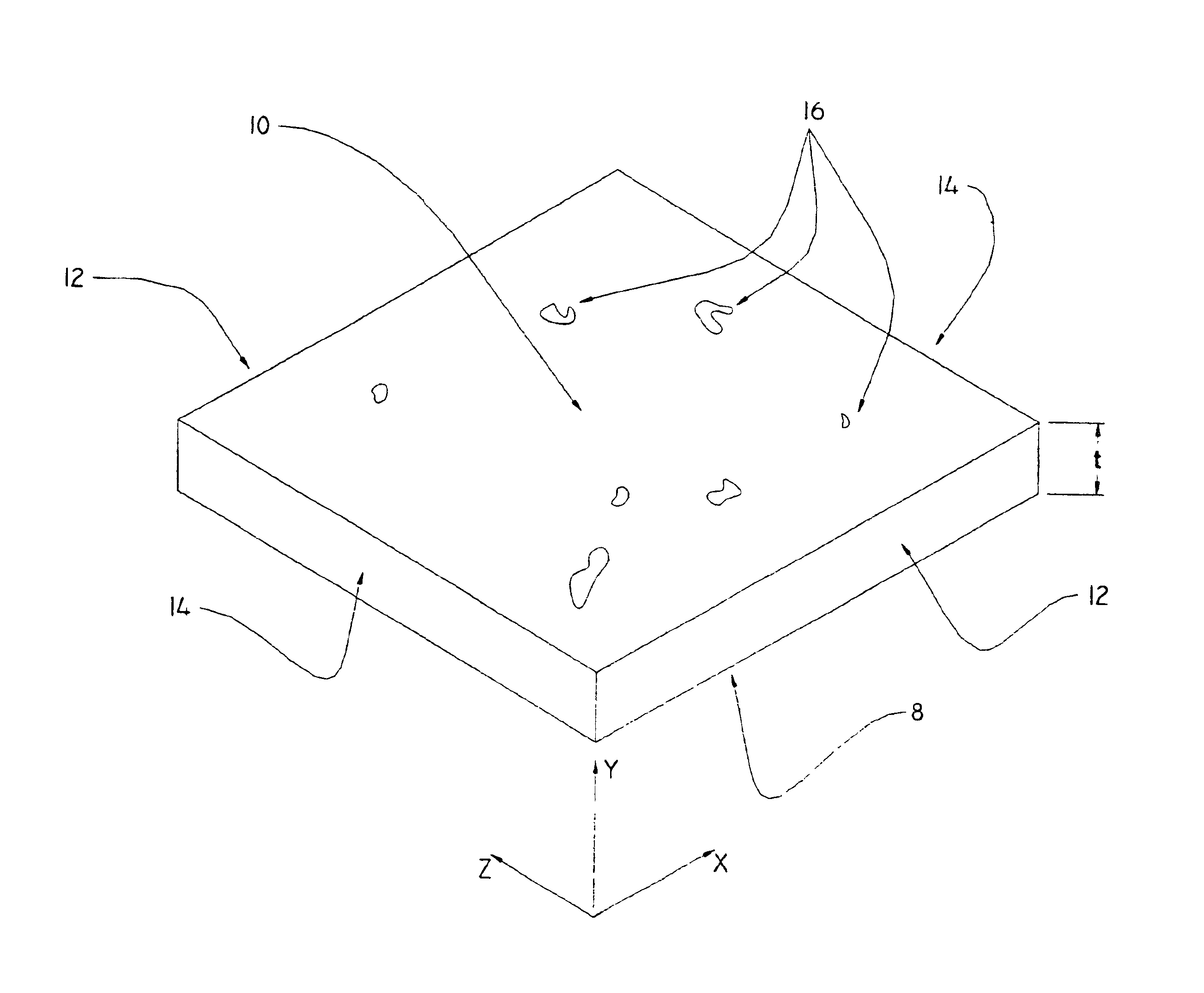
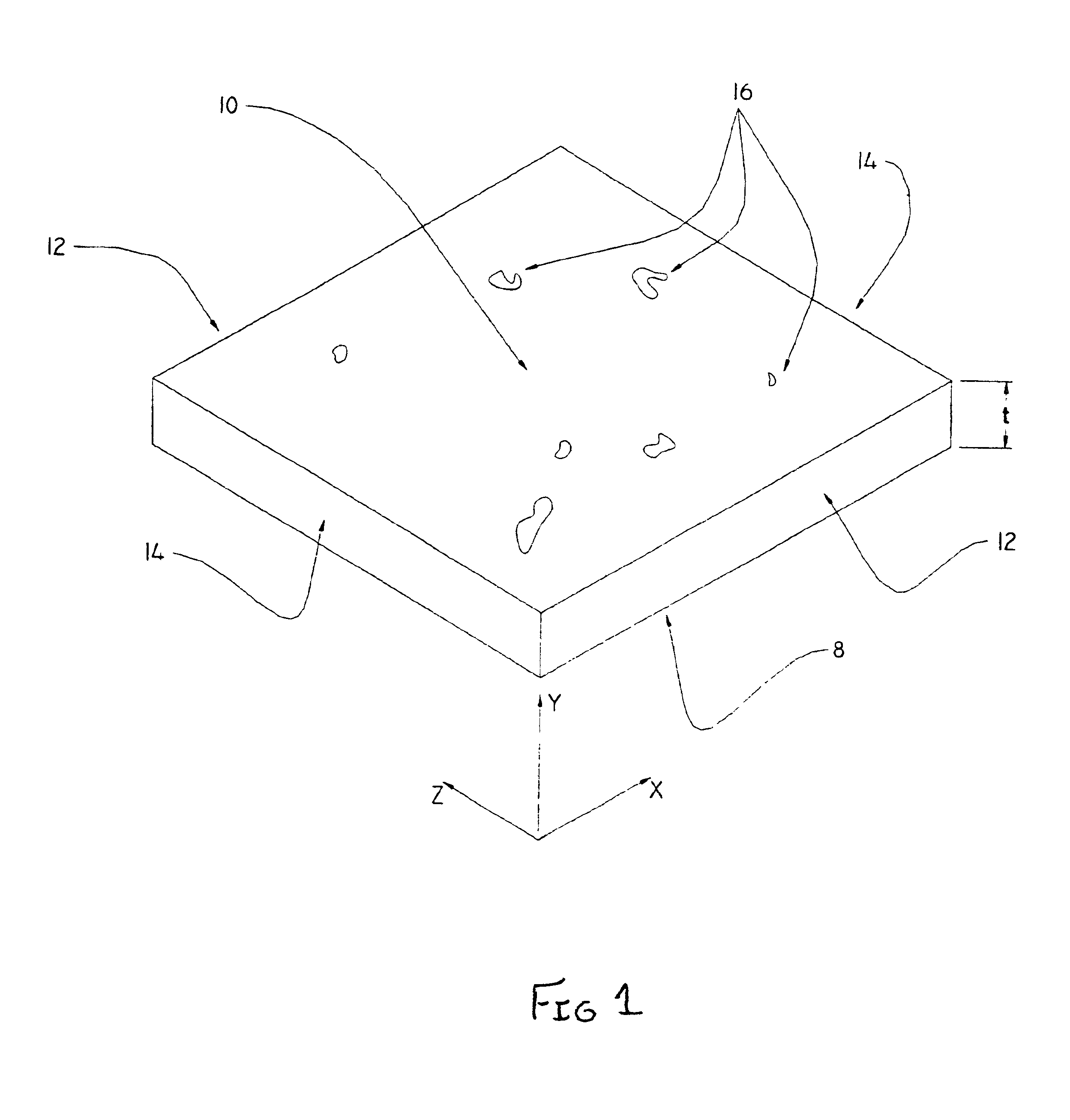
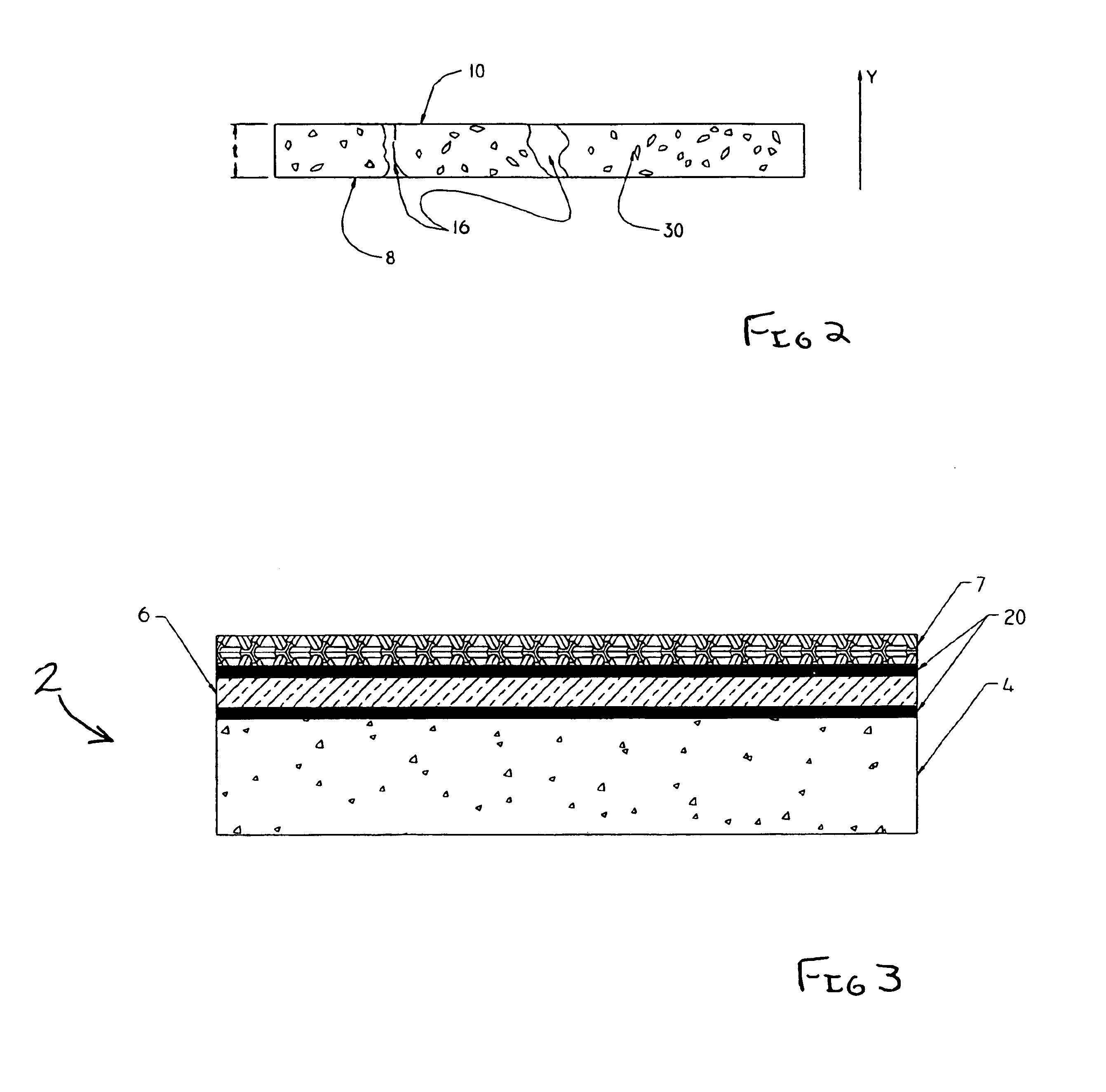
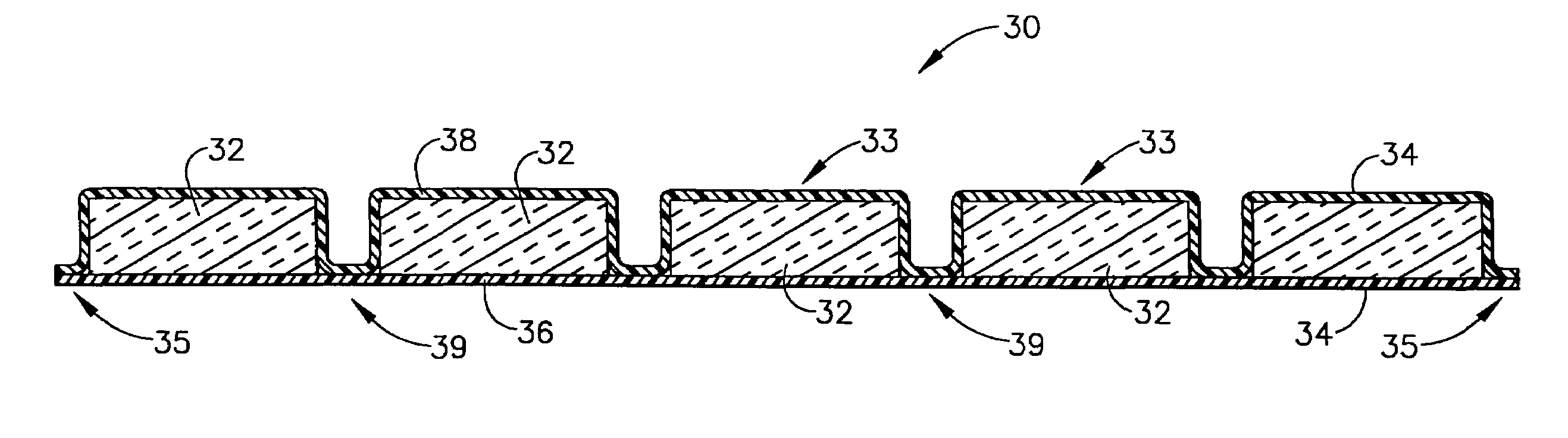
Patents
Literature
Hiro is an intelligent assistant for R&D personnel, combined with Patent DNA, to facilitate innovative research.
5517results about "Sound proofing" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
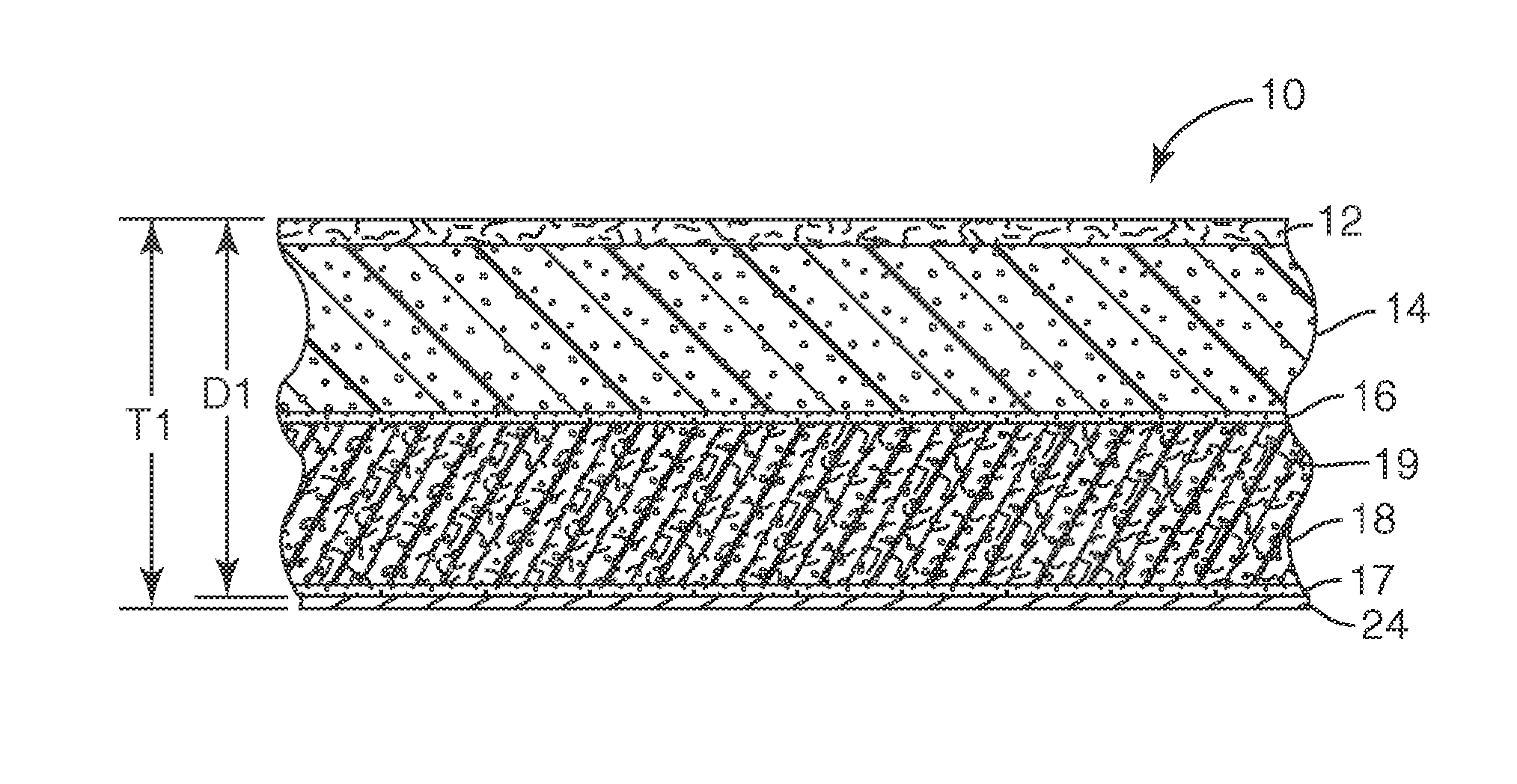
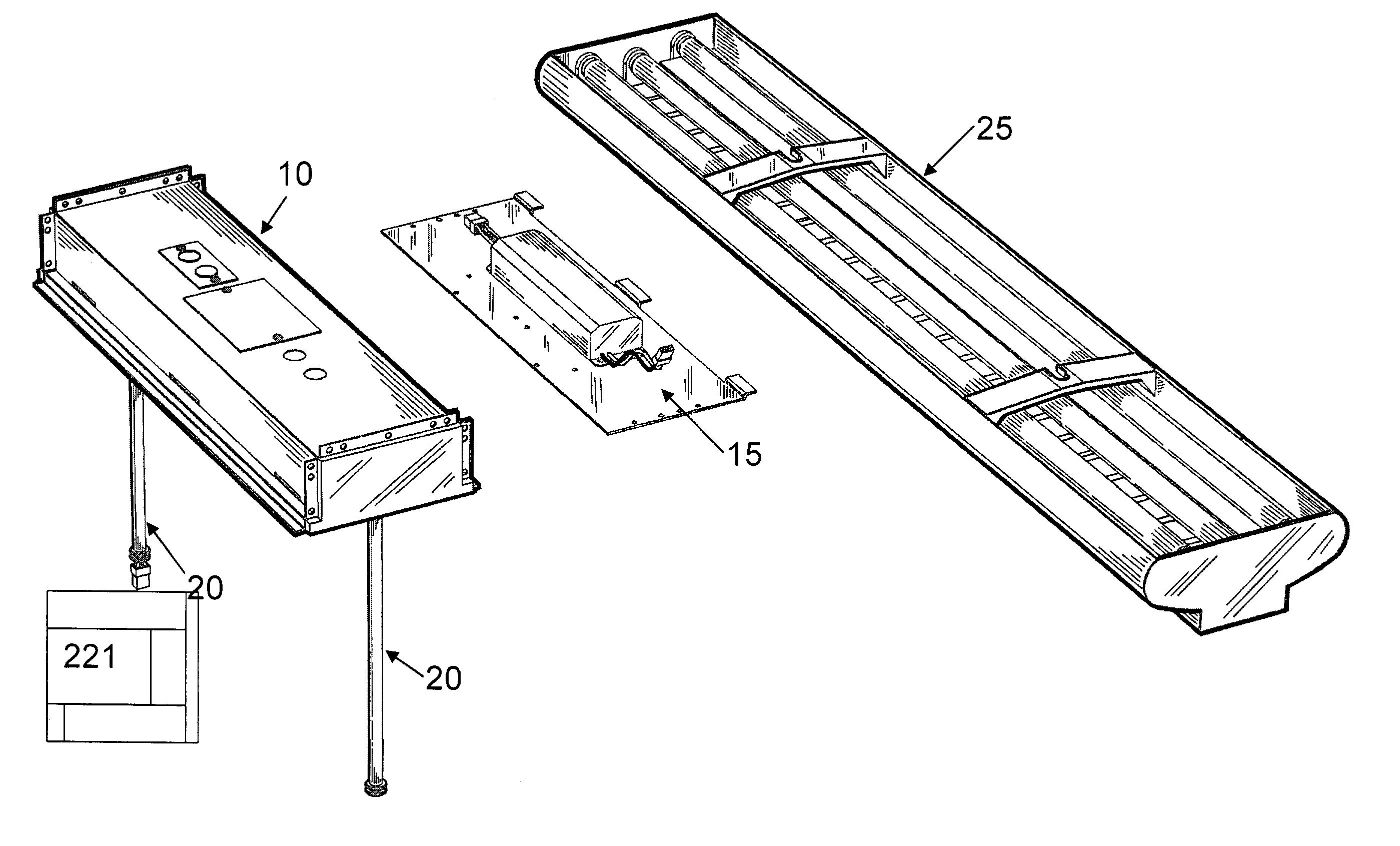
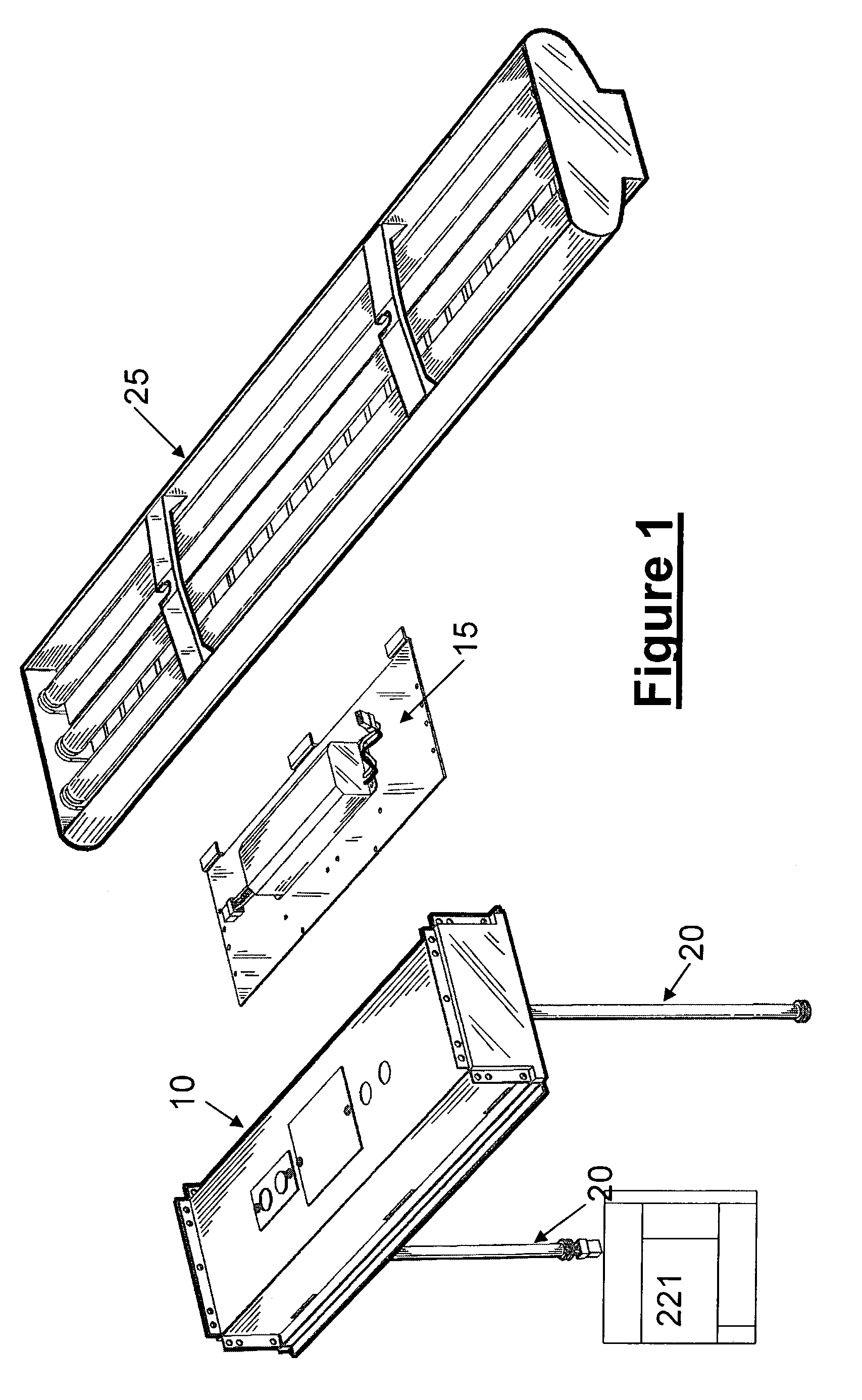
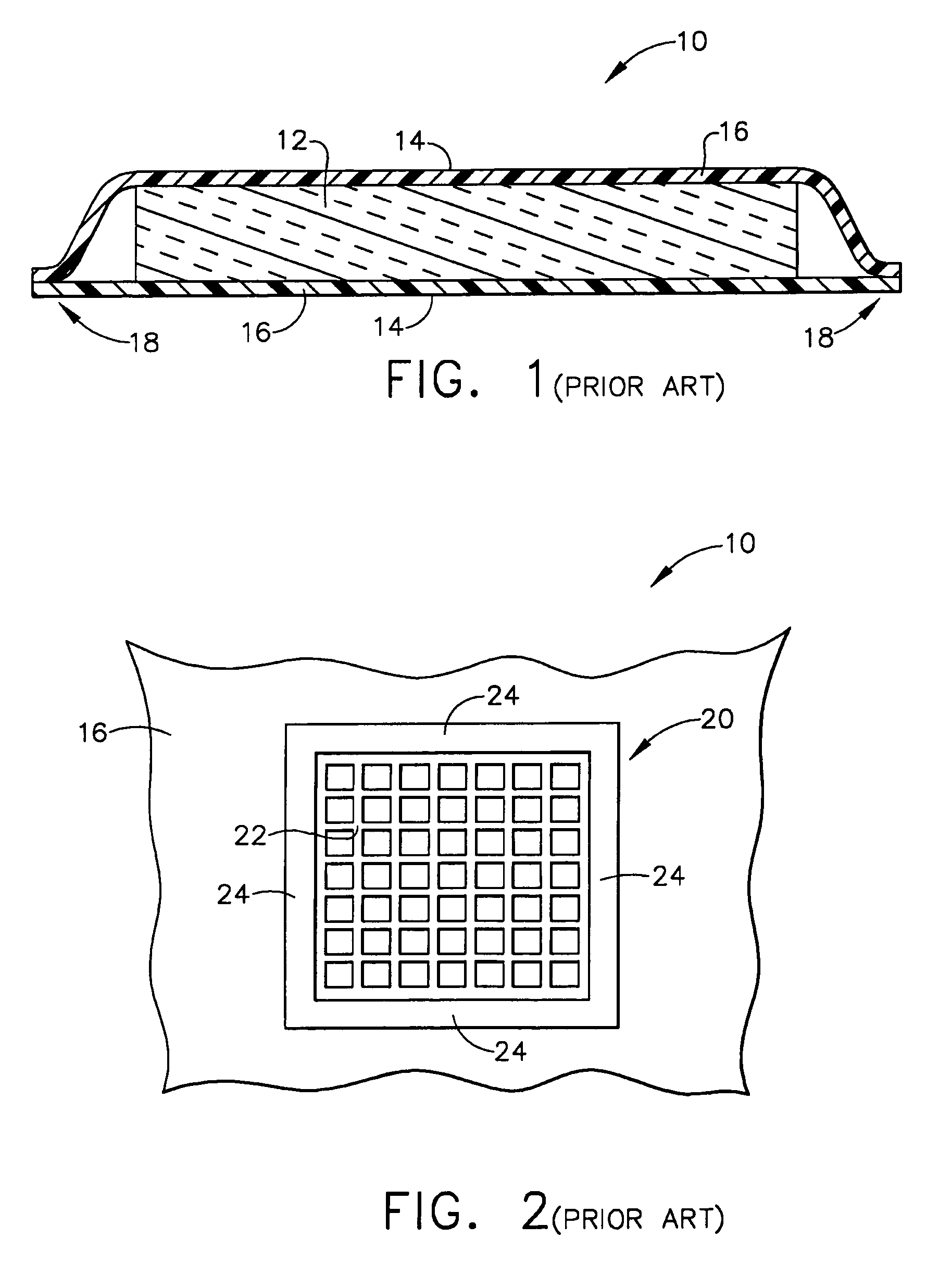
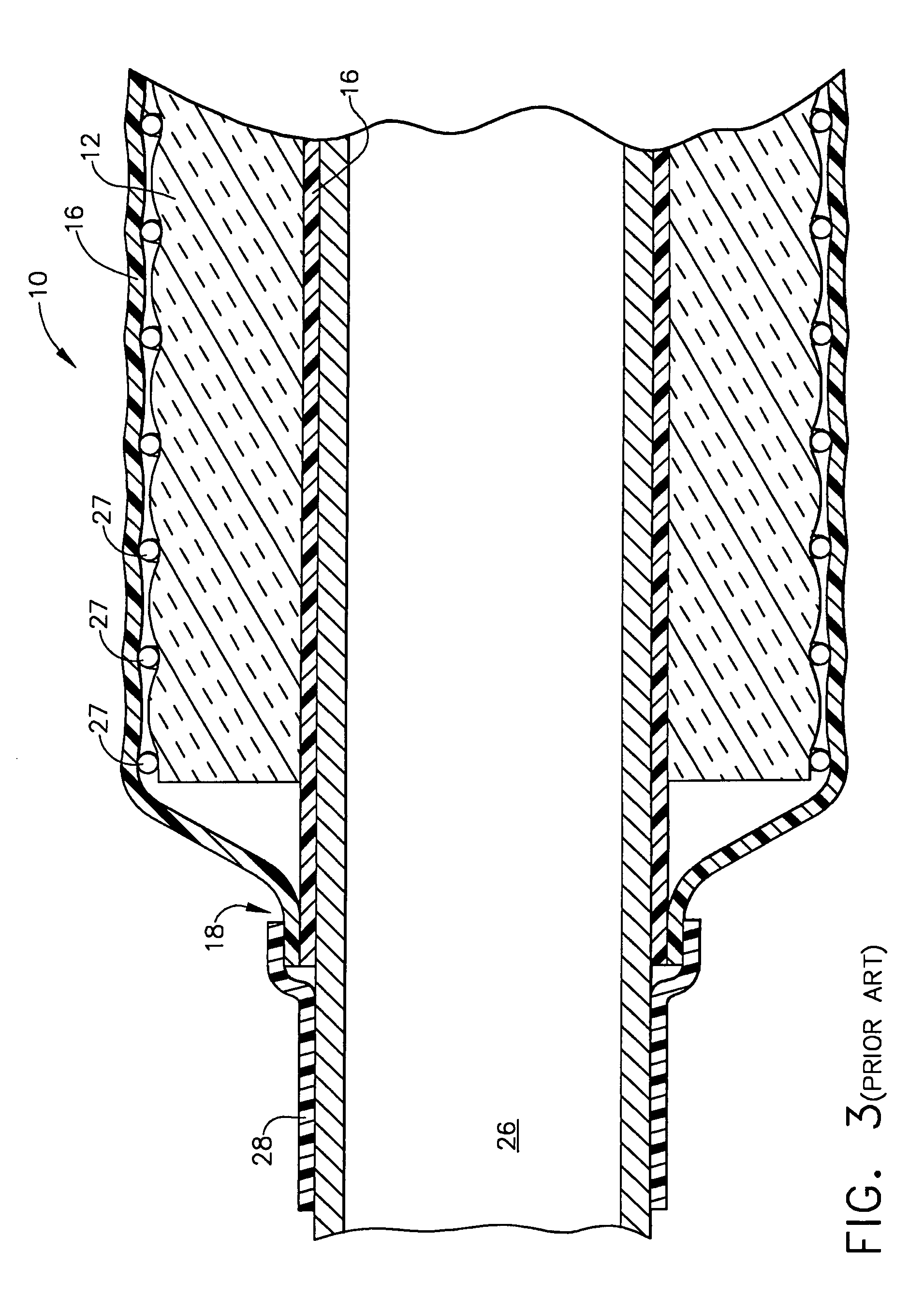
Modular ambient lighting system
InactiveUS6979097B2Support flexibilityEnabling changeCoupling device connectionsLight source combinationsTransformerElectrical connection
The invention is a modular ambient lighting system for providing lighting to the interior of the building. The system features three separate modules: (1) a support module, (2) a power module, and (3) a light fixture body module. The support module provides an electrical connection to the building and structural connection to the ceiling of the building. An interchangeable power module fits into a recess or “foot print” in the support module. The power module includes the electrical components of the lighting system (e.g. ballast, transformer, emergency batteries, etc). An interchangeable light fixture body module houses the lamp that can be configured to deliver direct, indirect, or direct / indirect illumination. The interchangeable features of the modules offers superior flexibility because of the ease to reconfigure the electrical operation of the light system, the type illumination delivered, or the aesthetics of the light system.
Owner:ELAM THOMAS E +1
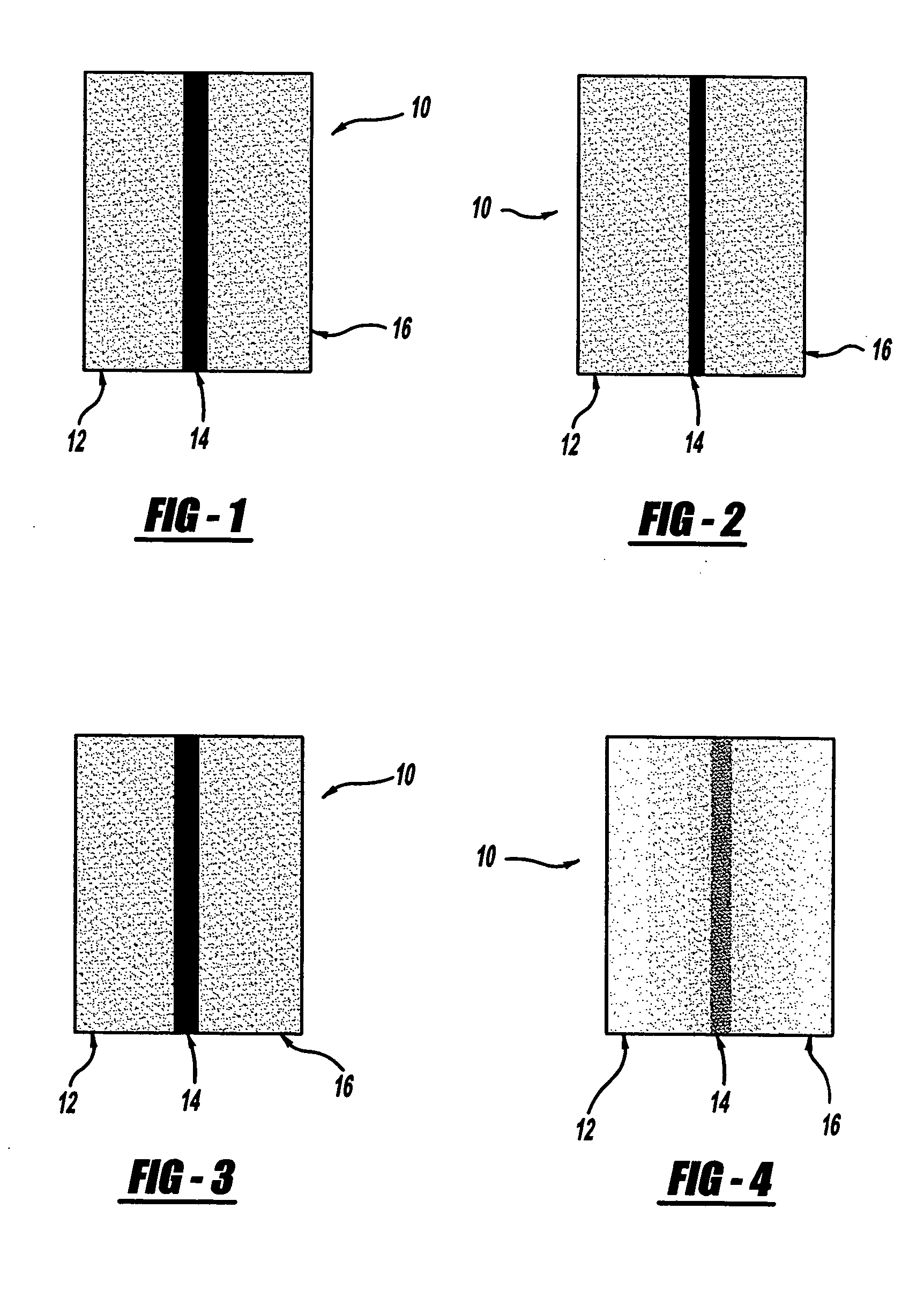
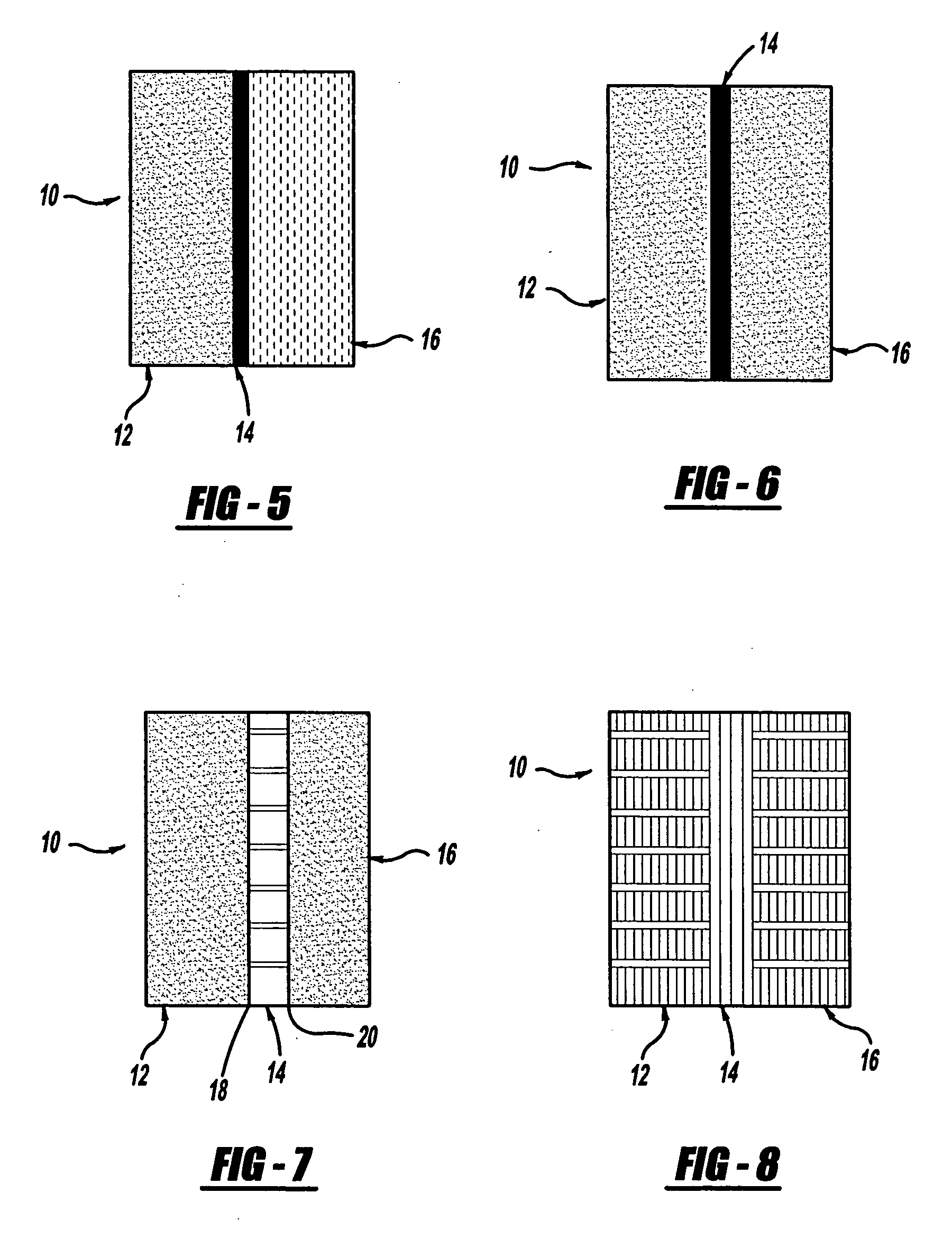
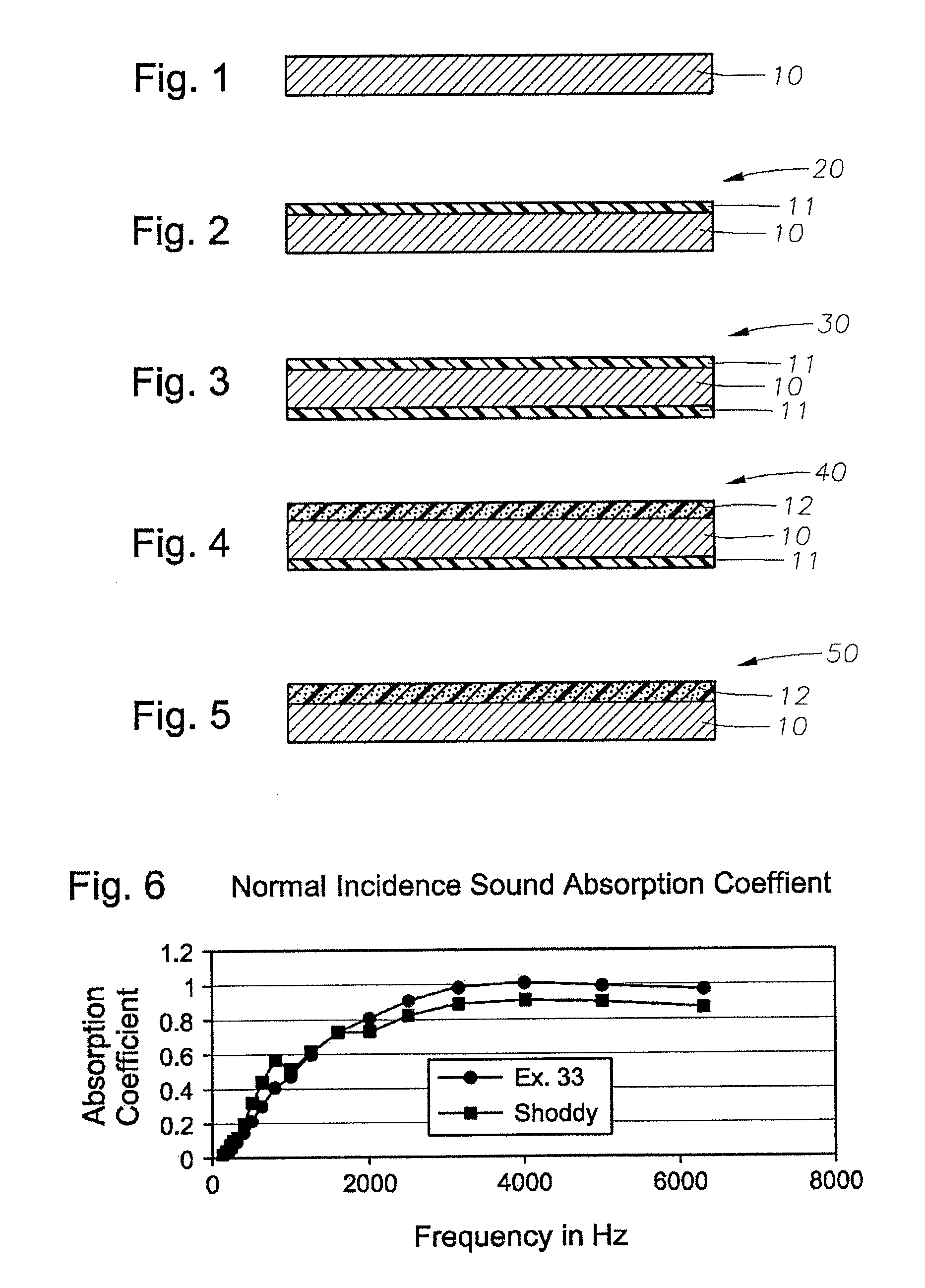
