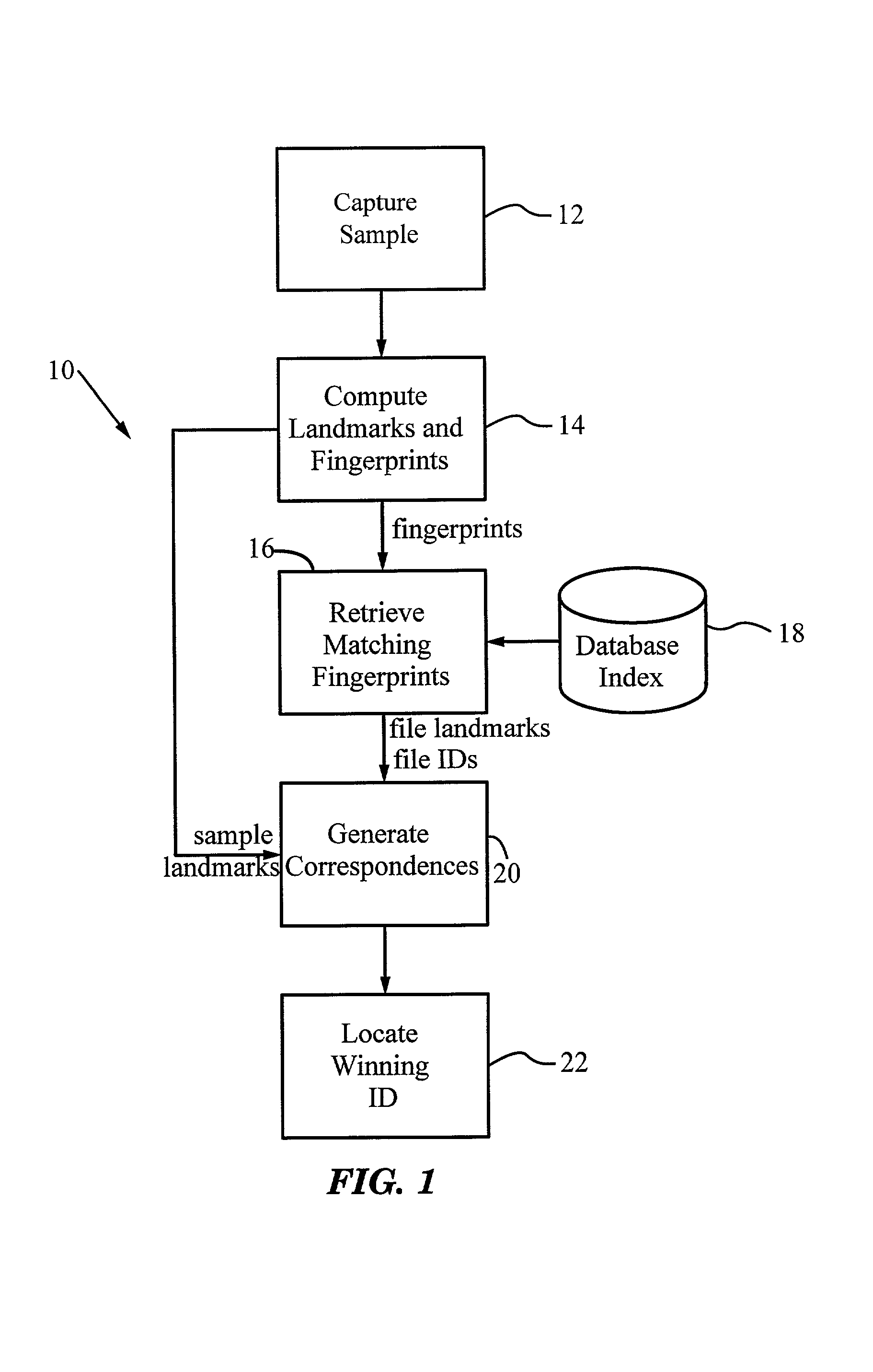
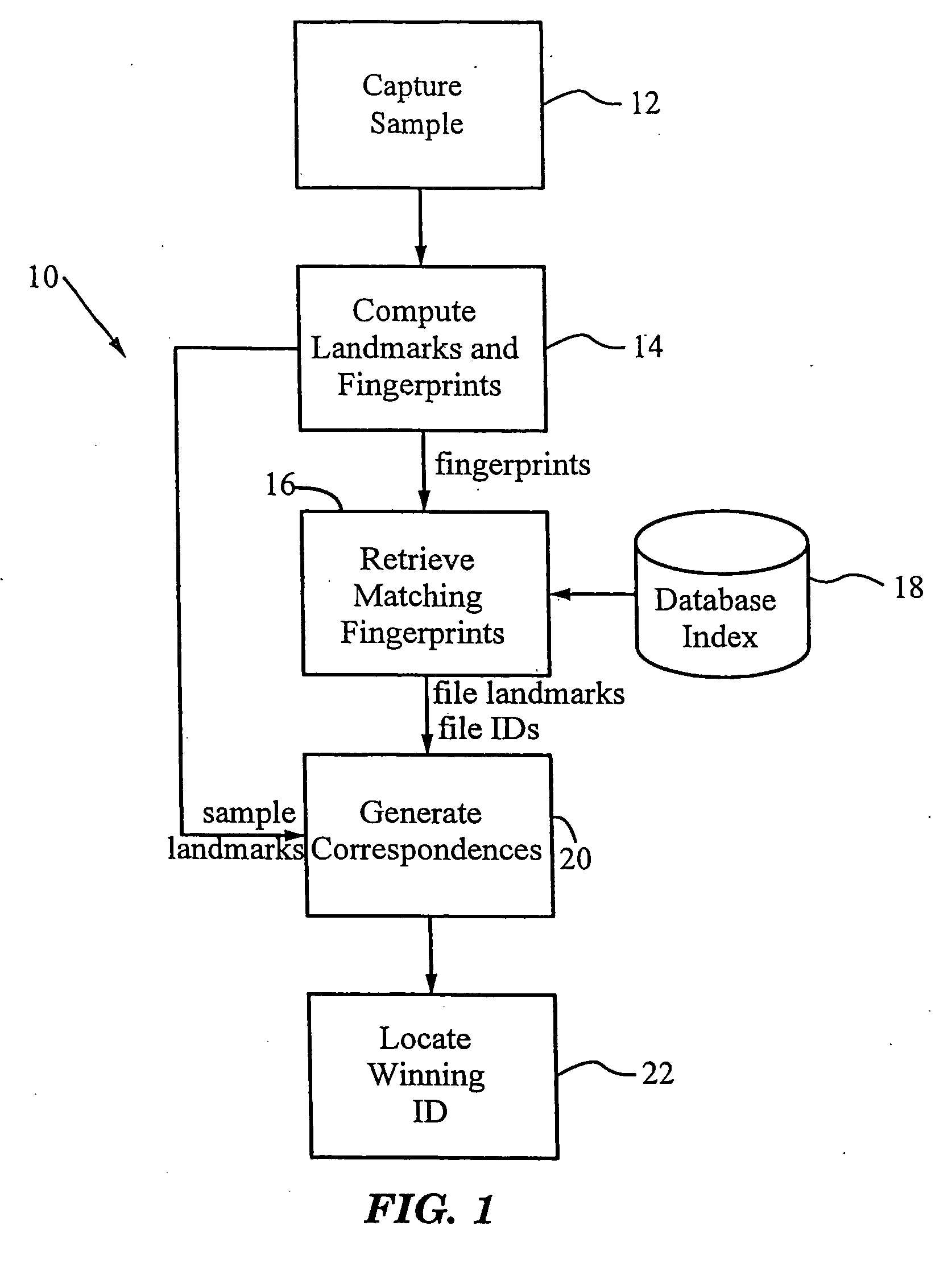
A method for recognizing an audio sample locates an audio file that most closely matches the audio sample from a database indexing a large set of original recordings. Each indexed audio file is represented in the database index by a set of landmark timepoints and associated fingerprints. Landmarks occur at reproducible locations within the file, while fingerprints represent features of the signal at or near the landmark timepoints. To perform recognition, landmarks and fingerprints are computed for the unknown sample and used to retrieve matching fingerprints from the database. For each file containing matching fingerprints, the landmarks are compared with landmarks of the sample at which the same fingerprints were computed. If a large number of corresponding landmarks are linearly related, i.e., if equivalent fingerprints of the sample and retrieved file have the same time evolution, then the file is identified with the sample. The method can be used for any type of sound or music, and is particularly effective for audio signals subject to linear and nonlinear distortion such as background noise, compression artifacts, or transmission dropouts. The sample can be identified in a time proportional to the logarithm of the number of entries in the database; given sufficient computational power, recognition can be performed in nearly real time as the sound is being sampled.
Owner:APPLE INC
Compressed low-resolution image restoration method based on combined deep network
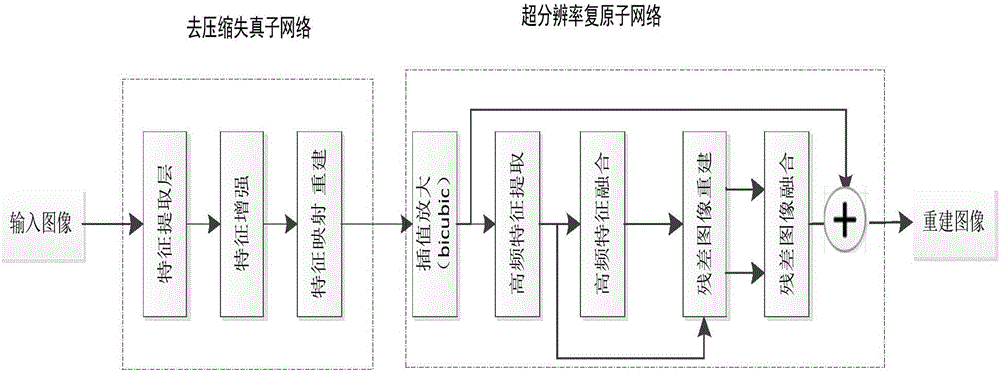
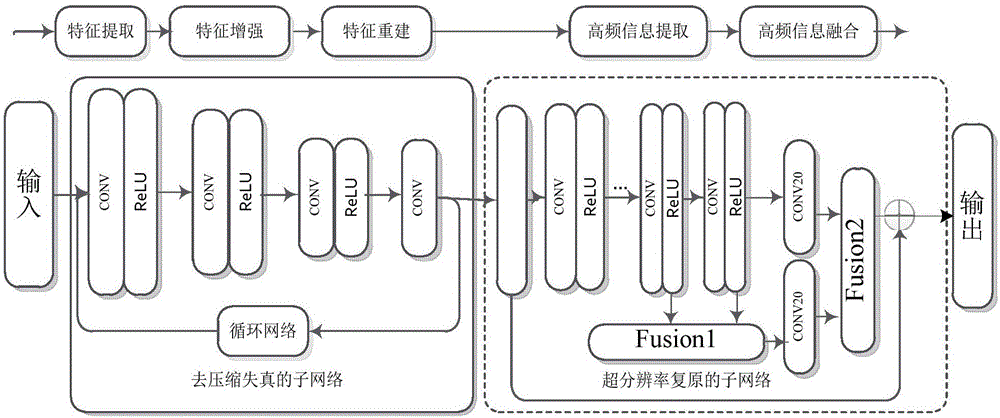
The present invention provides a compressed low-resolution image restoration method based on a combined deep network, belonging to the digital image / video signal processing field. The compressed low-resolution image restoration method based on the combined deep network starts from the aspect of the coprocessing of the compression artifact and downsampling factors to complete the restoration of a degraded image with the random combination of the compression artifact and the low resolution; the network provided by the invention comprises 28 convolution layers to establish a leptosomatic network structure, according to the idea of transfer learning, a model trained in advance employs a fine tuning mode to complete the training convergence of a greatly deep network so as to solve the problems of vanishing gradients and gradient explosion; the compressed low-resolution image restoration method completes the setting of the network model parameters through feature visualization, and the relation of the end-to-end learning degeneration feature and the ideal features omits the preprocessing and postprocessing; and finally, three important fusions are completed, namely the fusion of the feature figures with the same size, the fusion of residual images and the fusion of the high-frequency information and the high-frequency initial estimation figure, and the compressed low-resolution image restoration method can solve the super-resolution restoration problem of the low-resolution image with the compression artifact.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
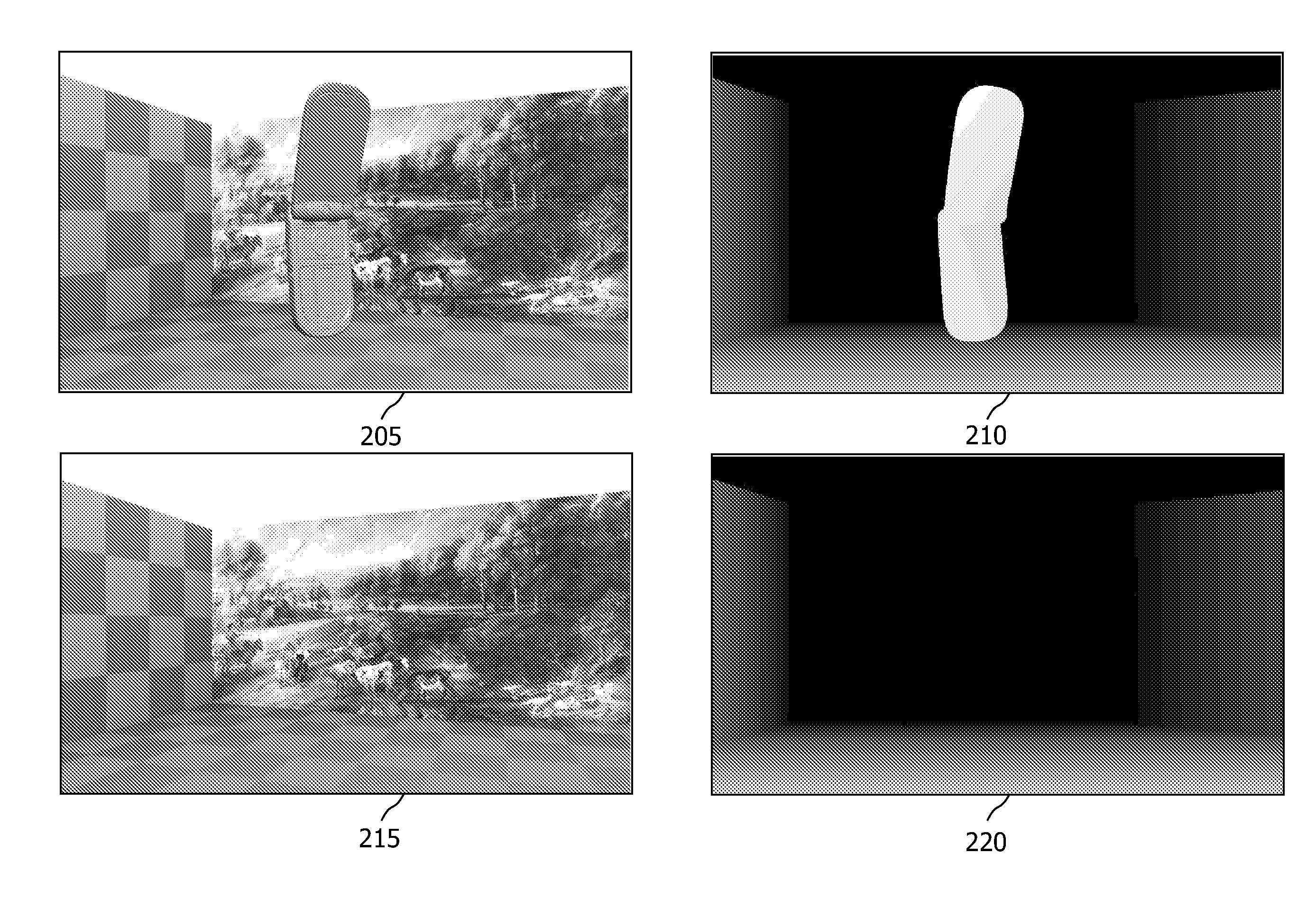
Method and device for processing a depth-map
InactiveUS20100215251A1Reduce the impact of noiseReduce compression artifactTelevision system detailsCharacter and pattern recognitionViewpointsCompression artifact
The present invention relates to a device and apparatus for processing a depth-map 710, the method comprising obtaining a depth-map 710 based on a lossy compressed depth-map, the depth-map 710 comprising depth information of a scene from a viewpoint, the scene comprising an object, obtaining occlusion information for the scene from the viewpoint, the occlusion information comprising information occluded by the object in the depth-map 710, and processing at least part of the depth information using at least part of the occlusion information in order to reduce compression artifacts in the depth-map 710.
Owner:KONINKLIJKE PHILIPS ELECTRONICS NV
System and methods for recognizing sound and music signals in high noise and distortion
InactiveUS20060122839A1High of distortionHigh levelDigital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionNonlinear distortionLinear correlation
A method for recognizing an audio sample locates an audio file that most closely matches the audio sample from a database indexing a large set of original recordings. Each indexed audio file is represented in the database index by a set of landmark timepoints and associated fingerprints. Landmarks occur at reproducible locations within the file, while fingerprints represent features of the signal at or near the landmark timepoints. To perform recognition, landmarks and fingerprints are computed for the unknown sample and used to retrieve matching fingerprints from the database. For each file containing matching fingerprints, the landmarks are compared with landmarks of the sample at which the same fingerprints were computed. If a large number of corresponding landmarks are linearly related, i.e., if equivalent fingerprints of the sample and retrieved file have the same time evolution, then the file is identified with the sample. The method can be used for any type of sound or music, and is particularly effective for audio signals subject to linear and nonlinear distortion such as background noise, compression artifacts, or transmission dropouts. The sample can be identified in a time proportional to the logarithm of the number of entries in the database; given sufficient computational power, recognition can be performed in nearly real time as the sound is being sampled.