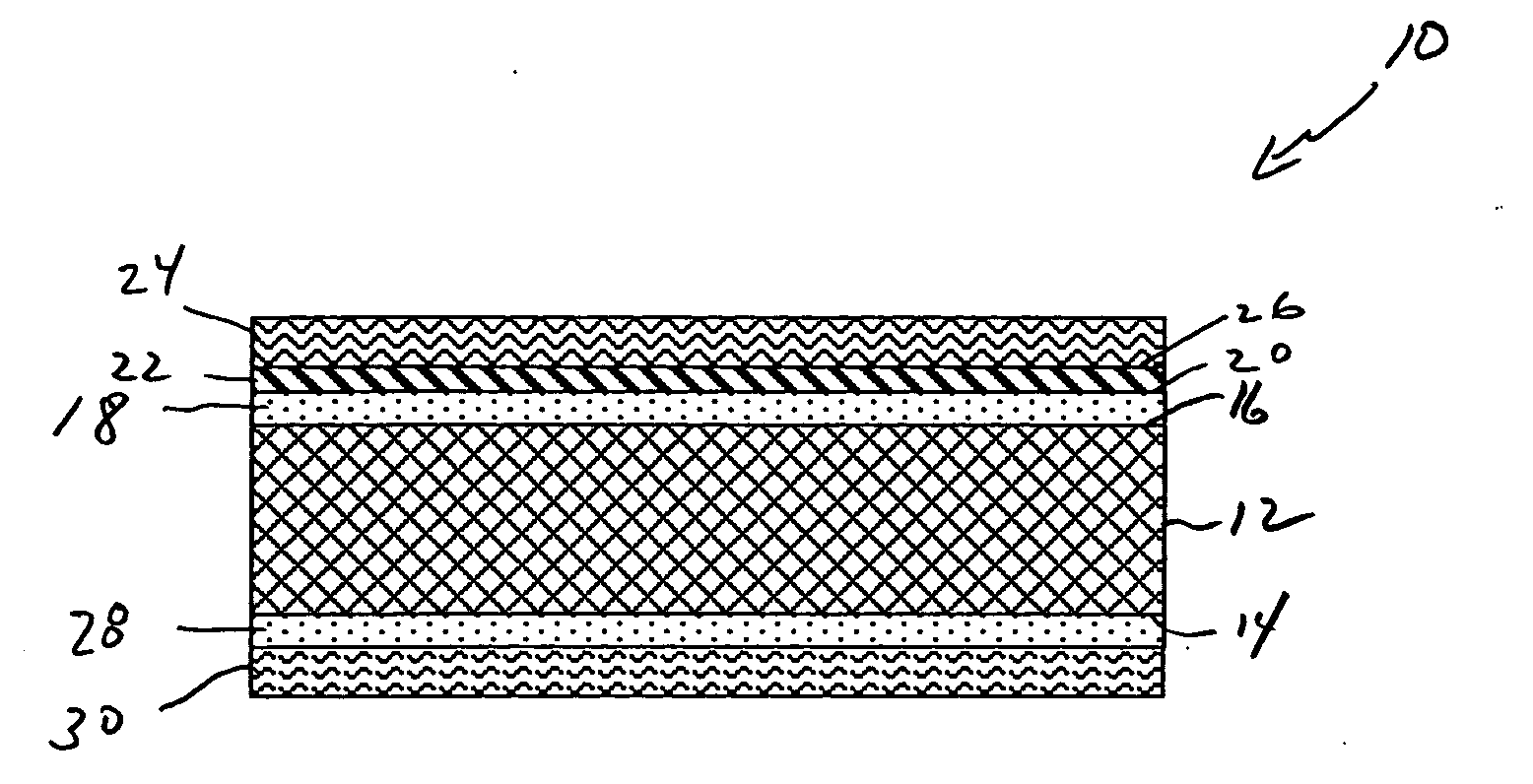
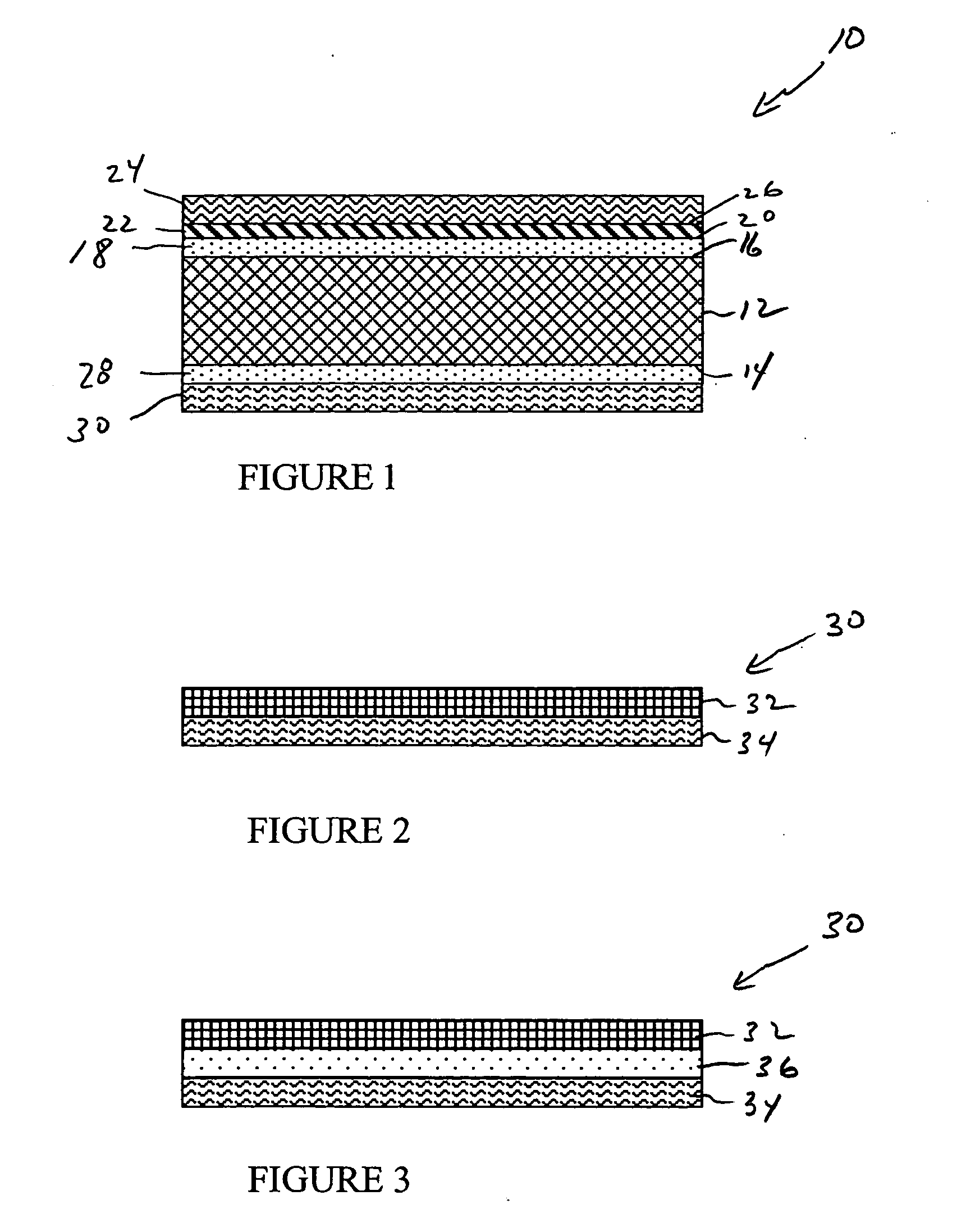
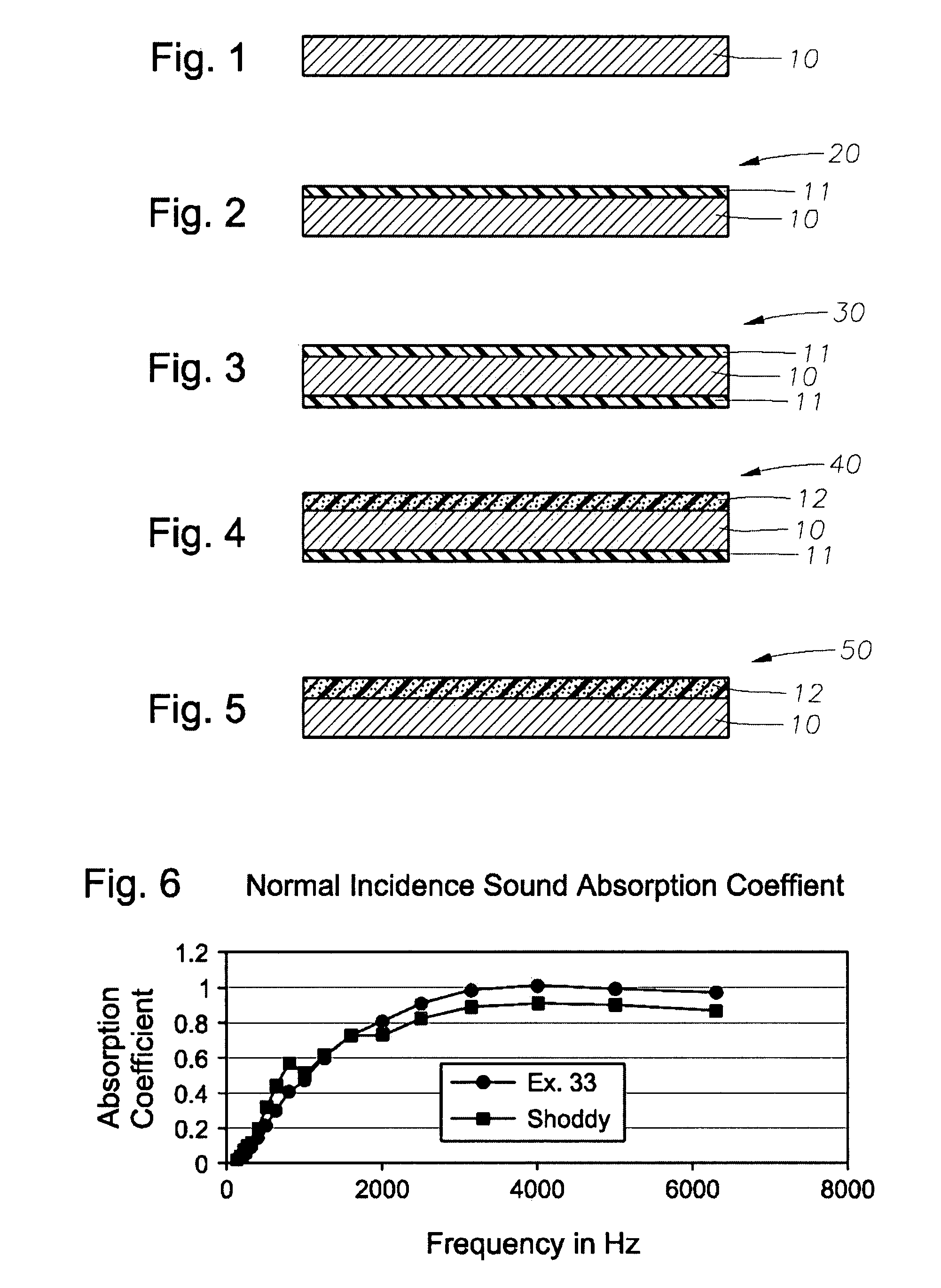
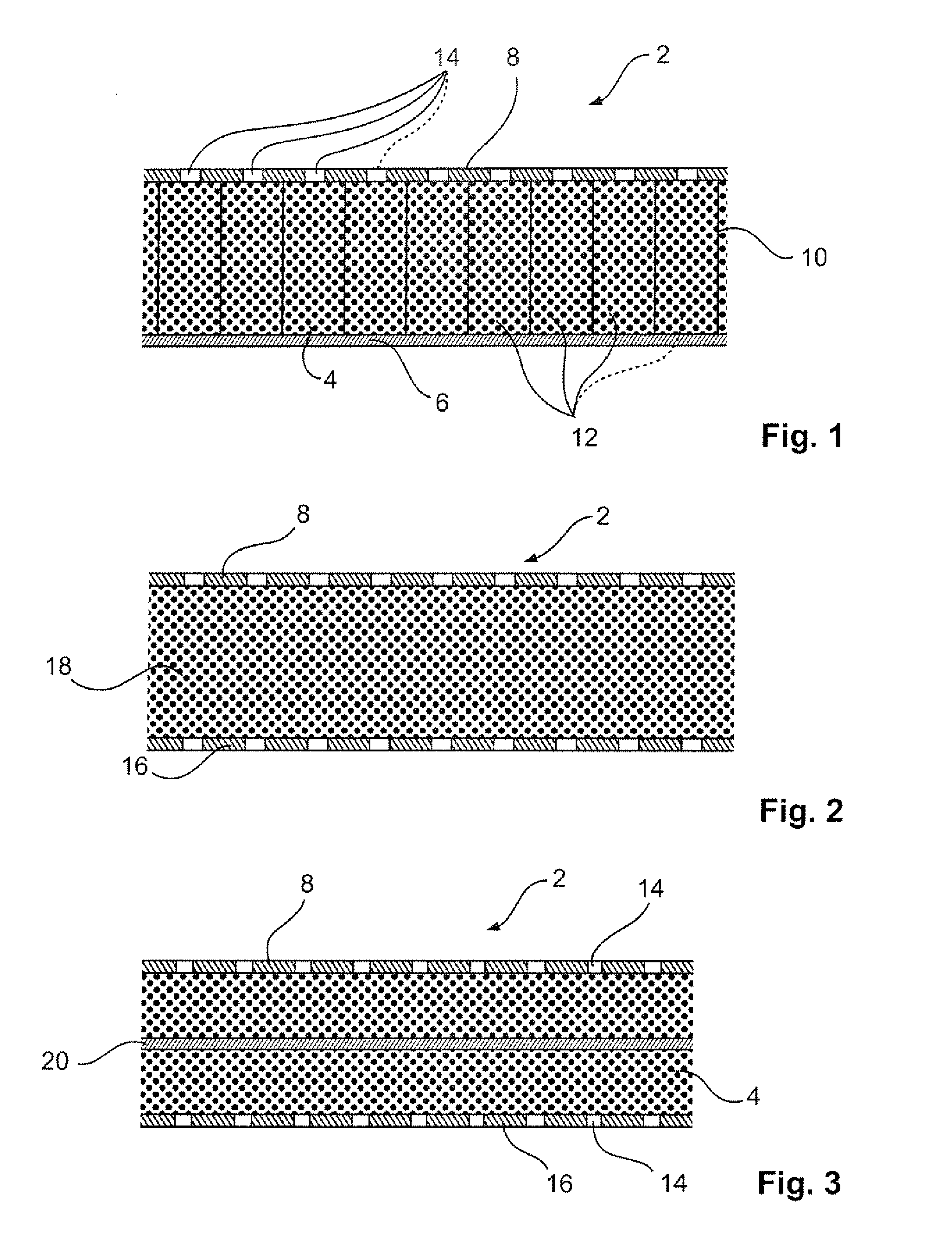
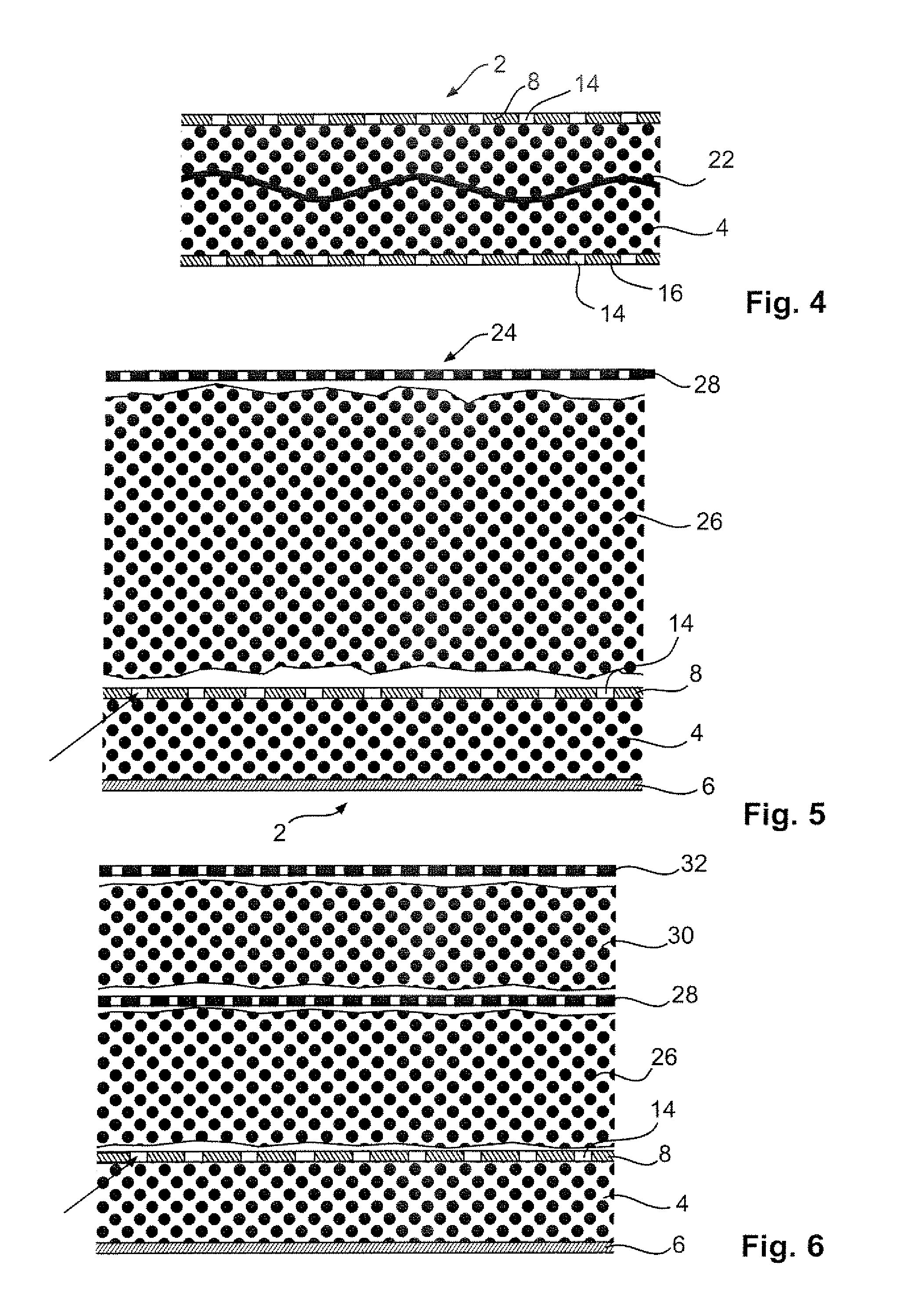
Sound insulating system
The present invention relates to a sound insulating system. The sound insulating system comprises a first sound absorbing layer. A barrier layer is positioned adjacent the first sound absorbing layer. A second absorbing layer is also provided and is adjacent the barrier layer.
Owner:DOW GLOBAL TECH LLC
Insulating sheathing with tough three-ply facers
InactiveUS6093481AImprove insulation performanceHighly controllableSynthetic resin layered productsHeat proofingPuncture resistanceHardness
A method for continuously manufacturing an insulation board by facing a foam-forming composition with one or two facing sheets to form a singly or doubly faced composite, at least one sheet comprising either a tough polymeric layer or a laminate of a tough polymeric layer with at least one other facing material, the tough polymeric layer of at least one sheet facing to the outside of the composite, and foaming and curing the faced foam-forming mixture to produce an insulation board having an exceptional hardness and puncture resistance.
Owner:THE DOW CHEM CO
Nonwoven material for acoustic insulation, and process for manufacture
An improved acoustically and thermally insulating composite material suitable for use in structures such as buildings, appliances, and the interior passenger compartments and exterior components of automotive vehicles, comprising at least one airlaid fibrous layer of controlled density and composition and incorporating suitable binding agents and additives as needed to meet expectations for noise abatement, fire, and mildew resistance. Separately, an airlaid structure which provides a reduced, controlled airflow therethrough useful for acoustic insulation is provided, and which includes a woven or nonwoven scrim.