Owner:APPLE INC
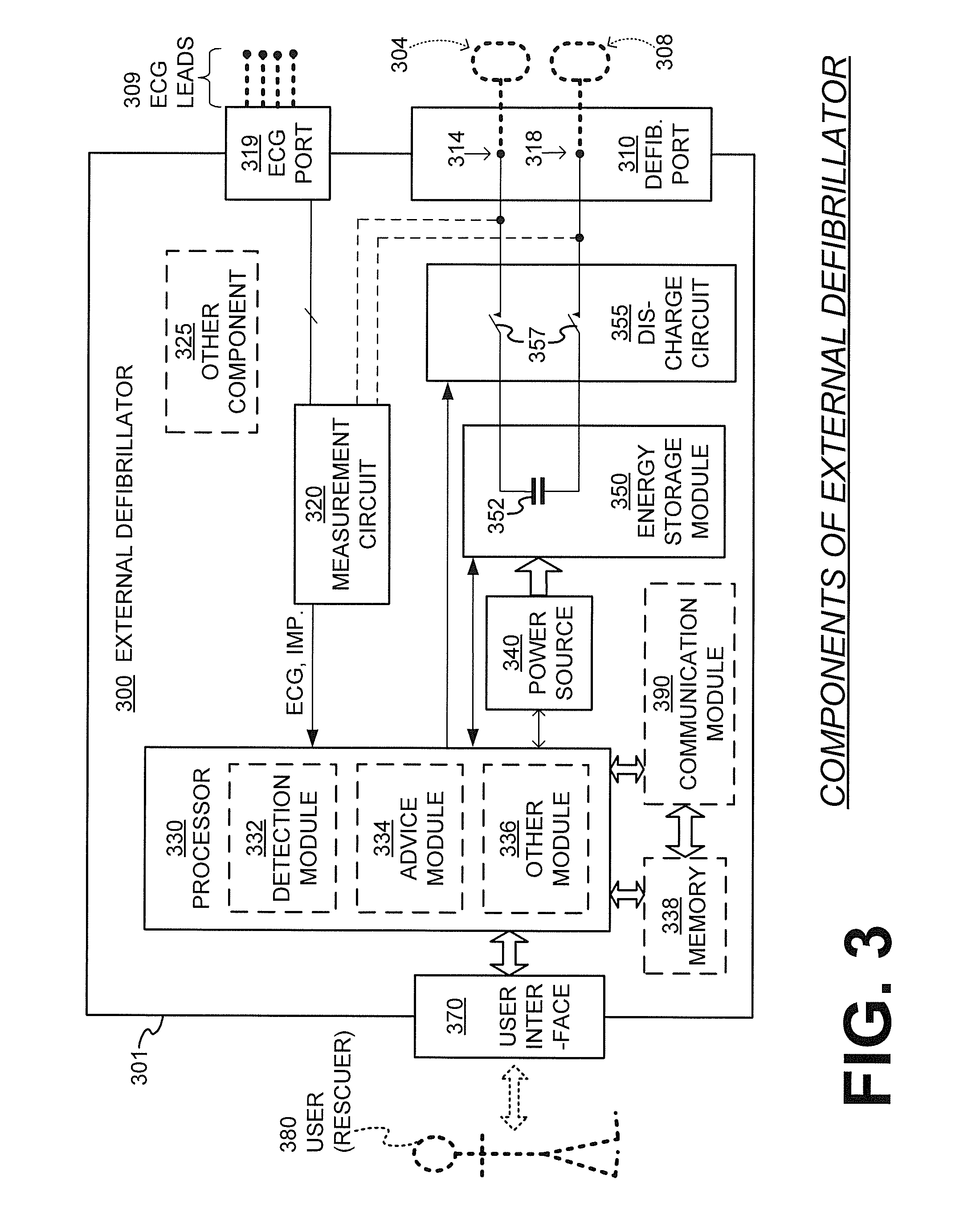
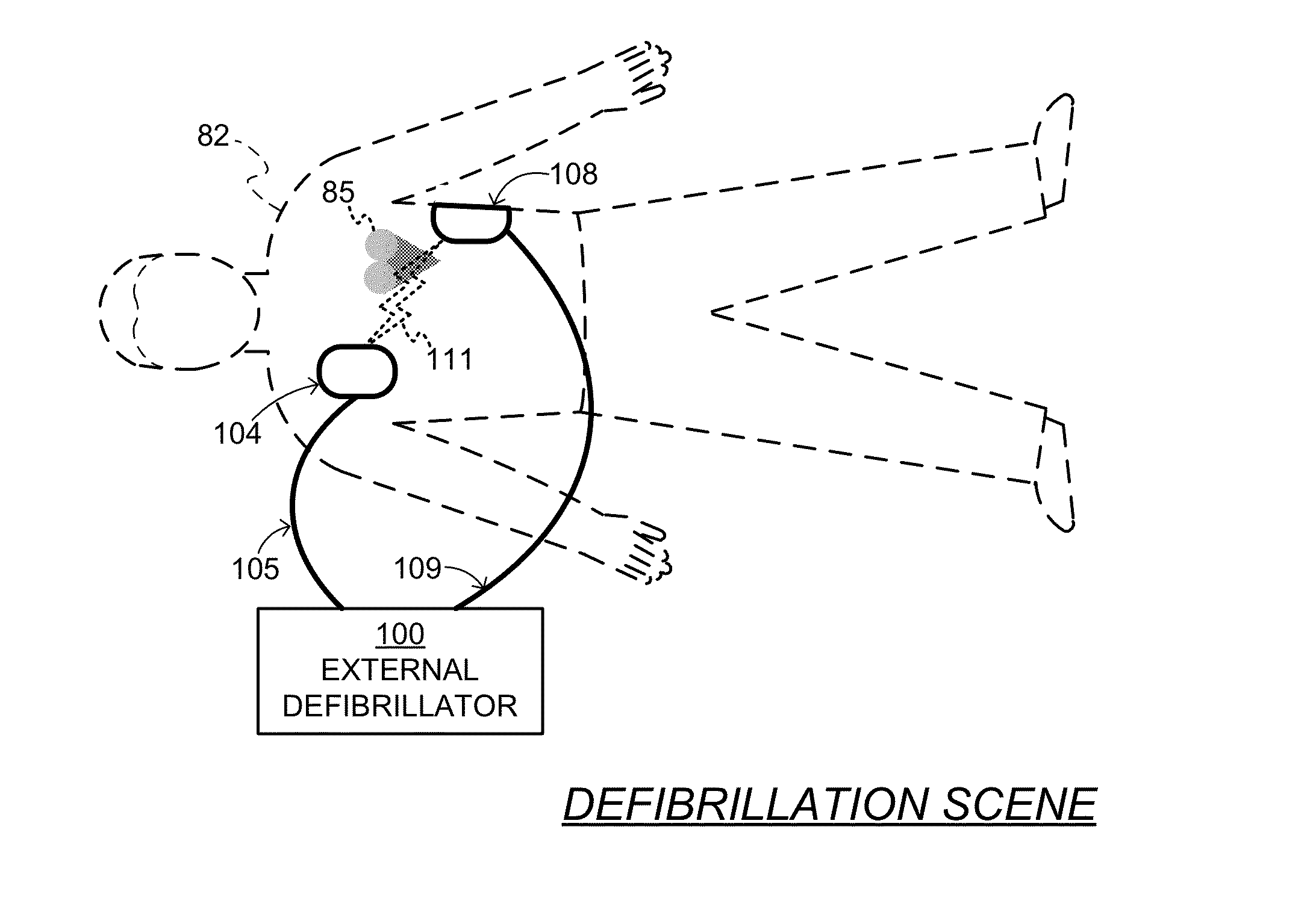
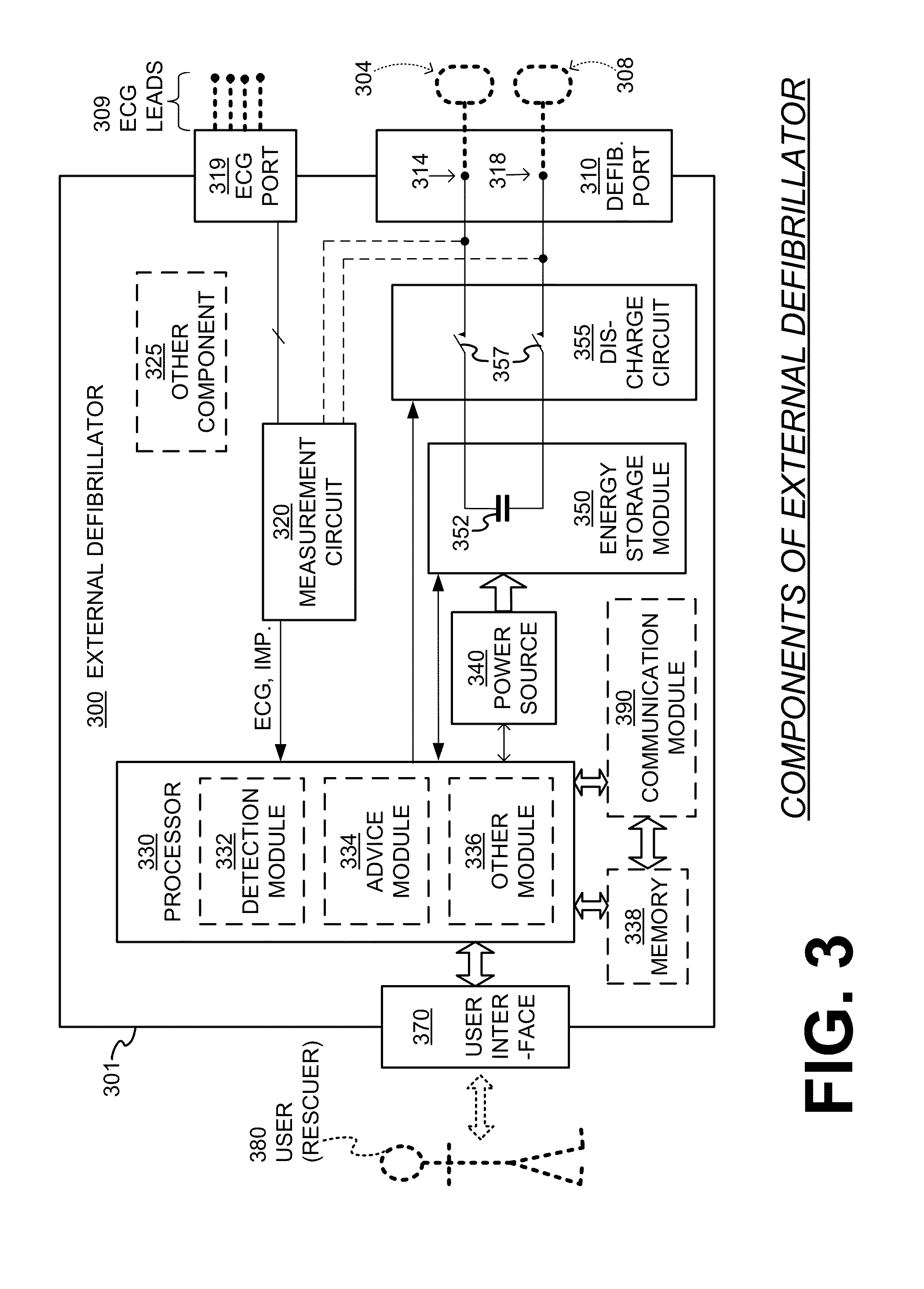
Filter mechanism for removing ECG artifact from mechanical chest compressions
ActiveUS20130296727A1Signal cleanElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringHarmonicCompression artifact
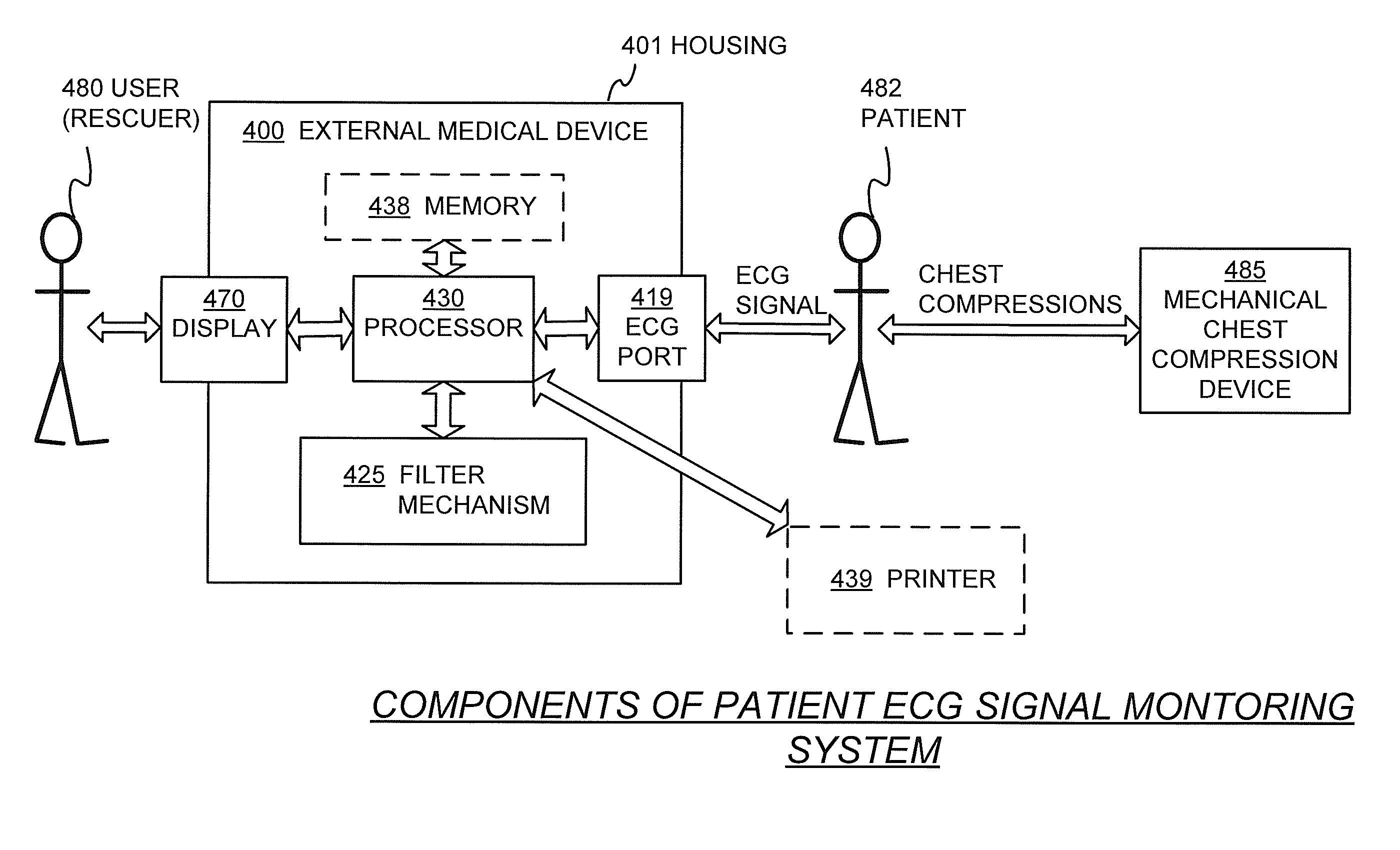
An external medical device can include a housing and a processor within the housing. The processor can be configured to receive an input signal for a patient receiving chest compressions from a mechanical chest compression device. The processor can also be configured to select at least one filter mechanism, the mechanical chest compression device having a chest compression frequency f. The processor can be further configured to apply the at least one filter mechanism to the signal to at least substantially remove chest compression artifacts from the signal, wherein the chest compression artifacts correspond to the chest compressions being delivered to the patient by the mechanical chest compression device, and wherein the at least one filter mechanism substantially rejects content in the frequency f plus content in at least one more frequency that is a higher harmonic to the frequency f.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
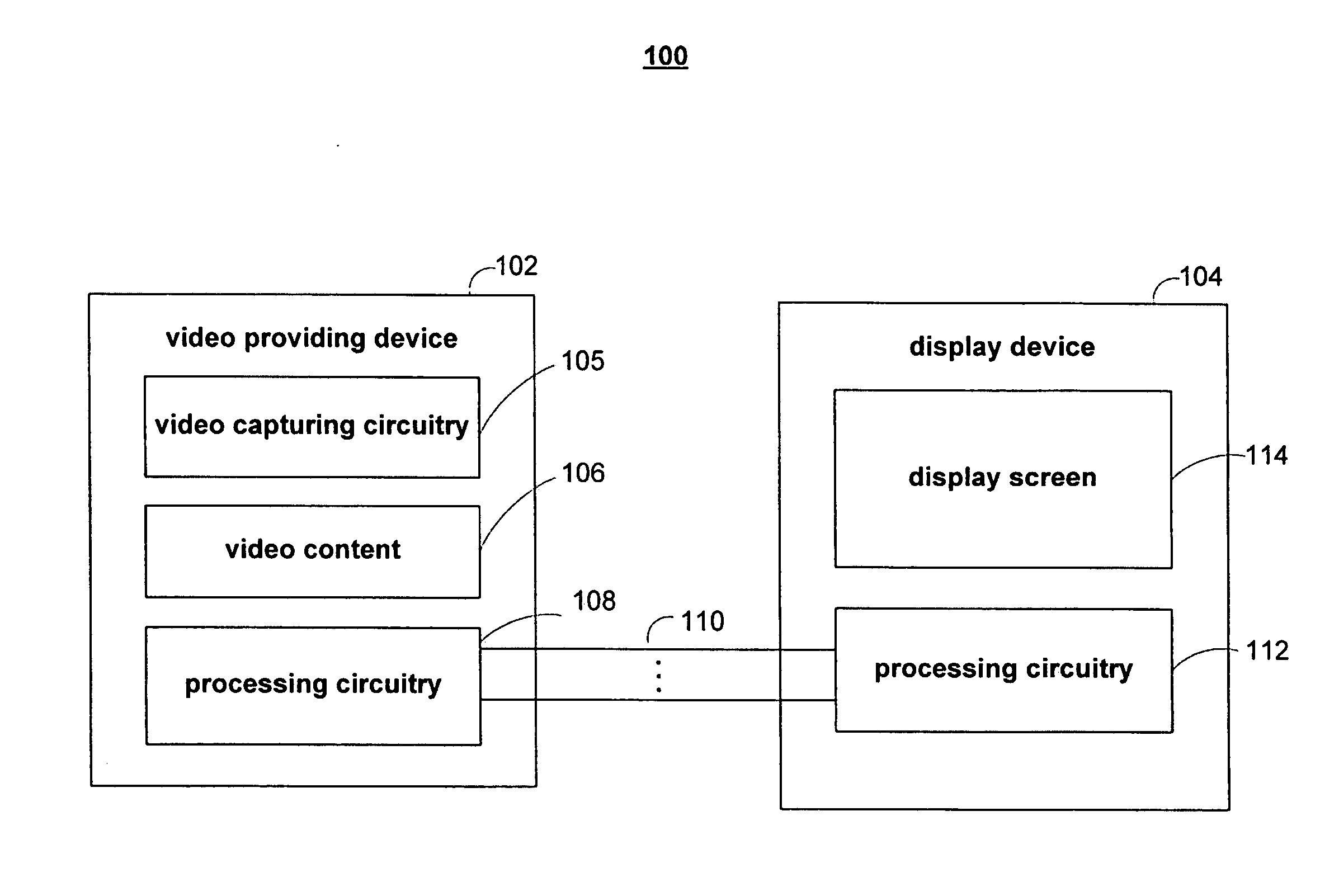
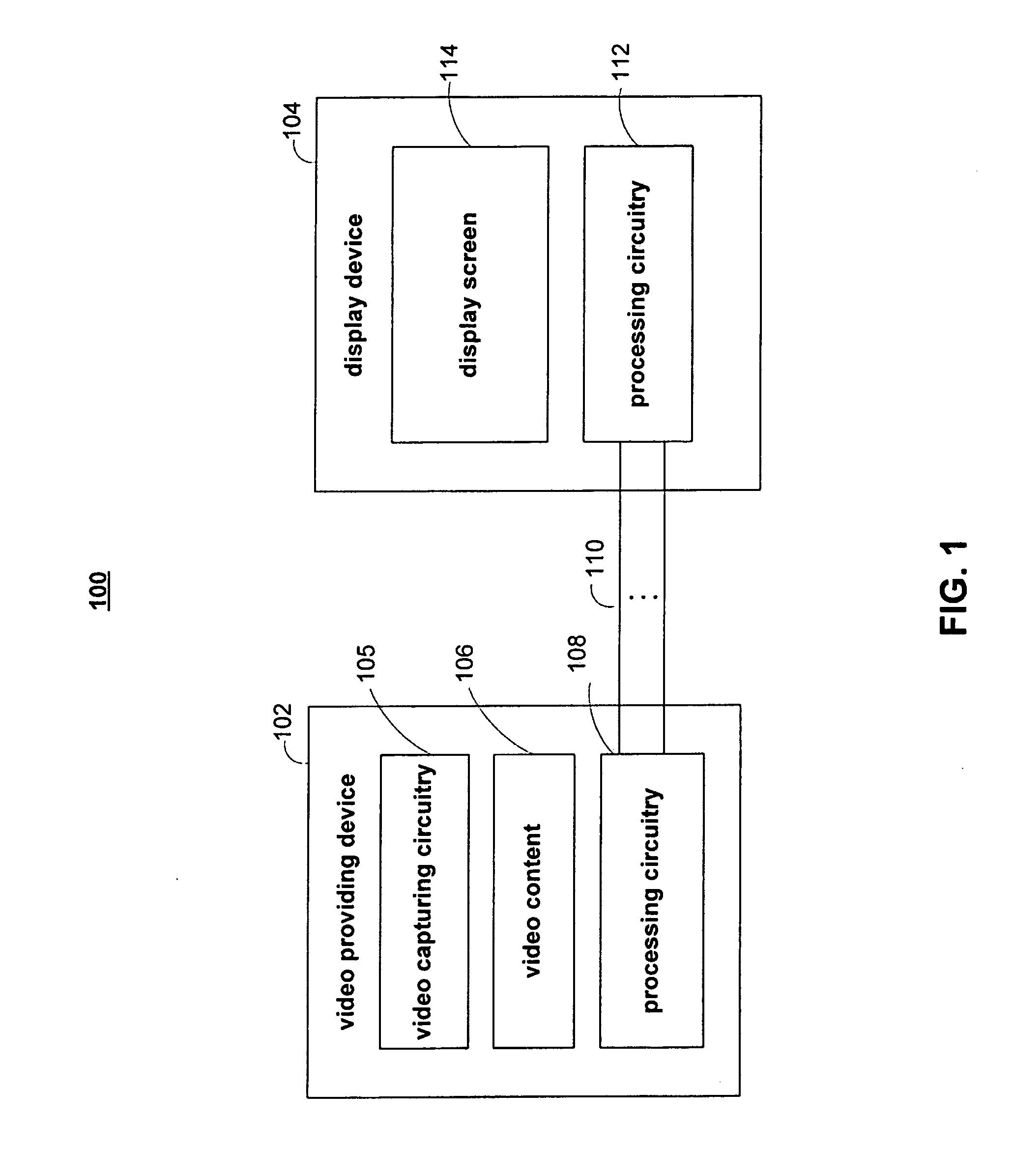
Methods and systems for improving low-resolution video
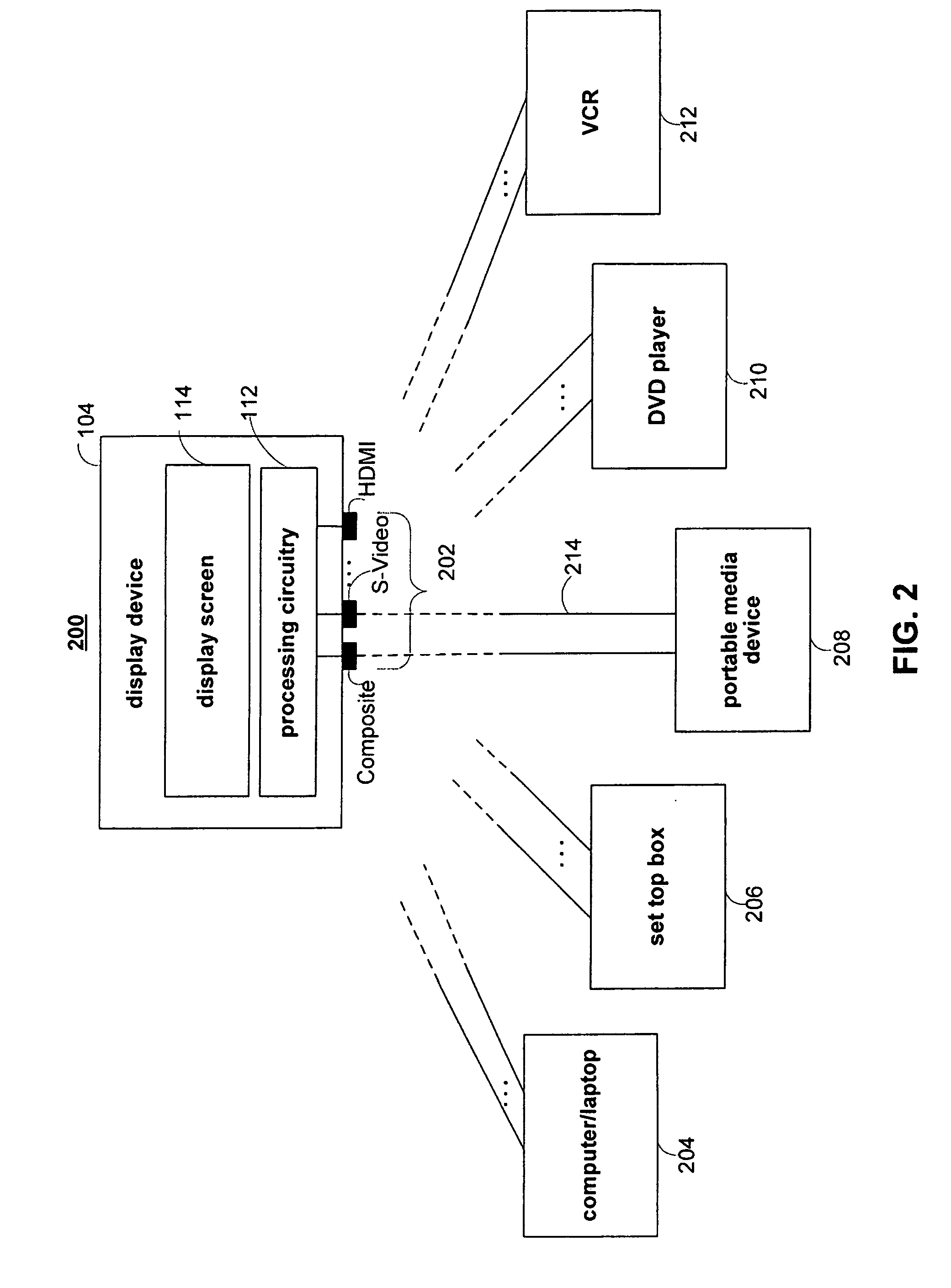
ActiveUS20080211959A1Improve visual appearanceHigh resolutionGeometric image transformationPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCompression artifactImage resolution
Systems and methods are provided for improving the visual quality of low-resolution video displayed on large-screen displays. A video format converter may be used to process a low-resolution video signal from a media providing device before the video is displayed. The video format converter may detect the true resolution of the video and deinterlace the video signal accordingly. For low-resolution videos that are also low in quality, the video format converter may reduce compression artifacts and apply techniques to enhance the appearance of the video.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC +1
System and method for electrocardiogram analysis and optimization of cardiopulmonary resuscitation and therapy delivery
ActiveUS20140107541A1Signal cleanElectrotherapyDiagnostic recording/measuringCompression artifactEmergency medicine