Owner:GLATFELTER CORP
Nonwoven containing acoustical insulation laminate
The present invention relates to an acoustical insulation material containing a first layer formed from a nonwoven web having a density of at least 50 kg / m3 wherein the nonwoven web is formed from thermoplastic [meltblown] fibers having an average fiber diameter of less than about 7 microns; and a second layer of a high loft material. The high loft material of the present invention provides bulk to the first layer and may or may not have sound attenuating properties. Examples of the high loft material include, for example, fiberglass and high loft nonwoven webs. Also disclosed in a method of attenuating sound waves passing from a sound source area to a second area. The method includes positioning an acoustical insulation material containing a first layer formed from a nonwoven web having a density of at least 50 kg / m3 wherein the nonwoven web is formed from thermoplastic [meltblown] fibers having an average fiber diameter of less than about 7 microns; and a second layer of a high loft material, between the sound source area and the second area.
Owner:KIMBERLY-CLARK WORLDWIDE INC
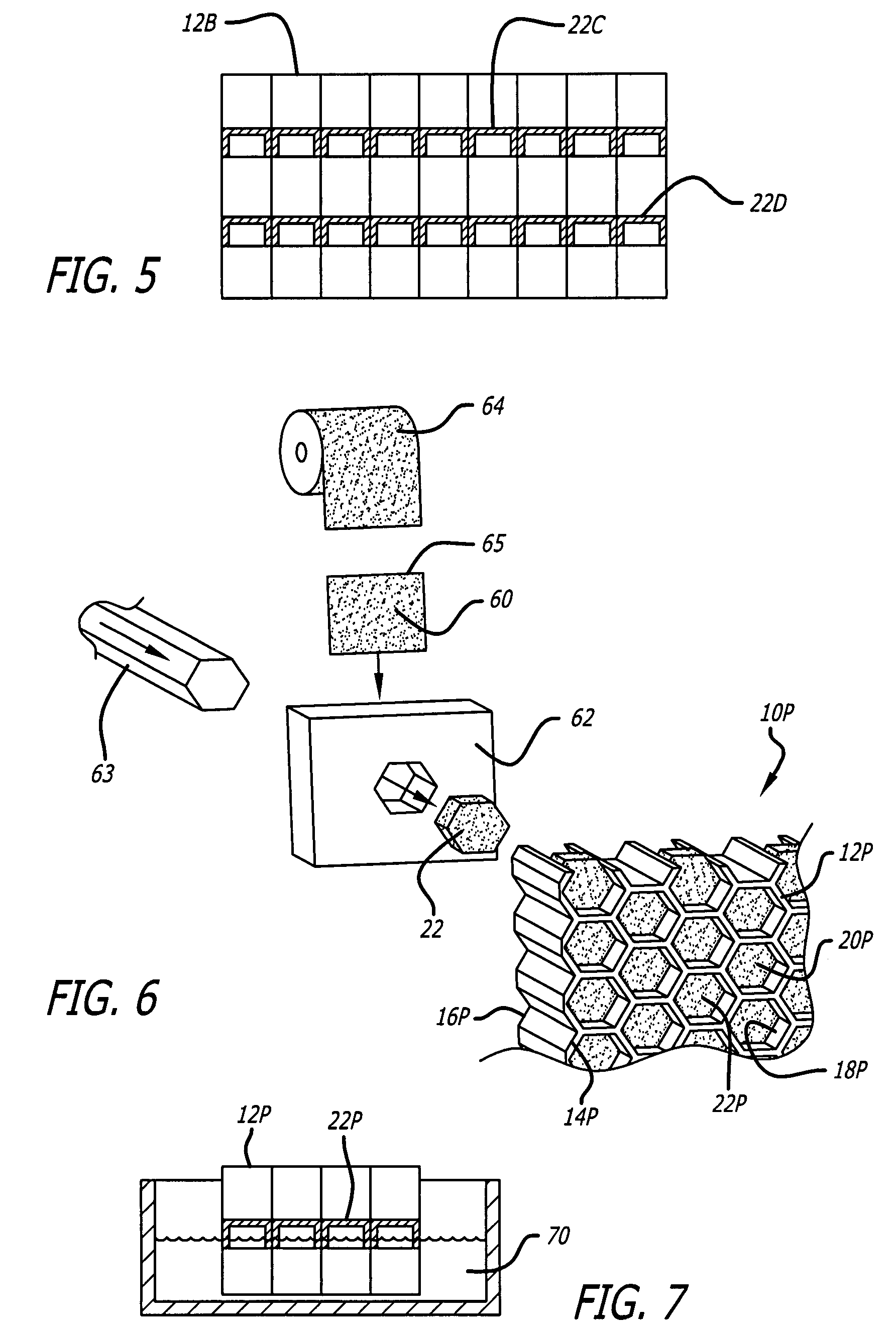
Sound attenuating structures
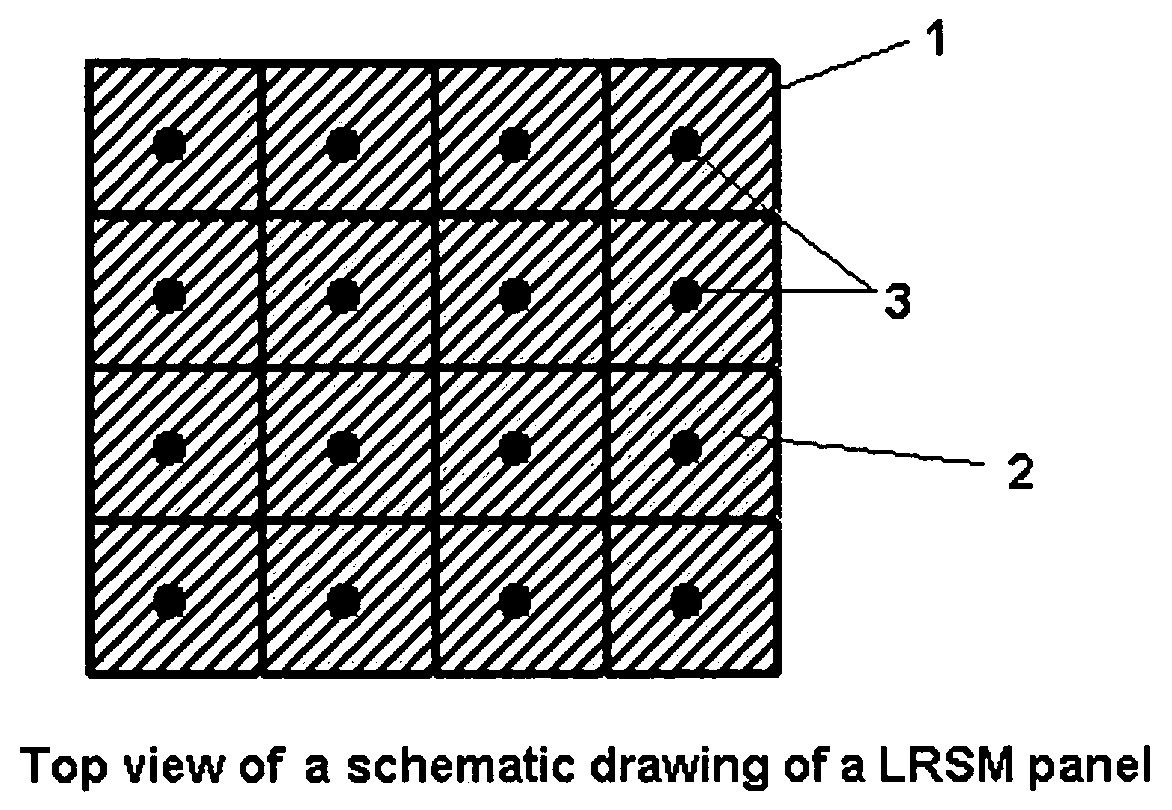
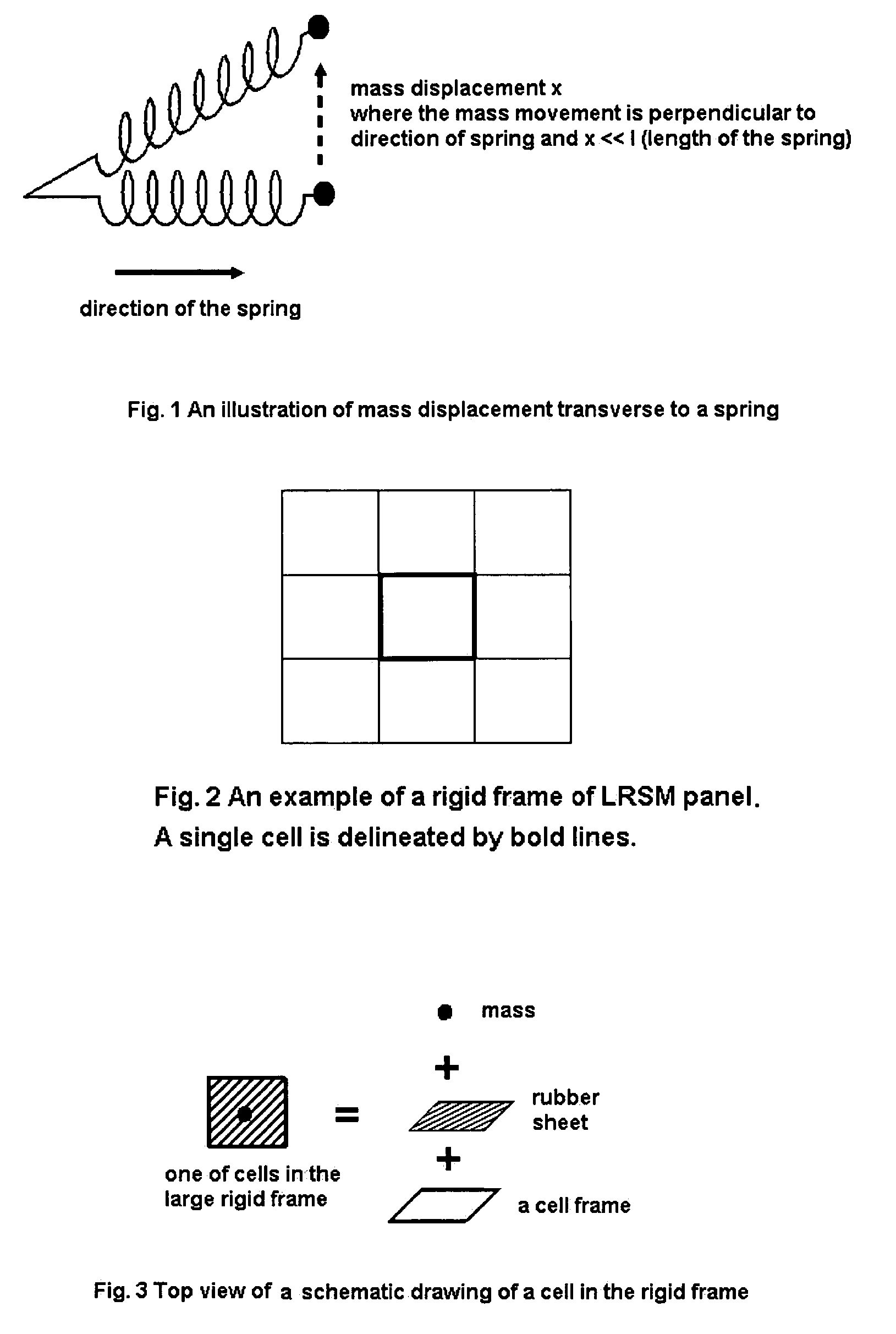
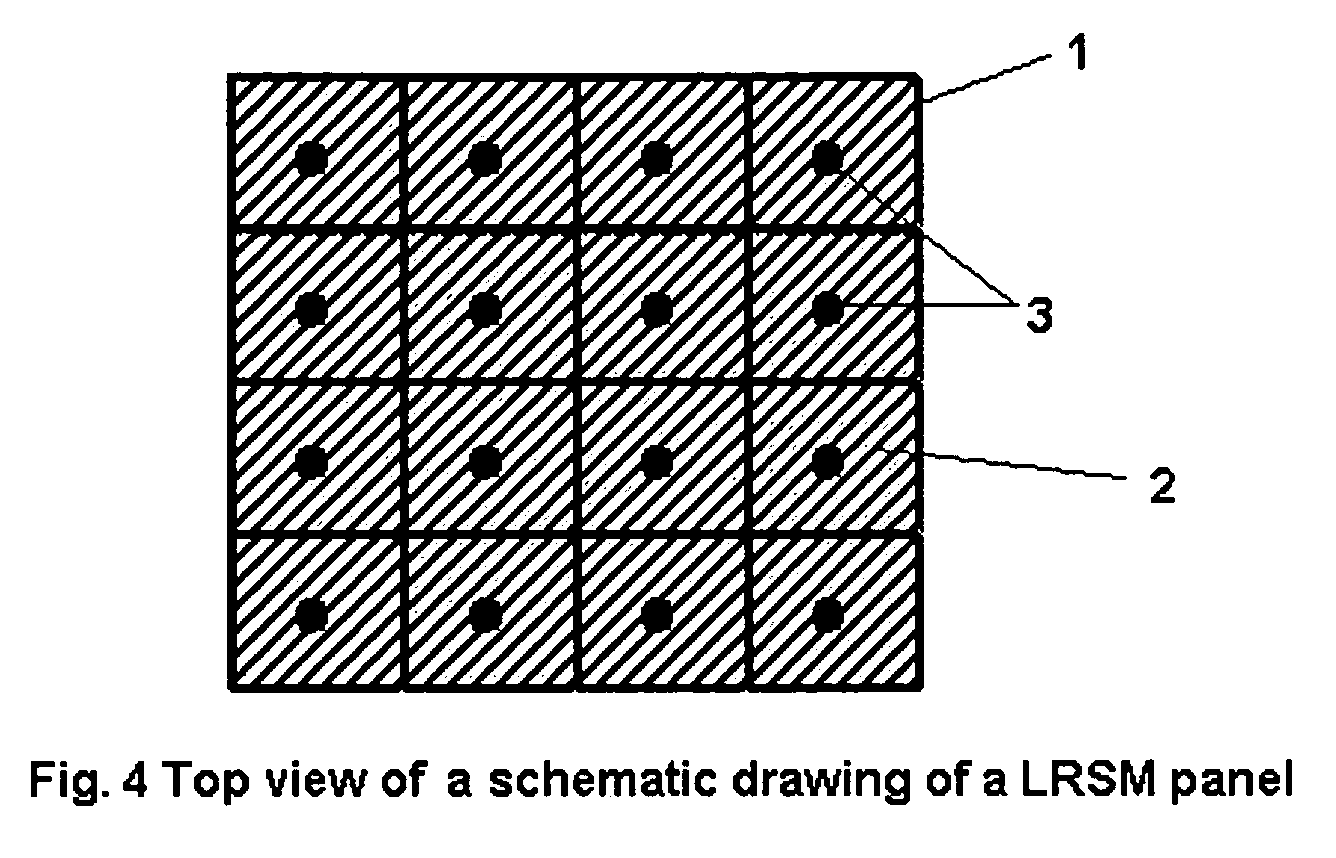
There is disclosed a sound attenuation panel comprising, a rigid frame divided into a plurality of individual cells, a sheet of a flexible material, and a plurality of weights. Each weight is fixed to the sheet of flexible material such that each cell is provided with a respective weight and the frequency of the sound attenuated can be controlled by suitable selecting the mass of the weight.