The system and method provide for electrocardiogram analysis and optimization of patient-customized cardiopulmonary resuscitation and therapy delivery. An external medical device includes a housing and a processor within the housing. The processor can be configured to receive an input signal for a patient receiving chest compressions and to select at least one filter mechanism and to apply the filter mechanism to the signal to at least substantially remove chest compression artifacts from the signal. A real time dynamic analysis of a cardiac rhythm is applied to adjust and integrate CPR prompting of a medical device. Real-time cardiac rhythm quality is facilitated using a rhythm assessment meter.
Owner:PHYSIO CONTROL INC
Methods and systems for improving low resolution and low frame rate video
ActiveUS20080198264A1Improve visual appearanceLow appearance requirementsTelevision system detailsPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesCompression artifactImage resolution
Systems and methods are provided for improving the visual quality of low resolution and / or low frame rate video content displayed on large-screen displays. A video format converter may be used to process a low resolution and / or low frame rate video signal from a media providing device before the video is displayed. The video format converter may detect the true resolution of the video and deinterlace the video signal accordingly. The video format converter may also determine the frame rate of a video and may increase the frame rate if the received frame rate is below a certain threshold. For videos that are also low in quality, the video format converter may reduce compression artifacts and apply techniques to enhance the appearance of the video.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC +1
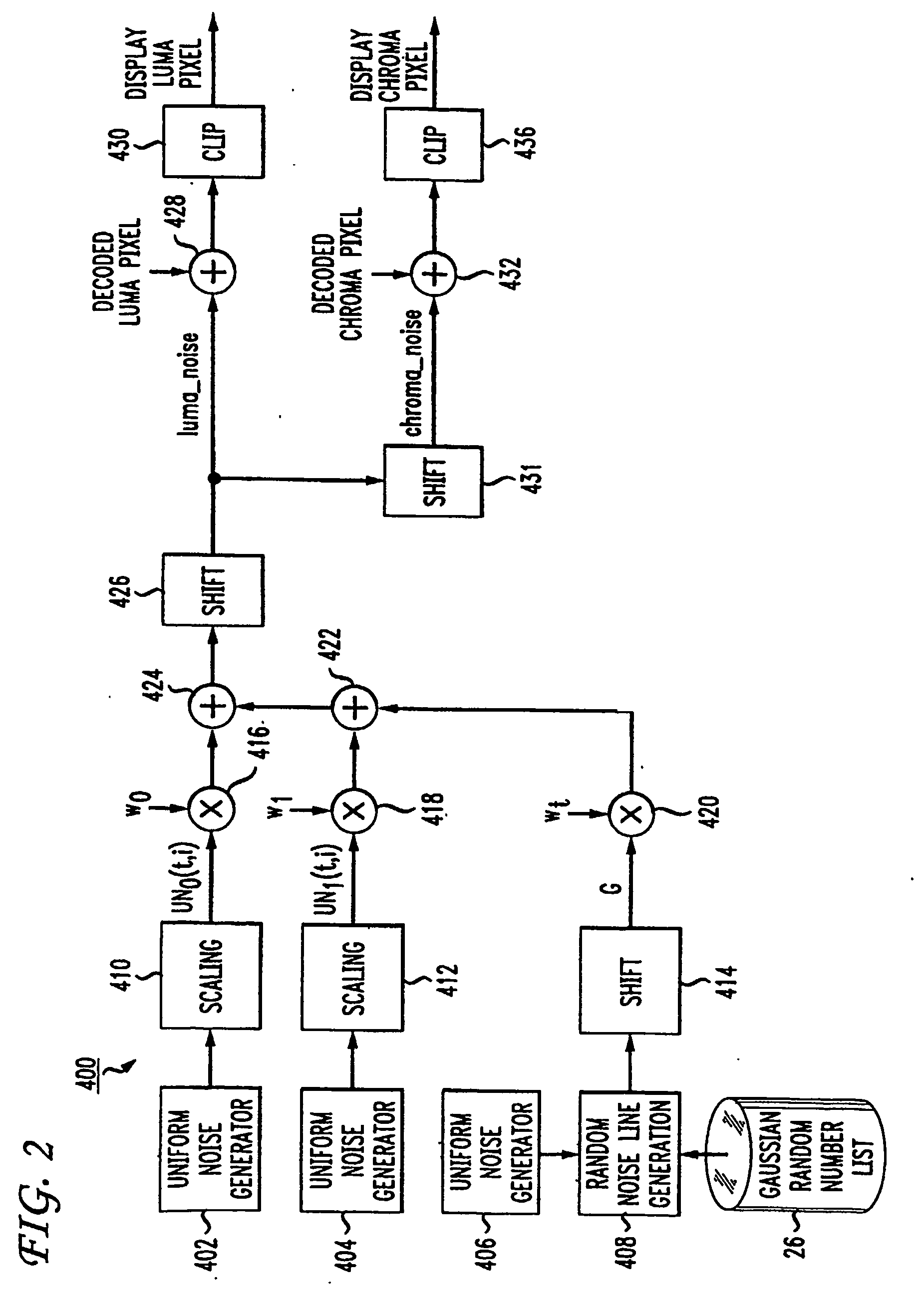
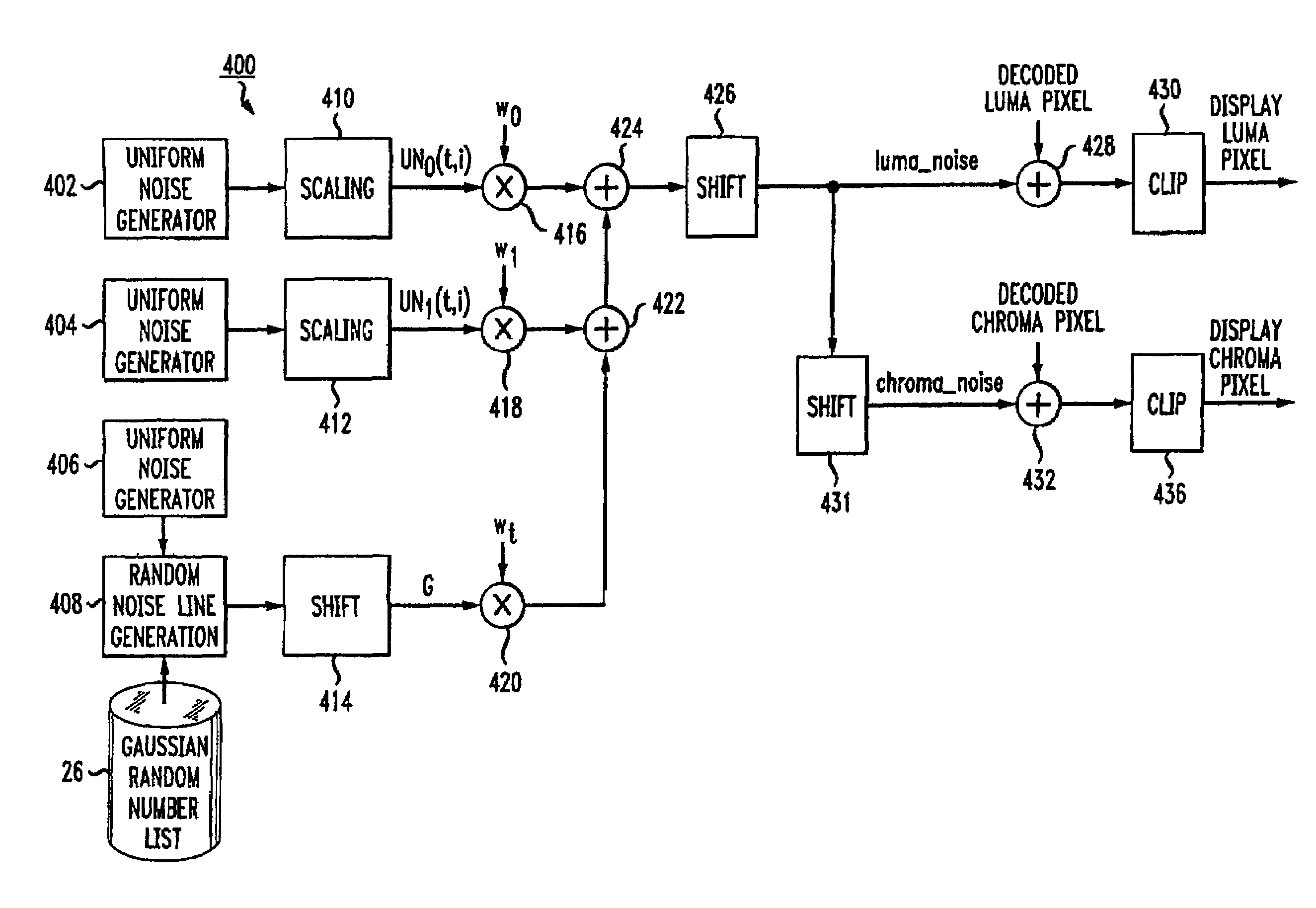
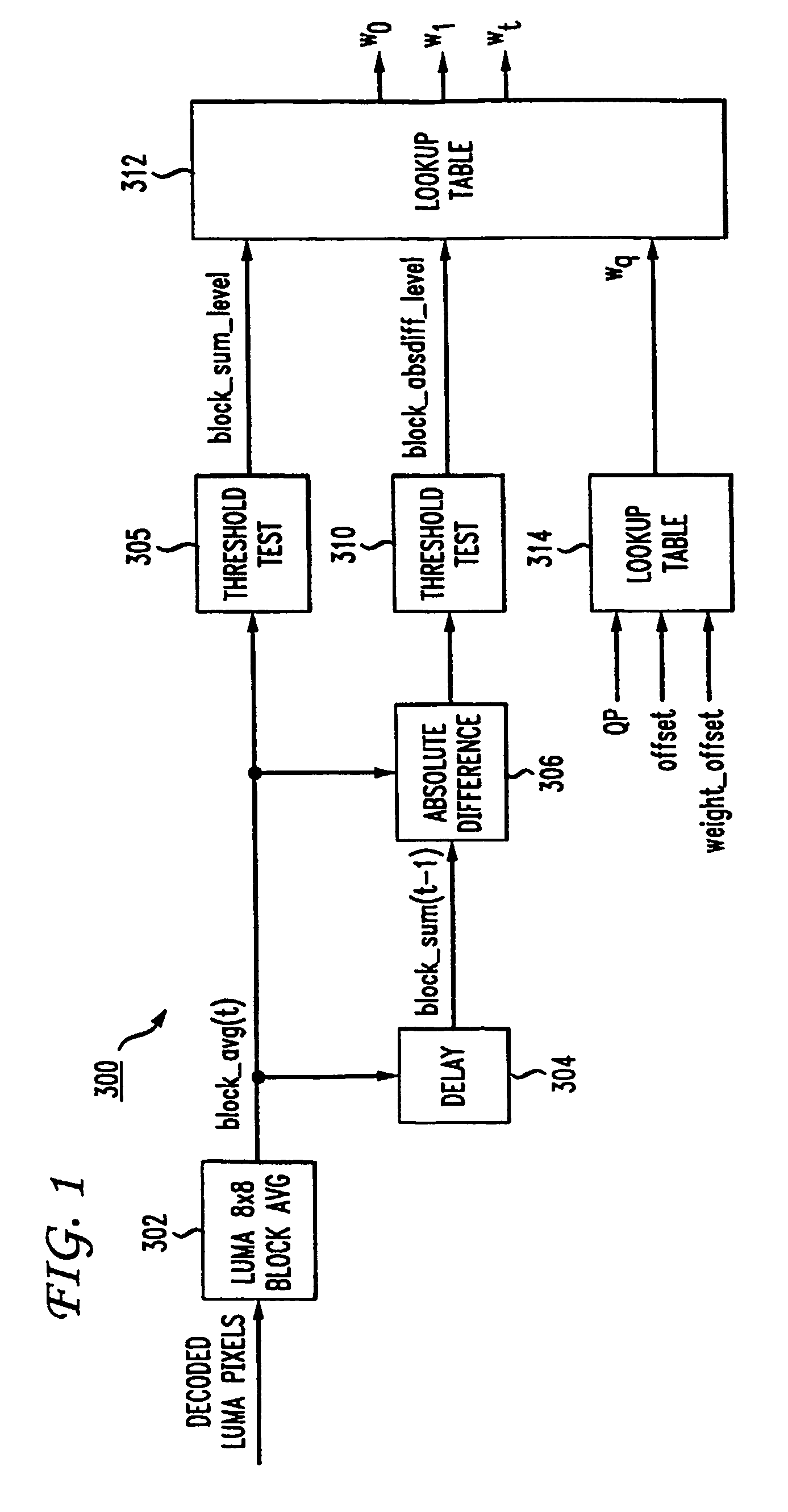
Technique for bit-accurate comfort noise addition
ActiveUS20070058866A1Reduce artifactsTelevision system detailsImage enhancementComfort noiseCompression artifact
The addition of comfort noise to an image serves to hide compression artifacts. To facilitate comfort noise addition, supplemental information accompanying a video image contains at least one parameter that specifies an attribute regarding comfort noise. Typically, the supplemental information includes parameters that function to turn the comfort noise on and off, as well as to indicate the level of noise to add, based on the expected level of compression artifacts.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
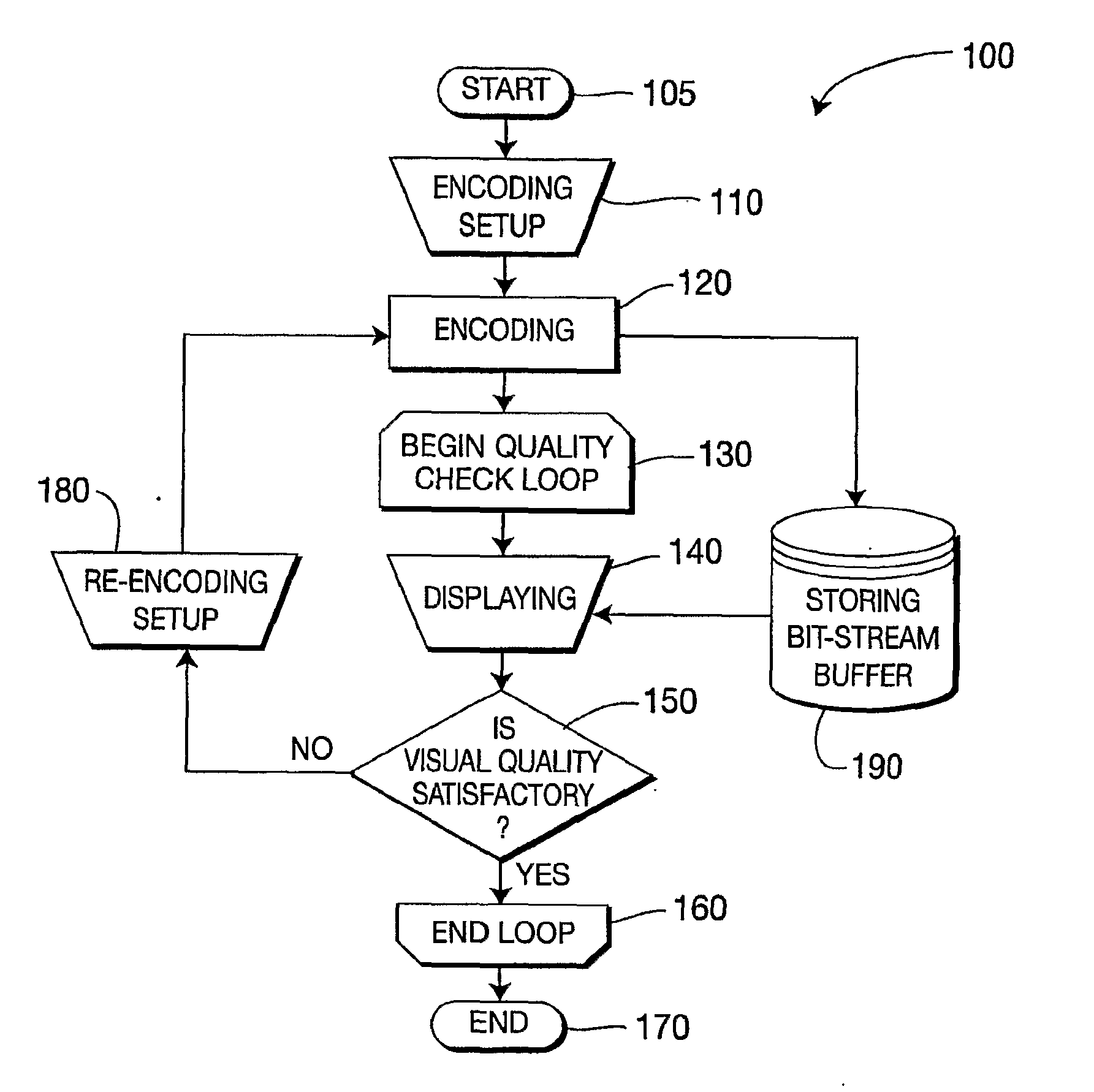
Methods and apparatus for enhanced performance in a multi-pass video recorder
ActiveUS20090323803A1Reduce generationImprove performanceColor television with pulse code modulationPulse modulation television signal transmissionVideo bitstreamCompression artifact