Owner:THE HONG KONG UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Nonwoven material for acoustic insulation, and process for manufacture
InactiveUS7837009B2Improve acoustic propertiesReduce weightLiquid surface applicatorsWallsMildewEngineering
An improved acoustically and thermally insulating fire-retardant composite material suitable for use in structures such as buildings, appliances, and the interior passenger compartments and exterior components of automotive vehicles is provided. The material is comprised of at least one airlaid fibrous layer of controlled density and composition and incorporating suitable binding agents and additives as needed to meet expectations for noise abatement, fire-retardancy, and mildew resistance. Separately, an airlaid structure which provides a reduced, controlled airflow therethrough useful for acoustic insulation is provided, and which includes a woven or nonwoven scrim. A process for the production of the fire retardant nonwoven material is also provided.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC NONWOVENS LLC
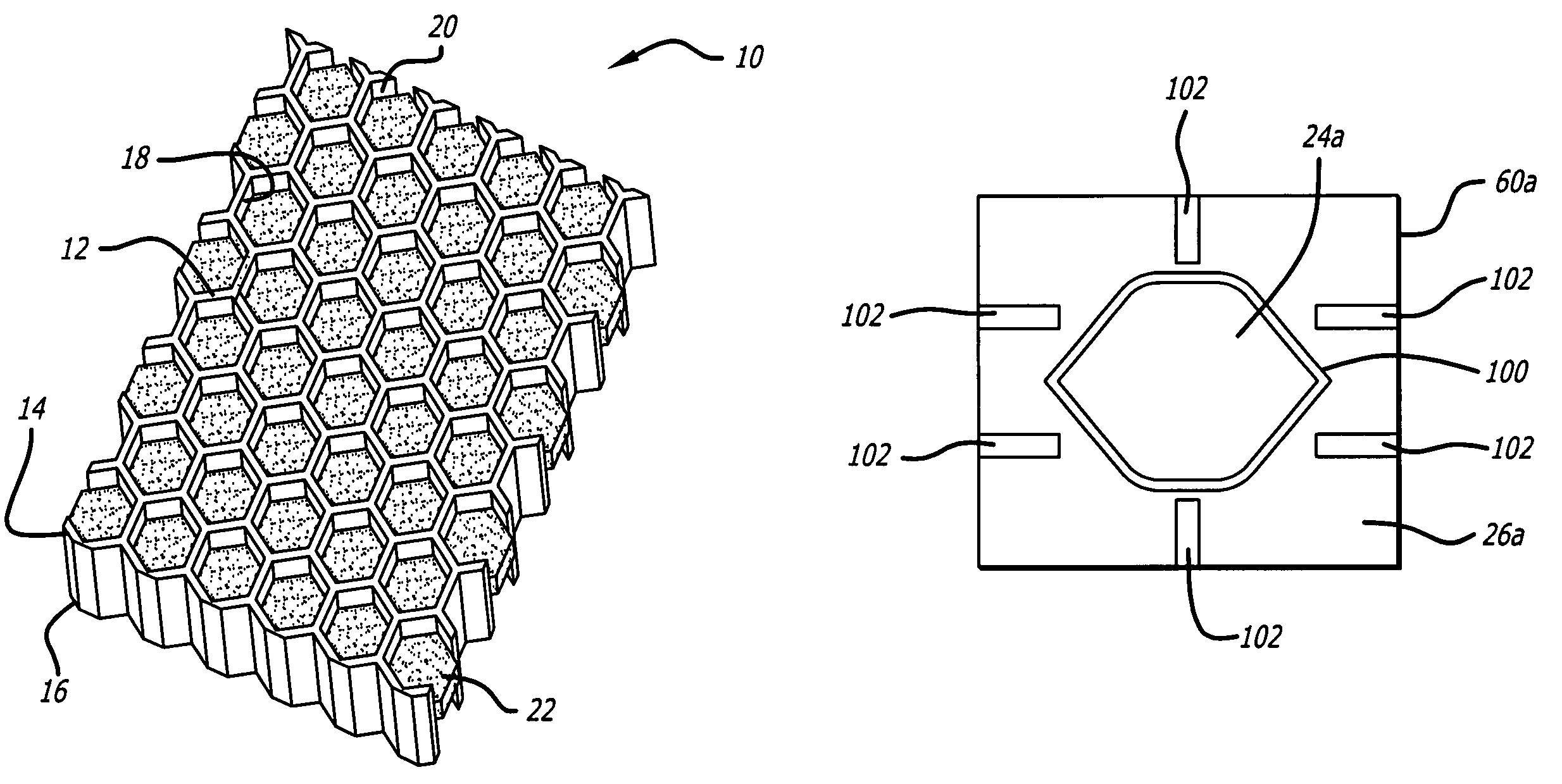
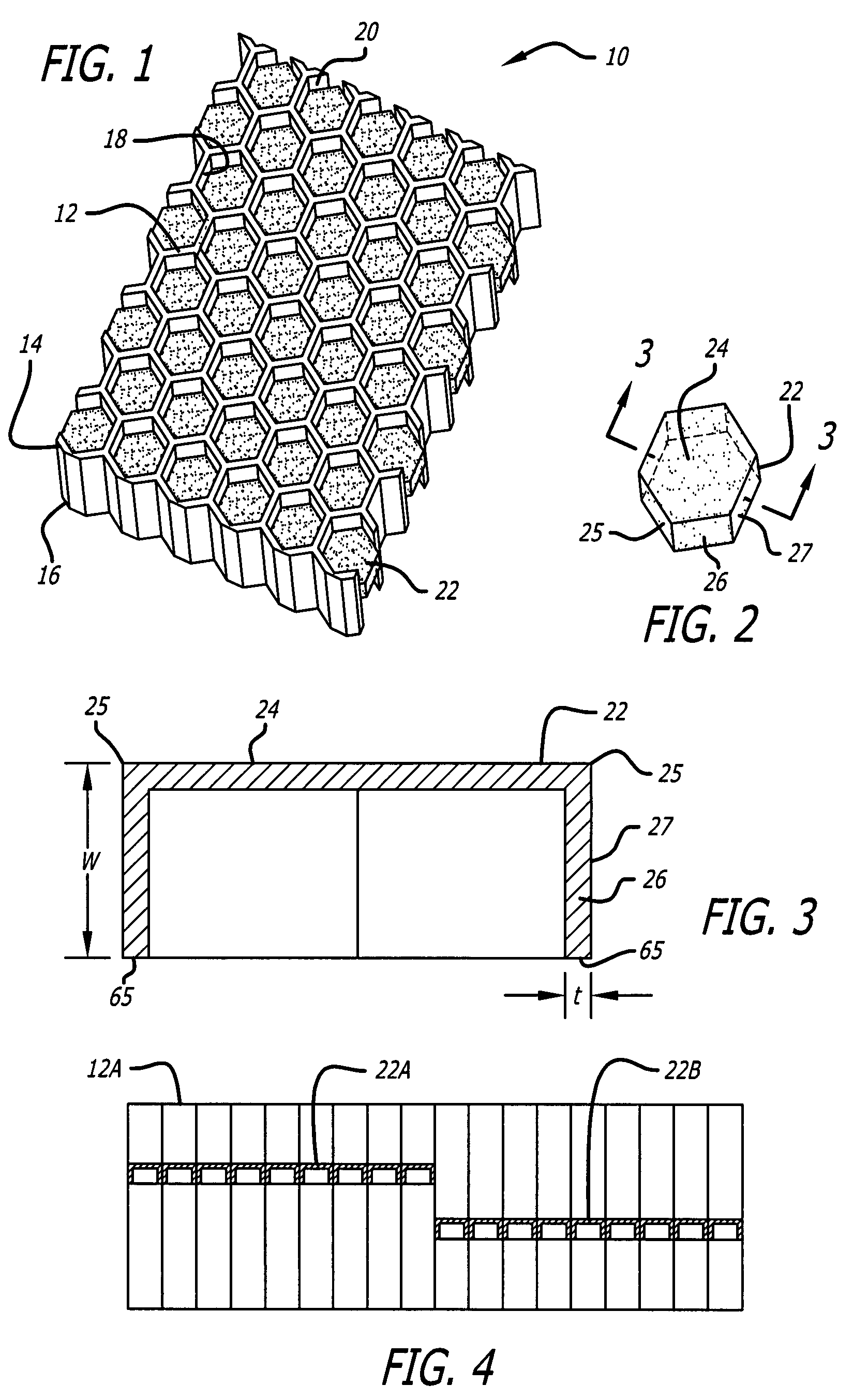
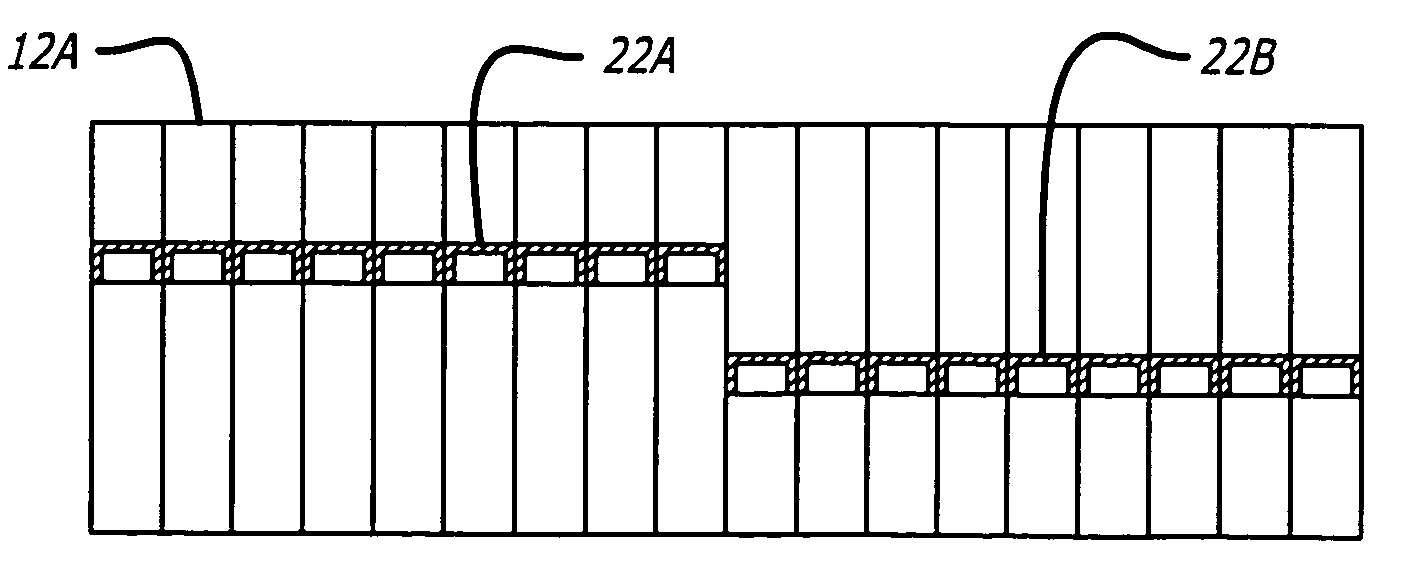
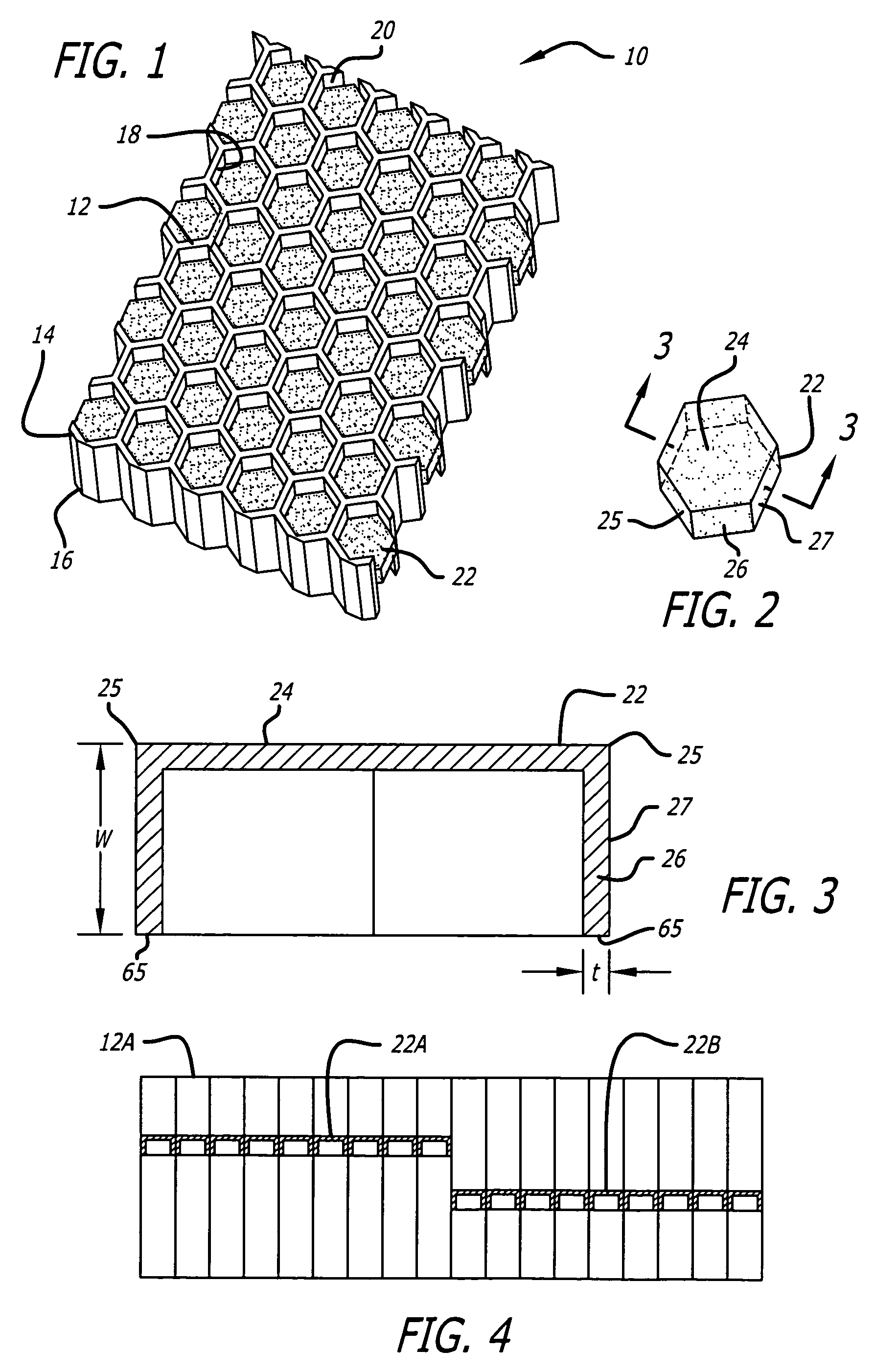
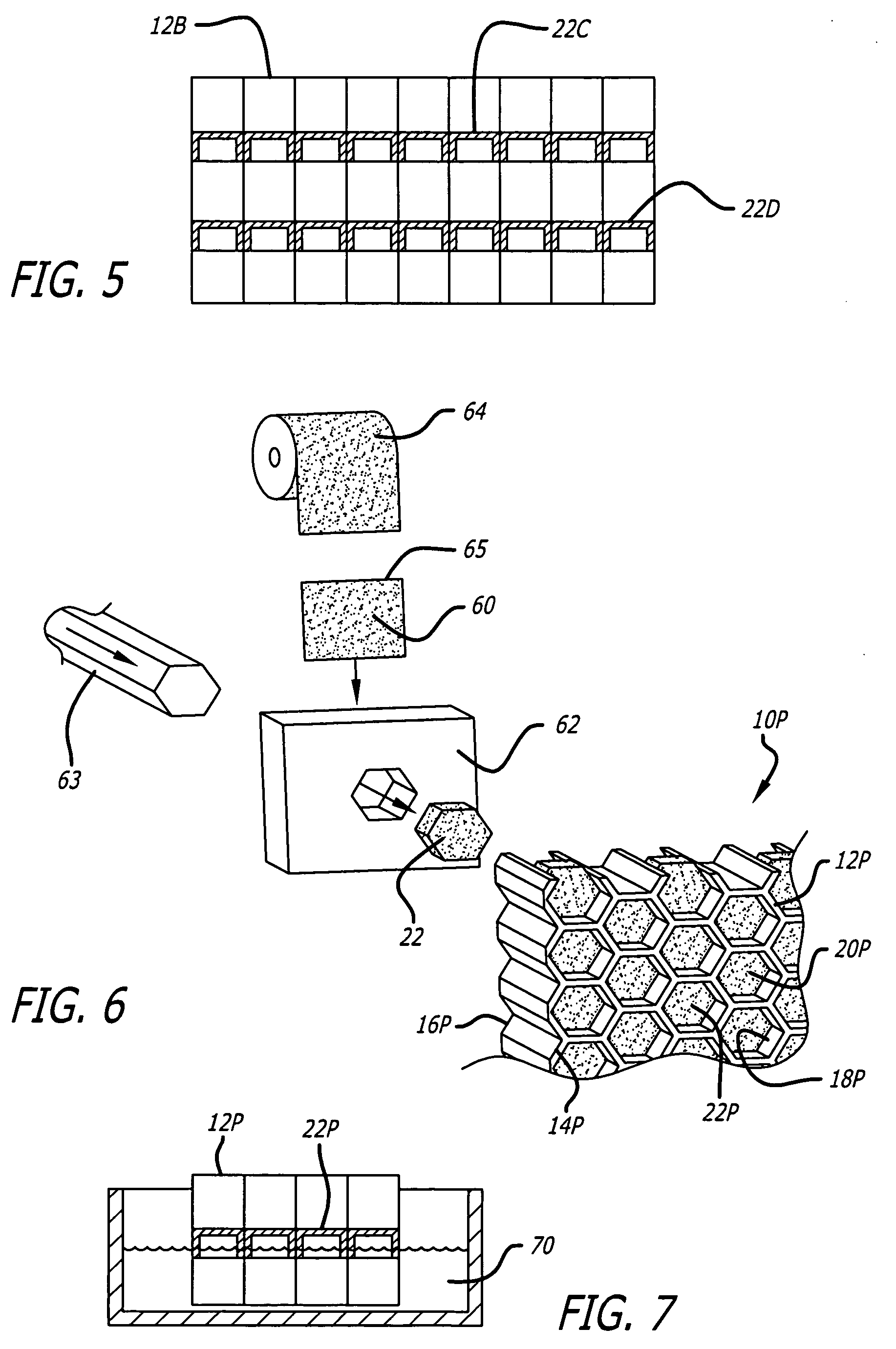
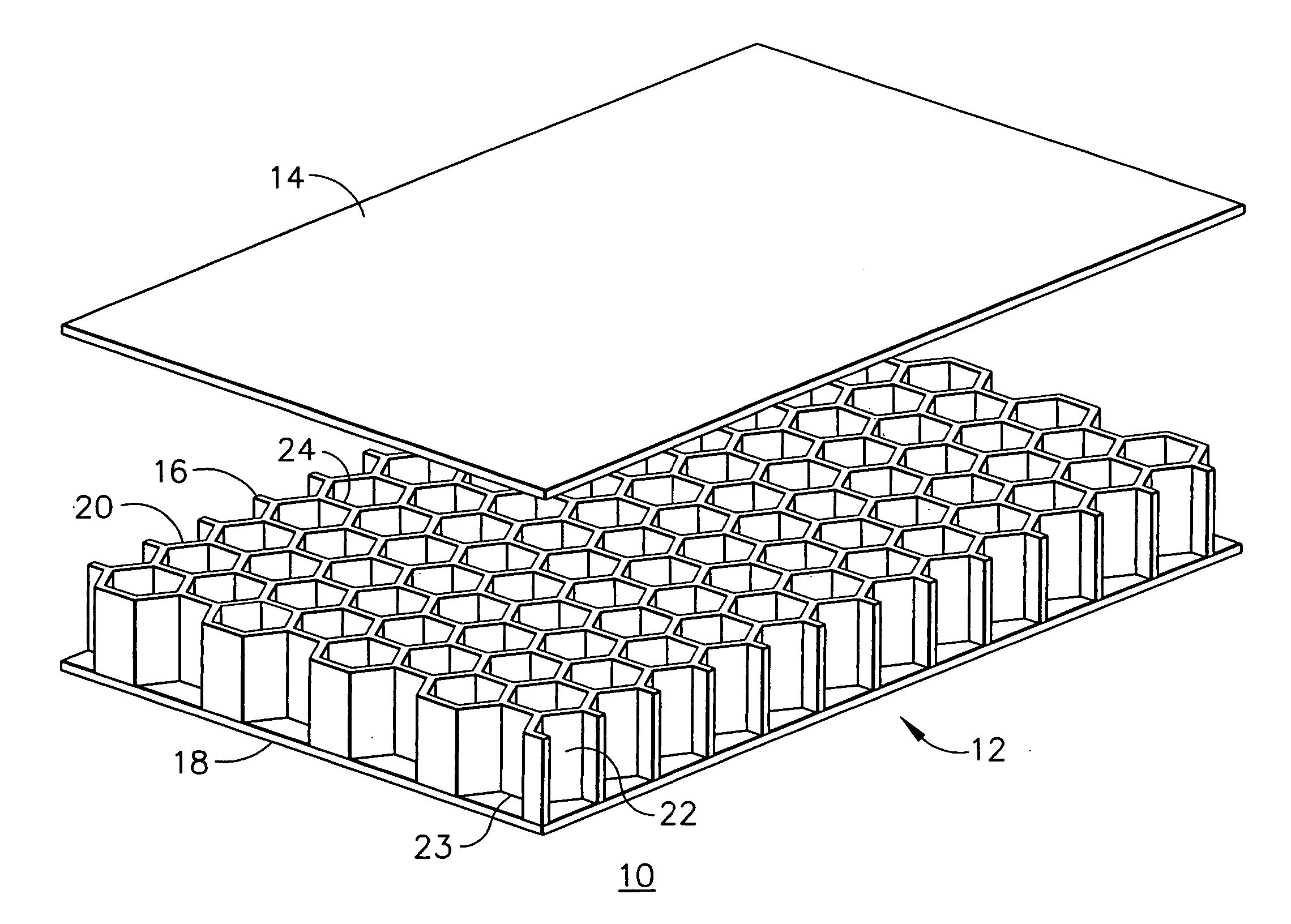
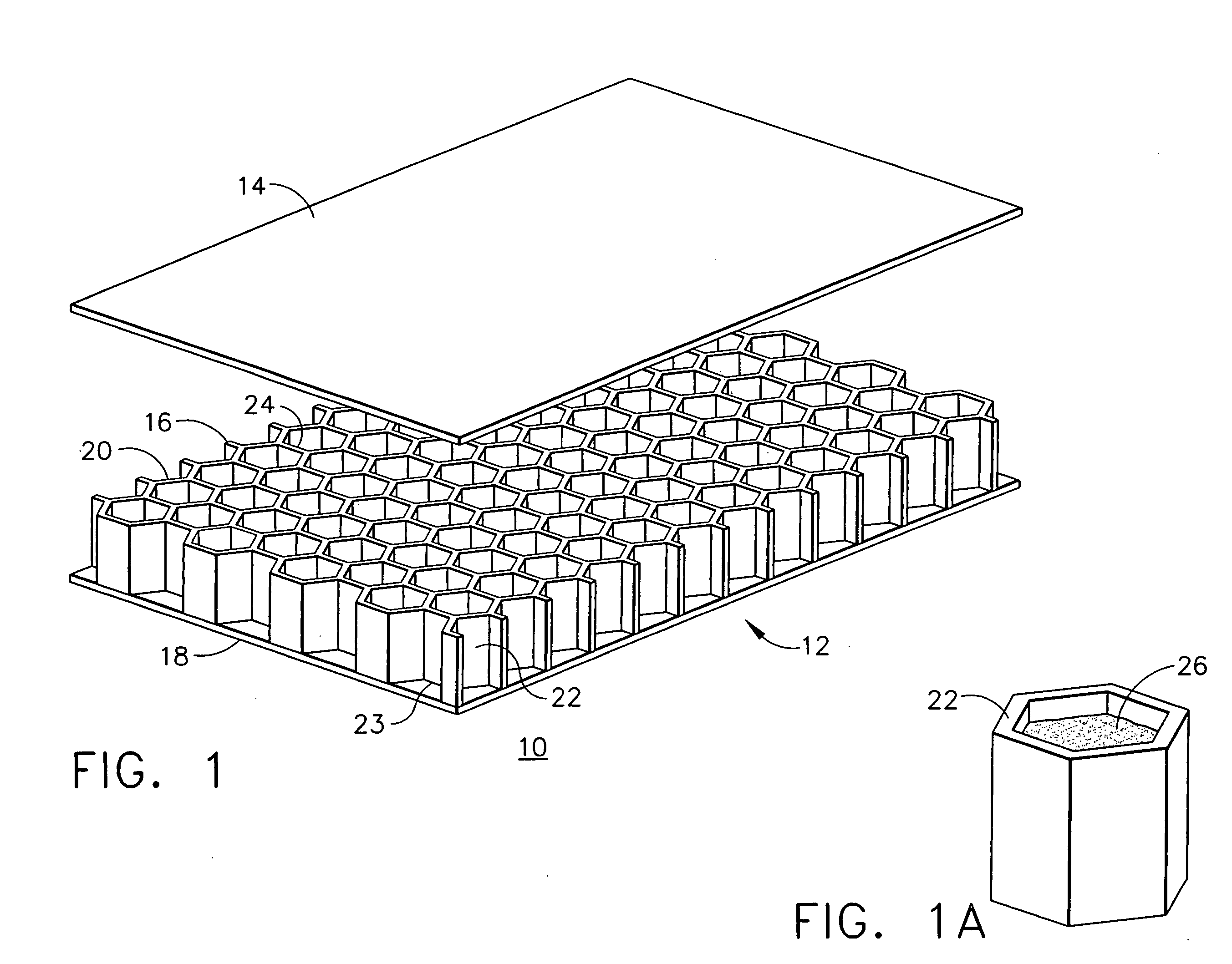
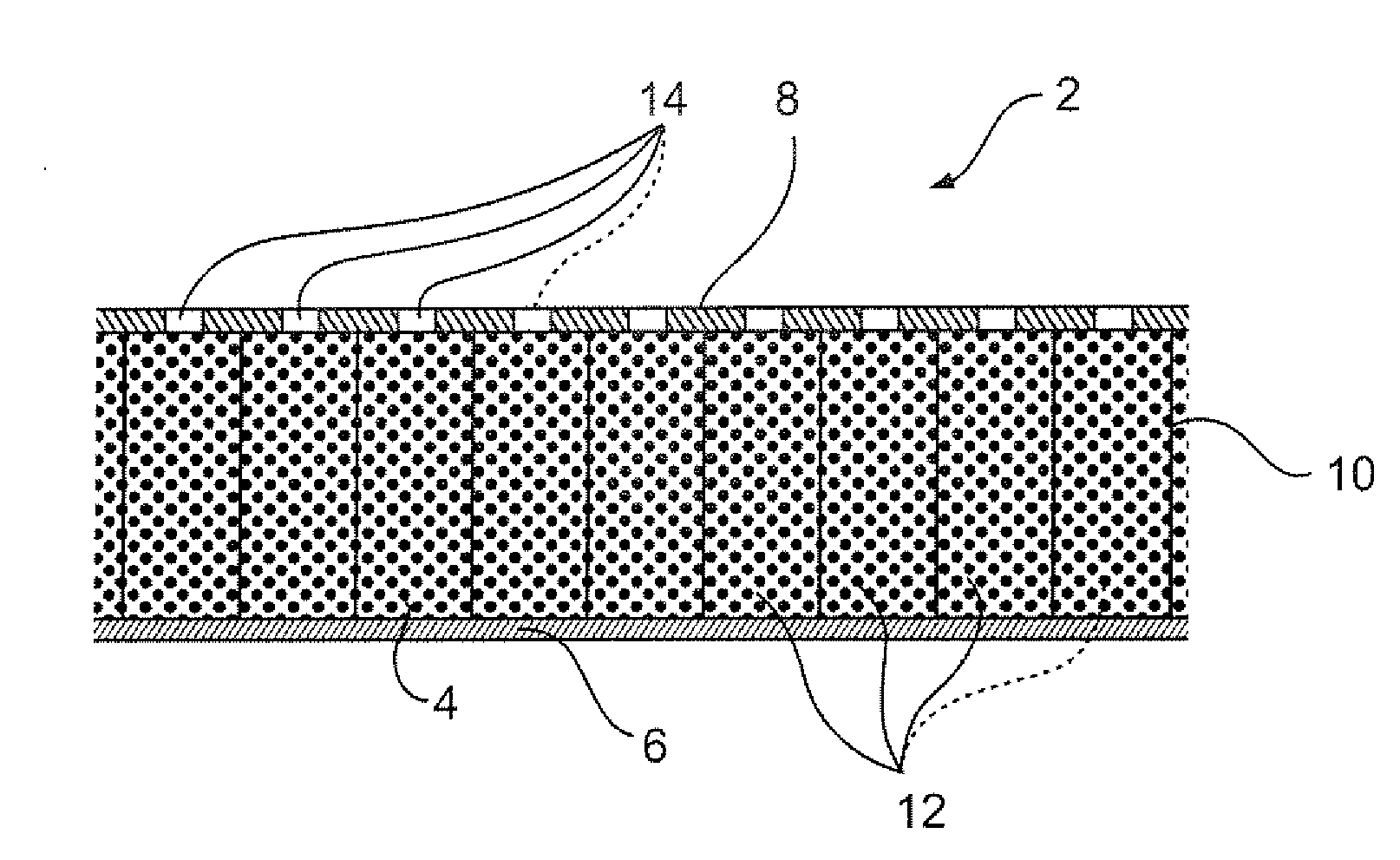
Acoustic septum cap honeycomb
Owner:HEXCEL
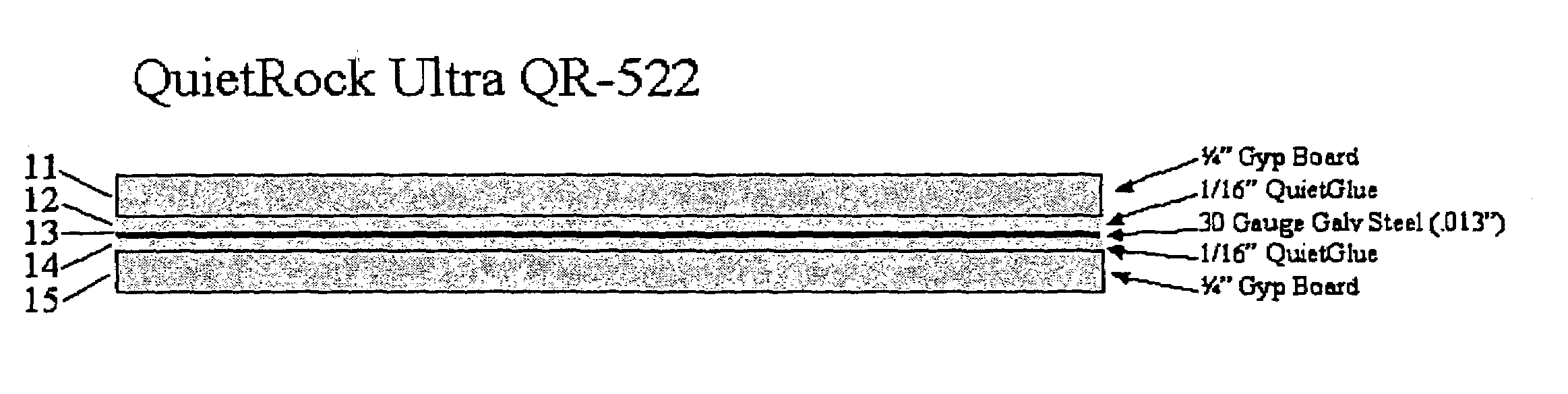
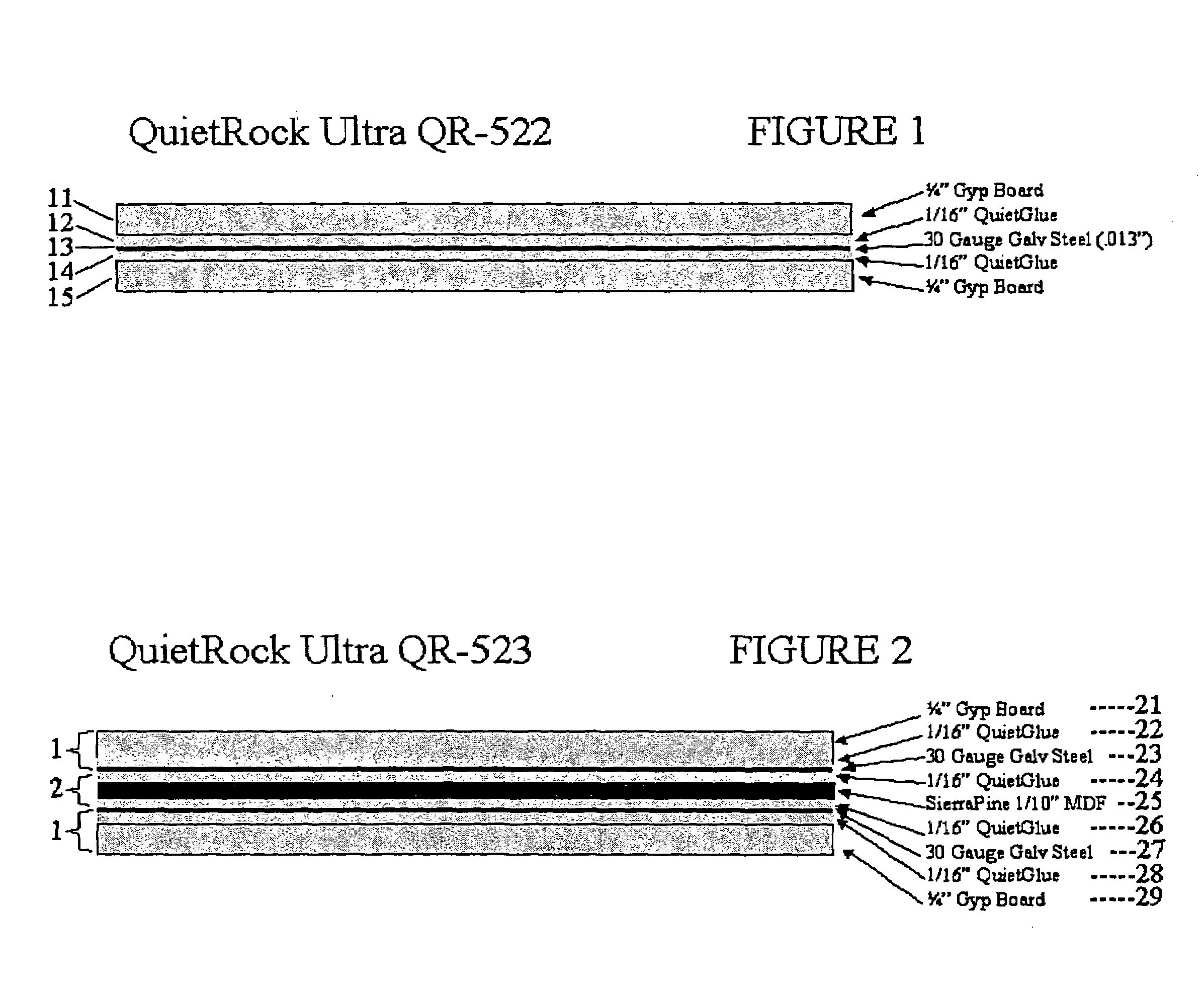
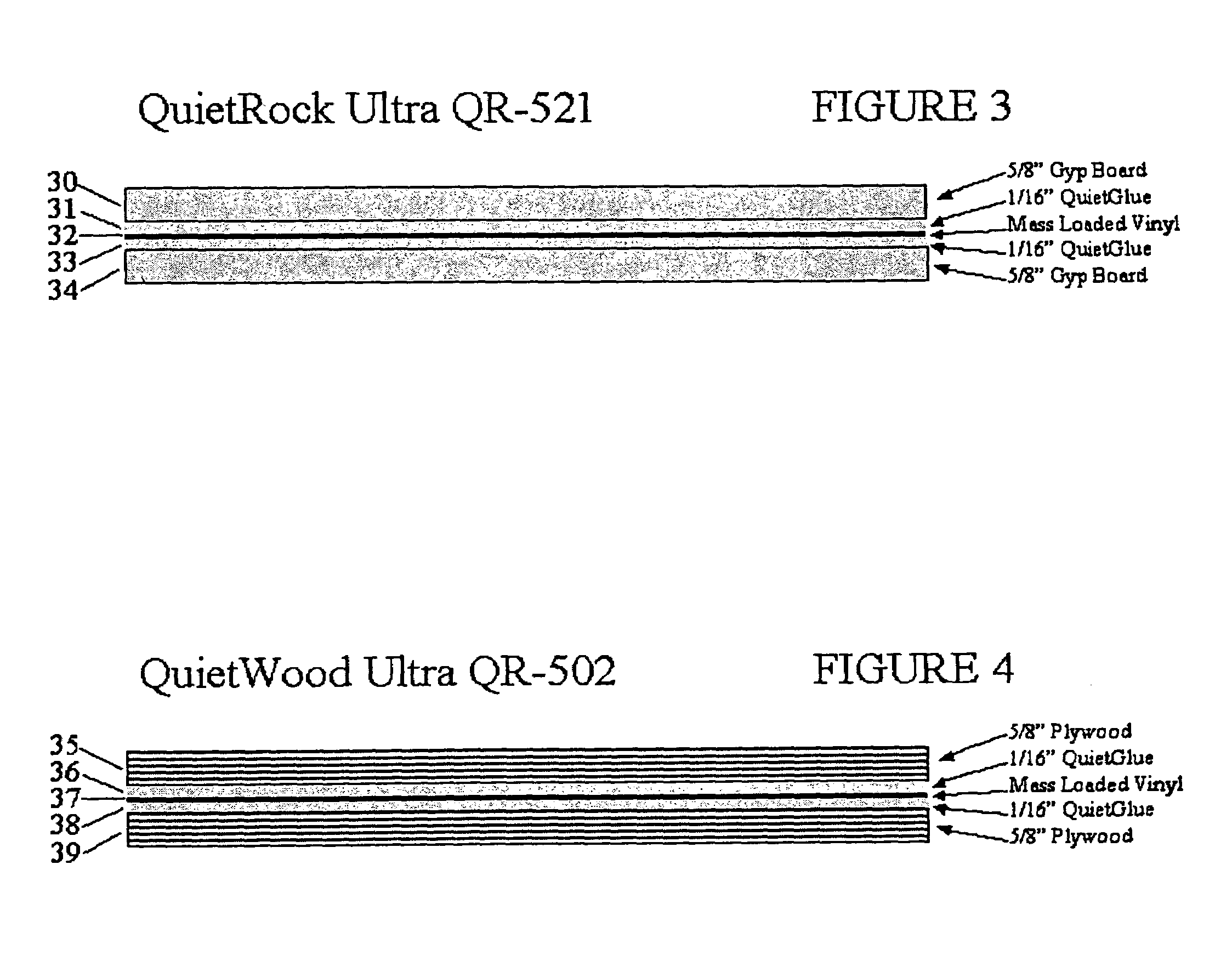
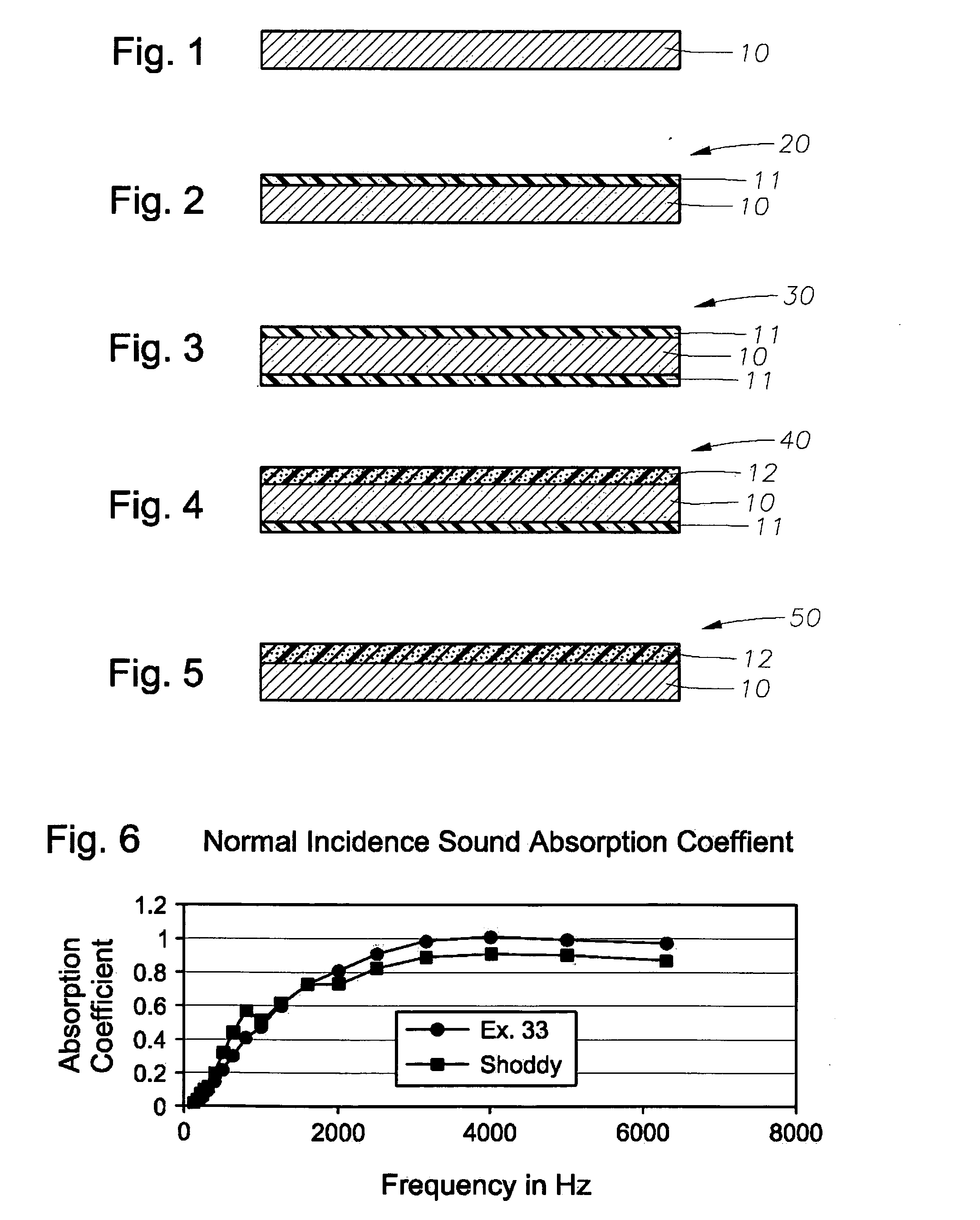
Acoustical sound proofing material and methods for manufacturing same
ActiveUS7181891B2Improve abilitiesReduce sound transmissionBuilding roofsCeilingsUltrasound attenuationCellulose
An improved acoustical damping wall (ceiling or floor) or door material comprises a laminar structure having as an integral part thereof one or more layers of viscoelastic material which also functions as a glue and one or more constraining layers, such as metal, cellulose, wood, or petroleum-based products such as plastic, vinyl, plastic or rubber. In one embodiment, standard wallboard, typically gypsum, comprises the external surfaces of the laminar structure; and one or more constraining layers are fabricated between the gypsum exterior. The resulting structure improves the attenuation of sound transmitted through the structure.