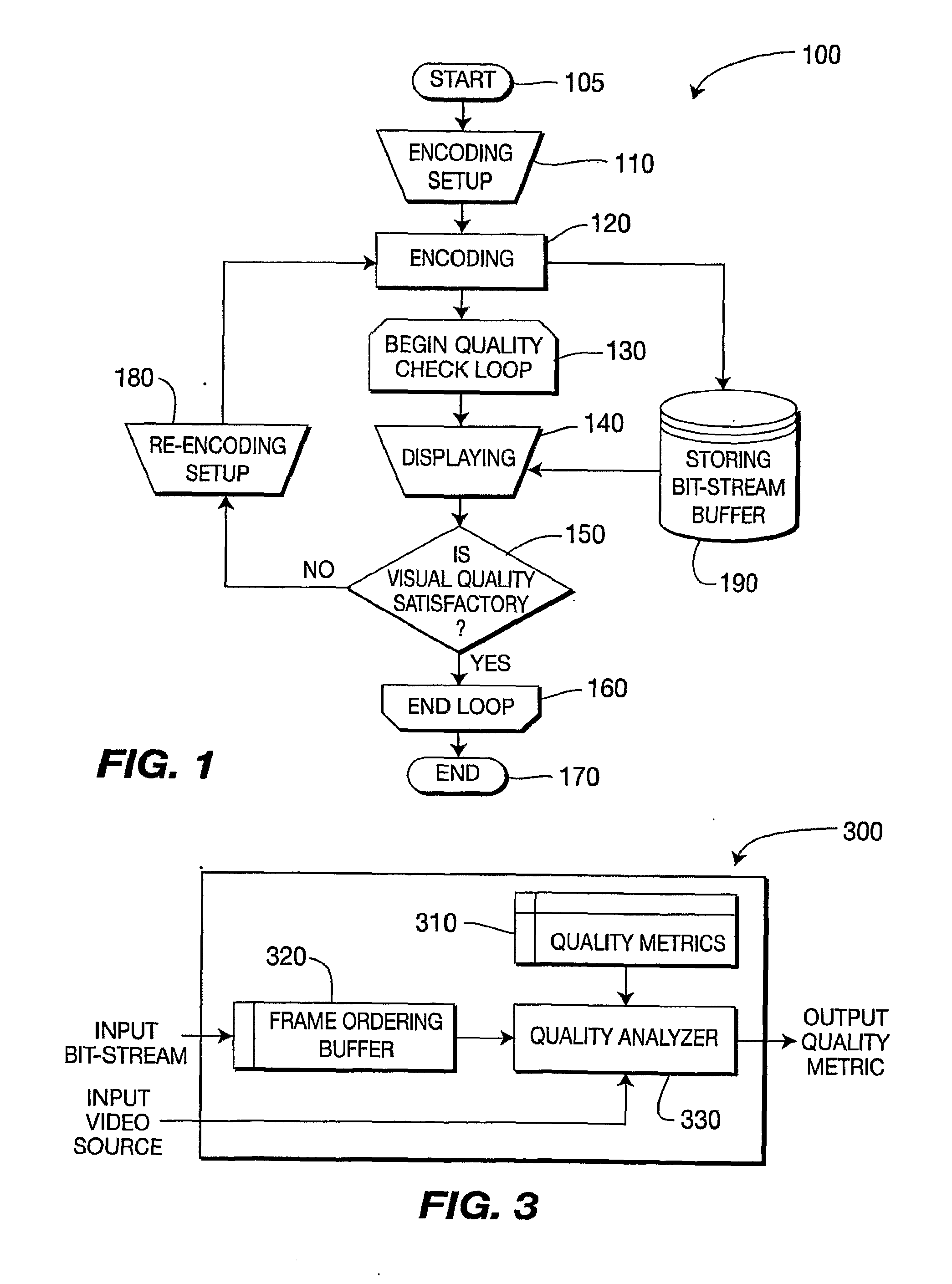
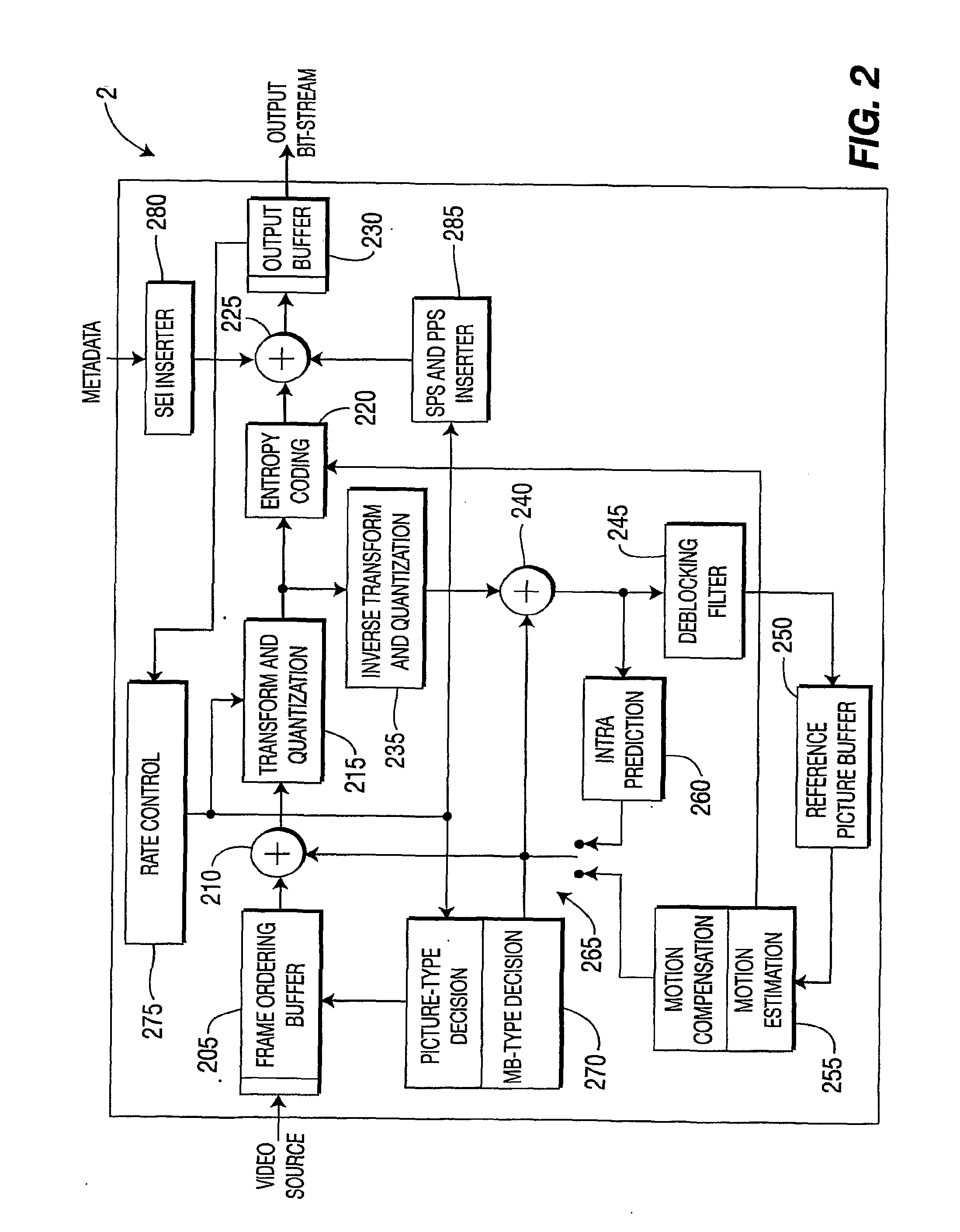
There are provided methods and apparatus for enhanced performance in a multi-pass video encoder. An apparatus includes a video encoder for encoding a video bitstream. The apparatus further includes a video quality analyzer, in signal communication with the encoder, for performing a video quality analysis of the video bitstream for a given encoding pass to detect encoder compression artifacts in the video bitstream, and providing to the encoder information relating to the encoder compression artifacts to enable a re-encoding setup of the encoder to reduce an occurrence of the encoder compression artifacts in subsequent re-encoding passes. At least one of the video quality analysis and the re-encoding setup are automated.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Methods and apparatus for removing compression artifacts in video sequences
InactiveUS6993191B2Cancel noiseIncrease amplitudeTelevision system detailsColor signal processing circuitsLow-pass filterCompression artifact
Techniques for removing ringing artifacts from video data. A deringing filter in accordance with the present invention preserves real image edges in a video frame, while smoothing out the interiors of objects. In one aspect, a 9-tap low-pass filter is applied to an adaptive processing window. The filter window is initialized with the values in a 3×3 mask centered on the position whose output is computed. Then all values that are very different from the central one are replaced with the central value. The deringing filter varies between 3×3 low-pass and identity, depending on how much the central value differs from its surrounding ones. A deblocking filter in accordance may also be suitably used in conjunction with the deringing filter.
Owner:ALTERA CORP
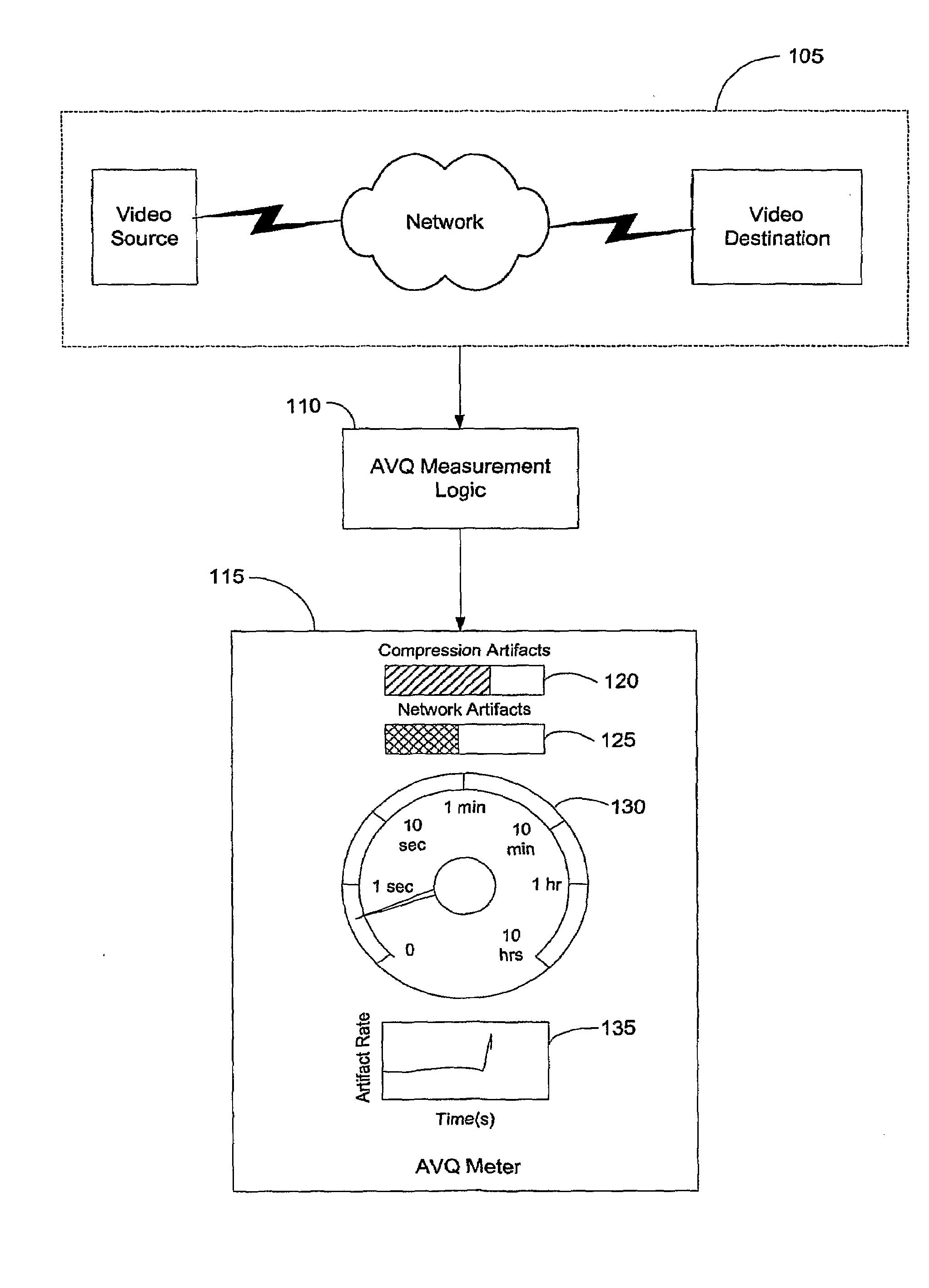
Automatic Video Quality Measurement System and Method Based on Spatial-Temporal Coherence Metrics
InactiveUS20090208140A1Abundant resourcesImage analysisPicture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPattern recognitionCompression artifact
An automatic video quality (AVQ) metric system for evaluating the quality of processed video and deriving an estimate of a subjectively determined function called Mean Time Between Failures (MTBF). The AVQ system has a blockiness metric, a streakiness metric, and a blurriness metric. The blockiness metric can be used to measure compression artifacts in processed video. The streakiness metric can be used to measure network artifacts in the processed video. The blurriness metric can measure the degradation (i.e., blurriness) of the images in the processed video to detect compression artifacts.