Owner:PACIFIC COAST BUILDING PRODS
Decorative interior sound absorbing panel
A multi-layered fiber reinforced thermoplastic sound absorbing panel includes a porous fiber reinforced thermoplastic core layer having a first surface and a second surface, and includes a thermoplastic material and from about 20 weight percent to about 80 weight percent fibers, a tie layer covering the second surface of the core layer and including a thermoplastic material, and a barrier layer covering the tie layer. The barrier layer includes a thermoplastic material having a melting temperature higher than the melting temperature of the core layer thermoplastic material. The tie layer bonds the barrier layer to the core layer. The panel also includes a non-woven layer including a fabric bonded to the barrier layer. The non-woven layer forms an outer surface of the panel.
Owner:HANWA AZDEL INC
Vibration dampening laminate
The present invention provides a vibration dampening laminate that is lightweight and has superior sound insulation and vibration dampening properties. The vibration dampening laminate comprises a constraining layer, a viscoelastic adhesive layer, a foam spacing layer and a pressure sensitive adhesive layer including a release layer. The pressure sensitive adhesive layer and release layer are contoured to fit a profile of the article being soundproofed and vibration dampened.
Owner:INT AUTOMOTIVE COMPONENTS GRP NORTH AMERICA INC
Structural composite material with improved acoustic and vibrational damping properties
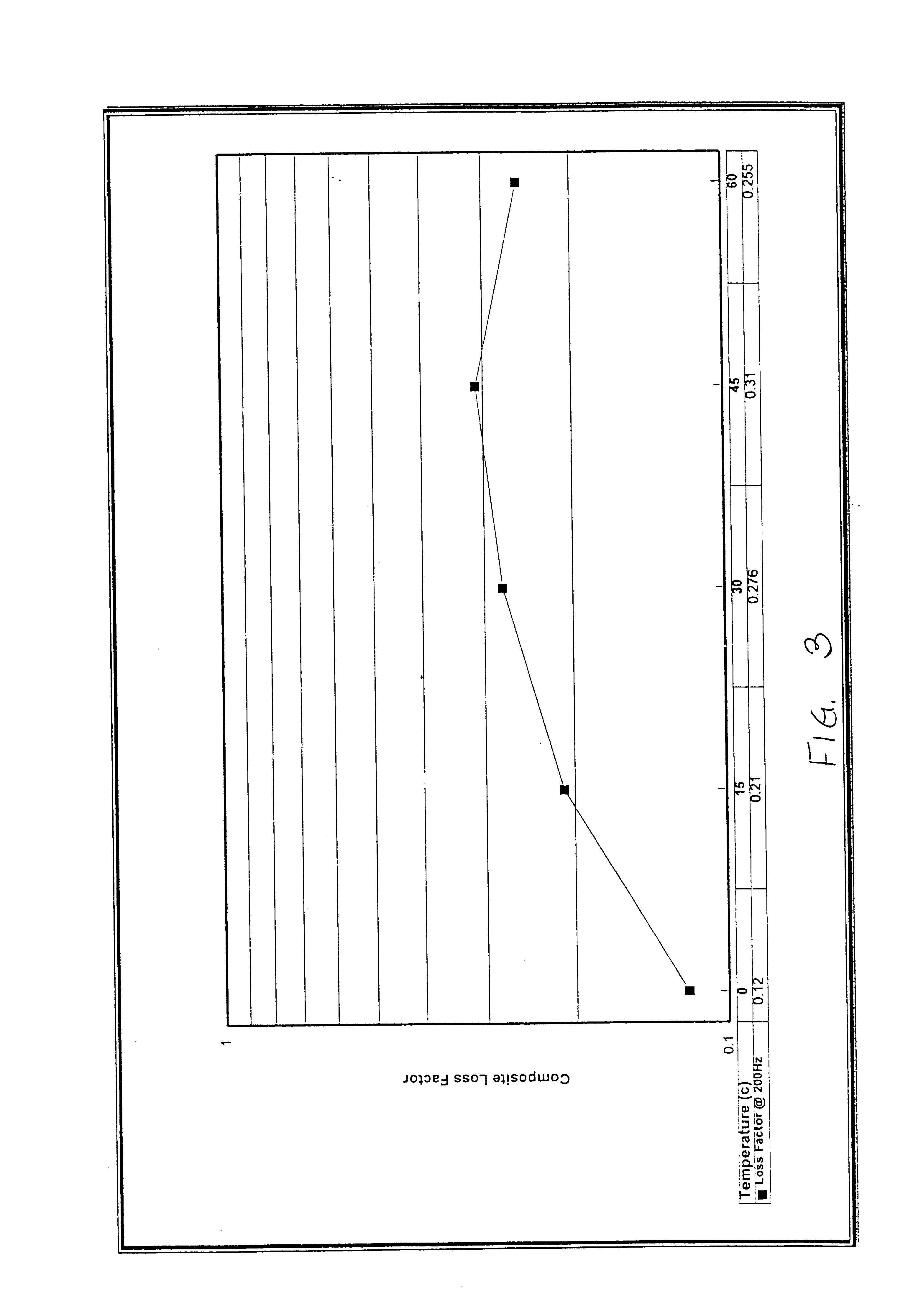
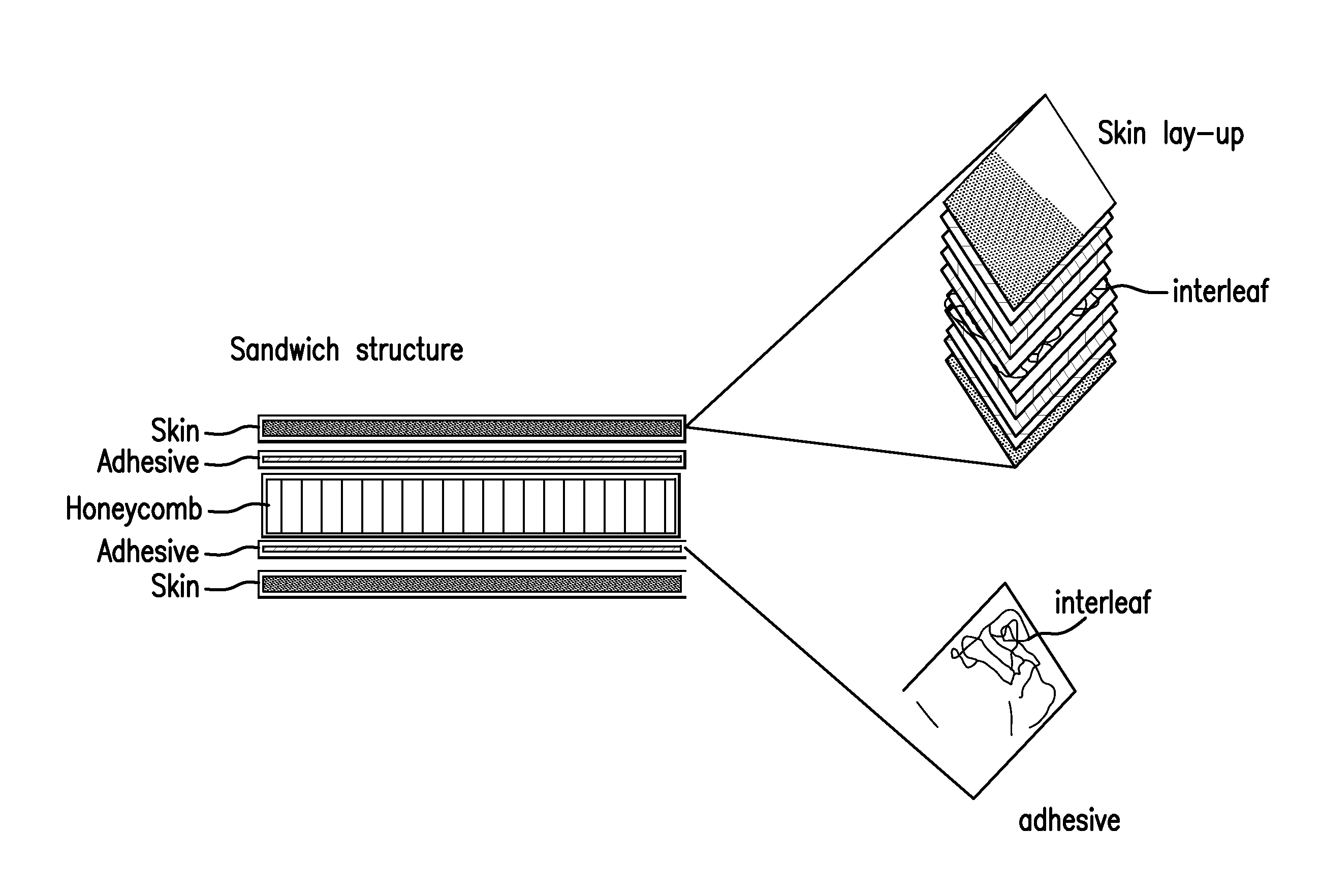
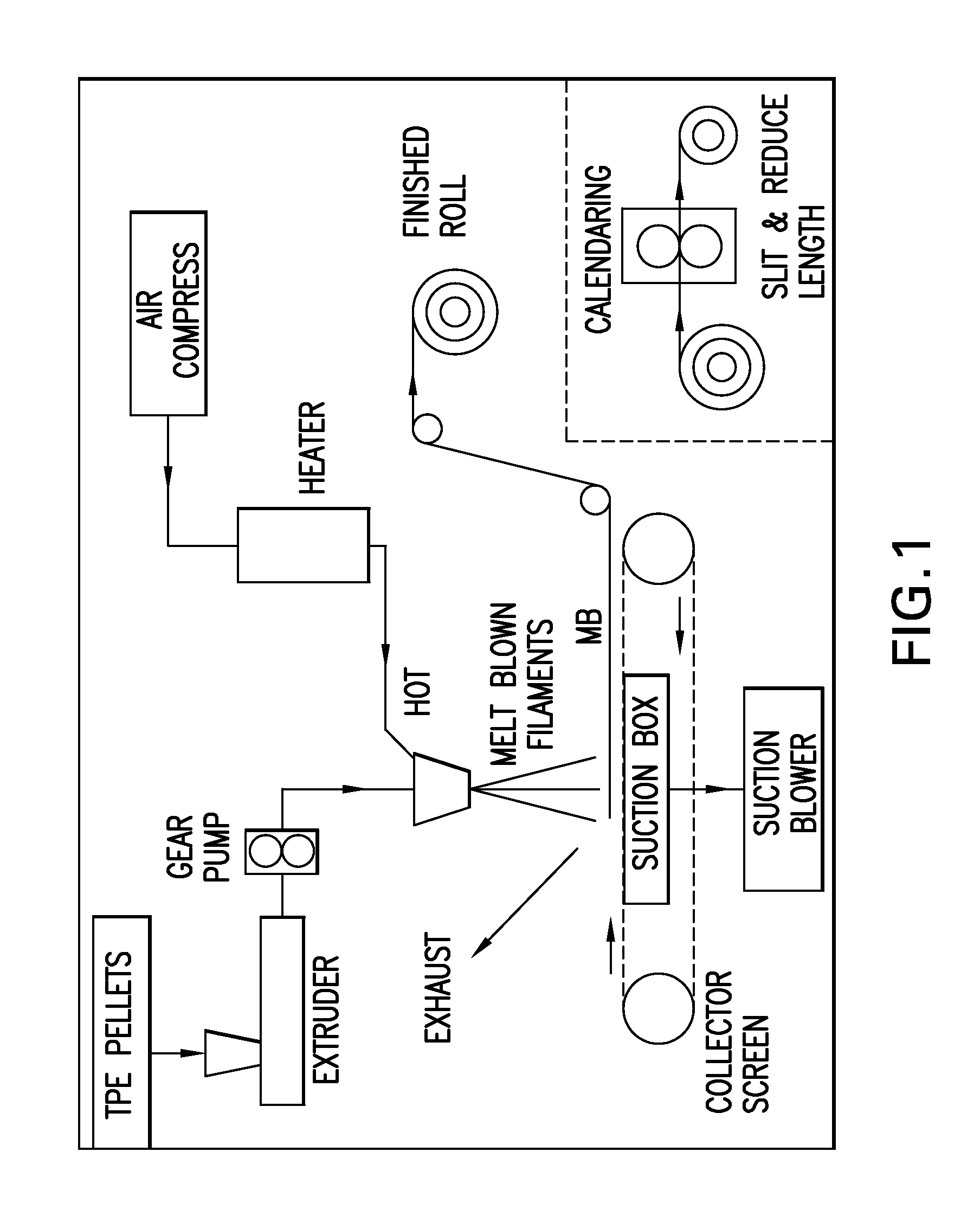
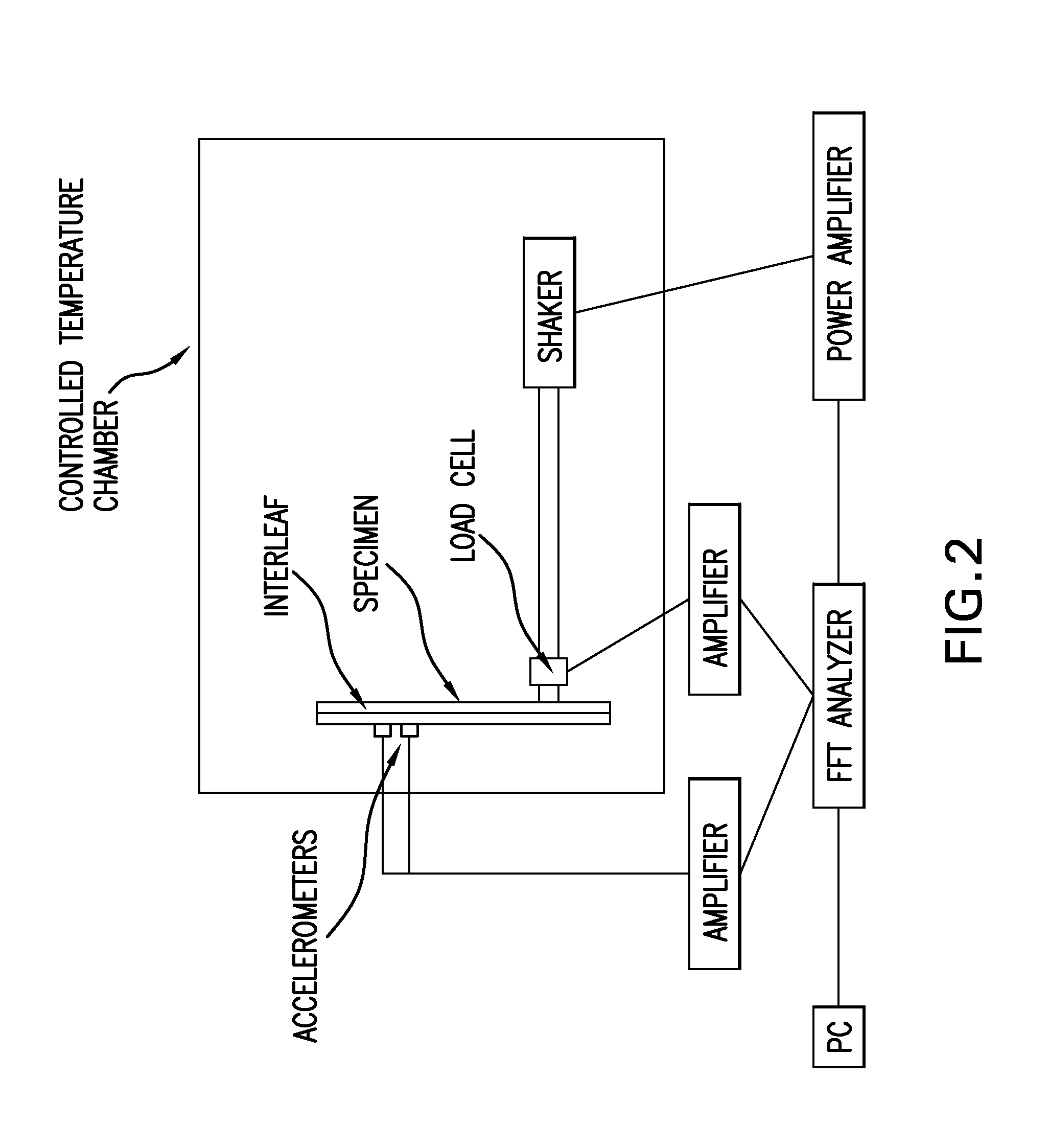
A composite material comprises a nonwoven layer having a viscoelastic interleaf, which may be positioned mid-ply therein.
Owner:CYTEC TECH CORP
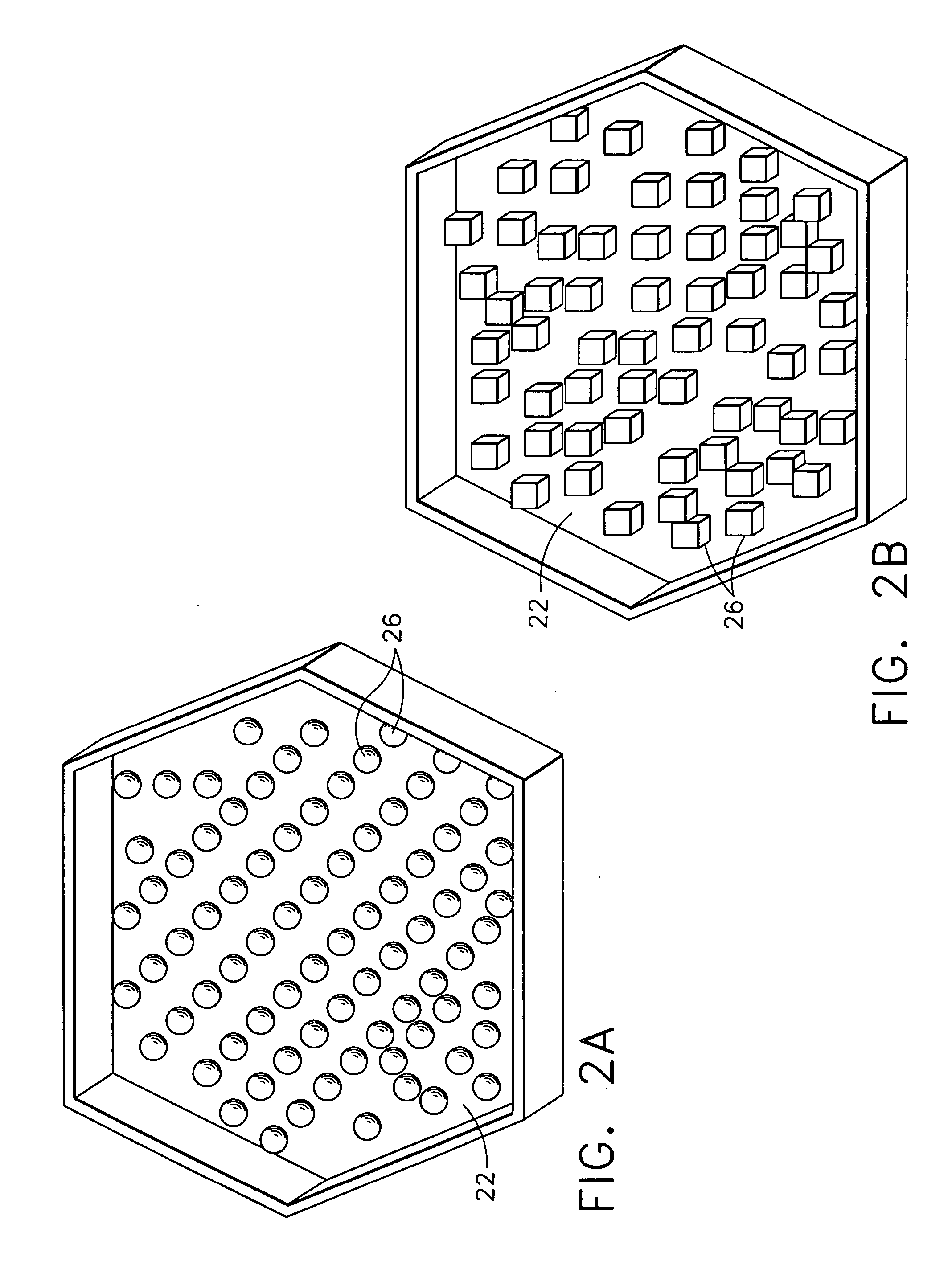
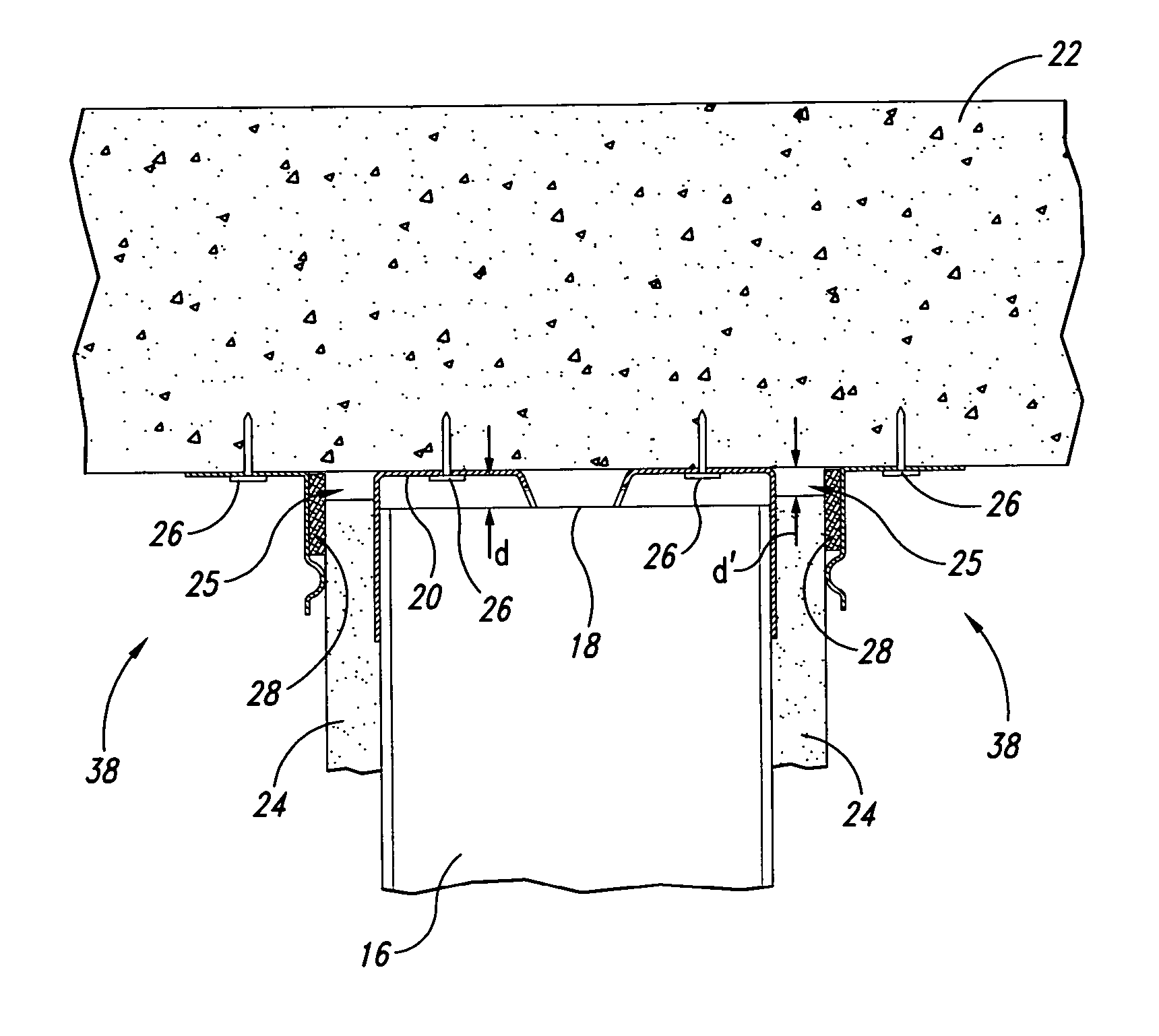
Acoustic septum cap honeycomb
An acoustic structure that includes a honeycomb having cells in which septum caps are located. The septum caps are formed from sheets of acoustic material and include a resonator portion and a flange portion. The flange portion has an anchoring surface that provides frictional engagement of the septum caps to the honeycomb cells when the caps are inserted into the honeycomb during fabrication of the acoustic structure. An adhesive is applied to the anchoring surface of the septum caps after the caps have been inserted into the honeycomb cells to provide a permanent bond.
Owner:HEXEL CORP
Fire retardant nonwoven material and process for manufacture
An improved acoustically and thermally insulating fire-retardant composite material suitable for use in structures such as buildings, appliances, and the interior passenger compartments and exterior components of automotive vehicles is provided. The material is comprised of at least one airlaid fibrous layer of controlled density and composition and incorporating suitable binding agents and additives as needed to meet expectations for noise abatement, fire-retardancy, and mildew resistance. Separately, an airlaid structure which provides a reduced, controlled airflow therethrough useful for acoustic insulation is provided, and which includes a woven or nonwoven scrim. A process for the production of the fire retardant nonwoven material is also provided.
Owner:GLATFELTER CORP
Acoustical gypsum board for ceiling panel
Low density acoustical gypsum boards having a perforated cover sheet that have good sound absorption properties and are generally clear of falling gypsum dust. The invention optionally provides a cover sheet having a pattern producing a textured visual effect particularly when viewed from a distance. The acoustical gypsum boards can be produced on modified existing gypsum board lines.
Owner:USG INTERIORS INC
Nonwoven material for acoustic insulation, and process for manufacture
InactiveUS20080121461A1Improve acoustic propertiesReduce weightLiquid surface applicatorsWallsVolumetric Mass DensityEngineering
An improved acoustically and thermally insulating fire-retardant composite material suitable for use in structures such as buildings, appliances, and the interior passenger compartments and exterior components of automotive vehicles is provided. The material is comprised of at least one airlaid fibrous layer of controlled density and composition and incorporating suitable binding agents and additives as needed to meet expectations for noise abatement, fire-retardancy, and mildew resistance. Separately, an airlaid structure which provides a reduced, controlled airflow therethrough useful for acoustic insulation is provided, and which includes a woven or nonwoven scrim. A process for the production of the fire retardant nonwoven material is also provided.
Owner:GEORGIA PACIFIC NONWOVENS LLC
Acoustical panel comprising interlocking matrix of set gypsum and method for making same
An acoustical panel comprising a continuous phase of an interlocking set gypsum matrix and a method of preparing an acoustical panel are disclosed.
Owner:UNITED STATES GYPSUM CO
Apparatus and method for aircraft cabin noise attenuation via non-obstructive particle damping
InactiveUS20050194210A1Increase dampingIncreased durabilityLayered productsFuselage insulationFilling materialsEngineering
An apparatus for reducing noise in an aircraft cabin is disclosed. The apparatus comprises a structure portion and filler material. The structure portion further comprises an internal member having at least one cavity disposed therein. Each of the at least one cavity of the structure portion are filled with the filler material.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
Head-of-wall fireblocks and related wall assemblies
Fireblock devices, wall assemblies and related methods useful for retarding the spread of smoke and fire through dynamic head-of-wall construction joints and gaps are disclosed herein. In one embodiment, the fireblock device is characterized by an elongated angled channel member having an elongated intumescent material strip, wherein the angled channel member is defined by an elongated top flange member connected to an elongated side flange member along a lengthwise edge, and wherein the top and side flange members define a right angle and a lengthwise interior corner region, and wherein the top and side flange members each have inner flange member surfaces that face inwardly with respect to the interior corner region, and outer flange member surfaces that face outwardly with respect to the interior corner region, and wherein the intumescent material strip is affixed on the outer flange member surface of the side flange member.
Owner:KLEIN JAMES ALAN
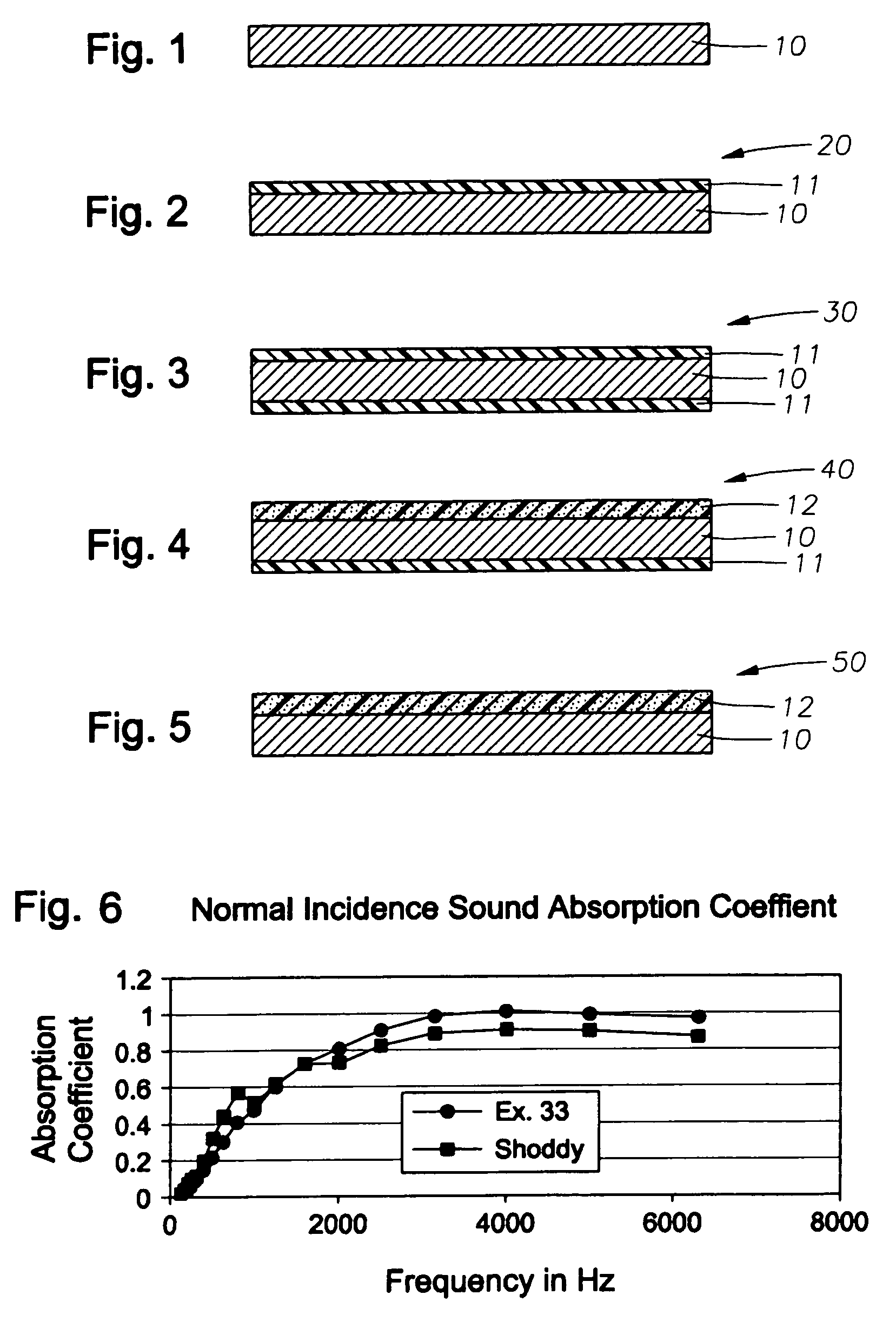
Sound absorbing material
InactiveUS20060225952A1Improve sound absorptionLow costSound proofingWoven fabricsMaterials scienceBulk density
A sound-absorbing material, wherein a non-woven fabric with a mass per unit area of 150 to 800 g / m2 and a bulk density of 0.01 to 0.2 g / cm3 and a surface material with an air permeability of not more than 50 cc / cm2 / sec measured according to JIS L-1096 are layered.
Owner:TAKAYASU CO LTD +2
Microperforated polymeric film for sound absorption and sound absorber using same
Microperforated polymeric films and sound absorbers using such films are provided. The microperforated polymeric films may be relatively thin and flexible and may further include holes having a narrowest diameter less than the film thickness and a widest diameter greater than the narrowest diameter. The microperforated polymeric films of a sound absorber may also have relatively large free span portions, which, in certain embodiments, may vibrate in response to incident sound waves.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
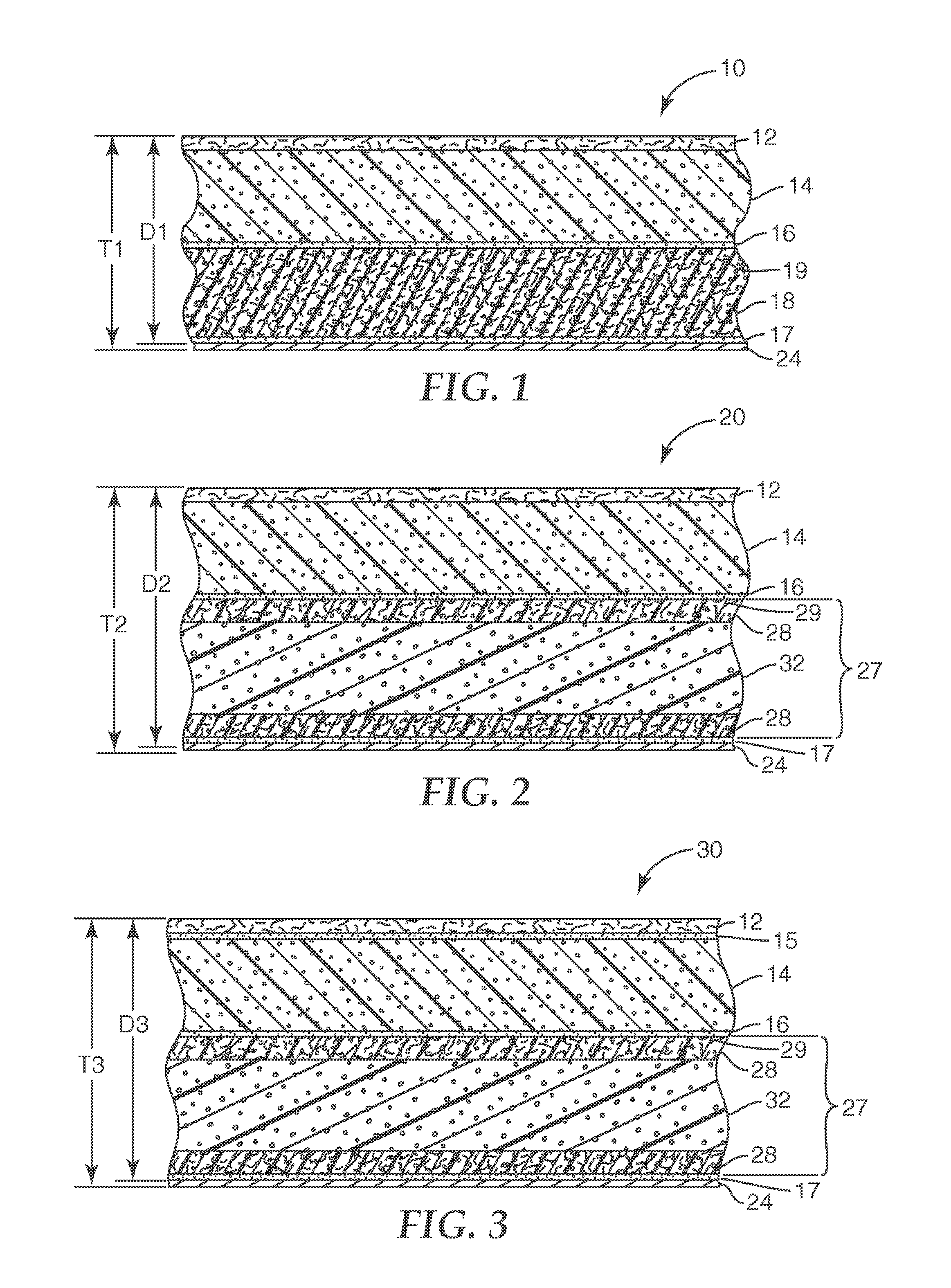
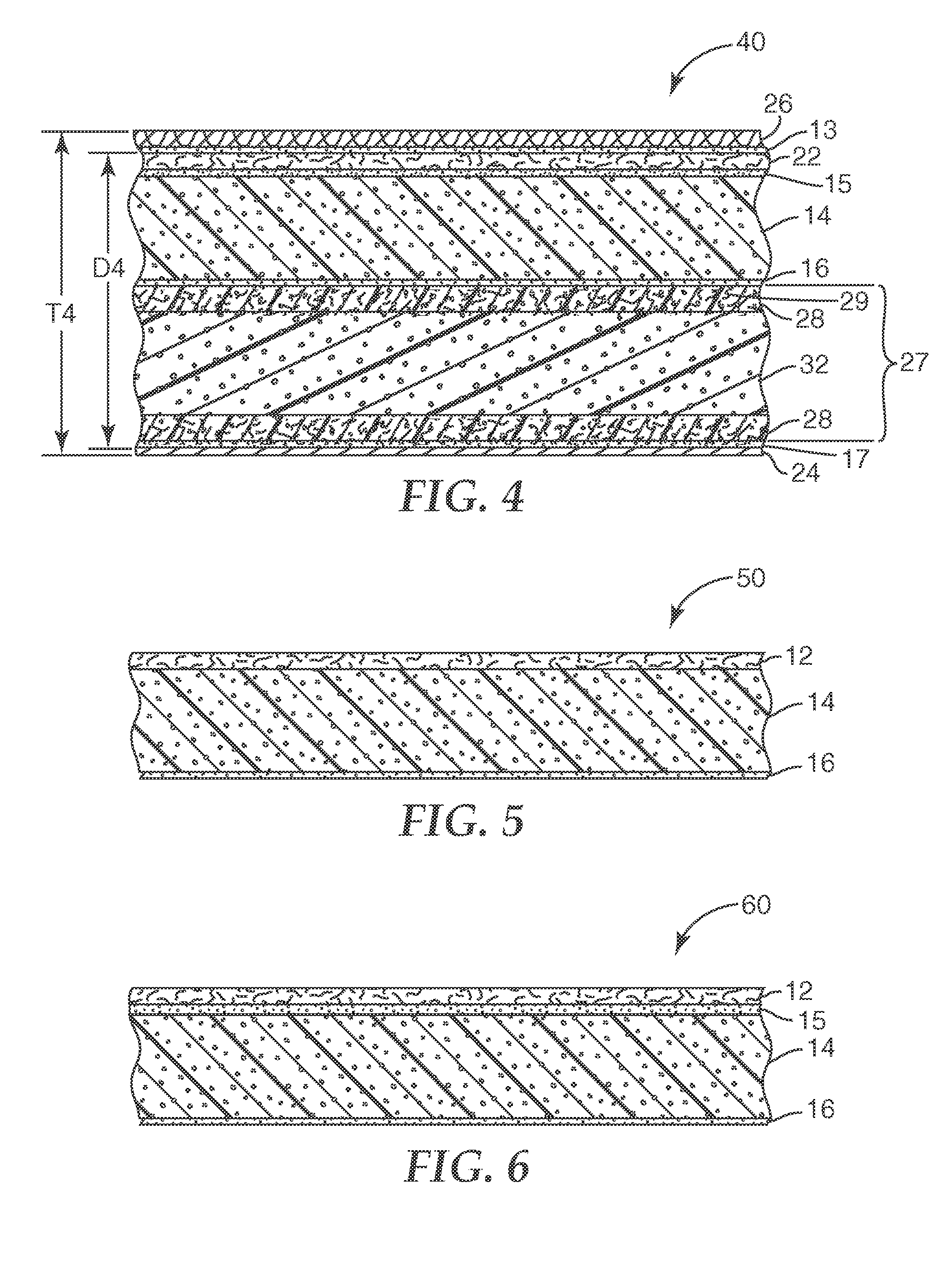
Sound absorptive multilayer composite
ActiveUS7320739B2Improve acoustic performanceIncreasing the thicknessMembranesSemi-permeable membranesOpen cellAirflow
A sound absorptive multilayer composite having an air-impermeable barrier, an air-permeable reinforcing core having an airflow resistance of at least about 100 mks Rayls and a thickness at least about ⅓ the final composite thickness, an air-permeable open cell foam or fibrous pad having an airflow resistance less than about 2000 mks Rayls and a thickness at least about 1 / 10 the final composite thickness and a semipermeable airflow-resistive membrane having an airflow resistance of about 500 to about 4000 mks Rayls can provide improved acoustic performance. For example, existing vehicular headliner designs may be improved by adding a properly chosen and properly positioned semipermeable airflow-resistive membrane, a properly chosen and properly positioned air-impermeable barrier, or a properly chosen and properly positioned open cell foam layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Impact sound insulation
InactiveUS6920723B2Minimizes height requirementAvoid damageSki bindingsCeilingsEngineeringUltimate tensile strength
A substrate for use in a flooring system which has a subfloor and a decorative upper layer. The substrate is made in a continuous sheet which has a bottom surface, a top surface, side surfaces and end surfaces. The top surface and the oppositely facing bottom surface are essentially parallel to each other and are spaced apart by the thickness of the substrate. Voids are provided in the substrate, the voids are provided between particles of rubber or other similar material. When the substrate is positioned between the subfloor and the decorative top layer, the particles of rubber provide the strength required to prevent deformation of the substrate in the direction of the thickness and the voids contribute to the sound dampening characteristics required to provide decibel reduction across the thickness of the substrate.
Owner:ECORE INT
Modularized insulation, systems, apparatus, and methods
ActiveUS7083147B2Prevent and minimize shiftingLaborFuselage bulkheadsFuselage insulationSkin surfaceSurface structure
Modularized insulation blanket for thermal and / or acoustical insulation. The modularized insulation blanket has a cover formed of a distal layer and proximal layer in sealed mated relationship. The distal and proximal layers are sealed along longitudinal and latitudinal heat-sealed seams that define a plurality of modules. The heat-sealed seam may be creased so as to be foldable and / or perforated to provide a tear line. Within the modules are batting blocks. The blankets may be attached to surface structures such as the interior skin surface of an aircraft fuselage, pipes or other structures with retention systems. The blankets may be formed in an apparatus including a platen, heat seal rollers or heating sealing mechanisms, and edge sealers.
Owner:THE BOEING CO
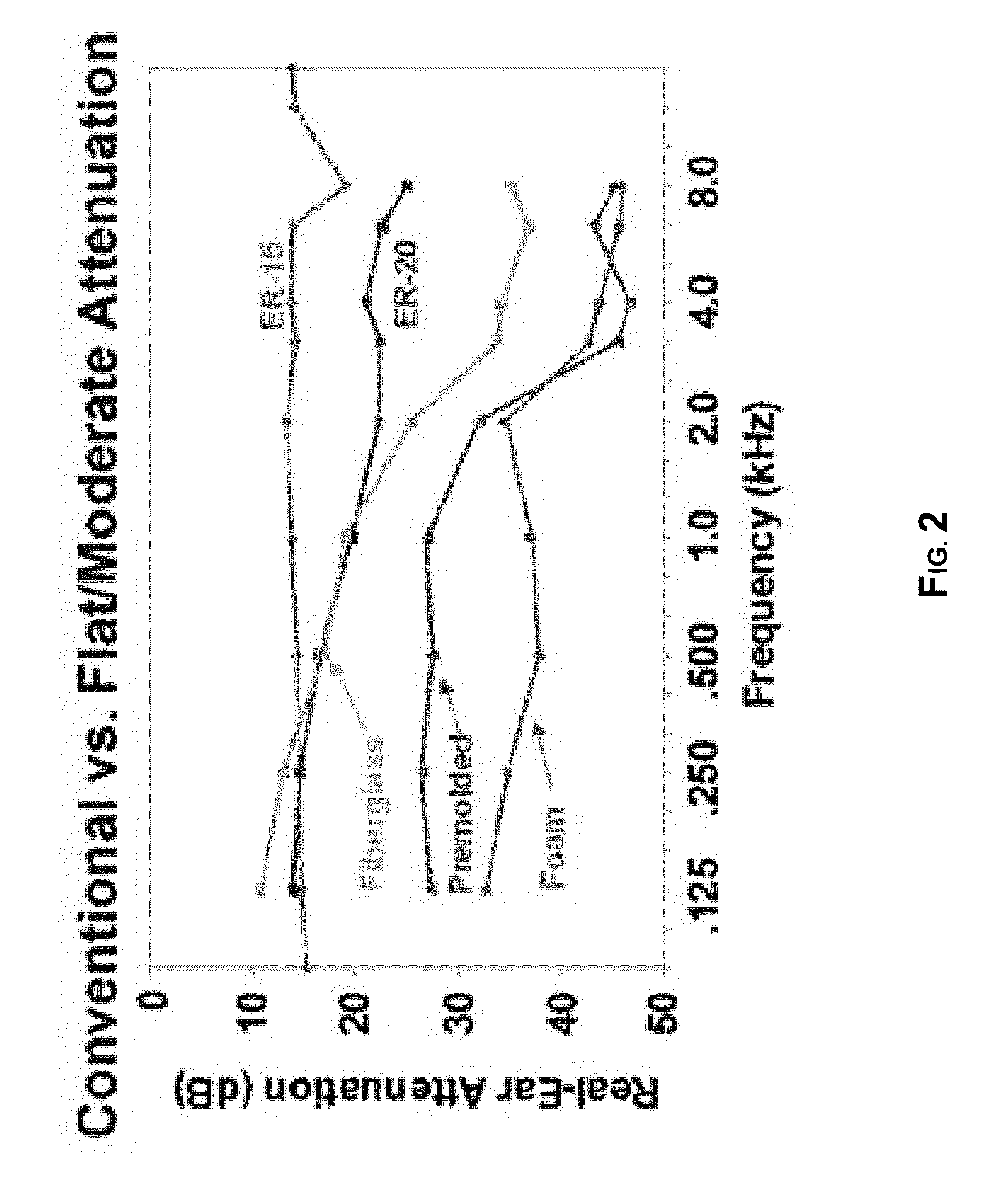
Method and structure for achieving spectrum-tunable and uniform attenuation
The present invention relates hearing protection devices for the human ear. More particularly, embodiments of the invention provide hearing protection devices capable of tunable acoustic attenuation. The invention relates further to ear plugs comprising a fluid-containing balloon for occlusion of the ear canal, which are capable of being adjusted for example by modifying fluid composition and / or fluid pressure within the balloon to vary attenuation at different frequencies of the audible sound spectrum. Other embodiments provide an earplug with fixed attenuation comprising: a body of compressible / expandable-recovery material shaped and sized to fit in an ear canal; and at least one chamber disposed within the body and comprising a filler material chosen from at least one of water, aphrons, water with solid or gelatinous particles suspended, and oil with particles suspended.