Owner:GEORGIA TECH RES CORP
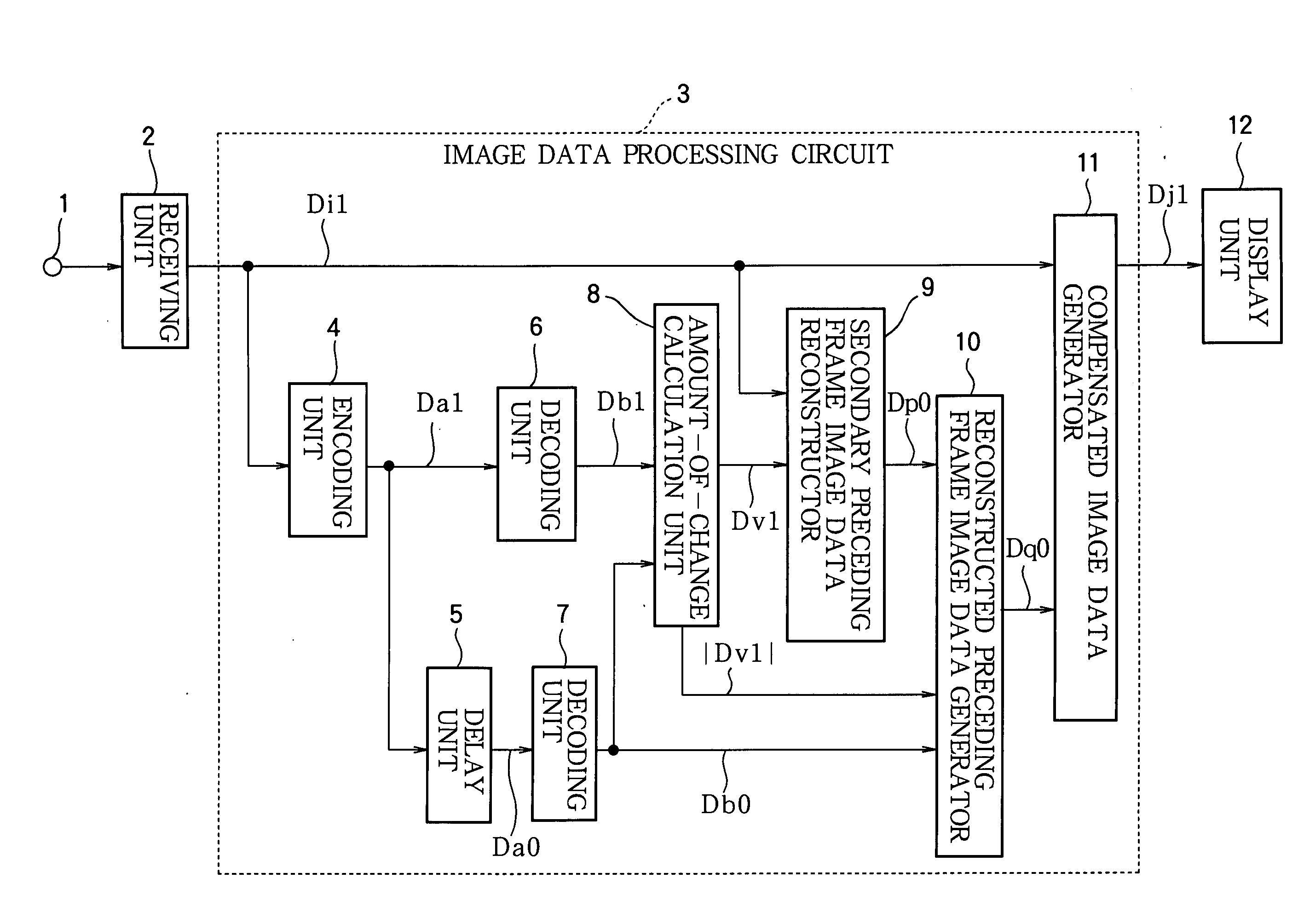
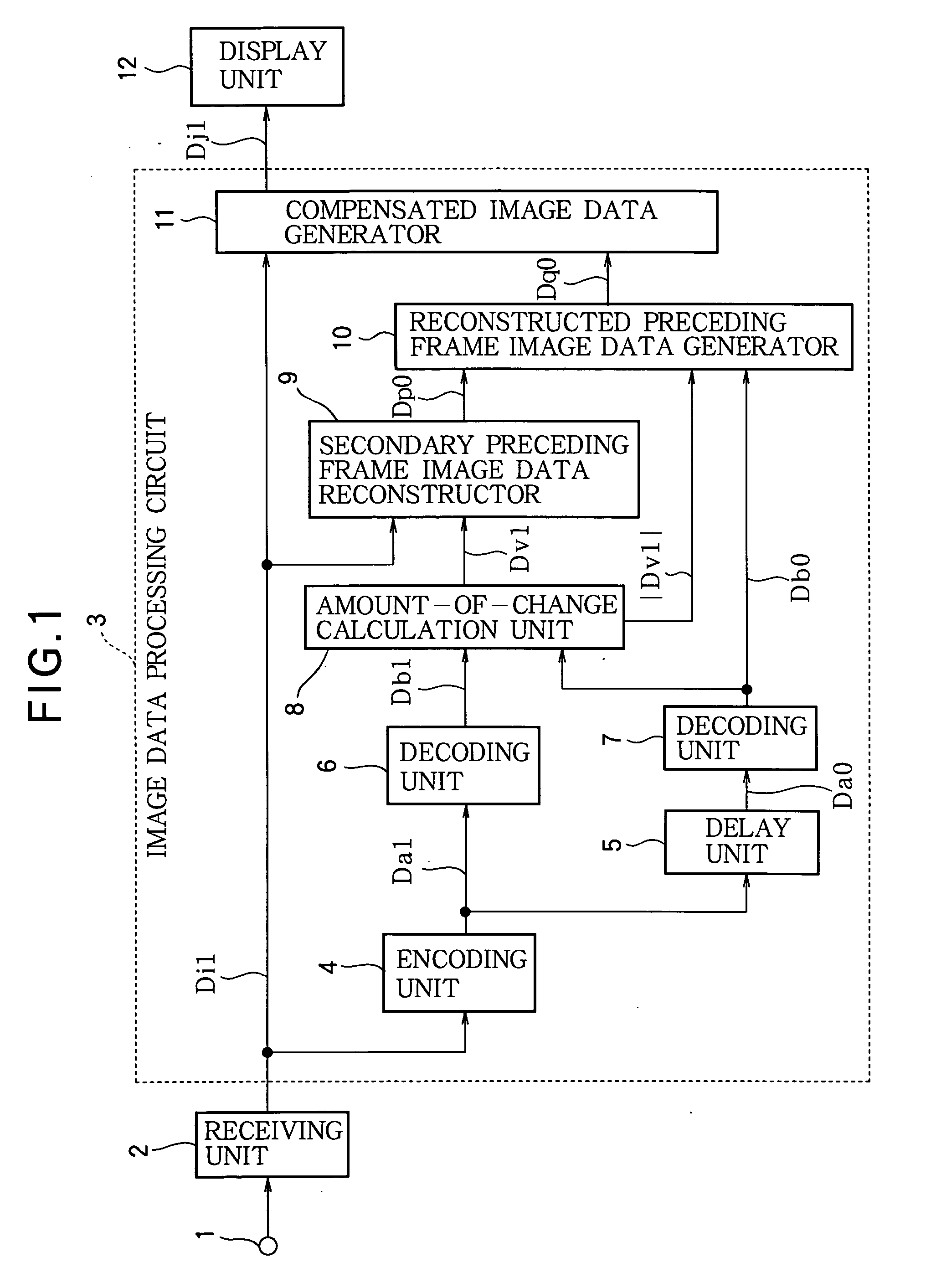
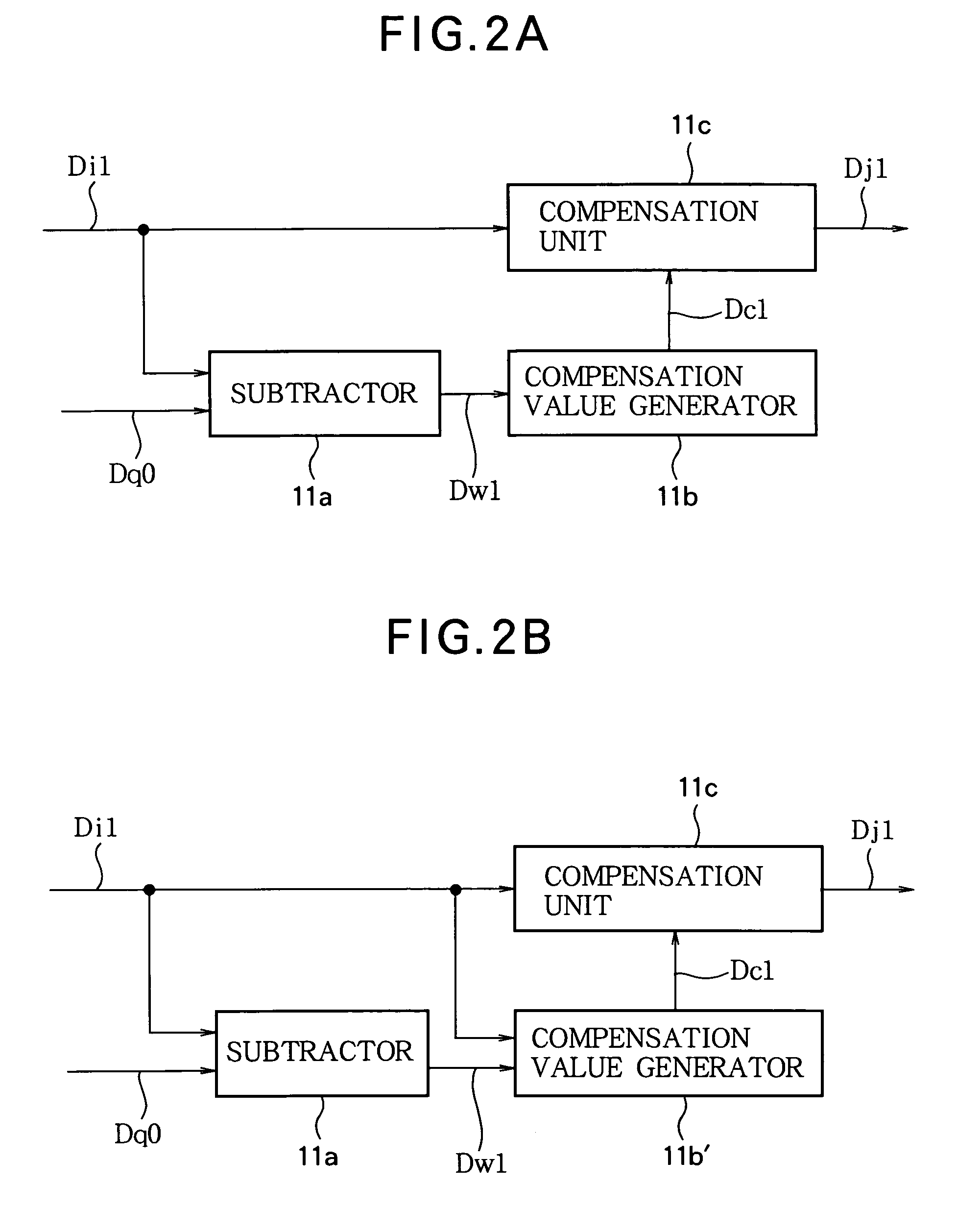
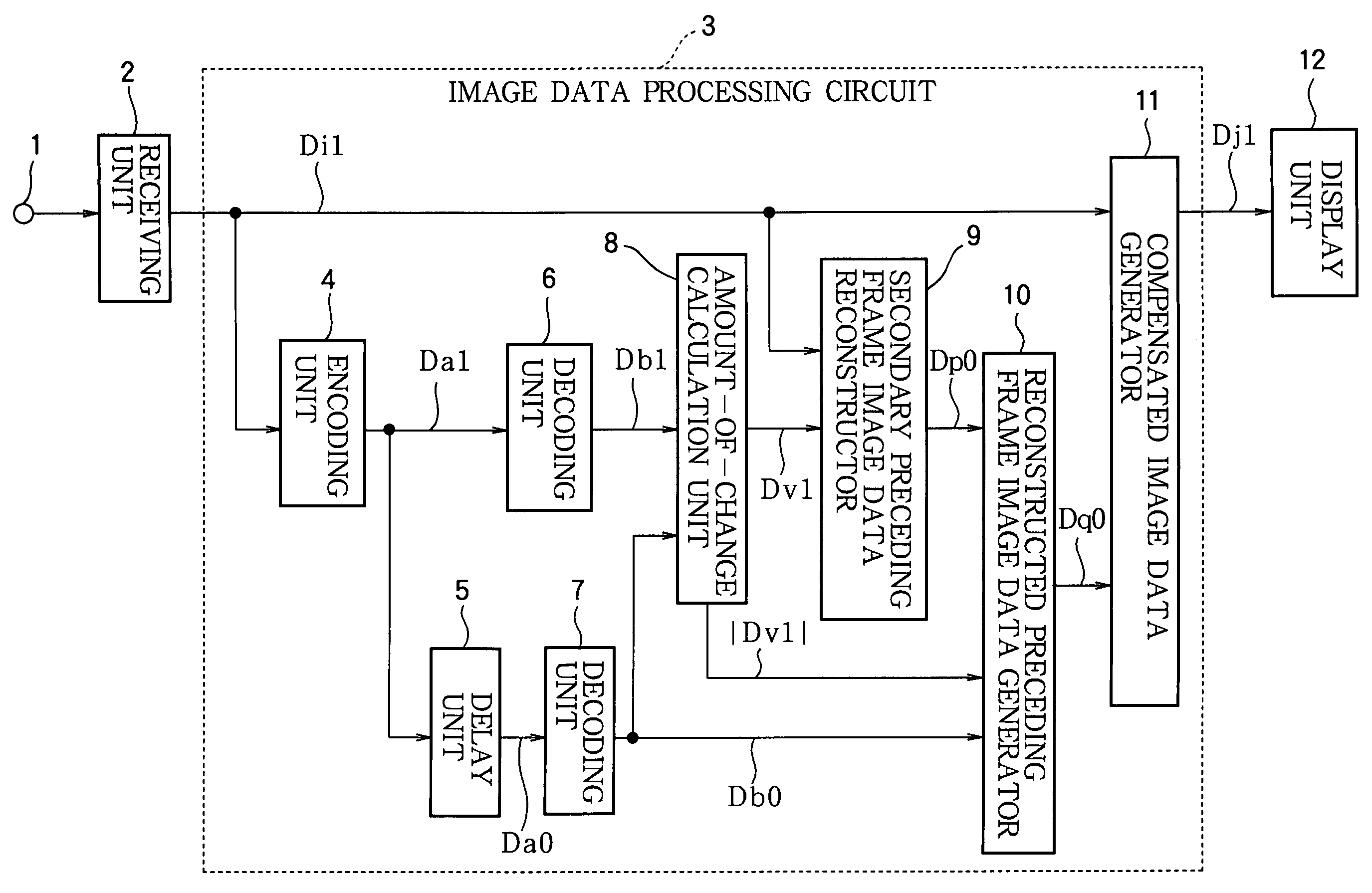
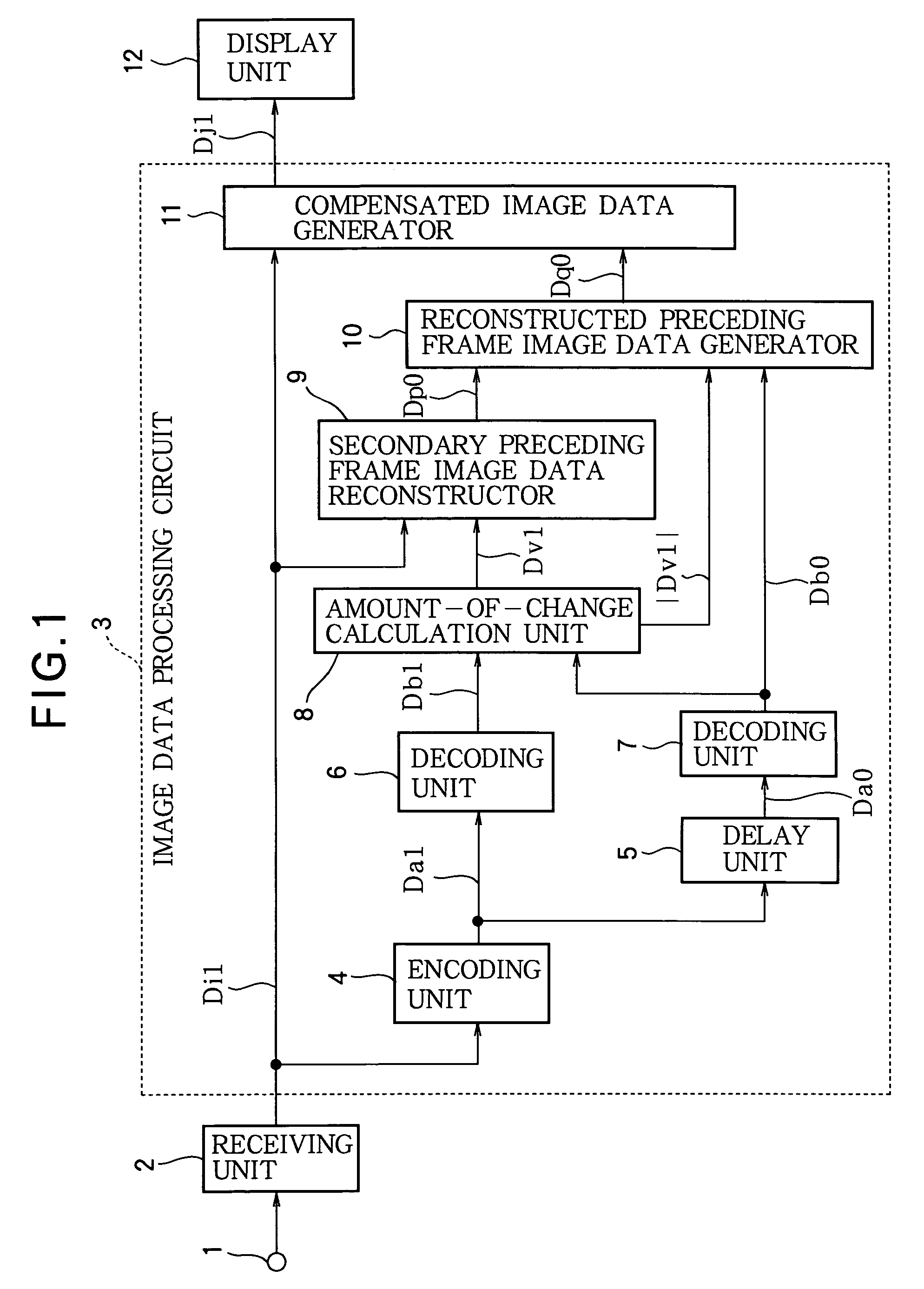
Image data processing method, and image data processing circuit
ActiveUS20040189565A1Reduce image sizeSmall sizeTelevision system detailsColor television detailsLiquid-crystal displayCompression artifact
Consecutive frames of image data are processed for display by, for example, a liquid crystal display. The image data are compressed, delayed, and decompressed to generate primary reconstructed data representing the preceding frame, and the amount of change from the preceding frame to the current frame is determined. Secondary reconstructed data are generated from the current frame image data according to the amount of change. Compensated image data are generated from the current frame image data and the primary and secondary reconstructed data; in this process, either the primary or the secondary reconstructed data may be selected according to the amount of change, or the primary and secondary reconstructed data may be combined according to the amount of change. The amount of memory needed to delay the image data can thereby be reduced without introducing compression artifacts when the amount of change is small.
Owner:TRIVALE TECH
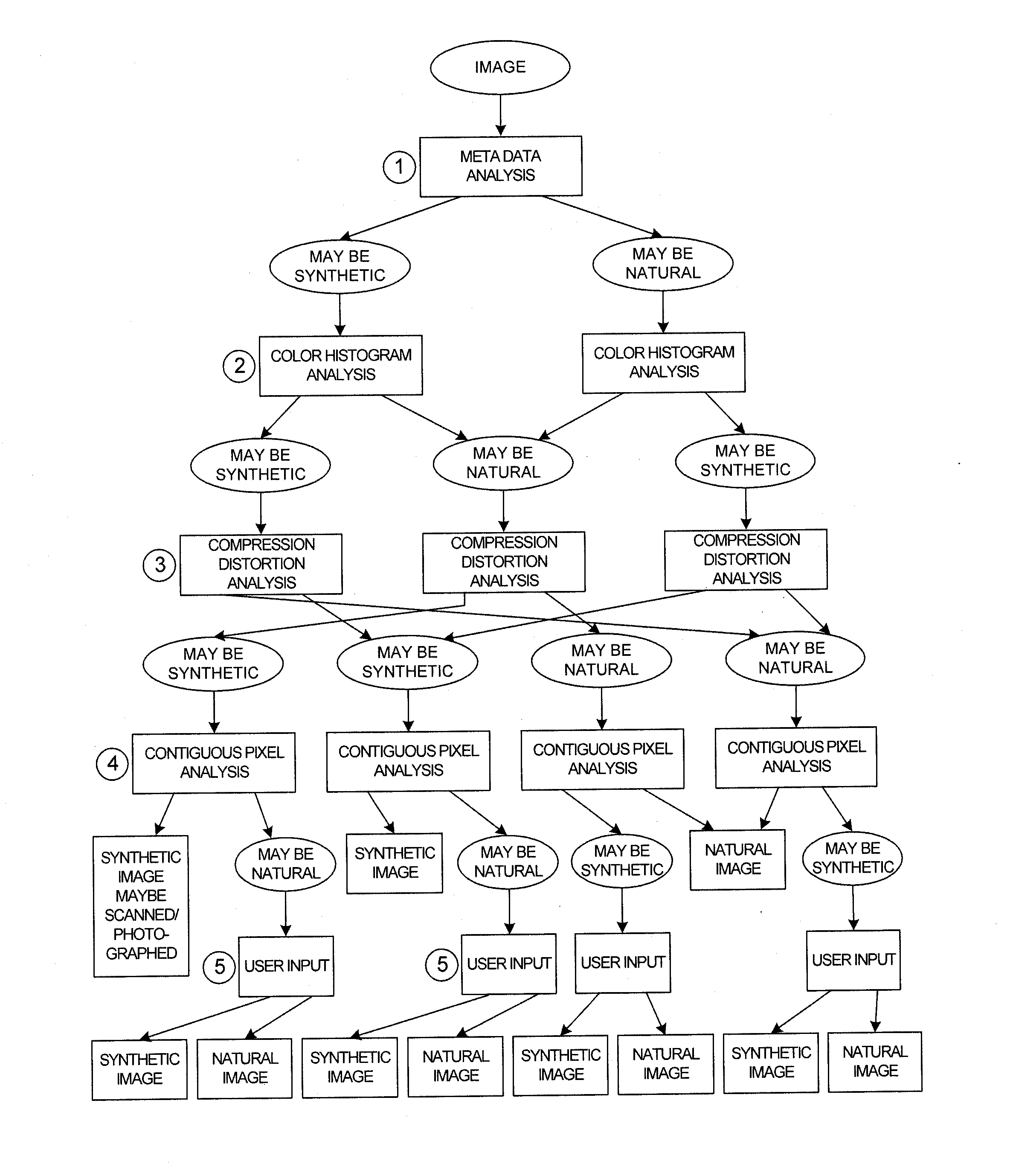
Methods and systems for differentiating synthetic and non-synthetic images
ActiveUS20140241629A1Well formedImage codingCharacter and pattern recognitionCompression artifactTranscoding
The techniques introduced here include a system and method for transcoding multimedia content based on the results of content analysis. The determination of specific transcoding parameters, used for transcoding multimedia content, can be performed by utilizing the results of content analysis of the multimedia content. One of the results of the content analysis is the determination of image type of any images included in the multimedia content. The content analysis uses one or more of several techniques, including analyzing content metadata, examining colors of contiguous pixels in the content, using histogram analysis, using compression distortion analysis, analyzing image edges, or examining user provided inputs. Transcoding the multimedia content can include adapting the content to the constraints in delivery and display, processing and storage of user computing devices.