Owner:VIRGINIA TECH INTPROP INC
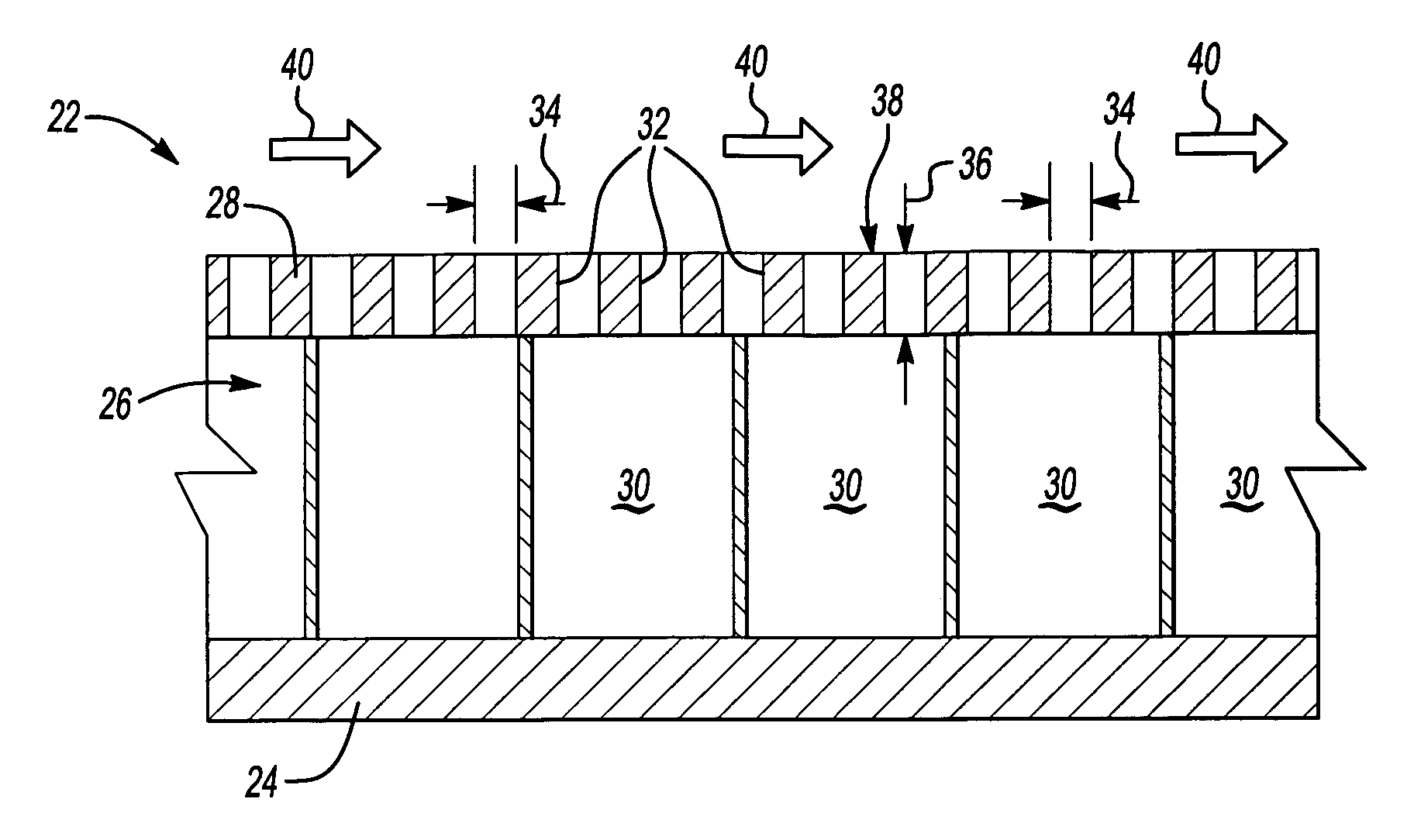
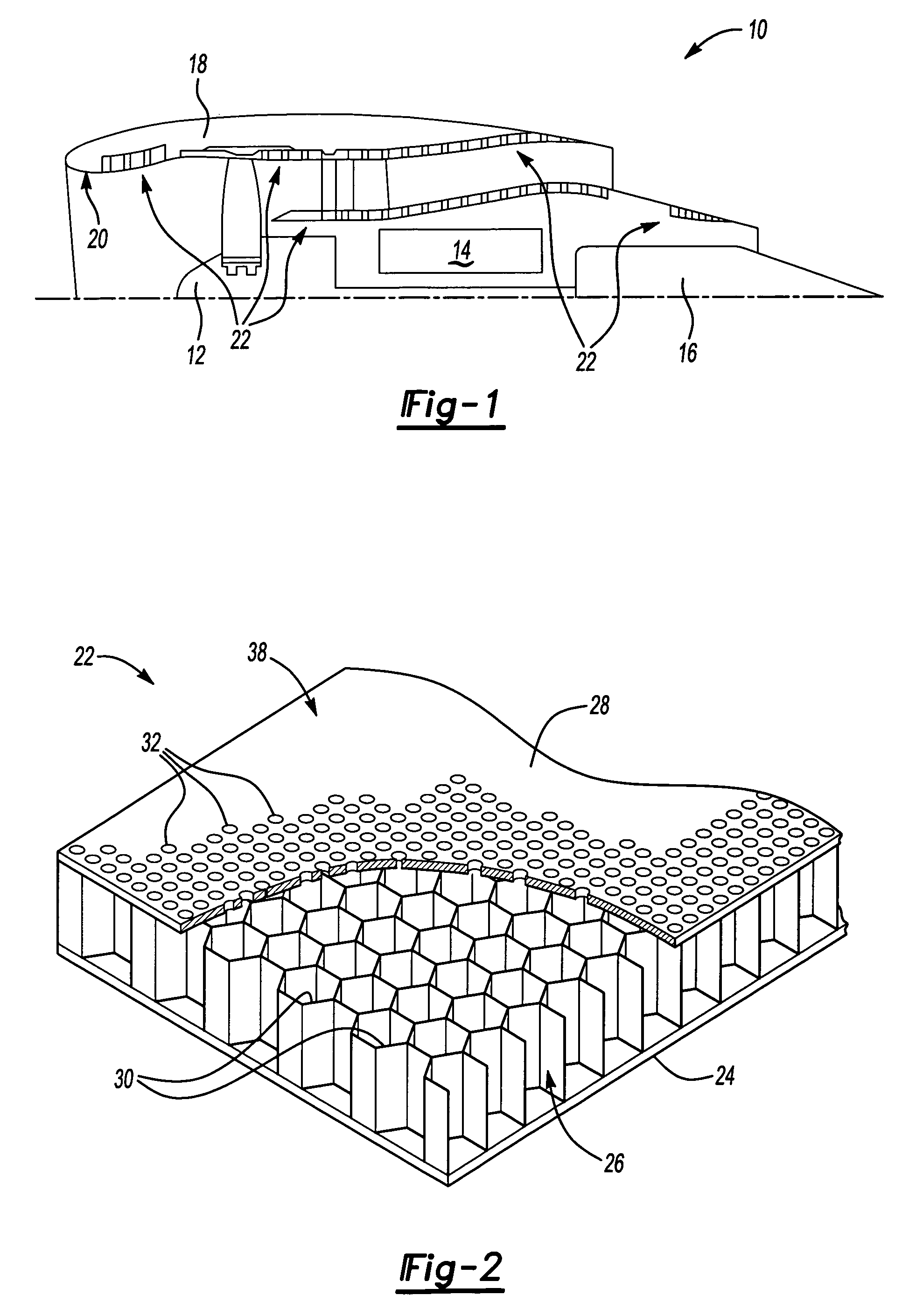
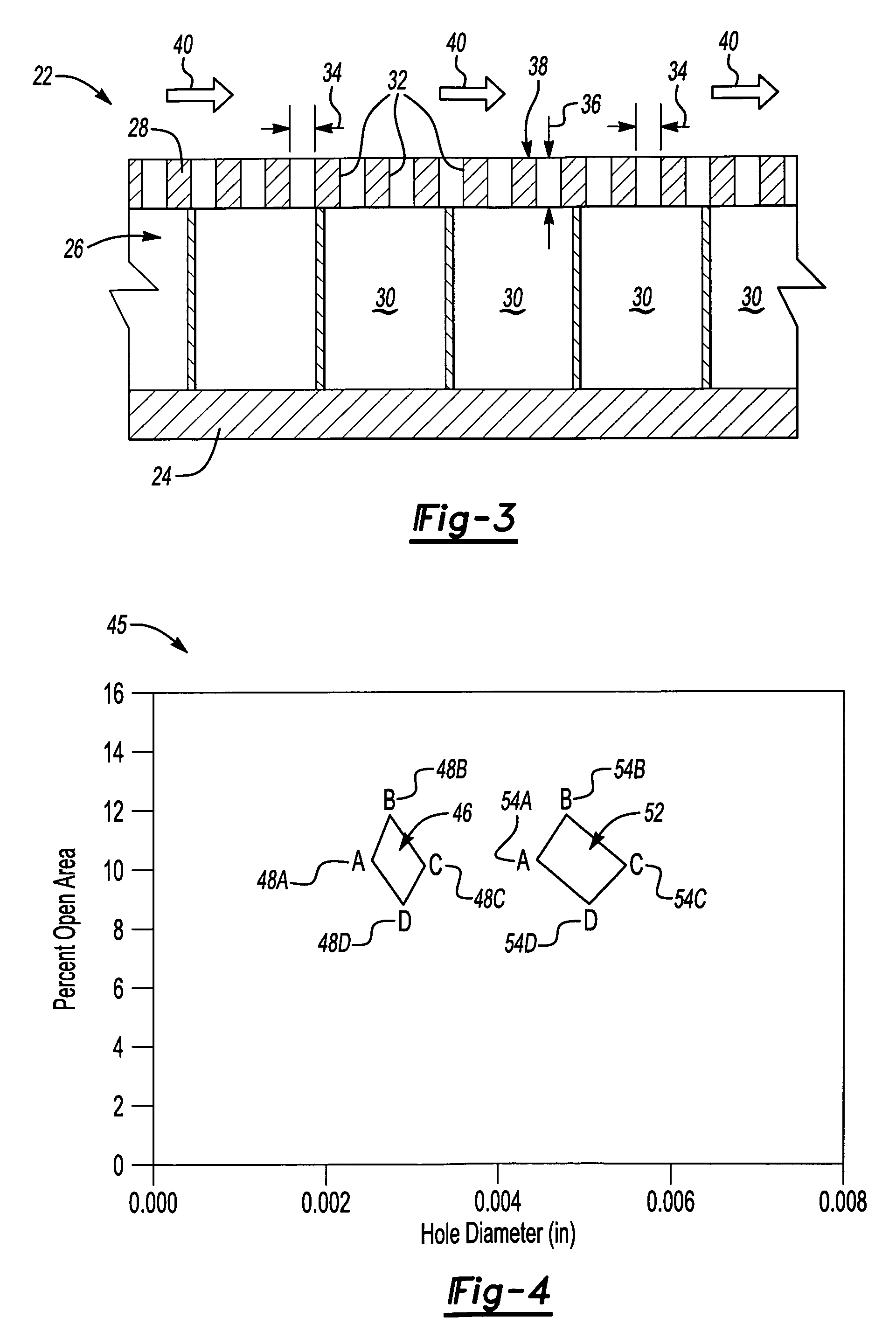
Acoustic resonator with impingement cooling tubes
Aspects of the invention are directed to an acoustic resonator with improved impingement cooling effectiveness. The resonator includes a plate with an inside face and an outside face. A plurality of passages extend through the plate. The resonator includes a side wall that extends from and about the plate. A plurality of cooling tubes are attached to the resonator plate such that an inner passage of each cooling tube is in fluid communication with a respective passage in the resonator plate. The resonator can be secured to a surface of a turbine engine combustor component to define a closed cavity. The ends of the cooling tubes are spaced from the surface. Thus, a coolant can enter the passages in the plate and can be directed to the surface so as to impingement cool the surface. The cooling tubes can minimize coolant loss by dispersion in the cavity.
Owner:SIEMENS ENERGY INC
Micro-perforated acoustic liner
ActiveUS7540354B2Drag minimizationPerformance maximizationEngine manufactureLayered productsEngineeringFace sheet
An example liner assembly includes a backing plate that supports a cellular structure covered by a perforated face sheet including a plurality of openings. Each of the plurality of openings is of a size determined to provide desired acoustic performance.
Owner:RTX CORP
Acoustically optimized cabin wall element
ActiveUS20090250293A1Improve efficiencyIncreasing weightWallsSynthetic resin layered productsEngineeringLow frequency
A wall element for the sound-insulating interior lining of a transport device, comprising at least one sandwich element, at least one insulation package and at least one absorber plane element. The sandwich element comprises at least one core layer, a first cover layer and a second cover layer, wherein the first cover layer and the second cover layer are each arranged on one side of the core layer. At least the first or the second cover layer is a microperforated layer; the sandwich element possesses a shear rigidity that is adjusted in such a way that the sandwich element comprises one or several coincidence boundary frequencies that are determined by the shear rigidity, which coincidence boundary frequencies are outside the frequency range that dominates the noise in the interior of the cabin; and the shear rigidity of the sandwich element at the same time is sufficient for said sandwich element to be used as an interior lining. Sound-insulating interior lining according to the aspects according to the invention provides adequate sound insulation also in the lower frequency range of below 500 Hz, without increasing the weight of the interior lining when compared to the weight of conventional interior linings.
Owner:AIRBUS OPERATIONS GMBH
Sound absorptive multilayer composite
InactiveUS20080073146A1Improve acoustic performanceIncreasing the thicknessSemi-permeable membranesMembranesMechanical engineeringOpen cell
A sound absorptive multilayer composite having an air-impermeable barrier, an air-permeable reinforcing core having an airflow resistance of at least about 100 mks Rayls and a thickness at least about ⅓ the final composite thickness, an air-permeable open cell foam or fibrous pad having an airflow resistance less than about 2000 mks Rayls and a thickness at least about 1 / 10 the final composite thickness and a semipermeable airflow-resistive membrane having an airflow resistance of about 500 to about 4000 mks Rayls can provide improved acoustic performance. For example, existing vehicular headliner designs may be improved by adding a properly chosen and properly positioned semipermeable airflow-resistive membrane, a properly chosen and properly positioned air-impermeable barrier, or a properly chosen and properly positioned open cell foam layer.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Sound-absorbing structure and sound-absorbing unit
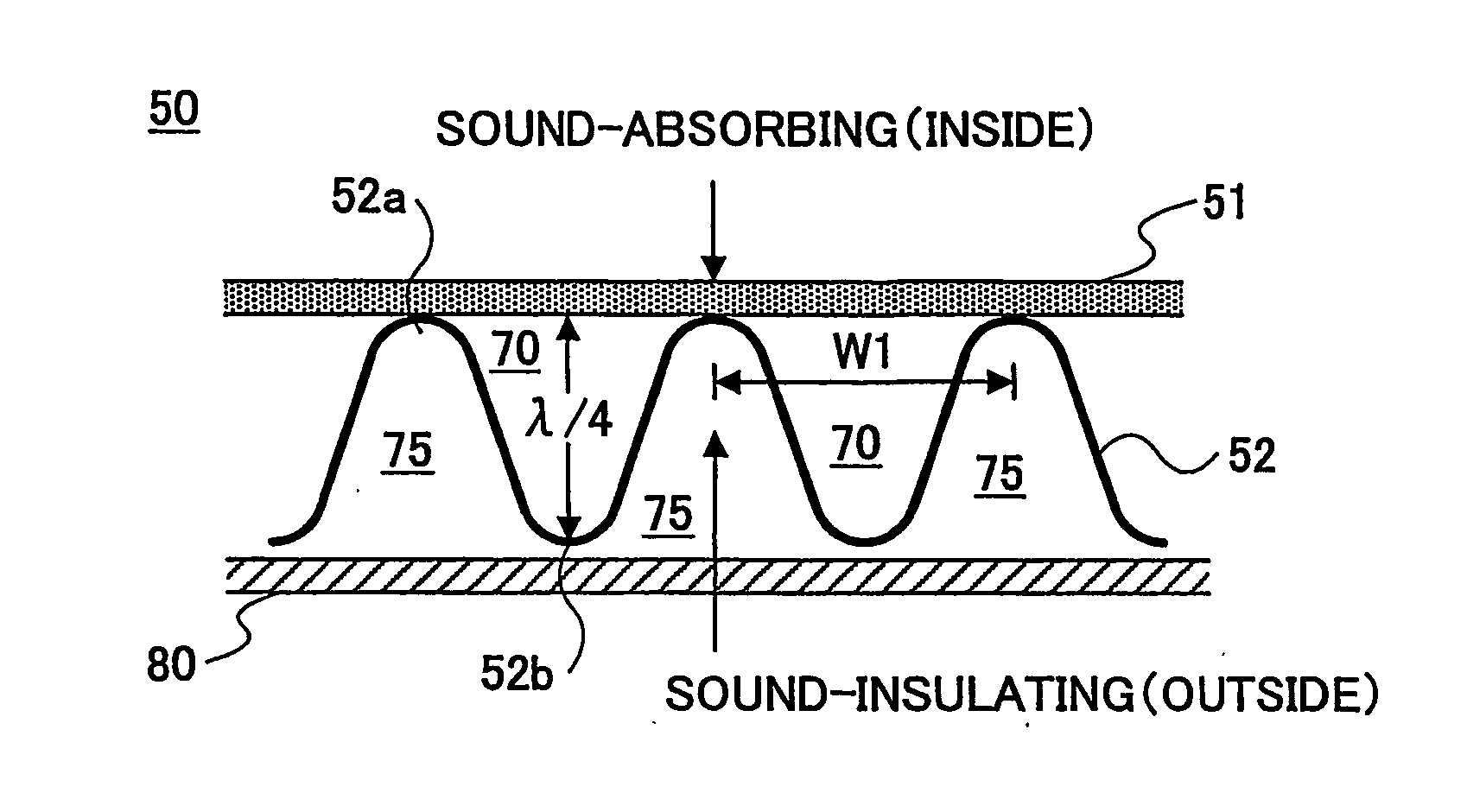
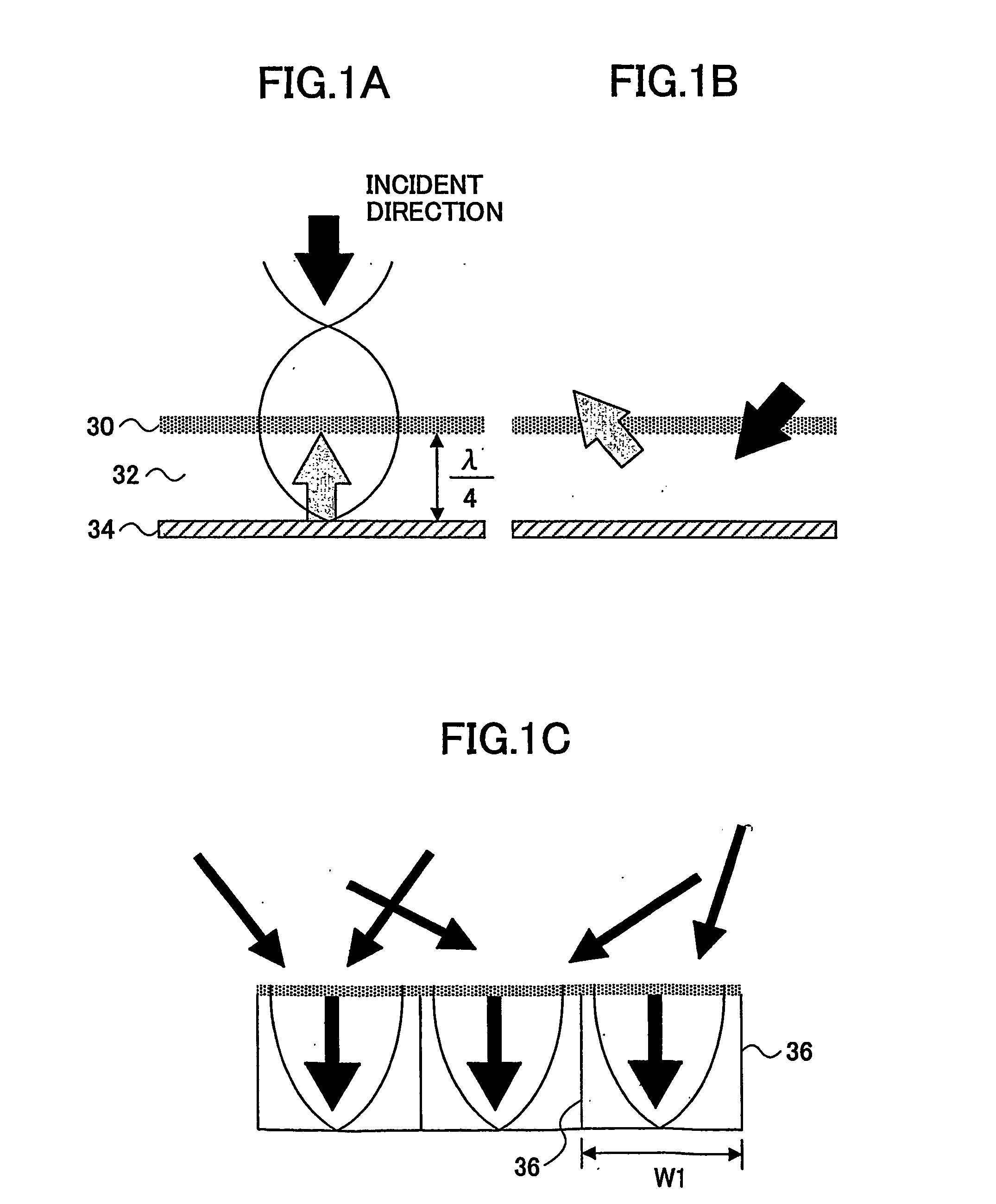
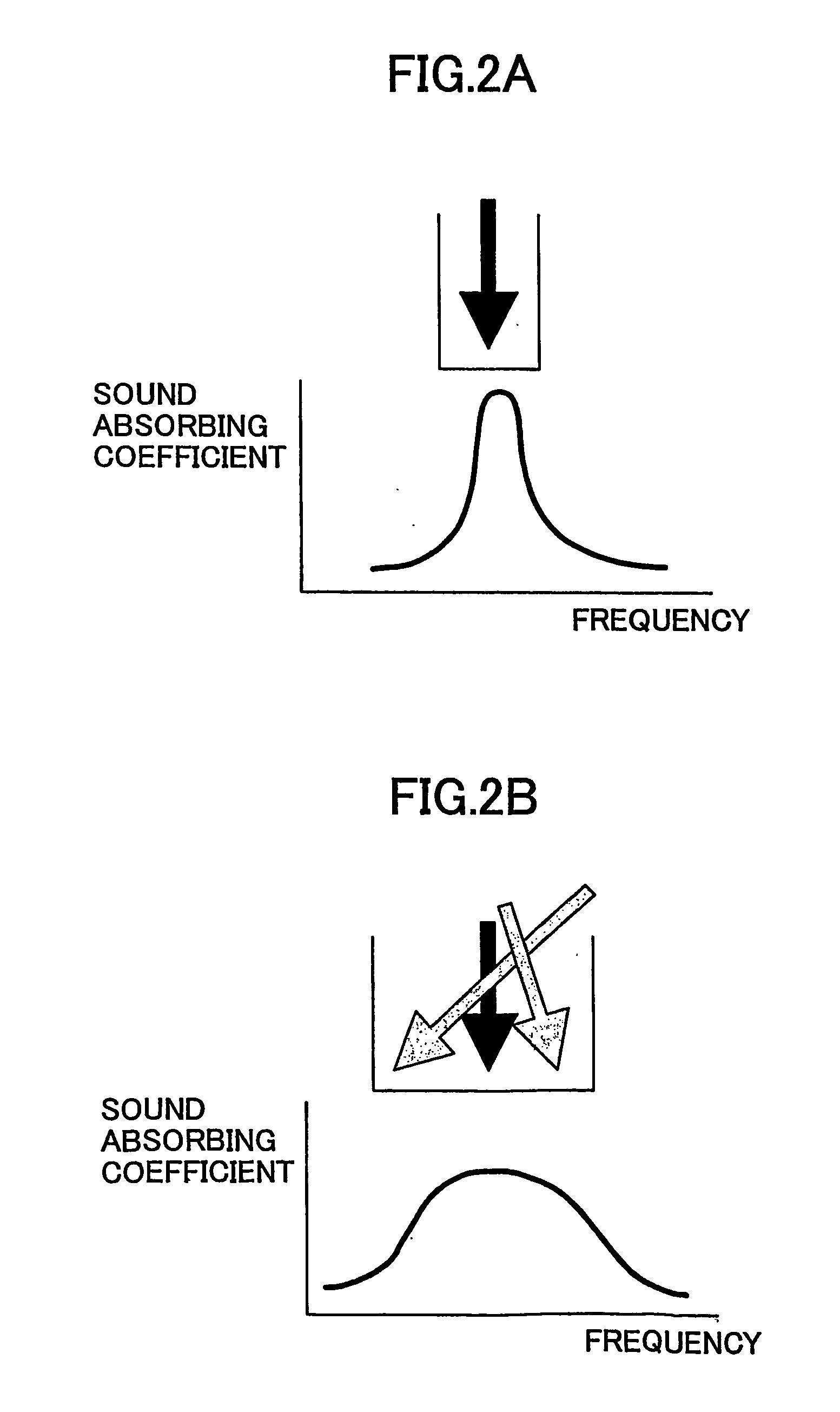
InactiveUS20050263346A1Effective sound absorptionImprove sound absorptionWallsVehicle componentsEngineering
Owner:TOYOTA JIDOSHA KK
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com