Owner:META PLATFORMS INC
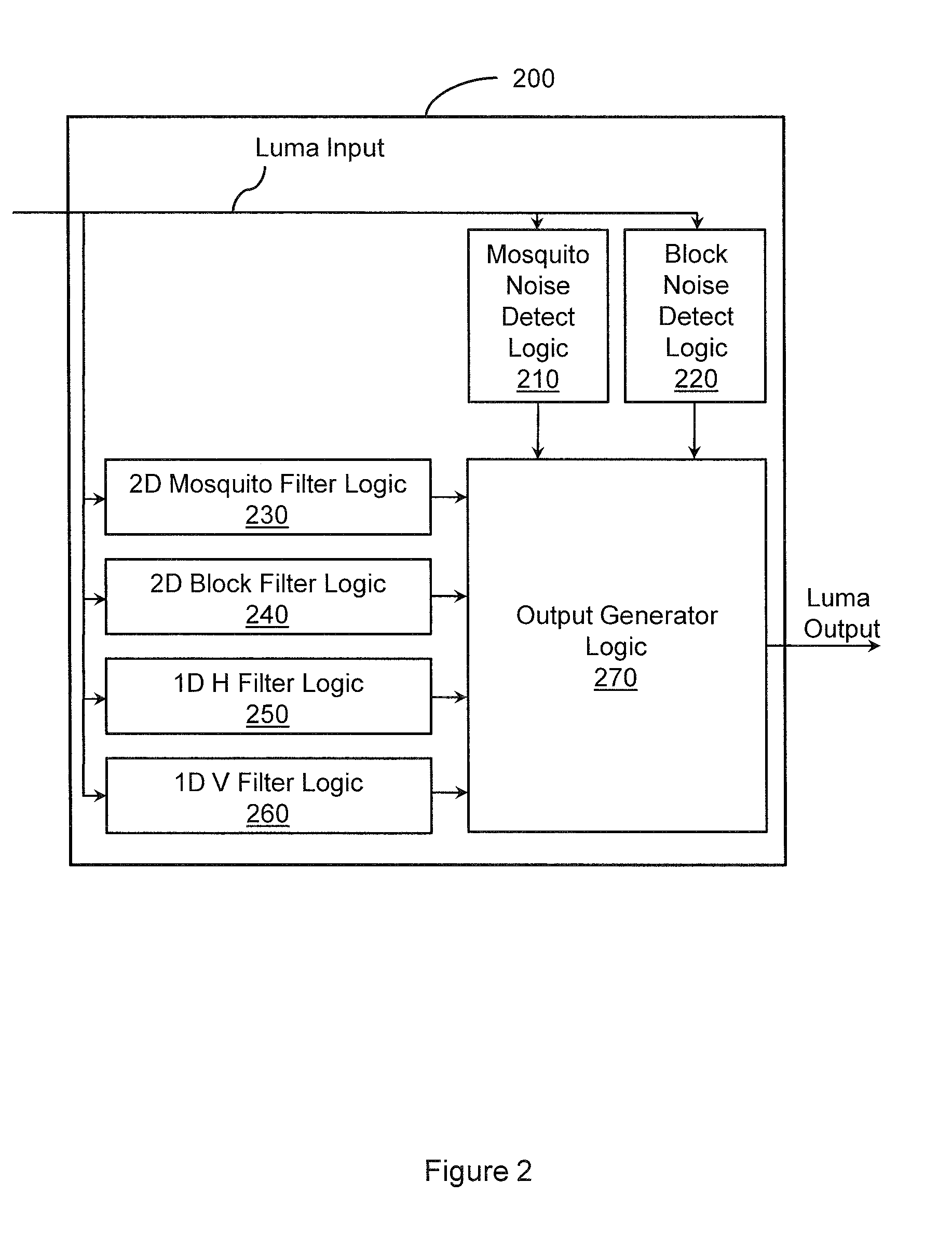
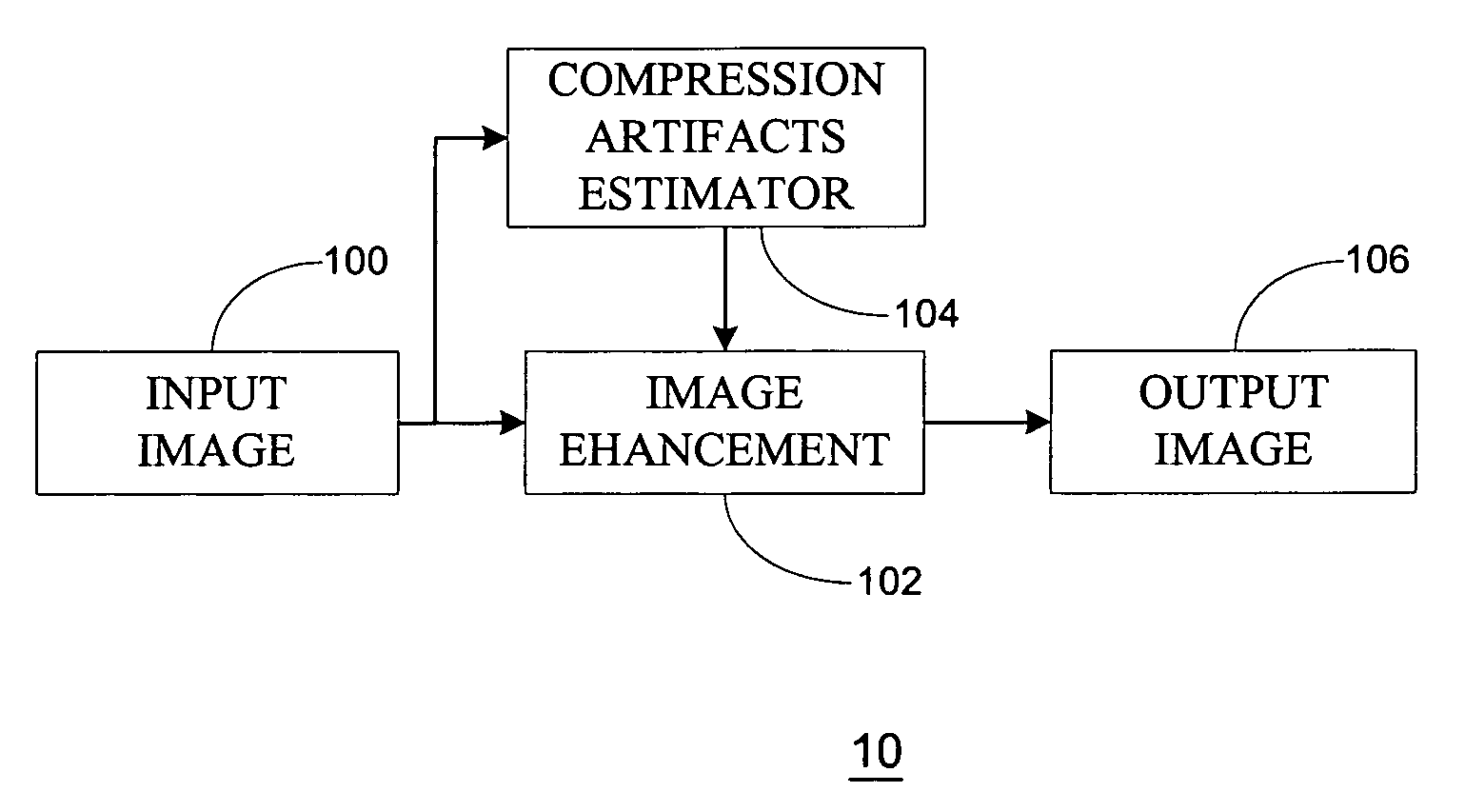
Reducing digital image noise
ActiveUS20100060749A1Improve image qualityReduce artifactsImage enhancementTelevision system detailsPattern recognitionCompression artifact
Devices, systems, methods, and other embodiments associated with reducing digital image noise are described. In one embodiment, a method includes determining, on a per pixel basis, mosquito noise values associated with pixels of a digital image. The method determines, on a per pixel basis, block noise values associated with the digital image. The method filters the digital image with a plurality of adaptive filters. A compression artifact in the digital image is reduced. The compression artifact is reduced by combining filter outputs from the plurality of adaptive filters. The filter outputs are combined based, at least in part, on the mosquito noise values and the block noise values.
Owner:SYNAPTICS INC +1
Video data quality assessment method and apparatus thereof
ActiveCN102740108AReduce computational complexityReal-time assessmentImage enhancementImage analysisPattern recognitionCompression artifact
Embodiments of the invention disclose a video data quality assessment method and an apparatus thereof. The video data quality assessment method comprises the following steps: acquiring a compression distortion parameter of video data; acquiring a frame damage distortion parameter; calculating a video quality parameter according to the compression distortion parameter and the frame damage distortion parameter, wherein the video quality parameter is a difference value of the compression distortion parameter and the frame damage distortion parameter.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
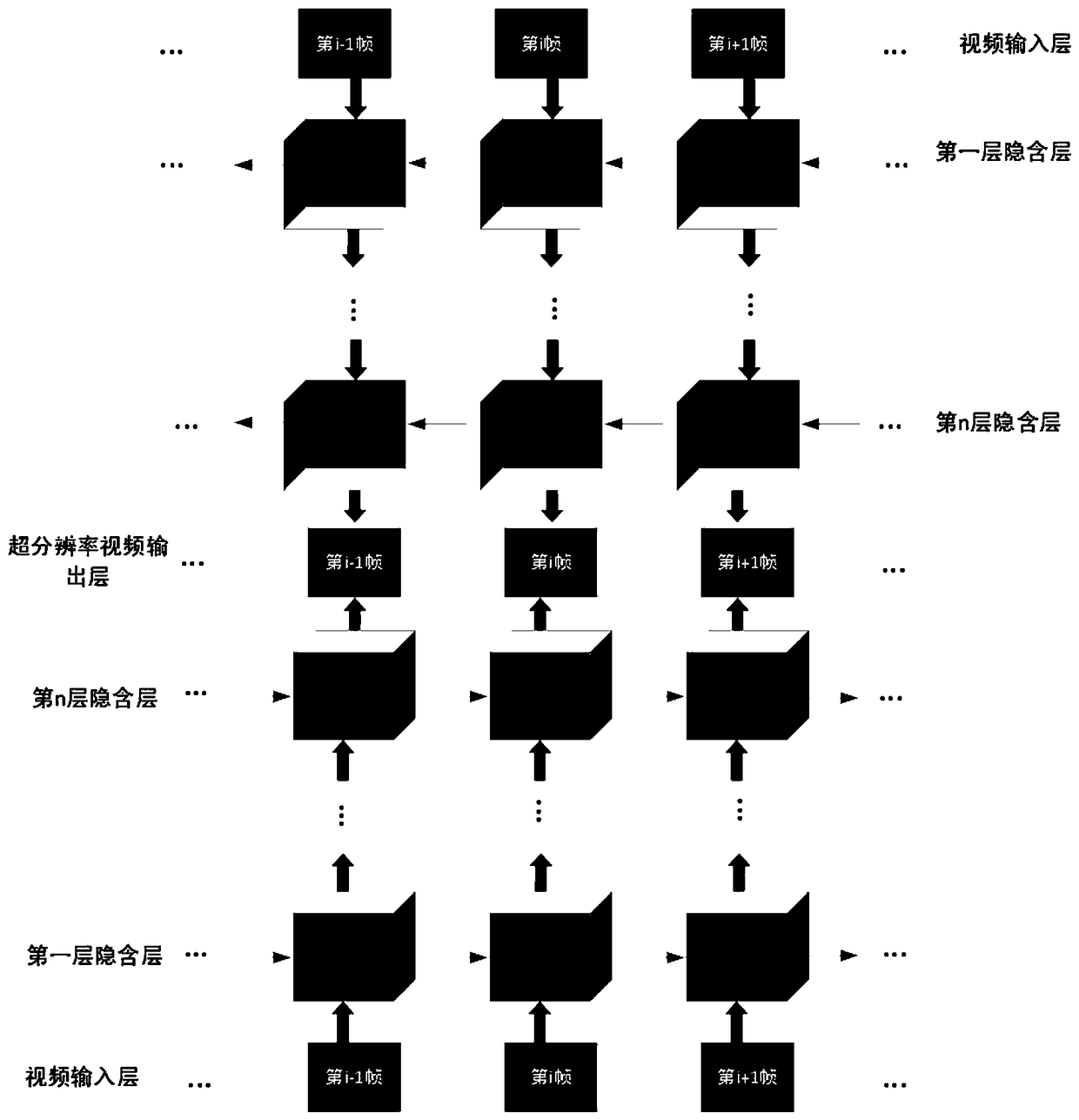
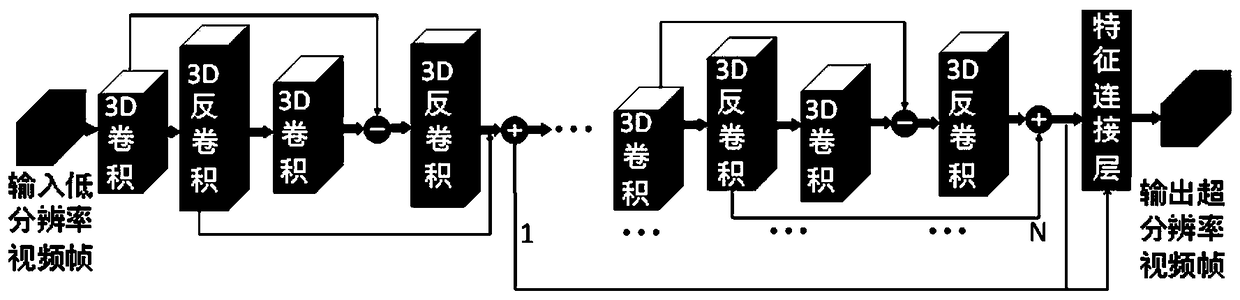
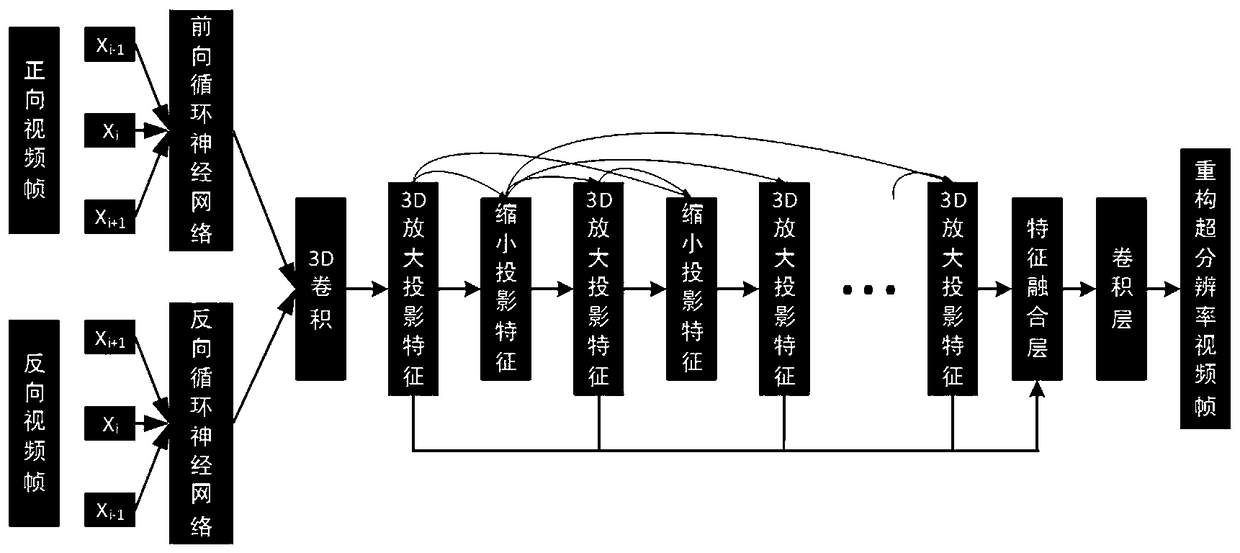
A video super-resolution reconstruction method based on depth learning
ActiveCN109102462ASuper-resolutionInternal combustion piston enginesGeometric image transformationCamera lensReconstruction method
The invention discloses a video super-resolution reconstruction method based on depth learning. The technical key points are: (1) continuous images are given under the same shot, the network predictsclearer video frame images; (2) using a bi-directional circulating neural network and a depth 3D back projection network; (3) the invention combines two networks into one network, and the network is used as a network (4) for in-depth learning video super-resolution reconstruction of the invention. The training data is labeled, and the processed data video frames are passed through the network to obtain a loss function. A final object of the present invention is to input temporal and spatial information of a low-resolution video frame predicted by a bi-directional circulating network, after the3D projection network re-predicts the details of the video frame, an optimal model is obtained after repeated training. The model is applied to remove the effects of the camera shake, the blur of theobject's fast motion, out-of-focus blur, lens optical blur, depth-of-field variation, compression distortion and noise, and other degradation factors.
Owner:CHINA JILIANG UNIV
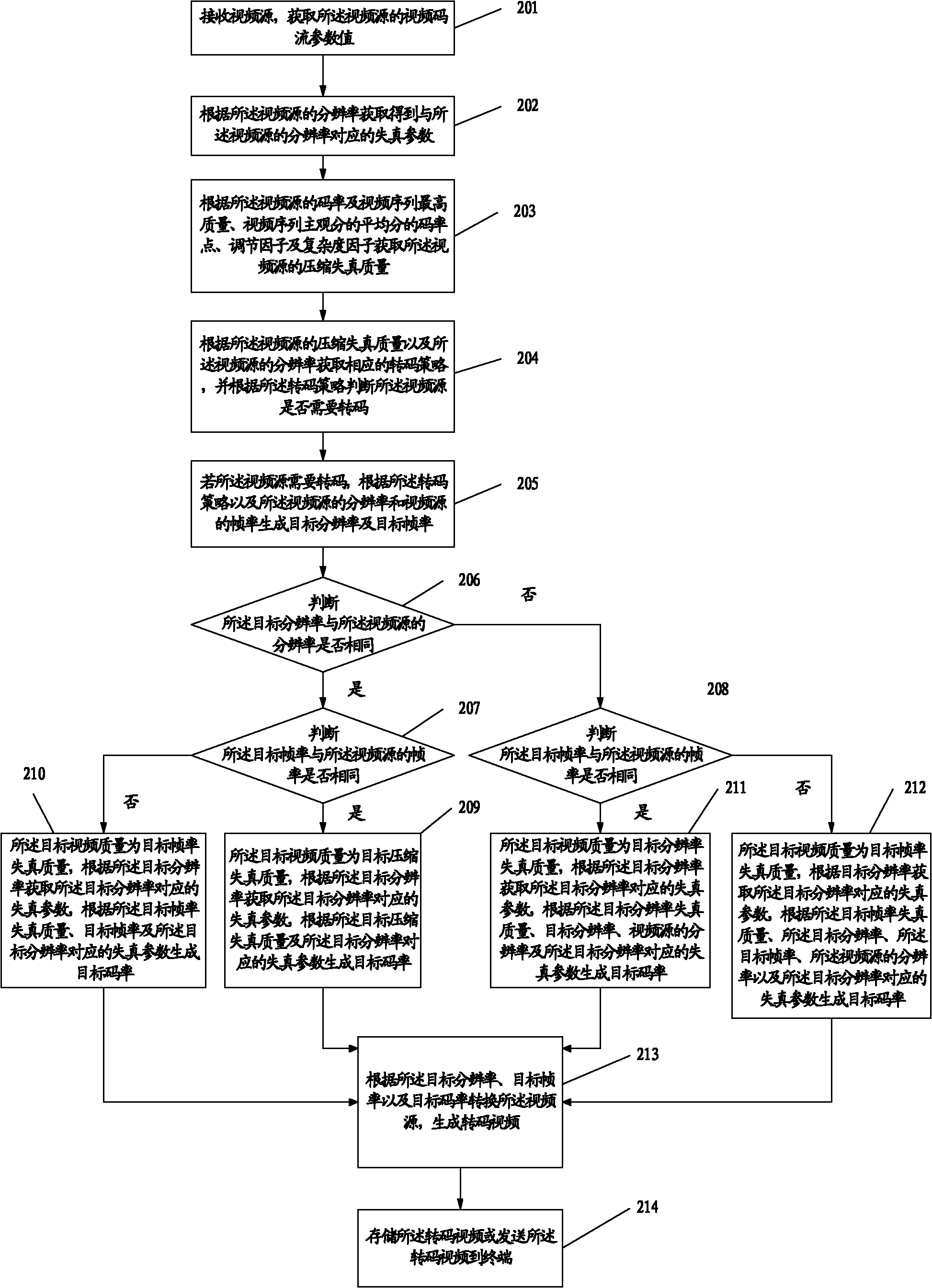
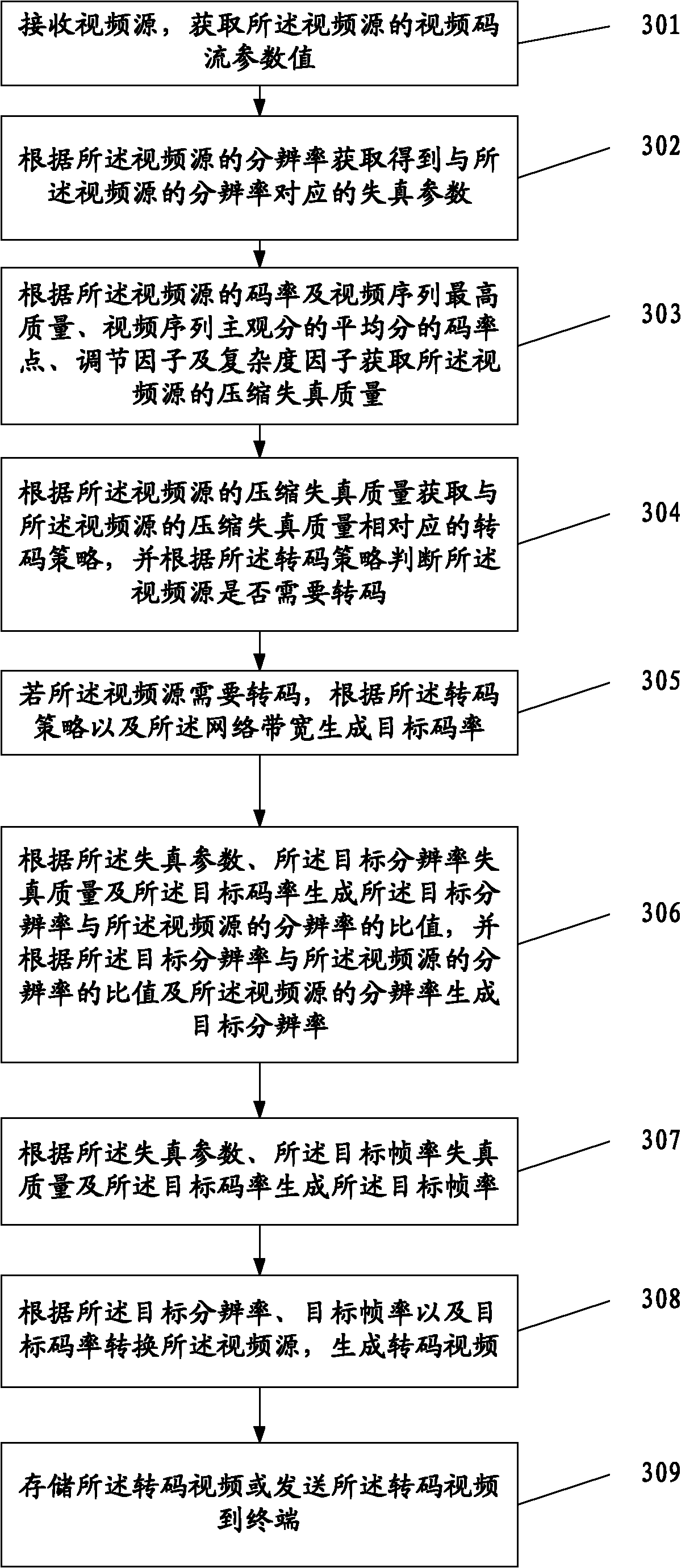
Video conversion method and device
ActiveCN103220550AImprove experiencePulse modulation television signal transmissionDigital video signal modificationTablet computerImage resolution
The invention discloses a video conversion method and device, and relates to the technical field of digital media. The video conversion method and device solves the problems that in the prior art, after a video is converted, a target video is low in quality, and poor in user experience. The method includes the steps of receiving a video source, obtaining compression artifact quality of the video source, obtaining transcoding strategies corresponding to the compression artifact quality of the video source according to the compression artifact quality of the video source, judging whether the video source needs transcoding according to the transcoding strategies, if yes, generating transcoding parameters according to the transcoding strategies, wherein the transcoding strategies comprise target video quality, and the transcoding parameters comprise a target resolution ratio, a target frame rate and a target code rate, converting the video source according to the target resolution ratio, the target frame rate and the target code rate, and generating a transcoded video. The video conversion method and device can be applied to network devices (like a network server) or terminal devices (like a telephone mobile terminal, a tablet computer and a notebook computer).
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
Technique for bit-accurate comfort noise addition
The addition of comfort noise to an image serves to hide compression artifacts. To facilitate comfort noise addition, supplemental information accompanying a video image contains at least one parameter that specifies an attribute regarding comfort noise. Typically, the supplemental information includes parameters that function to turn the comfort noise on and off, as well as to indicate the level of noise to add, based on the expected level of compression artifacts.
Owner:INTERDIGITAL MADISON PATENT HLDG
Method and device for measuring MPEG noise strength of compressed digital image
InactiveUS20070280552A1Easy to processImprove performanceCharacter and pattern recognitionDigital video signal modificationPattern recognitionCompression artifact
A method and system is provided for estimating the strength of block artifacts at each block boundary, based on global and local edge statistics computed from the input image (frame or field picture) in the spatial domain. Such a method systemically measures the strength of the compression artifacts that are associated with block-based compression / coding schemes such as JPEG, MPEG, and H.26x.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
A composite degraded image high-quality reconstruction method based on a generative adversarial network
ActiveCN109685072AReduce the amount of parametersEasy to trainImage enhancementCharacter and pattern recognitionIlluminanceCompression artifact
The invention discloses a composite degraded image high-quality reconstruction method based on a generative adversarial network. The method is mainly used for low-quality images with various quality reduction problems including haze, system noise, low illumination and compression distortion and the like. According to the method, a composite degraded image high-quality reconstruction method based on a generative adversarial network is established from the perspective of composite factor degraded image reconstruction, and reconstruction of a degraded image combined by factors such as haze, low illumination, compression, system noise and optical blurring can be completed; Secondly, an asymmetric generation network is adopted, so that the parameter quantity of the model is greatly reduced, andthe model is easy to train and use; Furthermore, the end-to-end idea is adopted, so that the architecture of the reconstruction system is simplified, and preprocessing and post-processing are omitted; And finally, the generation network is completely composed of convolution layers, and a composite degraded image with any size can be input for reconstruction.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF TECH
Method and appartus for model-based recovery of packet loss errors
ActiveUS20100275237A1Picture reproducers using cathode ray tubesPicture reproducers with optical-mechanical scanningPacket lossComputer graphics (images)
A media processor having a controller operable to recognize a portion of a video stream in an Interactive TV (iTV) network having video compression artifacts corresponding to a stored model and perform model-based video correction of the portion recognized using synthetically generated images of objects in a captured video scene. Other embodiments are disclosed.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP I L P
Method, system and apparatus for evaluating video quality
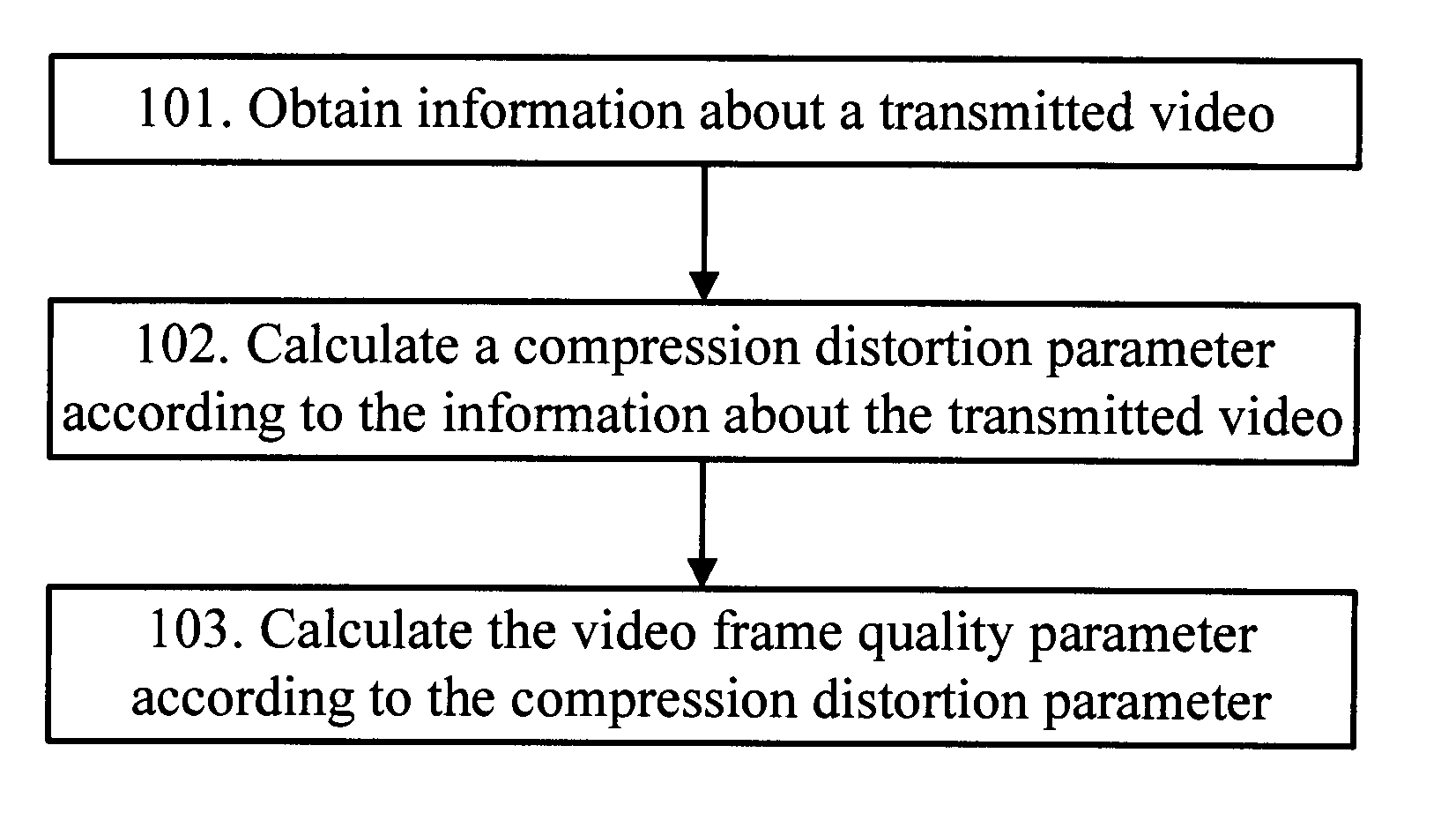
InactiveUS20110085605A1Improve accuracySave network resourcesColor television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionPattern recognitionPacket loss
A method, a system, and an apparatus for evaluating video quality are disclosed to improve accuracy of the evaluation. The method includes: obtaining information about a transmitted video; resolving the information about the transmitted video to obtain video frame parameters, where the video frame parameters include a compression distortion parameter and / or a video quality distortion parameter with packet loss; and calculating a video frame quality parameter according to the video frame parameters. An apparatus and a system for evaluating video quality are provided. The embodiments of the present invention improve accuracy of video quality evaluation without reference.
Owner:SNAPTRACK
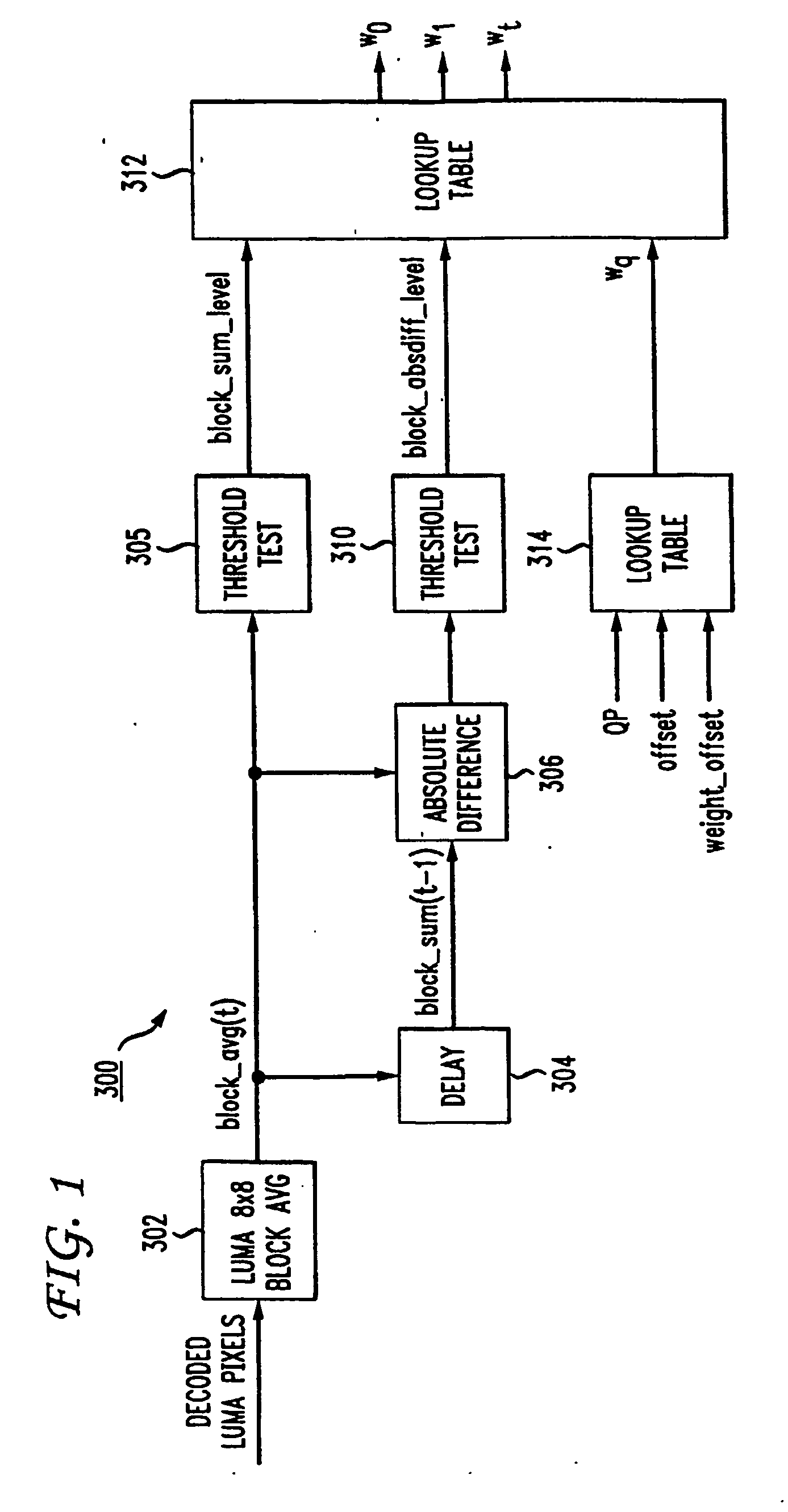
Spacial deblocking method using limited edge differences only to linearly correct blocking artifact
InactiveUS7277592B1Color television with pulse code modulationColor television with bandwidth reductionCompression artifactAlgorithm
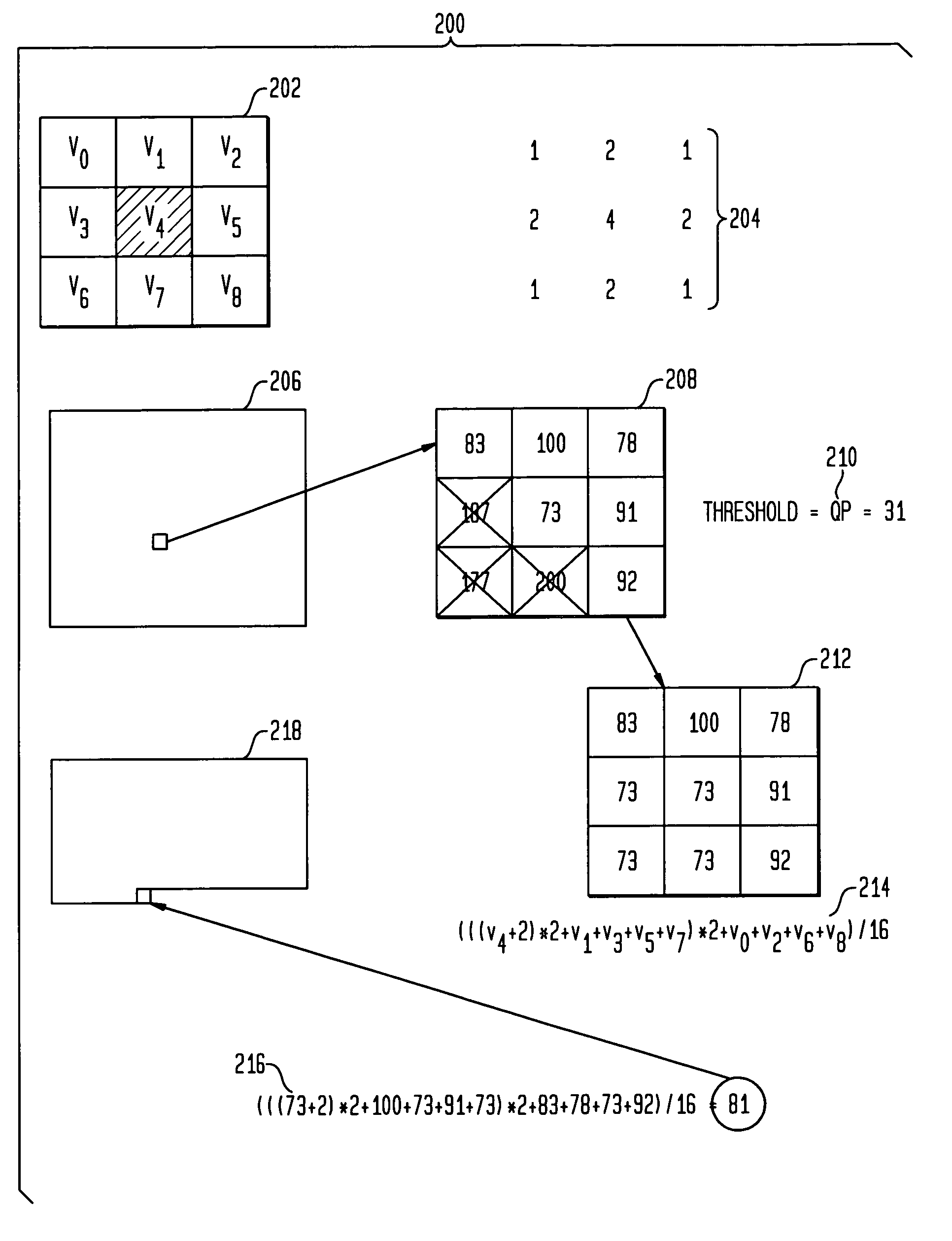
A de-blocking method smoothes pixels along a row or column that crosses a block boundary. Smoothing is performed to remove quantization or compression artifacts that appear on block edges when pixels in adjacent blocks are separately compressed. A maximum-allowed edge-pixel difference is generated from the quantization parameter QP. For each edge-crossing row or column, an edge difference is generated as half the difference between adjacent edge pixels in two blocks. This edge difference is compared to the maximum-allowed edge-pixel difference. When the edge difference is larger than the maximum-allowed edge-pixel difference, then the difference is limited to the maximum-allowed edge-pixel difference, since the pixel difference may be a real edge in the image. The limited or edge difference is then added or subtracted in decreasing amounts for several pixels in the row or column near the edge, smoothing the edge difference across several pixels, such as seven pixels.
Owner:REDROCK SEMICON
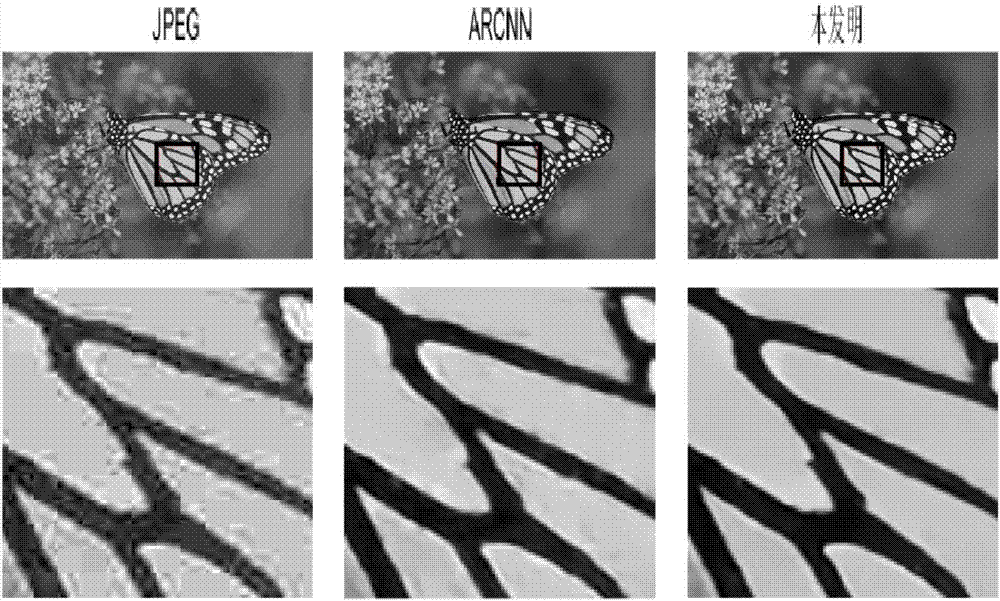
Compression artifacts removing method of image based on deep learning
ActiveCN107463989AEffective studyLearning techniques to effectively remove effectiveTelevision system detailsImage codingPattern recognitionData set
The invention discloses a compression artifacts removing method of an image based on deep learning. Artifacts generated in highly compression of the image can be effectively removed. The method is characterized in that firstly, by use of the newest deep learning technology, a deep residual error network is used as a basic module to be applied to a network model, so a gradient diffusion problem of the depth network model is effectively relieved, and meanwhile, base layer characteristics and high layer characteristics obtained in network learning are fused through skipping connection, so quite enriched characteristic information is provided for reconstruction of an artifacts removing image and the artifacts removing performance of the model is further improved; and secondly, the invention further provides a model selection scheme, so artifacts removing operation can be properly selected for proper models with compression artifacts in different degrees. According to the invention, two sets of public data sets are tested, so the performance of the provided method is remarkably improved than that of the current best artifacts removing algorithm.
Owner:福建帝视科技集团有限公司
Low-code-rate video coding and decoding method based on image reconstruction convolutional neural network
ActiveCN110087092AOvercoming the problem of low quality of upsampled imagesUpsampled image quality improvementDigital video signal modificationNeural architecturesVideo encodingImage resolution
The invention provides a low-code-rate video coding and decoding method based on an image reconstruction convolutional neural network. The method is used for solving the problem that in the prior art,a video is seriously compressed and distorted after being coded and decoded at a low code rate. The implementation steps are as follows: carrying out down-sampling operation on the input video to obtain a low-resolution video; and performing video encoding and decoding on the low-resolution video by using a standard X265 codec to obtain a decoded low-resolution video, inputting the decoded low-resolution video into the trained image reconstruction convolutional neural network, and then obtaining a reconstructed video with the same resolution as the input video. According to the invention, serious compression distortion caused by video coding and decoding can be effectively inhibited at a low code rate, and the video quality can be well improved.
Owner:XIDIAN UNIV
Image data processing method, and image data processing circuit
ActiveUS7403183B2Small sizeTelevision system detailsCathode-ray tube indicatorsLiquid-crystal displayCompression artifact
Consecutive frames of image data are processed for display by, for example, a liquid crystal display. The image data are compressed, delayed, and decompressed to generate primary reconstructed data representing the preceding frame, and the amount of change from the preceding frame to the current frame is determined. Secondary reconstructed data are generated from the current frame image data according to the amount of change. Compensated image data are generated from the current frame image data and the primary and secondary reconstructed data; in this process, either the primary or the secondary reconstructed data may be selected according to the amount of change, or the primary and secondary reconstructed data may be combined according to the amount of change. The amount of memory needed to delay the image data can thereby be reduced without introducing compression artifacts when the amount of change is small.
Owner:TRIVALE TECH
Robust reconstruction of high resolution grayscale images from a sequence of low-resolution frames (robust gray super-resolution)
InactiveUS20060291751A1Solution stableRemove image artifactGeometric image transformationCharacter and pattern recognitionCompression artifactImage resolution
A method for computing a high resolution gray-tone image from a sequence of low-resolution images uses an L1 norm minimization. In a preferred embodiment, the technique also uses a robust regularization based on a bilateral prior to deal with different data and noise models. This robust super-resolution technique uses the L1 norm both for the regularization and the data fusion terms. Whereas the former is responsible for edge preservation, the latter seeks robustness with respect to motion error, blur, outliers, and other kinds of errors not explicitly modeled in the fused images. This computationally inexpensive method is resilient against errors in motion and blur estimation, resulting in images with sharp edges. The method also reduces the effects of aliasing, noise and compression artifacts. The method's performance is superior to other super-resolution methods and has fast convergence.
Owner:UNIV OF CALIFORNIA SANTA CRUZ
JPEG artifact removal
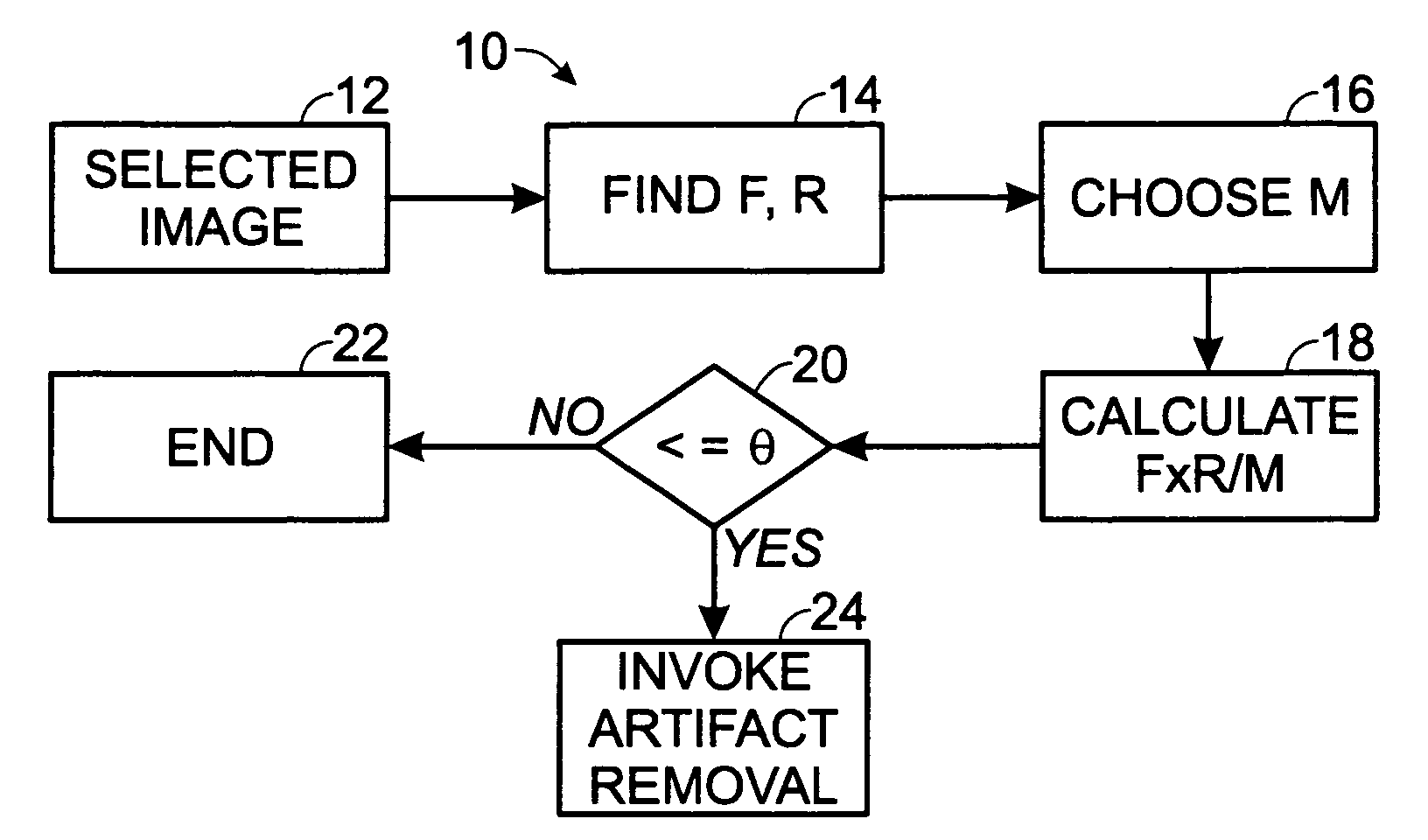
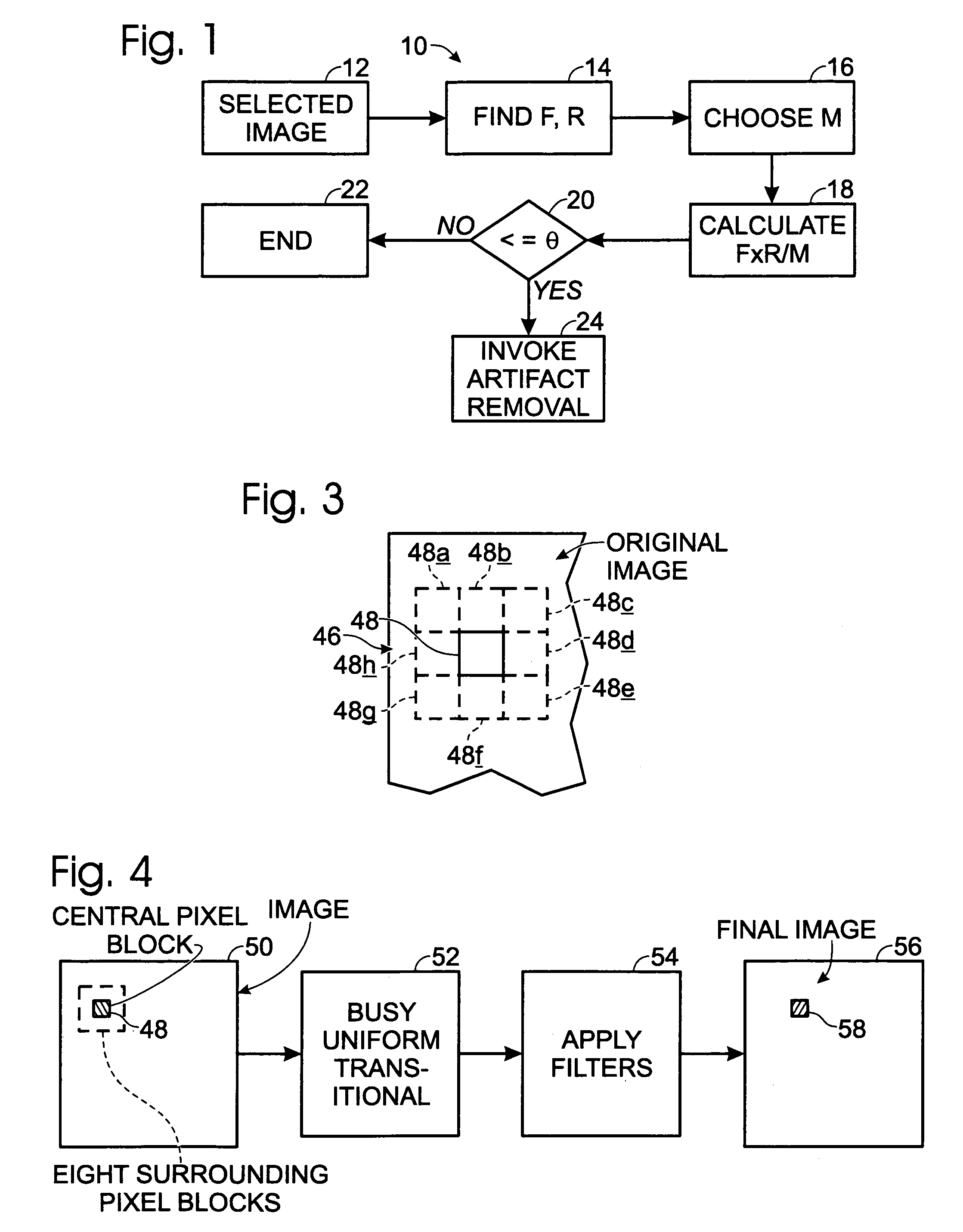
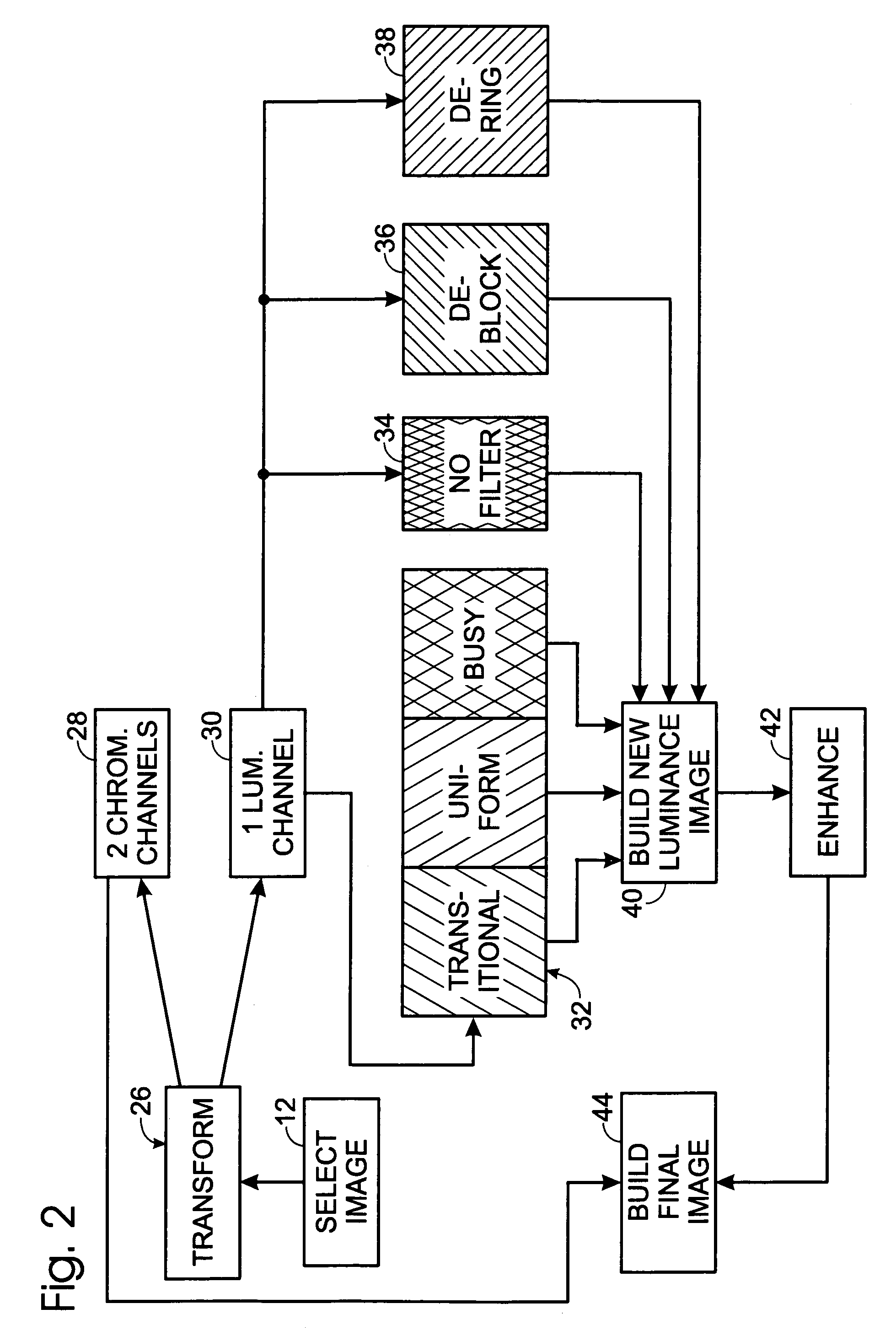
A system and methodology for removing JPEG-compression artifacts from color images, wherein a first-stage examination of the image takes place to determine, in accordance with several approaches, whether artifact removal is appropriate for the image. Following such examination and characterization, when an image is determined to be a candidate for artifact removal, pixel blocks in the image are examined so that they can be characterized as uniform, busy or transitional, and from these characterizations, appropriate filters, or no filter at all, are employed to prepare such pixels for insertion into a final artifact-removed output color image.
Owner:SHARP KK
A compression-distortion-oriented stereoscopic video quality objective evaluating method
ActiveCN104394403AImprove relevanceEffectively measure the degree of changeTelevision systemsSteroscopic systemsStereoscopic videoObjective quality
The invention discloses a compression-distortion-oriented stereoscopic video quality objective evaluating method comprising: dividing stereoscopic video quality into a left and right visual point quality section and a depth perception quality section. In the left and right visual point quality evaluating section, in view of a characteristic that a video image may generate a block effect and blur due to compression distortion, gradient information is extracted to be used as an image feature; meanwhile in view of a time-space domain visual characteristic of human eyes, left visual point quality and right visual point quality are obtained. In the depth perception quality evaluating section, by three dimensional wavelet transform, a low frequency component in a three dimensional parallax spatial diagram is extracted and the quality of the low frequency component is used as the depth perception quality of the stereoscopic video. At last, the left visual point quality and the right visual point quality are combined with the depth perception quality to obtain a final distortion stereoscopic video quality. The method has advantages of completing an object quality evaluation on the stereoscopic video from the view of the left and right visual point plane video quality and the view of the stereoscopic depth perception, and thereby effectively improving the correlation between an object evaluation result and a subject perception.
Owner:三联生活传媒有限公司
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com